Dispersion. February 12, 2014
|
|
|
- Leonard Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dispersion February 1, 014 In aterials, the dielectric constant and pereability are actually frequency dependent. This does not affect our results for single frequency odes, but when we have a superposition of frequencies it leads to dispersion. We begin with a siple odel for this behavior. The variation of the pereability is often quite weak, and we ay take µ = µ 0. Frequency dependence of the perittivity Recall that our earlier treatent of the dielectric constant began with electric dipole oent produced by a static electric field E in the presence of a linear restoring force, F = 0x, to produce a olecular polarization p ol = ex = ee 0 Then, if there are N olecules per unit volue with Z electrons per olecule, the dipole oent per unit volue is P = NZp ol χ e E so that Next, using χ e = NZe 0 D = E + P E = E + χ e E the dielectric constant is = 1 + χ e = 1 + NZe 0 This result changes when there is tie dependence to the electric field, with the dielectric constant showing frequency dependence. Suppose the aterial is sufficiently diffuse that the applied electric field is about equal to the electric field at each ato, and that the response of the atoic electrons ay be odeled as haronic. Again let x represent the displaceent of the charge fro equilibriu, and include daping, so that now we have [ ẍ + γẋ + 0x ] = ee x, t) 1
2 We assue everything here negligible agnetic effects, low-aplitude oscillations. enough to give iportant general features. Let the electric field vary haronically, E = E x) e it then the position of the electron with have the sae tie dependence, so and the electric dipole oent is [ iγ + 0] x = ee x) p = ex = e E 0 iγ) The odel is still Let there be N olecules per unit volue with Z electrons per olecule, with a fraction f i of the electrons having binding frequency i0 and daping γ i. This is reasonable since the different electrons in each olcule are bound differently to the nucleus. The total of all the f i should be the total nuber of electrons, i f i = Z. The dipole oent for each olecule is then p ol = i f i e i0 iγ i ) E Then, since the total dipole oent per unit volue is P = Np ol = χ e E, we have i Nf i e i0 iγ i ) E = χ e E Now, using D = E = E + P = E + χ e E, the dielectric constant is = 1 + χ e = 1 + N f i e i0 iγ i ) = 1 + Ne f i i0 iγ i This expression is accurate if f i, i0 and γ i are found quantu echanically. Anoolous dispersion and resonant absorption The frequency dependence of the dielectric constant has certain regular properties. iaginary parts, we have = + Ne = + Ne Re = + Ne I = Ne f i i0 iγ i ) f i i0 + iγ i i0 ) + γ i f i i0 ) i0 ) + γi f i γ i i0 ) + γ i Separating real and
3 and we note that the daping constant γ i is usually sall. At low frequencies, < i0 for all i, each ter in the real part of is positive and >. As the frequency increases, ore and ore of the ters becoe negative, until at high frequency, Re = Ne f i i0 i0 ) + γi and <. The real and iaginary parts of have peaks whenever is near one of the resonant frequencies, i0, of the olecule. At these frequencies, the corresponding ter of the denoinator becoes i0 ) + γ i γ i which is very sall but larger the higher the driving frequency). This produces a resonance peak in the iaginary part of, but since the ter is also changing sign in the real part, the peak is double positive for < i0 and negative once > i0. At these peaks, the aterial is absorbing energy fro the field the daping γ i plays an iportant role. The effect is easily seen fro the wave vector k. Suppose we have a plane wave travelling in the z direction, E = Ee ikz t), which passes near a resonant ato. Then k = µ Re + ii = µ 0 0 Re + ii Then, setting = c ε 0 k β + 1 iα we have β + 1 iα = c β + iαβ 1 4 α = c Re + ii ε 0 Re + ii ) so that and the electric field is given by β 1 4 α = c Re αβ = c I E = Ee ikz t) = Ee 1 αz e iβz t) The intensity of the wave, which varies as E then falls off as e αz 3
4 and α is called the attenuation constant. We see that the attenuation is larger near each resonant frequency, i0, where we expect the radiation to be exciting the electrons of the olecule. Relating this back to the resonance behavior, with α β, β β 1 4 α = c Re α = c β I I c Re Suppose, for siplicity, we have only a single resonance. Then with 0 so the attenuation constant is approxiately Re = 1 + Ne 0 0 ) + γ 1 I = Ne γ 0 ) + γ Ne γ α = Conductivity and low frequency behavior Ne c γ In a conductor there are free electrons. Since these have no restoring force, they ay be thought of as having a resonance frequency of zero. This akes the response of conductors at low frequency very different fro that of insulators. For insulators, the lowest resonant frequency is 10 > 0 and the equations above give a good approxiation to the actual response. For conductors, there is a very strong response at zero frequency. Consider the fraction of free electrons, f 0, separately, writing = + Ne = + Ne f i i0 iγ i f i i0 + Ne f 0 iγ i iγ 0 i 0 Ne f 0 = b + i γ 0 i) To see what is happening in ters of conduction, consider the Maxwell equation involving current, H D t = J We copare two different ways of handling this expression. First, let b be real so that if there are any other resonances they are far enough away in frequency to be negligible), and assue the ediu satisfies Oh s law, J = σe 4
5 Then, with the haronic applied field and a real dielectric constant, b, we would have H be) t = σe H + i b E = σe H = σ i b ) E = i b + iσ ) E Now copare this to the result without current but with the conduction electrons included in the dielectric constant. Then we have instead H D = 0 t H = ie Ne ) f 0 = i b + i E γ 0 i) Coparing the two expressions, we see that the effect of the zero-frequency resonance is the sae as a conductivity σ given by iσ Ne f 0 = i γ 0 i) σ = Ne f 0 γ 0 i) a result produced in 1900 by Drude. It requires substantial correction because the free electrons actually for a Feri gas. High frequency We expand our expression for the dielectric constant for i0 for all i. The denoinator is approxiately i0 iγ i and we have = + Ne Ne fi f i i0 iγ i Replacing the su over fractions by the atoic nuber, f i = Z, where = 1 NZe = 1 p p = NZe is called the plasa frequency. The plasa frequency depends only on NZ, the total nuber of electrons in the syste. Cobining with the wave nuber k, we have k = µε 5
6 k = 1 c = c 1 p ) so that = k c + p This provides a dispersion relation, k), for plasas. We will explore ore about dispersion relations soon. Exaple: Water Jackson has collected all available data to the date of first publication, anyway) on the index of refraction and attenuation coefficient of water as functions of frequency. The graphs on page 315 are fascinating! Take soe tie to digest what is going on. The window in the visible range is particularly interesting. 6
Q5 We know that a mass at the end of a spring when displaced will perform simple m harmonic oscillations with a period given by T = 2!
 Chapter 4.1 Q1 n oscillation is any otion in which the displaceent of a particle fro a fixed point keeps changing direction and there is a periodicity in the otion i.e. the otion repeats in soe way. In
Chapter 4.1 Q1 n oscillation is any otion in which the displaceent of a particle fro a fixed point keeps changing direction and there is a periodicity in the otion i.e. the otion repeats in soe way. In
13 Harmonic oscillator revisited: Dirac s approach and introduction to Second Quantization
 3 Haronic oscillator revisited: Dirac s approach and introduction to Second Quantization. Dirac cae up with a ore elegant way to solve the haronic oscillator proble. We will now study this approach. The
3 Haronic oscillator revisited: Dirac s approach and introduction to Second Quantization. Dirac cae up with a ore elegant way to solve the haronic oscillator proble. We will now study this approach. The
Chapter 1: Basics of Vibrations for Simple Mechanical Systems
 Chapter 1: Basics of Vibrations for Siple Mechanical Systes Introduction: The fundaentals of Sound and Vibrations are part of the broader field of echanics, with strong connections to classical echanics,
Chapter 1: Basics of Vibrations for Siple Mechanical Systes Introduction: The fundaentals of Sound and Vibrations are part of the broader field of echanics, with strong connections to classical echanics,
Lecture #8-3 Oscillations, Simple Harmonic Motion
 Lecture #8-3 Oscillations Siple Haronic Motion So far we have considered two basic types of otion: translation and rotation. But these are not the only two types of otion we can observe in every day life.
Lecture #8-3 Oscillations Siple Haronic Motion So far we have considered two basic types of otion: translation and rotation. But these are not the only two types of otion we can observe in every day life.
In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenomena. We will study the following topics:
 Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will study the following topics: Types of waves Aplitude, phase, frequency, period, propagation speed of a wave Mechanical
Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will study the following topics: Types of waves Aplitude, phase, frequency, period, propagation speed of a wave Mechanical
SRI LANKAN PHYSICS OLYMPIAD MULTIPLE CHOICE TEST 30 QUESTIONS ONE HOUR AND 15 MINUTES
 SRI LANKAN PHYSICS OLYMPIAD - 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE TEST QUESTIONS ONE HOUR AND 5 MINUTES INSTRUCTIONS This test contains ultiple choice questions. Your answer to each question ust be arked on the answer sheet
SRI LANKAN PHYSICS OLYMPIAD - 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE TEST QUESTIONS ONE HOUR AND 5 MINUTES INSTRUCTIONS This test contains ultiple choice questions. Your answer to each question ust be arked on the answer sheet
PHY 171. Lecture 14. (February 16, 2012)
 PHY 171 Lecture 14 (February 16, 212) In the last lecture, we looked at a quantitative connection between acroscopic and icroscopic quantities by deriving an expression for pressure based on the assuptions
PHY 171 Lecture 14 (February 16, 212) In the last lecture, we looked at a quantitative connection between acroscopic and icroscopic quantities by deriving an expression for pressure based on the assuptions
In this chapter we will study sound waves and concentrate on the following topics:
 Chapter 17 Waves II In this chapter we will study sound waves and concentrate on the following topics: Speed of sound waves Relation between displaceent and pressure aplitude Interference of sound waves
Chapter 17 Waves II In this chapter we will study sound waves and concentrate on the following topics: Speed of sound waves Relation between displaceent and pressure aplitude Interference of sound waves
Scattering and bound states
 Chapter Scattering and bound states In this chapter we give a review of quantu-echanical scattering theory. We focus on the relation between the scattering aplitude of a potential and its bound states
Chapter Scattering and bound states In this chapter we give a review of quantu-echanical scattering theory. We focus on the relation between the scattering aplitude of a potential and its bound states
IN A SENSE, every material is a composite, even if the
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1999 2075 Magnetis fro Conductors and Enhanced Nonlinear Phenoena J. B. Pendry, A. J. Holden, D. J. Robbins, and W. J. Stewart,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1999 2075 Magnetis fro Conductors and Enhanced Nonlinear Phenoena J. B. Pendry, A. J. Holden, D. J. Robbins, and W. J. Stewart,
P (t) = P (t = 0) + F t Conclusion: If we wait long enough, the velocity of an electron will diverge, which is obviously impossible and wrong.
 4 Phys520.nb 2 Drude theory ~ Chapter in textbook 2.. The relaxation tie approxiation Here we treat electrons as a free ideal gas (classical) 2... Totally ignore interactions/scatterings Under a static
4 Phys520.nb 2 Drude theory ~ Chapter in textbook 2.. The relaxation tie approxiation Here we treat electrons as a free ideal gas (classical) 2... Totally ignore interactions/scatterings Under a static
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electroagnetic Waves Physics 4 Maxwell s Equations Maxwell s equations suarize the relationships between electric and agnetic fields. A ajor consequence of these equations is that an accelerating charge
Electroagnetic Waves Physics 4 Maxwell s Equations Maxwell s equations suarize the relationships between electric and agnetic fields. A ajor consequence of these equations is that an accelerating charge
72. (30.2) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires.
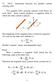 7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
 Pearson Education Liited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Esse CM0 JE England and Associated Copanies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Liited 04 All rights
Pearson Education Liited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Esse CM0 JE England and Associated Copanies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Liited 04 All rights
Physics 2107 Oscillations using Springs Experiment 2
 PY07 Oscillations using Springs Experient Physics 07 Oscillations using Springs Experient Prelab Read the following bacground/setup and ensure you are failiar with the concepts and theory required for
PY07 Oscillations using Springs Experient Physics 07 Oscillations using Springs Experient Prelab Read the following bacground/setup and ensure you are failiar with the concepts and theory required for
PH 221-2A Fall Waves - I. Lectures Chapter 16 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition)
 PH 1-A Fall 014 Waves - I Lectures 4-5 Chapter 16 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundaentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will
PH 1-A Fall 014 Waves - I Lectures 4-5 Chapter 16 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundaentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will
arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 1 Aug 2012
![arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 1 Aug 2012 arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 1 Aug 2012](/thumbs/72/68041909.jpg) ON THE INTERACTION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES WITH CONDUCTORS. B.V. Paranjape 1 and M. B. Paranjape 2 1 Professor Eeritus, Departent of Physics, University of Alberta and 2 Groupe de physique des particules,
ON THE INTERACTION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES WITH CONDUCTORS. B.V. Paranjape 1 and M. B. Paranjape 2 1 Professor Eeritus, Departent of Physics, University of Alberta and 2 Groupe de physique des particules,
The accelerated expansion of the universe is explained by quantum field theory.
 The accelerated expansion of the universe is explained by quantu field theory. Abstract. Forulas describing interactions, in fact, use the liiting speed of inforation transfer, and not the speed of light.
The accelerated expansion of the universe is explained by quantu field theory. Abstract. Forulas describing interactions, in fact, use the liiting speed of inforation transfer, and not the speed of light.
Physics 41 HW Set 1 Chapter 15 Serway 7 th Edition
 Physics HW Set Chapter 5 Serway 7 th Edition Conceptual Questions:, 3, 5,, 6, 9 Q53 You can take φ = π, or equally well, φ = π At t= 0, the particle is at its turning point on the negative side of equilibriu,
Physics HW Set Chapter 5 Serway 7 th Edition Conceptual Questions:, 3, 5,, 6, 9 Q53 You can take φ = π, or equally well, φ = π At t= 0, the particle is at its turning point on the negative side of equilibriu,
CHAPTER 4 TWO STANDARD SHORTCUTS USED TO TRANSFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC EQUATIONS 4.1 THE FREE-PARAMETER METHOD
 CHAPTER 4 TWO STANDARD SHORTCUTS USED TO TRANSFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC EQUATIONS The last several chapters have explained how the standard rules for changing units apply to electroagnetic physical quantities.
CHAPTER 4 TWO STANDARD SHORTCUTS USED TO TRANSFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC EQUATIONS The last several chapters have explained how the standard rules for changing units apply to electroagnetic physical quantities.
PY241 Solutions Set 9 (Dated: November 7, 2002)
 PY241 Solutions Set 9 (Dated: Noveber 7, 2002) 9-9 At what displaceent of an object undergoing siple haronic otion is the agnitude greatest for the... (a) velocity? The velocity is greatest at x = 0, the
PY241 Solutions Set 9 (Dated: Noveber 7, 2002) 9-9 At what displaceent of an object undergoing siple haronic otion is the agnitude greatest for the... (a) velocity? The velocity is greatest at x = 0, the
NB1140: Physics 1A - Classical mechanics and Thermodynamics Problem set 2 - Forces and energy Week 2: November 2016
 NB1140: Physics 1A - Classical echanics and Therodynaics Proble set 2 - Forces and energy Week 2: 21-25 Noveber 2016 Proble 1. Why force is transitted uniforly through a assless string, a assless spring,
NB1140: Physics 1A - Classical echanics and Therodynaics Proble set 2 - Forces and energy Week 2: 21-25 Noveber 2016 Proble 1. Why force is transitted uniforly through a assless string, a assless spring,
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechanics Physics 5 Lecture Oscillations (Chapter 6) What We Did Last Tie Analyzed the otion of a heavy top Reduced into -diensional proble of θ Qualitative behavior Precession + nutation Initial condition
Mechanics Physics 5 Lecture Oscillations (Chapter 6) What We Did Last Tie Analyzed the otion of a heavy top Reduced into -diensional proble of θ Qualitative behavior Precession + nutation Initial condition
Reading from Young & Freedman: For this topic, read the introduction to chapter 25 and sections 25.1 to 25.3 & 25.6.
 PHY10 Electricity Topic 6 (Lectures 9 & 10) Electric Current and Resistance n this topic, we will cover: 1) Current in a conductor ) Resistivity 3) Resistance 4) Oh s Law 5) The Drude Model of conduction
PHY10 Electricity Topic 6 (Lectures 9 & 10) Electric Current and Resistance n this topic, we will cover: 1) Current in a conductor ) Resistivity 3) Resistance 4) Oh s Law 5) The Drude Model of conduction
( ). One set of terms has a ω in
 Laptag Class Notes W. Gekelan Cold Plasa Dispersion relation Suer Let us go back to a single particle and see how it behaves in a high frequency electric field. We will use the force equation and Maxwell
Laptag Class Notes W. Gekelan Cold Plasa Dispersion relation Suer Let us go back to a single particle and see how it behaves in a high frequency electric field. We will use the force equation and Maxwell
Chapter 2: Introduction to Damping in Free and Forced Vibrations
 Chapter 2: Introduction to Daping in Free and Forced Vibrations This chapter ainly deals with the effect of daping in two conditions like free and forced excitation of echanical systes. Daping plays an
Chapter 2: Introduction to Daping in Free and Forced Vibrations This chapter ainly deals with the effect of daping in two conditions like free and forced excitation of echanical systes. Daping plays an
2. Electric Current. E.M.F. of a cell is defined as the maximum potential difference between the two electrodes of the
 2. Electric Current The net flow of charges through a etallic wire constitutes an electric current. Do you know who carries current? Current carriers In solid - the electrons in outerost orbit carries
2. Electric Current The net flow of charges through a etallic wire constitutes an electric current. Do you know who carries current? Current carriers In solid - the electrons in outerost orbit carries
Question 1. [14 Marks]
![Question 1. [14 Marks] Question 1. [14 Marks]](/thumbs/88/116022373.jpg) 6 Question 1. [14 Marks] R r T! A string is attached to the dru (radius r) of a spool (radius R) as shown in side and end views here. (A spool is device for storing string, thread etc.) A tension T is
6 Question 1. [14 Marks] R r T! A string is attached to the dru (radius r) of a spool (radius R) as shown in side and end views here. (A spool is device for storing string, thread etc.) A tension T is
OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
 OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES OSCILLATION IS AN EXAMPLE OF PERIODIC MOTION No stories this tie, we are going to get straight to the topic. We say that an event is Periodic in nature when it repeats itself in
OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES OSCILLATION IS AN EXAMPLE OF PERIODIC MOTION No stories this tie, we are going to get straight to the topic. We say that an event is Periodic in nature when it repeats itself in
Physics 207 Lecture 18. Physics 207, Lecture 18, Nov. 3 Goals: Chapter 14
 Physics 07, Lecture 18, Nov. 3 Goals: Chapter 14 Interrelate the physics and atheatics of oscillations. Draw and interpret oscillatory graphs. Learn the concepts of phase and phase constant. Understand
Physics 07, Lecture 18, Nov. 3 Goals: Chapter 14 Interrelate the physics and atheatics of oscillations. Draw and interpret oscillatory graphs. Learn the concepts of phase and phase constant. Understand
III.H Zeroth Order Hydrodynamics
 III.H Zeroth Order Hydrodynaics As a first approxiation, we shall assue that in local equilibriu, the density f 1 at each point in space can be represented as in eq.iii.56, i.e. f 0 1 p, q, t = n q, t
III.H Zeroth Order Hydrodynaics As a first approxiation, we shall assue that in local equilibriu, the density f 1 at each point in space can be represented as in eq.iii.56, i.e. f 0 1 p, q, t = n q, t
CHECKLIST. r r. Newton s Second Law. natural frequency ω o (rad.s -1 ) (Eq ) a03/p1/waves/waves doc 9:19 AM 29/03/05 1
 PHYS12 Physics 1 FUNDAMENTALS Module 3 OSCILLATIONS & WAVES Text Physics by Hecht Chapter 1 OSCILLATIONS Sections: 1.5 1.6 Exaples: 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 CHECKLIST Haronic otion, periodic otion, siple haronic
PHYS12 Physics 1 FUNDAMENTALS Module 3 OSCILLATIONS & WAVES Text Physics by Hecht Chapter 1 OSCILLATIONS Sections: 1.5 1.6 Exaples: 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 CHECKLIST Haronic otion, periodic otion, siple haronic
PH 221-1D Spring Oscillations. Lectures Chapter 15 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition)
 PH 1-1D Spring 013 Oscillations Lectures 35-37 Chapter 15 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundaentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 15 Oscillations In this chapter we will cover the following topics: Displaceent,
PH 1-1D Spring 013 Oscillations Lectures 35-37 Chapter 15 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundaentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 15 Oscillations In this chapter we will cover the following topics: Displaceent,
Feshbach Resonances in Ultracold Gases
 Feshbach Resonances in Ultracold Gases Sara L. Capbell MIT Departent of Physics Dated: May 5, 9) First described by Heran Feshbach in a 958 paper, Feshbach resonances describe resonant scattering between
Feshbach Resonances in Ultracold Gases Sara L. Capbell MIT Departent of Physics Dated: May 5, 9) First described by Heran Feshbach in a 958 paper, Feshbach resonances describe resonant scattering between
m A 1 m mgd k m v ( C) AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Oscillations
 P Physics Multiple Choice Practice Oscillations. ass, attached to a horizontal assless spring with spring constant, is set into siple haronic otion. Its axiu displaceent fro its equilibriu position is.
P Physics Multiple Choice Practice Oscillations. ass, attached to a horizontal assless spring with spring constant, is set into siple haronic otion. Its axiu displaceent fro its equilibriu position is.
Stern-Gerlach Experiment
 Stern-Gerlach Experient HOE: The Physics of Bruce Harvey This is the experient that is said to prove that the electron has an intrinsic agnetic oent. Hydrogen like atos are projected in a bea through a
Stern-Gerlach Experient HOE: The Physics of Bruce Harvey This is the experient that is said to prove that the electron has an intrinsic agnetic oent. Hydrogen like atos are projected in a bea through a
which is the moment of inertia mm -- the center of mass is given by: m11 r m2r 2
 Chapter 6: The Rigid Rotator * Energy Levels of the Rigid Rotator - this is the odel for icrowave/rotational spectroscopy - a rotating diatoic is odeled as a rigid rotator -- we have two atos with asses
Chapter 6: The Rigid Rotator * Energy Levels of the Rigid Rotator - this is the odel for icrowave/rotational spectroscopy - a rotating diatoic is odeled as a rigid rotator -- we have two atos with asses
Simple Harmonic Motion
 Reading: Chapter 15 Siple Haronic Motion Siple Haronic Motion Frequency f Period T T 1. f Siple haronic otion x ( t) x cos( t ). Aplitude x Phase Angular frequency Since the otion returns to its initial
Reading: Chapter 15 Siple Haronic Motion Siple Haronic Motion Frequency f Period T T 1. f Siple haronic otion x ( t) x cos( t ). Aplitude x Phase Angular frequency Since the otion returns to its initial
Lecture contents. Magnetic properties Diamagnetism Band paramagnetism Atomic paramagnetism. NNSE508 / NENG452 Lecture #14
 1 Lecture contents agnetic properties Diaagnetis and paraagnetis Atoic paraagnetis NNSE58 / NENG45 Lecture #14 agnetic units H /r V s 1 Wb T 1 T Wb T 1H A A Fro Treolet de Lacheisserie, 5 NNSE58 / NENG45
1 Lecture contents agnetic properties Diaagnetis and paraagnetis Atoic paraagnetis NNSE58 / NENG45 Lecture #14 agnetic units H /r V s 1 Wb T 1 T Wb T 1H A A Fro Treolet de Lacheisserie, 5 NNSE58 / NENG45
PH 221-3A Fall Waves - II. Lectures Chapter 17 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition)
 PH 221-3A Fall 2010 Waves - II Lectures 27-28 Chapter 17 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundaentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 17 Waves II In this chapter we will study sound waves and concentrate on
PH 221-3A Fall 2010 Waves - II Lectures 27-28 Chapter 17 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundaentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 17 Waves II In this chapter we will study sound waves and concentrate on
Recommended Reading. Entropy/Second law Thermodynamics
 Lecture 7. Entropy and the second law of therodynaics. Recoended Reading Entropy/econd law herodynaics http://en wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/entropy http://2ndlaw.oxy.edu/index.htl. his site
Lecture 7. Entropy and the second law of therodynaics. Recoended Reading Entropy/econd law herodynaics http://en wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/entropy http://2ndlaw.oxy.edu/index.htl. his site
= T. Oscillations and Waves. Example of an Oscillating System IB 12 IB 12
 Oscillation: the vibration of an object Oscillations and Waves Eaple of an Oscillating Syste A ass oscillates on a horizontal spring without friction as shown below. At each position, analyze its displaceent,
Oscillation: the vibration of an object Oscillations and Waves Eaple of an Oscillating Syste A ass oscillates on a horizontal spring without friction as shown below. At each position, analyze its displaceent,
Newton's Laws. Lecture 2 Key Concepts. Newtonian mechanics and relation to Kepler's laws The Virial Theorem Tidal forces Collision physics
 Lecture 2 Key Concepts Newtonian echanics and relation to Kepler's laws The Virial Theore Tidal forces Collision physics Newton's Laws 1) An object at rest will reain at rest and an object in otion will
Lecture 2 Key Concepts Newtonian echanics and relation to Kepler's laws The Virial Theore Tidal forces Collision physics Newton's Laws 1) An object at rest will reain at rest and an object in otion will
General Properties of Radiation Detectors Supplements
 Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent Yarouk University Chapter 4: General Properties of Radiation Detectors Suppleents Dr. Nidal M. Ershaidat Overview Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent
Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent Yarouk University Chapter 4: General Properties of Radiation Detectors Suppleents Dr. Nidal M. Ershaidat Overview Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent
2 Q 10. Likewise, in case of multiple particles, the corresponding density in 2 must be averaged over all
 Lecture 6 Introduction to kinetic theory of plasa waves Introduction to kinetic theory So far we have been odeling plasa dynaics using fluid equations. The assuption has been that the pressure can be either
Lecture 6 Introduction to kinetic theory of plasa waves Introduction to kinetic theory So far we have been odeling plasa dynaics using fluid equations. The assuption has been that the pressure can be either
Field Mass Generation and Control. Chapter 6. The famous two slit experiment proved that a particle can exist as a wave and yet
 111 Field Mass Generation and Control Chapter 6 The faous two slit experient proved that a particle can exist as a wave and yet still exhibit particle characteristics when the wavefunction is altered by
111 Field Mass Generation and Control Chapter 6 The faous two slit experient proved that a particle can exist as a wave and yet still exhibit particle characteristics when the wavefunction is altered by
which proves the motion is simple harmonic. Now A = a 2 + b 2 = =
 Worked out Exaples. The potential energy function for the force between two atos in a diatoic olecules can be expressed as follows: a U(x) = b x / x6 where a and b are positive constants and x is the distance
Worked out Exaples. The potential energy function for the force between two atos in a diatoic olecules can be expressed as follows: a U(x) = b x / x6 where a and b are positive constants and x is the distance
Quantum Ground States as Equilibrium Particle Vacuum Interaction States
 Quantu Ground States as Euilibriu article Vacuu Interaction States Harold E uthoff Abstract A rearkable feature of atoic ground states is that they are observed to be radiationless in nature despite (fro
Quantu Ground States as Euilibriu article Vacuu Interaction States Harold E uthoff Abstract A rearkable feature of atoic ground states is that they are observed to be radiationless in nature despite (fro
Optical Properties of Plasmas of High-Z Elements
 Forschungszentru Karlsruhe Techni und Uwelt Wissenschaftlishe Berichte FZK Optical Properties of Plasas of High-Z Eleents V.Tolach 1, G.Miloshevsy 1, H.Würz Project Kernfusion 1 Heat and Mass Transfer
Forschungszentru Karlsruhe Techni und Uwelt Wissenschaftlishe Berichte FZK Optical Properties of Plasas of High-Z Eleents V.Tolach 1, G.Miloshevsy 1, H.Würz Project Kernfusion 1 Heat and Mass Transfer
1B If the stick is pivoted about point P a distance h = 10 cm from the center of mass, the period of oscillation is equal to (in seconds)
 05/07/03 HYSICS 3 Exa #1 Use g 10 /s in your calculations. NAME Feynan lease write your nae also on the back side of this exa 1. 1A A unifor thin stick of ass M 0. Kg and length 60 c is pivoted at one
05/07/03 HYSICS 3 Exa #1 Use g 10 /s in your calculations. NAME Feynan lease write your nae also on the back side of this exa 1. 1A A unifor thin stick of ass M 0. Kg and length 60 c is pivoted at one
PHYS 1443 Section 003 Lecture #21 Wednesday, Nov. 19, 2003 Dr. Mystery Lecturer
 PHYS 443 Section 003 Lecture # Wednesday, Nov. 9, 003 Dr. Mystery Lecturer. Fluid Dyanics : Flow rate and Continuity Equation. Bernoulli s Equation 3. Siple Haronic Motion 4. Siple Bloc-Spring Syste 5.
PHYS 443 Section 003 Lecture # Wednesday, Nov. 9, 003 Dr. Mystery Lecturer. Fluid Dyanics : Flow rate and Continuity Equation. Bernoulli s Equation 3. Siple Haronic Motion 4. Siple Bloc-Spring Syste 5.
Simple Harmonic Motion
 Siple Haronic Motion Physics Enhanceent Prograe for Gifted Students The Hong Kong Acadey for Gifted Education and Departent of Physics, HKBU Departent of Physics Siple haronic otion In echanical physics,
Siple Haronic Motion Physics Enhanceent Prograe for Gifted Students The Hong Kong Acadey for Gifted Education and Departent of Physics, HKBU Departent of Physics Siple haronic otion In echanical physics,
V.N. Shilov a, *, A.V. Delgado b, F. Gonzalez-Caballero b, C. Grosse c
 Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicocheical and Engineering Aspects 192 (2001) 253 265 www.elsevier.co/locate/colsurfa Thin double layer theory of the wide-frequency range dielectric dispersion of suspensions
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicocheical and Engineering Aspects 192 (2001) 253 265 www.elsevier.co/locate/colsurfa Thin double layer theory of the wide-frequency range dielectric dispersion of suspensions
Pearson Physics Level 20 Unit IV Oscillatory Motion and Mechanical Waves: Unit IV Review Solutions
 Pearson Physics Level 0 Unit IV Oscillatory Motion and Mechanical Waves: Unit IV Review Solutions Student Book pages 440 443 Vocabulary. aplitude: axiu displaceent of an oscillation antinodes: points of
Pearson Physics Level 0 Unit IV Oscillatory Motion and Mechanical Waves: Unit IV Review Solutions Student Book pages 440 443 Vocabulary. aplitude: axiu displaceent of an oscillation antinodes: points of
Lecture 8 Symmetries, conserved quantities, and the labeling of states Angular Momentum
 Lecture 8 Syetries, conserved quantities, and the labeling of states Angular Moentu Today s Progra: 1. Syetries and conserved quantities labeling of states. hrenfest Theore the greatest theore of all ties
Lecture 8 Syetries, conserved quantities, and the labeling of states Angular Moentu Today s Progra: 1. Syetries and conserved quantities labeling of states. hrenfest Theore the greatest theore of all ties
ANALYSIS ON RESPONSE OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS TO PULSE SEQUENCES EXCITATION
 The 4 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering October -7, 8, Beijing, China ANALYSIS ON RESPONSE OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS TO PULSE SEQUENCES EXCITATION S. Li C.H. Zhai L.L. Xie Ph. D. Student, School of
The 4 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering October -7, 8, Beijing, China ANALYSIS ON RESPONSE OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS TO PULSE SEQUENCES EXCITATION S. Li C.H. Zhai L.L. Xie Ph. D. Student, School of
Course Information. Physics 1C Waves, optics and modern physics. Grades. Class Schedule. Clickers. Homework
 Course Inforation Physics 1C Waves, optics and odern physics Instructor: Melvin Oaura eail: oaura@physics.ucsd.edu Course Syllabus on the web page http://physics.ucsd.edu/ students/courses/fall2009/physics1c
Course Inforation Physics 1C Waves, optics and odern physics Instructor: Melvin Oaura eail: oaura@physics.ucsd.edu Course Syllabus on the web page http://physics.ucsd.edu/ students/courses/fall2009/physics1c
Periodic Motion is everywhere
 Lecture 19 Goals: Chapter 14 Interrelate the physics and atheatics of oscillations. Draw and interpret oscillatory graphs. Learn the concepts of phase and phase constant. Understand and use energy conservation
Lecture 19 Goals: Chapter 14 Interrelate the physics and atheatics of oscillations. Draw and interpret oscillatory graphs. Learn the concepts of phase and phase constant. Understand and use energy conservation
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION: NEWTON S LAW
 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION: NEWTON S LAW siple not siple PRIOR READING: Main 1.1, 2.1 Taylor 5.1, 5.2 http://www.yoops.org/twocw/it/nr/rdonlyres/physics/8-012fall-2005/7cce46ac-405d-4652-a724-64f831e70388/0/chp_physi_pndul.jpg
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION: NEWTON S LAW siple not siple PRIOR READING: Main 1.1, 2.1 Taylor 5.1, 5.2 http://www.yoops.org/twocw/it/nr/rdonlyres/physics/8-012fall-2005/7cce46ac-405d-4652-a724-64f831e70388/0/chp_physi_pndul.jpg
Oscillations: Review (Chapter 12)
 Oscillations: Review (Chapter 1) Oscillations: otions that are periodic in tie (i.e. repetitive) o Swinging object (pendulu) o Vibrating object (spring, guitar string, etc.) o Part of ediu (i.e. string,
Oscillations: Review (Chapter 1) Oscillations: otions that are periodic in tie (i.e. repetitive) o Swinging object (pendulu) o Vibrating object (spring, guitar string, etc.) o Part of ediu (i.e. string,
A GENERAL FORM FOR THE ELECTRIC FIELD LINES EQUATION CONCERNING AN AXIALLY SYMMETRIC CONTINUOUS CHARGE DISTRIBUTION
 A GENEAL FOM FO THE ELECTIC FIELD LINES EQUATION CONCENING AN AXIALLY SYMMETIC CONTINUOUS CHAGE DISTIBUTION BY MUGU B. ăuţ Abstract..By using an unexpected approach it results a general for for the electric
A GENEAL FOM FO THE ELECTIC FIELD LINES EQUATION CONCENING AN AXIALLY SYMMETIC CONTINUOUS CHAGE DISTIBUTION BY MUGU B. ăuţ Abstract..By using an unexpected approach it results a general for for the electric
Dr. Naser Abu-Zaid; Lecture notes in electromagnetic theory 1; Referenced to Engineering electromagnetics by Hayt, 8 th edition 2012; Text Book
 Text Book Dr. Naser Abu-Zaid Page 1 9/4/2012 Course syllabus Electroagnetic 2 (63374) Seester Language Copulsory / Elective Prerequisites Course Contents Course Objectives Learning Outcoes and Copetences
Text Book Dr. Naser Abu-Zaid Page 1 9/4/2012 Course syllabus Electroagnetic 2 (63374) Seester Language Copulsory / Elective Prerequisites Course Contents Course Objectives Learning Outcoes and Copetences
Physics 221B: Solution to HW # 6. 1) Born-Oppenheimer for Coupled Harmonic Oscillators
 Physics B: Solution to HW # 6 ) Born-Oppenheier for Coupled Haronic Oscillators This proble is eant to convince you of the validity of the Born-Oppenheier BO) Approxiation through a toy odel of coupled
Physics B: Solution to HW # 6 ) Born-Oppenheier for Coupled Haronic Oscillators This proble is eant to convince you of the validity of the Born-Oppenheier BO) Approxiation through a toy odel of coupled
Motion of Charges in Uniform E
 Motion of Charges in Unifor E and Fields Assue an ionized gas is acted upon by a unifor (but possibly tie-dependent) electric field E, and a unifor, steady agnetic field. These fields are assued to be
Motion of Charges in Unifor E and Fields Assue an ionized gas is acted upon by a unifor (but possibly tie-dependent) electric field E, and a unifor, steady agnetic field. These fields are assued to be
Damped Harmonic Motion
 Daped Haronic Motion PY154 Special Topics in Physics PY154 1 Driven Daped Haronic Motion What if we apply a haronic force?: F h Be it The total force is then: dx F Fh kx b dt d x dt Assue a solution of
Daped Haronic Motion PY154 Special Topics in Physics PY154 1 Driven Daped Haronic Motion What if we apply a haronic force?: F h Be it The total force is then: dx F Fh kx b dt d x dt Assue a solution of
Electromagnetic scattering. Graduate Course Electrical Engineering (Communications) 1 st Semester, Sharif University of Technology
 Electroagnetic scattering Graduate Course Electrical Engineering (Counications) 1 st Seester, 1388-1389 Sharif University of Technology Contents of lecture 5 Contents of lecture 5: Scattering fro a conductive
Electroagnetic scattering Graduate Course Electrical Engineering (Counications) 1 st Seester, 1388-1389 Sharif University of Technology Contents of lecture 5 Contents of lecture 5: Scattering fro a conductive
A toy model of quantum electrodynamics in (1 + 1) dimensions
 IOP PUBLISHING Eur. J. Phys. 29 (2008) 815 830 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICS doi:10.1088/0143-0807/29/4/014 A toy odel of quantu electrodynaics in (1 + 1) diensions ADBoozer Departent of Physics, California
IOP PUBLISHING Eur. J. Phys. 29 (2008) 815 830 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICS doi:10.1088/0143-0807/29/4/014 A toy odel of quantu electrodynaics in (1 + 1) diensions ADBoozer Departent of Physics, California
Force and dynamics with a spring, analytic approach
 Force and dynaics with a spring, analytic approach It ay strie you as strange that the first force we will discuss will be that of a spring. It is not one of the four Universal forces and we don t use
Force and dynaics with a spring, analytic approach It ay strie you as strange that the first force we will discuss will be that of a spring. It is not one of the four Universal forces and we don t use
Unit 14 Harmonic Motion. Your Comments
 Today s Concepts: Periodic Motion Siple - Mass on spring Daped Forced Resonance Siple - Pendulu Unit 1, Slide 1 Your Coents Please go through the three equations for siple haronic otion and phase angle
Today s Concepts: Periodic Motion Siple - Mass on spring Daped Forced Resonance Siple - Pendulu Unit 1, Slide 1 Your Coents Please go through the three equations for siple haronic otion and phase angle
III. Quantization of electromagnetic field
 III. Quantization of electroagnetic field Using the fraework presented in the previous chapter, this chapter describes lightwave in ters of quantu echanics. First, how to write a physical quantity operator
III. Quantization of electroagnetic field Using the fraework presented in the previous chapter, this chapter describes lightwave in ters of quantu echanics. First, how to write a physical quantity operator
More Oscillations! (Today: Harmonic Oscillators)
 More Oscillations! (oday: Haronic Oscillators) Movie assignent reinder! Final due HURSDAY April 20 Subit through ecapus Different rubric; reeber to chec it even if you got 00% on your draft: http://sarahspolaor.faculty.wvu.edu/hoe/physics-0
More Oscillations! (oday: Haronic Oscillators) Movie assignent reinder! Final due HURSDAY April 20 Subit through ecapus Different rubric; reeber to chec it even if you got 00% on your draft: http://sarahspolaor.faculty.wvu.edu/hoe/physics-0
[ ] ( t) ( ω ω. I. Part 3 Transitions and relation to observables. Left off at transition probability for absorbance: choose ω = ω mk
![[ ] ( t) ( ω ω. I. Part 3 Transitions and relation to observables. Left off at transition probability for absorbance: choose ω = ω mk [ ] ( t) ( ω ω. I. Part 3 Transitions and relation to observables. Left off at transition probability for absorbance: choose ω = ω mk](/thumbs/76/73935745.jpg) I. Part Transitions and relation to obserables I- Left off at transition probability for absorbance: coose k P ( t) k ( ) ( sin Ε 4 µ k ( [ k k ) t ) ] last ter is band sape f (t, f πt δ ( for t Long tie:
I. Part Transitions and relation to obserables I- Left off at transition probability for absorbance: coose k P ( t) k ( ) ( sin Ε 4 µ k ( [ k k ) t ) ] last ter is band sape f (t, f πt δ ( for t Long tie:
ma x = -bv x + F rod.
 Notes on Dynaical Systes Dynaics is the study of change. The priary ingredients of a dynaical syste are its state and its rule of change (also soeties called the dynaic). Dynaical systes can be continuous
Notes on Dynaical Systes Dynaics is the study of change. The priary ingredients of a dynaical syste are its state and its rule of change (also soeties called the dynaic). Dynaical systes can be continuous
Frequency dependence of the permittivity
 Frequency dependence of the permttvty February 7, 016 In materals, the delectrc constant and permeablty are actually frequency dependent. Ths does not affect our results for sngle frequency modes, but
Frequency dependence of the permttvty February 7, 016 In materals, the delectrc constant and permeablty are actually frequency dependent. Ths does not affect our results for sngle frequency modes, but
Some consequences of a Universal Tension arising from Dark Energy for structures from Atomic Nuclei to Galaxy Clusters
 unning Head: Universal Tension fro DE Article Type: Original esearch Soe consequences of a Universal Tension arising fro Dark Energy for structures fro Atoic Nuclei to Galaxy Clusters C Sivara Indian Institute
unning Head: Universal Tension fro DE Article Type: Original esearch Soe consequences of a Universal Tension arising fro Dark Energy for structures fro Atoic Nuclei to Galaxy Clusters C Sivara Indian Institute
Time Evolution of Matter States
 Tie Evolution of Matter States W. M. Hetherington February 15, 1 The Tie-Evolution Operat The tie-evolution of a wavefunction is deterined by the effect of a tie evolution operat through the relation Ψ
Tie Evolution of Matter States W. M. Hetherington February 15, 1 The Tie-Evolution Operat The tie-evolution of a wavefunction is deterined by the effect of a tie evolution operat through the relation Ψ
A NEW ELECTROSTATIC FIELD GEOMETRY. Jerry E. Bayles
 INTRODUCTION A NEW ELECTROSTATIC FIELD GEOMETRY by Jerry E Bayles The purpose of this paper is to present the electrostatic field in geoetrical ters siilar to that of the electrogravitational equation
INTRODUCTION A NEW ELECTROSTATIC FIELD GEOMETRY by Jerry E Bayles The purpose of this paper is to present the electrostatic field in geoetrical ters siilar to that of the electrogravitational equation
T m. Fapplied. Thur Oct 29. ω = 2πf f = (ω/2π) T = 1/f. k m. ω =
 Thur Oct 9 Assignent 10 Mass-Spring Kineatics (x, v, a, t) Dynaics (F,, a) Tie dependence Energy Pendulu Daping and Resonances x Acos( ωt) = v = Aω sin( ωt) a = Aω cos( ωt) ω = spring k f spring = 1 k
Thur Oct 9 Assignent 10 Mass-Spring Kineatics (x, v, a, t) Dynaics (F,, a) Tie dependence Energy Pendulu Daping and Resonances x Acos( ωt) = v = Aω sin( ωt) a = Aω cos( ωt) ω = spring k f spring = 1 k
Molecular Speeds. Real Gasses. Ideal Gas Law. Reasonable. Why the breakdown? P-V Diagram. Using moles. Using molecules
 Kinetic Theory of Gases Connect icroscopic properties (kinetic energy and oentu) of olecules to acroscopic state properties of a gas (teperature and pressure). P v v 3 3 3 But K v and P kt K v kt Teperature
Kinetic Theory of Gases Connect icroscopic properties (kinetic energy and oentu) of olecules to acroscopic state properties of a gas (teperature and pressure). P v v 3 3 3 But K v and P kt K v kt Teperature
CHAPTER 15: Vibratory Motion
 CHAPTER 15: Vibratory Motion courtesy of Richard White courtesy of Richard White 2.) 1.) Two glaring observations can be ade fro the graphic on the previous slide: 1.) The PROJECTION of a point on a circle
CHAPTER 15: Vibratory Motion courtesy of Richard White courtesy of Richard White 2.) 1.) Two glaring observations can be ade fro the graphic on the previous slide: 1.) The PROJECTION of a point on a circle
Supplementary Information for Design of Bending Multi-Layer Electroactive Polymer Actuators
 Suppleentary Inforation for Design of Bending Multi-Layer Electroactive Polyer Actuators Bavani Balakrisnan, Alek Nacev, and Elisabeth Sela University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 074 1 Analytical
Suppleentary Inforation for Design of Bending Multi-Layer Electroactive Polyer Actuators Bavani Balakrisnan, Alek Nacev, and Elisabeth Sela University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 074 1 Analytical
Many objects vibrate or oscillate an object on the end of a spring, a tuning
 An object attached to a coil spring can exhibit oscillatory otion. Many kinds of oscillatory otion are sinusoidal in tie, or nearly so, and are referred to as siple haronic otion. Real systes generally
An object attached to a coil spring can exhibit oscillatory otion. Many kinds of oscillatory otion are sinusoidal in tie, or nearly so, and are referred to as siple haronic otion. Real systes generally
Hee = ~ dxdy\jj+ (x) 'IJ+ (y) u (x- y) \jj (y) \jj (x), V, = ~ dx 'IJ+ (x) \jj (x) V (x), Hii = Z 2 ~ dx dy cp+ (x) cp+ (y) u (x- y) cp (y) cp (x),
 SOVIET PHYSICS JETP VOLUME 14, NUMBER 4 APRIL, 1962 SHIFT OF ATOMIC ENERGY LEVELS IN A PLASMA L. E. PARGAMANIK Khar'kov State University Subitted to JETP editor February 16, 1961; resubitted June 19, 1961
SOVIET PHYSICS JETP VOLUME 14, NUMBER 4 APRIL, 1962 SHIFT OF ATOMIC ENERGY LEVELS IN A PLASMA L. E. PARGAMANIK Khar'kov State University Subitted to JETP editor February 16, 1961; resubitted June 19, 1961
PH 222-2C Fall Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current. Lectures 18-19
 H - Fall 0 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent ectures 8-9 hapter 3 (Halliday/esnick/Walker, Fundaentals of hysics 8 th edition) hapter 3 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent
H - Fall 0 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent ectures 8-9 hapter 3 (Halliday/esnick/Walker, Fundaentals of hysics 8 th edition) hapter 3 Electroagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent
SOLVING LITERAL EQUATIONS. Bundle 1: Safety & Process Skills
 SOLVING LITERAL EQUATIONS Bundle 1: Safety & Process Skills Solving Literal Equations An equation is a atheatical sentence with an equal sign. The solution of an equation is a value for a variable that
SOLVING LITERAL EQUATIONS Bundle 1: Safety & Process Skills Solving Literal Equations An equation is a atheatical sentence with an equal sign. The solution of an equation is a value for a variable that
Problem Set 2. Chapter 1 Numerical:
 Chapter 1 Nuerical: roble Set 16. The atoic radius of xenon is 18 p. Is that consistent with its b paraeter of 5.15 1 - L/ol? Hint: what is the volue of a ole of xenon atos and how does that copare to
Chapter 1 Nuerical: roble Set 16. The atoic radius of xenon is 18 p. Is that consistent with its b paraeter of 5.15 1 - L/ol? Hint: what is the volue of a ole of xenon atos and how does that copare to
Lecture Frontier of complexity more is different Think of a spin - a multitude gives all sorts of magnetism due to interactions
 Lecture 1 Motivation for course The title of this course is condensed atter physics which includes solids and liquids (and occasionally gases). There are also interediate fors of atter, e.g., glasses,
Lecture 1 Motivation for course The title of this course is condensed atter physics which includes solids and liquids (and occasionally gases). There are also interediate fors of atter, e.g., glasses,
VIBRATING SYSTEMS. example. Springs obey Hooke s Law. Terminology. L 21 Vibration and Waves [ 2 ]
![VIBRATING SYSTEMS. example. Springs obey Hooke s Law. Terminology. L 21 Vibration and Waves [ 2 ] VIBRATING SYSTEMS. example. Springs obey Hooke s Law. Terminology. L 21 Vibration and Waves [ 2 ]](/thumbs/80/81911008.jpg) L 1 Vibration and Waves [ ] Vibrations (oscillations) resonance pendulu springs haronic otion Waves echanical waves sound waves usical instruents VIBRATING SYSTEMS Mass and spring on air trac Mass hanging
L 1 Vibration and Waves [ ] Vibrations (oscillations) resonance pendulu springs haronic otion Waves echanical waves sound waves usical instruents VIBRATING SYSTEMS Mass and spring on air trac Mass hanging
This exam is formed of three exercises in three pages numbered from 1 to 3 The use of non-programmable calculators is recommended.
 009 وزارة التربية والتعلين العالي الوديرية العاهة للتربية دائرة االهتحانات اهتحانات الشهادة الثانىية العاهة الفرع : علىم الحياة مسابقة في مادة الفيزياء المدة ساعتان االسن: الرقن: الدورة العادية للعام This
009 وزارة التربية والتعلين العالي الوديرية العاهة للتربية دائرة االهتحانات اهتحانات الشهادة الثانىية العاهة الفرع : علىم الحياة مسابقة في مادة الفيزياء المدة ساعتان االسن: الرقن: الدورة العادية للعام This
Chapter 4: Hypothesis of Diffusion-Limited Growth
 Suary This section derives a useful equation to predict quantu dot size evolution under typical organoetallic synthesis conditions that are used to achieve narrow size distributions. Assuing diffusion-controlled
Suary This section derives a useful equation to predict quantu dot size evolution under typical organoetallic synthesis conditions that are used to achieve narrow size distributions. Assuing diffusion-controlled
1.1 Heat and Mass transfer in daily life and process/mechanical engineering Heat transfer in daily life: Heating Cooling Cooking
 1. Introduction 1.1 Heat and Mass transfer in daily life and process/echanical engineering Heat transfer in daily life: Heating Cooling Cooking ransfer of heat along a teperature difference fro one syste
1. Introduction 1.1 Heat and Mass transfer in daily life and process/echanical engineering Heat transfer in daily life: Heating Cooling Cooking ransfer of heat along a teperature difference fro one syste
Chapter 12. Quantum gases Microcanonical ensemble
 Chapter 2 Quantu gases In classical statistical echanics, we evaluated therodynaic relations often for an ideal gas, which approxiates a real gas in the highly diluted liit. An iportant difference between
Chapter 2 Quantu gases In classical statistical echanics, we evaluated therodynaic relations often for an ideal gas, which approxiates a real gas in the highly diluted liit. An iportant difference between
Physics (Theory) CBSE Physics XII Board Paper SET C. General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory.
 Physics (Theory) [Tie allowed: 3 hours] [Maxiu arks:7] General Instructions: (i) All questions are copulsory. (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) There are 3 questions in total. Questions to 8 carry one ark each. Questions
Physics (Theory) [Tie allowed: 3 hours] [Maxiu arks:7] General Instructions: (i) All questions are copulsory. (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) There are 3 questions in total. Questions to 8 carry one ark each. Questions
Page 1. Physics 131: Lecture 22. Today s Agenda. SHM and Circles. Position
 Physics 3: ecture Today s genda Siple haronic otion Deinition Period and requency Position, velocity, and acceleration Period o a ass on a spring Vertical spring Energy and siple haronic otion Energy o
Physics 3: ecture Today s genda Siple haronic otion Deinition Period and requency Position, velocity, and acceleration Period o a ass on a spring Vertical spring Energy and siple haronic otion Energy o
Impurity effects on adatom density of state
 Ipurity effects on adato density of state HIROMU UE BA and SHOJI ICHIMURA Departent of Electronics, Faculty of Engineering Abstract The influence of both ipurity and surface states on the adato electronic
Ipurity effects on adato density of state HIROMU UE BA and SHOJI ICHIMURA Departent of Electronics, Faculty of Engineering Abstract The influence of both ipurity and surface states on the adato electronic
Kinetic Theory of Gases: Elementary Ideas
 Kinetic Theory of Gases: Eleentary Ideas 17th February 2010 1 Kinetic Theory: A Discussion Based on a Siplified iew of the Motion of Gases 1.1 Pressure: Consul Engel and Reid Ch. 33.1) for a discussion
Kinetic Theory of Gases: Eleentary Ideas 17th February 2010 1 Kinetic Theory: A Discussion Based on a Siplified iew of the Motion of Gases 1.1 Pressure: Consul Engel and Reid Ch. 33.1) for a discussion
Physics 201 Lecture 29
 Phsics 1 ecture 9 Goals ecture 9 v Describe oscillator otion in a siple pendulu v Describe oscillator otion with torques v Introduce daping in SHM v Discuss resonance v Final Ea Details l Sunda, Ma 13th
Phsics 1 ecture 9 Goals ecture 9 v Describe oscillator otion in a siple pendulu v Describe oscillator otion with torques v Introduce daping in SHM v Discuss resonance v Final Ea Details l Sunda, Ma 13th
dt dt THE AIR TRACK (II)
 THE AIR TRACK (II) References: [] The Air Track (I) - First Year Physics Laoratory Manual (PHY38Y and PHYY) [] Berkeley Physics Laoratory, nd edition, McGraw-Hill Book Copany [3] E. Hecht: Physics: Calculus,
THE AIR TRACK (II) References: [] The Air Track (I) - First Year Physics Laoratory Manual (PHY38Y and PHYY) [] Berkeley Physics Laoratory, nd edition, McGraw-Hill Book Copany [3] E. Hecht: Physics: Calculus,
COUPLED OSCILLATORS. Two identical pendulums
 COUPED OSCIATORS A real physical object can be rearded as a lare nuber of siple oscillators coupled toether (atos and olecules in solids. The question is: how does the couplin affect the behavior of each
COUPED OSCIATORS A real physical object can be rearded as a lare nuber of siple oscillators coupled toether (atos and olecules in solids. The question is: how does the couplin affect the behavior of each
Physics 2210 Fall smartphysics 20 Conservation of Angular Momentum 21 Simple Harmonic Motion 11/23/2015
 Physics 2210 Fall 2015 sartphysics 20 Conservation of Angular Moentu 21 Siple Haronic Motion 11/23/2015 Exa 4: sartphysics units 14-20 Midter Exa 2: Day: Fri Dec. 04, 2015 Tie: regular class tie Section
Physics 2210 Fall 2015 sartphysics 20 Conservation of Angular Moentu 21 Siple Haronic Motion 11/23/2015 Exa 4: sartphysics units 14-20 Midter Exa 2: Day: Fri Dec. 04, 2015 Tie: regular class tie Section
