Magnetic fields in the universe. Chiara Caprini, CEA Saclay
|
|
|
- Daisy Kerry Goodwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Magnetic fields in the universe Chiara Caprini, CEA Saclay
2 The problem: cannot explain the origin of magnetic fields observed in astrophysical objects Outline Observations and amplification by structure formation Possible generation mechanisms Model and evolution Primordial magnetic fields Constraint and observational effects (CMB)
3 Observations: observational techniques Zeeman splitting: direct measure from hydrogen emission lines, only for the Milky Way ν = eb/(2πm e ) Synchrotron radiation: plane of the sky component, needs independent measure of the electron density I(ν) B (1+α)/2 ν (1 α)/2 n e (E) = n 0 E α Faraday rotation: widely used - line of sight component, independent measure of electron density, several λ φ zs λ 2 = B µg ( ) n e l(z) rad cm 3 d kpc m 2 (Grasso and Rubinstein 2001, Giovannini 2003)
4 Observations: galactic magnetic fields General characteristics: B 2 tot = B 2 u + B 2 r B u µg B r several µg l corr kpc Structure: Axisymmetric or bisymmetric? Equipartition holds? Follows optical spiral arms? Dynamically important and not yet understood M51 (Zweibel and Heiles 1997, Han )
5 Observations: cluster magnetic fields General characteristics: B µg l corr kpc Examples: Synchrotron emission of cluster-wide diffuse sources: COMA Average value: B 0.1 1µG Faraday rotation of radio sources inside or behind the cluster + X-ray observation of the hot gas + simulations (Carilli and Taylor 2002) Abell 2382 (Guidetti et al 2007)
6 Observations: cluster magnetic fields B 3.3µG Kolmogorov spectrum Λ max 35kpc Hydra A: B 7µG Λ max 3kpc (Vogt and Ensslin 2005) M:!MM 0"I""$0+! ' J:76K25"""L M:!M* C@6D:;E2"F4G:7"H1:2;7<5"48" =>?7@"A"B-<9;: :2;7<5 M:!M'!"#"$%&'"(")&*"("*+"""", µ -""#"$*&."(")&*"(")&/+"012! M:!MN )&M M!M M) M)) 0""J012""L Very detailed MHD simulations (Dolag 2005, Dubois and Teyssier )
7 High redshift objects: (Athreya et al 98, Pentericci et al 02...) Faraday rotation in radio proto-galaxies and quasars at z>2 B µg l corr kpc Observations: summary Magnetic fields of order microgauss in all observed objects Correlated on scales of the order of the object size Probably grown in short times (or present previously) Ω B h 2 B2 8πρ c 0.06 Ω rad h 2 E gal B M EB ns M (R = 10 5 ly, h = 10 3 ly) (R = 10 6 cm, B = Gauss) ( ) 2 B 10 6 Gauss B 10 9 Gauss contributes 1% in the CMB (Durrer et al 99, Dolgov 03)
8 High electrical conductivity Observations: amplification Conservation of magnetic flux Amplification by structure collapse: B fin = B in ( Lin L fin ) 2 = B in ( ) 2/3 ρfin ρ in { Bgal in Bin clu Gauss 10 8 Gauss Amplification by galactic dynamo: INGREDIENTS: high conductivity, differential rotation, turbulence RESULTS: exponential growth up to equipartition, axisymmetric PROBLEMS: needs many rotations, reaches saturation? B gal in Gauss (t gal 10Gy) (Brandenburg and Subramanian 2005)
9 Possible generation mechanisms B 10 9 Gauss or Gauss at about 100 kpc Generation after recombination good: known physics bad: non-linear physics, correlation scale too small Generation prior to recombination CAUSAL: ACAUSAL: good: quite easy to get bad: correlation scale too small good: generated at any scale bad: not very predictive more than 100 primordial mechanisms but no preferred one (no amplitudes: depend on average method, evolution, parameters of the model...)
10 Generation after recombination BIERMANN BATTERY: B t = v B B 4πσ n e P e en 2 e galactic: shocks by SN explosions in proto-galaxies (problem: scale) both: radiation pressure at reionisation + density fluctuations EJECTION: galactic: from stars (problem: mean to zero) cluster: from galaxies and/or AGN (open questions: mix? amplitude?) CLUSTER: SMALL SCALE TURBULENT DYNAMO open questions: what generates it (mergers)? scale (reversal of the field, Faraday rotation)? (Hanaya et al 2005, Biermann and Galea 2003, Langer et al 2005, Colgate and Li 2000, Subramanian 2008, Schekochihin and Cowley )
11 Generation prior to recombination INFLATION: one needs to break conformal invariance of EM coupling of em field with the metric Turner and Widrow 1988 Bamba and Sasaki 2007 Campanelli et al 2008 coupling directly to the inflaton 1 4m 1 ( 2 (RF µνf µν + R µν F µα Fα ν + R µναβ F µν F αβ ) ) n R 4 m 2 F µνf µν, 1 ( ) α η F µνf µν 4 e αφ F µν F µν Ratra 1992, Bamba and Yokoyama introducing a charged scalar field (D µ φ) D µ φ m 2 φ φ 1 4 F µνf µν Turner and Widrow 1988, Calzetta et al 1998, Giovannini and Shaposhnikov 2000, Dimopoulos et al 2002, Prokopec et al 2004, Diaz-Gil et al inflation in string theory context Martin and Yokoyama 2007 f(φ)f µν F µν pre big bang, dynamical extra dimensions, non-linear em... Gasperini et al 1995, Kunze η 1
12 Generation prior to recombination PRIMORDIAL PHASE TRANSITIONS FIRST ORDER: charge separation at bubble walls + amplification by MHD turbulence (both EW and QCD) Hogan 1983, Quashnock et al 1989, Cheng and Olinto 1994, Baym et al 1996, Sigl et al 1996, Ahonen and Enqvist SECOND ORDER EW: generated by the symmetry breaking Vachaspati 1991, Davidson 1996, Grasso and Riotto 1997, Hindmarsh and Everett 1997, Tornkvist HELICITY GENERATION: H = 1 V EW baryogenesis: decay of EW strings V d 3 x A B h n b α Cornwall 1997, Vachaspati 2001, Copi et al coupling with a pseudoscalar φf µν F µν Field and Carroll 1998, Campanelli and Giannotti
13 Generation prior to recombination GENERATION BY VORTICITY t B + E = 0 B t E = 4πJ J = en(v p v e ) B = 4πen(Ω p Ω e ) electrons do Thomson scattering (Harrison 1973) vorticity by wiggly strings, superconducting strings or string loops Vachaspati and Vilenkin 1991, Davis and Dimopoulos 2005, Battefeld et al vorticity by second order perturbations Berezhiani and Dolgov 2003, Gopal and Sethi 2004, Matarrese et al 2004, Takahashi et al
14 Primordial magnetic fields: model break FRW symmetries π ij = (B 2 /3)h ij B i B j weak background field B 2 = O(0) ρ π ij, D i B j,... = O(1) Barrow, Maartens and Tsagas order 1/2 in perturbation B 2, π ij = O(1) Durrer et al homogeneous (Barrow et al ) or stochastic B i = 0 Power spectrum: B 2 0 B i (k)bj (q) = δ(k q)[ (δ ij ˆk iˆkj )S(k) + iɛ ijmˆkm A(k) ] Gaussian, homogeneous, isotropic and divergence free
15 Primordial magnetic fields: model energy density E B = 0 dk k 2 S(k) helicity density H = 0 dk ka(k) S(k) B + (k)b + ( k) + B (k)b ( k) A(k) B + (k)b + ( k) B (k)b ( k) parity even parity odd S(k) A(k) power spectra: Volume average: S(k) (λ n+3 B 2 λ)k n B λ (x) = 1 λ 3 B 2 λ = B 2 L d 3 y B(y)e (x y) 2 2λ 2 ( ) n+3 L λ A(k) (λ m+2 H λ )k m Hindmarsh and Everett 1997 line average: Bλ 2 = BL(L/λ) 2 surface average: Bλ 2 = BL(L/λ) 2 2
16 Primordial magnetic fields: model CONSTRAINT FOR A CAUSAL SPECTRUM: B i (x)b j (x + r) = 0 for r > L correlation function compact support L horizon power spectrum analytic B i (k)bj (q) = δ(k q)[ (δ ij ˆk iˆkj )S(k) + iɛ ijmˆkm A(k) ] k 0 : S(k) k 2, k 4... A(k) k, k 3... DIVERGENCE FREE IMPLIES NO WHITE NOISE λ Hogan 1973 B 2 λ = B 2 L ( ) n+3 L λ L no random walk leads to extra suppression at large scales
17 Primordial magnetic fields: evolution MHD: one relativistic fluid + em field (T µν f + T µν em) ;ν = 0 F µν ;ν = j µ F [µν;α] = 0 j µ + u ν j ν u µ = σf µν j ν conformal invariance in FRW flat spacetime induction equation: B t = (v B) + B 4πσ dφ dt = 1 4πσ S B ds dh dt = 1 4πσ V d 3 x B ( B) IDEAL MDH limit σ : flux and helicity are conserved B 2 a 4
18 Primordial magnetic fields: evolution 100 GeV 1 MeV 0.32 ev TURBULENT PHASE ν l νe Re = vl ν 1 VISCOUS PHASE σ T ν l γe σ T 3/2 Re 1 ReM Re 103 ( 100GeV T ) 4 ReM Re 1010 ( m e T ) 3/2 Turbulent cascade Alfvén waves in viscous fluid: damping of magnetic energy L > V A L Silk 20 ΩB Ω rad Mpc Jedamzik et al 1996, Ahonen and Enqvist 1996 Jedamzik et al 1996, Subramanian and Barrow 1997, Banerjee and Jedamzik 2004
19 Primordial magnetic fields: evolution TURBULENT PHASE non-helical field: DIRECT CASCADE E B (t) t 2(n+3)/(n+5) L B (t) t 2/(n+5) helical field: INVERSE CASCADE Magnetic energy is transferred to larger scales E B (t) t 2/3 L B (t) t 2/3 Christensson et al 2002, Banerjee and Jedamzik 2004, Campanelli
20 Primordial magnetic fields: constraint CONSTRAINT FROM GRAVITATIONAL WAVES AND NUCLEOSYNTHESIS GW spectrum always blue: bound on the integrated spectrum stronger than large scales (CMB) GW production takes place before dissipation: magnetic energy stored in GW GW production very efficient CAUSAL GENERATION AT 100 GeV: n = 2 B 0.1Mpc Gauss INFLATIONARY GENERATION AT 10^15 GeV: n = 0 n 3 B 0.1Mpc Gauss B 0.1Mpc 10 9 Gauss CC and Durrer 2001
21 Primordial magnetic fields: constraint δg µν = 8πGT B µν H 2 h GT B ḣ GT B /H ρ GW ḣ2 8πG Ω GW Ω2 B Ω rad S(k) (λ n+3 B 2 λ)k n Ω B (t) B2 λ ρ c (λk (t)) n+3 GW generated since the beginning: Ω GW Ω2 B (k ) Ω rad B 2 λ < ρ c (λk ) n+3 Ω rad NON HELICAL FIELD
22 Primordial magnetic fields: CMB effects l 2 C l ( ΩB Ω rad ) ( ) 4 B 10 9 Gauss MF energy momentum tensor: scalar, vector, tensor modes δg µν = 8πG(T µν + T B µν) (T µν + T Bµν ) ;ν = 0 MF + baryons: MHD waves (magnetosonic, Alfvén) (n 3) Vector mode (Alfvén waves) survives at scales: L V A L Silk V A ΩB Ω rad Subramanian and Barrow 2002 Temperature and B polarisation at high multipoles
23 Primordial magnetic fields: CMB effects Yamakazi et al 2008, Finelli et al 2008, Giovannini and Kunze 2007, Kahniashvili and Ratra 2006, Lewis 2004, Mack et al 2002, Koh and Lee
24 Primordial magnetic fields: CMB effects Parity odd cross-correlations from helical field l 2 C T B l l 2 C EB l at l = 50 Faraday rotation of CMB polarisation average rotation angle: Φ 2 ( B 10 9 Gauss ) ( 30GHz Pogosian et al 2001, CC et al ν ) 2 rotation of E in B: l 2 C B l at l = 10 4, ν = 30GHz Kosowsky and Loeb 1996, Campanelli et al 2004, Kosowsky et al Homogeneous field breaks isotropy a l+1,m a l 1,m Durrer et al 1998, Naselsky et al 2004 Stronger B polarisation from Faraday rotation, TB cross-correlation Scoccola et al 2004, Kristiansen and Ferreira
25 Conclusions The origin of MF observed in astrophysical objects is still unclear Observations: SKA radiotelescope: all-sky rotation measure survey evolution of magnetised structure from z>3 detect MF in the IGM? PLANCK: detect B polarisation and large multipoles parity-odd cross-correlations? non-gaussianity? LISA: GW signal from EW primordial fields Theory: deeper understanding of small scale dynamo processes are helical fields the solution? (not mentioned structure formation, cosmic rays...)
26 The alpha-omega mean field dynamo induction equation B t = (V B) B mean and random components = B + b V = V + v substituting and further averaging B t = ( V B ) + v b quasi-linear approximation + homogeneity and isotropy v b = α B β B β = τ α = τ v v 3 v2 3 field with poloidal and toroidal components α = α 0 z h B φ t B r t B e γt γ = α0 Ω = Ω B r = α B φ z h 2Gy 1 omega: poloidal into toroidal alpha: toroidal into poloidal B gal in Gauss (Brandenburg and Subramanian 2005)
Effects of primordial kinetic and magnetic helicity
 Effects of primordial kinetic and magnetic helicity Tina Kahniashvili 1. T. Kahniashvili and B.Ratra, 2005, PRD, 71, 103006 2. T. Kahniashvili, G. Gogoberidze, and B. Ratra, astro-ph/0505628, Phys. Rev.
Effects of primordial kinetic and magnetic helicity Tina Kahniashvili 1. T. Kahniashvili and B.Ratra, 2005, PRD, 71, 103006 2. T. Kahniashvili, G. Gogoberidze, and B. Ratra, astro-ph/0505628, Phys. Rev.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 8 Sep 2006
 Cosmic Magnetic Fields and the CMB Ruth Durrer arxiv:astro-ph/0609216v1 8 Sep 2006 Abstract Université de Genève, Ecole de Physique 24 Quai E. Ansermet, CH-1211 Genève Switzerland I describe the imprint
Cosmic Magnetic Fields and the CMB Ruth Durrer arxiv:astro-ph/0609216v1 8 Sep 2006 Abstract Université de Genève, Ecole de Physique 24 Quai E. Ansermet, CH-1211 Genève Switzerland I describe the imprint
EFFECTS OF HELICAL MAGNETIC FIELDS ON THE CMB
 EFFECTS OF HELICAL MAGNETIC FIELDS ON THE CMB KERSTIN KUNZE (UNIVERSITY OF SALAMANCA) KK, PRD 85 (2012) 083004 KK, PRD 83 (2011) 023006 OVERVIEW MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE STOCHASTIC HELICAL MAGNETIC
EFFECTS OF HELICAL MAGNETIC FIELDS ON THE CMB KERSTIN KUNZE (UNIVERSITY OF SALAMANCA) KK, PRD 85 (2012) 083004 KK, PRD 83 (2011) 023006 OVERVIEW MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE STOCHASTIC HELICAL MAGNETIC
Evolution and Signatures of Helical Magnetic Fields
 Evolution and Signatures of Helical Magnetic Fields Tina Kahniashvili McWilliams Center for Cosmology Carnegie Mellon University & Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory Ilia State University NORDITA June
Evolution and Signatures of Helical Magnetic Fields Tina Kahniashvili McWilliams Center for Cosmology Carnegie Mellon University & Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory Ilia State University NORDITA June
Magnetic fields in the early universe
 Magnetic fields in the early universe KandaswamySubramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. Heidelberg Joint Astronomical Colloquium, 1st December, 2009
Magnetic fields in the early universe KandaswamySubramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. Heidelberg Joint Astronomical Colloquium, 1st December, 2009
Primordial Magnetic Field Effects on CMB polarization
 Primordial Magnetic Field Effects on CMB polarization Tina Kahniashvili McWilliams Center for Cosmology Carnegie Mellon University, USA & Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory, Ilia Chavchavadze State University,
Primordial Magnetic Field Effects on CMB polarization Tina Kahniashvili McWilliams Center for Cosmology Carnegie Mellon University, USA & Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory, Ilia Chavchavadze State University,
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields
 Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
Polarized Relic Gravitational Waves
 Polarized Relic Gravitational Waves Tina Kahniashvili CCPP, New York University, USA & Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory, Georgia based on: T.K., G. Gogoberidze, and B.Ratra, PRL 2005, 2007 (in preparation),
Polarized Relic Gravitational Waves Tina Kahniashvili CCPP, New York University, USA & Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory, Georgia based on: T.K., G. Gogoberidze, and B.Ratra, PRL 2005, 2007 (in preparation),
Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations
 Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations Kerstin Kunze (University of Salamanca and IUFFyM) KK PRD 83 (2011) 023006; PRD 85 (2012) 083004; PRD 87 (2013) 103005; PRD 89 (2014) 103016, arxiv:1703.03650
Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations Kerstin Kunze (University of Salamanca and IUFFyM) KK PRD 83 (2011) 023006; PRD 85 (2012) 083004; PRD 87 (2013) 103005; PRD 89 (2014) 103016, arxiv:1703.03650
origin of large scale magnetic fields: physics of the early Universe? plasma astrophysics in the late Universe?
 Magnetic fields at > Galactic scales Martin Lemoine Institut d Astrophysique de Paris CNRS, Université Pierre & Marie Curie Questions related to large scale magnetic fields origin of large scale magnetic
Magnetic fields at > Galactic scales Martin Lemoine Institut d Astrophysique de Paris CNRS, Université Pierre & Marie Curie Questions related to large scale magnetic fields origin of large scale magnetic
GRAVITATIONAL WAVES FROM FIRST ORDER PHASE TRANSITIONS
 GRAVITATIONAL WAVES FROM FIRST ORDER PHASE TRANSITIONS Chiara Caprini IPhT, CEA Saclay (France) CC, R. Durrer and X. Siemens, arxiv:1007.1218 CC, R. Durrer and G. Servant, asxiv:0909.0622 CC, R. Durrer
GRAVITATIONAL WAVES FROM FIRST ORDER PHASE TRANSITIONS Chiara Caprini IPhT, CEA Saclay (France) CC, R. Durrer and X. Siemens, arxiv:1007.1218 CC, R. Durrer and G. Servant, asxiv:0909.0622 CC, R. Durrer
Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies
 Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe
 The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff Phys. Rev. D89:103001 arxiv:1304.4723 Hamburger Sternwarte, Hamburg University Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik
The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff Phys. Rev. D89:103001 arxiv:1304.4723 Hamburger Sternwarte, Hamburg University Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik
Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field
 Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Dolag, MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10 Neronov, Semikoz, MK, Ostapchenko, Elyiv 10 Introduction Mean free path of photons
Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Dolag, MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10 Neronov, Semikoz, MK, Ostapchenko, Elyiv 10 Introduction Mean free path of photons
Production of helical magnetic fields during baryogenesis
 Production of helical magnetic fields during baryogenesis Francesc Ferrer Washington University in Saint Louis ferrer@wustl.edu NORDITA. June 23, 25 Outline Introduction: Observations of Magnetic Fields
Production of helical magnetic fields during baryogenesis Francesc Ferrer Washington University in Saint Louis ferrer@wustl.edu NORDITA. June 23, 25 Outline Introduction: Observations of Magnetic Fields
Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe
 Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff 1 arxiv:1304.4723 Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik Schleicher 2, Günter Sigl 3 1 Hamburg University 2 Institut für Astrophysik,
Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff 1 arxiv:1304.4723 Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik Schleicher 2, Günter Sigl 3 1 Hamburg University 2 Institut für Astrophysik,
Galaxies 626. Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star
 Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
Probing Primordial Magnetic Fields with Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Probing Primordial Magnetic Fields with Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Department of Physics and Astrophysics University of Delhi IIT Madras, May 17, 2012 Collaborators: K. Subramanian, Pranjal
Probing Primordial Magnetic Fields with Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Department of Physics and Astrophysics University of Delhi IIT Madras, May 17, 2012 Collaborators: K. Subramanian, Pranjal
Magnetic Fields in Astrophysics: Origins and Evolution. Kinwah Wu Mullard Space Science Laboratory University College London
 Magnetic Fields in Astrophysics: Origins and Evolution Kinwah Wu Mullard Space Science Laboratory University College London Maxwell s equations covariant form in flat space time Lorentz force equation:
Magnetic Fields in Astrophysics: Origins and Evolution Kinwah Wu Mullard Space Science Laboratory University College London Maxwell s equations covariant form in flat space time Lorentz force equation:
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA
 Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS
 SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS MARTIN KRAUSE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE, UNIVERSITÄTSSTERNWARTE MÜNCHEN & MAX-PLANCK-INSTITUT FÜR EXTRATERRESTRISCHE PHYSIK COLLABORATORS: PAUL
SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS MARTIN KRAUSE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE, UNIVERSITÄTSSTERNWARTE MÜNCHEN & MAX-PLANCK-INSTITUT FÜR EXTRATERRESTRISCHE PHYSIK COLLABORATORS: PAUL
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters
 Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
Cosmological magnetic fields
 PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 55, No. 4 journal of October 2000 physics pp. 575 583 Cosmological magnetic fields ROY MAARTENS Relativity and Cosmology Group, School of Computer Science and
PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 55, No. 4 journal of October 2000 physics pp. 575 583 Cosmological magnetic fields ROY MAARTENS Relativity and Cosmology Group, School of Computer Science and
Microwave Background Polarization: Theoretical Perspectives
 Microwave Background Polarization: Theoretical Perspectives Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Pittsburgh CMBpol Technology Workshop Outline Tensor Perturbations and Microwave Polarization
Microwave Background Polarization: Theoretical Perspectives Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Pittsburgh CMBpol Technology Workshop Outline Tensor Perturbations and Microwave Polarization
Basics of MHD. Kandaswamy Subramanian a. Pune , India. a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics,
 Basics of MHD Kandaswamy Subramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The magnetic Universe, Feb 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Magnetic fields in Astrophysics MHD
Basics of MHD Kandaswamy Subramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The magnetic Universe, Feb 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Magnetic fields in Astrophysics MHD
Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters
 Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters Kandaswamy Subramanian Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Observing
Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters Kandaswamy Subramanian Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Observing
Really, really, what universe do we live in?
 Really, really, what universe do we live in? Fluctuations in cosmic microwave background Origin Amplitude Spectrum Cosmic variance CMB observations and cosmological parameters COBE, balloons WMAP Parameters
Really, really, what universe do we live in? Fluctuations in cosmic microwave background Origin Amplitude Spectrum Cosmic variance CMB observations and cosmological parameters COBE, balloons WMAP Parameters
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results. Alexander Schmah
 The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
Structures in the early Universe. Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4
 Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview Part 1: problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Part : Need for
Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview Part 1: problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Part : Need for
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields. Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn
 Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs
 Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
Evolution of primordial magnetic fields
 Astron. Nachr. / AN 334, No. 6, 537 542 (203) / DOI 0.002/asna.203893 Evolution of primordial magnetic fields R. Banerjee Hamburger Sternwarte, University of Hamburg, Gojenbergsweg 2, 2029 Hamburg, Germany
Astron. Nachr. / AN 334, No. 6, 537 542 (203) / DOI 0.002/asna.203893 Evolution of primordial magnetic fields R. Banerjee Hamburger Sternwarte, University of Hamburg, Gojenbergsweg 2, 2029 Hamburg, Germany
The Origin and Evolution of Cosmic Magnetism: Perspective from SKA. Luigina Feretti IRA - Bologna MCCT-SKADS School, Medicina,
 The Origin and Evolution of Cosmic Magnetism: Perspective from SKA Luigina Feretti IRA - Bologna MCCT-SKADS School, Medicina, 25 9-07 This topic is one of the 5 Key Science Projects of SKA, selected by
The Origin and Evolution of Cosmic Magnetism: Perspective from SKA Luigina Feretti IRA - Bologna MCCT-SKADS School, Medicina, 25 9-07 This topic is one of the 5 Key Science Projects of SKA, selected by
Second part of the talk
 Second part of the talk Homogeneous vs Inhomogeneous No matter where they come from, PMFs could have left an imprint on the CMB anisotropy pattern in temperature and polarization. In case of an homogeneous
Second part of the talk Homogeneous vs Inhomogeneous No matter where they come from, PMFs could have left an imprint on the CMB anisotropy pattern in temperature and polarization. In case of an homogeneous
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS. ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP. NOTES: (references therein)
 PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 9 Jul 1998
 Microwave Background Anisotropies from Alfvén waves arxiv:astro-ph/9807089v1 9 Jul 1998 R. Durrer, T. Kahniashvili and A. Yates Département de Physique Théorique, Université de Genève, 24 quai Ernest Ansermet,
Microwave Background Anisotropies from Alfvén waves arxiv:astro-ph/9807089v1 9 Jul 1998 R. Durrer, T. Kahniashvili and A. Yates Département de Physique Théorique, Université de Genève, 24 quai Ernest Ansermet,
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 9 Jun 2011
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 9 Jun 2011 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 9 Jun 2011](/thumbs/74/69912655.jpg) - Cosmic microwave background bispectrum of tensor passive modes induced from primordial magnetic fields Maresuke Shiraishi, 1, Daisuke Nitta, 1 Shuichiro Yokoyama, 1 Kiyotomo Ichiki, 1 and Keitaro Takahashi
- Cosmic microwave background bispectrum of tensor passive modes induced from primordial magnetic fields Maresuke Shiraishi, 1, Daisuke Nitta, 1 Shuichiro Yokoyama, 1 Kiyotomo Ichiki, 1 and Keitaro Takahashi
COSMOLOGY AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES. Chiara Caprini (APC)
 COSMOLOGY AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Chiara Caprini (APC) the direct detection of GW by the LIGO interferometers has opened a new era in Astronomy - we now have a new messenger bringing complementary informations
COSMOLOGY AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Chiara Caprini (APC) the direct detection of GW by the LIGO interferometers has opened a new era in Astronomy - we now have a new messenger bringing complementary informations
Concordance Cosmology and Particle Physics. Richard Easther (Yale University)
 Concordance Cosmology and Particle Physics Richard Easther (Yale University) Concordance Cosmology The standard model for cosmology Simplest model that fits the data Smallest number of free parameters
Concordance Cosmology and Particle Physics Richard Easther (Yale University) Concordance Cosmology The standard model for cosmology Simplest model that fits the data Smallest number of free parameters
3 Observational Cosmology Evolution from the Big Bang Lecture 2
 3 Observational Cosmology Evolution from the Big Bang Lecture 2 http://www.sr.bham.ac.uk/~smcgee/obscosmo/ Sean McGee smcgee@star.sr.bham.ac.uk http://www.star.sr.bham.ac.uk/~smcgee/obscosmo Nucleosynthesis
3 Observational Cosmology Evolution from the Big Bang Lecture 2 http://www.sr.bham.ac.uk/~smcgee/obscosmo/ Sean McGee smcgee@star.sr.bham.ac.uk http://www.star.sr.bham.ac.uk/~smcgee/obscosmo Nucleosynthesis
Soma De Post-doctoral Fellow, Arizona State University presentation at 27th Texas Symposium, Dec 11,2013
 Linear Polarization of CMB and 21cm & Circular Polarization of CMB Soma De Post-doctoral Fellow, Arizona State University presentation at 27th Texas Symposium, Dec 11,2013 Collaboration: Levon Pogosian
Linear Polarization of CMB and 21cm & Circular Polarization of CMB Soma De Post-doctoral Fellow, Arizona State University presentation at 27th Texas Symposium, Dec 11,2013 Collaboration: Levon Pogosian
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 27 Apr 2004
 KSUPT-04/2 March 2004 Looking for Cosmological Alfvén Waves in WMAP Data Gang Chen 1, Pia Mukherjee 2, Tina Kahniashvili 1,3, Bharat Ratra 1, and Yun Wang 2 arxiv:astro-ph/0403695v2 27 Apr 2004 ABSTRACT
KSUPT-04/2 March 2004 Looking for Cosmological Alfvén Waves in WMAP Data Gang Chen 1, Pia Mukherjee 2, Tina Kahniashvili 1,3, Bharat Ratra 1, and Yun Wang 2 arxiv:astro-ph/0403695v2 27 Apr 2004 ABSTRACT
Reduced MHD. Nick Murphy. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics. February 19, 2014
 Reduced MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 19, 2014 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics by Dalton
Reduced MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 19, 2014 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics by Dalton
Making Light from the Dark Universe
 Oxford University Physics Society, 1st May 2014 Talk Structure 1. Prelude: What is Dark Radiation? 2. Experimental motivation for dark radiation: CMB and BBN 3. Theoretical motivation for dark radiation:
Oxford University Physics Society, 1st May 2014 Talk Structure 1. Prelude: What is Dark Radiation? 2. Experimental motivation for dark radiation: CMB and BBN 3. Theoretical motivation for dark radiation:
INFLATION. - EARLY EXPONENTIAL PHASE OF GROWTH OF SCALE FACTOR (after T ~ TGUT ~ GeV)
 INFLATION - EARLY EXPONENTIAL PHASE OF GROWTH OF SCALE FACTOR (after T ~ TGUT ~ 10 15 GeV) -Phenomenologically similar to Universe with a dominant cosmological constant, however inflation needs to end
INFLATION - EARLY EXPONENTIAL PHASE OF GROWTH OF SCALE FACTOR (after T ~ TGUT ~ 10 15 GeV) -Phenomenologically similar to Universe with a dominant cosmological constant, however inflation needs to end
Generation of Large-Scale Magnetic Fields from Inflation in Teleparallelism
 VIIIth Rencontres du Vietnam - Beyond the Standard Model Generation of Large-Scale Magnetic Fields from Inflation in Teleparallelism Reference: JCAP 10 (2012) 058 Ling-Wei Luo Department of Physics, National
VIIIth Rencontres du Vietnam - Beyond the Standard Model Generation of Large-Scale Magnetic Fields from Inflation in Teleparallelism Reference: JCAP 10 (2012) 058 Ling-Wei Luo Department of Physics, National
 Caldwell, MK, Wadley (open) (flat) CMB determination of the geometry (MK, Spergel, and Sugiyama, 1994) Where did large scale structure (e.g., galaxies, clusters, larger-scale explosions clustering)
Caldwell, MK, Wadley (open) (flat) CMB determination of the geometry (MK, Spergel, and Sugiyama, 1994) Where did large scale structure (e.g., galaxies, clusters, larger-scale explosions clustering)
Baryon asymmetry from hypermagnetic helicity in inflationary cosmology
 Baryon asymmetry from hypermagnetic helicity in inflationary cosmology Reference: Physical Review D 74, 123504 (2006) [e-print arxiv:hep-ph/0611152] Particle and field seminar at National Tsing Hua University
Baryon asymmetry from hypermagnetic helicity in inflationary cosmology Reference: Physical Review D 74, 123504 (2006) [e-print arxiv:hep-ph/0611152] Particle and field seminar at National Tsing Hua University
Lecture 4. - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum (continued) - Polarisation
 Lecture 4 - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum (continued) - Polarisation Planck Collaboration (2016) Let s understand the peak heights Silk+Landau Damping Sachs-Wolfe
Lecture 4 - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum (continued) - Polarisation Planck Collaboration (2016) Let s understand the peak heights Silk+Landau Damping Sachs-Wolfe
The Early Universe John Peacock ESA Cosmic Vision Paris, Sept 2004
 The Early Universe John Peacock ESA Cosmic Vision Paris, Sept 2004 The history of modern cosmology 1917 Static via cosmological constant? (Einstein) 1917 Expansion (Slipher) 1952 Big Bang criticism (Hoyle)
The Early Universe John Peacock ESA Cosmic Vision Paris, Sept 2004 The history of modern cosmology 1917 Static via cosmological constant? (Einstein) 1917 Expansion (Slipher) 1952 Big Bang criticism (Hoyle)
Modern Cosmology Final Examination Solutions 60 Pts
 Modern Cosmology Final Examination Solutions 6 Pts Name:... Matr. Nr.:... February,. Observable Universe [4 Pts] 6 Pt: Complete the plot of Redshift vs Luminosity distance in the range < z < and plot (i)
Modern Cosmology Final Examination Solutions 6 Pts Name:... Matr. Nr.:... February,. Observable Universe [4 Pts] 6 Pt: Complete the plot of Redshift vs Luminosity distance in the range < z < and plot (i)
PRIMORDIAL MAGNETIC FIELDS WITH BPOL
 PRIMORDIAL MAGNETIC FIELDS WITH BPOL DANIELA PAOLETTI 1,2,3 & FABIO FINELLI 1,4 1 INAF/IASFBO Istituto di Astrofisica Spaziale e Fisica Cosmica di Bologna 2 Dipartimento di Fisica, Università degli Studi
PRIMORDIAL MAGNETIC FIELDS WITH BPOL DANIELA PAOLETTI 1,2,3 & FABIO FINELLI 1,4 1 INAF/IASFBO Istituto di Astrofisica Spaziale e Fisica Cosmica di Bologna 2 Dipartimento di Fisica, Università degli Studi
MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE
 ARTICLE MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE KANDASWAMY SUBRAMANIAN* The origin and maintenance of large scale magnetic fields in the Universe is discussed. A popular idea is that cosmic batteries generate
ARTICLE MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE KANDASWAMY SUBRAMANIAN* The origin and maintenance of large scale magnetic fields in the Universe is discussed. A popular idea is that cosmic batteries generate
Inflationary Cosmology and Alternatives
 Inflationary Cosmology and Alternatives V.A. Rubakov Institute for Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow and Department of paricle Physics abd Cosmology Physics Faculty Moscow State
Inflationary Cosmology and Alternatives V.A. Rubakov Institute for Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow and Department of paricle Physics abd Cosmology Physics Faculty Moscow State
Generation of Magnetic Fields in Cosmology. A.D. Dolgov
 Generation of Magnetic Fields in Cosmology A.D. Dolgov INFN, sezione di Ferrara Via Paradiso, 12-44100 Ferrara, Italy and ITEP, B. Cheremushkinskaya 25, Moscow, 117259, Russia Abstract Mechanisms of generation
Generation of Magnetic Fields in Cosmology A.D. Dolgov INFN, sezione di Ferrara Via Paradiso, 12-44100 Ferrara, Italy and ITEP, B. Cheremushkinskaya 25, Moscow, 117259, Russia Abstract Mechanisms of generation
arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 12 Jan 2014
![arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 12 Jan 2014 arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 12 Jan 2014](/thumbs/92/109664722.jpg) Galactic dynamo seeds from non-superconducting spin-polarised strings L.C.Garcia de Andrade 1 arxiv:1401.587v1 [gr-qc] 1 Jan 014 Abstract Earlier Enqvist and Olesen have shown that formation of ferromagnetic
Galactic dynamo seeds from non-superconducting spin-polarised strings L.C.Garcia de Andrade 1 arxiv:1401.587v1 [gr-qc] 1 Jan 014 Abstract Earlier Enqvist and Olesen have shown that formation of ferromagnetic
Cosmological observables and the nature of dark matter
 Cosmological observables and the nature of dark matter Shiv Sethi Raman Research Institute March 18, 2018 SDSS results: power... SDSS results: BAO at... Planck results:... Planck-SDSS comparison Summary
Cosmological observables and the nature of dark matter Shiv Sethi Raman Research Institute March 18, 2018 SDSS results: power... SDSS results: BAO at... Planck results:... Planck-SDSS comparison Summary
Triple unification of inflation, dark matter and dark energy
 Triple unification of inflation, dark matter and dark energy May 9, 2008 Leonard Susskind, The Anthropic Landscape of String Theory (2003) A. Liddle, A. Ureña-López, Inflation, dark matter and dark energy
Triple unification of inflation, dark matter and dark energy May 9, 2008 Leonard Susskind, The Anthropic Landscape of String Theory (2003) A. Liddle, A. Ureña-López, Inflation, dark matter and dark energy
Probing Cosmology and measuring the peculiar acceleration of binary black holes with LISA
 Probing Cosmology and measuring the peculiar acceleration of binary black holes with LISA Institut de Physique Théorique CEA-Saclay CNRS Université Paris-Saclay Probing cosmology with LISA Based on: Tamanini,
Probing Cosmology and measuring the peculiar acceleration of binary black holes with LISA Institut de Physique Théorique CEA-Saclay CNRS Université Paris-Saclay Probing cosmology with LISA Based on: Tamanini,
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences
 UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Exam for AST5220 Cosmology II Date: Tuesday, June 4th, 2013 Time: 09.00 13.00 The exam set consists of 13 pages. Appendix: Equation summary
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Exam for AST5220 Cosmology II Date: Tuesday, June 4th, 2013 Time: 09.00 13.00 The exam set consists of 13 pages. Appendix: Equation summary
Cosmic Microwave Background
 Cosmic Microwave Background Following recombination, photons that were coupled to the matter have had very little subsequent interaction with matter. Now observed as the cosmic microwave background. Arguably
Cosmic Microwave Background Following recombination, photons that were coupled to the matter have had very little subsequent interaction with matter. Now observed as the cosmic microwave background. Arguably
Parity violation in the Cosmic Microwave Background from a pseudoscalar inflaton
 Parity violation in the Cosmic Microwave Background from a pseudoscalar inflaton Lorenzo Sorbo UMass Amherst Padova, 17/02/2011 LS, 1101.1525 Plan of the talk Inflation, radiative stability and pseudo-nambu-goldstone
Parity violation in the Cosmic Microwave Background from a pseudoscalar inflaton Lorenzo Sorbo UMass Amherst Padova, 17/02/2011 LS, 1101.1525 Plan of the talk Inflation, radiative stability and pseudo-nambu-goldstone
IoP. An Introduction to the Science of Cosmology. Derek Raine. Ted Thomas. Series in Astronomy and Astrophysics
 Series in Astronomy and Astrophysics An Introduction to the Science of Cosmology Derek Raine Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Leicester, UK Ted Thomas Department of Physics and Astronomy
Series in Astronomy and Astrophysics An Introduction to the Science of Cosmology Derek Raine Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Leicester, UK Ted Thomas Department of Physics and Astronomy
Ringing in the New Cosmology
 Ringing in the New Cosmology 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 Boom98 CBI Maxima-1 DASI 500 1000 1500 l (multipole) Acoustic Peaks in the CMB Wayne Hu Temperature Maps CMB Isotropy Actual Temperature Data COBE 1992 Dipole
Ringing in the New Cosmology 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 Boom98 CBI Maxima-1 DASI 500 1000 1500 l (multipole) Acoustic Peaks in the CMB Wayne Hu Temperature Maps CMB Isotropy Actual Temperature Data COBE 1992 Dipole
From inflation to the CMB to today s universe. I - How it all begins
 From inflation to the CMB to today s universe I - How it all begins Raul Abramo Physics Institute - University of São Paulo abramo@fma.if.usp.br redshift Very brief cosmic history 10 9 200 s BBN 1 MeV
From inflation to the CMB to today s universe I - How it all begins Raul Abramo Physics Institute - University of São Paulo abramo@fma.if.usp.br redshift Very brief cosmic history 10 9 200 s BBN 1 MeV
Key: cosmological perturbations. With the LHC, we hope to be able to go up to temperatures T 100 GeV, age t second
 Lecture 3 With Big Bang nucleosynthesis theory and observations we are confident of the theory of the early Universe at temperatures up to T 1 MeV, age t 1 second With the LHC, we hope to be able to go
Lecture 3 With Big Bang nucleosynthesis theory and observations we are confident of the theory of the early Universe at temperatures up to T 1 MeV, age t 1 second With the LHC, we hope to be able to go
Galaxies and Cosmology
 F. Combes P. Boisse A. Mazure A. Blanchard Galaxies and Cosmology Translated by M. Seymour With 192 Figures Springer Contents General Introduction 1 1 The Classification and Morphology of Galaxies 5 1.1
F. Combes P. Boisse A. Mazure A. Blanchard Galaxies and Cosmology Translated by M. Seymour With 192 Figures Springer Contents General Introduction 1 1 The Classification and Morphology of Galaxies 5 1.1
Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium
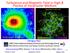 Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium Coma cluster of galaxies Dongsu Ryu UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) KASI (Korea Astronomy and Space
Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium Coma cluster of galaxies Dongsu Ryu UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) KASI (Korea Astronomy and Space
Cosmology II: The thermal history of the Universe
 .. Cosmology II: The thermal history of the Universe Ruth Durrer Département de Physique Théorique et CAP Université de Genève Suisse August 6, 2014 Ruth Durrer (Université de Genève) Cosmology II August
.. Cosmology II: The thermal history of the Universe Ruth Durrer Département de Physique Théorique et CAP Université de Genève Suisse August 6, 2014 Ruth Durrer (Université de Genève) Cosmology II August
Decaying Dark Matter, Bulk Viscosity, and Dark Energy
 Decaying Dark Matter, Bulk Viscosity, and Dark Energy Dallas, SMU; April 5, 2010 Outline Outline Standard Views Dark Matter Standard Views of Dark Energy Alternative Views of Dark Energy/Dark Matter Dark
Decaying Dark Matter, Bulk Viscosity, and Dark Energy Dallas, SMU; April 5, 2010 Outline Outline Standard Views Dark Matter Standard Views of Dark Energy Alternative Views of Dark Energy/Dark Matter Dark
POST-INFLATIONARY HIGGS RELAXATION AND THE ORIGIN OF MATTER- ANTIMATTER ASYMMETRY
 POST-INFLATIONARY HIGGS RELAXATION AND THE ORIGIN OF MATTER- ANTIMATTER ASYMMETRY LOUIS YANG ( 楊智軒 ) UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, LOS ANGELES (UCLA) DEC 27, 2016 NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY OUTLINE Big
POST-INFLATIONARY HIGGS RELAXATION AND THE ORIGIN OF MATTER- ANTIMATTER ASYMMETRY LOUIS YANG ( 楊智軒 ) UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, LOS ANGELES (UCLA) DEC 27, 2016 NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY OUTLINE Big
Physics 463, Spring 07. Formation and Evolution of Structure: Growth of Inhomogenieties & the Linear Power Spectrum
 Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 3 Formation and Evolution of Structure: Growth of Inhomogenieties & the Linear Power Spectrum last time: how fluctuations are generated and how the smooth Universe grows
Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 3 Formation and Evolution of Structure: Growth of Inhomogenieties & the Linear Power Spectrum last time: how fluctuations are generated and how the smooth Universe grows
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 24 Mar 2005
 Faraday Rotation of the Cosmic Microwave Background Polarization by a Stochastic Magnetic Field Arthur Kosowsky, 1, Tina Kahniashvili,, George Lavrelashvili, 3, and Bharat Ratra 4, 1 Department of Physics
Faraday Rotation of the Cosmic Microwave Background Polarization by a Stochastic Magnetic Field Arthur Kosowsky, 1, Tina Kahniashvili,, George Lavrelashvili, 3, and Bharat Ratra 4, 1 Department of Physics
Physical Cosmology 6/6/2016
 Physical Cosmology 6/6/2016 Alessandro Melchiorri alessandro.melchiorri@roma1.infn.it slides can be found here: oberon.roma1.infn.it/alessandro/cosmo2016 CMB anisotropies The temperature fluctuation in
Physical Cosmology 6/6/2016 Alessandro Melchiorri alessandro.melchiorri@roma1.infn.it slides can be found here: oberon.roma1.infn.it/alessandro/cosmo2016 CMB anisotropies The temperature fluctuation in
80 2 Observational Cosmology L and the mean energy
 80 2 Observational Cosmology fluctuations, short-wavelength modes have amplitudes that are suppressed because these modes oscillated as acoustic waves during the radiation epoch whereas the amplitude of
80 2 Observational Cosmology fluctuations, short-wavelength modes have amplitudes that are suppressed because these modes oscillated as acoustic waves during the radiation epoch whereas the amplitude of
Cosmic Strings. May 2, Safa Motesharrei University of Maryland
 Safa Motesharrei University of Maryland May 2, 2007 String Theory!! Cosmology Outline Why? What is a Topological Defect? Examples of Cosmological Defects Brief History Importance to String Theory Geometry
Safa Motesharrei University of Maryland May 2, 2007 String Theory!! Cosmology Outline Why? What is a Topological Defect? Examples of Cosmological Defects Brief History Importance to String Theory Geometry
Structures in the early Universe. Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4
 Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Need for an exponential
Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Need for an exponential
Lecture 3. - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum. - Polarisation of the CMB
 Lecture 3 - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum - Polarisation of the CMB Planck Collaboration (2016) Let s understand the peak heights Silk+Landau Damping Sachs-Wolfe Sound
Lecture 3 - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum - Polarisation of the CMB Planck Collaboration (2016) Let s understand the peak heights Silk+Landau Damping Sachs-Wolfe Sound
Oddities of the Universe
 Oddities of the Universe Koushik Dutta Theory Division, Saha Institute Physics Department, IISER, Kolkata 4th November, 2016 1 Outline - Basics of General Relativity - Expanding FRW Universe - Problems
Oddities of the Universe Koushik Dutta Theory Division, Saha Institute Physics Department, IISER, Kolkata 4th November, 2016 1 Outline - Basics of General Relativity - Expanding FRW Universe - Problems
El Universo en Expansion. Juan García-Bellido Inst. Física Teórica UAM Benasque, 12 Julio 2004
 El Universo en Expansion Juan García-Bellido Inst. Física Teórica UAM Benasque, 12 Julio 2004 5 billion years (you are here) Space is Homogeneous and Isotropic General Relativity An Expanding Universe
El Universo en Expansion Juan García-Bellido Inst. Física Teórica UAM Benasque, 12 Julio 2004 5 billion years (you are here) Space is Homogeneous and Isotropic General Relativity An Expanding Universe
Astr 2320 Thurs. May 7, 2015 Today s Topics Chapter 24: New Cosmology Problems with the Standard Model Cosmic Nucleosynthesis Particle Physics Cosmic
 Astr 2320 Thurs. May 7, 2015 Today s Topics Chapter 24: New Cosmology Problems with the Standard Model Cosmic Nucleosynthesis Particle Physics Cosmic Inflation Galaxy Formation 1 Chapter 24: #3 Chapter
Astr 2320 Thurs. May 7, 2015 Today s Topics Chapter 24: New Cosmology Problems with the Standard Model Cosmic Nucleosynthesis Particle Physics Cosmic Inflation Galaxy Formation 1 Chapter 24: #3 Chapter
Imprint of Scalar Dark Energy on CMB polarization
 Imprint of Scalar Dark Energy on CMB polarization Kin-Wang Ng ( 吳建宏 ) Institute of Physics & Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica, Taiwan Cosmology and Gravity Pre-workshop NTHU, Apr
Imprint of Scalar Dark Energy on CMB polarization Kin-Wang Ng ( 吳建宏 ) Institute of Physics & Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica, Taiwan Cosmology and Gravity Pre-workshop NTHU, Apr
Large-Scale Structure of the Galactic Magnetic Field. Marijke Haverkorn & Jo-Anne Brown NRAO/UC-Berkeley University of Calgary
 Large-Scale Structure of the Galactic Magnetic Field Marijke Haverkorn & Jo-Anne Brown NRAO/UC-Berkeley University of Calgary Outline On the Large-Scale Structure of the GMF... Why do we care? What do
Large-Scale Structure of the Galactic Magnetic Field Marijke Haverkorn & Jo-Anne Brown NRAO/UC-Berkeley University of Calgary Outline On the Large-Scale Structure of the GMF... Why do we care? What do
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
The Once and Future CMB
 The Once and Future CMB DOE, Jan. 2002 Wayne Hu The On(c)e Ring Original Power Spectra of Maps 64º Band Filtered Ringing in the New Cosmology Gravitational Ringing Potential wells = inflationary seeds
The Once and Future CMB DOE, Jan. 2002 Wayne Hu The On(c)e Ring Original Power Spectra of Maps 64º Band Filtered Ringing in the New Cosmology Gravitational Ringing Potential wells = inflationary seeds
Polarization from Rayleigh scattering
 Polarization from Rayleigh scattering Blue sky thinking for future CMB observations Previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
Polarization from Rayleigh scattering Blue sky thinking for future CMB observations Previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
Highlights from Planck 2013 cosmological results Paolo Natoli Università di Ferrara and ASI/ASDC DSU2013, Sissa, 17 October 2013
 Highlights from Planck 2013 cosmological results Paolo Natoli Università di Ferrara and ASI/ASDC DSU2013, Sissa, 17 October 2013 On behalf of the Planck collaboration Fluctuation and GW generator Fluctuation
Highlights from Planck 2013 cosmological results Paolo Natoli Università di Ferrara and ASI/ASDC DSU2013, Sissa, 17 October 2013 On behalf of the Planck collaboration Fluctuation and GW generator Fluctuation
The early and late time acceleration of the Universe
 The early and late time acceleration of the Universe Tomo Takahashi (Saga University) March 7, 2016 New Generation Quantum Theory -Particle Physics, Cosmology, and Chemistry- @Kyoto University The early
The early and late time acceleration of the Universe Tomo Takahashi (Saga University) March 7, 2016 New Generation Quantum Theory -Particle Physics, Cosmology, and Chemistry- @Kyoto University The early
Gravitation: Cosmology
 An Introduction to General Relativity Center for Relativistic Astrophysics School of Physics Georgia Institute of Technology Notes based on textbook: Spacetime and Geometry by S.M. Carroll Spring 2013
An Introduction to General Relativity Center for Relativistic Astrophysics School of Physics Georgia Institute of Technology Notes based on textbook: Spacetime and Geometry by S.M. Carroll Spring 2013
isocurvature modes Since there are two degrees of freedom in
 isocurvature modes Since there are two degrees of freedom in the matter-radiation perturbation, there must be a second independent perturbation mode to complement the adiabatic solution. This clearly must
isocurvature modes Since there are two degrees of freedom in the matter-radiation perturbation, there must be a second independent perturbation mode to complement the adiabatic solution. This clearly must
Cosmology and particle physics
 Cosmology and particle physics Lecture notes Timm Wrase Lecture 9 Inflation - part I Having discussed the thermal history of our universe and in particular its evolution at times larger than 10 14 seconds
Cosmology and particle physics Lecture notes Timm Wrase Lecture 9 Inflation - part I Having discussed the thermal history of our universe and in particular its evolution at times larger than 10 14 seconds
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 11 Apr 2013
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 11 Apr 2013 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 11 Apr 2013](/thumbs/78/77692476.jpg) Evolution of Primordial Magnetic Fields from Phase Transitions NORDITA-2012-96 arxiv:1212.0596v2 [astro-ph.co] 11 Apr 2013 Tina Kahniashvili, 1,2,3, Alexander G. Tevzadze, 4, Axel Brandenburg, 5,6, and
Evolution of Primordial Magnetic Fields from Phase Transitions NORDITA-2012-96 arxiv:1212.0596v2 [astro-ph.co] 11 Apr 2013 Tina Kahniashvili, 1,2,3, Alexander G. Tevzadze, 4, Axel Brandenburg, 5,6, and
An Estimator for statistical anisotropy from the CMB. CMB bispectrum
 An Estimator for statistical anisotropy from the CMB bispectrum 09/29/2012 1 2 3 4 5 6 ...based on: N. Bartolo, E. D., M. Liguori, S. Matarrese, A. Riotto JCAP 1201:029 N. Bartolo, E. D., S. Matarrese,
An Estimator for statistical anisotropy from the CMB bispectrum 09/29/2012 1 2 3 4 5 6 ...based on: N. Bartolo, E. D., M. Liguori, S. Matarrese, A. Riotto JCAP 1201:029 N. Bartolo, E. D., S. Matarrese,
Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy and Cosmology. Week 8
 Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy and Cosmology Week 8 Outline for Week 8 Primordial Nucleosynthesis Successes of the standard Big Bang model Olbers paradox/age of the Universe Hubble s law CMB Chemical/Physical
Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy and Cosmology Week 8 Outline for Week 8 Primordial Nucleosynthesis Successes of the standard Big Bang model Olbers paradox/age of the Universe Hubble s law CMB Chemical/Physical
The cosmic microwave background radiation
 The cosmic microwave background radiation László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 May 18, 2018. Origin of the cosmic microwave radiation Photons in the plasma are
The cosmic microwave background radiation László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 May 18, 2018. Origin of the cosmic microwave radiation Photons in the plasma are
Observations of Magnetic Fields in Intracluster Medium. Govoni Federica INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Cagliari
 Observations of Magnetic Fields in Intracluster Medium Govoni Federica INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Cagliari Collaborators: M. Murgia, L. Feretti, G. Giovannini, V. Vacca, A. Bonafede IAU 2012 China
Observations of Magnetic Fields in Intracluster Medium Govoni Federica INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Cagliari Collaborators: M. Murgia, L. Feretti, G. Giovannini, V. Vacca, A. Bonafede IAU 2012 China
Week 10: Theoretical predictions for the CMB temperature power spectrum
 Week 10: Theoretical predictions for the CMB temperature power spectrum April 5, 2012 1 Introduction Last week we defined various observable quantities to describe the statistics of CMB temperature fluctuations,
Week 10: Theoretical predictions for the CMB temperature power spectrum April 5, 2012 1 Introduction Last week we defined various observable quantities to describe the statistics of CMB temperature fluctuations,
Priming the BICEP. Wayne Hu Chicago, March BB
 Priming the BICEP 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.01 0 0.01 BB 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 Wayne Hu Chicago, March 2014 A BICEP Primer How do gravitational waves affect the CMB temperature and polarization spectrum?
Priming the BICEP 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.01 0 0.01 BB 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 Wayne Hu Chicago, March 2014 A BICEP Primer How do gravitational waves affect the CMB temperature and polarization spectrum?
Scale symmetry a link from quantum gravity to cosmology
 Scale symmetry a link from quantum gravity to cosmology scale symmetry fluctuations induce running couplings violation of scale symmetry well known in QCD or standard model Fixed Points Quantum scale symmetry
Scale symmetry a link from quantum gravity to cosmology scale symmetry fluctuations induce running couplings violation of scale symmetry well known in QCD or standard model Fixed Points Quantum scale symmetry
Moduli and Axions in the X-ray Universe
 Uppsala 20th November 2016 Talk Structure 1. Moduli and Axions in String Theory 2. The Cosmological Moduli Problem 3. A 0.1-1 kev Cosmic Axion Background 4. Observing a Cosmic Axion Background and the
Uppsala 20th November 2016 Talk Structure 1. Moduli and Axions in String Theory 2. The Cosmological Moduli Problem 3. A 0.1-1 kev Cosmic Axion Background 4. Observing a Cosmic Axion Background and the
