Cylindrical to rectangular coordinate transformation for planar phase front synthesis
|
|
|
- Myrtle Booth
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation Research Article Cylindrical to rectangular coordinate transforation for planar phase front synthesis ISSN Received on 6th July 207 Revised 9th October 207 Accepted on 28th Noveber 207 E-First on 2st February 208 doi: 0.049/iet-ap Seyed Hassan Sedighy, Caner Guclu 2, Mohaad Khalaj Airhosseini 3, Filippo Capolino 2 School of New Technologies, Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran 2 Departent of Electrical Engineering and Coputer Science, University of California at Irvine, Irvine, CA 92697, USA 3 School of Electrical Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran E-ail: sedighy@iust.ac.ir Abstract: Coordinate transforation technique is eployed to engineer a etaaterial slab that enables planar wave eission fro a planar or line localised source. First a rigorous cylindrical to rectangular coordinate transforation is applied resulting in with a sheet current generating a plane wave with ipedance atching at the boundary between the device and the surrounding ediu. Then, based on physical reasoning, the aterial constitutive paraeters are further reduced to having only one entry of the spatially varying pereability tensor instead of two entries as discussed in the references. This further reduction is equivalent to odifying the near field in the transfored doain. Finally, due to a specific u-near-zero condition near the origin, the sheet source is transfored to a localised one in the transfored doain and via full-wave siulations, the authors show that the field is still propagating as a plane wave. Moreover, the transission line () etaaterial ipleentation with discretised spatially varying pereability is designed. The capacitor- and inductor-loaded two-diensional grid is used to synthesise the required spatially varying relative pereability in the wavefront converter etaaterial slab. The etaaterial design is proven to successfully synthesise a planar wave front using a icrowave circuit siulator. Introduction The application of coordinate transforation in electroagnetics has received increasing attention in the last years. This technique, which relies on the for-invariance of Maxwell's equations through a spatial coordinate transforation, provides a ethodology to anipulate electroagnetic waves by engineering non-hoogeneous anisotropic constitutive paraeters, naely the perittivity and the pereability [ 4] based on a transforation schee. Novel applications of transforation electroagnetics also known as transforation optics include various devices such as the invisibility cloak [5], the electroagnetic concentrator [6, 7], illusion device [8], super absorber [9] and super scatter [0]. Here we present a directive eission device which can be integrated into antenna design as another application of the coordinate transforation. A coordinate transforation for converting cylindrical to plane waves was discussed in [], based on spatially dependent constitutive aterial paraeters, expressed as tensors in general. Moreover, as an application of the wave front conversion, a highly directive antenna was proposed in [2] by apping a half circle into a slab which needs infinite perittivity near the origin. A highly directive ulti-bea eission has been proposed in [3, 4] by proposing a wide triangle segent apping into narrow ones. A directive eission coposed of feeding source covered by an anisotropic coposite etaaterial has been proposed in [5, 6]. This structure is engineered by transforing a radiating cylindrical space into a rectangular one. A systeatic design procedure based on quasi-coordinate transforation technique has been proposed in [7] for the design of a lens antenna. In this procedure, the required three-diensional (3D) perittivity profile which is obtained by transforation of the tiny cells can liit the design and ipleentation. In this paper, a general coordinate transforation is applied to synthesise a etaaterial slab that enables planar TM-wave eission fro a planar or line localised source. The presented design also applies a reduction of constitutive paraeters which decreases the nuber of spatially dependent constitutive paraeters and at the sae tie preserves the advantages of the transforation schee such as eission with a planar wavefront IET Microw. Antennas Propag., 208, Vol. 2 Iss. 5, pp The Institution of Engineering and Technology 207 and wave atching to the surrounding space. This reduction procedure which is equivalent to odifying the near field in the transfored doain is justified analytically based on the Maxwell equations which have not been proved, previously. As a result, the final etaaterial design coprises constant constitutive paraeters with respect to position, except for only a single pereability tensor entry that varies only along a single principal direction (say x). Therefore, the resulting constitutive paraeters are siple and easy to ipleent in practice. Although our proposed transforation schee in general for is siilar to the ones proposed in [5, 6], the final proposed constructive paraeters are only spatially dependent in one direction copared with the ones introduced in these references which are spatially dependent in two directions. Moreover, the perfect ipedance atching at the outer boundary enhances our proposed slab perforance. In addition, as discussed in the next sections, due to a specific u-near-zero (MNZ) condition near the origin, the sheet source is transfored to a localised one in the transfored doain and therefore, the localised source can be planar or line eitter which enhances the design flexibility rather than the references works. The proposed schee of transforation is shown to successfully enable plane wave eission based on full-wave siulations. To validate the design concept with etaaterial ipleentation based on unit cells, the designed etaaterial slab with constitutive paraeters, (μ x, μ y, ε z ) is realised as a 2D transission line () etaaterial. For this purpose, the unit cells are loaded with sae proper luped reactive eleents to achieve the required effective pereability. Finally, the designed network is siulated at 00 MHz in a icrowave circuit siulator to validate the operation of the engineered etaaterial. We show that the transforation schee can be used for wavefront conversion even with discretisation of the spatial dependence function with respect to the etaaterial building block period for the ipleentation with a 2D etaaterial. The designed etaaterial requires the ipleentation of negative pereability which in principle cannot a wideband using foster circuit eleents. 84
2 The syste under investigation is invariant along the z-direction, thus it is essentially the 2D proble. Therefore assuing the presence of only transverse-to-z agnetic (TM) waves, the agnetic field has the x and y coponents and the electric field has only the z coponent. Effectively, only μ x, μ y and ε z in (2) govern the propagation of the TM waves (the subscripts x, y, and z denote the xx, yy, and zz entries of the tensors, respectively). As for the transforation schee, we adopt specific functions x = f ρ = wρ /R and y = g ϕ = Lϕ /π. Here the choice of g/ϕ and f /ρ as constants is otivated by having siple to ipleent functions. This leads to μ x = π L x, μ y = L π x, ε z = π L 2 R x (3) w Fig. Coordinate transforation schee fro virtual space to real space with cylindrical to rectangular coordinate transforation, where the colour coded lines illustrate the transforation apping Fig. 2 Required relative constitutive paraeters μ x, μ y and ε z for the ideal (dotted blue curves), odified (solid black curves) cases, and step-wise discretised μ x (dashed red curve) 2 Cylindrical to plane wave coordinate transforation The coordinate transforation concept is graphically shown in Fig.. For converting a cylindrical wave to a plane wave, the concentric circles in the virtual space x, y should be transfored to the parallel vertical lines in the real space x, y. There are various possible choices for this kind of transforation [2, 5, 6]. Here we start with a general schee which reads as x = f (ρ ) = f x 2 + y 2 (a) y = g(ϕ ) = g arctan y x (b) z = z (c) Assue that the virtual space (denoted by pried coordinates) is a vacuu, thus isotropic, (with relative perittivity and pereability as ε = I and μ = I, respectively, where I is the identity tensor). Based on the etric invariance of Maxwell's equations [, 3 5, 8, 9], the constitutive relative perittivity and pereability tensors of the ediu in the real space is ρ ( f /ρ ) ε = μ = g/ϕ ρ + z^z^. ( f /ρ )(g/ϕ ) x^x^ + g/ϕ ρ ( f /ρ ) y^ y^ (2) In the transfor schee, we expect the cylindrical wave in the virtual space to ap to plane wave propagation in the +x-direction in real space. The ipedance defined at x = w as μ y x = w ε z x = w η 0 = L πr η 0 (4) is required to be continuous between the slab and the free space at x = w. Indeed, when the slab is chosen with the diensions L/π = R = w =.5, the ipedance at x = w will be atched to the surrounding free space wave ipedance. For the chosen size, the perittivity and pereability (called direct paraeters fro now on) versus x are plotted in Fig. 2 with blue dashed curves. In order to validate the design forula, full-wave siulations based on the frequency-doain finite eleent ethod (ipleented via COMSOL Multi-Physics) are carried out for the design with the above direct paraeters. In the 2D siulation doain, the fields are invariant in the z-direction. The slab is excited by a z-directed surface current density (here referred to as sheet source) at x = 0. The sheet source corresponds to the line current in the virtual space noting that the origin of the virtual space aps to the edge of the etaaterial at the left (x = 0) side. The etaaterial doain is surrounded by vacuu on all sides of Fig. 2. Perfectly atched layers are ipleented at the boundary of the full-wave siulation doain to suppress reflections and iicking unbounded space. In Figs. 3a and b, we report E z and H y, respectively, in isotropic x y free space at a noinal frequency of 00 MHz, where the cylindrically eanating waves are observed fro a z-directed current line source. Then in Figs. 3c and d, we report the case after coordinate transforation, leading to the etaaterial slab excited by the sheet current. In practical cases, we consider a etaaterial slab only on one side of the source. In this case, ost of the power is eitted towards the free space side (the x direction) due to the high ipedance is seen fro the source sheet looking towards the etaaterial side (+x direction). This can be attributed to the growing μ y and decrease ε z close to x = 0. In order to eliinate the inefficient eission towards the etaaterial and to further siplify the spatial dependence of the constitutive paraeters, we ake another step of reduction in the constitutive paraeters under certain assuptions introduced hereafter (refer to Appendix for ore details). However, the reduction approach has been introduced in [20], here we focus on analytical prove of this approach. Let us look at the TM wave equation (derived in Appendix) in ters of the constitutive paraeters relevant to TM polarisation that vary only as a function of x ε z μ y 2 x 2E z + ε z μ x 2 y 2E z + ω 2 ε 0 μ 0 E z + ε z x μ y x E z = 0. Substituting the constitutive paraeters in (3) into (5) yields (5) IET Microw. Antennas Propag., 208, Vol. 2 Iss. 5, pp The Institution of Engineering and Technology
3 In (8), the constitutive paraeters only appear in two places as the products ε z μ x and ε z μ y which are, in general, the function of x. The wave equation in (8) guides us to ake another step in the reduction of the constitutive paraeters as μ x = μ x /a, μ y = μ y /a, and ε z = aε z (by using a spatially varying paraeter a) where the products ε z μ x and ε z μ y are sae as the products ε z μ x and ε z μ y, respectively. With the odified constitutive paraeters μ x, μ y, and ε z we can rewrite the wave equation as 2 ε z μ y x 2E z + 2 ε z μ x y 2E z + ω 2 μ 0 ε 0 E z + ε z x μ y x E z = 0 (9) Fig. 3 Noralised instantaneous z-polarised electric field (and y- polarised agnetic field in the second row) distribution in the x y plane for (a), (b)isotropic ediu, (c), (d) Converter slab using direct paraeters excited by a surface electric current sheet source at x = 0 along the edge of the etaaterial slab R/w 2 2 x 2E z + + R/w 2 x (π/l)(r/w)x 2 2 y 2E z + ω 2 μ 0 ε 0 E z x E z = 0. It can be observed that if we consider a plane wave solution (i.e. a wave not varying in y and z) of (6) this is not a plane wave with constant aplitude ainly because of the last ter, and indeed the field aplitude would vary in x. However, for large x, the solution tends to be that of a plane wave with a constant aplitude that propagates along x (guaranteeing that the second ter regarding the derivative with respect to y also vanishes). For large x, such a wave is a solution of the wave equation as (6) R/w 2 2 x 2E z + ω 2 μ 0 ε 0 E z = 0 (7) where the last ter in (6) has been neglected. This plane wave is consistent with the transforation in (2) because in the original x y doain [Fig. a], the corresponding cylindrical field solution is represented by Hankel function that near the origin does not behave siply as e jkρ / ρ due to near field represented by a logarithic function. Only far fro the origin, the cylindrical wave asyptotically behaves as e jkρ / ρ which corresponds to a pure plane wave in the transfored real space. Therefore, if in the transfored doain, we neglect the last ter of (6), the equation becoes the one that adits a constant-aplitude plane wave as a solution. We ai to ap ainly the propagative far-field fro the source in the virtual x y space onto a plane wave in the transfored space, whose far-field solution (i.e. for large x) is directly obtained by (5) after dropping its last ter. We will exploit this fact in siplifying the constitutive paraeters with the next step of odification. Rewriting (5) by neglecting the last ter, the TM wave equation in the etaaterial slab reduces to ε z μ y 2 x 2E z + ε z μ x 2 y 2E z + ω 2 ε 0 μ 0 E z = 0. (8) Note that the first line in (9) and the left-hand side ters in (5) are the sae since ε z μ x = ε z μ x and ε z μ y = ε z μ y. Moreover, by choosing μ y = μ y /a as a constant (thus a μ y ) we can guarantee that the last ter in (9) is zero. Accordingly, (8) and (9) becoe identical, and the etaaterial with the odified paraeters is expected to guide the waves in the sae anner as the original etaaterial under the approxiations that these equations are derived. Therefore the solution of (9) is asyptotically (for large x) equal to the one of (6). Eventually, we have defined a new step of odifying the constitutive paraeters without altering the wave equation of the propagation waves for large x, whose validity is also verified by full-wave siulations. Consider the three constitutive paraeters μ x, μ y, ε z that the TM waves propagation depends on, then divide μ x, μ y by a = μ y / χ and ultiply ε z by a = μ y / χ, where χ is a proper constant used for atching purposes. This further paraeter odification in the transfored doain keeps ε z μ x and ε z μ y functions intact. The odified relative constitutive paraeters are thus expressed as μ x = π L 2 χx 2, μ y = χ, ε z = R 2 w χ (0) Note that now only μ x depends on x whereas μ y and ε z are invariant with respect to position. A plane wave propagating along the x-direction at the aterial boundaries (in the real space) should be atched to the isotropic region to avoid reflection. This iplies that the ipedance TM wave propagating along the x-direction should be atched to the surrounding ediu's wave ipedance. Here the surrounding ediu is taken as a vacuu with the wave ipedance η 0, and the wave ipedance η TM = η 0 μ y /ε z should be atched to η 0 at x = w. Accordingly, the paraeter χ is set to be equal to R/w. With this condition, the final relative constitutive paraeters are siplified as μ x = Rπ2 wl 2 x2, μ y = R w, ε z = R w () In Fig. 2, the odified constitutive paraeters with L = 2R = 2w = 3, are reported with solid black curves where μ y = ε z. The only varying ter is μ x whose range is fro 0 to 2.5. Moreover, Fig. 2 shows a possible stepwise approxiation for the only varying paraeter μ x, which will be used in Section 3. The converter slab ade of etaaterial with the odified constitutive paraeters reported in Fig. 2 with solid black curves is also siulated in the full-wave environent. In Figs. 4a and b, we report a tie-shot of the z-polarised electric and agnetic field distribution at 00 MHz, respectively, using the etaaterial slab with odified paraeters excited by an electric current sheet. Note that this tie, the plane wave eanates in both + and x directions with equal aplitude. However, it is interesting to show that not only the electric surface current but also a line current source leads to plane wave eission when using the etaaterials slab. To this ai, we report the electric and agnetic field in Figs. 4c and d 86 IET Microw. Antennas Propag., 208, Vol. 2 Iss. 5, pp The Institution of Engineering and Technology 207
4 excited by a line source, all noralised by their respective axia at the plane wave regions. Strikingly, the slab is able to facilitate eission of a plane wave also by a line source. Note that for the transforation schee in Fig., every point in the cylindrical virtual space, except the origin, aps to a single point in the rectangular slab in the real space. The origin in the cylindrical virtual space, on the other hand, aps to the edge on y line in the rectangular real space. In the ideal transfored case, the z-directed line current at the origin in virtual space corresponds to a z-directed sheet current along the x = 0 side of the slab. However, we have shown that the etaaterial slab can lead to planar wave front radiation even for the line current at the origin. This can be attributed to the fact that a line current in the virtual space at an infinitesial distance fro the origin, eits cylindrical waves alost identical to the source at the origin; at the sae tie, it aps to a point at an infinitesial distance to the origin at the rectangular real space. Fro constitutive paraeters aspect, we observe that μx vanishes at the x = 0 edge of the slab. This corresponds to a resonance condition with MNZ where the field profile of the line source at y = 0 is transferred along the y-direction alost without losing intensity and in phase. The transforation schee introduced here would also hold for the dual case, where TE waves could be altered by siply ipleenting a single spatially-varying perittivity tensor entry. Fig. 4 Noralised instantaneous z-polarised electric field (and ypolarised agnetic field in the second row) distribution in the x y plane for (a), (b)converter slab using odified paraeters excited by a surface electric current sheet source at x = 0 along the edge of the etaaterial slab and (c), (d) Converter slab using odified paraeters excited by a line source at location (x, y) = (0, 0) 3 etaaterial synthesis For a etaaterial deonstration by synthesising the designed constitutive paraeters, a approach is selected. In the approach, for a 2D periodic esh grid loaded by series luped ipedance as shown in Fig. 5, the effective diagonal pereability and perittivity can be described by [2] μx, y μ0 = Ldis + Fig. 5 Unit cell of the etaaterial with luped series eleents Z y, x, jωd (a) Sketch ap of the converter etaaterial surrounded by ISO ediu, synthesised by grids ade of (b) capacitor loaded cell for μx < μxiso, (c) Isotropic cell with μx = μxiso, (d) Inductor loaded cell for μx > μxiso IET Microw. Antennas Propag., 208, Vol. 2 Iss. 5, pp The Institution of Engineering and Technology 207 (2) where Ldis (H/) and Cdis (F/) are the distributed (per-length) inductance and capacitance of the, respectively, d is the icrostrip grid period, and Z x, y are the series luped ipedances along the x and y directions, respectively. The surrounding isotropic ediu (ISO ediu) is ipleented as the isotropic grid (without series ipedance loading) shown in Fig. 6c. The unloaded icrostrip is the background ediu, so the constitutive paraeters in the slab are noralised by the ISO ediu's perittivity and pereability which are calculated by inserting Z x, y = 0 in (2) leading to μxiso μ0 = μyiso μ0 = Ldis and εzisoε0 = 2Cdis. In the designed slab, we need spatially varying μx, whereas the required μy and εz (relative to the isotropic background) are constant and equal to the isotropic surrounding ediu. Therefore, it is sufficient to load the icrostrip grid only along the y-direction, and then constitutive paraeters of the etaaterial slab are μx Zy =+, ISO jωdl μx dis Fig. 6 The sketch ap of the proposed converter εzε0 = 2Cdis μy = μyiso εz =. εziso (3) To synthesise the constitutive paraeters expressed in () with these relations, we chose L = 2R = 2w = 3 sae as the siulated case above. Note that the only spatially varying paraeter is μx = (π 2 /4) x/w 2 μxiso. To ipleent μx < μxiso, the should be loaded with capacitor (Fig. 6b) whereas for μx > μxiso, the should be loaded with inductor (Fig. 6d). The grid ade of.5 wide icrostrip line is designed on an FR4 substrate with relative perittivity εfr4 = 4.5, dielectric thickness h = Thus, the distributed inductance and capacitance of the icrostrip are Ldis = 306 nh/ and ISO Cdis = 28.5 pf leading to μxiso = 28.96ε0,, y = 0.243μ0 and εz respectively. The eshsize is chosen as d = 5 c which is less than λg /8 at the design frequency, 00 MHz, where λg =.3 is the 87
5 Table Design paraeters for the converter slab μ x /μ x ISO Region Loading type Coponent < x/w < 0. capacitor pf < x/w < 0.2 capacitor pf < x/w < 0.3 capacitor pf < x/w < 0.4 capacitor pf < x/w < 0.5 capacitor 3.2 pf < x/w < 0.6 capacitor pf 0.6 < x/w < 0.7 without loading none < x/w < 0.8 inductor nh < x/w < 0.9 inductor nh < x/w < inductor 5.66 nh Fig. 7 2D noralised voltage distribution in the network (a) tiso ediu, (b) Converter slab surrounded by ISO ediu equivalent guided wavelength in the isotropic grid. Also, the whole structure is shown in Fig. 6a consists of unit cells (3.98λ g 3.98λ g ) that the converter slab is ade by 0 20 (2.65λ g.32λ g ) cells. The continuous change of μ x with respect to x, cannot be applied to the 2D grid etaaterial since the structure is ade up of unit cells with finite diensions. The step-wise approxiation μ x is applied in such a way that each cell bears the value of μ x corresponding to the x-position of the cell's centre, as presented in Fig. 2. The odified paraeters sapled at the centre of each cell, are tabulated in Table, with the corresponding luped reactive series coponent required to realise the. The required values of μ x range fro 0 to 2.5, and this range of values are realised by three different types of unit cells: capacitor loaded grids shown in Fig. 6b for μ x < μ x ISO, isotropic grids shown in Fig. 6c for μ x = μ x ISO, and inductor loaded grids shown in Fig. 6d for μ x > μ x ISO. Also, based on () and (3), the required capacitors and inductors are calculated and tabulated in Table. The grids should be terinated with a proper ipedance to iniise the reflection fro the edges, iicking an unbounded environent. This proper terination ipedance can be coputed via Bloch theory [9] and it depends on the propagation direction of a Bloch wave. Based on the siulation results presented in Figs. 3 and 4, we expect to observe a wave with alost planar wavefront propagating in the x-direction inside the ISO ediu with the wavenuber k x = ω μ x ISO μ 0 ε z ISO ε 0. Therefore, the edges of the grid on x and +x sides are terinated by the ISO ediu noral-incidence Bloch ipedance of 29 Ω which atches the ain coponent of the spatial spectru of the waves propagating along the x-direction. Note that since the power is expected to propagate ainly along x, the power propagating along y is negligible. Therefore, we leave the y-direction edges of the ISO ediu open, which supports the plane wave propagating along the x-axis. On the other hand, when siulating the ISO ediu without the anisotropic slab, the choice of terination ipedances is strongly dependent on the terination point for which the incidence angle of the ain Bloch wave coponent varies as a function of position since the waves eanate cylindrically fro the source. The Bloch ipedance varies for propagation directions defined by (k x, k y ) pairs varying between 29 and 42 Ω on the edges along the x and y directions. We used the 34 Ω Bloch terination value as a weighted average of the required atching ipedances over the terination nodes at the edges of the ISO ediu. The axiu reflection coefficients turn out to be 0. and indeed as shown in the following results, the little isatch led to no observable reflection at the grid edges. We use a coercial icrowave circuit siulator (Agilent's Advanced Design Syste, ADS) to siulate the structure. An AC voltage source is used to excite the network, which is located half of the cell away fro the left slab boundary. First, we siulate the network without the converter slab, i.e. the source in the ISO ediu. The noralised voltage distribution of the grid nodes is plotted in Fig. 7a at 00 MHz. The cylindrical wavefront can be seen in this figure clearly. In Fig. 7b, the network with a converter slab surrounded by ISO ediu is siulated. The noralised voltage distribution at the grid nodes, i.e. the centre of the cells as shown in Fig. 5, is plotted in Fig. 7b. The designed slab converts the cylindrical to the planar wavefront. Coparing the noralised electric field distribution in Figs. 3 and 4 and noralised voltage distribution in Fig. 7 verifies the ability of the designed converter slab to convert the cylindrical wavefront to planar one. 4 Conclusion The coordinate transforation was applied for cylindrical to plane wavefront conversion. In addition to conventional transforation ethod, the constitutive paraeters are engineered in an additional step to further siplify the spatial dependence. The final constitutive paraeters are constant except only a single spatially varying paraeter. Therefore, the proposed constitutive paraeters, perittivity, and pereability are siple and easy to ipleent in practice. First using full-wave siulations of a bulk etaaterial slab, we proved that the designed etaaterial enables localised sources to eit planar waves. The etaaterial slab with single pereability tensor entry is shown to convert TM wave front via full-wave siulations. The dual case for converting TE waves by requiring only a single spatially-varying perittivity tensor entry could be also utilised since controlling perittivity could be ore convenient, depending on the frequency of operation. Finally, a etaaterial ade of a planar icrostrip line grid loaded with luped capacitors and inductors were used to synthesise the proposed etaaterial converter slab. Both the fullwave siulation of a bulk etaaterial slab and the circuit siulation of the grid verified the concept of circular to a planar wave converter that is also ipedance atched to the free space region. 88 IET Microw. Antennas Propag., 208, Vol. 2 Iss. 5, pp The Institution of Engineering and Technology 207
6 5 References [] Sedighy, S.H., Khalaj-Airhosseini, M.: Effect of optical transforation order on design of arbitrary polygonal invisible cloak, JOSA A, 202, 29, (2), pp [2] Kwon, D.-H., Werner, D.H.: Transforation electroagnetics: an overview of the theory and applications, IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag., 200, 52, pp [3] Leonhardt, U.: Optical conforal apping, Science, 2006, 32, pp [4] Leonhardt, U., Philbin, T.G.: Transforation optics and the geoetry of light, Prog. Opt., 2009, 53, pp [5] Pendry, J.B., Schurig, D., Sith, D.R.: Controlling electroagnetic fields, Science, 2006, 32, pp [6] Hasan Sedighy, S., Khalaj-Airhosseini, M.: Arbitrary n-sided irregular polygonal electroagnetic transfored edia, J. Opt. Soc. A. A, 202, 29, pp [7] Li, T., Huang, M., Yang, J., et al.: Three diensional electroagnetic concentrators with hoogeneous aterial paraeters, Prog. Electroagn. Res. M, 20, 8, pp [8] Lai, Y., Ng, J., Chen, H., et al.: Illusion optics: the optical transforation of an object into another object, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2009, 02, p [9] Ng, J., Chen, H., Chan, C.: Metaaterial frequency-selective superabsorber, Opt. Lett., 2009, 34, pp [0] Yang, T., Chen, H., Luo, X., et al.: Superscatterer: enhanceent of scattering with copleentary edia, Opt. Express, 2008, 6, (22), pp [] Jiang, W.X., Cui, T.J., Ma, H.F., et al.: Cylindrical-to-plane-wave conversion via ebedded optical transforation, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, 92, pp [2] Zhang, J., Luo, Y., Chen, H., et al.: Directive eission obtained by coordinate transforation, Prog. Electroagn. Res. (PIER), 2008, 8, pp [3] Jiang, Z.H., Gregory, M.D., Werner, D.H.: Experiental deonstration of a broadband transforation optics lens for highly directive ultibea eission, Phys. Rev. B, 20, 84, p. 65 [4] Wu, Q., Jiang, Z.H., Quevedo-Teruel, O., et al.: Transforation optics inspired ultibea lens antennas for broadband directive radiation, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., 203, 6, (2), pp [5] Tichit, P.H., Burokur, S.N., Gerain, D., et al.: Design and experiental deonstration of a high-directive eission with transforation optics, Phys. Rev. B, 20, 83, (5), p [6] Tichit, P.-H., Burokur, S., Gerain, D., et al.: Coordinate-transforationbased ultra-directive eission, Electron. Lett., 20, 47, pp [7] Ebrahipouri, M., Quevedo-Teruel, O.: Bespoke lenses based on quasiconforal transforation optics technique, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., 207, 65, (5), pp [8] Tang, C.A.W., Kallos, E., Song, W., et al.: Discrete coordinate transforation for designing all-dielectric flat antennas, IEEE Trans. Antenna Propag., 200, 58, pp [9] Cai, W., Chettiar, U.K., Kildishev, A.V., et al.: Optical cloaking with etaaterials, Nature Photonics, 2007,, pp [20] Schurig, D., Mock, J.J., Justice, B.J., et al.: Metaaterial electroagnetic cloak at icrowave frequencies, Science, 2006, 34, (580), pp [2] Wong, J.K., Balain, K.G., Eleftheriades, G.V.: Fields in planar anisotropic transission-line etaaterials, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., 2006, 54, pp Appendix The TM wave equation in ters of z-directed electric field is derived next. Assuing invariance along the z-axis together with diagonalisable constitutive paraeter tensors, Maxwell's equations can be separated for TM-to-z and TE-to-z waves. TM-to-z waves possess only H x, H y, and E z that satisfy the equations (derived fro the curl expression in Maxwell's equations) y E z = jωμ x H x, x E z = jωμ y H y, x H y (4) y H x = jωε z E z By anipulating the first two equations above as y jωμ 0 μ x y E z x jωμ y x E z = y H x = x H y (5) We can construct the suation ters on the left hand side of the last line in (4). Then the agnetic field coponents where the su of the left hand side of the equations in (5) is equal to jωε z E z. As such, the wave equation for the electric field is obtained as x μ y x E z + y μ x y E z + ω 2 μ 0 ε 0 ε z E z = 0 (6) Keeping in ind that pereabilities above are functions of x only in our transforation schee, the derivatives can be expanded to reach the wave equation given as ε z μ y 2 x 2E z + ε z μ x 2 y 2E z + ω 2 μ 0 ε 0 E z + ε z x μ y x E z = 0. (7) IET Microw. Antennas Propag., 208, Vol. 2 Iss. 5, pp The Institution of Engineering and Technology
IN A SENSE, every material is a composite, even if the
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1999 2075 Magnetis fro Conductors and Enhanced Nonlinear Phenoena J. B. Pendry, A. J. Holden, D. J. Robbins, and W. J. Stewart,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1999 2075 Magnetis fro Conductors and Enhanced Nonlinear Phenoena J. B. Pendry, A. J. Holden, D. J. Robbins, and W. J. Stewart,
Extraordinary Optical Transmission Induced by Excitation of a Magnetic Plasmon Propagation Mode in a Diatomic Chain of Slit-hole Resonators
 Extraordinary Optical Transission Induced by Excitation of a Magnetic Plason Propagation Mode in a Diatoic Chain of Slit-hole Resonators H. Liu 1, *, T. Li 1, Q. J. Wang 1, Z. H. Zhu 1, S. M. Wang 1, J.
Extraordinary Optical Transission Induced by Excitation of a Magnetic Plason Propagation Mode in a Diatoic Chain of Slit-hole Resonators H. Liu 1, *, T. Li 1, Q. J. Wang 1, Z. H. Zhu 1, S. M. Wang 1, J.
ECE280: Nano-Plasmonics and Its Applications. Week8. Negative Refraction & Plasmonic Metamaterials
 ECE8: Nano-Plasonics and Its Applications Week8 Negative Refraction & Plasonic Metaaterials Anisotropic Media c k k y y ω μ μ + Dispersion relation for TM wave isotropic anisotropic k r k i, S i S r θ
ECE8: Nano-Plasonics and Its Applications Week8 Negative Refraction & Plasonic Metaaterials Anisotropic Media c k k y y ω μ μ + Dispersion relation for TM wave isotropic anisotropic k r k i, S i S r θ
Modeling of Passive Elements with ASITIC. Prof. Ali M. Niknejad Berkeley Wireless Research Center University of California, Berkeley
 Modeling of Passive Eleents with ASITIC Prof. Ali M. Niknejad Berkeley Wireless Research Center University of California, Berkeley Outline of Presentation ASITIC Overview Electroagnetic Solution Approach
Modeling of Passive Eleents with ASITIC Prof. Ali M. Niknejad Berkeley Wireless Research Center University of California, Berkeley Outline of Presentation ASITIC Overview Electroagnetic Solution Approach
Directive Emission Obtained by Coordinate Transformation
 Directive Emission Obtained by Coordinate Transformation Jingjing Zhang 1, Yu Luo 1, Hongsheng Chen 1 2*, Lixin Ran 1, Bae-Ian Wu 2, and Jin Au Kong 1 2 1 The Electromagnetics Academy at Zhejiang University,
Directive Emission Obtained by Coordinate Transformation Jingjing Zhang 1, Yu Luo 1, Hongsheng Chen 1 2*, Lixin Ran 1, Bae-Ian Wu 2, and Jin Au Kong 1 2 1 The Electromagnetics Academy at Zhejiang University,
Infrared carpet cloak designed with uniform silicon grating structure
 Infrared carpet cloak designed with uniform silicon grating structure Xiaofei Xu, Yijun Feng, Yu Hao, Juming Zhao, Tian Jiang Department of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing Univerisity, Nanjing,
Infrared carpet cloak designed with uniform silicon grating structure Xiaofei Xu, Yijun Feng, Yu Hao, Juming Zhao, Tian Jiang Department of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing Univerisity, Nanjing,
Mutual capacitor and its applications
 Mutual capacitor and its applications Chun Li, Jason Li, Jieing Li CALSON Technologies, Toronto, Canada E-ail: calandli@yahoo.ca Published in The Journal of Engineering; Received on 27th October 2013;
Mutual capacitor and its applications Chun Li, Jason Li, Jieing Li CALSON Technologies, Toronto, Canada E-ail: calandli@yahoo.ca Published in The Journal of Engineering; Received on 27th October 2013;
Data-Driven Imaging in Anisotropic Media
 18 th World Conference on Non destructive Testing, 16- April 1, Durban, South Africa Data-Driven Iaging in Anisotropic Media Arno VOLKER 1 and Alan HUNTER 1 TNO Stieltjesweg 1, 6 AD, Delft, The Netherlands
18 th World Conference on Non destructive Testing, 16- April 1, Durban, South Africa Data-Driven Iaging in Anisotropic Media Arno VOLKER 1 and Alan HUNTER 1 TNO Stieltjesweg 1, 6 AD, Delft, The Netherlands
The Failure of Coaxial TEM Cells ASTM Standards Methods In H.F. Range
 The Failure of Coaxial TEM Cells ASTM Standards Methods In H.F. Range Mihai Badic HV/EMC Laboratory, Research Institute for Electrical Engineering - ICPE Bucharest, ROMAN badic@icpe.ro Mihai-Jo Marinescu
The Failure of Coaxial TEM Cells ASTM Standards Methods In H.F. Range Mihai Badic HV/EMC Laboratory, Research Institute for Electrical Engineering - ICPE Bucharest, ROMAN badic@icpe.ro Mihai-Jo Marinescu
Time-of-flight Identification of Ions in CESR and ERL
 Tie-of-flight Identification of Ions in CESR and ERL Eric Edwards Departent of Physics, University of Alabaa, Tuscaloosa, AL, 35486 (Dated: August 8, 2008) The accuulation of ion densities in the bea pipe
Tie-of-flight Identification of Ions in CESR and ERL Eric Edwards Departent of Physics, University of Alabaa, Tuscaloosa, AL, 35486 (Dated: August 8, 2008) The accuulation of ion densities in the bea pipe
th Annual IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference Aachen, Germany, Parallel Connection of Piezoelectric Transformers
 004 35th Annual IEEE ower Electronics Specialists Conference Aachen, Gerany, 004 arallel Connection of iezoelectric Transforers Svetlana Bronstein, Gregory Ivensky and Sa Ben-Yaakov* ower Electronics Laboratory
004 35th Annual IEEE ower Electronics Specialists Conference Aachen, Gerany, 004 arallel Connection of iezoelectric Transforers Svetlana Bronstein, Gregory Ivensky and Sa Ben-Yaakov* ower Electronics Laboratory
On the Mixed Discretization of the Time Domain Magnetic Field Integral Equation
 On the Mixed Discretization of the Tie Doain Magnetic Field Integral Equation H. A. Ülkü 1 I. Bogaert K. Cools 3 F. P. Andriulli 4 H. Bağ 1 Abstract Tie doain agnetic field integral equation (MFIE) is
On the Mixed Discretization of the Tie Doain Magnetic Field Integral Equation H. A. Ülkü 1 I. Bogaert K. Cools 3 F. P. Andriulli 4 H. Bağ 1 Abstract Tie doain agnetic field integral equation (MFIE) is
J. Electrical Systems x-x (xxx): x-xx. Regular paper. Reflected Signal on a Nonuniform Overhead Transmission Line at High Frequency
 A. Boudjeaa S. Tahi B. Bennaane T. B. Berbar B. Lehouidj J. Electrical Systes x-x (xxx): x-xx Regular paper Reflected Signal on a Nonunifor Overhead Transission Line at High Frequency The effect of the
A. Boudjeaa S. Tahi B. Bennaane T. B. Berbar B. Lehouidj J. Electrical Systes x-x (xxx): x-xx Regular paper Reflected Signal on a Nonunifor Overhead Transission Line at High Frequency The effect of the
HIGH RESOLUTION NEAR-FIELD MULTIPLE TARGET DETECTION AND LOCALIZATION USING SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES
 ICONIC 2007 St. Louis, O, USA June 27-29, 2007 HIGH RESOLUTION NEAR-FIELD ULTIPLE TARGET DETECTION AND LOCALIZATION USING SUPPORT VECTOR ACHINES A. Randazzo,. A. Abou-Khousa 2,.Pastorino, and R. Zoughi
ICONIC 2007 St. Louis, O, USA June 27-29, 2007 HIGH RESOLUTION NEAR-FIELD ULTIPLE TARGET DETECTION AND LOCALIZATION USING SUPPORT VECTOR ACHINES A. Randazzo,. A. Abou-Khousa 2,.Pastorino, and R. Zoughi
Engineering of Composite Media for Shields at Microwave Frequencies
 Engineering of Coposite Media for Shields at Microwave Frequencies Marina Koledintseva, Poorna Chander avva, ichard DuBroff, Jaes Drewniak EMC Laboratory, ECE Departent, University of Missouri-olla, olla,
Engineering of Coposite Media for Shields at Microwave Frequencies Marina Koledintseva, Poorna Chander avva, ichard DuBroff, Jaes Drewniak EMC Laboratory, ECE Departent, University of Missouri-olla, olla,
Accuracy of the Scaling Law for Experimental Natural Frequencies of Rectangular Thin Plates
 The 9th Conference of Mechanical Engineering Network of Thailand 9- October 005, Phuket, Thailand Accuracy of the caling Law for Experiental Natural Frequencies of Rectangular Thin Plates Anawat Na songkhla
The 9th Conference of Mechanical Engineering Network of Thailand 9- October 005, Phuket, Thailand Accuracy of the caling Law for Experiental Natural Frequencies of Rectangular Thin Plates Anawat Na songkhla
Coupling effect of magnetic polariton in perforated metal/dielectric layered metamaterials and its influence on negative refraction transmission
 Coupling effect of agnetic polariton in perforated etal/dielectric layered etaaterials and its influence on negative refraction transission T. Li, H. Liu, F. M. Wang, Z. G. Dong, and S. N. Zhu Departent
Coupling effect of agnetic polariton in perforated etal/dielectric layered etaaterials and its influence on negative refraction transission T. Li, H. Liu, F. M. Wang, Z. G. Dong, and S. N. Zhu Departent
A NEW ELECTROSTATIC FIELD GEOMETRY. Jerry E. Bayles
 INTRODUCTION A NEW ELECTROSTATIC FIELD GEOMETRY by Jerry E Bayles The purpose of this paper is to present the electrostatic field in geoetrical ters siilar to that of the electrogravitational equation
INTRODUCTION A NEW ELECTROSTATIC FIELD GEOMETRY by Jerry E Bayles The purpose of this paper is to present the electrostatic field in geoetrical ters siilar to that of the electrogravitational equation
Concealing arbitrary objects remotely with multi-folded transformation optics
 Concealing arbitrary objects remotely with multi-folded transformation optics B. Zheng 1, 2, 3, H. A. Madni 1, 2, 3, R. Hao 2, X. Zhang 2, X. Liu 1, E. Li 2* 1, 2, 3* and H. Chen 1 State Key Laboratory
Concealing arbitrary objects remotely with multi-folded transformation optics B. Zheng 1, 2, 3, H. A. Madni 1, 2, 3, R. Hao 2, X. Zhang 2, X. Liu 1, E. Li 2* 1, 2, 3* and H. Chen 1 State Key Laboratory
About the definition of parameters and regimes of active two-port networks with variable loads on the basis of projective geometry
 About the definition of paraeters and regies of active two-port networks with variable loads on the basis of projective geoetry PENN ALEXANDR nstitute of Electronic Engineering and Nanotechnologies "D
About the definition of paraeters and regies of active two-port networks with variable loads on the basis of projective geoetry PENN ALEXANDR nstitute of Electronic Engineering and Nanotechnologies "D
A Fiber Optic Phase Modulator with an Optical Frequency Shift of up to 20 GHz
 A Fiber Optic Phase Modulator with an Optical Frequency Shift of up to 0 GHz A.M.Maedov (1), A. L. Levin (), and V. T. Potapov (3) (1) Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics, Russian Acadey of
A Fiber Optic Phase Modulator with an Optical Frequency Shift of up to 0 GHz A.M.Maedov (1), A. L. Levin (), and V. T. Potapov (3) (1) Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics, Russian Acadey of
On the Radiation from a Short Current-Carrying Straight Wire Oriented Perpendicular to a Stratified Medium
 Progress In Electroagnetics Research, Vol. 159, 49 57, 17 On the Radiation fro a Short Current-Carrying Straight Wire Oriented Perpendicular to a Stratified Mediu Mauro Parise 1, * and Giulio Antonini
Progress In Electroagnetics Research, Vol. 159, 49 57, 17 On the Radiation fro a Short Current-Carrying Straight Wire Oriented Perpendicular to a Stratified Mediu Mauro Parise 1, * and Giulio Antonini
Singularity Extraction for Reflected Sommerfeld Integrals over Multilayered Media
 Telfor Journal, Vol. 6, No., 4. 7 Singularity Extraction for Reflected Soerfeld Integrals over Multilayered Media Vladiir V. Petrovic, Senior Meber, IEEE, Aleksandra J. Krneta, and Branko M. Kolundzija,
Telfor Journal, Vol. 6, No., 4. 7 Singularity Extraction for Reflected Soerfeld Integrals over Multilayered Media Vladiir V. Petrovic, Senior Meber, IEEE, Aleksandra J. Krneta, and Branko M. Kolundzija,
The source of THz radiation based on dielectric waveguide excited by sequence of electron bunches
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The source of THz radiation based on dielectric waveguide excited by sequence of electron bunches To cite this article: A M Altark and A D Kanareykin
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The source of THz radiation based on dielectric waveguide excited by sequence of electron bunches To cite this article: A M Altark and A D Kanareykin
A Study of Electromagnetic Wave Propagation. in the Foam Core Sandwich Structures
 ID-83 A Study of Electroagnetic Wave Propagation in the Foa Core Sandwich Structures H. J. Chun and H. S. Shin School of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering, Yonsei University 34, Shinchon-dong, Seodaeun-gu,
ID-83 A Study of Electroagnetic Wave Propagation in the Foa Core Sandwich Structures H. J. Chun and H. S. Shin School of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering, Yonsei University 34, Shinchon-dong, Seodaeun-gu,
Design of 25 KA Current Injection Transformer Core with Finite Element Method
 1 Design of 5 KA Current Injection Transforer Core ith Finite Eleent Method HOSSEIN HEYDARI, MOHSEN ARIANNEJAD, FARAMARZ FAGHIHI Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran Abstract.Since Current
1 Design of 5 KA Current Injection Transforer Core ith Finite Eleent Method HOSSEIN HEYDARI, MOHSEN ARIANNEJAD, FARAMARZ FAGHIHI Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran Abstract.Since Current
Kinetic Theory of Gases: Elementary Ideas
 Kinetic Theory of Gases: Eleentary Ideas 17th February 2010 1 Kinetic Theory: A Discussion Based on a Siplified iew of the Motion of Gases 1.1 Pressure: Consul Engel and Reid Ch. 33.1) for a discussion
Kinetic Theory of Gases: Eleentary Ideas 17th February 2010 1 Kinetic Theory: A Discussion Based on a Siplified iew of the Motion of Gases 1.1 Pressure: Consul Engel and Reid Ch. 33.1) for a discussion
PH 222-2C Fall Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current. Lectures 18-19
 H - Fall 0 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent ectures 8-9 hapter 3 (Halliday/esnick/Walker, Fundaentals of hysics 8 th edition) hapter 3 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent
H - Fall 0 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent ectures 8-9 hapter 3 (Halliday/esnick/Walker, Fundaentals of hysics 8 th edition) hapter 3 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent
SIMULATION OF THE HEATING STEP WITHIN THE THERMOFORMING PROCESS USING THE FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD
 SIMULATION OF THE HEATING STEP WITHIN THE THERMOFORMING PROCESS USING THE FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD A. Fertschej 1 *, G.R. Langecker 1 University of Leoben artur.fertschej@u-leoben.at; Franz-Josef Strasse
SIMULATION OF THE HEATING STEP WITHIN THE THERMOFORMING PROCESS USING THE FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD A. Fertschej 1 *, G.R. Langecker 1 University of Leoben artur.fertschej@u-leoben.at; Franz-Josef Strasse
Electromagnetic fields modeling of power line communication (PLC)
 Electroagnetic fields odeling of power line counication (PLC) Wei Weiqi UROP 3 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang echnological University E-ail: 4794486@ntu.edu.sg Keyword: power line
Electroagnetic fields odeling of power line counication (PLC) Wei Weiqi UROP 3 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang echnological University E-ail: 4794486@ntu.edu.sg Keyword: power line
2.141 Modeling and Simulation of Dynamic Systems Assignment #2
 2.141 Modeling and Siulation of Dynaic Systes Assignent #2 Out: Wednesday Septeber 20, 2006 Due: Wednesday October 4, 2006 Proble 1 The sketch shows a highly siplified diagra of a dry-dock used in ship
2.141 Modeling and Siulation of Dynaic Systes Assignent #2 Out: Wednesday Septeber 20, 2006 Due: Wednesday October 4, 2006 Proble 1 The sketch shows a highly siplified diagra of a dry-dock used in ship
Antipodal radiation pattern of a patch antenna combined with superstrate using transformation electromagnetics
 Antipodal radiation pattern of a patch antenna combined with superstrate using transformation electromagnetics Mark Clemente Arenas, Anne-Claire Lepage, Xavier Begaud To cite this version: Mark Clemente
Antipodal radiation pattern of a patch antenna combined with superstrate using transformation electromagnetics Mark Clemente Arenas, Anne-Claire Lepage, Xavier Begaud To cite this version: Mark Clemente
REPRODUCING KERNEL PARTICLE METHOD FOR CONDUCTION RADIATION INTERACTION IN 3D PARTICIPATING MEDIA
 Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Theral Sciences 2017, 1st ACTS March 26-30, 2017, Jeu Island, Korea ACTS-P00337 REPRODUCING KERNEL PARTICLE METHOD FOR CONDUCTION RADIATION INTERACTION IN 3D PARTICIPATING
Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Theral Sciences 2017, 1st ACTS March 26-30, 2017, Jeu Island, Korea ACTS-P00337 REPRODUCING KERNEL PARTICLE METHOD FOR CONDUCTION RADIATION INTERACTION IN 3D PARTICIPATING
Kinetic Theory of Gases: Elementary Ideas
 Kinetic Theory of Gases: Eleentary Ideas 9th February 011 1 Kinetic Theory: A Discussion Based on a Siplified iew of the Motion of Gases 1.1 Pressure: Consul Engel and Reid Ch. 33.1) for a discussion of
Kinetic Theory of Gases: Eleentary Ideas 9th February 011 1 Kinetic Theory: A Discussion Based on a Siplified iew of the Motion of Gases 1.1 Pressure: Consul Engel and Reid Ch. 33.1) for a discussion of
Inside-out electromagnetic cloaking
 Inside-out electromagnetic cloaking Nina A. Zharova 1,2, Ilya V. Shadrivov 1, and Yuri S. Kivshar 1 1 Nonlinear Physics Center, Research School of Physical Sciences and Engineering, Australian National
Inside-out electromagnetic cloaking Nina A. Zharova 1,2, Ilya V. Shadrivov 1, and Yuri S. Kivshar 1 1 Nonlinear Physics Center, Research School of Physical Sciences and Engineering, Australian National
Fast Montgomery-like Square Root Computation over GF(2 m ) for All Trinomials
 Fast Montgoery-like Square Root Coputation over GF( ) for All Trinoials Yin Li a, Yu Zhang a, a Departent of Coputer Science and Technology, Xinyang Noral University, Henan, P.R.China Abstract This letter
Fast Montgoery-like Square Root Coputation over GF( ) for All Trinoials Yin Li a, Yu Zhang a, a Departent of Coputer Science and Technology, Xinyang Noral University, Henan, P.R.China Abstract This letter
Simulated Effects of Soil Temperature and Salinity on Capacitance Sensor Measurements
 Sensors 2007, 7, 548-577 sensors ISSN 1424-8220 2007 by MDPI www.dpi.org/sensors Full Research Paper Siulated Effects of Soil Teperature and Salinity on Capacitance Sensor Measureents Mike Schwank 1, *
Sensors 2007, 7, 548-577 sensors ISSN 1424-8220 2007 by MDPI www.dpi.org/sensors Full Research Paper Siulated Effects of Soil Teperature and Salinity on Capacitance Sensor Measureents Mike Schwank 1, *
Two Dimensional Consolidations for Clay Soil of Non-Homogeneous and Anisotropic Permeability
 Two Diensional Consolidations for Clay Soil of Non-Hoogeneous and Anisotropic Pereability Ressol R. Shakir, Muhaed Majeed Thiqar University, College of Engineering, Thiqar, Iraq University of Technology,
Two Diensional Consolidations for Clay Soil of Non-Hoogeneous and Anisotropic Pereability Ressol R. Shakir, Muhaed Majeed Thiqar University, College of Engineering, Thiqar, Iraq University of Technology,
Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measurement Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES
 Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measureent Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES Belinda Lipa Codar Ocean Sensors 15 La Sandra Way, Portola Valley, CA 98 blipa@pogo.co
Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measureent Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES Belinda Lipa Codar Ocean Sensors 15 La Sandra Way, Portola Valley, CA 98 blipa@pogo.co
Electromagnetic scattering. Graduate Course Electrical Engineering (Communications) 1 st Semester, Sharif University of Technology
 Electroagnetic scattering Graduate Course Electrical Engineering (Counications) 1 st Seester, 1388-1389 Sharif University of Technology Contents of lecture 5 Contents of lecture 5: Scattering fro a conductive
Electroagnetic scattering Graduate Course Electrical Engineering (Counications) 1 st Seester, 1388-1389 Sharif University of Technology Contents of lecture 5 Contents of lecture 5: Scattering fro a conductive
This is a repository copy of Analytical optimisation of electromagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance motor.
 This is a repository copy of Analytical optiisation of electroagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance otor. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/907/
This is a repository copy of Analytical optiisation of electroagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance otor. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/907/
REDUCTION OF FINITE ELEMENT MODELS BY PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION
 ISSN 139 14X INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND CONTROL, 008, Vol.37, No.3 REDUCTION OF FINITE ELEMENT MODELS BY PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION Riantas Barauskas, Vidantas Riavičius Departent of Syste Analysis, Kaunas
ISSN 139 14X INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND CONTROL, 008, Vol.37, No.3 REDUCTION OF FINITE ELEMENT MODELS BY PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION Riantas Barauskas, Vidantas Riavičius Departent of Syste Analysis, Kaunas
Measuring orbital angular momentum superpositions of light by mode transformation
 CHAPTER 7 Measuring orbital angular oentu superpositions of light by ode transforation In chapter 6 we reported on a ethod for easuring orbital angular oentu (OAM) states of light based on the transforation
CHAPTER 7 Measuring orbital angular oentu superpositions of light by ode transforation In chapter 6 we reported on a ethod for easuring orbital angular oentu (OAM) states of light based on the transforation
Simulation and Analysis of Electromagnetic Transient Characteristics of Controllable Reactor of Transformer Type
 Siulation and Analysis of Electroagnetic Transient Characteristics of Controllable eactor of Transforer Type TIAN MINGXING, ZHAO QIANU, YIN JIANNING, LIU YIBIN Autoation and Electrical Engineering Lanzhou
Siulation and Analysis of Electroagnetic Transient Characteristics of Controllable eactor of Transforer Type TIAN MINGXING, ZHAO QIANU, YIN JIANNING, LIU YIBIN Autoation and Electrical Engineering Lanzhou
Chapter 2 General Properties of Radiation Detectors
 Med Phys 4RA3, 4RB3/6R3 Radioisotopes and Radiation Methodology -1 Chapter General Properties of Radiation Detectors Ionizing radiation is ost coonly detected by the charge created when radiation interacts
Med Phys 4RA3, 4RB3/6R3 Radioisotopes and Radiation Methodology -1 Chapter General Properties of Radiation Detectors Ionizing radiation is ost coonly detected by the charge created when radiation interacts
Noise Shielding Using Acoustic Metamaterials
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 53 (2010) pp. 560 564 c Chinese Physical Society and IOP Publishing Ltd Vol. 53, No. 3, March 15, 2010 Noise Shielding Using Acoustic Metamaterials LIU Bin ( Ê) and
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 53 (2010) pp. 560 564 c Chinese Physical Society and IOP Publishing Ltd Vol. 53, No. 3, March 15, 2010 Noise Shielding Using Acoustic Metamaterials LIU Bin ( Ê) and
Time-frequency plane behavioural studies of harmonic and chirp functions with fractional Fourier transform (FRFT)
 Maejo International Journal of Science and Technology Full Paper ISSN 95-7873 Available online at www.ijst.ju.ac.th Tie-frequency plane behavioural studies of haronic and chirp functions with fractional
Maejo International Journal of Science and Technology Full Paper ISSN 95-7873 Available online at www.ijst.ju.ac.th Tie-frequency plane behavioural studies of haronic and chirp functions with fractional
Using a De-Convolution Window for Operating Modal Analysis
 Using a De-Convolution Window for Operating Modal Analysis Brian Schwarz Vibrant Technology, Inc. Scotts Valley, CA Mark Richardson Vibrant Technology, Inc. Scotts Valley, CA Abstract Operating Modal Analysis
Using a De-Convolution Window for Operating Modal Analysis Brian Schwarz Vibrant Technology, Inc. Scotts Valley, CA Mark Richardson Vibrant Technology, Inc. Scotts Valley, CA Abstract Operating Modal Analysis
Figure 1: Equivalent electric (RC) circuit of a neurons membrane
 Exercise: Leaky integrate and fire odel of neural spike generation This exercise investigates a siplified odel of how neurons spike in response to current inputs, one of the ost fundaental properties of
Exercise: Leaky integrate and fire odel of neural spike generation This exercise investigates a siplified odel of how neurons spike in response to current inputs, one of the ost fundaental properties of
Random Vibration Fatigue Analysis with LS-DYNA
 1 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Siulation() Rando Vibration Fatigue Analysis with LS-DYNA Arnaud Ringeval 1, Yun Huang 1 CIMES, France 36 rue Marc Lefrancq, Les Ateliers Nuériques, 593 Valenciennes,
1 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Siulation() Rando Vibration Fatigue Analysis with LS-DYNA Arnaud Ringeval 1, Yun Huang 1 CIMES, France 36 rue Marc Lefrancq, Les Ateliers Nuériques, 593 Valenciennes,
EE5900 Spring Lecture 4 IC interconnect modeling methods Zhuo Feng
 EE59 Spring Parallel LSI AD Algoriths Lecture I interconnect odeling ethods Zhuo Feng. Z. Feng MTU EE59 So far we ve considered only tie doain analyses We ll soon see that it is soeties preferable to odel
EE59 Spring Parallel LSI AD Algoriths Lecture I interconnect odeling ethods Zhuo Feng. Z. Feng MTU EE59 So far we ve considered only tie doain analyses We ll soon see that it is soeties preferable to odel
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 97, , 2009
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 97, 407 416, 2009 PRACTICAL LIMITATIONS OF AN INVISIBILITY CLOAK B. L. Zhang Research Laboratory of Electronics Massachusetts Institute of Technology MA 02139,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 97, 407 416, 2009 PRACTICAL LIMITATIONS OF AN INVISIBILITY CLOAK B. L. Zhang Research Laboratory of Electronics Massachusetts Institute of Technology MA 02139,
Design and Experimental Research of Atomizer Based on Micro Abrasive Ultrasonic Polishing Bang-fu WANG, Yin ZHEN, Juan SONG and A-chun ZHU
 217 3rd International Conference on Applied Mechanics and Mechanical Autoation (AMMA 217) ISBN: 978-1-6595-479- Design and Experiental Research of Atoizer Based on Micro Abrasive Ultrasonic Polishing Bang-fu
217 3rd International Conference on Applied Mechanics and Mechanical Autoation (AMMA 217) ISBN: 978-1-6595-479- Design and Experiental Research of Atoizer Based on Micro Abrasive Ultrasonic Polishing Bang-fu
Analytical solution for the electric potential in arbitrary anisotropic layered media applying the set of Hankel transforms of integer order
 Geophysical Prospecting, 2006, 54, 651 661 Analytical solution for the electric potential in arbitrary anisotropic layered edia applying the set of Hankel transfors of integer order E. Pervago 1,A.Mousatov
Geophysical Prospecting, 2006, 54, 651 661 Analytical solution for the electric potential in arbitrary anisotropic layered edia applying the set of Hankel transfors of integer order E. Pervago 1,A.Mousatov
Efficient Filter Banks And Interpolators
 Efficient Filter Banks And Interpolators A. G. DEMPSTER AND N. P. MURPHY Departent of Electronic Systes University of Westinster 115 New Cavendish St, London W1M 8JS United Kingdo Abstract: - Graphical
Efficient Filter Banks And Interpolators A. G. DEMPSTER AND N. P. MURPHY Departent of Electronic Systes University of Westinster 115 New Cavendish St, London W1M 8JS United Kingdo Abstract: - Graphical
New Concept Conformal Antennas Utilizing Metamaterial and Transformation Optics
 New Concept Conformal Antennas Utilizing Metamaterial and Transformation Optics The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
New Concept Conformal Antennas Utilizing Metamaterial and Transformation Optics The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
P032 3D Seismic Diffraction Modeling in Multilayered Media in Terms of Surface Integrals
 P032 3D Seisic Diffraction Modeling in Multilayered Media in Ters of Surface Integrals A.M. Aizenberg (Institute of Geophysics SB RAS, M. Ayzenberg* (Norwegian University of Science & Technology, H.B.
P032 3D Seisic Diffraction Modeling in Multilayered Media in Ters of Surface Integrals A.M. Aizenberg (Institute of Geophysics SB RAS, M. Ayzenberg* (Norwegian University of Science & Technology, H.B.
A New Algorithm for Reactive Electric Power Measurement
 A. Abiyev, GAU J. Soc. & Appl. Sci., 2(4), 7-25, 27 A ew Algorith for Reactive Electric Power Measureent Adalet Abiyev Girne Aerican University, Departernt of Electrical Electronics Engineering, Mersin,
A. Abiyev, GAU J. Soc. & Appl. Sci., 2(4), 7-25, 27 A ew Algorith for Reactive Electric Power Measureent Adalet Abiyev Girne Aerican University, Departernt of Electrical Electronics Engineering, Mersin,
( ). One set of terms has a ω in
 Laptag Class Notes W. Gekelan Cold Plasa Dispersion relation Suer Let us go back to a single particle and see how it behaves in a high frequency electric field. We will use the force equation and Maxwell
Laptag Class Notes W. Gekelan Cold Plasa Dispersion relation Suer Let us go back to a single particle and see how it behaves in a high frequency electric field. We will use the force equation and Maxwell
Homogenous Optic-Null Medium Performs as Optical Surface Transformation
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 151, 169 173, 2015 Homogenous Optic-Null Medium Performs as Optical Surface Transformation Fei Sun 1 and Sailing He1, 2, * Abstract An optical surface transformation
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 151, 169 173, 2015 Homogenous Optic-Null Medium Performs as Optical Surface Transformation Fei Sun 1 and Sailing He1, 2, * Abstract An optical surface transformation
Terahertz Fabry-Perot interferometer constructed by metallic meshes with micrometer period and high ratio of linewidth/period
 Terahertz Fabry-Perot interferoeter constructed by etallic eshes with icroeter period and high ratio of linewidth/period Lu Zhengang 1,, Tan Jiubin, Fan Zhigang 1 1 Postdoctoral Research Station of Optical
Terahertz Fabry-Perot interferoeter constructed by etallic eshes with icroeter period and high ratio of linewidth/period Lu Zhengang 1,, Tan Jiubin, Fan Zhigang 1 1 Postdoctoral Research Station of Optical
From Active Metamaterials to Transformation Electromagnetics: AMULET from the academic's perspective
 From Active Metamaterials to Transformation Electromagnetics: AMULET from the academic's perspective Khalid Z. Rajab and Yang Hao School of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science, Queen Mary University
From Active Metamaterials to Transformation Electromagnetics: AMULET from the academic's perspective Khalid Z. Rajab and Yang Hao School of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science, Queen Mary University
Enhancing and suppressing radiation with some permeability-near-zero structures
 Enhancing and suppressing radiation with some permeability-near-zero structures Yi Jin 1,2 and Sailing He 1,2,3,* 1 Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical
Enhancing and suppressing radiation with some permeability-near-zero structures Yi Jin 1,2 and Sailing He 1,2,3,* 1 Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical
A Finite Element Propagation Model For Extracting Normal Incidence Impedance In Nonprogressive Acoustic Wave Fields
 NASA Technical Meorandu 110160 A Finite Eleent Propagation Model For Extracting Noral Incidence Ipedance In Nonprogressive Acoustic Wave Fields Willie R. Watson Langley Research Center, Hapton, Virginia
NASA Technical Meorandu 110160 A Finite Eleent Propagation Model For Extracting Noral Incidence Ipedance In Nonprogressive Acoustic Wave Fields Willie R. Watson Langley Research Center, Hapton, Virginia
ID 1163 CURE MONITORING OF THERMOSETTING RESIN COMPOSITES BY LACOMTECH DIELECTROMETRY
 ID 63 CURE MONITORING OF THERMOSETTING RESIN COMPOSITES BY LACOMTECH DIELECTROMETRY Jae Wook Kwon and Dai Gil Lee Departent of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology,
ID 63 CURE MONITORING OF THERMOSETTING RESIN COMPOSITES BY LACOMTECH DIELECTROMETRY Jae Wook Kwon and Dai Gil Lee Departent of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology,
Scattering by a Blade on a Metallic Plane
 UEMG #121474 Scattering by a Blade on a Metallic Plane DANILO ERRICOLO PIERGIORGIO L. E. USLENGHI BADRIA ELNOUR FRANCESCA MIOC QUERY SHEET QY: Au: Please check all artwork throughout article for correctness.
UEMG #121474 Scattering by a Blade on a Metallic Plane DANILO ERRICOLO PIERGIORGIO L. E. USLENGHI BADRIA ELNOUR FRANCESCA MIOC QUERY SHEET QY: Au: Please check all artwork throughout article for correctness.
Using EM To Estimate A Probablity Density With A Mixture Of Gaussians
 Using EM To Estiate A Probablity Density With A Mixture Of Gaussians Aaron A. D Souza adsouza@usc.edu Introduction The proble we are trying to address in this note is siple. Given a set of data points
Using EM To Estiate A Probablity Density With A Mixture Of Gaussians Aaron A. D Souza adsouza@usc.edu Introduction The proble we are trying to address in this note is siple. Given a set of data points
An Approximate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity Increase in the Intermediate Ballistics Period
 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity... 77 Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 205, 2(), 77-88 ISSN 2353-843 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction
An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity... 77 Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 205, 2(), 77-88 ISSN 2353-843 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction
Chapter 6 1-D Continuous Groups
 Chapter 6 1-D Continuous Groups Continuous groups consist of group eleents labelled by one or ore continuous variables, say a 1, a 2,, a r, where each variable has a well- defined range. This chapter explores:
Chapter 6 1-D Continuous Groups Continuous groups consist of group eleents labelled by one or ore continuous variables, say a 1, a 2,, a r, where each variable has a well- defined range. This chapter explores:
Research on Capacitance Current Compensation Scheme of Current Differential Protection of Complex Four-Circuit Transmission Lines on the Same Tower
 energies Article Research on apacitance urrent opensation Schee of urrent Differential Protection of oplex Four-ircuit Transission Lines on the Sae Tower ui Tang 1,2, * ID, Xianggen Yin 1,2 and Zhe Zhang
energies Article Research on apacitance urrent opensation Schee of urrent Differential Protection of oplex Four-ircuit Transission Lines on the Sae Tower ui Tang 1,2, * ID, Xianggen Yin 1,2 and Zhe Zhang
Supporting Online Material
 Supporting Online Material (A) Description of the suppleentary ovies Movie : Two-directional alignent of cells using 4-point electrodes. 0.08 % w/v yeast (S. cerevisiae) cells were assebled into D arrays
Supporting Online Material (A) Description of the suppleentary ovies Movie : Two-directional alignent of cells using 4-point electrodes. 0.08 % w/v yeast (S. cerevisiae) cells were assebled into D arrays
Structural-configurated magnetic plasmon bands in connected ring chains
 Structural-configurated agnetic plason bands in connected ring chains T. Li 1 *, R. X. Ye 1, C. Li 1, H. Liu 1, S. M. Wang 1, J. X. Cao 1, S. N. Zhu 1 *, and X. Zhang 2 1 National Laboratory of Solid State
Structural-configurated agnetic plason bands in connected ring chains T. Li 1 *, R. X. Ye 1, C. Li 1, H. Liu 1, S. M. Wang 1, J. X. Cao 1, S. N. Zhu 1 *, and X. Zhang 2 1 National Laboratory of Solid State
General Properties of Radiation Detectors Supplements
 Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent Yarouk University Chapter 4: General Properties of Radiation Detectors Suppleents Dr. Nidal M. Ershaidat Overview Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent
Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent Yarouk University Chapter 4: General Properties of Radiation Detectors Suppleents Dr. Nidal M. Ershaidat Overview Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent
Plasmonic metamaterial cloaking at optical frequencies
 Plasmonic metamaterial cloaking at optical frequencies F. Bilotti *, S. Tricarico, and L. Vegni Department of Applied Electronics, University Roma Tre Via della Vasca Navale 84, Rome 146, ITALY * Corresponding
Plasmonic metamaterial cloaking at optical frequencies F. Bilotti *, S. Tricarico, and L. Vegni Department of Applied Electronics, University Roma Tre Via della Vasca Navale 84, Rome 146, ITALY * Corresponding
RECIPROCAL INVISIBLE CLOAK WITH HOMOGE- NEOUS METAMATERIALS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 21, 15 115, 211 RECIPROCAL INVISIBLE CLOAK WITH HOMOGE- NEOUS METAMATERIALS J. J. Yang, M. Huang *, Y. L. Li, T. H. Li, and J. Sun School of Information Science
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 21, 15 115, 211 RECIPROCAL INVISIBLE CLOAK WITH HOMOGE- NEOUS METAMATERIALS J. J. Yang, M. Huang *, Y. L. Li, T. H. Li, and J. Sun School of Information Science
CHAPTER 4 TWO STANDARD SHORTCUTS USED TO TRANSFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC EQUATIONS 4.1 THE FREE-PARAMETER METHOD
 CHAPTER 4 TWO STANDARD SHORTCUTS USED TO TRANSFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC EQUATIONS The last several chapters have explained how the standard rules for changing units apply to electroagnetic physical quantities.
CHAPTER 4 TWO STANDARD SHORTCUTS USED TO TRANSFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC EQUATIONS The last several chapters have explained how the standard rules for changing units apply to electroagnetic physical quantities.
Polygonal Designs: Existence and Construction
 Polygonal Designs: Existence and Construction John Hegean Departent of Matheatics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 9405 Jeff Langford Departent of Matheatics, Drake University, Des Moines, IA 5011 G
Polygonal Designs: Existence and Construction John Hegean Departent of Matheatics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 9405 Jeff Langford Departent of Matheatics, Drake University, Des Moines, IA 5011 G
13.2 Fully Polynomial Randomized Approximation Scheme for Permanent of Random 0-1 Matrices
 CS71 Randoness & Coputation Spring 018 Instructor: Alistair Sinclair Lecture 13: February 7 Disclaier: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny accorded to foral publications. They ay
CS71 Randoness & Coputation Spring 018 Instructor: Alistair Sinclair Lecture 13: February 7 Disclaier: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny accorded to foral publications. They ay
ULTRASONIC WELDING OF COMPOSITE MATERAILS. ULTRASONIC BOOSTER DESIGN AND FEM SIMULATION
 ULTRASONIC WELDING OF COMPOSITE MATERAILS. ULTRASONIC BOOSTER DESIGN AND FEM SIMULATION Gh. AMZA, Zoia Apostolescu, Dan NITOI University Politehnica fro Bucharest, aza@aza.cais.pub.ro Keywords: ultrasonic,
ULTRASONIC WELDING OF COMPOSITE MATERAILS. ULTRASONIC BOOSTER DESIGN AND FEM SIMULATION Gh. AMZA, Zoia Apostolescu, Dan NITOI University Politehnica fro Bucharest, aza@aza.cais.pub.ro Keywords: ultrasonic,
Research and Experiments on Electromagnetic Field Induced by Two. Coaxial Solenoid Coils of Axially Mag-lev Driving Needle
 3rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Inforation Technology (ICMIT 16) Research and Experients on Electroagnetic Field Induced by Two Coaxial Solenoid Coils of Axially Mag-lev Driving Needle
3rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Inforation Technology (ICMIT 16) Research and Experients on Electroagnetic Field Induced by Two Coaxial Solenoid Coils of Axially Mag-lev Driving Needle
Intelligent Systems: Reasoning and Recognition. Perceptrons and Support Vector Machines
 Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley osig 1 Winter Seester 2018 Lesson 6 27 February 2018 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector achines Notation...2 Linear odels...3 Lines, Planes
Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley osig 1 Winter Seester 2018 Lesson 6 27 February 2018 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector achines Notation...2 Linear odels...3 Lines, Planes
ANALYSIS OF REFLECTOR AND HORN ANTENNAS USING MULTILEVEL FAST MULTIPOLE ALGORITHM
 European Congress on Coputational Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering ECCOMAS 2 Barcelona, 11-14 Septeber 2 ECCOMAS ANALYSIS OF REFLECTOR AND HORN ANTENNAS USING MULTILEVEL FAST MULTIPOLE ALGORITHM
European Congress on Coputational Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering ECCOMAS 2 Barcelona, 11-14 Septeber 2 ECCOMAS ANALYSIS OF REFLECTOR AND HORN ANTENNAS USING MULTILEVEL FAST MULTIPOLE ALGORITHM
Physics 139B Solutions to Homework Set 3 Fall 2009
 Physics 139B Solutions to Hoework Set 3 Fall 009 1. Consider a particle of ass attached to a rigid assless rod of fixed length R whose other end is fixed at the origin. The rod is free to rotate about
Physics 139B Solutions to Hoework Set 3 Fall 009 1. Consider a particle of ass attached to a rigid assless rod of fixed length R whose other end is fixed at the origin. The rod is free to rotate about
Extension of CSRSM for the Parametric Study of the Face Stability of Pressurized Tunnels
 Extension of CSRSM for the Paraetric Study of the Face Stability of Pressurized Tunnels Guilhe Mollon 1, Daniel Dias 2, and Abdul-Haid Soubra 3, M.ASCE 1 LGCIE, INSA Lyon, Université de Lyon, Doaine scientifique
Extension of CSRSM for the Paraetric Study of the Face Stability of Pressurized Tunnels Guilhe Mollon 1, Daniel Dias 2, and Abdul-Haid Soubra 3, M.ASCE 1 LGCIE, INSA Lyon, Université de Lyon, Doaine scientifique
arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 19 Jun 2008
![arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 19 Jun 2008 arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 19 Jun 2008](/thumbs/92/110994891.jpg) arxiv:0806.3231v1 [physics.optics] 19 Jun 2008 Necessary and sufficient conditions for reflectionless transformation media in an isotropic and homogenous background Wei Yan, Min Yan, Min Qiu Laboratory
arxiv:0806.3231v1 [physics.optics] 19 Jun 2008 Necessary and sufficient conditions for reflectionless transformation media in an isotropic and homogenous background Wei Yan, Min Yan, Min Qiu Laboratory
Physics Letters A 376 (2012) Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Physics Letters A.
 Physics Letters A 376 (01) 181 1817 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Physics Letters A www.elsevier.co/locate/pla The interaction between quantu dots and coupled agnetic plason in coupled
Physics Letters A 376 (01) 181 1817 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Physics Letters A www.elsevier.co/locate/pla The interaction between quantu dots and coupled agnetic plason in coupled
e-companion ONLY AVAILABLE IN ELECTRONIC FORM
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH doi 10.1287/opre.1070.0427ec pp. ec1 ec5 e-copanion ONLY AVAILABLE IN ELECTRONIC FORM infors 07 INFORMS Electronic Copanion A Learning Approach for Interactive Marketing to a Custoer
OPERATIONS RESEARCH doi 10.1287/opre.1070.0427ec pp. ec1 ec5 e-copanion ONLY AVAILABLE IN ELECTRONIC FORM infors 07 INFORMS Electronic Copanion A Learning Approach for Interactive Marketing to a Custoer
Dispersion. February 12, 2014
 Dispersion February 1, 014 In aterials, the dielectric constant and pereability are actually frequency dependent. This does not affect our results for single frequency odes, but when we have a superposition
Dispersion February 1, 014 In aterials, the dielectric constant and pereability are actually frequency dependent. This does not affect our results for single frequency odes, but when we have a superposition
Research Article Design of a Minimized Complementary Illusion Cloak with Arbitrary Position
 Antennas and Propagation Volume 25, Article ID 932495, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/25/932495 Research Article Design of a Minimized Complementary Illusion Cloak with Arbitrary Position Yan Shi, Lin Zhang,
Antennas and Propagation Volume 25, Article ID 932495, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/25/932495 Research Article Design of a Minimized Complementary Illusion Cloak with Arbitrary Position Yan Shi, Lin Zhang,
72. (30.2) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires.
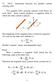 7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
A DESIGN GUIDE OF DOUBLE-LAYER CELLULAR CLADDINGS FOR BLAST ALLEVIATION
 International Journal of Aerospace and Lightweight Structures Vol. 3, No. 1 (2013) 109 133 c Research Publishing Services DOI: 10.3850/S201042862013000550 A DESIGN GUIDE OF DOUBLE-LAYER CELLULAR CLADDINGS
International Journal of Aerospace and Lightweight Structures Vol. 3, No. 1 (2013) 109 133 c Research Publishing Services DOI: 10.3850/S201042862013000550 A DESIGN GUIDE OF DOUBLE-LAYER CELLULAR CLADDINGS
Supplementary Information for Design of Bending Multi-Layer Electroactive Polymer Actuators
 Suppleentary Inforation for Design of Bending Multi-Layer Electroactive Polyer Actuators Bavani Balakrisnan, Alek Nacev, and Elisabeth Sela University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 074 1 Analytical
Suppleentary Inforation for Design of Bending Multi-Layer Electroactive Polyer Actuators Bavani Balakrisnan, Alek Nacev, and Elisabeth Sela University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 074 1 Analytical
Optical Forces Induced by Metal Nanoparticle Clusters
 Optical Forces Induced by Metal Nanoparticle Clusters Jordi Sancho-Parraon 1,2*, Salvador Bosch 2 1 Rudjer Boskovic Institute, Zagreb, Croatia 2 Applied Physics and Optics Departent, University of Barcelona,
Optical Forces Induced by Metal Nanoparticle Clusters Jordi Sancho-Parraon 1,2*, Salvador Bosch 2 1 Rudjer Boskovic Institute, Zagreb, Croatia 2 Applied Physics and Optics Departent, University of Barcelona,
WIRELESS DRIVE OF PIEZOELECTRIC COMPONENTS SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN 2011
 WIRELESS DRIVE OF PIEZOELECTRIC COMPONENTS SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN 011 WIRELESS DRIVE OF PIEZOELECTRIC COMPONENTS SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING 011 SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN WIRELESS
WIRELESS DRIVE OF PIEZOELECTRIC COMPONENTS SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN 011 WIRELESS DRIVE OF PIEZOELECTRIC COMPONENTS SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING 011 SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN WIRELESS
On Constant Power Water-filling
 On Constant Power Water-filling Wei Yu and John M. Cioffi Electrical Engineering Departent Stanford University, Stanford, CA94305, U.S.A. eails: {weiyu,cioffi}@stanford.edu Abstract This paper derives
On Constant Power Water-filling Wei Yu and John M. Cioffi Electrical Engineering Departent Stanford University, Stanford, CA94305, U.S.A. eails: {weiyu,cioffi}@stanford.edu Abstract This paper derives
Finite Element Analysis of Antennas and Phased Arrays in the Time Domain
 Finite Eleent Analysis of Antennas and Phased Arrays in the Tie Doain Jian-Ming Jin Center for Coputational Electroagnetics and Electroagnetics Laboratory Departent of Electrical and Coputer Engineering
Finite Eleent Analysis of Antennas and Phased Arrays in the Tie Doain Jian-Ming Jin Center for Coputational Electroagnetics and Electroagnetics Laboratory Departent of Electrical and Coputer Engineering
Statistical Logic Cell Delay Analysis Using a Current-based Model
 Statistical Logic Cell Delay Analysis Using a Current-based Model Hanif Fatei Shahin Nazarian Massoud Pedra Dept. of EE-Systes, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA 90089 {fatei, shahin,
Statistical Logic Cell Delay Analysis Using a Current-based Model Hanif Fatei Shahin Nazarian Massoud Pedra Dept. of EE-Systes, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA 90089 {fatei, shahin,
Reading from Young & Freedman: For this topic, read the introduction to chapter 25 and sections 25.1 to 25.3 & 25.6.
 PHY10 Electricity Topic 6 (Lectures 9 & 10) Electric Current and Resistance n this topic, we will cover: 1) Current in a conductor ) Resistivity 3) Resistance 4) Oh s Law 5) The Drude Model of conduction
PHY10 Electricity Topic 6 (Lectures 9 & 10) Electric Current and Resistance n this topic, we will cover: 1) Current in a conductor ) Resistivity 3) Resistance 4) Oh s Law 5) The Drude Model of conduction
Hysteresis model for magnetic materials using the Jiles-Atherton model
 Hysteresis odel for agnetic aterials using the Jiles-Atherton odel Predrag Petrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, pegi@ei.yu Nebojsa itrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, itar@tfc.tfc.kg.ac.yu
Hysteresis odel for agnetic aterials using the Jiles-Atherton odel Predrag Petrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, pegi@ei.yu Nebojsa itrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, itar@tfc.tfc.kg.ac.yu
ANALYSIS ON RESPONSE OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS TO PULSE SEQUENCES EXCITATION
 The 4 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering October -7, 8, Beijing, China ANALYSIS ON RESPONSE OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS TO PULSE SEQUENCES EXCITATION S. Li C.H. Zhai L.L. Xie Ph. D. Student, School of
The 4 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering October -7, 8, Beijing, China ANALYSIS ON RESPONSE OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS TO PULSE SEQUENCES EXCITATION S. Li C.H. Zhai L.L. Xie Ph. D. Student, School of
