Effects of Ball Groupings on Ball Passage Vibrations of a Linear Guideway Type Ball Bearing Pitching and Yawing Ball Passage Vibrations
|
|
|
- Delilah Webster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hiroyuki Ohta 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Nagaoka University of Technology, Kamitomioka, Nagaoka, Niigata, Japan ohta@mech.nagaokaut.ac.jp Yoshiki Kitajima LG Technology Department, NSK Precision Co., Ltd., 1-1 Ohnuma, Hanyu, Saitama, Japan Soichiro Kato LG Technology Department, NSK Precision Co., Ltd., 78 Toriba, Maebashi, Gunma, Japan Yutaka Igarashi Research Department, NSK Precision Co., Ltd., 78 Toriba, Maebashi, Gunma, Japan Effects of Ball Groupings on Ball Passage Vibrations of a Linear Guideway Type Ball Bearing Pitching and Yawing Ball Passage Vibrations The effects of ball groupings on the pitching and yawing ball passage vibrations of linear guideway type ball bearings (linear ball bearings) under low-speed operation were studied. For this study, the test linear ball bearings (which can retain the ball grouping in operation) with three types of ball groupings were manufactured, and the pitching and yawing ball passage vibrations of each test linear ball bearing were measured using a laser autocollimator. Moreover, a calculation method of the ball passage vibrations for a linear ball bearing with an arbitrary ball grouping was presented. According to the presented method the ball passage vibrations for three types of ball groupings were calculated. The experimental and calculated results show that the occurrence of the pitching and yawing ball passage vibrations was affected by the ball groupings. For the occurrence, the wave forms, and the amplitude of the pitching and yawing ball passage vibrations for the ball groupings, the calculated results based on the presented method almost matched the experimental results. DOI: / Keywords: ball bearing, linear bearing, ball passage vibration, ball grouping 1 Introduction Linear guideway type ball bearings linear ball bearings are widely used in machine tools, robots, and precision x-y tables 1. Although linear bearings have many advantages compared with sliding guides, they often lead to vibrations Ball passage vibrations periodical posture changes of the carriage with a ball passage frequency are typical vibrations of linear bearings. Kasai et al. 6 8 observed the ball passage vibrations of recirculating linear ball bearings in operation. They also pointed out that the ball passage vibration was reduced by using a carriage with crowning. Shimizu 9,10 presented the calculation method of ball passage vibrations of the table supported by the recirculating linear ball bearings. He also proposed an optimum circular crowning to reduce the ball passage vibration based on his experimental results. Ohta et al. 11 presented a theoretical design method of the crowning to reduce the ball passage vibrations of linear bearings. Kato and Matsumoto 12 showed a calculation method of the pitching and vertical ball passage vibrations for a ball grouping where the balls in the upper rows and in the lower rows are assumed to be staggered by half of the distance s between adjacent balls. They presumed that the ball passage vibrations are affected by ball groupings. Since the ball grouping in the recirculating linear ball bearings which were used in the previous studies is not retained in operation, it was difficult to evaluate the effects of the ball groupings on the ball passage vibrations. Therefore, the effects of the ball groupings on the ball passage vibrations have not yet been examined thoroughly. 1 Corresponding author. Contributed by the Tribology Division of ASME for publication in the JOURNAL OF TRIBOLOGY. Manuscript received June 14, 2006; final manuscript received September 18, Review conducted by Liming Chang. Paper presented at the STLE/ASME 2006 International Joint Tribology Conference, San Antonio, TX, October 22 25, In this paper, the effects of the ball groupings on the pitching and yawing ball passage vibrations under-low speed operation are examined by using the nonrecirculating linear ball bearings which can retain the ball grouping in operation. 2 Experiments 2.1 Test Bearings and Ball Groupings. In order to examine the effects of the ball groupings on the ball passage vibrations, nonrecirculating linear ball bearings were manufactured and used as test bearings. The photograph of a test linear ball bearing is shown in Fig. 1. One test bearing consists of one rail, one carriage, one retainer, and balls. The number of rows is four. In the test bearing, the ball grouping can be changed by changing the pocket locations in the retainer. All the test bearings are preloaded by oversizing of the balls. The test bearing specifications are shown in Table 1. The ball groupings of the test bearings are shown in Fig. 2. In Fig. 2, n 1 n 4 show the number of the loaded balls in the rows i=1 4, respectively. In this study, three types of ball groupings are considered as shown in Fig. 2. The features of each grouping are follows: 1. Ball grouping I. The ball locations in the two upper rows i=1,2 are shifted half the distance s between the adjacent balls to those in the two lower rows i=3,4 ; 2. Ball grouping II. The ball locations in the two left rows i =2,3 are shifted s/2 to those in the two right rows i =1,4 ; and 3. Ball grouping III. The ball locations in the second row i =2, in the third row i=3, and in the fourth row i=4 are shifted s/2, s/3, and s/5, to those in the first row i=1, respectively. 2.2 Experimental Method. The experimental apparatus is shown in Fig. 3. The rail of the test bearing is fixed on the concrete bed by bolts. The carriage of the test bearing is driven at a 188 / Vol. 129, JANUARY 2007 Copyright 2007 by ASME Transactions of the ASME
2 Fig. 1 Test bearing ball grouping I certain linear velocity. The pitching and yawing motion of the carriage was detected by using a laser autocollimator Chuo Precision Industrial Co., Ltd: LAC-S and a mirror, and was stored in a personal computer. The positive and negative directions of the pitching and yawing motion of the carriage were defined as shown in Fig. 3. Figure 4 shows the mounting position of the mirror. Because the gravitational center G m of the mirror was right above that of the carriage G c, the gravitational center G of the mirror attached the mirror was also right above G c. In the measurement using the laser autocollimator and the mirror, the motion caused by the deformation of the rail as well as the ball passage vibrations were detected 11. To avoid the effect of the motion caused by the deformation of the rail, a high pass filter was used. The cutoff frequency was 0.8f p, where f p is the ball passage frequency. The ball passage frequency f p is given by f p = V 2s 1 In the measurement, the linear velocity V of the carriage was varied in four steps in the range of m/s. Except for the vertical load caused by the weight of the carriage and mirror, external loads were not applied to the test bearing. The test bearings were lubricated with mineral oil ISO VG Experimental Results Table 1 Test bearing specifications Asssembly height m Carriage width m Carriage length L 1 m Carriage height m Rail width m Rail length L m Rail height m Ball diameter m Distance between adjacent balls s m Number of rows 4 Contact angle deg 50 Oversize of balls 0 m Crowning length L C m Crowing radius R m 1.1 Fig. 2 Ball arrangements The typical measured wave forms of the pitching and yawing ball passage vibrations are shown in Fig. 5. In Fig. 5, T p =1/ f p is the ball passage period. It is clear from Fig. 5 that the measured wave forms of the ball passage vibrations are affected by the ball groupings. In ball grouping I, the pitching ball passage vibration occurs, while the yawing ball passage vibration does not occur. In ball grouping II, the pitching ball passage vibration does not occur, while the yawing ball passage vibration occurs. In ball grouping III, both the pitching and yawing ball passage vibrations occur. The effect of the linear velocity V of the carriage on the measured rms amplitude of the ball passage vibrations in each ball grouping is shown in Fig. 6. It is clear from Fig. 6 that the measured amplitude of the pitching and yawing ball passage vibrations does not significantly change with linear velocity V, within the experimental condition linear velocity V= m/s. Journal of Tribology JANUARY 2007, Vol. 129 / 189
3 Fig. 3 Experimental apparatus 4 Discussion 4.1 Calculation Method of Ball Passage Vibrations for Linear Bearings with Arbitrary Ball Groupings. In this section, a calculation method of the ball passage vibrations for a linear bearing with an arbitrary ball grouping is discussed. Figure 7 shows the coordinate system for the test bearing. The coordinate system O-xyz is a moving coordinate which moves with the carriage in the longitudinal direction of the rail at the linear velocity V. The origin O of coordinates coincides with the position of the gravitational center G of the carriage with the mirror, on the condition that the distances between the races of the carriage and rail are equidistance reference condition. In Fig. 7, a is the distance from the origin O to the contact point of the upper rows of the carriage and the balls in the direction parallel to the z axis; b is the distance from the origin O to the contact point of the lower rows of the carriage and the balls in the direction parallel to the z axis; c is the distance from the origin O to the contact point of the rows of the carriage and the balls in the direction parallel to the y axis, is the contact angle; L 1 is the carriage body length; and L c ;is the crowning length. In the experiment in this study, only the vertical load caused by the weight of the carriage and mirror was applied to the test bearing. However, to present a wide use calculation method of Fig. 6 Effect of linear velocity on rms amplitude of ball passage vibrations Fig. 4 Center of gravity ball passage vibrations, we consider a loading condition in which the horizontal load F H, the vertical load F V, the rolling moment M R, the pitching moment M P, and the yawing moment M Y are applied to the carriage. Under the loading condition, the horizontal displacement u, the vertical displacement v, the rolling angle, the pitching angle, and the yawing angle occur as shown in Fig. 7, total contact deformation ij at jth ball in ith row is given by Fig. 5 Measured wave forms of ball passage vibrations V=1.67Ã10 4 m/s 190 / Vol. 129, JANUARY 2007 Transactions of the ASME
4 Table 2 Values of a, b, c, K, and W a m b m c m K N/m W N 9.92 Fig. 7 Coordinates of test bearing in integers which are not over Z Z real number. From the Hertzian theory, the normal force Q ij between jth ball and raceways of ith row is given by 13 Q ij = K 1.5 ij : ij 0 Q ij =0: ij 0 6 where K is the load deflection factor which is determined by the material and the geometry of the ball and the raceways. The static balance of the forces horizontal and vertical forces and moments rolling, pitching, and yawing moments can be written as n 1 Q 1j + n 2 n 3 Q 2j + n 4 Q 3j Q 4j cos = F H 7 1j = e u cos v sin + a cos + c sin x 1j sin + x 1j cos C x 1j 2j = e + u cos v sin a cos c sin x 2j sin x 2j cos C x 2j 3j = e + u cos + v sin b cos + c sin + x 3j sin x 3j cos C x 3j 4j = e u cos + v sin + b cos c sin + x 4j sin + x 4j cos C x 4j 2 where e is the total contact deformation of a ball on the straight area L 1 2L c of the raceways of the carriage under the reference condition. Considering the carriage flexibility under preloading, e is given by 6 e = where 0 is the oversize of the balls. In Eq. 2, C x is the crowning drop at x. For circular arc crownings, C x is given by 11 C x = R R 2 x + L 1 2 c 2 L : L 1 2 x L L c C x =0: L L c x L 1 2 L c C x = R R 2 x L 2 1 c 2 + L : L 1 2 L c x L 1 2 where R is the crowning radius. x ij is x coordinates of the jth ball in the ith row in the carriage under a certain linear velocity V, and int is given by x ij = j 1 s + x i0 + Vt 2 L 1 +2x i0 + Vt s 5 2s where t is time; s is the distance between the adjacent balls; x i0 is x coordinates of the first ball in the ith row at t=0; and L 1 /2 x i0 s L 1 /2. By setting x i0, an arbitrary ball grouping can be expressed. In Eq. 5, int Z represents the maximum 3 4 n 1 n 2 Q 1j n 1 Q 1j n 2 Q 2j + n 3 Q 3j + n 4 Q 4j sin = F V 8 n 3 n 4 Q 2j c sin + a cos + Q 3j Q 4j c sin b cos = M R n 1 n 2 n 3 n 4 Q 1jx 1j Q 2jx 2j + Q 3jx 3j + Q 4jx 4j sin = M P n 1 n 2 n 3 n 4 Q 1jx 1j Q 2jx 2j Q 3jx 3j + Q 4jx 4j cos = M Y By using Eqs. 2 11, the horizontal, vertical, rolling, pitching, and yawing ball passage vibrations for an arbitrary ball grouping can be calculated based on the static balance of the forces and moments. 4.2 Comparison of Experimental Results with Calculated Results. Based on the calculation method described in Sec. 4.1, the ball passage vibrations of the test bearings with ball groupings I III were calculated under the loading condition in the experiment F V = W, F H =M R =M P =M Y =0. In the calculations, the values listed in Tables 1 and 2, and the values of x i0 which correspond to the ball grouping listed in Table 3 were used. The value of K in Table 2 was calculated theoretically from the design values of the ball-race configuration and material properties of the Table 3 Values of x i0 for ball groupings I III Ball grouping x 10 x 20 x 30 x 40 I L 1 2 L 1 2 L 1 2+s 2 L 1 2+s 2 II L 1 2 L 1 2+s 2 L 1 2+s 2 L 1 2 III L 1 2 L 1 2+s 2 L 1 2+s 3 L 1 2+s 5 Journal of Tribology JANUARY 2007, Vol. 129 / 191
5 Fig. 8 Calculated wave forms of ball passage vibrations V=1.67Ã10 4 m/s test bearings, using Hertzian theory 13. The typical calculated wave forms of the ball passage vibrations for ball groupings I III are shown in Fig. 8. It is clear from Fig. 8 that the calculated wave forms of the ball passage vibrations are affected by the ball groupings. In ball grouping I, the vertical and pitching ball passage vibrations occur. In ball grouping II, the horizontal and yawing ball passage vibrations occur. In ball grouping III, the horizontal, vertical, rolling, pitching, and yawing ball passage vibrations occur. By comparing Figs. 8 and 5, it is clear that the calculated results on the occurrence, the time wave forms of the pitching, and yawing ball passage vibrations for ball groupings I III are almost matched with the experimental results. The calculated rms amplitude of the pitching and yawing ball passage vibrations is drawn in Fig. 6. The calculated rms amplitude of the yawing ball passage vibration in ball grouping I and that of the pitching ball passage vibration in ball grouping II are zero. From Fig. 6, it is clear that the calculated rms amplitude of the pitching and yawing ball passage vibrations is almost matched with the measured rms amplitude. The effect of ball groupings on the horizontal, vertical, and the rolling ball passage vibrations has not been verified in the experiment, since the autocollimator cannot measure the horizontal, vertical, and the rolling ball passage vibrations. This will be examined in a future study. 5 Conclusions The following conclusions are drawn from the experimental results and discussion: 1. The occurrence of the pitching and yawing ball passage vibrations were affected by the ball groupings; 2. The measured rms amplitude of the pitching and yawing ball passage vibrations did not significantly change with linear velocity V, within the experimental condition linear velocity V= m/s ; 3. Based on the static balance of forces and moments, a calculation method of the ball passage vibrations for a linear bearing with an arbitrary ball grouping was presented; and 4. For the occurrence, the time wave forms and rms amplitude of the pitching and yawing ball passage vibrations for the ball groupings, the calculated results based on the presented method were almost matched with the experimental results. Acknowledgment This research was supported in part by scientific research funds fundamental research C, No from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture, Japan. Nomenclature a distance from origin O to the contact point of the upper rows of the carriage and the balls in the direction parallel to the z axis m b distance from the origin O to the contact point of the lower rows of the carriage and the balls in the direction parallel to the z axis m c distance from the origin O to the contact point of the rows of the carriage and the balls in the direction parallel to the y axis m C x crowning drop at x m f p ball passage frequency Hz F H horizontal load N F V vertical load N M P pitching moment Nm M R rolling moment Nm M Y yawing moment Nm i row number j loaded ball number in a row 192 / Vol. 129, JANUARY 2007 Transactions of the ASME
6 K load deflection factor which is determined by the material and the geometry of the ball and the raceways N/m 3/2 L 1 carriage body length m L c crowning length m n 1 n 4 number of the loaded balls in the rows i=1 4, respectively. O-xyz Cartesian coordinates Q ij normal force Q ij between ith ball and raceways of jth row N R crowning radius m s distance between the adjacent balls m t time s T p ball passage period s u horizontal displacement of the ball passage vibration m v vertical displacement of the ball passage vibration m V linear velocity of the carriage m/s W total weight of the carriage and the mirror N x ij x coordinates of jth ball in ith row in the carriage under a certain linear velocity V Z real number contact angle deg pitching angle rad e total contact deformation of a ball on the straight area of the raceways of the carriage under the reference condition m References ij total contact deformation at jth ball in ith row m o oversizing of the balls m 1 The Japan Society for Precision Engineering, 2000, Present and Future Technology of Ultraprecision Positioning, FUJI Technosystem, Tokyo, Japan. 2 Teramachi, A., 2000, Introduction to Linear Systems, The Nikkan Kogyo Shimbun, Tokyo, Japan. 3 Grunau, A., and Giese, P., 1991, Scwingungsverhalten von Linearwalzfuhrungen für Werkzeugmashinen, Konstruktion, 43, pp Schneider, M., 1991, Statisches Und Dynamisches Verhalten Beim Einsatz Linearer Schienenführungen Auf Wälzlagerbasis Im Werkzeugmaschinenbau, Carl Hanser Verlag, Munchen, Wien, Germany. 5 Ohta, H., and Hayashi, E., 2000, Vibration of Linear Guideway Type Recirculating Linear Ball Bearings, J. Sound Vib., 235 5, pp Kasai, S., Tsukada, T., Ozawa, N., and Kato, S., 1985, Precision Linear Guides, NSK Tech. J., 645, pp Kasai, S., Tsukada, T., and Kato, S., 1987, Precision Linear Guides for Machine Tools, NSK Tech. J., 647, pp Kasai, S., Tsukada, T., and Kato, S., 1989, Recent Technical Trends of Linear Guides, NSK Tech. J., 649, pp Shimizu, S., 1990, Load Distribution and Accuracy/ Rigidity of Linear Motion Ball Guides System, J. Jpn. Soc. Precis. Eng., 56 8, pp Shimizu, S., 1992, Study on Accuracy Average Effect of Linear Motion Ball Guides System, J. Jpn. Soc. Precis. Eng., 58 11, pp Ohta, H., Kato, S., Matsumoto, J., and Nakano, K., 2005, A Design of Crowning to Reduce Ball Passage Vibrations of a Linear Guideway Type Recirculating Linear Ball Bearings, ASME J. Tribol., 127, pp Kato, S., and Matsumoto, J., 2000, Recent Developments in Highly Precise NSK Linear Guides, Motion & Control, 9, pp Harris, T. A., 2001, Rolling Bearing Analysis, 4th ed., Wiley, New York. Journal of Tribology JANUARY 2007, Vol. 129 / 193
Stability of Water-Lubricated, Hydrostatic, Conical Bearings With Spiral Grooves for High-Speed Spindles
 S. Yoshimoto Professor Science University of Tokyo, Department of Mechanical Engineering, 1-3 Kagurazaka Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo 16-8601 Japan S. Oshima Graduate Student Science University of Tokyo, Department
S. Yoshimoto Professor Science University of Tokyo, Department of Mechanical Engineering, 1-3 Kagurazaka Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo 16-8601 Japan S. Oshima Graduate Student Science University of Tokyo, Department
The basic dynamic load rating C is a statistical number and it is based on 90% of the bearings surviving 50 km of travel carrying the full load.
 Technical data Load Rating & Life Under normal conditions, the linear rail system can be damaged by metal fatigue as the result of repeated stress. The repeated stress causes flaking of the raceways and
Technical data Load Rating & Life Under normal conditions, the linear rail system can be damaged by metal fatigue as the result of repeated stress. The repeated stress causes flaking of the raceways and
Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis of a Hydrodynamic Journal Bearing Considering the Effect of a Rotating or Stationary Herringbone Groove
 G. H. Jang e-mail: ghjang@hanyang.ac.kr J. W. Yoon PREM, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul, 133-791, Korea Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis of a Hydrodynamic Journal Bearing Considering
G. H. Jang e-mail: ghjang@hanyang.ac.kr J. W. Yoon PREM, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul, 133-791, Korea Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis of a Hydrodynamic Journal Bearing Considering
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(7): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 4, 6(7): 44-4 Research Article ISSN : 975-784 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Analysis on static characteristics of linear rolling guide
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 4, 6(7): 44-4 Research Article ISSN : 975-784 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Analysis on static characteristics of linear rolling guide
Theoretical Study of Contact Angles of a Linear Guideway
 Copyright 2011 Tech Science Press SL, vol.5, no.3, pp.139-145, 2011 Theoretical Study of Contact Angles of a Linear Guideay D. Sha 1 Abstract: The contact angle affects the life and accuracy of a linear
Copyright 2011 Tech Science Press SL, vol.5, no.3, pp.139-145, 2011 Theoretical Study of Contact Angles of a Linear Guideay D. Sha 1 Abstract: The contact angle affects the life and accuracy of a linear
Calculating the Applied Load
 The LM Guide is capable of receiving loads and moments in all directions that are generated due to the mounting orientation, alignment, gravity center position of a traveling object, thrust position and
The LM Guide is capable of receiving loads and moments in all directions that are generated due to the mounting orientation, alignment, gravity center position of a traveling object, thrust position and
DEVELOPMENT OF SEISMIC ISOLATION TABLE COMPOSED OF AN X-Y TABLE AND WIRE ROPE ISOLATORS
 DEVELOPMENT OF SEISMIC ISOLATION TABLE COMPOSED OF AN X-Y TABLE AND WIRE ROPE ISOLATORS 7 Hirokazu SHIMODA, Norio NAGAI, Haruo SHIMOSAKA And Kenichiro OHMATA 4 SUMMARY In this study, a new type of isolation
DEVELOPMENT OF SEISMIC ISOLATION TABLE COMPOSED OF AN X-Y TABLE AND WIRE ROPE ISOLATORS 7 Hirokazu SHIMODA, Norio NAGAI, Haruo SHIMOSAKA And Kenichiro OHMATA 4 SUMMARY In this study, a new type of isolation
A 3D-ball bearing model for simulation of axial load variations
 A 3D-ball bearing model for simulation of axial load variations Petro Tkachuk and Jens Strackeljan Otto-von-Guericke-Universität Magdeburg, Fakultät für Maschinenbau Institut für Mechanik Universitätsplatz
A 3D-ball bearing model for simulation of axial load variations Petro Tkachuk and Jens Strackeljan Otto-von-Guericke-Universität Magdeburg, Fakultät für Maschinenbau Institut für Mechanik Universitätsplatz
VIBRATION TRANSMISSION THROUGH SELF-ALIGNING (SPHERICAL) ROLLING ELEMENT BEARINGS: THEORY AND EXPERIMENT
 Journal of Sound and Vibration (1998) 215(5), 997 1014 Article No. sv981579 VIBRATION TRANSMISSION THROUGH SELF-ALIGNING (SPHERICAL) ROLLING ELEMENT BEARINGS: THEORY AND EXPERIMENT T. J. ROYSTON AND I.
Journal of Sound and Vibration (1998) 215(5), 997 1014 Article No. sv981579 VIBRATION TRANSMISSION THROUGH SELF-ALIGNING (SPHERICAL) ROLLING ELEMENT BEARINGS: THEORY AND EXPERIMENT T. J. ROYSTON AND I.
New Representation of Bearings in LS-DYNA
 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Aerospace New Representation of Bearings in LS-DYNA Kelly S. Carney Samuel A. Howard NASA Glenn Research Center, Cleveland, OH 44135 Brad A. Miller
13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Aerospace New Representation of Bearings in LS-DYNA Kelly S. Carney Samuel A. Howard NASA Glenn Research Center, Cleveland, OH 44135 Brad A. Miller
C-Lube Linear Way ML Linear Way L ML LWL
 -Lube Linear ay ML Linear ay L MLLL -Lube Maintenance ree Series -Lube Linear ay ML ML long term maintenance free supported! The aquamarine end plate is the symbol of maintenance free. Identification umber
-Lube Linear ay ML Linear ay L MLLL -Lube Maintenance ree Series -Lube Linear ay ML ML long term maintenance free supported! The aquamarine end plate is the symbol of maintenance free. Identification umber
Stability Analysis of a Hydrodynamic Journal Bearing With Rotating Herringbone Grooves
 G. H. Jang e-mail: ghjang@hanyang.ac.kr J. W. Yoon PREM, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul, 33-79, Korea Stability Analysis of a Hydrodynamic Journal Bearing With Rotating
G. H. Jang e-mail: ghjang@hanyang.ac.kr J. W. Yoon PREM, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul, 33-79, Korea Stability Analysis of a Hydrodynamic Journal Bearing With Rotating
Auto collimator. Introduction. Objectives: Apparatus: Theory:
 Auto collimator Introduction An autocollimator is an optical instrument that is used to measure small angles with very high sensitivity. As such, the autocollimator has a wide variety of applications including
Auto collimator Introduction An autocollimator is an optical instrument that is used to measure small angles with very high sensitivity. As such, the autocollimator has a wide variety of applications including
NON-LINEAR BEARING STIFFNESS PARAMETER EXTRACTION FROM RANDOM RESPONSE IN FLEXIBLE ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEMS
 Journal of Sound and Vibration (1997) 3(3), 389 48 NON-LINEAR BEARING STIFFNESS PARAMETER EXTRACTION FROM RANDOM RESPONSE IN FLEXIBLE ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEMS Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian
Journal of Sound and Vibration (1997) 3(3), 389 48 NON-LINEAR BEARING STIFFNESS PARAMETER EXTRACTION FROM RANDOM RESPONSE IN FLEXIBLE ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEMS Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian
Evaluation of a surface acoustic wave motor with a multi-contact-point slider
 Smart Mater. Struct. 7 (1998) 305 311. Printed in the UK PII: S0964-1726(98)91230-7 Evaluation of a surface acoustic wave motor with a multi-contact-point slider Minoru Kuribayashi Kurosawa, Makoto Chiba
Smart Mater. Struct. 7 (1998) 305 311. Printed in the UK PII: S0964-1726(98)91230-7 Evaluation of a surface acoustic wave motor with a multi-contact-point slider Minoru Kuribayashi Kurosawa, Makoto Chiba
C-Lube Linear Way ML ML MLF
 Maintenance ree & U.S. PTTD C-Lube Linear ay Variation of C-Lube Linear ay Shape Length of slide unit Model code C-Lube Linear ay is a linear motion rolling guide, incorporating the C-Lube as a components
Maintenance ree & U.S. PTTD C-Lube Linear ay Variation of C-Lube Linear ay Shape Length of slide unit Model code C-Lube Linear ay is a linear motion rolling guide, incorporating the C-Lube as a components
Friction Properties of Surface with Circular Micro-patterns
 Friction Properties of Surface with Circular Micro-patterns Hideo Koguchi Mechanical Engineering, 603- Kamitomioka, Nagaoka Univ. of Tech., Nagaoka, Niigata, Japan Email: koguchi@mech.nagaokaut.ac.jp Takayoshi
Friction Properties of Surface with Circular Micro-patterns Hideo Koguchi Mechanical Engineering, 603- Kamitomioka, Nagaoka Univ. of Tech., Nagaoka, Niigata, Japan Email: koguchi@mech.nagaokaut.ac.jp Takayoshi
Journal of Physics: Conference Series. Related content. Recent citations PAPER OPEN ACCESS
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Ball's motion, sliding friction, and internal load distribution in a high-speed ball bearing subjected to a combined radial, thrust, and moment load,
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Ball's motion, sliding friction, and internal load distribution in a high-speed ball bearing subjected to a combined radial, thrust, and moment load,
KNIFE EDGE FLAT ROLLER
 EXPERIMENT N0. 1 To Determine jumping speed of cam Equipment: Cam Analysis Machine Aim: To determine jumping speed of Cam Formulae used: Upward inertial force = Wvω 2 /g Downward force = W + Ks For good
EXPERIMENT N0. 1 To Determine jumping speed of cam Equipment: Cam Analysis Machine Aim: To determine jumping speed of Cam Formulae used: Upward inertial force = Wvω 2 /g Downward force = W + Ks For good
PROCESS FOR SELECTING NB LINEAR SYSTEM
 The NB linear system is a linear motion mechanism which utilizes the recirculating movement of ball or roller elements to provide smooth and accurate linear travel. NB offers a wide range of linear motion
The NB linear system is a linear motion mechanism which utilizes the recirculating movement of ball or roller elements to provide smooth and accurate linear travel. NB offers a wide range of linear motion
Analysis of dynamic characteristics of a HDD spindle system supported by ball bearing due to temperature variation
 Analysis of dynamic characteristics of a HDD spindle system supported by ball bearing due to temperature variation G. H. Jang, D. K. Kim, J. H. Han, C. S. Kim Microsystem Technologies 9 (2003) 243 249
Analysis of dynamic characteristics of a HDD spindle system supported by ball bearing due to temperature variation G. H. Jang, D. K. Kim, J. H. Han, C. S. Kim Microsystem Technologies 9 (2003) 243 249
R-Plus System Frontespizio_R_PlusSystem.indd 1 11/06/ :32:02
 R-Plus System R-Plus System R-Plus system R-Plus system description Fig. R-Plus system R-Plus System is Rollon s series of rack & pinion driven actuators. Rollon R-Plus System series linear units are designed
R-Plus System R-Plus System R-Plus system R-Plus system description Fig. R-Plus system R-Plus System is Rollon s series of rack & pinion driven actuators. Rollon R-Plus System series linear units are designed
Nonlinear Rolling Element Bearings in MADYN 2000 Version 4.3
 - 1 - Nonlinear Rolling Element Bearings in MADYN 2000 Version 4.3 In version 4.3 nonlinear rolling element bearings can be considered for transient analyses. The nonlinear forces are calculated with a
- 1 - Nonlinear Rolling Element Bearings in MADYN 2000 Version 4.3 In version 4.3 nonlinear rolling element bearings can be considered for transient analyses. The nonlinear forces are calculated with a
Fine Alignment of the ATF Damping Ring
 Fine Alignment of the ATF Damping Ring M. Takano, S. Araki (a), Y. Funahashi (a), H. Hayano (a), T. Matsui (b), J. Urakawa (a) Toho University 2 2 1 Miyama, Funabashi, Chiba 275, Japan (a) KEK, High Energy
Fine Alignment of the ATF Damping Ring M. Takano, S. Araki (a), Y. Funahashi (a), H. Hayano (a), T. Matsui (b), J. Urakawa (a) Toho University 2 2 1 Miyama, Funabashi, Chiba 275, Japan (a) KEK, High Energy
Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive MKUVE15-KGT, MKUVE20-KGT
 Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive MKUVE15-KGT, MKUVE20-KGT Product overview Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive Actuators with ball monorail
Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive MKUVE15-KGT, MKUVE20-KGT Product overview Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive Actuators with ball monorail
STATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A PUMP IMPELLER WITH A BALANCING DEVICE PART I: STATIC ANALYSIS
 Int. J. of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 04, vol.9, No.3, pp.609-69 DOI: 0.478/ijame-04-004 STATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A PUMP IMPELLER WITH A BALANCING DEVICE PART I: STATIC ANALYSIS C. KUNDERA
Int. J. of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 04, vol.9, No.3, pp.609-69 DOI: 0.478/ijame-04-004 STATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A PUMP IMPELLER WITH A BALANCING DEVICE PART I: STATIC ANALYSIS C. KUNDERA
Analysis of Fluid Film Stiffness and Damping coefficient for A Circular Journal Bearing with Micropolar Fluid
 et International Journal on Emerging Technologies 5(1): 206-211(2014) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online) : 2249-3255 Analysis of Fluid Film Stiffness Damping coefficient for A Circular Journal
et International Journal on Emerging Technologies 5(1): 206-211(2014) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online) : 2249-3255 Analysis of Fluid Film Stiffness Damping coefficient for A Circular Journal
3.1 CONDITIONS FOR RIGID-BODY EQUILIBRIUM
 3.1 CONDITIONS FOR RIGID-BODY EQUILIBRIUM Consider rigid body fixed in the x, y and z reference and is either at rest or moves with reference at constant velocity Two types of forces that act on it, the
3.1 CONDITIONS FOR RIGID-BODY EQUILIBRIUM Consider rigid body fixed in the x, y and z reference and is either at rest or moves with reference at constant velocity Two types of forces that act on it, the
PROJECT 2 DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 41514
 PROJECT 2 DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 41514 Dynamics of Rotor-Bearing System Lateral Vibrations and Stability Threshold of Rotors Supported On Hydrodynamic Bearing and Ball Bearing. Ilmar Ferreira Santos, Prof.
PROJECT 2 DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 41514 Dynamics of Rotor-Bearing System Lateral Vibrations and Stability Threshold of Rotors Supported On Hydrodynamic Bearing and Ball Bearing. Ilmar Ferreira Santos, Prof.
Reduction of Mechanical Loss of Flywheel Energy Storage System with Spherical Spiral Groove Bearing
 Reduction of Mechanical Loss of Flywheel Energy Storage System with Spherical Spiral Groove Bearing Takeo Suuki, Takumi Masuda, Jun-ichi Itoh, Noboru Yamada Nagaoka University of Technology Nagaoka, Niigata,
Reduction of Mechanical Loss of Flywheel Energy Storage System with Spherical Spiral Groove Bearing Takeo Suuki, Takumi Masuda, Jun-ichi Itoh, Noboru Yamada Nagaoka University of Technology Nagaoka, Niigata,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia CIRP 36 (2015 ) CIRP 25th Design Conference Innovative Product Creation
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia CIRP 36 (2015 ) 111 116 CIRP 25th Design Conference Innovative Product Creation Machine stiffness rating: Characterization and evaluation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia CIRP 36 (2015 ) 111 116 CIRP 25th Design Conference Innovative Product Creation Machine stiffness rating: Characterization and evaluation
The SynchMotion. Retainer
 106 G99TE13-0809 Linear Guideways QE Series 2-9 QE Type Quiet Linear Guideway, with SynchMotion TM Technology The development of HIIN-QE linear guideway is based on a four-row circular-arc contact. The
106 G99TE13-0809 Linear Guideways QE Series 2-9 QE Type Quiet Linear Guideway, with SynchMotion TM Technology The development of HIIN-QE linear guideway is based on a four-row circular-arc contact. The
The Influence of location of balls and ball diameter difference in rolling bearings on the nonrepetitive runout (NRRO) of retainer revolution
 Precision Engineering 9 (005) 8 The Influence of location of balls and ball diameter difference in rolling bearings on the nonrepetitive runout (NRRO) of retainer revolution Shoji Noguchi a,, Kentaro Hiruma
Precision Engineering 9 (005) 8 The Influence of location of balls and ball diameter difference in rolling bearings on the nonrepetitive runout (NRRO) of retainer revolution Shoji Noguchi a,, Kentaro Hiruma
An Energy Circulation Driving Surface Acoustic Wave Motor
 An Energy Circulation Driving Surface Acoustic Wave Motor Minoru K. Kurosawa Tokyo Institute of Technology Yokohama, Japan mkur@ae.titech.ac.jp Purevdagva Nayanbuu Tokyo Institute of Technology Yokohama,
An Energy Circulation Driving Surface Acoustic Wave Motor Minoru K. Kurosawa Tokyo Institute of Technology Yokohama, Japan mkur@ae.titech.ac.jp Purevdagva Nayanbuu Tokyo Institute of Technology Yokohama,
Mechanical Vibrations Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Mechanical Vibrations Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 12 Signature analysis and preventive maintenance Lecture - 3 Field balancing
Mechanical Vibrations Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 12 Signature analysis and preventive maintenance Lecture - 3 Field balancing
Journal bearing performance and metrology issues
 of Achievements in Materials and Manufacturing Engineering VOLUME 3 ISSUE 1 January 009 Journal bearing performance and metrology issues S. Sharma a, *, D. Hargreaves b, W. Scott b a School of Engineering
of Achievements in Materials and Manufacturing Engineering VOLUME 3 ISSUE 1 January 009 Journal bearing performance and metrology issues S. Sharma a, *, D. Hargreaves b, W. Scott b a School of Engineering
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Rolling bearings Linear motion rolling bearings Part 2: Static load ratings
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 14728-2 First edition 2004-06-01 Rolling bearings Linear motion rolling bearings Part 2: Static load ratings Roulements Roulements à mouvement linéaire Partie 2: Charges statiques
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 14728-2 First edition 2004-06-01 Rolling bearings Linear motion rolling bearings Part 2: Static load ratings Roulements Roulements à mouvement linéaire Partie 2: Charges statiques
Identification Number
 Identification Number The specification of Micro Linear Way LWL is specified by the identification number, which consists of a model code, a size, a part code, a preload symbol, a classification symbol,
Identification Number The specification of Micro Linear Way LWL is specified by the identification number, which consists of a model code, a size, a part code, a preload symbol, a classification symbol,
Miniature Slide Guide Series with Retained Ball now Offers Complete Selection
 Miniature Slide Guide Series with Retained Ball now Offers Complete Selection Wide type of Miniature Slide Guide, providing greater allowable moment, is now available with retained ball structure. Due
Miniature Slide Guide Series with Retained Ball now Offers Complete Selection Wide type of Miniature Slide Guide, providing greater allowable moment, is now available with retained ball structure. Due
A nonlinear dynamic vibration model of defective bearings: The importance of modelling the finite size of rolling elements
 A nonlinear dynamic vibration model of defective bearings: The importance of modelling the finite size of rolling elements Alireza Moazenahmadi, Dick Petersen and Carl Howard School of Mechanical Engineering,
A nonlinear dynamic vibration model of defective bearings: The importance of modelling the finite size of rolling elements Alireza Moazenahmadi, Dick Petersen and Carl Howard School of Mechanical Engineering,
Chapter Objectives. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
 Chapter Objectives To develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body. To introduce the concept of the free-body diagram for a rigid body. To show how to solve rigid-body equilibrium problems using
Chapter Objectives To develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body. To introduce the concept of the free-body diagram for a rigid body. To show how to solve rigid-body equilibrium problems using
Analysis of Frictional Torque in Raceway Contacts of Tapered Roller Bearings
 Analysis of Frictional Torque in Raceway Contacts of Tapered Roller Bearings H. MATSUYAMA * S. KAMAMOTO ** * Bearing Research & Development Department, Research & Development Center **Mechatronic Systems
Analysis of Frictional Torque in Raceway Contacts of Tapered Roller Bearings H. MATSUYAMA * S. KAMAMOTO ** * Bearing Research & Development Department, Research & Development Center **Mechatronic Systems
AXTRUSION SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS. An approximate formula for estimating a bearing s stiffness is 1. P s A 2 h
 Appendix A AXTRUSION SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS A. Carriage Stiffness Estimates This section describes the steps to predict the stiffness performance of the carriage. First an accurate stiffness model of
Appendix A AXTRUSION SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS A. Carriage Stiffness Estimates This section describes the steps to predict the stiffness performance of the carriage. First an accurate stiffness model of
Chapter 2 Surface Acoustic Wave Motor Modeling and Motion Control
 Chapter 2 Surface Acoustic Wave Motor Modeling and Motion Control 1 Abstract For miniaturization of ultrasonic transducers, a surface acoustic wave device has an advantage in rigid mounting and high-power-density
Chapter 2 Surface Acoustic Wave Motor Modeling and Motion Control 1 Abstract For miniaturization of ultrasonic transducers, a surface acoustic wave device has an advantage in rigid mounting and high-power-density
Research Article Dynamic Carrying Capacity Analysis of Double-Row Four-Point Contact Ball Slewing Bearing
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 215, Article ID 8598, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/8598 Research Article Dynamic Carrying Capacity Analysis of Double-Row Four-Point Contact Ball Slewing
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 215, Article ID 8598, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/8598 Research Article Dynamic Carrying Capacity Analysis of Double-Row Four-Point Contact Ball Slewing
EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH REGARDING TRANSIENT REGIME OF KINEMATIC CHAINS INCLUDING PLANETARY TRANSMISSIONS USED IN INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS
 International Journal of Modern Manufacturing Technologies ISSN 2067 3604, Vol. VIII, No. 1 / 2016 EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH REGARDING TRANSIENT REGIME OF KINEMATIC CHAINS INCLUDING PLANETARY TRANSMISSIONS
International Journal of Modern Manufacturing Technologies ISSN 2067 3604, Vol. VIII, No. 1 / 2016 EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH REGARDING TRANSIENT REGIME OF KINEMATIC CHAINS INCLUDING PLANETARY TRANSMISSIONS
CYLINDRICAL ROLLER BEARINGS CARRYING THRUST LOAD
 CYLINDRICAL ROLLER BEARINGS CARRYING THRUST LOAD Gh. PRISACARU, Sp. CRETU, D. N. OLARU "Gh. Asachi Technical University, Department of Machine Design & Tribology, Bvd. D. Mangeron, 6-63, 66 Iasi, ROMANIA;
CYLINDRICAL ROLLER BEARINGS CARRYING THRUST LOAD Gh. PRISACARU, Sp. CRETU, D. N. OLARU "Gh. Asachi Technical University, Department of Machine Design & Tribology, Bvd. D. Mangeron, 6-63, 66 Iasi, ROMANIA;
Special edition paper
 Development of New Aseismatic Structure Using Escalators Kazunori Sasaki* Atsushi Hayashi* Hajime Yoshida** Toru Masuda* Aseismatic reinforcement work is often carried out in parallel with improvement
Development of New Aseismatic Structure Using Escalators Kazunori Sasaki* Atsushi Hayashi* Hajime Yoshida** Toru Masuda* Aseismatic reinforcement work is often carried out in parallel with improvement
Experimental Investigations of Whirl Speeds of a Rotor on Hydrodynamic Spiral Journal Bearings Under Flooded Lubrication
 International Conference on Fluid Dynamics and Thermodynamics Technologies (FDTT ) IPCSIT vol.33() () IACSIT Press, Singapore Experimental Investigations of Whirl Speeds of a Rotor on Hydrodynamic Spiral
International Conference on Fluid Dynamics and Thermodynamics Technologies (FDTT ) IPCSIT vol.33() () IACSIT Press, Singapore Experimental Investigations of Whirl Speeds of a Rotor on Hydrodynamic Spiral
Observation and analysis of the vibration and displacement signature of defective bearings due to various speeds and loads
 Observation and analysis of the vibration and displacement signature of defective bearings due to various speeds and loads Alireza-Moazen ahmadi a) Carl Howard b) Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Observation and analysis of the vibration and displacement signature of defective bearings due to various speeds and loads Alireza-Moazen ahmadi a) Carl Howard b) Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Inclined plane with protractor and pulley, roller, weight box, spring balance, spirit level, pan and thread.
 To find the downward force, along an inclined plane, acting on a roller due to gravity and study its relationship with the angle of inclination by plotting graph between force and sin θ. Inclined plane
To find the downward force, along an inclined plane, acting on a roller due to gravity and study its relationship with the angle of inclination by plotting graph between force and sin θ. Inclined plane
FATIGUE DAMAGE PROGRESSION IN PLASTICS DURING CYCLIC BALL INDENTATION
 FATIGUE DAMAGE PROGRESSION IN PLASTICS DURING CYCLIC BALL INDENTATION AKIO YONEZU, TAKAYASU HIRAKAWA, TAKESHI OGAWA and MIKIO TAKEMOTO Department of Mechanical Engineering, College of Science and Engineering,
FATIGUE DAMAGE PROGRESSION IN PLASTICS DURING CYCLIC BALL INDENTATION AKIO YONEZU, TAKAYASU HIRAKAWA, TAKESHI OGAWA and MIKIO TAKEMOTO Department of Mechanical Engineering, College of Science and Engineering,
Experimental test of static and dynamic characteristics of tilting-pad thrust bearings
 Special Issue Article Experimental test of static and dynamic characteristics of tilting-pad thrust bearings Advances in Mechanical Engineering 2015, Vol. 7(7) 1 8 Ó The Author(s) 2015 DOI: 10.1177/1687814015593878
Special Issue Article Experimental test of static and dynamic characteristics of tilting-pad thrust bearings Advances in Mechanical Engineering 2015, Vol. 7(7) 1 8 Ó The Author(s) 2015 DOI: 10.1177/1687814015593878
1 High precision, high rigidity positioning table
 TSHM CTHM 11 116 Precision Positioning Table H Ball screw TSH M Ball screw Slide table inear Way Bed inear Points 1 High precision, high rigidity positioning table High precision, high rigidity positioning
TSHM CTHM 11 116 Precision Positioning Table H Ball screw TSH M Ball screw Slide table inear Way Bed inear Points 1 High precision, high rigidity positioning table High precision, high rigidity positioning
CTV series CHARACTERISTICS LINEAR UNITS
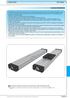 CTV series CHARACTERISTICS The CTV series describes s with a precision ball screw drive and two parallel, integrated, Zerobacklash rail guides. Compact dimensions allow high performance features such as,
CTV series CHARACTERISTICS The CTV series describes s with a precision ball screw drive and two parallel, integrated, Zerobacklash rail guides. Compact dimensions allow high performance features such as,
Influence of the Meniscus Force for Contact Recording Head Dynamics Over a Randomly Undulating Disk Surface
 864 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL. 39, NO. 2, MARCH 2003 Influence of the Meniscus Force for Contact Recording Head Dynamics Over a Randomly Undulating Disk Surface Hiroshige Matsuoka, Shigehisa
864 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL. 39, NO. 2, MARCH 2003 Influence of the Meniscus Force for Contact Recording Head Dynamics Over a Randomly Undulating Disk Surface Hiroshige Matsuoka, Shigehisa
3. Elastic Collision. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Theory. a) Kinetic Energy of a Rolling Ball
 ES 3. Elastic Collision 3.1 Introduction A collision is an interaction of two bodies during a short period of time, while momentum and energy are being exchanged. It is called an elastic collision if no
ES 3. Elastic Collision 3.1 Introduction A collision is an interaction of two bodies during a short period of time, while momentum and energy are being exchanged. It is called an elastic collision if no
Points. Precision Positioning Table TU. Variation. Major product specifications With flange
 9 0 Precision Positioning Table Ball screw inear Points lide table with high accuracy and high rigidity in a single structure lide table Compact and slim type positioning table with an original U-shaped
9 0 Precision Positioning Table Ball screw inear Points lide table with high accuracy and high rigidity in a single structure lide table Compact and slim type positioning table with an original U-shaped
SIMULATION FOR INSTABLE FLOATING OF HYDRODYNAMIC GUIDES DURING ACCELERATION AND AT CONSTANT VELOCITY 1. INTRODUCTION
 Journal of Machine Engineering, 08, Vol. 8, No., 5 5 ISSN 895-7595 (Print) ISSN 9-807 (Online) Received: December 07 / Accepted: 0 August 08 / Published online: 8 September 08 Yingying ZHANG * Volker WITTSTOCK
Journal of Machine Engineering, 08, Vol. 8, No., 5 5 ISSN 895-7595 (Print) ISSN 9-807 (Online) Received: December 07 / Accepted: 0 August 08 / Published online: 8 September 08 Yingying ZHANG * Volker WITTSTOCK
Examining the Adequacy of the Spectral Intensity Index for Running Safety Assessment of Railway Vehicles during Earthquakes
 October 1-17, 8, Beijing, China Examining the Adequacy of the Spectral Intensity Index for Running Safety Assessment of Railway Vehicles during Earthquakes Xiu LUO 1 and Takefumi MIYAMOTO 1 Dr. Eng., Senior
October 1-17, 8, Beijing, China Examining the Adequacy of the Spectral Intensity Index for Running Safety Assessment of Railway Vehicles during Earthquakes Xiu LUO 1 and Takefumi MIYAMOTO 1 Dr. Eng., Senior
PARAMETER ESTIMATION IN IMBALANCED NON-LINEAR ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEMS FROM RANDOM RESPONSE
 Journal of Sound and Vibration (1997) 208(1), 1 14 PARAMETER ESTIMATION IN IMBALANCED NON-LINEAR ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEMS FROM RANDOM RESPONSE Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology,
Journal of Sound and Vibration (1997) 208(1), 1 14 PARAMETER ESTIMATION IN IMBALANCED NON-LINEAR ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEMS FROM RANDOM RESPONSE Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology,
Modeling Method Analysis of the Friction Torque for High Speed Spindle Bearing
 MATEC Web of Conferences 75, 0308 (08) https://doi.org/0.05/matecconf/08750308 IFCAE-IOT 08 Modeling Method Analysis of the Friction Torque for High Speed Spindle Bearing Songsheng Li,, HuihangChen,, Haibing
MATEC Web of Conferences 75, 0308 (08) https://doi.org/0.05/matecconf/08750308 IFCAE-IOT 08 Modeling Method Analysis of the Friction Torque for High Speed Spindle Bearing Songsheng Li,, HuihangChen,, Haibing
Chapter 14 Periodic Motion
 Chapter 14 Periodic Motion 1 Describing Oscillation First, we want to describe the kinematical and dynamical quantities associated with Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM), for example, x, v x, a x, and F x.
Chapter 14 Periodic Motion 1 Describing Oscillation First, we want to describe the kinematical and dynamical quantities associated with Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM), for example, x, v x, a x, and F x.
General Explanation Ⅲ 1 Ⅲ 2
 General Explanation 1 2 Selection Procedure Selection of Linear Way and Linear Roller Way should be considered from the most important required matter to details in order. Typical procedure is shown below.
General Explanation 1 2 Selection Procedure Selection of Linear Way and Linear Roller Way should be considered from the most important required matter to details in order. Typical procedure is shown below.
Miniature (SEB Type) Tapped-Hole rail Types: Slide guides with clearance holes are standard and tapped holes are available upon request.
 Miniature (SE Type) The SE type slide guide is a linear motion bearing in which the ball elements roll along two tracking grooves. This is the smallest and lightest slide guide series offered by Nippon
Miniature (SE Type) The SE type slide guide is a linear motion bearing in which the ball elements roll along two tracking grooves. This is the smallest and lightest slide guide series offered by Nippon
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF TIE-ROD/TIE-BOLT ROTORS USING FEM
 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF TIE-ROD/TIE-BOLT ROTORS USING FEM J. E. Jam, F. Meisami Composite Materials and Technology Center Tehran, IRAN jejaam@gmail.com N. G. Nia Iran Polymer & Petrochemical Institute, Tehran,
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF TIE-ROD/TIE-BOLT ROTORS USING FEM J. E. Jam, F. Meisami Composite Materials and Technology Center Tehran, IRAN jejaam@gmail.com N. G. Nia Iran Polymer & Petrochemical Institute, Tehran,
DEVELOPMENT OF A REAL-TIME HYBRID EXPERIMENTAL SYSTEM USING A SHAKING TABLE
 DEVELOPMENT OF A REAL-TIME HYBRID EXPERIMENTAL SYSTEM USING A SHAKING TABLE Toshihiko HORIUCHI, Masahiko INOUE And Takao KONNO 3 SUMMARY A hybrid experimental method, in which an actuator-excited vibration
DEVELOPMENT OF A REAL-TIME HYBRID EXPERIMENTAL SYSTEM USING A SHAKING TABLE Toshihiko HORIUCHI, Masahiko INOUE And Takao KONNO 3 SUMMARY A hybrid experimental method, in which an actuator-excited vibration
DAMPING AND INERTIA COEFFICIENTS FOR TWO END SEALED SUEEZE FILM DAMPERS WITH A CENTRAL GROOVE: MEASUREMENTS AND PREDICTIONS
 2013 ASME Turbo Expo Conference, June 3-7 2013, San Antonio, TX, USA DAMPING AND INERTIA COEFFICIENTS FOR TWO END SEALED SUEEZE FILM DAMPERS WITH A CENTRAL GROOVE: MEASUREMENTS AND PREDICTIONS Luis San
2013 ASME Turbo Expo Conference, June 3-7 2013, San Antonio, TX, USA DAMPING AND INERTIA COEFFICIENTS FOR TWO END SEALED SUEEZE FILM DAMPERS WITH A CENTRAL GROOVE: MEASUREMENTS AND PREDICTIONS Luis San
MEEN 363 Notes Copyright, Dara W. Childs
 MEEN 363 Notes Copyright, Dara W. Childs Lecture 1. PARTICLE KINEMATICS IN A PLANE Kinematics: Geometric in nature, defines motion without regard to forces that cause motion or result from motion. Kinetics:
MEEN 363 Notes Copyright, Dara W. Childs Lecture 1. PARTICLE KINEMATICS IN A PLANE Kinematics: Geometric in nature, defines motion without regard to forces that cause motion or result from motion. Kinetics:
Improved 2D model of a ball bearing for the simulation of vibrations due to faults during run-up
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Improved D model of a ball bearing for the simulation of vibrations due to faults during run-up To cite this article: Matej Tadina and Miha Boltežar J. Phys.: Conf.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Improved D model of a ball bearing for the simulation of vibrations due to faults during run-up To cite this article: Matej Tadina and Miha Boltežar J. Phys.: Conf.
Experimental Study on the Velocity Dependent Drag Coefficient and Friction in an Automatic Ball Balancer
 TCHNISCH MCHANIK, 7, 1, (2017), 62 68 submitted: May 19, 2017 xperimental Study on the Velocity Dependent Drag Coefficient and Friction in an Automatic Ball Balancer L. Spannan, C. Daniel,. Woschke The
TCHNISCH MCHANIK, 7, 1, (2017), 62 68 submitted: May 19, 2017 xperimental Study on the Velocity Dependent Drag Coefficient and Friction in an Automatic Ball Balancer L. Spannan, C. Daniel,. Woschke The
Anisotropy of the Static Friction. of Plain-woven Filament Fabrics
 Anisotropy of the Static Friction of Plain-woven Filament Fabrics By Masayasu Ohsawa and Satoru Nam iki, Members, T M S J Faculty of Technology, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Koganei,
Anisotropy of the Static Friction of Plain-woven Filament Fabrics By Masayasu Ohsawa and Satoru Nam iki, Members, T M S J Faculty of Technology, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Koganei,
Parametrically Excited Vibration in Rolling Element Bearings
 Parametrically Ecited Vibration in Rolling Element Bearings R. Srinath ; A. Sarkar ; A. S. Sekhar 3,,3 Indian Institute of Technology Madras, India, 636 ABSTRACT A defect-free rolling element bearing has
Parametrically Ecited Vibration in Rolling Element Bearings R. Srinath ; A. Sarkar ; A. S. Sekhar 3,,3 Indian Institute of Technology Madras, India, 636 ABSTRACT A defect-free rolling element bearing has
Journal of Solid Mechanics and Materials Engineering
 and Materials Engineering Analysis of In-Plane Problems for an Isotropic Elastic Medium with Many Circular Holes or Rigid Inclusions Mutsumi MIYAGAWA, Jyo SHIMURA, Takuo SUZUKI and Takanobu TAMIYA Dept.of
and Materials Engineering Analysis of In-Plane Problems for an Isotropic Elastic Medium with Many Circular Holes or Rigid Inclusions Mutsumi MIYAGAWA, Jyo SHIMURA, Takuo SUZUKI and Takanobu TAMIYA Dept.of
Name: Fall 2014 CLOSED BOOK
 Name: Fall 2014 1. Rod AB with weight W = 40 lb is pinned at A to a vertical axle which rotates with constant angular velocity ω =15 rad/s. The rod position is maintained by a horizontal wire BC. Determine
Name: Fall 2014 1. Rod AB with weight W = 40 lb is pinned at A to a vertical axle which rotates with constant angular velocity ω =15 rad/s. The rod position is maintained by a horizontal wire BC. Determine
FEDSM99 S-291 AXIAL ROTOR OSCILLATIONS IN CRYOGENIC FLUID MACHINERY
 Proceedings of the 3 rd ASME/JSME Joint Fluids Engineering Conference 1999 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting July 18-23 1999, San Francisco, California FEDSM99 S-291 AXIAL ROTOR OSCILLATIONS
Proceedings of the 3 rd ASME/JSME Joint Fluids Engineering Conference 1999 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting July 18-23 1999, San Francisco, California FEDSM99 S-291 AXIAL ROTOR OSCILLATIONS
Balancing of Rotating Masses
 Balancing of Rotating Masses 1 Balancing of Rotating Masses m Consider first a single mass m moving in a circular arc of radius r with an angular velocity rad/s. The mass has a centripetal (centre 2 seeking)
Balancing of Rotating Masses 1 Balancing of Rotating Masses m Consider first a single mass m moving in a circular arc of radius r with an angular velocity rad/s. The mass has a centripetal (centre 2 seeking)
Theory of Structures
 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Postal Correspondence Course GATE, IES & PSUs Civil Engineering Theory of Structures C O N T E N T 1. ARCES... 3-14. ROLLING LOADS AND INFLUENCE LINES. 15-9 3. DETERMINACY AND INDETERMINACY..
SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Postal Correspondence Course GATE, IES & PSUs Civil Engineering Theory of Structures C O N T E N T 1. ARCES... 3-14. ROLLING LOADS AND INFLUENCE LINES. 15-9 3. DETERMINACY AND INDETERMINACY..
Tutorials. 1. Autocollimator. Angle Dekkor. General
 Tutorials 1. Autocollimator General An autocollimator is a Precise Optical Instrument for measurement of small angle deviations with very high sensitivity. Autocollimator is essentially an infinity telescope
Tutorials 1. Autocollimator General An autocollimator is a Precise Optical Instrument for measurement of small angle deviations with very high sensitivity. Autocollimator is essentially an infinity telescope
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR.
 LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
Appendix A Satellite Mechanical Loads
 Appendix A Satellite Mechanical Loads Mechanical loads can be static or dynamic. Static loads are constant or unchanging, and dynamic loads vary with time. Mechanical loads can also be external or self-contained.
Appendix A Satellite Mechanical Loads Mechanical loads can be static or dynamic. Static loads are constant or unchanging, and dynamic loads vary with time. Mechanical loads can also be external or self-contained.
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DEFINITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY Course Name : ENGINEERING MECHANICS Course Code : AAEB01 Program :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DEFINITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY Course Name : ENGINEERING MECHANICS Course Code : AAEB01 Program :
Selection Calculations For Linear & Rotary Actuators
 H-8 For Electric Linear Slides and Electric Cylinders First determine your series, then select your product. Select the actuator that you will use based on the following flow charts: Selection Procedure
H-8 For Electric Linear Slides and Electric Cylinders First determine your series, then select your product. Select the actuator that you will use based on the following flow charts: Selection Procedure
Methods of Analysis. Force or Flexibility Method
 INTRODUCTION: The structural analysis is a mathematical process by which the response of a structure to specified loads is determined. This response is measured by determining the internal forces or stresses
INTRODUCTION: The structural analysis is a mathematical process by which the response of a structure to specified loads is determined. This response is measured by determining the internal forces or stresses
Which one of the following correctly describes the velocities of the two bodies after the collision?
 Q1.In which of the following do both quantities have the same unit? Electrical resistivity and electrical resistance. Work function Planck constant Pressure and the Young modulus. cceleration and rate
Q1.In which of the following do both quantities have the same unit? Electrical resistivity and electrical resistance. Work function Planck constant Pressure and the Young modulus. cceleration and rate
Design and Research on Characteristics of a New Vibration Isolator with Quasi-zero-stiffness Shi Peicheng1, a, Nie Gaofa1, b
 International Conference on Mechanics, Materials and Structural Engineering (ICMMSE 2016 Design and Research on Characteristics of a New Vibration Isolator with Quasi-zero-stiffness Shi Peicheng1, a, Nie
International Conference on Mechanics, Materials and Structural Engineering (ICMMSE 2016 Design and Research on Characteristics of a New Vibration Isolator with Quasi-zero-stiffness Shi Peicheng1, a, Nie
Research on Crowning Profile to Obtain Maximum Load Carrying Capacity for Roller Bearings
 Research on Crowning Profile to Obtain Maximum Load Carrying Capacity for Roller Bearings S. KAMAMOTO * K. FUJIMOTO ** T. YAMAMOTO *** * Mechatronic Systems Research & Development Department, Research
Research on Crowning Profile to Obtain Maximum Load Carrying Capacity for Roller Bearings S. KAMAMOTO * K. FUJIMOTO ** T. YAMAMOTO *** * Mechatronic Systems Research & Development Department, Research
ROLLER BEARING FAILURES IN REDUCTION GEAR CAUSED BY INADEQUATE DAMPING BY ELASTIC COUPLINGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIONS
 ROLLER BEARIG FAILURES I REDUCTIO GEAR CAUSED BY IADEQUATE DAMPIG BY ELASTIC COUPLIGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIOS ~by Herbert Roeser, Trans Marine Propulsion Systems, Inc. Seattle Flexible couplings provide
ROLLER BEARIG FAILURES I REDUCTIO GEAR CAUSED BY IADEQUATE DAMPIG BY ELASTIC COUPLIGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIOS ~by Herbert Roeser, Trans Marine Propulsion Systems, Inc. Seattle Flexible couplings provide
Study of Stiffness of Linear Guide Pairs by Experiment and FEA
 World Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2016, 4, 115-128 http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjet ISSN Online: 2331-4249 ISSN Print: 2331-4222 Study of Stiffness of Linear Guide Pairs by Experiment and FEA
World Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2016, 4, 115-128 http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjet ISSN Online: 2331-4249 ISSN Print: 2331-4222 Study of Stiffness of Linear Guide Pairs by Experiment and FEA
The sound generated by a transverse impact of a ball on a circular
 J. Acoust. Soc. Jpn. (E) 1, 2 (1980) The sound generated by a transverse impact of a ball on a circular plate Toshio Takahagi*, Masayuki Yokoi*, and Mikio Nakai** *Junior College of Osaka Industrial University,
J. Acoust. Soc. Jpn. (E) 1, 2 (1980) The sound generated by a transverse impact of a ball on a circular plate Toshio Takahagi*, Masayuki Yokoi*, and Mikio Nakai** *Junior College of Osaka Industrial University,
Precision Ball Screw/Spline
 58-2E Models BNS-A, BNS, NS-A and NS Seal Outer ring Shim plate Seal Spline nut Seal Collar Shim plate Seal End cap Ball Outer ring Ball screw nut Outer ring Ball Retainer Retainer Outer ring Point of
58-2E Models BNS-A, BNS, NS-A and NS Seal Outer ring Shim plate Seal Spline nut Seal Collar Shim plate Seal End cap Ball Outer ring Ball screw nut Outer ring Ball Retainer Retainer Outer ring Point of
Physics 12. Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1
 Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
Robust shaft design to compensate deformation in the hub press fitting and disk clamping process of 2.5 HDDs
 DOI 10.1007/s00542-016-2850-2 TECHNICAL PAPER Robust shaft design to compensate deformation in the hub press fitting and disk clamping process of 2.5 HDDs Bumcho Kim 1,2 Minho Lee 3 Gunhee Jang 3 Received:
DOI 10.1007/s00542-016-2850-2 TECHNICAL PAPER Robust shaft design to compensate deformation in the hub press fitting and disk clamping process of 2.5 HDDs Bumcho Kim 1,2 Minho Lee 3 Gunhee Jang 3 Received:
Comparison of Models for Rolling Bearing Dynamic Capacity and Life
 2013 STLE Annual Meeting & Exhibition May 5-9, 2013 Detroit Marriott at the Renaissance Center Detroit, Michigan, USA Comparison of Models for Rolling Bearing Dynamic Capacity and Life Rolling-Element
2013 STLE Annual Meeting & Exhibition May 5-9, 2013 Detroit Marriott at the Renaissance Center Detroit, Michigan, USA Comparison of Models for Rolling Bearing Dynamic Capacity and Life Rolling-Element
Development of a probe traversing system for an open test section wind tunnel
 Development of a probe traversing system for an open test section wind tunnel Gépészet 2012 Conference 24 th of May, 2012 Section Energy 2. Árpád Varga Mechanical Engineering Modelling MSc, Contractual
Development of a probe traversing system for an open test section wind tunnel Gépészet 2012 Conference 24 th of May, 2012 Section Energy 2. Árpád Varga Mechanical Engineering Modelling MSc, Contractual
The Simulation of Dropped Objects on the Offshore Structure Liping SUN 1,a, Gang MA 1,b, Chunyong NIE 2,c, Zihan WANG 1,d
 Advanced Materials Research Online: 2011-09-02 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 339, pp 553-556 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.339.553 2011 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland The Simulation of Dropped Objects
Advanced Materials Research Online: 2011-09-02 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 339, pp 553-556 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.339.553 2011 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland The Simulation of Dropped Objects
Experimental Investigation of the Performances of a WRS-BTU Seismic Isolator
 , July 3-5, 2013, London, U.K. Experimental Investigation of the Performances of a WRS-BTU Seismic Isolator R. Brancati, G. Di Massa, S. Pagano, E. Rocca and S. Strano Abstract This paper describes an
, July 3-5, 2013, London, U.K. Experimental Investigation of the Performances of a WRS-BTU Seismic Isolator R. Brancati, G. Di Massa, S. Pagano, E. Rocca and S. Strano Abstract This paper describes an
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 STATICS AND MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr, John T. DeWolf David E Mazurek \Cawect Mc / iur/» Craw SugomcT Hilt Introduction 1 1.1 What is Mechanics? 2 1.2 Fundamental
STATICS AND MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr, John T. DeWolf David E Mazurek \Cawect Mc / iur/» Craw SugomcT Hilt Introduction 1 1.1 What is Mechanics? 2 1.2 Fundamental
Measuring vibration characteristics at large amplitude region of materials for high power ultrasonic vibration system
 Ultrasonics 38 (2000) 122 126 www.elsevier.nl/locate/ultras Measuring vibration characteristics at large amplitude region of materials for high power ultrasonic vibration system Kentaro Nakamura *, Kiyotsugu
Ultrasonics 38 (2000) 122 126 www.elsevier.nl/locate/ultras Measuring vibration characteristics at large amplitude region of materials for high power ultrasonic vibration system Kentaro Nakamura *, Kiyotsugu
( ) 5. Bearing internal load distribution and displacement. 5.1 Bearing internal load distribution
 5. internal load distribution and displacement 5. internal load distribution This section will begin by examing the effect of a radial load F r and an axial load F a applied on a single-row bearing with
5. internal load distribution and displacement 5. internal load distribution This section will begin by examing the effect of a radial load F r and an axial load F a applied on a single-row bearing with
