Dark Matter - III. Workshop Freudenstadt September 30, GRK 1694: Elementarteilchenphysik bei höchster Energie und höchster Präzision
|
|
|
- James Scott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dark Matter - III GRK 1694: Elementarteilchenphysik bei höchster Energie und höchster Präzision Workshop Freudenstadt 2015 September 30, 2015 Guido Drexlin, Institut für Experimentelle Kernphysik KIT University of the State of Baden-Württemberg and National Research Center of the Helmholtz Association
2 outline of today s final afternoon lecture Dark Matter 3: direct detection of dark matter - expected WIMP rates: SUSY (M c, s SI,SD) and astrophysics (F, v) - detection methods: 1- & 2- parameter experiments - underground experiments & background - DAMA s annual modulation - bolometers vs. LXe detectors - 2-phase liquid noble gas detectors: XENON100/1T/ DARWIN - conclusion multi-gev multi-gev e- MeV elastic WIMP-nucleus scattering in kev-range e- 2 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3 MeV
3 WIMP detection reaction kinematics: input from astrophysics & SUSY R N ASTRO nuclei F s r DM, local SI / SD Nnuclei s SI / SD 0 M ( c ) v SUSY c 0 c 0 s = 0,1 H, h Z WIMP properties: - kinetic energy (v) - local density r DM,local - flux F (from v & r DM,local ) 3 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3 N nuclei q q WIMP properties: - cross sections scalar s SI / axial s SD - mass M(c 0 )
4 WIMP number (rel. units) WIMP velocity profile WIMP energies from DM-halo - v ~ 10-3 c - E kin = ½ M c v 2 - M c = 100 GeV E kin < 100 kev E kin «M c isothermal WIMP velocity profile f(v) f (v) dv 2 4v e 3 v 0 d Maxwell-Boltzmann-velocity distribution v 2 / v v WIMP halo energies nuclear recoil energies E R kinetic energy (kev) 4 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
5 log dn / de WIMP scattering annual modulation modulation of WIMP recoil spectrum - superposition of velocity vectors v S (sun) & v E (earth) period: T = 1.00 year phase: j 0 = June, 2 WIMP wind June, 2 v(t) v0 v E cos(60 ) cos ( t t0) ~2-7% effect galactic plane December v E = 30 km/s December June recoil energy E 5 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
6 WIMP detection reaction kinematics: input from SUSY R N nuclei F s 1 level of partons: q, g DM, local SI / SD Nnuclei s SI / SD 0 M ( c ) c 0 - interaction with quarks, gluons c 0 coupling strength from SUSY model 2 level of nucleons: p, n q, g kinematics within the nucleons is determined by parton distributions (valence- & sea quarks) r v Xe-nucleus nucleon c 0 c 0 3 level of nuclear structure: Ar, Ge, Xe, c 0 - interaction on scale of nucleus (nuclear wave function) - reaction kinematics coherent nuclear recoil 6 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
7 neutralino scattering: scalar interaction scalar interaction: neutralino couples to mass distribution of the nucleus c 0 c 0 s = 0 H, h c 0 c 0 ~ q mechanism: - exchange of a light or a heavy higgs boson H, h - annihilation into squark (q-mixing) ~ q q q s = 0 q - also loop diagrams with (massless) gluons scalar c 0 interaction with a quark (s SI : spin independent) - quark- & gluon functions in nucleon: also heavy quarks contribute - coherent interaction ~ A 2 - s SI dominates the elastic c 0 -cross section in many SUSY models 7 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
8 neutralino scattering: spin-dependent axial-vector interaction: spin of neutralino couples to spin of nucleus c 0 c 0 s = 1 Z 0 J nucl. q q spin-dependent c 0 -interaction (s SD : spin dependent) - spin structure functions: nucleon spin (p,n) from partons - spin matrix elements: nucleons in nucleus ( mean p/n-spin in nucleus) - nuclear shell model: nuclear spin from coupled nucleons in shells 8 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
9 neutralino scattering: spin-dependent s SD ~ s 0 a p S p a n S n 2 J 1 J a p,n : WIMP-proton/neutron couplings (SUSY-model-dependent) J : spin of nucelus via unpaired nucleon (proton / neutron) due to pairing term (Bethe-Weizsäcker) S p,n :expectation value of proton/neutron spin (e.g. 5/2, 1/2) within nulcear shell model p coupling J=0 only J 0 targets are sensitive to spin-dependent WIMP-scattering examples of important target nuclei for s SD (sensitive to a p or a n ): detector type isotope fraction protons neutrons nucl. spin J coupling NaJ (scintillator) 23 Na /2 a p 127 I /2 a p LXe (TPC/scint.) 131 Xe 21.2 % /2 a n 129 Xe 26.4 % /2 a n Ge (bolometer) 73 Ge 7.8 % /2 a n p 9 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM
10 rate E > E r (events/kg/day) WIMP recoil spectra recoil spectrum for scalar interaction (coherent, form factor) dr de R ds ~ v f (v) dv de R recoil energies of nuclei on kev-scale astrophysics - WIMP-halo model (r CDM, v 0 ) : the larger v 0, the larger the rate - neutralino mass M c detector properties - nuclear target mass M N - nuclear structure (formfaktor F) - very low threshold (few kev) for heay target nuclei (Xe, J) recoil energy E r (kev) 10 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
11 WIMP cross section s [cm 2 ] WIMP plots comparison of results R N nuclei F s r DM, local SI / SD Nnuclei s SI / SD 0 M ( c ) v light WIMPs: nuclear recoil energy below threshold detector threshold E R small (Mc < M N ) heavy WIMPs: W CDM = 0.22 is fixed for large M c the WIMP fluss F decreases, less signal events SUSY region: to cover larger fraction: larger mass & smaller background optimum sensitivity SUSY WIMP mass M c (GeV) WIMP flux decreases 11 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
12 WIMP signal & background rate R N nuclei F s r DM, local SI / SD Nnuclei s SI / SD 0 M ( c ) v Gran Sasso shielding source and shielding events/kg/s events/kg/day natural gamma activity after passive shielding 10 2 cosmic muons at surface of earth expected CDM detection rate < Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
13 muon rate (muons/m 2 /year) underground labs muon rate & depth 10 6 muon rate and shielding depth Campo Imperatore DUSEL shallow WIPP Soudan LNGS Kamioka Baksan LSM Sudbury DUSEL - Homestake DUSEL Homestake (deep) depth (m water equivalent) 13 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
14 direct dark matter experiments Sanford: LUX, LZ SNOlab: PICASSO DEAP CLEAN Soudan: CDMS-II Boulby: ZEPLIN III, Drift Modane: Edelweiss LNGS: XENON 1T CRESST DarkSide50 DAMA/Libra Kamioka: XMASS Soudan: 2000 m.w.e SNOlab: 6000 m.w.e. Sanford: 4800 m.w.e Canfranc: ANAIS Rosebud ArDM Kamioka: 2700 m.w.e 14 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
15 Where are the detectors? 15 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin VL04
16 polyethylen extensive shielding example XENON100 Pb- & Cu-shielding in the XENON100 experiment - against gammas ( 235 U, 238 U, 232 Th, 237 Np, 40 K, ), neutrons (µ-induced) PE H 2 O/polyethylen Low-level Pb Cu Pb Cu LXe- TPC Pb Pb PE polyethylen 16 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
17 Radon background radon emanation in underground laboratories is substantial PE Pb a Cu LXe- TPC PE experiments 17 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
18 WIMP detection methods 1 parameter CRESST-I XMASS CLEAN Zeplin I phonons scintillation c 0 c 0 HDMS, DRIFT DAMA/Libra ANAIS NAIAD KIMS ionization 18 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
19 WIMP detection methods 2 parameters scintillation & phonons CRESST-II ROSEBUD CDMS Edelweiss c 0 c 0 XENON LUX WARP ArDM ZEPLIN II,III phonons & ionization ionization & scintillation 19 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
20 DAMA/LIBRA DArk MAtter experiment: NaJ scintillation detector array target: kg high-purity NaJ crystals (scintillators) E thres = 2 kev ee ( 20 kev recoil energy of 23 Na nucleus ) Read-out: 2 PMT s / crystal, light yield 5-7 p.e. / kev background: sehr geringe NaJ Eigenaktivität, shielding : concrete, paraffin, 15 cm Boliden-Pb, 10 cm Cu, 1-2 events/kev/kg/day NaJ crystals acrylic box N 2 atmosphere DAMA set-up at LNGS 20 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
21 residuals (events per day/kg/kev) DAMA annual modulation 7 years data taking ( kg-days) from January 1995 July 2002 modulation of event rate with T = 1a & expected phase (t 0 = June, 2) - signal directly above hardware threshold in region E = 2-6 kev - no modulation for E = 6-14 kev, statistical significance (CL) = 6.3 s - interpreted by DAMA as evidence for direct WIMP-detection (??) 0.1 t 0 = days, T = 1.00 a Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM measurement time (days)
22 XMASS - overview XMASS: strategy: Xenon detector for Weakly Interacting MASSive Particles operated in Kamioka mine in the Japanese alps gradual increase of Xe target mass improved self absorption of background via LXe (10-4 events/kg/kev/day) method: UV-scintillation light in liquid-xenon (LXe) (T = 165 K) at l = 175 nm, but: Rayleigh scattering limits position resolution 100 kg (3 kg fid.) Ø=0.3m 800 kg (100 kg fid.) Ø=0.8m 23 t (10 t fid.) Ø=2.5m 22 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
23 XMASS - results XMASS: strategy: Xenon detector for Weakly Interacting MASSive Particles operated in Kamioka mine in the Japanese alps gradual increase of Xe target mass improved self absorption of background via LXe (10-4 events/kg/kev/day) method: UV-scintillation light in liquid-xenon (LXe) (T = 165 K) at l = 175 nm, but: Rayleigh scattering limits position resolution status: new 2015 results with 832 kg x 16 months exclude DAMA/Libra 23 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
24 DAMA/Libra results excluded DAMA/Libra data (favoured regions) and exclusion limits from Xe-experiments (spin-independent iinteraction) NaJ Xe DAMA/Libra CDMS-II (Si) CRESST-II CoGeNT DAMA/Libra CRESST-II CDMS-II (Si) XENON-100 LUX LUX WIMP mass M c (GeV) WIMP mass M c (GeV) 24 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
25 2-phase detectors: mass vs. surface bolometers: only few kg, very low threshold large surface, good discrimination noble gases: leading technology for WIMPs deploy multi-ton detectors sensitivity of a dark matter experiment scales with its mass LXe Ge systematics & bg of a dark matter experiment scales with its surface bolometers liquid noble gases 25 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
26 cryogenic bolometers cryo-bolometer at low temperature in mk regime (CRESST, CDMS, ) advantages: - good sensitivity to nuclear recoils (phonons) - very low energy threshold - good energy resolution (~150 6 kev) - different target materials (Ge, Si, CaWO 4 ) - combine phonons with ionisation & scintillation: very good separation of gammas & electrons - modular set-up ( scalable & sequentiel extension replace sub-optimal single detectors, new detectors) Ge disadvantages: - extensive mk-cryotechnology (long runs) - limited target mass (~ 30 kg so far) - modular setup ( large inner surface) CaWO 4 26 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
27 Cryo-bolometers measurement principle principle of a cryogenic bolometer (µ-calorimeter): - energy deposition E R of recoil of target nucleus from c 0 -scattering leads to small, but measurable temperature increase DT in absorber - absorber (Ge, Si, CaWO 4 ) with masse M ~ g at T 0 = mk - thermometer to measure temperature increase DT in absorber - heat bath (weak couplinng) to decrease T(bolometer) to T 0 DT ER V C V important: small specific heat capacity C V of asorber limits mass M of a cryogenic bolometer to ~ 1kg heat bath 27 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
28 cross section s SI (GeV) Bolometers for low-mass region - future bolometer experiments (Super-CDMS, CRESST) will use few kg of detectors (Ge, Si) with low threshold to explore low-mass WIMP region CoGeNT DAMA/Libra CRESST-II CDMS-II (Si) XENON-100 LUX WIMP mass M c (GeV) 28 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
29 cross section s SI (GeV) Bolometers for low-mass region - future bolometer experiments (Super-CDMS, CRESST) will use few kg of detectors (Ge, Si) with low threshold to explore low-mass WIMP region CoGeNT DAMA/Libra CRESST-II CDMS-II (Si) XENON-100 LUX WIMP mass M c (GeV) 29 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
30 LSM Laboratoire Souterrain de Modane Fréjus (2900m) 4800 m.w.e. 4 muons/m 2 /day Italy France entry road tunnel NEMO-III 0nßß Ge gate Modane France Italy Nemo s.b. Höhe Abstand 1228 m 1263 m 1298 m 0 m 6210 m m Edelweiss 30 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
31 EDELWEISS Experiment Expérience pour détecter les WIMPs en Site Souterrain French-German experiment at LSM with Ge-/Si-bolometers : Edelweiss-I M = 1 kg 3 detectors : Edelweiss-II M = 4 kg 10 detectors 400 g each : Edelweiss-III M = 32 kg 40 detectors 800 g each cryostat 31 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
32 CDMS Cryogenic Dark Matter Search cryo-bolometers in the Soudan mine in North-Minnesota (2000 m.w.e) absorber: 250 g germanium (Ø = 7.5 cm, h = 1 cm) and 100 g Si-crystals ZIP-detector technology: Z-sensitive Ionisation and Phonon mediated detector signals: ballistic phonons ( TES: Al and W) use phonon-timing to discriminate against surface events Kryostat: 5 Türme ZIP detector with TES 32 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
33 Liquid noble gas detectors LXe & LAr detectors based on ultra-pure liquid noble gases - operated as 2-phase detectors: liquid & gaseous phase advantages: - large detector volumina (10 kg 100 kg 1 t 50 t ) - particle identification: chage & scintillation, pulse shape challenges: - low threshold, further reduction of background rate Z (A) properties of liquid noble gases as DM-detectors boiling T s [K] at p = 1 bar density at T s [g/cm 3 ] ionisation [e-/kev] scintillation [photons/ kev] scintillation light [l in nm] l-shifter Neon 10 (20) (WLS) Argon 18 (40) (WLS) Xenon 54(129/131) Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
34 2-phase LXe-experiments principles of LXe 2-phase-detectors: - scintillation light: detection via PMTs in LXe - ionisation signal: drift of electrons in E-field to Xe gas phase gas anode LXe S1 E R PMT Array S2 hn T drift 5 µs / cm electrons hn PMT array in LXe E ext E D signals S1 (prompt) & S2 (delayed): - S1: primary Xe-excitation due to recoiling nucleus (prompt scintillation light) - S2: detection of drifting electrons via extraction to gas phase, there acceleration of e - in strong field electro-luminescence via scattering processes of fast electrons off gas delayed light detection in upper PMT coincidence of S1 and S2: - S1 + S2: particle-id & point of interaction 34 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
35 particle identification (PID) discrimination among WIMP-recoils of Xe-nuclei & electron/gamma-bg particle identification: electron: S2/S1 is large (no quenching) WIMP: S2/S1 is small (less ionisation) energy of Xe-recoil: intensity S1 (primary excitation) position reconstruction: PMTs (x,y), drift time (z) WIMP drift time ratio S2/S1 used for PID MC-simulation of light signales WIMP scattering drifted electrons Kernrückstoß Gamma drift time primary scintillation: S1 secondary scintillation S2 35 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
36 XENON100 experiment XENON-100: at LNGS LXe-detector with 161 kg mass (~99 kg as veto, 62 kg as target) - detector: Ø = 30 cm, h = 30 cm (maximum drift distance for electrons) PMT for read-out of scintillation- & electro-luminescence- light - factor 100 less background (selection, cleaning, self absorption) factor 10 more mass than predecessor XENON10 LXe cryostat enclosure PMTs 36 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
37 XENON100 experiment XENON-100: measurements at LNGS upper PMT array lower PMT array 37 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
38 log (S2/S1) XENON100 experiment: results Inital results from XENON100: days of data taking: kg days - energy window for WIMPsearch: kev (Xe-recoil energy) 0.4 scintillation S1 (PE) events observed background expectation N bg = (1.0 ± 0.2) events s SI < cm 2 at WIMP-mass M c = 55 GeV energy (kev reoil energy ) 38 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
39 Large Underground Xenon (LUX) experiment 2-Phase-Xenon experiment at Sanford Lab: - similar technology as in XENON (S1-S2) H 2 O shielding instrumented as muon veto - detector with 370 kg mass (100 kg fiducial volume ) - expected initial WIMP-sensitivity: s SI = cm 2 (for R bg = 0.5 events/month/100 kg) thermosiphon watershield sources cryostat 39 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
40 WIMP-nucleon xsec s SI (cm 2 ) WIMP results: actual status DAMA (Na) CDMS (Si) excess: exclusion: DAMA, CRESST, CDMS (Si) LUX, XENON100, CDMS (Ge) CRESST LUX (±1s) WIMP mass (GeV) 40 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
41 XENON1T experiment next-generation-xenon experiment at LNGS: - construction period: autumn 2013 autumn total (active) LXe mass: 3.3 t (2.0 t), 1 m electron drift, inch PMTs - bg-goal: 100 x lower than XENON100 (~ evts to. -1 d -1 kev -1 ) 41 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
42 DARWIN R&D and design study DARWIN: Dark matter Wimp search in Noble liquids - goal: ultimate DM-experiment: tons LXe - reach sensitivity where bg is dominated by neutrinos s SI ~ cm 2 Experimental design parameters - TPC diameter > 2 m - electron drift length > 2 m - few x 10³ photosensors Physics goals - WIMP spectroscopy: mass and cross section - others: pp-neutrinos, 0nßß of 136 Xe, axions and ALPs, bosonic SuperWIMPs 42 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
43 s SI (cm 2 ) number of WIMP signals DARWIN R&D and design study DARWIN: Dark matter Wimp search in Noble liquids - goal: ultimate DM-experiment: tons LXe - reach sensitivity where bg is dominated by neutrinos WIMP events for M W = 100 GeV s SI = cm t Ar 1 t Xe sensitivity measuring time (years) 43 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
44 WIMP-nucleon xsec s SI (cm 2 ) actual & future WIMP sensitivities solar neutrinos (MeV) WIMP mass (GeV) neutrinos (multi-mev) LXe/LAr n s dominate background 44 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
45 Searching for dark matter a needle in a haystack 45 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
46 Conclusion 46 Sept. 30, 2015 G. Drexlin DM3
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches
 Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment
 The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments
 Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments Debasish Majumdar Astroparticle Physics and Cosmology Division Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata WIMP Hunting Going beyond gravity, three ways to detect
Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments Debasish Majumdar Astroparticle Physics and Cosmology Division Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata WIMP Hunting Going beyond gravity, three ways to detect
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases
 Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector. WIMP Search. Mani Tripathi, INPAC Meeting. Berkeley, May 5, 2007
 LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector WIMP Search Mani Tripathi INPAC Meeting Berkeley, New Collaboration Groups formerly in XENON10: Case Western, Brown, Livermore Natl. Lab (major fraction of the US
LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector WIMP Search Mani Tripathi INPAC Meeting Berkeley, New Collaboration Groups formerly in XENON10: Case Western, Brown, Livermore Natl. Lab (major fraction of the US
Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids
 Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Recontres de Moriond 2012, Cosmology Session, La Thuile, March 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Recontres de Moriond 2012, Cosmology Session, La Thuile, March 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
The XENON1T experiment
 The XENON1T experiment Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science For the XENON collaboration 1 The XENON1T experiment Direct detection with xenon The XENON project XENON1T/nT 2 Quick introduction and
The XENON1T experiment Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science For the XENON collaboration 1 The XENON1T experiment Direct detection with xenon The XENON project XENON1T/nT 2 Quick introduction and
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Dark Matter Search. Dark Matter
 Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Matter in the Universe - Composition ν too light => most of the is cold Ωmat = 0.27 0.04 u d of so far unknown weakly interacting, massive particles WIMPs normal baryonic
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Matter in the Universe - Composition ν too light => most of the is cold Ωmat = 0.27 0.04 u d of so far unknown weakly interacting, massive particles WIMPs normal baryonic
Direct Dark Matter Searches
 Direct Dark Matter Searches Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich What is? Invisibles12, GGI Florence, June 27th 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Direct Dark Matter Searches Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich What is? Invisibles12, GGI Florence, June 27th 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Status of DM Direct Detection. Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science
 Status of DM Direct Detection Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science DM evidence on one slide Thermal freeze out of dark matter in the standard cosmological model Weakly Interacting Massive Particles
Status of DM Direct Detection Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science DM evidence on one slide Thermal freeze out of dark matter in the standard cosmological model Weakly Interacting Massive Particles
Shedding Light on Dark Matter from Deep Underground with XENON. Kaixuan Ni (Columbia)
 Shedding Light on Dark Matter from Deep Underground with XENON Kaixuan Ni (Columbia) University of Maryland, 11-25-2008 A well-known mystery for astronomers Fritz Zwicky, The Astrophysical Journal, 85
Shedding Light on Dark Matter from Deep Underground with XENON Kaixuan Ni (Columbia) University of Maryland, 11-25-2008 A well-known mystery for astronomers Fritz Zwicky, The Astrophysical Journal, 85
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
The Direct Search for Dark Matter
 picture: Thomas Tuchan The Direct Search for Dark Matter with special emphasis on the XENON project Rafael F. Lang Purdue University rafael@purdue.edu IPMU Tokyo, March 8, 2013 1 baryon fraction Dark Matter
picture: Thomas Tuchan The Direct Search for Dark Matter with special emphasis on the XENON project Rafael F. Lang Purdue University rafael@purdue.edu IPMU Tokyo, March 8, 2013 1 baryon fraction Dark Matter
Dark Matter -- Astrophysical Evidences and Terrestrial Searches
 Dark Matter -- Astrophysical Evidences and Terrestrial Searches Klaus Eitel, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, KCETA, IK KIT University of the State of Baden-Württemberg and National Large-scale Research
Dark Matter -- Astrophysical Evidences and Terrestrial Searches Klaus Eitel, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, KCETA, IK KIT University of the State of Baden-Württemberg and National Large-scale Research
Direct detection: results from liquid noble-gas experiments
 Direct detection: results from liquid noble-gas experiments Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@mpi-hd.mpg.de DM@LHC Heidelberg, April 5th, 2018 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (MPIK) Liquid noble gases Heidelberg,
Direct detection: results from liquid noble-gas experiments Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@mpi-hd.mpg.de DM@LHC Heidelberg, April 5th, 2018 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (MPIK) Liquid noble gases Heidelberg,
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter
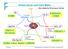 Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
Dark Matter Searches. Marijke Haffke University of Zürich
 University of Zürich Structure Ι. Introduction - Dark Matter - WIMPs Ι Ι. ΙΙΙ. ΙV. V. Detection - Philosophy & Methods - Direct Detection Detectors - Scintillators - Bolometer - Liquid Noble Gas Detectors
University of Zürich Structure Ι. Introduction - Dark Matter - WIMPs Ι Ι. ΙΙΙ. ΙV. V. Detection - Philosophy & Methods - Direct Detection Detectors - Scintillators - Bolometer - Liquid Noble Gas Detectors
XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector
 XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector Katsuki Hiraide, the university of Tokyo for the XMASS Collaboration October 3 rd, 2016 IPRD16@Siena, Italy 1 XMASS project XMASS: a multi purpose experiment
XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector Katsuki Hiraide, the university of Tokyo for the XMASS Collaboration October 3 rd, 2016 IPRD16@Siena, Italy 1 XMASS project XMASS: a multi purpose experiment
Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST
 Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST Marco Vignati 24 Ottobre 2011 0νDBD in Theory Nuclear process: (A,Z) (A,Z+2) + 2 e - Can only happen if lepton number is not conserved. The decay probability
Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST Marco Vignati 24 Ottobre 2011 0νDBD in Theory Nuclear process: (A,Z) (A,Z+2) + 2 e - Can only happen if lepton number is not conserved. The decay probability
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases
 Universität Zürich E-mail: marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Liquid noble gases have proven a great potential as detector medium for dark matter searches. Particles interacting in these media produce ionized and
Universität Zürich E-mail: marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Liquid noble gases have proven a great potential as detector medium for dark matter searches. Particles interacting in these media produce ionized and
A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results
 A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results I where we stand II recent results (CDMS, XENON10, etc) III DAMA results IV a bit about modulation V issues with DAMA results VI what to look for
A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results I where we stand II recent results (CDMS, XENON10, etc) III DAMA results IV a bit about modulation V issues with DAMA results VI what to look for
WIMP Dark Matter Search with XENON and DARWIN
 WIMP Dark Matter Search with XENON and DARWIN Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany XENON100 Rice University Houston, TX, USA http://xenon.physics.rice.edu 6th Patras Workshop Zurich July 7, 2010
WIMP Dark Matter Search with XENON and DARWIN Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany XENON100 Rice University Houston, TX, USA http://xenon.physics.rice.edu 6th Patras Workshop Zurich July 7, 2010
Looking for WIMPs A Review
 Looking for WIMPs A Review Beatriz E. Burrola Gabilondo There is currently a race to find out what dark matter actually is. Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs) are a strong candidate for dark
Looking for WIMPs A Review Beatriz E. Burrola Gabilondo There is currently a race to find out what dark matter actually is. Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs) are a strong candidate for dark
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter
 Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
Dark Matter Detection with XENON100 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future
 Dark Matter Detection with XENON0 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future http://xenon.astro.columbia.edu Kaixuan Ni Columbia University TeV Particle Astrophysics IHEP, Beijing, Sep.4-8, 008 The Challenges
Dark Matter Detection with XENON0 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future http://xenon.astro.columbia.edu Kaixuan Ni Columbia University TeV Particle Astrophysics IHEP, Beijing, Sep.4-8, 008 The Challenges
Dark Matter Search with XENON
 Dark Matter Search with XENON Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Universität Mainz, Seminar, May 2, 2012 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ 2 Baryonic Matter Dark Matter? Dark Energy????
Dark Matter Search with XENON Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Universität Mainz, Seminar, May 2, 2012 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ 2 Baryonic Matter Dark Matter? Dark Energy????
Direct Detection in the next five years: Experimental challenges and Phonon Mediated Detectors
 Direct Detection in the next five years: Experimental challenges and Phonon Mediated Detectors Complementarity between Dark Matter Searches & Collider Experiments Miniworkshop before SUSY06 at Irvine -
Direct Detection in the next five years: Experimental challenges and Phonon Mediated Detectors Complementarity between Dark Matter Searches & Collider Experiments Miniworkshop before SUSY06 at Irvine -
Chapter 12. Dark Matter
 Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal 128 Chapter 12 Dark Matter Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal Baryonic Dark Matter Brightness & Rotation Curve of NGC3198 Brightness Rotation Curve measured expected
Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal 128 Chapter 12 Dark Matter Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal Baryonic Dark Matter Brightness & Rotation Curve of NGC3198 Brightness Rotation Curve measured expected
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe physics beyond the standard model how to detect Dark Matter particles Josef Jochum Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen Kepler
Direct Search for Dark Matter Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe physics beyond the standard model how to detect Dark Matter particles Josef Jochum Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen Kepler
Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment. 1 Abstract. 2 Introduction
 Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory Columbia University New York, New York 10027 1 Abstract Observations on all fronts strongly
Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory Columbia University New York, New York 10027 1 Abstract Observations on all fronts strongly
Light Dark Matter and XENON100. For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University
 Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
DARWIN: dark matter WIMP search with noble liquids
 DARWIN: dark matter WIMP search with noble liquids Physik Institut, University of Zurich E-mail: laura.baudis@physik.uzh.ch DARWIN (DARk matter WImp search with Noble liquids) is an R&D and design study
DARWIN: dark matter WIMP search with noble liquids Physik Institut, University of Zurich E-mail: laura.baudis@physik.uzh.ch DARWIN (DARk matter WImp search with Noble liquids) is an R&D and design study
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 24 Jun 2004
 LATEST RESULTS OF THE EDELWEISS EXPERIMENT arxiv:astro-ph/46537v 24 Jun 24 V. SANGLARD for the Edelweiss collaboration Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, 4 rue Enrico Fermi, 69622 Villeurbanne, France
LATEST RESULTS OF THE EDELWEISS EXPERIMENT arxiv:astro-ph/46537v 24 Jun 24 V. SANGLARD for the Edelweiss collaboration Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, 4 rue Enrico Fermi, 69622 Villeurbanne, France
Dark Matter and the XENON Experiment
 Dark Matter and the XENON Experiment Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Lunch Seminar, Weizmann Institute of Science, November 4th, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ 2 3 95%
Dark Matter and the XENON Experiment Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Lunch Seminar, Weizmann Institute of Science, November 4th, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ 2 3 95%
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search. Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration
 SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX
 Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX we are a collaboration of 50+ scientists, please see http://lux.brown.edu for more information Peter Sorensen Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory DNP October
Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX we are a collaboration of 50+ scientists, please see http://lux.brown.edu for more information Peter Sorensen Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory DNP October
Direct dark matter search with XMASS. K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration
 Direct dark matter search with XMASS K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration Outline XMASS experiment. Single phase liquid xenon detector Many targets were searched with XMASS. WIMP search fiducialized volume.
Direct dark matter search with XMASS K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration Outline XMASS experiment. Single phase liquid xenon detector Many targets were searched with XMASS. WIMP search fiducialized volume.
Luca Grandi.
 Luca Grandi http://warp.pv.infn.it idm2004 - September 2004 Wimp Argon Programme Collaboration R. Brunetti, E. Calligarich, M. Cambiaghi, C. De Vecchi, R. Dolfini, L. Grandi, A. Menegolli, C. Montanari,
Luca Grandi http://warp.pv.infn.it idm2004 - September 2004 Wimp Argon Programme Collaboration R. Brunetti, E. Calligarich, M. Cambiaghi, C. De Vecchi, R. Dolfini, L. Grandi, A. Menegolli, C. Montanari,
Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments
 Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments Jingke Xu Princeton University June 7 th, 2013 1 Evidences for Dark Matter Rotation Curve Gravitational Lensing CMB Power Spectrum
Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments Jingke Xu Princeton University June 7 th, 2013 1 Evidences for Dark Matter Rotation Curve Gravitational Lensing CMB Power Spectrum
Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search
 Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search 1 LUX Goal: Direct Detection of Dark Matter WMAP 5-year data (2008) gives matter densities (Ω) based on best fit to Λ-CDM cosmological model: Ω
Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search 1 LUX Goal: Direct Detection of Dark Matter WMAP 5-year data (2008) gives matter densities (Ω) based on best fit to Λ-CDM cosmological model: Ω
Detectors for astroparticle physics
 Detectors for astroparticle physics Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Universität Zürich Kern und Teilchenphysik II, Zürich 07.05.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (UZH) Detectors for astroparticle
Detectors for astroparticle physics Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Universität Zürich Kern und Teilchenphysik II, Zürich 07.05.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (UZH) Detectors for astroparticle
Darkside-50, DarkSide-20k and the Global Collaboration to reach the Neutrino Floor with liquid argon
 Darkside-5, DarkSide-2k and the Global Collaboration to reach the Neutrino Floor with liquid argon Cristiano Galbiati Gran Sasso Science Institute and Princeton University The quest for dark matter with
Darkside-5, DarkSide-2k and the Global Collaboration to reach the Neutrino Floor with liquid argon Cristiano Galbiati Gran Sasso Science Institute and Princeton University The quest for dark matter with
DARWIN. Marc Schumann. U Freiburg PATRAS 2017 Thessaloniki, May 19,
 DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg PATRAS 2017 Thessaloniki, May 19, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Dark Matter Searches: Status spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions
DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg PATRAS 2017 Thessaloniki, May 19, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Dark Matter Searches: Status spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions
 Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
Recent results and status of the XENON program
 on behalf of the XENON Collaboration Subatech, Ecole des Mines de Nantes, CNRS/In2p3, Université de Nantes, Nantes, France E-mail: julien.masbou@subatech.in2p3.fr The XENON program aims at the direct detection
on behalf of the XENON Collaboration Subatech, Ecole des Mines de Nantes, CNRS/In2p3, Université de Nantes, Nantes, France E-mail: julien.masbou@subatech.in2p3.fr The XENON program aims at the direct detection
LARGE UNDERGROUND XENON
 LARGE UNDERGROUND XENON Cláudio Silva (LIP Coimbra) On behalf of the LUX Collaboration IDPASC Dark Matter Workshop 17 December 2011 1 THE LUX COLLABORATION Collaboration was formed in 2007 and fully funded
LARGE UNDERGROUND XENON Cláudio Silva (LIP Coimbra) On behalf of the LUX Collaboration IDPASC Dark Matter Workshop 17 December 2011 1 THE LUX COLLABORATION Collaboration was formed in 2007 and fully funded
Status of the EDELWEISS Dark Matter search
 Status of the EDELWEISS Dark Matter search KIT Institute Centre for Particle Nuclear and Physics Astroparticle Physics KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Research Center of
Status of the EDELWEISS Dark Matter search KIT Institute Centre for Particle Nuclear and Physics Astroparticle Physics KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Research Center of
Paolo Agnes Laboratoire APC, Université Paris 7 on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration. Dark Matter 2016 UCLA 17th - 19th February 2016
 Paolo Agnes Laboratoire APC, Université Paris 7 on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration Dark Matter 2016 UCLA 17th - 19th February 2016 The DarkSide program 2 Double Phase Liquid Argon TPC, a staged approach:
Paolo Agnes Laboratoire APC, Université Paris 7 on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration Dark Matter 2016 UCLA 17th - 19th February 2016 The DarkSide program 2 Double Phase Liquid Argon TPC, a staged approach:
The XMASS experiment. Y. Kishimoto for the XMASS collaboration March 24 th, 2014 Recontres de Moriond, Cosmology
 The XMASS experiment Y. Kishimoto for the XMASS collaboration March 24 th, 2014 Recontres de Moriond, Cosmology Contents Introduction to the XMASS Results from XMASS commissioning run Light mass WIMPs
The XMASS experiment Y. Kishimoto for the XMASS collaboration March 24 th, 2014 Recontres de Moriond, Cosmology Contents Introduction to the XMASS Results from XMASS commissioning run Light mass WIMPs
Dark matter search with the SABRE experiment
 Dark matter search with the SABRE experiment Giulia D Imperio* for the SABRE collaboration *INFN Roma 1 25-07-2017 TAUP 2017 Sudbury, Canada 1 Dark matter detection through annual modulation WIMP is one
Dark matter search with the SABRE experiment Giulia D Imperio* for the SABRE collaboration *INFN Roma 1 25-07-2017 TAUP 2017 Sudbury, Canada 1 Dark matter detection through annual modulation WIMP is one
DARK MATTER SEARCHES AT CANFRANC: ANAIS AND ROSEBUD: an update INTRODUCTION AND EXPERIMENTAL GOALS SUMMARY OF RECENT ACHIEVEMENTS AND EFFORTS
 DARK MATTER SEARCHES AT CANFRANC: ANAIS AND ROSEBUD: an update María Luisa Sarsa (Universidad de Zaragoza) On behalf of ANAIS & ROSEBUD Collaborations OUTLINE ANAIS INTRODUCTION AND EXPERIMENTAL GOALS
DARK MATTER SEARCHES AT CANFRANC: ANAIS AND ROSEBUD: an update María Luisa Sarsa (Universidad de Zaragoza) On behalf of ANAIS & ROSEBUD Collaborations OUTLINE ANAIS INTRODUCTION AND EXPERIMENTAL GOALS
Background and sensitivity predictions for XENON1T
 Background and sensitivity predictions for XENON1T Marco Selvi INFN - Sezione di Bologna (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Feb 19 th 016, UCLA Dark Matter 016 1 Outline Description of the detector;
Background and sensitivity predictions for XENON1T Marco Selvi INFN - Sezione di Bologna (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Feb 19 th 016, UCLA Dark Matter 016 1 Outline Description of the detector;
Status and Prospects of China JinPing Deep Underground Laboratory (CJPL) and China Dark Matter EXperiment (CDEX)
 Status and Prospects of China JinPing Deep Underground Laboratory (CJPL) and China Dark Matter EXperiment (CDEX) Qian Yue Department of Engineering Physics TsingHua University May 13, 2010 Outline: Survey
Status and Prospects of China JinPing Deep Underground Laboratory (CJPL) and China Dark Matter EXperiment (CDEX) Qian Yue Department of Engineering Physics TsingHua University May 13, 2010 Outline: Survey
Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors. David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011
 Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011 1 Summary LUX screening program limits background contributions
Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011 1 Summary LUX screening program limits background contributions
Introduction to Class and Dark Matter
 Introduction to Class and Dark Matter Prof. Luke A. Corwin PHYS 792 South Dakota School of Mines & Technology Jan. 14, 2014 (W1-1) L. Corwin, PHYS 792 (SDSM&T) Introduction Jan. 14, 2014 (W1-1) 1 / 22
Introduction to Class and Dark Matter Prof. Luke A. Corwin PHYS 792 South Dakota School of Mines & Technology Jan. 14, 2014 (W1-1) L. Corwin, PHYS 792 (SDSM&T) Introduction Jan. 14, 2014 (W1-1) 1 / 22
Nuclear Recoil Techniques for the Detection of Dark Matter
 Nuclear Recoil Techniques for the Detection of Dark Matter Uwe Oberlack Rice University Houston, TX The Cosmic Recipe Astrophysical observations reveal a dark universe. Cosmic Microwave Background. Geometry
Nuclear Recoil Techniques for the Detection of Dark Matter Uwe Oberlack Rice University Houston, TX The Cosmic Recipe Astrophysical observations reveal a dark universe. Cosmic Microwave Background. Geometry
Latest Results on Direct Detection of Dark Matter WIMPs - CDMS & SuperCDMS
 Latest Results on Direct Detection of Dark Matter WIMPs - CDMS & SuperCDMS TeV 2006, Madison - August 30, 2006 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS Summary of current status of Direct
Latest Results on Direct Detection of Dark Matter WIMPs - CDMS & SuperCDMS TeV 2006, Madison - August 30, 2006 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS Summary of current status of Direct
China JinPing underground Laboratory (CJPL) and China Darkmatter Experiment (CDEX) Qian Yue Tsinghua University Mar.24, 2011
 China JinPing underground Laboratory (CJPL) and China Darkmatter Experiment (CDEX) Qian Yue Tsinghua University Mar.24, 2011 Outline Survey of Low background Experiment in China The recent status of CJPL
China JinPing underground Laboratory (CJPL) and China Darkmatter Experiment (CDEX) Qian Yue Tsinghua University Mar.24, 2011 Outline Survey of Low background Experiment in China The recent status of CJPL
DARWIN. Marc Schumann. U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15,
 DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017
DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017
Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search
 Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search Federica Petricca on behalf of the CRESST collaboration: Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München TU München University of Oxford Universität
Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search Federica Petricca on behalf of the CRESST collaboration: Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München TU München University of Oxford Universität
SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS
 SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS David G. Cerdeño Institute for Theoretical Physics Universidad Autónoma de Madrid for the SuperCDMS Collaboration Hints for low-mass WIMPs in direct detection
SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS David G. Cerdeño Institute for Theoretical Physics Universidad Autónoma de Madrid for the SuperCDMS Collaboration Hints for low-mass WIMPs in direct detection
Low Background Experiments and Material Assay. Tessa Johnson NSSC Summer School July 2016
 Low Background Experiments and Material Assay Tessa Johnson NSSC Summer School July 2016 Outline How do we detect particles? Some interesting questions relating to particle physics How can particle detection
Low Background Experiments and Material Assay Tessa Johnson NSSC Summer School July 2016 Outline How do we detect particles? Some interesting questions relating to particle physics How can particle detection
DarkSide-50: performance and results from the first atmospheric argon run
 DarkSide-50: performance and results from the first atmospheric argon run Yann Guardincerri on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration August 27th, 2014 1 / 21 DarkSide Direct detection search for WIMP dark
DarkSide-50: performance and results from the first atmospheric argon run Yann Guardincerri on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration August 27th, 2014 1 / 21 DarkSide Direct detection search for WIMP dark
=> Ωmatter >> Ωbaryon
 Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Cryogenic Detectors CRESST Project Cosmic Microwave Background Matter-Density Ωmatter Anisotropy: Angular scale => geometry, Ωtot Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Cryogenic Detectors CRESST Project Cosmic Microwave Background Matter-Density Ωmatter Anisotropy: Angular scale => geometry, Ωtot Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe
New Physics Results from DarkSide-50. Masayuki Wada Princeton University on behalf of the DarkSide-50 Collaboration Feb
 New Physics Results from DarkSide5 Masayuki Wada Princeton University on behalf of the DarkSide5 Collaboration Feb. 8 Lake Louise Winter Institute 8 DETECTOR DARKSIDE 5 Radonfree (Rn levels < 5 mbq/m )
New Physics Results from DarkSide5 Masayuki Wada Princeton University on behalf of the DarkSide5 Collaboration Feb. 8 Lake Louise Winter Institute 8 DETECTOR DARKSIDE 5 Radonfree (Rn levels < 5 mbq/m )
DARK MATTER SEARCH AT BOULBY MINE
 DARK MATTER SEARCH AT BOULBY MINE R. LUSCHER on behalf of the Boulby Dark Matter Collaboration (RAL, Imperial College, Sheffield, UCLA, Texas A&M, Pisa, ITEP, Coimbra, Temple and Occidental) Rutherford
DARK MATTER SEARCH AT BOULBY MINE R. LUSCHER on behalf of the Boulby Dark Matter Collaboration (RAL, Imperial College, Sheffield, UCLA, Texas A&M, Pisa, ITEP, Coimbra, Temple and Occidental) Rutherford
Dark Matter, Low-Background Physics
 Dark Matter, Low-Background Physics RHUL Jocelyn Monroe Nov. 6, 2012 1. Evidence (Astrophysical Detection) 2. Candidates, Properties 3. Direct Detection (Particle Physics) 1 st Observation: 1930s Fritz
Dark Matter, Low-Background Physics RHUL Jocelyn Monroe Nov. 6, 2012 1. Evidence (Astrophysical Detection) 2. Candidates, Properties 3. Direct Detection (Particle Physics) 1 st Observation: 1930s Fritz
Direct Detection Lecture 2: Current Results
 Direct Detection Lecture 2: Current Results Outline I. Leading spin-independent measurements II. Leading spin-depending measurements III. Low Mass WIMP searches IV. Discussion on Calibration 43 Current
Direct Detection Lecture 2: Current Results Outline I. Leading spin-independent measurements II. Leading spin-depending measurements III. Low Mass WIMP searches IV. Discussion on Calibration 43 Current
Direct Detection of Dark Matter. Lauren Hsu Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics TRISEP Summer School, June 10, 2014
 Direct Detection of Dark Matter Lauren Hsu Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics TRISEP Summer School, June 10, 2014 Direct Detection of Dark Matter Lecture 1 How to detect dark matter Lecture 2 Review
Direct Detection of Dark Matter Lauren Hsu Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics TRISEP Summer School, June 10, 2014 Direct Detection of Dark Matter Lecture 1 How to detect dark matter Lecture 2 Review
Axion search with Dark Matter detector
 Axion search with Dark Matter detector Paolo Beltrame Durham IPPP, 14th March 2016 1 Direct DM search Dark matter (DM) Milky Way s halo => flux on Earth ~ 10 5 cm -2 s -1 ρχ ~ 0.3 GeV/cm 3 and 100 GeV/c
Axion search with Dark Matter detector Paolo Beltrame Durham IPPP, 14th March 2016 1 Direct DM search Dark matter (DM) Milky Way s halo => flux on Earth ~ 10 5 cm -2 s -1 ρχ ~ 0.3 GeV/cm 3 and 100 GeV/c
DarkSide-20k and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program. Giuliana Fiorillo Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli
 DarkSide-20k and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program Giuliana Fiorillo Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli UCLA DM Conference Los Angeles February 23, 2018 The case for DarkSide-20k
DarkSide-20k and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program Giuliana Fiorillo Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli UCLA DM Conference Los Angeles February 23, 2018 The case for DarkSide-20k
Latest results of EDELWEISS II
 Latest results of EDELWEISS II Ana Torrentó CEA/IRFU/SPP Saclay Rencontres de Moriond 2011 «EW and Unified Theories» WIMP search Motivated by the «WIMP miracle» Very small rate of WIMPnucleus scattering
Latest results of EDELWEISS II Ana Torrentó CEA/IRFU/SPP Saclay Rencontres de Moriond 2011 «EW and Unified Theories» WIMP search Motivated by the «WIMP miracle» Very small rate of WIMPnucleus scattering
WIMP Direct Detection: an outlook
 WIMP Direct Detection: an outlook Particle Cosmology Non baryonic dark matter WIMPs: a generic consequence of new physics at TeV scale 1 Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute
WIMP Direct Detection: an outlook Particle Cosmology Non baryonic dark matter WIMPs: a generic consequence of new physics at TeV scale 1 Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute
The Search for Dark Matter. Jim Musser
 The Search for Dark Matter Jim Musser Composition of the Universe Dark Matter There is an emerging consensus that the Universe is made of of roughly 70% Dark Energy, (see Stu s talk), 25% Dark Matter,
The Search for Dark Matter Jim Musser Composition of the Universe Dark Matter There is an emerging consensus that the Universe is made of of roughly 70% Dark Energy, (see Stu s talk), 25% Dark Matter,
The next generation dark matter hunter: XENON1T status and perspective
 The next generation dark matter hunter: XENON1T status and perspective A. Rizzo a on behalf of the XENON Collaboration Department of Astrophysics, Columbia University in the City of New York, USA Abstract.
The next generation dark matter hunter: XENON1T status and perspective A. Rizzo a on behalf of the XENON Collaboration Department of Astrophysics, Columbia University in the City of New York, USA Abstract.
Prospects for WIMP Dark Matter Direct Searches with XENON1T and DARWIN
 Via Lactea 2 (2008) Prospects for WIMP Dark Matter Direct Searches with XENON1T and DARWIN NASA/WMAP 8th Patras Workshop on Axions, WIMPs, and WISPs Chicago, 21-July-2012 http://xenon.physik.uni-mainz.de
Via Lactea 2 (2008) Prospects for WIMP Dark Matter Direct Searches with XENON1T and DARWIN NASA/WMAP 8th Patras Workshop on Axions, WIMPs, and WISPs Chicago, 21-July-2012 http://xenon.physik.uni-mainz.de
Recent results from PandaX- II and status of PandaX-4T
 Recent results from PandaX- II and status of PandaX-4T Jingkai Xia (Shanghai Jiao Tong University) On behalf of PandaX Collaboration August 2-5, Mini-Workshop@SJTU 2018/8/4 1 Outline Dark Matter direct
Recent results from PandaX- II and status of PandaX-4T Jingkai Xia (Shanghai Jiao Tong University) On behalf of PandaX Collaboration August 2-5, Mini-Workshop@SJTU 2018/8/4 1 Outline Dark Matter direct
DarkSide new results and prospects
 DarkSide new results and prospects Stefano Davini - INFN Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration La Thuile, March 20, 2018 The DarkSide WIMP-argon program at LNGS 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
DarkSide new results and prospects Stefano Davini - INFN Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration La Thuile, March 20, 2018 The DarkSide WIMP-argon program at LNGS 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
Dark Matter. and TPC Technologies
 Dark Matter and TPC Technologies The Physics Case for WIMPs Status of the Field:event by event discrimination Elements of a roadmap Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute for
Dark Matter and TPC Technologies The Physics Case for WIMPs Status of the Field:event by event discrimination Elements of a roadmap Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute for
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 15 Feb 2005
 The XENON Dark Matter Experiment Elena Aprile (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory, Columbia University, New York, New York 10027 age@astro.columbia.edu
The XENON Dark Matter Experiment Elena Aprile (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory, Columbia University, New York, New York 10027 age@astro.columbia.edu
The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III
 The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III Adam Cox Karlsruhe Institute for Technology (KIT) on behalf of the EDELWEISS Collaboration CEA, Saclay (IRFU and IRAMIS) IPNL (CNRS/IN2P3 and Université de
The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III Adam Cox Karlsruhe Institute for Technology (KIT) on behalf of the EDELWEISS Collaboration CEA, Saclay (IRFU and IRAMIS) IPNL (CNRS/IN2P3 and Université de
Direct Dark Matter and Axion Detection with CUORE
 Direct Dark Matter and Axion Detection with CUORE Marco Vignati University of Rome La Sapienza & INFN Rome on behalf of the CUORE collaboration Panic 11, July 5, MIT 988 TeO crystals Ton scale bolometric
Direct Dark Matter and Axion Detection with CUORE Marco Vignati University of Rome La Sapienza & INFN Rome on behalf of the CUORE collaboration Panic 11, July 5, MIT 988 TeO crystals Ton scale bolometric
Overview of Direct Detection Dark Matter Experiments
 Overview of Direct Detection Dark Matter Experiments Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX, USA E-mail: cooley@physics.smu.edu The past year has yielded several new results from the direct detection
Overview of Direct Detection Dark Matter Experiments Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX, USA E-mail: cooley@physics.smu.edu The past year has yielded several new results from the direct detection
Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background
 Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background A cryogenic detector for Dark Matter with heat (phonon) readout and light (scintillation) readout MPI, TUM, Oxford, Tübingen, LNGS What we re looking for: M W imp =
Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background A cryogenic detector for Dark Matter with heat (phonon) readout and light (scintillation) readout MPI, TUM, Oxford, Tübingen, LNGS What we re looking for: M W imp =
DarkSide. Bianca Bottino Università di Genova and INFN Sezione di Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration 1
 DarkSide Bianca Bottino Università di Genova and INFN Sezione di Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration 1 DARKSIDE MAIN FEATURES Dark Matter direct detection WIMP induced nuclear recoils Double
DarkSide Bianca Bottino Università di Genova and INFN Sezione di Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration 1 DARKSIDE MAIN FEATURES Dark Matter direct detection WIMP induced nuclear recoils Double
XENONNT AND BEYOND. Hardy Simgen. WIN 2015 MPIK Heidelberg. Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg
 XENONNT AND BEYOND Hardy Simgen Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg WIN 2015 MPIK Heidelberg THE XENON PROGRAM FOR DIRECT DARK MATTER SEARCH 1 THE PRESENT: XENON1T! LXe TPC under construction
XENONNT AND BEYOND Hardy Simgen Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg WIN 2015 MPIK Heidelberg THE XENON PROGRAM FOR DIRECT DARK MATTER SEARCH 1 THE PRESENT: XENON1T! LXe TPC under construction
Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project
 Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory/Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Menlo Park, CA 94025,
Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory/Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Menlo Park, CA 94025,
After LUX: The LZ Program. David Malling, Simon Fiorucci Brown University APS DPF Conference August 10, 2011
 After LUX: The LZ Program David Malling, Simon Fiorucci Brown University APS DPF Conference August 10, 2011 The LZ Program LZ LUX-ZEPLIN LUX (14 U.S. institutions) + new collaborators from ZEPLIN, other
After LUX: The LZ Program David Malling, Simon Fiorucci Brown University APS DPF Conference August 10, 2011 The LZ Program LZ LUX-ZEPLIN LUX (14 U.S. institutions) + new collaborators from ZEPLIN, other
The Neutron/WIMP Acceptance In XENON100
 The Neutron/WIMP Acceptance In XENON100 Symmetries and Fundamental Interactions 01 05 September 2014 Chiemsee Fraueninsel Boris Bauermeister on behalf of the XENON collaboration Boris.Bauermeister@uni-mainz.de
The Neutron/WIMP Acceptance In XENON100 Symmetries and Fundamental Interactions 01 05 September 2014 Chiemsee Fraueninsel Boris Bauermeister on behalf of the XENON collaboration Boris.Bauermeister@uni-mainz.de
Background simulations and shielding calculations
 Background simulations and shielding calculations Vitaly A. Kudryavtsev University of Sheffield Contributions from many others Outline Note 1: results are relevant to many experiments and techniques (mainly
Background simulations and shielding calculations Vitaly A. Kudryavtsev University of Sheffield Contributions from many others Outline Note 1: results are relevant to many experiments and techniques (mainly
PoS(EPS-HEP2017)074. Darkside Status and Prospects. Charles Jeff Martoff Temple University
 Temple University E-mail: cmartoff@gmail.com The DarkSide Dark Matter Search Program is a direct-detection search for dark matter using a Liquid Argon Time Projection Chamber. The detector is designed
Temple University E-mail: cmartoff@gmail.com The DarkSide Dark Matter Search Program is a direct-detection search for dark matter using a Liquid Argon Time Projection Chamber. The detector is designed
The XENON Dark Matter Project: Status of the XENON100 Phase. Elena Aprile Columbia University
 The XENON Dark Matter Project: Status of the XENON100 Phase Elena Aprile Columbia University 8th UCLA Symposium Marina del Rey, Feb 22, 2008 The XENON Dark Matter Phased Program Detect WIMPS through their
The XENON Dark Matter Project: Status of the XENON100 Phase Elena Aprile Columbia University 8th UCLA Symposium Marina del Rey, Feb 22, 2008 The XENON Dark Matter Phased Program Detect WIMPS through their
Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches
 Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches Tarek Saab University of Florida Tali Figueroa Northwestern University Calibration of Low Energy Particle Detectors
Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches Tarek Saab University of Florida Tali Figueroa Northwestern University Calibration of Low Energy Particle Detectors
Darkside and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program
 Darkside and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program Giuliana Fiorillo Università di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli PM2018-14th Pisa Meeting on Advanced Detectors DM direct detection WIMP χ Low mass
Darkside and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program Giuliana Fiorillo Università di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli PM2018-14th Pisa Meeting on Advanced Detectors DM direct detection WIMP χ Low mass
Search for Dark Matter with Liquid Argon and Pulse Shape Discrimination
 Search for Dark Matter with Liquid Argon and Pulse Shape Discrimination Results from DEAP-1 and Status of DEAP-3600 Pierre Gorel for the DEAP collaboration University of Alberta Dark matter Experiment
Search for Dark Matter with Liquid Argon and Pulse Shape Discrimination Results from DEAP-1 and Status of DEAP-3600 Pierre Gorel for the DEAP collaboration University of Alberta Dark matter Experiment
Direct Dark Matter Searches. General Overview LUX-ZEPLIN Hans Kraus, Oxford
 Direct Dark Matter Searches General Overview LUX-ZEPLIN Hans Kraus, Oxford How to detect dark matter 1. Direct detection (scattering XS) Nuclear (atomic) recoils from elastic scattering A- & J-dependence,
Direct Dark Matter Searches General Overview LUX-ZEPLIN Hans Kraus, Oxford How to detect dark matter 1. Direct detection (scattering XS) Nuclear (atomic) recoils from elastic scattering A- & J-dependence,
No combined analysis of all experiments available
 Compatibility between DAMA-CDMS CDMS-Edelweiss-Xenon10 - KIMS? No combined analysis of all experiments available However, some trivial considerations: * for m χ 25 GeV capture on DAMA is dominated by the
Compatibility between DAMA-CDMS CDMS-Edelweiss-Xenon10 - KIMS? No combined analysis of all experiments available However, some trivial considerations: * for m χ 25 GeV capture on DAMA is dominated by the
DARWIN. Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich. Aspera Technology Forum 2010, October 21-22, 2010
 21-22 DARWIN Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Aspera Technology Forum 2010, October 21-22, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ Dark Matter: Evidence & Detection NASA/WMAP
21-22 DARWIN Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Aspera Technology Forum 2010, October 21-22, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ Dark Matter: Evidence & Detection NASA/WMAP
PANDA-X A New Detector for Dark Matter Search. Karl Giboni Shanghai Jiao Tong University
 PANDA-X A New Detector for Dark Matter Search Karl Giboni Shanghai Jiao Tong University Seminar at KEK, Tsukuba Japan 3 February, 2011 Jin Ping Laboratory Newly constructed deep underground lab In the
PANDA-X A New Detector for Dark Matter Search Karl Giboni Shanghai Jiao Tong University Seminar at KEK, Tsukuba Japan 3 February, 2011 Jin Ping Laboratory Newly constructed deep underground lab In the
