Problem Set Number 5, j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014)
|
|
|
- Bertram Campbell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Problem Set Number 5, j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept.,Cambridge, MA 02139) Due Fri., October 24, October 17, Large µ limit for Liénard system #03 Statement: Large µ limit for Liénard system #03 A Liénard equation has the form ẍ + µ f (x) ẋ + g(x) = 0, (1.1) for some functions f and g. Here µ > 0 is a parameter. This can be re-written in the form d (ẋ + µ f(x)) + g(x) = 0. (1.2) Introduce y = 1 µ x 1 ẋ = µ (y f(x)) and ẏ = g(x). µ (1.3) 1 1 In this problem we will consider the case f(x) = x + x 3 x 5 and g(x) = x, (1.4) 3 60 with µ 1. Analyze the large µ limit for this system. In particular: 1. Are there any limit cycles? Are they stable, unstable, semi-stable? 2. Are there any critical points? Are they attractors, repellers? 3. Does the system have any global attractor? 4. Sketch the phase plane portrait. 1
2 2 2 Saddles and Conservative Systems Statement: Saddles and Conservative Systems Saddles for conservative systems are special, with the rate of expansion and contraction along the two principal directions equal. The purpose of this problem is to show this. Consider a phase plane autonomous system dy = f(x, y) and = g(x, y), (2.1) where both f and g have continuous partial derivatives. We will now assume: A. The origin x = y = 0 is an isolated critical point; in fact: a saddle, with eigenvalues for the linearized problem λ 1 > 0 > λ 2. B. The system is conservative near the origin. That is: there is a function E = E(x, y) (defined in a neighborhood of the origin) which is a constant on the orbits. Furthermore, assume that E is twice continuously differentiable, and that E = 0 (except at the origin). C. The origin is a true saddle for E that is det(d 2 E) < 0 at the origin. Show that: λ 1 = λ 2 which is equivalent to f x (0, 0) + g y (0, 0) = 0 (why?). Remark What does C mean? Since E is twice differentiable we can write 1 E = E 0 + a x b x y + c y 2 ( + o (x 2 + y 2 ) 1.5 ), (2.2) 2 2 where E 0, a, b, and c are constants. Then det(d 2 E) < 0 a c b 2 < 0 which means that the quadratic form Q = Q(x, y) = 1 a x 2 + b x y + 1 c y above in (2.2) is non-degenerate and non-definite. Thus: 1. The level lines for Q govern the local behavior of the level lines for E, and 2. Q has a saddle at the origin, so its level lines yield a saddle. Hence the surface z = E(x, y) has a saddle at the origin, dominated by the quadratic terms in its Taylor expansion. Example where this is not true: Consider the system ẋ = x and ẏ = 2 y, which has a saddle at the origin, and the conserved quantity E = y x 2. But the surface z = E(x, y) does not have a saddle at the origin. 1 Another example is provided by the system ẋ = x and ẏ = 3 y, also with a saddle at the origin and a conserved quantity: E = y x 3. In this case the surface z = E(x, y) has a saddle at the origin, but it is a very degenerate saddle. 2 Remark Note concerning E. From equation (2.2) is follows that ( ) ( ) ( ) a x + b y E = + o (x 2 a b x + y 2 ) = + o (x 2 + y 2 ). (2.3) b x + c y b c y Thus, because the matrix of coefficients is non-degenerate, E = 0 near (but not at) the origin. 1 By saddle we mean that the level lines E = 0 split the plane into four regions, and in each region E grows (decays) as we move away from the origin, with decay and growth alternating. 2 You would not like sitting on a horse saddle made following this design!
3 3 Hint Because E is conserved: Z = Z(x, y) = f E x + g E y 0. Explain why this. (2.4) On the other hand, because f and g are differentiable (and the origin is a critical point), we can write (for some constants α, β, γ, and δ): f = α x + β y + o (x 2 + y 2 ) and g = γ x + δ y + o (x 2 + y 2 ). (2.5) Substitute these expansions and (2.3), into (2.4) and conclude that 0 = α + δ = f x (0, 0) + g y (0, 0). This then implies λ 1 = λ 2 (why?), which is precisely what you are being asked to show. Remark General saddles. Modulo a nonsingular linear transformation of the dependent variables x and y, and a change in the time scale (possibly including a time reversal), the equations for a linear system with a saddle can always be written in the form ẋ = x and ẏ = ν y, where ν 1. (2.6) Conserved quantities for this last system must have the form E = f( x ν y), where f = f(ζ) is some arbitrary function. But then E x = sign(x) x (ν 1) y f ( x ν ν ν y) and Ey = x f ( x y), (2.7) so that E vanishes identically for x = 0, unless ν = 1, which corresponds to λ 1 = λ 2. 3 Uniqueness of the van der Pol oscillator limit cycle Statement: Uniqueness of the van der Pol oscillator limit cycle Consider the van der Pol equation d 2 x + µ (x 2 2 1) + x = 0, (3.1) where µ = 0 is a constant. Show that (3.1) has a unique limit cycle. The existence of, at least one, non-trivial 3 periodic orbit was shown in class. Hence, you need only show that there cannot be more than one such orbit. It follows (Poincaré-Bendixon theorem) that the limit cycle is a global attractor (repeller) for µ > 0 (µ < 0, resp.). Only one orbit (the critical point) does not approach the limit cycle as either t ±. Hints. h1. Index theory tells us that periodic orbits must enclose the (single) critical point x = ẋ = 0 in the phase plane (x, y) where y = ẋ. Hence, if the number of periodic orbits exceeds one, they will be nested. Any two successive ones will then delimit an annular region Ω, with the origin in the center hole. h2. The change t t reverses the sign of µ in (3.1). Hence, without loss of generality, assume µ < 0, and write dy the equation as = y and = x ɛ (1 x 2 ) y, where ɛ = µ > 0. (3.2) Then the origin is an attractor (node or spiral, depending on the size of ɛ), and the limit cycle is unstable. 3 Note that critical points are (trivial) periodic orbits.
4 4 h3. Study the behavior of the function E = 1 ( 2 x 2 + y 2) along the solutions to (3.2), and show that: } If (x, y) = (X(t), Y (t)) is a non-trivial periodic solution, then X 2 + Y 2 > 1 for all t. Thus the center hole for the item h.1 annular region Ω includes the unit disk x 2 (3.3) + y 2 1. To prove (3.3) you need to examine the sign of Ė in the unit disk. Be careful to provide a complete proof for (3.3), since along the segment y = 0 and 1 x 1 (where E = 0) a special argument is needed. h3. Find a function g = g(r), defined and smooth for r = x 2 + y 2 > 1, such that [ ] I = div (ẋ g, ẏ g) ẋ and ẏ as given by (3.2) (3.4) is non-negative for r > 1, and vanishes for x = ± 1 only. Note that g could have singularities when r 1 we do not care about what happens there. Sub-hint. The expression for I in (3.4) involves g and its derivative g. The trick is to pick g in terms of g and r so that the desired property applies. This will give you an ode for g, which you can solve. h4. Generalize Dulac s criterion to prove that there can be only one periodic orbit: (1) Assume that there is more than one periodic orbit, and consider the region Ω between any two consecutive ones, as defined in item h.1. (2) Integrate I, defined in (3.4), over Ω. Use Gauss theorem to reduce the integral to an integral over the boundary of Ω, which is made up by the two periodic orbits. This should yield a contradiction. It follows that the assumption in (1) must be false: there cannot be more than one periodic orbit. THE END.
5 MIT OpenCourseWare J / 2.036J Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos Fall 2014 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:
ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y), (x, y) D, can only have periodic solutions if (f,g) changes sign in D or if (f,g)=0in D.
 4 Periodic Solutions We have shown that in the case of an autonomous equation the periodic solutions correspond with closed orbits in phase-space. Autonomous two-dimensional systems with phase-space R
4 Periodic Solutions We have shown that in the case of an autonomous equation the periodic solutions correspond with closed orbits in phase-space. Autonomous two-dimensional systems with phase-space R
Practice Problems for Final Exam
 Math 1280 Spring 2016 Practice Problems for Final Exam Part 2 (Sections 6.6, 6.7, 6.8, and chapter 7) S o l u t i o n s 1. Show that the given system has a nonlinear center at the origin. ẋ = 9y 5y 5,
Math 1280 Spring 2016 Practice Problems for Final Exam Part 2 (Sections 6.6, 6.7, 6.8, and chapter 7) S o l u t i o n s 1. Show that the given system has a nonlinear center at the origin. ẋ = 9y 5y 5,
1. < 0: the eigenvalues are real and have opposite signs; the fixed point is a saddle point
 Solving a Linear System τ = trace(a) = a + d = λ 1 + λ 2 λ 1,2 = τ± = det(a) = ad bc = λ 1 λ 2 Classification of Fixed Points τ 2 4 1. < 0: the eigenvalues are real and have opposite signs; the fixed point
Solving a Linear System τ = trace(a) = a + d = λ 1 + λ 2 λ 1,2 = τ± = det(a) = ad bc = λ 1 λ 2 Classification of Fixed Points τ 2 4 1. < 0: the eigenvalues are real and have opposite signs; the fixed point
Stability of Dynamical systems
 Stability of Dynamical systems Stability Isolated equilibria Classification of Isolated Equilibria Attractor and Repeller Almost linear systems Jacobian Matrix Stability Consider an autonomous system u
Stability of Dynamical systems Stability Isolated equilibria Classification of Isolated Equilibria Attractor and Repeller Almost linear systems Jacobian Matrix Stability Consider an autonomous system u
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET. EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS. COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD
 CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: August 22, 2018, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Jan Meibohm,
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: August 22, 2018, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Jan Meibohm,
Problem Set Number 1, j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014)
 Problem Set Number 1, 18.385j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., Cambridge, MA 02139) September 9, 2014 Due Fri., September 19, 2014. 1 Get equation from phase line portrait problem
Problem Set Number 1, 18.385j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., Cambridge, MA 02139) September 9, 2014 Due Fri., September 19, 2014. 1 Get equation from phase line portrait problem
8.385 MIT (Rosales) Hopf Bifurcations. 2 Contents Hopf bifurcation for second order scalar equations. 3. Reduction of general phase plane case to seco
 8.385 MIT Hopf Bifurcations. Rodolfo R. Rosales Department of Mathematics Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Massachusetts MA 239 September 25, 999 Abstract In two dimensions a Hopf bifurcation
8.385 MIT Hopf Bifurcations. Rodolfo R. Rosales Department of Mathematics Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Massachusetts MA 239 September 25, 999 Abstract In two dimensions a Hopf bifurcation
A plane autonomous system is a pair of simultaneous first-order differential equations,
 Chapter 11 Phase-Plane Techniques 11.1 Plane Autonomous Systems A plane autonomous system is a pair of simultaneous first-order differential equations, ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y). This system has an equilibrium
Chapter 11 Phase-Plane Techniques 11.1 Plane Autonomous Systems A plane autonomous system is a pair of simultaneous first-order differential equations, ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y). This system has an equilibrium
Section 5. Graphing Systems
 Section 5. Graphing Systems 5A. The Phase Plane 5A-1. Find the critical points of each of the following non-linear autonomous systems. x = x 2 y 2 x = 1 x + y a) b) y = x xy y = y + 2x 2 5A-2. Write each
Section 5. Graphing Systems 5A. The Phase Plane 5A-1. Find the critical points of each of the following non-linear autonomous systems. x = x 2 y 2 x = 1 x + y a) b) y = x xy y = y + 2x 2 5A-2. Write each
Lectures on Periodic Orbits
 Lectures on Periodic Orbits 11 February 2009 Most of the contents of these notes can found in any typical text on dynamical systems, most notably Strogatz [1994], Perko [2001] and Verhulst [1996]. Complete
Lectures on Periodic Orbits 11 February 2009 Most of the contents of these notes can found in any typical text on dynamical systems, most notably Strogatz [1994], Perko [2001] and Verhulst [1996]. Complete
LECTURE 8: DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS 7
 15-382 COLLECTIVE INTELLIGENCE S18 LECTURE 8: DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS 7 INSTRUCTOR: GIANNI A. DI CARO GEOMETRIES IN THE PHASE SPACE Damped pendulum One cp in the region between two separatrix Separatrix Basin
15-382 COLLECTIVE INTELLIGENCE S18 LECTURE 8: DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS 7 INSTRUCTOR: GIANNI A. DI CARO GEOMETRIES IN THE PHASE SPACE Damped pendulum One cp in the region between two separatrix Separatrix Basin
Problem List MATH 5173 Spring, 2014
 Problem List MATH 5173 Spring, 2014 The notation p/n means the problem with number n on page p of Perko. 1. 5/3 [Due Wednesday, January 15] 2. 6/5 and describe the relationship of the phase portraits [Due
Problem List MATH 5173 Spring, 2014 The notation p/n means the problem with number n on page p of Perko. 1. 5/3 [Due Wednesday, January 15] 2. 6/5 and describe the relationship of the phase portraits [Due
Various lecture notes for
 Various lecture notes for 18385. R. R. Rosales. Department of Mathematics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts, MA 02139. September 17, 2012 Abstract Notes, both complete and/or
Various lecture notes for 18385. R. R. Rosales. Department of Mathematics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts, MA 02139. September 17, 2012 Abstract Notes, both complete and/or
MCE693/793: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems
 MCE693/793: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems Systems of Differential Equations Phase Plane Analysis Hanz Richter Mechanical Engineering Department Cleveland State University Systems of Nonlinear
MCE693/793: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems Systems of Differential Equations Phase Plane Analysis Hanz Richter Mechanical Engineering Department Cleveland State University Systems of Nonlinear
Problem set 7 Math 207A, Fall 2011 Solutions
 Problem set 7 Math 207A, Fall 2011 s 1. Classify the equilibrium (x, y) = (0, 0) of the system x t = x, y t = y + x 2. Is the equilibrium hyperbolic? Find an equation for the trajectories in (x, y)- phase
Problem set 7 Math 207A, Fall 2011 s 1. Classify the equilibrium (x, y) = (0, 0) of the system x t = x, y t = y + x 2. Is the equilibrium hyperbolic? Find an equation for the trajectories in (x, y)- phase
STABILITY. Phase portraits and local stability
 MAS271 Methods for differential equations Dr. R. Jain STABILITY Phase portraits and local stability We are interested in system of ordinary differential equations of the form ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y),
MAS271 Methods for differential equations Dr. R. Jain STABILITY Phase portraits and local stability We are interested in system of ordinary differential equations of the form ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y),
TWO DIMENSIONAL FLOWS. Lecture 5: Limit Cycles and Bifurcations
 TWO DIMENSIONAL FLOWS Lecture 5: Limit Cycles and Bifurcations 5. Limit cycles A limit cycle is an isolated closed trajectory [ isolated means that neighbouring trajectories are not closed] Fig. 5.1.1
TWO DIMENSIONAL FLOWS Lecture 5: Limit Cycles and Bifurcations 5. Limit cycles A limit cycle is an isolated closed trajectory [ isolated means that neighbouring trajectories are not closed] Fig. 5.1.1
EE222 - Spring 16 - Lecture 2 Notes 1
 EE222 - Spring 16 - Lecture 2 Notes 1 Murat Arcak January 21 2016 1 Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Essentially Nonlinear Phenomena Continued
EE222 - Spring 16 - Lecture 2 Notes 1 Murat Arcak January 21 2016 1 Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Essentially Nonlinear Phenomena Continued
ENGI Duffing s Equation Page 4.65
 ENGI 940 4. - Duffing s Equation Page 4.65 4. Duffing s Equation Among the simplest models of damped non-linear forced oscillations of a mechanical or electrical system with a cubic stiffness term is Duffing
ENGI 940 4. - Duffing s Equation Page 4.65 4. Duffing s Equation Among the simplest models of damped non-linear forced oscillations of a mechanical or electrical system with a cubic stiffness term is Duffing
BIFURCATION PHENOMENA Lecture 1: Qualitative theory of planar ODEs
 BIFURCATION PHENOMENA Lecture 1: Qualitative theory of planar ODEs Yuri A. Kuznetsov August, 2010 Contents 1. Solutions and orbits. 2. Equilibria. 3. Periodic orbits and limit cycles. 4. Homoclinic orbits.
BIFURCATION PHENOMENA Lecture 1: Qualitative theory of planar ODEs Yuri A. Kuznetsov August, 2010 Contents 1. Solutions and orbits. 2. Equilibria. 3. Periodic orbits and limit cycles. 4. Homoclinic orbits.
Hilbert s 16. problem
 Hilbert s 16. problem Aarhus University Aarhus 24 th March, 2017 Hilbert s Problem Does there exist (minimal) natural numbers H n, for n = 2, 3,..., such that any planar autonomous system of ODE s dx dt
Hilbert s 16. problem Aarhus University Aarhus 24 th March, 2017 Hilbert s Problem Does there exist (minimal) natural numbers H n, for n = 2, 3,..., such that any planar autonomous system of ODE s dx dt
Lecture 38. Almost Linear Systems
 Math 245 - Mathematics of Physics and Engineering I Lecture 38. Almost Linear Systems April 20, 2012 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 245, Lecture 38 April 20, 2012 1 / 11 Agenda Stability Properties of Linear
Math 245 - Mathematics of Physics and Engineering I Lecture 38. Almost Linear Systems April 20, 2012 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 245, Lecture 38 April 20, 2012 1 / 11 Agenda Stability Properties of Linear
Problem Set Number 2, j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014)
 Problem Set Number 2, 18.385j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept.,Cambridge, MA 02139) Due Mon., September 29, 2014. 1 Inverse function problem #01. Statement: Inverse function
Problem Set Number 2, 18.385j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept.,Cambridge, MA 02139) Due Mon., September 29, 2014. 1 Inverse function problem #01. Statement: Inverse function
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems
 B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 5. Global Bifurcations, Homoclinic chaos, Melnikov s method Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Motivation 1.1 The problem 1.2 A
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 5. Global Bifurcations, Homoclinic chaos, Melnikov s method Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Motivation 1.1 The problem 1.2 A
Solutions for B8b (Nonlinear Systems) Fake Past Exam (TT 10)
 Solutions for B8b (Nonlinear Systems) Fake Past Exam (TT 10) Mason A. Porter 15/05/2010 1 Question 1 i. (6 points) Define a saddle-node bifurcation and show that the first order system dx dt = r x e x
Solutions for B8b (Nonlinear Systems) Fake Past Exam (TT 10) Mason A. Porter 15/05/2010 1 Question 1 i. (6 points) Define a saddle-node bifurcation and show that the first order system dx dt = r x e x
Problem Set Number 02, j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2018)
 Problem Set Number 0, 18.385j/.036j MIT (Fall 018) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., room -337, Cambridge, MA 0139) September 6, 018 Due October 4, 018. Turn it in (by 3PM) at the Math. Problem Set
Problem Set Number 0, 18.385j/.036j MIT (Fall 018) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., room -337, Cambridge, MA 0139) September 6, 018 Due October 4, 018. Turn it in (by 3PM) at the Math. Problem Set
MIT (Spring 2014)
 18.311 MIT (Spring 014) Rodolfo R. Rosales February 13, 014. Problem Set # 01. Due: Mon. February 4. IMPORTANT: Turn in the regular and the special problems stapled in two SEPARATE packages. Print your
18.311 MIT (Spring 014) Rodolfo R. Rosales February 13, 014. Problem Set # 01. Due: Mon. February 4. IMPORTANT: Turn in the regular and the special problems stapled in two SEPARATE packages. Print your
1.7. Stability and attractors. Consider the autonomous differential equation. (7.1) ẋ = f(x),
 1.7. Stability and attractors. Consider the autonomous differential equation (7.1) ẋ = f(x), where f C r (lr d, lr d ), r 1. For notation, for any x lr d, c lr, we let B(x, c) = { ξ lr d : ξ x < c }. Suppose
1.7. Stability and attractors. Consider the autonomous differential equation (7.1) ẋ = f(x), where f C r (lr d, lr d ), r 1. For notation, for any x lr d, c lr, we let B(x, c) = { ξ lr d : ξ x < c }. Suppose
Problem Set Number 01, MIT (Winter-Spring 2018)
 Problem Set Number 01, 18.377 MIT (Winter-Spring 2018) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., room 2-337, Cambridge, MA 02139) February 28, 2018 Due Thursday, March 8, 2018. Turn it in (by 3PM) at the Math.
Problem Set Number 01, 18.377 MIT (Winter-Spring 2018) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., room 2-337, Cambridge, MA 02139) February 28, 2018 Due Thursday, March 8, 2018. Turn it in (by 3PM) at the Math.
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET. EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS. COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD
 CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: January 08, 2018, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Kristian
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: January 08, 2018, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Kristian
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET. EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS. COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD
 CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: January 14, 2019, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Kristian
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: January 14, 2019, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Kristian
2 Discrete growth models, logistic map (Murray, Chapter 2)
 2 Discrete growth models, logistic map (Murray, Chapter 2) As argued in Lecture 1 the population of non-overlapping generations can be modelled as a discrete dynamical system. This is an example of an
2 Discrete growth models, logistic map (Murray, Chapter 2) As argued in Lecture 1 the population of non-overlapping generations can be modelled as a discrete dynamical system. This is an example of an
8.1 Bifurcations of Equilibria
 1 81 Bifurcations of Equilibria Bifurcation theory studies qualitative changes in solutions as a parameter varies In general one could study the bifurcation theory of ODEs PDEs integro-differential equations
1 81 Bifurcations of Equilibria Bifurcation theory studies qualitative changes in solutions as a parameter varies In general one could study the bifurcation theory of ODEs PDEs integro-differential equations
Now I switch to nonlinear systems. In this chapter the main object of study will be
 Chapter 4 Stability 4.1 Autonomous systems Now I switch to nonlinear systems. In this chapter the main object of study will be ẋ = f(x), x(t) X R k, f : X R k, (4.1) where f is supposed to be locally Lipschitz
Chapter 4 Stability 4.1 Autonomous systems Now I switch to nonlinear systems. In this chapter the main object of study will be ẋ = f(x), x(t) X R k, f : X R k, (4.1) where f is supposed to be locally Lipschitz
Example of a Blue Sky Catastrophe
 PUB:[SXG.TEMP]TRANS2913EL.PS 16-OCT-2001 11:08:53.21 SXG Page: 99 (1) Amer. Math. Soc. Transl. (2) Vol. 200, 2000 Example of a Blue Sky Catastrophe Nikolaĭ Gavrilov and Andrey Shilnikov To the memory of
PUB:[SXG.TEMP]TRANS2913EL.PS 16-OCT-2001 11:08:53.21 SXG Page: 99 (1) Amer. Math. Soc. Transl. (2) Vol. 200, 2000 Example of a Blue Sky Catastrophe Nikolaĭ Gavrilov and Andrey Shilnikov To the memory of
Problem set 6 Math 207A, Fall 2011 Solutions. 1. A two-dimensional gradient system has the form
 Problem set 6 Math 207A, Fall 2011 s 1 A two-dimensional gradient sstem has the form x t = W (x,, x t = W (x, where W (x, is a given function (a If W is a quadratic function W (x, = 1 2 ax2 + bx + 1 2
Problem set 6 Math 207A, Fall 2011 s 1 A two-dimensional gradient sstem has the form x t = W (x,, x t = W (x, where W (x, is a given function (a If W is a quadratic function W (x, = 1 2 ax2 + bx + 1 2
Topic # /31 Feedback Control Systems. Analysis of Nonlinear Systems Lyapunov Stability Analysis
 Topic # 16.30/31 Feedback Control Systems Analysis of Nonlinear Systems Lyapunov Stability Analysis Fall 010 16.30/31 Lyapunov Stability Analysis Very general method to prove (or disprove) stability of
Topic # 16.30/31 Feedback Control Systems Analysis of Nonlinear Systems Lyapunov Stability Analysis Fall 010 16.30/31 Lyapunov Stability Analysis Very general method to prove (or disprove) stability of
A BENDIXSON DULAC THEOREM FOR SOME PIECEWISE SYSTEMS
 A BENDIXSON DULAC THEOREM FOR SOME PIECEWISE SYSTEMS LEONARDO P. C. DA CRUZ AND JOAN TORREGROSA Abstract. The Bendixson Dulac Theorem provides a criterion to find upper bounds for the number of limit cycles
A BENDIXSON DULAC THEOREM FOR SOME PIECEWISE SYSTEMS LEONARDO P. C. DA CRUZ AND JOAN TORREGROSA Abstract. The Bendixson Dulac Theorem provides a criterion to find upper bounds for the number of limit cycles
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems
 B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 1. Linear systems Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Linear systems 1.1 Differential Equations 1.2 Linear flows 1.3 Linear maps
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 1. Linear systems Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Linear systems 1.1 Differential Equations 1.2 Linear flows 1.3 Linear maps
ENGI 9420 Lecture Notes 4 - Stability Analysis Page Stability Analysis for Non-linear Ordinary Differential Equations
 ENGI 940 Lecture Notes 4 - Stability Analysis Page 4.01 4. Stability Analysis for Non-linear Ordinary Differential Equations A pair of simultaneous first order homogeneous linear ordinary differential
ENGI 940 Lecture Notes 4 - Stability Analysis Page 4.01 4. Stability Analysis for Non-linear Ordinary Differential Equations A pair of simultaneous first order homogeneous linear ordinary differential
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems
 B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 4. Bifurcations Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Local bifurcations for vector fields 1.1 The problem 1.2 The extended centre
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 4. Bifurcations Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Local bifurcations for vector fields 1.1 The problem 1.2 The extended centre
Nonlinear dynamics & chaos BECS
 Nonlinear dynamics & chaos BECS-114.7151 Phase portraits Focus: nonlinear systems in two dimensions General form of a vector field on the phase plane: Vector notation: Phase portraits Solution x(t) describes
Nonlinear dynamics & chaos BECS-114.7151 Phase portraits Focus: nonlinear systems in two dimensions General form of a vector field on the phase plane: Vector notation: Phase portraits Solution x(t) describes
Nonlinear Control Lecture 2:Phase Plane Analysis
 Nonlinear Control Lecture 2:Phase Plane Analysis Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Fall 2010 r. Farzaneh Abdollahi Nonlinear Control Lecture 2 1/53
Nonlinear Control Lecture 2:Phase Plane Analysis Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Fall 2010 r. Farzaneh Abdollahi Nonlinear Control Lecture 2 1/53
Lyapunov Stability Theory
 Lyapunov Stability Theory Peter Al Hokayem and Eduardo Gallestey March 16, 2015 1 Introduction In this lecture we consider the stability of equilibrium points of autonomous nonlinear systems, both in continuous
Lyapunov Stability Theory Peter Al Hokayem and Eduardo Gallestey March 16, 2015 1 Introduction In this lecture we consider the stability of equilibrium points of autonomous nonlinear systems, both in continuous
Math 1270 Honors ODE I Fall, 2008 Class notes # 14. x 0 = F (x; y) y 0 = G (x; y) u 0 = au + bv = cu + dv
 Math 1270 Honors ODE I Fall, 2008 Class notes # 1 We have learned how to study nonlinear systems x 0 = F (x; y) y 0 = G (x; y) (1) by linearizing around equilibrium points. If (x 0 ; y 0 ) is an equilibrium
Math 1270 Honors ODE I Fall, 2008 Class notes # 1 We have learned how to study nonlinear systems x 0 = F (x; y) y 0 = G (x; y) (1) by linearizing around equilibrium points. If (x 0 ; y 0 ) is an equilibrium
Lecture 5. Outline: Limit Cycles. Definition and examples How to rule out limit cycles. Poincare-Bendixson theorem Hopf bifurcations Poincare maps
 Lecture 5 Outline: Limit Cycles Definition and examples How to rule out limit cycles Gradient systems Liapunov functions Dulacs criterion Poincare-Bendixson theorem Hopf bifurcations Poincare maps Limit
Lecture 5 Outline: Limit Cycles Definition and examples How to rule out limit cycles Gradient systems Liapunov functions Dulacs criterion Poincare-Bendixson theorem Hopf bifurcations Poincare maps Limit
Chapter 6 Nonlinear Systems and Phenomena. Friday, November 2, 12
 Chapter 6 Nonlinear Systems and Phenomena 6.1 Stability and the Phase Plane We now move to nonlinear systems Begin with the first-order system for x(t) d dt x = f(x,t), x(0) = x 0 In particular, consider
Chapter 6 Nonlinear Systems and Phenomena 6.1 Stability and the Phase Plane We now move to nonlinear systems Begin with the first-order system for x(t) d dt x = f(x,t), x(0) = x 0 In particular, consider
Math 216 First Midterm 19 October, 2017
 Math 6 First Midterm 9 October, 7 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material that
Math 6 First Midterm 9 October, 7 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material that
Complex Dynamic Systems: Qualitative vs Quantitative analysis
 Complex Dynamic Systems: Qualitative vs Quantitative analysis Complex Dynamic Systems Chiara Mocenni Department of Information Engineering and Mathematics University of Siena (mocenni@diism.unisi.it) Dynamic
Complex Dynamic Systems: Qualitative vs Quantitative analysis Complex Dynamic Systems Chiara Mocenni Department of Information Engineering and Mathematics University of Siena (mocenni@diism.unisi.it) Dynamic
MIT Weakly Nonlinear Things: Oscillators.
 18.385 MIT Weakly Nonlinear Things: Oscillators. Department of Mathematics Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Massachusetts MA 02139 Abstract When nonlinearities are small there are various
18.385 MIT Weakly Nonlinear Things: Oscillators. Department of Mathematics Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Massachusetts MA 02139 Abstract When nonlinearities are small there are various
Part II. Dynamical Systems. Year
 Part II Year 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2017 34 Paper 1, Section II 30A Consider the dynamical system where β > 1 is a constant. ẋ = x + x 3 + βxy 2, ẏ = y + βx 2
Part II Year 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2017 34 Paper 1, Section II 30A Consider the dynamical system where β > 1 is a constant. ẋ = x + x 3 + βxy 2, ẏ = y + βx 2
System Control Engineering 0
 System Control Engineering 0 Koichi Hashimoto Graduate School of Information Sciences Text: Nonlinear Control Systems Analysis and Design, Wiley Author: Horacio J. Marquez Web: http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/~koichi/system_control/
System Control Engineering 0 Koichi Hashimoto Graduate School of Information Sciences Text: Nonlinear Control Systems Analysis and Design, Wiley Author: Horacio J. Marquez Web: http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/~koichi/system_control/
APPM 2360: Final Exam 10:30am 1:00pm, May 6, 2015.
 APPM 23: Final Exam :3am :pm, May, 25. ON THE FRONT OF YOUR BLUEBOOK write: ) your name, 2) your student ID number, 3) lecture section, 4) your instructor s name, and 5) a grading table for eight questions.
APPM 23: Final Exam :3am :pm, May, 25. ON THE FRONT OF YOUR BLUEBOOK write: ) your name, 2) your student ID number, 3) lecture section, 4) your instructor s name, and 5) a grading table for eight questions.
2.10 Saddles, Nodes, Foci and Centers
 2.10 Saddles, Nodes, Foci and Centers In Section 1.5, a linear system (1 where x R 2 was said to have a saddle, node, focus or center at the origin if its phase portrait was linearly equivalent to one
2.10 Saddles, Nodes, Foci and Centers In Section 1.5, a linear system (1 where x R 2 was said to have a saddle, node, focus or center at the origin if its phase portrait was linearly equivalent to one
7 Two-dimensional bifurcations
 7 Two-dimensional bifurcations As in one-dimensional systems: fixed points may be created, destroyed, or change stability as parameters are varied (change of topological equivalence ). In addition closed
7 Two-dimensional bifurcations As in one-dimensional systems: fixed points may be created, destroyed, or change stability as parameters are varied (change of topological equivalence ). In addition closed
April 13, We now extend the structure of the horseshoe to more general kinds of invariant. x (v) λ n v.
 April 3, 005 - Hyperbolic Sets We now extend the structure of the horseshoe to more general kinds of invariant sets. Let r, and let f D r (M) where M is a Riemannian manifold. A compact f invariant set
April 3, 005 - Hyperbolic Sets We now extend the structure of the horseshoe to more general kinds of invariant sets. Let r, and let f D r (M) where M is a Riemannian manifold. A compact f invariant set
MIT (Spring 2014)
 18.311 MIT (Spring 014) Rodolfo R. Rosales May 6, 014. Problem Set # 08. Due: Last day of lectures. IMPORTANT: Turn in the regular and the special problems stapled in two SEPARATE packages. Print your
18.311 MIT (Spring 014) Rodolfo R. Rosales May 6, 014. Problem Set # 08. Due: Last day of lectures. IMPORTANT: Turn in the regular and the special problems stapled in two SEPARATE packages. Print your
Calculus and Differential Equations II
 MATH 250 B Second order autonomous linear systems We are mostly interested with 2 2 first order autonomous systems of the form { x = a x + b y y = c x + d y where x and y are functions of t and a, b, c,
MATH 250 B Second order autonomous linear systems We are mostly interested with 2 2 first order autonomous systems of the form { x = a x + b y y = c x + d y where x and y are functions of t and a, b, c,
Random linear systems and simulation
 Random linear systems and simulation Bernardo Kulnig Pagnoncelli, Hélio Lopes and Carlos Frederico Borges Palmeira MAT. 8/06 Random linear systems and simulation BERNARDO KULNIG PAGNONCELLI, HÉLIO LOPES
Random linear systems and simulation Bernardo Kulnig Pagnoncelli, Hélio Lopes and Carlos Frederico Borges Palmeira MAT. 8/06 Random linear systems and simulation BERNARDO KULNIG PAGNONCELLI, HÉLIO LOPES
One dimensional Maps
 Chapter 4 One dimensional Maps The ordinary differential equation studied in chapters 1-3 provide a close link to actual physical systems it is easy to believe these equations provide at least an approximate
Chapter 4 One dimensional Maps The ordinary differential equation studied in chapters 1-3 provide a close link to actual physical systems it is easy to believe these equations provide at least an approximate
Applied Math Qualifying Exam 11 October Instructions: Work 2 out of 3 problems in each of the 3 parts for a total of 6 problems.
 Printed Name: Signature: Applied Math Qualifying Exam 11 October 2014 Instructions: Work 2 out of 3 problems in each of the 3 parts for a total of 6 problems. 2 Part 1 (1) Let Ω be an open subset of R
Printed Name: Signature: Applied Math Qualifying Exam 11 October 2014 Instructions: Work 2 out of 3 problems in each of the 3 parts for a total of 6 problems. 2 Part 1 (1) Let Ω be an open subset of R
Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience - Lecture 7. Bifurcations II.
 Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience - Lecture 7. Bifurcations II. Filip Piękniewski Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń, Poland Winter 2009/2010 Filip
Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience - Lecture 7. Bifurcations II. Filip Piękniewski Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń, Poland Winter 2009/2010 Filip
Chapter 4: First-order differential equations. Similarity and Transport Phenomena in Fluid Dynamics Christophe Ancey
 Chapter 4: First-order differential equations Similarity and Transport Phenomena in Fluid Dynamics Christophe Ancey Chapter 4: First-order differential equations Phase portrait Singular point Separatrix
Chapter 4: First-order differential equations Similarity and Transport Phenomena in Fluid Dynamics Christophe Ancey Chapter 4: First-order differential equations Phase portrait Singular point Separatrix
5.5 Deeper Properties of Continuous Functions
 5.5. DEEPER PROPERTIES OF CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS 195 5.5 Deeper Properties of Continuous Functions 5.5.1 Intermediate Value Theorem and Consequences When one studies a function, one is usually interested
5.5. DEEPER PROPERTIES OF CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS 195 5.5 Deeper Properties of Continuous Functions 5.5.1 Intermediate Value Theorem and Consequences When one studies a function, one is usually interested
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7)
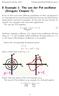 8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
An Undergraduate s Guide to the Hartman-Grobman and Poincaré-Bendixon Theorems
 An Undergraduate s Guide to the Hartman-Grobman and Poincaré-Bendixon Theorems Scott Zimmerman MATH181HM: Dynamical Systems Spring 2008 1 Introduction The Hartman-Grobman and Poincaré-Bendixon Theorems
An Undergraduate s Guide to the Hartman-Grobman and Poincaré-Bendixon Theorems Scott Zimmerman MATH181HM: Dynamical Systems Spring 2008 1 Introduction The Hartman-Grobman and Poincaré-Bendixon Theorems
The Higgins-Selkov oscillator
 The Higgins-Selkov oscillator May 14, 2014 Here I analyse the long-time behaviour of the Higgins-Selkov oscillator. The system is ẋ = k 0 k 1 xy 2, (1 ẏ = k 1 xy 2 k 2 y. (2 The unknowns x and y, being
The Higgins-Selkov oscillator May 14, 2014 Here I analyse the long-time behaviour of the Higgins-Selkov oscillator. The system is ẋ = k 0 k 1 xy 2, (1 ẏ = k 1 xy 2 k 2 y. (2 The unknowns x and y, being
Section 9.3 Phase Plane Portraits (for Planar Systems)
 Section 9.3 Phase Plane Portraits (for Planar Systems) Key Terms: Equilibrium point of planer system yꞌ = Ay o Equilibrium solution Exponential solutions o Half-line solutions Unstable solution Stable
Section 9.3 Phase Plane Portraits (for Planar Systems) Key Terms: Equilibrium point of planer system yꞌ = Ay o Equilibrium solution Exponential solutions o Half-line solutions Unstable solution Stable
Sample Solutions of Assignment 10 for MAT3270B
 Sample Solutions of Assignment 1 for MAT327B 1. For the following ODEs, (a) determine all critical points; (b) find the corresponding linear system near each critical point; (c) find the eigenvalues of
Sample Solutions of Assignment 1 for MAT327B 1. For the following ODEs, (a) determine all critical points; (b) find the corresponding linear system near each critical point; (c) find the eigenvalues of
EN Nonlinear Control and Planning in Robotics Lecture 3: Stability February 4, 2015
 EN530.678 Nonlinear Control and Planning in Robotics Lecture 3: Stability February 4, 2015 Prof: Marin Kobilarov 0.1 Model prerequisites Consider ẋ = f(t, x). We will make the following basic assumptions
EN530.678 Nonlinear Control and Planning in Robotics Lecture 3: Stability February 4, 2015 Prof: Marin Kobilarov 0.1 Model prerequisites Consider ẋ = f(t, x). We will make the following basic assumptions
Entrance Exam, Differential Equations April, (Solve exactly 6 out of the 8 problems) y + 2y + y cos(x 2 y) = 0, y(0) = 2, y (0) = 4.
 Entrance Exam, Differential Equations April, 7 (Solve exactly 6 out of the 8 problems). Consider the following initial value problem: { y + y + y cos(x y) =, y() = y. Find all the values y such that the
Entrance Exam, Differential Equations April, 7 (Solve exactly 6 out of the 8 problems). Consider the following initial value problem: { y + y + y cos(x y) =, y() = y. Find all the values y such that the
Math 312 Lecture Notes Linearization
 Math 3 Lecture Notes Linearization Warren Weckesser Department of Mathematics Colgate University 3 March 005 These notes discuss linearization, in which a linear system is used to approximate the behavior
Math 3 Lecture Notes Linearization Warren Weckesser Department of Mathematics Colgate University 3 March 005 These notes discuss linearization, in which a linear system is used to approximate the behavior
11 Chaos in Continuous Dynamical Systems.
 11 CHAOS IN CONTINUOUS DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS. 47 11 Chaos in Continuous Dynamical Systems. Let s consider a system of differential equations given by where x(t) : R R and f : R R. ẋ = f(x), The linearization
11 CHAOS IN CONTINUOUS DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS. 47 11 Chaos in Continuous Dynamical Systems. Let s consider a system of differential equations given by where x(t) : R R and f : R R. ẋ = f(x), The linearization
HW3 - Due 02/06. Each answer must be mathematically justified. Don t forget your name. 1 2, A = 2 2
 HW3 - Due 02/06 Each answer must be mathematically justified Don t forget your name Problem 1 Find a 2 2 matrix B such that B 3 = A, where A = 2 2 If A was diagonal, it would be easy: we would just take
HW3 - Due 02/06 Each answer must be mathematically justified Don t forget your name Problem 1 Find a 2 2 matrix B such that B 3 = A, where A = 2 2 If A was diagonal, it would be easy: we would just take
30 Surfaces and nondegenerate symmetric bilinear forms
 80 CHAPTER 3. COHOMOLOGY AND DUALITY This calculation is useful! Corollary 29.4. Let p, q > 0. Any map S p+q S p S q induces the zero map in H p+q ( ). Proof. Let f : S p+q S p S q be such a map. It induces
80 CHAPTER 3. COHOMOLOGY AND DUALITY This calculation is useful! Corollary 29.4. Let p, q > 0. Any map S p+q S p S q induces the zero map in H p+q ( ). Proof. Let f : S p+q S p S q be such a map. It induces
One Dimensional Dynamical Systems
 16 CHAPTER 2 One Dimensional Dynamical Systems We begin by analyzing some dynamical systems with one-dimensional phase spaces, and in particular their bifurcations. All equations in this Chapter are scalar
16 CHAPTER 2 One Dimensional Dynamical Systems We begin by analyzing some dynamical systems with one-dimensional phase spaces, and in particular their bifurcations. All equations in this Chapter are scalar
Chapter 7. Nonlinear Systems. 7.1 Introduction
 Nonlinear Systems Chapter 7 The scientist does not study nature because it is useful; he studies it because he delights in it, and he delights in it because it is beautiful. - Jules Henri Poincaré (1854-1912)
Nonlinear Systems Chapter 7 The scientist does not study nature because it is useful; he studies it because he delights in it, and he delights in it because it is beautiful. - Jules Henri Poincaré (1854-1912)
Solutions to Dynamical Systems 2010 exam. Each question is worth 25 marks.
 Solutions to Dynamical Systems exam Each question is worth marks [Unseen] Consider the following st order differential equation: dy dt Xy yy 4 a Find and classify all the fixed points of Hence draw the
Solutions to Dynamical Systems exam Each question is worth marks [Unseen] Consider the following st order differential equation: dy dt Xy yy 4 a Find and classify all the fixed points of Hence draw the
Advanced Partial Differential Equations with Applications
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.eu 18.306 Avance Partial Differential Equations with Applications Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.eu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.eu 18.306 Avance Partial Differential Equations with Applications Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.eu/terms.
Math 308 Final Exam Practice Problems
 Math 308 Final Exam Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems
Math 308 Final Exam Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems
MATH 415, WEEKS 7 & 8: Conservative and Hamiltonian Systems, Non-linear Pendulum
 MATH 415, WEEKS 7 & 8: Conservative and Hamiltonian Systems, Non-linear Pendulum Reconsider the following example from last week: dx dt = x y dy dt = x2 y. We were able to determine many qualitative features
MATH 415, WEEKS 7 & 8: Conservative and Hamiltonian Systems, Non-linear Pendulum Reconsider the following example from last week: dx dt = x y dy dt = x2 y. We were able to determine many qualitative features
Nonlinear Control Lecture 2:Phase Plane Analysis
 Nonlinear Control Lecture 2:Phase Plane Analysis Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Fall 2009 Farzaneh Abdollahi Nonlinear Control Lecture 2 1/68
Nonlinear Control Lecture 2:Phase Plane Analysis Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Fall 2009 Farzaneh Abdollahi Nonlinear Control Lecture 2 1/68
Answers to Problem Set Number MIT (Fall 2005).
 Answers to Problem Set Number 5. 18.305 MIT Fall 2005). D. Margetis and R. Rosales MIT, Math. Dept., Cambridge, MA 02139). November 23, 2005. Course TA: Nikos Savva, MIT, Dept. of Mathematics, Cambridge,
Answers to Problem Set Number 5. 18.305 MIT Fall 2005). D. Margetis and R. Rosales MIT, Math. Dept., Cambridge, MA 02139). November 23, 2005. Course TA: Nikos Savva, MIT, Dept. of Mathematics, Cambridge,
TWELVE LIMIT CYCLES IN A CUBIC ORDER PLANAR SYSTEM WITH Z 2 -SYMMETRY. P. Yu 1,2 and M. Han 1
 COMMUNICATIONS ON Website: http://aimsciences.org PURE AND APPLIED ANALYSIS Volume 3, Number 3, September 2004 pp. 515 526 TWELVE LIMIT CYCLES IN A CUBIC ORDER PLANAR SYSTEM WITH Z 2 -SYMMETRY P. Yu 1,2
COMMUNICATIONS ON Website: http://aimsciences.org PURE AND APPLIED ANALYSIS Volume 3, Number 3, September 2004 pp. 515 526 TWELVE LIMIT CYCLES IN A CUBIC ORDER PLANAR SYSTEM WITH Z 2 -SYMMETRY P. Yu 1,2
Principles of Optimal Control Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 16.323 Principles of Optimal Control Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 16.323 Lecture
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 16.323 Principles of Optimal Control Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 16.323 Lecture
MATH 215/255 Solutions to Additional Practice Problems April dy dt
 . For the nonlinear system MATH 5/55 Solutions to Additional Practice Problems April 08 dx dt = x( x y, dy dt = y(.5 y x, x 0, y 0, (a Show that if x(0 > 0 and y(0 = 0, then the solution (x(t, y(t of the
. For the nonlinear system MATH 5/55 Solutions to Additional Practice Problems April 08 dx dt = x( x y, dy dt = y(.5 y x, x 0, y 0, (a Show that if x(0 > 0 and y(0 = 0, then the solution (x(t, y(t of the
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET. EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS. COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD
 CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: April 06, 2018, at 14 00 18 00 Johanneberg Kristian
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: April 06, 2018, at 14 00 18 00 Johanneberg Kristian
A Mathematical Trivium
 A Mathematical Trivium V.I. Arnold 1991 1. Sketch the graph of the derivative and the graph of the integral of a function given by a freehand graph. 2. Find the limit lim x 0 sin tan x tan sin x arcsin
A Mathematical Trivium V.I. Arnold 1991 1. Sketch the graph of the derivative and the graph of the integral of a function given by a freehand graph. 2. Find the limit lim x 0 sin tan x tan sin x arcsin
PERIODIC SOLUTIONS WITH NONCONSTANT SIGN IN ABEL EQUATIONS OF THE SECOND KIND
 PERIODIC SOLUTIONS WITH NONCONSTANT SIGN IN ABEL EQUATIONS OF THE SECOND KIND JOSEP M. OLM, XAVIER ROS-OTON, AND TERE M. SEARA Abstract. The study of periodic solutions with constant sign in the Abel equation
PERIODIC SOLUTIONS WITH NONCONSTANT SIGN IN ABEL EQUATIONS OF THE SECOND KIND JOSEP M. OLM, XAVIER ROS-OTON, AND TERE M. SEARA Abstract. The study of periodic solutions with constant sign in the Abel equation
Answers to Problem Set Number MIT (Fall 2005).
 Answers to Problem Set Number 6. 18.305 MIT (Fall 2005). D. Margetis and R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., Cambridge, MA 02139). December 12, 2005. Course TA: Nikos Savva, MIT, Dept. of Mathematics, Cambridge,
Answers to Problem Set Number 6. 18.305 MIT (Fall 2005). D. Margetis and R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., Cambridge, MA 02139). December 12, 2005. Course TA: Nikos Savva, MIT, Dept. of Mathematics, Cambridge,
Linearization of Differential Equation Models
 Linearization of Differential Equation Models 1 Motivation We cannot solve most nonlinear models, so we often instead try to get an overall feel for the way the model behaves: we sometimes talk about looking
Linearization of Differential Equation Models 1 Motivation We cannot solve most nonlinear models, so we often instead try to get an overall feel for the way the model behaves: we sometimes talk about looking
Various lecture notes for
 Various lecture notes for 18306. R. R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., 2-337) April 14, 2014 Abstract Notes for MIT s 18.306 Advanced PDE with applications. Contents 1 First lecture. 3 Tomography. Use filtering
Various lecture notes for 18306. R. R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., 2-337) April 14, 2014 Abstract Notes for MIT s 18.306 Advanced PDE with applications. Contents 1 First lecture. 3 Tomography. Use filtering
Half of Final Exam Name: Practice Problems October 28, 2014
 Math 54. Treibergs Half of Final Exam Name: Practice Problems October 28, 24 Half of the final will be over material since the last midterm exam, such as the practice problems given here. The other half
Math 54. Treibergs Half of Final Exam Name: Practice Problems October 28, 24 Half of the final will be over material since the last midterm exam, such as the practice problems given here. The other half
Autonomous systems. Ordinary differential equations which do not contain the independent variable explicitly are said to be autonomous.
 Autonomous equations Autonomous systems Ordinary differential equations which do not contain the independent variable explicitly are said to be autonomous. i f i(x 1, x 2,..., x n ) for i 1,..., n As you
Autonomous equations Autonomous systems Ordinary differential equations which do not contain the independent variable explicitly are said to be autonomous. i f i(x 1, x 2,..., x n ) for i 1,..., n As you
Applied Dynamical Systems
 Applied Dynamical Systems Recommended Reading: (1) Morris W. Hirsch, Stephen Smale, and Robert L. Devaney. Differential equations, dynamical systems, and an introduction to chaos. Elsevier/Academic Press,
Applied Dynamical Systems Recommended Reading: (1) Morris W. Hirsch, Stephen Smale, and Robert L. Devaney. Differential equations, dynamical systems, and an introduction to chaos. Elsevier/Academic Press,
Nonlinear Autonomous Dynamical systems of two dimensions. Part A
 Nonlinear Autonomous Dynamical systems of two dimensions Part A Nonlinear Autonomous Dynamical systems of two dimensions x f ( x, y), x(0) x vector field y g( xy, ), y(0) y F ( f, g) 0 0 f, g are continuous
Nonlinear Autonomous Dynamical systems of two dimensions Part A Nonlinear Autonomous Dynamical systems of two dimensions x f ( x, y), x(0) x vector field y g( xy, ), y(0) y F ( f, g) 0 0 f, g are continuous
Poincaré Map, Floquet Theory, and Stability of Periodic Orbits
 Poincaré Map, Floquet Theory, and Stability of Periodic Orbits CDS140A Lecturer: W.S. Koon Fall, 2006 1 Poincaré Maps Definition (Poincaré Map): Consider ẋ = f(x) with periodic solution x(t). Construct
Poincaré Map, Floquet Theory, and Stability of Periodic Orbits CDS140A Lecturer: W.S. Koon Fall, 2006 1 Poincaré Maps Definition (Poincaré Map): Consider ẋ = f(x) with periodic solution x(t). Construct
Invariant manifolds of the Bonhoeffer-van der Pol oscillator
 Invariant manifolds of the Bonhoeffer-van der Pol oscillator R. Benítez 1, V. J. Bolós 2 1 Dpto. Matemáticas, Centro Universitario de Plasencia, Universidad de Extremadura. Avda. Virgen del Puerto 2. 10600,
Invariant manifolds of the Bonhoeffer-van der Pol oscillator R. Benítez 1, V. J. Bolós 2 1 Dpto. Matemáticas, Centro Universitario de Plasencia, Universidad de Extremadura. Avda. Virgen del Puerto 2. 10600,
Control Systems. Internal Stability - LTI systems. L. Lanari
 Control Systems Internal Stability - LTI systems L. Lanari outline LTI systems: definitions conditions South stability criterion equilibrium points Nonlinear systems: equilibrium points examples stable
Control Systems Internal Stability - LTI systems L. Lanari outline LTI systems: definitions conditions South stability criterion equilibrium points Nonlinear systems: equilibrium points examples stable
ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY HOMEWORK 3
 ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY HOMEWORK 3 (1) Consider the curve Y 2 = X 2 (X + 1). (a) Sketch the curve. (b) Determine the singular point P on C. (c) For all lines through P, determine the intersection multiplicity
ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY HOMEWORK 3 (1) Consider the curve Y 2 = X 2 (X + 1). (a) Sketch the curve. (b) Determine the singular point P on C. (c) For all lines through P, determine the intersection multiplicity
