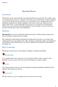
2.2t t 3 =1.2t+0.035' t= D, = f ? t 3 dt f ' 2 dt
|
|
|
- Brook Estella Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 5.5 Queuing Theory and Traffic Flow Analysis 159 EXAMPLE 5.8 After observing arrivals and departures at a highway toll booth over a 60-minute tim e period, an observer notes that the arrival and departure rates (or service rates) ar e deterministic, but instead of being uniform, they change over time according to a know n function. The arrival rate is given by the function A(t) = ?, and th e departure rate is given by du(t) = t, t is in minutes after the beginning of the observation period and A(t) and,u(t) are in vehicles per minute. Determine the total vehicle delay at the toll booth and the longest queue, assuming D/D/1 queuing. Note that this problem is an example of a time-dependent deterministic queue because th e deterministic arrival and departure rates change over time. Begin by computing the time to queue dissipation by equating vehicle arrivals and departures : ? dt = f l tdt 2.2t t 3 =1.2t+0.035' t= 0 which gives t = 61.8 minutes. Therefore, the total vehicle delay (the area between the arriva l and departure functions) i s D, = f ? t 3 dt f ' 2 dt =1.1? ' ' 3 Jr = (61.8) (61.8) (61.8) 2 = veh-min The queue length (in vehicles) at any time t is given by the functio n Q(t) = f e 2 dt t dt = t t Solving for the time at which the maximum queue length occurs, 'Q(t)= _ ' = 0 dt t = mi n Substituting with t = minutes gives the maximum queue length :
2 160 Chapter 5 Fundamentals of Traffic Flow and Queuing Theory Q(39.12) = t t 2 +t = (39.12) (39.12) = ve h MID/1 Queuin g The assumption of exponentially distributed times between the arrivals of successiv e vehicles (Poisson arrivals) will, in some cases, give a more realistic representation of traffic flow than the assumption of uniformly distributed arrival times. Therefore, th e M/D/1 queue (exponentially distributed arrivals, deterministic departures, and on e departure channel) has some important applications within the traffic analysis field. Although a graphical solution to an MID/1 queue is difficult, a mathematical solutio n is straightforward. Defining a new term (traffic intensity) for the ratio of averag e arrival to departure rates as p = traffic intensity, unitless, 2 = average arrival rate in vehicles per unit time, an d,u = average departure rate in vehicles per unit time, 2 p = (5.27) and assuming that p is less than 1, it can be shown that for an M/D/1 queue th e following queuing performance equations apply : p p 2 = (5.28) 2(1 p ) w= P 2,1 ( 1 p ) (5.29 ) t 2 p (5.30) 2/1(1 p) Q = average length of queue in vehicles, w = average waiting time in the queue, in unit time per vehicle, t = average time spent in the system (the summation of average waiting time in th e queue and average departure time), in unit time per vehicle, an d Other terms are as defined previously.
3 5.5 Queuing Theory and Traffic Flow Analysis 161 It is important to note that under the assumption that the traffic intensity is les s than 1 (2 <,u), the D/D/1 queue will predict no queue formation. However a queuing model that is derived based on random arrivals or departures, such as the M/D/ 1 queuing model, will predict queue formations under such conditions. Also, note tha t the M/D/ l queuing model presented here is based on steady-state conditions (constant average arrival and departure rates), with randomness arising from the assume d probability distribution of arrivals. This contrasts with the time-varying deterministi c queuing case, presented in Example 5.8, in which arrival and departure rates changed over time but randomness was not present. EXAMPLE 5.9 Consider the entrance to the recreational park described in Example 5.7. However, let the average arrival rate be 180 veh/h and Poisson distributed (exponential times betwee n arrivals) over the entire period from park opening time (8 :00 A.M.) until closing at dusk. Compute the average length of queue (in vehicles), average waiting time in the queue, an d average time spent in the system, assuming M/D/1 queuing. Putting arrival and departure rates into common units of vehicles per minute give s and 180 veh/h = 3 veh/min for all t 60 min/ h _ 60 s/min = 4 veh/min for all t 15 s/veh A 3 veh/mi n p= = =0.7 5 ft 4 veh/mi n For the average length of queue (in vehicles), Eq is applied : Q _ 2( ) =1.125veh For average waiting time in the queue, Eq give s w= 2(4)( ) = min/veh For average time spent in the system [queue time plus departure (service) time], Eq i s used :
4 162 Chapter 5 Fundamentals of Traffic Flow and Queuing Theory t _ 2(4)( ) = min/veh or, alternatively, because the departure (service) time is 1/,u (the 0.25 minutes it takes th e park attendant to distribute the brochure), = = min/ve h M/M/1 Queuing A queuing model that assumes one departure channel and exponentially distribute d departure times in addition to exponentially distributed arrival times (an M/M/1 queue) is applicable in some traffic applications. For example, exponentiall y distributed departure patterns might be a reasonable assumption at a toll booth, wher e some arriving drivers have the correct toll and can be processed quickly, and other s do not have the correct toll, producing a distribution of departures about some mea n departure rate. Under standard M/M/1 assumptions, it can be shown that th e following queuing performance equations apply (again assuming that p is less than 1) : (5.31 ) 2 w=,u (,u 2 ) (5.32 ) t= 1 (5.33 ) Q = average length of queue in vehicles, w = average waiting time in the queue, in unit time per vehicle, t = average time spent in the system (w + 1/,u), in unit time per vehicle, an d Other terms are as defined previously.
5 5.5 Queuing Theory and Traffic Flow Analysis 163 EXAMPLE 5.10 Assume that the park attendant in Examples 5.7 and 5.9 takes an average of 15 seconds t o distribute brochures, but the distribution time varies depending on whether park patron s have questions relating to park operating policies. Given an average arrival rate of 18 0 veh/h as in Example 5.9, compute the average length of queue (in vehicles), averag e waiting time in the queue, and average time spent in the system, assuming M/M/1 queuing. Using the average arrival rate, departure rate, and traffic intensity as determined in Exampl e 5.9, the average length of queue is (from Eq ) _ = 2.25 veh the average waiting time in the queue is (from Eq. 5.32) 3 w _ 4(4 3 ) = 0.75 min/ve h and the average time spent in the system is (from Eq ) t= = 1 min/ve h M/MIN Queuing A more general formulation of the M/M/1 queue is the M/M/N queue, N is th e total number of departure channels. M/M/N queuing is a reasonable assumption at tol l booths on turnpikes or at toll bridges, there is often more than one departur e channel available (more than one toll booth open). A parking lot is another example, with N being the number of parking stalls in the lot and the departure rate, p, being the exponentially distributed times of parking duration. M/M/N queuing is also frequently encountered in non-transportation applications such as checkout lines a t retail stores, security checks at airports, and so on. The following equations describe the operational characteristics of M/M/N queuing. Note that unlike the equations for M/D/1 and M/M/1, which require that the traffic intensity, p, be less than 1, the following equations allow p to be greater than 1 but apply only when p/n (which is called the utilization factor) is less than 1.
Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement Design
 Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement Design Speed Studies - Project Traffic Queuing Intersections Level of Service in Highways and
Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement Design Speed Studies - Project Traffic Queuing Intersections Level of Service in Highways and
CE351 Transportation Systems: Planning and Design
 CE351 Transportation Systems: Planning and Design TOPIC: Level of Service (LOS) at Traffic Signals 1 Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement
CE351 Transportation Systems: Planning and Design TOPIC: Level of Service (LOS) at Traffic Signals 1 Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement
EE 368. Weeks 3 (Notes)
 EE 368 Weeks 3 (Notes) 1 State of a Queuing System State: Set of parameters that describe the condition of the system at a point in time. Why do we need it? Average size of Queue Average waiting time How
EE 368 Weeks 3 (Notes) 1 State of a Queuing System State: Set of parameters that describe the condition of the system at a point in time. Why do we need it? Average size of Queue Average waiting time How
Signalized Intersection Delay Models
 Chapter 35 Signalized Intersection Delay Models 35.1 Introduction Signalized intersections are the important points or nodes within a system of highways and streets. To describe some measure of effectiveness
Chapter 35 Signalized Intersection Delay Models 35.1 Introduction Signalized intersections are the important points or nodes within a system of highways and streets. To describe some measure of effectiveness
Queueing Theory I Summary! Little s Law! Queueing System Notation! Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K "
 Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
MAT SYS 5120 (Winter 2012) Assignment 5 (not to be submitted) There are 4 questions.
 MAT 4371 - SYS 5120 (Winter 2012) Assignment 5 (not to be submitted) There are 4 questions. Question 1: Consider the following generator for a continuous time Markov chain. 4 1 3 Q = 2 5 3 5 2 7 (a) Give
MAT 4371 - SYS 5120 (Winter 2012) Assignment 5 (not to be submitted) There are 4 questions. Question 1: Consider the following generator for a continuous time Markov chain. 4 1 3 Q = 2 5 3 5 2 7 (a) Give
Introduction to queuing theory
 Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
CEE 320 Midterm Examination (50 minutes)
 CEE 320 Midterm Examination (50 minutes) Fall 2009 Please write your name on this cover. Please write your last name on all other exam pages This exam is NOT open book, but you are allowed to use one 8.5x11
CEE 320 Midterm Examination (50 minutes) Fall 2009 Please write your name on this cover. Please write your last name on all other exam pages This exam is NOT open book, but you are allowed to use one 8.5x11
PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research
 PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research Lecture 2.I Queuing Systems An Introduction Operations Research Models Deterministic Models Linear Programming Integer Programming Network Optimization
PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research Lecture 2.I Queuing Systems An Introduction Operations Research Models Deterministic Models Linear Programming Integer Programming Network Optimization
Traffic flow theory involves the development of mathematical relationships among
 CHAPTER 6 Fundamental Principles of Traffic Flow Traffic flow theory involves the development of mathematical relationships among the primary elements of a traffic stream: flow, density, and speed. These
CHAPTER 6 Fundamental Principles of Traffic Flow Traffic flow theory involves the development of mathematical relationships among the primary elements of a traffic stream: flow, density, and speed. These
Queuing Analysis. Chapter Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 Queuing Analysis Chapter 13 13-1 Chapter Topics Elements of Waiting Line Analysis The Single-Server Waiting Line System Undefined and Constant Service Times Finite Queue Length Finite Calling Problem The
Queuing Analysis Chapter 13 13-1 Chapter Topics Elements of Waiting Line Analysis The Single-Server Waiting Line System Undefined and Constant Service Times Finite Queue Length Finite Calling Problem The
5/15/18. Operations Research: An Introduction Hamdy A. Taha. Copyright 2011, 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The objective of queuing analysis is to offer a reasonably satisfactory service to waiting customers. Unlike the other tools of OR, queuing theory is not an optimization technique. Rather, it determines
The objective of queuing analysis is to offer a reasonably satisfactory service to waiting customers. Unlike the other tools of OR, queuing theory is not an optimization technique. Rather, it determines
Signalized Intersection Delay Models
 Signalized Intersection Delay Models Lecture Notes in Transportation Systems Engineering Prof. Tom V. Mathew Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Types of delay 2 2.1 Stopped Time Delay................................
Signalized Intersection Delay Models Lecture Notes in Transportation Systems Engineering Prof. Tom V. Mathew Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Types of delay 2 2.1 Stopped Time Delay................................
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems
 Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
1.225 Transportation Flow Systems Quiz (December 17, 2001; Duration: 3 hours)
 1.225 Transportation Flow Systems Quiz (December 17, 2001; Duration: 3 hours) Student Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This exam is open-book 2. No cooperation is permitted 3. Please write down your name
1.225 Transportation Flow Systems Quiz (December 17, 2001; Duration: 3 hours) Student Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This exam is open-book 2. No cooperation is permitted 3. Please write down your name
Cumulative Count Curve and Queueing Analysis
 Introduction Traffic flow theory (TFT) Zhengbing He, Ph.D., http://zhengbing.weebly.com School of traffic and transportation, Beijing Jiaotong University September 27, 2015 Introduction Outline 1 Introduction
Introduction Traffic flow theory (TFT) Zhengbing He, Ph.D., http://zhengbing.weebly.com School of traffic and transportation, Beijing Jiaotong University September 27, 2015 Introduction Outline 1 Introduction
Non Markovian Queues (contd.)
 MODULE 7: RENEWAL PROCESSES 29 Lecture 5 Non Markovian Queues (contd) For the case where the service time is constant, V ar(b) = 0, then the P-K formula for M/D/ queue reduces to L s = ρ + ρ 2 2( ρ) where
MODULE 7: RENEWAL PROCESSES 29 Lecture 5 Non Markovian Queues (contd) For the case where the service time is constant, V ar(b) = 0, then the P-K formula for M/D/ queue reduces to L s = ρ + ρ 2 2( ρ) where
Slides 9: Queuing Models
 Slides 9: Queuing Models Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical queuing model is: Queuing models provide the analyst with a powerful tool for designing
Slides 9: Queuing Models Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical queuing model is: Queuing models provide the analyst with a powerful tool for designing
Signalized Intersections
 Signalized Intersections Kelly Pitera October 23, 2009 Topics to be Covered Introduction/Definitions D/D/1 Queueing Phasing and Timing Plan Level of Service (LOS) Signal Optimization Conflicting Operational
Signalized Intersections Kelly Pitera October 23, 2009 Topics to be Covered Introduction/Definitions D/D/1 Queueing Phasing and Timing Plan Level of Service (LOS) Signal Optimization Conflicting Operational
ARE THE SEQUENCES OF BUS AND EARTHQUAKE ARRIVALS POISSON?
 Application Example 6 (Exponential and Poisson distributions) ARE THE SEQUENCES OF BUS AND EARTHQUAKE ARRIVALS POISSON? The Poisson Process The Poisson process is the simplest random distribution of points
Application Example 6 (Exponential and Poisson distributions) ARE THE SEQUENCES OF BUS AND EARTHQUAKE ARRIVALS POISSON? The Poisson Process The Poisson process is the simplest random distribution of points
Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems
 Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems John Shortle George Mason University February 28, 2018 Outline Why stochastic models matter M/M/1 queue Little s law Priority
Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems John Shortle George Mason University February 28, 2018 Outline Why stochastic models matter M/M/1 queue Little s law Priority
2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART IV: SIMULATION
 2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART IV: SIMULATION 22 Random Numbers A fundamental step in a simulation study is the generation of random numbers, where a random number represents the value of a random
2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART IV: SIMULATION 22 Random Numbers A fundamental step in a simulation study is the generation of random numbers, where a random number represents the value of a random
Introduction to queuing theory
 Introduction to queuing theory Queu(e)ing theory Queu(e)ing theory is the branch of mathematics devoted to how objects (packets in a network, people in a bank, processes in a CPU etc etc) join and leave
Introduction to queuing theory Queu(e)ing theory Queu(e)ing theory is the branch of mathematics devoted to how objects (packets in a network, people in a bank, processes in a CPU etc etc) join and leave
Chapter 10. Queuing Systems. D (Queuing Theory) Queuing theory is the branch of operations research concerned with waiting lines.
 Chapter 10 Queuing Systems D. 10. 1. (Queuing Theory) Queuing theory is the branch of operations research concerned with waiting lines. D. 10.. (Queuing System) A ueuing system consists of 1. a user source.
Chapter 10 Queuing Systems D. 10. 1. (Queuing Theory) Queuing theory is the branch of operations research concerned with waiting lines. D. 10.. (Queuing System) A ueuing system consists of 1. a user source.
Systems Simulation Chapter 6: Queuing Models
 Systems Simulation Chapter 6: Queuing Models Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr April 2, 2014 Introduction Introduction Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical
Systems Simulation Chapter 6: Queuing Models Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr April 2, 2014 Introduction Introduction Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical
λ λ λ In-class problems
 In-class problems 1. Customers arrive at a single-service facility at a Poisson rate of 40 per hour. When two or fewer customers are present, a single attendant operates the facility, and the service time
In-class problems 1. Customers arrive at a single-service facility at a Poisson rate of 40 per hour. When two or fewer customers are present, a single attendant operates the facility, and the service time
Networking = Plumbing. Queueing Analysis: I. Last Lecture. Lecture Outline. Jeremiah Deng. 29 July 2013
 Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
Signalized Intersection Delay Models
 hapter 56 Signalized Intersection Delay Models 56.1 Introduction Signalized intersections are the important points or nodes within a system of highways and streets. To describe some measure of effectiveness
hapter 56 Signalized Intersection Delay Models 56.1 Introduction Signalized intersections are the important points or nodes within a system of highways and streets. To describe some measure of effectiveness
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes. Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking
 Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
ISyE 2030 Practice Test 2
 1 NAME ISyE 2030 Practice Test 2 Summer 2005 This test is open notes, open books. You have exactly 75 minutes. 1. Short-Answer Questions (a) TRUE or FALSE? If arrivals occur according to a Poisson process
1 NAME ISyE 2030 Practice Test 2 Summer 2005 This test is open notes, open books. You have exactly 75 minutes. 1. Short-Answer Questions (a) TRUE or FALSE? If arrivals occur according to a Poisson process
Sandwich shop : a queuing net work with finite disposable resources queue and infinite resources queue
 Sandwich shop : a queuing net work with finite disposable resources queue and infinite resources queue Final project for ISYE 680: Queuing systems and Applications Hongtan Sun May 5, 05 Introduction As
Sandwich shop : a queuing net work with finite disposable resources queue and infinite resources queue Final project for ISYE 680: Queuing systems and Applications Hongtan Sun May 5, 05 Introduction As
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems
 Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Analytical Delay Models for Signalized Intersections
 Analytical Delay Models for Signalized Intersections Ali Payidar Akgungor and A. Graham R. Bullen INTRODUCTION Delay is the most important measure of effectiveness (MOE) at a signalized intersection because
Analytical Delay Models for Signalized Intersections Ali Payidar Akgungor and A. Graham R. Bullen INTRODUCTION Delay is the most important measure of effectiveness (MOE) at a signalized intersection because
Computer Networks More general queuing systems
 Computer Networks More general queuing systems Saad Mneimneh Computer Science Hunter College of CUNY New York M/G/ Introduction We now consider a queuing system where the customer service times have a
Computer Networks More general queuing systems Saad Mneimneh Computer Science Hunter College of CUNY New York M/G/ Introduction We now consider a queuing system where the customer service times have a
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing
 Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
Link Models for Circuit Switching
 Link Models for Circuit Switching The basis of traffic engineering for telecommunication networks is the Erlang loss function. It basically allows us to determine the amount of telephone traffic that can
Link Models for Circuit Switching The basis of traffic engineering for telecommunication networks is the Erlang loss function. It basically allows us to determine the amount of telephone traffic that can
Queueing Theory. VK Room: M Last updated: October 17, 2013.
 Queueing Theory VK Room: M1.30 knightva@cf.ac.uk www.vincent-knight.com Last updated: October 17, 2013. 1 / 63 Overview Description of Queueing Processes The Single Server Markovian Queue Multi Server
Queueing Theory VK Room: M1.30 knightva@cf.ac.uk www.vincent-knight.com Last updated: October 17, 2013. 1 / 63 Overview Description of Queueing Processes The Single Server Markovian Queue Multi Server
CHAPTER 3. CAPACITY OF SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS
 CHAPTER 3. CAPACITY OF SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS 1. Overview In this chapter we explore the models on which the HCM capacity analysis method for signalized intersections are based. While the method has
CHAPTER 3. CAPACITY OF SIGNALIZED INTERSECTIONS 1. Overview In this chapter we explore the models on which the HCM capacity analysis method for signalized intersections are based. While the method has
λ, µ, ρ, A n, W n, L(t), L, L Q, w, w Q etc. These
 Queuing theory models systems with servers and clients (presumably waiting in queues). Notation: there are many standard symbols like λ, µ, ρ, A n, W n, L(t), L, L Q, w, w Q etc. These represent the actual
Queuing theory models systems with servers and clients (presumably waiting in queues). Notation: there are many standard symbols like λ, µ, ρ, A n, W n, L(t), L, L Q, w, w Q etc. These represent the actual
Generation of Discrete Random variables
 Simulation Simulation is the imitation of the operation of a realworld process or system over time. The act of simulating something first requires that a model be developed; this model represents the key
Simulation Simulation is the imitation of the operation of a realworld process or system over time. The act of simulating something first requires that a model be developed; this model represents the key
Signalized Intersection Delay Models
 Transportation System Engineering 56. Signalized Intersection Delay Models Chapter 56 Signalized Intersection Delay Models 56.1 Introduction Signalized intersections are the important points or nodes within
Transportation System Engineering 56. Signalized Intersection Delay Models Chapter 56 Signalized Intersection Delay Models 56.1 Introduction Signalized intersections are the important points or nodes within
NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling
 NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling Queueing Theory II Chris Kirkbride Management Science 2017 Overview of Today s Sessions I Introduction to Queueing Modelling II Multiclass Queueing Models III Queueing Control
NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling Queueing Theory II Chris Kirkbride Management Science 2017 Overview of Today s Sessions I Introduction to Queueing Modelling II Multiclass Queueing Models III Queueing Control
Queueing Review. Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman 10/25/17. (mostly from BCNN) Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA
 1 / 26 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/25/17 2 / 26 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
1 / 26 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/25/17 2 / 26 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
Queuing Theory. The present section focuses on the standard vocabulary of Waiting Line Models.
 Queuing Theory Introduction Waiting lines are the most frequently encountered problems in everyday life. For example, queue at a cafeteria, library, bank, etc. Common to all of these cases are the arrivals
Queuing Theory Introduction Waiting lines are the most frequently encountered problems in everyday life. For example, queue at a cafeteria, library, bank, etc. Common to all of these cases are the arrivals
Traffic Flow Theory and Simulation
 Traffic Flow Theory and Simulation V.L. Knoop Lecture 2 Arrival patterns and cumulative curves Arrival patterns From microscopic to macroscopic 24-3-2014 Delft University of Technology Challenge the future
Traffic Flow Theory and Simulation V.L. Knoop Lecture 2 Arrival patterns and cumulative curves Arrival patterns From microscopic to macroscopic 24-3-2014 Delft University of Technology Challenge the future
Queueing Review. Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman 10/6/16. (mostly from BCNN) Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA
 1 / 24 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/6/16 2 / 24 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
1 / 24 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/6/16 2 / 24 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
Classification of Queuing Models
 Classification of Queuing Models Generally Queuing models may be completely specified in the following symbol form:(a/b/c):(d/e)where a = Probability law for the arrival(or inter arrival)time, b = Probability
Classification of Queuing Models Generally Queuing models may be completely specified in the following symbol form:(a/b/c):(d/e)where a = Probability law for the arrival(or inter arrival)time, b = Probability
Departure time choice equilibrium problem with partial implementation of congestion pricing
 Departure time choice equilibrium problem with partial implementation of congestion pricing Tokyo Institute of Technology Postdoctoral researcher Katsuya Sakai 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Method/Tool
Departure time choice equilibrium problem with partial implementation of congestion pricing Tokyo Institute of Technology Postdoctoral researcher Katsuya Sakai 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Method/Tool
57:022 Principles of Design II Final Exam Solutions - Spring 1997
 57:022 Principles of Design II Final Exam Solutions - Spring 1997 Part: I II III IV V VI Total Possible Pts: 52 10 12 16 13 12 115 PART ONE Indicate "+" if True and "o" if False: + a. If a component's
57:022 Principles of Design II Final Exam Solutions - Spring 1997 Part: I II III IV V VI Total Possible Pts: 52 10 12 16 13 12 115 PART ONE Indicate "+" if True and "o" if False: + a. If a component's
Batch Arrival Queuing Models with Periodic Review
 Batch Arrival Queuing Models with Periodic Review R. Sivaraman Ph.D. Research Scholar in Mathematics Sri Satya Sai University of Technology and Medical Sciences Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh National Awardee
Batch Arrival Queuing Models with Periodic Review R. Sivaraman Ph.D. Research Scholar in Mathematics Sri Satya Sai University of Technology and Medical Sciences Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh National Awardee
Chapter 6 Queueing Models. Banks, Carson, Nelson & Nicol Discrete-Event System Simulation
 Chapter 6 Queueing Models Banks, Carson, Nelson & Nicol Discrete-Event System Simulation Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queueing models. A simple but typical queueing model: Queueing
Chapter 6 Queueing Models Banks, Carson, Nelson & Nicol Discrete-Event System Simulation Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queueing models. A simple but typical queueing model: Queueing
CS418 Operating Systems
 CS418 Operating Systems Lecture 14 Queuing Analysis Textbook: Operating Systems by William Stallings 1 1. Why Queuing Analysis? If the system environment changes (like the number of users is doubled),
CS418 Operating Systems Lecture 14 Queuing Analysis Textbook: Operating Systems by William Stallings 1 1. Why Queuing Analysis? If the system environment changes (like the number of users is doubled),
I, A BRIEF REVIEW ON INFINITE QUEUE MODEL M.
 A BRIEF REVIEW ON INFINITE QUEUE MODEL M. Vasuki*, A. Dinesh Kumar** & G. Vijayaprabha** * Assistant Professor, Department of Mathematics, Srinivasan College of Arts and Science, Perambalur, Tamilnadu
A BRIEF REVIEW ON INFINITE QUEUE MODEL M. Vasuki*, A. Dinesh Kumar** & G. Vijayaprabha** * Assistant Professor, Department of Mathematics, Srinivasan College of Arts and Science, Perambalur, Tamilnadu
Discrete Event and Process Oriented Simulation (2)
 B. Maddah ENMG 622 Simulation 11/04/08 Discrete Event and Process Oriented Simulation (2) Discrete event hand simulation of an (s, S) periodic review inventory system Consider a retailer who sells a commodity
B. Maddah ENMG 622 Simulation 11/04/08 Discrete Event and Process Oriented Simulation (2) Discrete event hand simulation of an (s, S) periodic review inventory system Consider a retailer who sells a commodity
Probability and Statistics Concepts
 University of Central Florida Computer Science Division COT 5611 - Operating Systems. Spring 014 - dcm Probability and Statistics Concepts Random Variable: a rule that assigns a numerical value to each
University of Central Florida Computer Science Division COT 5611 - Operating Systems. Spring 014 - dcm Probability and Statistics Concepts Random Variable: a rule that assigns a numerical value to each
Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance
 Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance Marceau Coupechoux Telecom ParisTech, departement Informatique et Réseaux marceau.coupechoux@telecom-paristech.fr IT.2403 Modélisation
Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance Marceau Coupechoux Telecom ParisTech, departement Informatique et Réseaux marceau.coupechoux@telecom-paristech.fr IT.2403 Modélisation
The Timing Capacity of Single-Server Queues with Multiple Flows
 The Timing Capacity of Single-Server Queues with Multiple Flows Xin Liu and R. Srikant Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign March 14, 2003 Timing Channel Information
The Timing Capacity of Single-Server Queues with Multiple Flows Xin Liu and R. Srikant Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign March 14, 2003 Timing Channel Information
Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.
![Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0. Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.](/thumbs/95/124116804.jpg) IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
Traffic signal design-ii
 CHAPTER 4. TRAFFIC SIGNAL DESIGN-II NPTEL May 3, 007 Chapter 4 Traffic signal design-ii 4.1 Overview In the previous chapter, a simple design of cycle time was discussed. Here we will discuss how the cycle
CHAPTER 4. TRAFFIC SIGNAL DESIGN-II NPTEL May 3, 007 Chapter 4 Traffic signal design-ii 4.1 Overview In the previous chapter, a simple design of cycle time was discussed. Here we will discuss how the cycle
CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks. Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory
 CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory Definition Queuing system: a buffer (waiting room), service facility (one or more servers) a scheduling policy
CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory Definition Queuing system: a buffer (waiting room), service facility (one or more servers) a scheduling policy
Review of Queuing Models
 Review of Queuing Models Recitation, Apr. 1st Guillaume Roels 15.763J Manufacturing System and Supply Chain Design http://michael.toren.net/slides/ipqueue/slide001.html 2005 Guillaume Roels Outline Overview,
Review of Queuing Models Recitation, Apr. 1st Guillaume Roels 15.763J Manufacturing System and Supply Chain Design http://michael.toren.net/slides/ipqueue/slide001.html 2005 Guillaume Roels Outline Overview,
Queueing Theory and Simulation. Introduction
 Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University, Japan
Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University, Japan
Chapter 5: Special Types of Queuing Models
 Chapter 5: Special Types of Queuing Models Some General Queueing Models Discouraged Arrivals Impatient Arrivals Bulk Service and Bulk Arrivals OR37-Dr.Khalid Al-Nowibet 1 5.1 General Queueing Models 1.
Chapter 5: Special Types of Queuing Models Some General Queueing Models Discouraged Arrivals Impatient Arrivals Bulk Service and Bulk Arrivals OR37-Dr.Khalid Al-Nowibet 1 5.1 General Queueing Models 1.
Queueing systems. Renato Lo Cigno. Simulation and Performance Evaluation Queueing systems - Renato Lo Cigno 1
 Queueing systems Renato Lo Cigno Simulation and Performance Evaluation 2014-15 Queueing systems - Renato Lo Cigno 1 Queues A Birth-Death process is well modeled by a queue Indeed queues can be used to
Queueing systems Renato Lo Cigno Simulation and Performance Evaluation 2014-15 Queueing systems - Renato Lo Cigno 1 Queues A Birth-Death process is well modeled by a queue Indeed queues can be used to
Random Walk on a Graph
 IOR 67: Stochastic Models I Second Midterm xam, hapters 3 & 4, November 2, 200 SOLUTIONS Justify your answers; show your work.. Random Walk on a raph (25 points) Random Walk on a raph 2 5 F B 3 3 2 Figure
IOR 67: Stochastic Models I Second Midterm xam, hapters 3 & 4, November 2, 200 SOLUTIONS Justify your answers; show your work.. Random Walk on a raph (25 points) Random Walk on a raph 2 5 F B 3 3 2 Figure
Homework 1 - SOLUTION
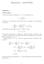 Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Control of Fork-Join Networks in Heavy-Traffic
 in Heavy-Traffic Asaf Zviran Based on MSc work under the guidance of Rami Atar (Technion) and Avishai Mandelbaum (Technion) Industrial Engineering and Management Technion June 2010 Introduction Network
in Heavy-Traffic Asaf Zviran Based on MSc work under the guidance of Rami Atar (Technion) and Avishai Mandelbaum (Technion) Industrial Engineering and Management Technion June 2010 Introduction Network
Readings: Finish Section 5.2
 LECTURE 19 Readings: Finish Section 5.2 Lecture outline Markov Processes I Checkout counter example. Markov process: definition. -step transition probabilities. Classification of states. Example: Checkout
LECTURE 19 Readings: Finish Section 5.2 Lecture outline Markov Processes I Checkout counter example. Markov process: definition. -step transition probabilities. Classification of states. Example: Checkout
MSA 640 Homework #2 Due September 17, points total / 20 points per question Show all work leading to your answers
 Name MSA 640 Homework #2 Due September 17, 2010 100 points total / 20 points per question Show all work leading to your answers 1. The annual demand for a particular type of valve is 3,500 units. The cost
Name MSA 640 Homework #2 Due September 17, 2010 100 points total / 20 points per question Show all work leading to your answers 1. The annual demand for a particular type of valve is 3,500 units. The cost
On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour
 On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour Bin Hu Saif Benjaafar Department of Operations and Management Science, Ross School of Business, University of Michigan at Ann Arbor,
On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour Bin Hu Saif Benjaafar Department of Operations and Management Science, Ross School of Business, University of Michigan at Ann Arbor,
CHAPTER 2. CAPACITY OF TWO-WAY STOP-CONTROLLED INTERSECTIONS
 CHAPTER 2. CAPACITY OF TWO-WAY STOP-CONTROLLED INTERSECTIONS 1. Overview In this chapter we will explore the models on which the HCM capacity analysis method for two-way stop-controlled (TWSC) intersections
CHAPTER 2. CAPACITY OF TWO-WAY STOP-CONTROLLED INTERSECTIONS 1. Overview In this chapter we will explore the models on which the HCM capacity analysis method for two-way stop-controlled (TWSC) intersections
IOE 202: lectures 11 and 12 outline
 IOE 202: lectures 11 and 12 outline Announcements Last time... Queueing models intro Performance characteristics of a queueing system Steady state analysis of an M/M/1 queueing system Other queueing systems,
IOE 202: lectures 11 and 12 outline Announcements Last time... Queueing models intro Performance characteristics of a queueing system Steady state analysis of an M/M/1 queueing system Other queueing systems,
Optimal Sleeping Mechanism for Multiple Servers with MMPP-Based Bursty Traffic Arrival
 1 Optimal Sleeping Mechanism for Multiple Servers with MMPP-Based Bursty Traffic Arrival Zhiyuan Jiang, Bhaskar Krishnamachari, Sheng Zhou, arxiv:1711.07912v1 [cs.it] 21 Nov 2017 Zhisheng Niu, Fellow,
1 Optimal Sleeping Mechanism for Multiple Servers with MMPP-Based Bursty Traffic Arrival Zhiyuan Jiang, Bhaskar Krishnamachari, Sheng Zhou, arxiv:1711.07912v1 [cs.it] 21 Nov 2017 Zhisheng Niu, Fellow,
A cork model for parking
 A cork model for parking Marco Alderighi U. Valle d Aosta SIET 2013 Venezia Marco Alderighi U. Valle d Aosta () Cork model SIET 2013 Venezia 1 / 26 The problem Many facilities, such as department stores,
A cork model for parking Marco Alderighi U. Valle d Aosta SIET 2013 Venezia Marco Alderighi U. Valle d Aosta () Cork model SIET 2013 Venezia 1 / 26 The problem Many facilities, such as department stores,
A TANDEM QUEUEING SYSTEM WITH APPLICATIONS TO PRICING STRATEGY. Wai-Ki Ching. Tang Li. Sin-Man Choi. Issic K.C. Leung
 Manuscript submitted to AIMS Journals Volume X, Number 0X, XX 00X Website: http://aimsciences.org pp. X XX A TANDEM QUEUEING SYSTEM WITH APPLICATIONS TO PRICING STRATEGY WAI-KI CHING SIN-MAN CHOI TANG
Manuscript submitted to AIMS Journals Volume X, Number 0X, XX 00X Website: http://aimsciences.org pp. X XX A TANDEM QUEUEING SYSTEM WITH APPLICATIONS TO PRICING STRATEGY WAI-KI CHING SIN-MAN CHOI TANG
Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits. IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015
 Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015 Outline Deterministic Fluid Models Directly From Data: Cumulative
Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015 Outline Deterministic Fluid Models Directly From Data: Cumulative
Conception of effective number of lanes as basis of traffic optimization
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 91 (016 ) 94 100 Information Technology and Quantitative Management (ITQM 016) Conception of effective number of lanes
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 91 (016 ) 94 100 Information Technology and Quantitative Management (ITQM 016) Conception of effective number of lanes
Queuing Theory. 3. Birth-Death Process. Law of Motion Flow balance equations Steady-state probabilities: , if
 1 Queuing Theory 3. Birth-Death Process Law of Motion Flow balance equations Steady-state probabilities: c j = λ 0λ 1...λ j 1 µ 1 µ 2...µ j π 0 = 1 1+ j=1 c j, if j=1 c j is finite. π j = c j π 0 Example
1 Queuing Theory 3. Birth-Death Process Law of Motion Flow balance equations Steady-state probabilities: c j = λ 0λ 1...λ j 1 µ 1 µ 2...µ j π 0 = 1 1+ j=1 c j, if j=1 c j is finite. π j = c j π 0 Example
Quiz Queue II. III. ( ) ( ) =1.3333
 Quiz Queue UMJ, a mail-order company, receives calls to place orders at an average of 7.5 minutes intervals. UMJ hires one operator and can handle each call in about every 5 minutes on average. The inter-arrival
Quiz Queue UMJ, a mail-order company, receives calls to place orders at an average of 7.5 minutes intervals. UMJ hires one operator and can handle each call in about every 5 minutes on average. The inter-arrival
The effect of probabilities of departure with time in a bank
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 3, Issue 7, July-2012 The effect of probabilities of departure with time in a bank Kasturi Nirmala, Shahnaz Bathul Abstract This paper
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 3, Issue 7, July-2012 The effect of probabilities of departure with time in a bank Kasturi Nirmala, Shahnaz Bathul Abstract This paper
Section 1.2: A Single Server Queue
 Section 12: A Single Server Queue Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course c 2006 Pearson Ed, Inc 0-13-142917-5 Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course Section 12: A Single Server Queue 1/ 30 Section
Section 12: A Single Server Queue Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course c 2006 Pearson Ed, Inc 0-13-142917-5 Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course Section 12: A Single Server Queue 1/ 30 Section
Tales of Time Scales. Ward Whitt AT&T Labs Research Florham Park, NJ
 Tales of Time Scales Ward Whitt AT&T Labs Research Florham Park, NJ New Book Stochastic-Process Limits An Introduction to Stochastic-Process Limits and Their Application to Queues Springer 2001 I won t
Tales of Time Scales Ward Whitt AT&T Labs Research Florham Park, NJ New Book Stochastic-Process Limits An Introduction to Stochastic-Process Limits and Their Application to Queues Springer 2001 I won t
A Study on Performance Analysis of Queuing System with Multiple Heterogeneous Servers
 UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA GENERAL EXAM REPORT A Study on Performance Analysis of Queuing System with Multiple Heterogeneous Servers Prepared by HUSNU SANER NARMAN husnu@ou.edu based on the papers 1) F. S.
UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA GENERAL EXAM REPORT A Study on Performance Analysis of Queuing System with Multiple Heterogeneous Servers Prepared by HUSNU SANER NARMAN husnu@ou.edu based on the papers 1) F. S.
Traffic Flow Theory & Simulation
 Traffic Flow Theory & Simulation S.P. Hoogendoorn Lecture 4 Shockwave theory Shockwave theory I: Introduction Applications of the Fundamental Diagram February 14, 2010 1 Vermelding onderdeel organisatie
Traffic Flow Theory & Simulation S.P. Hoogendoorn Lecture 4 Shockwave theory Shockwave theory I: Introduction Applications of the Fundamental Diagram February 14, 2010 1 Vermelding onderdeel organisatie
Queuing Theory. Queuing Theory. Fatih Cavdur April 27, 2015
 Queuing Theory Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr April 27, 2015 Introduction Introduction Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical model is the single-server
Queuing Theory Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr April 27, 2015 Introduction Introduction Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical model is the single-server
On the Resource/Performance Tradeoff in Large Scale Queueing Systems
 On the Resource/Performance Tradeoff in Large Scale Queueing Systems David Gamarnik MIT Joint work with Patrick Eschenfeldt, John Tsitsiklis and Martin Zubeldia (MIT) High level comments High level comments
On the Resource/Performance Tradeoff in Large Scale Queueing Systems David Gamarnik MIT Joint work with Patrick Eschenfeldt, John Tsitsiklis and Martin Zubeldia (MIT) High level comments High level comments
Data analysis and stochastic modeling
 Data analysis and stochastic modeling Lecture 7 An introduction to queueing theory Guillaume Gravier guillaume.gravier@irisa.fr with a lot of help from Paul Jensen s course http://www.me.utexas.edu/ jensen/ormm/instruction/powerpoint/or_models_09/14_queuing.ppt
Data analysis and stochastic modeling Lecture 7 An introduction to queueing theory Guillaume Gravier guillaume.gravier@irisa.fr with a lot of help from Paul Jensen s course http://www.me.utexas.edu/ jensen/ormm/instruction/powerpoint/or_models_09/14_queuing.ppt
Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains
 Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains Random variables describe the behaviour of a phenomenon independent of any specific sample space Distribution function (cdf, cumulative distribution function)
Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains Random variables describe the behaviour of a phenomenon independent of any specific sample space Distribution function (cdf, cumulative distribution function)
The Performance Impact of Delay Announcements
 The Performance Impact of Delay Announcements Taking Account of Customer Response IEOR 4615, Service Engineering, Professor Whitt Supplement to Lecture 21, April 21, 2015 Review: The Purpose of Delay Announcements
The Performance Impact of Delay Announcements Taking Account of Customer Response IEOR 4615, Service Engineering, Professor Whitt Supplement to Lecture 21, April 21, 2015 Review: The Purpose of Delay Announcements
Control experiments for a network of signalized intersections using the.q simulator
 Control experiments for a network of signalized intersections using the.q simulator Jennie Lioris Alexander A. Kurzhanskiy Pravin Varaiya California PATH, University of California, Berkeley Abstract: The
Control experiments for a network of signalized intersections using the.q simulator Jennie Lioris Alexander A. Kurzhanskiy Pravin Varaiya California PATH, University of California, Berkeley Abstract: The
Queuing Theory. Using the Math. Management Science
 Queuing Theory Using the Math 1 Markov Processes (Chains) A process consisting of a countable sequence of stages, that can be judged at each stage to fall into future states independent of how the process
Queuing Theory Using the Math 1 Markov Processes (Chains) A process consisting of a countable sequence of stages, that can be judged at each stage to fall into future states independent of how the process
A STUDY OF TRAFFIC PERFORMANCE MODELS UNDER AN INCIDENT CONDITION
 A STUDY OF TRAFFIC PERFORMANCE MODELS UNDER AN INCIDENT CONDITION We-Min Chow, IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center, Yorktown Heights, New York When an incident occurs on a roadway, traffic performance
A STUDY OF TRAFFIC PERFORMANCE MODELS UNDER AN INCIDENT CONDITION We-Min Chow, IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center, Yorktown Heights, New York When an incident occurs on a roadway, traffic performance
Delay of Incidents Consequences of Stochastic Incident Duration
 Delay of Incidents Consequences of Stochastic Incident Duration Victor L. Knoop 1, Serge P. Hoogendoorn 1, and Henk J. van Zuylen 1 Delft University of Technology & TRIL research School, Stevinweg 1, 68
Delay of Incidents Consequences of Stochastic Incident Duration Victor L. Knoop 1, Serge P. Hoogendoorn 1, and Henk J. van Zuylen 1 Delft University of Technology & TRIL research School, Stevinweg 1, 68
GI/M/1 and GI/M/m queuing systems
 GI/M/1 and GI/M/m queuing systems Dmitri A. Moltchanov moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/tlt-2716/ OUTLINE: GI/M/1 queuing system; Methods of analysis; Imbedded Markov chain approach; Waiting
GI/M/1 and GI/M/m queuing systems Dmitri A. Moltchanov moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/tlt-2716/ OUTLINE: GI/M/1 queuing system; Methods of analysis; Imbedded Markov chain approach; Waiting
Queueing Theory II. Summary. ! M/M/1 Output process. ! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages. ! General Distributions
 Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
Solutions. Some of the problems that might be encountered in collecting data on check-in times are:
 Solutions Chapter 7 E7.1 Some of the problems that might be encountered in collecting data on check-in times are: Need to collect separate data for each airline (time and cost). Need to collect data for
Solutions Chapter 7 E7.1 Some of the problems that might be encountered in collecting data on check-in times are: Need to collect separate data for each airline (time and cost). Need to collect data for
NICTA Short Course. Network Analysis. Vijay Sivaraman. Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains. Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1
 NICTA Short Course Network Analysis Vijay Sivaraman Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1 Outline Why a short course on mathematical analysis? Limited current course offering
NICTA Short Course Network Analysis Vijay Sivaraman Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1 Outline Why a short course on mathematical analysis? Limited current course offering
YORK UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS MATH , YEAR APPLIED OPTIMIZATION (TEST #4 ) (SOLUTIONS)
 YORK UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Instructor : Dr. Igor Poliakov MATH 4570 6.0, YEAR 2006-07 APPLIED OPTIMIZATION (TEST #4 ) (SOLUTIONS) March 29, 2007 Name (print)
YORK UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Instructor : Dr. Igor Poliakov MATH 4570 6.0, YEAR 2006-07 APPLIED OPTIMIZATION (TEST #4 ) (SOLUTIONS) March 29, 2007 Name (print)
CHAPTER 4. Networks of queues. 1. Open networks Suppose that we have a network of queues as given in Figure 4.1. Arrivals
 CHAPTER 4 Networks of queues. Open networks Suppose that we have a network of queues as given in Figure 4.. Arrivals Figure 4.. An open network can occur from outside of the network to any subset of nodes.
CHAPTER 4 Networks of queues. Open networks Suppose that we have a network of queues as given in Figure 4.. Arrivals Figure 4.. An open network can occur from outside of the network to any subset of nodes.
Impact of Day-to-Day Variability of Peak Hour Volumes on Signalized Intersection Performance
 Impact of Day-to-Day Variability of Peak Hour Volumes on Signalized Intersection Performance Bruce Hellinga, PhD, PEng Associate Professor (Corresponding Author) Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
Impact of Day-to-Day Variability of Peak Hour Volumes on Signalized Intersection Performance Bruce Hellinga, PhD, PEng Associate Professor (Corresponding Author) Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
