Isoperimetric inequalities and variations on Schwarz s Lemma
|
|
|
- Jonah Boone
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Isoperimetric inequalities and variations on Schwarz s Lemma joint work with M. van den Berg and T. Carroll May, 2010
2 Outline Schwarz s Lemma and variations Isoperimetric inequalities Proof
3 Classical Schwarz Lemma We begin with the classical form of Schwarz s Lemma. Let D = {z C : z < 1} and let f : D D be analytic with f (0) = 0. Then f (z) z and f (0) 1. Equality in either case implies f (z) = e iθ z for some θ R.
4 Classical Schwarz Lemma We begin with the classical form of Schwarz s Lemma. Let D = {z C : z < 1} and let f : D D be analytic with f (0) = 0. Then f (z) z and f (0) 1. Equality in either case implies f (z) = e iθ z for some θ R. We can rephrase this more geometrically by defining Rad(r) = sup f (z) f (0). z =r Then Schwarz s Lemma says Rad(r) r, and, in fact, its classical proof implies r 1 r Rad(r) is an increasing function for 0 < r < 1.
5 Variations on Schwarz s Lemma In 2008, Burckel, Marshall, Minda, Poggi-Corradini, and Ransford proved similar versions for n-diameter, logarithmic capacity, and area. They asked whether such a theorem holds for the first Dirichlet eigenvalue λ.
6 Variations on Schwarz s Lemma In 2008, Burckel, Marshall, Minda, Poggi-Corradini, and Ransford proved similar versions for n-diameter, logarithmic capacity, and area. They asked whether such a theorem holds for the first Dirichlet eigenvalue λ. Theorem (van den Berg, Carroll, ) Let f : D C be conformal. Then the function λ(f (rd)) r Φ λ (r) = = 1 λ(rd) j0 2 r 2 λ(f (rd)) (1) is strictly decreasing for 0 < r < 1, unless f is linear (in which case this function is constant).
7 Outline Schwarz s Lemma and variations Isoperimetric inequalities Proof
8 A key tool we use is the following isoperimetric inequality. Theorem Let D C be a bounded domain with Lipschitz boundary, and let φ be the first Dirichlet eigenfunction. Place the conformal metric ds 2 = φ 2 dz 2 on D, and let A = φ 2 dz 2, L = φ dz D be the area and perimeter (respectively) of D with respect to this conformal metric. Then D with equality if and only if D is a round disk. L 2 4πA, (2)
9 The metric φ 2 dz 2 is a singular metric on D, with singularities at the critical points of the eigenfunction φ. However, there are only finitely many of these singular points, all of which lie in the interior of D, and the metric vanishes to first order there.
10 The case of equality: the Bessel disk On the unit disk D, let φ 0 (r) = J 0 (j 0 r) be the first eigenfunction. We call the conformal metric ds 2 = φ 0 2 dz 2 = j 2 0 J2 1 (j 0r) dz 2 the Bessel metric on the disk. This metric has an isolated singularity at the origin. The curvature is everywhere positive, and goes to + as r 0 +, and (D, φ 0 2 dz 2 ) has total curvature 4π.
11 This is a graph of the conformal factor ρ(r) = j 0 J 1 (j 0 r):
12 This is a graph of the Gauss curvature, K = ρ 2 log(ρ), of the Bessel disk:
13 This is a graph of the Gauss-Bonnet integrand, KdA = log(ρ), of the Bessel disk:
14 There s a fairly large literature of isoperimetric inequalities on surfaces. Notable recent results include a pair of theorems due (separately) to Topping and Morgan-Hutchings-Howard. In each of their inequalities, they note that one gets equality for a rotationally symmetric on a disk where the curvature function is monotone. We note that the Bessel disk achieves equality in their inequalities, is rotationally symmetric, but its curvature is not monotone.
15 Outline Schwarz s Lemma and variations Isoperimetric inequalities Proof
16 We ll briefly sketch the proof of (2) and how one proves (1) using (2). Payne and Rayner proved an equivalent form of this isoperimetric inequality for the first eigenfunction: ( D ) 2 φda 4π φ 2 da. (3) λ D Their proof relies on the coarea formula and the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality, and is fairly similar to the classical proof of the Faber-Krahn inequality.
17 It is straightforward to see that (2) and (3) are equivalent. If η is the outward unit normal of D, then φ φ ds = D D η ds = φda D = λ φda Also, because φ is minimizes the Rayleigh quotient, φ 2 da = λ φ 2 da. D D D
18 Now we ll prove (1); recall Φ λ (r) = r 2 λ(f (rd)). To show that Φ λ is decreasing, we want to show that 0 dφ λ = 1 [2rλ(f dr j0 2 (rd)) + r 2 ddr ] λ(f (rd)), or, equivalently, j r λ(f (rd)) d (λ(f (rd))). (4) dr
19 A classical variation formula of Hadamard tells us d λ(f (rd))) = r dr 2π 0 ψ r 2 dθ, (5) where φ r is the eigenfunction of D r = f (rd) and ψ r = φ r f. We can normalize φ r so that D r φ 2 r da = 1.
20 By (2), ( r 2π 0 2 ( ) 2 ψ r dz ) = φ r ds D r 4π φ r 2 da D r = 4π ψ r 2 dz 2. rd
21 Now, using the normalization of φ r, 2 r λ(f (rd)) = 2 φ r 2 da = 2 r D r r ( r 2π ψ r (re iθ ) dθ 2π r 2π 0 0 rd ) 2 ψ r 2 dz 2 ψ r (re iθ ) 2 dθ = d λ(f (rd)). dr
22 Thanks!
arxiv: v1 [math.sp] 11 Jun 2010
![arxiv: v1 [math.sp] 11 Jun 2010 arxiv: v1 [math.sp] 11 Jun 2010](/thumbs/90/103465899.jpg) Isoperimetric Inequalities and Variations on Schwarz s Lemma Tom Carroll and Jesse Ratzkin arxiv:16.231v1 [math.sp] 11 Jun 21 University College Cork and University of Cape Town t.carroll@ucc.ie and j.ratzkin@ucc.ie
Isoperimetric Inequalities and Variations on Schwarz s Lemma Tom Carroll and Jesse Ratzkin arxiv:16.231v1 [math.sp] 11 Jun 21 University College Cork and University of Cape Town t.carroll@ucc.ie and j.ratzkin@ucc.ie
VOLUME INTEGRAL MEANS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS
 VOLUME INTEGRAL MEANS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS JIE XIAO AND KEHE ZHU ABSTRACT. The classical integral means of a holomorphic function f in the unit disk are defined by [ 1/p 1 2π f(re iθ ) dθ] p, r < 1.
VOLUME INTEGRAL MEANS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS JIE XIAO AND KEHE ZHU ABSTRACT. The classical integral means of a holomorphic function f in the unit disk are defined by [ 1/p 1 2π f(re iθ ) dθ] p, r < 1.
SOME REMARKS ABOUT ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS DEFINED ON AN ANNULUS. 1. Introduction. What else? Perimeter, eigenvalues of the Laplacian, etc...
 SOME REMARKS ABOUT ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS DEFINED ON AN ANNULUS PIETRO POGGI-CORRADINI Abstract. We show that some recent reformulations of the classical Schwarz Lemma and results of Landau and Toeplitz can
SOME REMARKS ABOUT ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS DEFINED ON AN ANNULUS PIETRO POGGI-CORRADINI Abstract. We show that some recent reformulations of the classical Schwarz Lemma and results of Landau and Toeplitz can
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
A Faber-Krahn type inequality for regular trees
 A Faber-Krahn type inequality for regular trees Josef Leydold leydold@statistikwu-wienacat Institut für Statistik, WU Wien Leydold 2003/02/13 A Faber-Krahn type inequality for regular trees p0/36 The Faber-Krahn
A Faber-Krahn type inequality for regular trees Josef Leydold leydold@statistikwu-wienacat Institut für Statistik, WU Wien Leydold 2003/02/13 A Faber-Krahn type inequality for regular trees p0/36 The Faber-Krahn
Regularity for functionals involving perimeter
 Regularity for functionals involving perimeter Guido De Philippis, Jimmy Lamboley, Michel Pierre, Bozhidar Velichkov Université Paris Dauphine, CEREMADE 22/11/16, CIRM Shape optimization, Isoperimetric
Regularity for functionals involving perimeter Guido De Philippis, Jimmy Lamboley, Michel Pierre, Bozhidar Velichkov Université Paris Dauphine, CEREMADE 22/11/16, CIRM Shape optimization, Isoperimetric
On the spectrum of the Hodge Laplacian and the John ellipsoid
 Banff, July 203 On the spectrum of the Hodge Laplacian and the John ellipsoid Alessandro Savo, Sapienza Università di Roma We give upper and lower bounds for the first eigenvalue of the Hodge Laplacian
Banff, July 203 On the spectrum of the Hodge Laplacian and the John ellipsoid Alessandro Savo, Sapienza Università di Roma We give upper and lower bounds for the first eigenvalue of the Hodge Laplacian
Math Theory of Partial Differential Equations Lecture 3-2: Spectral properties of the Laplacian. Bessel functions.
 Math 412-501 Theory of Partial ifferential Equations Lecture 3-2: Spectral properties of the Laplacian. Bessel functions. Eigenvalue problem: 2 φ + λφ = 0 in, ( αφ + β φ ) n = 0, where α, β are piecewise
Math 412-501 Theory of Partial ifferential Equations Lecture 3-2: Spectral properties of the Laplacian. Bessel functions. Eigenvalue problem: 2 φ + λφ = 0 in, ( αφ + β φ ) n = 0, where α, β are piecewise
Estimates in surfaces with positive constant Gauss curvature
 Estimates in surfaces with positive constant Gauss curvature J. A. Gálvez A. Martínez Abstract We give optimal bounds of the height, curvature, area and enclosed volume of K-surfaces in R 3 bounding a
Estimates in surfaces with positive constant Gauss curvature J. A. Gálvez A. Martínez Abstract We give optimal bounds of the height, curvature, area and enclosed volume of K-surfaces in R 3 bounding a
Shape optimization problems for variational functionals under geometric constraints
 Shape optimization problems for variational functionals under geometric constraints Ilaria Fragalà 2 nd Italian-Japanese Workshop Cortona, June 20-24, 2011 The variational functionals The first Dirichlet
Shape optimization problems for variational functionals under geometric constraints Ilaria Fragalà 2 nd Italian-Japanese Workshop Cortona, June 20-24, 2011 The variational functionals The first Dirichlet
The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and engineering.
 Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
Lecture 2: Isoperimetric methods for the curve-shortening flow and for the Ricci flow on surfaces
 Lecture 2: Isoperimetric methods for the curve-shortening flow and for the Ricci flow on surfaces Ben Andrews Mathematical Sciences Institute, Australian National University Winter School of Geometric
Lecture 2: Isoperimetric methods for the curve-shortening flow and for the Ricci flow on surfaces Ben Andrews Mathematical Sciences Institute, Australian National University Winter School of Geometric
Eigenvalue (mis)behavior on manifolds
 Bucknell University Lehigh University October 20, 2010 Outline 1 Isoperimetric inequalities 2 3 4 A little history Rayleigh quotients The Original Isoperimetric Inequality The Problem of Queen Dido: maximize
Bucknell University Lehigh University October 20, 2010 Outline 1 Isoperimetric inequalities 2 3 4 A little history Rayleigh quotients The Original Isoperimetric Inequality The Problem of Queen Dido: maximize
Shape optimization under convexity constraint
 Shape optimization under convexity constraint Jimmy LAMBOLEY University Paris-Dauphine with D. Bucur, G. Carlier, I. Fragalà, W. Gangbo, E. Harrell, A. Henrot, A. Novruzi, M. Pierre 07/10/2013, Ottawa
Shape optimization under convexity constraint Jimmy LAMBOLEY University Paris-Dauphine with D. Bucur, G. Carlier, I. Fragalà, W. Gangbo, E. Harrell, A. Henrot, A. Novruzi, M. Pierre 07/10/2013, Ottawa
Partial Differential Equations
 Partial Differential Equations Spring Exam 3 Review Solutions Exercise. We utilize the general solution to the Dirichlet problem in rectangle given in the textbook on page 68. In the notation used there
Partial Differential Equations Spring Exam 3 Review Solutions Exercise. We utilize the general solution to the Dirichlet problem in rectangle given in the textbook on page 68. In the notation used there
Review of complex analysis in one variable
 CHAPTER 130 Review of complex analysis in one variable This gives a brief review of some of the basic results in complex analysis. In particular, it outlines the background in single variable complex analysis
CHAPTER 130 Review of complex analysis in one variable This gives a brief review of some of the basic results in complex analysis. In particular, it outlines the background in single variable complex analysis
Extremal eigenvalue problems for surfaces
 Extremal eigenvalue problems for surfaces Richard Schoen Stanford University - Chen-Jung Hsu Lecture 3, Academia Sinica, ROC - December 4, 2013 Plan of Lecture The general lecture plan: Part 1: Introduction:
Extremal eigenvalue problems for surfaces Richard Schoen Stanford University - Chen-Jung Hsu Lecture 3, Academia Sinica, ROC - December 4, 2013 Plan of Lecture The general lecture plan: Part 1: Introduction:
Relative Isoperimetric Inequality Outside Convex Bodies
 Relative Isoperimetric Inequality Outside Convex Bodies Mohammad Ghomi (www.math.gatech.edu/ ghomi) Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, USA May 25, 2010, Tunis From Carthage to the World Joint work
Relative Isoperimetric Inequality Outside Convex Bodies Mohammad Ghomi (www.math.gatech.edu/ ghomi) Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, USA May 25, 2010, Tunis From Carthage to the World Joint work
Part IB. Further Analysis. Year
 Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
Lecture No 2 Degenerate Diffusion Free boundary problems
 Lecture No 2 Degenerate Diffusion Free boundary problems Columbia University IAS summer program June, 2009 Outline We will discuss non-linear parabolic equations of slow diffusion. Our model is the porous
Lecture No 2 Degenerate Diffusion Free boundary problems Columbia University IAS summer program June, 2009 Outline We will discuss non-linear parabolic equations of slow diffusion. Our model is the porous
Part 2 Continuous functions and their properties
 Part 2 Continuous functions and their properties 2.1 Definition Definition A function f is continuous at a R if, and only if, that is lim f (x) = f (a), x a ε > 0, δ > 0, x, x a < δ f (x) f (a) < ε. Notice
Part 2 Continuous functions and their properties 2.1 Definition Definition A function f is continuous at a R if, and only if, that is lim f (x) = f (a), x a ε > 0, δ > 0, x, x a < δ f (x) f (a) < ε. Notice
Topic 4 Notes Jeremy Orloff
 Topic 4 Notes Jeremy Orloff 4 auchy s integral formula 4. Introduction auchy s theorem is a big theorem which we will use almost daily from here on out. Right away it will reveal a number of interesting
Topic 4 Notes Jeremy Orloff 4 auchy s integral formula 4. Introduction auchy s theorem is a big theorem which we will use almost daily from here on out. Right away it will reveal a number of interesting
Nodal domains of Laplacian eigenfunctions
 Nodal domains of Laplacian eigenfunctions Yoni Rozenshein May 20 & May 27, 2014 Contents I Motivation, denitions, Courant's theorem and the Faber-Krahn inequality 1 1 Motivation / entertainment 2 1.1 The
Nodal domains of Laplacian eigenfunctions Yoni Rozenshein May 20 & May 27, 2014 Contents I Motivation, denitions, Courant's theorem and the Faber-Krahn inequality 1 1 Motivation / entertainment 2 1.1 The
Preliminary Exam 2018 Solutions to Morning Exam
 Preliminary Exam 28 Solutions to Morning Exam Part I. Solve four of the following five problems. Problem. Consider the series n 2 (n log n) and n 2 (n(log n)2 ). Show that one converges and one diverges
Preliminary Exam 28 Solutions to Morning Exam Part I. Solve four of the following five problems. Problem. Consider the series n 2 (n log n) and n 2 (n(log n)2 ). Show that one converges and one diverges
Foliations of hyperbolic space by constant mean curvature surfaces sharing ideal boundary
 Foliations of hyperbolic space by constant mean curvature surfaces sharing ideal boundary David Chopp and John A. Velling December 1, 2003 Abstract Let γ be a Jordan curve in S 2, considered as the ideal
Foliations of hyperbolic space by constant mean curvature surfaces sharing ideal boundary David Chopp and John A. Velling December 1, 2003 Abstract Let γ be a Jordan curve in S 2, considered as the ideal
are harmonic functions so by superposition
 J. Rauch Applied Complex Analysis The Dirichlet Problem Abstract. We solve, by simple formula, the Dirichlet Problem in a half space with step function boundary data. Uniqueness is proved by complex variable
J. Rauch Applied Complex Analysis The Dirichlet Problem Abstract. We solve, by simple formula, the Dirichlet Problem in a half space with step function boundary data. Uniqueness is proved by complex variable
PICARD S THEOREM STEFAN FRIEDL
 PICARD S THEOREM STEFAN FRIEDL Abstract. We give a summary for the proof of Picard s Theorem. The proof is for the most part an excerpt of [F]. 1. Introduction Definition. Let U C be an open subset. A
PICARD S THEOREM STEFAN FRIEDL Abstract. We give a summary for the proof of Picard s Theorem. The proof is for the most part an excerpt of [F]. 1. Introduction Definition. Let U C be an open subset. A
= 2 x y 2. (1)
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS PART 5: HARMONIC FUNCTIONS A Let me start by asking you a question. Suppose that f is an analytic function so that the CR-equation f/ z = 0 is satisfied. Let us write u and v for the real
COMPLEX ANALYSIS PART 5: HARMONIC FUNCTIONS A Let me start by asking you a question. Suppose that f is an analytic function so that the CR-equation f/ z = 0 is satisfied. Let us write u and v for the real
BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS ON A HALF SIERPINSKI GASKET
 BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS ON A HALF SIERPINSKI GASKET WEILIN LI AND ROBERT S. STRICHARTZ Abstract. We study boundary value problems for the Laplacian on a domain Ω consisting of the left half of the Sierpinski
BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS ON A HALF SIERPINSKI GASKET WEILIN LI AND ROBERT S. STRICHARTZ Abstract. We study boundary value problems for the Laplacian on a domain Ω consisting of the left half of the Sierpinski
L p Spaces and Convexity
 L p Spaces and Convexity These notes largely follow the treatments in Royden, Real Analysis, and Rudin, Real & Complex Analysis. 1. Convex functions Let I R be an interval. For I open, we say a function
L p Spaces and Convexity These notes largely follow the treatments in Royden, Real Analysis, and Rudin, Real & Complex Analysis. 1. Convex functions Let I R be an interval. For I open, we say a function
A dual form of the sharp Nash inequality and its weighted generalization
 A dual form of the sharp Nash inequality and its weighted generalization Elliott Lieb Princeton University Joint work with Eric Carlen, arxiv: 1704.08720 Kato conference, University of Tokyo September
A dual form of the sharp Nash inequality and its weighted generalization Elliott Lieb Princeton University Joint work with Eric Carlen, arxiv: 1704.08720 Kato conference, University of Tokyo September
An extremal eigenvalue problem for surfaces with boundary
 An extremal eigenvalue problem for surfaces with boundary Richard Schoen Stanford University - Conference in Geometric Analysis, UC Irvine - January 15, 2012 - Joint project with Ailana Fraser Plan of
An extremal eigenvalue problem for surfaces with boundary Richard Schoen Stanford University - Conference in Geometric Analysis, UC Irvine - January 15, 2012 - Joint project with Ailana Fraser Plan of
Differentiating Blaschke products
 Differentiating Blaschke products Oleg Ivrii April 14, 2017 Differentiating Blaschke Products Consider the following curious differentiation procedure: to a Blaschke product of degree d 1, F (z) = e iψ
Differentiating Blaschke products Oleg Ivrii April 14, 2017 Differentiating Blaschke Products Consider the following curious differentiation procedure: to a Blaschke product of degree d 1, F (z) = e iψ
Shape optimisation for the Robin Laplacian. an overview
 : an overview Group of Mathematical Physics University of Lisbon Geometric Spectral Theory Université de Neuchâtel Thursday, 22 June, 2017 The Robin eigenvalue problem Consider u = λu in Ω, u ν + αu =
: an overview Group of Mathematical Physics University of Lisbon Geometric Spectral Theory Université de Neuchâtel Thursday, 22 June, 2017 The Robin eigenvalue problem Consider u = λu in Ω, u ν + αu =
Isoperimetric Inequalities for the Cauchy-Dirichlet Heat Operator
 Filomat 32:3 (218), 885 892 https://doi.org/1.2298/fil183885k Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Isoperimetric Inequalities
Filomat 32:3 (218), 885 892 https://doi.org/1.2298/fil183885k Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Isoperimetric Inequalities
On the spectrum of the Laplacian
 On the spectrum of the Laplacian S. Kesavan Institute of Mathematical Sciences, CIT Campus, Taramani, Chennai - 600113. kesh@imsc.res.in July 1, 2013 S. Kesavan (IMSc) Spectrum of the Laplacian July 1,
On the spectrum of the Laplacian S. Kesavan Institute of Mathematical Sciences, CIT Campus, Taramani, Chennai - 600113. kesh@imsc.res.in July 1, 2013 S. Kesavan (IMSc) Spectrum of the Laplacian July 1,
REMARKS ON THE MEMBRANE AND BUCKLING EIGENVALUES FOR PLANAR DOMAINS. Leonid Friedlander
 REMARKS ON THE MEMBRANE AND BUCKLING EIGENVALUES FOR PLANAR DOMAINS Leonid Friedlander Abstract. I present a counter-example to the conjecture that the first eigenvalue of the clamped buckling problem
REMARKS ON THE MEMBRANE AND BUCKLING EIGENVALUES FOR PLANAR DOMAINS Leonid Friedlander Abstract. I present a counter-example to the conjecture that the first eigenvalue of the clamped buckling problem
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 2014
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 24 Homework 4 Solutions Exercise Do and hand in exercise, Chapter 3, p. 4. Solution. The exercise states: Show that if a
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 24 Homework 4 Solutions Exercise Do and hand in exercise, Chapter 3, p. 4. Solution. The exercise states: Show that if a
Transmission Eigenvalues in Inverse Scattering Theory
 Transmission Eigenvalues in Inverse Scattering Theory David Colton Department of Mathematical Sciences University of Delaware Newark, DE 19716, USA email: colton@math.udel.edu Research supported by a grant
Transmission Eigenvalues in Inverse Scattering Theory David Colton Department of Mathematical Sciences University of Delaware Newark, DE 19716, USA email: colton@math.udel.edu Research supported by a grant
Geometric inequalities for black holes
 Geometric inequalities for black holes Sergio Dain FaMAF-Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, CONICET, Argentina. 3 August, 2012 Einstein equations (vacuum) The spacetime is a four dimensional manifold M with
Geometric inequalities for black holes Sergio Dain FaMAF-Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, CONICET, Argentina. 3 August, 2012 Einstein equations (vacuum) The spacetime is a four dimensional manifold M with
Math 20C Homework 2 Partial Solutions
 Math 2C Homework 2 Partial Solutions Problem 1 (12.4.14). Calculate (j k) (j + k). Solution. The basic properties of the cross product are found in Theorem 2 of Section 12.4. From these properties, we
Math 2C Homework 2 Partial Solutions Problem 1 (12.4.14). Calculate (j k) (j + k). Solution. The basic properties of the cross product are found in Theorem 2 of Section 12.4. From these properties, we
Chapter 6: Residue Theory. Introduction. The Residue Theorem. 6.1 The Residue Theorem. 6.2 Trigonometric Integrals Over (0, 2π) Li, Yongzhao
 Outline Chapter 6: Residue Theory Li, Yongzhao State Key Laboratory of Integrated Services Networks, Xidian University June 7, 2009 Introduction The Residue Theorem In the previous chapters, we have seen
Outline Chapter 6: Residue Theory Li, Yongzhao State Key Laboratory of Integrated Services Networks, Xidian University June 7, 2009 Introduction The Residue Theorem In the previous chapters, we have seen
Gauss-Bonnet with Densities 10/16/09 1. The Gauss-Bonnet Formula on Surfaces with Densities. Frank Morgan and Ivan Corwin ! D
 Gauss-Bonnet with Densities 10/16/09 1 The Gauss-Bonnet Formula on Surfaces with Densities Frank Morgan and Ivan Corwin A classic, though somewhat anthropomorphic, question in mathematics is whether an
Gauss-Bonnet with Densities 10/16/09 1 The Gauss-Bonnet Formula on Surfaces with Densities Frank Morgan and Ivan Corwin A classic, though somewhat anthropomorphic, question in mathematics is whether an
Pseudo-Poincaré Inequalities and Applications to Sobolev Inequalities
 Pseudo-Poincaré Inequalities and Applications to Sobolev Inequalities Laurent Saloff-Coste Abstract Most smoothing procedures are via averaging. Pseudo-Poincaré inequalities give a basic L p -norm control
Pseudo-Poincaré Inequalities and Applications to Sobolev Inequalities Laurent Saloff-Coste Abstract Most smoothing procedures are via averaging. Pseudo-Poincaré inequalities give a basic L p -norm control
LAPLACE EQUATION. = 2 is call the Laplacian or del-square operator. In two dimensions, the expression of in rectangular and polar coordinates are
 LAPLACE EQUATION If a diffusion or wave problem is stationary (time independent), the pde reduces to the Laplace equation u = u =, an archetype of second order elliptic pde. = 2 is call the Laplacian or
LAPLACE EQUATION If a diffusion or wave problem is stationary (time independent), the pde reduces to the Laplace equation u = u =, an archetype of second order elliptic pde. = 2 is call the Laplacian or
Harmonic Analysis Homework 5
 Harmonic Analysis Homework 5 Bruno Poggi Department of Mathematics, University of Minnesota November 4, 6 Notation Throughout, B, r is the ball of radius r with center in the understood metric space usually
Harmonic Analysis Homework 5 Bruno Poggi Department of Mathematics, University of Minnesota November 4, 6 Notation Throughout, B, r is the ball of radius r with center in the understood metric space usually
IN SEARCH OF A MAHLER-TYPE INEQUALITY FOR THE EXTERNAL CONFORMAL RADIUS SPUR FINAL PAPER, SUMMER 2015
 IN SEARCH OF A MAHLER-TYPE INEQUALITY FOR THE EXTERNAL CONFORMAL RADIUS SPUR FINAL PAPER, SUMMER 2015 JINGWEN CHEN MENTOR: NICK STREHLKE 1. abstract If K is a convex set in the plane that contains the
IN SEARCH OF A MAHLER-TYPE INEQUALITY FOR THE EXTERNAL CONFORMAL RADIUS SPUR FINAL PAPER, SUMMER 2015 JINGWEN CHEN MENTOR: NICK STREHLKE 1. abstract If K is a convex set in the plane that contains the
SPECTRAL PROPERTIES OF THE LAPLACIAN ON BOUNDED DOMAINS
 SPECTRAL PROPERTIES OF THE LAPLACIAN ON BOUNDED DOMAINS TSOGTGEREL GANTUMUR Abstract. After establishing discrete spectra for a large class of elliptic operators, we present some fundamental spectral properties
SPECTRAL PROPERTIES OF THE LAPLACIAN ON BOUNDED DOMAINS TSOGTGEREL GANTUMUR Abstract. After establishing discrete spectra for a large class of elliptic operators, we present some fundamental spectral properties
Complex Analysis Qualifying Exam Solutions
 Complex Analysis Qualifying Exam Solutions May, 04 Part.. Let log z be the principal branch of the logarithm defined on G = {z C z (, 0]}. Show that if t > 0, then the equation log z = t has exactly one
Complex Analysis Qualifying Exam Solutions May, 04 Part.. Let log z be the principal branch of the logarithm defined on G = {z C z (, 0]}. Show that if t > 0, then the equation log z = t has exactly one
ISOPERIMETRIC INEQUALITY FOR FLAT SURFACES
 Proceedings of The Thirteenth International Workshop on Diff. Geom. 3(9) 3-9 ISOPERIMETRIC INEQUALITY FOR FLAT SURFACES JAIGYOUNG CHOE Korea Institute for Advanced Study, Seoul, 3-7, Korea e-mail : choe@kias.re.kr
Proceedings of The Thirteenth International Workshop on Diff. Geom. 3(9) 3-9 ISOPERIMETRIC INEQUALITY FOR FLAT SURFACES JAIGYOUNG CHOE Korea Institute for Advanced Study, Seoul, 3-7, Korea e-mail : choe@kias.re.kr
Problem 1A. Find the volume of the solid given by x 2 + z 2 1, y 2 + z 2 1. (Hint: 1. Solution: The volume is 1. Problem 2A.
 Problem 1A Find the volume of the solid given by x 2 + z 2 1, y 2 + z 2 1 (Hint: 1 1 (something)dz) Solution: The volume is 1 1 4xydz where x = y = 1 z 2 This integral has value 16/3 Problem 2A Let f(x)
Problem 1A Find the volume of the solid given by x 2 + z 2 1, y 2 + z 2 1 (Hint: 1 1 (something)dz) Solution: The volume is 1 1 4xydz where x = y = 1 z 2 This integral has value 16/3 Problem 2A Let f(x)
MA 412 Complex Analysis Final Exam
 MA 4 Complex Analysis Final Exam Summer II Session, August 9, 00.. Find all the values of ( 8i) /3. Sketch the solutions. Answer: We start by writing 8i in polar form and then we ll compute the cubic root:
MA 4 Complex Analysis Final Exam Summer II Session, August 9, 00.. Find all the values of ( 8i) /3. Sketch the solutions. Answer: We start by writing 8i in polar form and then we ll compute the cubic root:
Exact Solutions of the Einstein Equations
 Notes from phz 6607, Special and General Relativity University of Florida, Fall 2004, Detweiler Exact Solutions of the Einstein Equations These notes are not a substitute in any manner for class lectures.
Notes from phz 6607, Special and General Relativity University of Florida, Fall 2004, Detweiler Exact Solutions of the Einstein Equations These notes are not a substitute in any manner for class lectures.
Before you begin read these instructions carefully.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part IB Thursday, 6 June, 2013 9:00 am to 12:00 pm PAPER 3 Before you begin read these instructions carefully. Each question in Section II carries twice the number of marks of each
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part IB Thursday, 6 June, 2013 9:00 am to 12:00 pm PAPER 3 Before you begin read these instructions carefully. Each question in Section II carries twice the number of marks of each
Inequalities for the ADM-mass and capacity of asymptotically flat manifolds with minimal boundary
 Inequalities for the ADM-mass and capacity of asymptotically flat manifolds with minimal boundary Fernando Schwartz Abstract. We present some recent developments involving inequalities for the ADM-mass
Inequalities for the ADM-mass and capacity of asymptotically flat manifolds with minimal boundary Fernando Schwartz Abstract. We present some recent developments involving inequalities for the ADM-mass
Instructions: No books. No notes. Non-graphing calculators only. You are encouraged, although not required, to show your work.
 Exam 3 Math 850-007 Fall 04 Odenthal Name: Instructions: No books. No notes. Non-graphing calculators only. You are encouraged, although not required, to show your work.. Evaluate the iterated integral
Exam 3 Math 850-007 Fall 04 Odenthal Name: Instructions: No books. No notes. Non-graphing calculators only. You are encouraged, although not required, to show your work.. Evaluate the iterated integral
Sharp bounds for the bottom of the spectrum of Laplacians (and their associated stability estimates)
 Sharp bounds for the bottom of the spectrum of Laplacians (and their associated stability estimates) Lorenzo Brasco I2M Aix-Marseille Université lorenzo.brasco@univ-amu.fr http://www.latp.univ-mrs.fr/
Sharp bounds for the bottom of the spectrum of Laplacians (and their associated stability estimates) Lorenzo Brasco I2M Aix-Marseille Université lorenzo.brasco@univ-amu.fr http://www.latp.univ-mrs.fr/
Fatou s Theorem and minimal graphs
 Fatou s Theorem and minimal graphs José M. Espinar 1, Harold Rosenberg May 15, 2009 Institut de Mathématiques, Université Paris VII, 175 Rue du Chevaleret, 75013 Paris, France; e-mail: jespinar@ugr.es
Fatou s Theorem and minimal graphs José M. Espinar 1, Harold Rosenberg May 15, 2009 Institut de Mathématiques, Université Paris VII, 175 Rue du Chevaleret, 75013 Paris, France; e-mail: jespinar@ugr.es
Measuring Ellipsoids 1
 Measuring Ellipsoids 1 Igor Rivin Temple University 2 What is an ellipsoid? E = {x E n Ax = 1}, where A is a non-singular linear transformation of E n. Remark that Ax = Ax, Ax = x, A t Ax. The matrix Q
Measuring Ellipsoids 1 Igor Rivin Temple University 2 What is an ellipsoid? E = {x E n Ax = 1}, where A is a non-singular linear transformation of E n. Remark that Ax = Ax, Ax = x, A t Ax. The matrix Q
Murat Akman. The Brunn-Minkowski Inequality and a Minkowski Problem for Nonlinear Capacities. March 10
 The Brunn-Minkowski Inequality and a Minkowski Problem for Nonlinear Capacities Murat Akman March 10 Postdoc in HA Group and Postdoc at the University of Connecticut Minkowski Addition of Sets Let E 1
The Brunn-Minkowski Inequality and a Minkowski Problem for Nonlinear Capacities Murat Akman March 10 Postdoc in HA Group and Postdoc at the University of Connecticut Minkowski Addition of Sets Let E 1
Practice Final Solutions
 Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
1. Plurisubharmonic functions and currents The first part of the homework studies some properties of PSH functions.
 MATH 263: PROBLEM SET 2: PSH FUNCTIONS, HORMANDER S ESTIMATES AND VANISHING THEOREMS 1. Plurisubharmonic functions and currents The first part of the homework studies some properties of PSH functions.
MATH 263: PROBLEM SET 2: PSH FUNCTIONS, HORMANDER S ESTIMATES AND VANISHING THEOREMS 1. Plurisubharmonic functions and currents The first part of the homework studies some properties of PSH functions.
Sums of Reciprocal Eigenvalues
 Sums of Reciprocal Eigenvalues Bodo Dittmar Martin Luther niversity Halle-Wittenberg (Germany) E-mail: bodo.dittmar@mathematik.uni-halle.de Queen Dido Conference Carthage, Tunisia 200 Contens.Introduction
Sums of Reciprocal Eigenvalues Bodo Dittmar Martin Luther niversity Halle-Wittenberg (Germany) E-mail: bodo.dittmar@mathematik.uni-halle.de Queen Dido Conference Carthage, Tunisia 200 Contens.Introduction
u xx + u yy = 0. (5.1)
 Chapter 5 Laplace Equation The following equation is called Laplace equation in two independent variables x, y: The non-homogeneous problem u xx + u yy =. (5.1) u xx + u yy = F, (5.) where F is a function
Chapter 5 Laplace Equation The following equation is called Laplace equation in two independent variables x, y: The non-homogeneous problem u xx + u yy =. (5.1) u xx + u yy = F, (5.) where F is a function
Bounded point derivations on R p (X) and approximate derivatives
 Bounded point derivations on R p (X) and approximate derivatives arxiv:1709.02851v3 [math.cv] 21 Dec 2017 Stephen Deterding Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky Abstract It is shown that if
Bounded point derivations on R p (X) and approximate derivatives arxiv:1709.02851v3 [math.cv] 21 Dec 2017 Stephen Deterding Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky Abstract It is shown that if
ON THE REGULARITY OF SAMPLE PATHS OF SUB-ELLIPTIC DIFFUSIONS ON MANIFOLDS
 Bendikov, A. and Saloff-Coste, L. Osaka J. Math. 4 (5), 677 7 ON THE REGULARITY OF SAMPLE PATHS OF SUB-ELLIPTIC DIFFUSIONS ON MANIFOLDS ALEXANDER BENDIKOV and LAURENT SALOFF-COSTE (Received March 4, 4)
Bendikov, A. and Saloff-Coste, L. Osaka J. Math. 4 (5), 677 7 ON THE REGULARITY OF SAMPLE PATHS OF SUB-ELLIPTIC DIFFUSIONS ON MANIFOLDS ALEXANDER BENDIKOV and LAURENT SALOFF-COSTE (Received March 4, 4)
ANALYSIS QUALIFYING EXAM FALL 2017: SOLUTIONS. 1 cos(nx) lim. n 2 x 2. g n (x) = 1 cos(nx) n 2 x 2. x 2.
 ANALYSIS QUALIFYING EXAM FALL 27: SOLUTIONS Problem. Determine, with justification, the it cos(nx) n 2 x 2 dx. Solution. For an integer n >, define g n : (, ) R by Also define g : (, ) R by g(x) = g n
ANALYSIS QUALIFYING EXAM FALL 27: SOLUTIONS Problem. Determine, with justification, the it cos(nx) n 2 x 2 dx. Solution. For an integer n >, define g n : (, ) R by Also define g : (, ) R by g(x) = g n
Minimization of λ 2 (Ω) with a perimeter constraint
 Minimization of λ 2 (Ω) with a perimeter constraint Dorin Bucur Laboratoire de Mathématiques (LAMA) UMR 5127, Université de Savoie Campus Scientifique 73 376 Le-Bourget-Du-Lac, France email: dorin.bucur@univ-savoie.fr
Minimization of λ 2 (Ω) with a perimeter constraint Dorin Bucur Laboratoire de Mathématiques (LAMA) UMR 5127, Université de Savoie Campus Scientifique 73 376 Le-Bourget-Du-Lac, France email: dorin.bucur@univ-savoie.fr
18 Green s function for the Poisson equation
 8 Green s function for the Poisson equation Now we have some experience working with Green s functions in dimension, therefore, we are ready to see how Green s functions can be obtained in dimensions 2
8 Green s function for the Poisson equation Now we have some experience working with Green s functions in dimension, therefore, we are ready to see how Green s functions can be obtained in dimensions 2
David E. Barrett and Jeffrey Diller University of Michigan Indiana University
 A NEW CONSTRUCTION OF RIEMANN SURFACES WITH CORONA David E. Barrett and Jeffrey Diller University of Michigan Indiana University 1. Introduction An open Riemann surface X is said to satisfy the corona
A NEW CONSTRUCTION OF RIEMANN SURFACES WITH CORONA David E. Barrett and Jeffrey Diller University of Michigan Indiana University 1. Introduction An open Riemann surface X is said to satisfy the corona
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIABILITY IN R n.
 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIABILITY IN R n. MATANIA BEN-ARTZI April 2015 Functions here are defined on a subset T R n and take values in R m, where m can be smaller, equal or greater than n. The (open) ball
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIABILITY IN R n. MATANIA BEN-ARTZI April 2015 Functions here are defined on a subset T R n and take values in R m, where m can be smaller, equal or greater than n. The (open) ball
Complex Analysis Problems
 Complex Analysis Problems transcribed from the originals by William J. DeMeo October 2, 2008 Contents 99 November 2 2 2 200 November 26 4 3 2006 November 3 6 4 2007 April 6 7 5 2007 November 6 8 99 NOVEMBER
Complex Analysis Problems transcribed from the originals by William J. DeMeo October 2, 2008 Contents 99 November 2 2 2 200 November 26 4 3 2006 November 3 6 4 2007 April 6 7 5 2007 November 6 8 99 NOVEMBER
Note: Each problem is worth 14 points except numbers 5 and 6 which are 15 points. = 3 2
 Math Prelim II Solutions Spring Note: Each problem is worth points except numbers 5 and 6 which are 5 points. x. Compute x da where is the region in the second quadrant between the + y circles x + y and
Math Prelim II Solutions Spring Note: Each problem is worth points except numbers 5 and 6 which are 5 points. x. Compute x da where is the region in the second quadrant between the + y circles x + y and
EINDHOVEN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mathematics and Computer Science. CASA-Report November 2011
 EINDHOVEN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mathematics and Computer Science CASA-Report 11-54 November 2011 Existence of solutions to the diffusive VSC model by J. Hulshof, R. Nolet, G. Prokert Centre
EINDHOVEN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mathematics and Computer Science CASA-Report 11-54 November 2011 Existence of solutions to the diffusive VSC model by J. Hulshof, R. Nolet, G. Prokert Centre
Boundary value problems
 1 Introduction Boundary value problems Lecture 5 We have found that the electric potential is a solution of the partial differential equation; 2 V = ρ/ǫ 0 The above is Poisson s equation where ρ is the
1 Introduction Boundary value problems Lecture 5 We have found that the electric potential is a solution of the partial differential equation; 2 V = ρ/ǫ 0 The above is Poisson s equation where ρ is the
Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett/
 (February 9, 25) Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ (The present proof of this old result roughly follows the proof
(February 9, 25) Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ (The present proof of this old result roughly follows the proof
SECTION 3.6 THE CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN'S FUNCTION FOR THE TWO DIMENSIONAL OPERATOR WITH DIRICHLET BOUNDARY CONDITIONS
 SECTION 3.6 THE CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN'S FUNCTION FOR THE TWO DIMENSIONAL OPERATOR WITH DIRICHLET BOUNDARY CONDITIONS We now will construct a Green's function for the following problem: Find u such
SECTION 3.6 THE CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN'S FUNCTION FOR THE TWO DIMENSIONAL OPERATOR WITH DIRICHLET BOUNDARY CONDITIONS We now will construct a Green's function for the following problem: Find u such
Counting geodesic arcs in a fixed conjugacy class on negatively curved surfaces with boundary
 Counting geodesic arcs in a fixed conjugacy class on negatively curved surfaces with boundary Mark Pollicott Abstract We show how to derive an asymptotic estimates for the number of closed arcs γ on a
Counting geodesic arcs in a fixed conjugacy class on negatively curved surfaces with boundary Mark Pollicott Abstract We show how to derive an asymptotic estimates for the number of closed arcs γ on a
ON THE FOLIATION OF SPACE-TIME BY CONSTANT MEAN CURVATURE HYPERSURFACES
 ON THE FOLIATION OF SPACE-TIME BY CONSTANT MEAN CURVATURE HYPERSURFACES CLAUS GERHARDT Abstract. We prove that the mean curvature τ of the slices given by a constant mean curvature foliation can be used
ON THE FOLIATION OF SPACE-TIME BY CONSTANT MEAN CURVATURE HYPERSURFACES CLAUS GERHARDT Abstract. We prove that the mean curvature τ of the slices given by a constant mean curvature foliation can be used
An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010
 An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010 John P. D Angelo, Univ. of Illinois, Urbana IL 61801.
An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010 John P. D Angelo, Univ. of Illinois, Urbana IL 61801.
6.2 Important Theorems
 6.2. IMPORTANT THEOREMS 223 6.2 Important Theorems 6.2.1 Local Extrema and Fermat s Theorem Definition 6.2.1 (local extrema) Let f : I R with c I. 1. f has a local maximum at c if there is a neighborhood
6.2. IMPORTANT THEOREMS 223 6.2 Important Theorems 6.2.1 Local Extrema and Fermat s Theorem Definition 6.2.1 (local extrema) Let f : I R with c I. 1. f has a local maximum at c if there is a neighborhood
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5
 MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
Exercise 1 (Formula for connection 1-forms) Using the first structure equation, show that
 1 Stokes s Theorem Let D R 2 be a connected compact smooth domain, so that D is a smooth embedded circle. Given a smooth function f : D R, define fdx dy fdxdy, D where the left-hand side is the integral
1 Stokes s Theorem Let D R 2 be a connected compact smooth domain, so that D is a smooth embedded circle. Given a smooth function f : D R, define fdx dy fdxdy, D where the left-hand side is the integral
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm
 Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
carries the circle w 1 onto the circle z R and sends w = 0 to z = a. The function u(s(w)) is harmonic in the unit circle w 1 and we obtain
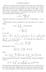 4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
Asymptotic Behaviour of λ-convex Sets in the Hyperbolic Plane
 Geometriae Dedicata 76: 75 89, 1999. 1999 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 75 Asymptotic Behaviour of λ-convex Sets in the Hyperbolic Plane EDUARDO GALLEGO and AGUSTÍ REVENTÓS Departament
Geometriae Dedicata 76: 75 89, 1999. 1999 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 75 Asymptotic Behaviour of λ-convex Sets in the Hyperbolic Plane EDUARDO GALLEGO and AGUSTÍ REVENTÓS Departament
Composition operators: the essential norm and norm-attaining
 Composition operators: the essential norm and norm-attaining Mikael Lindström Department of Mathematical Sciences University of Oulu Valencia, April, 2011 The purpose of this talk is to first discuss the
Composition operators: the essential norm and norm-attaining Mikael Lindström Department of Mathematical Sciences University of Oulu Valencia, April, 2011 The purpose of this talk is to first discuss the
A FABER-KRAHN INEQUALITY FOR THE CHEEGER CONSTANT OF N-GONS
 A FABER-KRAHN INEQUALITY FOR THE CHEEGER CONSTANT OF N-GONS DORIN BUCUR, ILARIA FRAGALÀ Abstract. We prove that the regular N-gon minimizes the Cheeger constant among polygons with a given area and N sides.
A FABER-KRAHN INEQUALITY FOR THE CHEEGER CONSTANT OF N-GONS DORIN BUCUR, ILARIA FRAGALÀ Abstract. We prove that the regular N-gon minimizes the Cheeger constant among polygons with a given area and N sides.
Your first day at work MATH 806 (Fall 2015)
 Your first day at work MATH 806 (Fall 2015) 1. Let X be a set (with no particular algebraic structure). A function d : X X R is called a metric on X (and then X is called a metric space) when d satisfies
Your first day at work MATH 806 (Fall 2015) 1. Let X be a set (with no particular algebraic structure). A function d : X X R is called a metric on X (and then X is called a metric space) when d satisfies
A proof for the full Fourier series on [ π, π] is given here.
![A proof for the full Fourier series on [ π, π] is given here. A proof for the full Fourier series on [ π, π] is given here.](/thumbs/75/72296360.jpg) niform convergence of Fourier series A smooth function on an interval [a, b] may be represented by a full, sine, or cosine Fourier series, and pointwise convergence can be achieved, except possibly at
niform convergence of Fourier series A smooth function on an interval [a, b] may be represented by a full, sine, or cosine Fourier series, and pointwise convergence can be achieved, except possibly at
MATH 220: INNER PRODUCT SPACES, SYMMETRIC OPERATORS, ORTHOGONALITY
 MATH 22: INNER PRODUCT SPACES, SYMMETRIC OPERATORS, ORTHOGONALITY When discussing separation of variables, we noted that at the last step we need to express the inhomogeneous initial or boundary data as
MATH 22: INNER PRODUCT SPACES, SYMMETRIC OPERATORS, ORTHOGONALITY When discussing separation of variables, we noted that at the last step we need to express the inhomogeneous initial or boundary data as
THE UNIFORMISATION THEOREM OF RIEMANN SURFACES
 THE UNIFORISATION THEORE OF RIEANN SURFACES 1. What is the aim of this seminar? Recall that a compact oriented surface is a g -holed object. (Classification of surfaces.) It can be obtained through a 4g
THE UNIFORISATION THEORE OF RIEANN SURFACES 1. What is the aim of this seminar? Recall that a compact oriented surface is a g -holed object. (Classification of surfaces.) It can be obtained through a 4g
Richard F. Bass Krzysztof Burdzy University of Washington
 ON DOMAIN MONOTONICITY OF THE NEUMANN HEAT KERNEL Richard F. Bass Krzysztof Burdzy University of Washington Abstract. Some examples are given of convex domains for which domain monotonicity of the Neumann
ON DOMAIN MONOTONICITY OF THE NEUMANN HEAT KERNEL Richard F. Bass Krzysztof Burdzy University of Washington Abstract. Some examples are given of convex domains for which domain monotonicity of the Neumann
Math 520a - Final take home exam - solutions
 Math 52a - Final take home exam - solutions 1. Let f(z) be entire. Prove that f has finite order if and only if f has finite order and that when they have finite order their orders are the same. Solution:
Math 52a - Final take home exam - solutions 1. Let f(z) be entire. Prove that f has finite order if and only if f has finite order and that when they have finite order their orders are the same. Solution:
Accumulation constants of iterated function systems with Bloch target domains
 Accumulation constants of iterated function systems with Bloch target domains September 29, 2005 1 Introduction Linda Keen and Nikola Lakic 1 Suppose that we are given a random sequence of holomorphic
Accumulation constants of iterated function systems with Bloch target domains September 29, 2005 1 Introduction Linda Keen and Nikola Lakic 1 Suppose that we are given a random sequence of holomorphic
ON THE ANALYTIC SYSTOLE OF RIEMANNIAN SURFACES OF FINITE TYPE
 ON THE ANALYTIC SYSTOLE O RIEMANNIAN SURACES O INITE TYPE WERNER BALLMANN, HENRIK MATTHIESEN, AND SUGATA MONDAL Abstract. In [2] we introduced, for a Riemannian surface S, the quantity Λ(S) := inf λ 0
ON THE ANALYTIC SYSTOLE O RIEMANNIAN SURACES O INITE TYPE WERNER BALLMANN, HENRIK MATTHIESEN, AND SUGATA MONDAL Abstract. In [2] we introduced, for a Riemannian surface S, the quantity Λ(S) := inf λ 0
THE HYPERBOLIC METRIC OF A RECTANGLE
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 26, 2001, 401 407 THE HYPERBOLIC METRIC OF A RECTANGLE A. F. Beardon University of Cambridge, DPMMS, Centre for Mathematical Sciences Wilberforce
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 26, 2001, 401 407 THE HYPERBOLIC METRIC OF A RECTANGLE A. F. Beardon University of Cambridge, DPMMS, Centre for Mathematical Sciences Wilberforce
Econ Lecture 3. Outline. 1. Metric Spaces and Normed Spaces 2. Convergence of Sequences in Metric Spaces 3. Sequences in R and R n
 Econ 204 2011 Lecture 3 Outline 1. Metric Spaces and Normed Spaces 2. Convergence of Sequences in Metric Spaces 3. Sequences in R and R n 1 Metric Spaces and Metrics Generalize distance and length notions
Econ 204 2011 Lecture 3 Outline 1. Metric Spaces and Normed Spaces 2. Convergence of Sequences in Metric Spaces 3. Sequences in R and R n 1 Metric Spaces and Metrics Generalize distance and length notions
Physics 2400 Midterm I Sample March 2017
 Physics 4 Midterm I Sample March 17 Question: 1 3 4 5 Total Points: 1 1 1 1 6 Gamma function. Leibniz s rule. 1. (1 points) Find positive x that minimizes the value of the following integral I(x) = x+1
Physics 4 Midterm I Sample March 17 Question: 1 3 4 5 Total Points: 1 1 1 1 6 Gamma function. Leibniz s rule. 1. (1 points) Find positive x that minimizes the value of the following integral I(x) = x+1
Blow-up Analysis of a Fractional Liouville Equation in dimension 1. Francesca Da Lio
 Blow-up Analysis of a Fractional Liouville Equation in dimension 1 Francesca Da Lio Outline Liouville Equation: Local Case Geometric Motivation Brezis & Merle Result Nonlocal Framework The Half-Laplacian
Blow-up Analysis of a Fractional Liouville Equation in dimension 1 Francesca Da Lio Outline Liouville Equation: Local Case Geometric Motivation Brezis & Merle Result Nonlocal Framework The Half-Laplacian
