ξ t = Fξ t 1 + v t. then λ is less than unity in absolute value. In the above expression, A denotes the determinant of the matrix, A. 1 y t 1.
|
|
|
- Delilah Gardner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Christiano FINC 520, Spring 2009 Homework 3, due Thursday, April In class, we discussed the p th order VAR: y t = c + φ 1 y t 1 + φ 2 y t φ p y t p + ε t, where ε t is a white noise with variance-covariance matrix, Ω, and orthogonal with y t s,s>0. Find a definition of ξ t, so that the VAR(p) can be written in the following VAR(1) form: ξ t = Fξ t 1 + v t. We assume that if λ satisfies λ p I n φ 1 λ p 1 φ 2 λ p 2... φ p =0, (1) then λ is less than unity in absolute value. In the above expression, A denotes the determinant of the matrix, A. 2. Write the VAR(p) in transposed form: y 0 t = x 0 tπ + ε 0 t, where x t = (np+1) 1 1 y t 1, y t p n (np+1) Π0 = h i c φ 1 φ p. Suppose we have data over the period t =1,..., T and write: Y = yt 0 y 0 1 y 0 2,X= x 0 T x 0 1 x 0 2,ε= ε 0 T ε 0 1 ε 0 2, 1
2 so that the VAR can be written as follows: Y T n = X T (np+1) Π + ε (np+1) n T n. Premultiply this by X 0 and then take expectations: Note that E [X 0 Y ]=E [X 0 X] Π + E [X 0 ε]. EX 0 ε = E TX t=1 x t ε 0 t =0, because of the assumed orthogonality properties of ε t. Then, Π = {E [X 0 X]} 1 E [X 0 Y ]. Ergodicity suggests using the following estimator for Π: ˆΠ =(X 0 X) 1 X 0 Y. (a) Compute ˆΠ using the data in the MATLAB m file that has been provided, with p =4. Let y t = R t log GDP t GDP t 1 π t, where R t denotes the 3 month Tbill rate, π t denotes the quarterly inflation rate and GDP t denotes Gross Domestic Product in quarter t. (b) Construct F, the matrix you constructed for question 1. Note how your way of handling the constant term causes there to be one eigenvalue equal to unity this matrix. Compute μ = Ey t = [I φ 1 φ 2 φ 3 φ 4 ] 1 c. Compare μ with: P [y t+500 y t,y t 1,...], Why should μ and this projection be so similar? 2
3 (c) Is the VAR(p) model you constructed covariance stationary and ergodic? Explain. (Hint: for this, you will want to know the roots of the polynomial in (1) and these can be found with Proposition 10.1 in the book.) (d) Construct a predicted time series on the long rate for the T = 201 quarters, 1955Q4-2005Q4. Graph it together with the actual 5 year rate, Rt. l To do this, you ll have to do the calculations discussed in class. However, the geometric sum formula described there will not work if you do it with the version of F in question 1,becausethathasaunitrootinit.YoucansimplyaddI + F F 19. How does the expectations hypothesis do? Do the same graph, only this time do it with y t = R t R l t log GDP t GDP t 1 π t. Do the results make any difference with this adjustment? 3. In question 2, I expect you to find that the predicted long rate falls too rapidly in the early 1980s. This could be because (i) the linear prediction of the short rate based on the VAR does not correspond with people s actual expectations, or (ii) because the term structure hypothesis itself is not good. The possibility, (ii) is explored in the work of Piazzesi and Schneider (see, e.g., Equilibrium Yield Curves, NBER working paper 12609) and the papers they cite. However, this takesustoofarafield of the subject matter of this course. Possibility (i) can be pursued in two ways. One could obtain survey data on forecasts of the short term interest rate and use those in place of P [R t+j Ω t ]in the formula for the long rate. This possibility would be fun to pursue, but would also take us too far off topic. Another way to attack (i) is to study the forecasts of the short rate that go into the calculation of the long rate in question (2). The idea is to see if they are any good. To investigate the quality of the forecast, you should graph the actual short rate data. At each two year interval you should graph the forecast of the short term rate that went into computing the predicted long term 3
4 rate. Thus, suppose t is a quarter when you compute the forecast. On the graph of the actual short term rate, you should also graph P [R t+j ξ t ], for j =0,.., 19. Because the forecasted and actual interest rates appear in the same graph you can see if there is a systematic problem with the forecasts of the short rate. For example, is there a tendency to under-predict the short rate in the early 1980s? Your graph will look a little messy, because the forecasts will appear like long hairs sprouting at two year intervals and wiggling along for 5 years. The hairs associated with different forecast dates will become intertwined and be a little hard to distinguish. Hopefully, it will still be possible to see something. 4. The forecasting procedure not only provides formulas for P [R t+j ξ t ], j>0, but it also provides estimates of the uncertainty of the forecast. To see this, note that R t+j P [R t+j ξ t ]=Dv t+j + DFv t+j DF j 1 v t+1, where D is a row vector defined in class. forecast error is: Then the variance of the v (j) var t (R t+j P [R t+j ξ t ]) = DV D 0 +DFV F 0 D DF j 1 V (F 0 ) j 1 D 0, where V is the variance covariance matrix of v t. This object can be constructed from the definition of v t andanestimateofv, ˆV,where ˆV = ˆε0ˆε T. Here, ˆε Y X ˆΠ. Consider the three dates, t 1 =1980Q1,t 2 =1982Q1 and t 3 =1985Q1. Produce three graphs, each containing the actual data as well as three other lines. Each of the three graphs corresponds to one of the dates, t i,i=1, 2, 3. Overlayedonthegraphwiththe actual data, graph P [R ti +j ξ t ], for j =0,..., 19, as well as P [R ti +j ξ t ] ± 2 q v (j), j=0,...,19. The graphs should be lined up so that P [R ti +j ξ t ]coincideswithr ti +j, as in question 3. Do the uncertainty bands about the forecasts seem plausible in light of the degree of fluctuations in the data? Do the uncertainty bands continue to expand, or does their width converge? 4
5 5. Consider the following time series representation for x t : x t = ρ x x t 1 + ε t,ρ x =0.9, σ ε =0.01. Inclasswehaveworkedoutthatthevarianceofx t is: E (x t ) 2 = σ2 x, 1 ρ 2 x and the τ th lag covariance is C (τ) =Ex t x t τ = ρ τ x Ex 2 t,τ=0, ±1, ±2,.... According to the discussion in class, the spectral density of x t is: S x ³ e iω = σ 2 x (1 ρ x e iω )(1 ρ x e iω ). Applying the inverse Fourier transform to this yields the covariances: C (τ) = 1 Z π ³ S x e iω e iωτ dω. 2π π (a) Consider two parameterizations of the x t process. One has the parameter values given above, and the other has ρ x =0.0 andσ ε set so that the variance of the two x t representations is the same. On the same figure, graph the spectral densities associated with the two representations of x t for ω (0,π). Also, generate 100 artificial time series observations from each representation. Note how the one with the higher value of ρ x generates a pattern of x t s that wanders around more lazily than does the representation with the smaller value of ρ x. That lazy pattern in the high-ρ x representation shows up as relatively more power in the lower frequencies of its spectrum. (b) Approximate the integral for C (τ) bythesumoftheareaofn rectangles, based on the Riemann sum interpretation of the integral. That is, if ω j =2πj/N, with j = (N/2) + 1,..., N/2, Z 1 π ³ S x e iω e iωτ dω 1 2π π 2π N/2 X j= (N/2)+1 S x ³ e iω j eiω j τ (ω j ω j 1 ).
6 Is it correct to work with the lower value of (N/2) + 1 for j, or with the lower value of (N/2)? Evaluate C (0),C(2),C(4) using the exact formulas above and the Riemann approximation for various values of N. What is the smallest values of N for which the Riemann approximation is good?
Principles of forecasting
 2.5 Forecasting Principles of forecasting Forecast based on conditional expectations Suppose we are interested in forecasting the value of y t+1 based on a set of variables X t (m 1 vector). Let y t+1
2.5 Forecasting Principles of forecasting Forecast based on conditional expectations Suppose we are interested in forecasting the value of y t+1 based on a set of variables X t (m 1 vector). Let y t+1
Vector Auto-Regressive Models
 Vector Auto-Regressive Models Laurent Ferrara 1 1 University of Paris Nanterre M2 Oct. 2018 Overview of the presentation 1. Vector Auto-Regressions Definition Estimation Testing 2. Impulse responses functions
Vector Auto-Regressive Models Laurent Ferrara 1 1 University of Paris Nanterre M2 Oct. 2018 Overview of the presentation 1. Vector Auto-Regressions Definition Estimation Testing 2. Impulse responses functions
VAR Models and Applications
 VAR Models and Applications Laurent Ferrara 1 1 University of Paris West M2 EIPMC Oct. 2016 Overview of the presentation 1. Vector Auto-Regressions Definition Estimation Testing 2. Impulse responses functions
VAR Models and Applications Laurent Ferrara 1 1 University of Paris West M2 EIPMC Oct. 2016 Overview of the presentation 1. Vector Auto-Regressions Definition Estimation Testing 2. Impulse responses functions
2.5 Forecasting and Impulse Response Functions
 2.5 Forecasting and Impulse Response Functions Principles of forecasting Forecast based on conditional expectations Suppose we are interested in forecasting the value of y t+1 based on a set of variables
2.5 Forecasting and Impulse Response Functions Principles of forecasting Forecast based on conditional expectations Suppose we are interested in forecasting the value of y t+1 based on a set of variables
Lecture 7a: Vector Autoregression (VAR)
 Lecture 7a: Vector Autoregression (VAR) 1 2 Big Picture We are done with univariate time series analysis Now we switch to multivariate analysis, that is, studying several time series simultaneously. VAR
Lecture 7a: Vector Autoregression (VAR) 1 2 Big Picture We are done with univariate time series analysis Now we switch to multivariate analysis, that is, studying several time series simultaneously. VAR
IDENTIFICATION OF ARMA MODELS
 IDENTIFICATION OF ARMA MODELS A stationary stochastic process can be characterised, equivalently, by its autocovariance function or its partial autocovariance function. It can also be characterised by
IDENTIFICATION OF ARMA MODELS A stationary stochastic process can be characterised, equivalently, by its autocovariance function or its partial autocovariance function. It can also be characterised by
... Econometric Methods for the Analysis of Dynamic General Equilibrium Models
 ... Econometric Methods for the Analysis of Dynamic General Equilibrium Models 1 Overview Multiple Equation Methods State space-observer form Three Examples of Versatility of state space-observer form:
... Econometric Methods for the Analysis of Dynamic General Equilibrium Models 1 Overview Multiple Equation Methods State space-observer form Three Examples of Versatility of state space-observer form:
Assessing Structural VAR s
 ... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Columbia, October 2005 1 Background Structural Vector Autoregressions Can be Used to Address the Following
... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Columbia, October 2005 1 Background Structural Vector Autoregressions Can be Used to Address the Following
Lecture 7a: Vector Autoregression (VAR)
 Lecture 7a: Vector Autoregression (VAR) 1 Big Picture We are done with univariate time series analysis Now we switch to multivariate analysis, that is, studying several time series simultaneously. VAR
Lecture 7a: Vector Autoregression (VAR) 1 Big Picture We are done with univariate time series analysis Now we switch to multivariate analysis, that is, studying several time series simultaneously. VAR
A Beginner s Introduction. Box-Jenkins Models
 A Beginner s Introduction To Box-Jenkins Models I. Introduction In their seminal work, Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control (1970, Holden Day), Professors Box and Jenkins introduced a set of time
A Beginner s Introduction To Box-Jenkins Models I. Introduction In their seminal work, Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control (1970, Holden Day), Professors Box and Jenkins introduced a set of time
Statistics 349(02) Review Questions
 Statistics 349(0) Review Questions I. Suppose that for N = 80 observations on the time series { : t T} the following statistics were calculated: _ x = 10.54 C(0) = 4.99 In addition the sample autocorrelation
Statistics 349(0) Review Questions I. Suppose that for N = 80 observations on the time series { : t T} the following statistics were calculated: _ x = 10.54 C(0) = 4.99 In addition the sample autocorrelation
Chapter 3 - Temporal processes
 STK4150 - Intro 1 Chapter 3 - Temporal processes Odd Kolbjørnsen and Geir Storvik January 23 2017 STK4150 - Intro 2 Temporal processes Data collected over time Past, present, future, change Temporal aspect
STK4150 - Intro 1 Chapter 3 - Temporal processes Odd Kolbjørnsen and Geir Storvik January 23 2017 STK4150 - Intro 2 Temporal processes Data collected over time Past, present, future, change Temporal aspect
Assessing Structural VAR s
 ... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Yale, October 2005 1 Background Structural Vector Autoregressions Can be Used to Address the Following Type
... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Yale, October 2005 1 Background Structural Vector Autoregressions Can be Used to Address the Following Type
Problem Set 1 Solution Sketches Time Series Analysis Spring 2010
 Problem Set 1 Solution Sketches Time Series Analysis Spring 2010 1. Construct a martingale difference process that is not weakly stationary. Simplest e.g.: Let Y t be a sequence of independent, non-identically
Problem Set 1 Solution Sketches Time Series Analysis Spring 2010 1. Construct a martingale difference process that is not weakly stationary. Simplest e.g.: Let Y t be a sequence of independent, non-identically
Problem Set 2 Solution Sketches Time Series Analysis Spring 2010
 Problem Set 2 Solution Sketches Time Series Analysis Spring 2010 Forecasting 1. Let X and Y be two random variables such that E(X 2 ) < and E(Y 2 )
Problem Set 2 Solution Sketches Time Series Analysis Spring 2010 Forecasting 1. Let X and Y be two random variables such that E(X 2 ) < and E(Y 2 )
Single Equation Linear GMM with Serially Correlated Moment Conditions
 Single Equation Linear GMM with Serially Correlated Moment Conditions Eric Zivot November 2, 2011 Univariate Time Series Let {y t } be an ergodic-stationary time series with E[y t ]=μ and var(y t )
Single Equation Linear GMM with Serially Correlated Moment Conditions Eric Zivot November 2, 2011 Univariate Time Series Let {y t } be an ergodic-stationary time series with E[y t ]=μ and var(y t )
Econometrics of Panel Data
 Econometrics of Panel Data Jakub Mućk Meeting # 9 Jakub Mućk Econometrics of Panel Data Meeting # 9 1 / 22 Outline 1 Time series analysis Stationarity Unit Root Tests for Nonstationarity 2 Panel Unit Root
Econometrics of Panel Data Jakub Mućk Meeting # 9 Jakub Mućk Econometrics of Panel Data Meeting # 9 1 / 22 Outline 1 Time series analysis Stationarity Unit Root Tests for Nonstationarity 2 Panel Unit Root
Assessing Structural VAR s
 ... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Background Structural Vector Autoregressions Can be Used to Address the Following Type of Question: How
... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Background Structural Vector Autoregressions Can be Used to Address the Following Type of Question: How
Reliability and Risk Analysis. Time Series, Types of Trend Functions and Estimates of Trends
 Reliability and Risk Analysis Stochastic process The sequence of random variables {Y t, t = 0, ±1, ±2 } is called the stochastic process The mean function of a stochastic process {Y t} is the function
Reliability and Risk Analysis Stochastic process The sequence of random variables {Y t, t = 0, ±1, ±2 } is called the stochastic process The mean function of a stochastic process {Y t} is the function
A primer on Structural VARs
 A primer on Structural VARs Claudia Foroni Norges Bank 10 November 2014 Structural VARs 1/ 26 Refresh: what is a VAR? VAR (p) : where y t K 1 y t = ν + B 1 y t 1 +... + B p y t p + u t, (1) = ( y 1t...
A primer on Structural VARs Claudia Foroni Norges Bank 10 November 2014 Structural VARs 1/ 26 Refresh: what is a VAR? VAR (p) : where y t K 1 y t = ν + B 1 y t 1 +... + B p y t p + u t, (1) = ( y 1t...
Structural VARs II. February 17, 2016
 Structural VARs II February 17, 216 Structural VARs Today: Long-run restrictions Two critiques of SVARs Blanchard and Quah (1989), Rudebusch (1998), Gali (1999) and Chari, Kehoe McGrattan (28). Recap:
Structural VARs II February 17, 216 Structural VARs Today: Long-run restrictions Two critiques of SVARs Blanchard and Quah (1989), Rudebusch (1998), Gali (1999) and Chari, Kehoe McGrattan (28). Recap:
Factor models. May 11, 2012
 Factor models May 11, 2012 Factor Models Macro economists have a peculiar data situation: Many data series, but usually short samples How can we utilize all this information without running into degrees
Factor models May 11, 2012 Factor Models Macro economists have a peculiar data situation: Many data series, but usually short samples How can we utilize all this information without running into degrees
Y t = log (employment t )
 Advanced Macroeconomics, Christiano Econ 416 Homework #7 Due: November 21 1. Consider the linearized equilibrium conditions of the New Keynesian model, on the slide, The Equilibrium Conditions in the handout,
Advanced Macroeconomics, Christiano Econ 416 Homework #7 Due: November 21 1. Consider the linearized equilibrium conditions of the New Keynesian model, on the slide, The Equilibrium Conditions in the handout,
Booth School of Business, University of Chicago Business 41914, Spring Quarter 2017, Mr. Ruey S. Tsay Midterm
 Booth School of Business, University of Chicago Business 41914, Spring Quarter 2017, Mr. Ruey S. Tsay Midterm Chicago Booth Honor Code: I pledge my honor that I have not violated the Honor Code during
Booth School of Business, University of Chicago Business 41914, Spring Quarter 2017, Mr. Ruey S. Tsay Midterm Chicago Booth Honor Code: I pledge my honor that I have not violated the Honor Code during
Econ 623 Econometrics II Topic 2: Stationary Time Series
 1 Introduction Econ 623 Econometrics II Topic 2: Stationary Time Series In the regression model we can model the error term as an autoregression AR(1) process. That is, we can use the past value of the
1 Introduction Econ 623 Econometrics II Topic 2: Stationary Time Series In the regression model we can model the error term as an autoregression AR(1) process. That is, we can use the past value of the
Covariance Stationary Time Series. Example: Independent White Noise (IWN(0,σ 2 )) Y t = ε t, ε t iid N(0,σ 2 )
 Covariance Stationary Time Series Stochastic Process: sequence of rv s ordered by time {Y t } {...,Y 1,Y 0,Y 1,...} Defn: {Y t } is covariance stationary if E[Y t ]μ for all t cov(y t,y t j )E[(Y t μ)(y
Covariance Stationary Time Series Stochastic Process: sequence of rv s ordered by time {Y t } {...,Y 1,Y 0,Y 1,...} Defn: {Y t } is covariance stationary if E[Y t ]μ for all t cov(y t,y t j )E[(Y t μ)(y
Prof. Dr. Roland Füss Lecture Series in Applied Econometrics Summer Term Introduction to Time Series Analysis
 Introduction to Time Series Analysis 1 Contents: I. Basics of Time Series Analysis... 4 I.1 Stationarity... 5 I.2 Autocorrelation Function... 9 I.3 Partial Autocorrelation Function (PACF)... 14 I.4 Transformation
Introduction to Time Series Analysis 1 Contents: I. Basics of Time Series Analysis... 4 I.1 Stationarity... 5 I.2 Autocorrelation Function... 9 I.3 Partial Autocorrelation Function (PACF)... 14 I.4 Transformation
Assessing Structural VAR s
 ... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Minneapolis, August 2005 1 Background In Principle, Impulse Response Functions from SVARs are useful as
... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Minneapolis, August 2005 1 Background In Principle, Impulse Response Functions from SVARs are useful as
A6523 Modeling, Inference, and Mining Jim Cordes, Cornell University
 A6523 Modeling, Inference, and Mining Jim Cordes, Cornell University Lecture 19 Modeling Topics plan: Modeling (linear/non- linear least squares) Bayesian inference Bayesian approaches to spectral esbmabon;
A6523 Modeling, Inference, and Mining Jim Cordes, Cornell University Lecture 19 Modeling Topics plan: Modeling (linear/non- linear least squares) Bayesian inference Bayesian approaches to spectral esbmabon;
Factor models. March 13, 2017
 Factor models March 13, 2017 Factor Models Macro economists have a peculiar data situation: Many data series, but usually short samples How can we utilize all this information without running into degrees
Factor models March 13, 2017 Factor Models Macro economists have a peculiar data situation: Many data series, but usually short samples How can we utilize all this information without running into degrees
An estimate of the long-run covariance matrix, Ω, is necessary to calculate asymptotic
 Chapter 6 ESTIMATION OF THE LONG-RUN COVARIANCE MATRIX An estimate of the long-run covariance matrix, Ω, is necessary to calculate asymptotic standard errors for the OLS and linear IV estimators presented
Chapter 6 ESTIMATION OF THE LONG-RUN COVARIANCE MATRIX An estimate of the long-run covariance matrix, Ω, is necessary to calculate asymptotic standard errors for the OLS and linear IV estimators presented
Modern Navigation. Thomas Herring
 12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Estimation methods Review of last class Restrict to basically linear estimation problems (also non-linear problems that are nearly linear) Restrict to parametric,
12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Estimation methods Review of last class Restrict to basically linear estimation problems (also non-linear problems that are nearly linear) Restrict to parametric,
1. Introduction. Hang Qian 1 Iowa State University
 Users Guide to the VARDAS Package Hang Qian 1 Iowa State University 1. Introduction The Vector Autoregression (VAR) model is widely used in macroeconomics. However, macroeconomic data are not always observed
Users Guide to the VARDAS Package Hang Qian 1 Iowa State University 1. Introduction The Vector Autoregression (VAR) model is widely used in macroeconomics. However, macroeconomic data are not always observed
For a stochastic process {Y t : t = 0, ±1, ±2, ±3, }, the mean function is defined by (2.2.1) ± 2..., γ t,
 CHAPTER 2 FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS This chapter describes the fundamental concepts in the theory of time series models. In particular, we introduce the concepts of stochastic processes, mean and covariance
CHAPTER 2 FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS This chapter describes the fundamental concepts in the theory of time series models. In particular, we introduce the concepts of stochastic processes, mean and covariance
Booth School of Business, University of Chicago Business 41914, Spring Quarter 2017, Mr. Ruey S. Tsay. Solutions to Midterm
 Booth School of Business, University of Chicago Business 41914, Spring Quarter 017, Mr Ruey S Tsay Solutions to Midterm Problem A: (51 points; 3 points per question) Answer briefly the following questions
Booth School of Business, University of Chicago Business 41914, Spring Quarter 017, Mr Ruey S Tsay Solutions to Midterm Problem A: (51 points; 3 points per question) Answer briefly the following questions
Class: Trend-Cycle Decomposition
 Class: Trend-Cycle Decomposition Macroeconometrics - Spring 2011 Jacek Suda, BdF and PSE June 1, 2011 Outline Outline: 1 Unobserved Component Approach 2 Beveridge-Nelson Decomposition 3 Spectral Analysis
Class: Trend-Cycle Decomposition Macroeconometrics - Spring 2011 Jacek Suda, BdF and PSE June 1, 2011 Outline Outline: 1 Unobserved Component Approach 2 Beveridge-Nelson Decomposition 3 Spectral Analysis
1 First-order di erence equation
 References Hamilton, J. D., 1994. Time Series Analysis. Princeton University Press. (Chapter 1,2) The task facing the modern time-series econometrician is to develop reasonably simple and intuitive models
References Hamilton, J. D., 1994. Time Series Analysis. Princeton University Press. (Chapter 1,2) The task facing the modern time-series econometrician is to develop reasonably simple and intuitive models
Økonomisk Kandidateksamen 2004 (I) Econometrics 2. Rettevejledning
 Økonomisk Kandidateksamen 2004 (I) Econometrics 2 Rettevejledning This is a closed-book exam (uden hjælpemidler). Answer all questions! The group of questions 1 to 4 have equal weight. Within each group,
Økonomisk Kandidateksamen 2004 (I) Econometrics 2 Rettevejledning This is a closed-book exam (uden hjælpemidler). Answer all questions! The group of questions 1 to 4 have equal weight. Within each group,
7. MULTIVARATE STATIONARY PROCESSES
 7. MULTIVARATE STATIONARY PROCESSES 1 1 Some Preliminary Definitions and Concepts Random Vector: A vector X = (X 1,..., X n ) whose components are scalar-valued random variables on the same probability
7. MULTIVARATE STATIONARY PROCESSES 1 1 Some Preliminary Definitions and Concepts Random Vector: A vector X = (X 1,..., X n ) whose components are scalar-valued random variables on the same probability
A. Recursively orthogonalized. VARs
 Orthogonalized VARs A. Recursively orthogonalized VAR B. Variance decomposition C. Historical decomposition D. Structural interpretation E. Generalized IRFs 1 A. Recursively orthogonalized Nonorthogonal
Orthogonalized VARs A. Recursively orthogonalized VAR B. Variance decomposition C. Historical decomposition D. Structural interpretation E. Generalized IRFs 1 A. Recursively orthogonalized Nonorthogonal
9) Time series econometrics
 30C00200 Econometrics 9) Time series econometrics Timo Kuosmanen Professor Management Science http://nomepre.net/index.php/timokuosmanen 1 Macroeconomic data: GDP Inflation rate Examples of time series
30C00200 Econometrics 9) Time series econometrics Timo Kuosmanen Professor Management Science http://nomepre.net/index.php/timokuosmanen 1 Macroeconomic data: GDP Inflation rate Examples of time series
ECON 4160, Spring term Lecture 12
 ECON 4160, Spring term 2013. Lecture 12 Non-stationarity and co-integration 2/2 Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics 13 Nov 2013 1 / 53 Introduction I So far we have considered: Stationary VAR, with deterministic
ECON 4160, Spring term 2013. Lecture 12 Non-stationarity and co-integration 2/2 Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics 13 Nov 2013 1 / 53 Introduction I So far we have considered: Stationary VAR, with deterministic
TIME SERIES AND FORECASTING. Luca Gambetti UAB, Barcelona GSE Master in Macroeconomic Policy and Financial Markets
 TIME SERIES AND FORECASTING Luca Gambetti UAB, Barcelona GSE 2014-2015 Master in Macroeconomic Policy and Financial Markets 1 Contacts Prof.: Luca Gambetti Office: B3-1130 Edifici B Office hours: email:
TIME SERIES AND FORECASTING Luca Gambetti UAB, Barcelona GSE 2014-2015 Master in Macroeconomic Policy and Financial Markets 1 Contacts Prof.: Luca Gambetti Office: B3-1130 Edifici B Office hours: email:
Empirical Market Microstructure Analysis (EMMA)
 Empirical Market Microstructure Analysis (EMMA) Lecture 3: Statistical Building Blocks and Econometric Basics Prof. Dr. Michael Stein michael.stein@vwl.uni-freiburg.de Albert-Ludwigs-University of Freiburg
Empirical Market Microstructure Analysis (EMMA) Lecture 3: Statistical Building Blocks and Econometric Basics Prof. Dr. Michael Stein michael.stein@vwl.uni-freiburg.de Albert-Ludwigs-University of Freiburg
New meeting times for Econ 210D Mondays 8:00-9:20 a.m. in Econ 300 Wednesdays 11:00-12:20 in Econ 300
 New meeting times for Econ 210D Mondays 8:00-9:20 a.m. in Econ 300 Wednesdays 11:00-12:20 in Econ 300 1 Identification using nonrecursive structure, long-run restrictions and heteroskedasticity 2 General
New meeting times for Econ 210D Mondays 8:00-9:20 a.m. in Econ 300 Wednesdays 11:00-12:20 in Econ 300 1 Identification using nonrecursive structure, long-run restrictions and heteroskedasticity 2 General
Stationary and nonstationary variables
 Stationary and nonstationary variables Stationary variable: 1. Finite and constant in time expected value: E (y t ) = µ < 2. Finite and constant in time variance: Var (y t ) = σ 2 < 3. Covariance dependent
Stationary and nonstationary variables Stationary variable: 1. Finite and constant in time expected value: E (y t ) = µ < 2. Finite and constant in time variance: Var (y t ) = σ 2 < 3. Covariance dependent
Vectors and Matrices Statistics with Vectors and Matrices
 Vectors and Matrices Statistics with Vectors and Matrices Lecture 3 September 7, 005 Analysis Lecture #3-9/7/005 Slide 1 of 55 Today s Lecture Vectors and Matrices (Supplement A - augmented with SAS proc
Vectors and Matrices Statistics with Vectors and Matrices Lecture 3 September 7, 005 Analysis Lecture #3-9/7/005 Slide 1 of 55 Today s Lecture Vectors and Matrices (Supplement A - augmented with SAS proc
Statistics & Data Sciences: First Year Prelim Exam May 2018
 Statistics & Data Sciences: First Year Prelim Exam May 2018 Instructions: 1. Do not turn this page until instructed to do so. 2. Start each new question on a new sheet of paper. 3. This is a closed book
Statistics & Data Sciences: First Year Prelim Exam May 2018 Instructions: 1. Do not turn this page until instructed to do so. 2. Start each new question on a new sheet of paper. 3. This is a closed book
Signals and Spectra - Review
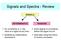 Signals and Spectra - Review SIGNALS DETERMINISTIC No uncertainty w.r.t. the value of a signal at any time Modeled by mathematical epressions RANDOM some degree of uncertainty before the signal occurs
Signals and Spectra - Review SIGNALS DETERMINISTIC No uncertainty w.r.t. the value of a signal at any time Modeled by mathematical epressions RANDOM some degree of uncertainty before the signal occurs
ECE302 Spring 2006 Practice Final Exam Solution May 4, Name: Score: /100
 ECE302 Spring 2006 Practice Final Exam Solution May 4, 2006 1 Name: Score: /100 You must show ALL of your work for full credit. This exam is open-book. Calculators may NOT be used. 1. As a function of
ECE302 Spring 2006 Practice Final Exam Solution May 4, 2006 1 Name: Score: /100 You must show ALL of your work for full credit. This exam is open-book. Calculators may NOT be used. 1. As a function of
Vector autoregressions, VAR
 1 / 45 Vector autoregressions, VAR Chapter 2 Financial Econometrics Michael Hauser WS17/18 2 / 45 Content Cross-correlations VAR model in standard/reduced form Properties of VAR(1), VAR(p) Structural VAR,
1 / 45 Vector autoregressions, VAR Chapter 2 Financial Econometrics Michael Hauser WS17/18 2 / 45 Content Cross-correlations VAR model in standard/reduced form Properties of VAR(1), VAR(p) Structural VAR,
Cointegrated VAR s. Eduardo Rossi University of Pavia. November Rossi Cointegrated VAR s Financial Econometrics / 56
 Cointegrated VAR s Eduardo Rossi University of Pavia November 2013 Rossi Cointegrated VAR s Financial Econometrics - 2013 1 / 56 VAR y t = (y 1t,..., y nt ) is (n 1) vector. y t VAR(p): Φ(L)y t = ɛ t The
Cointegrated VAR s Eduardo Rossi University of Pavia November 2013 Rossi Cointegrated VAR s Financial Econometrics - 2013 1 / 56 VAR y t = (y 1t,..., y nt ) is (n 1) vector. y t VAR(p): Φ(L)y t = ɛ t The
Questions and Answers on Unit Roots, Cointegration, VARs and VECMs
 Questions and Answers on Unit Roots, Cointegration, VARs and VECMs L. Magee Winter, 2012 1. Let ɛ t, t = 1,..., T be a series of independent draws from a N[0,1] distribution. Let w t, t = 1,..., T, be
Questions and Answers on Unit Roots, Cointegration, VARs and VECMs L. Magee Winter, 2012 1. Let ɛ t, t = 1,..., T be a series of independent draws from a N[0,1] distribution. Let w t, t = 1,..., T, be
18.06 Quiz 2 April 7, 2010 Professor Strang
 18.06 Quiz 2 April 7, 2010 Professor Strang Your PRINTED name is: 1. Your recitation number or instructor is 2. 3. 1. (33 points) (a) Find the matrix P that projects every vector b in R 3 onto the line
18.06 Quiz 2 April 7, 2010 Professor Strang Your PRINTED name is: 1. Your recitation number or instructor is 2. 3. 1. (33 points) (a) Find the matrix P that projects every vector b in R 3 onto the line
Cointegrating Regressions with Messy Regressors: J. Isaac Miller
 NASMES 2008 June 21, 2008 Carnegie Mellon U. Cointegrating Regressions with Messy Regressors: Missingness, Mixed Frequency, and Measurement Error J. Isaac Miller University of Missouri 1 Messy Data Example
NASMES 2008 June 21, 2008 Carnegie Mellon U. Cointegrating Regressions with Messy Regressors: Missingness, Mixed Frequency, and Measurement Error J. Isaac Miller University of Missouri 1 Messy Data Example
Switching Regime Estimation
 Switching Regime Estimation Series de Tiempo BIrkbeck March 2013 Martin Sola (FE) Markov Switching models 01/13 1 / 52 The economy (the time series) often behaves very different in periods such as booms
Switching Regime Estimation Series de Tiempo BIrkbeck March 2013 Martin Sola (FE) Markov Switching models 01/13 1 / 52 The economy (the time series) often behaves very different in periods such as booms
Spectral Analysis. Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania
 Spectral Analysis Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Why Spectral Analysis? We want to develop a theory to obtain the business cycle properties of the data. Burns and Mitchell (1946).
Spectral Analysis Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Why Spectral Analysis? We want to develop a theory to obtain the business cycle properties of the data. Burns and Mitchell (1946).
You must continuously work on this project over the course of four weeks.
 The project Five project topics are described below. You should choose one the projects. Maximum of two people per project is allowed. If two people are working on a topic they are expected to do double
The project Five project topics are described below. You should choose one the projects. Maximum of two people per project is allowed. If two people are working on a topic they are expected to do double
1 Class Organization. 2 Introduction
 Time Series Analysis, Lecture 1, 2018 1 1 Class Organization Course Description Prerequisite Homework and Grading Readings and Lecture Notes Course Website: http://www.nanlifinance.org/teaching.html wechat
Time Series Analysis, Lecture 1, 2018 1 1 Class Organization Course Description Prerequisite Homework and Grading Readings and Lecture Notes Course Website: http://www.nanlifinance.org/teaching.html wechat
It is easily seen that in general a linear combination of y t and x t is I(1). However, in particular cases, it can be I(0), i.e. stationary.
 6. COINTEGRATION 1 1 Cointegration 1.1 Definitions I(1) variables. z t = (y t x t ) is I(1) (integrated of order 1) if it is not stationary but its first difference z t is stationary. It is easily seen
6. COINTEGRATION 1 1 Cointegration 1.1 Definitions I(1) variables. z t = (y t x t ) is I(1) (integrated of order 1) if it is not stationary but its first difference z t is stationary. It is easily seen
Gold Rush Fever in Business Cycles
 Gold Rush Fever in Business Cycles Paul Beaudry, Fabrice Collard & Franck Portier University of British Columbia & Université de Toulouse UAB Seminar Barcelona November, 29, 26 The Klondike Gold Rush of
Gold Rush Fever in Business Cycles Paul Beaudry, Fabrice Collard & Franck Portier University of British Columbia & Université de Toulouse UAB Seminar Barcelona November, 29, 26 The Klondike Gold Rush of
Econometría 2: Análisis de series de Tiempo
 Econometría 2: Análisis de series de Tiempo Karoll GOMEZ kgomezp@unal.edu.co http://karollgomez.wordpress.com Segundo semestre 2016 IX. Vector Time Series Models VARMA Models A. 1. Motivation: The vector
Econometría 2: Análisis de series de Tiempo Karoll GOMEZ kgomezp@unal.edu.co http://karollgomez.wordpress.com Segundo semestre 2016 IX. Vector Time Series Models VARMA Models A. 1. Motivation: The vector
Assessing Structural VAR s
 ... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Zurich, September 2005 1 Background Structural Vector Autoregressions Address the Following Type of Question:
... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Zurich, September 2005 1 Background Structural Vector Autoregressions Address the Following Type of Question:
1 Outline. 1. Motivation. 2. SUR model. 3. Simultaneous equations. 4. Estimation
 1 Outline. 1. Motivation 2. SUR model 3. Simultaneous equations 4. Estimation 2 Motivation. In this chapter, we will study simultaneous systems of econometric equations. Systems of simultaneous equations
1 Outline. 1. Motivation 2. SUR model 3. Simultaneous equations 4. Estimation 2 Motivation. In this chapter, we will study simultaneous systems of econometric equations. Systems of simultaneous equations
5 Transfer function modelling
 MSc Further Time Series Analysis 5 Transfer function modelling 5.1 The model Consider the construction of a model for a time series (Y t ) whose values are influenced by the earlier values of a series
MSc Further Time Series Analysis 5 Transfer function modelling 5.1 The model Consider the construction of a model for a time series (Y t ) whose values are influenced by the earlier values of a series
Economics 618B: Time Series Analysis Department of Economics State University of New York at Binghamton
 Problem Set #1 1. Generate n =500random numbers from both the uniform 1 (U [0, 1], uniformbetween zero and one) and exponential λ exp ( λx) (set λ =2and let x U [0, 1]) b a distributions. Plot the histograms
Problem Set #1 1. Generate n =500random numbers from both the uniform 1 (U [0, 1], uniformbetween zero and one) and exponential λ exp ( λx) (set λ =2and let x U [0, 1]) b a distributions. Plot the histograms
VAR Model. (k-variate) VAR(p) model (in the Reduced Form): Y t-2. Y t-1 = A + B 1. Y t + B 2. Y t-p. + ε t. + + B p. where:
 VAR Model (k-variate VAR(p model (in the Reduced Form: where: Y t = A + B 1 Y t-1 + B 2 Y t-2 + + B p Y t-p + ε t Y t = (y 1t, y 2t,, y kt : a (k x 1 vector of time series variables A: a (k x 1 vector
VAR Model (k-variate VAR(p model (in the Reduced Form: where: Y t = A + B 1 Y t-1 + B 2 Y t-2 + + B p Y t-p + ε t Y t = (y 1t, y 2t,, y kt : a (k x 1 vector of time series variables A: a (k x 1 vector
Nonparametric Function Estimation with Infinite-Order Kernels
 Nonparametric Function Estimation with Infinite-Order Kernels Arthur Berg Department of Statistics, University of Florida March 15, 2008 Kernel Density Estimation (IID Case) Let X 1,..., X n iid density
Nonparametric Function Estimation with Infinite-Order Kernels Arthur Berg Department of Statistics, University of Florida March 15, 2008 Kernel Density Estimation (IID Case) Let X 1,..., X n iid density
Theoretical and Simulation-guided Exploration of the AR(1) Model
 Theoretical and Simulation-guided Exploration of the AR() Model Overview: Section : Motivation Section : Expectation A: Theory B: Simulation Section : Variance A: Theory B: Simulation Section : ACF A:
Theoretical and Simulation-guided Exploration of the AR() Model Overview: Section : Motivation Section : Expectation A: Theory B: Simulation Section : Variance A: Theory B: Simulation Section : ACF A:
Multivariate Time Series
 Multivariate Time Series Notation: I do not use boldface (or anything else) to distinguish vectors from scalars. Tsay (and many other writers) do. I denote a multivariate stochastic process in the form
Multivariate Time Series Notation: I do not use boldface (or anything else) to distinguish vectors from scalars. Tsay (and many other writers) do. I denote a multivariate stochastic process in the form
DSGE Methods. Estimation of DSGE models: GMM and Indirect Inference. Willi Mutschler, M.Sc.
 DSGE Methods Estimation of DSGE models: GMM and Indirect Inference Willi Mutschler, M.Sc. Institute of Econometrics and Economic Statistics University of Münster willi.mutschler@wiwi.uni-muenster.de Summer
DSGE Methods Estimation of DSGE models: GMM and Indirect Inference Willi Mutschler, M.Sc. Institute of Econometrics and Economic Statistics University of Münster willi.mutschler@wiwi.uni-muenster.de Summer
A time series is called strictly stationary if the joint distribution of every collection (Y t
 5 Time series A time series is a set of observations recorded over time. You can think for example at the GDP of a country over the years (or quarters) or the hourly measurements of temperature over a
5 Time series A time series is a set of observations recorded over time. You can think for example at the GDP of a country over the years (or quarters) or the hourly measurements of temperature over a
ECO 513 Fall 2009 C. Sims CONDITIONAL EXPECTATION; STOCHASTIC PROCESSES
 ECO 513 Fall 2009 C. Sims CONDIIONAL EXPECAION; SOCHASIC PROCESSES 1. HREE EXAMPLES OF SOCHASIC PROCESSES (I) X t has three possible time paths. With probability.5 X t t, with probability.25 X t t, and
ECO 513 Fall 2009 C. Sims CONDIIONAL EXPECAION; SOCHASIC PROCESSES 1. HREE EXAMPLES OF SOCHASIC PROCESSES (I) X t has three possible time paths. With probability.5 X t t, with probability.25 X t t, and
Final Examination Linear Partial Differential Equations. Matthew J. Hancock. Feb. 3, 2006
 Final Examination 8.303 Linear Partial ifferential Equations Matthew J. Hancock Feb. 3, 006 Total points: 00 Rules [requires student signature!]. I will use only pencils, pens, erasers, and straight edges
Final Examination 8.303 Linear Partial ifferential Equations Matthew J. Hancock Feb. 3, 006 Total points: 00 Rules [requires student signature!]. I will use only pencils, pens, erasers, and straight edges
Statistical signal processing
 Statistical signal processing Short overview of the fundamentals Outline Random variables Random processes Stationarity Ergodicity Spectral analysis Random variable and processes Intuition: A random variable
Statistical signal processing Short overview of the fundamentals Outline Random variables Random processes Stationarity Ergodicity Spectral analysis Random variable and processes Intuition: A random variable
Define y t+h t as the forecast of y t+h based on I t known parameters. The forecast error is. Forecasting
 Forecasting Let {y t } be a covariance stationary are ergodic process, eg an ARMA(p, q) process with Wold representation y t = X μ + ψ j ε t j, ε t ~WN(0,σ 2 ) j=0 = μ + ε t + ψ 1 ε t 1 + ψ 2 ε t 2 + Let
Forecasting Let {y t } be a covariance stationary are ergodic process, eg an ARMA(p, q) process with Wold representation y t = X μ + ψ j ε t j, ε t ~WN(0,σ 2 ) j=0 = μ + ε t + ψ 1 ε t 1 + ψ 2 ε t 2 + Let
DSGE-Models. Limited Information Estimation General Method of Moments and Indirect Inference
 DSGE-Models General Method of Moments and Indirect Inference Dr. Andrea Beccarini Willi Mutschler, M.Sc. Institute of Econometrics and Economic Statistics University of Münster willi.mutschler@uni-muenster.de
DSGE-Models General Method of Moments and Indirect Inference Dr. Andrea Beccarini Willi Mutschler, M.Sc. Institute of Econometrics and Economic Statistics University of Münster willi.mutschler@uni-muenster.de
This note introduces some key concepts in time series econometrics. First, we
 INTRODUCTION TO TIME SERIES Econometrics 2 Heino Bohn Nielsen September, 2005 This note introduces some key concepts in time series econometrics. First, we present by means of examples some characteristic
INTRODUCTION TO TIME SERIES Econometrics 2 Heino Bohn Nielsen September, 2005 This note introduces some key concepts in time series econometrics. First, we present by means of examples some characteristic
10. Time series regression and forecasting
 10. Time series regression and forecasting Key feature of this section: Analysis of data on a single entity observed at multiple points in time (time series data) Typical research questions: What is the
10. Time series regression and forecasting Key feature of this section: Analysis of data on a single entity observed at multiple points in time (time series data) Typical research questions: What is the
Approximate Counting and Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 Approximate Counting and Markov Chain Monte Carlo A Randomized Approach Arindam Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Delhi March 18, 2011 April 8, 2011 Arindam
Approximate Counting and Markov Chain Monte Carlo A Randomized Approach Arindam Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Delhi March 18, 2011 April 8, 2011 Arindam
2b Multivariate Time Series
 2b Multivariate Time Series Andrew Harvey Faculty of Economics, University of Cambridge May 2017 Andrew Harvey (Faculty of Economics, University of Cambridge) 2b Multivariate Time Series May 2017 1 / 28
2b Multivariate Time Series Andrew Harvey Faculty of Economics, University of Cambridge May 2017 Andrew Harvey (Faculty of Economics, University of Cambridge) 2b Multivariate Time Series May 2017 1 / 28
Lecture 6: Dynamic Models
 Lecture 6: Dynamic Models R.G. Pierse 1 Introduction Up until now we have maintained the assumption that X values are fixed in repeated sampling (A4) In this lecture we look at dynamic models, where the
Lecture 6: Dynamic Models R.G. Pierse 1 Introduction Up until now we have maintained the assumption that X values are fixed in repeated sampling (A4) In this lecture we look at dynamic models, where the
Econometrics I. Professor William Greene Stern School of Business Department of Economics 25-1/25. Part 25: Time Series
 Econometrics I Professor William Greene Stern School of Business Department of Economics 25-1/25 Econometrics I Part 25 Time Series 25-2/25 Modeling an Economic Time Series Observed y 0, y 1,, y t, What
Econometrics I Professor William Greene Stern School of Business Department of Economics 25-1/25 Econometrics I Part 25 Time Series 25-2/25 Modeling an Economic Time Series Observed y 0, y 1,, y t, What
Optimal Control of Nonlinear Econometric. Models with Rational Expectations
 Optimal Control of Nonlinear Econometric Models with Rational Expectations V. Blueschke-Nikolaeva a a Department of Economics, Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt Universitätsstrasse 65-67, A-9020 Klagenfurt,
Optimal Control of Nonlinear Econometric Models with Rational Expectations V. Blueschke-Nikolaeva a a Department of Economics, Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt Universitätsstrasse 65-67, A-9020 Klagenfurt,
10) Time series econometrics
 30C00200 Econometrics 10) Time series econometrics Timo Kuosmanen Professor, Ph.D. 1 Topics today Static vs. dynamic time series model Suprious regression Stationary and nonstationary time series Unit
30C00200 Econometrics 10) Time series econometrics Timo Kuosmanen Professor, Ph.D. 1 Topics today Static vs. dynamic time series model Suprious regression Stationary and nonstationary time series Unit
ECON 616: Lecture 1: Time Series Basics
 ECON 616: Lecture 1: Time Series Basics ED HERBST August 30, 2017 References Overview: Chapters 1-3 from Hamilton (1994). Technical Details: Chapters 2-3 from Brockwell and Davis (1987). Intuition: Chapters
ECON 616: Lecture 1: Time Series Basics ED HERBST August 30, 2017 References Overview: Chapters 1-3 from Hamilton (1994). Technical Details: Chapters 2-3 from Brockwell and Davis (1987). Intuition: Chapters
Combining Macroeconomic Models for Prediction
 Combining Macroeconomic Models for Prediction John Geweke University of Technology Sydney 15th Australasian Macro Workshop April 8, 2010 Outline 1 Optimal prediction pools 2 Models and data 3 Optimal pools
Combining Macroeconomic Models for Prediction John Geweke University of Technology Sydney 15th Australasian Macro Workshop April 8, 2010 Outline 1 Optimal prediction pools 2 Models and data 3 Optimal pools
Chapter 2. Some basic tools. 2.1 Time series: Theory Stochastic processes
 Chapter 2 Some basic tools 2.1 Time series: Theory 2.1.1 Stochastic processes A stochastic process is a sequence of random variables..., x 0, x 1, x 2,.... In this class, the subscript always means time.
Chapter 2 Some basic tools 2.1 Time series: Theory 2.1.1 Stochastic processes A stochastic process is a sequence of random variables..., x 0, x 1, x 2,.... In this class, the subscript always means time.
Regression of Time Series
 Mahlerʼs Guide to Regression of Time Series CAS Exam S prepared by Howard C. Mahler, FCAS Copyright 2016 by Howard C. Mahler. Study Aid 2016F-S-9Supplement Howard Mahler hmahler@mac.com www.howardmahler.com/teaching
Mahlerʼs Guide to Regression of Time Series CAS Exam S prepared by Howard C. Mahler, FCAS Copyright 2016 by Howard C. Mahler. Study Aid 2016F-S-9Supplement Howard Mahler hmahler@mac.com www.howardmahler.com/teaching
Univariate Time Series Analysis; ARIMA Models
 Econometrics 2 Fall 24 Univariate Time Series Analysis; ARIMA Models Heino Bohn Nielsen of4 Outline of the Lecture () Introduction to univariate time series analysis. (2) Stationarity. (3) Characterizing
Econometrics 2 Fall 24 Univariate Time Series Analysis; ARIMA Models Heino Bohn Nielsen of4 Outline of the Lecture () Introduction to univariate time series analysis. (2) Stationarity. (3) Characterizing
Forecasting with ARMA
 Forecasting with ARMA Eduardo Rossi University of Pavia October 2013 Rossi Forecasting Financial Econometrics - 2013 1 / 32 Mean Squared Error Linear Projection Forecast of Y t+1 based on a set of variables
Forecasting with ARMA Eduardo Rossi University of Pavia October 2013 Rossi Forecasting Financial Econometrics - 2013 1 / 32 Mean Squared Error Linear Projection Forecast of Y t+1 based on a set of variables
Time Series Analysis
 Time Series Analysis hm@imm.dtu.dk Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Technical University of Denmark DK-2800 Kgs. Lyngby 1 Outline of the lecture Chapter 9 Multivariate time series 2 Transfer function
Time Series Analysis hm@imm.dtu.dk Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Technical University of Denmark DK-2800 Kgs. Lyngby 1 Outline of the lecture Chapter 9 Multivariate time series 2 Transfer function
1.1. VARs, Wold representations and their limits
 1. Shocks Nr. 1 1.1. VARs, Wold representations and their limits A brief review of VARs. Assume a true model, in MA form: X = A 0 e + A 1 e( 1) + A 2 e( 2) +...; E(ee ) = I = (A 0 + A 1 L + A 2 L 2 +...)
1. Shocks Nr. 1 1.1. VARs, Wold representations and their limits A brief review of VARs. Assume a true model, in MA form: X = A 0 e + A 1 e( 1) + A 2 e( 2) +...; E(ee ) = I = (A 0 + A 1 L + A 2 L 2 +...)
8.2 Harmonic Regression and the Periodogram
 Chapter 8 Spectral Methods 8.1 Introduction Spectral methods are based on thining of a time series as a superposition of sinusoidal fluctuations of various frequencies the analogue for a random process
Chapter 8 Spectral Methods 8.1 Introduction Spectral methods are based on thining of a time series as a superposition of sinusoidal fluctuations of various frequencies the analogue for a random process
Econometrics of financial markets, -solutions to seminar 1. Problem 1
 Econometrics of financial markets, -solutions to seminar 1. Problem 1 a) Estimate with OLS. For any regression y i α + βx i + u i for OLS to be unbiased we need cov (u i,x j )0 i, j. For the autoregressive
Econometrics of financial markets, -solutions to seminar 1. Problem 1 a) Estimate with OLS. For any regression y i α + βx i + u i for OLS to be unbiased we need cov (u i,x j )0 i, j. For the autoregressive
Single Equation Linear GMM with Serially Correlated Moment Conditions
 Single Equation Linear GMM with Serially Correlated Moment Conditions Eric Zivot October 28, 2009 Univariate Time Series Let {y t } be an ergodic-stationary time series with E[y t ]=μ and var(y t )
Single Equation Linear GMM with Serially Correlated Moment Conditions Eric Zivot October 28, 2009 Univariate Time Series Let {y t } be an ergodic-stationary time series with E[y t ]=μ and var(y t )
Are Structural VARs Useful Guides for Developing Business Cycle Theories? by Larry Christiano
 Discussion of: Chari-Kehoe-McGrattan: Are Structural VARs Useful Guides for Developing Business Cycle Theories? by Larry Christiano 1 Chari-Kehoe-McGrattan: Are Structural VARs Useful Guides for Developing
Discussion of: Chari-Kehoe-McGrattan: Are Structural VARs Useful Guides for Developing Business Cycle Theories? by Larry Christiano 1 Chari-Kehoe-McGrattan: Are Structural VARs Useful Guides for Developing
Mixed frequency models with MA components
 Mixed frequency models with MA components Claudia Foroni a Massimiliano Marcellino b Dalibor Stevanović c a Deutsche Bundesbank b Bocconi University, IGIER and CEPR c Université du Québec à Montréal September
Mixed frequency models with MA components Claudia Foroni a Massimiliano Marcellino b Dalibor Stevanović c a Deutsche Bundesbank b Bocconi University, IGIER and CEPR c Université du Québec à Montréal September
5: MULTIVARATE STATIONARY PROCESSES
 5: MULTIVARATE STATIONARY PROCESSES 1 1 Some Preliminary Definitions and Concepts Random Vector: A vector X = (X 1,..., X n ) whose components are scalarvalued random variables on the same probability
5: MULTIVARATE STATIONARY PROCESSES 1 1 Some Preliminary Definitions and Concepts Random Vector: A vector X = (X 1,..., X n ) whose components are scalarvalued random variables on the same probability
ARDL Cointegration Tests for Beginner
 ARDL Cointegration Tests for Beginner Tuck Cheong TANG Department of Economics, Faculty of Economics & Administration University of Malaya Email: tangtuckcheong@um.edu.my DURATION: 3 HOURS On completing
ARDL Cointegration Tests for Beginner Tuck Cheong TANG Department of Economics, Faculty of Economics & Administration University of Malaya Email: tangtuckcheong@um.edu.my DURATION: 3 HOURS On completing
