Work and Energy. Sample Problem Set I Solutions ADDITIONAL PRACTICE E. Holt McDougal Physics i Sample Problem Set I
|
|
|
- Leo Goodwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sample Problem Set I Solutions Work and Energy ADDITIONAL PRACTICE E Holt McDougal Physics i Sample Problem Set I
2 Work and Energy continue Holt McDougal Physics ii Sample Problem Set I
3 Work and Energy Problem E CONSERVATION OF MECHANICAL ENERGY PROBLEM The largest apple ever grown had a mass of about 1.47 kg. Suppose you hold such an apple in your hand. You accidentally drop the apple, then manage to catch it just before it hits the ground. If the speed of the apple at that moment is 5.42 m/s, what is the kinetic energy of the apple? From what height did you drop it? SOLUTION 1. DEFINE Given: m = 1.47 kg g = 9.81 m/s 2 v = 5.42 m/s Unknown: KE =? h =? 2. PLAN Choose the equation(s) or situation: Use the equations for kinetic and gravitational potential energy. KE = 1 2 mv2 PE g = mgh The zero level for gravitational potential energy is the ground. Because the apple ends its fall at the zero level, the final gravitational potential energy is zero. PE g,f = 0 The initial gravitational potential energy is measured at the point from which the apple is released. PE g,i = mgh The apple is initially at rest, so the initial kinetic energy is zero. KE i = 0 The final kinetic energy is therefore: KE f = 1 2 mv2 3. CALCULATE Substitute the values into the equation(s) and solve: PE g,i = (1.47 kg)(9.81 m s 2 )h KE f = 1 2 (1.47 kg) 5.42 m 2 s Solving for KE yields the following result: KE = KE f = 1 2 (1.47 kg) 5.42 m 2 = 21.6 J s Holt McDougal Physics 1 Sample Problem Set I
4 Now use the principle of conservation for mechanical energy and the calculated quantity for KE f to evaluate h. ME i = ME f PE i + KE i = PE f + KE f PE i + 0 J = 0 J J mgh = 21.6 J 21.6 J h = (1.47 kg) 9.81 m = 1.50 m s 2 4. EVALUATE Note that the height of the apple can be determined without knowing the apple s mass. This is because the conservation equation reduces to the equation relating speed, acceleration, and displacement: v 2 = 2gh. ADDITIONAL PRACTICE 1. The largest watermelon ever grown had a mass of 118 kg. Suppose this watermelon were exhibited on a platform 5.00 m above the ground. After the exhibition, the watermelon is allowed to slide along to the ground along a smooth ramp. How high above the ground is the watermelon at the moment its kinetic energy is 4.61 kj? 2. One species of eucalyptus tree, Eucalyptus regnens, grows to heights similar to those attained by California redwoods. Suppose a bird sitting on top of one specimen of eucalyptus tree drops a nut. If the speed of the falling nut at the moment it is 50.0 m above the ground is 42.7 m/s, how tall is the tree? Do you need to know the mass of the nut to solve this problem? Disregard air resistance. 3. In 1989, Michel Menin of France walked on a tightrope suspended under a balloon nearly at an altitude of 3150 m above the ground. Suppose a coin falls from Menin s pocket during his walk. How high above the ground is the coin when its speed is 60.0 m/s? 4. In 1936, Col. Harry Froboess of Switzerland jumped into the ocean from the airship Graf Hindenburg, which was m above the water s surface. Assuming Froboess had a mass of 72.0 kg, what was his kinetic energy at the moment he was 30.0 m from the water s surface? What was his speed at that moment? Neglect the air resistance. 5. Suppose a motorcyclist rides a certain high-speed motorcycle. He reaches top speed and then coasts up a hill. The maximum height reached by the motorcyclist is m. If J of kinetic energy is dissipated by friction, what was the initial speed of the motorcycle? The combined mass of the motorcycle and motorcyclist is kg. Holt McDougal Physics 2 Sample Problem Set I
5 6. The deepest mine ever drilled has a depth of 12.3 km (by contrast, Mount Everest has height of 8.8 km). Suppose you drop a rock with a mass of g down the shaft of this mine. What would the rock s kinetic energy be after falling 3.2 km? What would the potential energy associated with the rock be at that same moment? Assume no air resistance and a constant free-fall acceleration. 7. Desperado, a roller coaster built in Nevada, has a vertical drop of 68.6 m. The roller coaster is designed so that the speed of the cars at the end of this drop is 35.6 m/s. Assume the cars are at rest at the start of the drop. What percent of the initial mechanical energy is dissipated by friction? Holt McDougal Physics 3 Sample Problem Set I
KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY. Chapter 6 (cont.)
 KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY Chapter 6 (cont.) The Two Types of Mechanical Energy Energy- the ability to do work- measured in joules Potential Energy- energy that arises because of an object s position
KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY Chapter 6 (cont.) The Two Types of Mechanical Energy Energy- the ability to do work- measured in joules Potential Energy- energy that arises because of an object s position
Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy
 Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy Level : Conceptual Physics Teacher : Kim Kinetic Energy (K) If an object is in motion, it has the energy of motion, or kinetic energy. The kinetic
Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy Level : Conceptual Physics Teacher : Kim Kinetic Energy (K) If an object is in motion, it has the energy of motion, or kinetic energy. The kinetic
5.3. Conservation of Energy
 5.3. Conservation of Energy Conservation of Energy Energy is never created or destroyed. Any time work is done, it is only transformed from one form to another: Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Gravitational,
5.3. Conservation of Energy Conservation of Energy Energy is never created or destroyed. Any time work is done, it is only transformed from one form to another: Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Gravitational,
Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy
 Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy Level : Physics I Teacher : Kim Work and Change in Energy If we rearrange the Work-Kinetic Energy theorem as follows K i +Fcosφ d = K f => Fcosφ d = K f - K i
Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy Level : Physics I Teacher : Kim Work and Change in Energy If we rearrange the Work-Kinetic Energy theorem as follows K i +Fcosφ d = K f => Fcosφ d = K f - K i
WEP-Energy. 2. If the speed of a car is doubled, the kinetic energy of the car is 1. quadrupled 2. quartered 3. doubled 4. halved
 1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
Honor Physics Final Exam Review. What is the difference between series, parallel, and combination circuits?
 Name Period Date Honor Physics Final Exam Review Circuits You should be able to: Calculate the total (net) resistance of a circuit. Calculate current in individual resistors and the total circuit current.
Name Period Date Honor Physics Final Exam Review Circuits You should be able to: Calculate the total (net) resistance of a circuit. Calculate current in individual resistors and the total circuit current.
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy Physics
 Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy Physics Work and Change in Energy If we rearrange the Work-Kinetic Energy theorem as follows Ki +Fcosφ d = Kf => Fcosφ d = Kf - Ki => Fcosφ d = K => Ki + ΣΣW =
Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy Physics Work and Change in Energy If we rearrange the Work-Kinetic Energy theorem as follows Ki +Fcosφ d = Kf => Fcosφ d = Kf - Ki => Fcosφ d = K => Ki + ΣΣW =
Question 8.1 Sign of the Energy II
 Question 8. Sign of the Energy II Is it possible for the gravitational potential energy of an object to be negative? a) yes b) no Question 8. Sign of the Energy II Is it possible for the gravitational
Question 8. Sign of the Energy II Is it possible for the gravitational potential energy of an object to be negative? a) yes b) no Question 8. Sign of the Energy II Is it possible for the gravitational
How does the total energy of the cart change as it goes down the inclined plane?
 Experiment 6 Conservation of Energy and the Work-Energy Theorem In this experiment you will explore the principle of conservation of mechanical energy. You will see that gravitational energy can be converted
Experiment 6 Conservation of Energy and the Work-Energy Theorem In this experiment you will explore the principle of conservation of mechanical energy. You will see that gravitational energy can be converted
Slide 1 / 113. Slide 2 / th Grade. Energy of Objects in Motion Classwork-Homework Slide 3 / 113. Classwork #1: Energy
 Slide 1 / 113 Slide 2 / 113 8th Grade Energy of Objects in Motion Classwork-Homework 2015-08-25 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 113 Classwork #1: Energy 1 Define Energy. Slide 4 / 113 2 What two things are necessary
Slide 1 / 113 Slide 2 / 113 8th Grade Energy of Objects in Motion Classwork-Homework 2015-08-25 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 113 Classwork #1: Energy 1 Define Energy. Slide 4 / 113 2 What two things are necessary
Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 2
 Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 1 3 problems from exam 2 6 problems 13.1 14.6 (including 14.5) 8 problems 1.1---9.6 Go through the
Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 1 3 problems from exam 2 6 problems 13.1 14.6 (including 14.5) 8 problems 1.1---9.6 Go through the
2. What would happen to his acceleration if his speed were half? Energy The ability to do work
 1. A 40 kilogram boy is traveling around a carousel with radius 0.5 meters at a constant speed of 1.7 meters per second. Calculate his centripetal acceleration. 2. What would happen to his acceleration
1. A 40 kilogram boy is traveling around a carousel with radius 0.5 meters at a constant speed of 1.7 meters per second. Calculate his centripetal acceleration. 2. What would happen to his acceleration
Student Exploration: Roller Coaster Physics
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Roller Coaster Physics Vocabulary: friction, gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy, momentum, velocity Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Roller Coaster Physics Vocabulary: friction, gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy, momentum, velocity Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
Conservation of Energy
 Lecture 3 Chapter 8 Physics I 03.0.04 Conservation of Energy Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physicsspring.html
Lecture 3 Chapter 8 Physics I 03.0.04 Conservation of Energy Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physicsspring.html
Ch 11 ENERGY and its CONSERVATION. work causes a change in the energy of a system KE (an increase or decrease in KE) ket.
 Ch 11 ENERGY and its CONSERVATION 11.1 The Many Forms of Energy work causes a change in the energy of a system W = KE (an increase or decrease in KE) work energy theorem object + work object work increase
Ch 11 ENERGY and its CONSERVATION 11.1 The Many Forms of Energy work causes a change in the energy of a system W = KE (an increase or decrease in KE) work energy theorem object + work object work increase
Potential and Kinetic Energy
 Potential and Kinetic Energy VELOCITY Velocity is a measure of how fast an object is traveling in a certain direction. Example: A bus traveling North at 150 m/s Example: A car is traveling 45 mph South.
Potential and Kinetic Energy VELOCITY Velocity is a measure of how fast an object is traveling in a certain direction. Example: A bus traveling North at 150 m/s Example: A car is traveling 45 mph South.
Multiple Choice Practice
 Class: Date: Multiple Choice Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An ice skater moving at 10.0 m/s coasts to a halt in 1.0 10 2 m on
Class: Date: Multiple Choice Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An ice skater moving at 10.0 m/s coasts to a halt in 1.0 10 2 m on
Lecture 5. Work Energy
 Lecture 5 Work Energy Work, Energy Work and energy are fundamental physical quantities in science. Work is done when a force moves an object through a distance. Energy is the ability to do work The unit
Lecture 5 Work Energy Work, Energy Work and energy are fundamental physical quantities in science. Work is done when a force moves an object through a distance. Energy is the ability to do work The unit
Physics 201, Midterm Exam 2, Fall Answer Key
 Physics 201, Midterm Exam 2, Fall 2006 Answer Key 1) A constant force is applied to a body that is already moving. The force is directed at an angle of 60 degrees to the direction of the body s velocity.
Physics 201, Midterm Exam 2, Fall 2006 Answer Key 1) A constant force is applied to a body that is already moving. The force is directed at an angle of 60 degrees to the direction of the body s velocity.
Name. Honors Physics AND POTENTIAL KINETIC
 KINETIC Name Honors Physics AND POTENTIAL Name Period Work and Energy Intro questions Read chapter 9 pages 144 146 (Section 9.1) 1. Define work in terms of physics? 2. In order to do work on an object,
KINETIC Name Honors Physics AND POTENTIAL Name Period Work and Energy Intro questions Read chapter 9 pages 144 146 (Section 9.1) 1. Define work in terms of physics? 2. In order to do work on an object,
The Story of Energy. Forms and Functions
 The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
Ch 5 Work and Energy
 Ch 5 Work and Energy Energy Provide a different (scalar) approach to solving some physics problems. Work Links the energy approach to the force (Newton s Laws) approach. Mechanical energy Kinetic energy
Ch 5 Work and Energy Energy Provide a different (scalar) approach to solving some physics problems. Work Links the energy approach to the force (Newton s Laws) approach. Mechanical energy Kinetic energy
MECHANICAL (TOTAL) ENERGY
 DO NOW: 1/19 If you haven t already, please take the short google form survey posted on Edmodo Please turn in your Work done by friction Lab in the top tray POTENTIAL ENERGY Stored energy An object that
DO NOW: 1/19 If you haven t already, please take the short google form survey posted on Edmodo Please turn in your Work done by friction Lab in the top tray POTENTIAL ENERGY Stored energy An object that
(A) 10 m (B) 20 m (C) 25 m (D) 30 m (E) 40 m
 PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
Name Class Date. In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 Assessment Chapter Test A ork and Energy MULTIPLE CHOICE In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. In which of the
Assessment Chapter Test A ork and Energy MULTIPLE CHOICE In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. In which of the
Today: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy. No Recitation Quiz this week
 Today: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy HW #4 due Thursday, 11:59 p.m. pm No Recitation Quiz this week 1 What is Energy? Mechanical Electromagnetic PHY 11 PHY 13 Chemical CHE 105 Nuclear PHY 555
Today: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy HW #4 due Thursday, 11:59 p.m. pm No Recitation Quiz this week 1 What is Energy? Mechanical Electromagnetic PHY 11 PHY 13 Chemical CHE 105 Nuclear PHY 555
The Story of Energy. Forms and Functions
 The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
CHAPTER 13.3 AND 13.4 ENERGY
 CHAPTER 13.3 AND 13.4 ENERGY Section 13.3 Energy Objective 1: What is the relationship between energy and work? Objective 2: Identify the energy of position. Objective 3: The factors that kinetic energy
CHAPTER 13.3 AND 13.4 ENERGY Section 13.3 Energy Objective 1: What is the relationship between energy and work? Objective 2: Identify the energy of position. Objective 3: The factors that kinetic energy
In an avalanche, a mass of loose snow, soil, or rock suddenly gives way and slides down the side of a mountain.
 ENERGY Energy Objective 1: What is the relationship between energy and work? Objective 2: Identify the energy of position. Objective 3: The factors that kinetic energy depends on Objective 4: What is non-mechanical
ENERGY Energy Objective 1: What is the relationship between energy and work? Objective 2: Identify the energy of position. Objective 3: The factors that kinetic energy depends on Objective 4: What is non-mechanical
Circular Orbits. Slide Pearson Education, Inc.
 Circular Orbits The figure shows a perfectly smooth, spherical, airless planet with one tower of height h. A projectile is launched parallel to the ground with speed v 0. If v 0 is very small, as in trajectory
Circular Orbits The figure shows a perfectly smooth, spherical, airless planet with one tower of height h. A projectile is launched parallel to the ground with speed v 0. If v 0 is very small, as in trajectory
At what point is the potential energy the highest for a pendulum? A) Potential energy is unrelated to height B) At the end of its path (1 & 5) C) At
 At what point is the potential energy the highest for a pendulum? A) Potential energy is unrelated to height B) At the end of its path (1 & 5) C) At the middle of its path (2 & 4) D) At the bottom of its
At what point is the potential energy the highest for a pendulum? A) Potential energy is unrelated to height B) At the end of its path (1 & 5) C) At the middle of its path (2 & 4) D) At the bottom of its
Work changes Energy. Do Work Son!
 1 Work changes Energy Do Work Son! 2 Do Work Son! 3 Work Energy Relationship 2 types of energy kinetic : energy of an object in motion potential: stored energy due to position or stored in a spring Work
1 Work changes Energy Do Work Son! 2 Do Work Son! 3 Work Energy Relationship 2 types of energy kinetic : energy of an object in motion potential: stored energy due to position or stored in a spring Work
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
2 possibilities. 2.) Work is done and... 1.) Work is done and... *** The function of work is to change energy ***
 Work-Energy Theorem and Energy Conservation *** The function of work is to change energy *** 2 possibilities 1.) Work is done and... or 2.) Work is done and... 1 EX: A 100 N box is 10 m above the ground
Work-Energy Theorem and Energy Conservation *** The function of work is to change energy *** 2 possibilities 1.) Work is done and... or 2.) Work is done and... 1 EX: A 100 N box is 10 m above the ground
Forces and two masses.
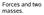 Forces and two masses. Atwood's Machine frictionless, massless pulley +a +a M 1 M 2 Atwood's Machine frictionless, massless pulley +a T +a m 1 a=t m 1 g 1 M 1 M 2 T m 2 a=m 2 g T 2 w 1 =m 1 g w 2 =m 2
Forces and two masses. Atwood's Machine frictionless, massless pulley +a +a M 1 M 2 Atwood's Machine frictionless, massless pulley +a T +a m 1 a=t m 1 g 1 M 1 M 2 T m 2 a=m 2 g T 2 w 1 =m 1 g w 2 =m 2
Lecture 10 Mechanical Energy Conservation; Power
 Potential energy Basic energy Lecture 10 Mechanical Energy Conservation; Power ACT: Zero net work The system of pulleys shown below is used to lift a bag of mass M at constant speed a distance h from the
Potential energy Basic energy Lecture 10 Mechanical Energy Conservation; Power ACT: Zero net work The system of pulleys shown below is used to lift a bag of mass M at constant speed a distance h from the
Chapter 7. The Conservation of Energy
 Chapter 7 The Conservation of Energy Consider an object dropped near the surface of the earth. If the distance is small then the gravitational force between the earth and the object will be nearly constant.
Chapter 7 The Conservation of Energy Consider an object dropped near the surface of the earth. If the distance is small then the gravitational force between the earth and the object will be nearly constant.
Section 1: Work, Power, and Machines. Preview Key Ideas Bellringer What Is Work? Math Skills Power Machines and Mechanical Advantage
 Section 1 Section 1: Work, Power, and Machines Preview Key Ideas Bellringer What Is Work? Math Skills Power Machines and Mechanical Advantage Section 1 Key Ideas How is work calculated? What is the relationship
Section 1 Section 1: Work, Power, and Machines Preview Key Ideas Bellringer What Is Work? Math Skills Power Machines and Mechanical Advantage Section 1 Key Ideas How is work calculated? What is the relationship
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations
 Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
WEP-Energy. 2. If the speed of a car is doubled, the kinetic energy of the car is 1. quadrupled 2. quartered 3. doubled 4. halved
 1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
Work, Power and Energy Worksheet. 2. Calculate the work done by a 47 N force pushing a kg pencil 0.25 m against a force of 23 N.
 Work, Power and Energy Worksheet Work and Power 1. Calculate the work done by a 47 N force pushing a pencil 0.26 m. 2. Calculate the work done by a 47 N force pushing a 0.025 kg pencil 0.25 m against a
Work, Power and Energy Worksheet Work and Power 1. Calculate the work done by a 47 N force pushing a pencil 0.26 m. 2. Calculate the work done by a 47 N force pushing a 0.025 kg pencil 0.25 m against a
AP1 WEP. Answer: E. The final velocities of the balls are given by v = 2gh.
 1. Bowling Ball A is dropped from a point halfway up a cliff. A second identical bowling ball, B, is dropped simultaneously from the top of the cliff. Comparing the bowling balls at the instant they reach
1. Bowling Ball A is dropped from a point halfway up a cliff. A second identical bowling ball, B, is dropped simultaneously from the top of the cliff. Comparing the bowling balls at the instant they reach
(A) 10 m (B) 20 m (C) 25 m (D) 30 m (E) 40 m
 Work/nergy 1. student throws a ball upward where the initial potential energy is 0. t a height of 15 meters the ball has a potential energy of 60 joules and is moving upward with a kinetic energy of 40
Work/nergy 1. student throws a ball upward where the initial potential energy is 0. t a height of 15 meters the ball has a potential energy of 60 joules and is moving upward with a kinetic energy of 40
Physics 20 Practice Problems for Exam 1 Fall 2014
 Physics 20 Practice Problems for Exam 1 Fall 2014 Multiple Choice Short Questions (1 pt ea.) Circle the best answer. 1. An apple falls from a tree and hits the ground 5 meters below. It hits the ground
Physics 20 Practice Problems for Exam 1 Fall 2014 Multiple Choice Short Questions (1 pt ea.) Circle the best answer. 1. An apple falls from a tree and hits the ground 5 meters below. It hits the ground
General Physics I Work & Energy
 General Physics I Work & Energy Forms of Energy Kinetic: Energy of motion. A car on the highway has kinetic energy. We have to remove this energy to stop it. The brakes of a car get HOT! This is an example
General Physics I Work & Energy Forms of Energy Kinetic: Energy of motion. A car on the highway has kinetic energy. We have to remove this energy to stop it. The brakes of a car get HOT! This is an example
Work and Energy Chapter 4 and 5
 Section 1 Work and Energy Chapter 4 and 5 Motion Read Chapter 4 pages 100 121 and Chapter 5 pages: 126-153 Objectives: - Distinguish between kinetic and potential energy; calculate kinetic energy, describe
Section 1 Work and Energy Chapter 4 and 5 Motion Read Chapter 4 pages 100 121 and Chapter 5 pages: 126-153 Objectives: - Distinguish between kinetic and potential energy; calculate kinetic energy, describe
Physics Regular 1617 Williams. Rollercoaster Physics: Energy
 Physics Regular 1617 Williams Rollercoaster Physics: Energy 1 2 Energy Coaster Calculation Sheet 1. Assume the coaster below is frictionless and that the first hill is depicted below. Fill in the table.
Physics Regular 1617 Williams Rollercoaster Physics: Energy 1 2 Energy Coaster Calculation Sheet 1. Assume the coaster below is frictionless and that the first hill is depicted below. Fill in the table.
This chapter covers all kinds of problems having to do with work in physics terms. Work
 Chapter 7 Working the Physics Way In This Chapter Understanding work Working with net force Calculating kinetic energy Handling potential energy Relating kinetic energy to work This chapter covers all
Chapter 7 Working the Physics Way In This Chapter Understanding work Working with net force Calculating kinetic energy Handling potential energy Relating kinetic energy to work This chapter covers all
CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY
 CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS (e) When the force is perpendicular to the displacement, as in C, there is no work When the force points in the same direction as the displacement,
CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS (e) When the force is perpendicular to the displacement, as in C, there is no work When the force points in the same direction as the displacement,
Gravitational Potential
 Gravitational Potential Energy Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Work Done Against Gravity Climbing stairs and lifting objects is work in both the scientific and everyday sense it is work done against the gravitational
Gravitational Potential Energy Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Work Done Against Gravity Climbing stairs and lifting objects is work in both the scientific and everyday sense it is work done against the gravitational
PSI AP Physics B Circular Motion
 PSI AP Physics B Circular Motion Multiple Choice 1. A ball is fastened to a string and is swung in a vertical circle. When the ball is at the highest point of the circle its velocity and acceleration directions
PSI AP Physics B Circular Motion Multiple Choice 1. A ball is fastened to a string and is swung in a vertical circle. When the ball is at the highest point of the circle its velocity and acceleration directions
Work Done by a Constant Force
 Work and Energy Work Done by a Constant Force In physics, work is described by what is accomplished when a force acts on an object, and the object moves through a distance. The work done by a constant
Work and Energy Work Done by a Constant Force In physics, work is described by what is accomplished when a force acts on an object, and the object moves through a distance. The work done by a constant
Conservation of Energy
 Robert Mathena/Fundamental Photographs, New York led-9 167 Conservation of Energy Key Term mechanical energy Conserved Quantities When we say that something is conserved, we mean that it remains constant.
Robert Mathena/Fundamental Photographs, New York led-9 167 Conservation of Energy Key Term mechanical energy Conserved Quantities When we say that something is conserved, we mean that it remains constant.
Lecture 10. Potential energy and conservation of energy
 Lecture 10 Potential energy and conservation of energy Today s Topics: Potential Energy and work done by conservative forces Work done by nonconservative forces Conservation of mechanical energy Potential
Lecture 10 Potential energy and conservation of energy Today s Topics: Potential Energy and work done by conservative forces Work done by nonconservative forces Conservation of mechanical energy Potential
Work. Work is the measure of energy transferred. Energy: the capacity to do work. W = F X d
 ENERGY CHAPTER 11 Work Work is the measure of energy transferred. Energy: the capacity to do work. W = F X d Units = Joules Work and energy transferred are equivalent in ideal systems. Two Types of Energy
ENERGY CHAPTER 11 Work Work is the measure of energy transferred. Energy: the capacity to do work. W = F X d Units = Joules Work and energy transferred are equivalent in ideal systems. Two Types of Energy
= 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ. T.E. initial. = T.E. Final. = P.E. final. + K.E. initial. + P.E. initial. K.E. initial =
 Practice Template K.E. = 1 2 mv2 P.E. height = mgh P.E. spring = 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ Energy Conservation T.E. initial = T.E. Final (1) Isolated system P.E. initial (2) Energy added E added
Practice Template K.E. = 1 2 mv2 P.E. height = mgh P.E. spring = 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ Energy Conservation T.E. initial = T.E. Final (1) Isolated system P.E. initial (2) Energy added E added
Name Class Date. Energy Energy
 CHAPTER 13 3 What Is Energy? SECTION Work and Energy KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How are energy and work related? Why is potential energy called energy of position?
CHAPTER 13 3 What Is Energy? SECTION Work and Energy KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How are energy and work related? Why is potential energy called energy of position?
KEY NNHS Introductory Physics: MCAS Review Packet #2
 2. Conservation of Energy and Momentum Broad Concept: The laws of conservation of energy and momentum provide alternate approaches to predict and describe the movement of objects. 1.) Which of the following
2. Conservation of Energy and Momentum Broad Concept: The laws of conservation of energy and momentum provide alternate approaches to predict and describe the movement of objects. 1.) Which of the following
Gravitational Potential Energy
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42148 1 Gravitational Potential Energy OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain gravitational
OpenStax-CNX module: m42148 1 Gravitational Potential Energy OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain gravitational
Physics Courseware Physics I Energy Conservation
 d Work work = Fd cos F Kinetic energy linear motion K. E. = mv Gravitational potential energy P. E. = mgh Physics Courseware Physics I Energy Conservation Problem.- A block is released from position A
d Work work = Fd cos F Kinetic energy linear motion K. E. = mv Gravitational potential energy P. E. = mgh Physics Courseware Physics I Energy Conservation Problem.- A block is released from position A
P = dw dt. P = F net. = W Δt. Conservative Force: P ave. Net work done by a conservative force on an object moving around every closed path is zero
 Power Forces Conservative Force: P ave = W Δt P = dw dt P = F net v Net work done by a conservative force on an object moving around every closed path is zero Non-conservative Force: Net work done by a
Power Forces Conservative Force: P ave = W Δt P = dw dt P = F net v Net work done by a conservative force on an object moving around every closed path is zero Non-conservative Force: Net work done by a
Work and Energy Energy Conservation
 Work and Energy Energy Conservation MidterM 1 statistics Mean = 16.48 Average = 2.74 2 Clicker Question #5 Rocket Science!!! The major principle of rocket propulsion is: a) Conservation of energy b) Conservation
Work and Energy Energy Conservation MidterM 1 statistics Mean = 16.48 Average = 2.74 2 Clicker Question #5 Rocket Science!!! The major principle of rocket propulsion is: a) Conservation of energy b) Conservation
Introduction to Mechanics Energy Conservation
 Introduction to Mechanics Energy Conservation Lana Sheridan De Anza College Mar 22, 2018 Last time conservative forces and potential energy energy diagrams mechanical energy energy conservation Overview
Introduction to Mechanics Energy Conservation Lana Sheridan De Anza College Mar 22, 2018 Last time conservative forces and potential energy energy diagrams mechanical energy energy conservation Overview
P8.14. m 1 > m 2. m 1 gh = 1 ( 2 m 1 + m 2 )v 2 + m 2 gh. 2( m 1. v = m 1 + m 2. 2 m 2v 2 Δh determined from. m 2 g Δh = 1 2 m 2v 2.
 . Two objects are connected by a light string passing over a light frictionless pulley as in Figure P8.3. The object of mass m is released from rest at height h. Using the principle of conservation of
. Two objects are connected by a light string passing over a light frictionless pulley as in Figure P8.3. The object of mass m is released from rest at height h. Using the principle of conservation of
In this lecture we will discuss three topics: conservation of energy, friction, and uniform circular motion.
 1 PHYS:100 LECTURE 9 MECHANICS (8) In this lecture we will discuss three topics: conservation of energy, friction, and uniform circular motion. 9 1. Conservation of Energy. Energy is one of the most fundamental
1 PHYS:100 LECTURE 9 MECHANICS (8) In this lecture we will discuss three topics: conservation of energy, friction, and uniform circular motion. 9 1. Conservation of Energy. Energy is one of the most fundamental
Exam 2--PHYS 101-Fall 2009
 ame: Class: Date: Exam 2PHYS 101Fall 2009 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider this figure of a roller coaster: At which of these points
ame: Class: Date: Exam 2PHYS 101Fall 2009 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider this figure of a roller coaster: At which of these points
Funsheet [ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS] Gu 2017
![Funsheet [ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS] Gu 2017 Funsheet [ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS] Gu 2017](/thumbs/83/87594120.jpg) Funsheet 6.1 6.2 [ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS] Gu 2017 State a 2 step energy transformation in each of the following situations. Include a bar chart. 1. A helicopter rises from the ground at constant speed.
Funsheet 6.1 6.2 [ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS] Gu 2017 State a 2 step energy transformation in each of the following situations. Include a bar chart. 1. A helicopter rises from the ground at constant speed.
What are two forms of Potential Energy that we commonly use? Explain Conservation of Energy and how we utilize it for problem-solving technics.
 Bell Ringer Define Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy, and Work. What are two forms of Potential Energy that we commonly use? Explain Conservation of Energy and how we utilize it for problem-solving technics.
Bell Ringer Define Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy, and Work. What are two forms of Potential Energy that we commonly use? Explain Conservation of Energy and how we utilize it for problem-solving technics.
1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B km C. 25 km D. 45 km E. 50 km
 Name: Physics I Mid Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Questions Date: Mr. Tiesler 1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B. 22.5 km C. 25 km D. 45 km
Name: Physics I Mid Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Questions Date: Mr. Tiesler 1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B. 22.5 km C. 25 km D. 45 km
PHYSICS 218 FINAL EXAM Fall, 2005 Sections
 PHYSICS 218 FINAL EXAM Fall, 2005 Sections 807-809 Name: Signature: Student ID: E-mail: Section Number: You have the full class period to complete the exam. Formulae are provided on the last page. You
PHYSICS 218 FINAL EXAM Fall, 2005 Sections 807-809 Name: Signature: Student ID: E-mail: Section Number: You have the full class period to complete the exam. Formulae are provided on the last page. You
WHAT IS ENERGY???? Energy can have many different meanings and. The ability of an object to do work. Measured in joules (J)
 WHAT IS ENERGY???? Energy can have many different meanings and forms The ability of an object to do work Measured in joules (J) N m = J Work in Progress So what is are the different types of energy? DIFFERENT
WHAT IS ENERGY???? Energy can have many different meanings and forms The ability of an object to do work Measured in joules (J) N m = J Work in Progress So what is are the different types of energy? DIFFERENT
PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy
 PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy Multiple-Choice questions 1. A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to accelerate
PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy Multiple-Choice questions 1. A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to accelerate
Conservation of Energy Review
 onservation of Energy Review Name: ate: 1. An electrostatic force exists between two +3.20 10 19 -coulomb point charges separated by a distance of 0.030 meter. As the distance between the two point charges
onservation of Energy Review Name: ate: 1. An electrostatic force exists between two +3.20 10 19 -coulomb point charges separated by a distance of 0.030 meter. As the distance between the two point charges
Physics 110 Homework Solutions Week #5
 Physics 110 Homework Solutions Week #5 Wednesday, October 7, 009 Chapter 5 5.1 C 5. A 5.8 B 5.34. A crate on a ramp a) x F N 15 F 30 o mg Along the x-axis we that F net = ma = Fcos15 mgsin30 = 500 cos15
Physics 110 Homework Solutions Week #5 Wednesday, October 7, 009 Chapter 5 5.1 C 5. A 5.8 B 5.34. A crate on a ramp a) x F N 15 F 30 o mg Along the x-axis we that F net = ma = Fcos15 mgsin30 = 500 cos15
ΣE before ± W = ΣE after
 The Law of Conservation of Energy The Law of Conservation of Energy states: Energy is never created nor destroyed just transformed into other forms of energy. OR ΣE before = ΣE after Yet if energy is added
The Law of Conservation of Energy The Law of Conservation of Energy states: Energy is never created nor destroyed just transformed into other forms of energy. OR ΣE before = ΣE after Yet if energy is added
Dynamics 4600:203 Homework 09 Due: April 04, 2008 Name:
 Dynamics 4600:03 Homework 09 Due: April 04, 008 Name: Please denote your answers clearly, i.e., box in, star, etc., and write neatly. There are no points for small, messy, unreadable work... please use
Dynamics 4600:03 Homework 09 Due: April 04, 008 Name: Please denote your answers clearly, i.e., box in, star, etc., and write neatly. There are no points for small, messy, unreadable work... please use
Chapter 5: Energy. Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy
 Chapter 5: Energy Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy Mechanical Chemical Thermal Electromagnetic Nuclear One form of energy can be converted to
Chapter 5: Energy Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy Mechanical Chemical Thermal Electromagnetic Nuclear One form of energy can be converted to
0J2 - Mechanics Lecture Notes 2
 0J2 - Mechanics Lecture Notes 2 Work, Power, Energy Work If a force is applied to a body, which then moves, we say the force does work. In 1D, if the force is constant with magnitude F, and the body moves
0J2 - Mechanics Lecture Notes 2 Work, Power, Energy Work If a force is applied to a body, which then moves, we say the force does work. In 1D, if the force is constant with magnitude F, and the body moves
Mechanical Energy Thermal Energy Chemical Energy Electrical Energy Electromagnetic Energy
 Physical Science PHYSICS UNIT 4 Study Guide. Chapter 15 - Energy Key Terms Energy Kinetic Energy Potential Gravitational Potential Elastic Potential Mechanical Energy Thermal Energy Chemical Energy Electrical
Physical Science PHYSICS UNIT 4 Study Guide. Chapter 15 - Energy Key Terms Energy Kinetic Energy Potential Gravitational Potential Elastic Potential Mechanical Energy Thermal Energy Chemical Energy Electrical
Exploring Potential Energy, Kinetic energy and Conservation of Energy: Part 1:
 WARM UP 3-4 mins: exploring energy with Phet Skate Park. Directions: 1) QUIETLY get a computer, and, with your partner,-search (Google) for: Phet Skate Park: Phet Skate Park 2) Click on the first link
WARM UP 3-4 mins: exploring energy with Phet Skate Park. Directions: 1) QUIETLY get a computer, and, with your partner,-search (Google) for: Phet Skate Park: Phet Skate Park 2) Click on the first link
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws
 Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Work and Energy continued
 Chapter 6 Work and Energy continued 6.2 The Work-Energy Theorem and Kinetic Energy Chapters 1 5 Motion equations were been developed, that relate the concepts of velocity, speed, displacement, time, and
Chapter 6 Work and Energy continued 6.2 The Work-Energy Theorem and Kinetic Energy Chapters 1 5 Motion equations were been developed, that relate the concepts of velocity, speed, displacement, time, and
AP Physics C: Work, Energy, and Power Practice
 AP Physics C: Work, Energy, and Power Practice 1981M2. A swing seat of mass M is connected to a fixed point P by a massless cord of length L. A child also of mass M sits on the seat and begins to swing
AP Physics C: Work, Energy, and Power Practice 1981M2. A swing seat of mass M is connected to a fixed point P by a massless cord of length L. A child also of mass M sits on the seat and begins to swing
Work and Potential Energy
 Work and Potential Energy One general type of energy is potential energy, U. It is the energy that can be associated with the configuration (or arrangement) of a system of objects that exert forces on
Work and Potential Energy One general type of energy is potential energy, U. It is the energy that can be associated with the configuration (or arrangement) of a system of objects that exert forces on
velocity, force and momentum are vectors, therefore direction matters!!!!!!!
 1 Momentum, p is mass times velocity: p = m v vector! unit: (p) = kg m/s Newton s second law: Force = time rate of change of momentum Net force F will produce change in momentum Δp of the object on which
1 Momentum, p is mass times velocity: p = m v vector! unit: (p) = kg m/s Newton s second law: Force = time rate of change of momentum Net force F will produce change in momentum Δp of the object on which
D) No, because of the way work is defined D) remains constant at zero. D) 0 J D) zero
 CHAPTER 6 REVIEW NAME 1) Can work be done on a system if there is no motion? A) Yes, if an outside force is provided. B) Yes, since motion is only relative. C) No, since a system which is not moving has
CHAPTER 6 REVIEW NAME 1) Can work be done on a system if there is no motion? A) Yes, if an outside force is provided. B) Yes, since motion is only relative. C) No, since a system which is not moving has
Tutorial 1 Calculating the Kinetic Energy of a Moving Object
 5. Energy As you learned in Section 5.1, mechanical work is done by applying orces on objects and displacing them. How are people, machines, and Earth able to do mechanical work? The answer is energy:
5. Energy As you learned in Section 5.1, mechanical work is done by applying orces on objects and displacing them. How are people, machines, and Earth able to do mechanical work? The answer is energy:
Science 10. Unit 4:Physics. Block: Name: Book 1: Kinetic & Potential Energy
 Science 10 Unit 4:Physics Book 1: Kinetic & Potential Energy Name: Block: 1 Brainstorm: Lesson 4.1 Intro to Energy + Kinetic Energy What is WORK? What is ENERGY? "in physics, we say that if you have done
Science 10 Unit 4:Physics Book 1: Kinetic & Potential Energy Name: Block: 1 Brainstorm: Lesson 4.1 Intro to Energy + Kinetic Energy What is WORK? What is ENERGY? "in physics, we say that if you have done
Physics Unit 4:Work & Energy Name:
 Name: Review and Preview We have come a long way in our study of mechanics. We started with the concepts of displacement and time, and built up to the more complex quantities of velocity and acceleration.
Name: Review and Preview We have come a long way in our study of mechanics. We started with the concepts of displacement and time, and built up to the more complex quantities of velocity and acceleration.
Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy Chap. 7 & 8
 Level : AP Physics Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy Chap. 7 & 8 Potential Energy of a System see p.191 in the textbook - Potential energy is the energy associated with the arrangement of a system
Level : AP Physics Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy Chap. 7 & 8 Potential Energy of a System see p.191 in the textbook - Potential energy is the energy associated with the arrangement of a system
Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 Name PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The quantity 1/2 mv2 is A) the potential energy of the object.
Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 Name PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The quantity 1/2 mv2 is A) the potential energy of the object.
Mechanical Energy - Grade 10 [CAPS] *
![Mechanical Energy - Grade 10 [CAPS] * Mechanical Energy - Grade 10 [CAPS] *](/thumbs/83/87872465.jpg) OpenStax-CNX module: m37174 1 Mechanical Energy - Grade 10 [CAPS] * Free High School Science Texts Project Based on Gravity and Mechanical Energy by Rory Adams Free High School Science Texts Project Sarah
OpenStax-CNX module: m37174 1 Mechanical Energy - Grade 10 [CAPS] * Free High School Science Texts Project Based on Gravity and Mechanical Energy by Rory Adams Free High School Science Texts Project Sarah
Chapter 6 Work and Energy
 Chapter 6 Work and Energy Midterm exams will be available next Thursday. Assignment 6 Textbook (Giancoli, 6 th edition), Chapter 6: Due on Thursday, November 5 1. On page 162 of Giancoli, problem 4. 2.
Chapter 6 Work and Energy Midterm exams will be available next Thursday. Assignment 6 Textbook (Giancoli, 6 th edition), Chapter 6: Due on Thursday, November 5 1. On page 162 of Giancoli, problem 4. 2.
Chapter 4. Energy. Work Power Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy. W = Fs Work = (force)(distance)
 Chapter 4 Energy In This Chapter: Work Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Work Work is a measure of the amount of change (in a general sense) that a force produces when it acts on a
Chapter 4 Energy In This Chapter: Work Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Work Work is a measure of the amount of change (in a general sense) that a force produces when it acts on a
Energy "is an abstract concept invented by scientists in the nineteenth century to describe quantitatively a wide variety of natural phenomena.
 Energy Energy "is an abstract concept invented by scientists in the nineteenth century to describe quantitatively a wide variety of natural phenomena." David Rose What is energy? Energy makes changes;
Energy Energy "is an abstract concept invented by scientists in the nineteenth century to describe quantitatively a wide variety of natural phenomena." David Rose What is energy? Energy makes changes;
Name: Class: Date: p 1 = p 2. Given m = 0.15 kg v i = 5.0 m/s v f = 3.0 m/s Solution
 Assessment Chapter Test A Teacher Notes and Answers Momentum and Collisions CHAPTER TEST A (GENERAL) 1. c 2. c 3. b 4. c 5. a p i = 4.0 kg m/s p f = 4.0 kg m/s p = p f p i = ( 4.0 kg m/s) 4.0 kg m/s =
Assessment Chapter Test A Teacher Notes and Answers Momentum and Collisions CHAPTER TEST A (GENERAL) 1. c 2. c 3. b 4. c 5. a p i = 4.0 kg m/s p f = 4.0 kg m/s p = p f p i = ( 4.0 kg m/s) 4.0 kg m/s =
- Conservation of Energy Notes Teacher Key -
 NAME: DATE: PERIOD: PHYSICS - Conservation of Energy Notes Teacher Key - - Is Energy Conserved? - Determine the max height that a 5kg cannonball will reach if fired vertically with an initial velocity
NAME: DATE: PERIOD: PHYSICS - Conservation of Energy Notes Teacher Key - - Is Energy Conserved? - Determine the max height that a 5kg cannonball will reach if fired vertically with an initial velocity
Name: Class: Date: d. none of the above
 Name: Class: Date: H Phys quiz Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the cause of an acceleration? a. speed b. inertia
Name: Class: Date: H Phys quiz Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the cause of an acceleration? a. speed b. inertia
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 07: WORK & ENERGY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com INTRO TO ENERGY & ENERGY FORMS ENERGY: A physical quantity without a precise definition. We don't know exactly WHAT it is, but we know HOW it works. - Energy "exists" in many forms;
!! www.clutchprep.com INTRO TO ENERGY & ENERGY FORMS ENERGY: A physical quantity without a precise definition. We don't know exactly WHAT it is, but we know HOW it works. - Energy "exists" in many forms;
