The Tectonics, Geology and Gold-Copper Metallogeny of New Guinea
|
|
|
- Ruby Mitchell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Tectonics, Geology and Gold-Copper Metallogeny of New Guinea STEVE GARWIN Independent Consultant Grasberg open-pit, circa th March, 2015 PACRIM 2015, Hong Kong China
2 Tectonic Elements, Cenozoic Magmatic Arcs and Major Au-Cu Deposits Shown on Sea-floor Bathymetry and DEM SE Asia and the W Pacific (Garwin et al., 2005 and Garwin, 2013)
3 GOLD DEPOSITS AGE & GOLD CONTENT SE Asia and the W Pacific Gold Content (tonnes) Wafi Golpu Age (million years)
4 Copper Content (1000 s tonnes) COPPER DEPOSITS AGE & Cu CONTENT SE Asia and the W Pacific Wafi Golpu (9000) Age (million years)
5 New Guinea Tectonic Framework Structural Preparation to Au-Cu mineralization Major plate reorganizations at c. 25 Ma and 5 Ma Maramuni arc and Medial New Guinea magmatic belt Miocene to Pleistocene magmatism (~ 20 1 Ma) Au-Cu mineralization from about 14 to 1 Ma Arc-transverse fault zones that control magmatism structural link to the mantle Mineralization follows southerly propagation of thrust-front Fault inversion along craton margin & crustal delamination Region of contraction / uplift / exhumation Structural settings favorable to focus heat- and fluid-flow
6 Tectonic Framework for New Guinea Presentday Wafi >10 M Oz Au Resource > 5 M Oz Au Resource Medial New Guinea Magmatic Belt (6 1 Ma) Maramuni Arc (Miocene) (Garwin et al., 2005; Garwin, 2013)
7 Major Gold and Copper Deposits / Districts (Garwin et al., 2005) >10 M Oz Au Resource > 5 M Oz Au Resource
8 New Guinea Regional Tectonic Setting Presentday >10 M Oz Au Resource > 5 M Oz Au Resource (Hall, 2002 and Garwin et al., 2005)
9 New Guinea Tectonic Reconstruction 25 Ma Arcs begin to collide with Australian plate. Ontong Java plateau collides with Melanesian arc. Sula Spur collides with Sundaland. PSF initiated In Bird s Head. (Hall, 2002 and Garwin et al., 2005)
10 New Guinea Tectonic Reconstruction 15 Ma SF splays cause collisions in eastern Sulawesi. S. Caroline arc terranes collide with New Guinea, but move in a leftlateral strike-slip zone. Subduction of the Solomon Sea beneath eastern New Guinea forms the Maramuni arc (c. 20 Ma). (Hall, 2002 and Garwin et al., 2005)
11 New Guinea Tectonic Reconstruction 5 Ma Bismarck sea opens. Woodlark basin spreading begins. Further accretion of arc terranes and significant uplift of mountains. Hinge rollback at the western end of New Guinea induces spreading in the Banda sea. (Hall, 2002 and Garwin et al., 2005) Australian craton approaches Indonesia, before collision with Banda arc at ~ 4 to 3 Ma.
12 New Guinea Tectonic Model Jurassic Architecture (Hill and Hall, 2003)
13 New Guinea Tectonic Models 25 and 15 Ma Arc collision with the continental margin of Australia. New Guinea margin changes from convergent to strike-slip dominant. 25 Ma Oblique subduction of the Solomon sea plate gave rise to Maramuni arc in eastern New Guinea. No south-dipping slab in western New Guinea at this time; a remnant slab may have dipped towards the north in Indonesia. 15 Ma Wafi, Freida (Hill and Hall, 2003)
14 New Guinea Tectonic Models 5 and 3-2 Ma 5 Ma Variable crust types effect extent of thrusting and uplift in western and eastern New Guinea. Convergence of the Caroline arc with New Guinea from about 12 Ma causes thrusting in the mobile belt and fold belt but ongoing strike-slip motion between the mobile belt and the accreted arc terranes. Plio-Pleistocene: local extensional reactivation of NEtrending basement faults provides link to mantle. Compression gives way to strike-slip faulting at 3-2 Ma. 3-2 Ma (Hill and Hall, 2003)
15 Papua New Guinea and Papua, Indonesia Au (Cu) Deposits and Settings (Garwin et al., 2005) Golpu >10 M Oz Au Resource > 5 M Oz Au Resource
16 Papua New Guinea Basement Faults and Cross- Sructures >10 M Oz Au Resource (Hill, 1991 and Gow and Walshe, 2005)
17 Neogene Thrust Inversion of Mesozoic Extensional Faults in Cratonic Basement Porgera Example (~ 6 Ma) (Hill et al., 2002)
18 Geodynamic Model for Structural Setting to Pliocene Cu-Au Deposits in Papuan Fold Belt of New Guinea (Hill et al., 2002)
19 Deposit and Magmatic Ages Versus Distance from Leading Basement Thrust 22 Maramuni Frieda 7 6 Wabu Porgera MNG 1 (Hill et al., 2002) and Davies (1991) Uplift / Exhumation rates of 0.7 to 1.7 mma- 1
20 Lithospheric-scale Cross Section for Central Range, Papuan Fold Belt Western New Guinea at 6 Ma. Comments Delamination commences at ~ 8 Ma and ceases at ~ 4 Ma ~ 1 mma 1 Thick-skinned Imbrication of cont. basement Craton GB PG Fold and Thrust Belt Thin-skinned Mapenduma anticline forms above reactivated normal faults Lithospheric mantle Asthenospheric mantle Transitional crust Mafic / alkaline magma pools near base of craton Early Jurassic oceanic crust Removal of lith. mantle leads to isostatic uplift (Cloos et al., 2005) Ideal setting for focused heatflow and intrusion-related mineralization
21 New Guinea Tectonic Framework Structural Preparation to Au-Cu Mineralization Major plate reorganizations at c. 25 Ma and 5 Ma Maramuni arc and Medial New Guinea magmatic belt Miocene to Pleistocene magmatism (~ 20 1 Ma) Au-Cu mineralization from about 14 to 1 Ma Arc-transverse fault zones that control magmatism structural link to the mantle Mineralization follows southerly propagation of thrust-front Fault inversion along craton margin & crustal delamination Region of contraction / uplift / exhumation Structural settings favorable to focus heat- and fluid-flow
22 New Guinea Gold-Copper Deposits Favorable Geological and Structural Settings Dilational zones in long-lived fault systems Zones of intersection between basement faults Basement high / dome / large-scale folds / horst-block Batholith / horst margins in zones of low mean-stress Reactive carbonate host-rocks as depositional traps
23 REFERENCES Carlile, J. C., and Mitchell, A. H. G., 1994, Magmatic arcs and associated gold and copper mineralization in Indonesia, in van Leeuwen T. M., Hedenquist, J. W., James, L. P., and Dow, J. A. S., eds., Mineral deposits of Indonesia; discoveries of the past 25 years., Journal of Geochemical Exploration v. 50; 1-3, p Cloos, M., Saphie, B., van Ufford, A.Q., Weiland, R.J., Warren, P.Q., and McMahon, T.P., 2005, Collisional delamination in New Guinea: The geotectonics of subducting slab breakoff, Geological Society of America, Special Paper 40, 50 p. Corbett, G. J., 1994, Regional structural control of selected Cu/Au occurrences in Papua New Guinea, in Rogerson, L., ed., Proceedings of the Papua New Guinea Geology, Mining and Exploration Conference: Lae, Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, Melbourne, p Corbett, G.J., and Leach, T.M., 1998, Southwest Pacific Rim gold-copper systems: Structure, alteration and mineralization, Society of Economic Geologists Special Publication 6, 240 p. Crowhurst, P. V., Hill, K. C., Foster, D. A., and Bennett, A. P., 1996, Thermochronological and geochemical constraints on the tectonic evolution of northern Papua New Guinea, in Hall, R., and Blundell Derek, J., eds., Tectonic evolution of Southeast Asia., 106. Geological Society Special Publications: London, United Kingdom, Geological Society of London, p Davies, H. L., 1991, Regional geologic setting of some mineral deposits of the New Guinea region, in Rogerson, R., ed., Proceedings of the Papua New Guinea Geology, Exploration and Mining Conference: Rabaul, Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, Melbourne, p Dow, D. B., 1977, A geological synthesis of Papua New Guinea: Australian Bureau of Mineral Resources Bulletin 201, Geology and Geophysics, 41 p. Dow, D. B., and Sukamto, R., 1984, Western Irian Jaya; the end-product of oblique plate convergence in the late Tertiary: Tectonophysics, v. 106, p
24 REFERENCES Fischer, M. W., and Warburton, J., 1996, The importance of pre-tertiary basin architecture for hydrocarbon accumulation in the Papuan fold and thrust belt; models, analogues and implications, in Buchanan Peter, G., ed., Petroleum exploration, development and production in Papua New Guinea; proceedings of the third PNG petroleum convention, Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea, PNG Chamber of Mines and Petroleum, p Garwin, S., Hall, R., and Watanabe, Y., Tectonic setting, geology and gold and copper mineralization in Cenozoic magmatic arcs of Southeast Asia and the west Pacific, in Hedenquist, J., Goldfarb, R. and Thompson, J. (eds.), Economic Geology 100 th Anniversary Volume, Society of Economic Geologists, p Garwin, S., 2013, Tectonic and structural controls to porphyry and epithermal mineralization in the Cenozoic magmatic arcs of Southeast Asia and the West Pacific, in Vearncombe, J. (compiler), Bulletin No. 57, Australian Institute of Geoscientists Symposium, May, 2013, Bali, Indonesia, p Gow, P.A., and Walshe, J.L., The role of pre-existing geologic architecture in the formation of giant porphyryrelated Cu + Au deposits: examples from New Guinea and Chile, Economic Geology, Society of Economic Geologists v. 100, pp Hall, R., 2002, Cenozoic geological and plate tectonic evolution of SE Asia and the SW Pacific: computer-based reconstructions, model and animations: Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, v. 20, p Hamilton, W., 1979, Tectonics of the Indonesian region: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper, v. 1078, p. 345 p. Hill, K. C., Kendrick, R. D., Crowhurst, P. V., and Gow, P. A., 2002, Copper-gold mineralisation in New Guinea; tectonics, lineaments, thermochronology and structure, in Korsch, R. J., ed., Geodynamics of Australia and its mineral systems; technologies, syntheses and regional studies, Blackwell Scientific Publications for the Geological Society of Australia. Melbourne, Australia, p Hill, K.C., and Hall, R., 2003, Mesozoic-Cenozoic evolution of Australia's New Guinea margin in a west Pacific context, Geological Society of America Special Papers, v. 372, p
25 REFERENCES Hutchison, C.S., 1989, Geological Evolution of Southeast Asia, Oxford Monographs on Geology and Geophysics, 13, Carendon Press, Oxford, United Kingdom, 368 p. McDowell, F. W., McMahon, T. P., Warren, P. Q., and Cloos, M., 1996, Pliocene Cu-Au-bearing igneous intrusions of the Gunung Bijih (Ertsberg) District, Irian Jaya, Indonesia; K-Ar geochronology: Journal of Geology, v. 104, p Pigram, C. J., and Davies, H. L., 1987, Terranes and the accretion history of the New Guinea Orogen: BMR Journal of Australian Geology and Geophysics, v. 10, p Rogerson, R., and McKee, C., 1990, Geology, volcanism and mineral deposits of Papua New Guinea, in Hughes, F. E., ed., Geology of the mineral deposits of Australia and Papua New Guinea; Volume 2., 14. Monograph Series - Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, p Sillitoe, R.H., and Hedenquist, J. W., 2003, Linkages between volcanotectonic settings, ore-fluid compositions, and epithermal precious-metal deposits, in Simmons, S. F., and Graham, I., eds., Giggenbach Volume, Special Publication 10, Society of Economic Geologists and Geochemical Society, p Weiland, R. J., and Cloos, M., 1996, Pliocene-Pleistocene asymmetric unroofing of the Irian fold belt, Irian Jaya, Indonesia; apatite fission-track thermochronology: Geological Society of America Bulletin, v. 108, p
Tectonic and Structural Controls to Porphyry and Epithermal Mineralization in Cenozoic Magmatic Arcs of SE Asia and the W Pacific
 Tectonic and Structural Controls to Porphyry and Epithermal Mineralization in Cenozoic Magmatic Arcs of SE Asia and the W Pacific STEVE GARWIN Independent Consultant sgar@iinet.net.au Grasberg, 24 Mt Cu
Tectonic and Structural Controls to Porphyry and Epithermal Mineralization in Cenozoic Magmatic Arcs of SE Asia and the W Pacific STEVE GARWIN Independent Consultant sgar@iinet.net.au Grasberg, 24 Mt Cu
The Sorong Fault Zone Kinematics: The Evidence of Divergence and Horsetail Structure at NW Bird's Head and Salawati Basin, West Papua, Indonesia*
 The Sorong Fault Zone Kinematics: The Evidence of Divergence and Horsetail Structure at NW Bird's Head and Salawati Basin, West Papua, Indonesia* Putri Riadini 1 and Benyamin Sapiie 2 Search and Discovery
The Sorong Fault Zone Kinematics: The Evidence of Divergence and Horsetail Structure at NW Bird's Head and Salawati Basin, West Papua, Indonesia* Putri Riadini 1 and Benyamin Sapiie 2 Search and Discovery
North America subducted under Rubia. Are there modern analogs for Hildebrand s model of North America subducting under Rubia?
 North America subducted under Rubia Are there modern analogs for Hildebrand s model of North America subducting under Rubia? In the Geological Society of America Special Papers Did Westward Subduction
North America subducted under Rubia Are there modern analogs for Hildebrand s model of North America subducting under Rubia? In the Geological Society of America Special Papers Did Westward Subduction
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education
 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
Topics Laramide Orogeny: Late Cretaceous to Early Eocene Reading: GSA DNAG volume 3, Ch. 6
 Topics Laramide Orogeny: Late Cretaceous to Early Eocene Reading: GSA DNAG volume 3, Ch. 6 Late Cretaceous to early Eocene New patterns developed 5 main regions Tectonic interpretations Post-Laramide events
Topics Laramide Orogeny: Late Cretaceous to Early Eocene Reading: GSA DNAG volume 3, Ch. 6 Late Cretaceous to early Eocene New patterns developed 5 main regions Tectonic interpretations Post-Laramide events
Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building
 Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building 1) A(n) fault has little or no vertical movements of the two blocks. A) stick slip B) oblique slip C) strike slip D) dip slip 2) In a(n) fault,
Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building 1) A(n) fault has little or no vertical movements of the two blocks. A) stick slip B) oblique slip C) strike slip D) dip slip 2) In a(n) fault,
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # Main Idea:
 Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
Evolution of Continents Chapter 20
 Evolution of Continents Chapter 20 Does not contain complete lecture notes. Mountain belts Orogenesis the processes that collectively produce a mountain belt Includes folding, thrust faulting, metamorphism,
Evolution of Continents Chapter 20 Does not contain complete lecture notes. Mountain belts Orogenesis the processes that collectively produce a mountain belt Includes folding, thrust faulting, metamorphism,
Global Tectonics. Kearey, Philip. Table of Contents ISBN-13: Historical perspective. 2. The interior of the Earth.
 Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Crustal Deformation and Mountain Building Chapter 17 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Jennifer
Essentials of Geology, 11e Crustal Deformation and Mountain Building Chapter 17 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Jennifer
Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms.
 Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
Geologic Structures. Changes in the shape and/or orientation of rocks in response to applied stress
 Geologic Structures Changes in the shape and/or orientation of rocks in response to applied stress Figure 15.19 Can be as big as a breadbox Or much bigger than a breadbox Three basic types Fractures >>>
Geologic Structures Changes in the shape and/or orientation of rocks in response to applied stress Figure 15.19 Can be as big as a breadbox Or much bigger than a breadbox Three basic types Fractures >>>
11.1 Rock Deformation
 Tarbuck Lutgens Mountain Building 11.1 Rock Deformation Factors Affecting Deformation Factors that influence the strength of a rock and how it will deform include temperature, confining pressure, rock
Tarbuck Lutgens Mountain Building 11.1 Rock Deformation Factors Affecting Deformation Factors that influence the strength of a rock and how it will deform include temperature, confining pressure, rock
Strike-Slip Faults. ! Fault motion is parallel to the strike of the fault.
 Strike-Slip Faults! Fault motion is parallel to the strike of the fault.! Usually vertical, no hanging-wall/footwall blocks.! Classified by the relative sense of motion. " Right lateral opposite block
Strike-Slip Faults! Fault motion is parallel to the strike of the fault.! Usually vertical, no hanging-wall/footwall blocks.! Classified by the relative sense of motion. " Right lateral opposite block
Overview of Indonesian Geothermal System
 Overview of Indonesian Geothermal System The Resources Beyond High Enthalpy Magmatic/Volcanic Systems By Dr.Eng. Suryantini ITB 4/3/2017 1 Outline Current Condition of Indonesian Geothermal Resources and
Overview of Indonesian Geothermal System The Resources Beyond High Enthalpy Magmatic/Volcanic Systems By Dr.Eng. Suryantini ITB 4/3/2017 1 Outline Current Condition of Indonesian Geothermal Resources and
Short course SC6: Porphyry copper-gold deposits in the circum-pacific and elsewhere
 Short course SC6: Porphyry copper-gold deposits in the circum-pacific and elsewhere Presenter Steve Garwin, email: sgar@iinet.net.au Date: Saturday 6 April one-day; 9:00 am - 5 pm Short course description
Short course SC6: Porphyry copper-gold deposits in the circum-pacific and elsewhere Presenter Steve Garwin, email: sgar@iinet.net.au Date: Saturday 6 April one-day; 9:00 am - 5 pm Short course description
Chapter 3. Geology & Tectonics
 Chapter 3 Geology & Tectonics 3.1 Geology The general geological features of Indonesia are shown in Figure 3.1. The basement formation is metamorphic and it is intruded with plutonic formations. They are
Chapter 3 Geology & Tectonics 3.1 Geology The general geological features of Indonesia are shown in Figure 3.1. The basement formation is metamorphic and it is intruded with plutonic formations. They are
Deformation of Rocks. Orientation of Deformed Rocks
 Deformation of Rocks Folds and faults are geologic structures caused by deformation. Structural geology is the study of the deformation of rocks and its effects. Fig. 7.1 Orientation of Deformed Rocks
Deformation of Rocks Folds and faults are geologic structures caused by deformation. Structural geology is the study of the deformation of rocks and its effects. Fig. 7.1 Orientation of Deformed Rocks
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 10 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 10 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 10 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Tectonic controls on magmatic-hydrothermal gold mineralization in the magmatic arcs of SE Asia and the SW Pacific
 Tectonic controls on magmatic-hydrothermal gold mineralization in the magmatic arcs of SE Asia and the SW Pacific M.E. Barley 1 and R. Hall 2 1 Centre for Exploration Targeting, School of Earth and Geographical
Tectonic controls on magmatic-hydrothermal gold mineralization in the magmatic arcs of SE Asia and the SW Pacific M.E. Barley 1 and R. Hall 2 1 Centre for Exploration Targeting, School of Earth and Geographical
Chapter 16. Mountain Building. Mountain Building. Mountains and Plate Tectonics. what s the connection?
 Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017
 ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
EXISTING GEOLOGICAL INFORMATION
 CHAPER 3 EXISTING GEOLOGICAL INFORMATION 3-1 General Geology of the Surrounding Area (1) General geology and ore deposits in Mongolia Geographically, Mongolia is a country located between Russia to the
CHAPER 3 EXISTING GEOLOGICAL INFORMATION 3-1 General Geology of the Surrounding Area (1) General geology and ore deposits in Mongolia Geographically, Mongolia is a country located between Russia to the
Cenozoic Magmatism and Mineral Deposits: Peru. Early Cenozoic. Cenozoic Tectonic Setting. Overview. Cenozoic Cordilleras
 Cenozoic Magmatism and Mineral Deposits: Peru Sarah Black Jay Zambito Chaudhry Ahmed Cenozoic Tectonic Setting Early Cenozoic http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/geology/tecall1_4.mov http://www.scotese.com/
Cenozoic Magmatism and Mineral Deposits: Peru Sarah Black Jay Zambito Chaudhry Ahmed Cenozoic Tectonic Setting Early Cenozoic http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/geology/tecall1_4.mov http://www.scotese.com/
Section 2: How Mountains Form
 Section 2: How Mountains Form Preview Objectives Mountain Ranges and Systems Plate Tectonics and Mountains Types of Mountains Objectives Identify the types of plate collisions that form mountains. Identify
Section 2: How Mountains Form Preview Objectives Mountain Ranges and Systems Plate Tectonics and Mountains Types of Mountains Objectives Identify the types of plate collisions that form mountains. Identify
Parts of the Sevier/ Laramide Orogeny
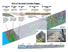 Parts of the Sevier/ Laramide Orogeny AA. Accretionary Prism BB. Forearc Basin Sediment scraped off of subducting plate Sediment derived from the volcanic arc CC. Volcanic Arc Magmatic intrusion into the
Parts of the Sevier/ Laramide Orogeny AA. Accretionary Prism BB. Forearc Basin Sediment scraped off of subducting plate Sediment derived from the volcanic arc CC. Volcanic Arc Magmatic intrusion into the
KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B
 GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
Mountain Building. Mountain Building
 Mountain Building Mountain building has occurred during the recent geologic past American Cordillera the western margin of the Americas from Cape Horn to Alaska Includes the Andes and Rocky Mountains Alpine
Mountain Building Mountain building has occurred during the recent geologic past American Cordillera the western margin of the Americas from Cape Horn to Alaska Includes the Andes and Rocky Mountains Alpine
Mountains are then built by deforming crust: Deformation & Mountain Building. Mountains form where stresses are high!
 Deformation & Mountain Building Where are mountains located? Deformation and Folding Mountain building Mountains form where stresses are high! Mountains form at all three types of plate boundaries where
Deformation & Mountain Building Where are mountains located? Deformation and Folding Mountain building Mountains form where stresses are high! Mountains form at all three types of plate boundaries where
Mineral Systems modelling in the Mount Isa Inlier, and its use in identification of permissive tracts for copper and lead/zinc mineralisation.
 Department of Natural Resources and Mines Mineral Systems modelling in the Mount Isa Inlier, and its use in identification of permissive tracts for copper and lead/zinc mineralisation. L.J.Hutton Geological
Department of Natural Resources and Mines Mineral Systems modelling in the Mount Isa Inlier, and its use in identification of permissive tracts for copper and lead/zinc mineralisation. L.J.Hutton Geological
Deformation of the Crust
 Deformation of the Crust Review Choose the best response. Write the letter of that choice in the space provided. 1. The state of balance between the thickness of the crust and the depth at which it rides
Deformation of the Crust Review Choose the best response. Write the letter of that choice in the space provided. 1. The state of balance between the thickness of the crust and the depth at which it rides
predictive mineral discovery*cooperative Research Centre A legacy for mineral exploration science Mineral Systems Q1 Architecture
 Mineral Systems Q1 Architecture 1 Key Parameter Mineral System Exploration is reflected in scale-dependent translation A. Gradient in hydraulic potential B. Permeability C. Solubility sensitivity to P,
Mineral Systems Q1 Architecture 1 Key Parameter Mineral System Exploration is reflected in scale-dependent translation A. Gradient in hydraulic potential B. Permeability C. Solubility sensitivity to P,
Directed Reading. Section: How Mountains Form MOUNTAIN RANGES AND SYSTEMS. Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How Mountains Form 1. How high is Mount Everest? a. about 1980 km above sea level b. more than 8 km below sea level c. more than 8 km above sea level d. more
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How Mountains Form 1. How high is Mount Everest? a. about 1980 km above sea level b. more than 8 km below sea level c. more than 8 km above sea level d. more
Plate Tectonics. Structure of the Earth
 Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
For personal use only
 Suite 2501 Level 25 St Martins Tower 31 Market Street Sydney NSW 2000 Australia (PO Box Q638 QVB Market Street NSW 1230 Australia) Tel: +61 (02) 9283 3880 ASX RELEASE GMN 05 March 2018 BONANZA GRADE TYPE
Suite 2501 Level 25 St Martins Tower 31 Market Street Sydney NSW 2000 Australia (PO Box Q638 QVB Market Street NSW 1230 Australia) Tel: +61 (02) 9283 3880 ASX RELEASE GMN 05 March 2018 BONANZA GRADE TYPE
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy)
 Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Mountains and Mountain Building: Chapter 11
 Mountains and Mountain Building: Chapter 11 Objectives: 1)Explain how some of Earth s major mountain belts formed 2) Compare and contrast active and passive continental margins 3) Explain how compression,
Mountains and Mountain Building: Chapter 11 Objectives: 1)Explain how some of Earth s major mountain belts formed 2) Compare and contrast active and passive continental margins 3) Explain how compression,
Geology of the Batemans Bay region. Geological evolution. The Lachlan Orogen
 Australian Journal of Earth Sciences 1 The word orogen is derived from the ancient Greek language word for mountain building. The Lachlan Orogen The rocks exposed in the Batemans Bay are part of the geological
Australian Journal of Earth Sciences 1 The word orogen is derived from the ancient Greek language word for mountain building. The Lachlan Orogen The rocks exposed in the Batemans Bay are part of the geological
Composition of the earth, Geologic Time, and Plate Tectonics
 Composition of the earth, Geologic Time, and Plate Tectonics Layers of the earth Chemical vs. Mechanical Chemical : Mechanical: 1) Core: Ni and Fe 2) Mantle: Mostly Peridotite 3) Crust: Many different
Composition of the earth, Geologic Time, and Plate Tectonics Layers of the earth Chemical vs. Mechanical Chemical : Mechanical: 1) Core: Ni and Fe 2) Mantle: Mostly Peridotite 3) Crust: Many different
FINAL EXAM Crustal Deformation CONVERGE DIVERGENT PLATES MANTLE PLUMES FLUX BASALTIC GRANITIC
 Crustal Deformation Reading: Chapter 10 Pages 283-304 Review Questions 4, 6, 7, 10, 12, 15, 18, 20 FINAL EXAM NOON TO 2 PM, TUESDAY DEC. 5 HERE: Natural Science 101 BRING A SCAN TRON TURN IN YOUR REVIEW
Crustal Deformation Reading: Chapter 10 Pages 283-304 Review Questions 4, 6, 7, 10, 12, 15, 18, 20 FINAL EXAM NOON TO 2 PM, TUESDAY DEC. 5 HERE: Natural Science 101 BRING A SCAN TRON TURN IN YOUR REVIEW
Continental Landscapes
 Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
The Lithosphere and the Tectonic System. The Structure of the Earth. Temperature 3000º ºC. Mantle
 The Lithosphere and the Tectonic System Objectives: Understand the structure of the planet Earth Review the geologic timescale as a point of reference for the history of the Earth Examine the major relief
The Lithosphere and the Tectonic System Objectives: Understand the structure of the planet Earth Review the geologic timescale as a point of reference for the history of the Earth Examine the major relief
Chapter 10: Deformation and Mountain Building. Fig. 10.1
 Chapter 10: Deformation and Mountain Building Fig. 10.1 OBJECTIVES Describe the processes of rock deformation and compare and contrast ductile and brittle behavior in rocks. Explain how strike and dip
Chapter 10: Deformation and Mountain Building Fig. 10.1 OBJECTIVES Describe the processes of rock deformation and compare and contrast ductile and brittle behavior in rocks. Explain how strike and dip
 Sedimentary Basin Analysis http://eqsun.geo.arizona.edu/geo5xx/geos517/ Sedimentary basins can be classified based on the type of plate motions (divergent, convergent), type of the lithosphere, distance
Sedimentary Basin Analysis http://eqsun.geo.arizona.edu/geo5xx/geos517/ Sedimentary basins can be classified based on the type of plate motions (divergent, convergent), type of the lithosphere, distance
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Structure of the western Brooks Range fold and thrust belt, Arctic Alaska
 Trabajos de Geología, Universidad de Oviedo, 29 : 218-222 (2009) Structure of the western Brooks Range fold and thrust belt, Arctic Alaska J. DE VERA 1* AND K. MCCLAY 2 1Now at: Shell, Rijswijk, Netherlands.
Trabajos de Geología, Universidad de Oviedo, 29 : 218-222 (2009) Structure of the western Brooks Range fold and thrust belt, Arctic Alaska J. DE VERA 1* AND K. MCCLAY 2 1Now at: Shell, Rijswijk, Netherlands.
Convergent plate boundaries. Objective to be able to explain the formation and key features of these zones.
 Convergent plate boundaries Objective to be able to explain the formation and key features of these zones. Destructive plate margins When plates collide due to convection currents/slab pull in the asthenosphere
Convergent plate boundaries Objective to be able to explain the formation and key features of these zones. Destructive plate margins When plates collide due to convection currents/slab pull in the asthenosphere
For personal use only
 12 September 2012 ASX RELEASE ASX Code: WAC FIRST PASS FIELD WORK COMPLETED AT PERU IOCG TARGETS Site visits and reconnaissance sampling has been completed at the Yauca and Chaparra Iron Oxide Copper Gold
12 September 2012 ASX RELEASE ASX Code: WAC FIRST PASS FIELD WORK COMPLETED AT PERU IOCG TARGETS Site visits and reconnaissance sampling has been completed at the Yauca and Chaparra Iron Oxide Copper Gold
Northern Chile, 170 km SE of Antofagasta Centred km S-SW of the giant La Escondida Mining District (BHP Billiton & Rio Tinto)
 October 2017 Block 3-Culebra is a large property block situated along the Domeyko Cordillera porphyry copper belt in northern Chile, which is host to some of the world s largest copper deposits and mines.
October 2017 Block 3-Culebra is a large property block situated along the Domeyko Cordillera porphyry copper belt in northern Chile, which is host to some of the world s largest copper deposits and mines.
Continental Margin Geology of Korea : Review and constraints on the opening of the East Sea (Japan Sea)
 Continental Margin Geology of Korea : Review and constraints on the opening of the East Sea (Japan Sea) Han-Joon Kim Marine Satellite & Observation Tech. Korea Ocean Research and Development Institute
Continental Margin Geology of Korea : Review and constraints on the opening of the East Sea (Japan Sea) Han-Joon Kim Marine Satellite & Observation Tech. Korea Ocean Research and Development Institute
For personal use only
 22 April 2013 Drilling to commence at Majada, Copper-Gold Prospect, Chile. Red Gum Resources Limited (ASX: RGX, Red Gum or the Company ) is pleased to announce that drilling of its Majada Copper-Gold Prospect,
22 April 2013 Drilling to commence at Majada, Copper-Gold Prospect, Chile. Red Gum Resources Limited (ASX: RGX, Red Gum or the Company ) is pleased to announce that drilling of its Majada Copper-Gold Prospect,
3. PLATE TECTONICS LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: PLATES
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: PLATES 3. PLATE TECTONICS The outer layers of the Earth are divided into the lithosphere and asthenosphere. The division is based on differences in mechanical properties
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: PLATES 3. PLATE TECTONICS The outer layers of the Earth are divided into the lithosphere and asthenosphere. The division is based on differences in mechanical properties
Basin Analysis. Stra-graphy
 Basin Analysis Stra-graphy Basin Analysis Basin analysis integrates program sedimentological, stra-graphic, and tectonic principals to develop a full understanding of the rocks that fill sedimentary basins.
Basin Analysis Stra-graphy Basin Analysis Basin analysis integrates program sedimentological, stra-graphic, and tectonic principals to develop a full understanding of the rocks that fill sedimentary basins.
The plate tectonics of Cenozoic SE Asia and the distribution of land and sea
 Cenozoic plate tectonics of SE Asia 99 The plate tectonics of Cenozoic SE Asia and the distribution of land and sea Robert Hall SE Asia Research Group, Department of Geology, Royal Holloway University
Cenozoic plate tectonics of SE Asia 99 The plate tectonics of Cenozoic SE Asia and the distribution of land and sea Robert Hall SE Asia Research Group, Department of Geology, Royal Holloway University
Contractional Tectonics: Convergence and Collision
 Contractional Tectonics: Convergence and Collision Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 4/12/2017 5:21 PM We Discuss Contractional Tectonics
Contractional Tectonics: Convergence and Collision Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 4/12/2017 5:21 PM We Discuss Contractional Tectonics
Plate Tectonics GEOL 101 Lecture 22 How Are Mountains Built?
 Plate Tectonics GEOL 101 Lecture 22 How Are Mountains Built? The Grand Tetons, Wyoming First a Brief Review of Sea Floor Spreading Prop: Test 3 Invitations Break-Up of a Continent and Origin of an Ocean
Plate Tectonics GEOL 101 Lecture 22 How Are Mountains Built? The Grand Tetons, Wyoming First a Brief Review of Sea Floor Spreading Prop: Test 3 Invitations Break-Up of a Continent and Origin of an Ocean
Plate Tectonics. By Destiny, Jarrek, Kaidence, and Autumn
 Plate Tectonics By Destiny, Jarrek, Kaidence, and Autumn .The Denali Fault and San Andreas Fault - The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly 1300 km (810 miles) through
Plate Tectonics By Destiny, Jarrek, Kaidence, and Autumn .The Denali Fault and San Andreas Fault - The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly 1300 km (810 miles) through
TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY BASINS, MECHANISM OF BASIN FORMATION & PETROLEUM HABITAT BY S. K.BISWAS
 TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY BASINS, MECHANISM OF BASIN FORMATION & PETROLEUM HABITAT BY S. K.BISWAS BASIN DEFINITION, CHARACTERISTICS & CLASSIFICATION A sedimentary basin is a structurally morphotectonic depression
TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY BASINS, MECHANISM OF BASIN FORMATION & PETROLEUM HABITAT BY S. K.BISWAS BASIN DEFINITION, CHARACTERISTICS & CLASSIFICATION A sedimentary basin is a structurally morphotectonic depression
Deep-Sea and Sub-Seafloor Resources: A Polymetallic Sulphide and Co-Mn Crust Perspective. Stephen Roberts
 Deep-Sea and Sub-Seafloor Resources: A Polymetallic Sulphide and Co-Mn Crust Perspective by Stephen Roberts The LRET Research Collegium Southampton, 16 July 7 September 2012 1 Deep-Sea and Sub-Seafloor
Deep-Sea and Sub-Seafloor Resources: A Polymetallic Sulphide and Co-Mn Crust Perspective by Stephen Roberts The LRET Research Collegium Southampton, 16 July 7 September 2012 1 Deep-Sea and Sub-Seafloor
Mesozoic-Cainozoic Evolution of Australia s New Guinea Margin. in a West Pacific Context *
 Mesozoic-Cainozoic Evolution of Australia s New Guinea Margin in a West Pacific Context * KEVIN C. HILL 1 AND ROBERT HALL 2 1 3D-GEO, School of Earth Sciences, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
Mesozoic-Cainozoic Evolution of Australia s New Guinea Margin in a West Pacific Context * KEVIN C. HILL 1 AND ROBERT HALL 2 1 3D-GEO, School of Earth Sciences, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
Chapter. Mountain Building
 Chapter Mountain Building 11.1 Rock Deformation Factors Affecting Deformation Factors that influence the strength of a rock and how it will deform include temperature, confining pressure, rock type, and
Chapter Mountain Building 11.1 Rock Deformation Factors Affecting Deformation Factors that influence the strength of a rock and how it will deform include temperature, confining pressure, rock type, and
Tectonic Setting, Geology, and Gold and Copper Mineralization in Cenozoic Magmatic Arcs of Southeast Asia and the West Pacific
 2005 Society of Economic Geologists, Inc. Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume pp. 891 930 Tectonic Setting, Geology, and Gold and Copper Mineralization in Cenozoic Magmatic Arcs of Southeast Asia
2005 Society of Economic Geologists, Inc. Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume pp. 891 930 Tectonic Setting, Geology, and Gold and Copper Mineralization in Cenozoic Magmatic Arcs of Southeast Asia
Mineral Systems and Exploration Targeting. T. Campbell McCuaig - Centre for Exploration Targeting
 Mineral Systems and Exploration Targeting T. Campbell McCuaig - Centre for Exploration Targeting Mineral Geoscience Masters October 2013 We will cover Mineral Systems as an organising framework to understand
Mineral Systems and Exploration Targeting T. Campbell McCuaig - Centre for Exploration Targeting Mineral Geoscience Masters October 2013 We will cover Mineral Systems as an organising framework to understand
Structural Evolution of Banda Arc, Eastern Indonesia: As a Future Indonesian Main Oil and Gas Development*
 Structural Evolution of Banda Arc, Eastern Indonesia: As a Future Indonesian Main Oil and Gas Development* Zaenal Holis 1, Agung Shirly Ponkarn 2, Agung Gunawan 2, Shinta Damayanti 2, and Brahmantyo K.
Structural Evolution of Banda Arc, Eastern Indonesia: As a Future Indonesian Main Oil and Gas Development* Zaenal Holis 1, Agung Shirly Ponkarn 2, Agung Gunawan 2, Shinta Damayanti 2, and Brahmantyo K.
Overview of the Seismic Source Characterization for the Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station
 Overview of the Seismic Source Characterization for the Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station Scott Lindvall SSC TI Team Lead Palo Verde SSC SSHAC Level 3 Project Tuesday, March 19, 2013 1 Questions from
Overview of the Seismic Source Characterization for the Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station Scott Lindvall SSC TI Team Lead Palo Verde SSC SSHAC Level 3 Project Tuesday, March 19, 2013 1 Questions from
PLATE TECTONICS. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Continental Drift- Wegener s Evidence
 Continental Drift PLATE TECTONICS E.B. Taylor (1910) and Alfred Wegener (1915) published on Continental Drift. Continental Drift Wegener s evidence 1. Fit of the Continents 2. Fossil Evidence 3. Rock Type
Continental Drift PLATE TECTONICS E.B. Taylor (1910) and Alfred Wegener (1915) published on Continental Drift. Continental Drift Wegener s evidence 1. Fit of the Continents 2. Fossil Evidence 3. Rock Type
Extension during late Neogene collision in east Indonesia and New Guinea
 Journal of the Virtual Explorer (2001), ISSN 1441-8126 Volume No. 4 Extension during late Neogene collision in east Indonesia and New Guinea ROBERT HALL SE Asia Research Group, Department of Geology, Royal
Journal of the Virtual Explorer (2001), ISSN 1441-8126 Volume No. 4 Extension during late Neogene collision in east Indonesia and New Guinea ROBERT HALL SE Asia Research Group, Department of Geology, Royal
Prospectivity Modelling of Mineralisation Systems in Papua New Guinea Using Weights of Evidence Techniques
 Prospectivity Modelling of Mineralisation Systems in Papua New Guinea Using Weights of Evidence Techniques K Peters 1 and G Partington 2 ABSTRACT A regional scale prospectivity model was developed for
Prospectivity Modelling of Mineralisation Systems in Papua New Guinea Using Weights of Evidence Techniques K Peters 1 and G Partington 2 ABSTRACT A regional scale prospectivity model was developed for
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway
 Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
CORPORATE UPDATE. Feasibility Study being finalised for completion towards the end of April.
 16 March 2018 Company Announcement Officer ASX Limited 20 Bridge Street SYDNEY NSW 2000 Highlights CORPORATE UPDATE Inaugural Bowdens Reserve Statement due early April. Feasibility Study being finalised
16 March 2018 Company Announcement Officer ASX Limited 20 Bridge Street SYDNEY NSW 2000 Highlights CORPORATE UPDATE Inaugural Bowdens Reserve Statement due early April. Feasibility Study being finalised
Geologic History of Texas: The Making of Texas Over 1.5 Billion Years
 # 4 Geologic History of Texas: The Making of Texas Over 1.5 Billion Years Dr. Richard Kyle March 24, 2000 Produced by and for Hot Science - Cool Talks by the Environmental Science Institute. We request
# 4 Geologic History of Texas: The Making of Texas Over 1.5 Billion Years Dr. Richard Kyle March 24, 2000 Produced by and for Hot Science - Cool Talks by the Environmental Science Institute. We request
The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and
 Earth s Structure The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and
Earth s Structure The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and
Predictive Mineral Discovery the Yilgarn gold story.. by Y4-A3-M9-F6 Project Members. predictive mineral discovery Cooperative Research Centre
 Predictive Mineral Discovery the Yilgarn gold story.. by Y4-A3-M9-F6 Project Members Continent Y4-A3-M9-F6 Craton Province Camp-district Deposit SESSION: YILGARN 11:20 Bruce Goleby Y4) Big system big picture:
Predictive Mineral Discovery the Yilgarn gold story.. by Y4-A3-M9-F6 Project Members Continent Y4-A3-M9-F6 Craton Province Camp-district Deposit SESSION: YILGARN 11:20 Bruce Goleby Y4) Big system big picture:
Aegeis deep structure & slab rollback in the Mediterranean
 Aegeis deep structure & slab rollback in the Mediterranean A paper for the Naxos field trip with Prof. Dr. Janos Urai, Summer Term 2014 Caspar Sinn, Martin Schlemmer August 31st, 2014 RWTH Aachen University,
Aegeis deep structure & slab rollback in the Mediterranean A paper for the Naxos field trip with Prof. Dr. Janos Urai, Summer Term 2014 Caspar Sinn, Martin Schlemmer August 31st, 2014 RWTH Aachen University,
SUMBA EXPLORATION UPDATE
 ASX RELEASE Tuesday, 23 November 2010 SUMBA EXPLORATION UPDATE Hillgrove Resources Limited (ASX:HGO) today announces a planned airborne geophysical survey, Pelitalira prospect progress and final results
ASX RELEASE Tuesday, 23 November 2010 SUMBA EXPLORATION UPDATE Hillgrove Resources Limited (ASX:HGO) today announces a planned airborne geophysical survey, Pelitalira prospect progress and final results
Towards a tectonic framework for the Gawler Craton. Martin Hand Justin Payne, Greg Swain, Karin Barovich, Rian Dutch, Anthony Reid, Mike Schwarz
 Martin Hand Justin Payne, Greg Swain, Karin Barovich, Rian Dutch, Anthony Reid, Mike Schwarz The tectonic evolution of is defined by two periods of tectonism both of which lead to apparent cratonisation.
Martin Hand Justin Payne, Greg Swain, Karin Barovich, Rian Dutch, Anthony Reid, Mike Schwarz The tectonic evolution of is defined by two periods of tectonism both of which lead to apparent cratonisation.
Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms
 Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms Structure of the Earth Lithosphere : earth s crust Asthenosphere : upper mantle zone where material is near its melting point & acts almost like liquid (appprox.
Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms Structure of the Earth Lithosphere : earth s crust Asthenosphere : upper mantle zone where material is near its melting point & acts almost like liquid (appprox.
PROCEEDINGS, INDONESIAN PETROLEUM ASSOCIATION Thirty-Eighth Annual Convention & Exhibition, May 2014
 IPA14-G-086 PROCEEDINGS, INDONESIAN PETROLEUM ASSOCIATION Thirty-Eighth Annual Convention & Exhibition, May 2014 DEVELOPMENT OF THE SORONG FAULT ZONE NORTH OF MISOOL EASTERN INDONESIA Afif Saputra* Robert
IPA14-G-086 PROCEEDINGS, INDONESIAN PETROLEUM ASSOCIATION Thirty-Eighth Annual Convention & Exhibition, May 2014 DEVELOPMENT OF THE SORONG FAULT ZONE NORTH OF MISOOL EASTERN INDONESIA Afif Saputra* Robert
The continental lithosphere
 Simplicity to complexity: The continental lithosphere Reading: Fowler p350-377 Sampling techniques Seismic refraction Bulk crustal properties, thickness velocity profiles Seismic reflection To image specific
Simplicity to complexity: The continental lithosphere Reading: Fowler p350-377 Sampling techniques Seismic refraction Bulk crustal properties, thickness velocity profiles Seismic reflection To image specific
WHAT IS PACRIM? To be held in Hong Kong in 2015 as a major initiative with the recently formed HK Branch.
 WHAT IS PACRIM? International congress of geoscience research and project case studies for mineralisation styles found around the Pacific Rim and from similar convergent tectonic settings through earth
WHAT IS PACRIM? International congress of geoscience research and project case studies for mineralisation styles found around the Pacific Rim and from similar convergent tectonic settings through earth
SCIENCE DISCOVERY GROWTH. Investor Presentation. Miga Arc Western Victoria s newly emerging copper belt
 SCIENCE DISCOVERY GROWTH Investor Presentation Miga Arc Western Victoria s newly emerging copper belt 23 October 2013 Forward-looking statement & disclaimer The information contained in this presentation
SCIENCE DISCOVERY GROWTH Investor Presentation Miga Arc Western Victoria s newly emerging copper belt 23 October 2013 Forward-looking statement & disclaimer The information contained in this presentation
Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Ch 19, Plate Tectonics Name
 Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Ch 19, Plate Tectonics Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The portion of a fracture
Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Ch 19, Plate Tectonics Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The portion of a fracture
10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves.
 Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
December 21, Chapter 11 mountain building E.notebook. Feb 19 8:19 AM. Feb 19 9:28 AM
 Mountains form along convergent plate boundaries. Typically (usually) if you look at a mountain range, you know that it is at a plate boundary (active continental margin) or has been some time in the past
Mountains form along convergent plate boundaries. Typically (usually) if you look at a mountain range, you know that it is at a plate boundary (active continental margin) or has been some time in the past
Geodynamics of congested subduction zones - implications for evolution of the Tasmanides
 Geodynamics of congested subduction zones - implications for evolution of the Tasmanides Pete Betts - School of Earth, Atmosphere, and environment, Monash University Louis Moresi Department of Earth Sciences,
Geodynamics of congested subduction zones - implications for evolution of the Tasmanides Pete Betts - School of Earth, Atmosphere, and environment, Monash University Louis Moresi Department of Earth Sciences,
Tectonic plates of the world
 Mountain Building Tectonic plates of the world ISOSTACY Isostatic Rebound crust rises as a result of removal of mass This iceberg also demonstrates the process of isostatic rebound. Types of Mountains
Mountain Building Tectonic plates of the world ISOSTACY Isostatic Rebound crust rises as a result of removal of mass This iceberg also demonstrates the process of isostatic rebound. Types of Mountains
Theory of Continental Drift
 Plate Tectonics Theory of Continental Drift Alfred Wegener suggested that continents had once been part of a supercontinent named Pangaea, that later broke up. The pieces moved apart over millions of years
Plate Tectonics Theory of Continental Drift Alfred Wegener suggested that continents had once been part of a supercontinent named Pangaea, that later broke up. The pieces moved apart over millions of years
Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009
 Name: Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009 Objective: Students will be introduced to the theory of plate tectonics and different styles of plate margins and interactions. Introduction The planet can be
Name: Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009 Objective: Students will be introduced to the theory of plate tectonics and different styles of plate margins and interactions. Introduction The planet can be
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES
 USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
Geology 15 West Valley College. Exam IV: Sierra Nevada
 Geology 15 West Valley College Name Exam IV: Sierra Nevada 1) On the diagram above, where is the Arc- Trench Gap? a. 1 and 3 c. 7 and 8 d. 6 e. 5 and 10 2) On the diagram above, where is the subduction
Geology 15 West Valley College Name Exam IV: Sierra Nevada 1) On the diagram above, where is the Arc- Trench Gap? a. 1 and 3 c. 7 and 8 d. 6 e. 5 and 10 2) On the diagram above, where is the subduction
6. In the diagram below, letters A and B represent locations near the edge of a continent.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
For personal use only
 ASX ANNOUNCEMENT ASX: IVG Date: 30 April 2012 Number: 030_300412 MARCH 2012 QUARTERLY REPORT SUMMARY Market Cap A$2.23m ($0.062 p/s) Issued Capital 36,006,006 Assay data and mineral alteration studies
ASX ANNOUNCEMENT ASX: IVG Date: 30 April 2012 Number: 030_300412 MARCH 2012 QUARTERLY REPORT SUMMARY Market Cap A$2.23m ($0.062 p/s) Issued Capital 36,006,006 Assay data and mineral alteration studies
Mesozoic Cenozoic evolution of Australia s New Guinea margin in a west Pacific context
 Geol. Soc. Australia Spec. Publ. 22, and Geol. Soc. America Spec. Pap. 372 (2003), 265 289 Mesozoic Cenozoic evolution of Australia s New Guinea margin in a west Pacific context K. C. HILL 1 * AND R. HALL
Geol. Soc. Australia Spec. Publ. 22, and Geol. Soc. America Spec. Pap. 372 (2003), 265 289 Mesozoic Cenozoic evolution of Australia s New Guinea margin in a west Pacific context K. C. HILL 1 * AND R. HALL
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Press & Siever, compressive forces. Compressive forces cause folding and faulting.
 Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Modelling Subduction Zone Seismogenic Hazards in Southeast Asia for Seismic Hazard Assessments
 Modelling Subduction Zone Seismogenic Hazards in Southeast Asia for Seismic Hazard Assessments Vicki-Ann Dimas 1,2 and Gary Gibson 3 1. Corresponding Author. Seismic Hazard Analyst, Seismology Research
Modelling Subduction Zone Seismogenic Hazards in Southeast Asia for Seismic Hazard Assessments Vicki-Ann Dimas 1,2 and Gary Gibson 3 1. Corresponding Author. Seismic Hazard Analyst, Seismology Research
TECTONIC AND STRUCTURAL CONTROLS ON INTRUSION- RELATED DEPOSITS IN THE NORTHERN PART OF SREDNA GORA ZONE, BULGARIA NIKOLAY PETROV & KAMELIA NEDKOVA
 TECTONIC AND STRUCTURAL CONTROLS ON INTRUSION- RELATED DEPOSITS IN THE NORTHERN PART OF SREDNA GORA ZONE, BULGARIA NIKOLAY PETROV & KAMELIA NEDKOVA INVESTIGATED AREA Praveshka Lakavica deposit Elatsite
TECTONIC AND STRUCTURAL CONTROLS ON INTRUSION- RELATED DEPOSITS IN THE NORTHERN PART OF SREDNA GORA ZONE, BULGARIA NIKOLAY PETROV & KAMELIA NEDKOVA INVESTIGATED AREA Praveshka Lakavica deposit Elatsite
OCN 201 Seafloor Spreading and Plate Tectonics. Question
 OCN 201 Seafloor Spreading and Plate Tectonics Question What was wrong from Wegener s theory of continental drift? A. The continents were once all connected in a single supercontinent B. The continents
OCN 201 Seafloor Spreading and Plate Tectonics Question What was wrong from Wegener s theory of continental drift? A. The continents were once all connected in a single supercontinent B. The continents
Learning Objectives (LO) What we ll learn today:!
 Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 13: Mountain Building Read: Chapter 10 Homework #11 due Tuesday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Define the types of stress that are present in the crust! 2. Define the
Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 13: Mountain Building Read: Chapter 10 Homework #11 due Tuesday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Define the types of stress that are present in the crust! 2. Define the
Plate Tectonics Practice Test
 Plate Tectonics Practice Test 1. What is the main idea Alfred Wegner proposed in the Theory of Continental Drift that he published in 1915? a. The continents float on a liquid layer that allows them to
Plate Tectonics Practice Test 1. What is the main idea Alfred Wegner proposed in the Theory of Continental Drift that he published in 1915? a. The continents float on a liquid layer that allows them to
Mineral Resources Research and Training at the University of Adelaide
 Mineral Resources Research and Training at the University of Adelaide David Giles School of Earth and Environmental Sciences Centre for Mineral Exploration Under Cover March 2007 Copyright 2007 The University
Mineral Resources Research and Training at the University of Adelaide David Giles School of Earth and Environmental Sciences Centre for Mineral Exploration Under Cover March 2007 Copyright 2007 The University
