Singularity Extraction for Reflected Sommerfeld Integrals over Multilayered Media
|
|
|
- Raymond Franklin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Telfor Journal, Vol. 6, No., 4. 7 Singularity Extraction for Reflected Soerfeld Integrals over Multilayered Media Vladiir V. Petrovic, Senior Meber, IEEE, Aleksandra J. Krneta, and Branko M. Kolundzija, Fellow, IEEE Abstract A new analytical-nuerical ethod based on singularity extraction is presented for efficient and accurate evaluation of one of the reflected Soerfeld integrals over ultilayered edia backed by a conducting (PEC) plane. Method is based on extraction of all the poles of the integrand. The ethod is deonstrated on one eleent of the tensor ultilayered Green s function, where only the singular part of the integrand, i.e. the reflection coefficient, is taken into consideration, as the cause of the largest calculation difficulties. It was also shown that the ethod practically eliinates all the branch cut singularities except for one. Keywords Soerfeld integrals, singularity extraction, ultilayered edia C I. INTRODUCTION ALCULATION of electroagnetic (EM) fields in the presence of a half-space or ultilayered edia, whose exact analytical solution is given by the so-called Soerfeld integrals, basically established by the classical paper [], is still in the focus of research. Applications are any. Historically the first was radio counication over the earth. Soe of the odern applications are ground penetrating radars for detecting buried objects, wall penetrating radars for detecting installations, aterial defects and inner cracks, through the wall iaging for security applications and geophysical search for gas and oil by using EM waves. However, the ost iportant ones are the increasingly growing application of the ultilayered printed circuit boards Paper received April 6, 4; accepted October, 4. Date of publication Noveber 5, 4. The associate editor coordinating the review of this anuscript and approving it for publication was Prof. George Paunovic. This paper is a revised and expanded version of the paper presented at the th Telecounications Foru TELFOR. The work presented here is partially supported by Serbian Ministry of Education, Science and Technical developent under the grant TR-5. V. Petrovic is with TES Electronic Solutions, Zettachring 8, 7567 Stuttgart, Gerany (phone: ; e-ail: vladiir.petrovic@gx.de). A. Krneta is with the School of Electrical Engineering, Univ. of Belgrade, Bul. kralja Aleksandra 7, Belgrade, Serbia (phone: ; e-ail: krneta@etf.rs). B. Kolundzija is with the School of Electrical Engineering, Univ. of Belgrade, Bul. kralja Aleksandra 7, Belgrade, Serbia (phone: ; e-ail: kol@etf.rs). (PCB) on icrowave and illieter-wave frequencies, where low-frequency approxiations and corresponding design ethods are not accurate enough. Moreover, such ultilayered PCBs often include printed or other antennas placed ostly on the top layer. A long series of scientific publications on this atter can be traced. A representative list of works can be found, e.g. in []. Both exact ethods (based on the Soerfeld integrals) and various approxiate ethods were developed. The goal of ost of these ethods is to provide an efficient and accurate evaluation of the Green function for a ultilayered structure. In this paper one of the reflected ultilayered Soerfeld integrals is chosen for deonstration of the ethod, naely the zz-coponent of a tensor Green function ( G ) for the agnetic vector-potential []. A II. ANALYTICAL FORM OF THE MULTILAYERED GREEN FUNCTION Consider a ultilayered structure, consisting of M layers ( M> ), where the botto layer is a perfectly conducting plane (Fig.). The structure is considered infinite and unifor in directions perpendicular to z-axis. Dielectric layers are non-agnetic and could be lossy or lossless, represented by their equivalent coplex perittivity, ε, and thickness, h, =,, M. r The upper half-space does not have to be vacuu, thus, in general, εr. A source and field point are above the structure and their utual position is denoted by heights z s and z f and the radial distance ρ, where any of these three relative coordinates can be zero or approach zero in the liiting case. If all the three coordinates approach zero the tensor Green function becoes singular (tends to infinity). The eleent of a tensor Green function chosen for deonstration of the ethod is g, whose copact (noralized) for [] is given by the Soerfeld integral g g = F( α, Z, Ρ) R ( α), () where Z= β( zs+ zf ), Ρ= βρ and β= ω ε µ. Function F( α, Z, Ρ ) coprises the Bessel function and an exponential function and its only singularity (in the coplex α -plane), as it contains the expression
2 8 Telfor Journal, Vol. 6, No., 4. u α =, is the branch point at α=. Function R ( α ) is often called a reflection coefficient, as it can be interpreted as a reflection coefficient for the plane wave incident to the ultilayered edia. z O M M source point Fig.. Layered edia backed by the PEC plane. For li R ( α) = R significant α iproveent of integral convergence is obtained when R ( α ) is represented as R ( α) = R+ R ( α) and the first of the resulting integrals solved analytically [4], jr F( α, Z, Ρ) R= Re / R, R= Ρ + Z. We will call function R ( α ) a reduced reflection coefficient. Extraction of this ter is iportant as the function R ( α ) for large arguents behaves as α [] and alone provides the convergence of the reaining z s integral, F( α, Z, Ρ) R ( α). This integral cannot be ρ h hm field point (PEC) ε r, µ ε r, µ ε r, µ ( ) solved analytically. More asyptotic ters could be extracted and the corresponding integrals solved analytically [], [5]. This will be addressed shortly later in the text. The oscillating nature of function F and its slow decay to zero for sall or zero values of Z ake its nuerical integration difficult. These two difficulties can, however, be solved in relatively standard and reported ways. A ore serious difficulty is that R ( α ) contains singularities in the for of poles and branch cut singularities (at points where the branch cuts of the ultivalued square root function starts). Every layer introduces one pair of these two types of singularities. For lossless layers these singularities are on the α -axis. For layers with sall losses (good dielectrics) they are very close to the α -axis, what is proven to be an even bigger difficulty for integration [4]. In this paper, the second, ore deanding, case will be chosen for deonstration of the ethod. In the ost deanding case of the Green function evaluation, and that is the case when all the three coordinates, z s, z f and ρ, approach zero, and, thus both Z and Ρ in () also approach zero, the F function is for z f ε, µ r, M - x sall arguents close to one and very slowly decaying. Thus, the integral, I = R ( α), () will be considered for deonstration of the proposed ethod. Due to α behavior of R ( α ) this integral is convergent. For solving the initial integral (), the ethod that will be presented can be cobined with techniques for efficient solving the integral if only function F is considered, leading to a hybrid and adaptive overall ethod, siilar to that reported in [], [4]. Function R ( α ) is given by the recurrence forula that is presented here according to [6] and after soe eleentary transforations, k z z+ + k th( uh) R=, z= k, k + z k + z th( u H ) () + =,, M, u z k, k, u, M= M = = α εr εr =,, M. Here th( ) is a hyperbolic tangent and H= βh. In the case that the botto layer is a PEC plane, is we considered in this work, k M=. In what follows we will consider also coplex values of α and will denote such a coplex variable as z. Fro the recurrence equations it can be seen that:. R is a function of (4) α, thus, any of its series expansions contains only even powers of α,. R ( z ) in the coplex plane has branch cut singularities at points ε, =,, M, where the function is r finite, but its derivative is infinite. It is also shown (e.g. in [7], [8]) that R( z ) has a nuber of poles in the second quadrant ( π/ < arg{ z} ). We will assue that locations of those poles, z, i=,, N, and their residuus can be efficiently nuerically deterined (e.g. as explained in [7]). To derive R ( α ) we need to obtain R i = li R ( α). For this reason we first obtain α liα th( uh) = liu th( uh) =. Next, for α, z= k for every and the result is k k εr εr R= liα =. (5) k + k ε + ε r r This is exactly the sae value as for the case when there is only one layer (the first) filling the whole lower halfspace. The value of R is the constant ter in the series expansion of R ( α ) around infinity (which is equivalent to expansion of R (/ x ) around x= ). As every expansion of R ( α ) has only even powers of α, the first ter in expansion of R ( α ) around infinity is the α ter, as already entioned.
3 Petrovic et al.: Singularity Extraction for Reflected Soerfeld Integrals over Multilayered Media 9 Fig.. Reduced reflection coefficient along the real axis. III. EXTRACTION OF POLES OF THE INTEGRAND As an exaple for deonstration of the ethod, in the rest of the paper, two-dielectric layered edia backed by a PEC plane ( M = ), with paraeters ε r= j (air), ε r= 9 j., ε r= 4 j., H =, H = will be considered. Graph of the reduced reflection coefficient R ( α ), for the chosen paraeters of the layered edia is shown in Fig., and in the coplex plane, denoted R ( z ), in Fig.. Large values of R ( α ) in Fig. are not infinite, because the three poles are soewhat displaced fro the real axis ( α -axis). However, direct nuerical integration of such a function, without the use of special ethods is highly inefficient. In the coplex plane, function R ( α ) has also branch cuts, one for each of the three functions u, equation (4), naely u,,. Each branch cut doubles the ultiplicity of the coplex functions (as the square root is a two-valued function). These branch cuts can be seen in Fig.4. The ulti-valued nature of R ( α ) is reoved by the condition π/ < arg{ z} + π/, but branch cut singularities (essential singularities) reain. following. In the coplex plane, function R ( z ) should be represented as R ( z) = R f ( z z ) + f ( z), (6) si i i= where z i are locations of poles, the pole singularities are copletely included in a properly chosen function f and R si are coefficients, directly connected to residuus of R ( z ). The reaining function f ( z ) is then considered for nuerical integration, possibly also after soe transforations. Function f ust provide that f ( z zi ) dz is convergent. The siplest choice for function f sees to be function i ( z z ). However, this does not lead to the convergence of the integral, as this function behaves in infinity as α. Instead, we considered the function e f ( x) =, (7) x whose priitive function is an exponential integral function, Ei( x ). Further properties of f ( x ) iportant x here are:. its residuu in the pole x = equals one,. its series expansion around infinity is identically equal to, and. for real arguents it is an odd function. Due to the first property, R si is the residuu of R ( z ). Due to the second property, series expansion of f ( z ) at infinity is the sae as of the function R ( z ). This is a very convenient property. Naely, the ajority of techniques for speeding up the integral convergence perfors the expansion of the integrand at infinity. By applying function (7), our ethod enables application of those techniques in an unchanged for. Fig.4. Branch cuts of the reduced reflection coefficient. Fig.. Absolute value of the reduced reflection coefficient in the coplex plane. The ethod of extracting poles fro the integrand is the Function f ( z ) has no poles and is depicted graphically, along the real, α-axis in Fig.5. Although with no poles it is obvious that it is not yet suited for nuerical integration due to its shape at α= (branch cut singularity).
4 4 Telfor Journal, Vol. 6, No., 4. IV. EXTRACTION OF BRANCH CUT SINGULARITIES OF THE INTEGRAND The reaining integrand, f ( z ) has, theoretically, branch cut singularities at points ε ri, i=,,, the first being at α = and the other two very close to α = and α =. Fro Fig.5 and also after the very detailed analysis around points α and α, we did not notice any significant singular behavior of the function. Eliination of those two branch cut singularities could be attributed to the fact that the already extracted poles were located very close to those branch cut singularities and that our extraction of those poles practically eliinated those singularities to. This property, which we observed also for other arrangeents and paraeters of the layered edia as in Fig., is not yet clearly reported or stated in the published work. This eans that only the essential singularity at α = needs to be extracted. This is efficiently and copletely done by the well-known change of variables [9], α= sinθ for < α< and α= ch( t) for α >. The transfored function f is depicted in Figs. 6 and 7. The size of the interval in which this change of variables is applied is not critical. We adopted, soewhat arbitrarily, α<. subintervals of length α=, by the use of different orders of the standard Gauss polynoial integration forula. Fig.8 shows the relative error of integration for:. direct integration of the reduced reflection coefficient, R ( α ),. direct integration after extracting the poles, i.e., direct integration of f ( α ) without the change of variables around α= and. as in point, only after a change of variables around α=. Convergence for the direct integration of R ( α ) is relatively slow. For the first accurate digit, a forula of the order about ust be applied. The fastest convergence, up to errors of about 5 has been achieved by the third ethod, resulting in 5 error of less than for the forula of the 5th order. The convergence of the second ethod is in between. Fig.7. Function f after the change of variables, for α<. Fig.5. Reflection coefficient after extraction of poles (function f ), along the real axis. Relative error.e+.e+.e-.e-.e-.e-4.e-5.e-6.e-7 Integration fro to 4 Integration forula order Fig.8. Relative error of integration. Fig.6. Function f after the change of variables, for α<. V. NUMERICAL RESULTS As a nuerical deonstration of the proposed ethod, the ethod is applied for integration in the interval (,4), in whose radius around a coplex origin all the initial singularities were located. Integration is perfored on VI. CONCLUSION The proposed ethod for extraction of singularities fro the reflection coefficient of the Soerfeld integrals for the ultilayered edia efficiently extracts the coplex poles of the reflection coefficient. As a side effect of the ethod, branch cut singularities are also practically reoved, except for the singularity at point (,) in the coplex plane, which is further reoved by a siple transforation. This enables efficient nuerical integration of the reaining integrand. The ethod does not change the behavior of the reflection coefficient function for large arguents, i.e. does not alter its series expansion around infinity, which could be very useful for further application of ethods for speeding up the convergence of the integral.
5 Petrovic et al.: Singularity Extraction for Reflected Soerfeld Integrals over Multilayered Media 4 REFERENCES [] A. Soerfeld A. "Über die Ausbreitung der Wellen in der Drachtlosen Telegraphie," Ann Phys Leipzig 99; 8 pp [] K. Michalski "Multilayered edia Green s functions in integral equation forulations," IEEE Trans AP 997, Vol. 45, pp [] V.V. Petrovic, A.R. Djordjevic, "General singularity extraction technique for reflected Soerfeld integrals," AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Counications, Vol.6, Sept 7, No.8 pp [4] A.R. Djordjevic, M.B. Bazdar, V.V Petrovic, D.I. Olcan, T.K. Sarkar, R.F. Harrington, Awas for Windows, ver... Analysis of wire antennas and scatterers, user s anual, Boston MA: Artech House;. [5] V.V. Petrovic, A.J.Krneta, B.M.Kolundzija, "Method for Iproving Convergence of the Reflected Soerfeld Integrals for a Multilayered Media," Proc. of Telfor Conference,... [6] J. Wait, Electroagnetic waves in Stratified Media, Oxford University Press, 996. [7] A. Alvarez, Applications of the integral equation technique to the analysis and synthesis of ultilayered printed shielded icrowave circuits and cavity backed antennas, PhD Thesis No.9, EPFL Lausanne 998. [8] D. Djurdjevic, B.D. Popovic, "Entire-doain analysis of thin-wire antennas in layered edia," IEE Proc.-Microw. Antennas Propag., Vol 4, No 4, 996. August. [9] B.D. Popovic, M.B. Dragovic, A.R. Djordjevic Analysis and synthesis of wire antennas and scatterers, Chichester, UK, Research Studies Press (Wiley), 98.
On the Radiation from a Short Current-Carrying Straight Wire Oriented Perpendicular to a Stratified Medium
 Progress In Electroagnetics Research, Vol. 159, 49 57, 17 On the Radiation fro a Short Current-Carrying Straight Wire Oriented Perpendicular to a Stratified Mediu Mauro Parise 1, * and Giulio Antonini
Progress In Electroagnetics Research, Vol. 159, 49 57, 17 On the Radiation fro a Short Current-Carrying Straight Wire Oriented Perpendicular to a Stratified Mediu Mauro Parise 1, * and Giulio Antonini
Electromagnetic scattering. Graduate Course Electrical Engineering (Communications) 1 st Semester, Sharif University of Technology
 Electroagnetic scattering Graduate Course Electrical Engineering (Counications) 1 st Seester, 1388-1389 Sharif University of Technology Contents of lecture 5 Contents of lecture 5: Scattering fro a conductive
Electroagnetic scattering Graduate Course Electrical Engineering (Counications) 1 st Seester, 1388-1389 Sharif University of Technology Contents of lecture 5 Contents of lecture 5: Scattering fro a conductive
SOLUTIONS. PROBLEM 1. The Hamiltonian of the particle in the gravitational field can be written as, x 0, + U(x), U(x) =
 SOLUTIONS PROBLEM 1. The Hailtonian of the particle in the gravitational field can be written as { Ĥ = ˆp2, x 0, + U(x), U(x) = (1) 2 gx, x > 0. The siplest estiate coes fro the uncertainty relation. If
SOLUTIONS PROBLEM 1. The Hailtonian of the particle in the gravitational field can be written as { Ĥ = ˆp2, x 0, + U(x), U(x) = (1) 2 gx, x > 0. The siplest estiate coes fro the uncertainty relation. If
Mutual capacitor and its applications
 Mutual capacitor and its applications Chun Li, Jason Li, Jieing Li CALSON Technologies, Toronto, Canada E-ail: calandli@yahoo.ca Published in The Journal of Engineering; Received on 27th October 2013;
Mutual capacitor and its applications Chun Li, Jason Li, Jieing Li CALSON Technologies, Toronto, Canada E-ail: calandli@yahoo.ca Published in The Journal of Engineering; Received on 27th October 2013;
Symbolic Analysis as Universal Tool for Deriving Properties of Non-linear Algorithms Case study of EM Algorithm
 Acta Polytechnica Hungarica Vol., No., 04 Sybolic Analysis as Universal Tool for Deriving Properties of Non-linear Algoriths Case study of EM Algorith Vladiir Mladenović, Miroslav Lutovac, Dana Porrat
Acta Polytechnica Hungarica Vol., No., 04 Sybolic Analysis as Universal Tool for Deriving Properties of Non-linear Algoriths Case study of EM Algorith Vladiir Mladenović, Miroslav Lutovac, Dana Porrat
2 Q 10. Likewise, in case of multiple particles, the corresponding density in 2 must be averaged over all
 Lecture 6 Introduction to kinetic theory of plasa waves Introduction to kinetic theory So far we have been odeling plasa dynaics using fluid equations. The assuption has been that the pressure can be either
Lecture 6 Introduction to kinetic theory of plasa waves Introduction to kinetic theory So far we have been odeling plasa dynaics using fluid equations. The assuption has been that the pressure can be either
Scattering by a Blade on a Metallic Plane
 UEMG #121474 Scattering by a Blade on a Metallic Plane DANILO ERRICOLO PIERGIORGIO L. E. USLENGHI BADRIA ELNOUR FRANCESCA MIOC QUERY SHEET QY: Au: Please check all artwork throughout article for correctness.
UEMG #121474 Scattering by a Blade on a Metallic Plane DANILO ERRICOLO PIERGIORGIO L. E. USLENGHI BADRIA ELNOUR FRANCESCA MIOC QUERY SHEET QY: Au: Please check all artwork throughout article for correctness.
Electromagnetic fields modeling of power line communication (PLC)
 Electroagnetic fields odeling of power line counication (PLC) Wei Weiqi UROP 3 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang echnological University E-ail: 4794486@ntu.edu.sg Keyword: power line
Electroagnetic fields odeling of power line counication (PLC) Wei Weiqi UROP 3 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang echnological University E-ail: 4794486@ntu.edu.sg Keyword: power line
lecture 37: Linear Multistep Methods: Absolute Stability, Part I lecture 38: Linear Multistep Methods: Absolute Stability, Part II
 lecture 37: Linear Multistep Methods: Absolute Stability, Part I lecture 3: Linear Multistep Methods: Absolute Stability, Part II 5.7 Linear ultistep ethods: absolute stability At this point, it ay well
lecture 37: Linear Multistep Methods: Absolute Stability, Part I lecture 3: Linear Multistep Methods: Absolute Stability, Part II 5.7 Linear ultistep ethods: absolute stability At this point, it ay well
A GENERAL FORM FOR THE ELECTRIC FIELD LINES EQUATION CONCERNING AN AXIALLY SYMMETRIC CONTINUOUS CHARGE DISTRIBUTION
 A GENEAL FOM FO THE ELECTIC FIELD LINES EQUATION CONCENING AN AXIALLY SYMMETIC CONTINUOUS CHAGE DISTIBUTION BY MUGU B. ăuţ Abstract..By using an unexpected approach it results a general for for the electric
A GENEAL FOM FO THE ELECTIC FIELD LINES EQUATION CONCENING AN AXIALLY SYMMETIC CONTINUOUS CHAGE DISTIBUTION BY MUGU B. ăuţ Abstract..By using an unexpected approach it results a general for for the electric
The Weierstrass Approximation Theorem
 36 The Weierstrass Approxiation Theore Recall that the fundaental idea underlying the construction of the real nubers is approxiation by the sipler rational nubers. Firstly, nubers are often deterined
36 The Weierstrass Approxiation Theore Recall that the fundaental idea underlying the construction of the real nubers is approxiation by the sipler rational nubers. Firstly, nubers are often deterined
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines
 Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley ENSIAG 2 / osig 1 Second Seester 2012/2013 Lesson 20 2 ay 2013 Kernel ethods and Support Vector achines Contents Kernel Functions...2 Quadratic
Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley ENSIAG 2 / osig 1 Second Seester 2012/2013 Lesson 20 2 ay 2013 Kernel ethods and Support Vector achines Contents Kernel Functions...2 Quadratic
Anisotropic reference media and the possible linearized approximations for phase velocities of qs waves in weakly anisotropic media
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS D: APPLIED PHYSICS J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 5 00 007 04 PII: S00-770867-6 Anisotropic reference edia and the possible linearized approxiations for phase
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS D: APPLIED PHYSICS J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 5 00 007 04 PII: S00-770867-6 Anisotropic reference edia and the possible linearized approxiations for phase
A Simplified Analytical Approach for Efficiency Evaluation of the Weaving Machines with Automatic Filling Repair
 Proceedings of the 6th SEAS International Conference on Siulation, Modelling and Optiization, Lisbon, Portugal, Septeber -4, 006 0 A Siplified Analytical Approach for Efficiency Evaluation of the eaving
Proceedings of the 6th SEAS International Conference on Siulation, Modelling and Optiization, Lisbon, Portugal, Septeber -4, 006 0 A Siplified Analytical Approach for Efficiency Evaluation of the eaving
Intelligent Systems: Reasoning and Recognition. Perceptrons and Support Vector Machines
 Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley osig 1 Winter Seester 2018 Lesson 6 27 February 2018 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector achines Notation...2 Linear odels...3 Lines, Planes
Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley osig 1 Winter Seester 2018 Lesson 6 27 February 2018 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector achines Notation...2 Linear odels...3 Lines, Planes
P032 3D Seismic Diffraction Modeling in Multilayered Media in Terms of Surface Integrals
 P032 3D Seisic Diffraction Modeling in Multilayered Media in Ters of Surface Integrals A.M. Aizenberg (Institute of Geophysics SB RAS, M. Ayzenberg* (Norwegian University of Science & Technology, H.B.
P032 3D Seisic Diffraction Modeling in Multilayered Media in Ters of Surface Integrals A.M. Aizenberg (Institute of Geophysics SB RAS, M. Ayzenberg* (Norwegian University of Science & Technology, H.B.
Analytical solution for the electric potential in arbitrary anisotropic layered media applying the set of Hankel transforms of integer order
 Geophysical Prospecting, 2006, 54, 651 661 Analytical solution for the electric potential in arbitrary anisotropic layered edia applying the set of Hankel transfors of integer order E. Pervago 1,A.Mousatov
Geophysical Prospecting, 2006, 54, 651 661 Analytical solution for the electric potential in arbitrary anisotropic layered edia applying the set of Hankel transfors of integer order E. Pervago 1,A.Mousatov
Efficient Filter Banks And Interpolators
 Efficient Filter Banks And Interpolators A. G. DEMPSTER AND N. P. MURPHY Departent of Electronic Systes University of Westinster 115 New Cavendish St, London W1M 8JS United Kingdo Abstract: - Graphical
Efficient Filter Banks And Interpolators A. G. DEMPSTER AND N. P. MURPHY Departent of Electronic Systes University of Westinster 115 New Cavendish St, London W1M 8JS United Kingdo Abstract: - Graphical
a a a a a a a m a b a b
 Algebra / Trig Final Exa Study Guide (Fall Seester) Moncada/Dunphy Inforation About the Final Exa The final exa is cuulative, covering Appendix A (A.1-A.5) and Chapter 1. All probles will be ultiple choice
Algebra / Trig Final Exa Study Guide (Fall Seester) Moncada/Dunphy Inforation About the Final Exa The final exa is cuulative, covering Appendix A (A.1-A.5) and Chapter 1. All probles will be ultiple choice
Data-Driven Imaging in Anisotropic Media
 18 th World Conference on Non destructive Testing, 16- April 1, Durban, South Africa Data-Driven Iaging in Anisotropic Media Arno VOLKER 1 and Alan HUNTER 1 TNO Stieltjesweg 1, 6 AD, Delft, The Netherlands
18 th World Conference on Non destructive Testing, 16- April 1, Durban, South Africa Data-Driven Iaging in Anisotropic Media Arno VOLKER 1 and Alan HUNTER 1 TNO Stieltjesweg 1, 6 AD, Delft, The Netherlands
Role of rf electric and magnetic fields in heating of micro-protrusions in accelerating structures. Gregory S. Nusinovich and Thomas M. Antonsen, Jr.
 Role of rf electric and agnetic fields in heating of icro-protrusions in accelerating structures. Gregory S. Nusinovich and Thoas M. Antonsen, Jr. Abstract It is known that high-gradient operation in etallic
Role of rf electric and agnetic fields in heating of icro-protrusions in accelerating structures. Gregory S. Nusinovich and Thoas M. Antonsen, Jr. Abstract It is known that high-gradient operation in etallic
In this chapter, we consider several graph-theoretic and probabilistic models
 THREE ONE GRAPH-THEORETIC AND STATISTICAL MODELS 3.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter, we consider several graph-theoretic and probabilistic odels for a social network, which we do under different assuptions
THREE ONE GRAPH-THEORETIC AND STATISTICAL MODELS 3.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter, we consider several graph-theoretic and probabilistic odels for a social network, which we do under different assuptions
Supplementary Information for Design of Bending Multi-Layer Electroactive Polymer Actuators
 Suppleentary Inforation for Design of Bending Multi-Layer Electroactive Polyer Actuators Bavani Balakrisnan, Alek Nacev, and Elisabeth Sela University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 074 1 Analytical
Suppleentary Inforation for Design of Bending Multi-Layer Electroactive Polyer Actuators Bavani Balakrisnan, Alek Nacev, and Elisabeth Sela University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 074 1 Analytical
Chapter 6 1-D Continuous Groups
 Chapter 6 1-D Continuous Groups Continuous groups consist of group eleents labelled by one or ore continuous variables, say a 1, a 2,, a r, where each variable has a well- defined range. This chapter explores:
Chapter 6 1-D Continuous Groups Continuous groups consist of group eleents labelled by one or ore continuous variables, say a 1, a 2,, a r, where each variable has a well- defined range. This chapter explores:
Anton Bourdine. 1. Introduction. and approximate propagation constants by following simple ratio (Equation (32.22) in [1]):
![Anton Bourdine. 1. Introduction. and approximate propagation constants by following simple ratio (Equation (32.22) in [1]): Anton Bourdine. 1. Introduction. and approximate propagation constants by following simple ratio (Equation (32.22) in [1]):](/thumbs/92/109365953.jpg) Matheatical Probles in Engineering olue 5, Article ID 843, pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/5/843 Research Article Fast and Siple Method for Evaluation of Polarization Correction to Propagation Constant of
Matheatical Probles in Engineering olue 5, Article ID 843, pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/5/843 Research Article Fast and Siple Method for Evaluation of Polarization Correction to Propagation Constant of
Hysteresis model for magnetic materials using the Jiles-Atherton model
 Hysteresis odel for agnetic aterials using the Jiles-Atherton odel Predrag Petrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, pegi@ei.yu Nebojsa itrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, itar@tfc.tfc.kg.ac.yu
Hysteresis odel for agnetic aterials using the Jiles-Atherton odel Predrag Petrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, pegi@ei.yu Nebojsa itrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, itar@tfc.tfc.kg.ac.yu
Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measurement Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES
 Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measureent Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES Belinda Lipa Codar Ocean Sensors 15 La Sandra Way, Portola Valley, CA 98 blipa@pogo.co
Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measureent Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES Belinda Lipa Codar Ocean Sensors 15 La Sandra Way, Portola Valley, CA 98 blipa@pogo.co
Fixed-to-Variable Length Distribution Matching
 Fixed-to-Variable Length Distribution Matching Rana Ali Ajad and Georg Böcherer Institute for Counications Engineering Technische Universität München, Gerany Eail: raa2463@gail.co,georg.boecherer@tu.de
Fixed-to-Variable Length Distribution Matching Rana Ali Ajad and Georg Böcherer Institute for Counications Engineering Technische Universität München, Gerany Eail: raa2463@gail.co,georg.boecherer@tu.de
Hermite s Rule Surpasses Simpson s: in Mathematics Curricula Simpson s Rule. Should be Replaced by Hermite s
 International Matheatical Foru, 4, 9, no. 34, 663-686 Herite s Rule Surpasses Sipson s: in Matheatics Curricula Sipson s Rule Should be Replaced by Herite s Vito Lapret University of Lublana Faculty of
International Matheatical Foru, 4, 9, no. 34, 663-686 Herite s Rule Surpasses Sipson s: in Matheatics Curricula Sipson s Rule Should be Replaced by Herite s Vito Lapret University of Lublana Faculty of
Curious Bounds for Floor Function Sums
 1 47 6 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 1 (018), Article 18.1.8 Curious Bounds for Floor Function Sus Thotsaporn Thanatipanonda and Elaine Wong 1 Science Division Mahidol University International
1 47 6 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 1 (018), Article 18.1.8 Curious Bounds for Floor Function Sus Thotsaporn Thanatipanonda and Elaine Wong 1 Science Division Mahidol University International
EE5900 Spring Lecture 4 IC interconnect modeling methods Zhuo Feng
 EE59 Spring Parallel LSI AD Algoriths Lecture I interconnect odeling ethods Zhuo Feng. Z. Feng MTU EE59 So far we ve considered only tie doain analyses We ll soon see that it is soeties preferable to odel
EE59 Spring Parallel LSI AD Algoriths Lecture I interconnect odeling ethods Zhuo Feng. Z. Feng MTU EE59 So far we ve considered only tie doain analyses We ll soon see that it is soeties preferable to odel
Fast Montgomery-like Square Root Computation over GF(2 m ) for All Trinomials
 Fast Montgoery-like Square Root Coputation over GF( ) for All Trinoials Yin Li a, Yu Zhang a, a Departent of Coputer Science and Technology, Xinyang Noral University, Henan, P.R.China Abstract This letter
Fast Montgoery-like Square Root Coputation over GF( ) for All Trinoials Yin Li a, Yu Zhang a, a Departent of Coputer Science and Technology, Xinyang Noral University, Henan, P.R.China Abstract This letter
Rationality Problems of the Principles of Equivalence and General Relativity
 Rationality Probles of the Principles of Equivalence and General Relativity Mei Xiaochun (Departent of Physics, Fuzhou University, E-ail: xc1@163.co Tel:86-591-8761414) (N.7-B, South Building, Zhongfu
Rationality Probles of the Principles of Equivalence and General Relativity Mei Xiaochun (Departent of Physics, Fuzhou University, E-ail: xc1@163.co Tel:86-591-8761414) (N.7-B, South Building, Zhongfu
New upper bound for the B-spline basis condition number II. K. Scherer. Institut fur Angewandte Mathematik, Universitat Bonn, Bonn, Germany.
 New upper bound for the B-spline basis condition nuber II. A proof of de Boor's 2 -conjecture K. Scherer Institut fur Angewandte Matheati, Universitat Bonn, 535 Bonn, Gerany and A. Yu. Shadrin Coputing
New upper bound for the B-spline basis condition nuber II. A proof of de Boor's 2 -conjecture K. Scherer Institut fur Angewandte Matheati, Universitat Bonn, 535 Bonn, Gerany and A. Yu. Shadrin Coputing
Multi-Scale/Multi-Resolution: Wavelet Transform
 Multi-Scale/Multi-Resolution: Wavelet Transfor Proble with Fourier Fourier analysis -- breaks down a signal into constituent sinusoids of different frequencies. A serious drawback in transforing to the
Multi-Scale/Multi-Resolution: Wavelet Transfor Proble with Fourier Fourier analysis -- breaks down a signal into constituent sinusoids of different frequencies. A serious drawback in transforing to the
Non-Parametric Non-Line-of-Sight Identification 1
 Non-Paraetric Non-Line-of-Sight Identification Sinan Gezici, Hisashi Kobayashi and H. Vincent Poor Departent of Electrical Engineering School of Engineering and Applied Science Princeton University, Princeton,
Non-Paraetric Non-Line-of-Sight Identification Sinan Gezici, Hisashi Kobayashi and H. Vincent Poor Departent of Electrical Engineering School of Engineering and Applied Science Princeton University, Princeton,
lecture 36: Linear Multistep Mehods: Zero Stability
 95 lecture 36: Linear Multistep Mehods: Zero Stability 5.6 Linear ultistep ethods: zero stability Does consistency iply convergence for linear ultistep ethods? This is always the case for one-step ethods,
95 lecture 36: Linear Multistep Mehods: Zero Stability 5.6 Linear ultistep ethods: zero stability Does consistency iply convergence for linear ultistep ethods? This is always the case for one-step ethods,
Ch 12: Variations on Backpropagation
 Ch 2: Variations on Backpropagation The basic backpropagation algorith is too slow for ost practical applications. It ay take days or weeks of coputer tie. We deonstrate why the backpropagation algorith
Ch 2: Variations on Backpropagation The basic backpropagation algorith is too slow for ost practical applications. It ay take days or weeks of coputer tie. We deonstrate why the backpropagation algorith
A Simple Regression Problem
 A Siple Regression Proble R. M. Castro March 23, 2 In this brief note a siple regression proble will be introduced, illustrating clearly the bias-variance tradeoff. Let Y i f(x i ) + W i, i,..., n, where
A Siple Regression Proble R. M. Castro March 23, 2 In this brief note a siple regression proble will be introduced, illustrating clearly the bias-variance tradeoff. Let Y i f(x i ) + W i, i,..., n, where
Feature Extraction Techniques
 Feature Extraction Techniques Unsupervised Learning II Feature Extraction Unsupervised ethods can also be used to find features which can be useful for categorization. There are unsupervised ethods that
Feature Extraction Techniques Unsupervised Learning II Feature Extraction Unsupervised ethods can also be used to find features which can be useful for categorization. There are unsupervised ethods that
Hyperbolic Horn Helical Mass Spectrometer (3HMS) James G. Hagerman Hagerman Technology LLC & Pacific Environmental Technologies April 2005
 Hyperbolic Horn Helical Mass Spectroeter (3HMS) Jaes G Hageran Hageran Technology LLC & Pacific Environental Technologies April 5 ABSTRACT This paper describes a new type of ass filter based on the REFIMS
Hyperbolic Horn Helical Mass Spectroeter (3HMS) Jaes G Hageran Hageran Technology LLC & Pacific Environental Technologies April 5 ABSTRACT This paper describes a new type of ass filter based on the REFIMS
A Study of Electromagnetic Wave Propagation. in the Foam Core Sandwich Structures
 ID-83 A Study of Electroagnetic Wave Propagation in the Foa Core Sandwich Structures H. J. Chun and H. S. Shin School of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering, Yonsei University 34, Shinchon-dong, Seodaeun-gu,
ID-83 A Study of Electroagnetic Wave Propagation in the Foa Core Sandwich Structures H. J. Chun and H. S. Shin School of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering, Yonsei University 34, Shinchon-dong, Seodaeun-gu,
. The univariate situation. It is well-known for a long tie that denoinators of Pade approxiants can be considered as orthogonal polynoials with respe
 PROPERTIES OF MULTIVARIATE HOMOGENEOUS ORTHOGONAL POLYNOMIALS Brahi Benouahane y Annie Cuyt? Keywords Abstract It is well-known that the denoinators of Pade approxiants can be considered as orthogonal
PROPERTIES OF MULTIVARIATE HOMOGENEOUS ORTHOGONAL POLYNOMIALS Brahi Benouahane y Annie Cuyt? Keywords Abstract It is well-known that the denoinators of Pade approxiants can be considered as orthogonal
ON THE TWO-LEVEL PRECONDITIONING IN LEAST SQUARES METHOD
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE YEREVAN STATE UNIVERSITY Physical and Matheatical Sciences 04,, p. 7 5 ON THE TWO-LEVEL PRECONDITIONING IN LEAST SQUARES METHOD M a t h e a t i c s Yu. A. HAKOPIAN, R. Z. HOVHANNISYAN
PROCEEDINGS OF THE YEREVAN STATE UNIVERSITY Physical and Matheatical Sciences 04,, p. 7 5 ON THE TWO-LEVEL PRECONDITIONING IN LEAST SQUARES METHOD M a t h e a t i c s Yu. A. HAKOPIAN, R. Z. HOVHANNISYAN
Model Fitting. CURM Background Material, Fall 2014 Dr. Doreen De Leon
 Model Fitting CURM Background Material, Fall 014 Dr. Doreen De Leon 1 Introduction Given a set of data points, we often want to fit a selected odel or type to the data (e.g., we suspect an exponential
Model Fitting CURM Background Material, Fall 014 Dr. Doreen De Leon 1 Introduction Given a set of data points, we often want to fit a selected odel or type to the data (e.g., we suspect an exponential
Lecture #8-3 Oscillations, Simple Harmonic Motion
 Lecture #8-3 Oscillations Siple Haronic Motion So far we have considered two basic types of otion: translation and rotation. But these are not the only two types of otion we can observe in every day life.
Lecture #8-3 Oscillations Siple Haronic Motion So far we have considered two basic types of otion: translation and rotation. But these are not the only two types of otion we can observe in every day life.
Some Perspective. Forces and Newton s Laws
 Soe Perspective The language of Kineatics provides us with an efficient ethod for describing the otion of aterial objects, and we ll continue to ake refineents to it as we introduce additional types of
Soe Perspective The language of Kineatics provides us with an efficient ethod for describing the otion of aterial objects, and we ll continue to ake refineents to it as we introduce additional types of
Modeling of Low Power Multilayer Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser
 International Journal of Optics and Applications 15, 5(5): 155-16 DOI: 1.593/j.optics.1555.3 Modeling of Low Power Multilayer Vertical Cavity Surface Eitting Laser Shashad Akther Khan *, M. A. Hasnayeen
International Journal of Optics and Applications 15, 5(5): 155-16 DOI: 1.593/j.optics.1555.3 Modeling of Low Power Multilayer Vertical Cavity Surface Eitting Laser Shashad Akther Khan *, M. A. Hasnayeen
Scattering and bound states
 Chapter Scattering and bound states In this chapter we give a review of quantu-echanical scattering theory. We focus on the relation between the scattering aplitude of a potential and its bound states
Chapter Scattering and bound states In this chapter we give a review of quantu-echanical scattering theory. We focus on the relation between the scattering aplitude of a potential and its bound states
A NEW ELECTROSTATIC FIELD GEOMETRY. Jerry E. Bayles
 INTRODUCTION A NEW ELECTROSTATIC FIELD GEOMETRY by Jerry E Bayles The purpose of this paper is to present the electrostatic field in geoetrical ters siilar to that of the electrogravitational equation
INTRODUCTION A NEW ELECTROSTATIC FIELD GEOMETRY by Jerry E Bayles The purpose of this paper is to present the electrostatic field in geoetrical ters siilar to that of the electrogravitational equation
13 Harmonic oscillator revisited: Dirac s approach and introduction to Second Quantization
 3 Haronic oscillator revisited: Dirac s approach and introduction to Second Quantization. Dirac cae up with a ore elegant way to solve the haronic oscillator proble. We will now study this approach. The
3 Haronic oscillator revisited: Dirac s approach and introduction to Second Quantization. Dirac cae up with a ore elegant way to solve the haronic oscillator proble. We will now study this approach. The
Physics 2107 Oscillations using Springs Experiment 2
 PY07 Oscillations using Springs Experient Physics 07 Oscillations using Springs Experient Prelab Read the following bacground/setup and ensure you are failiar with the concepts and theory required for
PY07 Oscillations using Springs Experient Physics 07 Oscillations using Springs Experient Prelab Read the following bacground/setup and ensure you are failiar with the concepts and theory required for
In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenomena. We will study the following topics:
 Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will study the following topics: Types of waves Aplitude, phase, frequency, period, propagation speed of a wave Mechanical
Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will study the following topics: Types of waves Aplitude, phase, frequency, period, propagation speed of a wave Mechanical
72. (30.2) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires.
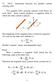 7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
Dispersive power. of Prism
 Dispersive power of Pris 1 Dispersive Power of Pris Experient No. Object : To deterine the dispersive power of the aterial of a pris by spectroeter. Apparatus : Spectroeter, pris, spirit level, reading
Dispersive power of Pris 1 Dispersive Power of Pris Experient No. Object : To deterine the dispersive power of the aterial of a pris by spectroeter. Apparatus : Spectroeter, pris, spirit level, reading
This model assumes that the probability of a gap has size i is proportional to 1/i. i.e., i log m e. j=1. E[gap size] = i P r(i) = N f t.
![This model assumes that the probability of a gap has size i is proportional to 1/i. i.e., i log m e. j=1. E[gap size] = i P r(i) = N f t. This model assumes that the probability of a gap has size i is proportional to 1/i. i.e., i log m e. j=1. E[gap size] = i P r(i) = N f t.](/thumbs/73/69472191.jpg) CS 493: Algoriths for Massive Data Sets Feb 2, 2002 Local Models, Bloo Filter Scribe: Qin Lv Local Models In global odels, every inverted file entry is copressed with the sae odel. This work wells when
CS 493: Algoriths for Massive Data Sets Feb 2, 2002 Local Models, Bloo Filter Scribe: Qin Lv Local Models In global odels, every inverted file entry is copressed with the sae odel. This work wells when
Force and dynamics with a spring, analytic approach
 Force and dynaics with a spring, analytic approach It ay strie you as strange that the first force we will discuss will be that of a spring. It is not one of the four Universal forces and we don t use
Force and dynaics with a spring, analytic approach It ay strie you as strange that the first force we will discuss will be that of a spring. It is not one of the four Universal forces and we don t use
Reducing Vibration and Providing Robustness with Multi-Input Shapers
 29 Aerican Control Conference Hyatt Regency Riverfront, St. Louis, MO, USA June -2, 29 WeA6.4 Reducing Vibration and Providing Robustness with Multi-Input Shapers Joshua Vaughan and Willia Singhose Abstract
29 Aerican Control Conference Hyatt Regency Riverfront, St. Louis, MO, USA June -2, 29 WeA6.4 Reducing Vibration and Providing Robustness with Multi-Input Shapers Joshua Vaughan and Willia Singhose Abstract
ORIGAMI CONSTRUCTIONS OF RINGS OF INTEGERS OF IMAGINARY QUADRATIC FIELDS
 #A34 INTEGERS 17 (017) ORIGAMI CONSTRUCTIONS OF RINGS OF INTEGERS OF IMAGINARY QUADRATIC FIELDS Jürgen Kritschgau Departent of Matheatics, Iowa State University, Aes, Iowa jkritsch@iastateedu Adriana Salerno
#A34 INTEGERS 17 (017) ORIGAMI CONSTRUCTIONS OF RINGS OF INTEGERS OF IMAGINARY QUADRATIC FIELDS Jürgen Kritschgau Departent of Matheatics, Iowa State University, Aes, Iowa jkritsch@iastateedu Adriana Salerno
Page 1 Lab 1 Elementary Matrix and Linear Algebra Spring 2011
 Page Lab Eleentary Matri and Linear Algebra Spring 0 Nae Due /03/0 Score /5 Probles through 4 are each worth 4 points.. Go to the Linear Algebra oolkit site ransforing a atri to reduced row echelon for
Page Lab Eleentary Matri and Linear Algebra Spring 0 Nae Due /03/0 Score /5 Probles through 4 are each worth 4 points.. Go to the Linear Algebra oolkit site ransforing a atri to reduced row echelon for
( ). One set of terms has a ω in
 Laptag Class Notes W. Gekelan Cold Plasa Dispersion relation Suer Let us go back to a single particle and see how it behaves in a high frequency electric field. We will use the force equation and Maxwell
Laptag Class Notes W. Gekelan Cold Plasa Dispersion relation Suer Let us go back to a single particle and see how it behaves in a high frequency electric field. We will use the force equation and Maxwell
HIGH RESOLUTION NEAR-FIELD MULTIPLE TARGET DETECTION AND LOCALIZATION USING SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES
 ICONIC 2007 St. Louis, O, USA June 27-29, 2007 HIGH RESOLUTION NEAR-FIELD ULTIPLE TARGET DETECTION AND LOCALIZATION USING SUPPORT VECTOR ACHINES A. Randazzo,. A. Abou-Khousa 2,.Pastorino, and R. Zoughi
ICONIC 2007 St. Louis, O, USA June 27-29, 2007 HIGH RESOLUTION NEAR-FIELD ULTIPLE TARGET DETECTION AND LOCALIZATION USING SUPPORT VECTOR ACHINES A. Randazzo,. A. Abou-Khousa 2,.Pastorino, and R. Zoughi
Rational Filter Wavelets*
 Ž Journal of Matheatical Analysis and Applications 39, 744 1999 Article ID jaa19996550, available online at http:wwwidealibraryco on Rational Filter Wavelets* Kuang Zheng and Cui Minggen Departent of Matheatics,
Ž Journal of Matheatical Analysis and Applications 39, 744 1999 Article ID jaa19996550, available online at http:wwwidealibraryco on Rational Filter Wavelets* Kuang Zheng and Cui Minggen Departent of Matheatics,
Engineering of Composite Media for Shields at Microwave Frequencies
 Engineering of Coposite Media for Shields at Microwave Frequencies Marina Koledintseva, Poorna Chander avva, ichard DuBroff, Jaes Drewniak EMC Laboratory, ECE Departent, University of Missouri-olla, olla,
Engineering of Coposite Media for Shields at Microwave Frequencies Marina Koledintseva, Poorna Chander avva, ichard DuBroff, Jaes Drewniak EMC Laboratory, ECE Departent, University of Missouri-olla, olla,
About the definition of parameters and regimes of active two-port networks with variable loads on the basis of projective geometry
 About the definition of paraeters and regies of active two-port networks with variable loads on the basis of projective geoetry PENN ALEXANDR nstitute of Electronic Engineering and Nanotechnologies "D
About the definition of paraeters and regies of active two-port networks with variable loads on the basis of projective geoetry PENN ALEXANDR nstitute of Electronic Engineering and Nanotechnologies "D
3D acoustic wave modeling with a time-space domain dispersion-relation-based Finite-difference scheme
 P-8 3D acoustic wave odeling with a tie-space doain dispersion-relation-based Finite-difference schee Yang Liu * and rinal K. Sen State Key Laboratory of Petroleu Resource and Prospecting (China University
P-8 3D acoustic wave odeling with a tie-space doain dispersion-relation-based Finite-difference schee Yang Liu * and rinal K. Sen State Key Laboratory of Petroleu Resource and Prospecting (China University
J. Electrical Systems x-x (xxx): x-xx. Regular paper. Reflected Signal on a Nonuniform Overhead Transmission Line at High Frequency
 A. Boudjeaa S. Tahi B. Bennaane T. B. Berbar B. Lehouidj J. Electrical Systes x-x (xxx): x-xx Regular paper Reflected Signal on a Nonunifor Overhead Transission Line at High Frequency The effect of the
A. Boudjeaa S. Tahi B. Bennaane T. B. Berbar B. Lehouidj J. Electrical Systes x-x (xxx): x-xx Regular paper Reflected Signal on a Nonunifor Overhead Transission Line at High Frequency The effect of the
Extraordinary Optical Transmission Induced by Excitation of a Magnetic Plasmon Propagation Mode in a Diatomic Chain of Slit-hole Resonators
 Extraordinary Optical Transission Induced by Excitation of a Magnetic Plason Propagation Mode in a Diatoic Chain of Slit-hole Resonators H. Liu 1, *, T. Li 1, Q. J. Wang 1, Z. H. Zhu 1, S. M. Wang 1, J.
Extraordinary Optical Transission Induced by Excitation of a Magnetic Plason Propagation Mode in a Diatoic Chain of Slit-hole Resonators H. Liu 1, *, T. Li 1, Q. J. Wang 1, Z. H. Zhu 1, S. M. Wang 1, J.
On the Mixed Discretization of the Time Domain Magnetic Field Integral Equation
 On the Mixed Discretization of the Tie Doain Magnetic Field Integral Equation H. A. Ülkü 1 I. Bogaert K. Cools 3 F. P. Andriulli 4 H. Bağ 1 Abstract Tie doain agnetic field integral equation (MFIE) is
On the Mixed Discretization of the Tie Doain Magnetic Field Integral Equation H. A. Ülkü 1 I. Bogaert K. Cools 3 F. P. Andriulli 4 H. Bağ 1 Abstract Tie doain agnetic field integral equation (MFIE) is
Iterative Decoding of LDPC Codes over the q-ary Partial Erasure Channel
 1 Iterative Decoding of LDPC Codes over the q-ary Partial Erasure Channel Rai Cohen, Graduate Student eber, IEEE, and Yuval Cassuto, Senior eber, IEEE arxiv:1510.05311v2 [cs.it] 24 ay 2016 Abstract In
1 Iterative Decoding of LDPC Codes over the q-ary Partial Erasure Channel Rai Cohen, Graduate Student eber, IEEE, and Yuval Cassuto, Senior eber, IEEE arxiv:1510.05311v2 [cs.it] 24 ay 2016 Abstract In
Lectures 8 & 9: The Z-transform.
 Lectures 8 & 9: The Z-transfor. 1. Definitions. The Z-transfor is defined as a function series (a series in which each ter is a function of one or ore variables: Z[] where is a C valued function f : N
Lectures 8 & 9: The Z-transfor. 1. Definitions. The Z-transfor is defined as a function series (a series in which each ter is a function of one or ore variables: Z[] where is a C valued function f : N
Antenna Saturation Effects on MIMO Capacity
 Antenna Saturation Effects on MIMO Capacity T S Pollock, T D Abhayapala, and R A Kennedy National ICT Australia Research School of Inforation Sciences and Engineering The Australian National University,
Antenna Saturation Effects on MIMO Capacity T S Pollock, T D Abhayapala, and R A Kennedy National ICT Australia Research School of Inforation Sciences and Engineering The Australian National University,
7. Renormalization and universality in pionless EFT
 Renoralization and universality in pionless EFT (last revised: October 6, 04) 7 7. Renoralization and universality in pionless EFT Recall the scales of nuclear forces fro Section 5: Pionless EFT is applicable
Renoralization and universality in pionless EFT (last revised: October 6, 04) 7 7. Renoralization and universality in pionless EFT Recall the scales of nuclear forces fro Section 5: Pionless EFT is applicable
IN A SENSE, every material is a composite, even if the
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1999 2075 Magnetis fro Conductors and Enhanced Nonlinear Phenoena J. B. Pendry, A. J. Holden, D. J. Robbins, and W. J. Stewart,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1999 2075 Magnetis fro Conductors and Enhanced Nonlinear Phenoena J. B. Pendry, A. J. Holden, D. J. Robbins, and W. J. Stewart,
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechanics Physics 5 Lecture Oscillations (Chapter 6) What We Did Last Tie Analyzed the otion of a heavy top Reduced into -diensional proble of θ Qualitative behavior Precession + nutation Initial condition
Mechanics Physics 5 Lecture Oscillations (Chapter 6) What We Did Last Tie Analyzed the otion of a heavy top Reduced into -diensional proble of θ Qualitative behavior Precession + nutation Initial condition
A Better Algorithm For an Ancient Scheduling Problem. David R. Karger Steven J. Phillips Eric Torng. Department of Computer Science
 A Better Algorith For an Ancient Scheduling Proble David R. Karger Steven J. Phillips Eric Torng Departent of Coputer Science Stanford University Stanford, CA 9435-4 Abstract One of the oldest and siplest
A Better Algorith For an Ancient Scheduling Proble David R. Karger Steven J. Phillips Eric Torng Departent of Coputer Science Stanford University Stanford, CA 9435-4 Abstract One of the oldest and siplest
DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS *
 IJST, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. M1, pp 89-100 Printed in The Islaic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shira University DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS
IJST, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. M1, pp 89-100 Printed in The Islaic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shira University DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS
MAKE SURE TA & TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START
 Laboratory Section: Last Revised on Deceber 15, 2014 Partners Naes: Grade: EXPERIMENT 8 Electron Beas 0. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. Nae the 2 forces that are equated in order to derive the charge to
Laboratory Section: Last Revised on Deceber 15, 2014 Partners Naes: Grade: EXPERIMENT 8 Electron Beas 0. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. Nae the 2 forces that are equated in order to derive the charge to
The Failure of Coaxial TEM Cells ASTM Standards Methods In H.F. Range
 The Failure of Coaxial TEM Cells ASTM Standards Methods In H.F. Range Mihai Badic HV/EMC Laboratory, Research Institute for Electrical Engineering - ICPE Bucharest, ROMAN badic@icpe.ro Mihai-Jo Marinescu
The Failure of Coaxial TEM Cells ASTM Standards Methods In H.F. Range Mihai Badic HV/EMC Laboratory, Research Institute for Electrical Engineering - ICPE Bucharest, ROMAN badic@icpe.ro Mihai-Jo Marinescu
Fairness via priority scheduling
 Fairness via priority scheduling Veeraruna Kavitha, N Heachandra and Debayan Das IEOR, IIT Bobay, Mubai, 400076, India vavitha,nh,debayan}@iitbacin Abstract In the context of ulti-agent resource allocation
Fairness via priority scheduling Veeraruna Kavitha, N Heachandra and Debayan Das IEOR, IIT Bobay, Mubai, 400076, India vavitha,nh,debayan}@iitbacin Abstract In the context of ulti-agent resource allocation
Optical Properties of Plasmas of High-Z Elements
 Forschungszentru Karlsruhe Techni und Uwelt Wissenschaftlishe Berichte FZK Optical Properties of Plasas of High-Z Eleents V.Tolach 1, G.Miloshevsy 1, H.Würz Project Kernfusion 1 Heat and Mass Transfer
Forschungszentru Karlsruhe Techni und Uwelt Wissenschaftlishe Berichte FZK Optical Properties of Plasas of High-Z Eleents V.Tolach 1, G.Miloshevsy 1, H.Würz Project Kernfusion 1 Heat and Mass Transfer
Extension of CSRSM for the Parametric Study of the Face Stability of Pressurized Tunnels
 Extension of CSRSM for the Paraetric Study of the Face Stability of Pressurized Tunnels Guilhe Mollon 1, Daniel Dias 2, and Abdul-Haid Soubra 3, M.ASCE 1 LGCIE, INSA Lyon, Université de Lyon, Doaine scientifique
Extension of CSRSM for the Paraetric Study of the Face Stability of Pressurized Tunnels Guilhe Mollon 1, Daniel Dias 2, and Abdul-Haid Soubra 3, M.ASCE 1 LGCIE, INSA Lyon, Université de Lyon, Doaine scientifique
Time-of-flight Identification of Ions in CESR and ERL
 Tie-of-flight Identification of Ions in CESR and ERL Eric Edwards Departent of Physics, University of Alabaa, Tuscaloosa, AL, 35486 (Dated: August 8, 2008) The accuulation of ion densities in the bea pipe
Tie-of-flight Identification of Ions in CESR and ERL Eric Edwards Departent of Physics, University of Alabaa, Tuscaloosa, AL, 35486 (Dated: August 8, 2008) The accuulation of ion densities in the bea pipe
Inspection; structural health monitoring; reliability; Bayesian analysis; updating; decision analysis; value of information
 Cite as: Straub D. (2014). Value of inforation analysis with structural reliability ethods. Structural Safety, 49: 75-86. Value of Inforation Analysis with Structural Reliability Methods Daniel Straub
Cite as: Straub D. (2014). Value of inforation analysis with structural reliability ethods. Structural Safety, 49: 75-86. Value of Inforation Analysis with Structural Reliability Methods Daniel Straub
MA304 Differential Geometry
 MA304 Differential Geoetry Hoework 4 solutions Spring 018 6% of the final ark 1. The paraeterised curve αt = t cosh t for t R is called the catenary. Find the curvature of αt. Solution. Fro hoework question
MA304 Differential Geoetry Hoework 4 solutions Spring 018 6% of the final ark 1. The paraeterised curve αt = t cosh t for t R is called the catenary. Find the curvature of αt. Solution. Fro hoework question
Supporting Information for Supression of Auger Processes in Confined Structures
 Supporting Inforation for Supression of Auger Processes in Confined Structures George E. Cragg and Alexander. Efros Naval Research aboratory, Washington, DC 20375, USA 1 Solution of the Coupled, Two-band
Supporting Inforation for Supression of Auger Processes in Confined Structures George E. Cragg and Alexander. Efros Naval Research aboratory, Washington, DC 20375, USA 1 Solution of the Coupled, Two-band
A Note on the Applied Use of MDL Approximations
 A Note on the Applied Use of MDL Approxiations Daniel J. Navarro Departent of Psychology Ohio State University Abstract An applied proble is discussed in which two nested psychological odels of retention
A Note on the Applied Use of MDL Approxiations Daniel J. Navarro Departent of Psychology Ohio State University Abstract An applied proble is discussed in which two nested psychological odels of retention
Dr. Naser Abu-Zaid; Lecture notes in electromagnetic theory 1; Referenced to Engineering electromagnetics by Hayt, 8 th edition 2012; Text Book
 Text Book Dr. Naser Abu-Zaid Page 1 9/4/2012 Course syllabus Electroagnetic 2 (63374) Seester Language Copulsory / Elective Prerequisites Course Contents Course Objectives Learning Outcoes and Copetences
Text Book Dr. Naser Abu-Zaid Page 1 9/4/2012 Course syllabus Electroagnetic 2 (63374) Seester Language Copulsory / Elective Prerequisites Course Contents Course Objectives Learning Outcoes and Copetences
Chaotic Coupled Map Lattices
 Chaotic Coupled Map Lattices Author: Dustin Keys Advisors: Dr. Robert Indik, Dr. Kevin Lin 1 Introduction When a syste of chaotic aps is coupled in a way that allows the to share inforation about each
Chaotic Coupled Map Lattices Author: Dustin Keys Advisors: Dr. Robert Indik, Dr. Kevin Lin 1 Introduction When a syste of chaotic aps is coupled in a way that allows the to share inforation about each
This is a repository copy of Analytical optimisation of electromagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance motor.
 This is a repository copy of Analytical optiisation of electroagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance otor. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/907/
This is a repository copy of Analytical optiisation of electroagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance otor. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/907/
CHAPTER 4 TWO STANDARD SHORTCUTS USED TO TRANSFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC EQUATIONS 4.1 THE FREE-PARAMETER METHOD
 CHAPTER 4 TWO STANDARD SHORTCUTS USED TO TRANSFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC EQUATIONS The last several chapters have explained how the standard rules for changing units apply to electroagnetic physical quantities.
CHAPTER 4 TWO STANDARD SHORTCUTS USED TO TRANSFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC EQUATIONS The last several chapters have explained how the standard rules for changing units apply to electroagnetic physical quantities.
13.2 Fully Polynomial Randomized Approximation Scheme for Permanent of Random 0-1 Matrices
 CS71 Randoness & Coputation Spring 018 Instructor: Alistair Sinclair Lecture 13: February 7 Disclaier: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny accorded to foral publications. They ay
CS71 Randoness & Coputation Spring 018 Instructor: Alistair Sinclair Lecture 13: February 7 Disclaier: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny accorded to foral publications. They ay
P (t) = P (t = 0) + F t Conclusion: If we wait long enough, the velocity of an electron will diverge, which is obviously impossible and wrong.
 4 Phys520.nb 2 Drude theory ~ Chapter in textbook 2.. The relaxation tie approxiation Here we treat electrons as a free ideal gas (classical) 2... Totally ignore interactions/scatterings Under a static
4 Phys520.nb 2 Drude theory ~ Chapter in textbook 2.. The relaxation tie approxiation Here we treat electrons as a free ideal gas (classical) 2... Totally ignore interactions/scatterings Under a static
Comparison of Stability of Selected Numerical Methods for Solving Stiff Semi- Linear Differential Equations
 International Journal of Applied Science and Technology Vol. 7, No. 3, Septeber 217 Coparison of Stability of Selected Nuerical Methods for Solving Stiff Sei- Linear Differential Equations Kwaku Darkwah
International Journal of Applied Science and Technology Vol. 7, No. 3, Septeber 217 Coparison of Stability of Selected Nuerical Methods for Solving Stiff Sei- Linear Differential Equations Kwaku Darkwah
Descent polynomials. Mohamed Omar Department of Mathematics, Harvey Mudd College, 301 Platt Boulevard, Claremont, CA , USA,
 Descent polynoials arxiv:1710.11033v2 [ath.co] 13 Nov 2017 Alexander Diaz-Lopez Departent of Matheatics and Statistics, Villanova University, 800 Lancaster Avenue, Villanova, PA 19085, USA, alexander.diaz-lopez@villanova.edu
Descent polynoials arxiv:1710.11033v2 [ath.co] 13 Nov 2017 Alexander Diaz-Lopez Departent of Matheatics and Statistics, Villanova University, 800 Lancaster Avenue, Villanova, PA 19085, USA, alexander.diaz-lopez@villanova.edu
Physics 215 Winter The Density Matrix
 Physics 215 Winter 2018 The Density Matrix The quantu space of states is a Hilbert space H. Any state vector ψ H is a pure state. Since any linear cobination of eleents of H are also an eleent of H, it
Physics 215 Winter 2018 The Density Matrix The quantu space of states is a Hilbert space H. Any state vector ψ H is a pure state. Since any linear cobination of eleents of H are also an eleent of H, it
DESIGN OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS HAVING MAXIMALLY FLAT RESPONSE AT LOW FREQUENCIES
 DESIGN OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS HAVING MAXIMALLY FLAT RESPONSE AT LOW FREQUENCIES V.Raachran, Ravi P.Raachran C.S.Gargour Departent of Electrical Coputer Engineering, Concordia University, Montreal, QC, CANADA,
DESIGN OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS HAVING MAXIMALLY FLAT RESPONSE AT LOW FREQUENCIES V.Raachran, Ravi P.Raachran C.S.Gargour Departent of Electrical Coputer Engineering, Concordia University, Montreal, QC, CANADA,
Keywords: Estimator, Bias, Mean-squared error, normality, generalized Pareto distribution
 Testing approxiate norality of an estiator using the estiated MSE and bias with an application to the shape paraeter of the generalized Pareto distribution J. Martin van Zyl Abstract In this work the norality
Testing approxiate norality of an estiator using the estiated MSE and bias with an application to the shape paraeter of the generalized Pareto distribution J. Martin van Zyl Abstract In this work the norality
Interferometry in dissipative media: Addressing the shallow sea problem for Seabed Logging applications
 Evert Slob and Kees Wapenaar, Departent of Geotechnology, Delft University of Technology Roel Snieder, Center for Wave Phenoena and Departent of Geophysics, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY We derive interferoetric
Evert Slob and Kees Wapenaar, Departent of Geotechnology, Delft University of Technology Roel Snieder, Center for Wave Phenoena and Departent of Geophysics, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY We derive interferoetric
KONINKL. NEDERL. AKADEMIE VAN WETENSCHAPPEN AMSTERDAM Reprinted from Proceedings, Series A, 61, No. 1 and Indag. Math., 20, No.
 KONINKL. NEDERL. AKADEMIE VAN WETENSCHAPPEN AMSTERDAM Reprinted fro Proceedings, Series A, 6, No. and Indag. Math., 20, No., 95 8 MATHEMATIC S ON SEQUENCES OF INTEGERS GENERATED BY A SIEVIN G PROCES S
KONINKL. NEDERL. AKADEMIE VAN WETENSCHAPPEN AMSTERDAM Reprinted fro Proceedings, Series A, 6, No. and Indag. Math., 20, No., 95 8 MATHEMATIC S ON SEQUENCES OF INTEGERS GENERATED BY A SIEVIN G PROCES S
