Design and Performance of the Cornell ERL DC Photoemission Gun
|
|
|
- Ferdinand Hart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Design and Performance of the Cornell ERL DC Photoemission Gun K. Smolenski, I. Bazarov, B. Dunham, H. Li, Y. Li, X. Liu, D. Ouzounov, C. Sinclair CLASSE, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, U.S.A. Abstract. Cornell University is planning to build an Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) X-ray facility. For an ERL, it is well known that the x-ray beam brightness for the users is mainly determined by the initial electron beam emittance provided by the injector To address technical challenges of producing very low emittance beams at high average current as required for an ERL, Cornell University has proposed a prototype injector with 5-15 MeV beam energy, 100 ma maximum average current and 77 pc/bunch. In this article, we describe the design, construction and initial results for a DC photoemission gun now under operation. Keywords: DC high voltage GaAs photogun. Energy recovery linac. PACS: Bx, Ps, p, t, Bm INTRODUCTION An electron injector for an ERL-based light source has many challenges. To provide the x-ray beam quality that users demand for the future, the injector needs to meet the requirements show in Table 1 [1]. TABLE 1. Injector Requirements (values in ( ) are goals for the prototype system of this paper) Beam Energy Charge per bunch Average Current Bunch Length Transverse Emittance Operating Frequency (5-15) MeV 77 (77) pc 100 (100) ma 2-3 (2-3) ps 0.3 (2) nm 1.3 (1.3) GHz At Cornell University, we have undertaken a program to develop and test such an injector (see Fig. 1) towards realization of this difficult set of requirements. The design was based on detailed simulations using genetic algorithms to find the optimum solutions to the multi-parameter design space [2]. The electron source is a DC photoemission gun using a GaAs cathode, providing a 1.3 GHz bunch train of 77 pc^unch with a ps 'beer can' distribution. This is followed by a short section CY\\A9, SpinPhysics, If? International Spin Physics Symposium edited by D. G. Crabb, D. B. Day, S. Liuti, X. Zheng, M. Poelker, and Y. Prok 2009 American Institute of Physics /09/$
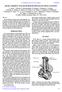
2 for emittance compensation solenoids and a normal conducting buncher cavity [3]. The beam is then accelerated through a cryomodule containing five 2-cell niobium superconducting RF (SRF) cavities, each with individual control of phase and gradient. The cavities have two opposing 50 kw input couplers to feed in 100 kw per cavity. The available RF power allows for either 100 ma at 5 MeV or 33 ma at 15 MeV. After the SRF cavities, an extensive suite of diagnostics allows for a complete characterization of the transverse and longitudinal phase space of the beam. The beam is terminated in an aluminum dump with a capacity for disposing 600 kw of average power. The current status of the complete injector commissioning and beam performance has been reported elsewhere. [4] quads ^ ICM buncher FIGURE 1. The layout of the Cornell prototype ERL injector. DC PHOTOEMISSION GUN Based on the experience of other labs [5] and of the authors, DC photoemission guns provide the best chance of producing the low emittance, high average power beam to meet the needs of an ERL. The present record for average current belongs to the Boeing normal conducting RF (NCRF) gun [6] at 32 ma (25% duty factor), and while other projects continue to push for higher current with NCRF guns, no improvements have been realized. Work on SRF guns has made excellent progress recently [7], but the prospect of obtaining 100 ma average current is still many years away. The DC gun used for the Jefferson Lab FEL project [5] has reliably provided 135 pc bunches at an average current of ~9 ma, and an extension of that technology is the most likely path to meet the needs of an ERL injector in the near future. High Voltage Gun Common sense dictates that high initial beam energy and high electric field at the cathode are necessary to overcome the space charge forces in bunched beams and obtain the best possible emittance. Simulations [2] show that higher gun voltage is important for obtaining low emittance up to a certain point, after which the improvement is relatively small. Thus, a DC gun operating in the range of kv should meet the emittance goals with the appropriate cathode. To minimize dark current at the operating voltage, the gun must be processed to roughly 25% above the operating value; consequently the Cornell gun has been designed to withstand a 750 kv maximum voltage. A schematic cutaway of the Cornell DC photoemission gun is shown in Fig. 2, and was designed to meet the requirements in Table 2. The gun was operated for over a year using a test beamline to measure the performance of the gun and cathode before 1078
3 mating it to the rest of the injector Details of these measurements have been pubhshed elsewhere [8, 9], with the main result that the emittance measurements at 77 pc^unch and 250 kv beam energy match the simulations very closely, giving confidence that the simulations for the entire system are valid. Two difficulties observed involved the laser profile and laser stability. Tails in the phase space distribution were traced (through simulation) to non-uniformities and laser stability across the 'flat-top' laser distribution and variations in the distribution over time. The pointing stability of the laser at the cathode was also an issue, causing jumps in the phase space measurements. The laser itself is stable to im rms, but this increases upon demagnification to the cathode. We have since purchased an active position stabilization device (MRC Systems GmbH) which will reduce the position jitter at the cathode to < 10 j,m rms. TABLE 2. DC Gun and Laser Requirements Operating voltage Maximum voltage Average Current Vacuum during operation External SF^ pressure Laser wavelength Laser pulse shape Laser pulse length Phase jitter kv 750 kv 100 ma <lxlo-"torr 4atm 520 nm 'beer can' ps < 1 ps All guns of this type suffer from the problem of controlling field emitted electrons from the high voltage surfaces. These electrons can land on the insulator, and if the charge builds up punch-through can occur, causing a vacuum leak. We purchased an insulator with an internal resistive coating (CPI, Inc.) to bleed off these electrons, but it has only been successful up to 450 kv during processing, above which punchthrough occurs. In addition, the coating has not adhered well, leaving a layer of dust on the electrodes, certain demise for reaching 750 kv. Two such insulators have been built and tested with similar damage occurring to both. Correlation between the location of edges of the segmented electrode support stalk and the vacuum breaches caused by punch-through have led to the adoption of a single piece stalk to replace the one shown in fig. 2. Colleagues at Daresbury Lab [10] have built an insulator using a new material from Morgan Advanced Ceramics (AL-970CD) which is more resistant to field emitted electrons, at least up to 500 kv. We are in the process of obtaining a new insulator using this material, and are also investigating the use of segmented insulators [II] which completely block the line of sight between the electrodes and the insulator, but have a much more complicated mechanical structure. For now, we are hmiting the gun voltage to 300 kv to reduce the chance of damage, until a spare is obtained. 1079
4 If one can make electrodes that do not field emit, the insulator design is not so important - this is the Holy Grail for gun design (and for SRF cavities). We have built the present gun emulating the best techniques known for cavity cleaning, namely electro-polishing followed by high pressure rinsing. In a test chamber, gradients of 30 MV/m have been routinely reached on large area electrodes, but these results have not been reproduced in the real gun, most likely due to dust contamination from the insulator coating inch flange V -750 kv Insulator Electron beam GaAs Cathode Laser input FIGURE 2. The Cornell Photoemission Gun. Laser System To produce 100 ma from a GaAs cathode with a 1% QE, over 20 Watts of laser power at 520 nm is required at the cathode (2 W for 10% QE). Accounting for possible losses in the laser transport and beam shaping, a laser with 40 W of average power is desired. The system must provide pulses at a repetition rate of 1.3 GHz 1080
5 synchronized to the RF master clock (with a timing jitter < 1 ps), and a configurable pulse shape in time and space for minimizing the electron beam emittance. We have chosen to use a Yb-doped fiber laser system to meet these requirements [12]. Initially, the oscillator was made in-house, but difficulties were encountered in accurately synchronizing it to the RF system. Subsequently, a commercial fiber laser 'clock' was purchased from PriTel Inc. They modified a standard product to work at our pulse repetition rate. The laser is triggered by the RF master clock signal, and the jitter between the output pulse the clock signal is less than 500 fs. The pulses are fed to a single mode fiber amplifier where the pulse energy is boosted to 150 nj, low enough to prevent any nonlinear distortion. The pulse energy is further increased through amplification in a double clad large mode area fiber amplifier built to work in nearly single mode regime. Currently we have implemented only one such stage and achieved average power of 35 watts at 1040 nm (27 nj pulse energy). The IR pulses are frequency doubled in a LBO crystal to produce pulses centered at 520 nm and energy of 9 nj (12 W average power). Additional thermal management is needed to reach higher powers. Laser shaping of the pulses has been described in detail elsewhere in these proceedings [13]. Photocathode Materials A perfect photocathode for an accelerator electron source would have high efficiency at a convenient laser wavelength, fast response time, long lifetime and a low thermal emittance. Unfortunately, no such cathode exists today, although the search continues. A number of different photocathodes meet some of these criteria, so tradeoffs have to be made depending on the requirements of the particular system. For an ERL, obtaining 100 ma average current means high quantum efficiency (QE) photocathodes are a necessity. Semiconductor photocathodes are currently the best choice for high QE and low emittance. Examples are GaAs, Cs2Te, GaN, and K2CsSb. Both Cs2Te and GaN show promise but require UV hght but there are no laser systems available to produce enough average power in the UV Both GaAs and K2CsSb have 5-10% QE for -520 nm light, where high average power lasers are readily available. At Cornell, we have chosen to use GaAs, but are still considering other cathodes depending on the application. As mentioned earlier, it is possible to recover the intrinsic thermal emittance from the cathode using a carefully designed emittance compensation scheme for the bunch charges of interest to an ERL [2]. Of all the cathodes available, GaAs has the lowest thermal emittance [7], so is the cathode of choice for an ERL. Unfortunately, the QE is near a minimum when the thermal emittance is smallest (close to the band gap), thus unsuitable for high average current. In addition, it is well known that at -780 nm a fast laser pulse will generate an electron beam with a ps tail, which is not acceptable for low emittance operation. For shorter wavelengths (-520nm) recent measurements [10] show that the response time is quite fast (-1 ps) as long as the QE is not too high (< 10%). This points out some of the tradeoffs one has to make even when using GaAs, and we have chosen an operating wavelength of 520 nm as the best compromise between QE, thermal emittance and response time. 1081
6 The last important parameter is cathode lifetime. The cathodes described above are all sensitive to chemical poisoning to some extent, and require ultra-high vacuum. GaAs is the most sensitive, unfortunately, requiring vacuum levels < 10"" Torr for successful operation. An additional lifetime limiter is ion back-bombardment which further reduces QE. The electron beam can ionize residual gas molecules anywhere along their path, which can then be accelerated back towards the cathode surface. Jefferson Lab [14] has carried out extensive measurements at 10 ma average current, and has measured cathode lifetimes as high as 10^ C/cm^ (the amount of charge extracted per cm^ when the QE has fallen by 1/e). One can use this data to estimate that a 10 W maximum power laser system should be able to provide 100 ma over 100 hours with a 1.8 mm diameter laser spot [15]. Such performance has not been demonstrated yet, and it is certainly an optimistic estimate. Vacuum System In order to meet the extreme vacuum levels required for sufficient cathode lifetime both reductions in outgassing and massive pumping have been implemented. The stainless steel vacuum vessel and all stainless internal components including the electrodes have been air-fired for 100 hours at 400 C to reduce their hydrogen outgassing rate, the primary residual gas constituent [16]. A typical 160 C vacuum bake follows assembly of the gun. The pumping scheme consists of a 400 1/sec Perkin-Elmer ion pump and 20 NEG modules lining the walls of the gun vessel. The NEG modules are of the WP1650-ST 707 type supplied by SAES Getters and provide approximately 15,000 1/sec of pumping for hydrogen. Typical static pressure in the gun is below 6x10"'^ mbar. Small vacuum leaks have opened at the Conflat flange joints between the insulator and the gun vessel during processing, perhaps caused by heating of the gasket by field emission. New triple point protection rings that cover the vacuum joint were installed and no further leaks have occurred. Cathode Preparation System A modular cathode preparation system is attached to rear of the gun vessel to load, clean, prepare, and store the semiconductor cathodes. Vacuum isolation between each chamber (load lock, hydrogen cleaning and heating, cathode surface preparation) allows for multiple cathodes to be accommodated at once. For example a backup cathode could be heat cleaned at the same time the primary cathode is being cesiated. Its design allows for flexibility in the cathode material and is extensible for future cathode material development. Im long orthogonal manipulator arms transfer the cathode pucks between processing chambers and also move the prepared cathode into the electrode structure. COMMISSIONING RESULTS AND PLANS Processing of the electrode structure at a rate of IkV/Hr. has been successful only to 450KV where punch through occurred (as described earher). The gun typically 1082
7 operates at 250 kv and we are not pushing the voltage higher until a backup insulator is acquired. Now in operation for two years, the gun routinely provides pulsed beams of varying bunch charge for diagnostic measurements. Average current as high as 20mA at 250kV has been achieved for short periods. The near term plans include extensive sets of phase space measurements along with the push for higher currents. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was supported by NSF grant PHY REFERENCES 1. S. M. Gruner and M. Tigner, Eds., "Study for a proposed Phase I Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) synchrotron light source at Cornell University", CHESS Technical Memo , Jefferson Laboratory Report No. JLAB ACT (2001). 2. I.V. Bazarov, et al, "Multivariate optimization of a High Brightness DC Gun Photoinjector", PRST AB, 8, (2005). 3. S. Belomestnykh, et al., "Commissioning of the Cornell ERL Injector RE Systems", 2008 European Particle Ace. Conf, Genoa, Italy (2008). 4. B. Dunham, et al., "Eirst Tests of the Cornell University ERL Injector", Linac 08 Proceedings, In Press (2008). 5. C. Hernandez-Garcia, et al, "A High Average Current DC GaAs Photocathode Gun for ERLs and EELs", 2005 Particle Ace. Conf, Knoxville, TN, (2005). 6. D. Dowell, etal, Nucl. Instr Meth. A356, 167 (1995). 7. A. Arnold, et al, "Development of a Superconducting RE Photoinjector", Nucl. Instr Meth., A 577, 440 (2007). 8. I. Bazarov et al., "Thermal emittance and response time measurements of negative electron affinity photocathodes", J. Appl. Phys., 103 (2008) I. Bazarov et al, "Efficient temporal shaping of electron distributions for high brightness photoemission guns", PRST AB 11 (2008) R.J. Smith, Daresbury Lab, personal communication. 11. J. Haimson, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. NS 22, 1354 ( D. Ouzounov, et al, "The Laser System for the ERL Electron Source at Cornell", 2007 Particle Ace. Conf, Albuquerque, NM, (2007). 13.D. Ouzounov, et al. These Proceedings. 1083
FIRST TESTS OF THE CORNELL UNIVERSITY ERL INJECTOR*
 FIRST TESTS OF THE CORNELL UNIVERSITY ERL INJECTOR* B. Dunham #, I. Bazarov, S. Belomestnykh, M. Billing, E. Chojnacki, Z. Conway, J. Dobbins, R. Ehrlich, M. Forster, S. Gruner, G. Hoffstaetter, V. Kostroun,
FIRST TESTS OF THE CORNELL UNIVERSITY ERL INJECTOR* B. Dunham #, I. Bazarov, S. Belomestnykh, M. Billing, E. Chojnacki, Z. Conway, J. Dobbins, R. Ehrlich, M. Forster, S. Gruner, G. Hoffstaetter, V. Kostroun,
ICFA ERL Workshop Jefferson Laboratory March 19-23, 2005 Working Group 1 summary Ilan Ben-Zvi & Ivan Bazarov
 ICFA ERL Workshop Jefferson Laboratory March 19-23, 2005 Working Group 1 summary Ilan Ben-Zvi & Ivan Bazarov Sincere thanks to all WG1 participants: Largest group, very active participation. This summary
ICFA ERL Workshop Jefferson Laboratory March 19-23, 2005 Working Group 1 summary Ilan Ben-Zvi & Ivan Bazarov Sincere thanks to all WG1 participants: Largest group, very active participation. This summary
INITIAL BEAM RESULTS FROM THE CORNELL HIGH-CURRENT ERL INJECTOR PROTOTYPE
 INITIAL BEAM RESULTS FROM THE CORNELL HIGH-CURRENT ERL INJECTOR PROTOTYPE I. Bazarov, S. Belomestnykh, E. Chojnacki, J. Dobbins, B. Dunham, R. Ehrlich, M. Forster, C. Gulliford, G. Hoffstaetter, H. Li,
INITIAL BEAM RESULTS FROM THE CORNELL HIGH-CURRENT ERL INJECTOR PROTOTYPE I. Bazarov, S. Belomestnykh, E. Chojnacki, J. Dobbins, B. Dunham, R. Ehrlich, M. Forster, C. Gulliford, G. Hoffstaetter, H. Li,
New Electron Source for Energy Recovery Linacs
 New Electron Source for Energy Recovery Linacs Ivan Bazarov 20m Cornell s photoinjector: world s brightest electron source 1 Outline Uses of high brightness electron beams Physics of brightness High brightness
New Electron Source for Energy Recovery Linacs Ivan Bazarov 20m Cornell s photoinjector: world s brightest electron source 1 Outline Uses of high brightness electron beams Physics of brightness High brightness
Present status and future of DC photoemission electron guns for high power, high brightness applications
 Present status and future of DC photoemission electron guns for high power, high brightness applications DC photoemission electron guns using GaAs cathodes have been in use to produce polarized electrons
Present status and future of DC photoemission electron guns for high power, high brightness applications DC photoemission electron guns using GaAs cathodes have been in use to produce polarized electrons
Jlab FEL Photoemission DC Guns
 Jlab FEL Photoemission DC Guns Fay Hannon On behalf of the FEL team FLS 2010, 2 nd March 2 Operational Guns 1. FEL Gun 60m Gun Test Stand (GTS) 2. Backup gun, test stand with beam characterization beamline
Jlab FEL Photoemission DC Guns Fay Hannon On behalf of the FEL team FLS 2010, 2 nd March 2 Operational Guns 1. FEL Gun 60m Gun Test Stand (GTS) 2. Backup gun, test stand with beam characterization beamline
HIGH CURRENT AND HIGH BRIGHTNESS ELECTRON SOURCES
 HIGH CURRENT AND HIGH BRIGHTNESS ELECTRON SOURCES F. Loehl, I. Bazarov, S. Belomestnykh, M. Billing, E. Chojnacki, Z. Conway, J. Dobbins, B. Dunham, R. Ehrlich, M. Forster, S. M. Gruner, C. Gulliford,
HIGH CURRENT AND HIGH BRIGHTNESS ELECTRON SOURCES F. Loehl, I. Bazarov, S. Belomestnykh, M. Billing, E. Chojnacki, Z. Conway, J. Dobbins, B. Dunham, R. Ehrlich, M. Forster, S. M. Gruner, C. Gulliford,
Present status and future of DC photoemission electron guns for high power, high brightness applications
 Present status and future of DC photoemission electron guns for high power, high brightness applications DC photoemission electron guns using GaAs cathodes have been in use to produce polarized electrons
Present status and future of DC photoemission electron guns for high power, high brightness applications DC photoemission electron guns using GaAs cathodes have been in use to produce polarized electrons
ERL09 WG1 DC-Gun KEK JAEA
 ERL09 WG1 DC-Gun KEK Cornell JLAB CEBAF JAEA JLAB FEL Daresbury Cornell Gun DC Photocathode Gun -750 kv Cathode Preparation and Load Lock 16.5 inch flange Insulator 750 kv, 100 ma HVPS Drive Laser Focusing
ERL09 WG1 DC-Gun KEK Cornell JLAB CEBAF JAEA JLAB FEL Daresbury Cornell Gun DC Photocathode Gun -750 kv Cathode Preparation and Load Lock 16.5 inch flange Insulator 750 kv, 100 ma HVPS Drive Laser Focusing
SRF GUN CHARACTERIZATION - PHASE SPACE AND DARK CURRENT MEASUREMENTS AT ELBE*
 SRF GUN CHARACTERIZATION - PHASE SPACE AND DARK CURRENT MEASUREMENTS AT ELBE* E. Panofski #, A. Jankowiak, T. Kamps, Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin, Berlin, Germany P.N. Lu, J. Teichert, Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf,
SRF GUN CHARACTERIZATION - PHASE SPACE AND DARK CURRENT MEASUREMENTS AT ELBE* E. Panofski #, A. Jankowiak, T. Kamps, Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin, Berlin, Germany P.N. Lu, J. Teichert, Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf,
Emittance and photocathodes
 Cornell Laboratory for Accelerator-based ScienceS and Education () Emittance and photocathodes Ivan Bazarov Where we are today Injector performance Ongoing work Venues for improvements Next generation
Cornell Laboratory for Accelerator-based ScienceS and Education () Emittance and photocathodes Ivan Bazarov Where we are today Injector performance Ongoing work Venues for improvements Next generation
THE LCLS-II INJECTOR DESIGN*
 THE LCLS-II INJECTOR DESIGN* J.F. Schmerge #, A. Brachmann, D. Dowell, A. Fry, R.K. Li, Z. Li, T. Raubenheimer, T. Vecchione, F. Zhou, SLAC, Menlo Park, CA 94025, USA A. Bartnik, I. Bazarov, B. Dunham,
THE LCLS-II INJECTOR DESIGN* J.F. Schmerge #, A. Brachmann, D. Dowell, A. Fry, R.K. Li, Z. Li, T. Raubenheimer, T. Vecchione, F. Zhou, SLAC, Menlo Park, CA 94025, USA A. Bartnik, I. Bazarov, B. Dunham,
A Polarized Electron PWT Photoinjector for the ILC
 2005 ALCPG & ILC Workshops Snowmass, U.S.A. A Polarized Electron PWT Photoinjector for the ILC David Yu, Yan Luo, Alexei Smirnov, DULY Research Inc., Rancho Palos Verdes, CA 90275 Ivan Bazarov, Cornell
2005 ALCPG & ILC Workshops Snowmass, U.S.A. A Polarized Electron PWT Photoinjector for the ILC David Yu, Yan Luo, Alexei Smirnov, DULY Research Inc., Rancho Palos Verdes, CA 90275 Ivan Bazarov, Cornell
Multivariate Optimization of High Brightness High Current DC Photoinjector. Ivan Bazarov
 Multivariate Optimization of High Brightness High Current DC Photoinjector Ivan Bazarov Talk Outline: Motivation Evolutionary Algorithms Optimization Results 1 ERL Injector 750 kv DC Gun Goal: provide
Multivariate Optimization of High Brightness High Current DC Photoinjector Ivan Bazarov Talk Outline: Motivation Evolutionary Algorithms Optimization Results 1 ERL Injector 750 kv DC Gun Goal: provide
Using IMPACT T to perform an optimization of a DC gun system Including merger
 Using IMPACT T to perform an optimization of a DC gun system Including merger Xiaowei Dong and Michael Borland Argonne National Laboratory Presented at ERL09 workshop June 10th, 2009 Introduction An energy
Using IMPACT T to perform an optimization of a DC gun system Including merger Xiaowei Dong and Michael Borland Argonne National Laboratory Presented at ERL09 workshop June 10th, 2009 Introduction An energy
Toward an Energy Recovery Linac x-ray source at Cornell University
 1 Toward an Energy Recovery Linac x-ray source at Cornell University Georg Hoffstaetter Cornell Physics Dept. / LEPP The ERL principle Limits of ERLs Studies for an x-ray ERL Ivan Bazarov LEPP / CHESS
1 Toward an Energy Recovery Linac x-ray source at Cornell University Georg Hoffstaetter Cornell Physics Dept. / LEPP The ERL principle Limits of ERLs Studies for an x-ray ERL Ivan Bazarov LEPP / CHESS
The New Superconducting RF Photoinjector a High-Average Current & High-Brightness Gun
 The New Superconducting RF Photoinjector a High-Average Current & High-Brightness Gun Jochen Teichert for the BESSY-DESY-FZD-MBI collaboration and the ELBE crew High-Power Workshop, UCLA, Los Angeles 14
The New Superconducting RF Photoinjector a High-Average Current & High-Brightness Gun Jochen Teichert for the BESSY-DESY-FZD-MBI collaboration and the ELBE crew High-Power Workshop, UCLA, Los Angeles 14
Overview of Photoinjectors for Future Light Sources
 Cornell Laboratory for Accelerator-based ScienceS and Education () Overview of Photoinjectors for Future Light Sources Ivan Bazarov Main dump T-map during 35 ma high current running GaAs QE(%) map after
Cornell Laboratory for Accelerator-based ScienceS and Education () Overview of Photoinjectors for Future Light Sources Ivan Bazarov Main dump T-map during 35 ma high current running GaAs QE(%) map after
Magnetized Beam Update (LDRD)
 Magnetized Beam Update (LDRD) JLEIC Collaboration Meeting March 29, 2016 Riad Suleiman and Matt Poelker Outline Magnetized Bunched Electron Beam Requirements Magnetized Sources JLEIC Magnetized Beam LDRD
Magnetized Beam Update (LDRD) JLEIC Collaboration Meeting March 29, 2016 Riad Suleiman and Matt Poelker Outline Magnetized Bunched Electron Beam Requirements Magnetized Sources JLEIC Magnetized Beam LDRD
Accelerator R&D Opportunities: Sources and Linac. Developing expertise. D. Rubin, Cornell University
 Accelerator R&D Opportunities: Sources and Linac D. Rubin, Cornell University Electron and positron sources Requirements Status of R&D Linac Modeling of beam dynamics Development of diagnostic and tuning
Accelerator R&D Opportunities: Sources and Linac D. Rubin, Cornell University Electron and positron sources Requirements Status of R&D Linac Modeling of beam dynamics Development of diagnostic and tuning
A Polarized Electron PWT Photoinjector for the ILC
 2005 ALCPG & ILC Workshops Snowmass, U.S.A. A Polarized Electron PWT Photoinjector for the ILC David Yu, Yan Luo, Alexei Smirnov, DULY Research Inc., Rancho Palos Verdes, CA 90275 Ivan Bazarov, Cornell
2005 ALCPG & ILC Workshops Snowmass, U.S.A. A Polarized Electron PWT Photoinjector for the ILC David Yu, Yan Luo, Alexei Smirnov, DULY Research Inc., Rancho Palos Verdes, CA 90275 Ivan Bazarov, Cornell
Multivariate Optimization of High Brightness High Current DC Photoinjector. Ivan Bazarov Cornell University
 Multivariate Optimization of High Brightness High Current DC Photoinjector Ivan Bazarov Cornell University Talk Outline: Motivation Parallel Evolutionary Algorithms Results & Outlook Ivan Bazarov, Multivariate
Multivariate Optimization of High Brightness High Current DC Photoinjector Ivan Bazarov Cornell University Talk Outline: Motivation Parallel Evolutionary Algorithms Results & Outlook Ivan Bazarov, Multivariate
Shaping Electrostatic Conditions in the Stalk of the ERL -750 kv Electron Gun
 Shaping Electrostatic Conditions in the Stalk of the ERL -750 kv Electron Gun David Stone Carnegie Mellon University Advisors: Karl Smolenski and Bruce Dunham Cornell University Laboratory for Elementary-Particle
Shaping Electrostatic Conditions in the Stalk of the ERL -750 kv Electron Gun David Stone Carnegie Mellon University Advisors: Karl Smolenski and Bruce Dunham Cornell University Laboratory for Elementary-Particle
A Review of ERL Prototype Experience and Light Source Design Challenges. Susan Smith Accelerator Physics ASTeC CCLRC Daresbury Laboratory
 A Review of ERL Prototype Experience and Light Source Design Challenges Susan Smith Accelerator Physics ASTeC CCLRC Daresbury Laboratory Content Existing light source ERLs JLAB experience Challenges of
A Review of ERL Prototype Experience and Light Source Design Challenges Susan Smith Accelerator Physics ASTeC CCLRC Daresbury Laboratory Content Existing light source ERLs JLAB experience Challenges of
WORLDWIDE ERL R&D OVERVIEW INCLUDING JLAMP, BNL, AND CORNELL ERLS *
 WORLDWIDE ERL R&D OVERVIEW INCLUDING JLAMP, BNL, AND CORNELL ERLS * George R. Neil, Jefferson Laboratory, Newport News, VA, 23606, USA Abstract Energy Recovering Linacs have become an important approach
WORLDWIDE ERL R&D OVERVIEW INCLUDING JLAMP, BNL, AND CORNELL ERLS * George R. Neil, Jefferson Laboratory, Newport News, VA, 23606, USA Abstract Energy Recovering Linacs have become an important approach
Linacs. Susan Smith. Daresbury Laboratory Mami and Beyond
 Energy Recovery Linacs Susan Smith ASTeC/Cockcroft Daresbury Laboratory Mami and Beyond Introduction to ERLs Contents Operational ERLs Applications Challenges ERL Prototypes and R&D Summary 2 Introduction
Energy Recovery Linacs Susan Smith ASTeC/Cockcroft Daresbury Laboratory Mami and Beyond Introduction to ERLs Contents Operational ERLs Applications Challenges ERL Prototypes and R&D Summary 2 Introduction
Applications of High Brightness Beams: Energy Recovered Linacs
 Applications of High Brightness Beams: Energy Recovered Linacs G. A. Krafft Jefferson Lab Schematic Representation of Accelerator Types RF Installation Beam injector and dump Beamline Ring Linac Recirculating
Applications of High Brightness Beams: Energy Recovered Linacs G. A. Krafft Jefferson Lab Schematic Representation of Accelerator Types RF Installation Beam injector and dump Beamline Ring Linac Recirculating
What is an Energy Recovery Linac and Why is there one in your Future?
 What is an Energy Recovery Linac and Why is there one in your Future? Sol M. Gruner CHESS, Physics Dept. Cornell University Ithaca, NY 14853 Outline 1. Who needs another synchrotron source? 2. What is
What is an Energy Recovery Linac and Why is there one in your Future? Sol M. Gruner CHESS, Physics Dept. Cornell University Ithaca, NY 14853 Outline 1. Who needs another synchrotron source? 2. What is
Experimental Measurements of the ORION Photoinjector Drive Laser Oscillator Subsystem
 Experimental Measurements of the ORION Photoinjector Drive Laser Oscillator Subsystem D.T Palmer and R. Akre Laser Issues for Electron RF Photoinjectors October 23-25, 2002 Stanford Linear Accelerator
Experimental Measurements of the ORION Photoinjector Drive Laser Oscillator Subsystem D.T Palmer and R. Akre Laser Issues for Electron RF Photoinjectors October 23-25, 2002 Stanford Linear Accelerator
ERL upgrade of an existing X-ray facility: CHESS at CESR
 ERL-5-8 ERL upgrade of an existing X-ray facility: CHESS at CESR G.H. Hoffstaetter Abstract Cornell University has proposed an Energy-Recovery Linac (ERL) based synchrotron-light facility which uses 5GeV,
ERL-5-8 ERL upgrade of an existing X-ray facility: CHESS at CESR G.H. Hoffstaetter Abstract Cornell University has proposed an Energy-Recovery Linac (ERL) based synchrotron-light facility which uses 5GeV,
Cornell Injector Performance
 Cornell Injector Performance Adam Bartnik 1 Cornell Injector Performance as an ERL injector 2 Cornell Injector Performance as an ERL injector as an FEL injector (e.g. LCLS-II) as an injector for EIC applications
Cornell Injector Performance Adam Bartnik 1 Cornell Injector Performance as an ERL injector 2 Cornell Injector Performance as an ERL injector as an FEL injector (e.g. LCLS-II) as an injector for EIC applications
Experimental Optimization of Electron Beams for Generating THz CTR and CDR with PITZ
 Experimental Optimization of Electron Beams for Generating THz CTR and CDR with PITZ Introduction Outline Optimization of Electron Beams Calculations of CTR/CDR Pulse Energy Summary & Outlook Prach Boonpornprasert
Experimental Optimization of Electron Beams for Generating THz CTR and CDR with PITZ Introduction Outline Optimization of Electron Beams Calculations of CTR/CDR Pulse Energy Summary & Outlook Prach Boonpornprasert
CsK 2 Sb PHOTOCATHODE DEVELOPMENT FOR. Martin Schmeißer, Julius Kühn, Thorsten Kamps, Andreas Jankowiak Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin
 CsK 2 Sb PHOTOCATHODE DEVELOPMENT FOR Martin Schmeißer, Julius Kühn, Thorsten Kamps, Andreas Jankowiak Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin 1 PHOTOCATHODES Photoinjector for berlinpro Aim: 0.5 mm mrad emittance from
CsK 2 Sb PHOTOCATHODE DEVELOPMENT FOR Martin Schmeißer, Julius Kühn, Thorsten Kamps, Andreas Jankowiak Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin 1 PHOTOCATHODES Photoinjector for berlinpro Aim: 0.5 mm mrad emittance from
Optics considerations for
 Optics considerations for ERL x-ray x sources Georg H. Hoffstaetter* Physics Department Cornell University Ithaca / NY Georg.Hoffstaetter@cornell.edu 1. Overview of Parameters 2. Critical Topics 3. Phase
Optics considerations for ERL x-ray x sources Georg H. Hoffstaetter* Physics Department Cornell University Ithaca / NY Georg.Hoffstaetter@cornell.edu 1. Overview of Parameters 2. Critical Topics 3. Phase
4GLS Status. Susan L Smith ASTeC Daresbury Laboratory
 4GLS Status Susan L Smith ASTeC Daresbury Laboratory Contents ERLP Introduction Status (Kit on site ) Plan 4GLS (Conceptual Design) Concept Beam transport Injectors SC RF FELs Combining Sources May 2006
4GLS Status Susan L Smith ASTeC Daresbury Laboratory Contents ERLP Introduction Status (Kit on site ) Plan 4GLS (Conceptual Design) Concept Beam transport Injectors SC RF FELs Combining Sources May 2006
Review of proposals of ERL injector cryomodules. S. Belomestnykh
 Review of proposals of ERL injector cryomodules S. Belomestnykh ERL 2005 JLab, March 22, 2005 Introduction In this presentation we will review injector cryomodule designs either already existing or under
Review of proposals of ERL injector cryomodules S. Belomestnykh ERL 2005 JLab, March 22, 2005 Introduction In this presentation we will review injector cryomodule designs either already existing or under
The Cornell University Photoinjector
 The Cornell University Photoinjector L. Cultrera On behalf of ERL team Outline The Cornell ERL R&D program The photoinjector Photocathode lab SRF development Achieved Milestones Beam brightness and High
The Cornell University Photoinjector L. Cultrera On behalf of ERL team Outline The Cornell ERL R&D program The photoinjector Photocathode lab SRF development Achieved Milestones Beam brightness and High
High Accuracy Adaptive (transverse) Laser and Electron Beam Shaping. Jared Maxson Cornell University ERL 2015, BNL
 High Accuracy Adaptive (transverse) Laser and Electron Beam Shaping and a bit about DC gun emittance vs. gun gap Jared Maxson Cornell University ERL 2015, BNL Outline I. Motivation: Why do you want from
High Accuracy Adaptive (transverse) Laser and Electron Beam Shaping and a bit about DC gun emittance vs. gun gap Jared Maxson Cornell University ERL 2015, BNL Outline I. Motivation: Why do you want from
WG2 on ERL light sources CHESS & LEPP
 Charge: WG2 on ERL light sources Address and try to answer a list of critical questions for ERL light sources. Session leaders can approach each question by means of (a) (Very) short presentations (b)
Charge: WG2 on ERL light sources Address and try to answer a list of critical questions for ERL light sources. Session leaders can approach each question by means of (a) (Very) short presentations (b)
Diagnostic Systems for Characterizing Electron Sources at the Photo Injector Test Facility at DESY, Zeuthen site
 1 Diagnostic Systems for Characterizing Electron Sources at the Photo Injector Test Facility at DESY, Zeuthen site Sakhorn Rimjaem (on behalf of the PITZ team) Motivation Photo Injector Test Facility at
1 Diagnostic Systems for Characterizing Electron Sources at the Photo Injector Test Facility at DESY, Zeuthen site Sakhorn Rimjaem (on behalf of the PITZ team) Motivation Photo Injector Test Facility at
Initial Emittance Measurements for Polarized Electron Gun with NEA-GaAs Type Photocathode
 Initial Emittance Measurements for Polarized Electron Gun with NEA-GaAs Type Photocathode Naoto Yamamoto*, M. Yamamoto*, R. Sakai*, T. Nakanishi*, S. Okumi*, M. Kuwahara*, K. Tamagaki*, T. Morino*, A.
Initial Emittance Measurements for Polarized Electron Gun with NEA-GaAs Type Photocathode Naoto Yamamoto*, M. Yamamoto*, R. Sakai*, T. Nakanishi*, S. Okumi*, M. Kuwahara*, K. Tamagaki*, T. Morino*, A.
Multiparameter optimization of an ERL. injector
 Multiparameter optimization of an ERL injector R. Hajima a, R. Nagai a a Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, Tokai-mura, Ibaraki 319 1195 Japan Abstract We present multiparameter optimization of an
Multiparameter optimization of an ERL injector R. Hajima a, R. Nagai a a Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, Tokai-mura, Ibaraki 319 1195 Japan Abstract We present multiparameter optimization of an
Update on Development of High Current Bunched Electron Beam from Magnetized DC Photogun
 Update on Development of High Current Bunched Electron Beam from Magnetized DC Photogun JLEIC Collaboration Meeting October 6, 2016 Riad Suleiman and Matt Poelker Magnetized Cooling JLEIC bunched magnetized
Update on Development of High Current Bunched Electron Beam from Magnetized DC Photogun JLEIC Collaboration Meeting October 6, 2016 Riad Suleiman and Matt Poelker Magnetized Cooling JLEIC bunched magnetized
Accelerator Physics Issues of ERL Prototype
 Accelerator Physics Issues of ERL Prototype Ivan Bazarov, Geoffrey Krafft Cornell University TJNAF ERL site visit (Mar 7-8, ) Part I (Bazarov). Optics. Space Charge Emittance Compensation in the Injector
Accelerator Physics Issues of ERL Prototype Ivan Bazarov, Geoffrey Krafft Cornell University TJNAF ERL site visit (Mar 7-8, ) Part I (Bazarov). Optics. Space Charge Emittance Compensation in the Injector
Novel, Hybrid RF Injector as a High-average. Dinh Nguyen. Lloyd Young
 Novel, Hybrid RF Injector as a High-average average-current Electron Source Dinh Nguyen Los Alamos National Laboratory Lloyd Young TechSource Energy Recovery Linac Workshop Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator
Novel, Hybrid RF Injector as a High-average average-current Electron Source Dinh Nguyen Los Alamos National Laboratory Lloyd Young TechSource Energy Recovery Linac Workshop Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator
ERL FOR LOW ENERGY ELECTRON COOLING AT RHIC (LEREC)*
 ERL FOR LOW ENERGY ELECTRON COOLING AT RHIC (LEREC)* J. Kewisch, M. Blaskiewicz, A. Fedotov, D. Kayran, C. Montag, V. Ranjbar Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, New York Abstract Low-energy RHIC Electron
ERL FOR LOW ENERGY ELECTRON COOLING AT RHIC (LEREC)* J. Kewisch, M. Blaskiewicz, A. Fedotov, D. Kayran, C. Montag, V. Ranjbar Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, New York Abstract Low-energy RHIC Electron
Low Energy RHIC electron Cooling (LEReC)
 Low Energy RHIC electron Cooling (LEReC) LEReC overview: project goal and cooling approach Alexei Fedotov MEIC Collaboration Meeting 30 31 LEReC Project Mission/Purpose The purpose of the LEReC is to provide
Low Energy RHIC electron Cooling (LEReC) LEReC overview: project goal and cooling approach Alexei Fedotov MEIC Collaboration Meeting 30 31 LEReC Project Mission/Purpose The purpose of the LEReC is to provide
Status of linear collider designs:
 Status of linear collider designs: Electron and positron sources Design overview, principal open issues G. Dugan March 11, 2002 Electron sourcesfor 500 GeV CM machines Parameter TESLA NLC CLIC Cycle rate
Status of linear collider designs: Electron and positron sources Design overview, principal open issues G. Dugan March 11, 2002 Electron sourcesfor 500 GeV CM machines Parameter TESLA NLC CLIC Cycle rate
Joe Grames, Center for Injectors & Sources
 Polarized Electron Sources at JLab Joe Grames, Center for Injectors & Sources OUTLINE o Motivation o Photoemission from GaAs o Spin polarized electrons o Extreme High Vacuum (XHV) o High frequency/power
Polarized Electron Sources at JLab Joe Grames, Center for Injectors & Sources OUTLINE o Motivation o Photoemission from GaAs o Spin polarized electrons o Extreme High Vacuum (XHV) o High frequency/power
Magnetized Beam LDRD. Abdullah Mamun On behalf of JLab Injector Group. JLEIC Collaboration Meeting Spring 2018, March 26-28,, Jefferson Lab
 Magnetized Beam LDRD Abdullah Mamun On behalf of JLab Injector Group JLEIC Collaboration Meeting Spring 2018, March 26-28,, Jefferson Lab Outline Magnetized Bunched-Beam Electron Cooling LDRD Magnetized
Magnetized Beam LDRD Abdullah Mamun On behalf of JLab Injector Group JLEIC Collaboration Meeting Spring 2018, March 26-28,, Jefferson Lab Outline Magnetized Bunched-Beam Electron Cooling LDRD Magnetized
High average current photo injector (PHIN) for the CLIC Test Facility at CERN
 High average current photo injector (PHIN) for the CLIC Test Facility at CERN CLIC and CTF3 motivation Photo injectors, PHIN Emittance measurements Long pulse operation, time resolved measurements Cathode
High average current photo injector (PHIN) for the CLIC Test Facility at CERN CLIC and CTF3 motivation Photo injectors, PHIN Emittance measurements Long pulse operation, time resolved measurements Cathode
DIAGNOSTIC TEST-BEAM-LINE FOR THE MESA INJECTOR
 DIAGNOSTIC TEST-BEAM-LINE FOR THE MESA INJECTOR I.Alexander,K.Aulenbacher,V.Bechthold,B.Ledroit,C.Matejcek InstitutfürKernphysik,JohannesGutenberg-Universität,D-55099Mainz,Germany Abstract With the test-beam-line
DIAGNOSTIC TEST-BEAM-LINE FOR THE MESA INJECTOR I.Alexander,K.Aulenbacher,V.Bechthold,B.Ledroit,C.Matejcek InstitutfürKernphysik,JohannesGutenberg-Universität,D-55099Mainz,Germany Abstract With the test-beam-line
Recent Status of Polarized Electron Sources at Nagoya University
 Recent Status of Polarized Electron Sources at Nagoya University M. Kuwahara, N. Yamamoto, F. Furuta, T. Nakanishi, S. Okumi, M. Yamamoto, M. Kuriki *, T. Ujihara ** and K. Takeda ** Graduate School of
Recent Status of Polarized Electron Sources at Nagoya University M. Kuwahara, N. Yamamoto, F. Furuta, T. Nakanishi, S. Okumi, M. Yamamoto, M. Kuriki *, T. Ujihara ** and K. Takeda ** Graduate School of
What have we learned from the LCLS injector?*
 SLAC-PUB-14644 LCLS-TN-11-4 October 19, 2011 What have we learned from the LCLS injector?* Feng Zhou and Axel Brachmann for the LCLS injector team The LCLS injector reliably delivered a high quality electron
SLAC-PUB-14644 LCLS-TN-11-4 October 19, 2011 What have we learned from the LCLS injector?* Feng Zhou and Axel Brachmann for the LCLS injector team The LCLS injector reliably delivered a high quality electron
Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) Science Workshop
 Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) Science Workshop Sol M. Gruner, CHESS & Physics Dept. Objective: Examine science possible with an ERL x-ray source. Ques.: Ans.: Why do this? Need for more and better SR machines.
Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) Science Workshop Sol M. Gruner, CHESS & Physics Dept. Objective: Examine science possible with an ERL x-ray source. Ques.: Ans.: Why do this? Need for more and better SR machines.
Diagnostics Needs for Energy Recovery Linacs
 Diagnostics Needs for Energy Recovery Linacs Georg H. Hoffstaetter Cornell Laboratory for Accelerator-based Sciences and Education & Physics Department Cornell University, Ithaca New York 14853-2501 gh77@cornell.edu
Diagnostics Needs for Energy Recovery Linacs Georg H. Hoffstaetter Cornell Laboratory for Accelerator-based Sciences and Education & Physics Department Cornell University, Ithaca New York 14853-2501 gh77@cornell.edu
Beam Emittance in the ERL Injector Prototype
 Beam Emittance in the ERL Injector Prototype Peter Battaglino Physics Department, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, 53 (Dated: August 8, 3) The number of parameters which influence the beam emittance
Beam Emittance in the ERL Injector Prototype Peter Battaglino Physics Department, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, 53 (Dated: August 8, 3) The number of parameters which influence the beam emittance
Geometry Optimization of DC and SRF Guns to Maximize Beam Brightness
 Geometry Optimization of and SRF Guns to Maximize Beam Brightness M.N. Lakshmanan and I.V. Bazarov, CLASSE, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA T. Miyajima, Photon Factory, KEK, Tsukuba, Japan Abstract
Geometry Optimization of and SRF Guns to Maximize Beam Brightness M.N. Lakshmanan and I.V. Bazarov, CLASSE, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA T. Miyajima, Photon Factory, KEK, Tsukuba, Japan Abstract
Design of an RF Photo-Gun (PHIN)
 Design of an RF Photo-Gun (PHIN) R. Roux 1, G. Bienvenu 1, C. Prevost 1, B. Mercier 1 1) CNRS-IN2P3-LAL, Orsay, France Abstract In this note we show the results of the RF simulations performed with a 2-D
Design of an RF Photo-Gun (PHIN) R. Roux 1, G. Bienvenu 1, C. Prevost 1, B. Mercier 1 1) CNRS-IN2P3-LAL, Orsay, France Abstract In this note we show the results of the RF simulations performed with a 2-D
SwissFEL INJECTOR DESIGN: AN AUTOMATIC PROCEDURE
 Proceedings of FEL03, New York, NY, USA SwissFEL INJECTOR DESIGN: AN AUTOMATIC PROCEDURE S. Bettoni, M. Pedrozzi, S. Reiche, PSI, Villigen, Switzerland Abstract The first section of FEL injectors driven
Proceedings of FEL03, New York, NY, USA SwissFEL INJECTOR DESIGN: AN AUTOMATIC PROCEDURE S. Bettoni, M. Pedrozzi, S. Reiche, PSI, Villigen, Switzerland Abstract The first section of FEL injectors driven
Modeling of the secondary electron emission in rf photocathode guns
 Modeling of the secondary electron emission in rf photocathode guns J.-H. Han, DESY Zeuthen 8 June 2004 Joint Uni. Hamburg and DESY Accelerator Physics Seminar Contents 1. Necessity of secondary electron
Modeling of the secondary electron emission in rf photocathode guns J.-H. Han, DESY Zeuthen 8 June 2004 Joint Uni. Hamburg and DESY Accelerator Physics Seminar Contents 1. Necessity of secondary electron
VELA/CLARA as Advanced Accelerator Studies Test-bed at Daresbury Lab.
 VELA/CLARA as Advanced Accelerator Studies Test-bed at Daresbury Lab. Yuri Saveliev on behalf of VELA and CLARA teams STFC, ASTeC, Cockcroft Institute Daresbury Lab., UK Outline VELA (Versatile Electron
VELA/CLARA as Advanced Accelerator Studies Test-bed at Daresbury Lab. Yuri Saveliev on behalf of VELA and CLARA teams STFC, ASTeC, Cockcroft Institute Daresbury Lab., UK Outline VELA (Versatile Electron
BALKAN PHYSICS LETTERS Bogazici University Press 15 November 2016 BPL, 24, , pp , (2016)
 139 BALKAN PHYSICS LETTERS Bogazici University Press 15 November 2016 BPL, 24, 241016, pp. 139 145, (2016) VACUUM STUDIES ON ELECTRON GUN AND INJECTOR LINE OF TARLA FACILITY E. COŞGUN, E.P. DEMİRCİ, Ö.
139 BALKAN PHYSICS LETTERS Bogazici University Press 15 November 2016 BPL, 24, 241016, pp. 139 145, (2016) VACUUM STUDIES ON ELECTRON GUN AND INJECTOR LINE OF TARLA FACILITY E. COŞGUN, E.P. DEMİRCİ, Ö.
Simulations of the IR/THz Options at PITZ (High-gain FEL and CTR)
 Case Study of IR/THz source for Pump-Probe Experiment at the European XFEL Simulations of the IR/THz Options at PITZ (High-gain FEL and CTR) Introduction Outline Simulations of High-gain FEL (SASE) Simulation
Case Study of IR/THz source for Pump-Probe Experiment at the European XFEL Simulations of the IR/THz Options at PITZ (High-gain FEL and CTR) Introduction Outline Simulations of High-gain FEL (SASE) Simulation
LCLS Injector Prototyping at the GTF
 LCLS Injector Prototyping at at the GTF John John Schmerge, SLAC SLAC November 3, 3, 23 23 GTF GTF Description Summary of of Previous Measurements Longitudinal Emittance Transverse Emittance Active LCLS
LCLS Injector Prototyping at at the GTF John John Schmerge, SLAC SLAC November 3, 3, 23 23 GTF GTF Description Summary of of Previous Measurements Longitudinal Emittance Transverse Emittance Active LCLS
Present status of 200keV polarized electron gun at Nagoya University
 Present status of 200keV polarized electron gun at Nagoya University Nagoya University Masahiro Yamamoto, N. Yamamoto, T. Nakanishi, S. Okumi, F. Furuta, M. Miyamoto, M. Kuwahara, K. Naniwa, K. Yasui KEK
Present status of 200keV polarized electron gun at Nagoya University Nagoya University Masahiro Yamamoto, N. Yamamoto, T. Nakanishi, S. Okumi, F. Furuta, M. Miyamoto, M. Kuwahara, K. Naniwa, K. Yasui KEK
Commissioning of the new Injector Laser System for the Short Pulse Project at FLASH
 Commissioning of the new Injector Laser System for the Short Pulse Project at FLASH Uni Hamburg tim.plath@desy.de 05.11.2013 Supported by BMBF under contract 05K10GU2 & FS FLASH 301 Motivation short pulses
Commissioning of the new Injector Laser System for the Short Pulse Project at FLASH Uni Hamburg tim.plath@desy.de 05.11.2013 Supported by BMBF under contract 05K10GU2 & FS FLASH 301 Motivation short pulses
Development status of non-destructive assay of nuclear material by using laser Compton scattered gamma-rays
 Development status of non-destructive assay of nuclear material by using laser Compton scattered gamma-rays Ryoichi Hajima Japan Atomic Energy Agency IZEST Tokyo 2013 Nov. 18, 2013 Collaborators Quantum
Development status of non-destructive assay of nuclear material by using laser Compton scattered gamma-rays Ryoichi Hajima Japan Atomic Energy Agency IZEST Tokyo 2013 Nov. 18, 2013 Collaborators Quantum
Status of Proof-of-Principle Experiment of Coherent Electron Cooling at BNL
 Status of Proof-of-Principle Experiment of Coherent Electron Cooling at BNL Outline 2 Why we doing it? What is Coherent electron Cooling System description Subsystem performance Plan for Run 18 e-n Luminosity
Status of Proof-of-Principle Experiment of Coherent Electron Cooling at BNL Outline 2 Why we doing it? What is Coherent electron Cooling System description Subsystem performance Plan for Run 18 e-n Luminosity
Emittance and Quantum Efficiency Measurements from a 1.6 cell S- Band Photocathode RF Gun with Mg Cathode *
 LCLS-TN-4-3 SLAC PUB 763 September, 4 Emittance and Quantum Efficiency Measurements from a.6 cell S- Band Photocathode RF Gun with Mg Cathode * J.F. Schmerge, J.M. Castro, J.E. Clendenin, D.H. Dowell,
LCLS-TN-4-3 SLAC PUB 763 September, 4 Emittance and Quantum Efficiency Measurements from a.6 cell S- Band Photocathode RF Gun with Mg Cathode * J.F. Schmerge, J.M. Castro, J.E. Clendenin, D.H. Dowell,
Reduction of thermal emittance of rf guns *
 SLAC-PUB-884 LCLS TN 99-8 October 1999 Reduction of thermal emittance of rf guns * J. E. Clendenin, T. Kotseroglou, G. A. Mulhollan, D. T. Palmer, and J. F. Schmerge Stanford Linear Accelerator Center,
SLAC-PUB-884 LCLS TN 99-8 October 1999 Reduction of thermal emittance of rf guns * J. E. Clendenin, T. Kotseroglou, G. A. Mulhollan, D. T. Palmer, and J. F. Schmerge Stanford Linear Accelerator Center,
ASTRA simulations of the slice longitudinal momentum spread along the beamline for PITZ
 ASTRA simulations of the slice longitudinal momentum spread along the beamline for PITZ Orlova Ksenia Lomonosov Moscow State University GSP-, Leninskie Gory, Moscow, 11999, Russian Federation Email: ks13orl@list.ru
ASTRA simulations of the slice longitudinal momentum spread along the beamline for PITZ Orlova Ksenia Lomonosov Moscow State University GSP-, Leninskie Gory, Moscow, 11999, Russian Federation Email: ks13orl@list.ru
Photoinjector design for the LCLS
 SLAC-PUB-8962 LCLS-TN-01-05 Revised November 2001 Photoinjector design for the LCLS P.R. Bolton a, J.E. Clendenin a, D.H. Dowell a, M. Ferrario b, A.S. Fisher a, S.M. Gierman a, R.E. Kirby a, P. Krejcik
SLAC-PUB-8962 LCLS-TN-01-05 Revised November 2001 Photoinjector design for the LCLS P.R. Bolton a, J.E. Clendenin a, D.H. Dowell a, M. Ferrario b, A.S. Fisher a, S.M. Gierman a, R.E. Kirby a, P. Krejcik
Investigations on the electron bunch distribution in the longitudinal phase space at a laser driven RF-electron source for the European X-FEL
 Juliane Rönsch Universität Hamburg / DESY Investigations on the electron bunch distribution in the longitudinal phase space at a laser driven RF-electron source for the European X-FEL 5/27/2009 1 Contents
Juliane Rönsch Universität Hamburg / DESY Investigations on the electron bunch distribution in the longitudinal phase space at a laser driven RF-electron source for the European X-FEL 5/27/2009 1 Contents
Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) Properties. Physics Dept. & Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source (CHESS) Ithaca, NY Cornell University
 Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) Properties Sol M. Gruner Physics Dept. & Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source (CHESS) Cornell University Ithaca, NY 14853-2501 Acknowledgements T. Allen (Special thanks to
Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) Properties Sol M. Gruner Physics Dept. & Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source (CHESS) Cornell University Ithaca, NY 14853-2501 Acknowledgements T. Allen (Special thanks to
Overview of Energy Recovery Linacs
 Overview of Energy Recovery Linacs Ivan Bazarov Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source Talk Outline: Historical Perspective Parameter Space Operational ERLs & Funded Projects Challenges ERL Concept: conventional
Overview of Energy Recovery Linacs Ivan Bazarov Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source Talk Outline: Historical Perspective Parameter Space Operational ERLs & Funded Projects Challenges ERL Concept: conventional
Towards a Low Emittance X-ray FEL at PSI
 Towards a Low Emittance X-ray FEL at PSI A. Adelmann, A. Anghel, R.J. Bakker, M. Dehler, R. Ganter, C. Gough, S. Ivkovic, F. Jenni, C. Kraus, S.C. Leemann, A. Oppelt, F. Le Pimpec, K. Li, P. Ming, B. Oswald,
Towards a Low Emittance X-ray FEL at PSI A. Adelmann, A. Anghel, R.J. Bakker, M. Dehler, R. Ganter, C. Gough, S. Ivkovic, F. Jenni, C. Kraus, S.C. Leemann, A. Oppelt, F. Le Pimpec, K. Li, P. Ming, B. Oswald,
Georg Hoffstaetter Cornell Physics Dept. / CLASSE Cornell s ERL team
 1 R&D toward an ERL Georg Hoffstaetter Cornell Physics Dept. / Cornell s ERL team DC-gun R&D CW linac R&D SRF injector R&D Undulator R&D 2 Cornell history: The ERL principle Energy recovery needs continuously
1 R&D toward an ERL Georg Hoffstaetter Cornell Physics Dept. / Cornell s ERL team DC-gun R&D CW linac R&D SRF injector R&D Undulator R&D 2 Cornell history: The ERL principle Energy recovery needs continuously
Photo Injector Test facility at DESY, Zeuthen site
 Photo Injector Test facility at DESY, Zeuthen site PITZ EXPERIENCE ON THE EXPERIMENTAL OPTIMIZATION OF THE RF PHOTO INJECTOR FOR THE EUROPEAN XFEL Mikhail Krasilnikov (DESY) for the PITZ Team FEL 2013
Photo Injector Test facility at DESY, Zeuthen site PITZ EXPERIENCE ON THE EXPERIMENTAL OPTIMIZATION OF THE RF PHOTO INJECTOR FOR THE EUROPEAN XFEL Mikhail Krasilnikov (DESY) for the PITZ Team FEL 2013
Development of reliable and sophisticated photo injector system and future plan
 Development of reliable and sophisticated photo injector system and future plan Hiromitsu Tomizawa Accelerator Division, Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI/SPring-8) Kouto, Sayo-cho,
Development of reliable and sophisticated photo injector system and future plan Hiromitsu Tomizawa Accelerator Division, Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI/SPring-8) Kouto, Sayo-cho,
3D Laser Pulse Shaping for the Cornell ERL Photoinjector. August 9 th, 2012 Sierra Cook Advisors: Adam Bartnik, Ivan Bazarov, Jared Maxson
 3D Laser Pulse Shaping for the Cornell ERL Photoinjector August 9 th, 2012 Sierra Cook Advisors: Adam Bartnik, Ivan Bazarov, Jared Maxson Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) Accelerating Bunch Decelerating Bunch
3D Laser Pulse Shaping for the Cornell ERL Photoinjector August 9 th, 2012 Sierra Cook Advisors: Adam Bartnik, Ivan Bazarov, Jared Maxson Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) Accelerating Bunch Decelerating Bunch
Accelerators and Lasers In Combined Experiments Susan Smith Daresbury Laboratory
 ALICE iagnostics Accelerators and Lasers In Combined Experiments Susan Smith aresbury Laboratory Contents Quick Review of ALICE iagnostics Extended injector line ALICE to EMMA transfer line EMMA ebpm Other
ALICE iagnostics Accelerators and Lasers In Combined Experiments Susan Smith aresbury Laboratory Contents Quick Review of ALICE iagnostics Extended injector line ALICE to EMMA transfer line EMMA ebpm Other
Summary, Working Group 1: Electron guns and injector designs
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 557 (2006) 337 344 www.elsevier.com/locate/nima Summary, Working Group 1: Electron guns and injector designs I. Ben-Zvi a,, I.V. Bazarov b a Brookhaven
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 557 (2006) 337 344 www.elsevier.com/locate/nima Summary, Working Group 1: Electron guns and injector designs I. Ben-Zvi a,, I.V. Bazarov b a Brookhaven
ELIC Design. Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators. Jefferson Lab. Second Electron-Ion Collider Workshop Jefferson Lab March 15-17, 2004
 ELIC Design Ya. Derbenev, K. Beard, S. Chattopadhyay, J. Delayen, J. Grames, A. Hutton, G. Krafft, R. Li, L. Merminga, M. Poelker, E. Pozdeyev, B. Yunn, Y. Zhang Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators
ELIC Design Ya. Derbenev, K. Beard, S. Chattopadhyay, J. Delayen, J. Grames, A. Hutton, G. Krafft, R. Li, L. Merminga, M. Poelker, E. Pozdeyev, B. Yunn, Y. Zhang Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators
Alignment requirement for the SRF cavities of the LCLS-II injector LCLSII-TN /16/2014
 Alignment requirement for the SRF cavities of the LCLS-II injector LCLS-II TN-14-16 12/16/2014 R. K. Li, C. Papadopoulos, T. O. Raubenheimer, J. F. Schmerge, and F. Zhou December 16, 2014 LCLSII-TN-14-16
Alignment requirement for the SRF cavities of the LCLS-II injector LCLS-II TN-14-16 12/16/2014 R. K. Li, C. Papadopoulos, T. O. Raubenheimer, J. F. Schmerge, and F. Zhou December 16, 2014 LCLSII-TN-14-16
Free-electron laser SACLA and its basic. Yuji Otake, on behalf of the members of XFEL R&D division RIKEN SPring-8 Center
 Free-electron laser SACLA and its basic Yuji Otake, on behalf of the members of XFEL R&D division RIKEN SPring-8 Center Light and Its Wavelength, Sizes of Material Virus Mosquito Protein Bacteria Atom
Free-electron laser SACLA and its basic Yuji Otake, on behalf of the members of XFEL R&D division RIKEN SPring-8 Center Light and Its Wavelength, Sizes of Material Virus Mosquito Protein Bacteria Atom
X-band Experience at FEL
 X-band Experience at FERMI@Elettra FEL Gerardo D Auria Elettra - Sincrotrone Trieste GdA_TIARA Workshop, Ångström Laboratory, June 17-19, 2013 1 Outline The FERMI@Elettra FEL project Machine layout and
X-band Experience at FERMI@Elettra FEL Gerardo D Auria Elettra - Sincrotrone Trieste GdA_TIARA Workshop, Ångström Laboratory, June 17-19, 2013 1 Outline The FERMI@Elettra FEL project Machine layout and
USPAS Course on Recirculated and Energy Recovered Linacs
 USPAS Course on Recirculated and Energy Recovered Linacs I. V. Bazarov Cornell University G. A. Krafft and L. Merminga Jefferson Lab Computer Class: Space Charge in DC Gun ERL Injector USPAS 2005 Recirculated
USPAS Course on Recirculated and Energy Recovered Linacs I. V. Bazarov Cornell University G. A. Krafft and L. Merminga Jefferson Lab Computer Class: Space Charge in DC Gun ERL Injector USPAS 2005 Recirculated
Development of Cs 2 Te photocathode RF gun system for compact THz SASE-FEL
 Development of Cs 2 Te photocathode RF gun system for compact THz SASE-FEL R. Kuroda, H. Ogawa, N. Sei, H. Toyokawa, K. Yagi-Watanabe, M. Yasumoto, M. Koike, K. Yamada, T. Yanagida*, T. Nakajyo*, F. Sakai*
Development of Cs 2 Te photocathode RF gun system for compact THz SASE-FEL R. Kuroda, H. Ogawa, N. Sei, H. Toyokawa, K. Yagi-Watanabe, M. Yasumoto, M. Koike, K. Yamada, T. Yanagida*, T. Nakajyo*, F. Sakai*
Delta undulator magnet: concept and project status
 Delta undulator magnet: concept and project status Part I: concept and model construction* Alexander Temnykh, CLASSE, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, USA Part - II: beam test at ATF in BNL + M. Babzien,
Delta undulator magnet: concept and project status Part I: concept and model construction* Alexander Temnykh, CLASSE, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, USA Part - II: beam test at ATF in BNL + M. Babzien,
ELIC: A High Luminosity And Efficient Spin Manipulation Electron-Light Ion Collider Based At CEBAF
 ELIC: A High Luminosity And Efficient Spin Manipulation Electron-Light Ion Collider Based At CEBAF Lia Merminga and Yaroslav Derbenev Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators, Jefferson Laboratory,
ELIC: A High Luminosity And Efficient Spin Manipulation Electron-Light Ion Collider Based At CEBAF Lia Merminga and Yaroslav Derbenev Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators, Jefferson Laboratory,
Transverse emittance measurements on an S-band photocathode rf electron gun * Abstract
 SLAC PUB 8963 LCLS-01-06 October 2001 Transverse emittance measurements on an S-band photocathode rf electron gun * J.F. Schmerge, P.R. Bolton, J.E. Clendenin, F.-J. Decker, D.H. Dowell, S.M. Gierman,
SLAC PUB 8963 LCLS-01-06 October 2001 Transverse emittance measurements on an S-band photocathode rf electron gun * J.F. Schmerge, P.R. Bolton, J.E. Clendenin, F.-J. Decker, D.H. Dowell, S.M. Gierman,
Jim Clark, Matt Poelker, Steve Covert, Phil Adderley, Riad Suleiman, John Hansknecht, Marcy Stutzman, Joe Grames
 CEBAF Polarized Electron Source Jim Clark, Matt Poelker, Steve Covert, Phil Adderley, Riad Suleiman, John Hansknecht, Marcy Stutzman, Joe Grames JLAB Summer Lecture Series, June 23 rd 2011 What you are
CEBAF Polarized Electron Source Jim Clark, Matt Poelker, Steve Covert, Phil Adderley, Riad Suleiman, John Hansknecht, Marcy Stutzman, Joe Grames JLAB Summer Lecture Series, June 23 rd 2011 What you are
Electron sources for accelerators
 Electron sources for accelerators Carlos Hernandez-Garcia, Patrick G. O Shea, and Marcy L. Stutzman Photoemission shines as a source of the bright electron beams required for free-electron lasers and particle-physics
Electron sources for accelerators Carlos Hernandez-Garcia, Patrick G. O Shea, and Marcy L. Stutzman Photoemission shines as a source of the bright electron beams required for free-electron lasers and particle-physics
OVERVIEW OF ENERGY RECOVERY LINACS
 OVERVIEW OF ENERGY RECOVERY LINACS Ivan V. Bazarov, LEPP/CHESS, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA Abstract Existing Energy Recovery Linacs (ERLs) are successfully operated as kw-class average power
OVERVIEW OF ENERGY RECOVERY LINACS Ivan V. Bazarov, LEPP/CHESS, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA Abstract Existing Energy Recovery Linacs (ERLs) are successfully operated as kw-class average power
E E L C E T C R T O R N O N SO S U O R U C R E C S E S A N A D N D INJ N EC E T C O T R O S
 ELECTRON SOURCES AND INJECTORS Fernando Sannibale Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory 1 ELECTRON SOURCES AND INJECTORS Lecture 1: The role of electron sources and injectors in light source Requirements
ELECTRON SOURCES AND INJECTORS Fernando Sannibale Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory 1 ELECTRON SOURCES AND INJECTORS Lecture 1: The role of electron sources and injectors in light source Requirements
Waseda University. Design of High Brightness Laser-Compton Light Source for EUV Lithography Research in Shorter Wavelength Region
 Waseda University Research Institute for Science and Engineering Design of High Brightness Laser-Compton Light Source for EUV Lithography Research in Shorter Wavelength Region Research Institute for Science
Waseda University Research Institute for Science and Engineering Design of High Brightness Laser-Compton Light Source for EUV Lithography Research in Shorter Wavelength Region Research Institute for Science
Jim Clark, Matt Poelker, Steve Covert, Phil Adderley, Riad Suleiman, John Hansknecht, Marcy Stutzman, Joe Grames
 CEBAF Polarized Electron Source Jim Clark, Matt Poelker, Steve Covert, Phil Adderley, Riad Suleiman, John Hansknecht, Marcy Stutzman, Joe Grames JLAB Summer Lecture Series, July 17 th 2012 How do we see
CEBAF Polarized Electron Source Jim Clark, Matt Poelker, Steve Covert, Phil Adderley, Riad Suleiman, John Hansknecht, Marcy Stutzman, Joe Grames JLAB Summer Lecture Series, July 17 th 2012 How do we see
Simulations of the IR/THz source at PITZ (SASE FEL and CTR)
 Simulations of the IR/THz source at PITZ (SASE FEL and CTR) Introduction Outline Simulations of SASE FEL Simulations of CTR Summary Issues for Discussion Mini-Workshop on THz Option at PITZ DESY, Zeuthen
Simulations of the IR/THz source at PITZ (SASE FEL and CTR) Introduction Outline Simulations of SASE FEL Simulations of CTR Summary Issues for Discussion Mini-Workshop on THz Option at PITZ DESY, Zeuthen
PAL LINAC UPGRADE FOR A 1-3 Å XFEL
 PAL LINAC UPGRADE FOR A 1-3 Å XFEL J. S. Oh, W. Namkung, Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, POSTECH, Pohang 790-784, Korea Y. Kim, Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY, D-603 Hamburg, Germany Abstract With
PAL LINAC UPGRADE FOR A 1-3 Å XFEL J. S. Oh, W. Namkung, Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, POSTECH, Pohang 790-784, Korea Y. Kim, Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY, D-603 Hamburg, Germany Abstract With
