On the Radiation from a Short Current-Carrying Straight Wire Oriented Perpendicular to a Stratified Medium
|
|
|
- Winifred King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Progress In Electroagnetics Research, Vol. 159, 49 57, 17 On the Radiation fro a Short Current-Carrying Straight Wire Oriented Perpendicular to a Stratified Mediu Mauro Parise 1, * and Giulio Antonini Abstract In a previous work, iproved full-wave analytical expressions have been derived for the Soerfeld Integrals (SIs) describing electroagnetic radiation fro a short vertical straight wire located in close proxiity to a conductive soil. Such forulas ensure high accuracy of the result of the coputation, as well as tie savings respect to conventional techniques used to evaluate the SIs, but unfortunately ay be used only when both source and field points are located at the air-ediu interface. The scope of this paper is to overcoe the liitations iplied by the previous approach, and provide series-for expressions for the generated field coponents that are valid for an arbitrarily stratified ediu and for any position of the vertical wire antenna and observation point in the air space above it. The expressions follow fro the analytical evaluation of the integral representation for the agnetic vector potential, perfored through contour integration after substituting an equivalent pole set for each branch cut of the integrand. Validity, efficiency and accuracy of the developed forulas are illustrated through nuerical exaples. 1. INTRODUCTION The study of the radiation characteristics of dipole antennas situated in proxiity to stratified edia has attracted the interest of several scientists in the past years 1 ]. This is because electric dipoles are extensively used in a variety of engineering applications, especially in the areas of close-to-thesurface radio counication, geophysical prospecting, radio reote sensing, and hypetheria 7, 11 15,, 3]. Despite the nuber of contributions fro researchers, to date accurate analytical expressions for the fields, valid regardless of the operating frequency, can be derived only under the assuption that both the source and the observation points lie on the surface of the aterial ediu 1, 3]. If this condition cannot be et, closed-for expressions for the fields ay still be obtained, but at the price of introducing approxiations that liit their applicability to electrically dense edia 4 7, 11] or specified frequency ranges 4 6, 17 ]. Exaples of contributions in this direction are the solutions valid for the quasi-static, inderediate, and far-field frequency ranges, which result fro reducing the Soerfeld integrals to fors aenable to asyptotic techniques such as the saddle-point ethod 13, 17 ]. The present paper focuses on the proble of a short current-carrying straight wire oriented perpendicular to a stratified ground. The scope of the work is to overcoe the liitations iplied by the approach described in 1, 3], and deterine exact analytical expressions for the generated fields that are valid for any position of the source and observation points in the air space above the ediu. To accoplish this task, first the direct field and the ideal reflected field are extracted fro the integral representation for the agnetic vector potential. Next, the reaining part of the agnetic vector potential is written as the su of branch-cut integrals and closed-contour integrals around the poles of the integrand. Finally, the hyperbolic branch cuts are extracted fro the integrands of the Received 9 April 17, Accepted June 17, Scheduled 3 June 17 * Corresponding author: Mauro Parise (.parise@unicapus.it). 1 Unit of Electrical Engineering, University Capus Bio-Medico of Roe, Italy. Departent of Industrial Engineering, Coputer Science and Econoics, University of L Aquila, Italy.
2 5 Parise and Antonini branch-cut integrals and replaced equivalent pole sets 3], so as to ake it possible analytical integration. Each field coponent is given as the su of two exponential ters (describing the direct and the ideal reflected fields) and three fast convergent sequences of residue sus, that represent the above surface ground wave, the lateral wave and the surface waves. The obtained forulas for the fields offer advantages in ters of tie savings respect to standard nuerical integration procedures. Moreover, investigating the expressions for the different contributions to the fields, as well as their outcoes, allows to gain useful insight into the physics of the proble, and this feature akes the proposed solution advantageous over nuerical siulation tools eployed to solve electroagnetic boundary value probles.. FORMULATION OF THE PROBLEM The geoetrical configuration under study is sketched in Fig. 1. The eitter, odeled as a vertical electric dipole of oent 1 e jωt A, is located at height h above an N-layer conducting ediu. The nth layer of the ediu has dielectric perittivity ɛ n, electrical conductivity σ n,andthickness d n =z n z n 1,beingz n the position of the upper bound of the layer. The botto or first layer is assued to be a sei-infinite region. The agnetic pereability is everywhere equal to that of free space μ. We introduce a cylindrical coordinate syste (ρ, ϕ, z) such that the air-ediu interface coincides the plane z= and the short wire antenna is placed on the z axis. The syetry about the z axis iplies that the electroagnetic field originates fro a z-directed agnetic vector potential 17]. As a consequence, the field coponents produced in the air space ay be expressed as E ρ = jω A k ρ z, (1) E z = jω ( k ρ + 1 ) A, () ρ ρ H ϕ = 1 A μ ρ, (3) z ρ P z-h μ, ε h z N z N-1 z N- μ, ε N, σ N μ, ε N-1, σ N-1 x ϕ ρ y z z 1 μ, ε, σ μ, ε 1, σ 1 Figure 1. Sketch of a short straight wire oriented perpendicular to a stratified ediu.
3 Progress In Electroagnetics Research, Vol. 159, where A is the non-null coponent of the vector potential, given by ] A (ρ, z, h) = μ e jk R 4π R e jkr R + A s (ρ, z, h), (4) being A s (ρ, z, h) = μ e u (z+h) Z λ H (1) 4π Z + ẐN (λρ)dλ (5) u and R = ρ +(z h), R = ρ +(z + h), (6) u n = λ kn, Reu n ]>, (7) kn = ω μ n ɛ n jωμ n σ n. (8) In Eq. (4), the two exponential ters represent the priary field and the ideal field reflected by the ediu (that is the field of a negative iage), while A s is a correction ter caused by the iperfect conductivity of the layered half-space. On the other hand, Z n is the intrinsic ipedance of the nth layer (n= denotes free space), given by u n Z n =, (9) σ n + jωɛ n while Ẑn is the surface ipedance at z=z n, defined by the recursive forula Ẑ n 1 + Z n tanh(u n d n ) Ẑ n =Z n Z n + Ẑn 1tanh(u, n=,...,n, (1) n d n ) Ẑ 1 =Z 1. (11) The ai of this paper is to analytically evaluate Eq. (5) and, subsequently, the field coponents in Eqs. (1) (3). To this end, it is first convenient to rewrite Eq. (5) as A s (ρ, z, h) = μ 4π G (u,u 1,λ,z,h) H (1) (λρ)λdλ, (1) G (u,u 1,λ,z,h)= e u (z+h) Z, (13) u Z + ẐN where the dependence on the square roots u,u 3,...,u N has not been ade explicit to signify that the function G is even in such quantities 17]. Next, proceeding as in 17, 4] akes it possible to defor the integration contour so that it is wrapped around the singularities of the integrand located in the upper-half of the coplex plane, as shown in Fig. (a). This leads to express A s as A s (ρ, z, h)=...]+...]+...]=i ( 1) + I () + I (1), (14) λ ( 1) k k 1 that is as the su of two branch-cut integrals associated k and k 1 plus a nuber of closedcontour integrals around the poles of G, thatisλ ( 1) 1,λ ( 1),λ ( 1) 3,... Notice that the integral along the upper infinite sei-circle has been neglected in Eq. (14). In fact, this contribution cannot but be identically zero, because the Hankel function in the integrand decays exponentially increasing λ in the upper half-plane. The explicit for of I ( 1) ay be easily obtained through residue calculus. It yields I ( 1) = jμ ] A ( 1) (z,h) H (1) λ ( 1) ρ, (15)
4 5 Parise and Antonini λ- plane λ ( 1) I λ Integration path I λ k 1 λ ( 1) 1 generated poles ( n ) λ 1 ( n ) λ ( n ) λ arc of upper sei-circle k (a) o Re λ suppressed branch line (b) Figure. (a) Defored integration contour and (b) branch cut equivalent pole set. where A ( 1) is the residue of the function λg at λ=λ ( 1) A ( 1) (z,h)=r ( 1) λ λ G(u,u 1,λ,z,h)] = li λ λ ( 1),thatis λ λ ( 1) ] λg(u,u 1,λ,z,h). (16) On the other hand, each of the integrals I () and I (1) ay be evaluated by extracting the relevant branch cut fro the integrand and replacing it an equivalent set of poles. Branch-cut extraction procedure consists of decoposing G into its even and odd parts respect to u or u 1. For instance, I () requires a decoposition of G respect to u, as follows G (u,u 1,λ,z,h)=G () e (λ, z, h)+g () o (λ, z, h) u, (17) where G () e and G () o are even function of u,givenby G () e (λ, z, h) = 1 G (u,u 1,λ,z,h)+G( u,u 1,λ,z,h)], (18) G () o (λ, z, h) = 1 G (u,u 1,λ,z,h) G ( u,u 1,λ,z,h)]. (19) u Since G () e does not exhibit any branch cut running fro k, it will not contribute to I (). As a consequence, it yields I () = μ G () o (λ, z, h) u H (1) (λρ)λdλ, () 4π k and, analogously, for I 1 one obtains I (1) = μ G (1) o (λ, z, h) u 1 H (1) (λρ)λdλ, (1) 4π k 1 G (1) o (λ, z, h)= 1 G (u,u 1,λ,z,h) G (u, u 1,λ,z,h)]. () u 1 Pole sets equivalent to the extracted branch cuts ay be deterined by iteratively applying the square root algorith to the coputation of the square roots u and u 1, as described in 1, 3, 4]. At the lth iteration, the square root algorith generates the following partial-fraction representation for u n 3] ( ) ] l 1 u n = l u n + M l h r n λ λ +, (3) h= =1
5 Progress In Electroagnetics Research, Vol. 159, being M l = l 1 1, and = kn t, (4) r n = 1 M l +1 ( ) l t ] h M l l+1 t h h t ] 1, (5) h= ( π ) t =tan l. (6) Substituting Eq. (3) in the nth branch-cut integral I (n) and closing the integration contour the arc of upper infinite sei-circle coprised between its ends, as sketched in Fig. (b), allows to obtain a closed-contour integral around the s. In fact, such poles lie on the suppressed branch line. Since the residue of Eq. (3) at λ= is equal to one obtains and, after letting A (n) in copact for as I (n) = jμ li λ =1 (z,h)=r n G (n) o λ h=1 h ] u n = r n, n =, 1, (7) r n G (n) o (λ, z, h) H (1) ]λ=λ (λρ), n =, 1, (8) (n) A s (ρ, z, h)= jμ ],z,h,n=, 1, expression (14) for A s ay be rewritten 1 n= 1 =1 A (n) (z,h) H(1) ] ρ, (9) where the first M l poles of the pole set corresponding to n= 1 have been considered. It is understood that the nubering of the λ ( 1) s is arranged so that I λ ( 1) 1 < I λ ( 1) < I λ ( 1) 3 <...and so on, which eans that higher-order poles correspond to highly attenuated waves. Finally, use of Eqs. (4) and (9) in Eqs. (1) (3) gives rise to the following expressions for the fields E ρ = E ρ ζ=z h E ρ ζ=z+h + Eρ s, (3) E z = E z ζ=z h E z ζ=z+h + Ez s, (31) H ϕ = H ϕ ζ=z h H ϕ ζ=z+h + Hϕ, s (3) being E ρ = ρζe jk r ( 3+3jk 4πjωɛ r 5 r k r), (33) r= ρ +ζ,and E z = e jk r 4πjωɛ r 5 ( ζ ρ ) (1 + jk r)+ρ k r], (34) H ϕ = ρe jk r 4πr 3 (1 + jk r), (35) E s ρ = 1 ωɛ E s z = 1 ωɛ H s ϕ = j 1 1 n= 1 =1 1 n= 1 =1 n= 1 =1 A(n) H(1) 1 da (n) ] dz H(1) 1 ρ, (36) ] ] A (n) H(1) ρ, (37) ρ ], (38)
6 54 Parise and Antonini R ( 1) λ u λg(u,u 1,λ,z)], n = 1 da (n) ] dz = r n G () e λ (),z, n = ] r n u G (1) o λ (1),z, n =1 (39) where account has been taken of the identities 1] ( ρ + 1 ρ ρ dh (1) (λρ) dρ = λh (1) 1 (λρ), (4) ) H (1) (λρ) = λ H (1) (λρ). (41) Each of the expressions (36) (38) consists of three sequences of residue sus, which converge as l is increased in virtue of convergence of the square root algorith. The residue sus associated n= and n=1 describe the above-surface ground and lateral waves, respectively. Such contributions, together the direct field and the ideal reflected field, labelled a subscript in Eqs. (3) (3), constitute the space wave radiated by the antenna. The rest of the generated field consists of surface waves, and is described by the residue sus associated n= 1 in Eqs. (36) (38). Expressions (3) (3) allow to overcoe the liitations iplied by the previously published square-root-algorith-based solution to the sae proble 1, 4]. In fact, they allow to relax the assuption that both source and observation points lie at the air-ediu interface. At the sae tie, as will be clarified in Sec. 3, the derived expressions ensure a high level of accuracy and offer advantages in ters of tie savings respect to standard nuerical techniques conventionally used for evaluating Soerfeld-type integrals. 3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Priary objective of this section is to show the convergence of the sequences in Eqs. (36) (38) as the nuber of iterations l of the square root algorith is increased. To this goal, we use Eq. (31) to copute the aplitude-frequency spectru of the E z -field generated by a unit-oent straight wire antenna lying on the top surface of a two-layer conductive ground. The field point is at height z=5 above the ediu and at radial distance ρ=3 fro the eitter, while the electroagnetic and geoetric paraeters of the layers of the ediu are assued to be σ 1 =1 S/, ɛ 1 =1ɛ, d 1 =4, σ =1 S/, and ɛ =5ɛ. The results of the siulations, depicted in Fig. 3, are copared the data arising fro nuerically evaluating Eq. () through the Gauss-Kronrod quadrature rule 5]. As is seen, when l is increased the outcoes fro Eq. (31) rapidly converge to the exact nuerical data, denoted by points, and convergence is faster at higher frequencies. Moreover, perfect agreeent between analytical and nuerical data is observed when truncating the sequences of residue sus in Eq. (37) at l=1, that is when each residue su is coposed of M 1 = 11 1=47 residues. It should be noted that, in general, the three contributions to Eq. (37) do not have the sae ipact on the E z -field strength. For instance, if the field point is located at height z=5 fro the top surface of the ediu, one would expect that the effects of surface and lateral waves, associated n= 1 and n=1, respectively, are negligible respect to that of the ground wave (n=). This point is clarified by Fig. 4, which depicts the agnitude of E z and those of the relevant ground-wave, lateral-wave, and surface-wave ters against the radial distance ρ fro the eitter. The paraeters of the ediu are taken to be the sae as in the previous exaple, and the operating frequency is assued to be 1 khz. Again, the sequences of the residue sus have been truncated at l=1. Fro the analysis of the plotted curves it eerges that the aplitude of the E z -field substantially coincides that of the ground-wave field over the considered interval, and that the surface waves suffer fro a ild attenuation increasing ρ. Instead, the agnitude of the lateral wave rapidly goes down below the plot scale as ρ grows up. Finally, it should be observed that direct and ideal reflected fields cannot contribute to the total E z -field, since they cancel out each other because of the position of the eitter at the air-ediu interface.
7 Progress In Electroagnetics Research, Vol. 159, E z (V/) Frequency (Hz) exact l=5 l=6 l=7 l=1 Figure 3. Profiles of E z against frequency. Outcoes fro the proposed solution are copared the data arising fro nuerical integration of the field integral. E z (V/) total gw lw sw Radial distance fro the source, ρ () Figure 4. Profile of E ρ against ρ. Separate contributions of ground wave (gw), lateral wave (lw), and surface waves (sw) to the total field. One would ask whether the derived solution is advantageous in ters of coputation tie over previous solutions and standard nuerical integration procedures. This aspect is illustrated in Table 1, which shows the tie taken by the proposed ethod, the Gauss-Kronrod quadrature rule, and King s well-established solution 7], to calculate the radial distribution of the vertical electric field that a straight wire antenna lying on a hoogeneous ediu produces at z=5. Here, the operating frequency is 1 MHz, while the electroagnetic paraeters of the ediu are taken to be σ 1 =.1 S/ and ɛ 1 =3 ɛ. Table 1 is structured as follows. The second colun contains tie cost data corresponding to Table 1. Coputation ties and accuracy of the proposed and conventional approaches. Approach Tie consuption (s) Speed-up RMS rel. error (%) Gaussian rule King s approach Proposed solution z () ρ () (a) z () ρ () (b) Figure 5. Contour plots of (a) E ρ and (b) E z versus ρ and z, coputed for σ 1 =.1 S/ and ɛ 1 =3 ɛ by applying the proposed approach (solid isolines). Outcoes fro King s approach are denoted by dashed isolines.
8 56 Parise and Antonini siulations running on a single-core 1.8 GHz PC. The third colun shows the ratio of the tie taken by the proposed expression for E z and the Gaussian rule to that required by King s solution (speed-up offered by King s approach). Finally, the fourth colun contains the root-ean-square (RMS) relative errors resulting fro using the proposed and King s solution in place of Gaussian quadrature rule. Fro a glance at the data in Table 1 it is deduced that, accuracy being equal, using Eq. (37) rather than Gaussian quadrature perits to obtain significant tie savings. On the other hand, King s approach iplies iniu tie cost, but the price to be paid for its usage is the loss of accuracy. This is also confired by the contour plots sketched in Fig. 5, which depict the agnitudes of E ρ (Fig. 5(a)) and E z (Fig. 5(b)) versus ρ and z (the antenna is still positioned at height h=). For both the contour plots, a significant discrepancy is observed between the solid isolines associated the proposed solution and the dashed isolines arising fro King s approach. The aount of the discrepancy depends on the conductivity of the ediu, and higher values of the conductivity ake it possible to reduce the discrepancy. For instance, assuing σ 1 =1 S/ and ɛ 1 =1 ɛ leads to the contour plots illustrated in Fig. 6, characterized by solid and dashed isolines alost overlapping. Bad accuracy of King s solution for low values of the conductivity is explained by the failure of the assuptions k 1 ρ 1 andk / k 1 1, underlying its derivation. z () ρ () (a) z () ρ () (b) Figure 6. Contour plots of (a) E ρ and (b) E z versus ρ and z, coputed for σ 1 =1 S/ and ɛ 1 =1 ɛ by applying the proposed approach (solid isolines). Outcoes fro King s approach are denoted by dashed isolines. 4. CONCLUSION This paper presents an explicit solution, in series for, for the fields fro a short current-carrying straight wire oriented perpendicular to a stratified ediu. The solution arises fro the analytical evaluation of the integral representation for the agnetic vector potential, carried out through contour integration upon substituting an equivalent pole set for each branch cut exhibited by the integrand. Each field coponent is expressed as the su of five contributions, naely the direct, the ideal reflected, the ground-wave, the lateral-wave, and the surface-wave fields. The latter three ters are given as convergent sequences of residue sus. Perfored nuerical siulations confir the correctness of the developed theory. It has been shown how the proposed forulas are accurate and significantly less tie consuing than conventional nuerical integration procedures. REFERENCES 1. Soerfeld, A., On the propagation of waves in wireless telegraphy, Annals of Physics, Vol. 81, , Baños, A., Dipole Radiation in the Presence of a Conducting Half-space, Pergaon Press, Oxford, NY, 1966.
9 Progress In Electroagnetics Research, Vol. 159, Durrani, S. H., Air to undersea counication electric dipoles, IRE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, Vol. 1, 54 58, Moore, R. K. and W. E. Blair, Dipole radiation in a conducting half space, Journal of Research of the National Bureau of Standards-D Radio Propagation, Vol. 65D, No. 6, , Wait, J. R., The electroagnetic fields of a horizontal dipole in the presence of a conducting half-space, Canadian Journal of Physics, Vol. 39, , Bannister, P. R., Quasi-static fields of dipole antennas at the earth s surface, Radio Science, Vol. 1, , King,R.W.P.,M.Owens,andT.T.Wu,Lateral Electroagnetic Waves: Theory and Applications to Counications, Geophysical Exploration, and Reote Sensing, Springer-Verlag, New York, King, R. W. P., S. S. Sandler, and L. C. Shen, The electroagnetic field of a vertical electric dipole over the earth or sea, IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, Vol. 4, , King, R. W. P., Electroagnetic field of a vertical dipole over an iperfectly conducting halfspace, Radio Science, Vol. 5, , Parise, M., An exact series representation for the EM field fro a vertical electric dipole on an iperfectly conducting half-space, Journal of Electroagnetic Waves and Applications, Vol. 8, No. 8, 93 94, Wait, J. R., Electroagnetic Waves in Stratified Media, Pergaon Press, New York, Parise, M., Second-order forulation for the quasi-static field fro a vertical electric dipole on a lossy half-space, Progress In Electroagnetics Research, Vol. 136, 59 51, Kong, J. A., Electroagnetic Wave Theory, John Wiley & Sons, New York, Ward, S. H. and G. W. Hohann, Electroagnetic theory for geophysical applications, Electroagnetic Methods in Applied Geophysics, Vol. 1, , Society of Exploration Geophysicists, Tulsa, OK, Balanis, C. A., Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design, nd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York, Wait, J. R., Radiation fro a vertical electric dipole over a stratified ground, Transactions of the IRE Antennas and Propagation, Vol. 1, No. 1, 9 11, Wait, J. R., Influence of a sub-surface insulating layer on electroagnetic ground wave propagation, IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, Vol. 14, No. 6, , Wait, J. R., Asyptotic theory for dipole radiation in the presence of a lossy slab lying on a conducting half-space, IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, Vol. 15, No. 5, , Kong, J. A., L. C. Shen, and L. Tsang, Field of an antenna suberged in a dissipative dielectric ediu, IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, Vol. 5, No. 6, , Fuller, J. A. and J. R. Wait, A pulsed dipole in the earth, Transient Electroagnetic Fields, 37 69, Springer, New York, Parise, M., An exact series representation for the EM field fro a circular loop antenna on a lossy half-space, IEEE Antennas and Wireless Prop. Letters, Vol. 13, 3 6, 14.. Parise, M., Exact EM field excited by a short horizontal wire antenna lying on a conducting soil, AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Counications, Vol. 7, , Parise, M., Iproved Babylonian square root algorith-based analytical expressions for the surface-to-surface solution to the Soerfeld half-space proble, IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, Vol. 63, No. 1, , Parise, M., On the surface fields of a sall circular loop antenna placed on plane stratified earth, International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, Vol. 15, 1 8, Patterson, T. N. L., The optiu addition of points to quadrature forulae, Matheatics of Coputation, Vol., , 1968.
Quasi-static Vertical Magnetic Field of a Large Horizontal Circular Loop Located at the Earth s Surface
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 9 34, 16 Quasi-static Vertical Magnetic Field of a Large Horizontal Circular Loop Located at the Earth s Surface Mauro Parise * Abstract In this work,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 9 34, 16 Quasi-static Vertical Magnetic Field of a Large Horizontal Circular Loop Located at the Earth s Surface Mauro Parise * Abstract In this work,
Singularity Extraction for Reflected Sommerfeld Integrals over Multilayered Media
 Telfor Journal, Vol. 6, No., 4. 7 Singularity Extraction for Reflected Soerfeld Integrals over Multilayered Media Vladiir V. Petrovic, Senior Meber, IEEE, Aleksandra J. Krneta, and Branko M. Kolundzija,
Telfor Journal, Vol. 6, No., 4. 7 Singularity Extraction for Reflected Soerfeld Integrals over Multilayered Media Vladiir V. Petrovic, Senior Meber, IEEE, Aleksandra J. Krneta, and Branko M. Kolundzija,
Electromagnetic scattering. Graduate Course Electrical Engineering (Communications) 1 st Semester, Sharif University of Technology
 Electroagnetic scattering Graduate Course Electrical Engineering (Counications) 1 st Seester, 1388-1389 Sharif University of Technology Contents of lecture 5 Contents of lecture 5: Scattering fro a conductive
Electroagnetic scattering Graduate Course Electrical Engineering (Counications) 1 st Seester, 1388-1389 Sharif University of Technology Contents of lecture 5 Contents of lecture 5: Scattering fro a conductive
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD OF A HORIZONTAL IN- FINITELY LONG MAGNETIC LINE SOURCE OVER THE EARTH COATED WITH A DIELECTRIC LAYER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 31, 55 64, 2012 ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD OF A HORIZONTAL IN- FINITELY LONG MAGNETIC LINE SOURCE OVER THE EARTH COATED WITH A DIELECTRIC LAYER Y.-J. Zhi
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 31, 55 64, 2012 ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD OF A HORIZONTAL IN- FINITELY LONG MAGNETIC LINE SOURCE OVER THE EARTH COATED WITH A DIELECTRIC LAYER Y.-J. Zhi
J. Electrical Systems x-x (xxx): x-xx. Regular paper. Reflected Signal on a Nonuniform Overhead Transmission Line at High Frequency
 A. Boudjeaa S. Tahi B. Bennaane T. B. Berbar B. Lehouidj J. Electrical Systes x-x (xxx): x-xx Regular paper Reflected Signal on a Nonunifor Overhead Transission Line at High Frequency The effect of the
A. Boudjeaa S. Tahi B. Bennaane T. B. Berbar B. Lehouidj J. Electrical Systes x-x (xxx): x-xx Regular paper Reflected Signal on a Nonunifor Overhead Transission Line at High Frequency The effect of the
lecture 36: Linear Multistep Mehods: Zero Stability
 95 lecture 36: Linear Multistep Mehods: Zero Stability 5.6 Linear ultistep ethods: zero stability Does consistency iply convergence for linear ultistep ethods? This is always the case for one-step ethods,
95 lecture 36: Linear Multistep Mehods: Zero Stability 5.6 Linear ultistep ethods: zero stability Does consistency iply convergence for linear ultistep ethods? This is always the case for one-step ethods,
Model Fitting. CURM Background Material, Fall 2014 Dr. Doreen De Leon
 Model Fitting CURM Background Material, Fall 014 Dr. Doreen De Leon 1 Introduction Given a set of data points, we often want to fit a selected odel or type to the data (e.g., we suspect an exponential
Model Fitting CURM Background Material, Fall 014 Dr. Doreen De Leon 1 Introduction Given a set of data points, we often want to fit a selected odel or type to the data (e.g., we suspect an exponential
Physics 139B Solutions to Homework Set 3 Fall 2009
 Physics 139B Solutions to Hoework Set 3 Fall 009 1. Consider a particle of ass attached to a rigid assless rod of fixed length R whose other end is fixed at the origin. The rod is free to rotate about
Physics 139B Solutions to Hoework Set 3 Fall 009 1. Consider a particle of ass attached to a rigid assless rod of fixed length R whose other end is fixed at the origin. The rod is free to rotate about
Dr. Naser Abu-Zaid; Lecture notes in electromagnetic theory 1; Referenced to Engineering electromagnetics by Hayt, 8 th edition 2012; Text Book
 Text Book Dr. Naser Abu-Zaid Page 1 9/4/2012 Course syllabus Electroagnetic 2 (63374) Seester Language Copulsory / Elective Prerequisites Course Contents Course Objectives Learning Outcoes and Copetences
Text Book Dr. Naser Abu-Zaid Page 1 9/4/2012 Course syllabus Electroagnetic 2 (63374) Seester Language Copulsory / Elective Prerequisites Course Contents Course Objectives Learning Outcoes and Copetences
Data-Driven Imaging in Anisotropic Media
 18 th World Conference on Non destructive Testing, 16- April 1, Durban, South Africa Data-Driven Iaging in Anisotropic Media Arno VOLKER 1 and Alan HUNTER 1 TNO Stieltjesweg 1, 6 AD, Delft, The Netherlands
18 th World Conference on Non destructive Testing, 16- April 1, Durban, South Africa Data-Driven Iaging in Anisotropic Media Arno VOLKER 1 and Alan HUNTER 1 TNO Stieltjesweg 1, 6 AD, Delft, The Netherlands
Figure 1: Equivalent electric (RC) circuit of a neurons membrane
 Exercise: Leaky integrate and fire odel of neural spike generation This exercise investigates a siplified odel of how neurons spike in response to current inputs, one of the ost fundaental properties of
Exercise: Leaky integrate and fire odel of neural spike generation This exercise investigates a siplified odel of how neurons spike in response to current inputs, one of the ost fundaental properties of
IN A SENSE, every material is a composite, even if the
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1999 2075 Magnetis fro Conductors and Enhanced Nonlinear Phenoena J. B. Pendry, A. J. Holden, D. J. Robbins, and W. J. Stewart,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1999 2075 Magnetis fro Conductors and Enhanced Nonlinear Phenoena J. B. Pendry, A. J. Holden, D. J. Robbins, and W. J. Stewart,
Chaotic Coupled Map Lattices
 Chaotic Coupled Map Lattices Author: Dustin Keys Advisors: Dr. Robert Indik, Dr. Kevin Lin 1 Introduction When a syste of chaotic aps is coupled in a way that allows the to share inforation about each
Chaotic Coupled Map Lattices Author: Dustin Keys Advisors: Dr. Robert Indik, Dr. Kevin Lin 1 Introduction When a syste of chaotic aps is coupled in a way that allows the to share inforation about each
Scattering by a Blade on a Metallic Plane
 UEMG #121474 Scattering by a Blade on a Metallic Plane DANILO ERRICOLO PIERGIORGIO L. E. USLENGHI BADRIA ELNOUR FRANCESCA MIOC QUERY SHEET QY: Au: Please check all artwork throughout article for correctness.
UEMG #121474 Scattering by a Blade on a Metallic Plane DANILO ERRICOLO PIERGIORGIO L. E. USLENGHI BADRIA ELNOUR FRANCESCA MIOC QUERY SHEET QY: Au: Please check all artwork throughout article for correctness.
P032 3D Seismic Diffraction Modeling in Multilayered Media in Terms of Surface Integrals
 P032 3D Seisic Diffraction Modeling in Multilayered Media in Ters of Surface Integrals A.M. Aizenberg (Institute of Geophysics SB RAS, M. Ayzenberg* (Norwegian University of Science & Technology, H.B.
P032 3D Seisic Diffraction Modeling in Multilayered Media in Ters of Surface Integrals A.M. Aizenberg (Institute of Geophysics SB RAS, M. Ayzenberg* (Norwegian University of Science & Technology, H.B.
Analytical solution for the electric potential in arbitrary anisotropic layered media applying the set of Hankel transforms of integer order
 Geophysical Prospecting, 2006, 54, 651 661 Analytical solution for the electric potential in arbitrary anisotropic layered edia applying the set of Hankel transfors of integer order E. Pervago 1,A.Mousatov
Geophysical Prospecting, 2006, 54, 651 661 Analytical solution for the electric potential in arbitrary anisotropic layered edia applying the set of Hankel transfors of integer order E. Pervago 1,A.Mousatov
SOLUTIONS. PROBLEM 1. The Hamiltonian of the particle in the gravitational field can be written as, x 0, + U(x), U(x) =
 SOLUTIONS PROBLEM 1. The Hailtonian of the particle in the gravitational field can be written as { Ĥ = ˆp2, x 0, + U(x), U(x) = (1) 2 gx, x > 0. The siplest estiate coes fro the uncertainty relation. If
SOLUTIONS PROBLEM 1. The Hailtonian of the particle in the gravitational field can be written as { Ĥ = ˆp2, x 0, + U(x), U(x) = (1) 2 gx, x > 0. The siplest estiate coes fro the uncertainty relation. If
DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS *
 IJST, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. M1, pp 89-100 Printed in The Islaic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shira University DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS
IJST, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. M1, pp 89-100 Printed in The Islaic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shira University DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS
13 Harmonic oscillator revisited: Dirac s approach and introduction to Second Quantization
 3 Haronic oscillator revisited: Dirac s approach and introduction to Second Quantization. Dirac cae up with a ore elegant way to solve the haronic oscillator proble. We will now study this approach. The
3 Haronic oscillator revisited: Dirac s approach and introduction to Second Quantization. Dirac cae up with a ore elegant way to solve the haronic oscillator proble. We will now study this approach. The
3D acoustic wave modeling with a time-space domain dispersion-relation-based Finite-difference scheme
 P-8 3D acoustic wave odeling with a tie-space doain dispersion-relation-based Finite-difference schee Yang Liu * and rinal K. Sen State Key Laboratory of Petroleu Resource and Prospecting (China University
P-8 3D acoustic wave odeling with a tie-space doain dispersion-relation-based Finite-difference schee Yang Liu * and rinal K. Sen State Key Laboratory of Petroleu Resource and Prospecting (China University
MSEC MODELING OF DEGRADATION PROCESSES TO OBTAIN AN OPTIMAL SOLUTION FOR MAINTENANCE AND PERFORMANCE
 Proceeding of the ASME 9 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference MSEC9 October 4-7, 9, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA MSEC9-8466 MODELING OF DEGRADATION PROCESSES TO OBTAIN AN OPTIMAL
Proceeding of the ASME 9 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference MSEC9 October 4-7, 9, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA MSEC9-8466 MODELING OF DEGRADATION PROCESSES TO OBTAIN AN OPTIMAL
Dispersion. February 12, 2014
 Dispersion February 1, 014 In aterials, the dielectric constant and pereability are actually frequency dependent. This does not affect our results for single frequency odes, but when we have a superposition
Dispersion February 1, 014 In aterials, the dielectric constant and pereability are actually frequency dependent. This does not affect our results for single frequency odes, but when we have a superposition
lecture 37: Linear Multistep Methods: Absolute Stability, Part I lecture 38: Linear Multistep Methods: Absolute Stability, Part II
 lecture 37: Linear Multistep Methods: Absolute Stability, Part I lecture 3: Linear Multistep Methods: Absolute Stability, Part II 5.7 Linear ultistep ethods: absolute stability At this point, it ay well
lecture 37: Linear Multistep Methods: Absolute Stability, Part I lecture 3: Linear Multistep Methods: Absolute Stability, Part II 5.7 Linear ultistep ethods: absolute stability At this point, it ay well
EE5900 Spring Lecture 4 IC interconnect modeling methods Zhuo Feng
 EE59 Spring Parallel LSI AD Algoriths Lecture I interconnect odeling ethods Zhuo Feng. Z. Feng MTU EE59 So far we ve considered only tie doain analyses We ll soon see that it is soeties preferable to odel
EE59 Spring Parallel LSI AD Algoriths Lecture I interconnect odeling ethods Zhuo Feng. Z. Feng MTU EE59 So far we ve considered only tie doain analyses We ll soon see that it is soeties preferable to odel
A method to determine relative stroke detection efficiencies from multiplicity distributions
 A ethod to deterine relative stroke detection eiciencies ro ultiplicity distributions Schulz W. and Cuins K. 2. Austrian Lightning Detection and Inoration Syste (ALDIS), Kahlenberger Str.2A, 90 Vienna,
A ethod to deterine relative stroke detection eiciencies ro ultiplicity distributions Schulz W. and Cuins K. 2. Austrian Lightning Detection and Inoration Syste (ALDIS), Kahlenberger Str.2A, 90 Vienna,
Research and Experiments on Electromagnetic Field Induced by Two. Coaxial Solenoid Coils of Axially Mag-lev Driving Needle
 3rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Inforation Technology (ICMIT 16) Research and Experients on Electroagnetic Field Induced by Two Coaxial Solenoid Coils of Axially Mag-lev Driving Needle
3rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Inforation Technology (ICMIT 16) Research and Experients on Electroagnetic Field Induced by Two Coaxial Solenoid Coils of Axially Mag-lev Driving Needle
Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measurement Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES
 Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measureent Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES Belinda Lipa Codar Ocean Sensors 15 La Sandra Way, Portola Valley, CA 98 blipa@pogo.co
Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measureent Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES Belinda Lipa Codar Ocean Sensors 15 La Sandra Way, Portola Valley, CA 98 blipa@pogo.co
Multi-Scale/Multi-Resolution: Wavelet Transform
 Multi-Scale/Multi-Resolution: Wavelet Transfor Proble with Fourier Fourier analysis -- breaks down a signal into constituent sinusoids of different frequencies. A serious drawback in transforing to the
Multi-Scale/Multi-Resolution: Wavelet Transfor Proble with Fourier Fourier analysis -- breaks down a signal into constituent sinusoids of different frequencies. A serious drawback in transforing to the
An Approximate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity Increase in the Intermediate Ballistics Period
 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity... 77 Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 205, 2(), 77-88 ISSN 2353-843 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction
An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity... 77 Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 205, 2(), 77-88 ISSN 2353-843 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction
A Simple Regression Problem
 A Siple Regression Proble R. M. Castro March 23, 2 In this brief note a siple regression proble will be introduced, illustrating clearly the bias-variance tradeoff. Let Y i f(x i ) + W i, i,..., n, where
A Siple Regression Proble R. M. Castro March 23, 2 In this brief note a siple regression proble will be introduced, illustrating clearly the bias-variance tradeoff. Let Y i f(x i ) + W i, i,..., n, where
The Transactional Nature of Quantum Information
 The Transactional Nature of Quantu Inforation Subhash Kak Departent of Coputer Science Oklahoa State University Stillwater, OK 7478 ABSTRACT Inforation, in its counications sense, is a transactional property.
The Transactional Nature of Quantu Inforation Subhash Kak Departent of Coputer Science Oklahoa State University Stillwater, OK 7478 ABSTRACT Inforation, in its counications sense, is a transactional property.
Faraday's Law Warm Up
 Faraday's Law-1 Faraday's Law War Up 1. Field lines of a peranent agnet For each peranent agnet in the diagra below draw several agnetic field lines (or a agnetic vector field if you prefer) corresponding
Faraday's Law-1 Faraday's Law War Up 1. Field lines of a peranent agnet For each peranent agnet in the diagra below draw several agnetic field lines (or a agnetic vector field if you prefer) corresponding
On Constant Power Water-filling
 On Constant Power Water-filling Wei Yu and John M. Cioffi Electrical Engineering Departent Stanford University, Stanford, CA94305, U.S.A. eails: {weiyu,cioffi}@stanford.edu Abstract This paper derives
On Constant Power Water-filling Wei Yu and John M. Cioffi Electrical Engineering Departent Stanford University, Stanford, CA94305, U.S.A. eails: {weiyu,cioffi}@stanford.edu Abstract This paper derives
The source of THz radiation based on dielectric waveguide excited by sequence of electron bunches
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The source of THz radiation based on dielectric waveguide excited by sequence of electron bunches To cite this article: A M Altark and A D Kanareykin
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The source of THz radiation based on dielectric waveguide excited by sequence of electron bunches To cite this article: A M Altark and A D Kanareykin
Two Dimensional Consolidations for Clay Soil of Non-Homogeneous and Anisotropic Permeability
 Two Diensional Consolidations for Clay Soil of Non-Hoogeneous and Anisotropic Pereability Ressol R. Shakir, Muhaed Majeed Thiqar University, College of Engineering, Thiqar, Iraq University of Technology,
Two Diensional Consolidations for Clay Soil of Non-Hoogeneous and Anisotropic Pereability Ressol R. Shakir, Muhaed Majeed Thiqar University, College of Engineering, Thiqar, Iraq University of Technology,
Role of rf electric and magnetic fields in heating of micro-protrusions in accelerating structures. Gregory S. Nusinovich and Thomas M. Antonsen, Jr.
 Role of rf electric and agnetic fields in heating of icro-protrusions in accelerating structures. Gregory S. Nusinovich and Thoas M. Antonsen, Jr. Abstract It is known that high-gradient operation in etallic
Role of rf electric and agnetic fields in heating of icro-protrusions in accelerating structures. Gregory S. Nusinovich and Thoas M. Antonsen, Jr. Abstract It is known that high-gradient operation in etallic
Feature Extraction Techniques
 Feature Extraction Techniques Unsupervised Learning II Feature Extraction Unsupervised ethods can also be used to find features which can be useful for categorization. There are unsupervised ethods that
Feature Extraction Techniques Unsupervised Learning II Feature Extraction Unsupervised ethods can also be used to find features which can be useful for categorization. There are unsupervised ethods that
IN modern society that various systems have become more
 Developent of Reliability Function in -Coponent Standby Redundant Syste with Priority Based on Maxiu Entropy Principle Ryosuke Hirata, Ikuo Arizono, Ryosuke Toohiro, Satoshi Oigawa, and Yasuhiko Takeoto
Developent of Reliability Function in -Coponent Standby Redundant Syste with Priority Based on Maxiu Entropy Principle Ryosuke Hirata, Ikuo Arizono, Ryosuke Toohiro, Satoshi Oigawa, and Yasuhiko Takeoto
Generalized Rayleigh Wave Dispersion in a Covered Half-space Made of Viscoelastic Materials
 Copyright 7 Tech Science Press CMC vol.53 no.4 pp.37-34 7 Generalized Rayleigh Wave Dispersion in a Covered Half-space Made of Viscoelastic Materials S.D. Akbarov and M. Negin 3 Abstract: Dispersion of
Copyright 7 Tech Science Press CMC vol.53 no.4 pp.37-34 7 Generalized Rayleigh Wave Dispersion in a Covered Half-space Made of Viscoelastic Materials S.D. Akbarov and M. Negin 3 Abstract: Dispersion of
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines
 Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley ENSIAG 2 / osig 1 Second Seester 2012/2013 Lesson 20 2 ay 2013 Kernel ethods and Support Vector achines Contents Kernel Functions...2 Quadratic
Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley ENSIAG 2 / osig 1 Second Seester 2012/2013 Lesson 20 2 ay 2013 Kernel ethods and Support Vector achines Contents Kernel Functions...2 Quadratic
HIGH RESOLUTION NEAR-FIELD MULTIPLE TARGET DETECTION AND LOCALIZATION USING SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES
 ICONIC 2007 St. Louis, O, USA June 27-29, 2007 HIGH RESOLUTION NEAR-FIELD ULTIPLE TARGET DETECTION AND LOCALIZATION USING SUPPORT VECTOR ACHINES A. Randazzo,. A. Abou-Khousa 2,.Pastorino, and R. Zoughi
ICONIC 2007 St. Louis, O, USA June 27-29, 2007 HIGH RESOLUTION NEAR-FIELD ULTIPLE TARGET DETECTION AND LOCALIZATION USING SUPPORT VECTOR ACHINES A. Randazzo,. A. Abou-Khousa 2,.Pastorino, and R. Zoughi
Electromagnetic fields modeling of power line communication (PLC)
 Electroagnetic fields odeling of power line counication (PLC) Wei Weiqi UROP 3 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang echnological University E-ail: 4794486@ntu.edu.sg Keyword: power line
Electroagnetic fields odeling of power line counication (PLC) Wei Weiqi UROP 3 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang echnological University E-ail: 4794486@ntu.edu.sg Keyword: power line
REDUCTION OF FINITE ELEMENT MODELS BY PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION
 ISSN 139 14X INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND CONTROL, 008, Vol.37, No.3 REDUCTION OF FINITE ELEMENT MODELS BY PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION Riantas Barauskas, Vidantas Riavičius Departent of Syste Analysis, Kaunas
ISSN 139 14X INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND CONTROL, 008, Vol.37, No.3 REDUCTION OF FINITE ELEMENT MODELS BY PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION Riantas Barauskas, Vidantas Riavičius Departent of Syste Analysis, Kaunas
Now multiply the left-hand-side by ω and the right-hand side by dδ/dt (recall ω= dδ/dt) to get:
 Equal Area Criterion.0 Developent of equal area criterion As in previous notes, all powers are in per-unit. I want to show you the equal area criterion a little differently than the book does it. Let s
Equal Area Criterion.0 Developent of equal area criterion As in previous notes, all powers are in per-unit. I want to show you the equal area criterion a little differently than the book does it. Let s
72. (30.2) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires.
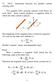 7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
13.2 Fully Polynomial Randomized Approximation Scheme for Permanent of Random 0-1 Matrices
 CS71 Randoness & Coputation Spring 018 Instructor: Alistair Sinclair Lecture 13: February 7 Disclaier: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny accorded to foral publications. They ay
CS71 Randoness & Coputation Spring 018 Instructor: Alistair Sinclair Lecture 13: February 7 Disclaier: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny accorded to foral publications. They ay
Numerical Studies of a Nonlinear Heat Equation with Square Root Reaction Term
 Nuerical Studies of a Nonlinear Heat Equation with Square Root Reaction Ter Ron Bucire, 1 Karl McMurtry, 1 Ronald E. Micens 2 1 Matheatics Departent, Occidental College, Los Angeles, California 90041 2
Nuerical Studies of a Nonlinear Heat Equation with Square Root Reaction Ter Ron Bucire, 1 Karl McMurtry, 1 Ronald E. Micens 2 1 Matheatics Departent, Occidental College, Los Angeles, California 90041 2
Interferometry in dissipative media: Addressing the shallow sea problem for Seabed Logging applications
 Evert Slob and Kees Wapenaar, Departent of Geotechnology, Delft University of Technology Roel Snieder, Center for Wave Phenoena and Departent of Geophysics, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY We derive interferoetric
Evert Slob and Kees Wapenaar, Departent of Geotechnology, Delft University of Technology Roel Snieder, Center for Wave Phenoena and Departent of Geophysics, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY We derive interferoetric
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electroagnetic Waves Physics 4 Maxwell s Equations Maxwell s equations suarize the relationships between electric and agnetic fields. A ajor consequence of these equations is that an accelerating charge
Electroagnetic Waves Physics 4 Maxwell s Equations Maxwell s equations suarize the relationships between electric and agnetic fields. A ajor consequence of these equations is that an accelerating charge
Research Article Rapidly-Converging Series Representations of a Mutual-Information Integral
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Counications and Networking Volue 11, Article ID 5465, 6 pages doi:1.54/11/5465 Research Article Rapidly-Converging Series Representations of a Mutual-Inforation
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Counications and Networking Volue 11, Article ID 5465, 6 pages doi:1.54/11/5465 Research Article Rapidly-Converging Series Representations of a Mutual-Inforation
Solving initial value problems by residual power series method
 Theoretical Matheatics & Applications, vol.3, no.1, 13, 199-1 ISSN: 179-9687 (print), 179-979 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 13 Solving initial value probles by residual power series ethod Mohaed H. Al-Sadi
Theoretical Matheatics & Applications, vol.3, no.1, 13, 199-1 ISSN: 179-9687 (print), 179-979 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 13 Solving initial value probles by residual power series ethod Mohaed H. Al-Sadi
Intelligent Systems: Reasoning and Recognition. Perceptrons and Support Vector Machines
 Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley osig 1 Winter Seester 2018 Lesson 6 27 February 2018 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector achines Notation...2 Linear odels...3 Lines, Planes
Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley osig 1 Winter Seester 2018 Lesson 6 27 February 2018 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector achines Notation...2 Linear odels...3 Lines, Planes
Fast Montgomery-like Square Root Computation over GF(2 m ) for All Trinomials
 Fast Montgoery-like Square Root Coputation over GF( ) for All Trinoials Yin Li a, Yu Zhang a, a Departent of Coputer Science and Technology, Xinyang Noral University, Henan, P.R.China Abstract This letter
Fast Montgoery-like Square Root Coputation over GF( ) for All Trinoials Yin Li a, Yu Zhang a, a Departent of Coputer Science and Technology, Xinyang Noral University, Henan, P.R.China Abstract This letter
Keywords: Estimator, Bias, Mean-squared error, normality, generalized Pareto distribution
 Testing approxiate norality of an estiator using the estiated MSE and bias with an application to the shape paraeter of the generalized Pareto distribution J. Martin van Zyl Abstract In this work the norality
Testing approxiate norality of an estiator using the estiated MSE and bias with an application to the shape paraeter of the generalized Pareto distribution J. Martin van Zyl Abstract In this work the norality
A DESIGN GUIDE OF DOUBLE-LAYER CELLULAR CLADDINGS FOR BLAST ALLEVIATION
 International Journal of Aerospace and Lightweight Structures Vol. 3, No. 1 (2013) 109 133 c Research Publishing Services DOI: 10.3850/S201042862013000550 A DESIGN GUIDE OF DOUBLE-LAYER CELLULAR CLADDINGS
International Journal of Aerospace and Lightweight Structures Vol. 3, No. 1 (2013) 109 133 c Research Publishing Services DOI: 10.3850/S201042862013000550 A DESIGN GUIDE OF DOUBLE-LAYER CELLULAR CLADDINGS
A comparative study of conventional arrays of resistivity prospecting with differential arrays
 Geol. Soc. MaLaYJia, Bulletin 39, JuLy 1996,. pp. 105-111 A coparative study of conventional arrays of resistivity prospecting with differential arrays SHARMA K.K. AND JAYASHREE S. Departent of Applied
Geol. Soc. MaLaYJia, Bulletin 39, JuLy 1996,. pp. 105-111 A coparative study of conventional arrays of resistivity prospecting with differential arrays SHARMA K.K. AND JAYASHREE S. Departent of Applied
Intelligent Systems: Reasoning and Recognition. Artificial Neural Networks
 Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley MOSIG M1 Winter Seester 2018 Lesson 7 1 March 2018 Outline Artificial Neural Networks Notation...2 Introduction...3 Key Equations... 3 Artificial
Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley MOSIG M1 Winter Seester 2018 Lesson 7 1 March 2018 Outline Artificial Neural Networks Notation...2 Introduction...3 Key Equations... 3 Artificial
AN APPLICATION OF CUBIC B-SPLINE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD FOR THE BURGERS EQUATION
 Aksan, E..: An Applıcatıon of Cubıc B-Splıne Fınıte Eleent Method for... THERMAL SCIECE: Year 8, Vol., Suppl., pp. S95-S S95 A APPLICATIO OF CBIC B-SPLIE FIITE ELEMET METHOD FOR THE BRGERS EQATIO by Eine
Aksan, E..: An Applıcatıon of Cubıc B-Splıne Fınıte Eleent Method for... THERMAL SCIECE: Year 8, Vol., Suppl., pp. S95-S S95 A APPLICATIO OF CBIC B-SPLIE FIITE ELEMET METHOD FOR THE BRGERS EQATIO by Eine
CHAPTER 4 TWO STANDARD SHORTCUTS USED TO TRANSFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC EQUATIONS 4.1 THE FREE-PARAMETER METHOD
 CHAPTER 4 TWO STANDARD SHORTCUTS USED TO TRANSFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC EQUATIONS The last several chapters have explained how the standard rules for changing units apply to electroagnetic physical quantities.
CHAPTER 4 TWO STANDARD SHORTCUTS USED TO TRANSFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC EQUATIONS The last several chapters have explained how the standard rules for changing units apply to electroagnetic physical quantities.
Anisotropic reference media and the possible linearized approximations for phase velocities of qs waves in weakly anisotropic media
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS D: APPLIED PHYSICS J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 5 00 007 04 PII: S00-770867-6 Anisotropic reference edia and the possible linearized approxiations for phase
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS D: APPLIED PHYSICS J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 5 00 007 04 PII: S00-770867-6 Anisotropic reference edia and the possible linearized approxiations for phase
Ferromagnetism. So that once magnetized the material will stay that way even in the absence of external current it is a permanent magnet.
 Ferroagnetis We now turn to the case where is not proportional to. We distinguish two cases: soft and hard ferroagnets. In a soft ferroagnet a graph of vs looks like If is now reduced, will retrace the
Ferroagnetis We now turn to the case where is not proportional to. We distinguish two cases: soft and hard ferroagnets. In a soft ferroagnet a graph of vs looks like If is now reduced, will retrace the
A new type of lower bound for the largest eigenvalue of a symmetric matrix
 Linear Algebra and its Applications 47 7 9 9 www.elsevier.co/locate/laa A new type of lower bound for the largest eigenvalue of a syetric atrix Piet Van Mieghe Delft University of Technology, P.O. Box
Linear Algebra and its Applications 47 7 9 9 www.elsevier.co/locate/laa A new type of lower bound for the largest eigenvalue of a syetric atrix Piet Van Mieghe Delft University of Technology, P.O. Box
Spine Fin Efficiency A Three Sided Pyramidal Fin of Equilateral Triangular Cross-Sectional Area
 Proceedings of the 006 WSEAS/IASME International Conference on Heat and Mass Transfer, Miai, Florida, USA, January 18-0, 006 (pp13-18) Spine Fin Efficiency A Three Sided Pyraidal Fin of Equilateral Triangular
Proceedings of the 006 WSEAS/IASME International Conference on Heat and Mass Transfer, Miai, Florida, USA, January 18-0, 006 (pp13-18) Spine Fin Efficiency A Three Sided Pyraidal Fin of Equilateral Triangular
Hysteresis model for magnetic materials using the Jiles-Atherton model
 Hysteresis odel for agnetic aterials using the Jiles-Atherton odel Predrag Petrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, pegi@ei.yu Nebojsa itrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, itar@tfc.tfc.kg.ac.yu
Hysteresis odel for agnetic aterials using the Jiles-Atherton odel Predrag Petrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, pegi@ei.yu Nebojsa itrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, itar@tfc.tfc.kg.ac.yu
This is a repository copy of Analytical optimisation of electromagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance motor.
 This is a repository copy of Analytical optiisation of electroagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance otor. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/907/
This is a repository copy of Analytical optiisation of electroagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance otor. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/907/
Comparison of Stability of Selected Numerical Methods for Solving Stiff Semi- Linear Differential Equations
 International Journal of Applied Science and Technology Vol. 7, No. 3, Septeber 217 Coparison of Stability of Selected Nuerical Methods for Solving Stiff Sei- Linear Differential Equations Kwaku Darkwah
International Journal of Applied Science and Technology Vol. 7, No. 3, Septeber 217 Coparison of Stability of Selected Nuerical Methods for Solving Stiff Sei- Linear Differential Equations Kwaku Darkwah
2 Q 10. Likewise, in case of multiple particles, the corresponding density in 2 must be averaged over all
 Lecture 6 Introduction to kinetic theory of plasa waves Introduction to kinetic theory So far we have been odeling plasa dynaics using fluid equations. The assuption has been that the pressure can be either
Lecture 6 Introduction to kinetic theory of plasa waves Introduction to kinetic theory So far we have been odeling plasa dynaics using fluid equations. The assuption has been that the pressure can be either
Monitoring and system identification of suspension bridges: An alternative approach
 Monitoring and syste identification of suspension bridges: An alternative approach Erdal Şafak Boğaziçi University, Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Reseach Institute, Istanbul, Turkey Abstract This
Monitoring and syste identification of suspension bridges: An alternative approach Erdal Şafak Boğaziçi University, Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Reseach Institute, Istanbul, Turkey Abstract This
A Simplified Analytical Approach for Efficiency Evaluation of the Weaving Machines with Automatic Filling Repair
 Proceedings of the 6th SEAS International Conference on Siulation, Modelling and Optiization, Lisbon, Portugal, Septeber -4, 006 0 A Siplified Analytical Approach for Efficiency Evaluation of the eaving
Proceedings of the 6th SEAS International Conference on Siulation, Modelling and Optiization, Lisbon, Portugal, Septeber -4, 006 0 A Siplified Analytical Approach for Efficiency Evaluation of the eaving
Hyperbolic Horn Helical Mass Spectrometer (3HMS) James G. Hagerman Hagerman Technology LLC & Pacific Environmental Technologies April 2005
 Hyperbolic Horn Helical Mass Spectroeter (3HMS) Jaes G Hageran Hageran Technology LLC & Pacific Environental Technologies April 5 ABSTRACT This paper describes a new type of ass filter based on the REFIMS
Hyperbolic Horn Helical Mass Spectroeter (3HMS) Jaes G Hageran Hageran Technology LLC & Pacific Environental Technologies April 5 ABSTRACT This paper describes a new type of ass filter based on the REFIMS
ANALYSIS OF REFLECTOR AND HORN ANTENNAS USING MULTILEVEL FAST MULTIPOLE ALGORITHM
 European Congress on Coputational Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering ECCOMAS 2 Barcelona, 11-14 Septeber 2 ECCOMAS ANALYSIS OF REFLECTOR AND HORN ANTENNAS USING MULTILEVEL FAST MULTIPOLE ALGORITHM
European Congress on Coputational Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering ECCOMAS 2 Barcelona, 11-14 Septeber 2 ECCOMAS ANALYSIS OF REFLECTOR AND HORN ANTENNAS USING MULTILEVEL FAST MULTIPOLE ALGORITHM
N-Point. DFTs of Two Length-N Real Sequences
 Coputation of the DFT of In ost practical applications, sequences of interest are real In such cases, the syetry properties of the DFT given in Table 5. can be exploited to ake the DFT coputations ore
Coputation of the DFT of In ost practical applications, sequences of interest are real In such cases, the syetry properties of the DFT given in Table 5. can be exploited to ake the DFT coputations ore
Rotation-induced superstructure in slow-light waveguides with mode-degeneracy: optical gyroscopes with exponential sensitivity
 1216 J. Opt. Soc. A. B/ Vol. 24, No. 5/ May 2007 Steinberg et al. Rotation-induced superstructure in slow-light waveguides with ode-degeneracy: optical gyroscopes with exponential sensitivity Ben Z. Steinberg,
1216 J. Opt. Soc. A. B/ Vol. 24, No. 5/ May 2007 Steinberg et al. Rotation-induced superstructure in slow-light waveguides with ode-degeneracy: optical gyroscopes with exponential sensitivity Ben Z. Steinberg,
Numerically repeated support splitting and merging phenomena in a porous media equation with strong absorption. Kenji Tomoeda
 Journal of Math-for-Industry, Vol. 3 (C-), pp. Nuerically repeated support splitting and erging phenoena in a porous edia equation with strong absorption To the eory of y friend Professor Nakaki. Kenji
Journal of Math-for-Industry, Vol. 3 (C-), pp. Nuerically repeated support splitting and erging phenoena in a porous edia equation with strong absorption To the eory of y friend Professor Nakaki. Kenji
A remark on a success rate model for DPA and CPA
 A reark on a success rate odel for DPA and CPA A. Wieers, BSI Version 0.5 andreas.wieers@bsi.bund.de Septeber 5, 2018 Abstract The success rate is the ost coon evaluation etric for easuring the perforance
A reark on a success rate odel for DPA and CPA A. Wieers, BSI Version 0.5 andreas.wieers@bsi.bund.de Septeber 5, 2018 Abstract The success rate is the ost coon evaluation etric for easuring the perforance
MICROWAVE SCATTERING AND ABSORPTION BY A MULTILAYERED LOSSY METAMATERIAL-GLASS CYLINDER
 Progress In Electroagnetics Research, Vol. 105, 103 118, 2010 MICROWAVE SCATTERING AND ABSORPTION BY A MULTILAYERED LOSSY METAMATERIAL-GLASS CYLINDER J. Bucinskas Physics Departent Vilnius University Vilnius,
Progress In Electroagnetics Research, Vol. 105, 103 118, 2010 MICROWAVE SCATTERING AND ABSORPTION BY A MULTILAYERED LOSSY METAMATERIAL-GLASS CYLINDER J. Bucinskas Physics Departent Vilnius University Vilnius,
Chapter 2: Introduction to Damping in Free and Forced Vibrations
 Chapter 2: Introduction to Daping in Free and Forced Vibrations This chapter ainly deals with the effect of daping in two conditions like free and forced excitation of echanical systes. Daping plays an
Chapter 2: Introduction to Daping in Free and Forced Vibrations This chapter ainly deals with the effect of daping in two conditions like free and forced excitation of echanical systes. Daping plays an
Department of Physics Preliminary Exam January 3 6, 2006
 Departent of Physics Preliinary Exa January 3 6, 2006 Day 1: Classical Mechanics Tuesday, January 3, 2006 9:00 a.. 12:00 p.. Instructions: 1. Write the answer to each question on a separate sheet of paper.
Departent of Physics Preliinary Exa January 3 6, 2006 Day 1: Classical Mechanics Tuesday, January 3, 2006 9:00 a.. 12:00 p.. Instructions: 1. Write the answer to each question on a separate sheet of paper.
A NEW ELECTROSTATIC FIELD GEOMETRY. Jerry E. Bayles
 INTRODUCTION A NEW ELECTROSTATIC FIELD GEOMETRY by Jerry E Bayles The purpose of this paper is to present the electrostatic field in geoetrical ters siilar to that of the electrogravitational equation
INTRODUCTION A NEW ELECTROSTATIC FIELD GEOMETRY by Jerry E Bayles The purpose of this paper is to present the electrostatic field in geoetrical ters siilar to that of the electrogravitational equation
Motion of Charges in Uniform E
 Motion of Charges in Unifor E and Fields Assue an ionized gas is acted upon by a unifor (but possibly tie-dependent) electric field E, and a unifor, steady agnetic field. These fields are assued to be
Motion of Charges in Unifor E and Fields Assue an ionized gas is acted upon by a unifor (but possibly tie-dependent) electric field E, and a unifor, steady agnetic field. These fields are assued to be
ma x = -bv x + F rod.
 Notes on Dynaical Systes Dynaics is the study of change. The priary ingredients of a dynaical syste are its state and its rule of change (also soeties called the dynaic). Dynaical systes can be continuous
Notes on Dynaical Systes Dynaics is the study of change. The priary ingredients of a dynaical syste are its state and its rule of change (also soeties called the dynaic). Dynaical systes can be continuous
Chapter 2. Small-Signal Model Parameter Extraction Method
 Chapter Sall-Signal Model Paraeter Extraction Method In this chapter, we introduce a new paraeter extraction technique for sall-signal HBT odeling. Figure - shows the sall-signal equivalent circuit of
Chapter Sall-Signal Model Paraeter Extraction Method In this chapter, we introduce a new paraeter extraction technique for sall-signal HBT odeling. Figure - shows the sall-signal equivalent circuit of
Supporting Online Material
 Supporting Online Material (A) Description of the suppleentary ovies Movie : Two-directional alignent of cells using 4-point electrodes. 0.08 % w/v yeast (S. cerevisiae) cells were assebled into D arrays
Supporting Online Material (A) Description of the suppleentary ovies Movie : Two-directional alignent of cells using 4-point electrodes. 0.08 % w/v yeast (S. cerevisiae) cells were assebled into D arrays
The Energy Flux Method for Reverberation: Modeling and Inversion
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A Approved for public release; distribution is unliited The Energy Flux Method for Reverberation: Modeling and Inversion Ji-Xun Zhou School of Mechanical Engineering Georgia Institute
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A Approved for public release; distribution is unliited The Energy Flux Method for Reverberation: Modeling and Inversion Ji-Xun Zhou School of Mechanical Engineering Georgia Institute
Chapter 1: Basics of Vibrations for Simple Mechanical Systems
 Chapter 1: Basics of Vibrations for Siple Mechanical Systes Introduction: The fundaentals of Sound and Vibrations are part of the broader field of echanics, with strong connections to classical echanics,
Chapter 1: Basics of Vibrations for Siple Mechanical Systes Introduction: The fundaentals of Sound and Vibrations are part of the broader field of echanics, with strong connections to classical echanics,
2. Electric Current. E.M.F. of a cell is defined as the maximum potential difference between the two electrodes of the
 2. Electric Current The net flow of charges through a etallic wire constitutes an electric current. Do you know who carries current? Current carriers In solid - the electrons in outerost orbit carries
2. Electric Current The net flow of charges through a etallic wire constitutes an electric current. Do you know who carries current? Current carriers In solid - the electrons in outerost orbit carries
Problem T1. Main sequence stars (11 points)
 Proble T1. Main sequence stars 11 points Part. Lifetie of Sun points i..7 pts Since the Sun behaves as a perfectly black body it s total radiation power can be expressed fro the Stefan- Boltzann law as
Proble T1. Main sequence stars 11 points Part. Lifetie of Sun points i..7 pts Since the Sun behaves as a perfectly black body it s total radiation power can be expressed fro the Stefan- Boltzann law as
NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE TYRE/ROAD CONTACT
 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE TYRE/ROAD CONTACT PACS REFERENCE: 43.5.LJ Krister Larsson Departent of Applied Acoustics Chalers University of Technology SE-412 96 Sweden Tel: +46 ()31 772 22 Fax: +46 ()31
NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE TYRE/ROAD CONTACT PACS REFERENCE: 43.5.LJ Krister Larsson Departent of Applied Acoustics Chalers University of Technology SE-412 96 Sweden Tel: +46 ()31 772 22 Fax: +46 ()31
COS 424: Interacting with Data. Written Exercises
 COS 424: Interacting with Data Hoework #4 Spring 2007 Regression Due: Wednesday, April 18 Written Exercises See the course website for iportant inforation about collaboration and late policies, as well
COS 424: Interacting with Data Hoework #4 Spring 2007 Regression Due: Wednesday, April 18 Written Exercises See the course website for iportant inforation about collaboration and late policies, as well
entropy ISSN by MDPI
 Entropy, 007, 9, 118-131 Full Research Paper entropy ISSN 1099-4300 007 by MDPI www.dpi.org/entropy On Darcy-Brinkan Equation: Viscous Flow Between Two Parallel Plates Packed with Regular Square Arrays
Entropy, 007, 9, 118-131 Full Research Paper entropy ISSN 1099-4300 007 by MDPI www.dpi.org/entropy On Darcy-Brinkan Equation: Viscous Flow Between Two Parallel Plates Packed with Regular Square Arrays
Simulated Effects of Soil Temperature and Salinity on Capacitance Sensor Measurements
 Sensors 2007, 7, 548-577 sensors ISSN 1424-8220 2007 by MDPI www.dpi.org/sensors Full Research Paper Siulated Effects of Soil Teperature and Salinity on Capacitance Sensor Measureents Mike Schwank 1, *
Sensors 2007, 7, 548-577 sensors ISSN 1424-8220 2007 by MDPI www.dpi.org/sensors Full Research Paper Siulated Effects of Soil Teperature and Salinity on Capacitance Sensor Measureents Mike Schwank 1, *
PERIODIC STEADY STATE ANALYSIS, EFFECTIVE VALUE,
 PERIODIC SEADY SAE ANALYSIS, EFFECIVE VALUE, DISORSION FACOR, POWER OF PERIODIC CURRENS t + Effective value of current (general definition) IRMS i () t dt Root Mean Square, in Czech boo denoted I he value
PERIODIC SEADY SAE ANALYSIS, EFFECIVE VALUE, DISORSION FACOR, POWER OF PERIODIC CURRENS t + Effective value of current (general definition) IRMS i () t dt Root Mean Square, in Czech boo denoted I he value
Hybrid System Identification: An SDP Approach
 49th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control Deceber 15-17, 2010 Hilton Atlanta Hotel, Atlanta, GA, USA Hybrid Syste Identification: An SDP Approach C Feng, C M Lagoa, N Ozay and M Sznaier Abstract The
49th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control Deceber 15-17, 2010 Hilton Atlanta Hotel, Atlanta, GA, USA Hybrid Syste Identification: An SDP Approach C Feng, C M Lagoa, N Ozay and M Sznaier Abstract The
PH 222-2C Fall Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current. Lectures 18-19
 H - Fall 0 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent ectures 8-9 hapter 3 (Halliday/esnick/Walker, Fundaentals of hysics 8 th edition) hapter 3 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent
H - Fall 0 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent ectures 8-9 hapter 3 (Halliday/esnick/Walker, Fundaentals of hysics 8 th edition) hapter 3 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent
Stern-Gerlach Experiment
 Stern-Gerlach Experient HOE: The Physics of Bruce Harvey This is the experient that is said to prove that the electron has an intrinsic agnetic oent. Hydrogen like atos are projected in a bea through a
Stern-Gerlach Experient HOE: The Physics of Bruce Harvey This is the experient that is said to prove that the electron has an intrinsic agnetic oent. Hydrogen like atos are projected in a bea through a
PH 221-2A Fall Waves - I. Lectures Chapter 16 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition)
 PH 1-A Fall 014 Waves - I Lectures 4-5 Chapter 16 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundaentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will
PH 1-A Fall 014 Waves - I Lectures 4-5 Chapter 16 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundaentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will
A Note on the Applied Use of MDL Approximations
 A Note on the Applied Use of MDL Approxiations Daniel J. Navarro Departent of Psychology Ohio State University Abstract An applied proble is discussed in which two nested psychological odels of retention
A Note on the Applied Use of MDL Approxiations Daniel J. Navarro Departent of Psychology Ohio State University Abstract An applied proble is discussed in which two nested psychological odels of retention
Seismic Analysis of Structures by TK Dutta, Civil Department, IIT Delhi, New Delhi.
 Seisic Analysis of Structures by K Dutta, Civil Departent, II Delhi, New Delhi. Module 5: Response Spectru Method of Analysis Exercise Probles : 5.8. or the stick odel of a building shear frae shown in
Seisic Analysis of Structures by K Dutta, Civil Departent, II Delhi, New Delhi. Module 5: Response Spectru Method of Analysis Exercise Probles : 5.8. or the stick odel of a building shear frae shown in
Numerical Solution of the MRLW Equation Using Finite Difference Method. 1 Introduction
 ISSN 1749-3889 print, 1749-3897 online International Journal of Nonlinear Science Vol.1401 No.3,pp.355-361 Nuerical Solution of the MRLW Equation Using Finite Difference Method Pınar Keskin, Dursun Irk
ISSN 1749-3889 print, 1749-3897 online International Journal of Nonlinear Science Vol.1401 No.3,pp.355-361 Nuerical Solution of the MRLW Equation Using Finite Difference Method Pınar Keskin, Dursun Irk
In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenomena. We will study the following topics:
 Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will study the following topics: Types of waves Aplitude, phase, frequency, period, propagation speed of a wave Mechanical
Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will study the following topics: Types of waves Aplitude, phase, frequency, period, propagation speed of a wave Mechanical
