Prof. S. Yip. Graduate Students. D. E. Crane M. D. Lubin
|
|
|
- Britney Lily Grant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 XVI. INTERACTION OF LASER RADIATION WITH PLASMAS AND NONADIABATIC MOTION OF PARTICLES IN MAGNETIC FIELDS Academic and Research Staff Prof. D. J. Rose Prof. T. H. Dupree Prof. L. M. Prof. S. Yip Lidsky T. S. Brown J. D. Callen H. Ching Graduate Students D. E. Crane M. D. Lubin R. W. Moir M. Murakami A. A. Offenberger A. INCOHERENT SCATTERING OF LIGHT FROM A PLASMA IV The N 2 -CO 2 laser development for the plasma scattering experiment -3 has been completed; the optical detecting scheme has been finalized; and, after delivery of a i bandpass filter centered at 10.6 t, noise measurements were made to determine the NEP of our mercury-doped Ge detector. The final, and greatly simplified, laser design is indicated in Fig. XVI-1. Two VACUUM PUMP I CATHODE "DOUBLE TOUGH" PYREX O-RING SEALS ALL PARTS S.S. NOTE: ENDS SYMMETRICAL EXCEPT FOR GAS INLET AND VACUUM PORT SIZES Fig. XVI-1. Detail of laser discharge tube. coaxially mounted equal lengths of "Double Tough" Pyrex tubing, 10 ft long and 1 in. and 2 in. I. D., with compressive O-ring sealing to the end flanges, form the discharge region and coolant channel. The flanges incorporate the O-ring mounted NaC1 Brewster *This work was supported by the United States Atomic Energy Commission (Contract AT(30-1)-3285). QPR No
2 windows, vacuum fitting and gas inlet ports, cathode and anode for the discharge, and are directly cooled by passing the cooling water through them. The discharge tube and mirrors are mounted on a 4-in. Al H-beam. The discharge conditions are 100 ma at 12 kv in a gas mixture of 1 Torr CO 2, 1 Torr N 2, and 4 Torr He. The mirrors have a separation of 4 m; one being an Aucoated B. S. C. glass, the other a flat Ge mirror. The Au mirror has a 1-mm central hole for alignment purposes when using an He-Ne laser. The Ge mirror, 2-mm thick, has a front surface reflectivity of 36%0 (index of refraction n= 4) and the back surface has a ZnS antireflection coating. The output power is ~100 watts at [, with essential stability on a single rotational transition. At lower power levels, or with slightly detuned mirrors, other rotational lines (~200 A separation) appear. The output is multimode longitudinally and transversely, but this is of no consequence in our scattering experiment. Using a Au-coated mirror with 1-cm hole coupling yields an even higher power level, but does not give the single rotational line stability that the Ge mirror affords. The optics for detecting the scattered radiation from the plasma is indicated in Fig. XVI-2, with the exception of substituting mirrors for lenses in collecting and VIEWING FOCUSING LENS GAS LIQUID HELIUM CRYOSTAT MERCURY DOPED GERMANIUM MIRRORDETECTOR BLOCKING FILTER COLLIMATING MIRROR FABRY-PEROT INTERFEROMETER PLASMA LASER BEAM DUMP Fig. XVI-2. Laser-plasma scattering-detection optics. rendering the scattered radiation parallel for wavelength analysis. We found that spherical aberration in the KC1 lenses was the limiting factor in utilizing all available scattered light. A redesign, with mirrors substituted for lenses, indicates far less spherical aberration and hence much better collection efficiency. The large mirror sub- -2 tends rr X 10 sr at the scattering point in the plasma. The mirror assembly QPR No
3 is under construction. The Fabry-Perot interferometer uses Ge plates with 96% ZnS reflective coatings, which affords a 20 A bandpass. The central wavelength is to be pressure-tuned by using ethane, which will afford a spectral scan of 1400 A. This range will enable measurement of the plasma-frequency satellite resonances, as well as temperature measurements from the Doppler-shifted intensity spectrum. An NaC1 lens with small spherical aberration focuses the spectrally analyzed radiation onto an Hg-doped Ge detector cooled to 4 0 K. A Ge substrate blocking filter of bandpass mounted in the 4 K cryostat blocks all orders from the Fabry-Perot, except one, and additionally limits the 3000K black-body radiation seen by the detector The measured NEP is 2 X 10 with a responsivity of 8 X 10 volts watt and watt cps - /2, source impedance of 1.5 M, compared with an unblocked detector of NEP = watt cps - 1 /2 and responsivity = volt watt - 1. A considerable improvement has been achieved. The anticipated scattered power levels are 4 x watt; this indicates detection bandwidths of 1/25 cps for a S/N = 1. The laser radiation is chopped before focusing into the scattering volume, and the scattered signal is detected synchronously by using an FET impedance-matching preamplifier and Princeton Applied Research HR-8 lock-in amplifier. The detector noise is well above pre-amplifier noise, and is the limiting factor in this experiment. The scattered light collecting mirrors are being set up and the only outstanding question will be that of laser beam dump efficiency. References A. A. Offenberger 1. A. A. Offenberger, Quarterly Progress Report No. 78, Research Laboratory of Electronics, M.I.T., July 15, 1965, pp A. A. Offenberger, Quarterly Progress Report No. 79, Research Laboratory of Electronics, M. I. T., October 15, 1965, pp A. A. Offenberger, Quarterly Progress Report No. 81, Research Laboratory of Electronics, M.I.T., April 15, 1966, pp B. ELECTRON DIFFUSION IN THE HELICALLY PERTURBED MAGNETIC FIELD OF THE M. I.T. STELLARATOR Electrons of 1500 volts are being injected and trapped in a torus for an average of 100 transits. The trapped electrons diffuse outward toward the walls of the torus and are collected in an azimuthally symmetric charge detector. After an initial transient, the current at the collector decays exponentially after the injection current is switched off. This type of behavior implies a random walk of the electrons toward the walls. The QPR No
4 R average number of transits N, where R is the radius of the vacuum wall, and (Ar) is the average square change in the particle's radial position in one transit. (Ar) Z is produced by perturbation fields (waves), as well as gas scattering, scattering from the Stellarator fields in the U-bends, and noncancellation of the toroidal drifts. The perturbing fields are varied while the others are kept as constant as possible; thus their effects can be subtracted out. The electrons diffuse to the torus in real space, but the perturbing fields produce velocity-space diffusion and almost no real-space diffusion of the guiding centers. The drift cancellation in the U-bends is velocity-dependent and hence converts velocity diffusion into real-space diffusion. The average number of transits then becomes N 2 v N loss cone in velocity coordinates, where v i loss cone is the perpendicular (to B) velocity at which the electron will be lost rapidly. (Avvl)Z ) is the squared change in perpendicular velocity in one transit averaged over all possible initial entrance velocity-space angle (phase average). The loss cone (v_ loss cone ) in a torus is not simply defined as in a mirror device, and depends on the drift-cancellation method that is used; however, it does not vary with a change in perturbation field strength, and hence we can measure the dependence of (Av)Z on perturbation field strength, keeping vi loss cone constant. We plan to measure the loss cone (vi loss ), but, at present, we use it as an adjustable parameter to fit the data. The perturbation field used for this experiment was a static transverse magnetic field rotating in space with a varying pitch length. A theoretical prediction of the lifetime for weak perturbations is the following. 1 where A\B F~)-1 F(zo) N= z 2 (1) v 1 loss cone 2 V o A- LP 2 o Tz 2 a r o QPR No
5 z Zo 2 o4 / F(zo) = tan TL - a cos 2L B = field for resonance for 1. 5 kv electrons o = 61.2 Gauss r = Larmor radius at the resonant field for v = 0 a = cm = Percentage of electron energy for which the perturbed field has been designed to convert parallel (to B) energy to transverse energy (or vice versa) = 80% L = length of perturbed-field region = 1 meter Po = resonant pitch length for vi = 0, = 13.4 cm z = position at 0-z <z L. o which an electron with v, = 0 is in resonance for a given B z, SLOPE = 1.6 ERROR BARS INDICATE RANDOM ERRORS ONLY SLOPE = I1 7 I I I 1 l i 1 I I 1 1, Fig. XVI-3. Diffusion coefficient vs perturbation field strength. QPR No
6 The raw data from the experiment was the average number of transits, N(BL ) N(B I ) N(o) where N is N(o) = oo. the average number of transits attributable to the perturbation field with Figure XVI-3 shows experimental results for Eq. 1, with BI varied and all else fixed. Equation 1 predicts a square-law dependence of the number of transits on perturbation field strength. The dependence goes from a 1. 6 power law to something higher (possible square law) at fields below BL/B z = The large error bars 10, z z THEORY, EQUATION 1 O 0 EXPERIMENTAL DATA FOR B 1 =0.89 GAUSS A EXPERIMENTAL DATA TAKEN AT BL = 2.67 GAUSS AND 0 EXTRAPOLATED TO 0.89 GAUSS BY A -POWER LAW AS IS SUGGESTED BY THE DATA OF FIG. XVI I I I I B z GAUSS Fig. XVI-4. Lifetime vs magnetic field strength. QPR No
7 result from the small difference of large numbers in Eq. 2 for weak perturbation (that is, N(B 1 ) = N(o)). Clark and Lidsky 2 predict N cc [B3/2] - 1 for sufficiently large Bj, which is in agreement with the region of Fig. XVI-3 above B 1 /B z = 1. 3%. The dependence of Eq. 1 on B was checked experimentally; it is given in Fig. XVI-4 for a constant value of BI= Gauss. By changing B z, the resonance point was shifted. B z = 61.2 Gauss corresponds to resonance at the left of Fig. XVI-4 (z 0 = 100 cm), while B z = 137 Gauss corresponds to resonance at z 0 = 0 for electrons with v.l = 0. An approximate fit to the data was found for vloss/v = 1. Researchers have proposed the use of perturbation fields for nonadiabatic traps, whereby molecular ions are trapped by a resonant field. Before that are lost by the inverse trapping process, collisions can break up an appreciable fraction of the molecular ions into atomic ions with half the mass, for instance. Figure XVI-4 gives experimental results that are equivalent to changing the mass of the particles. A molecular ion, H 2 say, would behave like an electron in resonance at 61.2 Gauss. An atomic ion of half the mass would be in resonance at Gauss and, from Fig. XVI-4, we see that the atomic ion would have a lifetime 100 times longer then the molecular ion. In this perturbed field the pitch changed by more than a factor of 2, so the atomic ion equivalent electrons were still in resonance with a portion of the perturbed field. During the next quarter we shall investigate diffusion from perturbed fields in the transition region between resonant and nonresonant fields. Also, we plan to measure the size of the loss cone in our torus. R. W. Moir, L. M. Lidsky References 1. R. C. Wingerson, T. H. Dupree, and D. J. Rose, Phys. Fluids 7, 1475 (1964); see Eq. (58). 2. L. M. Lidsky, J. F. Clarke, and D. J. Rose, "Experimental and Numerical Investigations of Velocity Diffusion in a Nonadiabatic Injection System," Paper No. 5L-9, Eighth Annual Meeting of the Division of Plasma Physics, Boston, Mass., November 1966; J. F. Clarke and L. M. Lidsky, "Nonclassical Diffusion Produced by a Resonant Helical Magnetic Field Perturbation," Paper No ; J. F. Clarke,, Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Nuclear Engineering, M. I. T., June QPR No
8
Academic and Research Staff. Prof. T. H. Dupree Prof. L. M. Lidsky Prof. N. L. Oleson. Graduate Students
 XXV. INTERACTION OF LASER RADIATION WITH PLASMAS AND NONADIABATIC MOTION OF PARTICLES IN MAGNETIC FIELDS Academic and Research Staff Prof. T. H. Dupree Prof. L. M. Lidsky Prof. N. L. Oleson Graduate Students
XXV. INTERACTION OF LASER RADIATION WITH PLASMAS AND NONADIABATIC MOTION OF PARTICLES IN MAGNETIC FIELDS Academic and Research Staff Prof. T. H. Dupree Prof. L. M. Lidsky Prof. N. L. Oleson Graduate Students
Stimulated Emission Devices: LASERS
 Stimulated Emission Devices: LASERS 1. Stimulated Emission and Photon Amplification E 2 E 2 E 2 hυ hυ hυ In hυ Out hυ E 1 E 1 E 1 (a) Absorption (b) Spontaneous emission (c) Stimulated emission The Principle
Stimulated Emission Devices: LASERS 1. Stimulated Emission and Photon Amplification E 2 E 2 E 2 hυ hυ hυ In hυ Out hυ E 1 E 1 E 1 (a) Absorption (b) Spontaneous emission (c) Stimulated emission The Principle
Experiment 3 1. The Michelson Interferometer and the He- Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado
 Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He- Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado The Michelson interferometer is one example of an optical interferometer.
Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He- Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado The Michelson interferometer is one example of an optical interferometer.
(b) Spontaneous emission. Absorption, spontaneous (random photon) emission and stimulated emission.
 Lecture 10 Stimulated Emission Devices Lasers Stimulated emission and light amplification Einstein coefficients Optical fiber amplifiers Gas laser and He-Ne Laser The output spectrum of a gas laser Laser
Lecture 10 Stimulated Emission Devices Lasers Stimulated emission and light amplification Einstein coefficients Optical fiber amplifiers Gas laser and He-Ne Laser The output spectrum of a gas laser Laser
Measurements of rotational transform due to noninductive toroidal current using motional Stark effect spectroscopy in the Large Helical Device
 REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS 76, 053505 2005 Measurements of rotational transform due to noninductive toroidal current using motional Stark effect spectroscopy in the Large Helical Device K. Ida, a
REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS 76, 053505 2005 Measurements of rotational transform due to noninductive toroidal current using motional Stark effect spectroscopy in the Large Helical Device K. Ida, a
B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F)
 B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F) Note : Attempt FIVE questions in all taking least two questions from each Part. All questions carry equal marks Part-A Q. 1. (a) What are Newton's
B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F) Note : Attempt FIVE questions in all taking least two questions from each Part. All questions carry equal marks Part-A Q. 1. (a) What are Newton's
What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light
 What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light amplification) Optical Resonator Cavity (greatly increase
What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light amplification) Optical Resonator Cavity (greatly increase
Internal magnetic field measurement in tokamak plasmas using a Zeeman polarimeter
 PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 55, Nos 5 & 6 journal of Nov. & Dec. 2000 physics pp. 751 756 Internal magnetic field measurement in tokamak plasmas using a Zeeman polarimeter M JAGADEESHWARI
PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 55, Nos 5 & 6 journal of Nov. & Dec. 2000 physics pp. 751 756 Internal magnetic field measurement in tokamak plasmas using a Zeeman polarimeter M JAGADEESHWARI
Atomic magnetometers: new twists to the old story. Michael Romalis Princeton University
 Atomic magnetometers: new twists to the old story Michael Romalis Princeton University Outline K magnetometer Elimination of spin-exchange relaxation Experimental setup Magnetometer performance Theoretical
Atomic magnetometers: new twists to the old story Michael Romalis Princeton University Outline K magnetometer Elimination of spin-exchange relaxation Experimental setup Magnetometer performance Theoretical
Astronomy 203 practice final examination
 Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Modern optics Lasers
 Chapter 13 Phys 322 Lecture 36 Modern optics Lasers Reminder: Please complete the online course evaluation Last lecture: Review discussion (no quiz) LASER = Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of
Chapter 13 Phys 322 Lecture 36 Modern optics Lasers Reminder: Please complete the online course evaluation Last lecture: Review discussion (no quiz) LASER = Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of
Academic and Research Staff. Prof. R. Weiss. Graduate Students. G. D. Blum T. R. Brown S. Ezekiel
 VII. GRAVITATION RESEARCH Academic and Research Staff Prof. R. Weiss Graduate Students G. D. Blum T. R. Brown S. Ezekiel RESEARCH OBJECTIVES Research in this group is concerned with an experimental investigation
VII. GRAVITATION RESEARCH Academic and Research Staff Prof. R. Weiss Graduate Students G. D. Blum T. R. Brown S. Ezekiel RESEARCH OBJECTIVES Research in this group is concerned with an experimental investigation
1. Consider the biconvex thick lens shown in the figure below, made from transparent material with index n and thickness L.
 Optical Science and Engineering 2013 Advanced Optics Exam Answer all questions. Begin each question on a new blank page. Put your banner ID at the top of each page. Please staple all pages for each individual
Optical Science and Engineering 2013 Advanced Optics Exam Answer all questions. Begin each question on a new blank page. Put your banner ID at the top of each page. Please staple all pages for each individual
Measuring Laser Diode Optical Power with an Integrating Sphere
 Measuring Laser Diode Optical Power with an Integrating Sphere Introduction Characterizing radiant sources like laser diodes accurately depends on the ability to measure their optical power output accurately.
Measuring Laser Diode Optical Power with an Integrating Sphere Introduction Characterizing radiant sources like laser diodes accurately depends on the ability to measure their optical power output accurately.
Laser Types Two main types depending on time operation Continuous Wave (CW) Pulsed operation Pulsed is easier, CW more useful
 What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light amplification) Optical Resonator Cavity (greatly increase
What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light amplification) Optical Resonator Cavity (greatly increase
First Beam Profile Measurements Based on Light Radiation of Atoms Excited by the Particle Beam
 First Beam Profile Measurements Based on Light Radiation of Atoms Excited by the Particle Beam Jürgen Dietrich Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH Bensheim, October 19, 2004 COSY Overview COSY accelerates (polarised)
First Beam Profile Measurements Based on Light Radiation of Atoms Excited by the Particle Beam Jürgen Dietrich Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH Bensheim, October 19, 2004 COSY Overview COSY accelerates (polarised)
Laser Types Two main types depending on time operation Continuous Wave (CW) Pulsed operation Pulsed is easier, CW more useful
 Main Requirements of the Laser Optical Resonator Cavity Laser Gain Medium of 2, 3 or 4 level types in the Cavity Sufficient means of Excitation (called pumping) eg. light, current, chemical reaction Population
Main Requirements of the Laser Optical Resonator Cavity Laser Gain Medium of 2, 3 or 4 level types in the Cavity Sufficient means of Excitation (called pumping) eg. light, current, chemical reaction Population
Interface (backside) & Extraction Lens
 Plasma Interface Interface (backside) & Extraction Lens Extraction Lens (-2000 volts) ION OPTICS Tip of the sampler cone is positioned to be in the region of maximum ionization Ions no longer under control
Plasma Interface Interface (backside) & Extraction Lens Extraction Lens (-2000 volts) ION OPTICS Tip of the sampler cone is positioned to be in the region of maximum ionization Ions no longer under control
LIST OF TOPICS BASIC LASER PHYSICS. Preface xiii Units and Notation xv List of Symbols xvii
 ate LIST OF TOPICS Preface xiii Units and Notation xv List of Symbols xvii BASIC LASER PHYSICS Chapter 1 An Introduction to Lasers 1.1 What Is a Laser? 2 1.2 Atomic Energy Levels and Spontaneous Emission
ate LIST OF TOPICS Preface xiii Units and Notation xv List of Symbols xvii BASIC LASER PHYSICS Chapter 1 An Introduction to Lasers 1.1 What Is a Laser? 2 1.2 Atomic Energy Levels and Spontaneous Emission
LASER APPLICATIONS XII. QPR No Academic Research Staff. Ezekiel. Prof. S. Graduate Students
 XII. LASER APPLICATIONS Academic Research Staff Prof. S. Ezekiel Graduate Students L. A. Hackel J. A. Monjes J. P. Sullivan P. D. Henshaw T. J. Ryan D. G. Youmans J. W. Stafurik RESEARCH OBJECTIVES Our
XII. LASER APPLICATIONS Academic Research Staff Prof. S. Ezekiel Graduate Students L. A. Hackel J. A. Monjes J. P. Sullivan P. D. Henshaw T. J. Ryan D. G. Youmans J. W. Stafurik RESEARCH OBJECTIVES Our
2. OPERATIONAL CONDITIONS
 1. INTRODUCTION This device was designed for modern physics labs of colleges and graduate schools. It demonstrates the influence of a magnetic field on light, known as Zeeman Effect, and reveals the behavior
1. INTRODUCTION This device was designed for modern physics labs of colleges and graduate schools. It demonstrates the influence of a magnetic field on light, known as Zeeman Effect, and reveals the behavior
Fabry-Perot Interferometer for atmospheric monitoring useful for EAS detection E.Fokitis 1, K. Patrinos 1, Z. Nikitaki 1
 Fabry-Perot Interferometer for atmospheric monitoring useful for EAS detection E.Fokitis 1, K. Patrinos 1, Z. Nikitaki 1 ABSTRACT A piezotunable Fabry-Perot interferometer is studied as a candidate Doppler
Fabry-Perot Interferometer for atmospheric monitoring useful for EAS detection E.Fokitis 1, K. Patrinos 1, Z. Nikitaki 1 ABSTRACT A piezotunable Fabry-Perot interferometer is studied as a candidate Doppler
Speed of Light in Air
 Speed of Light in Air Electromagnetic waves represent energy in the form of oscillating electric and magnetic fields which propagate through vacuum with a speed c = 2.9979246x10 8 m/s. Electromagnetic
Speed of Light in Air Electromagnetic waves represent energy in the form of oscillating electric and magnetic fields which propagate through vacuum with a speed c = 2.9979246x10 8 m/s. Electromagnetic
Lasers & Holography. Ulrich Heintz Brown University. 4/5/2016 Ulrich Heintz - PHYS 1560 Lecture 10 1
 Lasers & Holography Ulrich Heintz Brown University 4/5/2016 Ulrich Heintz - PHYS 1560 Lecture 10 1 Lecture schedule Date Topic Thu, Jan 28 Introductory meeting Tue, Feb 2 Safety training Thu, Feb 4 Lab
Lasers & Holography Ulrich Heintz Brown University 4/5/2016 Ulrich Heintz - PHYS 1560 Lecture 10 1 Lecture schedule Date Topic Thu, Jan 28 Introductory meeting Tue, Feb 2 Safety training Thu, Feb 4 Lab
Academic and Research Staff. Prof. T. H. Dupree Prof. L. M. Lidsky Prof. N. L. Oleson. Graduate Students
 XV. INTERACTION OF LASER RADIATION WITH PLASMAS AND NONADIABATIC MOTION OF PARTICLES IN MAGNETIC FIELDS Academic and Research Staff Prof. T. H. Dupree Prof. L. M. Lidsy Prof. N. L. Oleson Graduate Students
XV. INTERACTION OF LASER RADIATION WITH PLASMAS AND NONADIABATIC MOTION OF PARTICLES IN MAGNETIC FIELDS Academic and Research Staff Prof. T. H. Dupree Prof. L. M. Lidsy Prof. N. L. Oleson Graduate Students
Introduction. Procedure. In this experiment, you'll use the interferometer to EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Lens 18mm FL. Component holder.
 12-7137A Precision Interferometer Experiment 1: Introduction to Interferometry EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Basic Interferometer (OS-9255A) Laser (OS-9171) Laser Alignment Bench (OS-9172) Interferometer Accessories
12-7137A Precision Interferometer Experiment 1: Introduction to Interferometry EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Basic Interferometer (OS-9255A) Laser (OS-9171) Laser Alignment Bench (OS-9172) Interferometer Accessories
Zeeman Effect. Alex Povilus Physics 441- Fall 2003 December 20, 2003
 Zeeman Effect Alex Povilus Physics 441- Fall 2003 December 20, 2003 Abstract The Zeeman Effect is observed by application of a strong magnetic field to a mercury vapor cell and exciting transitions by
Zeeman Effect Alex Povilus Physics 441- Fall 2003 December 20, 2003 Abstract The Zeeman Effect is observed by application of a strong magnetic field to a mercury vapor cell and exciting transitions by
Measurement of lower hybrid waves using microwave scattering technique in Alcator C-Mod
 Measurement of lower hybrid waves using microwave scattering technique in Alcator C-Mod S. Baek, R. Parker, S. Shiraiwa, A. Dominguez, E. Marmar, G. Wallace, G. J. Kramer* Plasma Science and Fusion Center,
Measurement of lower hybrid waves using microwave scattering technique in Alcator C-Mod S. Baek, R. Parker, S. Shiraiwa, A. Dominguez, E. Marmar, G. Wallace, G. J. Kramer* Plasma Science and Fusion Center,
Highly Efficient and Anomalous Charge Transfer in van der Waals Trilayer Semiconductors
 Highly Efficient and Anomalous Charge Transfer in van der Waals Trilayer Semiconductors Frank Ceballos 1, Ming-Gang Ju 2 Samuel D. Lane 1, Xiao Cheng Zeng 2 & Hui Zhao 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Highly Efficient and Anomalous Charge Transfer in van der Waals Trilayer Semiconductors Frank Ceballos 1, Ming-Gang Ju 2 Samuel D. Lane 1, Xiao Cheng Zeng 2 & Hui Zhao 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy,
JRE Group of Institutions ASSIGNMENT # 1 Special Theory of Relativity
 ASSIGNMENT # 1 Special Theory of Relativity 1. What was the objective of conducting the Michelson-Morley experiment? Describe the experiment. How is the negative result of the experiment interpreted? 2.
ASSIGNMENT # 1 Special Theory of Relativity 1. What was the objective of conducting the Michelson-Morley experiment? Describe the experiment. How is the negative result of the experiment interpreted? 2.
PHY410 Optics Exam #3
 PHY410 Optics Exam #3 NAME: 1 2 Multiple Choice Section - 5 pts each 1. A continuous He-Ne laser beam (632.8 nm) is chopped, using a spinning aperture, into 500 nanosecond pulses. Compute the resultant
PHY410 Optics Exam #3 NAME: 1 2 Multiple Choice Section - 5 pts each 1. A continuous He-Ne laser beam (632.8 nm) is chopped, using a spinning aperture, into 500 nanosecond pulses. Compute the resultant
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 17.
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 17 Optical Sources- Introduction to LASER Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar,
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 17 Optical Sources- Introduction to LASER Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar,
Lab #13: Polarization
 Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
Unit-2 LASER. Syllabus: Properties of lasers, types of lasers, derivation of Einstein A & B Coefficients, Working He-Ne and Ruby lasers.
 Unit-2 LASER Syllabus: Properties of lasers, types of lasers, derivation of Einstein A & B Coefficients, Working He-Ne and Ruby lasers. Page 1 LASER: The word LASER is acronym for light amplification by
Unit-2 LASER Syllabus: Properties of lasers, types of lasers, derivation of Einstein A & B Coefficients, Working He-Ne and Ruby lasers. Page 1 LASER: The word LASER is acronym for light amplification by
Optical Techniques for Gravitational-Wave Detection
 Optical Techniques for Gravitational-Wave Detection M. Tacca Nikhef - Amsterdam Nikhef- 2017 July 14th Born in Novara (Italy) Introducing Myself PostDoc Fellow @ Nikhef (since July 2017) Laurea & PhD @
Optical Techniques for Gravitational-Wave Detection M. Tacca Nikhef - Amsterdam Nikhef- 2017 July 14th Born in Novara (Italy) Introducing Myself PostDoc Fellow @ Nikhef (since July 2017) Laurea & PhD @
Application Note GA-301E. MBMS for Preformed Ions. Extrel CMS, 575 Epsilon Drive, Pittsburgh, PA I. SAMPLING A CHEMICAL SOUP
 Application Note MBMS for Preformed Ions, 575 Epsilon Drive, Pittsburgh, PA 15238 (Poster Presented at 45th ASMS Conference on Mass Spectrometry, June 1-5, 1997) In order to accurately characterize a plasma
Application Note MBMS for Preformed Ions, 575 Epsilon Drive, Pittsburgh, PA 15238 (Poster Presented at 45th ASMS Conference on Mass Spectrometry, June 1-5, 1997) In order to accurately characterize a plasma
Physics 610. Adv Particle Physics. April 7, 2014
 Physics 610 Adv Particle Physics April 7, 2014 Accelerators History Two Principles Electrostatic Cockcroft-Walton Van de Graaff and tandem Van de Graaff Transformers Cyclotron Betatron Linear Induction
Physics 610 Adv Particle Physics April 7, 2014 Accelerators History Two Principles Electrostatic Cockcroft-Walton Van de Graaff and tandem Van de Graaff Transformers Cyclotron Betatron Linear Induction
Chapter-4 Stimulated emission devices LASERS
 Semiconductor Laser Diodes Chapter-4 Stimulated emission devices LASERS The Road Ahead Lasers Basic Principles Applications Gas Lasers Semiconductor Lasers Semiconductor Lasers in Optical Networks Improvement
Semiconductor Laser Diodes Chapter-4 Stimulated emission devices LASERS The Road Ahead Lasers Basic Principles Applications Gas Lasers Semiconductor Lasers Semiconductor Lasers in Optical Networks Improvement
Neutral Beam-Ion Prompt Loss Induced by Alfvén Eigenmodes in DIII-D
 Neutral Beam-Ion Prompt Loss Induced by Alfvén Eigenmodes in DIII-D by X. Chen,1 M.E. Austin,2 R.K. Fisher,3 W.W. Heidbrink,1 G.J. Kramer,4 R. Nazikian,4 D.C. Pace,3 C.C. Petty,3 M.A. Van Zeeland3 1University
Neutral Beam-Ion Prompt Loss Induced by Alfvén Eigenmodes in DIII-D by X. Chen,1 M.E. Austin,2 R.K. Fisher,3 W.W. Heidbrink,1 G.J. Kramer,4 R. Nazikian,4 D.C. Pace,3 C.C. Petty,3 M.A. Van Zeeland3 1University
Nuclear spin maser with a novel masing mechanism and its application to the search for an atomic EDM in 129 Xe
 Nuclear spin maser with a novel masing mechanism and its application to the search for an atomic EDM in 129 Xe A. Yoshimi RIKEN K. Asahi, S. Emori, M. Tsukui, RIKEN, Tokyo Institute of Technology Nuclear
Nuclear spin maser with a novel masing mechanism and its application to the search for an atomic EDM in 129 Xe A. Yoshimi RIKEN K. Asahi, S. Emori, M. Tsukui, RIKEN, Tokyo Institute of Technology Nuclear
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS
 PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS C. A. Bennett University of North Carolina At Asheville WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS Preface 1 The Physics of Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS C. A. Bennett University of North Carolina At Asheville WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS Preface 1 The Physics of Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
Visualization of Xe and Sn Atoms Generated from Laser-Produced Plasma for EUV Light Source
 3rd International EUVL Symposium NOVEMBER 1-4, 2004 Miyazaki, Japan Visualization of Xe and Sn Atoms Generated from Laser-Produced Plasma for EUV Light Source H. Tanaka, A. Matsumoto, K. Akinaga, A. Takahashi
3rd International EUVL Symposium NOVEMBER 1-4, 2004 Miyazaki, Japan Visualization of Xe and Sn Atoms Generated from Laser-Produced Plasma for EUV Light Source H. Tanaka, A. Matsumoto, K. Akinaga, A. Takahashi
Characterization and Stabilization of Opto Power Fiber-Coupled Laser Diode Arrays. Abstract
 Characterization and Stabilization of Opto Power Fiber-Coupled Laser Diode Arrays D. F. Phillips, G. P. Wong, D. Bear, R. E. Stoner and R. L. Walsworth Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge,
Characterization and Stabilization of Opto Power Fiber-Coupled Laser Diode Arrays D. F. Phillips, G. P. Wong, D. Bear, R. E. Stoner and R. L. Walsworth Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge,
Measurement of EEDF and Distribution of Primary Electron in a Bucket Ion Source
 Fourth IAEA Technical Meeting on "Negative Ion Based NBIs" May 9-11 2005, Padova - Italy Measurement of EEDF and Distribution of Primary Electron in a Bucket Ion Source S. Miyamoto, F. Kanayama, T. Minami,
Fourth IAEA Technical Meeting on "Negative Ion Based NBIs" May 9-11 2005, Padova - Italy Measurement of EEDF and Distribution of Primary Electron in a Bucket Ion Source S. Miyamoto, F. Kanayama, T. Minami,
Gauss Modes. Paul Fulda
 Interferometry Interferometry with with LaguerreLaguerreGauss Gauss Modes Modes Paul Paul Fulda Fulda University University of of Birmingham Birmingham E.T. E.T. WP3 WP3 Meeting Meeting -- -- 09/06/2009
Interferometry Interferometry with with LaguerreLaguerreGauss Gauss Modes Modes Paul Paul Fulda Fulda University University of of Birmingham Birmingham E.T. E.T. WP3 WP3 Meeting Meeting -- -- 09/06/2009
Lasers... the optical cavity
 Lasers... the optical cavity history principle, intuitive aspects, characteristics 2 levels systems Ti: Helium Al2O3 - Neon model-locked laser laser VCSEL bragg mirrors cleaved facets 13 ptical and/or
Lasers... the optical cavity history principle, intuitive aspects, characteristics 2 levels systems Ti: Helium Al2O3 - Neon model-locked laser laser VCSEL bragg mirrors cleaved facets 13 ptical and/or
Laser Spectroscopy on Bunched Radioactive Ion Beams
 Laser Spectroscopy on Bunched Radioactive Ion Beams Jon Billowes University of Manchester Balkan School on Nuclear Physics, Bodrum 2004 Lecture 1. 1.1 Nuclear moments 1.2 Hyperfine interaction in free
Laser Spectroscopy on Bunched Radioactive Ion Beams Jon Billowes University of Manchester Balkan School on Nuclear Physics, Bodrum 2004 Lecture 1. 1.1 Nuclear moments 1.2 Hyperfine interaction in free
Digital Holographic Measurement of Nanometric Optical Excitation on Soft Matter by Optical Pressure and Photothermal Interactions
 Ph.D. Dissertation Defense September 5, 2012 Digital Holographic Measurement of Nanometric Optical Excitation on Soft Matter by Optical Pressure and Photothermal Interactions David C. Clark Digital Holography
Ph.D. Dissertation Defense September 5, 2012 Digital Holographic Measurement of Nanometric Optical Excitation on Soft Matter by Optical Pressure and Photothermal Interactions David C. Clark Digital Holography
Laboratory #29: Spectrometer
 INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS, P309 LABORATORY Laboratory #29: Spectrometer Goal: Learn to adjust an optical spectrometer, use a transmission grating to measure known spectral lines of mercury,
INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS, P309 LABORATORY Laboratory #29: Spectrometer Goal: Learn to adjust an optical spectrometer, use a transmission grating to measure known spectral lines of mercury,
Lasers and Electro-optics
 Lasers and Electro-optics Second Edition CHRISTOPHER C. DAVIS University of Maryland III ^0 CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface to the Second Edition page xv 1 Electromagnetic waves, light, and lasers 1
Lasers and Electro-optics Second Edition CHRISTOPHER C. DAVIS University of Maryland III ^0 CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface to the Second Edition page xv 1 Electromagnetic waves, light, and lasers 1
The Michelson Interferometer and the He-Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado
 Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He-Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado In the experiment, two different types of measurements will be made with
Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He-Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado In the experiment, two different types of measurements will be made with
Fiber Gratings p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Bragg Diffraction p. 2 Photosensitivity p. 3 Fabrication Techniques p. 4 Single-Beam Internal Technique p.
 Preface p. xiii Fiber Gratings p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Bragg Diffraction p. 2 Photosensitivity p. 3 Fabrication Techniques p. 4 Single-Beam Internal Technique p. 4 Dual-Beam Holographic Technique p. 5
Preface p. xiii Fiber Gratings p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Bragg Diffraction p. 2 Photosensitivity p. 3 Fabrication Techniques p. 4 Single-Beam Internal Technique p. 4 Dual-Beam Holographic Technique p. 5
Light Scattering Study of Poly (dimethyl siloxane) in Liquid and Supercritical CO 2.
 Supplemental Information. Light Scattering Study of Poly (dimethyl siloxane) in Liquid and Supercritical CO 2. Pascal André, Sarah L. Folk, Mireille Adam, Michael Rubinstein, and Joseph M. DeSimone Technical
Supplemental Information. Light Scattering Study of Poly (dimethyl siloxane) in Liquid and Supercritical CO 2. Pascal André, Sarah L. Folk, Mireille Adam, Michael Rubinstein, and Joseph M. DeSimone Technical
Status of the LHCb RICH detector and the HPD
 Beauty 2005 Status of the LHCb RICH detector and the HPD Tito Bellunato Università degli Studi di Milano Bicocca & INFN On behalf of the LHCb RICH group Assisi 23 June Assisi 2005 23 June Tito Bellunato
Beauty 2005 Status of the LHCb RICH detector and the HPD Tito Bellunato Università degli Studi di Milano Bicocca & INFN On behalf of the LHCb RICH group Assisi 23 June Assisi 2005 23 June Tito Bellunato
The Plasma Phase. Chapter 1. An experiment - measure and understand transport processes in a plasma. Chapter 2. An introduction to plasma physics
 The Plasma Phase Chapter 1. An experiment - measure and understand transport processes in a plasma Three important vugraphs What we have just talked about The diagnostics Chapter 2. An introduction to
The Plasma Phase Chapter 1. An experiment - measure and understand transport processes in a plasma Three important vugraphs What we have just talked about The diagnostics Chapter 2. An introduction to
Determining thermal noise limiting properties of thin films
 Determining thermal noise limiting properties of thin films Courtney Linn Institute for Gravitational Research University of Glasgow Summer 2011 Abstract In order to make thermally stable mirrors to be
Determining thermal noise limiting properties of thin films Courtney Linn Institute for Gravitational Research University of Glasgow Summer 2011 Abstract In order to make thermally stable mirrors to be
Flow dynamics and plasma heating of spheromaks in SSX
 Flow dynamics and plasma heating of spheromaks in SSX M. R. Brown and C. D. Cothran, D. Cohen, J. Horwitz, and V. Chaplin Department of Physics and Astronomy Center for Magnetic Self Organization Swarthmore
Flow dynamics and plasma heating of spheromaks in SSX M. R. Brown and C. D. Cothran, D. Cohen, J. Horwitz, and V. Chaplin Department of Physics and Astronomy Center for Magnetic Self Organization Swarthmore
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. ECE426F Optical Engineering. Final Exam. Dec. 17, 2003.
 Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE426F Optical Engineering Final Exam Dec. 17, 2003 Exam Type: D (Close-book + one 2-sided aid sheet + a non-programmable calculator)
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE426F Optical Engineering Final Exam Dec. 17, 2003 Exam Type: D (Close-book + one 2-sided aid sheet + a non-programmable calculator)
ERL FACILITY AT CERN FOR APPLICATIONS
 ERL FACILITY AT CERN FOR APPLICATIONS Erk Jensen (CERN) Big thanks to contributors: A. Bogacz (JLAB), O. Brüning, R. Calaga, V. Chetvertkova, E. Cormier (CELIA), R. Jones, M. Klein, A. Valloni, D. Pellegrini,
ERL FACILITY AT CERN FOR APPLICATIONS Erk Jensen (CERN) Big thanks to contributors: A. Bogacz (JLAB), O. Brüning, R. Calaga, V. Chetvertkova, E. Cormier (CELIA), R. Jones, M. Klein, A. Valloni, D. Pellegrini,
Study of Distributed Ion-Pumps in CESR 1
 Study of Distributed Ion-Pumps in CESR 1 Yulin Li, Roberto Kersevan, Nariman Mistry Laboratory of Nuclear Studies, Cornell University Ithaca, NY 153-001 Abstract It is desirable to reduce anode voltage
Study of Distributed Ion-Pumps in CESR 1 Yulin Li, Roberto Kersevan, Nariman Mistry Laboratory of Nuclear Studies, Cornell University Ithaca, NY 153-001 Abstract It is desirable to reduce anode voltage
A Multi-beamlet Injector for Heavy Ion Fusion: Experiments and Modeling
 A Multi-beamlet Injector for Heavy Ion Fusion: Experiments and Modeling G.A. Westenskow, D.P. Grote; LLNL J.W. Kwan, F. Bieniosek; LBNL PAC07 - FRYAB01 Albuquerque, New Mexico June 29, 2007 This work has
A Multi-beamlet Injector for Heavy Ion Fusion: Experiments and Modeling G.A. Westenskow, D.P. Grote; LLNL J.W. Kwan, F. Bieniosek; LBNL PAC07 - FRYAB01 Albuquerque, New Mexico June 29, 2007 This work has
laser with Q-switching for generation of terahertz radiation Multiline CO 2 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Multiline CO 2 laser with Q-switching for generation of terahertz radiation To cite this article: A A Ionin et al 2017 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 941 012004
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Multiline CO 2 laser with Q-switching for generation of terahertz radiation To cite this article: A A Ionin et al 2017 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 941 012004
Formation of High-b ECH Plasma and Inward Particle Diffusion in RT-1
 J Fusion Energ (2010) 29:553 557 DOI 10.1007/s10894-010-9327-6 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Formation of High-b ECH Plasma and Inward Particle Diffusion in RT-1 H. Saitoh Z. Yoshida J. Morikawa Y. Yano T. Mizushima
J Fusion Energ (2010) 29:553 557 DOI 10.1007/s10894-010-9327-6 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Formation of High-b ECH Plasma and Inward Particle Diffusion in RT-1 H. Saitoh Z. Yoshida J. Morikawa Y. Yano T. Mizushima
Homework 1. Property LASER Incandescent Bulb
 Homework 1 Solution: a) LASER light is spectrally pure, single wavelength, and they are coherent, i.e. all the photons are in phase. As a result, the beam of a laser light tends to stay as beam, and not
Homework 1 Solution: a) LASER light is spectrally pure, single wavelength, and they are coherent, i.e. all the photons are in phase. As a result, the beam of a laser light tends to stay as beam, and not
1. INTRODUCTION 2. EXPERIMENTAL SET-UP CHARACTERIZATION OF A TUBULAR PLASMA REACTOR WITH EXTERNAL ANNULAR ELECTRODES
 Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 57, No. 3, P. 390-395, 2005 CHARACTERIZATION OF A TUBULAR PLASMA REACTOR WITH EXTERNAL ANNULAR ELECTRODES C. PETCU, B. MITU, G. DINESCU National Institute for Lasers,
Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 57, No. 3, P. 390-395, 2005 CHARACTERIZATION OF A TUBULAR PLASMA REACTOR WITH EXTERNAL ANNULAR ELECTRODES C. PETCU, B. MITU, G. DINESCU National Institute for Lasers,
Comparison of hollow cathode and Penning discharges for metastable He production
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 11 (2002) 426 430 Comparison of hollow cathode and Penning discharges for metastable He production PLASMA SOURCES SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY PII:
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 11 (2002) 426 430 Comparison of hollow cathode and Penning discharges for metastable He production PLASMA SOURCES SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY PII:
EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET AND SOFT X-RAY LASERS
 Chapter 7 EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET AND SOFT X-RAY LASERS Hot dense plasma lasing medium d θ λ λ Visible laser pump Ch07_00VG.ai The Processes of Absorption, Spontaneous Emission, and Stimulated Emission Absorption
Chapter 7 EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET AND SOFT X-RAY LASERS Hot dense plasma lasing medium d θ λ λ Visible laser pump Ch07_00VG.ai The Processes of Absorption, Spontaneous Emission, and Stimulated Emission Absorption
Observation of Electron Trapping in an Intense Laser Beam
 Observation of Electron Trapping in an Intense Laser Beam Since the discovery of the ponderomotive force over 4 years ago, it has been known that charged particles interacting with an oscillating electromagnetic
Observation of Electron Trapping in an Intense Laser Beam Since the discovery of the ponderomotive force over 4 years ago, it has been known that charged particles interacting with an oscillating electromagnetic
Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap
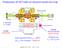 Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap I=450 ma E= 5 kev axially: electrodes radially: electron beam space charge total trap potential U trap 200 V (U trap ion charge) 10000 ev 15000 A/cm 2 n
Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap I=450 ma E= 5 kev axially: electrodes radially: electron beam space charge total trap potential U trap 200 V (U trap ion charge) 10000 ev 15000 A/cm 2 n
Zeeman Effect - Lab exercises 24
 Zeeman Effect - Lab exercises 24 Pieter Zeeman Franziska Beyer August 2010 1 Overview and Introduction The Zeeman effect consists of the splitting of energy levels of atoms if they are situated in a magnetic
Zeeman Effect - Lab exercises 24 Pieter Zeeman Franziska Beyer August 2010 1 Overview and Introduction The Zeeman effect consists of the splitting of energy levels of atoms if they are situated in a magnetic
Characterization of the VIIRS Blackbody Emittance
 Characterization of the VIIRS Blackbody Emittance Jeremy Kloepfer, Chris Taylor, and Vijay Murgai jeremiah_kloepfer@raytheon.com Conference on Characterization and Radiometric Calibration for Remote Sensing,
Characterization of the VIIRS Blackbody Emittance Jeremy Kloepfer, Chris Taylor, and Vijay Murgai jeremiah_kloepfer@raytheon.com Conference on Characterization and Radiometric Calibration for Remote Sensing,
University of Groningen. Laser Spectroscopy of Trapped Ra+ Ion Versolato, Oscar Oreste
 University of Groningen Laser Spectroscopy of Trapped Ra+ Ion Versolato, Oscar Oreste IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Laser Spectroscopy of Trapped Ra+ Ion Versolato, Oscar Oreste IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
Chapter9. Amplification of light. Lasers Part 2
 Chapter9. Amplification of light. Lasers Part 06... Changhee Lee School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Seoul National Univ. chlee7@snu.ac.kr /9 9. Stimulated emission and thermal radiation The
Chapter9. Amplification of light. Lasers Part 06... Changhee Lee School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Seoul National Univ. chlee7@snu.ac.kr /9 9. Stimulated emission and thermal radiation The
Effect of secondary beam neutrals on MSE: theory
 Effect of secondary beam neutrals on MSE: theory S. Scott (PPPL) J. Ko, I. Hutchinson (PSFC/MIT) H. Yuh (Nova Photonics) Poster NP8.87 49 th Annual Meeting, DPP-APS Orlando, FL November 27 Abstract A standard
Effect of secondary beam neutrals on MSE: theory S. Scott (PPPL) J. Ko, I. Hutchinson (PSFC/MIT) H. Yuh (Nova Photonics) Poster NP8.87 49 th Annual Meeting, DPP-APS Orlando, FL November 27 Abstract A standard
The Design and Fabrication of a 6 Tesla EBIT Solenoid
 LBNL-40462 SCMAG-593 The Design and Fabrication of a 6 Tesla EBIT Solenoid 1. Introduction M. A. Green a, S. M. Dardin a, R. E. Marrs b, E. Magee b, S. K. Mukhergee a a Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory,
LBNL-40462 SCMAG-593 The Design and Fabrication of a 6 Tesla EBIT Solenoid 1. Introduction M. A. Green a, S. M. Dardin a, R. E. Marrs b, E. Magee b, S. K. Mukhergee a a Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory,
Spectroscopic Measurements of Optical Elements For Submillimeter Receivers
 5- Abstract Spectroscopic Measurements of Optical Elements For Submillimeter Receivers J. Kawamura, S. Paine, and D. C. Papa Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 60 Garden Street Cambridge, Massachusetts
5- Abstract Spectroscopic Measurements of Optical Elements For Submillimeter Receivers J. Kawamura, S. Paine, and D. C. Papa Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 60 Garden Street Cambridge, Massachusetts
Light as Wave Motion p. 1 Huygens' Ideas p. 2 Newton's Ideas p. 8 Complex Numbers p. 10 Simple Harmonic Motion p. 11 Polarized Waves in a Stretched
 Introduction p. xvii Light as Wave Motion p. 1 Huygens' Ideas p. 2 Newton's Ideas p. 8 Complex Numbers p. 10 Simple Harmonic Motion p. 11 Polarized Waves in a Stretched String p. 16 Velocities of Mechanical
Introduction p. xvii Light as Wave Motion p. 1 Huygens' Ideas p. 2 Newton's Ideas p. 8 Complex Numbers p. 10 Simple Harmonic Motion p. 11 Polarized Waves in a Stretched String p. 16 Velocities of Mechanical
Helioseismology. Jesper Schou Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research
 Helioseismology Jesper Schou Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research schou@mps.mpg.de Page 1 of 60 Helioseismology The study of the Sun using waves Similar to Earth seismology Sounds waves are trapped
Helioseismology Jesper Schou Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research schou@mps.mpg.de Page 1 of 60 Helioseismology The study of the Sun using waves Similar to Earth seismology Sounds waves are trapped
Chapter 2 Correlation Force Spectroscopy
 Chapter 2 Correlation Force Spectroscopy Correlation Force Spectroscopy: Rationale In principle, the main advantage of correlation force spectroscopy (CFS) over onecantilever atomic force microscopy (AFM)
Chapter 2 Correlation Force Spectroscopy Correlation Force Spectroscopy: Rationale In principle, the main advantage of correlation force spectroscopy (CFS) over onecantilever atomic force microscopy (AFM)
Assessment of the Azimuthal Homogeneity of the Neutral Gas in a Hall Effect Thruster using Electron Beam Fluorescence
 Assessment of the Azimuthal Homogeneity of the Neutral Gas in a Hall Effect Thruster using Electron Beam Fluorescence IEPC-2015-91059 / ISTS-2015-b-91059 Presented at Joint Conference of 30th International
Assessment of the Azimuthal Homogeneity of the Neutral Gas in a Hall Effect Thruster using Electron Beam Fluorescence IEPC-2015-91059 / ISTS-2015-b-91059 Presented at Joint Conference of 30th International
OPTI 511R, Spring 2018 Problem Set 10 Prof. R.J. Jones Due Thursday, April 19
 OPTI 511R, Spring 2018 Problem Set 10 Prof. R.J. Jones Due Thursday, April 19 1. (a) Suppose you want to use a lens focus a Gaussian laser beam of wavelength λ in order to obtain a beam waist radius w
OPTI 511R, Spring 2018 Problem Set 10 Prof. R.J. Jones Due Thursday, April 19 1. (a) Suppose you want to use a lens focus a Gaussian laser beam of wavelength λ in order to obtain a beam waist radius w
Physics Common Assessment Unit 5-8 3rd Nine Weeks
 1) What is the direction of the force(s) that maintain(s) circular motion? A) one force pulls the object inward toward the radial center while another force pushes the object at a right angle to the first
1) What is the direction of the force(s) that maintain(s) circular motion? A) one force pulls the object inward toward the radial center while another force pushes the object at a right angle to the first
GA A22722 CENTRAL THOMSON SCATTERING UPGRADE ON DIII D
 GA A22722 CENTRAL THOMSON SCATTERING UPGRADE ON DIII D by D.G. NILSON, T.N. CARLSTROM, C.L. HSIEH, B.W. STALLARD, and R.E. STOCKDALE NOVEMBER 1997 DISCLAIMER This report was prepared as an account of work
GA A22722 CENTRAL THOMSON SCATTERING UPGRADE ON DIII D by D.G. NILSON, T.N. CARLSTROM, C.L. HSIEH, B.W. STALLARD, and R.E. STOCKDALE NOVEMBER 1997 DISCLAIMER This report was prepared as an account of work
A Multipass Optics for Quantum-Well-Pumped Semiconductor Disk Lasers
 Multipass-Pumped Semiconductor Disk Lasers 37 A Multipass Optics for Quantum-Well-Pumped Semiconductor Disk Lasers Markus Polanik The pump absorption of quantum-well-pumped semiconductor disk lasers can
Multipass-Pumped Semiconductor Disk Lasers 37 A Multipass Optics for Quantum-Well-Pumped Semiconductor Disk Lasers Markus Polanik The pump absorption of quantum-well-pumped semiconductor disk lasers can
EE485 Introduction to Photonics
 Pattern formed by fluorescence of quantum dots EE485 Introduction to Photonics Photon and Laser Basics 1. Photon properties 2. Laser basics 3. Characteristics of laser beams Reading: Pedrotti 3, Sec. 1.2,
Pattern formed by fluorescence of quantum dots EE485 Introduction to Photonics Photon and Laser Basics 1. Photon properties 2. Laser basics 3. Characteristics of laser beams Reading: Pedrotti 3, Sec. 1.2,
F.G. Major. The Quantum Beat. The Physical Principles of Atomic Clocks. With 230 Illustrations. Springer
 F.G. Major The Quantum Beat The Physical Principles of Atomic Clocks With 230 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface Chapter 1. Celestial and Mechanical Clocks 1 1.1 Cyclic Events in Nature 1 1.2 The
F.G. Major The Quantum Beat The Physical Principles of Atomic Clocks With 230 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface Chapter 1. Celestial and Mechanical Clocks 1 1.1 Cyclic Events in Nature 1 1.2 The
QPR No. 80 VIII. NOISE IN ELECTRON DEVICES. Academic and Research Staff. Prof. H. A. Haus Prof. P. Penfield, Jr. Prof. R. P. Rafuse.
 VIII. NOISE IN ELECTRON DEVICES Academic and Research Staff Prof. H. A. Haus Prof. P. Penfield, Jr. Prof. R. P. Rafuse Graduate Students J. L. Doane H. J. Pauwels R. L. Guldi V. K. Prabhu RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
VIII. NOISE IN ELECTRON DEVICES Academic and Research Staff Prof. H. A. Haus Prof. P. Penfield, Jr. Prof. R. P. Rafuse Graduate Students J. L. Doane H. J. Pauwels R. L. Guldi V. K. Prabhu RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
= 6 (1/ nm) So what is probability of finding electron tunneled into a barrier 3 ev high?
 STM STM With a scanning tunneling microscope, images of surfaces with atomic resolution can be readily obtained. An STM uses quantum tunneling of electrons to map the density of electrons on the surface
STM STM With a scanning tunneling microscope, images of surfaces with atomic resolution can be readily obtained. An STM uses quantum tunneling of electrons to map the density of electrons on the surface
The ISIS Penning H - SPS and Diagnostic Developments at RAL
 The ISIS Penning H - SPS and Diagnostic Developments at RAL D.C. Faircloth 1, A.P. Letchford 1, J. Pozimski 1+2, M.O. Whitehead 1, T. Wood 1, S. Jolly 2, P. Savage 2, M. Haigh 3, J. Morrison 3, I. Yew
The ISIS Penning H - SPS and Diagnostic Developments at RAL D.C. Faircloth 1, A.P. Letchford 1, J. Pozimski 1+2, M.O. Whitehead 1, T. Wood 1, S. Jolly 2, P. Savage 2, M. Haigh 3, J. Morrison 3, I. Yew
ION THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY IN TORSATRONS. R. E. Potok, P. A. Politzer, and L. M. Lidsky. April 1980 PFC/JA-80-10
 ION THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY IN TORSATRONS R. E. Potok, P. A. Politzer, and L. M. Lidsky April 1980 PFC/JA-80-10 ION THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY IN TORSATRONS R.E. Potok, P.A. Politzer, and L.M. Lidsky Plasma Fusion
ION THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY IN TORSATRONS R. E. Potok, P. A. Politzer, and L. M. Lidsky April 1980 PFC/JA-80-10 ION THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY IN TORSATRONS R.E. Potok, P.A. Politzer, and L.M. Lidsky Plasma Fusion
Optics, Light and Lasers
 Dieter Meschede Optics, Light and Lasers The Practical Approach to Modern Aspects of Photonics and Laser Physics Second, Revised and Enlarged Edition BICENTENNIAL.... n 4 '':- t' 1 8 0 7 $W1LEY 2007 tri
Dieter Meschede Optics, Light and Lasers The Practical Approach to Modern Aspects of Photonics and Laser Physics Second, Revised and Enlarged Edition BICENTENNIAL.... n 4 '':- t' 1 8 0 7 $W1LEY 2007 tri
by Wood,I Fuchtbauer2 and others; and for mercury, cadmium, lead, The apparatus used in the present work with zinc was similar to that
 738 PHYSICS: J. G. WINANS PRoc. N. A. S. approaches the normal effect more and more closely as k, increases, so that this also would probably resemble a normal triplet. The patterns which we should expect
738 PHYSICS: J. G. WINANS PRoc. N. A. S. approaches the normal effect more and more closely as k, increases, so that this also would probably resemble a normal triplet. The patterns which we should expect
Some Topics in Optics
 Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
MODERN OPTICS. P47 Optics: Unit 9
 MODERN OPTICS P47 Optics: Unit 9 Course Outline Unit 1: Electromagnetic Waves Unit 2: Interaction with Matter Unit 3: Geometric Optics Unit 4: Superposition of Waves Unit 5: Polarization Unit 6: Interference
MODERN OPTICS P47 Optics: Unit 9 Course Outline Unit 1: Electromagnetic Waves Unit 2: Interaction with Matter Unit 3: Geometric Optics Unit 4: Superposition of Waves Unit 5: Polarization Unit 6: Interference
What can laser light do for (or to) me?
 What can laser light do for (or to) me? Phys 1020, Day 15: Questions? Refection, refraction LASERS: 14.3 Next Up: Finish lasers Cameras and optics 1 Eyes to web: Final Project Info Light travels more slowly
What can laser light do for (or to) me? Phys 1020, Day 15: Questions? Refection, refraction LASERS: 14.3 Next Up: Finish lasers Cameras and optics 1 Eyes to web: Final Project Info Light travels more slowly
Charge readout and double phase
 Charge readout and double phase Vyacheslav Galymov IPN Lyon 1 st annual meeting AIDA-2020 Liquid argon double-phase TPC Concept of double-phase LAr TPC (Not to scale) Anode 0V 2 mm Collection field 5kV/cm
Charge readout and double phase Vyacheslav Galymov IPN Lyon 1 st annual meeting AIDA-2020 Liquid argon double-phase TPC Concept of double-phase LAr TPC (Not to scale) Anode 0V 2 mm Collection field 5kV/cm
Lepton beam polarisation for the HERA experiments ZEUS and H1
 Lepton beam polarisation for the HERA experiments ZEUS and H1 Polarisation at collider machines The HERA storage ring The HERA polarimeters The collider experiments ZEUS and H1 The HERA II upgrade Data
Lepton beam polarisation for the HERA experiments ZEUS and H1 Polarisation at collider machines The HERA storage ring The HERA polarimeters The collider experiments ZEUS and H1 The HERA II upgrade Data
Reference literature. (See: CHEM 2470 notes, Module 8 Textbook 6th ed., Chapters )
 September 17, 2018 Reference literature (See: CHEM 2470 notes, Module 8 Textbook 6th ed., Chapters 13-14 ) Reference.: https://slideplayer.com/slide/8354408/ Spectroscopy Usual Wavelength Type of Quantum
September 17, 2018 Reference literature (See: CHEM 2470 notes, Module 8 Textbook 6th ed., Chapters 13-14 ) Reference.: https://slideplayer.com/slide/8354408/ Spectroscopy Usual Wavelength Type of Quantum
LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER:
 LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER: 111-22-3333 MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to give some practice in using
LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER: 111-22-3333 MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to give some practice in using
Particle Transport and Edge Dynamo in the MST RFP
 Particle Transport and Edge Dynamo in the ST RFP International RFP Workshop 28 February 2000, adison, WI D. J. Den Hartog Department of Physics University of Wisconsin adison In collaboration with J. K.
Particle Transport and Edge Dynamo in the ST RFP International RFP Workshop 28 February 2000, adison, WI D. J. Den Hartog Department of Physics University of Wisconsin adison In collaboration with J. K.
