Transactions on Engineering Sciences vol 1, 1993 WIT Press, ISSN
|
|
|
- Adele Madeline Brown
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Theoretical and experimental analysis of the rolling contact between two cylinders coated with multilayered, viscoelastic rubber G.F.M. Braat^, J.J. Kalker" "Delft University of Technology, Department of Technical Mathematics and Informatics, The Netherlands **0ce Nederland B.V. Research & Development, Department of Analytical Measurements, Venlo, The Netherlands ABSTRACT The rolling contact of cylinders coated with a rubber layer is studied. The rubber layer consists of one or more sublayers with different elastic and geometrical properties. Each sublayer may be viscoelastic. The numerical results are verified by experiments. A contactless measurement technique, Laser-Doppler Anemometry, is applied to measure the velocity in and outside the contact region. INTRODUCTION The frictional contact between rolling cylinders coated with one or more rubber layers has many applications in industry. For example in copiers these mechanical elements (or nips) frequently occur and are used to transport paper or to transfer the image onto the paper. The half-space approximation, which is based on the frictionless theory of Hertz\ is one of the methods that can be used to describe the underlying contact problem. Johnson^ summarizes this theory with friction. However, the half-space approximation is only applicable under certain conditions, i.e. the thickness d of the layer is large with respect to the dimensions of the contact region a. Meijers^ gives a solution for the frictionless indentation problem of a rigid cylinder and an elastic layer, founded on a rigid base, in terms of an infinite series for two cases (a/2d < 1) and (a/2d > 1). For thin, single layers the simplified theory of Kalker* may be applied. Frictional rolling contact of viscoelastic cylinders has been studied by Hunter^ The material is modelled as a viscoelastic halfspace with one relaxation time. The two-
2 120 Contact Mechanics dimensional^ and three-dimensional viscoelastic rolling contact problem has been treated by Wang. Kalker gives a numerical method to solve the problem of rolling contact of viscoelastic, multilayered cylinders on which this paper is based. Here we will briefly discuss the numerical model and present the numerical results. The computations are compared with experimental results. The measurements are obtained with the Laser-Doppler technique, which is a contactless method to measure velocities. Roller 1 sublayer 3 sublayer sublayi D Roller 2 Figure 1. Two multilayered cylinders in rolling contact STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM In figure 1 we see a two-dimensional cross-section of two multilayered cylinders in contact. A coordinate frame xz is attached. The upper and lower cylinder (roller 1 and 2 respectively) are pressed together by a normal force F^ which causes an approach 6 of the axles. A torque M^ applied to the axles of the rollers causes a tangential force F^ applied by the adjacent body (i.e. paper or rubber surface) to the surface of roller a. The friction between the contacting surfaces is modelled by Coulomb's Law of Friction. V^ is the circumferential velocity of roller a. The difference between Vj and V^ is called creepage. It is assumed that the cylinders are rolling steadily, i.e. there is no explicit time dependence. The deformations of the rubber material are assumed to be small relative to the dimensions of the body (radius /? ). The theory of linear elasticity and viscoelasticity is applied.
3 Contact Mechanics 121 Viscoelastic properties are modelled with a simple three-parameter spring-dashpot model, the Standard Linear Solid, which is discussed in many textbooks on viscoelasticity, e.g. Findley\ The constitutive equation for such a linear viscoelastic material is given by: 0 + T CJ = EQ + (EQ + k ) T U) where T is the relaxation time, derivative. Q and k are the elastic moduli and (') is the time THE SOLUTION METHOD The numerical algorithm, which solves this contact problem, consists of two main parts: The determination of the influence functions and the contact algorithm. Influence functions or Green's functions are characteristic functions for the rubber material. They are determined by a Fourier transformation of the governing equations of elasticity and the boundary conditions with respect to x. The boundary conditions are summarized. Firstly the normal and tangential contact stress distributions (i.e. a(x)ao;(x,0) and i(x)&ixz(x,0)) are assumed to be known in advance. They will be determined by the contact algorithm. Secondly the displacements w/x,z), w/x,z) and the stresses o/%,z), T^z) are continuous at an interface z=d$ between two sublayers. The index s indicates a sublayer number and d$ is the cumulative thickness of sublayer 1 to s. Finally at the boundary between rubber layer and rigid cylinder (z-d), the displacements vanish: u^(x,d) = u^x,d) = 0. If one of the sublayers is viscoelastic, the Correspondence Principle^ is applied: The governing equations for the elastic and the viscoelastic problem are similar in the Fourier domain. In the Fourier domain, the transformed stresses and displacements at an arbitrary position z are expressed in terms of the Fourier transformed contact stresses:, z) (2), Z) or briefly by:, z) (3) An analytical inverse Fourier transformation of equation (3) is rather difficult because the explicit expressions for S^co, z) are very complicated. Therefore a numerical inverse transformation is preferred. The interval of integration is divided into two parts. The first interval u)e[0,oj is divided into small non-equidistant elements on which the influence functions are approximated by a second order polynomial, see figure 2. If the curve has a high gradient, the element width is small. On the second interval coe[qc,^) the influence functions are replaced by a limit function^. In the spatial domain, the potential contact region is divided into elements Ax on which the stresses and displacements are assumed to be constant. The midpoints are
4 122 Contact Mechanics one quadratic interpolation element subinterval 2 subinterval 1 subinterval 0 A ( > - A c»>0 / 4 A o> = A G>0 / 2 Aco A nw ( ) = =nwg AAw Figure 2. Non-equidistant inverse Fourier Transformation. given by x^=kax. The contact stresses p/xj are determined by the contact algorithm, which computes the normal and tangential stress distributions, the approach and the creepage. The normal and tangential contact conditions are solved separately by NORM and TANG, two algorithms, designed by Kalker". The contact problem has a non-linear geometry. After the calculation of the deformed state, the deformed surfaces do not coincide. This is the geometryproblem, which has its origin in two phenomena: Firstly, when the influence numbers are calculated, the rubber layers are assumed to be horizontal, while in the real geometry they are curved, see figure 1. Secondly, in the expression for the distance between the deformed surfaces (normal contact conditions), the tangential displacements are not taken into account^: + U- (i)/(x)\ U^ (2)/ ' (X)\ O * v (4} / where h(x) is the distance in the undeformed state. Expression (4) is called the approximate distance. This problem is solved by the addition of a correction e(x) to the expression for the approximate distance. The correction is determined after each completed contact iteration and repeated until convergence of e(x) has been reached. In fact the numerical problem is solved now. The inverse Fourier transform of (3) and the contact stresses determined by the contact algorithm, give the relevant quantities /fo,z) for an arbitrary z-coordinate by: EXPERIMENTS WITH LASER DOPPLER ANEMOMETRY Numerical results become more valid if they are verified by experiment. The purpose is to measure velocities locally at an arbitrary surface point x in and outside the contact region. Laser-Doppler Anemometry (LDA) is a technique to measure velocities of moving particles. It is an optical method with the advantage that it is contactless. The principles of LDA are discussed in Durst^.
5 Contact Mechanics 123 The measured velocity at x is denoted by v^x) and can be related to the computed normal strain in the ^-direction, e/%), by: (6) dt = -V This relation holds only for steady state rolling, where V is the rolling velocity. The basic idea is to focus two coherent laser beams by a converging lens. The region of intersection is called the measuring volume. When a moving particle is crossing this measuring volume, it scatters light from both laser beams with different frequencies, according to the Doppler-effect. rubber layer black roller (A) (B) Figure 3. Laser-Doppler measurements: (A). Particle moves through the measuring volume, (B). Laser beams focussed into the contact region The difference between these frequencies is the Doppler-frequency / which is related to the velocity of the particle. A scheme of the experimental set-up is given in figure 3, where one of the rollers is completely transparent, while the other is black. The measuring volume is placed in the contact region by using two mirrors A and B of which the latter can be rotated about the y-axis (i.e. the axle of the glass roller). The rotation of the lower mirror causes the measuring volume to be displaced along the circumference of the outer surface of the glass roller. Hence we are able to scan the surface and to perform measurements at different positions. For detailed information on the experimental part of this research work, the reader is referred to NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS In this section an impression is given of the capabilities of the numerical algorithm, which have been implemented in a computer program, MULTILAYER. We examine a configuration which has two sublayers on the upper roller. The intermediate layer is relatively soft and thick (E=2.0 Nlmm\ d-4.0 mm), while the
6 124 Contact Mechanics d = mm * d = 0.2 mm x [mm] Figure 4. Normal stress distribution for a configuration with two sublayers toplayer is relatively hard (E=5500 Nlmnf). The thickness is varied (d=0, 0.025, 0.1 and 0.2 mm). The other roller is rigid. In figure 4 we see the normal stress distribution in the contact region. Peak stresses arise at the edges of the contact region, which are due to the bending of the upper layer. The peak values are proportional to the thickness of the toplayer. A similar result is obtained by Johnson^ for the indentation of a plate on an elastic foundation by a rigid cylinder. elastic, F? = 1.0 N/mm viscoelastic, F = 0.0 N/mm normal stress (A) normal stress Figure 5. Contour-lines of o^(x,z) for an elastic and a viscoelastic configuration In figure 5 an elastic configuration is compared with a viscoelastic configuration. The numerical data are: E=2.0 N/mm*, d=4.0 mm. v = 0.5,,,=7.0 Nlmm\ k=3.0 N/mm, x=0.007 s and V=100.0 mm/s. A contour-plot is shown of the normal stress distribution or,. From the shape of the contour-lines we can see that the elastic situation with tangential force shows a similar behaviour as the viscoelastic case, without tangential force. The normal stress is asymmetrical and hence rolling is resisted by a moment about the axle of the upper roller. (B)
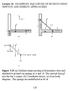
7 o.os r t0.13 Contact Mechanics 125 o.oo Figure 6. Comparison between numerical and experimental results. /. F^ = 0.74 TV/mm, 0) F^ = 0.0 TV/mm, %) F^= 0.05 TV/mm In figure 6 the comparison between numerical and experimental results for configuration I is shown. Configuration I means that only the glass roller is covered with one single transparent rubber layer. The black roller is rigid. In figure 6B a tangential force is applied: A slip region occurs at the trailing (left) edge of the contact region. The numerical data for this configuration are: E=0.91 Nlmnr, d-2.0 mm, v=0.5, R,=50.0 mm and R2=25.0 mm. The coefficient of friction is 2.7, which has been measured in a separate set-up. enlargement with optimization o.n 0.60 o.oo Figure 7. Comparison between numerical and experimental results. Configuration II: F\ = 7.78 N/mm, (A) Fj = 0.0 N/mm, (B) Fj= 0.53 N/mm In figure 7 the results for configuration II are shown. Here the black roller is covered with a black (carbon-filled) rubber layer (E-2.04 N/mm^, d-2.7 mm). The strain in the contact region is not constant in this case. The coefficient of friction is 2.8. In the numerical results of figure 7 we see also the influence of the geometrical optimization. The agreement is better if the geometry is optimized, especially when a tangential force is applied, as indicated in figure 7B. Finally the transparent rubber layer of configuration I is replaced by a two-layer rubber coating (configuration III). The toplayer is very thin and relatively hard (d=0.020 mm, E=2.04 Nlmnf), while the intermeadiate layer is thick and soft (d-2.3 mm, E=0.83 Nlmnf).
8 126 Contact Mechanics o.oo Figure 8. Comparison between numerical and experimental results. Configuration III: F» = 1.78 N/mm, (A) F? = 0.0 N/mm, (B) F^ 0.53 N/mm CONCLUSIONS In this paper a numerical and experimental analysis is given of the contact between multilayered, viscoelastic, rolling cylinders. It has been demonstrated that the agreement between for theory and experiment is very satisfactory for three different configurations, with and without tangential force. The linear model is adequate enough to model this contact problem. The geometrical optimization has improved the agreement between theory and experiment. The viscoelastic model is suitable to obtain qualitative results. REFERENCES [1] H. Hertz, Uber die Beriihrung fester elastischer Korper. Journal fur reine und angewandte Mathematik. 92, pp , 1882 [2] K.L. Johnson, Contact Mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge U.K., 1985 [3] P. Meijers, The contact problem of a rigid cylinder on an elastic layer. Applied Science Research, 18, pp , 1968 [4] J.J. Kalker, The simplified theory of rolling contact. Delft Progress Report, 1, pp. 1-10, 1973 [5] S.C. Hunter, The rolling contact of a rigid cylinder with a viscoelastic half-space. Journal of Applied Mechanics. 28, pp , 1961 [6] G. Wang, Rollkontakt zweier viskoelastischer Walzen mil Coulombscher Reibung. PhD Thesis, Berlin, 1991 [7] G. Wang, J.J. Kalker, Threedimensional Rolling contact of two viscoelastic bodies. Proceedings of the Contact Mechanics International Symposium (Ed. A. Curnier), Presse Polytechnique Universitaire Press Romandes, pp , 1992 [8] J.J. Kalker, Viscoelastic multilayered cylinders rolling with dry friction. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 58, pp , 1991 [9] W.N. Findley, J.S. Lai, K. Onaran, Creep and Relaxation of Nonlinear Viscoelastic Materials. Dover Publications Inc., New York, 1976 [10] G.F.M. Braat, Theory and experiments on multilayered, viscoelastic cylinders in rolling contact. PhD Thesis, Delft, to be published in June 1993 [11] J.J. Kalker, Three-dimensional Elastic Bodies in Rolling Contact. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Boston, London, 1990 [12] F. Durst, A. Melling, J.H. Whitelaw, Principles and Practise of Laser-Doppler Anemometry. Academic Press, London, 1981 [13] G.F.M. Braat, H.G.J. Rutten, Application of Laser-Doppler Anemometry in nips (in Dutch). Mikroniek, 1, 1993
Computational Modelling of the Surface Roughness Effects on the Thermal-elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Problem
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow Prague, Czech Republic, August 11-12, 2014 Paper No. 192 Computational Modelling of the Surface Roughness Effects on the Thermal-elastohydrodynamic
Proceedings of the International Conference on Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow Prague, Czech Republic, August 11-12, 2014 Paper No. 192 Computational Modelling of the Surface Roughness Effects on the Thermal-elastohydrodynamic
5.5 Exercises for This Chapter Two-Axle Vehicle on Cosine Track Two-Axle Vehicle on Generally Periodic Track...
 Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 The Basic Function of the Wheel/rail System.... 1 1.2 Significance of Dynamics on the Operation of Rail Vehicles... 2 1.3 On the History of Research in the Field of Railway
Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 The Basic Function of the Wheel/rail System.... 1 1.2 Significance of Dynamics on the Operation of Rail Vehicles... 2 1.3 On the History of Research in the Field of Railway
CONTACT USING FRICTION HYSTERESIS UDC Adrian Kraft, Roman Pohrt
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Series: Mechanical Engineering Vol. 14, N o 2, 2016, pp. 159-168 Original scientific paper 1REDUCTION OF RESIDUAL SHEAR STRESS IN THE LOADED CONTACT USING FRICTION HYSTERESIS UDC 531.4
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Series: Mechanical Engineering Vol. 14, N o 2, 2016, pp. 159-168 Original scientific paper 1REDUCTION OF RESIDUAL SHEAR STRESS IN THE LOADED CONTACT USING FRICTION HYSTERESIS UDC 531.4
USE OF A LINEAR VISCOELASTIC CONSTITUTIVE LAW TO MODEL THE TIME DEPENDENT BEHAVIOUR OF ORTHOTROPIC GLASSFIBRE REINFORCED PLASTIC
 USE OF A LINEAR VISCOELASTIC CONSTITUTIVE LAW TO MODEL THE TIME DEPENDENT BEHAVIOUR OF ORTHOTROPIC GLASSFIBRE REINFORCED PLASTIC Roland. M. Hinterhoelzl 1, Guenther Schullerer 1, Kurt Moser 1 1 Institut
USE OF A LINEAR VISCOELASTIC CONSTITUTIVE LAW TO MODEL THE TIME DEPENDENT BEHAVIOUR OF ORTHOTROPIC GLASSFIBRE REINFORCED PLASTIC Roland. M. Hinterhoelzl 1, Guenther Schullerer 1, Kurt Moser 1 1 Institut
A Nonlinear Dynamic Model for Single-axle Wheelsets with Profiled Wheels and Rails
 Proceedings of the International Conference of Control, Dynamic Systems, and Robotics Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, May 15-16 2014 Paper No. 60 A Nonlinear Dynamic Model for Single-axle Wheelsets with Profiled
Proceedings of the International Conference of Control, Dynamic Systems, and Robotics Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, May 15-16 2014 Paper No. 60 A Nonlinear Dynamic Model for Single-axle Wheelsets with Profiled
Steady state rolling contact of cylinders with viscoelastic layers M. Tervonen Department of Mechanical Engineering, University
 Steady state rolling contact of cylinders with viscoelastic layers M. Tervonen Department of Mechanical Engineering, University ABSTRACT The finite element method is used to solve the steady state rolling
Steady state rolling contact of cylinders with viscoelastic layers M. Tervonen Department of Mechanical Engineering, University ABSTRACT The finite element method is used to solve the steady state rolling
EFFECT OF STRAIN HARDENING ON ELASTIC-PLASTIC CONTACT BEHAVIOUR OF A SPHERE AGAINST A RIGID FLAT A FINITE ELEMENT STUDY
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 2009 (ICME2009) 26-28 December 2009, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME09- EFFECT OF STRAIN HARDENING ON ELASTIC-PLASTIC CONTACT BEHAVIOUR OF A
Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 2009 (ICME2009) 26-28 December 2009, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME09- EFFECT OF STRAIN HARDENING ON ELASTIC-PLASTIC CONTACT BEHAVIOUR OF A
The Dynamic Stress State of the Wheel-Rail Contact
 Proceedings of the 2nd IASME / WSEAS International Conference on Continuum Mechanics (CM'07), Portoroz, Slovenia, May 15-17, 2007 127 The Dynamic Stress State of the Wheel-Rail Contact XIN ZHAO *, ZILI
Proceedings of the 2nd IASME / WSEAS International Conference on Continuum Mechanics (CM'07), Portoroz, Slovenia, May 15-17, 2007 127 The Dynamic Stress State of the Wheel-Rail Contact XIN ZHAO *, ZILI
A simple model for elastic and viscoelastic punch. indentation problems with experimental validation
 A simple model for elastic and viscoelastic punch indentation problems with experimental validation A. SAMEUR, H. P. YIN, D. DUHAMEL, V. VILKE Université Paris-Est, Institut Navier, LAMI, Ecole Nationale
A simple model for elastic and viscoelastic punch indentation problems with experimental validation A. SAMEUR, H. P. YIN, D. DUHAMEL, V. VILKE Université Paris-Est, Institut Navier, LAMI, Ecole Nationale
Finite element analysis of indentation experiments J.M. Olaf Fraunhofer-Insitut fur Werkstoffmechanik, Wohlerstr. 11, D-W Freiburg, Germany
 Finite element analysis of indentation experiments J.M. Olaf Fraunhofer-Insitut fur Werkstoffmechanik, Wohlerstr. 11, D-W- 7800 Freiburg, Germany ABSTRACT There are only a few methods suitable for a quantitative
Finite element analysis of indentation experiments J.M. Olaf Fraunhofer-Insitut fur Werkstoffmechanik, Wohlerstr. 11, D-W- 7800 Freiburg, Germany ABSTRACT There are only a few methods suitable for a quantitative
For an imposed stress history consisting of a rapidly applied step-function jump in
 Problem 2 (20 points) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 0239 2.002 MECHANICS AND MATERIALS II SOLUTION for QUIZ NO. October 5, 2003 For
Problem 2 (20 points) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 0239 2.002 MECHANICS AND MATERIALS II SOLUTION for QUIZ NO. October 5, 2003 For
New Representation of Bearings in LS-DYNA
 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Aerospace New Representation of Bearings in LS-DYNA Kelly S. Carney Samuel A. Howard NASA Glenn Research Center, Cleveland, OH 44135 Brad A. Miller
13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Aerospace New Representation of Bearings in LS-DYNA Kelly S. Carney Samuel A. Howard NASA Glenn Research Center, Cleveland, OH 44135 Brad A. Miller
Steady rolling contact and resistance of a cylinder on a viscoelastic foundation by an integral equation algorithm
 Graduate Theses and Dissertations Iowa State University Capstones, Theses and Dissertations 29 Steady rolling contact and resistance of a cylinder on a viscoelastic foundation by an integral equation algorithm
Graduate Theses and Dissertations Iowa State University Capstones, Theses and Dissertations 29 Steady rolling contact and resistance of a cylinder on a viscoelastic foundation by an integral equation algorithm
FLAC3D analysis on soil moving through piles
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 211 FLAC3D analysis on soil moving through piles E H. Ghee Griffith University
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 211 FLAC3D analysis on soil moving through piles E H. Ghee Griffith University
SEMM Mechanics PhD Preliminary Exam Spring Consider a two-dimensional rigid motion, whose displacement field is given by
 SEMM Mechanics PhD Preliminary Exam Spring 2014 1. Consider a two-dimensional rigid motion, whose displacement field is given by u(x) = [cos(β)x 1 + sin(β)x 2 X 1 ]e 1 + [ sin(β)x 1 + cos(β)x 2 X 2 ]e
SEMM Mechanics PhD Preliminary Exam Spring 2014 1. Consider a two-dimensional rigid motion, whose displacement field is given by u(x) = [cos(β)x 1 + sin(β)x 2 X 1 ]e 1 + [ sin(β)x 1 + cos(β)x 2 X 2 ]e
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Simulation of severe wheel-rail wear Zi-Li Li & Joost J. Kalker Delft University of Technology Subfaculty of Technical Mathematics and Informatics Faculty ofinformation Technology and Systems MeWweg 4
Simulation of severe wheel-rail wear Zi-Li Li & Joost J. Kalker Delft University of Technology Subfaculty of Technical Mathematics and Informatics Faculty ofinformation Technology and Systems MeWweg 4
Ch. 10: Fundamental of contact between solids
 Ch. 10: Fundamental of contact between solids Actual surface is not smooth. At atomic scale, there are always defects at surface, such as vacancies, ledges, kinks, terraces. In micro or macro scale, roughness
Ch. 10: Fundamental of contact between solids Actual surface is not smooth. At atomic scale, there are always defects at surface, such as vacancies, ledges, kinks, terraces. In micro or macro scale, roughness
Transactions on Engineering Sciences vol 14, 1997 WIT Press, ISSN
 On the Computation of Elastic Elastic Rolling Contact using Adaptive Finite Element Techniques B. Zastrau^, U. Nackenhorst*,J. Jarewski^ ^Institute of Mechanics and Informatics, Technical University Dresden,
On the Computation of Elastic Elastic Rolling Contact using Adaptive Finite Element Techniques B. Zastrau^, U. Nackenhorst*,J. Jarewski^ ^Institute of Mechanics and Informatics, Technical University Dresden,
Analysis of Flexible Media Transport Characteristics of Crown Roller and Its Application to Design
 Copyright c 28 ICCES ICCES, vol.7, no.1, pp.23-42 Analysis of Flexible Media Transport Characteristics of Crown Roller and Its Application to Design Iizuka Yoichiro 1, Hiroshi Yamaura Summary Crown rollers
Copyright c 28 ICCES ICCES, vol.7, no.1, pp.23-42 Analysis of Flexible Media Transport Characteristics of Crown Roller and Its Application to Design Iizuka Yoichiro 1, Hiroshi Yamaura Summary Crown rollers
Fine adhesive particles A contact model including viscous damping
 Fine adhesive particles A contact model including viscous damping CHoPS 2012 - Friedrichshafen 7 th International Conference for Conveying and Handling of Particulate Solids Friedrichshafen, 12 th September
Fine adhesive particles A contact model including viscous damping CHoPS 2012 - Friedrichshafen 7 th International Conference for Conveying and Handling of Particulate Solids Friedrichshafen, 12 th September
Review of Strain Energy Methods and Introduction to Stiffness Matrix Methods of Structural Analysis
 uke University epartment of Civil and Environmental Engineering CEE 42L. Matrix Structural Analysis Henri P. Gavin Fall, 22 Review of Strain Energy Methods and Introduction to Stiffness Matrix Methods
uke University epartment of Civil and Environmental Engineering CEE 42L. Matrix Structural Analysis Henri P. Gavin Fall, 22 Review of Strain Energy Methods and Introduction to Stiffness Matrix Methods
46th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference April 2005 Austin, Texas
 th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics & Materials Conference - April, Austin, Texas AIAA - AIAA - Bi-stable Cylindrical Space Frames H Ye and S Pellegrino University of Cambridge, Cambridge,
th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics & Materials Conference - April, Austin, Texas AIAA - AIAA - Bi-stable Cylindrical Space Frames H Ye and S Pellegrino University of Cambridge, Cambridge,
8. Contact Mechanics DE2-EA 2.1: M4DE. Dr Connor Myant 2017/2018
 DE2-EA 2.1: M4DE Dr Connor Myant 2017/2018 8. Contact Mechanics Comments and corrections to connor.myant@imperial.ac.uk Lecture resources may be found on Blackboard and at http://connormyant.com Contents
DE2-EA 2.1: M4DE Dr Connor Myant 2017/2018 8. Contact Mechanics Comments and corrections to connor.myant@imperial.ac.uk Lecture resources may be found on Blackboard and at http://connormyant.com Contents
STEEL JOINTS - COMPONENT METHOD APPLICATION
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 5 (54) - 2012 Series 1: Special Issue No. 1 STEEL JOINTS - COPONENT ETHOD APPLICATION D. RADU 1 Abstract: As long as the rotation joint stiffness
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 5 (54) - 2012 Series 1: Special Issue No. 1 STEEL JOINTS - COPONENT ETHOD APPLICATION D. RADU 1 Abstract: As long as the rotation joint stiffness
Non-Linear Finite Element Methods in Solid Mechanics Attilio Frangi, Politecnico di Milano, February 17, 2017, Lesson 5
 Non-Linear Finite Element Methods in Solid Mechanics Attilio Frangi, attilio.frangi@polimi.it Politecnico di Milano, February 17, 2017, Lesson 5 1 Politecnico di Milano, February 17, 2017, Lesson 5 2 Outline
Non-Linear Finite Element Methods in Solid Mechanics Attilio Frangi, attilio.frangi@polimi.it Politecnico di Milano, February 17, 2017, Lesson 5 1 Politecnico di Milano, February 17, 2017, Lesson 5 2 Outline
Mechatronics. MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1
 Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION (Section 17.2)
 PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION (Section 17.2) We will limit our study of planar kinetics to rigid bodies that are symmetric with respect to a fixed reference plane. As discussed in Chapter 16, when
PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION (Section 17.2) We will limit our study of planar kinetics to rigid bodies that are symmetric with respect to a fixed reference plane. As discussed in Chapter 16, when
The Finite Element Method for Mechonics of Solids with ANSYS Applicotions
 The Finite Element Method for Mechonics of Solids with ANSYS Applicotions ELLIS H. DILL 0~~F~~~~"P Boca Raton London New Vork CRC Press is an imprint 01 the Taylor & Francis Group, an Informa business
The Finite Element Method for Mechonics of Solids with ANSYS Applicotions ELLIS H. DILL 0~~F~~~~"P Boca Raton London New Vork CRC Press is an imprint 01 the Taylor & Francis Group, an Informa business
PHY 001 (Physics I) Lecture 7
 PHY 001 (Physics I) Instructor: Dr. Mohamed Fouad Salem mohamed.salem@gmail.com Textbook University Physics, 12 th edition, Young and Freedman Course Material Website http://meryesk.wordpress.com/phy001/
PHY 001 (Physics I) Instructor: Dr. Mohamed Fouad Salem mohamed.salem@gmail.com Textbook University Physics, 12 th edition, Young and Freedman Course Material Website http://meryesk.wordpress.com/phy001/
A multiscale framework for lubrication analysis of bearings with textured surface
 A multiscale framework for lubrication analysis of bearings with textured surface *Leiming Gao 1), Gregory de Boer 2) and Rob Hewson 3) 1), 3) Aeronautics Department, Imperial College London, London, SW7
A multiscale framework for lubrication analysis of bearings with textured surface *Leiming Gao 1), Gregory de Boer 2) and Rob Hewson 3) 1), 3) Aeronautics Department, Imperial College London, London, SW7
LINEAR AND NONLINEAR SHELL THEORY. Contents
 LINEAR AND NONLINEAR SHELL THEORY Contents Strain-displacement relations for nonlinear shell theory Approximate strain-displacement relations: Linear theory Small strain theory Small strains & moderate
LINEAR AND NONLINEAR SHELL THEORY Contents Strain-displacement relations for nonlinear shell theory Approximate strain-displacement relations: Linear theory Small strain theory Small strains & moderate
Identification of model parameters from elastic/elasto-plastic spherical indentation
 Thomas Niederkofler a, Andreas Jäger a, Roman Lackner b a Institute for Mechanics of Materials and Structures (IMWS), Department of Civil Engineering, Vienna University of Technology, Vienna, Austria b
Thomas Niederkofler a, Andreas Jäger a, Roman Lackner b a Institute for Mechanics of Materials and Structures (IMWS), Department of Civil Engineering, Vienna University of Technology, Vienna, Austria b
Lecture 31. EXAMPLES: EQUATIONS OF MOTION USING NEWTON AND ENERGY APPROACHES
 Lecture 31. EXAMPLES: EQUATIONS OF MOTION USING NEWTON AND ENERGY APPROACHES Figure 5.29 (a) Uniform beam moving in frictionless slots and attached to ground via springs at A and B. The vertical force
Lecture 31. EXAMPLES: EQUATIONS OF MOTION USING NEWTON AND ENERGY APPROACHES Figure 5.29 (a) Uniform beam moving in frictionless slots and attached to ground via springs at A and B. The vertical force
3 2 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) 3. a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1
 Math Problem a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1 3 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) = Au( t) with u (0) =. 3 1 u 1 =, u 1 3 = b- True or false and why 1. if A is
Math Problem a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1 3 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) = Au( t) with u (0) =. 3 1 u 1 =, u 1 3 = b- True or false and why 1. if A is
Rigid Flexible Contact Analysis of an Inflated Membrane Balloon with Various Contact Conditions
 roceedings Rigid Flexible Contact Analysis of an Inflated Membrane Balloon with Various Contact Conditions MengXiong Liu and XiDe Li * Department of Engineering Mechanics, Tghua University, Beijing 100084,
roceedings Rigid Flexible Contact Analysis of an Inflated Membrane Balloon with Various Contact Conditions MengXiong Liu and XiDe Li * Department of Engineering Mechanics, Tghua University, Beijing 100084,
Chapter 12. Static Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Cite this paper as follows:
 Cite this paper as follows: Naughton P.J. and O Kelly B.C. 2001. An overview of the University College Dublin hollow cylinder apparatus. Proceedings of the 14th Young European Geotechnical Engineer s Conference,
Cite this paper as follows: Naughton P.J. and O Kelly B.C. 2001. An overview of the University College Dublin hollow cylinder apparatus. Proceedings of the 14th Young European Geotechnical Engineer s Conference,
Notes on Rubber Friction
 Notes on Rubber Friction 2011 A G Plint Laws of Friction: In dry sliding between a given pair of materials under steady conditions, the coefficient of friction may be almost constant. This is the basis
Notes on Rubber Friction 2011 A G Plint Laws of Friction: In dry sliding between a given pair of materials under steady conditions, the coefficient of friction may be almost constant. This is the basis
COMPOSITE PLATE THEORIES
 CHAPTER2 COMPOSITE PLATE THEORIES 2.1 GENERAL Analysis of composite plates is usually done based on one of the following the ries. 1. Equivalent single-layer theories a. Classical laminate theory b. Shear
CHAPTER2 COMPOSITE PLATE THEORIES 2.1 GENERAL Analysis of composite plates is usually done based on one of the following the ries. 1. Equivalent single-layer theories a. Classical laminate theory b. Shear
(MPa) compute (a) The traction vector acting on an internal material plane with normal n ( e1 e
 EN10: Continuum Mechanics Homework : Kinetics Due 1:00 noon Friday February 4th School of Engineering Brown University 1. For the Cauchy stress tensor with components 100 5 50 0 00 (MPa) compute (a) The
EN10: Continuum Mechanics Homework : Kinetics Due 1:00 noon Friday February 4th School of Engineering Brown University 1. For the Cauchy stress tensor with components 100 5 50 0 00 (MPa) compute (a) The
The Finite Element Method for Solid and Structural Mechanics
 The Finite Element Method for Solid and Structural Mechanics Sixth edition O.C. Zienkiewicz, CBE, FRS UNESCO Professor of Numerical Methods in Engineering International Centre for Numerical Methods in
The Finite Element Method for Solid and Structural Mechanics Sixth edition O.C. Zienkiewicz, CBE, FRS UNESCO Professor of Numerical Methods in Engineering International Centre for Numerical Methods in
OPTICAL DETECTION OF SHORT COLLISION TIMES
 The 14 th International Conference of the Slovenian Society for Non-Destructive Testing»Application of Contemporary Non-Destructive Testing in Engineering«September 4-6, 2017, Bernardin, Slovenia More
The 14 th International Conference of the Slovenian Society for Non-Destructive Testing»Application of Contemporary Non-Destructive Testing in Engineering«September 4-6, 2017, Bernardin, Slovenia More
Analysis of a portal steel frame subject to fire by use of a truss model
 Analysis of a portal steel frame subject to fire by use of a truss model P. G. Papadopoulos & A. Mathiopoulou Department of Civil Engineering, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece Abstract A plane
Analysis of a portal steel frame subject to fire by use of a truss model P. G. Papadopoulos & A. Mathiopoulou Department of Civil Engineering, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece Abstract A plane
University of Huddersfield Repository
 University of Huddersfield Repository Pislaru, Crinela Modelling and Simulation of the Dynamic Behaviour of Wheel-Rail Interface Original Citation Pislaru, Crinela (2012) Modelling and Simulation of the
University of Huddersfield Repository Pislaru, Crinela Modelling and Simulation of the Dynamic Behaviour of Wheel-Rail Interface Original Citation Pislaru, Crinela (2012) Modelling and Simulation of the
Determining thermal noise limiting properties of thin films
 Determining thermal noise limiting properties of thin films Courtney Linn Institute for Gravitational Research University of Glasgow Summer 2011 Abstract In order to make thermally stable mirrors to be
Determining thermal noise limiting properties of thin films Courtney Linn Institute for Gravitational Research University of Glasgow Summer 2011 Abstract In order to make thermally stable mirrors to be
Simulation in Computer Graphics Elastic Solids. Matthias Teschner
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Elastic Solids Matthias Teschner Outline Introduction Elastic forces Miscellaneous Collision handling Visualization University of Freiburg Computer Science Department 2
Simulation in Computer Graphics Elastic Solids Matthias Teschner Outline Introduction Elastic forces Miscellaneous Collision handling Visualization University of Freiburg Computer Science Department 2
Non-linear and time-dependent material models in Mentat & MARC. Tutorial with Background and Exercises
 Non-linear and time-dependent material models in Mentat & MARC Tutorial with Background and Exercises Eindhoven University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Piet Schreurs July 7, 2009
Non-linear and time-dependent material models in Mentat & MARC Tutorial with Background and Exercises Eindhoven University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Piet Schreurs July 7, 2009
Lecture 2: Stresses in Pavements
 Lecture 2: Stresses in Pavements Stresses in Layered Systems At any point, 9 stresses exist. They are 3 normal stresses (s z, s r, s t ) and 6 shearing stresses ( t rz = t zr, t rt = t tr, and t tz = t
Lecture 2: Stresses in Pavements Stresses in Layered Systems At any point, 9 stresses exist. They are 3 normal stresses (s z, s r, s t ) and 6 shearing stresses ( t rz = t zr, t rt = t tr, and t tz = t
Advanced Structural Analysis EGF Section Properties and Bending
 Advanced Structural Analysis EGF316 3. Section Properties and Bending 3.1 Loads in beams When we analyse beams, we need to consider various types of loads acting on them, for example, axial forces, shear
Advanced Structural Analysis EGF316 3. Section Properties and Bending 3.1 Loads in beams When we analyse beams, we need to consider various types of loads acting on them, for example, axial forces, shear
STICK-SLIP WHIRL INTERACTION IN DRILLSTRING DYNAMICS
 STICK-SLIP WHIRL INTERACTION IN DRILLSTRING DYNAMICS R. I. Leine, D. H. van Campen Department of Mechanical Engineering, Eindhoven University of Technology, P. O. Box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven, The Netherlands
STICK-SLIP WHIRL INTERACTION IN DRILLSTRING DYNAMICS R. I. Leine, D. H. van Campen Department of Mechanical Engineering, Eindhoven University of Technology, P. O. Box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven, The Netherlands
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SEMESTER: III SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A
 DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
VIBRATION AND DAMPING ANALYSIS OF FIBER REINFORCED COMPOSITE MATERIAL CONICAL SHELLS
 VIBRATION AND DAMPING ANALYSIS OF FIBER REINFORCED COMPOSITE MATERIAL CONICAL SHELLS Mechanical Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi 110 016, India (Received 22 January 1992,
VIBRATION AND DAMPING ANALYSIS OF FIBER REINFORCED COMPOSITE MATERIAL CONICAL SHELLS Mechanical Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi 110 016, India (Received 22 January 1992,
Analysis of CMC-Supported Embankments Considering Soil Arching
 Analysis of CMC-Supported Embankments Considering Soil Arching Balaka Ghosh 1, Behzad Fatahi 2, Hadi Khabbaz 3, and A. H. M. Kamruzzaman 4 1 PhD Candidate, School of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
Analysis of CMC-Supported Embankments Considering Soil Arching Balaka Ghosh 1, Behzad Fatahi 2, Hadi Khabbaz 3, and A. H. M. Kamruzzaman 4 1 PhD Candidate, School of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
Arbitrary Normal and Tangential Loading Sequences for Circular Hertzian Contact
 Arbitrary Normal and Tangential Loading Sequences for Circular Hertzian Contact Philip P. Garland 1 and Robert J. Rogers 2 1 School of Biomedical Engineering, Dalhousie University, Canada 2 Department
Arbitrary Normal and Tangential Loading Sequences for Circular Hertzian Contact Philip P. Garland 1 and Robert J. Rogers 2 1 School of Biomedical Engineering, Dalhousie University, Canada 2 Department
UNIT- I Thin plate theory, Structural Instability:
 UNIT- I Thin plate theory, Structural Instability: Analysis of thin rectangular plates subject to bending, twisting, distributed transverse load, combined bending and in-plane loading Thin plates having
UNIT- I Thin plate theory, Structural Instability: Analysis of thin rectangular plates subject to bending, twisting, distributed transverse load, combined bending and in-plane loading Thin plates having
CHAPTER THREE SYMMETRIC BENDING OF CIRCLE PLATES
 CHAPTER THREE SYMMETRIC BENDING OF CIRCLE PLATES * Governing equations in beam and plate bending ** Solution by superposition 1.1 From Beam Bending to Plate Bending 1.2 Governing Equations For Symmetric
CHAPTER THREE SYMMETRIC BENDING OF CIRCLE PLATES * Governing equations in beam and plate bending ** Solution by superposition 1.1 From Beam Bending to Plate Bending 1.2 Governing Equations For Symmetric
Mechanics of Materials II. Chapter III. A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection
 Mechanics of Materials II Chapter III A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection Outline Introduction Assumtions and limitations Axial loading Torsion of circular shafts
Mechanics of Materials II Chapter III A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection Outline Introduction Assumtions and limitations Axial loading Torsion of circular shafts
Advanced Friction Modeling in Sheet Metal Forming
 Advanced Friction Modeling in Sheet Metal Forming J.Hol 1,a, M.V. Cid Alfaro 2, T. Meinders 3, J. Huétink 3 1 Materials innovation institute (M2i), P.O. box 58, 26 GA Delft, The Netherlands 2 Tata Steel
Advanced Friction Modeling in Sheet Metal Forming J.Hol 1,a, M.V. Cid Alfaro 2, T. Meinders 3, J. Huétink 3 1 Materials innovation institute (M2i), P.O. box 58, 26 GA Delft, The Netherlands 2 Tata Steel
Finite Element Analysis of Compression of Thin, High Modulus, Cylindrical Shells with Low-Modulus Core
 Finite Element Analysis of Compression of Thin, High Modulus, Cylindrical Shells with Low-Modulus Core Robert S. Joseph Design Engineering Analysis Corporation, McMurray, PA ABSTRACT Long, cylindrical
Finite Element Analysis of Compression of Thin, High Modulus, Cylindrical Shells with Low-Modulus Core Robert S. Joseph Design Engineering Analysis Corporation, McMurray, PA ABSTRACT Long, cylindrical
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer
 CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
Exploiting pattern transformation to tune phononic band gaps in a two-dimensional granular crystal
 Exploiting pattern transformation to tune phononic band gaps in a two-dimensional granular crystal The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
Exploiting pattern transformation to tune phononic band gaps in a two-dimensional granular crystal The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
Exam paper: Biomechanics
 Exam paper: Biomechanics Tuesday August 10th 2010; 9.00-12.00 AM Code: 8W020 Biomedical Engineering Department, Eindhoven University of Technology The exam comprises 10 problems. Every problem has a maximum
Exam paper: Biomechanics Tuesday August 10th 2010; 9.00-12.00 AM Code: 8W020 Biomedical Engineering Department, Eindhoven University of Technology The exam comprises 10 problems. Every problem has a maximum
The Effect of Coefficient of Restitution for Two Collision Models
 The Effect of Coefficient of Restitution for Two Collision Models ALACI STELIAN 1, FILOTE CONSTANTIN 2, CIORNEI FLORINA-CARMEN 1 1 Mechanics and Technologies Department 2 The Computers, Electronics and
The Effect of Coefficient of Restitution for Two Collision Models ALACI STELIAN 1, FILOTE CONSTANTIN 2, CIORNEI FLORINA-CARMEN 1 1 Mechanics and Technologies Department 2 The Computers, Electronics and
RHEOLOGY Principles, Measurements, and Applications. Christopher W. Macosko
 RHEOLOGY Principles, Measurements, and Applications I -56081-5'79~5 1994 VCH Publishers. Inc. New York Part I. CONSTITUTIVE RELATIONS 1 1 l Elastic Solid 5 1.1 Introduction 5 1.2 The Stress Tensor 8 1.2.1
RHEOLOGY Principles, Measurements, and Applications I -56081-5'79~5 1994 VCH Publishers. Inc. New York Part I. CONSTITUTIVE RELATIONS 1 1 l Elastic Solid 5 1.1 Introduction 5 1.2 The Stress Tensor 8 1.2.1
ARTICLE A-8000 STRESSES IN PERFORATED FLAT PLATES
 ARTICLE A-8000 STRESSES IN PERFORATED FLAT PLATES Delete endnote 18, which says "Express metric values in exponential form" A-8100 INTRODUCTION A-8110 SCOPE (a) This Article contains a method of analysis
ARTICLE A-8000 STRESSES IN PERFORATED FLAT PLATES Delete endnote 18, which says "Express metric values in exponential form" A-8100 INTRODUCTION A-8110 SCOPE (a) This Article contains a method of analysis
Problem Set Number 01, MIT (Winter-Spring 2018)
 Problem Set Number 01, 18.377 MIT (Winter-Spring 2018) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., room 2-337, Cambridge, MA 02139) February 28, 2018 Due Thursday, March 8, 2018. Turn it in (by 3PM) at the Math.
Problem Set Number 01, 18.377 MIT (Winter-Spring 2018) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., room 2-337, Cambridge, MA 02139) February 28, 2018 Due Thursday, March 8, 2018. Turn it in (by 3PM) at the Math.
GATE SOLUTIONS E N G I N E E R I N G
 GATE SOLUTIONS C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G From (1987-018) Office : F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110016 Phone : 011-65064 Mobile : 81309090, 9711853908 E-mail: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
GATE SOLUTIONS C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G From (1987-018) Office : F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110016 Phone : 011-65064 Mobile : 81309090, 9711853908 E-mail: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
PRESSURE VESSELS & PRESSURE CABINS FOR BLENDED WING BODIES
 PRESSURE VESSELS & PRESSURE CABINS FOR BLENDED WING BODIES F.J.J.M.M. Geuskens, O.K. Bergsma 2, S. Koussios 2 & A. Beukers 3 PhD Researcher, 2 Associate professor, 3 Professor / DPCS, TU Delft Kluyverweg,
PRESSURE VESSELS & PRESSURE CABINS FOR BLENDED WING BODIES F.J.J.M.M. Geuskens, O.K. Bergsma 2, S. Koussios 2 & A. Beukers 3 PhD Researcher, 2 Associate professor, 3 Professor / DPCS, TU Delft Kluyverweg,
U.S. South America Workshop. Mechanics and Advanced Materials Research and Education. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. August 2 6, Steven L.
 Computational Modeling of Composite and Functionally Graded Materials U.S. South America Workshop Mechanics and Advanced Materials Research and Education Rio de Janeiro, Brazil August 2 6, 2002 Steven
Computational Modeling of Composite and Functionally Graded Materials U.S. South America Workshop Mechanics and Advanced Materials Research and Education Rio de Janeiro, Brazil August 2 6, 2002 Steven
Module 7: Micromechanics Lecture 29: Background of Concentric Cylinder Assemblage Model. Introduction. The Lecture Contains
 Introduction In this lecture we are going to introduce a new micromechanics model to determine the fibrous composite effective properties in terms of properties of its individual phases. In this model
Introduction In this lecture we are going to introduce a new micromechanics model to determine the fibrous composite effective properties in terms of properties of its individual phases. In this model
A Basic Study on Wheel Flange Climbing using Model Wheelset
 IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 3, No. 2 / June 2010, pp. 60-67 The Korean Society for Railway A Basic Study on Wheel Flange Climbing using Model Wheelset Yosuke Nagumo*, Katsuya Tanifuji and
IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 3, No. 2 / June 2010, pp. 60-67 The Korean Society for Railway A Basic Study on Wheel Flange Climbing using Model Wheelset Yosuke Nagumo*, Katsuya Tanifuji and
Mechanical Engineering Ph.D. Preliminary Qualifying Examination Solid Mechanics February 25, 2002
 student personal identification (ID) number on each sheet. Do not write your name on any sheet. #1. A homogeneous, isotropic, linear elastic bar has rectangular cross sectional area A, modulus of elasticity
student personal identification (ID) number on each sheet. Do not write your name on any sheet. #1. A homogeneous, isotropic, linear elastic bar has rectangular cross sectional area A, modulus of elasticity
Modelling of railway vehicle movement considering non-ideal geometry of wheels and rails
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (2007) 489-498 Modelling of railway vehicle movement considering non-ideal geometry of wheels and rails R. Jandora a, a Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, rno University
Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (2007) 489-498 Modelling of railway vehicle movement considering non-ideal geometry of wheels and rails R. Jandora a, a Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, rno University
STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS
 1 UNIT I STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define: Stress When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The
1 UNIT I STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define: Stress When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The
Figure 43. Some common mechanical systems involving contact.
 33 Demonstration: experimental surface measurement ADE PhaseShift Whitelight Interferometer Surface measurement Surface characterization - Probability density function - Statistical analyses - Autocorrelation
33 Demonstration: experimental surface measurement ADE PhaseShift Whitelight Interferometer Surface measurement Surface characterization - Probability density function - Statistical analyses - Autocorrelation
Transactions on Engineering Sciences vol 1, 1993 WIT Press, ISSN
 Contact analysis in clamping-roller free-wheel clutches K. Diirkopp, W. Jorden Laboratorium fur Konstruktionslehre, Uni-GH- Paderborn, D~4 790 Paderborn, Germany ABSTRACT Free-wheels are coupling devices
Contact analysis in clamping-roller free-wheel clutches K. Diirkopp, W. Jorden Laboratorium fur Konstruktionslehre, Uni-GH- Paderborn, D~4 790 Paderborn, Germany ABSTRACT Free-wheels are coupling devices
Three-dimensional thermo-mechanical analysis of layered elasticlplastic solids
 Three-dimensional thermo-mechanical analysis of layered elasticlplastic solids W. Peng & Y.-T. Hsia Seagate Technology, U.S.A. Abstract At high temperature a layered solid undergoes intense thermal loading
Three-dimensional thermo-mechanical analysis of layered elasticlplastic solids W. Peng & Y.-T. Hsia Seagate Technology, U.S.A. Abstract At high temperature a layered solid undergoes intense thermal loading
A New Method of Analysis of Continuous Skew Girder Bridges
 A New Method of Analysis of Continuous Skew Girder Bridges Dr. Salem Awad Ramoda Hadhramout University of Science & Technology Mukalla P.O.Box : 50511 Republic of Yemen ABSTRACT One three girder two span
A New Method of Analysis of Continuous Skew Girder Bridges Dr. Salem Awad Ramoda Hadhramout University of Science & Technology Mukalla P.O.Box : 50511 Republic of Yemen ABSTRACT One three girder two span
Module 4 : Deflection of Structures Lecture 4 : Strain Energy Method
 Module 4 : Deflection of Structures Lecture 4 : Strain Energy Method Objectives In this course you will learn the following Deflection by strain energy method. Evaluation of strain energy in member under
Module 4 : Deflection of Structures Lecture 4 : Strain Energy Method Objectives In this course you will learn the following Deflection by strain energy method. Evaluation of strain energy in member under
Experimental research on electrical resistance of microcontacts
 Experimental research on electrical resistance of microcontacts Cristina Iliuţă, Viorel Ciornei Ştefan cel Mare University, Suceava, Romania tina_criss2005@yahoo.com Abstract: Contact resistance between
Experimental research on electrical resistance of microcontacts Cristina Iliuţă, Viorel Ciornei Ştefan cel Mare University, Suceava, Romania tina_criss2005@yahoo.com Abstract: Contact resistance between
Introductory guide to measuring the mechanical properties of nanoobjects/particles
 Jeremias Seppä MIKES Metrology, VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Ltd P.O. Box 1000, FI-02044 VTT, Finland Contents: AFM Cantilever calibration F-d curves and cantilever bending Hitting the particles
Jeremias Seppä MIKES Metrology, VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Ltd P.O. Box 1000, FI-02044 VTT, Finland Contents: AFM Cantilever calibration F-d curves and cantilever bending Hitting the particles
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
LIMIT LOAD OF A MASONRY ARCH BRIDGE BASED ON FINITE ELEMENT FRICTIONAL CONTACT ANALYSIS
 5 th GRACM International Congress on Computational Mechanics Limassol, 29 June 1 July, 2005 LIMIT LOAD OF A MASONRY ARCH BRIDGE BASED ON FINITE ELEMENT FRICTIONAL CONTACT ANALYSIS G.A. Drosopoulos I, G.E.
5 th GRACM International Congress on Computational Mechanics Limassol, 29 June 1 July, 2005 LIMIT LOAD OF A MASONRY ARCH BRIDGE BASED ON FINITE ELEMENT FRICTIONAL CONTACT ANALYSIS G.A. Drosopoulos I, G.E.
Moment Area Method. 1) Read
 Moment Area Method Lesson Objectives: 1) Identify the formulation and sign conventions associated with the Moment Area method. 2) Derive the Moment Area method theorems using mechanics and mathematics.
Moment Area Method Lesson Objectives: 1) Identify the formulation and sign conventions associated with the Moment Area method. 2) Derive the Moment Area method theorems using mechanics and mathematics.
Physics 141 Rotational Motion 2 Page 1. Rotational Motion 2
 Physics 141 Rotational Motion 2 Page 1 Rotational Motion 2 Right handers, go over there, left handers over here. The rest of you, come with me.! Yogi Berra Torque Motion of a rigid body, like motion of
Physics 141 Rotational Motion 2 Page 1 Rotational Motion 2 Right handers, go over there, left handers over here. The rest of you, come with me.! Yogi Berra Torque Motion of a rigid body, like motion of
Chapter Rotational Motion
 26 Chapter Rotational Motion 1. Initial angular velocity of a circular disc of mass M is ω 1. Then two small spheres of mass m are attached gently to diametrically opposite points on the edge of the disc.
26 Chapter Rotational Motion 1. Initial angular velocity of a circular disc of mass M is ω 1. Then two small spheres of mass m are attached gently to diametrically opposite points on the edge of the disc.
UNLOADING OF AN ELASTIC-PLASTIC LOADED SPHERICAL CONTACT
 2004 AIMETA International Tribology Conference, September 14-17, 2004, Rome, Italy UNLOADING OF AN ELASTIC-PLASTIC LOADED SPHERICAL CONTACT Yuri KLIGERMAN( ), Yuri Kadin( ), Izhak ETSION( ) Faculty of
2004 AIMETA International Tribology Conference, September 14-17, 2004, Rome, Italy UNLOADING OF AN ELASTIC-PLASTIC LOADED SPHERICAL CONTACT Yuri KLIGERMAN( ), Yuri Kadin( ), Izhak ETSION( ) Faculty of
IN-PLANE VIBRATIONS OF CIRCULAR CURVED BEAMS WITH A TRANSVERSE OPEN CRACK 1. INTRODUCTION
 Mathematical and Computational Applications, Vol. 11, No. 1, pp. 1-10, 006. Association for Scientific Research IN-PLANE VIBRATIONS OF CIRCULAR CURVED BEAMS WITH A TRANSVERSE OPEN CRACK Department of Mechanical
Mathematical and Computational Applications, Vol. 11, No. 1, pp. 1-10, 006. Association for Scientific Research IN-PLANE VIBRATIONS OF CIRCULAR CURVED BEAMS WITH A TRANSVERSE OPEN CRACK Department of Mechanical
A NEW SIMPLIFIED AND EFFICIENT TECHNIQUE FOR FRACTURE BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS OF CONCRETE STRUCTURES
 Fracture Mechanics of Concrete Structures Proceedings FRAMCOS-3 AEDFCATO Publishers, D-79104 Freiburg, Germany A NEW SMPLFED AND EFFCENT TECHNQUE FOR FRACTURE BEHAVOR ANALYSS OF CONCRETE STRUCTURES K.
Fracture Mechanics of Concrete Structures Proceedings FRAMCOS-3 AEDFCATO Publishers, D-79104 Freiburg, Germany A NEW SMPLFED AND EFFCENT TECHNQUE FOR FRACTURE BEHAVOR ANALYSS OF CONCRETE STRUCTURES K.
CHAPTER -6- BENDING Part -1-
 Ishik University / Sulaimani Civil Engineering Department Mechanics of Materials CE 211 CHAPTER -6- BENDING Part -1-1 CHAPTER -6- Bending Outlines of this chapter: 6.1. Chapter Objectives 6.2. Shear and
Ishik University / Sulaimani Civil Engineering Department Mechanics of Materials CE 211 CHAPTER -6- BENDING Part -1-1 CHAPTER -6- Bending Outlines of this chapter: 6.1. Chapter Objectives 6.2. Shear and
Experimental Investigation of Fully Plastic Contact of a Sphere Against a Hard Flat
 J. Jamari e-mail: j.jamari@ctw.utwente.nl D. J. Schipper University of Twente, Surface Technology and Tribology, Faculty of Engineering Technology, Drienerloolaan 5, Postbus 17, 7500 AE, Enschede, The
J. Jamari e-mail: j.jamari@ctw.utwente.nl D. J. Schipper University of Twente, Surface Technology and Tribology, Faculty of Engineering Technology, Drienerloolaan 5, Postbus 17, 7500 AE, Enschede, The
Elastic impact of a sphere with an elastic half-space: numerical modeling and comparison with experiment
 Elastic impact of a sphere with an elastic half-space: numerical modeling and comparison with experiment I.A. Lyashenko 1,, E. Willert 1, V.L. Popov 1,3,4 1 Berlin University of Technology, 163 Berlin,
Elastic impact of a sphere with an elastic half-space: numerical modeling and comparison with experiment I.A. Lyashenko 1,, E. Willert 1, V.L. Popov 1,3,4 1 Berlin University of Technology, 163 Berlin,
Influence of forced material in roller compactor parameters I.
 1 Portál pre odborné publikovanie ISSN 1338-0087 Influence of forced material in roller compactor parameters I. Krok Alexander Elektrotechnika, Strojárstvo 24.08.2009 In the chemical, pharmaceutical and
1 Portál pre odborné publikovanie ISSN 1338-0087 Influence of forced material in roller compactor parameters I. Krok Alexander Elektrotechnika, Strojárstvo 24.08.2009 In the chemical, pharmaceutical and
Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions Why do we have to make the assumption that plane sections plane? How about bars with non-axis symmetric cross section? The formulae derived look very similar to beam and axial
Frequently Asked Questions Why do we have to make the assumption that plane sections plane? How about bars with non-axis symmetric cross section? The formulae derived look very similar to beam and axial
Estimation of damping capacity of rubber vibration isolators under harmonic excitation
 Estimation of damping capacity of rubber vibration isolators under harmonic excitation Svetlana Polukoshko Ventspils University College, Engineering Research Institute VSRC, Ventspils, Latvia E-mail: pol.svet@inbox.lv
Estimation of damping capacity of rubber vibration isolators under harmonic excitation Svetlana Polukoshko Ventspils University College, Engineering Research Institute VSRC, Ventspils, Latvia E-mail: pol.svet@inbox.lv
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE INELASTIC SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC STRUCTURES WITH ENERGY DISSIPATORS
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE INELASTIC SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC STRUCTURES WITH ENERGY DISSIPATORS ABSTRACT : P Mata1, AH Barbat1, S Oller1, R Boroschek2 1 Technical University of Catalonia, Civil Engineering
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE INELASTIC SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC STRUCTURES WITH ENERGY DISSIPATORS ABSTRACT : P Mata1, AH Barbat1, S Oller1, R Boroschek2 1 Technical University of Catalonia, Civil Engineering
Stiffness Matrices, Spring and Bar Elements
 CHAPTER Stiffness Matrices, Spring and Bar Elements. INTRODUCTION The primary characteristics of a finite element are embodied in the element stiffness matrix. For a structural finite element, the stiffness
CHAPTER Stiffness Matrices, Spring and Bar Elements. INTRODUCTION The primary characteristics of a finite element are embodied in the element stiffness matrix. For a structural finite element, the stiffness
Photoelasticity of Glass
 H. Aben, C. GuiUemet Photoelasticity of Glass With 218 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents Preface v Part One The Basics of Photoelasticity
H. Aben, C. GuiUemet Photoelasticity of Glass With 218 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents Preface v Part One The Basics of Photoelasticity
A fatigue limit diagram for plastic rail clips
 Computers in Railways XIV 839 A fatigue limit diagram for plastic rail clips S. Tamagawa, H. Kataoka & T. Deshimaru Department of Track Structures and Components, Railway Technical Research Institute,
Computers in Railways XIV 839 A fatigue limit diagram for plastic rail clips S. Tamagawa, H. Kataoka & T. Deshimaru Department of Track Structures and Components, Railway Technical Research Institute,
Analysis of forming- Slipline Field Method
 Analysis of forming- Slipline Field Method R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401 Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 7 Table of Contents 1.
Analysis of forming- Slipline Field Method R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401 Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 7 Table of Contents 1.
