New Physics Results from DarkSide-50. Masayuki Wada Princeton University on behalf of the DarkSide-50 Collaboration Feb
|
|
|
- Patrick Jack McDonald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 New Physics Results from DarkSide5 Masayuki Wada Princeton University on behalf of the DarkSide5 Collaboration Feb. 8 Lake Louise Winter Institute 8
2 DETECTOR DARKSIDE 5 Radonfree (Rn levels < 5 mbq/m ) Assembly Clean Room,tonne Water Cherenkov Cosmic Ray Veto tonne Liquid Scintillator Neutron and γ s Veto Veto efficiency > 99.% Inner detector TPC
3 r e DARKSIDE5 THE TIMEPROJECTION CHAMBER (TPC) e e Electron Recoil (ER) acquired charge acquired charge time S Nuclear Recoil (NR) S (S) (S) (S) (S) time S/S ratio and Pulse Shape Discrimination (PSD) WIMPs will generate nuclear recoils (NRs) DM S S n WIMPlike signal! E drift xy position from S light fraction E mult S e e e S z t drift liquid argon (L)
4 DARKSIDE5 PULSE SHAPE DISCRIMINATION M. G. Boulay and A. Hime, Astropart. Phys. 5 (6) 79 4 Electron and nuclear recoils produce different excitation densities in the argon, leading to different ratios of singlet and triplet excitation states τsinglet ~ 7 ns τtriplet ~ 5 ns f9 ~. Electron Recoil (ER) PSD parameter F9: Ratio of detected light in the first 9 ns, compared to the total signal ~ Fraction of singlet states NR band f9 ~.7 Nuclear Recoil (NR) WIMPlike signal! ER band AmBe calibration data
5 A Blind Analysis of 54 livedays of data f S [PE] Blinding box (red outline) shown with 7day data: PR D 9, 8 (6) Goal: design an analysis that will have <. event of background in the tobedesigned search box. (Final box chosen: dashed red) 5
6 Nuclear Recoil BG Events / [5 PE] Surface α decays Energy [MeV] Degraded: under TPB Data Po Rn 8 Po Full energy in L Background rejection: S < 46 Selfvetoing in DS5! Small or no S Long scintillation tail from TPB Neutrons S [PE] n + B α + 7 Li Background rejection: TPC: multiscatter LS Veto n + B α + 7 Li + γ 6 Measured n efficiency with AmC for TPC singlenr:.9964±.4 Cosmogenics: Water Cherenkov Veto Neutrons in data counted
7 Electron Recoil BG S+Cherenkov S + Cherenkov events are Dangerous!! f Energy [kev nr ] Li(p,n) in SCENE 4 AmBe in DarkSide5 Cherenkov light is all in prompt. Move regular scintillation events into NR band S [PE] Background rejection: Underground S fraction in max PMT PSD: f9 = S fraction in first 9 ns Design cut to reduce ER to <.8 event of background 7 Background Est. Survive Surface a decays All. Cuts Cosmogenic n <. Radiogenic n <.5 ER S+Cherenkov.8* Total.9±.4 Goal achieved: open the box!
8 Final Data Set Energy [kev nr ] f % 5% 99% S [PE] 8 arxiv: 8.798
9 9% C.L. Exclusion Limits [cm ] Dark MatterNucleon σ SI [TeV/c ] M χ DarkSide5 (8) PANDAXII (7) XENONT (7) DEAP6 (proj.) LZ (proj.) WARP (7) DarkSide5 (5) DEAP6 (7) DarkSidek (t yr LUX (7) XENONT (proj.) XENONnT (proj.) proj.) DarkSidek (t yr proj.) Future tonne GADMC Detector (ktyr proj.) Future tonne GADMC detector (ktyr proj.) 9 arxiv: 8.798
10 Low Mass Dark Matter Search Ionization Only Analyses arxiv: arxiv:
11 Ionization Measurements Scintillation signal (S): threshold at ~ kevee / 6 kevnr weak sensitivity to low mass WIMPs. Ionization signal (S): threshold <. kevee /.4 kevnr Sensitive to low mass WIMPs!! Use Ionization (S) Only. PMTs have zero dark rate at 88K Gain in the gas region (~7 e/e ) Sensitive to a single extracted electron Radioactivity rate in the detector is remarkably low No need of PSD The electron yield for nuclear recoils increases at low energy kg day] Acceptance Detection Efficiency MC Simulation Fiducialization Trigger efficiency S Identification (f <.5) 9 Ne 4 (Analysis Threshold for six Inner PMTs) S [PE] The efficiency is flat above the analysis threshold of number of electrons >4. S yield from Singleelectrons Center PMT DS5 DATA Getter Off Getter On Fit Ext. e Ext. e 's Detection efficiency: estimated from Data + MC S light distribution pattern among PMTs S waveform including longitudinal diffusion due to drifting Events /[.5 N e S=PE Fiducialization: use volume under 7 central PMTs In DS5, we can detect down to single electron. arxiv: Ne S/η, ηc = PE/e N e One electron creates ± PE at the center PMT Number of electrons
12 Energy scale for ER and NR 7 provides two xrays,.8 kev and.7 kev. Decayed out with 5 day halflife and not remain in the last 5days data set. Good agreement of BR with expected value. Confirmation of the trigger efficiency and acceptance AmBe and AmC neutron sources are used to extract ionization yield at ROI. The difference between other measured points is take as systematics arxiv: day] kg /kev nr ] Events / [.5 N e [e Q y Ionization Yield E [kev nr ] 9 E Xe [kev nr ] Electron Recoil Energy Scale N e Xe Data Xe Model First days Last 5 days Single S(5 d) S + S(5 d) LUX 6 7 ZEPLINIII XENON Manzur et al. XENON 9 Aprile et al. 6 Bezrukov et al. kg day] Events /[N e Data ARIS SCENE AmBe AmC ARIS SCENE Joshi et al. 4 Joshi et al. 4 Cross Calibrated N e ε L/K BR Ratio =. ±. 7.7 kev Nuclear Recoil Energy Scale Xenon 7.8 kev Ne=47.9 Number of electrons gon Reduced Energy NR ionization yield is obtained by fitting AmBe and AmC neutron calibration data
13 Background and WIMP Signals Fit the BG components at high energy in the same dataset (field V/ cm) Events/[ kev] High Energy Spectra 5 4 Th 4 K 8 U low 5 9 U Cryo 6 Co 8 U up 85 Kr DATA Put constraints on the rate of BG at ROI BG events in ROI are modeled with ER Ionization yield and detector response. The excess of events due to tail of the delayed electrons are not modeled as BG. WIMP recoil spectra are modeled with day] kg Energy [kev] WIMP Search ROI E [kevnr 45 ] 4 DM spectra σ χ = M χ =.5 GeV/c M χ =5. GeV/c M χ =. GeV/c cm Extrapolation at low energy, ok within few % E [kevee] Data G4DS MC All Cryostat γrays PMTs γrays Kr day] kg NR Energy Quenching Ionization Detector Response Events / [N e Excess of events due to tail of delayed electrons Those events were also observed in XENON N e Ana. Thres. Mχ 4 GeV arxiv: Ana. Thres. Mχ 4 GeV Number of electrons Events / [kevee
14 8 9% C.L. Exclusion Limits [cm ] 9 No Quenching Fluctuation Dark MatterNucleon σ SI Binomial Fluctuation DarkSide5 DarkSide5 Binomial DarkSide5 No Quenching Fluctuation NEWSG 8 LUX 7 XENONT 7 PICO6 7 PICASSO 7 CRESSTIII 7 CDMSLite 7 PandaXII 6 XENON 6 CDEX 6 DAMIC 6 CRESSTII 5 SuperCDMS 4 COGENT CDMSlite 4 CDMS CRESST DAMA/LIBRA 8 Neutrino Floor 5 M χ 4 [GeV/c ] Profile Likelihood Method is used Uncertainties from both WIMP signals (NR ionization yield, single electron yields) and BG spectrum (rates, ER ionization yield) Due to lack of knowledge about fluctuation at low recoil energy, two cases are considered. Binomial fluctuation for NR energy quenching, ionization, and recombination processes. No Fluctuation for NR energy quenching process. Corresponding to apply hard cut off in quenched energy ~.6 kevnr. 4 arxiv:
15 SubGeV Dark Matter Search arxiv: Light DM scatter off electrons DM signals are also ER. The same measured spectrum as the WIMP search is used. kg day] Events / [N e E [kevee] FDM = 6 DM spectra σ χ = M χ = MeV/c M χ = MeV/c M χ = MeV/c cm Data G4DS MC All Cryostat γrays PMTs γrays Kr N e Two extreme cases of Dark Matter formfactor are considered kg day] E [kevee] FDM /q DM spectra σ χ = M χ = MeV/c M χ = MeV/c M χ = MeV/c cm Data G4DS MC All Cryostat γrays PMTs γrays Kr FDM= heavy mediator FDM /q light mediator Events / [N e N e
16 SubGeV Dark Matter Exclusion Limits arxiv: [cm ] FDM = FDM /q [cm ] Dark MatterElectron σ e 7 8 F DM = DarkSide5 XENON XENON Dark MatterElectron σ e 4 5 F DM /q DarkSide5 XENON XENON 9 M χ [MeV] 6 M χ [MeV] Profile Likelihood Method is used Uncertainties from ER ionization yield and single electron yields are included both DM spectra and BG spectra. Rates uncertainties are included in BG spectra. In the case of a heavy mediator, FDM =, we improve the exclusion limit in the range from MeV/c to 7 MeV/c. 6
17 Summary Blind Analysis is successfully done with 54 livedays of data. Pulse Shape Discrimination (f9) is strong discriminator and necessary for BG free WIMP search at high mass. Liquid gon is also sensitive to low mass WIMPs and subgev DM. Next generation DarkSidek is coming! arxiv: arxiv: arxiv:
18 Thank You! 8
19 Additional Rejection S/S f Energy [kev nr ] % 5% 99%. S/S cut with 5% acceptance + R< cm radial cut S [PE]
20 Energy [kev nr ] SingleScatter Unresolved MultiScatter NR Acceptance Total cut acceptance f 9 NR Acceptance Overall NR Acceptance Events / [. f9] Scintillation + FusedSilica Cherenkov Scintillation + PTFE Cherenkov S [PE] f f Radiogenic Cosmogenic Fission candidate 5% NR acceptance S [PE] Drift time [µs] Reconstructed radius [cm] 8 6 4
21 NR Ionization Yields AmBe neutron source 9 AmC neutron source Events / N e AmBe Data G4DS Fit Single S S + S Events / N e Am C Data G4DS Fit Single S S + S 4 Am C γ N e number of electrons N e number of electrons MC + Ionization model [] fit to NR data from AmBe and AmC. The systematic discrepancy between the extracted and measured ionization yield is taken as systematic uncertainty. /kev nr ] [e Q y E [kev nr ] 9 E Xe [kev nr ] Xe Data Xe Model LUX 6 ZEPLINIII XENON Manzur et al. XENON 9 Aprile et al. 6 Bezrukov et al. Data Xenon ARIS SCENE AmBe AmC ARIS SCENE Joshi et al. 4 Joshi et al. 4 Cross Calibrated ε gon [] F. Bezrukov, F. Kahlhoefer, and M. Lindner, Astropart. Phys. 5, 9 ().
22 Quality +Trgtime +Ssat f 9.9 Entries Integral.9794e e S [PE] Trigtime: the first pulse is within expected trigger time window Ssat: S pulse is not saturated
23 +Npulses f Entries Integral 4.e S [PE] Npulses: number of pulse is or if there is S (echo of S). Most of surface events are gone.
24 +4µs fid f 9.9 Entries 4474 Integral.88e S [PE] 4us fid: remove 4 us from top and bottom in t_drift. Lots of γs from PMTs, unresolved S+S events, and surface close to top are removed. 4
25 +Spmf f 9.9 Entries 8895 Integral.7e S [PE] Spmf: fraction of prompt light in the maximum PMT is less than a threshold, which is a function of t_drift and S Remove scintillation + Cherenkov events from Fused Silica 5
26 f 9.9 +min Suncorr Entries 8664 Integral.695e S [PE] min Suncorr: S have PE This is more like quality cut, but remove surface events, which number of electrons are reduced by the surface effect. 6
27 +xyrecon f 9.9 Entries 8556 Integral.688e S [PE] xyrecon: reasonable xy reconstructed values (reconstruction does not failed) 7
28 f 9.9 +S F9 Entries 8556 Integral.688e S [PE] s F9: F9 of S pulse <. Remove S + S pileup events 8
29 f min S/S Entries Integral.68e S [PE] min S/S: S/S need to be above threshold, which is a function of S. Remove strangely small S events, like surface events. 9
30 f max S/S Entries Integral 5.4e S [PE] max S/S: S/S need to be below threshold, which is a function of S. Remove strangely large S events, which we don t expect, but applied as a safety net.
31 f S i9/i Entries Integral 5.8e S [PE] S i9/i: S have reasonable rise time. Remove events in which S is actually S+S pulses.
32 f S TBA Entries Integral 5.9e S [PE] S TBA: zposition from S TopBottom asymmetry agrees with t_drift. Remove random pileup S and S.
33 f TPB Tail Entries Integral 5.97e S [PE] TPB Tail: remove events, which have long tail of scintillation caused by TPB scintillation. Remove surface events, in which alpha goes through TPB layer.
34 f NLL Entries 5445 Integral 5.66e S [PE] NLL: Negative Log Likelihood cut, which compare event position from S light distribution among PMTs and event position from t_drift and S xy. Remove Cherenkov + scintillation events which deposit energy in separate locations. 4
35 +R f 9.9 Entries 6687 Integral.576e S [PE] R : Radial cut as a function of t_drift 5
36 +Veto f 9 Entries Integral.58e S [PE] Veto: all veto cuts Remove neutrons 6
DarkSide new results and prospects
 DarkSide new results and prospects Stefano Davini - INFN Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration La Thuile, March 20, 2018 The DarkSide WIMP-argon program at LNGS 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
DarkSide new results and prospects Stefano Davini - INFN Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration La Thuile, March 20, 2018 The DarkSide WIMP-argon program at LNGS 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
Darkside-50, DarkSide-20k and the Global Collaboration to reach the Neutrino Floor with liquid argon
 Darkside-5, DarkSide-2k and the Global Collaboration to reach the Neutrino Floor with liquid argon Cristiano Galbiati Gran Sasso Science Institute and Princeton University The quest for dark matter with
Darkside-5, DarkSide-2k and the Global Collaboration to reach the Neutrino Floor with liquid argon Cristiano Galbiati Gran Sasso Science Institute and Princeton University The quest for dark matter with
Paolo Agnes Laboratoire APC, Université Paris 7 on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration. Dark Matter 2016 UCLA 17th - 19th February 2016
 Paolo Agnes Laboratoire APC, Université Paris 7 on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration Dark Matter 2016 UCLA 17th - 19th February 2016 The DarkSide program 2 Double Phase Liquid Argon TPC, a staged approach:
Paolo Agnes Laboratoire APC, Université Paris 7 on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration Dark Matter 2016 UCLA 17th - 19th February 2016 The DarkSide program 2 Double Phase Liquid Argon TPC, a staged approach:
Darkside and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program
 Darkside and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program Giuliana Fiorillo Università di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli PM2018-14th Pisa Meeting on Advanced Detectors DM direct detection WIMP χ Low mass
Darkside and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program Giuliana Fiorillo Università di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli PM2018-14th Pisa Meeting on Advanced Detectors DM direct detection WIMP χ Low mass
DarkSide. Bianca Bottino Università di Genova and INFN Sezione di Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration 1
 DarkSide Bianca Bottino Università di Genova and INFN Sezione di Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration 1 DARKSIDE MAIN FEATURES Dark Matter direct detection WIMP induced nuclear recoils Double
DarkSide Bianca Bottino Università di Genova and INFN Sezione di Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration 1 DARKSIDE MAIN FEATURES Dark Matter direct detection WIMP induced nuclear recoils Double
The XENON1T experiment
 The XENON1T experiment Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science For the XENON collaboration 1 The XENON1T experiment Direct detection with xenon The XENON project XENON1T/nT 2 Quick introduction and
The XENON1T experiment Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science For the XENON collaboration 1 The XENON1T experiment Direct detection with xenon The XENON project XENON1T/nT 2 Quick introduction and
DarkSide-50: performance and results from the first atmospheric argon run
 DarkSide-50: performance and results from the first atmospheric argon run Yann Guardincerri on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration August 27th, 2014 1 / 21 DarkSide Direct detection search for WIMP dark
DarkSide-50: performance and results from the first atmospheric argon run Yann Guardincerri on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration August 27th, 2014 1 / 21 DarkSide Direct detection search for WIMP dark
Background and sensitivity predictions for XENON1T
 Background and sensitivity predictions for XENON1T Marco Selvi INFN - Sezione di Bologna (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Feb 19 th 016, UCLA Dark Matter 016 1 Outline Description of the detector;
Background and sensitivity predictions for XENON1T Marco Selvi INFN - Sezione di Bologna (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Feb 19 th 016, UCLA Dark Matter 016 1 Outline Description of the detector;
PoS(EPS-HEP2017)074. Darkside Status and Prospects. Charles Jeff Martoff Temple University
 Temple University E-mail: cmartoff@gmail.com The DarkSide Dark Matter Search Program is a direct-detection search for dark matter using a Liquid Argon Time Projection Chamber. The detector is designed
Temple University E-mail: cmartoff@gmail.com The DarkSide Dark Matter Search Program is a direct-detection search for dark matter using a Liquid Argon Time Projection Chamber. The detector is designed
Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments
 Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments Jingke Xu Princeton University June 7 th, 2013 1 Evidences for Dark Matter Rotation Curve Gravitational Lensing CMB Power Spectrum
Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments Jingke Xu Princeton University June 7 th, 2013 1 Evidences for Dark Matter Rotation Curve Gravitational Lensing CMB Power Spectrum
Background Characterization and Rejection in the LZ Detector. David Malling Brown University IDM 2012 July 25, 2012
 Background Characterization and Rejection in the LZ Detector David Malling Brown University IDM 2012 July 25, 2012 LZ Construction 2 Background Sources Ti cryostats 1500 kg
Background Characterization and Rejection in the LZ Detector David Malling Brown University IDM 2012 July 25, 2012 LZ Construction 2 Background Sources Ti cryostats 1500 kg
DarkSide-20k and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program. Giuliana Fiorillo Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli
 DarkSide-20k and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program Giuliana Fiorillo Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli UCLA DM Conference Los Angeles February 23, 2018 The case for DarkSide-20k
DarkSide-20k and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program Giuliana Fiorillo Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli UCLA DM Conference Los Angeles February 23, 2018 The case for DarkSide-20k
Light Dark Matter and XENON100. For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University
 Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS
 SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS David G. Cerdeño Institute for Theoretical Physics Universidad Autónoma de Madrid for the SuperCDMS Collaboration Hints for low-mass WIMPs in direct detection
SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS David G. Cerdeño Institute for Theoretical Physics Universidad Autónoma de Madrid for the SuperCDMS Collaboration Hints for low-mass WIMPs in direct detection
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases
 Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
DarkSide-20k and the Darkside Program for Dark Matter Searches
 DarkSide-20k and the Darkside Program for Dark Matter Searches Cristiano Galbiati Princeton University APC Paris Diderot GDR Neutrinos LPSC Grenoble June 6, 2016 DarkSide-20k Institutions [cm 2 ] σ 41
DarkSide-20k and the Darkside Program for Dark Matter Searches Cristiano Galbiati Princeton University APC Paris Diderot GDR Neutrinos LPSC Grenoble June 6, 2016 DarkSide-20k Institutions [cm 2 ] σ 41
Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search
 Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search 1 LUX Goal: Direct Detection of Dark Matter WMAP 5-year data (2008) gives matter densities (Ω) based on best fit to Λ-CDM cosmological model: Ω
Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search 1 LUX Goal: Direct Detection of Dark Matter WMAP 5-year data (2008) gives matter densities (Ω) based on best fit to Λ-CDM cosmological model: Ω
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 31 Oct 2015 Alden Fan 1
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 31 Oct 2015 Alden Fan 1 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 31 Oct 2015 Alden Fan 1](/thumbs/95/125151835.jpg) DPF2015-240 November 4, 2015 Status and Results from DarkSide-50 arxiv:1511.00676v1 [physics.ins-det] 31 Oct 2015 Alden Fan 1 Physics and Astronomy Department University of California, Los Angeles, CA
DPF2015-240 November 4, 2015 Status and Results from DarkSide-50 arxiv:1511.00676v1 [physics.ins-det] 31 Oct 2015 Alden Fan 1 Physics and Astronomy Department University of California, Los Angeles, CA
XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector
 XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector Katsuki Hiraide, the university of Tokyo for the XMASS Collaboration October 3 rd, 2016 IPRD16@Siena, Italy 1 XMASS project XMASS: a multi purpose experiment
XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector Katsuki Hiraide, the university of Tokyo for the XMASS Collaboration October 3 rd, 2016 IPRD16@Siena, Italy 1 XMASS project XMASS: a multi purpose experiment
Status of the XENON100 Dark Matter Search
 Status of the XENON Dark Matter Search Guillaume Plante Columbia University on behalf of the XENON Collaboration Exploring Low-Mass Dark Matter Candidates - PITT PACC - November 146, 211 XENON Collaboration
Status of the XENON Dark Matter Search Guillaume Plante Columbia University on behalf of the XENON Collaboration Exploring Low-Mass Dark Matter Candidates - PITT PACC - November 146, 211 XENON Collaboration
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions
 Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector. WIMP Search. Mani Tripathi, INPAC Meeting. Berkeley, May 5, 2007
 LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector WIMP Search Mani Tripathi INPAC Meeting Berkeley, New Collaboration Groups formerly in XENON10: Case Western, Brown, Livermore Natl. Lab (major fraction of the US
LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector WIMP Search Mani Tripathi INPAC Meeting Berkeley, New Collaboration Groups formerly in XENON10: Case Western, Brown, Livermore Natl. Lab (major fraction of the US
The Neutron/WIMP Acceptance In XENON100
 The Neutron/WIMP Acceptance In XENON100 Symmetries and Fundamental Interactions 01 05 September 2014 Chiemsee Fraueninsel Boris Bauermeister on behalf of the XENON collaboration Boris.Bauermeister@uni-mainz.de
The Neutron/WIMP Acceptance In XENON100 Symmetries and Fundamental Interactions 01 05 September 2014 Chiemsee Fraueninsel Boris Bauermeister on behalf of the XENON collaboration Boris.Bauermeister@uni-mainz.de
Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids
 Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Recontres de Moriond 2012, Cosmology Session, La Thuile, March 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Recontres de Moriond 2012, Cosmology Session, La Thuile, March 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
XENON100. Marc Schumann. Physik Institut, Universität Zürich. IDM 2010, Montpellier, July 26 th,
 XENON100 Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich IDM 2010, Montpellier, July 26 th, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ Why WIMP search with Xenon? efficient, fast scintillator (178nm)
XENON100 Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich IDM 2010, Montpellier, July 26 th, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ Why WIMP search with Xenon? efficient, fast scintillator (178nm)
UCLA Dark Matter 2014 Symposium. Origins and Distributions of the Backgrounds. 15 min
 S. Fiorucci Brown University UCLA Dark Matter 2014 Symposium Origins and Distributions of the Backgrounds 15 min What is a signal for LUX? Nuclear recoil Single scatter Signal Low energy, typically < 25
S. Fiorucci Brown University UCLA Dark Matter 2014 Symposium Origins and Distributions of the Backgrounds 15 min What is a signal for LUX? Nuclear recoil Single scatter Signal Low energy, typically < 25
DARWIN. Marc Schumann. U Freiburg PATRAS 2017 Thessaloniki, May 19,
 DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg PATRAS 2017 Thessaloniki, May 19, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Dark Matter Searches: Status spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions
DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg PATRAS 2017 Thessaloniki, May 19, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Dark Matter Searches: Status spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions
Recent results from PandaX- II and status of PandaX-4T
 Recent results from PandaX- II and status of PandaX-4T Jingkai Xia (Shanghai Jiao Tong University) On behalf of PandaX Collaboration August 2-5, Mini-Workshop@SJTU 2018/8/4 1 Outline Dark Matter direct
Recent results from PandaX- II and status of PandaX-4T Jingkai Xia (Shanghai Jiao Tong University) On behalf of PandaX Collaboration August 2-5, Mini-Workshop@SJTU 2018/8/4 1 Outline Dark Matter direct
Search for Dark Matter with Liquid Argon and Pulse Shape Discrimination
 Search for Dark Matter with Liquid Argon and Pulse Shape Discrimination Results from DEAP-1 and Status of DEAP-3600 Pierre Gorel for the DEAP collaboration University of Alberta Dark matter Experiment
Search for Dark Matter with Liquid Argon and Pulse Shape Discrimination Results from DEAP-1 and Status of DEAP-3600 Pierre Gorel for the DEAP collaboration University of Alberta Dark matter Experiment
Background Studies for the XENON100 Experiment. Alexander Kish Physics Institute, University of Zürich Doktorandenseminar August 30, 2010 UZH
 Background Studies for the XENON100 Experiment Alexander Kish Physics Institute, University of Zürich Doktorandenseminar August 30, 2010 UZH The XENON dark matter search program Target Volume 62 kg Total
Background Studies for the XENON100 Experiment Alexander Kish Physics Institute, University of Zürich Doktorandenseminar August 30, 2010 UZH The XENON dark matter search program Target Volume 62 kg Total
Direct detection: results from liquid noble-gas experiments
 Direct detection: results from liquid noble-gas experiments Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@mpi-hd.mpg.de DM@LHC Heidelberg, April 5th, 2018 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (MPIK) Liquid noble gases Heidelberg,
Direct detection: results from liquid noble-gas experiments Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@mpi-hd.mpg.de DM@LHC Heidelberg, April 5th, 2018 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (MPIK) Liquid noble gases Heidelberg,
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment
 The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
Nuclear Recoil Scintillation and Ionization Yields in Liquid Xenon
 Nuclear Recoil Scintillation and Ionization Yields in Liquid Xenon Dan McKinsey Yale University Physics Department February, 011 Indirect and Direct Detection of Dark Matter Aspen Center of Physics Energy
Nuclear Recoil Scintillation and Ionization Yields in Liquid Xenon Dan McKinsey Yale University Physics Department February, 011 Indirect and Direct Detection of Dark Matter Aspen Center of Physics Energy
Hands on DarkSide-50: Low Energy Calibration
 Hands on DarkSide-50: Low Energy Calibration Kyungwon Kim Seoul National University IBS Center for Underground Physics E-mail: kwkim@hep1.snu.ac.kr University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Triangle Universities
Hands on DarkSide-50: Low Energy Calibration Kyungwon Kim Seoul National University IBS Center for Underground Physics E-mail: kwkim@hep1.snu.ac.kr University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Triangle Universities
Results from DarkSide-50 with underground argon
 Dark Matter 2016 Los Angeles, CA 17-19 February 2016 Results from DarkSide-50 with underground argon Alden Fan UCLA for the DarkSide collaboration 1 DarkSide WIMP dark matter search using direct detection
Dark Matter 2016 Los Angeles, CA 17-19 February 2016 Results from DarkSide-50 with underground argon Alden Fan UCLA for the DarkSide collaboration 1 DarkSide WIMP dark matter search using direct detection
Dark Matter Search Results from the Silicon Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment
 Dark Matter Search Results from the Silicon Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment Kevin A. McCarthy Massachusetts Institute of Technology On behalf of the SuperCDMS and CDMS Collaborations
Dark Matter Search Results from the Silicon Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment Kevin A. McCarthy Massachusetts Institute of Technology On behalf of the SuperCDMS and CDMS Collaborations
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter
 Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
DARWIN. Marc Schumann. U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15,
 DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017
DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017
Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors. David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011
 Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011 1 Summary LUX screening program limits background contributions
Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011 1 Summary LUX screening program limits background contributions
Status of DM Direct Detection. Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science
 Status of DM Direct Detection Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science DM evidence on one slide Thermal freeze out of dark matter in the standard cosmological model Weakly Interacting Massive Particles
Status of DM Direct Detection Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science DM evidence on one slide Thermal freeze out of dark matter in the standard cosmological model Weakly Interacting Massive Particles
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches
 Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
The DarkSide-50 Outer Detectors
 The DarkSide-50 Outer Detectors Shawn Westerdale Princeton University (for the DarkSide Collaboration) TAUP 2015 Torino Thursday, Sept 10, 2015 The DarkSide-50 Experiment Located in Hall C of Laboratori
The DarkSide-50 Outer Detectors Shawn Westerdale Princeton University (for the DarkSide Collaboration) TAUP 2015 Torino Thursday, Sept 10, 2015 The DarkSide-50 Experiment Located in Hall C of Laboratori
Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX
 Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX we are a collaboration of 50+ scientists, please see http://lux.brown.edu for more information Peter Sorensen Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory DNP October
Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX we are a collaboration of 50+ scientists, please see http://lux.brown.edu for more information Peter Sorensen Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory DNP October
Current and Future of WIMP Search in DarkSide
 Current and Future of WIMP Search in DarkSide Masayuki Wada Princeton University on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration March 20 2017 52nd Rencontres de Moriond Conference 1 DarkSide Program Direct detection
Current and Future of WIMP Search in DarkSide Masayuki Wada Princeton University on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration March 20 2017 52nd Rencontres de Moriond Conference 1 DarkSide Program Direct detection
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 15 Feb 2005
 The XENON Dark Matter Experiment Elena Aprile (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory, Columbia University, New York, New York 10027 age@astro.columbia.edu
The XENON Dark Matter Experiment Elena Aprile (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory, Columbia University, New York, New York 10027 age@astro.columbia.edu
Recent Progress from the DEAP-3600 Dark Matter Direct Detection Experiment
 Recent Progress from the DEAP-3600 Dark Matter Direct Detection Experiment Jocelyn Monroe, Royal Holloway University of London IPA2014 August 22, 2014 Outline 1. DEAP-3600 Detector 2. Experimental Technique
Recent Progress from the DEAP-3600 Dark Matter Direct Detection Experiment Jocelyn Monroe, Royal Holloway University of London IPA2014 August 22, 2014 Outline 1. DEAP-3600 Detector 2. Experimental Technique
Axion search with Dark Matter detector
 Axion search with Dark Matter detector Paolo Beltrame Durham IPPP, 14th March 2016 1 Direct DM search Dark matter (DM) Milky Way s halo => flux on Earth ~ 10 5 cm -2 s -1 ρχ ~ 0.3 GeV/cm 3 and 100 GeV/c
Axion search with Dark Matter detector Paolo Beltrame Durham IPPP, 14th March 2016 1 Direct DM search Dark matter (DM) Milky Way s halo => flux on Earth ~ 10 5 cm -2 s -1 ρχ ~ 0.3 GeV/cm 3 and 100 GeV/c
Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search
 Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search Federica Petricca on behalf of the CRESST collaboration: Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München TU München University of Oxford Universität
Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search Federica Petricca on behalf of the CRESST collaboration: Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München TU München University of Oxford Universität
TWO-PHASE DETECTORS USING THE NOBLE LIQUID XENON. Henrique Araújo Imperial College London
 TWO-PHASE DETECTORS USING THE NOBLE LIQUID XENON Henrique Araújo Imperial College London Oxford University 18 th October 2016 OUTLINE Two-phase xenon for (dark) radiation detection Instrumenting a liquid
TWO-PHASE DETECTORS USING THE NOBLE LIQUID XENON Henrique Araújo Imperial College London Oxford University 18 th October 2016 OUTLINE Two-phase xenon for (dark) radiation detection Instrumenting a liquid
Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment. 1 Abstract. 2 Introduction
 Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory Columbia University New York, New York 10027 1 Abstract Observations on all fronts strongly
Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory Columbia University New York, New York 10027 1 Abstract Observations on all fronts strongly
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search. Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration
 SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
LARGE UNDERGROUND XENON
 LARGE UNDERGROUND XENON Cláudio Silva (LIP Coimbra) On behalf of the LUX Collaboration IDPASC Dark Matter Workshop 17 December 2011 1 THE LUX COLLABORATION Collaboration was formed in 2007 and fully funded
LARGE UNDERGROUND XENON Cláudio Silva (LIP Coimbra) On behalf of the LUX Collaboration IDPASC Dark Matter Workshop 17 December 2011 1 THE LUX COLLABORATION Collaboration was formed in 2007 and fully funded
Current status of LUX Dark Matter Experiment
 Current status of LUX Dark Matter Experiment by A. Lyashenko Yale University On behalf of LUX collaboration LUX Large Underground Xenon experiment LUX Collaboration: Yale, CWRU, UC Santa Barbara, Brown,
Current status of LUX Dark Matter Experiment by A. Lyashenko Yale University On behalf of LUX collaboration LUX Large Underground Xenon experiment LUX Collaboration: Yale, CWRU, UC Santa Barbara, Brown,
Direct Detection of! sub-gev Dark Matter
 Direct Detection of! sub-gev Dark Matter Rouven Essig C.N. Yang Institute for Theoretical Physics, Stony Brook Sackler Conference, Harvard, May 18, 2014 An ongoing program Direct Detection of sub-gev Dark
Direct Detection of! sub-gev Dark Matter Rouven Essig C.N. Yang Institute for Theoretical Physics, Stony Brook Sackler Conference, Harvard, May 18, 2014 An ongoing program Direct Detection of sub-gev Dark
The LZ Experiment Tom Shutt SLAC. SURF South Dakota
 The LZ Experiment Tom Shutt SLAC SURF South Dakota 1 LUX - ZEPLIN 31 Institutions, ~200 people 7 ton LXe TPC ( tons LXe total) University of Alabama University at Albany SUNY Berkeley Lab (LBNL), UC Berkeley
The LZ Experiment Tom Shutt SLAC SURF South Dakota 1 LUX - ZEPLIN 31 Institutions, ~200 people 7 ton LXe TPC ( tons LXe total) University of Alabama University at Albany SUNY Berkeley Lab (LBNL), UC Berkeley
Direct dark matter search with XMASS. K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration
 Direct dark matter search with XMASS K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration Outline XMASS experiment. Single phase liquid xenon detector Many targets were searched with XMASS. WIMP search fiducialized volume.
Direct dark matter search with XMASS K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration Outline XMASS experiment. Single phase liquid xenon detector Many targets were searched with XMASS. WIMP search fiducialized volume.
LOW ENERGY SOLAR NEUTRINOS WITH BOREXINO. Lea Di Noto on behalf of the Borexino collaboration
 LOW ENERGY SOLAR NEUTRINOS WITH BOREXINO Lea Di Noto on behalf of the Borexino collaboration Vulcano Workshop 20 th -26 th May 2018 [cm -2 s -1 MeV -1 ] SOLAR NEUTRINOS Electrons neutrinos are produced
LOW ENERGY SOLAR NEUTRINOS WITH BOREXINO Lea Di Noto on behalf of the Borexino collaboration Vulcano Workshop 20 th -26 th May 2018 [cm -2 s -1 MeV -1 ] SOLAR NEUTRINOS Electrons neutrinos are produced
The XENON Project. M. Selvi The XENON project
 The XENON Project M. Selvi Assemblea di Sezione 2011 Dark matter in the Universe Dark matter properties: what we know Direct WIMP search Direct WIMP search Direct WIMP detection Why Xenon? A double-phase
The XENON Project M. Selvi Assemblea di Sezione 2011 Dark matter in the Universe Dark matter properties: what we know Direct WIMP search Direct WIMP search Direct WIMP detection Why Xenon? A double-phase
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter
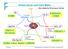 Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
Calibration of Single Phase Liquid Argon Detectors
 Calibration of Single Phase Liquid Argon Detectors Kimberly J. Palladino MIT MiniCLEAN Collaboration 1 Outline Single Phase Liquid Argon technique Calibration Goals Internal calibration sources External
Calibration of Single Phase Liquid Argon Detectors Kimberly J. Palladino MIT MiniCLEAN Collaboration 1 Outline Single Phase Liquid Argon technique Calibration Goals Internal calibration sources External
ANAIS: Status and prospects
 LSC Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc ANAIS: Status and prospects Miguel Ángel Oliván on behalf of the ANAIS team Universidad de Zaragoza Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc RICAP 2014 Roma International
LSC Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc ANAIS: Status and prospects Miguel Ángel Oliván on behalf of the ANAIS team Universidad de Zaragoza Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc RICAP 2014 Roma International
Studies of the XENON100 Electromagnetic Background
 Studies of the XENON100 Electromagnetic Background Daniel Mayani Physik-Institut University of Zurich PhD Seminar PSI, August 26-27, 2015 Searching for elusive particles The main challenge for experiments
Studies of the XENON100 Electromagnetic Background Daniel Mayani Physik-Institut University of Zurich PhD Seminar PSI, August 26-27, 2015 Searching for elusive particles The main challenge for experiments
WIMP Dark Matter Search with XENON and DARWIN
 WIMP Dark Matter Search with XENON and DARWIN Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany XENON100 Rice University Houston, TX, USA http://xenon.physics.rice.edu 6th Patras Workshop Zurich July 7, 2010
WIMP Dark Matter Search with XENON and DARWIN Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany XENON100 Rice University Houston, TX, USA http://xenon.physics.rice.edu 6th Patras Workshop Zurich July 7, 2010
Prospects for WIMP Dark Matter Direct Searches with XENON1T and DARWIN
 Via Lactea 2 (2008) Prospects for WIMP Dark Matter Direct Searches with XENON1T and DARWIN NASA/WMAP 8th Patras Workshop on Axions, WIMPs, and WISPs Chicago, 21-July-2012 http://xenon.physik.uni-mainz.de
Via Lactea 2 (2008) Prospects for WIMP Dark Matter Direct Searches with XENON1T and DARWIN NASA/WMAP 8th Patras Workshop on Axions, WIMPs, and WISPs Chicago, 21-July-2012 http://xenon.physik.uni-mainz.de
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases
 Universität Zürich E-mail: marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Liquid noble gases have proven a great potential as detector medium for dark matter searches. Particles interacting in these media produce ionized and
Universität Zürich E-mail: marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Liquid noble gases have proven a great potential as detector medium for dark matter searches. Particles interacting in these media produce ionized and
After LUX: The LZ Program. David Malling, Simon Fiorucci Brown University APS DPF Conference August 10, 2011
 After LUX: The LZ Program David Malling, Simon Fiorucci Brown University APS DPF Conference August 10, 2011 The LZ Program LZ LUX-ZEPLIN LUX (14 U.S. institutions) + new collaborators from ZEPLIN, other
After LUX: The LZ Program David Malling, Simon Fiorucci Brown University APS DPF Conference August 10, 2011 The LZ Program LZ LUX-ZEPLIN LUX (14 U.S. institutions) + new collaborators from ZEPLIN, other
Understanding Ionization, Scintillation Light, and the Energy Scale
 Understanding Ionization, Scintillation Light, and the Energy Scale In Noble Element Detectors http://nest.physics.ucdavis.edu/site/ Matthew Szydagis, UC Davis University of Connecticut 12/09/13 1 Why
Understanding Ionization, Scintillation Light, and the Energy Scale In Noble Element Detectors http://nest.physics.ucdavis.edu/site/ Matthew Szydagis, UC Davis University of Connecticut 12/09/13 1 Why
Enectalí Figueroa-Feliciano
 School and Workshop on Dark Matter and Neutrino Detection Dark Matter Direct Detection Lecture 3 Enectalí Figueroa-Feliciano!113 Outline Lecture 1: The dark matter problem WIMP and WIMP-like DM detection
School and Workshop on Dark Matter and Neutrino Detection Dark Matter Direct Detection Lecture 3 Enectalí Figueroa-Feliciano!113 Outline Lecture 1: The dark matter problem WIMP and WIMP-like DM detection
A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results
 A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results I where we stand II recent results (CDMS, XENON10, etc) III DAMA results IV a bit about modulation V issues with DAMA results VI what to look for
A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results I where we stand II recent results (CDMS, XENON10, etc) III DAMA results IV a bit about modulation V issues with DAMA results VI what to look for
Direct Dark Matter Searches
 Direct Dark Matter Searches Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich What is? Invisibles12, GGI Florence, June 27th 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Direct Dark Matter Searches Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich What is? Invisibles12, GGI Florence, June 27th 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
The relevance of XENON10 constraints in this low-mass region has been questioned [15] C.E. Aalseth et al. arxiv: v1
![The relevance of XENON10 constraints in this low-mass region has been questioned [15] C.E. Aalseth et al. arxiv: v1 The relevance of XENON10 constraints in this low-mass region has been questioned [15] C.E. Aalseth et al. arxiv: v1](/thumbs/88/116252430.jpg) The relevance of XENON10 constraints in this low-mass region has been questioned [15] C.E. Aalseth et al. arxiv:1001.2834v1 Peter Sorensen LLNL on behalf of the XENON10 Collaboration at UC Davis HEFTI
The relevance of XENON10 constraints in this low-mass region has been questioned [15] C.E. Aalseth et al. arxiv:1001.2834v1 Peter Sorensen LLNL on behalf of the XENON10 Collaboration at UC Davis HEFTI
Direct Detection: Liquid Nobles
 Direct Detection: Liquid Nobles Dan Akerib SLAC National Accelerator Lab and Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology Stanford University LUX / LZ collaborations! 9 September 2015 WIMPs
Direct Detection: Liquid Nobles Dan Akerib SLAC National Accelerator Lab and Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology Stanford University LUX / LZ collaborations! 9 September 2015 WIMPs
The Direct Search for Dark Matter
 picture: Thomas Tuchan The Direct Search for Dark Matter with special emphasis on the XENON project Rafael F. Lang Purdue University rafael@purdue.edu IPMU Tokyo, March 8, 2013 1 baryon fraction Dark Matter
picture: Thomas Tuchan The Direct Search for Dark Matter with special emphasis on the XENON project Rafael F. Lang Purdue University rafael@purdue.edu IPMU Tokyo, March 8, 2013 1 baryon fraction Dark Matter
Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project
 Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory/Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Menlo Park, CA 94025,
Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory/Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Menlo Park, CA 94025,
Low Energy Particles in Noble Liquids
 Low Energy Particles in Noble Liquids Antonio J. Melgarejo Fernandez Columbia University Invisibles School, July 14th 2013, Durham Explaining the title I Noble gases are a group of elements found at the
Low Energy Particles in Noble Liquids Antonio J. Melgarejo Fernandez Columbia University Invisibles School, July 14th 2013, Durham Explaining the title I Noble gases are a group of elements found at the
Recent Results from the PandaX Experiment
 Recent Results from the PandaX Experiment Changbo Fu Shanghai Jiao Tong University On Behalf of Collaboration 25May2017 1 Outline 1. Introduciton Dark Matter: WIMPs, Axion, PandaX at China Jinping Underground
Recent Results from the PandaX Experiment Changbo Fu Shanghai Jiao Tong University On Behalf of Collaboration 25May2017 1 Outline 1. Introduciton Dark Matter: WIMPs, Axion, PandaX at China Jinping Underground
PandaX Dark Matter Search
 PandaX Dark Matter Search Xiangdong Ji Shanghai Jiao Tong University University of Maryland On Behalf of the PandaX Collaboration 2017/8/7 1 Outline Introduction to WIMP search and liquid xenon experiments
PandaX Dark Matter Search Xiangdong Ji Shanghai Jiao Tong University University of Maryland On Behalf of the PandaX Collaboration 2017/8/7 1 Outline Introduction to WIMP search and liquid xenon experiments
Liquefied noble gases as targets for light dark matter
 Liquefied noble gases as targets for light dark matter Dan McKinsey Yale University Physics Department May 1, 2010 HEFTI Workshop on Light Dark Matter UC Davis The Noble Liquid Revolution Noble liquids
Liquefied noble gases as targets for light dark matter Dan McKinsey Yale University Physics Department May 1, 2010 HEFTI Workshop on Light Dark Matter UC Davis The Noble Liquid Revolution Noble liquids
Outline. Dark Matter Physics at SNOLAB: And Future Prospects. Overview of SNOLAB DarkMatter Program. Status of Current Experiments
 Outline Dark Matter Physics at SNOLAB: And Future Prospects Overview of SNOLAB DarkMatter Program Status of Current Experiments The G2 Down Select Process Crystal Ball Gazing where will we be in 2020?
Outline Dark Matter Physics at SNOLAB: And Future Prospects Overview of SNOLAB DarkMatter Program Status of Current Experiments The G2 Down Select Process Crystal Ball Gazing where will we be in 2020?
Oddities of light production in the noble elements. James Nikkel
 Oddities of light production in the noble elements James Nikkel 1 2 What is a scintillator? Particle with Energy Photons Stuff 3 What is a scintillator? We would like: Nphotons = Y Eincoming With Y as
Oddities of light production in the noble elements James Nikkel 1 2 What is a scintillator? Particle with Energy Photons Stuff 3 What is a scintillator? We would like: Nphotons = Y Eincoming With Y as
Searches for Low-Mass WIMPs with CDMS II and SuperCDMS
 Searches for Low-Mass WIMPs with CDMS II and SuperCDMS SuperCDMS Science Coordinator Syracuse University arxiv: 1304.4279 1304.3706 1203.1309 A New Order 0.01% Visible H, He 0.5% ENERGY Metals Dark Matter
Searches for Low-Mass WIMPs with CDMS II and SuperCDMS SuperCDMS Science Coordinator Syracuse University arxiv: 1304.4279 1304.3706 1203.1309 A New Order 0.01% Visible H, He 0.5% ENERGY Metals Dark Matter
Scintillation efficiency measurement of Na recoils in NaI(Tl) below the DAMA/LIBRA energy threshold
 Scintillation efficiency measurement of Na recoils in NaI(Tl) below the DAMA/LIBRA energy threshold Jingke Xu, Princeton (now @LLNL) Sept 24, 2015 2015 LowECal Workshop, Chicago, IL Outline 1. Overview
Scintillation efficiency measurement of Na recoils in NaI(Tl) below the DAMA/LIBRA energy threshold Jingke Xu, Princeton (now @LLNL) Sept 24, 2015 2015 LowECal Workshop, Chicago, IL Outline 1. Overview
Detectors for astroparticle physics
 Detectors for astroparticle physics Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Universität Zürich Kern und Teilchenphysik II, Zürich 07.05.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (UZH) Detectors for astroparticle
Detectors for astroparticle physics Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Universität Zürich Kern und Teilchenphysik II, Zürich 07.05.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (UZH) Detectors for astroparticle
Supernova Neutrino Physics with XENON1T and Beyond
 Supernova Neutrino Physics with XENON1T and Beyond Shayne Reichard* University of Zurich nueclipse 2017 August 22 R. F. Lang*, C. McCabe, M. Selvi*, and I. Tamborra Phys. Rev. D94, arxiv:1606.09243 *Members
Supernova Neutrino Physics with XENON1T and Beyond Shayne Reichard* University of Zurich nueclipse 2017 August 22 R. F. Lang*, C. McCabe, M. Selvi*, and I. Tamborra Phys. Rev. D94, arxiv:1606.09243 *Members
Daya Bay and joint reactor neutrino analysis
 Daya Bay and joint reactor neutrino analysis Logan Lebanowski (Tsinghua University) on behalf of the Daya Bay collaboration 2016/11/4 - NNN16, Beijing 1 Contents Daya Bay Reactor Neutrino Experiment Introduction
Daya Bay and joint reactor neutrino analysis Logan Lebanowski (Tsinghua University) on behalf of the Daya Bay collaboration 2016/11/4 - NNN16, Beijing 1 Contents Daya Bay Reactor Neutrino Experiment Introduction
LZ and Direct Dark Matter Detection. Kimberly J. Palladino May 1, 2018
 LZ and Direct Dark Matter Detection Kimberly J. Palladino May 1, 2018 What is the universe made of? Abell 2218 Reconciling what we measure on Earth with what we see in the cosmos 2 Outline Dark Matter
LZ and Direct Dark Matter Detection Kimberly J. Palladino May 1, 2018 What is the universe made of? Abell 2218 Reconciling what we measure on Earth with what we see in the cosmos 2 Outline Dark Matter
Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches
 Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches Tarek Saab University of Florida Tali Figueroa Northwestern University Calibration of Low Energy Particle Detectors
Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches Tarek Saab University of Florida Tali Figueroa Northwestern University Calibration of Low Energy Particle Detectors
Direct Detection Lecture 2: Current Results
 Direct Detection Lecture 2: Current Results Outline I. Leading spin-independent measurements II. Leading spin-depending measurements III. Low Mass WIMP searches IV. Discussion on Calibration 43 Current
Direct Detection Lecture 2: Current Results Outline I. Leading spin-independent measurements II. Leading spin-depending measurements III. Low Mass WIMP searches IV. Discussion on Calibration 43 Current
SIGN: A Pressurized Noble Gas Approach to WIMP Detection
 SIGN: A Pressurized Noble Gas Approach to WIMP Detection J.T. White Texas A&M University Dark Side of the Universe U. Minnesota, 6/7/2007 Why Gaseous Nobles? Original Motivation: Neon Electron mobility
SIGN: A Pressurized Noble Gas Approach to WIMP Detection J.T. White Texas A&M University Dark Side of the Universe U. Minnesota, 6/7/2007 Why Gaseous Nobles? Original Motivation: Neon Electron mobility
Dark Matter Search with XENON
 Dark Matter Search with XENON Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Universität Mainz, Seminar, May 2, 2012 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ 2 Baryonic Matter Dark Matter? Dark Energy????
Dark Matter Search with XENON Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Universität Mainz, Seminar, May 2, 2012 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ 2 Baryonic Matter Dark Matter? Dark Energy????
The XENON Dark Matter Project: Status of the XENON100 Phase. Elena Aprile Columbia University
 The XENON Dark Matter Project: Status of the XENON100 Phase Elena Aprile Columbia University 8th UCLA Symposium Marina del Rey, Feb 22, 2008 The XENON Dark Matter Phased Program Detect WIMPS through their
The XENON Dark Matter Project: Status of the XENON100 Phase Elena Aprile Columbia University 8th UCLA Symposium Marina del Rey, Feb 22, 2008 The XENON Dark Matter Phased Program Detect WIMPS through their
DARK MATTER SEARCH AT BOULBY MINE
 DARK MATTER SEARCH AT BOULBY MINE R. LUSCHER on behalf of the Boulby Dark Matter Collaboration (RAL, Imperial College, Sheffield, UCLA, Texas A&M, Pisa, ITEP, Coimbra, Temple and Occidental) Rutherford
DARK MATTER SEARCH AT BOULBY MINE R. LUSCHER on behalf of the Boulby Dark Matter Collaboration (RAL, Imperial College, Sheffield, UCLA, Texas A&M, Pisa, ITEP, Coimbra, Temple and Occidental) Rutherford
Dark Matter Search * in China
 Dark Matter Search * in China Jianglai Liu 刘江来 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Member of the PandaX collaboration * Disclaimer: focused on direct detection The 7th Workshop on Hadron Physics in China and
Dark Matter Search * in China Jianglai Liu 刘江来 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Member of the PandaX collaboration * Disclaimer: focused on direct detection The 7th Workshop on Hadron Physics in China and
Doojin Kim University of Wisconsin, WI November 14th, 2017
 Doojin Kim, WI November 14th, 2017 Based on DK, J.-C. Park, S. Shin, PRL119, 161801 (2017) G. Giudice, DK, J.-C. Park, S. Shin, 1711. xxxxx Doojin Kim, WI November 14th, 2017 Based on DK, J.-C. Park, S.
Doojin Kim, WI November 14th, 2017 Based on DK, J.-C. Park, S. Shin, PRL119, 161801 (2017) G. Giudice, DK, J.-C. Park, S. Shin, 1711. xxxxx Doojin Kim, WI November 14th, 2017 Based on DK, J.-C. Park, S.
Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background
 Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background A cryogenic detector for Dark Matter with heat (phonon) readout and light (scintillation) readout MPI, TUM, Oxford, Tübingen, LNGS What we re looking for: M W imp =
Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background A cryogenic detector for Dark Matter with heat (phonon) readout and light (scintillation) readout MPI, TUM, Oxford, Tübingen, LNGS What we re looking for: M W imp =
New developments in dark matter direct detection experiments
 New developments in dark matter direct detection experiments Christopher M c Cabe SLAP!, Kasteel Woerden 11th October 2017 Outline Why direct detection? New developments with Large detectors Small detectors
New developments in dark matter direct detection experiments Christopher M c Cabe SLAP!, Kasteel Woerden 11th October 2017 Outline Why direct detection? New developments with Large detectors Small detectors
BubXe: a liquid xenon bubble chamber for Dark Matter detection!
 BubXe: a liquid xenon bubble chamber for Dark Matter detection Jeremy Mock, on behalf of Cecilia Levy and Matthew Szydagis SUNY Albany Direct DM Search Today 3 detection channels (light, charge, heat):
BubXe: a liquid xenon bubble chamber for Dark Matter detection Jeremy Mock, on behalf of Cecilia Levy and Matthew Szydagis SUNY Albany Direct DM Search Today 3 detection channels (light, charge, heat):
Prospects for kev-dm searches with the GERDA experiment
 Physik-Institut Prospects for kev-dm searches with the GERDA experiment Roman Hiller for the GERDA collaboration 29/03/2017 Page 1 GERDA concept Cleanroom Lock systen Enriched 76 Ge detectors Cryostat
Physik-Institut Prospects for kev-dm searches with the GERDA experiment Roman Hiller for the GERDA collaboration 29/03/2017 Page 1 GERDA concept Cleanroom Lock systen Enriched 76 Ge detectors Cryostat
First results on neutrinoless double beta decay of 82 Se with CUPID-0
 First results on neutrinoless double beta decay of 82 Se with CUPID-0 Lorenzo Pagnanini on behalf of the CUPID-0 collaboration 30 th Rencontres de Blois CUPID: a next generation experiment CUPID (CUORE
First results on neutrinoless double beta decay of 82 Se with CUPID-0 Lorenzo Pagnanini on behalf of the CUPID-0 collaboration 30 th Rencontres de Blois CUPID: a next generation experiment CUPID (CUORE
Axion and axion-like particle searches in LUX and LZ. Maria Francesca Marzioni
 Axion and axion-like particle searches in LUX and LZ Maria Francesca Marzioni PPE All Group meeting 06/06/2016 Outline Why are we interested in axions How can we detect axions with a xenon TPC Axion signal
Axion and axion-like particle searches in LUX and LZ Maria Francesca Marzioni PPE All Group meeting 06/06/2016 Outline Why are we interested in axions How can we detect axions with a xenon TPC Axion signal
