Honor Physics Final Exam Review. What is the difference between series, parallel, and combination circuits?
|
|
|
- Miles Campbell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Period Date Honor Physics Final Exam Review Circuits You should be able to: Calculate the total (net) resistance of a circuit. Calculate current in individual resistors and the total circuit current. Calculate the voltage (drop) across resistors. Calculate the power dissipated by each resistor. Questions to Consider: What is the difference between series, parallel, and combination circuits? Which equations apply to calculate power, voltage, current, and resistance when resistors are wired in parallel OR series? Momentum You should be able to: Identify the physics principles involved in collisions. Questions to Consider: What physics principles explain how the egg drop project works? What is momentum and how is it related to impulse? Work, Power & Energy You should be able to: Calculate gravitational potential, elastic potential, and kinetic energy. Apply conservation of energy to calculate velocity, height, OR distance (that a spring compresses). Questions to Consider: What are the transformations of energy during a roller coaster ride? Which equations apply to calculate GPE, EPE, and KE? What is conservation of energy and how does it apply to a roller coaster ride? Projectile Motion You should be able to: Calculate the range a projectile travels. Understand how launch angle affects the range of a projectile. Calculate the total time a projectile is in the air. Questions to Consider: Which equations apply to a projectile launched at an angle? How do you calculate the total time a projectile is in the air? How does launch angle affect range? 1 P a g e
2 Simple Harmonic Motion You should be able to: Plot a graph of total energy as a function of position. Plot a graph of kinetic energy OR elastic potential energy as a function of position. Determine displacement given a graph of energy as a function of position. Calculate the spring constant, potential energy, and kinetic energy given a graph of energy as a function of position. Determine the location of a spring given a graph of energy as a function of position. Questions to Consider: What are the transformations of energy for an oscillating mass-spring system? What does conservation of energy tell us about the total energy of the mass-spring system? Where do the maximum and minimum values of elastic potential and kinetic energy occur during an oscillation of the mass-spring system? P a g e
3 Free Response 1 - Solve each problem, showing all work. Partial credit may be given. V IR Series Circuits Parallel Circuits V VT V1 V V3... VT V1 V V3... P IV I R R I T I1 I I 3... I T I1 I I 3... REq R1 R R R R R R EQ Three resistors are arranged in a circuit as shown above. The battery has an unknown but constant Voltage, V, and a negligible internal resistance. The current I in resistor R 3 is a. Determine the equivalent resistance of the three resistors. b. Determine the voltage of the battery. c. Determine the potential difference (voltage drop) across resistor R 3. d. Determine the potential difference (voltage drop) across resistor R 1. e. Determine the power dissipated in resistor R 1. f. Determine the current through resistor R. 3 P a g e
4 Free Response - Solve each problem, showing all work. Partial credit may be given. Use the circuit in the diagram to answer the following questions. a. What is the net resistance in the circuit? b. What is the current through the battery? c. What is the current through the 3 Ω resistor? d. What is the current through the 4 Ω resistor? e. What is the voltage drop across the Ω resistor? f. What is the power dissipation of the 3 Ω resistor? 4 P a g e
5 Free Response 3 - Solve each problem, showing all work. Partial credit may be given. T = t N = 1 f GPE = mgh KE = 1 mv Mass-Spring T = p m k Pendulum T l g f = N t = 1 T F spring = -kx EPE = 1 kx f = 1 p k m f 1 g l A 1.0 kg mass is attached to a horizontal spring which undergoes SHM. The graph of EPE as a function of position is shown. The total energy of the oscillating system is 0.8 J. a. Draw and label on the graph the total energy as a function of position. b. Draw and label on the graph the graph of kinetic energy as a function of position. c. What is the maximum displacement of the oscillating mass? d. What is the spring constant of the system? e. What is the potential energy at the position of 4 cm? f. What is the kinetic energy at the position of 4 cm? EPE g. Find the location of the oscillating mass when its potential energy is 0. J. h. What is the period of one oscillation? 5 P a g e
6 Free Response 4 - Solve each problem, showing all work. Partial credit may be given. A 0.5 kg mass is attached to a horizontal spring which undergoes SHM. The graph of EPE as a function of position is shown. The total energy of the oscillating system is 0.3 J. i. Draw and label on the graph the total energy as a function of position. j. Draw and label on the graph the graph of kinetic energy as a function of position. k. What is the maximum displacement of the oscillating mass? l. What is the spring constant of the system? m. What is the potential energy at the position of 0 cm? n. What is the kinetic energy at the position of 0 cm? o. Find the location of the oscillating mass when its potential energy is 0. J. 6 P a g e
7 Free Response 5 & 6 - Solve each problem, showing all work. Partial credit may be given. A roller coaster starts from rest at the top of a 90 m hill. How fast will it be going at the bottom of the hill, if there is no friction? A spring gun has a spring constant of 175 N/m. How fast will a 0.0 kg dart go if the spring is compressed m? 7 P a g e
8 Free Response 7 - Solve each problem, showing all work. Partial credit may be given. 1 KE mv Eo E f 1 GPE mgh EPE kx A roller coaster of mass 400 kg starts its ride from rest at point A. Point A is located at a height of 90 m above the lowest point on the track. The car rolls down the incline and follows the track around a loop of radius 30 m. Ignore friction force. a. What is the gravitational potential energy of the car at point A? b. Calculate the speed of the car at point C. c. Calculate the speed of the car at point B. 8 P a g e
9 Free Response 8 - Solve each problem, showing all work. Partial credit may be given. A track consists of an arc and a straight horizontal path. A kg block is released from rest at point A. At point B it has a velocity of 5 m/s. Then it collides and sticks to an identical block at rest and they slide into and compress a spring with a spring constant of 00 N/m. Ignore friction between the block and the track surface. a. What is the vertical distance (height) between point A and point B? b. If the velocity of the blocks after the collision is /5 m/s determine how far do the blocks compress the spring before coming to a momentary stop? 9 P a g e
10 Free Response 9 The rifles in the figures are being fired horizontally (straight outward, off platforms). The bullets fired from the rifles are all identical, but the rifles propel the bullets at different speeds. The speed of each bullet and the height of each platform are given. All of the bullets miss the targets and hit the ground. 10 P a g e
11 Free Response 10 Cannonballs of different masses are shot from cannons at various angles above the horizontal. The velocity of each cannonball as it leaves the cannon is given, along with the horizontal component of that velocity, which is the same. 11 P a g e
12 Free Response 11 Cannonballs with different masses are shot from cannons at various angles above the horizontal. The velocity of each cannonball as it leaves the cannon is given, along with the same vertical component of that velocity. 1 P a g e
Energy Conservation AP
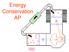 Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
AP Physics C. Momentum. Free Response Problems
 AP Physics C Momentum Free Response Problems 1. A bullet of mass m moves at a velocity v 0 and collides with a stationary block of mass M and length L. The bullet emerges from the block with a velocity
AP Physics C Momentum Free Response Problems 1. A bullet of mass m moves at a velocity v 0 and collides with a stationary block of mass M and length L. The bullet emerges from the block with a velocity
AP Physics B Summer Assignment
 BERGEN COUNTY TECHNICAL SCHOOL AP Physics B Summer Assignment 2011 Solve all problems on separate paper. This will be due the first week of school. If you need any help you can e-mail Mr. Zavorotniy at
BERGEN COUNTY TECHNICAL SCHOOL AP Physics B Summer Assignment 2011 Solve all problems on separate paper. This will be due the first week of school. If you need any help you can e-mail Mr. Zavorotniy at
CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY
 CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS (e) When the force is perpendicular to the displacement, as in C, there is no work When the force points in the same direction as the displacement,
CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS (e) When the force is perpendicular to the displacement, as in C, there is no work When the force points in the same direction as the displacement,
(A) 10 m (B) 20 m (C) 25 m (D) 30 m (E) 40 m
 Work/nergy 1. student throws a ball upward where the initial potential energy is 0. t a height of 15 meters the ball has a potential energy of 60 joules and is moving upward with a kinetic energy of 40
Work/nergy 1. student throws a ball upward where the initial potential energy is 0. t a height of 15 meters the ball has a potential energy of 60 joules and is moving upward with a kinetic energy of 40
Summer AP Assignment 2016
 Summer AP Assignment 2016 Mr. Michael Wichart (Rm. 109) wichart.m@woodstown.org Summer Assignment Goals The main goal of this assignment is to review some of the material that was taught during Honors
Summer AP Assignment 2016 Mr. Michael Wichart (Rm. 109) wichart.m@woodstown.org Summer Assignment Goals The main goal of this assignment is to review some of the material that was taught during Honors
AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum)
 AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum) 1980M2. A block of mass m slides at velocity v o across a horizontal frictionless surface toward a large curved movable ramp
AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum) 1980M2. A block of mass m slides at velocity v o across a horizontal frictionless surface toward a large curved movable ramp
(A) 10 m (B) 20 m (C) 25 m (D) 30 m (E) 40 m
 PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics
 AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will the motorcycle
AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will the motorcycle
If there is now a constant air resistance force of 35 N, what is the new maximum height the ball attains?
 A 1kg ball is launched straight up into the air with an initial speed of 64 m/s. Using only energy considerations, determine the maximum height the ball attains assuming there is no air resistance. If
A 1kg ball is launched straight up into the air with an initial speed of 64 m/s. Using only energy considerations, determine the maximum height the ball attains assuming there is no air resistance. If
October 24. Linear Momentum: - It is a vector which may require breaking it into components
 October 24 Linear Momentum: - It is a vector which may require breaking it into components Newton s First Law: A body continues with Constant Linear Momentum unless it is acted upon by a Net External Force.
October 24 Linear Momentum: - It is a vector which may require breaking it into components Newton s First Law: A body continues with Constant Linear Momentum unless it is acted upon by a Net External Force.
The graph shows how an external force applied to an object of mass 2.0 kg varies with time. The object is initially at rest.
 T2-2 [195 marks] 1. The graph shows how an external force applied to an object of mass 2.0 kg varies with time. The object is initially at rest. What is the speed of the object after 0.60 s? A. 7.0 ms
T2-2 [195 marks] 1. The graph shows how an external force applied to an object of mass 2.0 kg varies with time. The object is initially at rest. What is the speed of the object after 0.60 s? A. 7.0 ms
St. Joseph s Anglo-Chinese School
 Time allowed:.5 hours Take g = 0 ms - if necessary. St. Joseph s Anglo-Chinese School 008 009 First Term Examination Form 6 ASL Physics Section A (40%) Answer ALL questions in this section. Write your
Time allowed:.5 hours Take g = 0 ms - if necessary. St. Joseph s Anglo-Chinese School 008 009 First Term Examination Form 6 ASL Physics Section A (40%) Answer ALL questions in this section. Write your
Energy Problem Solving Techniques.
 1 Energy Problem Solving Techniques www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Introduction Gravitational Potential Energy Problem Solving GPE, KE and EPE Problem Solving Conservation of Energy Problem Solving
1 Energy Problem Solving Techniques www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Introduction Gravitational Potential Energy Problem Solving GPE, KE and EPE Problem Solving Conservation of Energy Problem Solving
PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy
 PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy Multiple-Choice questions 1. A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to accelerate
PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy Multiple-Choice questions 1. A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to accelerate
i. Indicate on the figure the point P at which the maximum speed of the car is attained. ii. Calculate the value vmax of this maximum speed.
 1. A 0.20 kg object moves along a straight line. The net force acting on the object varies with the object's displacement as shown in the graph above. The object starts from rest at displacement x = 0
1. A 0.20 kg object moves along a straight line. The net force acting on the object varies with the object's displacement as shown in the graph above. The object starts from rest at displacement x = 0
Momentum Practice Problems
 Momentum Practice Problems PSI AP Physics C Name Multiple Choice 1. A steel ball and a piece of clay have equal mass. They are dropped from the same height on a horizontal steel platform. The ball bounces
Momentum Practice Problems PSI AP Physics C Name Multiple Choice 1. A steel ball and a piece of clay have equal mass. They are dropped from the same height on a horizontal steel platform. The ball bounces
Energy in Collisions Problems AP Physics C
 1. A bullet of mass m and velocity v 0 is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface. The bullet penetrates the block and emerges with a velocity
1. A bullet of mass m and velocity v 0 is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface. The bullet penetrates the block and emerges with a velocity
Physics 201, Midterm Exam 2, Fall Answer Key
 Physics 201, Midterm Exam 2, Fall 2006 Answer Key 1) A constant force is applied to a body that is already moving. The force is directed at an angle of 60 degrees to the direction of the body s velocity.
Physics 201, Midterm Exam 2, Fall 2006 Answer Key 1) A constant force is applied to a body that is already moving. The force is directed at an angle of 60 degrees to the direction of the body s velocity.
Practice Problems for Exam 2 Solutions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 008 Practice Problems for Exam Solutions Part I Concept Questions: Circle your answer. 1) A spring-loaded toy dart gun
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 008 Practice Problems for Exam Solutions Part I Concept Questions: Circle your answer. 1) A spring-loaded toy dart gun
2 possibilities. 2.) Work is done and... 1.) Work is done and... *** The function of work is to change energy ***
 Work-Energy Theorem and Energy Conservation *** The function of work is to change energy *** 2 possibilities 1.) Work is done and... or 2.) Work is done and... 1 EX: A 100 N box is 10 m above the ground
Work-Energy Theorem and Energy Conservation *** The function of work is to change energy *** 2 possibilities 1.) Work is done and... or 2.) Work is done and... 1 EX: A 100 N box is 10 m above the ground
AP Physics C - Mechanics
 Slide 1 / 84 Slide 2 / 84 P Physics C - Mechanics Energy Problem Solving Techniques 2015-12-03 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 84 Introduction Gravitational Potential Energy Problem Solving GPE,
Slide 1 / 84 Slide 2 / 84 P Physics C - Mechanics Energy Problem Solving Techniques 2015-12-03 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 84 Introduction Gravitational Potential Energy Problem Solving GPE,
PRACTICE TEST for Midterm Exam
 South Pasadena AP Physics PRACTICE TEST for Midterm Exam FORMULAS Name Period Date / / d = vt d = v o t + ½ at 2 d = v o + v 2 t v = v o + at v 2 = v 2 o + 2ad v = v x 2 + v y 2 = tan 1 v y v v x = v cos
South Pasadena AP Physics PRACTICE TEST for Midterm Exam FORMULAS Name Period Date / / d = vt d = v o t + ½ at 2 d = v o + v 2 t v = v o + at v 2 = v 2 o + 2ad v = v x 2 + v y 2 = tan 1 v y v v x = v cos
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations
 Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
P = dw dt. P = F net. = W Δt. Conservative Force: P ave. Net work done by a conservative force on an object moving around every closed path is zero
 Power Forces Conservative Force: P ave = W Δt P = dw dt P = F net v Net work done by a conservative force on an object moving around every closed path is zero Non-conservative Force: Net work done by a
Power Forces Conservative Force: P ave = W Δt P = dw dt P = F net v Net work done by a conservative force on an object moving around every closed path is zero Non-conservative Force: Net work done by a
Part I Review Unit Review Name Momentum and Impulse
 Part I Review Unit Review Name Momentum and Impulse 1. A 5.00-kilogram block slides along a horizontal, frictionless surface at 10.0 meters per second for 4.00 seconds. The magnitude of the block's momentum
Part I Review Unit Review Name Momentum and Impulse 1. A 5.00-kilogram block slides along a horizontal, frictionless surface at 10.0 meters per second for 4.00 seconds. The magnitude of the block's momentum
Slide 1 / 76. Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems
 Slide 1 / 76 Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems Slide 2 / 76 1 A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to
Slide 1 / 76 Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems Slide 2 / 76 1 A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to
PHYSICS 218 FINAL EXAM Fall, 2005 Sections
 PHYSICS 218 FINAL EXAM Fall, 2005 Sections 807-809 Name: Signature: Student ID: E-mail: Section Number: You have the full class period to complete the exam. Formulae are provided on the last page. You
PHYSICS 218 FINAL EXAM Fall, 2005 Sections 807-809 Name: Signature: Student ID: E-mail: Section Number: You have the full class period to complete the exam. Formulae are provided on the last page. You
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion. Preparation for unit test
 Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
Final Exam Review Topics/Problems
 Final Exam Review Topics/Problems Units/Sig Figs Look at conversions Review sig figs Motion and Forces Newton s Laws X(t), v(t), a(t) graphs: look at F, displacement, accel, average velocity Boat problems/vector
Final Exam Review Topics/Problems Units/Sig Figs Look at conversions Review sig figs Motion and Forces Newton s Laws X(t), v(t), a(t) graphs: look at F, displacement, accel, average velocity Boat problems/vector
the spring is compressed and x is the compression
 Lecture 4 Spring problem and conservation of mechanical energy Hooke's Law The restoring force exerted by the spring is directly proportional to its displacement. The restoring force acts in a direction
Lecture 4 Spring problem and conservation of mechanical energy Hooke's Law The restoring force exerted by the spring is directly proportional to its displacement. The restoring force acts in a direction
Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review
 Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review 1600 kg 800 kg 9 m/s truck with mass 1600 kg collides with a car with mass 800 kg at rest. They stick together and continue to move to the right. 1. What is
Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review 1600 kg 800 kg 9 m/s truck with mass 1600 kg collides with a car with mass 800 kg at rest. They stick together and continue to move to the right. 1. What is
Energy Storage and Transfer Model: Review Sheet
 Name Energy Storage and Transfer Model: Review Sheet Date Pd 1. A softball (m = 180 g) traveling at 22.3 m/s moves a fielder's glove backward 25 cm when the ball is caught. a. Construct an energy bar graph
Name Energy Storage and Transfer Model: Review Sheet Date Pd 1. A softball (m = 180 g) traveling at 22.3 m/s moves a fielder's glove backward 25 cm when the ball is caught. a. Construct an energy bar graph
Lecture 18: Work and Energy. Today s Agenda
 Lecture 18: Work and Energy Work and Energy Definition of work Examples Today s Agenda Definition of Mechanical Energy Conservation of Mechanical Energy Conservative forces Physics 201: Lecture 10, Pg
Lecture 18: Work and Energy Work and Energy Definition of work Examples Today s Agenda Definition of Mechanical Energy Conservation of Mechanical Energy Conservative forces Physics 201: Lecture 10, Pg
v (m/s) 10 d. displacement from 0-4 s 28 m e. time interval during which the net force is zero 0-2 s f. average velocity from 0-4 s 7 m/s x (m) 20
 Physics Final Exam Mechanics Review Answers 1. Use the velocity-time graph below to find the: a. velocity at 2 s 6 m/s v (m/s) 1 b. acceleration from -2 s 6 c. acceleration from 2-4 s 2 m/s 2 2 4 t (s)
Physics Final Exam Mechanics Review Answers 1. Use the velocity-time graph below to find the: a. velocity at 2 s 6 m/s v (m/s) 1 b. acceleration from -2 s 6 c. acceleration from 2-4 s 2 m/s 2 2 4 t (s)
Phys101 Lectures 9 and 10 Conservation of Mechanical Energy
 Phys101 Lectures 9 and 10 Conservation of Mechanical Energy Key points: Conservative and Nonconservative Forces Potential Energy Generalized work-energy principle Mechanical Energy and Its Conservation
Phys101 Lectures 9 and 10 Conservation of Mechanical Energy Key points: Conservative and Nonconservative Forces Potential Energy Generalized work-energy principle Mechanical Energy and Its Conservation
Chapter 7. The Conservation of Energy
 Chapter 7 The Conservation of Energy Consider an object dropped near the surface of the earth. If the distance is small then the gravitational force between the earth and the object will be nearly constant.
Chapter 7 The Conservation of Energy Consider an object dropped near the surface of the earth. If the distance is small then the gravitational force between the earth and the object will be nearly constant.
= 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ. T.E. initial. = T.E. Final. = P.E. final. + K.E. initial. + P.E. initial. K.E. initial =
 Practice Template K.E. = 1 2 mv2 P.E. height = mgh P.E. spring = 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ Energy Conservation T.E. initial = T.E. Final (1) Isolated system P.E. initial (2) Energy added E added
Practice Template K.E. = 1 2 mv2 P.E. height = mgh P.E. spring = 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ Energy Conservation T.E. initial = T.E. Final (1) Isolated system P.E. initial (2) Energy added E added
D) No, because of the way work is defined D) remains constant at zero. D) 0 J D) zero
 CHAPTER 6 REVIEW NAME 1) Can work be done on a system if there is no motion? A) Yes, if an outside force is provided. B) Yes, since motion is only relative. C) No, since a system which is not moving has
CHAPTER 6 REVIEW NAME 1) Can work be done on a system if there is no motion? A) Yes, if an outside force is provided. B) Yes, since motion is only relative. C) No, since a system which is not moving has
1. A 1,160-kg car traveling initially with a speed of 25.0 m/s in an easterly direction crashes into the rear end of a
 Collisions Worksheet Honors: Name: Date: 1. A 1,160-kg car traveling initially with a speed of 25.0 m/s in an easterly direction crashes into the rear end of a 9,900-kg truck moving in the same direction
Collisions Worksheet Honors: Name: Date: 1. A 1,160-kg car traveling initially with a speed of 25.0 m/s in an easterly direction crashes into the rear end of a 9,900-kg truck moving in the same direction
frictionless horizontal surface. The bullet penetrates the block and emerges with a velocity of o
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Momentum and Impulse 1976B2. A bullet of mass m and velocity v o is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface.
AP Physics Free Response Practice Momentum and Impulse 1976B2. A bullet of mass m and velocity v o is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface.
AP Physics C. Work and Energy. Free-Response Problems. (Without Calculus)
 AP Physics C Work and Energy Free-Response Problems (Without Calculus) 1. A block with a mass m =10 kg is released from rest and slides a distance d = 5 m down a frictionless plane inclined at an angle
AP Physics C Work and Energy Free-Response Problems (Without Calculus) 1. A block with a mass m =10 kg is released from rest and slides a distance d = 5 m down a frictionless plane inclined at an angle
AP Physics 2 - Summer Assignment
 AP Physics 2 - Summer Assignment This assignment is due on the first day of school. You must show all your work in all steps. This material is review of First Year Physics and will be covered in its entirety
AP Physics 2 - Summer Assignment This assignment is due on the first day of school. You must show all your work in all steps. This material is review of First Year Physics and will be covered in its entirety
1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B km C. 25 km D. 45 km E. 50 km
 Name: Physics I Mid Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Questions Date: Mr. Tiesler 1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B. 22.5 km C. 25 km D. 45 km
Name: Physics I Mid Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Questions Date: Mr. Tiesler 1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B. 22.5 km C. 25 km D. 45 km
Work and Potential Energy
 Work and Potential Energy One general type of energy is potential energy, U. It is the energy that can be associated with the configuration (or arrangement) of a system of objects that exert forces on
Work and Potential Energy One general type of energy is potential energy, U. It is the energy that can be associated with the configuration (or arrangement) of a system of objects that exert forces on
SOLUTIONS Aug 2016 exam TFY4102
 SOLUTIONS Aug 2016 exam TFY4102 1) In a perfectly ELASTIC collision between two perfectly rigid objects A) the momentum of each object is conserved. B) the kinetic energy of each object is conserved. C)
SOLUTIONS Aug 2016 exam TFY4102 1) In a perfectly ELASTIC collision between two perfectly rigid objects A) the momentum of each object is conserved. B) the kinetic energy of each object is conserved. C)
(A) 0 (B) mv (C) 2mv (D) 2mv sin θ (E) 2mv cos θ
 Physics 1 Lesson 8 Forces and Momentum Homework Outcomes 1. Define linear momentum. 2. Determine the total linear momentum of a system. 3. Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to solve problems. 4.
Physics 1 Lesson 8 Forces and Momentum Homework Outcomes 1. Define linear momentum. 2. Determine the total linear momentum of a system. 3. Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to solve problems. 4.
Physics 1 Second Midterm Exam (AM) 2/25/2010
 Physics Second Midterm Eam (AM) /5/00. (This problem is worth 40 points.) A roller coaster car of m travels around a vertical loop of radius R. There is no friction and no air resistance. At the top of
Physics Second Midterm Eam (AM) /5/00. (This problem is worth 40 points.) A roller coaster car of m travels around a vertical loop of radius R. There is no friction and no air resistance. At the top of
Exam I, Physics 117-Spring 2003, Mon. 3/10/2003
 General Instructions Exam I, Physics 117-Spring 2003, Mon. 3/10/2003 Instructor: Dr. S. Liberati There are a total of five problems in this exam. All problems carry equal weights. Do all the five problems
General Instructions Exam I, Physics 117-Spring 2003, Mon. 3/10/2003 Instructor: Dr. S. Liberati There are a total of five problems in this exam. All problems carry equal weights. Do all the five problems
Chapter 8 Conservation of Energy. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 8 Conservation of Energy Units of Chapter 8 Conservative and Nonconservative Forces Potential Energy Mechanical Energy and Its Conservation Problem Solving Using Conservation of Mechanical Energy
Chapter 8 Conservation of Energy Units of Chapter 8 Conservative and Nonconservative Forces Potential Energy Mechanical Energy and Its Conservation Problem Solving Using Conservation of Mechanical Energy
Curso Física Básica Experimental I Cuestiones Tema IV. Trabajo y energía.
 1. A body of mass m slides a distance d along a horizontal surface. How much work is done by gravity? A) mgd B) zero C) mgd D) One cannot tell from the given information. E) None of these is correct. 2.
1. A body of mass m slides a distance d along a horizontal surface. How much work is done by gravity? A) mgd B) zero C) mgd D) One cannot tell from the given information. E) None of these is correct. 2.
Preparing for Six Flags Physics Concepts
 Preparing for Six Flags Physics Concepts uniform means constant, unchanging At a uniform speed, the distance traveled is given by Distance = speed x time At uniform velocity, the displacement is given
Preparing for Six Flags Physics Concepts uniform means constant, unchanging At a uniform speed, the distance traveled is given by Distance = speed x time At uniform velocity, the displacement is given
Name & Surname:... No:... Class: 11 /...
 METU D. F. HIGH SCHOOL 2017-2018 ACADEMIC YEAR, 1 st SEMESTER GRADE 11 / PHYSICS REVIEW FOR GENERAL EXAM-3 UNIFORMLY ACCELERATED MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS, ENERGY, IMPULSE & MOMENTUM & TORQUE DECEMBER 2017
METU D. F. HIGH SCHOOL 2017-2018 ACADEMIC YEAR, 1 st SEMESTER GRADE 11 / PHYSICS REVIEW FOR GENERAL EXAM-3 UNIFORMLY ACCELERATED MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS, ENERGY, IMPULSE & MOMENTUM & TORQUE DECEMBER 2017
What are two forms of Potential Energy that we commonly use? Explain Conservation of Energy and how we utilize it for problem-solving technics.
 Bell Ringer Define Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy, and Work. What are two forms of Potential Energy that we commonly use? Explain Conservation of Energy and how we utilize it for problem-solving technics.
Bell Ringer Define Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy, and Work. What are two forms of Potential Energy that we commonly use? Explain Conservation of Energy and how we utilize it for problem-solving technics.
Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 8 Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy Potential energy Conservation of energy conservative forces Conservation of energy friction Conservation of energy external
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 8 Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy Potential energy Conservation of energy conservative forces Conservation of energy friction Conservation of energy external
EXAM 3 SOLUTIONS. NAME: SECTION: AU Username: Read each question CAREFULLY and answer all parts. Work MUST be shown to receive credit.
 EXAM 3 SOLUTIONS NAME: SECTION: AU Username: Print your name: Printing your name above acknowledges that you are subject to the AU Academic Honesty Policy Instructions: Read each question CAREFULLY and
EXAM 3 SOLUTIONS NAME: SECTION: AU Username: Print your name: Printing your name above acknowledges that you are subject to the AU Academic Honesty Policy Instructions: Read each question CAREFULLY and
Mechanics. Time (s) Distance (m) Velocity (m/s) Acceleration (m/s 2 ) = + displacement/time.
 Mechanics Symbols: Equations: Kinematics The Study of Motion s = distance or displacement v = final speed or velocity u = initial speed or velocity a = average acceleration s u+ v v v u v= also v= a =
Mechanics Symbols: Equations: Kinematics The Study of Motion s = distance or displacement v = final speed or velocity u = initial speed or velocity a = average acceleration s u+ v v v u v= also v= a =
Physics I (Navitas) FINAL EXAM Fall 2015
 95.141 Physics I (Navitas) FINAL EXAM Fall 2015 Name, Last Name First Name Student Identification Number: Write your name at the top of each page in the space provided. Answer all questions, beginning
95.141 Physics I (Navitas) FINAL EXAM Fall 2015 Name, Last Name First Name Student Identification Number: Write your name at the top of each page in the space provided. Answer all questions, beginning
Physics 12 January 2001 Provincial Examination
 Physics 12 January 2001 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE Organizers CURRICULUM: Sub-Organizers 1. Vector Kinematics in Two Dimensions A, B and Dynamics and Vector Dynamics C, D 2. Work,
Physics 12 January 2001 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE Organizers CURRICULUM: Sub-Organizers 1. Vector Kinematics in Two Dimensions A, B and Dynamics and Vector Dynamics C, D 2. Work,
Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 Name PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The quantity 1/2 mv2 is A) the potential energy of the object.
Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 Name PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The quantity 1/2 mv2 is A) the potential energy of the object.
LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS
 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS Chapter 9 Units of Chapter 9 Linear Momentum Momentum and Newton s Second Law Impulse Conservation of Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Center of Mass
LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS Chapter 9 Units of Chapter 9 Linear Momentum Momentum and Newton s Second Law Impulse Conservation of Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Center of Mass
https://njctl.org/courses/science/ap-physics-c-mechanics/attachments/summerassignment-3/
 AP Physics C Summer Assignment 2017 1. Complete the problem set that is online, entitled, AP C Physics C Summer Assignment 2017. I also gave you a copy of the problem set. You may work in groups as a matter
AP Physics C Summer Assignment 2017 1. Complete the problem set that is online, entitled, AP C Physics C Summer Assignment 2017. I also gave you a copy of the problem set. You may work in groups as a matter
AP PHYSICS 1 UNIT 4 / FINAL 1 PRACTICE TEST
 AP PHYSICS 1 UNIT 4 / FINAL 1 PRACTICE TEST NAME FREE RESPONSE PROBLEMS Put all answers on this test. Show your work for partial credit. Circle or box your answers. Include the correct units and the correct
AP PHYSICS 1 UNIT 4 / FINAL 1 PRACTICE TEST NAME FREE RESPONSE PROBLEMS Put all answers on this test. Show your work for partial credit. Circle or box your answers. Include the correct units and the correct
PRACTICE TEST for Midterm Exam
 South Pasadena AP Physics PRACTICE TEST for Midterm Exam FORMULAS Name Period Date / / d = vt d = v ot + ½ at d = v o + v t v = v o + at v = v o + ad v = v x + v y = tan 1 v y v v x = v cos v y = v sin
South Pasadena AP Physics PRACTICE TEST for Midterm Exam FORMULAS Name Period Date / / d = vt d = v ot + ½ at d = v o + v t v = v o + at v = v o + ad v = v x + v y = tan 1 v y v v x = v cos v y = v sin
AP Physics 1 Lesson 9 Homework Outcomes. Name
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 9 Homework Outcomes Name Date 1. Define uniform circular motion. 2. Determine the tangential velocity of an object moving with uniform circular motion. 3. Determine the centripetal
AP Physics 1 Lesson 9 Homework Outcomes Name Date 1. Define uniform circular motion. 2. Determine the tangential velocity of an object moving with uniform circular motion. 3. Determine the centripetal
AP Mechanics Summer Assignment
 2012-2013 AP Mechanics Summer Assignment To be completed in summer Submit for grade in September Name: Date: Equations: Kinematics (For #1 and #2 questions: use following equations only. Need to show derivation
2012-2013 AP Mechanics Summer Assignment To be completed in summer Submit for grade in September Name: Date: Equations: Kinematics (For #1 and #2 questions: use following equations only. Need to show derivation
Momentum, Work and Energy Review
 Momentum, Work and Energy Review 1.5 Momentum Be able to: o solve simple momentum and impulse problems o determine impulse from the area under a force-time graph o solve problems involving the impulse-momentum
Momentum, Work and Energy Review 1.5 Momentum Be able to: o solve simple momentum and impulse problems o determine impulse from the area under a force-time graph o solve problems involving the impulse-momentum
Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review
 Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review 1600 kg 800 kg 9 m/s A truck with mass 1600 kg collides with a car with mass 800 kg at rest. They stick together and continue to move to the right. 1. What is
Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review 1600 kg 800 kg 9 m/s A truck with mass 1600 kg collides with a car with mass 800 kg at rest. They stick together and continue to move to the right. 1. What is
Phys101 Lectures 9 and 10 Conservation of Mechanical Energy
 Phys101 Lectures 9 and 10 Conservation of Mechanical Energy Key points: Conservative and Nonconservative Forces Potential Energy Generalized work-energy principle Mechanical Energy and Its Conservation
Phys101 Lectures 9 and 10 Conservation of Mechanical Energy Key points: Conservative and Nonconservative Forces Potential Energy Generalized work-energy principle Mechanical Energy and Its Conservation
Impulse,Momentum, CM Practice Questions
 Name: Date: 1. A 12.0-kilogram cart is moving at a speed of 0.25 meter per second. After the speed of the cart is tripled, the inertia of the cart will be A. unchanged B. one-third as great C. three times
Name: Date: 1. A 12.0-kilogram cart is moving at a speed of 0.25 meter per second. After the speed of the cart is tripled, the inertia of the cart will be A. unchanged B. one-third as great C. three times
Choose the best answer for Questions 1-15 below. Mark your answer on your scantron form using a #2 pencil.
 Name: ID #: Section #: PART I: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Choose the best answer for Questions 1-15 below. Mark your answer on your scantron form using a #2 pencil. 1. A 55.0-kg box rests on a horizontal
Name: ID #: Section #: PART I: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Choose the best answer for Questions 1-15 below. Mark your answer on your scantron form using a #2 pencil. 1. A 55.0-kg box rests on a horizontal
Extra credit assignment #4 It can be handed in up until one class before Test 4 (check your course outline). It will NOT be accepted after that.
 Extra credit assignment #4 It can be handed in up until one class before Test 4 (check your course outline). It will NOT be accepted after that. NAME: 4. Units of power include which of the following?
Extra credit assignment #4 It can be handed in up until one class before Test 4 (check your course outline). It will NOT be accepted after that. NAME: 4. Units of power include which of the following?
Physics 110 Homework Solutions Week #5
 Physics 110 Homework Solutions Week #5 Wednesday, October 7, 009 Chapter 5 5.1 C 5. A 5.8 B 5.34. A crate on a ramp a) x F N 15 F 30 o mg Along the x-axis we that F net = ma = Fcos15 mgsin30 = 500 cos15
Physics 110 Homework Solutions Week #5 Wednesday, October 7, 009 Chapter 5 5.1 C 5. A 5.8 B 5.34. A crate on a ramp a) x F N 15 F 30 o mg Along the x-axis we that F net = ma = Fcos15 mgsin30 = 500 cos15
Unit 4 Work, Power & Conservation of Energy Workbook
 Name: Per: AP Physics C Semester 1 - Mechanics Unit 4 Work, Power & Conservation of Energy Workbook Unit 4 - Work, Power, & Conservation of Energy Supplements to Text Readings from Fundamentals of Physics
Name: Per: AP Physics C Semester 1 - Mechanics Unit 4 Work, Power & Conservation of Energy Workbook Unit 4 - Work, Power, & Conservation of Energy Supplements to Text Readings from Fundamentals of Physics
Center of Mass & Linear Momentum
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)
![Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a) Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)](/thumbs/83/87594074.jpg) Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
Today s lecture. WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY Physics
 Today s lecture Review of chapters 1-14 Note: I m taking for granted that you ll still know SI/cgs units, order-of-magnitude estimates, etc., so I m focusing on problems. Velocity and acceleration (1d)
Today s lecture Review of chapters 1-14 Note: I m taking for granted that you ll still know SI/cgs units, order-of-magnitude estimates, etc., so I m focusing on problems. Velocity and acceleration (1d)
FINAL EXAM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS
 Physics 10 Spring 009 George Williams FINAL EXAM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS A data sheet is provided. Table 10- from your text is assumed, and will be provided on the final exam. 1. A rock is thrown downward from
Physics 10 Spring 009 George Williams FINAL EXAM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS A data sheet is provided. Table 10- from your text is assumed, and will be provided on the final exam. 1. A rock is thrown downward from
Physics 103, Practice Midterm Exam 2
 Physics 103, Practice Midterm Exam 2 1) A rock of mass m is whirled in a horizontal circle on a string of length L. The period of its motion is T seconds. If the length of the string is increased to 4L
Physics 103, Practice Midterm Exam 2 1) A rock of mass m is whirled in a horizontal circle on a string of length L. The period of its motion is T seconds. If the length of the string is increased to 4L
The world is charged with the grandeur of God.
 Name: Course: HS Physics Date: Mr. Szopiak FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Final Exam Focus on Dynamic Systems Forces and their Effect on Particle Motion Conservation of Energy Transferring and Converting Energy
Name: Course: HS Physics Date: Mr. Szopiak FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Final Exam Focus on Dynamic Systems Forces and their Effect on Particle Motion Conservation of Energy Transferring and Converting Energy
Topic 1: Newtonian Mechanics Energy & Momentum
 Work (W) the amount of energy transferred by a force acting through a distance. Scalar but can be positive or negative ΔE = W = F! d = Fdcosθ Units N m or Joules (J) Work, Energy & Power Power (P) the
Work (W) the amount of energy transferred by a force acting through a distance. Scalar but can be positive or negative ΔE = W = F! d = Fdcosθ Units N m or Joules (J) Work, Energy & Power Power (P) the
Test Booklet. Subject: SC, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics. Student name:
 Test ooklet Subject: S, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics Student name: uthor: North arolina istrict: North arolina Released Tests Printed: Monday July 09, 2012 1 n object is launched across a room.
Test ooklet Subject: S, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics Student name: uthor: North arolina istrict: North arolina Released Tests Printed: Monday July 09, 2012 1 n object is launched across a room.
3.The wrecking crane shown is moving toward a brick wall that is to be torn down.
 Test Name: Physics Practice Test Section 1 1.Which of the following best classifies a material that has extremely low conductivity? 1. A. semiconductor B. insulator C. metalloid D. conductor 2.Which of
Test Name: Physics Practice Test Section 1 1.Which of the following best classifies a material that has extremely low conductivity? 1. A. semiconductor B. insulator C. metalloid D. conductor 2.Which of
Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 2
 Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 1 3 problems from exam 2 6 problems 13.1 14.6 (including 14.5) 8 problems 1.1---9.6 Go through the
Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 1 3 problems from exam 2 6 problems 13.1 14.6 (including 14.5) 8 problems 1.1---9.6 Go through the
23. A force in the negative direction of an x-axis is applied for 27ms to a 0.40kg ball initially moving at 14m/s in the positive direction of the
 23. A force in the negative direction of an x-axis is applied for 27ms to a 0.40kg ball initially moving at 14m/s in the positive direction of the axis. The force varies in magnitude, and the impulse has
23. A force in the negative direction of an x-axis is applied for 27ms to a 0.40kg ball initially moving at 14m/s in the positive direction of the axis. The force varies in magnitude, and the impulse has
AP* Circular & Gravitation Free Response Questions
 1992 Q1 AP* Circular & Gravitation Free Response Questions A 0.10-kilogram solid rubber ball is attached to the end of a 0.80-meter length of light thread. The ball is swung in a vertical circle, as shown
1992 Q1 AP* Circular & Gravitation Free Response Questions A 0.10-kilogram solid rubber ball is attached to the end of a 0.80-meter length of light thread. The ball is swung in a vertical circle, as shown
Topic 2 Revision questions Paper
 Topic 2 Revision questions Paper 1 3.1.2018 1. [1 mark] The graph shows the variation of the acceleration a of an object with time t. What is the change in speed of the object shown by the graph? A. 0.5
Topic 2 Revision questions Paper 1 3.1.2018 1. [1 mark] The graph shows the variation of the acceleration a of an object with time t. What is the change in speed of the object shown by the graph? A. 0.5
Momentum in 1-Dimension
 Momentum in 1-Dimension Level : Physics I Date : Warm-up Questions If you were in a car that was out of control and had to choose between hitting a concrete wall or a haystack to stop, which would you
Momentum in 1-Dimension Level : Physics I Date : Warm-up Questions If you were in a car that was out of control and had to choose between hitting a concrete wall or a haystack to stop, which would you
Honors Physics Final Exam Review. Symbol Units Units (if applicable)
 Honors Physics Final Exam Review Name: Date: Write the symbol and the SI units for each of the following: Symbol Units Units (if applicable) 1) Time 2) Distance 3) Speed 4) Displacement 5) Velocity 6)
Honors Physics Final Exam Review Name: Date: Write the symbol and the SI units for each of the following: Symbol Units Units (if applicable) 1) Time 2) Distance 3) Speed 4) Displacement 5) Velocity 6)
Exam 2: Equation Summary
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.01 Physics Fall Term 2012 Exam 2: Equation Summary Newton s Second Law: Force, Mass, Acceleration: Newton s Third Law: Center of Mass: Velocity
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.01 Physics Fall Term 2012 Exam 2: Equation Summary Newton s Second Law: Force, Mass, Acceleration: Newton s Third Law: Center of Mass: Velocity
s_3x03 Page 1 Physics Samples
 Physics Samples KE, PE, Springs 1. A 1.0-kilogram rubber ball traveling east at 4.0 meters per second hits a wall and bounces back toward the west at 2.0 meters per second. Compared to the kinetic energy
Physics Samples KE, PE, Springs 1. A 1.0-kilogram rubber ball traveling east at 4.0 meters per second hits a wall and bounces back toward the west at 2.0 meters per second. Compared to the kinetic energy
Potential Energy. Uo = mgh. Apply the Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem: F = - mg x = - (h - ho) ΔK = W = Fx ½ mv 2 - ½ mvo 2 = (-mg ) [- (ho - h)]
![Potential Energy. Uo = mgh. Apply the Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem: F = - mg x = - (h - ho) ΔK = W = Fx ½ mv 2 - ½ mvo 2 = (-mg ) [- (ho - h)] Potential Energy. Uo = mgh. Apply the Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem: F = - mg x = - (h - ho) ΔK = W = Fx ½ mv 2 - ½ mvo 2 = (-mg ) [- (ho - h)]](/thumbs/92/108491604.jpg) Physics 17 Part F Potential Energy U = mgh Apply the Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem: F = - mg x = - (h - ho) ΔK = W = Fx ½ mv 2 - ½ mvo 2 = (-mg ) [- (ho - h)] Re-written: ½ mv 2 + mgh = ½ mvo 2 + mgho Ko
Physics 17 Part F Potential Energy U = mgh Apply the Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem: F = - mg x = - (h - ho) ΔK = W = Fx ½ mv 2 - ½ mvo 2 = (-mg ) [- (ho - h)] Re-written: ½ mv 2 + mgh = ½ mvo 2 + mgho Ko
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Department of Physics. Final Exam 041. Answer key - First choice is the correct answer
 King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Department of Physics MSK Final Exam 041 Answer key - First choice is the correct answer Q1 A 20 kg uniform ladder is leaning against a frictionless wall
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Department of Physics MSK Final Exam 041 Answer key - First choice is the correct answer Q1 A 20 kg uniform ladder is leaning against a frictionless wall
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist
 Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
CHAPTER 6 TEST REVIEW -- MARKSCHEME
 Force (N) AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER
Force (N) AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER
PLK VICWOOD K.T. CHONG SIXTH FORM COLLEGE Form Six Second Term Final Examination ( ) Physics A-Level Paper 1 Question/Answer Book A
 05-06/F. 6 Final Exam/AL Physics/Paper 1/P.1 PLK VICWOOD K.T. CHONG SIXTH FORM COLLEGE Form Six Second Term Final Examination (2005-2006) A Physics A-Level Paper 1 Question/Answer Book A Time Allowed:
05-06/F. 6 Final Exam/AL Physics/Paper 1/P.1 PLK VICWOOD K.T. CHONG SIXTH FORM COLLEGE Form Six Second Term Final Examination (2005-2006) A Physics A-Level Paper 1 Question/Answer Book A Time Allowed:
Old Exams Questions Ch. 8 T072 Q2.: Q5. Q7.
 Old Exams Questions Ch. 8 T072 Q2.: A ball slides without friction around a loop-the-loop (see Fig 2). A ball is released, from rest, at a height h from the left side of the loop of radius R. What is the
Old Exams Questions Ch. 8 T072 Q2.: A ball slides without friction around a loop-the-loop (see Fig 2). A ball is released, from rest, at a height h from the left side of the loop of radius R. What is the
University of Houston Mathematics Contest: Physics Exam 2017
 Unless otherwise specified, please use g as the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth. Vectors x, y, and z are unit vectors along x, y, and z, respectively. Let G be the universal gravitational
Unless otherwise specified, please use g as the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth. Vectors x, y, and z are unit vectors along x, y, and z, respectively. Let G be the universal gravitational
AP PHYSICS 1. Energy 2016 EDITION
 AP PHYSICS 1 Energy 2016 EDITION Copyright 2016 National Math + Initiative, Dallas, Texas. All rights reserved. Visit us online at www.nms.org. 1 Pre-Assessment Questions Consider a system which could
AP PHYSICS 1 Energy 2016 EDITION Copyright 2016 National Math + Initiative, Dallas, Texas. All rights reserved. Visit us online at www.nms.org. 1 Pre-Assessment Questions Consider a system which could
11th Grade. Review for General Exam-3. decreases. smaller than. remains the same
 1. An object is thrown horizontally with a speed of v from point M and hits point E on the vertical wall after t seconds as shown in the figure. (Ignore air friction.). Two objects M and S are thrown as
1. An object is thrown horizontally with a speed of v from point M and hits point E on the vertical wall after t seconds as shown in the figure. (Ignore air friction.). Two objects M and S are thrown as
