Classical Mechanics Lecture 20
|
|
|
- Isabella Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Classical Mechanics Lecture 20 Today s Concepts: A) Angular Momentum B) Precession Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 1
2 Work is of two kinds: first, altering the posi>on of at or near the earth's surface rela>vely to other such second, telling other people to do so. The first kind is unpleasant and ill paid; the second is pleasant and highly paid. from In Praise of Idleness by Bertrand Russell
3 Torques and Gyroscopes Mechanical Universe: Episode 20
4 Your Comments I did not completely understand how the torque causes an object to move and have a precession frequency. [ hbp:// ] S**t just got real. Can we spend the whole class spinning the Nres again? How do we determine the direcnon of precession? This is all REALLY confusing!!! Please help! I am doing so so on angular momentum, but quanntanve problems, or some sort of pracnse worksheet would help lots. OMG this is so hard I spent my whole evening to study physics, I have no entertainment :( Can you upload lecture 14 on webct? [ hbp:// Lect14.pdf ] Is there a case analogous to perfectly elasnc collisions in rotanonal kinemancs? Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 2
5 Precession demos will be almost guaranteed to BLOW THEIR MINDS! But we're definitely going to need to go over precession a few Nmes with physical examples. Angular momentum isn't that bad, but I'm snll having issues with parallel axis theorem that are screwing me up in the later homework i don't understand how we can include rotanon direcnon in calculanng the precession direcnon. lets go over this one more Nme, I get it all, just would be great to have some demos This video seems to help picture the Gyroscope much beber than what was depicted in the slides.hbp:// But it seems like physics might just be gefng interesnng again :) Can we go over how to find the direcnon of precession? I need precession help GyraNon and precession is snll unclear. physics yo! das doowwwwwn This is gefng stupidly hard... Your Comments Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 2
6 Student on Stool There are no external torques ac>ng on the student- stool system, so angular momentum will be conserved. Ini>ally: L i = I i ω i Finally: L f = I f ω f ω i ω f I i I f L i L f Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 3
7 Clicker Question A student sits on a freely turning stool and rotates with constant angular velocity ω 1. She pulls her arms in and her angular velocity increases to ω 2. In doing this her kine>c energy: A) Increases B) Decreases C) Stays the same ω i ω f I i I f L i L f Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 4
8 (using L = Iω) L is conserved: I f < I i K f > K i K increases! ω i ω f I i I f L i L f Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 5
9 Since the student has to force her arms to move toward her body, she must be doing posi>ve work! The work/kine>c energy theorem states that this will increase the kine>c energy of the system! ω i ω f I i I f L i L f Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 6
10 I would like to see the student siyng in the chair with a top in a real life demo. Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 7
11 Clicker Question (like CheckPoint) A puck slides in a circular path on a horizontal fric>onless table. It is held at a constant radius by a string threaded through a fric>onless hole at the center of the table. If you pull on the string such that the radius decreases by a factor of 2, by what factor does the angular velocity of the puck increase? A) 2 B) 4 C) 8 Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 8
12 Clicker Question Since the string is pulled through a hole at the center of rotation, there is no torque: Angular momentum is conserved. R 2 = L 2 = I 2! 2 = m! 2 2 R Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 9
13 Food for thought (not on any test) R We just used to find But So how do we get an α without a τ? usually 0, but not now Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 10
14 Food for thought (not on any test) Now suppose τ EXT = 0: So in this case we can have an α without an external torque! Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 11
15 Precession The magnitude of the torque about the pivot is τ = Mgd. The direcnon of this torque at the instant shown is out of the page (using the right hand rule). ~ ext = d ~L dt The change in angular momentum at the instant shown must also be out of the page! Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 13
16 Precession Aerial View dφ pivot τ EXT Ω Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 14
17 Precession In this example: Direc>on: The >p of L moves in the direc>on of τ. Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 15
18 CheckPoint A disk is spinning with angular velocity ω on a pivoted horizontal axle as shown. Gravity acts down. In which direc>on does precession cause the disk to move? A) Out of the page B) Into the page C) Up D) Down Torque is out of the page Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 16
19 CheckPoint In which direc>on does point? A B Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 17
20 CheckPoint In which direc>on does precession cause the disk to move? A) Into the page B) Out of the page C) Up D) Down Torque is out of the page A) The torque provided by gravity is going out of the page. Therefore, L must change out of the page. However, since L is in the opposite direcnon of the axel when drawn from the pivot, precession must make the disk go into the page. B) Gravity exerts a net torque out of the page, so the disk precesses in a direcnon out of the page. D) Torque is down so precession is down Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 18
21 Clicker Question A disk is spinning with angular velocity ω on a pivoted horizontal axle as shown. If the mass of the disk were doubled but its radius and angular velocity were kept the same: A) The angular momentum of the disk Quadruples B) The angular momentum of the disk Doubles C) The torque about the pivot doubles D) Both A and C E) Both B and C L = Iω Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 19
22 CheckPoint A disk is spinning with angular velocity ω on a pivoted horizontal axle as shown. Gravity acts down and the disk has a precession frequency Ω. If the mass of the disk were doubled but its radius and angular velocity were kept the same, the precession frequency would: A) Increase B) Decrease C) Stay the same Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 20
23 CheckPoint If the mass of the disk were doubled but its radius and angular velocity were kept the same, the precession frequency would A) Increase B) Decrease C) Stay the same A) torque due to weight increases in the numerator. B) When mass is doubled, angular momentum doubles, so precession frequency decreases. C) Increasing the mass increases both the angular momentum and the torque equally, so the precession frequency stays the same Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 21
24 Clicker Question A disk is spinning with angular velocity ω on a pivoted horizontal axle as shown. If the radius of the disk were doubled but its mass and angular velocity were kept the same: A) The angular momentum of the disk Quadruples B) The angular momentum of the disk Doubles C) The torque about the pivot doubles D) Both A and C C) Both B and C L = Iω Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 22
25 CheckPoint A disk is spinning with angular velocity ω on a pivoted horizontal axle as shown. Gravity acts down and the disk has a precession frequency Ω. If the radius of the disk were doubled but its mass and angular velocity were kept the same, the precession frequency would A) Increase B) Decrease C) Stay the same Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 23
26 CheckPoint If the radius of the disk were doubled but its mass and angular velocity were kept the same, the precession frequency would A) Increase B) Decrease C) Stay the same A) The moment of inerna would increase, so the angular momentum would increase, so omega would also increase B) If you increase radius, you increase angular momentum, and thus decrease the precession frequency. C) the frequency would remain the same because the radius has no impact on the frequency Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 24
27 All of this stuff doesn't really seem pracncal. If you can't prove me wrong then we should all just get A's for this secnon of the course. (see 2:30) PracNcal ApplicaNon: Keeps you from falling off your bike when you ride using no hands! Riding straight (τ = 0) Lean Lek (τ out of page) Lean Right (τ into page) Wheel steers straight Wheel steers lek Wheel steers right Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 25
28 d Mg Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 26
29 L (using right hand rule) Mechanics Lecture 20, Slide 27
Last 6 lectures are easier
 Your Comments I love you. Seriously. I do. And you never post it. I felt really bad whilst completing the checkpoint for this. This stuff is way above my head and I struggled with the concept of precession.
Your Comments I love you. Seriously. I do. And you never post it. I felt really bad whilst completing the checkpoint for this. This stuff is way above my head and I struggled with the concept of precession.
Chapter 11. Today. Last Wednesday. Precession from Pre- lecture. Solving problems with torque
 Chapter 11 Last Wednesday Solving problems with torque Work and power with torque Angular momentum Conserva5on of angular momentum Today Precession from Pre- lecture Study the condi5ons for equilibrium
Chapter 11 Last Wednesday Solving problems with torque Work and power with torque Angular momentum Conserva5on of angular momentum Today Precession from Pre- lecture Study the condi5ons for equilibrium
PHYSICS 220. Lecture 15. Textbook Sections Lecture 15 Purdue University, Physics 220 1
 PHYSICS 220 Lecture 15 Angular Momentum Textbook Sections 9.3 9.6 Lecture 15 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Last Lecture Overview Torque = Force that causes rotation τ = F r sin θ Work done by torque
PHYSICS 220 Lecture 15 Angular Momentum Textbook Sections 9.3 9.6 Lecture 15 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Last Lecture Overview Torque = Force that causes rotation τ = F r sin θ Work done by torque
Classical Mechanics Lecture 7
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 7 Today s Concepts: Work & Kine6c Energy Mechanics Lecture 7, Slide 1 Notices Midterm Exam Friday Feb 8 will cover stuff we do un6l today. 10 mul6ple choice + 2 problems, 2
Classical Mechanics Lecture 7 Today s Concepts: Work & Kine6c Energy Mechanics Lecture 7, Slide 1 Notices Midterm Exam Friday Feb 8 will cover stuff we do un6l today. 10 mul6ple choice + 2 problems, 2
Classical Mechanics Lecture 7
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 7 Today s Concepts: Work & Kine6c Energy Mechanics Lecture 7, Slide 1 Karate Will not do Session 3 of Unit 8. It is a Karate thing. We will only mark Session 2 of unit 8. You
Classical Mechanics Lecture 7 Today s Concepts: Work & Kine6c Energy Mechanics Lecture 7, Slide 1 Karate Will not do Session 3 of Unit 8. It is a Karate thing. We will only mark Session 2 of unit 8. You
Classical Mechanics Lecture 7
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 7 UNIT 10: WORK AND ENERGY Approximate Classroom Time: Three 100 minute sessions Today s Concepts: Work & Kine6c Energy ES "Knowing is not enough; we must apply. Willing is
Classical Mechanics Lecture 7 UNIT 10: WORK AND ENERGY Approximate Classroom Time: Three 100 minute sessions Today s Concepts: Work & Kine6c Energy ES "Knowing is not enough; we must apply. Willing is
Last Time: Finish Ch 9 Start Ch 10 Today: Chapter 10
 Last Time: Finish Ch 9 Start Ch 10 Today: Chapter 10 Monday Ch 9 examples Rota:on of a rigid body Torque and angular accelera:on Today Solving problems with torque Work and power with torque Angular momentum
Last Time: Finish Ch 9 Start Ch 10 Today: Chapter 10 Monday Ch 9 examples Rota:on of a rigid body Torque and angular accelera:on Today Solving problems with torque Work and power with torque Angular momentum
Gyroscopes and statics
 Gyroscopes and statics Announcements: Welcome back from Spring Break! CAPA due Friday at 10pm We will finish Chapter 11 in H+R on angular momentum and start Chapter 12 on stability. Friday we will begin
Gyroscopes and statics Announcements: Welcome back from Spring Break! CAPA due Friday at 10pm We will finish Chapter 11 in H+R on angular momentum and start Chapter 12 on stability. Friday we will begin
Your Comments. Mechanics Lecture 19, Slide 1
 Your Comments i studied so hard for exam... and i did so bad :'( why physics u no love me. When we say a system will conserve angular momentum, does the solar system count? Say the sun suddenly expands
Your Comments i studied so hard for exam... and i did so bad :'( why physics u no love me. When we say a system will conserve angular momentum, does the solar system count? Say the sun suddenly expands
Classical Mechanics Lecture 17
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 17 Today s Concept: Angular Momentum Mechanics Lecture 19, Slide 1 So does L=r x p or L= Iω? Your Comments I would appreciate if I was not treated as a point par8cle, Why does
Classical Mechanics Lecture 17 Today s Concept: Angular Momentum Mechanics Lecture 19, Slide 1 So does L=r x p or L= Iω? Your Comments I would appreciate if I was not treated as a point par8cle, Why does
Physics 131: Lecture 22. Today s Agenda
 Physics 131: Lecture 22 Today s Agenda Rotational dynamics Torque = I Angular Momentum Physics 201: Lecture 10, Pg 1 An Unfair Race A frictionless block and a rolling (without slipping) disk are released
Physics 131: Lecture 22 Today s Agenda Rotational dynamics Torque = I Angular Momentum Physics 201: Lecture 10, Pg 1 An Unfair Race A frictionless block and a rolling (without slipping) disk are released
Review for 3 rd Midterm
 Review for 3 rd Midterm Midterm is on 4/19 at 7:30pm in the same rooms as before You are allowed one double sided sheet of paper with any handwritten notes you like. The moment-of-inertia about the center-of-mass
Review for 3 rd Midterm Midterm is on 4/19 at 7:30pm in the same rooms as before You are allowed one double sided sheet of paper with any handwritten notes you like. The moment-of-inertia about the center-of-mass
Classical Mechanics Lecture 9
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 9 Today's Concepts: a) Energy and Fric6on b) Poten6al energy & force Mechanics Lecture 9, Slide 1 Some comments about the course Spring examples with numbers Bring out a spring!
Classical Mechanics Lecture 9 Today's Concepts: a) Energy and Fric6on b) Poten6al energy & force Mechanics Lecture 9, Slide 1 Some comments about the course Spring examples with numbers Bring out a spring!
Your Comments. That s the plan
 Your Comments I love physics as much as the next gal, but I was wondering. Why don't we get class off the day after an evening exam? What if the ladder has friction with the wall? Things were complicated
Your Comments I love physics as much as the next gal, but I was wondering. Why don't we get class off the day after an evening exam? What if the ladder has friction with the wall? Things were complicated
Angular Momentum L = I ω
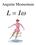 Angular Momentum L = Iω If no NET external Torques act on a system then Angular Momentum is Conserved. Linitial = I ω = L final = Iω Angular Momentum L = Iω Angular Momentum L = I ω A Skater spins with
Angular Momentum L = Iω If no NET external Torques act on a system then Angular Momentum is Conserved. Linitial = I ω = L final = Iω Angular Momentum L = Iω Angular Momentum L = I ω A Skater spins with
Chapter 11. Angular Momentum
 Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Angular Momentum The Vector Nature of Rotation Torque and Angular Momentum Conservation of Angular Momentum MFMcGraw-PHY 2425 Chap_11Ha_Angular_Momentum-Revised 10/13/2012 2
Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Angular Momentum The Vector Nature of Rotation Torque and Angular Momentum Conservation of Angular Momentum MFMcGraw-PHY 2425 Chap_11Ha_Angular_Momentum-Revised 10/13/2012 2
Physics 131: Lecture 22. Today s Agenda
 Physics 131: Lecture Today s Agenda Rotational dynamics Torque = I Angular Momentum Physics 01: Lecture 10, Pg 1 An Unfair Race A frictionless block and a rolling (without slipping) disk are released at
Physics 131: Lecture Today s Agenda Rotational dynamics Torque = I Angular Momentum Physics 01: Lecture 10, Pg 1 An Unfair Race A frictionless block and a rolling (without slipping) disk are released at
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 21
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 21 Chapter 8: Torque and Angular Momentum 8.2 Torque 8.4 Equilibrium Revisited 8.8 Angular Momentum Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 Midterm Exam 2 Wednesday, April 6, 6:30
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 21 Chapter 8: Torque and Angular Momentum 8.2 Torque 8.4 Equilibrium Revisited 8.8 Angular Momentum Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 Midterm Exam 2 Wednesday, April 6, 6:30
Kinetic Energy of Rolling
 Kinetic Energy of Rolling A solid disk and a hoop (with the same mass and radius) are released from rest and roll down a ramp from a height h. Which one is moving faster at the bottom of the ramp? A. they
Kinetic Energy of Rolling A solid disk and a hoop (with the same mass and radius) are released from rest and roll down a ramp from a height h. Which one is moving faster at the bottom of the ramp? A. they
PHY131H1F - Class 18. Torque of a quick push
 Today: Today, Chapter 11: PHY131H1F - Class 18 Angular velocity and Angular acceleration vectors Torque and the Vector Cross Product Angular Momentum Conservation of Angular Momentum Gyroscopes and Precession
Today: Today, Chapter 11: PHY131H1F - Class 18 Angular velocity and Angular acceleration vectors Torque and the Vector Cross Product Angular Momentum Conservation of Angular Momentum Gyroscopes and Precession
Angular Momentum. Objectives CONSERVATION OF ANGULAR MOMENTUM
 Angular Momentum CONSERVATION OF ANGULAR MOMENTUM Objectives Calculate the angular momentum vector for a moving particle Calculate the angular momentum vector for a rotating rigid object where angular
Angular Momentum CONSERVATION OF ANGULAR MOMENTUM Objectives Calculate the angular momentum vector for a moving particle Calculate the angular momentum vector for a rotating rigid object where angular
Work and kinetic Energy
 Work and kinetic Energy Problem 66. M=4.5kg r = 0.05m I = 0.003kgm 2 Q: What is the velocity of mass m after it dropped a distance h? (No friction) h m=0.6kg mg Work and kinetic Energy Problem 66. M=4.5kg
Work and kinetic Energy Problem 66. M=4.5kg r = 0.05m I = 0.003kgm 2 Q: What is the velocity of mass m after it dropped a distance h? (No friction) h m=0.6kg mg Work and kinetic Energy Problem 66. M=4.5kg
Angular Momentum System of Particles Concept Questions
 Question 1: Angular Momentum Angular Momentum System of Particles Concept Questions A non-symmetric body rotates with an angular speed ω about the z axis. Relative to the origin 1. L 0 is constant. 2.
Question 1: Angular Momentum Angular Momentum System of Particles Concept Questions A non-symmetric body rotates with an angular speed ω about the z axis. Relative to the origin 1. L 0 is constant. 2.
If rigid body = few particles I = m i. If rigid body = too-many-to-count particles I = I COM. KE rot. = 1 2 Iω 2
 2 If rigid body = few particles I = m i r i If rigid body = too-many-to-count particles Sum Integral Parallel Axis Theorem I = I COM + Mh 2 Energy of rota,onal mo,on KE rot = 1 2 Iω 2 [ KE trans = 1 2
2 If rigid body = few particles I = m i r i If rigid body = too-many-to-count particles Sum Integral Parallel Axis Theorem I = I COM + Mh 2 Energy of rota,onal mo,on KE rot = 1 2 Iω 2 [ KE trans = 1 2
Review session for Exam 2 Monday 3/25 6:00 PM in Loomis 151 (here) Print out/bring Exam 2, Fall 2005
 Physics 101: Lecture 16 Rolling Objects and Angular Momentum No checkpoints today. Review session for Exam 2 Monday 3/25 6:00 PM in Loomis 151 (here) Print out/bring Exam 2, Fall 2005 Linear and Angular
Physics 101: Lecture 16 Rolling Objects and Angular Momentum No checkpoints today. Review session for Exam 2 Monday 3/25 6:00 PM in Loomis 151 (here) Print out/bring Exam 2, Fall 2005 Linear and Angular
PHYS 185 Final Exam December 4, 2012
 PHYS 185 Final Exam December 4, 2012 Name: Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for an answer, continue on the back of the page. Please make an effort
PHYS 185 Final Exam December 4, 2012 Name: Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for an answer, continue on the back of the page. Please make an effort
Chapter 10: Dynamics of Rotational Motion
 Chapter 10: Dynamics of Rotational Motion What causes an angular acceleration? The effectiveness of a force at causing a rotation is called torque. QuickCheck 12.5 The four forces shown have the same strength.
Chapter 10: Dynamics of Rotational Motion What causes an angular acceleration? The effectiveness of a force at causing a rotation is called torque. QuickCheck 12.5 The four forces shown have the same strength.
Rolling without slipping Angular Momentum Conservation of Angular Momentum. Physics 201: Lecture 19, Pg 1
 Physics 131: Lecture Today s Agenda Rolling without slipping Angular Momentum Conservation o Angular Momentum Physics 01: Lecture 19, Pg 1 Rolling Without Slipping Rolling is a combination o rotation and
Physics 131: Lecture Today s Agenda Rolling without slipping Angular Momentum Conservation o Angular Momentum Physics 01: Lecture 19, Pg 1 Rolling Without Slipping Rolling is a combination o rotation and
Classical Mechanics Lecture 16
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 16 Today s Concepts: a) Rolling Kine6c Energy b) Angular Accelera6on Physics 211 Lecture 16, Slide 1 Thoughts from the Present & Past Can we do that cookie 6n demo again, but
Classical Mechanics Lecture 16 Today s Concepts: a) Rolling Kine6c Energy b) Angular Accelera6on Physics 211 Lecture 16, Slide 1 Thoughts from the Present & Past Can we do that cookie 6n demo again, but
Cutnell/Johnson Physics
 Cutnell/Johnson Physics Classroom Response System Questions Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics Interactive Lecture Questions 9.1.1. You are using a wrench in an attempt to loosen a nut by applying a force as
Cutnell/Johnson Physics Classroom Response System Questions Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics Interactive Lecture Questions 9.1.1. You are using a wrench in an attempt to loosen a nut by applying a force as
Classical Mechanics Lecture 21
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 21 Today s Concept: Simple Harmonic Mo7on: Mass on a Spring Mechanics Lecture 21, Slide 1 The Mechanical Universe, Episode 20: Harmonic Motion http://www.learner.org/vod/login.html?pid=565
Classical Mechanics Lecture 21 Today s Concept: Simple Harmonic Mo7on: Mass on a Spring Mechanics Lecture 21, Slide 1 The Mechanical Universe, Episode 20: Harmonic Motion http://www.learner.org/vod/login.html?pid=565
Midterm 3 Thursday April 13th
 Welcome back to Physics 215 Today s agenda: Angular momentum Rolling without slipping Midterm Review Physics 215 Spring 2017 Lecture 12-2 1 Midterm 3 Thursday April 13th Material covered: Ch 9 Ch 12 Lectures
Welcome back to Physics 215 Today s agenda: Angular momentum Rolling without slipping Midterm Review Physics 215 Spring 2017 Lecture 12-2 1 Midterm 3 Thursday April 13th Material covered: Ch 9 Ch 12 Lectures
Rolling, Torque, Angular Momentum
 Chapter 11 Rolling, Torque, Angular Momentum Copyright 11.2 Rolling as Translational and Rotation Combined Motion of Translation : i.e.motion along a straight line Motion of Rotation : rotation about a
Chapter 11 Rolling, Torque, Angular Momentum Copyright 11.2 Rolling as Translational and Rotation Combined Motion of Translation : i.e.motion along a straight line Motion of Rotation : rotation about a
Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics Tuesday, September 17, 2013
 Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics Tuesday, September 17, 2013 10:00 PM The fundamental idea of Newtonian dynamics is that "things happen for a reason;" to be more specific, there is no need to explain rest
Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics Tuesday, September 17, 2013 10:00 PM The fundamental idea of Newtonian dynamics is that "things happen for a reason;" to be more specific, there is no need to explain rest
ω = ω 0 θ = θ + ω 0 t αt ( ) Rota%onal Kinema%cs: ( ONLY IF α = constant) v = ω r ω ω r s = θ r v = d θ dt r = ω r + a r = a a tot + a t = a r
 θ (t) ( θ 1 ) Δ θ = θ 2 s = θ r ω (t) = d θ (t) dt v = d θ dt r = ω r v = ω r α (t) = d ω (t) dt = d 2 θ (t) dt 2 a tot 2 = a r 2 + a t 2 = ω 2 r 2 + αr 2 a tot = a t + a r = a r ω ω r a t = α r ( ) Rota%onal
θ (t) ( θ 1 ) Δ θ = θ 2 s = θ r ω (t) = d θ (t) dt v = d θ dt r = ω r v = ω r α (t) = d ω (t) dt = d 2 θ (t) dt 2 a tot 2 = a r 2 + a t 2 = ω 2 r 2 + αr 2 a tot = a t + a r = a r ω ω r a t = α r ( ) Rota%onal
Classical Mechanics Lecture 15
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 5 Today s Concepts: a) Parallel Axis Theorem b) Torque & Angular Acceleration Mechanics Lecture 5, Slide Unit 4 Main Points Mechanics Lecture 4, Slide Unit 4 Main Points Mechanics
Classical Mechanics Lecture 5 Today s Concepts: a) Parallel Axis Theorem b) Torque & Angular Acceleration Mechanics Lecture 5, Slide Unit 4 Main Points Mechanics Lecture 4, Slide Unit 4 Main Points Mechanics
Angular Momentum L = I ω
 Angular Momentum L = Iω If no NET external Torques act on a system then Angular Momentum is Conserved. Linitial = I ω = L final = Iω Angular Momentum L = Iω Angular Momentum L = I ω A Skater spins with
Angular Momentum L = Iω If no NET external Torques act on a system then Angular Momentum is Conserved. Linitial = I ω = L final = Iω Angular Momentum L = Iω Angular Momentum L = I ω A Skater spins with
Exam 3 Practice Solutions
 Exam 3 Practice Solutions Multiple Choice 1. A thin hoop, a solid disk, and a solid sphere, each with the same mass and radius, are at rest at the top of an inclined plane. If all three are released at
Exam 3 Practice Solutions Multiple Choice 1. A thin hoop, a solid disk, and a solid sphere, each with the same mass and radius, are at rest at the top of an inclined plane. If all three are released at
NAME. (2) Choose the graph below that represents the velocity vs. time for constant, nonzero acceleration in one dimension.
 (1) The figure shows a lever (which is a uniform bar, length d and mass M), hinged at the bottom and supported steadily by a rope. The rope is attached a distance d/4 from the hinge. The two angles are
(1) The figure shows a lever (which is a uniform bar, length d and mass M), hinged at the bottom and supported steadily by a rope. The rope is attached a distance d/4 from the hinge. The two angles are
Physics 8 Friday, November 4, 2011
 Physics 8 Friday, November 4, 2011 Please turn in Homework 7. I will hand out solutions once everyone is here. The handout also includes HW8 and a page or two of updates to the equation sheet needed to
Physics 8 Friday, November 4, 2011 Please turn in Homework 7. I will hand out solutions once everyone is here. The handout also includes HW8 and a page or two of updates to the equation sheet needed to
Classical Mechanics Lecture 3
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 3 Today's Concepts: Newton s Laws a) Accelera=on is caused by forces b) Force changes momentum c) Forces always come in pairs d) Good reference frames Mechanics Lecture 3, Slide
Classical Mechanics Lecture 3 Today's Concepts: Newton s Laws a) Accelera=on is caused by forces b) Force changes momentum c) Forces always come in pairs d) Good reference frames Mechanics Lecture 3, Slide
Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum
 AP Physics C Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum Introduction: Rolling: In the last unit we studied the rotation of a rigid body about a fixed axis. We will now extend our study to include cases where
AP Physics C Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum Introduction: Rolling: In the last unit we studied the rotation of a rigid body about a fixed axis. We will now extend our study to include cases where
Stability of rotating objects
 PHY131H1F - Hour 28 Today: We finish up Chapter 9! 9.5 Rotational Kinetic Energy (skip 9.6 on Tides and Earth s day) Stability of rotating objects If the rider's balance shifts a bit, the bike + rider
PHY131H1F - Hour 28 Today: We finish up Chapter 9! 9.5 Rotational Kinetic Energy (skip 9.6 on Tides and Earth s day) Stability of rotating objects If the rider's balance shifts a bit, the bike + rider
Physics 2210 Fall smartphysics Rotational Statics 11/18/2015
 Physics 2210 Fall 2015 smartphysics 17-18 Rotational Statics 11/18/2015 τ TT = L T 1 sin 150 = 1 T 2 1L Poll 11-18-01 τ TT = L 2 T 2 sin 150 = 1 4 T 2L 150 150 τ gg = L 2 MM sin +90 = 1 2 MMM +90 MM τ
Physics 2210 Fall 2015 smartphysics 17-18 Rotational Statics 11/18/2015 τ TT = L T 1 sin 150 = 1 T 2 1L Poll 11-18-01 τ TT = L 2 T 2 sin 150 = 1 4 T 2L 150 150 τ gg = L 2 MM sin +90 = 1 2 MMM +90 MM τ
Chapter 8 - Rotational Dynamics and Equilibrium REVIEW
 Pagpalain ka! (Good luck, in Filipino) Date Chapter 8 - Rotational Dynamics and Equilibrium REVIEW TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) When a rigid body
Pagpalain ka! (Good luck, in Filipino) Date Chapter 8 - Rotational Dynamics and Equilibrium REVIEW TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) When a rigid body
Stuff you asked about:
 Stuff you asked about: Instrumental illness Can you go over the change in momentum with respect to the change in time being used to calcuate the net force in depth more during the lecture. We never really
Stuff you asked about: Instrumental illness Can you go over the change in momentum with respect to the change in time being used to calcuate the net force in depth more during the lecture. We never really
Classical Mechanics Lecture 8
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 8 Name St.No. - Date(YY/MM/DD) / / Section Today's Concepts: a) Poten)al Energy b) Mechanical Energy UNIT 11: ENERGY CONSERVATION Approximate Classroom Time: Two 100 minute
Classical Mechanics Lecture 8 Name St.No. - Date(YY/MM/DD) / / Section Today's Concepts: a) Poten)al Energy b) Mechanical Energy UNIT 11: ENERGY CONSERVATION Approximate Classroom Time: Two 100 minute
A solid disk and a ring roll down an incline. The ring is slower than the disk if
 A solid disk and a ring roll down an incline. The ring is slower than the disk if A. mring= mdisk, where m is the mass. B. rring = rdisk, where r is the radius. C. mring = mdisk and rring = rdisk. D.The
A solid disk and a ring roll down an incline. The ring is slower than the disk if A. mring= mdisk, where m is the mass. B. rring = rdisk, where r is the radius. C. mring = mdisk and rring = rdisk. D.The
Rotational Dynamics. A wrench floats weightlessly in space. It is subjected to two forces of equal and opposite magnitude: Will the wrench accelerate?
 Rotational Dynamics A wrench floats weightlessly in space. It is subjected to two forces of equal and opposite magnitude: Will the wrench accelerate? A. yes B. no C. kind of? Rotational Dynamics 10.1-3
Rotational Dynamics A wrench floats weightlessly in space. It is subjected to two forces of equal and opposite magnitude: Will the wrench accelerate? A. yes B. no C. kind of? Rotational Dynamics 10.1-3
Physics 2210 Fall smartphysics Conservation of Angular Momentum 11/20/2015
 Physics 2210 Fall 2015 smartphysics 19-20 Conservation of Angular Momentum 11/20/2015 Poll 11-18-03 In the two cases shown above identical ladders are leaning against frictionless walls and are not sliding.
Physics 2210 Fall 2015 smartphysics 19-20 Conservation of Angular Momentum 11/20/2015 Poll 11-18-03 In the two cases shown above identical ladders are leaning against frictionless walls and are not sliding.
Rolling, Torque & Angular Momentum
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 11 Rolling, Torque & Angular Momentum Rolling motion Torque Angular momentum Conservation of angular momentum 1. A uniform hoop (ring) is rolling smoothly from the
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 11 Rolling, Torque & Angular Momentum Rolling motion Torque Angular momentum Conservation of angular momentum 1. A uniform hoop (ring) is rolling smoothly from the
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes
 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes Physics 2414 - Strauss Formulas: v = l / t = r θ / t = rω a T = v / t = r ω / t =rα a C = v 2 /r = ω 2 r ω = ω 0 + αt θ = ω 0 t +(1/2)αt 2 θ = (1/2)(ω 0 +ω)t ω 2 = ω 0 2 +2αθ τ
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes Physics 2414 - Strauss Formulas: v = l / t = r θ / t = rω a T = v / t = r ω / t =rα a C = v 2 /r = ω 2 r ω = ω 0 + αt θ = ω 0 t +(1/2)αt 2 θ = (1/2)(ω 0 +ω)t ω 2 = ω 0 2 +2αθ τ
Chapter 8 Lecture. Pearson Physics. Rotational Motion and Equilibrium. Prepared by Chris Chiaverina Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 8 Lecture Pearson Physics Rotational Motion and Equilibrium Prepared by Chris Chiaverina Chapter Contents Describing Angular Motion Rolling Motion and the Moment of Inertia Torque Static Equilibrium
Chapter 8 Lecture Pearson Physics Rotational Motion and Equilibrium Prepared by Chris Chiaverina Chapter Contents Describing Angular Motion Rolling Motion and the Moment of Inertia Torque Static Equilibrium
Chapter 11. Angular Momentum
 Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Angular Momentum Angular momentum plays a key role in rotational dynamics. There is a principle of conservation of angular momentum. In analogy to the principle of conservation
Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Angular Momentum Angular momentum plays a key role in rotational dynamics. There is a principle of conservation of angular momentum. In analogy to the principle of conservation
Classical Mechanics Lecture 8
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 8 Today's Concepts: a) Poten2al Energy b) Mechanical Energy Mechanics Lecture 8, Slide 1 Stuff you asked about: Gravity is the law. violators will be brought down. How were
Classical Mechanics Lecture 8 Today's Concepts: a) Poten2al Energy b) Mechanical Energy Mechanics Lecture 8, Slide 1 Stuff you asked about: Gravity is the law. violators will be brought down. How were
Physics 111. Tuesday, November 2, Rotational Dynamics Torque Angular Momentum Rotational Kinetic Energy
 ics Tuesday, ember 2, 2002 Ch 11: Rotational Dynamics Torque Angular Momentum Rotational Kinetic Energy Announcements Wednesday, 8-9 pm in NSC 118/119 Sunday, 6:30-8 pm in CCLIR 468 Announcements This
ics Tuesday, ember 2, 2002 Ch 11: Rotational Dynamics Torque Angular Momentum Rotational Kinetic Energy Announcements Wednesday, 8-9 pm in NSC 118/119 Sunday, 6:30-8 pm in CCLIR 468 Announcements This
Q: What does angular momentum mean? What is its equation for calculation?
 Ch 10: Conservation of Angular Momentum Reeeeecap. Q: What does angular velocity mean? What is its symbol? A: The rate of change of angular displacement.. Q: What does angular acceleration mean? What is
Ch 10: Conservation of Angular Momentum Reeeeecap. Q: What does angular velocity mean? What is its symbol? A: The rate of change of angular displacement.. Q: What does angular acceleration mean? What is
Classical Mechanics Lecture 5
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 5 Today s Concepts: a) Free Body Diagrams b) Force due to strings c) Force due to springs d) Force due to gravity Mechanics Lecture 5, Slide 1 Stuff you asked about:! the change
Classical Mechanics Lecture 5 Today s Concepts: a) Free Body Diagrams b) Force due to strings c) Force due to springs d) Force due to gravity Mechanics Lecture 5, Slide 1 Stuff you asked about:! the change
Chapter 11 Angular Momentum; General Rotation. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 11 Angular Momentum; General Rotation ! L = I!! Units of Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Objects Rotating About a Fixed Axis Vector Cross Product; Torque as a Vector Angular Momentum of a Particle
Chapter 11 Angular Momentum; General Rotation ! L = I!! Units of Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Objects Rotating About a Fixed Axis Vector Cross Product; Torque as a Vector Angular Momentum of a Particle
It will be most difficult for the ant to adhere to the wheel as it revolves past which of the four points? A) I B) II C) III D) IV
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 16 Homework Newton s First and Second Law of Rotational Motion Outcomes Define rotational inertia, torque, and center of gravity. State and explain Newton s first Law of Motion as it
AP Physics 1 Lesson 16 Homework Newton s First and Second Law of Rotational Motion Outcomes Define rotational inertia, torque, and center of gravity. State and explain Newton s first Law of Motion as it
Lectures. Today: Rolling and Angular Momentum in ch 12. Complete angular momentum (chapter 12) and begin equilibrium (chapter 13)
 Lectures Today: Rolling and Angular Momentum in ch 1 Homework 6 due Next time: Complete angular momentum (chapter 1) and begin equilibrium (chapter 13) By Monday, will post at website Sample midterm II
Lectures Today: Rolling and Angular Momentum in ch 1 Homework 6 due Next time: Complete angular momentum (chapter 1) and begin equilibrium (chapter 13) By Monday, will post at website Sample midterm II
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 8
 Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 8 1. If the beaters on a mixer make 800 revolutions in 5 minutes, what is the average rotational speed of the beaters? a. 2.67 rev/min b. 16.8
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 8 1. If the beaters on a mixer make 800 revolutions in 5 minutes, what is the average rotational speed of the beaters? a. 2.67 rev/min b. 16.8
W13D1-1 Reading Quiz and Concept Questions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 2009 W13D1-1 Reading Quiz and Concept Questions A person spins a tennis ball on a string in a horizontal circle (so that
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 2009 W13D1-1 Reading Quiz and Concept Questions A person spins a tennis ball on a string in a horizontal circle (so that
Chapter 8. Rotational Motion
 Chapter 8 Rotational Motion Rotational Work and Energy W = Fs = s = rθ Frθ Consider the work done in rotating a wheel with a tangential force, F, by an angle θ. τ = Fr W =τθ Rotational Work and Energy
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion Rotational Work and Energy W = Fs = s = rθ Frθ Consider the work done in rotating a wheel with a tangential force, F, by an angle θ. τ = Fr W =τθ Rotational Work and Energy
Name: Date: Period: AP Physics C Rotational Motion HO19
 1.) A wheel turns with constant acceleration 0.450 rad/s 2. (9-9) Rotational Motion H19 How much time does it take to reach an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s, starting from rest? Through how many revolutions
1.) A wheel turns with constant acceleration 0.450 rad/s 2. (9-9) Rotational Motion H19 How much time does it take to reach an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s, starting from rest? Through how many revolutions
PHYSICS. Chapter 12 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 12 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 12 Rotation of a Rigid Body IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn to understand and apply the physics
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 12 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 12 Rotation of a Rigid Body IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn to understand and apply the physics
Last Time: Ch 3 Today: Relative Motion and Ch 4
 Last Time: Ch 3 Today: Relative Motion and Ch 4 Chapter 3 Finish Rela+ve Mo+on Chapter 4 Forces Newton s 1 st Law Newton s 2 nd Law Free body diagrams Examples (if we get that far) Prelecture: Ques2on
Last Time: Ch 3 Today: Relative Motion and Ch 4 Chapter 3 Finish Rela+ve Mo+on Chapter 4 Forces Newton s 1 st Law Newton s 2 nd Law Free body diagrams Examples (if we get that far) Prelecture: Ques2on
8.012 Physics I: Classical Mechanics Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.012 Physics I: Classical Mechanics Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.012 Physics I: Classical Mechanics Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
Show all work in answering the following questions. Partial credit may be given for problems involving calculations.
 Physics 3210, Spring 2018 Final Exam Name: Signature: UID: Please read the following before continuing: Show all work in answering the following questions. Partial credit may be given for problems involving
Physics 3210, Spring 2018 Final Exam Name: Signature: UID: Please read the following before continuing: Show all work in answering the following questions. Partial credit may be given for problems involving
Circular Motion, Pt 2: Angular Dynamics. Mr. Velazquez AP/Honors Physics
 Circular Motion, Pt 2: Angular Dynamics Mr. Velazquez AP/Honors Physics Formulas: Angular Kinematics (θ must be in radians): s = rθ Arc Length 360 = 2π rads = 1 rev ω = θ t = v t r Angular Velocity α av
Circular Motion, Pt 2: Angular Dynamics Mr. Velazquez AP/Honors Physics Formulas: Angular Kinematics (θ must be in radians): s = rθ Arc Length 360 = 2π rads = 1 rev ω = θ t = v t r Angular Velocity α av
MITOCW 18. Quiz Review From Optional Problem Set 8
 MITOCW 18. Quiz Review From Optional Problem Set 8 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational
MITOCW 18. Quiz Review From Optional Problem Set 8 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational
A uniform rod of length L and Mass M is attached at one end to a frictionless pivot. If the rod is released from rest from the horizontal position,
 A dentist s drill starts from rest. After 3.20 s of constant angular acceleration, it turns at a rate of 2.51 10 4 rev/min. (a) Find the drill s angular acceleration. (b) Determine the angle (in radians)
A dentist s drill starts from rest. After 3.20 s of constant angular acceleration, it turns at a rate of 2.51 10 4 rev/min. (a) Find the drill s angular acceleration. (b) Determine the angle (in radians)
The student will be able to: the torque of an applied force and solve related problems.
 Honors Physics Assignment Rotational Mechanics Reading Chapters 10 and 11 Objectives/HW: Assignment #1 M: Assignment #2 M: Assignment #3 M: Assignment #4 M: 1 2 3 #1-5 #6-10 #14, 15, 17, 18, 20-23 #24,
Honors Physics Assignment Rotational Mechanics Reading Chapters 10 and 11 Objectives/HW: Assignment #1 M: Assignment #2 M: Assignment #3 M: Assignment #4 M: 1 2 3 #1-5 #6-10 #14, 15, 17, 18, 20-23 #24,
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium. 1. Give explanation of torque in own words after doing balance-the-torques lab as an inquiry introduction
 Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium Name 1. Give explanation of torque in own words after doing balance-the-torques lab as an inquiry introduction 1. The distance between a turning axis and the
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium Name 1. Give explanation of torque in own words after doing balance-the-torques lab as an inquiry introduction 1. The distance between a turning axis and the
New Course Webpage (To be setup by this weekend) h>p://people.physics.tamu.edu/tyana/phys218/
 Important Informa+on Instructor: Dr. Ty S(egler Office: ENPH 211 (Office Hours TBD) Email: tyana@physics.tamu.edu New Course Webpage (To be setup by this weekend) h>p://people.physics.tamu.edu/tyana/phys218/
Important Informa+on Instructor: Dr. Ty S(egler Office: ENPH 211 (Office Hours TBD) Email: tyana@physics.tamu.edu New Course Webpage (To be setup by this weekend) h>p://people.physics.tamu.edu/tyana/phys218/
Angular Momentum Conservation of Angular Momentum
 Lecture 22 Chapter 12 Physics I Angular Momentum Conservation of Angular Momentum Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will continue discussing rotational
Lecture 22 Chapter 12 Physics I Angular Momentum Conservation of Angular Momentum Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will continue discussing rotational
Conservation of Angular Momentum
 Lecture 23 Chapter 12 Physics I Conservation of Angular Momentum Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will continue discussing rotational dynamics
Lecture 23 Chapter 12 Physics I Conservation of Angular Momentum Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will continue discussing rotational dynamics
Physics 7A Lecture 2 Fall 2014 Midterm 2 Solutions. November 9, 2014
 Physics 7A Lecture 2 Fall 204 Midterm 2 Solutions November 9, 204 Lecture 2 Midterm 2 Problem Solution Our general strategy is to use energy conservation, keeping in mind that the force of friction will
Physics 7A Lecture 2 Fall 204 Midterm 2 Solutions November 9, 204 Lecture 2 Midterm 2 Problem Solution Our general strategy is to use energy conservation, keeping in mind that the force of friction will
Exam Results. Your scores will be posted before midnight tonight. Score Range = Approx. le<er Grade = A = B = C = D 0 34 = F
 Exam Results Your scores will be posted before midnight tonight. Score Range = Approx. le
Exam Results Your scores will be posted before midnight tonight. Score Range = Approx. le
Exam 3 Results !"#$%&%'()*+(,-./0% 123+#435%%6789:% Approximate Grade Cutoffs Ø A Ø B Ø C Ø D Ø 0 24 F
 Exam 3 Results Approximate Grade Cutos Ø 75-1 A Ø 55 74 B Ø 35 54 C Ø 5 34 D Ø 4 F '$!" '#!" '!!" &!" %!" $!" #!"!"!"#$%&%'()*+(,-./% 13+#435%%6789:%!()" )('!" '!(')" ')(#!" #!(#)" #)(*!" *!(*)" *)($!"
Exam 3 Results Approximate Grade Cutos Ø 75-1 A Ø 55 74 B Ø 35 54 C Ø 5 34 D Ø 4 F '$!" '#!" '!!" &!" %!" $!" #!"!"!"#$%&%'()*+(,-./% 13+#435%%6789:%!()" )('!" '!(')" ')(#!" #!(#)" #)(*!" *!(*)" *)($!"
Classical Mechanics Lecture 13
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 13 Today s Concepts: a) More on Elas5c Collisions b) Average Force during Collisions Mechanics Lecture 13, Slide 1 Your comments: good I'd like to go over the energy of a system
Classical Mechanics Lecture 13 Today s Concepts: a) More on Elas5c Collisions b) Average Force during Collisions Mechanics Lecture 13, Slide 1 Your comments: good I'd like to go over the energy of a system
Angular Motion Unit Exam Practice
 Angular Motion Unit Exam Practice Multiple Choice. Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If you whirl a tin can on the end of a string and the string suddenly
Angular Motion Unit Exam Practice Multiple Choice. Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If you whirl a tin can on the end of a string and the string suddenly
Review questions. Before the collision, 70 kg ball is stationary. Afterward, the 30 kg ball is stationary and 70 kg ball is moving to the right.
 Review questions Before the collision, 70 kg ball is stationary. Afterward, the 30 kg ball is stationary and 70 kg ball is moving to the right. 30 kg 70 kg v (a) Is this collision elastic? (b) Find the
Review questions Before the collision, 70 kg ball is stationary. Afterward, the 30 kg ball is stationary and 70 kg ball is moving to the right. 30 kg 70 kg v (a) Is this collision elastic? (b) Find the
Recap I. Angular position: Angular displacement: s. Angular velocity: Angular Acceleration:
 Recap I Angular position: Angular displacement: s Angular velocity: Angular Acceleration: Every point on a rotating rigid object has the same angular, but not the same linear motion! Recap II Circular
Recap I Angular position: Angular displacement: s Angular velocity: Angular Acceleration: Every point on a rotating rigid object has the same angular, but not the same linear motion! Recap II Circular
Lab 5: Rotational Motion II
 Lab 5: Rotational Motion II Written October-November 1986 by Nancy Bronder '86, Tom Budka '89, Bob Hamwey GS, D. Mook revised by Mook, K. Muenchinger '93 and E. Pleger '94 July-November 1991 and by Melissa
Lab 5: Rotational Motion II Written October-November 1986 by Nancy Bronder '86, Tom Budka '89, Bob Hamwey GS, D. Mook revised by Mook, K. Muenchinger '93 and E. Pleger '94 July-November 1991 and by Melissa
Rotation. Kinematics Rigid Bodies Kinetic Energy. Torque Rolling. featuring moments of Inertia
 Rotation Kinematics Rigid Bodies Kinetic Energy featuring moments of Inertia Torque Rolling Angular Motion We think about rotation in the same basic way we do about linear motion How far does it go? How
Rotation Kinematics Rigid Bodies Kinetic Energy featuring moments of Inertia Torque Rolling Angular Motion We think about rotation in the same basic way we do about linear motion How far does it go? How
Rotational Kinetic Energy
 Lecture 17, Chapter 10: Rotational Energy and Angular Momentum 1 Rotational Kinetic Energy Consider a rigid body rotating with an angular velocity ω about an axis. Clearly every point in the rigid body
Lecture 17, Chapter 10: Rotational Energy and Angular Momentum 1 Rotational Kinetic Energy Consider a rigid body rotating with an angular velocity ω about an axis. Clearly every point in the rigid body
Chapter 8: Dynamics in a plane
 8.1 Dynamics in 2 Dimensions p. 210-212 Chapter 8: Dynamics in a plane 8.2 Velocity and Acceleration in uniform circular motion (a review of sec. 4.6) p. 212-214 8.3 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion
8.1 Dynamics in 2 Dimensions p. 210-212 Chapter 8: Dynamics in a plane 8.2 Velocity and Acceleration in uniform circular motion (a review of sec. 4.6) p. 212-214 8.3 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion
 PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
End-of-Chapter Exercises
 End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. Figure 11.21 shows four different cases involving a
End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. Figure 11.21 shows four different cases involving a
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 11. Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 11 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 11 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion
 PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
Chapter 12. Rotation of a Rigid Body
 Chapter 12. Rotation of a Rigid Body Not all motion can be described as that of a particle. Rotation requires the idea of an extended object. This diver is moving toward the water along a parabolic trajectory,
Chapter 12. Rotation of a Rigid Body Not all motion can be described as that of a particle. Rotation requires the idea of an extended object. This diver is moving toward the water along a parabolic trajectory,
43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms,
 43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms, A) her moment of inertia increases and her rotational kinetic energy remains the same.
43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms, A) her moment of inertia increases and her rotational kinetic energy remains the same.
Wiley Plus. Final Assignment (5) Is Due Today: Before 11 pm!
 Wiley Plus Final Assignment (5) Is Due Today: Before 11 pm! Final Exam Review December 9, 009 3 What about vector subtraction? Suppose you are given the vector relation A B C RULE: The resultant vector
Wiley Plus Final Assignment (5) Is Due Today: Before 11 pm! Final Exam Review December 9, 009 3 What about vector subtraction? Suppose you are given the vector relation A B C RULE: The resultant vector
ENGINEERING COUNCIL DYNAMICS OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS D225 TUTORIAL 6 - GYROSCOPES. On completion of this tutorial you should be able to
 ENGINEERING COUNCIL DYNAMICS OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS D225 TUTORIAL 6 - GYROSCOPES This tutorial examines linear and angular motion. The work is then linked with earlier studies of materials and mechanisms
ENGINEERING COUNCIL DYNAMICS OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS D225 TUTORIAL 6 - GYROSCOPES This tutorial examines linear and angular motion. The work is then linked with earlier studies of materials and mechanisms
Classical Mechanics Lecture 13
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 13 Today s Concepts: a) More on Elas5c Collisions b) Average Force during Collisions Mechanics Lecture 13, Slide 1 Your comments: This section was pretty good. Easy to understand.
Classical Mechanics Lecture 13 Today s Concepts: a) More on Elas5c Collisions b) Average Force during Collisions Mechanics Lecture 13, Slide 1 Your comments: This section was pretty good. Easy to understand.
Equilibrium. For an object to remain in equilibrium, two conditions must be met. The object must have no net force: and no net torque:
 Equilibrium For an object to remain in equilibrium, two conditions must be met. The object must have no net force: F v = 0 and no net torque: v τ = 0 Worksheet A uniform rod with a length L and a mass
Equilibrium For an object to remain in equilibrium, two conditions must be met. The object must have no net force: F v = 0 and no net torque: v τ = 0 Worksheet A uniform rod with a length L and a mass
The student will be able to: 1 Determine the torque of an applied force and solve related problems.
 Honors Physics Assignment Rotational Mechanics Reading Chapters 10 and 11 Objectives/HW The student will be able to: HW: 1 Determine the torque of an applied force and solve related problems. (t = rx r
Honors Physics Assignment Rotational Mechanics Reading Chapters 10 and 11 Objectives/HW The student will be able to: HW: 1 Determine the torque of an applied force and solve related problems. (t = rx r
LECTURE 17. Prof. Paul
 LECTURE 17 Prof. Paul Announcements Exam II, two weeks away Cumulative (you must know concepts from first exam) On your hw I just handed back, (#38) I may have INCORRECTLY stated that it s wrong to use
LECTURE 17 Prof. Paul Announcements Exam II, two weeks away Cumulative (you must know concepts from first exam) On your hw I just handed back, (#38) I may have INCORRECTLY stated that it s wrong to use
