Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 2
|
|
|
- Shawn Bond
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 1 3 problems from exam 2 6 problems (including 14.5) 8 problems Go through the homework, discussion and clicker quizzes problems carefully.
2 HITT RF Remote Login Procedure: The radio channel number for this room is 07 (zero, seven). It is STRONGLY recommended to login your remote for every class just to be sure it is on the correct radio channel and working before class. 1. PRESS AND HOLD THE DOWN ARROW KEY until the GREEN light on the remote turns RED. 2. PRESS THE 0 KEY and you will see the RED light flash GREEN. 3. PRESS THE 7 KEY and you will see the RED light flash GREEN. 4. PRESS AND RELEASE THE DOWN ARROW KEY again and you will see the red light search for the receiver, if it BLINKS GREEN MULTIPLE TIMES you are logged in.
3 Ch Ch. 3 Units: Look what is given, convert all numbers to SI units, then substitute in your final formula! Vectors: (Scalars vs Vectors) Addition Subtraction
4 Linear Motion with const. a Displacement vs. distance Velocity vs. speed Average velocity vs. average speed Kinematic Equations v = v + at o o x = v t + 1 at v = v + 2a x x = v average o 2 vo + v t = 2 f t
5 Projectile motion x- uniform motion y- constant acceleration Relative Velocity: v r = v r v r AB AE EB
6 Example Car moving at 25 m/s hits the brakes & stops in a distance of 25 m What was the car s (uniform) acceleration? A m/s 2 B m/s 2 C. 1.0 m/s 2 D. 50 m/s 2 E. -50 m/s 2 How long did it take to stop?
7 Example A ball is launched straight upward with an initial speed of 20 m/s. How long does it take to return? A. 10 s B. 8 s C. 6 s D. 4 s E. 2 s How high did it go?
8 How far before the plane gets to the hikers does the rescuer need to drop the parcel? A. 180 m B. 150 m C. 120 m D. 100 m E. 50 m 125 m 30 m/s
9 Ch. 4 Newton s Laws Force Vector Add forces 1 st law 2 nd law 3 rd law Equilibrium Friction r r r r F = F + F + F +... net r F = ma r net Free-body Diagram!!
10 Example Woman pulls 75 kg sled at an angle 42 with constant velocity along a flat road. (µk=0.1) What is the tension in the pulling rope? m T Ground
11 Example Block being pulled up a hill. What tension must rope have before block moves? (m=10kg, θ=25, µs=0.6) y max f s n T x y T x mg θ
12 Ch. 5 Work and Energy Work KE PE W-KE Theorem Conservation WE theorem Power W (Fcos θ) x Wnet = KEf KEi = KE KE + PE = KE + PE i i f f W = ( KE KE) nc f i + ( PE PE) = 0 f i
13 76. A 2.00-kg block situated on a rough incline is connected to a spring of negligible mass having a spring constant of 100 N/m (Fig. P5.76). The block is released from rest when the spring is unstretched, and the pulley is frictionless. The block moves 20.0 cm down the incline before coming to rest. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between block and incline. A B C D
14
15 The launching mechanism of a toy gun consists of a Hooke s law spring of unknown spring constant. If the spring is compressed a distance of m and the gun fired vertically, the gun can launch a 20.0-g projectile from rest to a maximum height of 20.0 m above the starting point of the projectile. Neglecting all resistive forces, determine the spring constant N/m N/m N/m N/m
16 W nc = KE + PE g + PE s W nc = 0 KE = 0 PE g = - PE s PE gf PE gi = PE si PE sf mgh = (1/2)kx 2 k = (2mgh)/x 2
17 Ch. 6 Momentum, M. Cons. r r p = mv Momentum Impulse Impulse momentum theorem Conservation collisions r I = F t Ft = = p r F( t 2 t1) = p p f i
18 A 20-kg object sitting at rest is struck in a head-on collision with a 10-kg object initially moving at +5.0 m/s. If the 10- kg object moving at +1.0 m/s after the collision. Find the velocity of the 20-kg object after the collision. a m/s b m/s c m/s d m/s
19 An 8.00 g bullet is fired into a 280 g block that is initially at rest at the edge of a table of 1.00 m height. The bullet remains in the block, and after the impact the block lands d = 2.1 m from the bottom of the table. Determine the initial speed of the bullet. A m/s B m/s C m/s D. 166 m/s Scanned solutions 2
20 Linear vs Rotation Linear Motion coordinate x velocity v acceleration a θ ω α Rotational Motion angle angular velocity angular acceleration mass m force F 1 st Newton s Law F=0: v=const 2 nd Newton s Law F = ma Ι τ τ=0: ω=const τ = Iα moment of inertia torque Kinetic Energy KE = ½mv 2 Momentum p = mv KE = ½Iω 2 Kinetic Energy L= Iω Angular Momentum
21 Analogies Between Linear and Rotational Motion Relations between angular and linear quantities s a = r θ; = rα; v t a c t = rω = v r 2 2 = rω
22 The planet is rotating about the vertical axis with constant angular velocity ω. What is the acceleration of the mass m at point A. R A A. 0 B m B. g C. ω 2 R
23 The planet is rotating about the vertical axis with constant angular velocity ω. What is the acceleration of the mass m at point B. R A A. 0 B m B. g C. ω 2 R
24 Part of a roller-coaster ride involves coasting down an incline and entering a loop 8.00 m in diameter. For safety considerations, the roller coaster's speed at the top of the loop must be such that the force of the seat on a rider is equal in magnitude to the rider's weight. From what height above the bottom of the loop must the roller coaster descend to satisfy this requirement? A.12.0 m B m C m D.100 m Scanned solutions 3
25 A wheel undergoes constant angular acceleration. Find the angular acceleration if the initial angular velocity is zero and the final angular velocity after 10 s is 100 rad/s. A.1 rad/s 2 B.10 rad/s 2 C.100 rad/s 2 ω f = ω i + αt 100 = α D.1000 rad/s 2
26 1. Choose origin P 2. Find distance of the point P (where the force is being applied to the beam) from the origin O. This is the value of r. θ F Fsinθ 3. Find the angle θ the force F makes with the beam i.e. think of the beam as the x-axis. O 4. Find the component of the force F which is perpendicular to the beam i.e. think of the beam as the x-axis and find the y-component of F which is Fsinθ.
27 5. Torque τ = r F sin θ P θ Fsinθ 6. If the force F is tending to rotate the beam clockwise then τ is negative. F O
28 A 100-N uniform ladder rests against a smooth vertical wall. The coefficient of static friction between ladder and floor is What minimum angle can the ladder make with the floor before it slips? A. 42 o B. 22 o C. 18 o D. 51 o E. 39 o
29 Example: a ladder against a wall What minimum angle can the ladder make with the floor before it slips? P x F = 0 f s P = 0 F y = 0 n mg = 0 τ = 0 L PLsin θ mg sin(90 θ ) = 2 fs = µ sn = µ smg y 0 x N θ f s mg L µ s mglsin θ mg cosθ = 0 µ s sinθ cosθ = 0 1 tan θ = 2µ s
30 Rolling down incline Energy conservation Linear velocity and angular speed are related v=rω 1 mgh = mv Iω mgh = mv + ( ) v = ( m (1 I gh = + ) v 2 2 mr Smaller I/mR 2, bigger v, faster!! 1 2 I R 2 h I R 2 ) v 2 v
31 Example ω i ω f
32 Example: solution
33 Example, cont. a. How much work was done by the elephant if the radius of the carousel is 2 m? b. How much work was done to the elephant? c. How much work was done to the carousel?
34 The puck has a mass of kg. Its original distance from the center of rotation is 0.4 m and it moves with a speed of 0.8 m/s. The string is pulled downward 0.15 m through the hole in the frictionless table. Determine the work done on the puck. What is the angular momentum of the puck?
35 A sample of blood is placed in a centrifuge of radius 13.0 cm. The mass of a red blood cell is 3.0 X kg, and the magnitude of the force acting on it as it settles out of the plasma is 4.0 X N. At how many revolutions per second should the centrifuge be operated? 161 rev/s
36 The Earth has a radius of about 6400 km. At what altitude is the acceleration of gravity about 1/9 that of g (acceleration of gravity at the surface of the Earth = 9.8 m/s 2 )? A km B km C km D km E. 12,800 km g = G ME r 2 M E = kg G = x N m² /kg² Gravitational force from multiple masses
37 The Earth has a radius of about 6400 km. If an object is dropped from 12,800 km above Earth s surface, what is its speed when it hits Earth s surface? A. 1 km/s B. 3 km/s C. 6 km/s D. 9 km/s E km/s PE g M Em = G r M E = kg G = x N m² /kg²
38 Ch. 9 Solid and Fluid Elastic Modulus Fluid Pressure Pascal s Principle Archimedes Principle
39 39. A 1.00-kg beaker containing 2.00 kg of oil (density = 916 kg/m 3 ) rests on a scale. A 2.00-kg block of iron (density = kg/m 3 )is suspended from a spring scale and is completely submerged in the oil (Fig. P9.39). Find the equilibrium readings of both scales.
40 43. A 1.00-kg beaker containing 2.00 kg of oil (density = 916 kg/m 3 ) rests on a scale. A 2.00-kg block of iron (density = kg/m 3 )is suspended from a spring scale and is completely submerged in the oil (Fig. P9.39). Find the equilibrium readings of both scales. Will the reading of the upper scale be 1. Less than weight of iron 2. Greater than weight of iron 3. Equal to weight of iron
41 43. A 1.00-kg beaker containing 2.00 kg of oil (density = 916 kg/m 3 ) rests on a scale. A 2.00-kg block of iron (density = kg/m 3 )is suspended from a spring scale and is completely submerged in the oil (Fig. P9.39). Find the equilibrium readings of both scales. Will the reading of the lower scale be 1. Less than weight of beaker + oil 2. Greater than weight of beaker + oil 3. Equal to weight of beaker + oil
42 Example problem: Iceberg What percentage of the volume of an iceberg can be seen above the surface of the sea? F m B f = g ρ V V f f V V V V V f = above above w = g ρ ρ = Mg = ρ f V = 1 ice V V Vg f = 1 ρ ρ f = 0.10 = 10%
43 At a distance d from an automobile the sound intensity is 10-7 W/m 2. Find intensity level. How about 3d? Or 1000 automobiles?
Mechanics II. Which of the following relations among the forces W, k, N, and F must be true?
 Mechanics II 1. By applying a force F on a block, a person pulls a block along a rough surface at constant velocity v (see Figure below; directions, but not necessarily magnitudes, are indicated). Which
Mechanics II 1. By applying a force F on a block, a person pulls a block along a rough surface at constant velocity v (see Figure below; directions, but not necessarily magnitudes, are indicated). Which
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2011 EXAM #2 SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 2, 2011
 PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
(A) 10 m (B) 20 m (C) 25 m (D) 30 m (E) 40 m
 PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
 King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Physics Department Physics 101 Recitation Term 131 Fall 013 Quiz # 4 Section 10 A 1.50-kg block slides down a frictionless 30.0 incline, starting from rest.
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Physics Department Physics 101 Recitation Term 131 Fall 013 Quiz # 4 Section 10 A 1.50-kg block slides down a frictionless 30.0 incline, starting from rest.
Exam 3 Practice Solutions
 Exam 3 Practice Solutions Multiple Choice 1. A thin hoop, a solid disk, and a solid sphere, each with the same mass and radius, are at rest at the top of an inclined plane. If all three are released at
Exam 3 Practice Solutions Multiple Choice 1. A thin hoop, a solid disk, and a solid sphere, each with the same mass and radius, are at rest at the top of an inclined plane. If all three are released at
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion. Preparation for unit test
 Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2010 EXAM #1 Solutions WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 29, 2010
 PHYSICS 1, FALL 010 EXAM 1 Solutions WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 9, 010 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In
PHYSICS 1, FALL 010 EXAM 1 Solutions WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 9, 010 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym
 FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 13 pages. Make sure none are missing 2.
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 13 pages. Make sure none are missing 2.
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Monday, 14 December 2015, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym
 FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 111, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Monday, 14 December 015, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 13 pages. Make sure none are missing. There
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 111, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Monday, 14 December 015, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 13 pages. Make sure none are missing. There
Topic 1: Newtonian Mechanics Energy & Momentum
 Work (W) the amount of energy transferred by a force acting through a distance. Scalar but can be positive or negative ΔE = W = F! d = Fdcosθ Units N m or Joules (J) Work, Energy & Power Power (P) the
Work (W) the amount of energy transferred by a force acting through a distance. Scalar but can be positive or negative ΔE = W = F! d = Fdcosθ Units N m or Joules (J) Work, Energy & Power Power (P) the
Wiley Plus. Final Assignment (5) Is Due Today: Before 11 pm!
 Wiley Plus Final Assignment (5) Is Due Today: Before 11 pm! Final Exam Review December 9, 009 3 What about vector subtraction? Suppose you are given the vector relation A B C RULE: The resultant vector
Wiley Plus Final Assignment (5) Is Due Today: Before 11 pm! Final Exam Review December 9, 009 3 What about vector subtraction? Suppose you are given the vector relation A B C RULE: The resultant vector
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Saturday, 14 December 2013, 1PM to 4 PM, AT 1003
 FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Saturday, 14 December 2013, 1PM to 4 PM, AT 1003 NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 14 pages. Make sure none are missing 2. There is
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Saturday, 14 December 2013, 1PM to 4 PM, AT 1003 NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 14 pages. Make sure none are missing 2. There is
PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy
 PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy Multiple-Choice questions 1. A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to accelerate
PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy Multiple-Choice questions 1. A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to accelerate
(1) +0.2 m/s (2) +0.4 m/s (3) +0.6 m/s (4) +1 m/s (5) +0.8 m/s
 77777 77777 Instructor: Biswas/Ihas/Whiting PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2, 120 minutes November 13, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized
77777 77777 Instructor: Biswas/Ihas/Whiting PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2, 120 minutes November 13, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized
On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
 Instructor(s): Profs. D. Reitze, H. Chan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2 April 2, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Instructor(s): Profs. D. Reitze, H. Chan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2 April 2, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
PH1104/PH114S MECHANICS
 PH04/PH4S MECHANICS SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 06-07 SOLUTION MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS. (B) For freely falling bodies, the equation v = gh holds. v is proportional to h, therefore v v = h h = h h =.. (B).5i
PH04/PH4S MECHANICS SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 06-07 SOLUTION MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS. (B) For freely falling bodies, the equation v = gh holds. v is proportional to h, therefore v v = h h = h h =.. (B).5i
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 130) Lecture 0 Rotational dynamics equilibrium nd Newton s Law for rotational motion rolling Exam II review http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy130/ Lightning Review Last lecture:
General Physics (PHY 130) Lecture 0 Rotational dynamics equilibrium nd Newton s Law for rotational motion rolling Exam II review http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy130/ Lightning Review Last lecture:
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Department of Physics. Final Exam 041. Answer key - First choice is the correct answer
 King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Department of Physics MSK Final Exam 041 Answer key - First choice is the correct answer Q1 A 20 kg uniform ladder is leaning against a frictionless wall
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Department of Physics MSK Final Exam 041 Answer key - First choice is the correct answer Q1 A 20 kg uniform ladder is leaning against a frictionless wall
Circular Motion, Pt 2: Angular Dynamics. Mr. Velazquez AP/Honors Physics
 Circular Motion, Pt 2: Angular Dynamics Mr. Velazquez AP/Honors Physics Formulas: Angular Kinematics (θ must be in radians): s = rθ Arc Length 360 = 2π rads = 1 rev ω = θ t = v t r Angular Velocity α av
Circular Motion, Pt 2: Angular Dynamics Mr. Velazquez AP/Honors Physics Formulas: Angular Kinematics (θ must be in radians): s = rθ Arc Length 360 = 2π rads = 1 rev ω = θ t = v t r Angular Velocity α av
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws
 Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
HITT RF Remote Login Procedure:
 HITT RF Remote Login Procedure: The radio channel number for this room is 07 (zero, seven). It is STRONGLY recommended to login your remote for every class just to be sure it is on the correct radio channel
HITT RF Remote Login Procedure: The radio channel number for this room is 07 (zero, seven). It is STRONGLY recommended to login your remote for every class just to be sure it is on the correct radio channel
. d. v A v B. e. none of these.
 General Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, the essential
General Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, the essential
UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA
 PAGE NO.: 1 of 6 + Formula Sheet Equal marks for all questions. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will look
PAGE NO.: 1 of 6 + Formula Sheet Equal marks for all questions. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will look
Figure 1 Answer: = m
 Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Write your name legibly on the top right hand corner of this paper
 NAME Phys 631 Summer 2007 Quiz 2 Tuesday July 24, 2007 Instructor R. A. Lindgren 9:00 am 12:00 am Write your name legibly on the top right hand corner of this paper No Books or Notes allowed Calculator
NAME Phys 631 Summer 2007 Quiz 2 Tuesday July 24, 2007 Instructor R. A. Lindgren 9:00 am 12:00 am Write your name legibly on the top right hand corner of this paper No Books or Notes allowed Calculator
4) Vector = and vector = What is vector = +? A) B) C) D) E)
 1) Suppose that an object is moving with constant nonzero acceleration. Which of the following is an accurate statement concerning its motion? A) In equal times its speed changes by equal amounts. B) In
1) Suppose that an object is moving with constant nonzero acceleration. Which of the following is an accurate statement concerning its motion? A) In equal times its speed changes by equal amounts. B) In
Department of Physics
 Department of Physics PHYS101-051 FINAL EXAM Test Code: 100 Tuesday, 4 January 006 in Building 54 Exam Duration: 3 hrs (from 1:30pm to 3:30pm) Name: Student Number: Section Number: Page 1 1. A car starts
Department of Physics PHYS101-051 FINAL EXAM Test Code: 100 Tuesday, 4 January 006 in Building 54 Exam Duration: 3 hrs (from 1:30pm to 3:30pm) Name: Student Number: Section Number: Page 1 1. A car starts
Chapter 5: Energy. Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy
 Chapter 5: Energy Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy Mechanical Chemical Thermal Electromagnetic Nuclear One form of energy can be converted to
Chapter 5: Energy Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy Mechanical Chemical Thermal Electromagnetic Nuclear One form of energy can be converted to
Dynamics 4600:203 Homework 09 Due: April 04, 2008 Name:
 Dynamics 4600:03 Homework 09 Due: April 04, 008 Name: Please denote your answers clearly, i.e., box in, star, etc., and write neatly. There are no points for small, messy, unreadable work... please use
Dynamics 4600:03 Homework 09 Due: April 04, 008 Name: Please denote your answers clearly, i.e., box in, star, etc., and write neatly. There are no points for small, messy, unreadable work... please use
Solution Only gravity is doing work. Since gravity is a conservative force mechanical energy is conserved:
 8) roller coaster starts with a speed of 8.0 m/s at a point 45 m above the bottom of a dip (see figure). Neglecting friction, what will be the speed of the roller coaster at the top of the next slope,
8) roller coaster starts with a speed of 8.0 m/s at a point 45 m above the bottom of a dip (see figure). Neglecting friction, what will be the speed of the roller coaster at the top of the next slope,
Your Name: PHYSICS 101 MIDTERM. Please circle your section 1 9 am Galbiati 2 10 am Kwon 3 11 am McDonald 4 12:30 pm McDonald 5 12:30 pm Kwon
 1 Your Name: PHYSICS 101 MIDTERM October 26, 2006 2 hours Please circle your section 1 9 am Galbiati 2 10 am Kwon 3 11 am McDonald 4 12:30 pm McDonald 5 12:30 pm Kwon Problem Score 1 /13 2 /20 3 /20 4
1 Your Name: PHYSICS 101 MIDTERM October 26, 2006 2 hours Please circle your section 1 9 am Galbiati 2 10 am Kwon 3 11 am McDonald 4 12:30 pm McDonald 5 12:30 pm Kwon Problem Score 1 /13 2 /20 3 /20 4
Honor Physics Final Exam Review. What is the difference between series, parallel, and combination circuits?
 Name Period Date Honor Physics Final Exam Review Circuits You should be able to: Calculate the total (net) resistance of a circuit. Calculate current in individual resistors and the total circuit current.
Name Period Date Honor Physics Final Exam Review Circuits You should be able to: Calculate the total (net) resistance of a circuit. Calculate current in individual resistors and the total circuit current.
Review for 3 rd Midterm
 Review for 3 rd Midterm Midterm is on 4/19 at 7:30pm in the same rooms as before You are allowed one double sided sheet of paper with any handwritten notes you like. The moment-of-inertia about the center-of-mass
Review for 3 rd Midterm Midterm is on 4/19 at 7:30pm in the same rooms as before You are allowed one double sided sheet of paper with any handwritten notes you like. The moment-of-inertia about the center-of-mass
Your Name: PHYSICS 101 MIDTERM. Please Circle your section 1 9 am Galbiati 2 10 am Wang 3 11 am Hasan 4 12:30 am Hasan 5 12:30 pm Olsen
 1 Your Name: PHYSICS 101 MIDTERM October 27, 2005 2 hours Please Circle your section 1 9 am Galbiati 2 10 am Wang 3 11 am Hasan 4 12:30 am Hasan 5 12:30 pm Olsen Problem Score 1 /16 2 /16 3 /16 4 /18 5
1 Your Name: PHYSICS 101 MIDTERM October 27, 2005 2 hours Please Circle your section 1 9 am Galbiati 2 10 am Wang 3 11 am Hasan 4 12:30 am Hasan 5 12:30 pm Olsen Problem Score 1 /16 2 /16 3 /16 4 /18 5
Phys 1401: General Physics I
 1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 1402 c. PHYS 2425 d. PHYS 2426 2. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam 2 c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of the exam is this?
1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 1402 c. PHYS 2425 d. PHYS 2426 2. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam 2 c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of the exam is this?
E 490 FE Exam Prep. Engineering Mechanics
 E 490 FE Exam Prep Engineering Mechanics 2008 E 490 Course Topics Statics Newton s Laws of Motion Resultant Force Systems Moment of Forces and Couples Equilibrium Pulley Systems Trusses Centroid of an
E 490 FE Exam Prep Engineering Mechanics 2008 E 490 Course Topics Statics Newton s Laws of Motion Resultant Force Systems Moment of Forces and Couples Equilibrium Pulley Systems Trusses Centroid of an
Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy?
 Tuesday, June 15, 2010 Page: 1 Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy? A) ML 2 /T 2 B) LT 2 /M C) MLT D) M 2 L 3 T E) ML/T 2 Q2. Two cars are initially 150 kilometers
Tuesday, June 15, 2010 Page: 1 Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy? A) ML 2 /T 2 B) LT 2 /M C) MLT D) M 2 L 3 T E) ML/T 2 Q2. Two cars are initially 150 kilometers
Exam II. Spring 2004 Serway & Jewett, Chapters Fill in the bubble for the correct answer on the answer sheet. next to the number.
 Agin/Meyer PART I: QUALITATIVE Exam II Spring 2004 Serway & Jewett, Chapters 6-10 Assigned Seat Number Fill in the bubble for the correct answer on the answer sheet. next to the number. NO PARTIAL CREDIT:
Agin/Meyer PART I: QUALITATIVE Exam II Spring 2004 Serway & Jewett, Chapters 6-10 Assigned Seat Number Fill in the bubble for the correct answer on the answer sheet. next to the number. NO PARTIAL CREDIT:
Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3
 Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3 Information and Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above. Please write and bubble your Name and Student Id number on
Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3 Information and Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above. Please write and bubble your Name and Student Id number on
Slide 1 / 76. Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems
 Slide 1 / 76 Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems Slide 2 / 76 1 A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to
Slide 1 / 76 Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems Slide 2 / 76 1 A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to
Chapter 6: Work and Kinetic Energy
 Chapter 6: Work and Kinetic Energy Suppose you want to find the final velocity of an object being acted on by a variable force. Newton s 2 nd law gives the differential equation (for 1D motion) dv dt =
Chapter 6: Work and Kinetic Energy Suppose you want to find the final velocity of an object being acted on by a variable force. Newton s 2 nd law gives the differential equation (for 1D motion) dv dt =
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
Review questions. Before the collision, 70 kg ball is stationary. Afterward, the 30 kg ball is stationary and 70 kg ball is moving to the right.
 Review questions Before the collision, 70 kg ball is stationary. Afterward, the 30 kg ball is stationary and 70 kg ball is moving to the right. 30 kg 70 kg v (a) Is this collision elastic? (b) Find the
Review questions Before the collision, 70 kg ball is stationary. Afterward, the 30 kg ball is stationary and 70 kg ball is moving to the right. 30 kg 70 kg v (a) Is this collision elastic? (b) Find the
Solution to Problem. Part A. x m. x o = 0, y o = 0, t = 0. Part B m m. range
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS: Final Exam, December 4 Monday, GYM, 6 to 9 PM Problem A Physics Professor did a daredevil stunt in his spare time. In the figure below he tries to cross a river from a 53 ramp at an
PRACTICE PROBLEMS: Final Exam, December 4 Monday, GYM, 6 to 9 PM Problem A Physics Professor did a daredevil stunt in his spare time. In the figure below he tries to cross a river from a 53 ramp at an
AP Physics. Harmonic Motion. Multiple Choice. Test E
 AP Physics Harmonic Motion Multiple Choice Test E A 0.10-Kg block is attached to a spring, initially unstretched, of force constant k = 40 N m as shown below. The block is released from rest at t = 0 sec.
AP Physics Harmonic Motion Multiple Choice Test E A 0.10-Kg block is attached to a spring, initially unstretched, of force constant k = 40 N m as shown below. The block is released from rest at t = 0 sec.
r r Sample Final questions for PS 150
 Sample Final questions for PS 150 1) Which of the following is an accurate statement? A) Rotating a vector about an axis passing through the tip of the vector does not change the vector. B) The magnitude
Sample Final questions for PS 150 1) Which of the following is an accurate statement? A) Rotating a vector about an axis passing through the tip of the vector does not change the vector. B) The magnitude
Final Exam Spring 2014 May 05, 2014
 95.141 Final Exam Spring 2014 May 05, 2014 Section number Section instructor Last/First name Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Answer all questions, beginning each new question in the space provided.
95.141 Final Exam Spring 2014 May 05, 2014 Section number Section instructor Last/First name Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Answer all questions, beginning each new question in the space provided.
Practice Test for Midterm Exam
 A.P. Physics Practice Test for Midterm Exam Kinematics 1. Which of the following statements are about uniformly accelerated motion? Select two answers. a) If an object s acceleration is constant then it
A.P. Physics Practice Test for Midterm Exam Kinematics 1. Which of the following statements are about uniformly accelerated motion? Select two answers. a) If an object s acceleration is constant then it
1 MR SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 2013
 SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
Forces of Friction Contact between bodies with a relative velocity produces friction opposite
 Forces of Friction Contact between bodies with a relative velocity produces friction Friction is proportional to the normal force The force of static friction is generally greater than the force of kinetic
Forces of Friction Contact between bodies with a relative velocity produces friction Friction is proportional to the normal force The force of static friction is generally greater than the force of kinetic
Phys 1401: General Physics I
 1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 1402 c. PHYS 2425 d. PHYS 2426 2. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam 2 c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of the exam is this?
1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 1402 c. PHYS 2425 d. PHYS 2426 2. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam 2 c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of the exam is this?
St. Joseph s Anglo-Chinese School
 Time allowed:.5 hours Take g = 0 ms - if necessary. St. Joseph s Anglo-Chinese School 008 009 First Term Examination Form 6 ASL Physics Section A (40%) Answer ALL questions in this section. Write your
Time allowed:.5 hours Take g = 0 ms - if necessary. St. Joseph s Anglo-Chinese School 008 009 First Term Examination Form 6 ASL Physics Section A (40%) Answer ALL questions in this section. Write your
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
Static Equilibrium, Gravitation, Periodic Motion
 This test covers static equilibrium, universal gravitation, and simple harmonic motion, with some problems requiring a knowledge of basic calculus. Part I. Multiple Choice 1. 60 A B 10 kg A mass of 10
This test covers static equilibrium, universal gravitation, and simple harmonic motion, with some problems requiring a knowledge of basic calculus. Part I. Multiple Choice 1. 60 A B 10 kg A mass of 10
Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 8 Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy Potential energy Conservation of energy conservative forces Conservation of energy friction Conservation of energy external
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 8 Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy Potential energy Conservation of energy conservative forces Conservation of energy friction Conservation of energy external
Physics-MC Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1.
 Physics-MC 2006-7 Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1. 3. 2. Three blocks of equal mass are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure above. A constant force F is applied to block
Physics-MC 2006-7 Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1. 3. 2. Three blocks of equal mass are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure above. A constant force F is applied to block
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
Physics 12 Final Exam Review Booklet # 1
 Physics 12 Final Exam Review Booklet # 1 1. Which is true of two vectors whose sum is zero? (C) 2. Which graph represents an object moving to the left at a constant speed? (C) 3. Which graph represents
Physics 12 Final Exam Review Booklet # 1 1. Which is true of two vectors whose sum is zero? (C) 2. Which graph represents an object moving to the left at a constant speed? (C) 3. Which graph represents
Today s lecture. WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY Physics
 Today s lecture Review of chapters 1-14 Note: I m taking for granted that you ll still know SI/cgs units, order-of-magnitude estimates, etc., so I m focusing on problems. Velocity and acceleration (1d)
Today s lecture Review of chapters 1-14 Note: I m taking for granted that you ll still know SI/cgs units, order-of-magnitude estimates, etc., so I m focusing on problems. Velocity and acceleration (1d)
Power: Sources of Energy
 Chapter 5 Energy Power: Sources of Energy Tidal Power SF Bay Tidal Power Project Main Ideas (Encyclopedia of Physics) Energy is an abstract quantity that an object is said to possess. It is not something
Chapter 5 Energy Power: Sources of Energy Tidal Power SF Bay Tidal Power Project Main Ideas (Encyclopedia of Physics) Energy is an abstract quantity that an object is said to possess. It is not something
Chapter 10. Rotation
 Chapter 10 Rotation Rotation Rotational Kinematics: Angular velocity and Angular Acceleration Rotational Kinetic Energy Moment of Inertia Newton s nd Law for Rotation Applications MFMcGraw-PHY 45 Chap_10Ha-Rotation-Revised
Chapter 10 Rotation Rotation Rotational Kinematics: Angular velocity and Angular Acceleration Rotational Kinetic Energy Moment of Inertia Newton s nd Law for Rotation Applications MFMcGraw-PHY 45 Chap_10Ha-Rotation-Revised
Concept Question: Normal Force
 Concept Question: Normal Force Consider a person standing in an elevator that is accelerating upward. The upward normal force N exerted by the elevator floor on the person is 1. larger than 2. identical
Concept Question: Normal Force Consider a person standing in an elevator that is accelerating upward. The upward normal force N exerted by the elevator floor on the person is 1. larger than 2. identical
6. Find the net torque on the wheel in Figure about the axle through O if a = 10.0 cm and b = 25.0 cm.
 1. During a certain period of time, the angular position of a swinging door is described by θ = 5.00 + 10.0t + 2.00t 2, where θ is in radians and t is in seconds. Determine the angular position, angular
1. During a certain period of time, the angular position of a swinging door is described by θ = 5.00 + 10.0t + 2.00t 2, where θ is in radians and t is in seconds. Determine the angular position, angular
Exam 2 Solutions. PHY2048 Spring 2017
 Exam Solutions. The figure shows an overhead view of three horizontal forces acting on a cargo canister that was initially stationary but that now moves across a frictionless floor. The force magnitudes
Exam Solutions. The figure shows an overhead view of three horizontal forces acting on a cargo canister that was initially stationary but that now moves across a frictionless floor. The force magnitudes
Sample Physics Placement Exam
 Sample Physics 130-1 Placement Exam A. Multiple Choice Questions: 1. A cable is used to take construction equipment from the ground to the top of a tall building. During the trip up, when (if ever) is
Sample Physics 130-1 Placement Exam A. Multiple Choice Questions: 1. A cable is used to take construction equipment from the ground to the top of a tall building. During the trip up, when (if ever) is
A) 4.0 m/s B) 5.0 m/s C) 0 m/s D) 3.0 m/s E) 2.0 m/s. Ans: Q2.
 Coordinator: Dr. W. Al-Basheer Thursday, July 30, 2015 Page: 1 Q1. A constant force F ( 7.0ˆ i 2.0 ˆj ) N acts on a 2.0 kg block, initially at rest, on a frictionless horizontal surface. If the force causes
Coordinator: Dr. W. Al-Basheer Thursday, July 30, 2015 Page: 1 Q1. A constant force F ( 7.0ˆ i 2.0 ˆj ) N acts on a 2.0 kg block, initially at rest, on a frictionless horizontal surface. If the force causes
Physics UCSB TR 2:00-3:15 lecture Final Exam Wednesday 3/17/2010
 Physics @ UCSB TR :00-3:5 lecture Final Eam Wednesday 3/7/00 Print your last name: Print your first name: Print your perm no.: INSTRUCTIONS: DO NOT START THE EXAM until you are given instructions to do
Physics @ UCSB TR :00-3:5 lecture Final Eam Wednesday 3/7/00 Print your last name: Print your first name: Print your perm no.: INSTRUCTIONS: DO NOT START THE EXAM until you are given instructions to do
PSI AP Physics B Dynamics
 PSI AP Physics B Dynamics Multiple-Choice questions 1. After firing a cannon ball, the cannon moves in the opposite direction from the ball. This an example of: A. Newton s First Law B. Newton s Second
PSI AP Physics B Dynamics Multiple-Choice questions 1. After firing a cannon ball, the cannon moves in the opposite direction from the ball. This an example of: A. Newton s First Law B. Newton s Second
Rotational Dynamics continued
 Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics continued 9.4 Newton s Second Law for Rotational Motion About a Fixed Axis ROTATIONAL ANALOG OF NEWTON S SECOND LAW FOR A RIGID BODY ROTATING ABOUT A FIXED AXIS I = ( mr 2
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics continued 9.4 Newton s Second Law for Rotational Motion About a Fixed Axis ROTATIONAL ANALOG OF NEWTON S SECOND LAW FOR A RIGID BODY ROTATING ABOUT A FIXED AXIS I = ( mr 2
CHAPTER 6 TEST REVIEW -- MARKSCHEME
 Force (N) AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER
Force (N) AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER
Phys101 Second Major-152 Zero Version Coordinator: Dr. W. Basheer Monday, March 07, 2016 Page: 1
 Phys101 Second Major-15 Zero Version Coordinator: Dr. W. Basheer Monday, March 07, 016 Page: 1 Q1. Figure 1 shows two masses; m 1 = 4.0 and m = 6.0 which are connected by a massless rope passing over a
Phys101 Second Major-15 Zero Version Coordinator: Dr. W. Basheer Monday, March 07, 016 Page: 1 Q1. Figure 1 shows two masses; m 1 = 4.0 and m = 6.0 which are connected by a massless rope passing over a
3. How long must a 100 N net force act to produce a change in momentum of 200 kg m/s? (A) 0.25 s (B) 0.50 s (C) 1.0 s (D) 2.0 s (E) 4.
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Momentum and Impulse 1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass,
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Momentum and Impulse 1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass,
Translational Motion Rotational Motion Equations Sheet
 PHYSICS 01 Translational Motion Rotational Motion Equations Sheet LINEAR ANGULAR Time t t Displacement x; (x = rθ) θ Velocity v = Δx/Δt; (v = rω) ω = Δθ/Δt Acceleration a = Δv/Δt; (a = rα) α = Δω/Δt (
PHYSICS 01 Translational Motion Rotational Motion Equations Sheet LINEAR ANGULAR Time t t Displacement x; (x = rθ) θ Velocity v = Δx/Δt; (v = rω) ω = Δθ/Δt Acceleration a = Δv/Δt; (a = rα) α = Δω/Δt (
Final Exam Name: Box# Physics
 Final Exam Name: Box# Physics 160-01 1) A certain airplane has a speed of 400.0 km/h and is diving at an angle of 30.0 below the horizontal when a radar decoy is released. The plane is 800 m high when
Final Exam Name: Box# Physics 160-01 1) A certain airplane has a speed of 400.0 km/h and is diving at an angle of 30.0 below the horizontal when a radar decoy is released. The plane is 800 m high when
AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics
 AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will the motorcycle
AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will the motorcycle
Practice Problems for Exam 2 Solutions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 008 Practice Problems for Exam Solutions Part I Concept Questions: Circle your answer. 1) A spring-loaded toy dart gun
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 008 Practice Problems for Exam Solutions Part I Concept Questions: Circle your answer. 1) A spring-loaded toy dart gun
Choose the best answer for Questions 1-15 below. Mark your answer on your scantron form using a #2 pencil.
 Name: ID #: Section #: PART I: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Choose the best answer for Questions 1-15 below. Mark your answer on your scantron form using a #2 pencil. 1. A 55.0-kg box rests on a horizontal
Name: ID #: Section #: PART I: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Choose the best answer for Questions 1-15 below. Mark your answer on your scantron form using a #2 pencil. 1. A 55.0-kg box rests on a horizontal
Q1. For a completely inelastic two-body collision the kinetic energy of the objects after the collision is the same as:
 Coordinator: Dr.. Naqvi Monday, January 05, 015 Page: 1 Q1. For a completely inelastic two-body collision the kinetic energy of the objects after the collision is the same as: ) (1/) MV, where M is the
Coordinator: Dr.. Naqvi Monday, January 05, 015 Page: 1 Q1. For a completely inelastic two-body collision the kinetic energy of the objects after the collision is the same as: ) (1/) MV, where M is the
Phys101 Second Major-173 Zero Version Coordinator: Dr. M. Al-Kuhaili Thursday, August 02, 2018 Page: 1. = 159 kw
 Coordinator: Dr. M. Al-Kuhaili Thursday, August 2, 218 Page: 1 Q1. A car, of mass 23 kg, reaches a speed of 29. m/s in 6.1 s starting from rest. What is the average power used by the engine during the
Coordinator: Dr. M. Al-Kuhaili Thursday, August 2, 218 Page: 1 Q1. A car, of mass 23 kg, reaches a speed of 29. m/s in 6.1 s starting from rest. What is the average power used by the engine during the
Physics 53 Summer Final Exam. Solutions
 Final Exam Solutions In questions or problems not requiring numerical answers, express the answers in terms of the symbols given, and standard constants such as g. If numbers are required, use g = 10 m/s
Final Exam Solutions In questions or problems not requiring numerical answers, express the answers in terms of the symbols given, and standard constants such as g. If numbers are required, use g = 10 m/s
43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms,
 43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms, A) her moment of inertia increases and her rotational kinetic energy remains the same.
43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms, A) her moment of inertia increases and her rotational kinetic energy remains the same.
TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES. PHYS 1111, Exam 2 Section 1 Version 1 November 2, 2005 Total Weight: 100 points
 TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS 1111, Exam Section 1 Version 1 November, 005 Total Weight: 100 points 1. Check your examination for completeness prior to starting.
TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS 1111, Exam Section 1 Version 1 November, 005 Total Weight: 100 points 1. Check your examination for completeness prior to starting.
Translational vs Rotational. m x. Connection Δ = = = = = = Δ = = = = = = Δ =Δ = = = = = 2 / 1/2. Work
 Translational vs Rotational / / 1/ Δ m x v dx dt a dv dt F ma p mv KE mv Work Fd / / 1/ θ ω θ α ω τ α ω ω τθ Δ I d dt d dt I L I KE I Work / θ ω α τ Δ Δ c t s r v r a v r a r Fr L pr Connection Translational
Translational vs Rotational / / 1/ Δ m x v dx dt a dv dt F ma p mv KE mv Work Fd / / 1/ θ ω θ α ω τ α ω ω τθ Δ I d dt d dt I L I KE I Work / θ ω α τ Δ Δ c t s r v r a v r a r Fr L pr Connection Translational
ΣF=ma SECOND LAW. Make a freebody diagram for EVERY problem!
 PHYSICS HOMEWORK #31 SECOND LAW ΣF=ma NEWTON S LAWS Newton s Second Law of Motion The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force applied, inversely proportional to the mass of the
PHYSICS HOMEWORK #31 SECOND LAW ΣF=ma NEWTON S LAWS Newton s Second Law of Motion The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force applied, inversely proportional to the mass of the
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations
 Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
Slide 1 / 76. Slide 2 / 76. Slide 3 / 76. Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems A 1,800 B 5,000 E 300,000. A Fdcos θ - μ mgd B Fdcos θ.
 Slide 1 / 76 Work & nergy Multiple hoice Problems 1 driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to accelerate the sports
Slide 1 / 76 Work & nergy Multiple hoice Problems 1 driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to accelerate the sports
Important: This test consists of 15 multiple choice problems, each worth points.
 Physics 214 Practice Exam 1 C Fill in on the OPSCAN sheet: 1) Name 2) Student identification number 3) Exam number as 01 4) Sign the OPSCAN sheet Important: This test consists of 15 multiple choice problems,
Physics 214 Practice Exam 1 C Fill in on the OPSCAN sheet: 1) Name 2) Student identification number 3) Exam number as 01 4) Sign the OPSCAN sheet Important: This test consists of 15 multiple choice problems,
Topic 2 Revision questions Paper
 Topic 2 Revision questions Paper 1 3.1.2018 1. [1 mark] The graph shows the variation of the acceleration a of an object with time t. What is the change in speed of the object shown by the graph? A. 0.5
Topic 2 Revision questions Paper 1 3.1.2018 1. [1 mark] The graph shows the variation of the acceleration a of an object with time t. What is the change in speed of the object shown by the graph? A. 0.5
Physics 221. Exam III Spring f S While the cylinder is rolling up, the frictional force is and the cylinder is rotating
 Physics 1. Exam III Spring 003 The situation below refers to the next three questions: A solid cylinder of radius R and mass M with initial velocity v 0 rolls without slipping up the inclined plane. N
Physics 1. Exam III Spring 003 The situation below refers to the next three questions: A solid cylinder of radius R and mass M with initial velocity v 0 rolls without slipping up the inclined plane. N
We define angular displacement, θ, and angular velocity, ω. What's a radian?
 We define angular displacement, θ, and angular velocity, ω Units: θ = rad ω = rad/s What's a radian? Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius note: counterclockwise is + clockwise
We define angular displacement, θ, and angular velocity, ω Units: θ = rad ω = rad/s What's a radian? Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius note: counterclockwise is + clockwise
Forces of Rolling. 1) Ifobjectisrollingwith a com =0 (i.e.no netforces), then v com =ωr = constant (smooth roll)
 Physics 2101 Section 3 March 12 rd : Ch. 10 Announcements: Mid-grades posted in PAW Quiz today I will be at the March APS meeting the week of 15-19 th. Prof. Rich Kurtz will help me. Class Website: http://www.phys.lsu.edu/classes/spring2010/phys2101-3/
Physics 2101 Section 3 March 12 rd : Ch. 10 Announcements: Mid-grades posted in PAW Quiz today I will be at the March APS meeting the week of 15-19 th. Prof. Rich Kurtz will help me. Class Website: http://www.phys.lsu.edu/classes/spring2010/phys2101-3/
CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION
 62 CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION 63 Up to now we have described the motion of particles using quantities like displacement, velocity and acceleration. These quantities
62 CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION 63 Up to now we have described the motion of particles using quantities like displacement, velocity and acceleration. These quantities
Momentum Circular Motion and Gravitation Rotational Motion Fluid Mechanics
 Momentum Circular Motion and Gravitation Rotational Motion Fluid Mechanics Momentum Momentum Collisions between objects can be evaluated using the laws of conservation of energy and of momentum. Momentum
Momentum Circular Motion and Gravitation Rotational Motion Fluid Mechanics Momentum Momentum Collisions between objects can be evaluated using the laws of conservation of energy and of momentum. Momentum
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
Work and kinetic Energy
 Work and kinetic Energy Problem 66. M=4.5kg r = 0.05m I = 0.003kgm 2 Q: What is the velocity of mass m after it dropped a distance h? (No friction) h m=0.6kg mg Work and kinetic Energy Problem 66. M=4.5kg
Work and kinetic Energy Problem 66. M=4.5kg r = 0.05m I = 0.003kgm 2 Q: What is the velocity of mass m after it dropped a distance h? (No friction) h m=0.6kg mg Work and kinetic Energy Problem 66. M=4.5kg
Energy Conservation AP
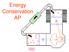 Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
24/06/13 Forces ( F.Robilliard) 1
 R Fr F W 24/06/13 Forces ( F.Robilliard) 1 Mass: So far, in our studies of mechanics, we have considered the motion of idealised particles moving geometrically through space. Why a particular particle
R Fr F W 24/06/13 Forces ( F.Robilliard) 1 Mass: So far, in our studies of mechanics, we have considered the motion of idealised particles moving geometrically through space. Why a particular particle
Physics 12. Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1
 Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
Physics 201 Final Exam
 Physics 201 Final Exam Information and Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above. Please write and bubble your Name and Student Id number on your
Physics 201 Final Exam Information and Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above. Please write and bubble your Name and Student Id number on your
= y(x, t) =A cos (!t + kx)
 A harmonic wave propagates horizontally along a taut string of length L = 8.0 m and mass M = 0.23 kg. The vertical displacement of the string along its length is given by y(x, t) = 0. m cos(.5 t + 0.8
A harmonic wave propagates horizontally along a taut string of length L = 8.0 m and mass M = 0.23 kg. The vertical displacement of the string along its length is given by y(x, t) = 0. m cos(.5 t + 0.8
