PROCESS FOR SELECTING NB LINEAR SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Gyles Murphy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The NB linear system is a linear motion mechanism which utilizes the recirculating movement of ball or roller elements to provide smooth and accurate linear travel. NB offers a wide range of linear motion products that may contribute to the size and weight reduction of machinery and other equipment, while providing dependable performance in highprecision equipment. ADVANTAGES Low Friction and Excellent Response: The dynamic friction of rolling ball or roller elements is substantially lower than that of full-face surface sliding friction. Since the difference between rolling dynamic and static friction is small, motion response is excellent and results in superior dependable movement. This also allows for easy fabrication of mechanisms requiring precise positioning or highspeed acceleration. High Precision and Smooth Movement: The NB linear system is designed for smooth rolling movements. The rolling element's raceway contact surface is finished through high-precision grinding. The recirculating movement of the rolling elements allow for continuous high-precision linear movement without clearance. High Load Capacity and Long Travel Life: Although the NB linear system is designed to be compact, the use of large rolling elements and machined raceway surface results in high load capacity and long travel life. Ease of Installation: The NB linear system shortens machining and assembly time when compared with that of a full face surface sliding bearing system. Variety of Models: A wide variety of models and types of NB systems are available for just about any shape or material option. This permits the selection of the best appropriate linear component for any application. Eng-1
2 SLIDE GUIDE PROCESS FOR SELECTING NB LINEAR SYSTEM NG NG Determine the application conditions Decide system shape Pre-select the size and number of linear systems Calculate load Determine static load OK Compute life OK Identify machine to be used, application conditions environmental conditions, and desired accuracy * slide guide * ball spline * slide way * slide bush Pre-select the size and number based on balance of machinery systems and other equipment as well as past experience *Calculate load on each system *Calculate average variable load. (Ref. to page Eng. 6-8) Determine basic static load and allowable moment by applying static safety factor (Ref. to page Eng..) Compute rated life and compare to required life. (Ref. to page Eng. 4.) BALL SPLINE ROTARY BALL SPLINE TOPBALL PRODUCTS SLIDE BUSH SLIDE UNIT STROKE BUSH SLIDEROTARYBUSH NG NG Determine pre-load and accuracy OK Select lubrication and dust prevention method OK Confirm the clearance needed around the equipment OK Decide pre-load and accuracy based on the operating conditions. (Refer to product description for each model and type.) Select lubrication and dust prevention method (seal or bellows) Confirm clearance by considering, machine size, and access space needed for installation and maintenance SLIDE SHAFT SLIDE WAY SLIDE TABLE GONIO WAY Selection completed Eng-2 ACTUATOR SLIDE SCREW
3 ALLOWABLE LOAD Load and Moment: A load may be exerted to a linear system as depicted in Figure 1-1. In addition, a moment may be applied to a slide guide. Each type of load addressed by NB is described as follows. Basic Static Load Rating and Allowable Static Moment: Under excess or impact load conditions applied to a linear system while it is stationary or moving slowly, a permanent deformation occurs on either the rolling surface or the rolling elements. When this deformation exceeds a predictable level, it becomes a source of vibration and acoustic noise during operation and will also result in rough motion and shortens life. To prevent this permanent deformation and deterioration in movement accuracy, a basic static load rating (Co) is given as an allowable load. This basic static load rating is defined as the static load that results in the maximum allowable stress at the center of the contact surface between the rolling elements and the rolling surface. The sum of the permanent deformation of the rolling elements and that of the rolling surface is 1/10,000 the diameter of the rolling elements. In linear systems, a moment may also be present when applied in addition to the static load. The allowable static moment is defined by MP, MY, and MR, which are illustrated in Figure 1-1. Allowable Load and Static Safety Factor: The basic static load rating and allowable static moment define the maximum static load in each direction. These maximum static loads are not necessarily applicable depending on the operating conditions, the mounting accuracy, and the required motion accuracy. Therefore, an allowable load with a safety factor that covers these factors must be obtained. In general, the minimum static safety factor is based on the values as listed in Table 1-1. Allowable load Pmax. Co/fs (1) Allowable moment Mmax. (MP,MY,MR)/fs (2) fs : static safety factor Co : basic static load rating(n) Pmax. : allowable load(n) MP,MR,MY : allowable static moment(n m) Mmax. : allowable moment(n m) Eng- Figure 1-1 Load and Moment load direction of moment pitch yaw roll rated loads C and Co Table 1-1 Minimum Static Safety Factor operating conditions normal smooth motion required vibration/impact loading static safety factor
4 SLIDE GUIDE LIFE Life of a Linear System: If a linear system reciprocates when it is under a load, a continuous stress acts on it, ultimately causing flaking of its rolling elements and/or rolling surfaces due to material fatigue, making it inoperable. The distance a linear system travels before this flaking condition first occurs is called the life of the system. A linear system can also become inoperable due to sintering, cracking, pitting, or rusting. These factors are differentiated from those affecting the life because they are related to installation accuracy, operating environment, or the selected lubrication method of the installer. Rated Life: Even when two linear systems are manufactured at the same time, have the same part number, and are used under identical conditions, their lifetimes can differ due to differences in their fatigue failure characteristics. This prevents determining the life of any particular linear system. Therefore, the rated life is determined statistically and is defined as the distance 90% of linear systems travel before experiencing flaking. Rated Basic Dynamic Load and Rated Basic Dynamic Torque: The life of a linear system is expressed in terms of the distance traveled. Therefore, the life of a linear system is calculated using the allowable load that corresponds to a certain distance traveled. This allowable load is a measure of the system's performance relative to the applied load and is called the rated basic dynamic load. It is defined as a constant-direction load with a magnitude corresponding to a life of 50x10 m. In some cases or linear systems, the basic dynamic load rating may vary depending on the direction of the applied force. In the NB Linear System catalog, the value of the basic dynamic load rating is assumed when a force is applied from directly above and is indicated in the dimension tables. For ball splines, the linear motion may involve torque loading, so the basic dynamic torque rating is defined in a similar fashion. Eng-4 Rated Life Estimation: The rated lifetime estimation depends on the type of rolling element used. Both Equations () and (4) are used for ball and roller elements respectively. In cases when torque loading is applied, Equation (5) is to be used. When a ball is used as the rolling element, C L = ( ) 50 () P When a roller is used as the rolling element, C 10/ L = 50 (4) P When torque loading is applied, L : rated life(km) C : basic dynamic load rating(n) P : applied load(n) CT : basic dynamic torque rating(n m) T : applied torque(n m) Numerous variables, such as guide rail accuracy, mounting conditions, operating conditions, vibration and shock while under linear motion affect an actual application. Therefore, calculating the actual applied load accurately is extremely difficult. In general, the calculation is simplified by using coefficients representing these effects. These coefficients include hardness (fh), temperature (ft), contact (fc), and applied load (fw). By using these coefficients, Equations () (5) can be expressed by Equations (6) (8). When a ball is used as the rolling element, ( ) fh ft fc C L = 50 (6) fw P When a roller is used as the rolling element, ( ) 10/ L = C fh ft fc 50 (7) fw P When torque loading is applied, L = ( ) CT ( ) L = 50 (5) T fh ft fc CT ( ) T 50 (8) fw L : rated life(km) fh : hardness coefficient fc : contact coefficient fw : applied load coefficient P : applied load(n) C : basic dynamic load rating (N) CT : basic dynamic torque rating(n m) T : applied torque(n m) BALL SPLINE ROTARY BALL SPLINE TOPBALL PRODUCTS SLIDE BUSH SLIDE UNIT STROKE BUSH SLIDEROTARYBUSH SLIDE SHAFT SLIDE WAY SLIDE TABLE GONIO WAY ACTUATOR SLIDE SCREW
5 If the distance traveled per unit time is known, the life can be expressed in terms of time, which may be easier to understand. The relationship between the stroke distance, the stroke frequency per minuit, and the life time is expressed by Equation (9) Hardness Coefficient (fh): In a linear system, the guide rail serves the same purpose as an inner race of a ball bearing. Therefore, the hardness of the guide rail plays an important role in determining the rated load. If the surface hardness is less than HRC58, the rated load is reduced. NB uses an advanced heat treatment method to maintain an appropriate level of hardness. However, if guide rails with inadequate hardness must be used, the rated load must be re-calibrated based on the hardness coefficients given in Figure 1-2. Temperature Coefficient (ft): NB linear systems are heat treated to reduce the amount of wear. Therefore, if the operating temperature exceeds 100, hardness is reduced and the life of the system is shortened. The variation in hardness with temperature is shown in Figure 1-. Contact Coefficient (fc): When two or more linear systems are used in contact with each other, the variation in each system and the accuracy of the mounting surfaces must be taken into consideration. In general, the coefficient values given in Table 1-2 should be used to compute the life. Applied Load Coefficient (fw): When computing the applied load, the weight of the mass, inertial force, moment resulting from the motion, and the variation with time should be accurately estimated. However, it is very difficult to accurately estimate the applied load due to the existence of numerous variables, including the start/stop conditions of the reciprocating motion and of the shock/vibration. Estimation is simplified by using the values given in Table 1-. L 10 Lh = (9) 2 s n1 60 Lh : life time(hr) s : stroke distance(m) n1 : stroke frequency per min.(cpm) Figure 1-2 Hardness Coefficient Hardness Coefficient, fh Tracking Surface Hardness, HRC Figure 1- Temperature Coefficient Temperature Coefficient, ft Temperature of Linear System ( ) Table 1-2 Contact Coefficient number of linear systems in contact contact coefficient and applied to a single shaft Table 1- Applied Load Coefficient operating condition loading condition velocity no shock/vibration 15 m/min or less low shock/vibration 60 m/min or less high shock/vibration 60 m/min or more fc applied load coefficient, fw Eng-5
6 SLIDE GUIDE Method for Determining Applied Load: Typical cases that linear systems are set and the equations for determining the applied load for each case example are summarized in Table 1-4. W : applied load (N) P1 - P4 : load applied to linear system (N) X,Y : linear system span (mm) x, y, : distance to load applied or to working center of gravity (mm) g : gravitational acceleration (9.8 x 10 mm/s 2 ) V : velocity (mm/s) t1 : duration of acceleration (sec) t : duration of deceleration (sec) Table 1-4 Method for Determining Applied Load (1) 2 horizontal shafts condition applied load computation formula BALL SPLINE ROTARY BALL SPLINE TOPBALL PRODUCTS SLIDE BUSH SLIDE UNIT under static conditions or constant velocity motion 2 horizontal shafts, over-hang 2 horizontal shafts moving rails Note: If the calculation results in a negative value, the loading direction is in the opposite direction, but with the same computed magnitude. STROKE BUSH SLIDEROTARYBUSH SLIDE SHAFT SLIDE WAY SLIDE TABLE GONIO WAY Eng-6 ACTUATOR SLIDE SCREW
7 Table 1-5 Method for Determining Applied Load (2) 2 vertical/side shafts condition applied load computation formula under static conditions or constant velocity motion 2 vertical shafts thrust force thrust force 2 horizontal shafts velocity V velocity profile under acceleration under constant acceleration conditions G:center of gravity time T thrust force direction of movement thrust force under deceleration under constant velocity motion g:gravitational acceleration Eng-7
8 SLIDE GUIDE Average Applied Load: The load applied to a linear system generally varies with the distance traveled depending on how the system is used. This includes the start/stop processes of the reciprocating motion. The average applied load is used to compute the life corresponding to the actual application conditions. 1. When the load varies in a step manner with the distance traveled (Figure 1-4) and 1 is the distance traveled under load P1, 2 is the distance traveled under load P2, and n is the distance traveled under load Pn, the average applied load, Pm is obtained by the following equation Pm = 1 (P1 1+P2 2 +Pn n) (4) Pm : average applied load (N) : total distance traveled (m) Figure 1-4 Applied Load Varies Stepwise Figure 1-5 Applied Load Varies Linearly BALL SPLINE ROTARY BALL SPLINE TOPBALL PRODUCTS SLIDE BUSH SLIDE UNIT 2. When the applied load varies linearly with the distance traveled (Figure 1-5), the average applied load, Pm is approximated by the following equation. 1 Pm (Pmin+2Pmax) (5) Figure 1-6 Applied Load Varies Sine-Curve STROKE BUSH SLIDEROTARYBUSH Pm : minimum applied load (N) Pmax : maximum applied load (N). When the applied load draws a sine-curve as shown by Figures 1-6 (a) and (b), the average applied load, Pm, is approximated by the following equations. Figure 1-6(a) Pm 0.65Pmax (6) Figure 1-6(b) Pm 0.75Pmax (7) SLIDE SHAFT SLIDE WAY SLIDE TABLE GONIO WAY Eng-8 ACTUATOR SLIDE SCREW
9 RIGIDITY AND PRE-LOAD Effect of Pre-load and Rigidity: The rigidity of a linear system must be taken into consideration when it is to be used in high-precision positioning devices or high-precision machinery. Preloaded slide guides and ball splines, which use a ball as the rolling element, are available upon request to meet the need for greater rigidity. If a force is applied to the ball elements without a pre-load, an elastic deformation proportional to the applied force to the 2/ power will result. W (8) 2/ : elastic deformation W : applied force Therefore, the elastic deformation is relatively large during the initial loading stage, however then becomes smaller as the load increases. The contact angles for all of the ball elements in SGL slide guides are the same as shown in Figure 1-7. Therefore, if the pre-load (P1) applied results in an elastic deformation of 1, the deformation will vary linearly with the applied load until the elastic deformation of the ball element on the other side cross the race becomes zero, as depicted in Figure 1-8. This permits the determination of the deformation of linear systems. The ratio between the applied load and the elastic deformation is defined as the rigidity of the system. Equation (9) can be used to determine the elastic deformation with an applied load of up to 2.8 times the pre-load. 2/ 2/ P 1 P 2 (9) P P 1 k : constant P1 : pre-load P2 : applied load when the pre-load becomes 0 Contact NB for further information on rigidity. Types of Pre-Load and its Specification: Pre-load is categorized into three primary ranges: normal, light, and medium. At NB, pre-load is applied by installing rolling elements that are slightly larger than normal. Therefore, the specification of the preload is expressed by a negative gap value. Figure 1-7 Contact Structure of SGL Slide Guide Figure 1-8 Applied Load vs. Elastic Deformation of Steel Balls elastic deformation P :pre-load P2:applied load at zero pre-load applied load P no pre-load with pre-load Eng-9
10 SLIDE GUIDE FRICTIONAL RESISTANCE AND REQUIRED THRUST The static friction of a linear system is extremely low. Since the difference between the static and dynamic friction is marginal, stable motion can be achieved from low to high velocity. The frictional resistance (required thrust) can be obtained from the load and the seal resistance unique to each type of system using the following equation: F = W + f (10) F : frictional resistance(n) : dynamic frictional coefficient W : applied load(n) f : seal resistance(n) The dynamic friction coefficient varies with the applied load, pre-load, viscosity of the lubricant, and other factors. However, the values given in Table 1-6 are used for the normal loading condition (20% of basic dynamic load rating) without any pre-load. The seal resistance depends on the seal-lip condition as well as on the condition of the lubricant and does not change proportionally with the applied load, which commonly is expressed by a constant value of 2 to 5 N. Table 1-6 Dynamic Friction Coefficient type slide guide ball spline rotary ball spline slide bush slide unit stroke bush slide rotary bush slide way slide table major types SGL SGW SEB SER SSP SPR GM SM KB SW SMA SME SR RK SV SVW SVT SYT dynamic friction coefficient( ) BALL SPLINE ROTARY BALL SPLINE TOPBALL PRODUCTS SLIDE BUSH SLIDE UNIT STROKE BUSH SLIDEROTARYBUSH dynamic friction coefficient Figure 1-9 Applied Load vs. Dynamic Friction Coefficient load ratio P/C Eng-10 P applied load C basic dynamic load rating SLIDE SHAFT SLIDE WAY SLIDE TABLE GONIO WAY ACTUATOR SLIDE SCREW
11 OPERATING ENVIRONMENT Temperature Range: NB linear systems are heat-treated in order to harden the surface. Because of this, if the temperature of the system exceeds 100, the hardness and rated load will be reduced (refer to page Eng. 5, hardness coefficient). If resin is used in any one of the components, the system cannot be used in a high-temperature environment. The recommended operating temperature ranges for each type of linear system are listed in Table 1-7. Table 1-7 Material Type and Recommended Temperature Range component material includes resin operating temperature range slide guide SEB-A/SEBS-B/SGL/SGW ball spline SSP/SSPF/SSPB rotary ball spline SPR GM/SM G/KB G/ slide bush SW G/SMS G/ KBS G/SWS G SMA G/AK G/RB/RBW/ slide unit TKA/TWA/CE/CD stroke bush slide rotary bush RK slide way slide table slide screw steel SER SM/KB/SW SMA/AK/SWA SR/SRB SRE SV/SVW/RV SVT/SYT SS stainless SEBS-BM/SERS SMS/KBS/SWS SMSA/AKS/SWSA SVS/SVWS SYTS/SYBS * If the system is made of stainless steel and has a seal, the temperature should be below 120 ** Contact NB if system is to be used at temperatures beyond the recommended temperature ranges. other SVTS** Temperature conversion equation 5 9 C= (F-2) F=2+ C 9 5 Operating Environment: Dust and perticle debris will adversely affect the motion characteristics of a linear system. They can also cause abnormally fast wear. In a normal operating environment, the use of seals may prevent adverse effects to the linear system. However, the linear system should be well protected by using bellows or a protective cover when it is used in an extremely hostile environment. (Figure 1-10) Figure 1-10 Example of Dust Prevention Devices bellows cover Eng-11
12 SLIDE GUIDE LUBRICATION The objective of lubrication includes the reduction of friction between the rolling elements and the rolling surfaces, prevention of pitting, reduction of wear, and the prevention of rusting by forming a film over the surfaces. To maximize the performance of a linear system, a lubrication method and a lubricant appropriate for the operating environment should be selected. Methods of lubrication include oil lubrication and grease lubrication. For oil lubrication, turbine oil conforming to ISO standard VG2-68 is also recommended. For grease lubrication, lithium soap based grease is recommended. A rust preventative oil that does not adversely affect the lubricant is applied in a slide bush. The slide bush should be lubricated before it is placed into service. Products with raceway grooves, such as slide guides, are delivered pre-lublicated with grease and may be installed and used without further lubrication. Through operation lublicant is dispersed, so it is advisable to re-lubricate periodically based upon apprication usage. NOTES ON HANDLING NB linear systems are precision, machined components and should be handled with care. K GREASE K grease is a low dust generation lubricant for linear systems that provides long-term and stable dust control. This particular type has very few impurities, yet its lubricating effect, contamination control, and rust prevention characteristics are equivalent to that of lithium soap grease. Main Property Appearance Yellow white Thickening agent Ureic Base oil Composition oil Consistency 280(No.2) Operating temperature range BALL SPLINE ROTARY BALL SPLINE TOPBALL PRODUCTS SLIDE BUSH SLIDE UNIT STROKE BUSH SLIDEROTARYBUSH SLIDE SHAFT To preserve the accuracy and performance expected. Any shock load caused by rough handling (such as dropping or hitting with hammer) may cause a scar on the raceway which will hinder smooth movement and shorten expected travel life. To obtain best results, it is critical to ensure accurate installation. During installation misalignment should be avoided by taking into consideration parallelism of the system. For a linear system to deliver its best performance, ensure that the housing, shaft, and guide rail mounting surfaces all have proper and accurate dimensions. Eng-12 SLIDE WAY SLIDE TABLE GONIO WAY ACTUATOR SLIDE SCREW
The basic dynamic load rating C is a statistical number and it is based on 90% of the bearings surviving 50 km of travel carrying the full load.
 Technical data Load Rating & Life Under normal conditions, the linear rail system can be damaged by metal fatigue as the result of repeated stress. The repeated stress causes flaking of the raceways and
Technical data Load Rating & Life Under normal conditions, the linear rail system can be damaged by metal fatigue as the result of repeated stress. The repeated stress causes flaking of the raceways and
Miniature (SEB Type) Tapped-Hole rail Types: Slide guides with clearance holes are standard and tapped holes are available upon request.
 Miniature (SE Type) The SE type slide guide is a linear motion bearing in which the ball elements roll along two tracking grooves. This is the smallest and lightest slide guide series offered by Nippon
Miniature (SE Type) The SE type slide guide is a linear motion bearing in which the ball elements roll along two tracking grooves. This is the smallest and lightest slide guide series offered by Nippon
Identification Number
 Identification Number The specification of Micro Linear Way LWL is specified by the identification number, which consists of a model code, a size, a part code, a preload symbol, a classification symbol,
Identification Number The specification of Micro Linear Way LWL is specified by the identification number, which consists of a model code, a size, a part code, a preload symbol, a classification symbol,
Example of Calculating the Nominal Life
 Condition (Horizontal Installation) Assumed model number : KR 5520A LM Guide unit (C = 800N, C 0 = 6900N) Ball Screw unit (C a = 620N, C 0a = 9290N) Bearing unit(fixed Side) (C a = 7600N, P 0a = 990N)
Condition (Horizontal Installation) Assumed model number : KR 5520A LM Guide unit (C = 800N, C 0 = 6900N) Ball Screw unit (C a = 620N, C 0a = 9290N) Bearing unit(fixed Side) (C a = 7600N, P 0a = 990N)
General Explanation Ⅲ 1 Ⅲ 2
 General Explanation 1 2 Selection Procedure Selection of Linear Way and Linear Roller Way should be considered from the most important required matter to details in order. Typical procedure is shown below.
General Explanation 1 2 Selection Procedure Selection of Linear Way and Linear Roller Way should be considered from the most important required matter to details in order. Typical procedure is shown below.
Miniature Slide Guide Series with Retained Ball now Offers Complete Selection
 Miniature Slide Guide Series with Retained Ball now Offers Complete Selection Wide type of Miniature Slide Guide, providing greater allowable moment, is now available with retained ball structure. Due
Miniature Slide Guide Series with Retained Ball now Offers Complete Selection Wide type of Miniature Slide Guide, providing greater allowable moment, is now available with retained ball structure. Due
R-Plus System Frontespizio_R_PlusSystem.indd 1 11/06/ :32:02
 R-Plus System R-Plus System R-Plus system R-Plus system description Fig. R-Plus system R-Plus System is Rollon s series of rack & pinion driven actuators. Rollon R-Plus System series linear units are designed
R-Plus System R-Plus System R-Plus system R-Plus system description Fig. R-Plus system R-Plus System is Rollon s series of rack & pinion driven actuators. Rollon R-Plus System series linear units are designed
The SynchMotion. Retainer
 106 G99TE13-0809 Linear Guideways QE Series 2-9 QE Type Quiet Linear Guideway, with SynchMotion TM Technology The development of HIIN-QE linear guideway is based on a four-row circular-arc contact. The
106 G99TE13-0809 Linear Guideways QE Series 2-9 QE Type Quiet Linear Guideway, with SynchMotion TM Technology The development of HIIN-QE linear guideway is based on a four-row circular-arc contact. The
LINEAR SYSTEM LINEAR SYSTEM. Decide system type ADVANTAGES. Calculate load. Determine static load OK. Compute rated life OK. Selection completed
 The NB linear system is a linear motion mechanism which utilizes the motion of ball and/or roller elements. NB offers a wide range of linear motion products of high precision quality that contribute to
The NB linear system is a linear motion mechanism which utilizes the motion of ball and/or roller elements. NB offers a wide range of linear motion products of high precision quality that contribute to
( ) Calculating the Nominal Life. Nominal Life Equation for an LM Guide Using Balls. Nominal Life Equation for the Oil-Free LM Guide L = ( C L =
 Point of Selection The service life of an LM Guide is subject to variations even under the same operational conditions. Therefore, it is necessary to use the nominal life defi ned below as a reference
Point of Selection The service life of an LM Guide is subject to variations even under the same operational conditions. Therefore, it is necessary to use the nominal life defi ned below as a reference
Points. Precision Positioning Table TU. Variation. Major product specifications With flange
 9 0 Precision Positioning Table Ball screw inear Points lide table with high accuracy and high rigidity in a single structure lide table Compact and slim type positioning table with an original U-shaped
9 0 Precision Positioning Table Ball screw inear Points lide table with high accuracy and high rigidity in a single structure lide table Compact and slim type positioning table with an original U-shaped
S.C. Rulmenti S.A. Barlad Romania Republicii Street No
 SELECTION OF BEARING SIZE Basic load ratings The size of a bearing is selected considering the load in the used rolling bearing and also depends on the operational rating life and prescribed operating
SELECTION OF BEARING SIZE Basic load ratings The size of a bearing is selected considering the load in the used rolling bearing and also depends on the operational rating life and prescribed operating
Selection Calculations For Linear & Rotary Actuators
 H-8 For Electric Linear Slides and Electric Cylinders First determine your series, then select your product. Select the actuator that you will use based on the following flow charts: Selection Procedure
H-8 For Electric Linear Slides and Electric Cylinders First determine your series, then select your product. Select the actuator that you will use based on the following flow charts: Selection Procedure
Precision Ball Screw/Spline
 58-2E Models BNS-A, BNS, NS-A and NS Seal Outer ring Shim plate Seal Spline nut Seal Collar Shim plate Seal End cap Ball Outer ring Ball screw nut Outer ring Ball Retainer Retainer Outer ring Point of
58-2E Models BNS-A, BNS, NS-A and NS Seal Outer ring Shim plate Seal Spline nut Seal Collar Shim plate Seal End cap Ball Outer ring Ball screw nut Outer ring Ball Retainer Retainer Outer ring Point of
ENGINEERING INFORMATION TABLE OF CONTENTS SHAFT AND HOUSING FITS LUBRICATION LIFE AND LOAD RATINGS RADIAL CLEARANCE CHART
 ENGINEERING INFORMATION TABLE OF CONTENTS ENGINEERING INFORMATION SHAFT AND HOUSING FITS LUBRICATION LIFE AND LOAD RATINGS RADIAL CLEARANCE CHART SHAFT AND HOUSING FITS FOR METRIC RADIAL BALL AND ROLLER
ENGINEERING INFORMATION TABLE OF CONTENTS ENGINEERING INFORMATION SHAFT AND HOUSING FITS LUBRICATION LIFE AND LOAD RATINGS RADIAL CLEARANCE CHART SHAFT AND HOUSING FITS FOR METRIC RADIAL BALL AND ROLLER
Cam Roller Guides. The Drive and Control Company. Service Automation. Electric Drives and Controls. Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies
 Industrial Hydraulics Electric Drives and Controls Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Pneumatics Service Automation Mobile Hydraulics Cam Roller Guides The Drive and Control Company Linear Motion
Industrial Hydraulics Electric Drives and Controls Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Pneumatics Service Automation Mobile Hydraulics Cam Roller Guides The Drive and Control Company Linear Motion
Linear guide drives. Synchronous shafts The use of synchronous shafts enables several linear axes to be operated with one drive.
 Linear guide drives Drive concept The linear guides are driven via the hollow shaft in the drive head. The drive head is used to directly install a motor or alternatively (in connection with a center shaft)
Linear guide drives Drive concept The linear guides are driven via the hollow shaft in the drive head. The drive head is used to directly install a motor or alternatively (in connection with a center shaft)
SLIDE GUIDE SGL TYPE SLIDE GUIDE BLOCK TYPES ACCURACY
 SGL YPE he N slide is a linear motion earing utilizing the rotational motion of all elements along four rows of raceway grooves. It can e used in various applications due to its compactness and high load
SGL YPE he N slide is a linear motion earing utilizing the rotational motion of all elements along four rows of raceway grooves. It can e used in various applications due to its compactness and high load
C-Lube Linear Way ML ML MLF
 Maintenance ree & U.S. PTTD C-Lube Linear ay Variation of C-Lube Linear ay Shape Length of slide unit Model code C-Lube Linear ay is a linear motion rolling guide, incorporating the C-Lube as a components
Maintenance ree & U.S. PTTD C-Lube Linear ay Variation of C-Lube Linear ay Shape Length of slide unit Model code C-Lube Linear ay is a linear motion rolling guide, incorporating the C-Lube as a components
 Identification The of -Lube Linear Roller Way Super MX is identified by the identification, which consists of model code, size, part code, material symbol preload symbol, classification symbol, interchangeable
Identification The of -Lube Linear Roller Way Super MX is identified by the identification, which consists of model code, size, part code, material symbol preload symbol, classification symbol, interchangeable
Ball Reverser. Ball Reverser Actuator. FLENNOR Power Transmission Products. Patented
 Ball Reverser FLENNOR Power Transmission Products Ball Reverser Actuator Patented Ball Reverser Principle General Information NORCO'S Ball Reverser Actuator is a unique actuator which provides automatic
Ball Reverser FLENNOR Power Transmission Products Ball Reverser Actuator Patented Ball Reverser Principle General Information NORCO'S Ball Reverser Actuator is a unique actuator which provides automatic
SLIDE GUIDE SGL TYPE SLIDE GUIDE BLOCK TYPES ACCURACY
 SGL YPE he N slide is a linear motion earing utilizing the rotational motion of all elements along four rows of raceway grooves. It can e used in various applications due to its compactness and high load
SGL YPE he N slide is a linear motion earing utilizing the rotational motion of all elements along four rows of raceway grooves. It can e used in various applications due to its compactness and high load
Sliding Bearings. Fig.(1) (a) Full-journal bearing and (b) partial-journal bearing
 Sliding Bearings The goal of a bearing is to provide relative positioning and rotational freedom while transmitting a load between two parts, commonly a shaft and its housing. The object of lubrication
Sliding Bearings The goal of a bearing is to provide relative positioning and rotational freedom while transmitting a load between two parts, commonly a shaft and its housing. The object of lubrication
BEARINGS Pillow Blocks
 The bearing size is usually selected according to the required bearing life and reliability under a specified type of load charged on the bearing. The load applied to the bearing operating under a static
The bearing size is usually selected according to the required bearing life and reliability under a specified type of load charged on the bearing. The load applied to the bearing operating under a static
General Explanation Ⅲ 1 Ⅲ 2
 General Explanation 1 2 Load Rating and Life Life of linear motion rolling guides Even in normal operational status, a linear motion rolling guide will reach the end of its life after a certain period
General Explanation 1 2 Load Rating and Life Life of linear motion rolling guides Even in normal operational status, a linear motion rolling guide will reach the end of its life after a certain period
Drive Units with Ball Screw Drives R310EN 3304 ( ) The Drive & Control Company
 Drive Units with Ball Screw Drives R310EN 3304 (2007.05) The Drive & Control Company Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear Bushings and Shafts Precision Ball
Drive Units with Ball Screw Drives R310EN 3304 (2007.05) The Drive & Control Company Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear Bushings and Shafts Precision Ball
MonocarrierTM Monocarrier
 Monocarrier TM Significantly saves designing load of machinery through an integration of linear motion components in one unit. Demonstrates high performance in a wide range of applications, including assembling
Monocarrier TM Significantly saves designing load of machinery through an integration of linear motion components in one unit. Demonstrates high performance in a wide range of applications, including assembling
SKF actuators available for quick delivery. Selection guide
 SKF actuators available for quick delivery Selection guide A wide range of SKF actuators available for quick delivery Industrial actuator 24 Volt DC Load range 1 000 to 4 000 N Speed range 5 to 52 mm/s
SKF actuators available for quick delivery Selection guide A wide range of SKF actuators available for quick delivery Industrial actuator 24 Volt DC Load range 1 000 to 4 000 N Speed range 5 to 52 mm/s
Monoca rrier TM CBLOCK C1-C22 C23-C68 C69-C88
 C-1 TM 1. Features C1 2. Classifications and Series C. Optional Components C. Selection of.1. Procedures for Selecting C.2. Rigidity C.. Maximum Speed C.. Accuracy Grade C.. Stroke and Ball Screw Lead
C-1 TM 1. Features C1 2. Classifications and Series C. Optional Components C. Selection of.1. Procedures for Selecting C.2. Rigidity C.. Maximum Speed C.. Accuracy Grade C.. Stroke and Ball Screw Lead
The SKF model for calculating the frictional moment
 The SKF model for calculating the frictional moment The SKF model for calculating the frictional moment Bearing friction is not constant and depends on certain tribological phenomena that occur in the
The SKF model for calculating the frictional moment The SKF model for calculating the frictional moment Bearing friction is not constant and depends on certain tribological phenomena that occur in the
Selection Calculations For Motorized Actuators
 Selection Calculations/ Selection Calculations For Linear Slides and Cylinders Select from the EZS Series, EZS Series for Cleanroom Use, EZC Series First determine your series, then select your model.
Selection Calculations/ Selection Calculations For Linear Slides and Cylinders Select from the EZS Series, EZS Series for Cleanroom Use, EZC Series First determine your series, then select your model.
Calculating the Applied Load
 The LM Guide is capable of receiving loads and moments in all directions that are generated due to the mounting orientation, alignment, gravity center position of a traveling object, thrust position and
The LM Guide is capable of receiving loads and moments in all directions that are generated due to the mounting orientation, alignment, gravity center position of a traveling object, thrust position and
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Rolling bearings Thermal speed rating Calculation and coefficients
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 1512 First edition 200-12-01 Rolling bearings Thermal speed rating Calculation and coefficients Roulements Vitesse de référence thermique Calculs et facteurs de correction Reference
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 1512 First edition 200-12-01 Rolling bearings Thermal speed rating Calculation and coefficients Roulements Vitesse de référence thermique Calculs et facteurs de correction Reference
Linear Recirculating Ball Bearings
 inear Recirculating Ball Bearings NIKOR 1. 2. 3.... 7. Technical Information Recirculating ball bearing, rawn shell esign, compact type, series kh inear Recirculating Ball Bearing precision series type
inear Recirculating Ball Bearings NIKOR 1. 2. 3.... 7. Technical Information Recirculating ball bearing, rawn shell esign, compact type, series kh inear Recirculating Ball Bearing precision series type
CTV series CHARACTERISTICS LINEAR UNITS
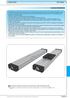 CTV series CHARACTERISTICS The CTV series describes s with a precision ball screw drive and two parallel, integrated, Zerobacklash rail guides. Compact dimensions allow high performance features such as,
CTV series CHARACTERISTICS The CTV series describes s with a precision ball screw drive and two parallel, integrated, Zerobacklash rail guides. Compact dimensions allow high performance features such as,
Bearing Internal Clearance and Preload
 . Bearing Internal Clearance and Preload. Bearing internal clearance Bearing internal clearance is the amount of internal free movement before mounting. As shown in Fig.., when either the inner ring or
. Bearing Internal Clearance and Preload. Bearing internal clearance Bearing internal clearance is the amount of internal free movement before mounting. As shown in Fig.., when either the inner ring or
Chapter 11. Bearing Types. Bearing Load. The Reliability Goal. Selection of Tapered Roller Bearings
 Chapter 11 Rolling Contact Bearing Bearing Types Bearing Life Bearing Load Bearing Survival The Reliability Goal Selection of Ball and Straight Roller Bearings Selection of Tapered Roller Bearings 1 Introduction
Chapter 11 Rolling Contact Bearing Bearing Types Bearing Life Bearing Load Bearing Survival The Reliability Goal Selection of Ball and Straight Roller Bearings Selection of Tapered Roller Bearings 1 Introduction
C-Lube Linear Way ML Linear Way L ML LWL
 -Lube Linear ay ML Linear ay L MLLL -Lube Maintenance ree Series -Lube Linear ay ML ML long term maintenance free supported! The aquamarine end plate is the symbol of maintenance free. Identification umber
-Lube Linear ay ML Linear ay L MLLL -Lube Maintenance ree Series -Lube Linear ay ML ML long term maintenance free supported! The aquamarine end plate is the symbol of maintenance free. Identification umber
Replacement of Grid Coupling with Bush Pin Coupling in Blower
 Replacement of Grid Coupling with Bush Pin Coupling in Blower Ramees Rahman A 1, Dr S Sankar 2 Dr K S Senthil Kumar 3 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, NCERC, Thrissure, Kerala, India
Replacement of Grid Coupling with Bush Pin Coupling in Blower Ramees Rahman A 1, Dr S Sankar 2 Dr K S Senthil Kumar 3 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, NCERC, Thrissure, Kerala, India
Tribology Prof. Dr. Harish Hirani Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Tribology Prof. Dr. Harish Hirani Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. # 29 Rolling Element Bearings (Contd.) Welcome to 29 th lecture of video course
Tribology Prof. Dr. Harish Hirani Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. # 29 Rolling Element Bearings (Contd.) Welcome to 29 th lecture of video course
Product Description. Further highlights. Outstanding features. 4 Bosch Rexroth Corporation Miniature Linear Modules R310A 2418 (2009.
 4 Bosch Rexroth orporation Miniature Linear Modules R310A 2418 (2009.05) Product Description Outstanding features Rexroth Miniature Linear Modules are precise, ready-to-install linear motion systems that
4 Bosch Rexroth orporation Miniature Linear Modules R310A 2418 (2009.05) Product Description Outstanding features Rexroth Miniature Linear Modules are precise, ready-to-install linear motion systems that
 Identification The specification of C-Lube Linear ay is identified by the identification, which consists of a model code, a size, a part code, a material code, a preload symbol, a classification symbol,
Identification The specification of C-Lube Linear ay is identified by the identification, which consists of a model code, a size, a part code, a material code, a preload symbol, a classification symbol,
second PLSA line R310EN 3308 ( )
 01_1 Planetary st Headline_36 Screw Assemblies pt/14.4 mm second PLSA line R310EN 3308 (2011-09) 2 Planetary Screw Assemblies PLSA Planetary Screw Assemblies PLSA Product Overview 3 Nuts, Screws, Screw
01_1 Planetary st Headline_36 Screw Assemblies pt/14.4 mm second PLSA line R310EN 3308 (2011-09) 2 Planetary Screw Assemblies PLSA Planetary Screw Assemblies PLSA Product Overview 3 Nuts, Screws, Screw
Identification system for short product names. Changes/amendments at a glance. 2 Bosch Rexroth AG OBB omega modules R ( )
 Omega Modules OBB 2 OBB omega modules R9990079 (206-05) Identification system for short product names Short product name Example: O B B - 085 - N N - System = Omega module Guideway = Ball Rail System Drive
Omega Modules OBB 2 OBB omega modules R9990079 (206-05) Identification system for short product names Short product name Example: O B B - 085 - N N - System = Omega module Guideway = Ball Rail System Drive
STAF Linear Guide. STAF Linear Guide Integrated Rail for Non Cage Type and Cage Type.
 STAF Linear Guide STAF Linear Guide Integrated Rail for Non Cage Type and Cage Type www.staf.com.tw A. Terms of Linear Guide 1-1 Main Factors a. Lifetime and Load of Linear Guide Selection of linear guide
STAF Linear Guide STAF Linear Guide Integrated Rail for Non Cage Type and Cage Type www.staf.com.tw A. Terms of Linear Guide 1-1 Main Factors a. Lifetime and Load of Linear Guide Selection of linear guide
Dynamic Analysis for Needle Roller Bearings Under Planetary Motion
 NTN TECHNICAL REVIEW No.75 2007 Technical Paper Dynamic Analysis for Needle Roller Bearings Under Planetary Motion Tomoya SAKAGUCHI A dynamic analysis tool for needle roller bearings in planetary gear
NTN TECHNICAL REVIEW No.75 2007 Technical Paper Dynamic Analysis for Needle Roller Bearings Under Planetary Motion Tomoya SAKAGUCHI A dynamic analysis tool for needle roller bearings in planetary gear
( ) 5. Bearing internal load distribution and displacement. 5.1 Bearing internal load distribution
 5. internal load distribution and displacement 5. internal load distribution This section will begin by examing the effect of a radial load F r and an axial load F a applied on a single-row bearing with
5. internal load distribution and displacement 5. internal load distribution This section will begin by examing the effect of a radial load F r and an axial load F a applied on a single-row bearing with
Ball screw. Linear. Coupling cover. 1Positioning table of a structure with enhanced sealing property. 3 High corrosion resistance
 Cleanroom Precision Positioning Table TC Ball screw TC EB Slide table inear Way Side cover Stainless sheet Motor bracket inear Coupling cover Pipe threads for suction connector Points ight weight, low
Cleanroom Precision Positioning Table TC Ball screw TC EB Slide table inear Way Side cover Stainless sheet Motor bracket inear Coupling cover Pipe threads for suction connector Points ight weight, low
Load Washers. Force. for Forces of 7, kn. F z. Type 9001A A 9081B, 9091B
 Force Load Washers for Forces of 7,5... 1 200 kn Type 9001A... 9071A 9081B, 9091B 1-component force sensor for measuring dynamic and quasistatic forces in z direction. F z Calibrated measuring range 100
Force Load Washers for Forces of 7,5... 1 200 kn Type 9001A... 9071A 9081B, 9091B 1-component force sensor for measuring dynamic and quasistatic forces in z direction. F z Calibrated measuring range 100
Planetary Screw Assemblies PLSA
 Planetary Screw Assemblies PLSA Ernst-Sachs-Straße 100 97424 Schweinfurt Tel. +49 9721 937-0 Fax +49 9721 937-275 www.boschrexroth.com Catalog "Planetary Screw Assemblies PLSA" R310XX 3308 (2014.01) Dear
Planetary Screw Assemblies PLSA Ernst-Sachs-Straße 100 97424 Schweinfurt Tel. +49 9721 937-0 Fax +49 9721 937-275 www.boschrexroth.com Catalog "Planetary Screw Assemblies PLSA" R310XX 3308 (2014.01) Dear
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 8 Balancing Lecture - 1 Introduce To Rigid Rotor Balancing Till
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 8 Balancing Lecture - 1 Introduce To Rigid Rotor Balancing Till
Product description. Compact Modules. Characteristic features. Further highlights
 4 Compact Modules Product description Characteristic features Five fine-tuned sizes based on a compact precision aluminum profile with two integrated pre-tensioned ball rail systems Identical external
4 Compact Modules Product description Characteristic features Five fine-tuned sizes based on a compact precision aluminum profile with two integrated pre-tensioned ball rail systems Identical external
AF SERIES AWEA MECHANTRONIC CO., LTD. High Performance Vertical Machining Center AGENT ISO 9001 ISO 14001
 AWEA MECHANTRONIC CO., LTD. HEADQUARTERS 629, Suezhetou Section, Kwanpu Rd., Wenshan Li, Hsinpu, Hsinchu, Taiwan TEL : +886-3-88-191 FAX : +886-3-88-19 Website : www.awea.com CENTRAL TAIWAN SCIENCE PARK
AWEA MECHANTRONIC CO., LTD. HEADQUARTERS 629, Suezhetou Section, Kwanpu Rd., Wenshan Li, Hsinpu, Hsinchu, Taiwan TEL : +886-3-88-191 FAX : +886-3-88-19 Website : www.awea.com CENTRAL TAIWAN SCIENCE PARK
SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling.
 SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling. Find: Determine the value of the critical speed of rotation for the shaft. Schematic and
SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling. Find: Determine the value of the critical speed of rotation for the shaft. Schematic and
ADVANCED MOTION TECHNOLOGIES CORP.
 LINEAR GUIDEWAY ADVANCED MOTION TECHNOLOGIES COR. No.7, Lane 89, Chung Shan Rd., Shen Kang Hsiang, Taichung Hsien 49, Taiwan TEL: +886464 FAX: +8864686 Email: amt.info@pmiamt.com.tw Web site: www.pmiamt.com
LINEAR GUIDEWAY ADVANCED MOTION TECHNOLOGIES COR. No.7, Lane 89, Chung Shan Rd., Shen Kang Hsiang, Taichung Hsien 49, Taiwan TEL: +886464 FAX: +8864686 Email: amt.info@pmiamt.com.tw Web site: www.pmiamt.com
AE / AER Series. AER Series
 AE / AER Series Characteristic Highlights True helical gear design Precision helical gearing increases tooth to tooth contact ratio by over % vs spur gearing. The helix angle produces smooth and quiet
AE / AER Series Characteristic Highlights True helical gear design Precision helical gearing increases tooth to tooth contact ratio by over % vs spur gearing. The helix angle produces smooth and quiet
FOUR-POINT CONTACT SLEWING RINGS - without gear [ O ]
![FOUR-POINT CONTACT SLEWING RINGS - without gear [ O ] FOUR-POINT CONTACT SLEWING RINGS - without gear [ O ]](/thumbs/96/126795264.jpg) FOUR-POINT CONTACT SLEWING RINGS - without gear [ O ] Number of the Loading Boundary Dimensions Static Ax.Basic Load Rating Designation Weight Abutment Dimensions Curve d D T C oa G J 1 J 2 N 1 N 2 n 1
FOUR-POINT CONTACT SLEWING RINGS - without gear [ O ] Number of the Loading Boundary Dimensions Static Ax.Basic Load Rating Designation Weight Abutment Dimensions Curve d D T C oa G J 1 J 2 N 1 N 2 n 1
CYLINDRICAL ROLLER BEARINGS CARRYING THRUST LOAD
 CYLINDRICAL ROLLER BEARINGS CARRYING THRUST LOAD Gh. PRISACARU, Sp. CRETU, D. N. OLARU "Gh. Asachi Technical University, Department of Machine Design & Tribology, Bvd. D. Mangeron, 6-63, 66 Iasi, ROMANIA;
CYLINDRICAL ROLLER BEARINGS CARRYING THRUST LOAD Gh. PRISACARU, Sp. CRETU, D. N. OLARU "Gh. Asachi Technical University, Department of Machine Design & Tribology, Bvd. D. Mangeron, 6-63, 66 Iasi, ROMANIA;
Coating K = TFE wear resist, dry lubricant Kerkote X = Special coating, (Example: Kerkote with grease)
 HAYD: 0 WGS0 Low Profile, Screw Driven Slide WGS0 Linear Rail with Hybrid 000 Series Size Single and Double Stacks and 000 Series Size Single and Double Stacks Kerk Motorized WGS Linear Slide utilizes
HAYD: 0 WGS0 Low Profile, Screw Driven Slide WGS0 Linear Rail with Hybrid 000 Series Size Single and Double Stacks and 000 Series Size Single and Double Stacks Kerk Motorized WGS Linear Slide utilizes
TABLE OF CONTENT Scope 2 Alignment Systems and Procedures 2 Balancing 8 Lubrication System 10 Preservation of Spare Parts 12
 Page : 1 of 21 Project Engineering Standard www.klmtechgroup.com KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru Malaysia TABLE OF CONTENT Scope 2 Alignment
Page : 1 of 21 Project Engineering Standard www.klmtechgroup.com KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru Malaysia TABLE OF CONTENT Scope 2 Alignment
SIMULATION FOR INSTABLE FLOATING OF HYDRODYNAMIC GUIDES DURING ACCELERATION AND AT CONSTANT VELOCITY 1. INTRODUCTION
 Journal of Machine Engineering, 08, Vol. 8, No., 5 5 ISSN 895-7595 (Print) ISSN 9-807 (Online) Received: December 07 / Accepted: 0 August 08 / Published online: 8 September 08 Yingying ZHANG * Volker WITTSTOCK
Journal of Machine Engineering, 08, Vol. 8, No., 5 5 ISSN 895-7595 (Print) ISSN 9-807 (Online) Received: December 07 / Accepted: 0 August 08 / Published online: 8 September 08 Yingying ZHANG * Volker WITTSTOCK
Dynamics of Machinery
 Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Series MHY2/MHW Angular Gripper. Cam actuation style is now standardized! MHZ2 MHZJ2 MHQ MHL2 MHR MHK MHS MHC2 MHT2 MHY2 MHW2 MRHQ 2.
 18 Angular Gripper Cam Style Rack & Pinion Style Series / Cam actuation style is now standardized! 2.8-1 18 Angular Gripper 18 Angular Gripper Series / Cam Style Rack & Pinion Style Series / Series MHY/Cam
18 Angular Gripper Cam Style Rack & Pinion Style Series / Cam actuation style is now standardized! 2.8-1 18 Angular Gripper 18 Angular Gripper Series / Cam Style Rack & Pinion Style Series / Series MHY/Cam
Planetary Screw Assemblies PLSA
 Planetary Screw Assemblies PLSA R310EN 3308 (2011-09) The Drive & Control Company C/ Centauro, 13 Área Empresarial Las Cubiertas 28971-Griñón (Madrid) T. 0034 91 126 6627 info@diversiatec.com www.diversiatec.com
Planetary Screw Assemblies PLSA R310EN 3308 (2011-09) The Drive & Control Company C/ Centauro, 13 Área Empresarial Las Cubiertas 28971-Griñón (Madrid) T. 0034 91 126 6627 info@diversiatec.com www.diversiatec.com
UNIT-I (FORCE ANALYSIS)
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEACH AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME2302 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY III YEAR/ V SEMESTER UNIT-I (FORCE ANALYSIS) PART-A (2 marks)
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEACH AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME2302 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY III YEAR/ V SEMESTER UNIT-I (FORCE ANALYSIS) PART-A (2 marks)
Flexible Mechanical Elements
 lexible Mechanical Elements INTRODUCTION Belts, ropes, chains, and other similar elastic or flexible machine elements are used in conveying systems and in the transmission of power over comparatively long
lexible Mechanical Elements INTRODUCTION Belts, ropes, chains, and other similar elastic or flexible machine elements are used in conveying systems and in the transmission of power over comparatively long
Chapter 12. Static Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
1 High precision, high rigidity positioning table
 TSHM CTHM 11 116 Precision Positioning Table H Ball screw TSH M Ball screw Slide table inear Way Bed inear Points 1 High precision, high rigidity positioning table High precision, high rigidity positioning
TSHM CTHM 11 116 Precision Positioning Table H Ball screw TSH M Ball screw Slide table inear Way Bed inear Points 1 High precision, high rigidity positioning table High precision, high rigidity positioning
Friction in Anti-friction Bearings
 Tribology Prof. Dr. Harish Hirani Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. # 32 Friction of Rolling Element Bearing Welcome to thirty second lecture of video
Tribology Prof. Dr. Harish Hirani Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. # 32 Friction of Rolling Element Bearing Welcome to thirty second lecture of video
ZF Maschinenantriebe GmbH Industrial Drives. Planetary gearboxes Economy Series for Servomotors
 ZF Maschinenantriebe GmbH Industrial rives Planetary gearboxes Economy Series for Servomotors 2 ZF-uoplan 2K Two-speed Gearboxes ZF-Ecolift Elevator Gearboxes ZF-Servoplan G ompact Gearbox ZF-Tiratron
ZF Maschinenantriebe GmbH Industrial rives Planetary gearboxes Economy Series for Servomotors 2 ZF-uoplan 2K Two-speed Gearboxes ZF-Ecolift Elevator Gearboxes ZF-Servoplan G ompact Gearbox ZF-Tiratron
Hydraulic Fundamentals Hydraulics Definition Advent of Oil Hydraulics Pascal s Law Pressure
 Fluidsys Training Centre, Bangalore offers an extensive range of skill-based and industry-relevant courses in the field of Pneumatics and Hydraulics. For more details, please visit the website: https://fluidsys.org
Fluidsys Training Centre, Bangalore offers an extensive range of skill-based and industry-relevant courses in the field of Pneumatics and Hydraulics. For more details, please visit the website: https://fluidsys.org
Chapter 3. Experimentation and Data Acquisition
 48 Chapter 3 Experimentation and Data Acquisition In order to achieve the objectives set by the present investigation as mentioned in the Section 2.5, an experimental set-up has been fabricated by mounting
48 Chapter 3 Experimentation and Data Acquisition In order to achieve the objectives set by the present investigation as mentioned in the Section 2.5, an experimental set-up has been fabricated by mounting
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF OVERLOAD ABSORBING GEAR COUPLINGS
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 9, Issue 12, December 2018, pp. 1240 1255, Article ID: IJMET_09_12_126 Available online at http://www.ia aeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 9, Issue 12, December 2018, pp. 1240 1255, Article ID: IJMET_09_12_126 Available online at http://www.ia aeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=
Modeling Method Analysis of the Friction Torque for High Speed Spindle Bearing
 MATEC Web of Conferences 75, 0308 (08) https://doi.org/0.05/matecconf/08750308 IFCAE-IOT 08 Modeling Method Analysis of the Friction Torque for High Speed Spindle Bearing Songsheng Li,, HuihangChen,, Haibing
MATEC Web of Conferences 75, 0308 (08) https://doi.org/0.05/matecconf/08750308 IFCAE-IOT 08 Modeling Method Analysis of the Friction Torque for High Speed Spindle Bearing Songsheng Li,, HuihangChen,, Haibing
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Rolling bearings Linear motion rolling bearings Part 2: Static load ratings
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 14728-2 First edition 2004-06-01 Rolling bearings Linear motion rolling bearings Part 2: Static load ratings Roulements Roulements à mouvement linéaire Partie 2: Charges statiques
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 14728-2 First edition 2004-06-01 Rolling bearings Linear motion rolling bearings Part 2: Static load ratings Roulements Roulements à mouvement linéaire Partie 2: Charges statiques
Maintenance Free C-Sleeve Linear Way ML ME MH MUL
 Maintenance ree C-Sleeve Linear ay M M MUL CAT-A e aim to be a Technology-Developing company taking customer-need as primary source for the development. ith our original technologies and creativities,
Maintenance ree C-Sleeve Linear ay M M MUL CAT-A e aim to be a Technology-Developing company taking customer-need as primary source for the development. ith our original technologies and creativities,
SNL plummer block housings, 2, 3, 5 and 6 series Other bearing housings Large SNL plummer block housings
 Bearing housings SNL plummer block housings, 2, 3, 5 and 6 series... 1033 Other bearing housings... 1058 Large SNL plummer block housings... 1058 SONL plummer block housings... 1059 SDG plummer block housings...
Bearing housings SNL plummer block housings, 2, 3, 5 and 6 series... 1033 Other bearing housings... 1058 Large SNL plummer block housings... 1058 SONL plummer block housings... 1059 SDG plummer block housings...
Single cam type. Double cam type. Grip force N. Type Model/size Stroke Screw type straight style. Screw type tee style
 Type Model/size Stroke -SS-0-N. -SS-0-N. Single cam type -SS- 7. -SS-. -SS-4. -SD-0 Double cam type -SD- -SD-4. Screw type straight style Screw type tee style -FS- -FT- -FS- -FT- 0.9 1. 1.. 1. 4 Grip forcen
Type Model/size Stroke -SS-0-N. -SS-0-N. Single cam type -SS- 7. -SS-. -SS-4. -SD-0 Double cam type -SD- -SD-4. Screw type straight style Screw type tee style -FS- -FT- -FS- -FT- 0.9 1. 1.. 1. 4 Grip forcen
Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive MKUVE15-KGT, MKUVE20-KGT
 Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive MKUVE15-KGT, MKUVE20-KGT Product overview Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive Actuators with ball monorail
Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive MKUVE15-KGT, MKUVE20-KGT Product overview Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive Actuators with ball monorail
Improvement in the Design & Manufacturing of Twin Worm Self Locking Technique and applications
 Improvement in the Design & Manufacturing of Twin Worm Self Locking Technique and applications Prof. P.B. Kadam 1, Prof. M.R. Todkar 2 1 Assistant Professor, Mechanical Engineering Department, T.K.I.E.T.Warananagar,
Improvement in the Design & Manufacturing of Twin Worm Self Locking Technique and applications Prof. P.B. Kadam 1, Prof. M.R. Todkar 2 1 Assistant Professor, Mechanical Engineering Department, T.K.I.E.T.Warananagar,
Vane Type Rotary Actuators Series Variations
 Vane Type Rotary Actuators Series Variations Vane Type Exterior CRB Series 0,, 0,, CRBU Series 0,, 0,, CRB Series, 6, 80, Has a compact body with exterior dimensions that do not change regardless of the
Vane Type Rotary Actuators Series Variations Vane Type Exterior CRB Series 0,, 0,, CRBU Series 0,, 0,, CRB Series, 6, 80, Has a compact body with exterior dimensions that do not change regardless of the
RGS08 Linear Rails: RGS08 Non-Motorized With and Without Guide Screw. RGS08 Non-Motorized Linear Rails
 RGS08 RGS08 Non-Motorized With and Without Guide RGS08 Non-Motorized Linear Rails RG Series linear rails are available: RGS08 Non-Motorized, -driven linear rail RGS08 Non-Motorized linear rail without
RGS08 RGS08 Non-Motorized With and Without Guide RGS08 Non-Motorized Linear Rails RG Series linear rails are available: RGS08 Non-Motorized, -driven linear rail RGS08 Non-Motorized linear rail without
Key words: Polymeric Composite Bearing, Clearance, FEM
 A study on the effect of the clearance on the contact stresses and kinematics of polymeric composite journal bearings under reciprocating sliding conditions Abstract The effect of the clearance on the
A study on the effect of the clearance on the contact stresses and kinematics of polymeric composite journal bearings under reciprocating sliding conditions Abstract The effect of the clearance on the
Journal of Physics: Conference Series. Related content. Recent citations PAPER OPEN ACCESS
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Ball's motion, sliding friction, and internal load distribution in a high-speed ball bearing subjected to a combined radial, thrust, and moment load,
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Ball's motion, sliding friction, and internal load distribution in a high-speed ball bearing subjected to a combined radial, thrust, and moment load,
Online Calculation of Guide Rings for Hydraulic Cylinders
 Online Calculation of Guide Rings for Hydraulic Cylinders Fietz Roland Haraldsson Anna 1 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Guide Rings General Information / Introduction Guide Rings Synthetic Materials Demarcation
Online Calculation of Guide Rings for Hydraulic Cylinders Fietz Roland Haraldsson Anna 1 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Guide Rings General Information / Introduction Guide Rings Synthetic Materials Demarcation
Scattered Energy of Vibration a novel parameter for rotating shaft vibration assessment
 5 th Australasian Congress on Applied Mechanics, ACAM 007 10-1 December 007, Brisbane, Australia Scattered Energy of Vibration a novel parameter for rotating shaft vibration assessment Abdul Md Mazid Department
5 th Australasian Congress on Applied Mechanics, ACAM 007 10-1 December 007, Brisbane, Australia Scattered Energy of Vibration a novel parameter for rotating shaft vibration assessment Abdul Md Mazid Department
BS-ISO helical gear fatigue life estimation and debris analysis validation
 BS-ISO helical gear fatigue life estimation and debris analysis validation Muhammad Ali Khan 1, a, Dennis Cooper 2 and Andrew Starr 1 1 Extreme loading and design research group, School of Mechanical,
BS-ISO helical gear fatigue life estimation and debris analysis validation Muhammad Ali Khan 1, a, Dennis Cooper 2 and Andrew Starr 1 1 Extreme loading and design research group, School of Mechanical,
Glossary Innovative Measurement Solutions
 Glossary GLOSSARY OF TERMS FOR TRANSDUCERS, LOAD CELLS AND WEIGH MODULES This purpose of this document is to provide a comprehensive, alphabetical list of terms and definitions commonly employed in the
Glossary GLOSSARY OF TERMS FOR TRANSDUCERS, LOAD CELLS AND WEIGH MODULES This purpose of this document is to provide a comprehensive, alphabetical list of terms and definitions commonly employed in the
VOLUMEC. Valve Position Indicator 5
 VOLUMEC Valve Position Indicator 5 2 KRACHT CORP. 8600 S Wilkinson Way Unit A Perrysburg, OH 43551 USA P +1 419 874 1000 F +1 419 874 1006 flowmeters@krachtcorp.com www.krachtcorp.com VOLUMEC Valve Position
VOLUMEC Valve Position Indicator 5 2 KRACHT CORP. 8600 S Wilkinson Way Unit A Perrysburg, OH 43551 USA P +1 419 874 1000 F +1 419 874 1006 flowmeters@krachtcorp.com www.krachtcorp.com VOLUMEC Valve Position
Overview. Dry Friction Wedges Flatbelts Screws Bearings Rolling Resistance
 Friction Chapter 8 Overview Dry Friction Wedges Flatbelts Screws Bearings Rolling Resistance Dry Friction Friction is defined as a force of resistance acting on a body which prevents slipping of the body
Friction Chapter 8 Overview Dry Friction Wedges Flatbelts Screws Bearings Rolling Resistance Dry Friction Friction is defined as a force of resistance acting on a body which prevents slipping of the body
Agricultural Science 1B Principles & Processes in Agriculture. Mike Wheatland
 Agricultural Science 1B Principles & Processes in Agriculture Mike Wheatland (m.wheatland@physics.usyd.edu.au) Outline - Lectures weeks 9-12 Chapter 6: Balance in nature - description of energy balance
Agricultural Science 1B Principles & Processes in Agriculture Mike Wheatland (m.wheatland@physics.usyd.edu.au) Outline - Lectures weeks 9-12 Chapter 6: Balance in nature - description of energy balance
MECTROL CORPORATION 9 NORTHWESTERN DRIVE, SALEM, NH PHONE FAX TIMING BELT THEORY
 MECTRO CORPORATION 9 NORTHWESTERN DRIVE, SAEM, NH 03079 PHONE 603-890-55 FAX 603-890-66 TIMING BET THEORY Copyright 997, 999, 00 Mectrol Corporation. All rights reserved. April 00 Timing Belt Theory Introduction
MECTRO CORPORATION 9 NORTHWESTERN DRIVE, SAEM, NH 03079 PHONE 603-890-55 FAX 603-890-66 TIMING BET THEORY Copyright 997, 999, 00 Mectrol Corporation. All rights reserved. April 00 Timing Belt Theory Introduction
Force - a push or a pull A force described by its strength and by the direction in which it acts The SI unit for force is the newton (N)
 Forces Force - a push or a pull A force described by its strength and by the direction in which it acts The SI unit for force is the newton (N) The direction and strength of forces can be represented by
Forces Force - a push or a pull A force described by its strength and by the direction in which it acts The SI unit for force is the newton (N) The direction and strength of forces can be represented by
Not all thin-section bearings are created equal. KAYDON new capacity calculations. Robert Roos, Scott Hansen
 Not all thin-section bearings are created equal KAYDON new capacity calculations Robert Roos, Scott Hansen A white paper from KAYDON Bearings Division Table of Contents Abstract... pg. Introduction...
Not all thin-section bearings are created equal KAYDON new capacity calculations Robert Roos, Scott Hansen A white paper from KAYDON Bearings Division Table of Contents Abstract... pg. Introduction...
Design against fluctuating load
 Design against fluctuating load In many applications, the force acting on the spring is not constants but varies in magnitude with time. The valve springs of automotive engine subjected to millions of
Design against fluctuating load In many applications, the force acting on the spring is not constants but varies in magnitude with time. The valve springs of automotive engine subjected to millions of
RGS06 Linear Rails: RGS06 Non-Motorized With and Without Guide Screw. RGS06 Non-Motorized Linear Rails
 on-motorized With and Without Guide on-motorized Linear Rails RG Series linear rails are available: on-motorized, -driven linear rail on-motorized, Wide format, -driven linear rail on-motorized, Wide format,
on-motorized With and Without Guide on-motorized Linear Rails RG Series linear rails are available: on-motorized, -driven linear rail on-motorized, Wide format, -driven linear rail on-motorized, Wide format,
Peltier Application Note
 Peltier Application Note Early 19th century scientists, Thomas Seebeck and Jean Peltier, first discovered the phenomena that are the basis for today s thermoelectric industry. Seebeck found that if you
Peltier Application Note Early 19th century scientists, Thomas Seebeck and Jean Peltier, first discovered the phenomena that are the basis for today s thermoelectric industry. Seebeck found that if you
MAINTENANCE EVALUATION CHECKLIST HYDRAULIC ELEVATORS
 Manufacturer: Model: Evaluation Performed By: INTRODUCTION: This checklist will enable the user to make an objective appraisal of the condition of the equipment. Given the variety and complexity of the
Manufacturer: Model: Evaluation Performed By: INTRODUCTION: This checklist will enable the user to make an objective appraisal of the condition of the equipment. Given the variety and complexity of the
A nonlinear dynamic vibration model of defective bearings: The importance of modelling the finite size of rolling elements
 A nonlinear dynamic vibration model of defective bearings: The importance of modelling the finite size of rolling elements Alireza Moazenahmadi, Dick Petersen and Carl Howard School of Mechanical Engineering,
A nonlinear dynamic vibration model of defective bearings: The importance of modelling the finite size of rolling elements Alireza Moazenahmadi, Dick Petersen and Carl Howard School of Mechanical Engineering,
1.3 Working temperature T 200,0 1.4 Working environment. F... Guided seating. Light service. Cold formed springs. Music wire ASTM A228
 Helical cylindrical compression spring of round wires and bars i ii? 1.0 Calculation without errors. Project information Input parameters section Selection of load conditions, spring operational and production
Helical cylindrical compression spring of round wires and bars i ii? 1.0 Calculation without errors. Project information Input parameters section Selection of load conditions, spring operational and production
