Lower bounds for lowest eigenvalues
|
|
|
- Barrie Clarke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lower bounds for lowest eigenvalues Peter Dole DRAFT Version 0.3A dated September 994 UNDER CONSTRUCTION GNU FDL Introduction In this abortive paper, we will discuss how to find lower bounds for lowest eigenvalues. The aim will be to get across the basic ideas, so we will discuss onl the simplest cases, and we won t worr about matters like exactl how man derivatives we are demanding of our functions. The work described here is joint work with Bob Brooks and Bob Kohn. Caveat. I seem to recall that I was changing the notation around when I turned to other things, so there ma be some inconsistencies. Also, ou ll note the the stor breaks off abruptl near the end. Continuous version Consider a nice bounded domain Ω in the Euclidean plane. A positive number λ is an eigenvalue of the positive Laplacian ( ) = x + Copright (C) 994 Peter G. Dole. Permission is granted to cop, distribute and/or modif this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, as published b the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts.
2 if there exists a function u (other than the zero function) such that and u = λu u Ω = 0. We label the eigenvalues 0 < λ 0 < λ λ.... The lowest eigenvalue λ 0 is simple, and the corresponding eigenfunction u 0 does not change sign in the interior of Ω. B taking u 0 0 and u 0 =, we get a unique lowest eigenfunction u 0. The lowest eigenvalue λ 0 is the minimum of the Raleigh quotient: λ 0 = u min u = min u = u. These minima are attained when u = u 0, and since u 0 0 we can, if we wish, add the additional constraint u 0 to the classes of functions over which we take these minima. Theorem. λ 0 = sup(λ v, v v λ) = sup inf( v v ). v Proof. Suppose v v λ. Then λ u = = u ( v) u v u u v u v u u + uv u.
3 Thus On the other hand, if we put λ 0 sup(λ v, v v λ). v 0 = u 0 u 0 then and v 0 = u 0 + u 0 u 0 u 0 v 0 v 0 = u 0 u 0 = λ 0. Corollar. Let γ 0 = sup(γ w, w γ, w ). Then Let Proof. Suppose λ 0 γ 0 4. w γ, w. v = γ w. Then ) v v γ γ ( γ = γ 4. 3
4 Then Corollar (Cheeger s inequalit). Let χ 0 = min D Ω length( D). area(d) λ 0 χ 0 4. Proof. B the max-flow min-cut theorem, γ 0 = χ 0. Generalized continuous version Now introduce conductivit tensor σ and capacit function ρ: In this setting the Laplacian becomes and the eigenvalue equation becomes u = ρ (σ u) (σ u) = λρu. Now λ 0 = u (σ u) min ρu = min ρu = u (σ u) and our theorem becomes: Theorem. λ 0 = sup(λ v, v v σ v λρ) = sup inf( v ρ ( v v σ v)). 4
5 In this case, the choice of v that achieves the supremum is Discrete version v 0 = σ u 0 u 0. Let Ω = Ω intω be a graph with adjacenc matrix C(x, ) and valence function D(x) = C(x, ). A positive number λ is an eigenvalue of the discrete Laplacian, where if and u(x) = D(x) C(x, )(u(x) u()) u = λu u Ω = 0. We label the eigenvalues 0 < λ 0 < λ λ.... The lowest eigenvalue λ 0 is simple, and the corresponding eigenfunction u 0 does not change sign in the interior of Ω. B taking u 0 0 and x u 0 (x) =, we get a unique lowest eigenfunction u 0. The lowest eigenvalue λ 0 is the minimum of the Raleigh quotient: λ 0 = x, C(x, )(u(x) u()) min x D(x)u(x) = min x u(x) = x, C(x, )(u(x) u()). These minima are attained when u = u 0, and since u 0 0 we can, if we wish, add the additional constraint u 0 to the classes of functions over which we take these minima. 5
6 Theorem. λ 0 = sup{λ η : intω Ω [0, ), intω η(x,)η(,x) Ω C(x,)( η(x,)) λd(x) } = sup η H inf x intω C(x, )( η(x, )), D(x) Ω where H = {η, intω Ω [0, ) intω η(x, )η(, x) }. Proof. Suppose η H and for ever x intω, For an u with u Ω = 0, λ x u(x) x C(x, )( η(x, )) λ. u(x) C(x, )( η(x, )) = C(x, )u(x) C(x, )η(x, )u(x) x, = C(x, ) [ u(x) + u() η(x, )u(x) η(, x)u() ] x, C(x, ) [ u(x) + u() η(x, )u(x) ] x, η(x, ) u() = C(x, ) u(x) + u() η(x, )u(x) x, η(x, ) u() u(x)u() = C(x, ) (u(x) u()) η(x, )u(x) x, η(x, ) u() C(x, )(u(x) u()). x, (This isn t quite right, of course, since we ve been too cavalier about what happens when Ω, but not to worr... ) 6
7 On the other hand, if we set we have η 0 (x, ) = u 0() u 0 (x) C(x, )( η 0 (x, )) = ( C(x, ) u ) 0() u 0 (x) = u 0(x) u 0 (x) = λ 0. If we think of setting v(x, ) = C(x, )( η(x, )), we can get a form of this principle that is in a certain sense the discrete limit of the continuous variational principle: Corollar. λ 0 = sup{λ v : intω Ω R, v(x, ) C(x, ), Ω v(x,) λd(x) } v(x,) v(,x)+v(x,)v(,x)/c(x,) 0 Proof. Set η(x, ) = v(x, ) C(x, ). More later We ve run out of steam, and we haven t even covered the discrete Cheeger inequalit et.... 7
Math Lecture 23 Notes
 Math 1010 - Lecture 23 Notes Dylan Zwick Fall 2009 In today s lecture we ll expand upon the concept of radicals and radical expressions, and discuss how we can deal with equations involving these radical
Math 1010 - Lecture 23 Notes Dylan Zwick Fall 2009 In today s lecture we ll expand upon the concept of radicals and radical expressions, and discuss how we can deal with equations involving these radical
Surface Integrals (6A)
 Surface Integrals (6A) Surface Integral Stokes' Theorem Copright (c) 2012 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to cop, distribute and/or modif this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation
Surface Integrals (6A) Surface Integral Stokes' Theorem Copright (c) 2012 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to cop, distribute and/or modif this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation
Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 2. The Laplacian. Daniel A. Spielman September 4, x T M x. ψ i = arg min
 Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 2 The Laplacian Daniel A. Spielman September 4, 2015 Disclaimer These notes are not necessarily an accurate representation of what happened in class. The notes written before
Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 2 The Laplacian Daniel A. Spielman September 4, 2015 Disclaimer These notes are not necessarily an accurate representation of what happened in class. The notes written before
SPECTRAL PROPERTIES OF THE LAPLACIAN ON BOUNDED DOMAINS
 SPECTRAL PROPERTIES OF THE LAPLACIAN ON BOUNDED DOMAINS TSOGTGEREL GANTUMUR Abstract. After establishing discrete spectra for a large class of elliptic operators, we present some fundamental spectral properties
SPECTRAL PROPERTIES OF THE LAPLACIAN ON BOUNDED DOMAINS TSOGTGEREL GANTUMUR Abstract. After establishing discrete spectra for a large class of elliptic operators, we present some fundamental spectral properties
Surface Integrals (6A)
 urface Integrals (6A) urface Integral tokes' Theorem Copright (c) 2012 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to cop, distribute and/or modif this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License,
urface Integrals (6A) urface Integral tokes' Theorem Copright (c) 2012 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to cop, distribute and/or modif this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License,
The Kemeny constant of a Markov chain
 The Kemeny constant of a Markov chain Peter Doyle Version 1.0 dated 14 September 009 GNU FDL Abstract Given an ergodic finite-state Markov chain, let M iw denote the mean time from i to equilibrium, meaning
The Kemeny constant of a Markov chain Peter Doyle Version 1.0 dated 14 September 009 GNU FDL Abstract Given an ergodic finite-state Markov chain, let M iw denote the mean time from i to equilibrium, meaning
1 GSW Gaussian Elimination
 Gaussian elimination is probabl the simplest technique for solving a set of simultaneous linear equations, such as: = A x + A x + A x +... + A x,,,, n n = A x + A x + A x +... + A x,,,, n n... m = Am,x
Gaussian elimination is probabl the simplest technique for solving a set of simultaneous linear equations, such as: = A x + A x + A x +... + A x,,,, n n = A x + A x + A x +... + A x,,,, n n... m = Am,x
Project IV Fourier Series
 Project IV Fourier Series Robert Jerrard Goal of the project To develop understanding of how many terms of a Fourier series are required in order to well-approximate the original function, and of the differences
Project IV Fourier Series Robert Jerrard Goal of the project To develop understanding of how many terms of a Fourier series are required in order to well-approximate the original function, and of the differences
Review of Lecture 5. F = GMm r 2. = m dv dt Expressed in terms of altitude x = r R, we have. mv dv dx = GMm. (R + x) 2. Max altitude. 2GM v 2 0 R.
 Review of Lecture 5 Models could involve just one or two equations (e.g. orbit calculation), or hundreds of equations (as in climate modeling). To model a vertical cannon shot: F = GMm r 2 = m dv dt Expressed
Review of Lecture 5 Models could involve just one or two equations (e.g. orbit calculation), or hundreds of equations (as in climate modeling). To model a vertical cannon shot: F = GMm r 2 = m dv dt Expressed
Maximal Functions in Analysis
 Maximal Functions in Analysis Robert Fefferman June, 5 The University of Chicago REU Scribe: Philip Ascher Abstract This will be a self-contained introduction to the theory of maximal functions, which
Maximal Functions in Analysis Robert Fefferman June, 5 The University of Chicago REU Scribe: Philip Ascher Abstract This will be a self-contained introduction to the theory of maximal functions, which
Harmonic Functions and the Spectrum of the Laplacian on the Sierpinski Carpet
 Harmonic Functions and the Spectrum of the Laplacian on the Sierpinski Carpet Matthew Begué, Tristan Kalloniatis, & Robert Strichartz October 3, 2010 Construction of SC The Sierpinski Carpet, SC, is constructed
Harmonic Functions and the Spectrum of the Laplacian on the Sierpinski Carpet Matthew Begué, Tristan Kalloniatis, & Robert Strichartz October 3, 2010 Construction of SC The Sierpinski Carpet, SC, is constructed
Course Description for Real Analysis, Math 156
 Course Description for Real Analysis, Math 156 In this class, we will study elliptic PDE, Fourier analysis, and dispersive PDE. Here is a quick summary of the topics will study study. They re described
Course Description for Real Analysis, Math 156 In this class, we will study elliptic PDE, Fourier analysis, and dispersive PDE. Here is a quick summary of the topics will study study. They re described
THE GREEN FUNCTION. Contents
 THE GREEN FUNCTION CRISTIAN E. GUTIÉRREZ NOVEMBER 5, 203 Contents. Third Green s formula 2. The Green function 2.. Estimates of the Green function near the pole 2 2.2. Symmetry of the Green function 3
THE GREEN FUNCTION CRISTIAN E. GUTIÉRREZ NOVEMBER 5, 203 Contents. Third Green s formula 2. The Green function 2.. Estimates of the Green function near the pole 2 2.2. Symmetry of the Green function 3
The Mean Value Theorem
 Math 31A Discussion Session Week 6 Notes February 9 and 11, 2016 This week we ll discuss some (unsurprising) properties of the derivative, and then try to use some of these properties to solve a real-world
Math 31A Discussion Session Week 6 Notes February 9 and 11, 2016 This week we ll discuss some (unsurprising) properties of the derivative, and then try to use some of these properties to solve a real-world
Math 1320, Section 10 Quiz IV Solutions 20 Points
 Math 1320, Section 10 Quiz IV Solutions 20 Points Please answer each question. To receive full credit you must show all work and give answers in simplest form. Cell phones and graphing calculators are
Math 1320, Section 10 Quiz IV Solutions 20 Points Please answer each question. To receive full credit you must show all work and give answers in simplest form. Cell phones and graphing calculators are
Convex Optimization. Convex Analysis - Functions
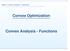 Convex Optimization Convex Analsis - Functions p. 1 A function f : K R n R is convex, if K is a convex set and x, K,x, λ (,1) we have f(λx+(1 λ)) λf(x)+(1 λ)f(). (x, f(x)) (,f()) x - strictl convex,
Convex Optimization Convex Analsis - Functions p. 1 A function f : K R n R is convex, if K is a convex set and x, K,x, λ (,1) we have f(λx+(1 λ)) λf(x)+(1 λ)f(). (x, f(x)) (,f()) x - strictl convex,
Multivariate Topological Data Analysis
 Cleveland State University November 20, 2008, Duke University joint work with Gunnar Carlsson (Stanford), Peter Kim and Zhiming Luo (Guelph), and Moo Chung (Wisconsin Madison) Framework Ideal Truth (Parameter)
Cleveland State University November 20, 2008, Duke University joint work with Gunnar Carlsson (Stanford), Peter Kim and Zhiming Luo (Guelph), and Moo Chung (Wisconsin Madison) Framework Ideal Truth (Parameter)
Higher Order ODE's (3A) Young Won Lim 7/8/14
 Higher Order ODE's (3A) Copyright (c) 2011-2014 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or
Higher Order ODE's (3A) Copyright (c) 2011-2014 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or
2.4 The Extreme Value Theorem and Some of its Consequences
 2.4 The Extreme Value Theorem and Some of its Consequences The Extreme Value Theorem deals with the question of when we can be sure that for a given function f, (1) the values f (x) don t get too big or
2.4 The Extreme Value Theorem and Some of its Consequences The Extreme Value Theorem deals with the question of when we can be sure that for a given function f, (1) the values f (x) don t get too big or
Geometric bounds for Steklov eigenvalues
 Geometric bounds for Steklov eigenvalues Luigi Provenzano École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Switzerland Joint work with Joachim Stubbe June 20, 2017 luigi.provenzano@epfl.ch (EPFL) Steklov eigenvalues
Geometric bounds for Steklov eigenvalues Luigi Provenzano École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Switzerland Joint work with Joachim Stubbe June 20, 2017 luigi.provenzano@epfl.ch (EPFL) Steklov eigenvalues
LESSON 35: EIGENVALUES AND EIGENVECTORS APRIL 21, (1) We might also write v as v. Both notations refer to a vector.
 LESSON 5: EIGENVALUES AND EIGENVECTORS APRIL 2, 27 In this contet, a vector is a column matri E Note 2 v 2, v 4 5 6 () We might also write v as v Both notations refer to a vector (2) A vector can be man
LESSON 5: EIGENVALUES AND EIGENVECTORS APRIL 2, 27 In this contet, a vector is a column matri E Note 2 v 2, v 4 5 6 () We might also write v as v Both notations refer to a vector (2) A vector can be man
Hermitian vs. Riemannian Geometry
 Hermitian vs. Riemannian Geometry Gabe Khan 1 1 Department of Mathematics The Ohio State University GSCAGT, May 2016 Outline of the talk Complex curves Background definitions What happens if the metric
Hermitian vs. Riemannian Geometry Gabe Khan 1 1 Department of Mathematics The Ohio State University GSCAGT, May 2016 Outline of the talk Complex curves Background definitions What happens if the metric
The knee-jerk mapping
 arxiv:math/0606068v [math.pr] 2 Jun 2006 The knee-jerk mapping Peter G. Doyle Jim Reeds Version dated 5 October 998 GNU FDL Abstract We claim to give the definitive theory of what we call the kneejerk
arxiv:math/0606068v [math.pr] 2 Jun 2006 The knee-jerk mapping Peter G. Doyle Jim Reeds Version dated 5 October 998 GNU FDL Abstract We claim to give the definitive theory of what we call the kneejerk
Preface. Implicit Differentiation. y =
 Preface Here are the solutions to the practice problems for m Calculus I notes. Some solutions will have more or less detail than other solutions. The level of detail in each solution will depend up on
Preface Here are the solutions to the practice problems for m Calculus I notes. Some solutions will have more or less detail than other solutions. The level of detail in each solution will depend up on
Approximation of Continuous Functions
 Approximation of Continuous Functions Francis J. Narcowich October 2014 1 Modulus of Continuit Recall that ever function continuous on a closed interval < a x b < is uniforml continuous: For ever ɛ > 0,
Approximation of Continuous Functions Francis J. Narcowich October 2014 1 Modulus of Continuit Recall that ever function continuous on a closed interval < a x b < is uniforml continuous: For ever ɛ > 0,
On the approximation of the principal eigenvalue for a class of nonlinear elliptic operators
 On the approximation of the principal eigenvalue for a class of nonlinear elliptic operators Fabio Camilli ("Sapienza" Università di Roma) joint work with I.Birindelli ("Sapienza") I.Capuzzo Dolcetta ("Sapienza")
On the approximation of the principal eigenvalue for a class of nonlinear elliptic operators Fabio Camilli ("Sapienza" Università di Roma) joint work with I.Birindelli ("Sapienza") I.Capuzzo Dolcetta ("Sapienza")
Eigenvalue (mis)behavior on manifolds
 Bucknell University Lehigh University October 20, 2010 Outline 1 Isoperimetric inequalities 2 3 4 A little history Rayleigh quotients The Original Isoperimetric Inequality The Problem of Queen Dido: maximize
Bucknell University Lehigh University October 20, 2010 Outline 1 Isoperimetric inequalities 2 3 4 A little history Rayleigh quotients The Original Isoperimetric Inequality The Problem of Queen Dido: maximize
Lesson 29 MA Nick Egbert
 Lesson 9 MA 16 Nick Egbert Overview In this lesson we build on the previous two b complicating our domains of integration and discussing the average value of functions of two variables. Lesson So far the
Lesson 9 MA 16 Nick Egbert Overview In this lesson we build on the previous two b complicating our domains of integration and discussing the average value of functions of two variables. Lesson So far the
Rev Name Date. Solve each of the following equations for y by isolating the square and using the square root property.
 Rev 8-8-3 Name Date TI-8 GC 3 Using GC to Graph Parabolae that are Not Functions of Objectives: Recall the square root propert Practice solving a quadratic equation f Graph the two parts of a hizontal
Rev 8-8-3 Name Date TI-8 GC 3 Using GC to Graph Parabolae that are Not Functions of Objectives: Recall the square root propert Practice solving a quadratic equation f Graph the two parts of a hizontal
Math 2930 Worksheet Equilibria and Stability
 Math 2930 Worksheet Equilibria and Stabilit Week 3 September 7, 2017 Question 1. (a) Let C be the temperature (in Fahrenheit) of a cup of coffee that is cooling off to room temperature. Which of the following
Math 2930 Worksheet Equilibria and Stabilit Week 3 September 7, 2017 Question 1. (a) Let C be the temperature (in Fahrenheit) of a cup of coffee that is cooling off to room temperature. Which of the following
Preliminary draft only: please check for final version
 ARE211, Fall2012 ANALYSIS6: TUE, SEP 11, 2012 PRINTED: AUGUST 22, 2012 (LEC# 6) Contents 1. Analysis (cont) 1 1.9. Continuous Functions 1 1.9.1. Weierstrass (extreme value) theorem 3 1.10. An inverse image
ARE211, Fall2012 ANALYSIS6: TUE, SEP 11, 2012 PRINTED: AUGUST 22, 2012 (LEC# 6) Contents 1. Analysis (cont) 1 1.9. Continuous Functions 1 1.9.1. Weierstrass (extreme value) theorem 3 1.10. An inverse image
Harmonic Functions and the Spectrum of the Laplacian on the Sierpinski Carpet
 Harmonic Functions and the Spectrum of the Laplacian on the Sierpinski Carpet Matthew Begué, Tristan Kalloniatis, & Robert Strichartz October 4, 2011 Norbert Wiener Center Seminar Construction of the Sierpinski
Harmonic Functions and the Spectrum of the Laplacian on the Sierpinski Carpet Matthew Begué, Tristan Kalloniatis, & Robert Strichartz October 4, 2011 Norbert Wiener Center Seminar Construction of the Sierpinski
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c
 Wave Phenomena Phsics 15c Lecture 13 Multi-Dimensional Waves (H&L Chapter 7) Term Paper Topics! Have ou found a topic for the paper?! 2/3 of the class have, or have scheduled a meeting with me! If ou haven
Wave Phenomena Phsics 15c Lecture 13 Multi-Dimensional Waves (H&L Chapter 7) Term Paper Topics! Have ou found a topic for the paper?! 2/3 of the class have, or have scheduled a meeting with me! If ou haven
Short note on compact operators - Monday 24 th March, Sylvester Eriksson-Bique
 Short note on compact operators - Monday 24 th March, 2014 Sylvester Eriksson-Bique 1 Introduction In this note I will give a short outline about the structure theory of compact operators. I restrict attention
Short note on compact operators - Monday 24 th March, 2014 Sylvester Eriksson-Bique 1 Introduction In this note I will give a short outline about the structure theory of compact operators. I restrict attention
Polynomial approximation and Splines
 Polnomial approimation and Splines 1. Weierstrass approimation theorem The basic question we ll look at toda is how to approimate a complicated function f() with a simpler function P () f() P () for eample,
Polnomial approimation and Splines 1. Weierstrass approimation theorem The basic question we ll look at toda is how to approimate a complicated function f() with a simpler function P () f() P () for eample,
One-Dimensional Dynamics
 One-Dimensional Dnamics We aim to characterize the dnamics completel describe the phase portrait) of the one-dimensional autonomous differential equation Before proceeding we worr about 1.1) having a solution.
One-Dimensional Dnamics We aim to characterize the dnamics completel describe the phase portrait) of the one-dimensional autonomous differential equation Before proceeding we worr about 1.1) having a solution.
Linear Programming. Maximize the function. P = Ax + By + C. subject to the constraints. a 1 x + b 1 y < c 1 a 2 x + b 2 y < c 2
 Linear Programming Man real world problems require the optimization of some function subject to a collection of constraints. Note: Think of optimizing as maimizing or minimizing for MATH1010. For eample,
Linear Programming Man real world problems require the optimization of some function subject to a collection of constraints. Note: Think of optimizing as maimizing or minimizing for MATH1010. For eample,
The heat equation in time dependent domains with Neumann boundary conditions
 The heat equation in time dependent domains with Neumann boundary conditions Chris Burdzy Zhen-Qing Chen John Sylvester Abstract We study the heat equation in domains in R n with insulated fast moving
The heat equation in time dependent domains with Neumann boundary conditions Chris Burdzy Zhen-Qing Chen John Sylvester Abstract We study the heat equation in domains in R n with insulated fast moving
Higher Order ODE's (3A) Young Won Lim 7/7/14
 Higher Order ODE's (3A) Copyright (c) 2011-2014 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or
Higher Order ODE's (3A) Copyright (c) 2011-2014 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c
 Wave Phenomena Phsics 15c Lecture 13 Multi-Dimensional Waves (H&L Chapter 7) Term Paper Topics! Have ou found a topic for the paper?! 2/3 of the class have, or have scheduled a meeting with me! If ou haven
Wave Phenomena Phsics 15c Lecture 13 Multi-Dimensional Waves (H&L Chapter 7) Term Paper Topics! Have ou found a topic for the paper?! 2/3 of the class have, or have scheduled a meeting with me! If ou haven
On the p-laplacian and p-fluids
 LMU Munich, Germany Lars Diening On the p-laplacian and p-fluids Lars Diening On the p-laplacian and p-fluids 1/50 p-laplacian Part I p-laplace and basic properties Lars Diening On the p-laplacian and
LMU Munich, Germany Lars Diening On the p-laplacian and p-fluids Lars Diening On the p-laplacian and p-fluids 1/50 p-laplacian Part I p-laplace and basic properties Lars Diening On the p-laplacian and
Eigenfunctions for versions of the p-laplacian
 Eigenfunctions for versions of the p-laplacian Bernd Kawohl Universität zu Köln www.mi.uni-koeln.de/ kawohl *Joint work with C. Nitsch, L.Esposito, C.Trombetti and others B. Kawohl (Universität zu Köln)
Eigenfunctions for versions of the p-laplacian Bernd Kawohl Universität zu Köln www.mi.uni-koeln.de/ kawohl *Joint work with C. Nitsch, L.Esposito, C.Trombetti and others B. Kawohl (Universität zu Köln)
Notes for CS542G (Iterative Solvers for Linear Systems)
 Notes for CS542G (Iterative Solvers for Linear Systems) Robert Bridson November 20, 2007 1 The Basics We re now looking at efficient ways to solve the linear system of equations Ax = b where in this course,
Notes for CS542G (Iterative Solvers for Linear Systems) Robert Bridson November 20, 2007 1 The Basics We re now looking at efficient ways to solve the linear system of equations Ax = b where in this course,
Oblique derivative problems for elliptic and parabolic equations, Lecture II
 of the for elliptic and parabolic equations, Lecture II Iowa State University July 22, 2011 of the 1 2 of the of the As a preliminary step in our further we now look at a special situation for elliptic.
of the for elliptic and parabolic equations, Lecture II Iowa State University July 22, 2011 of the 1 2 of the of the As a preliminary step in our further we now look at a special situation for elliptic.
The Ricci Flow Approach to 3-Manifold Topology. John Lott
 The Ricci Flow Approach to 3-Manifold Topology John Lott Two-dimensional topology All of the compact surfaces that anyone has ever seen : These are all of the compact connected oriented surfaces without
The Ricci Flow Approach to 3-Manifold Topology John Lott Two-dimensional topology All of the compact surfaces that anyone has ever seen : These are all of the compact connected oriented surfaces without
Lecture 12: Introduction to Spectral Graph Theory, Cheeger s inequality
 CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Spring 2016 Lecture 12: Introduction to Spectral Graph Theory, Cheeger s inequality Lecturer: Shayan Oveis Gharan May 4th Scribe: Gabriel Cadamuro Disclaimer:
CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Spring 2016 Lecture 12: Introduction to Spectral Graph Theory, Cheeger s inequality Lecturer: Shayan Oveis Gharan May 4th Scribe: Gabriel Cadamuro Disclaimer:
Completeness, Eigenvalues, and the Calculus of Variations
 Completeness, Eigenvalues, and the Calculus of Variations MA 436 Kurt Bryan 1 Introduction Our goal here is to prove that ϕ k (x) = 2 sin(kπx) for k = 1, 2, 3,... form a complete orthogonal family of functions
Completeness, Eigenvalues, and the Calculus of Variations MA 436 Kurt Bryan 1 Introduction Our goal here is to prove that ϕ k (x) = 2 sin(kπx) for k = 1, 2, 3,... form a complete orthogonal family of functions
Higher Order ODE's (3A) Young Won Lim 12/27/15
 Higher Order ODE's (3A) Copyright (c) 2011-2015 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or
Higher Order ODE's (3A) Copyright (c) 2011-2015 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or
Background Complex Analysis (1A) Young Won Lim 9/2/14
 Background Complex Analsis (1A) Copright (c) 2014 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to cop, distribute and/or modif this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or
Background Complex Analsis (1A) Copright (c) 2014 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to cop, distribute and/or modif this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or
Chapter 6: Inverse Trig Functions
 Haberman MTH Section I: The Trigonometric Functions Chapter 6: Inverse Trig Functions As we studied in MTH, the inverse of a function reverses the roles of the inputs and the outputs (For more information
Haberman MTH Section I: The Trigonometric Functions Chapter 6: Inverse Trig Functions As we studied in MTH, the inverse of a function reverses the roles of the inputs and the outputs (For more information
Introduction to Empirical Processes and Semiparametric Inference Lecture 08: Stochastic Convergence
 Introduction to Empirical Processes and Semiparametric Inference Lecture 08: Stochastic Convergence Michael R. Kosorok, Ph.D. Professor and Chair of Biostatistics Professor of Statistics and Operations
Introduction to Empirical Processes and Semiparametric Inference Lecture 08: Stochastic Convergence Michael R. Kosorok, Ph.D. Professor and Chair of Biostatistics Professor of Statistics and Operations
If electrons moved in simple orbits, p and x could be determined, but this violates the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle.
 CHEM 2060 Lecture 18: Particle in a Box L18-1 Atomic Orbitals If electrons moved in simple orbits, p and x could be determined, but this violates the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. We can only talk
CHEM 2060 Lecture 18: Particle in a Box L18-1 Atomic Orbitals If electrons moved in simple orbits, p and x could be determined, but this violates the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. We can only talk
5.7 Start Thinking. 5.7 Warm Up. 5.7 Cumulative Review Warm Up
 .7 Start Thinking Graph the linear inequalities < + and > 9 on the same coordinate plane. What does the area shaded for both inequalities represent? What does the area shaded for just one of the inequalities
.7 Start Thinking Graph the linear inequalities < + and > 9 on the same coordinate plane. What does the area shaded for both inequalities represent? What does the area shaded for just one of the inequalities
Chapter 8 Notes SN AA U2C8
 Chapter 8 Notes SN AA U2C8 Name Period Section 8-: Eploring Eponential Models Section 8-2: Properties of Eponential Functions In Chapter 7, we used properties of eponents to determine roots and some of
Chapter 8 Notes SN AA U2C8 Name Period Section 8-: Eploring Eponential Models Section 8-2: Properties of Eponential Functions In Chapter 7, we used properties of eponents to determine roots and some of
Singular Diffusion Equations With Nonuniform Driving Force. Y. Giga University of Tokyo (Joint work with M.-H. Giga) July 2009
 Singular Diffusion Equations With Nonuniform Driving Force Y. Giga University of Tokyo (Joint work with M.-H. Giga) July 2009 1 Contents 0. Introduction 1. Typical Problems 2. Variational Characterization
Singular Diffusion Equations With Nonuniform Driving Force Y. Giga University of Tokyo (Joint work with M.-H. Giga) July 2009 1 Contents 0. Introduction 1. Typical Problems 2. Variational Characterization
1 Adjacency matrix and eigenvalues
 CSC 5170: Theory of Computational Complexity Lecture 7 The Chinese University of Hong Kong 1 March 2010 Our objective of study today is the random walk algorithm for deciding if two vertices in an undirected
CSC 5170: Theory of Computational Complexity Lecture 7 The Chinese University of Hong Kong 1 March 2010 Our objective of study today is the random walk algorithm for deciding if two vertices in an undirected
Complex Functions (1A) Young Won Lim 2/22/14
 Complex Functions (1A) Copyright (c) 2011-2014 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or
Complex Functions (1A) Copyright (c) 2011-2014 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or
Lecture 10: Powers of Matrices, Difference Equations
 Lecture 10: Powers of Matrices, Difference Equations Difference Equations A difference equation, also sometimes called a recurrence equation is an equation that defines a sequence recursively, i.e. each
Lecture 10: Powers of Matrices, Difference Equations Difference Equations A difference equation, also sometimes called a recurrence equation is an equation that defines a sequence recursively, i.e. each
Positive stationary solutions of eq. with p-laplace operator
 Positive stationary solutions of equations with p-laplace operator joint paper with Mateusz MACIEJEWSKI Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń, Poland Geometry in Dynamics (6th European Congress of Mathematics),
Positive stationary solutions of equations with p-laplace operator joint paper with Mateusz MACIEJEWSKI Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń, Poland Geometry in Dynamics (6th European Congress of Mathematics),
6.2 Deeper Properties of Continuous Functions
 6.2. DEEPER PROPERTIES OF CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS 69 6.2 Deeper Properties of Continuous Functions 6.2. Intermediate Value Theorem and Consequences When one studies a function, one is usually interested in
6.2. DEEPER PROPERTIES OF CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS 69 6.2 Deeper Properties of Continuous Functions 6.2. Intermediate Value Theorem and Consequences When one studies a function, one is usually interested in
Existence Theory: Green s Functions
 Chapter 5 Existence Theory: Green s Functions In this chapter we describe a method for constructing a Green s Function The method outlined is formal (not rigorous) When we find a solution to a PDE by constructing
Chapter 5 Existence Theory: Green s Functions In this chapter we describe a method for constructing a Green s Function The method outlined is formal (not rigorous) When we find a solution to a PDE by constructing
Isoperimetric Inequalities for the Cauchy-Dirichlet Heat Operator
 Filomat 32:3 (218), 885 892 https://doi.org/1.2298/fil183885k Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Isoperimetric Inequalities
Filomat 32:3 (218), 885 892 https://doi.org/1.2298/fil183885k Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Isoperimetric Inequalities
3 Algebraic Methods. we can differentiate both sides implicitly to obtain a differential equation involving x and y:
 3 Algebraic Methods b The first appearance of the equation E Mc 2 in Einstein s handwritten notes. So far, the only general class of differential equations that we know how to solve are directly integrable
3 Algebraic Methods b The first appearance of the equation E Mc 2 in Einstein s handwritten notes. So far, the only general class of differential equations that we know how to solve are directly integrable
Mt. Douglas Secondary
 Foundations of Math 11 Section 7.1 Quadratic Functions 31 7.1 Quadratic Functions Mt. Douglas Secondar Quadratic functions are found in everda situations, not just in our math classroom. Tossing a ball
Foundations of Math 11 Section 7.1 Quadratic Functions 31 7.1 Quadratic Functions Mt. Douglas Secondar Quadratic functions are found in everda situations, not just in our math classroom. Tossing a ball
7. Numerical Solutions of the TISE
 7. Numerical Solutions of the TISE Copyright c 2015 2016, Daniel V. Schroeder Besides the infinite square well, there aren t many potentials V (x) for which you can find the energies and eigenfunctions
7. Numerical Solutions of the TISE Copyright c 2015 2016, Daniel V. Schroeder Besides the infinite square well, there aren t many potentials V (x) for which you can find the energies and eigenfunctions
Calculus: What is a Limit? (understanding epislon-delta proofs)
 Calculus: What is a Limit? (understanding epislon-delta proofs) Here is the definition of a limit: Suppose f is a function. We say that Lim aa ff() = LL if for every εε > 0 there is a δδ > 0 so that if
Calculus: What is a Limit? (understanding epislon-delta proofs) Here is the definition of a limit: Suppose f is a function. We say that Lim aa ff() = LL if for every εε > 0 there is a δδ > 0 so that if
u(0) = u 0, u(1) = u 1. To prove what we want we introduce a new function, where c = sup x [0,1] a(x) and ɛ 0:
![u(0) = u 0, u(1) = u 1. To prove what we want we introduce a new function, where c = sup x [0,1] a(x) and ɛ 0: u(0) = u 0, u(1) = u 1. To prove what we want we introduce a new function, where c = sup x [0,1] a(x) and ɛ 0:](/thumbs/73/68755519.jpg) 6. Maximum Principles Goal: gives properties of a solution of a PDE without solving it. For the two-point boundary problem we shall show that the extreme values of the solution are attained on the boundary.
6. Maximum Principles Goal: gives properties of a solution of a PDE without solving it. For the two-point boundary problem we shall show that the extreme values of the solution are attained on the boundary.
Introduction to Formal Verification Methods Exercise 4
 Introduction to Formal Verification Methods Exercise 4 Guy Katz, 301062063 May 30, 2013 Question 1 We argue that there exists a weakly fair non-progress cycle in the given model. ssuming weak fairness,
Introduction to Formal Verification Methods Exercise 4 Guy Katz, 301062063 May 30, 2013 Question 1 We argue that there exists a weakly fair non-progress cycle in the given model. ssuming weak fairness,
Chapter 18 Quadratic Function 2
 Chapter 18 Quadratic Function Completed Square Form 1 Consider this special set of numbers - the square numbers or the set of perfect squares. 4 = = 9 = 3 = 16 = 4 = 5 = 5 = Numbers like 5, 11, 15 are
Chapter 18 Quadratic Function Completed Square Form 1 Consider this special set of numbers - the square numbers or the set of perfect squares. 4 = = 9 = 3 = 16 = 4 = 5 = 5 = Numbers like 5, 11, 15 are
1 Review: symmetric matrices, their eigenvalues and eigenvectors
 Cornell University, Fall 2012 Lecture notes on spectral methods in algorithm design CS 6820: Algorithms Studying the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of matrices has powerful consequences for at least three
Cornell University, Fall 2012 Lecture notes on spectral methods in algorithm design CS 6820: Algorithms Studying the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of matrices has powerful consequences for at least three
1 + x 1/2. b) For what values of k is g a quasi-concave function? For what values of k is g a concave function? Explain your answers.
 Questions and Answers from Econ 0A Final: Fall 008 I have gone to some trouble to explain the answers to all of these questions, because I think that there is much to be learned b working through them
Questions and Answers from Econ 0A Final: Fall 008 I have gone to some trouble to explain the answers to all of these questions, because I think that there is much to be learned b working through them
Single-Predicate Derivations
 Single-Predicate Derivations Let s do some derivations. Start with an easy one: Practice #1: Fb, Gb Ⱶ (ꓱx)(Fx Gx) Imagine that I have a frog named Bob. The above inference might go like this: Bob is friendly.
Single-Predicate Derivations Let s do some derivations. Start with an easy one: Practice #1: Fb, Gb Ⱶ (ꓱx)(Fx Gx) Imagine that I have a frog named Bob. The above inference might go like this: Bob is friendly.
Edge Detection PSY 5018H: Math Models Hum Behavior, Prof. Paul Schrater, Spring 2005
 Edge Detection PSY 5018H: Math Models Hum Behavior, Prof. Paul Schrater, Spring 2005 Gradients and edges Points of sharp change in an image are interesting: change in reflectance change in object change
Edge Detection PSY 5018H: Math Models Hum Behavior, Prof. Paul Schrater, Spring 2005 Gradients and edges Points of sharp change in an image are interesting: change in reflectance change in object change
Mobius transformations and AdS 3 geometry
 Mobius transformations and AdS 3 geometr Jeffre Danciger September 1, 010 1 PSL (R + Rτ) and its action on AdS 3 Let B be the real algebra generated b an element τ, with τ = +1. As a vector space B = R
Mobius transformations and AdS 3 geometr Jeffre Danciger September 1, 010 1 PSL (R + Rτ) and its action on AdS 3 Let B be the real algebra generated b an element τ, with τ = +1. As a vector space B = R
Paul Schrimpf. October 18, UBC Economics 526. Unconstrained optimization. Paul Schrimpf. Notation and definitions. First order conditions
 Unconstrained UBC Economics 526 October 18, 2013 .1.2.3.4.5 Section 1 Unconstrained problem x U R n F : U R. max F (x) x U Definition F = max x U F (x) is the maximum of F on U if F (x) F for all x U and
Unconstrained UBC Economics 526 October 18, 2013 .1.2.3.4.5 Section 1 Unconstrained problem x U R n F : U R. max F (x) x U Definition F = max x U F (x) is the maximum of F on U if F (x) F for all x U and
Quantum wires, orthogonal polynomials and Diophantine approximation
 Quantum wires, orthogonal polynomials and Diophantine approximation Introduction Quantum Mechanics (QM) is a linear theory Main idea behind Quantum Information (QI): use the superposition principle of
Quantum wires, orthogonal polynomials and Diophantine approximation Introduction Quantum Mechanics (QM) is a linear theory Main idea behind Quantum Information (QI): use the superposition principle of
Last week we looked at limits generally, and at finding limits using substitution.
 Math 1314 ONLINE Week 4 Notes Lesson 4 Limits (continued) Last week we looked at limits generally, and at finding limits using substitution. Indeterminate Forms What do you do when substitution gives you
Math 1314 ONLINE Week 4 Notes Lesson 4 Limits (continued) Last week we looked at limits generally, and at finding limits using substitution. Indeterminate Forms What do you do when substitution gives you
Functions. 1. Any set of ordered pairs is a relation. Graph each set of ordered pairs. A. B. C.
 Functions 1. Any set of ordered pairs is a relation. Graph each set of ordered pairs. A. x y B. x y C. x y -3-6 -2-1 -3 6-1 -3-3 0-2 4 0-1 6 3-1 1 3 5-2 1 0 0 5 6-1 4 1 1 A. B. C. 2. A function is a special
Functions 1. Any set of ordered pairs is a relation. Graph each set of ordered pairs. A. x y B. x y C. x y -3-6 -2-1 -3 6-1 -3-3 0-2 4 0-1 6 3-1 1 3 5-2 1 0 0 5 6-1 4 1 1 A. B. C. 2. A function is a special
Relative entropies, suitable weak solutions, and weak-strong uniqueness for the compressible Navier-Stokes system
 Relative entropies, suitable weak solutions, and weak-strong uniqueness for the compressible Navier-Stokes system Institute of Mathematics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, Prague joint work
Relative entropies, suitable weak solutions, and weak-strong uniqueness for the compressible Navier-Stokes system Institute of Mathematics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, Prague joint work
2 Two-Point Boundary Value Problems
 2 Two-Point Boundary Value Problems Another fundamental equation, in addition to the heat eq. and the wave eq., is Poisson s equation: n j=1 2 u x 2 j The unknown is the function u = u(x 1, x 2,..., x
2 Two-Point Boundary Value Problems Another fundamental equation, in addition to the heat eq. and the wave eq., is Poisson s equation: n j=1 2 u x 2 j The unknown is the function u = u(x 1, x 2,..., x
f(x) = 2x 2 + 2x - 4
 4-1 Graphing Quadratic Functions What You ll Learn Scan the tet under the Now heading. List two things ou will learn about in the lesson. 1. Active Vocabular 2. New Vocabular Label each bo with the terms
4-1 Graphing Quadratic Functions What You ll Learn Scan the tet under the Now heading. List two things ou will learn about in the lesson. 1. Active Vocabular 2. New Vocabular Label each bo with the terms
Next is material on matrix rank. Please see the handout
 B90.330 / C.005 NOTES for Wednesday 0.APR.7 Suppose that the model is β + ε, but ε does not have the desired variance matrix. Say that ε is normal, but Var(ε) σ W. The form of W is W w 0 0 0 0 0 0 w 0
B90.330 / C.005 NOTES for Wednesday 0.APR.7 Suppose that the model is β + ε, but ε does not have the desired variance matrix. Say that ε is normal, but Var(ε) σ W. The form of W is W w 0 0 0 0 0 0 w 0
Mathematic 108, Fall 2015: Solutions to assignment #7
 Mathematic 08, Fall 05: Solutions to assignment #7 Problem # Suppose f is a function with f continuous on the open interval I and so that f has a local maximum at both x = a and x = b for a, b I with a
Mathematic 08, Fall 05: Solutions to assignment #7 Problem # Suppose f is a function with f continuous on the open interval I and so that f has a local maximum at both x = a and x = b for a, b I with a
Preliminary draft only: please check for final version
 ARE211, Fall2012 CALCULUS4: THU, OCT 11, 2012 PRINTED: AUGUST 22, 2012 (LEC# 15) Contents 3. Univariate and Multivariate Differentiation (cont) 1 3.6. Taylor s Theorem (cont) 2 3.7. Applying Taylor theory:
ARE211, Fall2012 CALCULUS4: THU, OCT 11, 2012 PRINTED: AUGUST 22, 2012 (LEC# 15) Contents 3. Univariate and Multivariate Differentiation (cont) 1 3.6. Taylor s Theorem (cont) 2 3.7. Applying Taylor theory:
Conductance, the Normalized Laplacian, and Cheeger s Inequality
 Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 6 Conductance, the Normalized Laplacian, and Cheeger s Inequality Daniel A. Spielman September 17, 2012 6.1 About these notes These notes are not necessarily an accurate representation
Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 6 Conductance, the Normalized Laplacian, and Cheeger s Inequality Daniel A. Spielman September 17, 2012 6.1 About these notes These notes are not necessarily an accurate representation
QUALIFYING EXAMINATION Harvard University Department of Mathematics Tuesday September 21, 2004 (Day 1)
 QUALIFYING EXAMINATION Harvard University Department of Mathematics Tuesday September 21, 2004 (Day 1) Each of the six questions is worth 10 points. 1) Let H be a (real or complex) Hilbert space. We say
QUALIFYING EXAMINATION Harvard University Department of Mathematics Tuesday September 21, 2004 (Day 1) Each of the six questions is worth 10 points. 1) Let H be a (real or complex) Hilbert space. We say
Stanford University CS366: Graph Partitioning and Expanders Handout 13 Luca Trevisan March 4, 2013
 Stanford University CS366: Graph Partitioning and Expanders Handout 13 Luca Trevisan March 4, 2013 Lecture 13 In which we construct a family of expander graphs. The problem of constructing expander graphs
Stanford University CS366: Graph Partitioning and Expanders Handout 13 Luca Trevisan March 4, 2013 Lecture 13 In which we construct a family of expander graphs. The problem of constructing expander graphs
Integration and Differentiation Limit Interchange Theorems
 Integration and Differentiation Limit Interchange Theorems James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University March 11, 2018 Outline 1 A More
Integration and Differentiation Limit Interchange Theorems James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University March 11, 2018 Outline 1 A More
Learn how to use Desmos
 Learn how to use Desmos Maclaurin and Taylor series 1 Go to www.desmos.com. Create an account (click on bottom near top right of screen) Change the grid settings (click on the spanner) to 1 x 3, 1 y 12
Learn how to use Desmos Maclaurin and Taylor series 1 Go to www.desmos.com. Create an account (click on bottom near top right of screen) Change the grid settings (click on the spanner) to 1 x 3, 1 y 12
Higher Order ODE's, (3A)
 Higher Order ODE's, (3A) Initial Value Problems, and Boundary Value Problems Copyright (c) 2011-2015 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms
Higher Order ODE's, (3A) Initial Value Problems, and Boundary Value Problems Copyright (c) 2011-2015 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms
Eigenvalues of 2-edge-coverings
 Eigenvalues of -edge-coverings Steve Butler October 3, 007 Abstract A -edge-covering between G and H is an onto homomorphism from the vertices of G to the vertices of H so that each edge is covered twice
Eigenvalues of -edge-coverings Steve Butler October 3, 007 Abstract A -edge-covering between G and H is an onto homomorphism from the vertices of G to the vertices of H so that each edge is covered twice
SUBELLIPTIC CORDES ESTIMATES
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 00, Number 0, Pages 000 000 S 000-9939XX0000-0 SUBELLIPTIC CORDES ESTIMATES Abstract. We prove Cordes type estimates for subelliptic linear partial
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 00, Number 0, Pages 000 000 S 000-9939XX0000-0 SUBELLIPTIC CORDES ESTIMATES Abstract. We prove Cordes type estimates for subelliptic linear partial
Hypothesis Testing: The Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test
 Hypothesis Testing: The Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test Consider testing the hypotheses H 0 : θ Θ 0 H 1 : θ Θ \ Θ 0 Definition: The Generalized Likelihood Ratio (GLR Let L(θ be a likelihood for a random
Hypothesis Testing: The Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test Consider testing the hypotheses H 0 : θ Θ 0 H 1 : θ Θ \ Θ 0 Definition: The Generalized Likelihood Ratio (GLR Let L(θ be a likelihood for a random
REMARKS ON THE MEMBRANE AND BUCKLING EIGENVALUES FOR PLANAR DOMAINS. Leonid Friedlander
 REMARKS ON THE MEMBRANE AND BUCKLING EIGENVALUES FOR PLANAR DOMAINS Leonid Friedlander Abstract. I present a counter-example to the conjecture that the first eigenvalue of the clamped buckling problem
REMARKS ON THE MEMBRANE AND BUCKLING EIGENVALUES FOR PLANAR DOMAINS Leonid Friedlander Abstract. I present a counter-example to the conjecture that the first eigenvalue of the clamped buckling problem
Symmetry and symmetry breaking of extremal functions in some interpolation inequalities: an overview
 Symmetry and symmetry breaking of extremal functions in some interpolation inequalities: an overview Jean Dolbeault dolbeaul@ceremade.dauphine.fr CEREMADE CNRS & Université Paris-Dauphine http://www.ceremade.dauphine.fr/
Symmetry and symmetry breaking of extremal functions in some interpolation inequalities: an overview Jean Dolbeault dolbeaul@ceremade.dauphine.fr CEREMADE CNRS & Université Paris-Dauphine http://www.ceremade.dauphine.fr/
Isoperimetric inequalities and variations on Schwarz s Lemma
 Isoperimetric inequalities and variations on Schwarz s Lemma joint work with M. van den Berg and T. Carroll May, 2010 Outline Schwarz s Lemma and variations Isoperimetric inequalities Proof Classical Schwarz
Isoperimetric inequalities and variations on Schwarz s Lemma joint work with M. van den Berg and T. Carroll May, 2010 Outline Schwarz s Lemma and variations Isoperimetric inequalities Proof Classical Schwarz
BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS ON A HALF SIERPINSKI GASKET
 BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS ON A HALF SIERPINSKI GASKET WEILIN LI AND ROBERT S. STRICHARTZ Abstract. We study boundary value problems for the Laplacian on a domain Ω consisting of the left half of the Sierpinski
BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS ON A HALF SIERPINSKI GASKET WEILIN LI AND ROBERT S. STRICHARTZ Abstract. We study boundary value problems for the Laplacian on a domain Ω consisting of the left half of the Sierpinski
5.5 Deeper Properties of Continuous Functions
 5.5. DEEPER PROPERTIES OF CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS 195 5.5 Deeper Properties of Continuous Functions 5.5.1 Intermediate Value Theorem and Consequences When one studies a function, one is usually interested
5.5. DEEPER PROPERTIES OF CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS 195 5.5 Deeper Properties of Continuous Functions 5.5.1 Intermediate Value Theorem and Consequences When one studies a function, one is usually interested
5.7 Differential Equations: Separation of Variables Calculus
 5.7 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: SEPARATION OF VARIABLES In the last section we discussed the method of separation of variables to solve a differential equation. In this section we have 4 basic goals. (1) Verif
5.7 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: SEPARATION OF VARIABLES In the last section we discussed the method of separation of variables to solve a differential equation. In this section we have 4 basic goals. (1) Verif
Math Practice Final - solutions
 Math 151 - Practice Final - solutions 2 1-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Problem 1 Indicate the following from looking at the graph of f(x) above. All answers are small integers, ±, or DNE for does not exist. a) lim x 1
Math 151 - Practice Final - solutions 2 1-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Problem 1 Indicate the following from looking at the graph of f(x) above. All answers are small integers, ±, or DNE for does not exist. a) lim x 1
