Lecture 5. Outline: Limit Cycles. Definition and examples How to rule out limit cycles. Poincare-Bendixson theorem Hopf bifurcations Poincare maps
|
|
|
- Logan Boyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 5 Outline: Limit Cycles Definition and examples How to rule out limit cycles Gradient systems Liapunov functions Dulacs criterion Poincare-Bendixson theorem Hopf bifurcations Poincare maps
2 Limit Cycles DEF: A limit cycle is an isolated closed trajectory. Examples: Heart beat, pacemaker neurons, daily rhythms in body temperature, chemical reactions,...
3 Limit Cycles Are inherently a non-linear phenomenon What about closed orbits in linear systems? x= A x They can have solutions that are closed orbits! Linearity implies: if x(t) is a solution so is c x(t) Amplitude is determined by ICs, any small perturbation persists forever purely complex eigenvalues In contrast: in limit cycles in nonlinear systems the structure of the system determines the amplitude and shape of the limit cycle.
4 Examples (1) Not hard to construct examples of limit cycles in polar coordinates Θ = 1 ṙ = r(1 r 2 ) x(t), y(t) -> sine or cosine, -> periodic functions in x And y directions
5 Van der Pol Oscillator ẍ+μ(x 2 1) ẋ+ x=0 dx/dt nonlinear damping term Equation arose in connection with nonlinear electrical circuits used in the first radios Damping term Causes large aplitude osci's to decay, but pumps them back if they become too small VdP osci has a unique stable LC for each µ>0 x
6 What to do? Suppose we want to analyze a given 2d flow Rule out existence of limit cycles Index theory (last lecture) We know the system belongs to a class of systems that cannot have LCs (-> e.g. Gradient systems) Construct Liapunov function Dulac's criterion... Prove existence of a LC Poincare-Bendixson theorem
7 Gradient Systems DEF: A gradient system is a system that can be written in the form ẋ= V. V is then called a potential function. Remarks: In components: Every 1d system is a gradient system How to check if a 2d system is a gradient system? If ẋ = f (x, y) ẏ = g(x, y) ẋ = x V (x, y) ẏ = y V (x, y) is a gs, then: f / y= g / x
8 Example Gradient Systems Is (1) a gradient system? If so, find a potential. Check condition f / y=1+2x ẋ = y+2xy ẏ = x+ x 2 y 2 (1) f / y= g / x g/ x=1+2x Find potential? Partial integration. V x = y+2xy V = xy x 2 y+c ( y) V y = x+ x 2 C y ( y)= ẏ= x+ x 2 y 2 dc /dy = y 2 C ( y)=1/3 y 3 V (x, y)= xy x 2 y+1 /3 y 3
9 Gradient Systems THEOREM: Closed orbits are impossible in gradient systems. Proof: Suppose there is a closed orbit. Consider change in V after one circuit. On the one hand: V=0 (V is a scalar) On the other hand: Δ V = T dv 0 dt dt= T 0 ( V x)dt T Δ V = 0 x 2 dt<0 (contradiction)
10 Liapunov Functions Occasionally possible to find energy-like functions that decrease along trajectories DEF: Consider a system dx/dt=f(x) with a fixed point at x*. A Liapunov function is a cont. diff. real-valued function V(x), such that: V(x)>0 for all x x* and V(x*)=0 (V is pos. definite) dv/dt<0 for all x x* (all trajectories are downhill towards x*) Then x* is globally asymptotically stable. In particular the system has no limit cycles.
11 Liapunov Functions Proof : Why does the existence of a Liapunov function rule out closed orbits? Consider change of V along a closed orbit. V is real-valued, after one circuit one should have V=0 On the other hand: Δ V = 0 T dv dt dt <0 Existence of a LF implies that trajectories move monotonically down the graph of V toward x*
12 Liapunov Functions Problem: How to find Liapunov functions? No general method, requires divine inspiration :-) Often sums of squares work... ẋ = x+ 4y ẏ = x y 3 (2) Ansatz: V (x, y)=x 2 +a y 2 V =2 ẋ x+2a ẏ y=2 x( x+4y )+2ay ( x y 3 ) = 2x 2 +8xy 2ay 4 2axy Choose a=4 = 2x 2 8y 4
13 Liapunov Functions Is V (x, y)=x 2 +4y 2 a Liapunov function for (2)? V > 0 for all (x,y)!=(x*,y*)=(0,0) V(0,0)=0 dv/dt < 0 for (x,y)!=(0,0) by construction. Theorem above then implies that (0,0) is globally asymptotically stable.
14 Dulac's Criterion Let dx/dt=f(x) be a cont. diff. VF in a simply connected subset R of the plane. If there exists a cont. diff. real-valued function g(x) such that (g ẋ) has one sign throughout R then there are no closed orbits lying entirely in R. A (g x)da = C g x ndl 0 =0 since x n
15 Dulac in Practice... Requires a real-valued function g with the above properties Same problem as with Liapunov functions No general method to find g, divine inspiration... So far: negative results (ruling out limit cycles). How to prove that limit cycles must exist?
16 Poincare Bendixson Theorem Suppose R is a closed bounded subset of the plane and dx/dt=f(x) is a cont. diff. VF on an open set containing R R does not contain any fixed points There exists a traj. that is confined in R Then, either C is a closed orbit or C spirals toward one. R contains a closed orbit.
17 P-B-T Limits types of behaviour in the phase plane: Fixed points, oscillations Self-sustaining oscillations, but no chaos! PBT in applications: First two conditions are easy to show Often hard to construct a trapping region to prove existence of a confined trajectory Situation often simpler, if system has simple representation in polar coordinates
18 P-B-T in Action Consider: ṙ = r(1 r 2 )+μ r cosθ Θ = 1 Does the closed orbit at r=1 survive for small µ? 2 r max (1 r max )+μ r max cos Θ<0 e.g. r max > 1+μ 2 r min (1 r min e.g. r min < 1 μ )+μ r min cosθ>0 There must be a limit cycle in μ <r < μ
19 Hopf Bifurcations How can a FP lose stability? Stable node Transcritical, Saddle node, Pitchfork bifurcations Stable spiral Hopf bifurcations
20 Supercritical Hopf Bifurcation Below bif. point: small oscillations gradually abating Above bif. point: small oscillations gradually built up to small amplitude Stable spiral changes into an unstable spiral surrounded by a small elliptical limit cycle
21 Supercritical Hopf Example (0) ṙ = μ r r 3 µ controls stability of FP Θ = ω+br 2 ω controls frequency of rotations B controls dependence of frequency on amplitude for large amplitudes µ<0: origin is stable spiral µ=0: origin still is weak stable spiral µ>0: origin unstable spiral + limit cycle at r= μ
22 Supercritical Hopf Example (1) What happens to eigenvalues? In cartesian coordinates... x=r cosθ y=r sin Θ ẋ=ṙ cosθ r Θsin Θ =(μ r r 3 )cos Θ r(ω+br 2 )sin Θ =(μ [ x 2 + y 2 ]) x (ω+b[ x 2 + y 2 ]) y =μ x ω y +cubic terms... ẏ=ω x+μ y+cubic terms J = ( μ ω ) λ=μ±iω ω μ
23 Supercritical Hopf Bifurcation Example illustrates two general rules: Size of LC grows continuously from zero μ μ C Frequency of limit cycle at birth is given by Im(λ) at µ c However: Eigenvalues generally don't cross x=0 in straight lines At birth limit cycle generally is an ellipse (not circle as in example)
24 Subcritical Hopf Bifurcations ṙ = μ r+r 3 r 5 Cubic term now destabilizing! Θ = ω+br 2
25 FP of P correspond to closed orbits Poincare maps Useful for studying swirling flows dx/dt=f(x) n dim. flow, S n-1 dim. surface of section transverse to flow Poincare map is a mapping of S to itself obtained by following trajectories from one intersection with S to the next, i.e. if x k is kth intersection, then: x k+1 =P(x k ).
26 Poincare maps (1) Converts problems about closed orbits (tough) into problems about fixed points of a map (easy ) E.g. stability of limit cycle -> stability of fixed point of Poincare map However: typically impossible to find a formula for P
27 Example Poincare map for Θ = 1 ṙ = r(1 r 2 ) Let S be positive x axis, time of flight for one return is t=2π. r 1 r 0 dr r(1 r 2 ) = 0 2 π dt=2 π r 1 =(1+e 4 π (r 0 2 1)) 1/ 2 P(r)=(1+e 4 π (r 2 1 /2 1)) Fixed points? r * =P(r * ) r * =1
28 Cobweb Construction r* is stable and unique -> system has stable limit cycle given by the circle r=1.
29 Linear Stability of Closed Orbits Given a system dx/dt=f(x) with a closed orbit. Is it stable? -> Is corresponding fixed point of Poincare map stable? Explore fate of an infinitesimal perturbation v 0. x * +v 1 =P( x * +v 0 ) =P(x * )+[ DP( x * )] v 0 +O( v 0 2 ) v 1 =[DP( x * )] v 0 DP(x*) is linearized Poincare map at x*
30 Linear Stability of Closed Orbits The closed orbit is linearly stable if and only if for all eigenvalues of DP(x*), λ i,i=1,...,n-1 it holds λ i <1. n 1 v = 0 j=1 v j, 0 e j v 1 =DP(x * ) n 1 v k =...= j=1 v j,0 (λ j ) k e j The eigenvalues λ i are also called the characteristic or Floquet multipliers of the closed orbit. In general, requires numerical integration... n 1 j =1 n 1 v j, 0 e = j j =1 v j, 0 λ j e j
31 Summary You should remember: What a limit cycle is and why it is only found in nonlinear systems Conditions under which there cannot be a limit cycle Gradient systems and Liapunov functions The Poincare Bendixson theorem and why it is important Hopf bifurcations Poincare maps and how to argue about stability of closed orbits
TWO DIMENSIONAL FLOWS. Lecture 5: Limit Cycles and Bifurcations
 TWO DIMENSIONAL FLOWS Lecture 5: Limit Cycles and Bifurcations 5. Limit cycles A limit cycle is an isolated closed trajectory [ isolated means that neighbouring trajectories are not closed] Fig. 5.1.1
TWO DIMENSIONAL FLOWS Lecture 5: Limit Cycles and Bifurcations 5. Limit cycles A limit cycle is an isolated closed trajectory [ isolated means that neighbouring trajectories are not closed] Fig. 5.1.1
1. < 0: the eigenvalues are real and have opposite signs; the fixed point is a saddle point
 Solving a Linear System τ = trace(a) = a + d = λ 1 + λ 2 λ 1,2 = τ± = det(a) = ad bc = λ 1 λ 2 Classification of Fixed Points τ 2 4 1. < 0: the eigenvalues are real and have opposite signs; the fixed point
Solving a Linear System τ = trace(a) = a + d = λ 1 + λ 2 λ 1,2 = τ± = det(a) = ad bc = λ 1 λ 2 Classification of Fixed Points τ 2 4 1. < 0: the eigenvalues are real and have opposite signs; the fixed point
Practice Problems for Final Exam
 Math 1280 Spring 2016 Practice Problems for Final Exam Part 2 (Sections 6.6, 6.7, 6.8, and chapter 7) S o l u t i o n s 1. Show that the given system has a nonlinear center at the origin. ẋ = 9y 5y 5,
Math 1280 Spring 2016 Practice Problems for Final Exam Part 2 (Sections 6.6, 6.7, 6.8, and chapter 7) S o l u t i o n s 1. Show that the given system has a nonlinear center at the origin. ẋ = 9y 5y 5,
Lecture 6. Lorenz equations and Malkus' waterwheel Some properties of the Lorenz Eq.'s Lorenz Map Towards definitions of:
 Lecture 6 Chaos Lorenz equations and Malkus' waterwheel Some properties of the Lorenz Eq.'s Lorenz Map Towards definitions of: Chaos, Attractors and strange attractors Transient chaos Lorenz Equations
Lecture 6 Chaos Lorenz equations and Malkus' waterwheel Some properties of the Lorenz Eq.'s Lorenz Map Towards definitions of: Chaos, Attractors and strange attractors Transient chaos Lorenz Equations
STABILITY. Phase portraits and local stability
 MAS271 Methods for differential equations Dr. R. Jain STABILITY Phase portraits and local stability We are interested in system of ordinary differential equations of the form ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y),
MAS271 Methods for differential equations Dr. R. Jain STABILITY Phase portraits and local stability We are interested in system of ordinary differential equations of the form ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y),
LECTURE 8: DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS 7
 15-382 COLLECTIVE INTELLIGENCE S18 LECTURE 8: DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS 7 INSTRUCTOR: GIANNI A. DI CARO GEOMETRIES IN THE PHASE SPACE Damped pendulum One cp in the region between two separatrix Separatrix Basin
15-382 COLLECTIVE INTELLIGENCE S18 LECTURE 8: DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS 7 INSTRUCTOR: GIANNI A. DI CARO GEOMETRIES IN THE PHASE SPACE Damped pendulum One cp in the region between two separatrix Separatrix Basin
7 Two-dimensional bifurcations
 7 Two-dimensional bifurcations As in one-dimensional systems: fixed points may be created, destroyed, or change stability as parameters are varied (change of topological equivalence ). In addition closed
7 Two-dimensional bifurcations As in one-dimensional systems: fixed points may be created, destroyed, or change stability as parameters are varied (change of topological equivalence ). In addition closed
Part II. Dynamical Systems. Year
 Part II Year 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2017 34 Paper 1, Section II 30A Consider the dynamical system where β > 1 is a constant. ẋ = x + x 3 + βxy 2, ẏ = y + βx 2
Part II Year 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2017 34 Paper 1, Section II 30A Consider the dynamical system where β > 1 is a constant. ẋ = x + x 3 + βxy 2, ẏ = y + βx 2
ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y), (x, y) D, can only have periodic solutions if (f,g) changes sign in D or if (f,g)=0in D.
 4 Periodic Solutions We have shown that in the case of an autonomous equation the periodic solutions correspond with closed orbits in phase-space. Autonomous two-dimensional systems with phase-space R
4 Periodic Solutions We have shown that in the case of an autonomous equation the periodic solutions correspond with closed orbits in phase-space. Autonomous two-dimensional systems with phase-space R
Lecture 3 : Bifurcation Analysis
 Lecture 3 : Bifurcation Analysis D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis October - December 2008 D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis General settings 4 basic bifurcations (as long as there is only one unstable mode!) steady state
Lecture 3 : Bifurcation Analysis D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis October - December 2008 D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis General settings 4 basic bifurcations (as long as there is only one unstable mode!) steady state
EE222 - Spring 16 - Lecture 2 Notes 1
 EE222 - Spring 16 - Lecture 2 Notes 1 Murat Arcak January 21 2016 1 Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Essentially Nonlinear Phenomena Continued
EE222 - Spring 16 - Lecture 2 Notes 1 Murat Arcak January 21 2016 1 Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Essentially Nonlinear Phenomena Continued
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET. EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS. COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD
 CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: August 22, 2018, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Jan Meibohm,
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: August 22, 2018, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Jan Meibohm,
MATH 415, WEEK 11: Bifurcations in Multiple Dimensions, Hopf Bifurcation
 MATH 415, WEEK 11: Bifurcations in Multiple Dimensions, Hopf Bifurcation 1 Bifurcations in Multiple Dimensions When we were considering one-dimensional systems, we saw that subtle changes in parameter
MATH 415, WEEK 11: Bifurcations in Multiple Dimensions, Hopf Bifurcation 1 Bifurcations in Multiple Dimensions When we were considering one-dimensional systems, we saw that subtle changes in parameter
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems
 B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 4. Bifurcations Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Local bifurcations for vector fields 1.1 The problem 1.2 The extended centre
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 4. Bifurcations Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Local bifurcations for vector fields 1.1 The problem 1.2 The extended centre
Lectures on Periodic Orbits
 Lectures on Periodic Orbits 11 February 2009 Most of the contents of these notes can found in any typical text on dynamical systems, most notably Strogatz [1994], Perko [2001] and Verhulst [1996]. Complete
Lectures on Periodic Orbits 11 February 2009 Most of the contents of these notes can found in any typical text on dynamical systems, most notably Strogatz [1994], Perko [2001] and Verhulst [1996]. Complete
= F ( x; µ) (1) where x is a 2-dimensional vector, µ is a parameter, and F :
 1 Bifurcations Richard Bertram Department of Mathematics and Programs in Neuroscience and Molecular Biophysics Florida State University Tallahassee, Florida 32306 A bifurcation is a qualitative change
1 Bifurcations Richard Bertram Department of Mathematics and Programs in Neuroscience and Molecular Biophysics Florida State University Tallahassee, Florida 32306 A bifurcation is a qualitative change
154 Chapter 9 Hints, Answers, and Solutions The particular trajectories are highlighted in the phase portraits below.
 54 Chapter 9 Hints, Answers, and Solutions 9. The Phase Plane 9.. 4. The particular trajectories are highlighted in the phase portraits below... 3. 4. 9..5. Shown below is one possibility with x(t) and
54 Chapter 9 Hints, Answers, and Solutions 9. The Phase Plane 9.. 4. The particular trajectories are highlighted in the phase portraits below... 3. 4. 9..5. Shown below is one possibility with x(t) and
2 Discrete growth models, logistic map (Murray, Chapter 2)
 2 Discrete growth models, logistic map (Murray, Chapter 2) As argued in Lecture 1 the population of non-overlapping generations can be modelled as a discrete dynamical system. This is an example of an
2 Discrete growth models, logistic map (Murray, Chapter 2) As argued in Lecture 1 the population of non-overlapping generations can be modelled as a discrete dynamical system. This is an example of an
(8.51) ẋ = A(λ)x + F(x, λ), where λ lr, the matrix A(λ) and function F(x, λ) are C k -functions with k 1,
 2.8.7. Poincaré-Andronov-Hopf Bifurcation. In the previous section, we have given a rather detailed method for determining the periodic orbits of a two dimensional system which is the perturbation of a
2.8.7. Poincaré-Andronov-Hopf Bifurcation. In the previous section, we have given a rather detailed method for determining the periodic orbits of a two dimensional system which is the perturbation of a
2.10 Saddles, Nodes, Foci and Centers
 2.10 Saddles, Nodes, Foci and Centers In Section 1.5, a linear system (1 where x R 2 was said to have a saddle, node, focus or center at the origin if its phase portrait was linearly equivalent to one
2.10 Saddles, Nodes, Foci and Centers In Section 1.5, a linear system (1 where x R 2 was said to have a saddle, node, focus or center at the origin if its phase portrait was linearly equivalent to one
Problem Set 5 Solutions
 Problem Set 5 Solutions Dorian Abbot APM47 0/8/04. (a) We consider π θ π. The pendulum pointin down corresponds to θ=0 and the pendulum pointin up corresponds to θ π. Define ν θ. The system can be rewritten:
Problem Set 5 Solutions Dorian Abbot APM47 0/8/04. (a) We consider π θ π. The pendulum pointin down corresponds to θ=0 and the pendulum pointin up corresponds to θ π. Define ν θ. The system can be rewritten:
Problem set 7 Math 207A, Fall 2011 Solutions
 Problem set 7 Math 207A, Fall 2011 s 1. Classify the equilibrium (x, y) = (0, 0) of the system x t = x, y t = y + x 2. Is the equilibrium hyperbolic? Find an equation for the trajectories in (x, y)- phase
Problem set 7 Math 207A, Fall 2011 s 1. Classify the equilibrium (x, y) = (0, 0) of the system x t = x, y t = y + x 2. Is the equilibrium hyperbolic? Find an equation for the trajectories in (x, y)- phase
Chapter 7. Nonlinear Systems. 7.1 Introduction
 Nonlinear Systems Chapter 7 The scientist does not study nature because it is useful; he studies it because he delights in it, and he delights in it because it is beautiful. - Jules Henri Poincaré (1854-1912)
Nonlinear Systems Chapter 7 The scientist does not study nature because it is useful; he studies it because he delights in it, and he delights in it because it is beautiful. - Jules Henri Poincaré (1854-1912)
Nonlinear Control Lecture 2:Phase Plane Analysis
 Nonlinear Control Lecture 2:Phase Plane Analysis Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Fall 2010 r. Farzaneh Abdollahi Nonlinear Control Lecture 2 1/53
Nonlinear Control Lecture 2:Phase Plane Analysis Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Fall 2010 r. Farzaneh Abdollahi Nonlinear Control Lecture 2 1/53
Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics. Laurette Tuckerman PMMH-ESPCI-CNRS
 Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics Laurette Tuckerman PMMH-ESPCI-CNRS laurette@pmmh.espci.fr Dynamical Systems: A Basic Primer 1 1 Basic bifurcations 1.1 Fixed points and linear
Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics Laurette Tuckerman PMMH-ESPCI-CNRS laurette@pmmh.espci.fr Dynamical Systems: A Basic Primer 1 1 Basic bifurcations 1.1 Fixed points and linear
Sample Solutions of Assignment 10 for MAT3270B
 Sample Solutions of Assignment 1 for MAT327B 1. For the following ODEs, (a) determine all critical points; (b) find the corresponding linear system near each critical point; (c) find the eigenvalues of
Sample Solutions of Assignment 1 for MAT327B 1. For the following ODEs, (a) determine all critical points; (b) find the corresponding linear system near each critical point; (c) find the eigenvalues of
Models Involving Interactions between Predator and Prey Populations
 Models Involving Interactions between Predator and Prey Populations Matthew Mitchell Georgia College and State University December 30, 2015 Abstract Predator-prey models are used to show the intricate
Models Involving Interactions between Predator and Prey Populations Matthew Mitchell Georgia College and State University December 30, 2015 Abstract Predator-prey models are used to show the intricate
THREE DIMENSIONAL SYSTEMS. Lecture 6: The Lorenz Equations
 THREE DIMENSIONAL SYSTEMS Lecture 6: The Lorenz Equations 6. The Lorenz (1963) Equations The Lorenz equations were originally derived by Saltzman (1962) as a minimalist model of thermal convection in a
THREE DIMENSIONAL SYSTEMS Lecture 6: The Lorenz Equations 6. The Lorenz (1963) Equations The Lorenz equations were originally derived by Saltzman (1962) as a minimalist model of thermal convection in a
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET. EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS. COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD
 CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: January 08, 2018, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Kristian
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: January 08, 2018, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Kristian
Entrance Exam, Differential Equations April, (Solve exactly 6 out of the 8 problems) y + 2y + y cos(x 2 y) = 0, y(0) = 2, y (0) = 4.
 Entrance Exam, Differential Equations April, 7 (Solve exactly 6 out of the 8 problems). Consider the following initial value problem: { y + y + y cos(x y) =, y() = y. Find all the values y such that the
Entrance Exam, Differential Equations April, 7 (Solve exactly 6 out of the 8 problems). Consider the following initial value problem: { y + y + y cos(x y) =, y() = y. Find all the values y such that the
Dynamical systems tutorial. Gregor Schöner, INI, RUB
 Dynamical systems tutorial Gregor Schöner, INI, RUB Dynamical systems: Tutorial the word dynamics time-varying measures range of a quantity forces causing/accounting for movement => dynamical systems dynamical
Dynamical systems tutorial Gregor Schöner, INI, RUB Dynamical systems: Tutorial the word dynamics time-varying measures range of a quantity forces causing/accounting for movement => dynamical systems dynamical
Nonlinear dynamics & chaos BECS
 Nonlinear dynamics & chaos BECS-114.7151 Phase portraits Focus: nonlinear systems in two dimensions General form of a vector field on the phase plane: Vector notation: Phase portraits Solution x(t) describes
Nonlinear dynamics & chaos BECS-114.7151 Phase portraits Focus: nonlinear systems in two dimensions General form of a vector field on the phase plane: Vector notation: Phase portraits Solution x(t) describes
Systems Biology: A Personal View XX. Biological oscillators: Hopf Bifurcation & Glycolysis. Sitabhra Sinha IMSc Chennai
 Systems Biology: A Personal View XX. Biological oscillators: Hopf Bifurcation & Glycolysis Sitabhra Sinha IMSc Chennai www.bio.brandeis.edu Oscillations in the Chlorine dioxide-iodine- Malonic Acid (ClO
Systems Biology: A Personal View XX. Biological oscillators: Hopf Bifurcation & Glycolysis Sitabhra Sinha IMSc Chennai www.bio.brandeis.edu Oscillations in the Chlorine dioxide-iodine- Malonic Acid (ClO
One Dimensional Dynamical Systems
 16 CHAPTER 2 One Dimensional Dynamical Systems We begin by analyzing some dynamical systems with one-dimensional phase spaces, and in particular their bifurcations. All equations in this Chapter are scalar
16 CHAPTER 2 One Dimensional Dynamical Systems We begin by analyzing some dynamical systems with one-dimensional phase spaces, and in particular their bifurcations. All equations in this Chapter are scalar
Non-Linear Dynamics Homework Solutions Week 6
 Non-Linear Dynamics Homework Solutions Week 6 Chris Small March 6, 2007 Please email me at smachr09@evergreen.edu with any questions or concerns reguarding these solutions. 6.8.3 Locate annd find the index
Non-Linear Dynamics Homework Solutions Week 6 Chris Small March 6, 2007 Please email me at smachr09@evergreen.edu with any questions or concerns reguarding these solutions. 6.8.3 Locate annd find the index
Half of Final Exam Name: Practice Problems October 28, 2014
 Math 54. Treibergs Half of Final Exam Name: Practice Problems October 28, 24 Half of the final will be over material since the last midterm exam, such as the practice problems given here. The other half
Math 54. Treibergs Half of Final Exam Name: Practice Problems October 28, 24 Half of the final will be over material since the last midterm exam, such as the practice problems given here. The other half
Poincaré Map, Floquet Theory, and Stability of Periodic Orbits
 Poincaré Map, Floquet Theory, and Stability of Periodic Orbits CDS140A Lecturer: W.S. Koon Fall, 2006 1 Poincaré Maps Definition (Poincaré Map): Consider ẋ = f(x) with periodic solution x(t). Construct
Poincaré Map, Floquet Theory, and Stability of Periodic Orbits CDS140A Lecturer: W.S. Koon Fall, 2006 1 Poincaré Maps Definition (Poincaré Map): Consider ẋ = f(x) with periodic solution x(t). Construct
Solutions to Dynamical Systems 2010 exam. Each question is worth 25 marks.
 Solutions to Dynamical Systems exam Each question is worth marks [Unseen] Consider the following st order differential equation: dy dt Xy yy 4 a Find and classify all the fixed points of Hence draw the
Solutions to Dynamical Systems exam Each question is worth marks [Unseen] Consider the following st order differential equation: dy dt Xy yy 4 a Find and classify all the fixed points of Hence draw the
Problem Set Number 5, j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014)
 Problem Set Number 5, 18.385j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept.,Cambridge, MA 02139) Due Fri., October 24, 2014. October 17, 2014 1 Large µ limit for Liénard system #03 Statement:
Problem Set Number 5, 18.385j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept.,Cambridge, MA 02139) Due Fri., October 24, 2014. October 17, 2014 1 Large µ limit for Liénard system #03 Statement:
Solutions for B8b (Nonlinear Systems) Fake Past Exam (TT 10)
 Solutions for B8b (Nonlinear Systems) Fake Past Exam (TT 10) Mason A. Porter 15/05/2010 1 Question 1 i. (6 points) Define a saddle-node bifurcation and show that the first order system dx dt = r x e x
Solutions for B8b (Nonlinear Systems) Fake Past Exam (TT 10) Mason A. Porter 15/05/2010 1 Question 1 i. (6 points) Define a saddle-node bifurcation and show that the first order system dx dt = r x e x
Limit Cycles II. Prof. Ned Wingreen MOL 410/510. How to prove a closed orbit exists?
 Limit Cycles II Prof. Ned Wingreen MOL 410/510 How to prove a closed orbit eists? numerically Poincaré-Bendison Theorem: If 1. R is a closed, bounded subset of the plane. = f( ) is a continuously differentiable
Limit Cycles II Prof. Ned Wingreen MOL 410/510 How to prove a closed orbit eists? numerically Poincaré-Bendison Theorem: If 1. R is a closed, bounded subset of the plane. = f( ) is a continuously differentiable
8.385 MIT (Rosales) Hopf Bifurcations. 2 Contents Hopf bifurcation for second order scalar equations. 3. Reduction of general phase plane case to seco
 8.385 MIT Hopf Bifurcations. Rodolfo R. Rosales Department of Mathematics Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Massachusetts MA 239 September 25, 999 Abstract In two dimensions a Hopf bifurcation
8.385 MIT Hopf Bifurcations. Rodolfo R. Rosales Department of Mathematics Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Massachusetts MA 239 September 25, 999 Abstract In two dimensions a Hopf bifurcation
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET. EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS. COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD
 CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: January 14, 2019, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Kristian
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: January 14, 2019, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Kristian
Problem List MATH 5173 Spring, 2014
 Problem List MATH 5173 Spring, 2014 The notation p/n means the problem with number n on page p of Perko. 1. 5/3 [Due Wednesday, January 15] 2. 6/5 and describe the relationship of the phase portraits [Due
Problem List MATH 5173 Spring, 2014 The notation p/n means the problem with number n on page p of Perko. 1. 5/3 [Due Wednesday, January 15] 2. 6/5 and describe the relationship of the phase portraits [Due
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7)
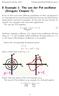 8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
A plane autonomous system is a pair of simultaneous first-order differential equations,
 Chapter 11 Phase-Plane Techniques 11.1 Plane Autonomous Systems A plane autonomous system is a pair of simultaneous first-order differential equations, ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y). This system has an equilibrium
Chapter 11 Phase-Plane Techniques 11.1 Plane Autonomous Systems A plane autonomous system is a pair of simultaneous first-order differential equations, ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y). This system has an equilibrium
Modelling biological oscillations
 Modelling biological oscillations Shan He School for Computational Science University of Birmingham Module 06-23836: Computational Modelling with MATLAB Outline Outline of Topics Van der Pol equation Van
Modelling biological oscillations Shan He School for Computational Science University of Birmingham Module 06-23836: Computational Modelling with MATLAB Outline Outline of Topics Van der Pol equation Van
UNIVERSITY of LIMERICK
 UNIVERSITY of LIMERICK OLLSCOIL LUIMNIGH Faculty of Science and Engineering Department of Mathematics & Statistics END OF SEMESTER ASSESSMENT PAPER MODULE CODE: MS08 SEMESTER: Spring 0 MODULE TITLE: Dynamical
UNIVERSITY of LIMERICK OLLSCOIL LUIMNIGH Faculty of Science and Engineering Department of Mathematics & Statistics END OF SEMESTER ASSESSMENT PAPER MODULE CODE: MS08 SEMESTER: Spring 0 MODULE TITLE: Dynamical
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET. EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS. COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD
 CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: April 06, 2018, at 14 00 18 00 Johanneberg Kristian
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: April 06, 2018, at 14 00 18 00 Johanneberg Kristian
Lotka Volterra Predator-Prey Model with a Predating Scavenger
 Lotka Volterra Predator-Prey Model with a Predating Scavenger Monica Pescitelli Georgia College December 13, 2013 Abstract The classic Lotka Volterra equations are used to model the population dynamics
Lotka Volterra Predator-Prey Model with a Predating Scavenger Monica Pescitelli Georgia College December 13, 2013 Abstract The classic Lotka Volterra equations are used to model the population dynamics
Nonlinear Control Lecture 2:Phase Plane Analysis
 Nonlinear Control Lecture 2:Phase Plane Analysis Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Fall 2009 Farzaneh Abdollahi Nonlinear Control Lecture 2 1/68
Nonlinear Control Lecture 2:Phase Plane Analysis Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Fall 2009 Farzaneh Abdollahi Nonlinear Control Lecture 2 1/68
ME 680- Spring Geometrical Analysis of 1-D Dynamical Systems
 ME 680- Spring 2014 Geometrical Analysis of 1-D Dynamical Systems 1 Geometrical Analysis of 1-D Dynamical Systems Logistic equation: n = rn(1 n) velocity function Equilibria or fied points : initial conditions
ME 680- Spring 2014 Geometrical Analysis of 1-D Dynamical Systems 1 Geometrical Analysis of 1-D Dynamical Systems Logistic equation: n = rn(1 n) velocity function Equilibria or fied points : initial conditions
Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience - Lecture 7. Bifurcations II.
 Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience - Lecture 7. Bifurcations II. Filip Piękniewski Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń, Poland Winter 2009/2010 Filip
Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience - Lecture 7. Bifurcations II. Filip Piękniewski Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń, Poland Winter 2009/2010 Filip
Edward Lorenz. Professor of Meteorology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 The Lorenz system Edward Lorenz Professor of Meteorology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology In 1963 derived a three dimensional system in efforts to model long range predictions for the weather
The Lorenz system Edward Lorenz Professor of Meteorology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology In 1963 derived a three dimensional system in efforts to model long range predictions for the weather
Chapter 6 Nonlinear Systems and Phenomena. Friday, November 2, 12
 Chapter 6 Nonlinear Systems and Phenomena 6.1 Stability and the Phase Plane We now move to nonlinear systems Begin with the first-order system for x(t) d dt x = f(x,t), x(0) = x 0 In particular, consider
Chapter 6 Nonlinear Systems and Phenomena 6.1 Stability and the Phase Plane We now move to nonlinear systems Begin with the first-order system for x(t) d dt x = f(x,t), x(0) = x 0 In particular, consider
Solution to Homework #5 Roy Malka 1. Questions 2,3,4 of Homework #5 of M. Cross class. dv (x) dx
 Solution to Homework #5 Roy Malka. Questions 2,,4 of Homework #5 of M. Cross class. Bifurcations: (M. Cross) Consider the bifurcations of the stationary solutions of a particle undergoing damped one dimensional
Solution to Homework #5 Roy Malka. Questions 2,,4 of Homework #5 of M. Cross class. Bifurcations: (M. Cross) Consider the bifurcations of the stationary solutions of a particle undergoing damped one dimensional
Introduction to Applied Nonlinear Dynamical Systems and Chaos
 Stephen Wiggins Introduction to Applied Nonlinear Dynamical Systems and Chaos Second Edition With 250 Figures 4jj Springer I Series Preface v L I Preface to the Second Edition vii Introduction 1 1 Equilibrium
Stephen Wiggins Introduction to Applied Nonlinear Dynamical Systems and Chaos Second Edition With 250 Figures 4jj Springer I Series Preface v L I Preface to the Second Edition vii Introduction 1 1 Equilibrium
Section 9.3 Phase Plane Portraits (for Planar Systems)
 Section 9.3 Phase Plane Portraits (for Planar Systems) Key Terms: Equilibrium point of planer system yꞌ = Ay o Equilibrium solution Exponential solutions o Half-line solutions Unstable solution Stable
Section 9.3 Phase Plane Portraits (for Planar Systems) Key Terms: Equilibrium point of planer system yꞌ = Ay o Equilibrium solution Exponential solutions o Half-line solutions Unstable solution Stable
Section 5. Graphing Systems
 Section 5. Graphing Systems 5A. The Phase Plane 5A-1. Find the critical points of each of the following non-linear autonomous systems. x = x 2 y 2 x = 1 x + y a) b) y = x xy y = y + 2x 2 5A-2. Write each
Section 5. Graphing Systems 5A. The Phase Plane 5A-1. Find the critical points of each of the following non-linear autonomous systems. x = x 2 y 2 x = 1 x + y a) b) y = x xy y = y + 2x 2 5A-2. Write each
BIFURCATION PHENOMENA Lecture 1: Qualitative theory of planar ODEs
 BIFURCATION PHENOMENA Lecture 1: Qualitative theory of planar ODEs Yuri A. Kuznetsov August, 2010 Contents 1. Solutions and orbits. 2. Equilibria. 3. Periodic orbits and limit cycles. 4. Homoclinic orbits.
BIFURCATION PHENOMENA Lecture 1: Qualitative theory of planar ODEs Yuri A. Kuznetsov August, 2010 Contents 1. Solutions and orbits. 2. Equilibria. 3. Periodic orbits and limit cycles. 4. Homoclinic orbits.
Nonlinear Autonomous Systems of Differential
 Chapter 4 Nonlinear Autonomous Systems of Differential Equations 4.0 The Phase Plane: Linear Systems 4.0.1 Introduction Consider a system of the form x = A(x), (4.0.1) where A is independent of t. Such
Chapter 4 Nonlinear Autonomous Systems of Differential Equations 4.0 The Phase Plane: Linear Systems 4.0.1 Introduction Consider a system of the form x = A(x), (4.0.1) where A is independent of t. Such
ENGI Duffing s Equation Page 4.65
 ENGI 940 4. - Duffing s Equation Page 4.65 4. Duffing s Equation Among the simplest models of damped non-linear forced oscillations of a mechanical or electrical system with a cubic stiffness term is Duffing
ENGI 940 4. - Duffing s Equation Page 4.65 4. Duffing s Equation Among the simplest models of damped non-linear forced oscillations of a mechanical or electrical system with a cubic stiffness term is Duffing
Contents lecture 6 2(17) Automatic Control III. Summary of lecture 5 (I/III) 3(17) Summary of lecture 5 (II/III) 4(17) H 2, H synthesis pros and cons:
 Contents lecture 6 (7) Automatic Control III Lecture 6 Linearization and phase portraits. Summary of lecture 5 Thomas Schön Division of Systems and Control Department of Information Technology Uppsala
Contents lecture 6 (7) Automatic Control III Lecture 6 Linearization and phase portraits. Summary of lecture 5 Thomas Schön Division of Systems and Control Department of Information Technology Uppsala
Section 5.4 (Systems of Linear Differential Equation); 9.5 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors, cont d
 Section 5.4 (Systems of Linear Differential Equation); 9.5 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors, cont d July 6, 2009 Today s Session Today s Session A Summary of This Session: Today s Session A Summary of This
Section 5.4 (Systems of Linear Differential Equation); 9.5 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors, cont d July 6, 2009 Today s Session Today s Session A Summary of This Session: Today s Session A Summary of This
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems
 B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 5. Global Bifurcations, Homoclinic chaos, Melnikov s method Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Motivation 1.1 The problem 1.2 A
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 5. Global Bifurcations, Homoclinic chaos, Melnikov s method Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Motivation 1.1 The problem 1.2 A
Math 266: Phase Plane Portrait
 Math 266: Phase Plane Portrait Long Jin Purdue, Spring 2018 Review: Phase line for an autonomous equation For a single autonomous equation y = f (y) we used a phase line to illustrate the equilibrium solutions
Math 266: Phase Plane Portrait Long Jin Purdue, Spring 2018 Review: Phase line for an autonomous equation For a single autonomous equation y = f (y) we used a phase line to illustrate the equilibrium solutions
Chaos. Lendert Gelens. KU Leuven - Vrije Universiteit Brussel Nonlinear dynamics course - VUB
 Chaos Lendert Gelens KU Leuven - Vrije Universiteit Brussel www.gelenslab.org Nonlinear dynamics course - VUB Examples of chaotic systems: the double pendulum? θ 1 θ θ 2 Examples of chaotic systems: the
Chaos Lendert Gelens KU Leuven - Vrije Universiteit Brussel www.gelenslab.org Nonlinear dynamics course - VUB Examples of chaotic systems: the double pendulum? θ 1 θ θ 2 Examples of chaotic systems: the
Nonlinear systems, chaos and control in Engineering
 Nonlinear systems, chaos and control in Engineering Module 1 block 3 One-dimensional nonlinear systems Cristina Masoller Cristina.masoller@upc.edu http://www.fisica.edu.uy/~cris/ Schedule Flows on the
Nonlinear systems, chaos and control in Engineering Module 1 block 3 One-dimensional nonlinear systems Cristina Masoller Cristina.masoller@upc.edu http://www.fisica.edu.uy/~cris/ Schedule Flows on the
Dynamics and Bifurcations in Predator-Prey Models with Refuge, Dispersal and Threshold Harvesting
 Dynamics and Bifurcations in Predator-Prey Models with Refuge, Dispersal and Threshold Harvesting August 2012 Overview Last Model ẋ = αx(1 x) a(1 m)xy 1+c(1 m)x H(x) ẏ = dy + b(1 m)xy 1+c(1 m)x (1) where
Dynamics and Bifurcations in Predator-Prey Models with Refuge, Dispersal and Threshold Harvesting August 2012 Overview Last Model ẋ = αx(1 x) a(1 m)xy 1+c(1 m)x H(x) ẏ = dy + b(1 m)xy 1+c(1 m)x (1) where
Lecture - 11 Bendixson and Poincare Bendixson Criteria Van der Pol Oscillator
 Nonlinear Dynamical Systems Prof. Madhu. N. Belur and Prof. Harish. K. Pillai Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 11 Bendixson and Poincare Bendixson Criteria
Nonlinear Dynamical Systems Prof. Madhu. N. Belur and Prof. Harish. K. Pillai Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 11 Bendixson and Poincare Bendixson Criteria
nonlinear oscillators. method of averaging
 Physics 4 Spring 7 nonlinear oscillators. method of averaging lecture notes, spring semester 7 http://www.phys.uconn.edu/ rozman/courses/p4_7s/ Last modified: April, 7 Oscillator with nonlinear friction
Physics 4 Spring 7 nonlinear oscillators. method of averaging lecture notes, spring semester 7 http://www.phys.uconn.edu/ rozman/courses/p4_7s/ Last modified: April, 7 Oscillator with nonlinear friction
Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos
 Ian Eisenman eisenman@fas.harvard.edu Geological Museum 101, 6-6352 Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos Review of some of the topics covered in homework problems, based on section notes. December, 2005 Contents
Ian Eisenman eisenman@fas.harvard.edu Geological Museum 101, 6-6352 Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos Review of some of the topics covered in homework problems, based on section notes. December, 2005 Contents
3 Stability and Lyapunov Functions
 CDS140a Nonlinear Systems: Local Theory 02/01/2011 3 Stability and Lyapunov Functions 3.1 Lyapunov Stability Denition: An equilibrium point x 0 of (1) is stable if for all ɛ > 0, there exists a δ > 0 such
CDS140a Nonlinear Systems: Local Theory 02/01/2011 3 Stability and Lyapunov Functions 3.1 Lyapunov Stability Denition: An equilibrium point x 0 of (1) is stable if for all ɛ > 0, there exists a δ > 0 such
Feedback-mediated oscillatory coexistence in the chemostat
 Feedback-mediated oscillatory coexistence in the chemostat Patrick De Leenheer and Sergei S. Pilyugin Department of Mathematics, University of Florida deleenhe,pilyugin@math.ufl.edu 1 Introduction We study
Feedback-mediated oscillatory coexistence in the chemostat Patrick De Leenheer and Sergei S. Pilyugin Department of Mathematics, University of Florida deleenhe,pilyugin@math.ufl.edu 1 Introduction We study
APPPHYS217 Tuesday 25 May 2010
 APPPHYS7 Tuesday 5 May Our aim today is to take a brief tour of some topics in nonlinear dynamics. Some good references include: [Perko] Lawrence Perko Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems (Springer-Verlag
APPPHYS7 Tuesday 5 May Our aim today is to take a brief tour of some topics in nonlinear dynamics. Some good references include: [Perko] Lawrence Perko Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems (Springer-Verlag
Difference Resonances in a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator involving time. delay
 Difference Resonances in a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator involving time delay This paper was published in the journal Chaos, Solitions & Fractals, vol.4, no., pp.975-98, Oct 9 J.C. Ji, N. Zhang,
Difference Resonances in a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator involving time delay This paper was published in the journal Chaos, Solitions & Fractals, vol.4, no., pp.975-98, Oct 9 J.C. Ji, N. Zhang,
MCE693/793: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems
 MCE693/793: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems Lyapunov Stability - I Hanz Richter Mechanical Engineering Department Cleveland State University Definition of Stability - Lyapunov Sense Lyapunov
MCE693/793: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems Lyapunov Stability - I Hanz Richter Mechanical Engineering Department Cleveland State University Definition of Stability - Lyapunov Sense Lyapunov
The Higgins-Selkov oscillator
 The Higgins-Selkov oscillator May 14, 2014 Here I analyse the long-time behaviour of the Higgins-Selkov oscillator. The system is ẋ = k 0 k 1 xy 2, (1 ẏ = k 1 xy 2 k 2 y. (2 The unknowns x and y, being
The Higgins-Selkov oscillator May 14, 2014 Here I analyse the long-time behaviour of the Higgins-Selkov oscillator. The system is ẋ = k 0 k 1 xy 2, (1 ẏ = k 1 xy 2 k 2 y. (2 The unknowns x and y, being
Bifurcation and Stability Analysis of a Prey-predator System with a Reserved Area
 ISSN 746-733, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 8 ( No. 4, pp. 85-9 Bifurcation and Stability Analysis of a Prey-predator System with a Reserved Area Debasis Mukherjee Department
ISSN 746-733, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 8 ( No. 4, pp. 85-9 Bifurcation and Stability Analysis of a Prey-predator System with a Reserved Area Debasis Mukherjee Department
Lecture 3. Dynamical Systems in Continuous Time
 Lecture 3. Dynamical Systems in Continuous Time University of British Columbia, Vancouver Yue-Xian Li November 2, 2017 1 3.1 Exponential growth and decay A Population With Generation Overlap Consider a
Lecture 3. Dynamical Systems in Continuous Time University of British Columbia, Vancouver Yue-Xian Li November 2, 2017 1 3.1 Exponential growth and decay A Population With Generation Overlap Consider a
2D-Volterra-Lotka Modeling For 2 Species
 Majalat Al-Ulum Al-Insaniya wat - Tatbiqiya 2D-Volterra-Lotka Modeling For 2 Species Alhashmi Darah 1 University of Almergeb Department of Mathematics Faculty of Science Zliten Libya. Abstract The purpose
Majalat Al-Ulum Al-Insaniya wat - Tatbiqiya 2D-Volterra-Lotka Modeling For 2 Species Alhashmi Darah 1 University of Almergeb Department of Mathematics Faculty of Science Zliten Libya. Abstract The purpose
Computer Problems for Methods of Solving Ordinary Differential Equations
 Computer Problems for Methods of Solving Ordinary Differential Equations 1. Have a computer make a phase portrait for the system dx/dt = x + y, dy/dt = 2y. Clearly indicate critical points and separatrices.
Computer Problems for Methods of Solving Ordinary Differential Equations 1. Have a computer make a phase portrait for the system dx/dt = x + y, dy/dt = 2y. Clearly indicate critical points and separatrices.
Math 345 Intro to Math Biology Lecture 7: Models of System of Nonlinear Difference Equations
 Math 345 Intro to Math Biology Lecture 7: Models of System of Nonlinear Difference Equations Junping Shi College of William and Mary, USA Equilibrium Model: x n+1 = f (x n ), here f is a nonlinear function
Math 345 Intro to Math Biology Lecture 7: Models of System of Nonlinear Difference Equations Junping Shi College of William and Mary, USA Equilibrium Model: x n+1 = f (x n ), here f is a nonlinear function
APPM 2360: Final Exam 10:30am 1:00pm, May 6, 2015.
 APPM 23: Final Exam :3am :pm, May, 25. ON THE FRONT OF YOUR BLUEBOOK write: ) your name, 2) your student ID number, 3) lecture section, 4) your instructor s name, and 5) a grading table for eight questions.
APPM 23: Final Exam :3am :pm, May, 25. ON THE FRONT OF YOUR BLUEBOOK write: ) your name, 2) your student ID number, 3) lecture section, 4) your instructor s name, and 5) a grading table for eight questions.
22.2. Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors 22.2 Introduction Many applications of matrices in both engineering and science utilize eigenvalues and, sometimes, eigenvectors. Control theory, vibration
Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors 22.2 Introduction Many applications of matrices in both engineering and science utilize eigenvalues and, sometimes, eigenvectors. Control theory, vibration
Linear and Nonlinear Oscillators (Lecture 2)
 Linear and Nonlinear Oscillators (Lecture 2) January 25, 2016 7/441 Lecture outline A simple model of a linear oscillator lies in the foundation of many physical phenomena in accelerator dynamics. A typical
Linear and Nonlinear Oscillators (Lecture 2) January 25, 2016 7/441 Lecture outline A simple model of a linear oscillator lies in the foundation of many physical phenomena in accelerator dynamics. A typical
MAS212 Scientific Computing and Simulation
 MAS212 Scientific Computing and Simulation Dr. Sam Dolan School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Sheffield Autumn 2017 http://sam-dolan.staff.shef.ac.uk/mas212/ G18 Hicks Building s.dolan@sheffield.ac.uk
MAS212 Scientific Computing and Simulation Dr. Sam Dolan School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Sheffield Autumn 2017 http://sam-dolan.staff.shef.ac.uk/mas212/ G18 Hicks Building s.dolan@sheffield.ac.uk
Mathematical Model of Forced Van Der Pol s Equation
 Mathematical Model of Forced Van Der Pol s Equation TO Tsz Lok Wallace LEE Tsz Hong Homer December 9, Abstract This work is going to analyze the Forced Van Der Pol s Equation which is used to analyze the
Mathematical Model of Forced Van Der Pol s Equation TO Tsz Lok Wallace LEE Tsz Hong Homer December 9, Abstract This work is going to analyze the Forced Van Der Pol s Equation which is used to analyze the
CONTROLLING IN BETWEEN THE LORENZ AND THE CHEN SYSTEMS
 International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol. 12, No. 6 (22) 1417 1422 c World Scientific Publishing Company CONTROLLING IN BETWEEN THE LORENZ AND THE CHEN SYSTEMS JINHU LÜ Institute of Systems
International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol. 12, No. 6 (22) 1417 1422 c World Scientific Publishing Company CONTROLLING IN BETWEEN THE LORENZ AND THE CHEN SYSTEMS JINHU LÜ Institute of Systems
Chapter 4. Systems of ODEs. Phase Plane. Qualitative Methods
 Chapter 4 Systems of ODEs. Phase Plane. Qualitative Methods Contents 4.0 Basics of Matrices and Vectors 4.1 Systems of ODEs as Models 4.2 Basic Theory of Systems of ODEs 4.3 Constant-Coefficient Systems.
Chapter 4 Systems of ODEs. Phase Plane. Qualitative Methods Contents 4.0 Basics of Matrices and Vectors 4.1 Systems of ODEs as Models 4.2 Basic Theory of Systems of ODEs 4.3 Constant-Coefficient Systems.
Chapter #4 EEE8086-EEE8115. Robust and Adaptive Control Systems
 Chapter #4 Robust and Adaptive Control Systems Nonlinear Dynamics.... Linear Combination.... Equilibrium points... 3 3. Linearisation... 5 4. Limit cycles... 3 5. Bifurcations... 4 6. Stability... 6 7.
Chapter #4 Robust and Adaptive Control Systems Nonlinear Dynamics.... Linear Combination.... Equilibrium points... 3 3. Linearisation... 5 4. Limit cycles... 3 5. Bifurcations... 4 6. Stability... 6 7.
Math 232, Final Test, 20 March 2007
 Math 232, Final Test, 20 March 2007 Name: Instructions. Do any five of the first six questions, and any five of the last six questions. Please do your best, and show all appropriate details in your solutions.
Math 232, Final Test, 20 March 2007 Name: Instructions. Do any five of the first six questions, and any five of the last six questions. Please do your best, and show all appropriate details in your solutions.
MCE693/793: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems
 MCE693/793: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems Systems of Differential Equations Phase Plane Analysis Hanz Richter Mechanical Engineering Department Cleveland State University Systems of Nonlinear
MCE693/793: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems Systems of Differential Equations Phase Plane Analysis Hanz Richter Mechanical Engineering Department Cleveland State University Systems of Nonlinear
Numerical techniques: Deterministic Dynamical Systems
 Numerical techniques: Deterministic Dynamical Systems Henk Dijkstra Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Utrecht, The Netherlands Transition behavior
Numerical techniques: Deterministic Dynamical Systems Henk Dijkstra Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Utrecht, The Netherlands Transition behavior
Chapter 1, Section 1.2, Example 9 (page 13) and Exercise 29 (page 15). Use the Uniqueness Tool. Select the option ẋ = x
 Use of Tools from Interactive Differential Equations with the texts Fundamentals of Differential Equations, 5th edition and Fundamentals of Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems, 3rd edition
Use of Tools from Interactive Differential Equations with the texts Fundamentals of Differential Equations, 5th edition and Fundamentals of Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems, 3rd edition
Clearly the passage of an eigenvalue through to the positive real half plane leads to a qualitative change in the phase portrait, i.e.
 Bifurcations We have already seen how the loss of stiffness in a linear oscillator leads to instability. In a practical situation the stiffness may not degrade in a linear fashion, and instability may
Bifurcations We have already seen how the loss of stiffness in a linear oscillator leads to instability. In a practical situation the stiffness may not degrade in a linear fashion, and instability may
Dynamical Systems & Lyapunov Stability
 Dynamical Systems & Lyapunov Stability Harry G. Kwatny Department of Mechanical Engineering & Mechanics Drexel University Outline Ordinary Differential Equations Existence & uniqueness Continuous dependence
Dynamical Systems & Lyapunov Stability Harry G. Kwatny Department of Mechanical Engineering & Mechanics Drexel University Outline Ordinary Differential Equations Existence & uniqueness Continuous dependence
PHY411 Lecture notes Part 4
 PHY411 Lecture notes Part 4 Alice Quillen February 1, 2016 Contents 0.1 Introduction.................................... 2 1 Bifurcations of one-dimensional dynamical systems 2 1.1 Saddle-node bifurcation.............................
PHY411 Lecture notes Part 4 Alice Quillen February 1, 2016 Contents 0.1 Introduction.................................... 2 1 Bifurcations of one-dimensional dynamical systems 2 1.1 Saddle-node bifurcation.............................
arxiv: v1 [nlin.ao] 19 May 2017
![arxiv: v1 [nlin.ao] 19 May 2017 arxiv: v1 [nlin.ao] 19 May 2017](/thumbs/74/70757831.jpg) Feature-rich bifurcations in a simple electronic circuit Debdipta Goswami 1, and Subhankar Ray 2, 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742, USA
Feature-rich bifurcations in a simple electronic circuit Debdipta Goswami 1, and Subhankar Ray 2, 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742, USA
Additive resonances of a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator
 Additive resonances of a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator This paper has been published in Journal of Sound and Vibration vol. 5 issue - 8 pp.-. J.C. Ji N. Zhang Faculty of Engineering University
Additive resonances of a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator This paper has been published in Journal of Sound and Vibration vol. 5 issue - 8 pp.-. J.C. Ji N. Zhang Faculty of Engineering University
