Observing Climate - Surface
|
|
|
- Sharleen Nicholson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Observing Climate - Surface 3-1 Density Science Concepts Definition Mass Gas Laws Behavior of Gases Boyle s Law Charles Law Ideal Gas Law Adiabatic Ascent Energy - Potential Energy The Earth System (Kump, Kastin & Crane) Chap. 4 (p. 57)
2 Density 3-2 Definition MASS per unit volume not weight per unit volume - Mass ==> inertia - Weight ==> force as a result of gravity Don't usually measure atmospheric density Units g / cm 3 slug / in 3 Conversion 1 lb-mass / in 3 = gm / cm 3 Standard Atmosphere Surface Value At mb and 15 C, the atmospheric density is 1.23 kg / m 3
3 3-3 Boyle s Law ( Pressure * Volume ) is proportional to a constant if the temperature is kept constant during the process p 1 * V 1 = constant = p 2 * V 2 If density (ρ) is the mass / volume then ρ = m / V or solving for V, V = m / ρ. Replacing V in Boyle s Law by its equivalent m / ρ yields p 1 * m 1 / ρ 1 = constant = p 2 * m 2 / ρ 2 Robert Boyle ~jr/ if the mass within the volume remains physlist.html unchanged while the pressure and volume change, then m 1 = m 2 and can be canceled. Thus, we are left with p 1 / ρ 1 = constant = p 2 / ρ 2
4 3-4 Boyle s Law (Con t) Example - Take a balloon initially at pressure p 1 = 1000 mb and volume V 1 = 1 m 3. Reduce the pressure, while keeping the temperature constant, until the pressure is p 2 = 500 mb. What is the new volume, V 2? p 1 * V 1 = p 2 * V 2 ( 1000 mb ) * (1 m 3 ) = ( 500 mb ) * V 2 V 2 = [ 1000 (1) / 500 ] m 3 *mb / mb V 2 = 2.00 m 3 The balloon is now twice as large and the air half as dense.
5 3-5 Laws of Physics Example - Boyle s Law > p 1 * V 1 = constant = p 2 * V 2 How are these different from societal laws? What do laws of physics tell us? Can we prove a law of physics is true? When you can measure what you are speaking about, and express it in numbers, you know something about it; but when you cannot express it in numbers, your knowledge is of a meager and unsatisfactory kind; it may be the beginning of knowledge, but you have scarcely, in your thoughts, advanced to the state of science. Lord Kelvin ( )
6 3-6 Charles Law ( Volume / Temperature ) is proportional to a constant if the pressure is kept constant during the process. Note the temperature must be in Kelvin. V 1 / T 1 = constant = V 2 / T 2 or as with Boyle s Law in terms of density ρ 1 * T 1 = constant = ρ 2 * T 2 Jacques Charles
7 3-7 Charles Law (Con t) Example - Take a balloon initially at temperature T 1 = 17 C and volume V 1 = 1 m 3. Add heat, while keeping the pressure constant, until the temperature is T 2 = 37 C. What is the new volume, V 2? V 1 / T 1 = V 2 / T 2 ( 1 m 3 ) / [ ( ) K ] = V 2 / [ ( ) K ] V 2 = [ 1 ( 310 ) / 290 ] m 3 * K / K V 2 = 1.07 m 3 The balloon is now 7% larger and the air 7% less dense.
8 3-8 Ideal Gas Law or Equation of State Combining Boyle s and Charles Law ( p 1 * V 1 ) / T 1 = constant = ( p 2 * V 2 ) / T 2 or as with Boyle s Law p 1 / ( ρ 1 * T 1 ) = constant = p 2 / ( ρ 2 * T 2 ) Note the constant, R depends on the gas. For dry air R = Joules / kg - K.
9 3-9 Ideal Gas Law or Equation of State (Con t) Consequences of the Gas Law Parcel of air - Imaginary bubble or glob of air - Envision parcel having invisible, limp skin - Skin expands or contracts without effort. Thus, pressure inside parcel equals that outside the parcel Skin is heat tight (adiabatic) and water tight
10 3-10 Ideal Gas Law or Equation of State (Con t) Consequences of the Gas Law (Con t) - As an air parcel rises in the atmosphere > Because atmospheric pressure decreases as one ascends, the parcel s pressure decreases > Its volume increases > Its density decreases > Its temperature decreases
11 3-11 Ideal Gas Law or Equation of State (Con t) Consequences of the Gas Law (Con t) - As an air parcel subsides or sinks in the atmosphere > Because atmospheric pressure increases as one descends, the parcel s pressure increases > Its volume decreases > Its density increases > Its temperature increases - Warm air is less dense than cold air, if the pressure is the same
12 3-12 Ideal Gas Law or Equation of State (Con t) Consequences of the Gas Law (Con t) - If the surface pressure is equal for both locations, then the pressure aloft over the warm air is higher than the pressure aloft over the cold air. Aloft Surface Cold Warm - Unequal pressure at the same height causes the air to move. Thus, air in high pressure regions is forced toward lower pressure regions.
Pressure and the Gas Laws
 ressure and the Gas Laws H. Schmid, Indiana University Gas ressure Gas molecules inside a volume (e.g. a balloon) are constantly moving around freely. During this molecular motion they frequently collide
ressure and the Gas Laws H. Schmid, Indiana University Gas ressure Gas molecules inside a volume (e.g. a balloon) are constantly moving around freely. During this molecular motion they frequently collide
ATMO/OPTI 656b Spring 09. Physical properties of the atmosphere
 The vertical structure of the atmosphere. Physical properties of the atmosphere To first order, the gas pressure at the bottom of an atmospheric column balances the downward force of gravity on the column.
The vertical structure of the atmosphere. Physical properties of the atmosphere To first order, the gas pressure at the bottom of an atmospheric column balances the downward force of gravity on the column.
--Lord Kelvin, May 3rd, 1883
 When you can measure what you are speaking about and express it in numbers, you know something about it; but when you cannot measure it, when you cannot express it in numbers, you knowledge is of a meager
When you can measure what you are speaking about and express it in numbers, you know something about it; but when you cannot measure it, when you cannot express it in numbers, you knowledge is of a meager
Lecture 1. Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions. Pressure gradient + force force
 Lecture 3 Lecture 1 Basic dynamics Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions Acceleration = Pressure Coriolis + gravity + friction gradient + force force This set of equations is the
Lecture 3 Lecture 1 Basic dynamics Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions Acceleration = Pressure Coriolis + gravity + friction gradient + force force This set of equations is the
Temperature (T) degrees Celsius ( o C) arbitrary scale from 0 o C at melting point of ice to 100 o C at boiling point of water Also (Kelvin, K) = o C
 1 2 3 4 Temperature (T) degrees Celsius ( o C) arbitrary scale from 0 o C at melting point of ice to 100 o C at boiling point of water Also (Kelvin, K) = o C plus 273.15 0 K is absolute zero, the minimum
1 2 3 4 Temperature (T) degrees Celsius ( o C) arbitrary scale from 0 o C at melting point of ice to 100 o C at boiling point of water Also (Kelvin, K) = o C plus 273.15 0 K is absolute zero, the minimum
Lecture 3: Light and Temperature
 Lecture 3: Light and Temperature terrestrial radiative cooling Solar radiative warming (Light) Global Temperature atmosphere ocean land Light Temperature Different forms of energy Energy conservation energy,
Lecture 3: Light and Temperature terrestrial radiative cooling Solar radiative warming (Light) Global Temperature atmosphere ocean land Light Temperature Different forms of energy Energy conservation energy,
The Behaviour of the Atmosphere
 3 The Behaviour of the Atmosphere Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: apply the ideal gas law and the concept of hydrostatic balance to the atmosphere (pp. 49 54); apply
3 The Behaviour of the Atmosphere Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: apply the ideal gas law and the concept of hydrostatic balance to the atmosphere (pp. 49 54); apply
Introduction. Lecture 6: Water in Atmosphere. How Much Heat Is Brought Upward By Water Vapor?
 Lecture 6: Water in Atmosphere Introduction Over 70% of the planet is covered by water Water is unique in that it can simultaneously exist in all three states (solid, liquid, gas) at the same temperature
Lecture 6: Water in Atmosphere Introduction Over 70% of the planet is covered by water Water is unique in that it can simultaneously exist in all three states (solid, liquid, gas) at the same temperature
CHAPTER 2 ATMOSPHERIC PHYSICS
 CHAPTER 2 ATMOSPHERIC PHYSICS The science of physics is devoted to finding, defining, and reaching solutions to problems. It is the basic science that deals with motion, force, and energy. Physics, therefore,
CHAPTER 2 ATMOSPHERIC PHYSICS The science of physics is devoted to finding, defining, and reaching solutions to problems. It is the basic science that deals with motion, force, and energy. Physics, therefore,
Lecture 3: Convection
 EESC V2100 The Climate System spring 2004 Lecture 3: Convection Yochanan Kushnir Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Palisades, NY 10964, USA kushnir@ldeo.columbia.edu Layers of the
EESC V2100 The Climate System spring 2004 Lecture 3: Convection Yochanan Kushnir Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Palisades, NY 10964, USA kushnir@ldeo.columbia.edu Layers of the
Final Examination. Part A Answer ONLY TWELVE QUESTIONS in Part A. (Each question is 3 points)
 ATS 210 Spring Term 2001 NAME: Final Examination This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. Calculators may be used. All answers should be written on the examination paper. Use the final sheet for any
ATS 210 Spring Term 2001 NAME: Final Examination This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. Calculators may be used. All answers should be written on the examination paper. Use the final sheet for any
Chapter 6. Cloud Development and Forms
 Cloud Formation Chapter 6 Cloud Development and Forms Condensation (i.e. clouds,fog) results from: Diabatic cooling (important for fog) Adiabatic cooling (important for clouds) Clouds form due to adiabatic
Cloud Formation Chapter 6 Cloud Development and Forms Condensation (i.e. clouds,fog) results from: Diabatic cooling (important for fog) Adiabatic cooling (important for clouds) Clouds form due to adiabatic
The Ideal Gas Equation
 If you pump too much air into a party balloon, the pressure of the air inside will burst it with a loud bang. Put one into the fridge and it will shrink a bit. You have carried out two simple experiments
If you pump too much air into a party balloon, the pressure of the air inside will burst it with a loud bang. Put one into the fridge and it will shrink a bit. You have carried out two simple experiments
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 6 Laws about gases
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 6 Laws about gases Charles law Volume is directly proportional to temperature. V = ct, where c > 0 is constant. French balloonist Jacque Charles noticed that
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 6 Laws about gases Charles law Volume is directly proportional to temperature. V = ct, where c > 0 is constant. French balloonist Jacque Charles noticed that
Unit 3 - Part 2: Gas Laws. Objective - learn the main gas laws that all molecules follow.
 Unit 3 - Part 2: Gas Laws Objective - learn the main gas laws that all molecules follow. Pressure - Pressure = Force / Area Created by collisions of the gas molecules with each other and with surfaces.
Unit 3 - Part 2: Gas Laws Objective - learn the main gas laws that all molecules follow. Pressure - Pressure = Force / Area Created by collisions of the gas molecules with each other and with surfaces.
Equation of state of ideal gases
 Objective Equation of state of ideal gases F a constant amount of gas (air) investigate the crelation of 1. Volume and pressure at constant temperature (Boyles law) 2. Volume and temperature at constant
Objective Equation of state of ideal gases F a constant amount of gas (air) investigate the crelation of 1. Volume and pressure at constant temperature (Boyles law) 2. Volume and temperature at constant
Unit 10: Gases. Section 1: Kinetic Molecular Theory and the Combined Gas Law
 Unit 10: Gases Section 1: Kinetic Molecular Theory and the Combined Gas Law Introduction Molecules in a gas behave uniquely Gas molecules move rapidly and expand to fill their space Kinetic Molecular Theory:
Unit 10: Gases Section 1: Kinetic Molecular Theory and the Combined Gas Law Introduction Molecules in a gas behave uniquely Gas molecules move rapidly and expand to fill their space Kinetic Molecular Theory:
Scientists and Their Discoveries: The Ideal Gas Law Poster Illustrated Teacher's Guide
 Scientists and Their Discoveries: The Ideal Gas Law Poster Illustrated Teacher's Guide #35-1170 Paper #35-1171 Laminated Background Gas Law Basics Matter most frequently takes the form of a solid, liquid,
Scientists and Their Discoveries: The Ideal Gas Law Poster Illustrated Teacher's Guide #35-1170 Paper #35-1171 Laminated Background Gas Law Basics Matter most frequently takes the form of a solid, liquid,
1. The vertical structure of the atmosphere. Temperature profile.
 Lecture 4. The structure of the atmosphere. Air in motion. Objectives: 1. The vertical structure of the atmosphere. Temperature profile. 2. Temperature in the lower atmosphere: dry adiabatic lapse rate.
Lecture 4. The structure of the atmosphere. Air in motion. Objectives: 1. The vertical structure of the atmosphere. Temperature profile. 2. Temperature in the lower atmosphere: dry adiabatic lapse rate.
Chapter 11. Preview. Lesson Starter Objectives Pressure and Force Dalton s Law of Partial Pressures
 Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Pressure and Force Dalton s Law of Partial Pressures Section 1 Gases and Pressure Lesson Starter Make a list of gases you already know about. Separate your list into elements,
Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Pressure and Force Dalton s Law of Partial Pressures Section 1 Gases and Pressure Lesson Starter Make a list of gases you already know about. Separate your list into elements,
GAS LAWS. Boyle s Law: Investigating the dependence of Volume on Pressure (Temperature kept constant)
 1 GAS LAWS Boyle s Law: Investigating the dependence of Volume on Pressure (Temperature kept constant) The diagram below shows the apparatus which gives a direct reading for both the volume and pressure
1 GAS LAWS Boyle s Law: Investigating the dependence of Volume on Pressure (Temperature kept constant) The diagram below shows the apparatus which gives a direct reading for both the volume and pressure
3-3: The Behavior of Gases. 8 th Grade Physical Sciences
 8 th Grade Physical Sciences How Gas Behaves To understand how a gas behaves, we must first remind ourselves about volume, temperature, and pressure Volume How much space it takes up m 3 - meters cubed
8 th Grade Physical Sciences How Gas Behaves To understand how a gas behaves, we must first remind ourselves about volume, temperature, and pressure Volume How much space it takes up m 3 - meters cubed
Quasi-Geostrophic ω-equation. 1. The atmosphere is approximately hydrostatic. 2. The atmosphere is approximately geostrophic.
 Quasi-Geostrophic ω-equation For large-scale flow in the atmosphere, we have learned about two very important characteristics:. The atmosphere is approximately hydrostatic.. The atmosphere is approximately
Quasi-Geostrophic ω-equation For large-scale flow in the atmosphere, we have learned about two very important characteristics:. The atmosphere is approximately hydrostatic.. The atmosphere is approximately
Topic 2: Heat Affects Matter in Different Ways
 Topic 2: Heat Affects Matter in Different Ways 1 2.1 States of Matter and the Particle Model of Matter A. States of 1. Matter is made up of tiny particles and exist in 3 states:, and. 2. Matter can change
Topic 2: Heat Affects Matter in Different Ways 1 2.1 States of Matter and the Particle Model of Matter A. States of 1. Matter is made up of tiny particles and exist in 3 states:, and. 2. Matter can change
2. Usually, the air pressure inside a building is the air pressure outside the building. a. greater than b. about the same as c.
 CHAPTER 5 AIR PRESSURE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The magnitude of pressure exerted by the gas molecules composing air depends on a. the mass of the air molecules. b. the pull of gravity. c. the kinetic
CHAPTER 5 AIR PRESSURE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The magnitude of pressure exerted by the gas molecules composing air depends on a. the mass of the air molecules. b. the pull of gravity. c. the kinetic
ATMO/OPTI 656b Spring 08. Physical Properties of the Atmosphere
 Physical Properties of the Atmosphere Thin as a piece of paper The atmosphere is a very thin layer above the solid Earth and its oceans. This is true of the atmospheres of all of the terrestrial planets.
Physical Properties of the Atmosphere Thin as a piece of paper The atmosphere is a very thin layer above the solid Earth and its oceans. This is true of the atmospheres of all of the terrestrial planets.
density (in g/l) = molar mass in grams / molar volume in liters (i.e., 22.4 L)
 Unit 9: The Gas Laws 9.5 1. Write the formula for the density of any gas at STP. Name: KEY Text Questions from Corwin density (in g/l) = molar mass in grams / molar volume in liters (i.e., 22.4 L) Ch.
Unit 9: The Gas Laws 9.5 1. Write the formula for the density of any gas at STP. Name: KEY Text Questions from Corwin density (in g/l) = molar mass in grams / molar volume in liters (i.e., 22.4 L) Ch.
Archimedes Principle
 Archimedes Principle applies in air the more air an object displaces, the greater the buoyant force on it if an object displaces its weight, it hovers at a constant altitude if an object displaces less
Archimedes Principle applies in air the more air an object displaces, the greater the buoyant force on it if an object displaces its weight, it hovers at a constant altitude if an object displaces less
The Gas Laws. Types of Variation. What type of variation is it? Write the equation of the line.
 The Gas Laws 1) Types of Variation 2) Boyle's Law + P V Investigation 3) Charles' Law + T V Thought Lab 4) Lussac's Law + T P Investigation 5) The Combined Gas Law 6) Avogadro and the Universal Gas Law
The Gas Laws 1) Types of Variation 2) Boyle's Law + P V Investigation 3) Charles' Law + T V Thought Lab 4) Lussac's Law + T P Investigation 5) The Combined Gas Law 6) Avogadro and the Universal Gas Law
The Gas Laws-Part I The Gaseous State
 The Gas Laws-Part I The Gaseous State The States of Matter The Distinction of Gases from Liquids and Solids 1. Gas volume changes greatly with pressure. 2. Gas volume changes greatly with temperature.
The Gas Laws-Part I The Gaseous State The States of Matter The Distinction of Gases from Liquids and Solids 1. Gas volume changes greatly with pressure. 2. Gas volume changes greatly with temperature.
PHYSICS 151 Notes for Online Lecture #33
 PHYSICS 151 otes for Online Lecture #33 Moving From Fluids o Gases here is a quantity called compressibility that helps distinguish between solids, liquids and gases. If you squeeze a solid with your hands,
PHYSICS 151 otes for Online Lecture #33 Moving From Fluids o Gases here is a quantity called compressibility that helps distinguish between solids, liquids and gases. If you squeeze a solid with your hands,
METEO 431: Atmospheric Thermodynamics
 METEO 431: Atmospheric Thermodynamics Final Exam (100 points) INSTRUCTIONS: Please write as legibly as you can and make sure your thoughts are organized. I am looking for your understanding of the key
METEO 431: Atmospheric Thermodynamics Final Exam (100 points) INSTRUCTIONS: Please write as legibly as you can and make sure your thoughts are organized. I am looking for your understanding of the key
Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten. Chapter 10. Gases.
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 10 Characteristics of Unlike liquids and solids, they Expand to fill their containers.
Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 10 Characteristics of Unlike liquids and solids, they Expand to fill their containers.
Chemistry Section Review 2.2
 Chemistry Section Review 2.2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Standards of measurement are chosen because they a. can be related to everyday
Chemistry Section Review 2.2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Standards of measurement are chosen because they a. can be related to everyday
Properties of Matter. Heat. Summary
 Properties of Matter Heat Summary Heat is a form of energy that is measured in joules (J). The temperature of an object is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in the object and is
Properties of Matter Heat Summary Heat is a form of energy that is measured in joules (J). The temperature of an object is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in the object and is
CHM Units and Dimensional Analysis (r14) Charles Taylor 1/6
 CHM 110 - Units and Dimensional Analysis (r14) - 2014 Charles Taylor 1/6 Introduction Units are critical in all measurements. If you don't tell someone a unit when you tell them a number, they're not likely
CHM 110 - Units and Dimensional Analysis (r14) - 2014 Charles Taylor 1/6 Introduction Units are critical in all measurements. If you don't tell someone a unit when you tell them a number, they're not likely
What Do You Think? Investigate GOALS. [Catch art: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx] Part A: Volume and Temperature of a Gas
![What Do You Think? Investigate GOALS. [Catch art: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx] Part A: Volume and Temperature of a Gas What Do You Think? Investigate GOALS. [Catch art: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx] Part A: Volume and Temperature of a Gas](/thumbs/74/70031344.jpg) Activity 4 Hot-Air Balloons [Catch art: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx] GOALS In this activity you will: Investigate the relationship between temperature and volume of a gas. Understand why the Kelvin scale is used
Activity 4 Hot-Air Balloons [Catch art: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx] GOALS In this activity you will: Investigate the relationship between temperature and volume of a gas. Understand why the Kelvin scale is used
Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition
 Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition Air is a combination of many gases, each with its own unique characteristics. About 99 percent of the atmosphere is composed of nitrogen and oxygen, with the
Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition Air is a combination of many gases, each with its own unique characteristics. About 99 percent of the atmosphere is composed of nitrogen and oxygen, with the
CPO Science Foundations of Physics. Unit 8, Chapter 27
 CPO Science Foundations of Physics Unit 8, Chapter 27 Unit 8: Matter and Energy Chapter 27 The Physical Properties of Matter 27.1 Properties of Solids 27.2 Properties of Liquids and Fluids 27.3 Properties
CPO Science Foundations of Physics Unit 8, Chapter 27 Unit 8: Matter and Energy Chapter 27 The Physical Properties of Matter 27.1 Properties of Solids 27.2 Properties of Liquids and Fluids 27.3 Properties
Integrated Science Force Test
 Integrated Science Force Test Name: Answer Key For multiple-choice, please circle the correct letter. For short answer, be sure to use complete sentences and lots of details. To get full credit, you must
Integrated Science Force Test Name: Answer Key For multiple-choice, please circle the correct letter. For short answer, be sure to use complete sentences and lots of details. To get full credit, you must
Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1
 Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1 About Water on the Earth: The Hydrological Cycle Review 3-states of water, phase change and Latent Heat Indices of Water Vapor Content in the
Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1 About Water on the Earth: The Hydrological Cycle Review 3-states of water, phase change and Latent Heat Indices of Water Vapor Content in the
There are three phases of matter: Solid, liquid and gas
 FLUIDS: Gases and Liquids Chapter 4 of text There are three phases of matter: Solid, liquid and gas Solids: Have form, constituents ( atoms and molecules) are in fixed positions (though they can vibrate
FLUIDS: Gases and Liquids Chapter 4 of text There are three phases of matter: Solid, liquid and gas Solids: Have form, constituents ( atoms and molecules) are in fixed positions (though they can vibrate
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004
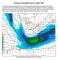 Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
MATTER AND HEAT. Chapter 4 OUTLINE GOALS
 Chapter 4 MATTER AND HEAT OUTLINE Temperature and Heat 4.1 Temperature 4.2 Heat 4.3 Metabolic Energy Fluids 4.4 Density 4.5 Pressure 4.6 Buoyancy 4.7 The Gas Laws Kinetic Theory of Matter 4.8 Kinetic Theory
Chapter 4 MATTER AND HEAT OUTLINE Temperature and Heat 4.1 Temperature 4.2 Heat 4.3 Metabolic Energy Fluids 4.4 Density 4.5 Pressure 4.6 Buoyancy 4.7 The Gas Laws Kinetic Theory of Matter 4.8 Kinetic Theory
Vocabulary. Pressure Absolute zero Charles Law Boyle s Law (take a moment to look up and record definitions in your notes)
 The Gas Laws Vocabulary Pressure Absolute zero Charles Law Boyle s Law (take a moment to look up and record definitions in your notes) Key Concepts What causes gas pressure in a closed container? What
The Gas Laws Vocabulary Pressure Absolute zero Charles Law Boyle s Law (take a moment to look up and record definitions in your notes) Key Concepts What causes gas pressure in a closed container? What
I. Convective Available Potential Energy (CAPE)
 Reading 4: Procedure Summary-- Calcluating CAPE, Lifted Index and Strength of Maximum Convective Updraft CAPE Calculation Lifted Index Calculation Maximum Updraft Strength Calculation I. Convective Available
Reading 4: Procedure Summary-- Calcluating CAPE, Lifted Index and Strength of Maximum Convective Updraft CAPE Calculation Lifted Index Calculation Maximum Updraft Strength Calculation I. Convective Available
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans
![Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans](/thumbs/96/128963638.jpg) Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Unrestrained Expansion - A Source of Entropy Louis M. Michaud, Vortex Engine Submitted to AGU Fall 2005 meeting
 Unrestrained Expansion - A Source of Entropy Louis M. Michaud, Vortex Engine Submitted to AGU Fall 2005 meeting Abstract The paper examines the role of unrestrained expansion in atmospheric entropy production.
Unrestrained Expansion - A Source of Entropy Louis M. Michaud, Vortex Engine Submitted to AGU Fall 2005 meeting Abstract The paper examines the role of unrestrained expansion in atmospheric entropy production.
Atmospheric Pressure and Wind Frode Stordal, University of Oslo
 Chapter 4 Lecture Understanding Weather and Climate Seventh Edition Atmospheric Pressure and Wind Frode Stordal, University of Oslo Redina L. Herman Western Illinois University The Concept of Pressure
Chapter 4 Lecture Understanding Weather and Climate Seventh Edition Atmospheric Pressure and Wind Frode Stordal, University of Oslo Redina L. Herman Western Illinois University The Concept of Pressure
Lecture 7. Science A-30 February 21, 2008 Air may be forced to move up or down in the atmosphere by mechanical forces (wind blowing over an obstacle,
 Lecture 7. Science A-30 February 21, 2008 Air may be forced to move up or down in the atmosphere by mechanical forces (wind blowing over an obstacle, like a mountain) or by buoyancy forces. Air that is
Lecture 7. Science A-30 February 21, 2008 Air may be forced to move up or down in the atmosphere by mechanical forces (wind blowing over an obstacle, like a mountain) or by buoyancy forces. Air that is
Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics
 12.818 Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics Lodovica Illari 1 Background The Earth is bathed in radiation from the Sun whose intensity peaks in the visible. In order to maintain energy balance
12.818 Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics Lodovica Illari 1 Background The Earth is bathed in radiation from the Sun whose intensity peaks in the visible. In order to maintain energy balance
F = ma. ATS 150 Global Climate Change Winds and Weather. Scott Denning CSU CMMAP 1. Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook
 Winds and Weather Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook Circulation of the atmosphere and oceans are driven by energy imbalances Energy Imbalances What Makes the Wind Blow? Three real forces (gravity,
Winds and Weather Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook Circulation of the atmosphere and oceans are driven by energy imbalances Energy Imbalances What Makes the Wind Blow? Three real forces (gravity,
Robert Boyle ( ), who is often considered
 L A B 4 BOYLE S LAW Differentiation Robert Boyle (1627 1691), who is often considered the founder of modern chemistry, made studies of acids and bases, the calcination of metals, combustion, the nature
L A B 4 BOYLE S LAW Differentiation Robert Boyle (1627 1691), who is often considered the founder of modern chemistry, made studies of acids and bases, the calcination of metals, combustion, the nature
I. Convective Available Potential Energy (CAPE)
 Calculating CAPE, Lifted Index and Strength of Maximum Convective Updraft CAPE Calculation Lifted Index Calculation Maximum Updraft Strength Calculation I. Convective Available Potential Energy (CAPE)
Calculating CAPE, Lifted Index and Strength of Maximum Convective Updraft CAPE Calculation Lifted Index Calculation Maximum Updraft Strength Calculation I. Convective Available Potential Energy (CAPE)
ATMO551a Fall Vertical Structure of Earth s Atmosphere
 Vertical Structure of Earth s Atmosphere Thin as a piece of paper The atmosphere is a very thin layer above the solid Earth and its oceans. This is true of the atmospheres of all of the terrestrial planets.
Vertical Structure of Earth s Atmosphere Thin as a piece of paper The atmosphere is a very thin layer above the solid Earth and its oceans. This is true of the atmospheres of all of the terrestrial planets.
Unit Outline. I. Introduction II. Gas Pressure III. Gas Laws IV. Gas Law Problems V. Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases VI.
 Unit 10: Gases Unit Outline I. Introduction II. Gas Pressure III. Gas Laws IV. Gas Law Problems V. Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases VI. Real Gases I. Opening thoughts Have you ever: Seen a hot air balloon?
Unit 10: Gases Unit Outline I. Introduction II. Gas Pressure III. Gas Laws IV. Gas Law Problems V. Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases VI. Real Gases I. Opening thoughts Have you ever: Seen a hot air balloon?
Gases and Gas Laws. Relationships of the Physical Properties of Gases. What is a gas?
 What is a gas? For pure substances, there are many different phases of matter, but only three that we interact with at common temperature and pressures solids, liquids and gases. We can differentiate the
What is a gas? For pure substances, there are many different phases of matter, but only three that we interact with at common temperature and pressures solids, liquids and gases. We can differentiate the
First Law of Thermodynamics
 First Law of Thermodynamics September 11, 2013 The first law of thermodynamics is the conservation of energy applied to thermal systems. Here, we develop the principles of thermodynamics for a discrete
First Law of Thermodynamics September 11, 2013 The first law of thermodynamics is the conservation of energy applied to thermal systems. Here, we develop the principles of thermodynamics for a discrete
What is a change of state? What happens during a change of state? What can happen when a substance loses or gains energy?
 CHAPTER 3 3 Changes of State SECTION States of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a change of state? What happens during a change
CHAPTER 3 3 Changes of State SECTION States of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a change of state? What happens during a change
Temperature, Thermal Energy and Heat
 Temperature You use the words hot and cold to describe temperature. Something is hot when its temperature is high. When you heat water on a stove, its temperature increases. How are temperature and heat
Temperature You use the words hot and cold to describe temperature. Something is hot when its temperature is high. When you heat water on a stove, its temperature increases. How are temperature and heat
Chapter 4 Water Vapor
 Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
the energy of motion!
 What are the molecules of matter doing all the time?! Heat and Temperature! Notes! All matter is composed of continually jiggling atoms or molecules! The jiggling is! If something is vibrating, what kind
What are the molecules of matter doing all the time?! Heat and Temperature! Notes! All matter is composed of continually jiggling atoms or molecules! The jiggling is! If something is vibrating, what kind
Introduction to Skew-T Diagrams
 Introduction to Skew-T Diagrams Have a think about a few things I m going to throw to you it will hopefully make you think a little outside the square! - LIs of -15 can give you clear skies - LIs of 0
Introduction to Skew-T Diagrams Have a think about a few things I m going to throw to you it will hopefully make you think a little outside the square! - LIs of -15 can give you clear skies - LIs of 0
RSPT 1060 OBJECTIVES. MODULE C Lesson #4 GAS LAWS OBJECTIVES SUPPORTIVE READINGS. Gas Laws. Web Sites
 RSP 060 MODULE C Lesson #4 GAS LAWS OBJECIVES At the end of this module, the student should be able to Define terms associated with gas laws. Define Boyle s Law. Describe the relationship between volume,
RSP 060 MODULE C Lesson #4 GAS LAWS OBJECIVES At the end of this module, the student should be able to Define terms associated with gas laws. Define Boyle s Law. Describe the relationship between volume,
Lecture 5: Precipitation
 Lecture 5: Precipitation Key Questions 1. What physical concepts control the formation of precipitation (air pressure, expanding gases and cooling, and vapor pressure)? 2. What are some air mass lifting
Lecture 5: Precipitation Key Questions 1. What physical concepts control the formation of precipitation (air pressure, expanding gases and cooling, and vapor pressure)? 2. What are some air mass lifting
Gas Laws. Labs, Activities & Demonstrations:
 Add Important Gas Laws Page: 60 NGSS Standards: N/A Gas Laws MA Curriculum Frameworks (006): N/A AP Physics Learning Objectives: 3.4.C., 3.4.C., 4.C.3., 7.A.3.3, 7.B.. Knowledge/Understanding: Skills:
Add Important Gas Laws Page: 60 NGSS Standards: N/A Gas Laws MA Curriculum Frameworks (006): N/A AP Physics Learning Objectives: 3.4.C., 3.4.C., 4.C.3., 7.A.3.3, 7.B.. Knowledge/Understanding: Skills:
Student Review Packet Answer Key
 Student Review acket Answer Key. Convert the following temperatures as indicated. a 0 o C to K 73 K e atm to ka 0.3 ka (s.f. = 00 b -0 o C to K 63 K f 0.878 atm to ka 88.9 ka c 45 o C to K 38 K g 3. atm
Student Review acket Answer Key. Convert the following temperatures as indicated. a 0 o C to K 73 K e atm to ka 0.3 ka (s.f. = 00 b -0 o C to K 63 K f 0.878 atm to ka 88.9 ka c 45 o C to K 38 K g 3. atm
SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 2009/2010. MAPH Physical Meteorology
 SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 2009/2010 MAPH 40240 Physical Meteorology Extern examiner: Professor Keith Shine Head of School: Professor Micheal O Searcoid Examiner: Dr. Rodrigo Caballero Time Allowed: 2 hours
SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 2009/2010 MAPH 40240 Physical Meteorology Extern examiner: Professor Keith Shine Head of School: Professor Micheal O Searcoid Examiner: Dr. Rodrigo Caballero Time Allowed: 2 hours
1. Water Vapor in Air
 1. Water Vapor in Air Water appears in all three phases in the earth s atmosphere - solid, liquid and vapor - and it is one of the most important components, not only because it is essential to life, but
1. Water Vapor in Air Water appears in all three phases in the earth s atmosphere - solid, liquid and vapor - and it is one of the most important components, not only because it is essential to life, but
Study Guide for Chapters 2, 3, and 10
 Study Guide for Chapters 2, 3, and 10 1. What is matter? Where can it be found? Anything that has mass and takes up space. 2. What units are used to measure volume? Liters and meters cubed 3. How would
Study Guide for Chapters 2, 3, and 10 1. What is matter? Where can it be found? Anything that has mass and takes up space. 2. What units are used to measure volume? Liters and meters cubed 3. How would
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Tidal forces in general are the result of A) unequal forces acting on different parts
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Tidal forces in general are the result of A) unequal forces acting on different parts
General Atmospheric Circulation
 General Atmospheric Circulation Take away Concepts and Ideas Global circulation: The mean meridional (N-S) circulation Trade winds and westerlies The Jet Stream Earth s climate zones Monsoonal climate
General Atmospheric Circulation Take away Concepts and Ideas Global circulation: The mean meridional (N-S) circulation Trade winds and westerlies The Jet Stream Earth s climate zones Monsoonal climate
Physics 115 Future Physics Midterm Review Exam will be closed book; no calculators; no computers.
 Physics 115 Future Physics Midterm Review 2016 Exam will be closed book; no calculators; no computers. You can bring a 3 x 5 index card with whatever notes and equations you want written on ONE SIDE ONLY.
Physics 115 Future Physics Midterm Review 2016 Exam will be closed book; no calculators; no computers. You can bring a 3 x 5 index card with whatever notes and equations you want written on ONE SIDE ONLY.
ESS 111 Climate & Global Change. Week 1 Weather vs Climate Structure of the Atmosphere Global Wind Belts
 ESS 111 Climate & Global Change Week 1 Weather vs Climate Structure of the Atmosphere Global Wind Belts Weather is the state of the atmosphere at a given place and time. For example, right now, the temperature
ESS 111 Climate & Global Change Week 1 Weather vs Climate Structure of the Atmosphere Global Wind Belts Weather is the state of the atmosphere at a given place and time. For example, right now, the temperature
MP203 Statistical and Thermal Physics. Jon-Ivar Skullerud and James Smith
 MP203 Statistical and Thermal Physics Jon-Ivar Skullerud and James Smith October 3, 2017 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Temperature and thermal equilibrium.................... 4 1.1.1 The zeroth law of
MP203 Statistical and Thermal Physics Jon-Ivar Skullerud and James Smith October 3, 2017 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Temperature and thermal equilibrium.................... 4 1.1.1 The zeroth law of
CONVERGENCE, DIVERGENCE, AND VORTICITY
 CHAPTER 1 CONVERGENCE, DIVERGENCE, AND VORTICITY In your reading of the AG2 manual, volume 1, you became familiar with the terms convergence, divergence, and vorticity when used in relation to surface
CHAPTER 1 CONVERGENCE, DIVERGENCE, AND VORTICITY In your reading of the AG2 manual, volume 1, you became familiar with the terms convergence, divergence, and vorticity when used in relation to surface
Chapter 3 Phases of Matter Physical Science
 Chapter 3 Phases of Matter Physical Science CH 3- States of Matter 1 What makes up matter? What is the difference between a solid, a liquid, and a gas? What kind of energy do all particles of matter have?
Chapter 3 Phases of Matter Physical Science CH 3- States of Matter 1 What makes up matter? What is the difference between a solid, a liquid, and a gas? What kind of energy do all particles of matter have?
The Gas Laws. Section 1.2 (7th and 8th editions) Individual Gases Boyle s Law Charles Law. Perfect (Ideal) Gas Equation
 The Gas Laws Section 1.2 (7th and 8th editions) Individual Gases Boyle s Law Charles Law Perfect (Ideal) Gas Equation Mixtures of Gases Dalton s Law Mole Fractions Last updated: Sept. 14, 2009; minor edits
The Gas Laws Section 1.2 (7th and 8th editions) Individual Gases Boyle s Law Charles Law Perfect (Ideal) Gas Equation Mixtures of Gases Dalton s Law Mole Fractions Last updated: Sept. 14, 2009; minor edits
AT 620 Notes. These notes were prepared by Prof. Steven A. Rutledge. (and adapted slightly for the Fall 2009 course, and again slightly for this year)
 AT 620 Notes These notes were prepared by Prof. Steven A. Rutledge (and adapted slightly for the Fall 2009 course, and again slightly for this year) You may access Prof. Cotton s notes, password cloud9
AT 620 Notes These notes were prepared by Prof. Steven A. Rutledge (and adapted slightly for the Fall 2009 course, and again slightly for this year) You may access Prof. Cotton s notes, password cloud9
Numerical Example An air parcel with mass of 1 kg rises adiabatically from sea level to an altitude of 3 km. What is its temperature change?
 Numerical Example An air parcel with mass of 1 kg rises adiabatically from sea level to an altitude of 3 km. What is its temperature change? From the 1 st law, T = -g/c p z + Q/m air /c p Here, Q = 0,
Numerical Example An air parcel with mass of 1 kg rises adiabatically from sea level to an altitude of 3 km. What is its temperature change? From the 1 st law, T = -g/c p z + Q/m air /c p Here, Q = 0,
EAS 370: Applied Atmospheric Physics. Lecture Notes. Andrew B.G. Bush Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences University of Alberta
 EAS 370: Applied Atmospheric Physics Lecture Notes Andrew B.G. Bush Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences University of Alberta 1. BASIC THERMODYNAMIC CONCEPTS Why study atmospheric thermodynamics?
EAS 370: Applied Atmospheric Physics Lecture Notes Andrew B.G. Bush Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences University of Alberta 1. BASIC THERMODYNAMIC CONCEPTS Why study atmospheric thermodynamics?
3.2 Units of Measurement > Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement. 3.2 Units of Measurement. 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements
 Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements 3.2 Units of Measurement 3.3 Solving Conversion Problems 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements 3.2 Units of Measurement 3.3 Solving Conversion Problems 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
Monteverdi Metr 201 Quiz #4 100 pts.
 DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES Name San Francisco State University April 27, 2012 Monteverdi Metr 201 Quiz #4 100 pts. A. Definitions. (5 points each for a total of 25 points in this section). (a) Convective
DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES Name San Francisco State University April 27, 2012 Monteverdi Metr 201 Quiz #4 100 pts. A. Definitions. (5 points each for a total of 25 points in this section). (a) Convective
Introduction to Atmospheric Circulation
 Introduction to Atmospheric Circulation Start rotating table Cloud Fraction Dice Results from http://eos.atmos.washington.edu/erbe/ from http://eos.atmos.washington.edu/erbe/ from http://eos.atmos.washington.edu/erbe/
Introduction to Atmospheric Circulation Start rotating table Cloud Fraction Dice Results from http://eos.atmos.washington.edu/erbe/ from http://eos.atmos.washington.edu/erbe/ from http://eos.atmos.washington.edu/erbe/
Thermal Properties and Ideal Gases: Boyle's law and Charle's law *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m39083 1 Thermal Properties and Ideal Gases: Boyle's law and Charle's law * Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
OpenStax-CNX module: m39083 1 Thermal Properties and Ideal Gases: Boyle's law and Charle's law * Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
Observing Climate - Upper Air
 Observing Climate - Upper Air 3-1 Water (Con t) Clouds Types - Classification Base height Coverage Science Concepts Definition The Earth System (Kump, Kastin & Crane) Chap. 3 (pp. 48-49) 3-2 What do we
Observing Climate - Upper Air 3-1 Water (Con t) Clouds Types - Classification Base height Coverage Science Concepts Definition The Earth System (Kump, Kastin & Crane) Chap. 3 (pp. 48-49) 3-2 What do we
VIII. CLOUDS AND STABILITY:
 VIII. CLOUDS AND STABILITY: A. Cloud Classification: 1) Clouds are classified with respect to the height of the cloud base --- low, middle, or high. a. Strato is the first prefix used to indicate cloud
VIII. CLOUDS AND STABILITY: A. Cloud Classification: 1) Clouds are classified with respect to the height of the cloud base --- low, middle, or high. a. Strato is the first prefix used to indicate cloud
Lab #3: Stability and Dispersion. Fall 2014 Due Tuesday, November 25, 2014
 NAME ID number Disc. Day and Time Lab #3: Stability and Dispersion Atmospheric Sciences 2L Fall 2014 Due Tuesday, November 25, 2014 In this lab, we will test the stability of a simulated atmospheric environment
NAME ID number Disc. Day and Time Lab #3: Stability and Dispersion Atmospheric Sciences 2L Fall 2014 Due Tuesday, November 25, 2014 In this lab, we will test the stability of a simulated atmospheric environment
Electricity and Energy 1 Content Statements
 Keep this in good condition, it will help you pass your final exams. The school will only issue one paper copy per pupil. An e-copy will be placed on the school s web-site. Electricity and Energy 1 Content
Keep this in good condition, it will help you pass your final exams. The school will only issue one paper copy per pupil. An e-copy will be placed on the school s web-site. Electricity and Energy 1 Content
AST111 PROBLEM SET 6 SOLUTIONS
 AST111 PROBLEM SET 6 SOLUTIONS Homework problems 1. Ideal gases in pressure balance Consider a parcel of molecular hydrogen at a temperature of 100 K in proximity to a parcel of ionized hydrogen at a temperature
AST111 PROBLEM SET 6 SOLUTIONS Homework problems 1. Ideal gases in pressure balance Consider a parcel of molecular hydrogen at a temperature of 100 K in proximity to a parcel of ionized hydrogen at a temperature
Unit 3: 4/14/2015. Meteorology. Meteorologist. Research. The Earth s Atmosphere How do we collect information on the atmosphere?
 Unit 3: Meteorology The word meteorology is from Greek, metéōros, meaning "lofty; high (in the sky)" Where are they? Why is there no weather? Meteorology Meteorology is the study of the atmosphere, atmospheric
Unit 3: Meteorology The word meteorology is from Greek, metéōros, meaning "lofty; high (in the sky)" Where are they? Why is there no weather? Meteorology Meteorology is the study of the atmosphere, atmospheric
Heat & Temperature. What are heat & temperature and how do they relate?
 Heat & Temperature What are heat & temperature and how do they relate? SPS7. Students will relate transformations and flow of energy within a system. a. Identify energy transformations within a system
Heat & Temperature What are heat & temperature and how do they relate? SPS7. Students will relate transformations and flow of energy within a system. a. Identify energy transformations within a system
P sat = A exp [B( 1/ /T)] B= 5308K. A=6.11 mbar=vapor press. 0C.
![P sat = A exp [B( 1/ /T)] B= 5308K. A=6.11 mbar=vapor press. 0C. P sat = A exp [B( 1/ /T)] B= 5308K. A=6.11 mbar=vapor press. 0C.](/thumbs/79/79184286.jpg) Lecture 5. Water and water vapor in the atmosphere 14 Feb 2008 Review of buoyancy, with an unusual demonstration of Archimedes principle. Water is a polar molecule that forms hydrogen bonds. Consequently
Lecture 5. Water and water vapor in the atmosphere 14 Feb 2008 Review of buoyancy, with an unusual demonstration of Archimedes principle. Water is a polar molecule that forms hydrogen bonds. Consequently
Lecture 2. Professor Hicks General Chemistry (CHE131) Spring Units. units are like apples and oranges. any number of
 Lecture 2 Professor Hicks General Chemistry (CHE131) Spring 2009 1 Units units are like apples and oranges any number of 1 inch any number! kilograms things with different types of units cannot be equated
Lecture 2 Professor Hicks General Chemistry (CHE131) Spring 2009 1 Units units are like apples and oranges any number of 1 inch any number! kilograms things with different types of units cannot be equated
OCEAN/ESS 410. Class 3. Understanding Conductive Cooling: A Thought Experiment. Write your answers on the exercise sheet
 Class 3. Understanding Conductive Cooling: A Thought Experiment Write your answers on the exercise sheet While looking at the global bathymetry maps you will have noticed that mid-ocean ridges or ocean
Class 3. Understanding Conductive Cooling: A Thought Experiment Write your answers on the exercise sheet While looking at the global bathymetry maps you will have noticed that mid-ocean ridges or ocean
The Basic Gas Laws Properties of gases Stephen Lower (2011)
 The Basic Gas Laws Properties of gases Stephen Lower (2011) The "pneumatic" era of chemistry began with the discovery of the vacuum around 1650 which clearly established that gases are a form of matter.
The Basic Gas Laws Properties of gases Stephen Lower (2011) The "pneumatic" era of chemistry began with the discovery of the vacuum around 1650 which clearly established that gases are a form of matter.
Week 1 Temperature, Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. (Ch. 19 of Serway&J.)
 Week 1 Temperature, Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. (Ch. 19 of Serway&J.) (Syllabus) Temperature Thermal Expansion Temperature and Heat Heat and Work The first Law Heat Transfer Temperature Thermodynamics:
Week 1 Temperature, Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. (Ch. 19 of Serway&J.) (Syllabus) Temperature Thermal Expansion Temperature and Heat Heat and Work The first Law Heat Transfer Temperature Thermodynamics:
2. If the volume of a container holding a gas is reduced, what will happen to the presure within the container?
 1. Which gas law states that the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its Kelvin temperature if the pressure is kept constant? A. Boyle s law B. Charles law C. Dalton s law D. Gay-Lussac
1. Which gas law states that the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its Kelvin temperature if the pressure is kept constant? A. Boyle s law B. Charles law C. Dalton s law D. Gay-Lussac
ESS15 Lecture 10. Winds and weather The Coriolis force Global circulations of atmosphere & ocean Weather vs. Climate
 ESS15 Lecture 10 Winds and weather The Coriolis force Global circulations of atmosphere & ocean Weather vs. Climate Earth s energy imbalances, winds, and the global circulation of the atmopshere. Please
ESS15 Lecture 10 Winds and weather The Coriolis force Global circulations of atmosphere & ocean Weather vs. Climate Earth s energy imbalances, winds, and the global circulation of the atmopshere. Please
