Arctic Ocean-Sea Ice-Climate Interactions
|
|
|
- George Goodwin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Arctic Ocean-Sea Ice-Climate Interactions
2 Sea Ice Ice extent waxes and wanes with the seasons. Ice extent is at a maximum in March (typically 14 million square km, about twice the area of the contiguous United States) and about half that in September [data from NSIDC].
3 Ice extent is declining in all months, but most rapidly in September, the end of the melt season [courtesy NSIDC, Boulder, CO]. The modern satellite record starts in Ice extent for earlier years is determined from earlier types of satellite data (back to1972), aircraft and ship reports. Records back to 1953 are pretty good.
4 September ice extent (all colored regions) and anomalies in ice concentration (see color bar) for the years 2002 through Each panel shows the median September ice extent. Concentration anomalies and median extent are referenced to the period [courtesy NSIDC, Boulder, CO]. All of these Septembers were characterized by extreme negative anomalies in ice extent.
5 Sea ice formation, types and morphology
6 Temperature versus density plot for fresh water and ice at standard atmospheric pressure [from Maykut, 1985, by permission of Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington, Seattle, WA]. Water density increases with decreasing temperature until 3.98 deg. C. With further cooling, density decreases. Hence as a fresh water column cools from the surface, it initially sets up convection (overturning). One the entire column is at the temperature of maximum density, further cooling leads to a stable (stratified) situation (with the colder, lighter water at the top), and ice can form.
7 Courtesy John Wettlaufer, presented at 2007 Woods Hole GFD summer program
8 The effect of salinity on the temperature of maximum density (dashed curve) and the freezing point temperature (solid curve) [from Maykut, 1985, by permission of Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington, Seattle, WA]. With salinities above 24.7 psu (most ocean water is higher than this), the temperature of maximum density equals the freezing point of water. Salt in solution also depresses the freezing point. At 35 psu, the freezing point of water is -1.8 deg. C. Cooling at the surface increases the water density, and there will be overturning. However, because of pre-existing strong density gradients, only the top m of the water column needs to cool to the temperature of maximum density before ice can form.
9 At high water temperatures (> several C), density depends mainly on temperature. However, at water low temperatures near freezing (such as in the Arctic), density depends mainly on salinity
10 Temperature and salinity profiles for the Beaufort Sea and near the pole. The y-axis is depth in decibars (dbar), which closely approximates depth in meters [courtesy of J. Morison, Polar Science Center, University of Washington, Seattle, WA]. Note the low salinity very near the surface (the fresh surface layer), and the rapid increase in salinity from the surface downwards. This makes the water column stable (low density water at the top), which allows sea ice to readily form.
11 Terminology of oceanographers Thermocline: Strong vertical temperature gradient Halocline: Strong vertical salinity gradient Pycnocline: Strong vertical density gradient In the Arctic, the halocline forms the pycnocline
12 Sea ice formation sequence: frazil ice (small platelets, needles, < 3-4 mm) grease ice (1-10 cm thick) pancake ice pack ice
13 Courtesy John Wettlaufer, presented at 2007 Woods Hole GFD summer program
14 Top: Frazil ice, small needle-like ice crystals, typically 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter, suspended in water, represent the first stages of sea ice growth; they merge under calm conditions to form thin sheets of grease ice on the surface. Bottom: Grease ice [courtesy NSIDC, see for more]
15 Grease ice and small pancake ice Virginia Institute of Marine Science,
16 Small and medium pancake ice Virginia Institute of Marine Science,
17 Medium pancake ice Virginia Institute of Marine Science,
18 Large pancake ice forming pack ice Virginia Institute of Marine Science,
19 Pack ice Virginia Institute of Marine Science,
20 Iceberg in pack ice Virginia Institute of Marine Science,
21 Ridged (left) and undeformed (right) first-year ice, near Barrow. Ridging results from velocity convergence [photo by M. Serreze].
22 Top: Multiyear ice, defined as ice that has survived at least one melt season. Multiyear ice has a very low salinity (2 psu or so) and is a suitable source of drinking water. Bottom: A summer melt pond on sea ice. This is a shallow one. A deep one on multiyear ice can drown a snow machine [courtesy NSIDC, see for more.
23 Courtesy John Wettlaufer, presented at 2007 Woods Hole GFD summer program
24 Courtesy John Wettlaufer, presented at 2007 Woods Hole GFD summer program
25 Ice concentration for the Arctic and peripheral seas (see color bar) for the period 5-11 January, 1994, based on the analysis of the National Ice Center [courtesy K. Knowles, NSIDC]
26 Sea ice motion, thickness and deformation
27 Mean annual sea ice drift in the Arctic, based on data from the IABP, the North Pole program and other sources with overlay of sea level pressure from NCEP/NCAR [ice drift field courtesy of I. Rigor, Polar Science Center, University of Washington, Seattle, WA]. Since ice responds to wind forcing, the mean drift pattern broadly relates to the sea level pressure distribution. Ice export from the Arctic Ocean to the North Atlantic is primarily through Fram Strait, between Greenland and Svalbard.
28 Ice motion can be quite variable at daily to monthly time scales. This map shows the mean pattern of sea ice drift in the Arctic for January 1991 based on SSM/I retrievals with overlay of mean sea level pressure from NCEP/NCAR [ice drift field courtesy of C. Fowler, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO, sea level pressure field by the authors].
29 Mean pattern of sea ice drift in the Arctic for January 1989 based on SSM/I retrievals with overlay of sea level pressure from NCEP/NCAR [ice drift field courtesy of C. Fowler, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO, sea level pressure field by the authors]. Note the very different pattern of ice motion compared to that shown on the previous slide.
30 MODIS satellite image showing the shear zone along the coast of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. North is roughly to the right. Axel Heiburg Island is at the bottom. The image covers an area of approximately 526 km by 376 km, with a resolution of 250 m [courtesy of T. Haran, NSIDC, Boulder, CO].
31 Estimated distribution of mean winter sea ice thickness in the Arctic based in part on under-ice submarine sonar data [from Bourke and Garrett, 1987, by permission of Elsevier]. The ice is thickest along the coast of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago where the mean drift pattern promotes ridging.
32 Ice thickness estimated for the late winters of 2006, 2007 and 2008 based on measurements taken by NASA's ICESat laser altimeter [from NSIDC, courtesy of Ron Kwok, JPL]. Thickness can vary quite a bit from year to year. This variability seems to be superposed upon a downward trend in ice thickness over recent decades.
33 Time series of sea ice divergence (in percent per day) in the vicinity of the SHEBA station calculated at four different spatial scales (average sizes) centered on the station, based on the RADARSAT RGPS [from Stern and Moritz, 2002, by permission of AGU]. Divergence (positive values in the plot) results on openings (leads) that in winter may quickly refreeze. Convergence results in closing (increased ice concentration) and ridging. Convergence/divergence is quite episodic in nature, with big events typically associated with the passage of weather systems and their associated wind patterns.
34 A pressure ridge in the Chukchi Sea resulting from convergent ice motion. This one is about 3 m wide and about 3 m high. Virginia Institute of Marine Science, Pice.html?svr=www See ridging animation:
35 Lead in Chukchi Sea about 25 m wide Virginia Institute of Marine Science,
36 Case studies: September ice extent for 2007 vs. 2008
37 Sept 14, 2008: 4.51 million sq. km Ice extent for September 2007 and 2008 was the lowest and second lowest, respectively, recorded in the satellite area. The map shows ice extent for at the September 2008 minimum (bluish) and for 2007 (yellow line), The time series at the bottom snow September ice extent from 1979 through 2008 and daily extent for 2007, 2008 and from climatology [from Serreze et al., 2008]. Sept 16, 2007: 4.13 million sq. km
38 Even More Young, Thin Ice than in Spring 2007 Estimated Ice Age from Tracking Algorithm The setup: For both years the melt season started out with lots of young, thin ice prone to melting out in summer [courtesy J. Maslanik, Univ. CO Boulder]
39 As seen in fields of temperature anomalies at the 925 hpa level, the melt season (May-August) was warm in 2008 (lots of melt) but not as warm as in This helps to explain the slightly higher ice extent for September 2008 compared to 2007 [J. Stroeve, NSIDC, and NOAA Climate Diagnostics Center]. The Melt Season was Not as Warm as in 2007
40 The warmer conditions over the 2007 melt season are related to a dipole anomaly circulation of the atmosphere at sea level, with high pressure centered north of the Beaufort Sea and low pressure over Eurasia. Winds between these two pressure features were strong and from the south, hence bringing in lots of heat into the Chukchi and East Siberian seas. The southerly winds also pushed ice away from the shore, leaving areas of open water. There was a also a dipole circulation in summer 2008, but not as well developed [J. Stroeve, NSIDC and NOAA Climate Diagnostics Center].
41 Compare and contrast the previous slides with the 925 hpa temperature anomaly and sea level pressure fields averaged for May-August of Air temperature anomalies are negative over much of the Arctic Ocean. There is no dipole anomaly, but rather a mean low pressure cell over the central Arctic Ocean. Sea ice extent in September 1996 was the highest for that month in the satellite record [NOAA Climate Diagnostics Center].
42 Sept 14, 2008: 4.51 million sq. km Ice extent for September 2007 and 2008 was the lowest and second lowest, respectively, recorded in the satellite area. The map shows ice extent for at the September 2008 minimum (bluish) and for 2007 (yellow line), The time series at the bottom snow September ice extent from 1979 through 2008 and daily extent for 2007, 2008 and from climatology [from Serreze et al., 2008]; Sept 16, 2007: 4.13 million sq. km
43 The Fram Strait outflow, the thermohaline circulation and the Arctic back door
44 Blue paths represent deepwater currents, red paths represent surface currents [courtesy Wikipdia]. Warm surface waters in the north Atlantic travel northward and then cool and sink in the Greenland/Iceland/Norwegian seas (the GIN seas). Disruption of this sinking in the GIN seas could have widespread climate effects. Changes in freshwater export via Fram Strait is a potential source of disruption. See the animation:
45 The Mean Annual Freshwater Budget of the Arctic The biggest oceanic sinks of freshwater in the Arctic Ocean are the transports of ice and low salinity water through Fram Strait and of low salinity water through the straits of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The biggest oceanic source of freshwater is the import of low salinity water through Bering Strait. From Serreze et al., 2006
46 Mean annual cycle of the ice volume flux through Fram Strait. The dotted line shows the parameterized mean monthly flux. The solid line shows the volume flux adjusted for the mean ice thickness observed from using upwardlooking sonar [from Vinje, 2001, by permission of AMS]. There is about a factor of two difference in the flux between winter and summer.
47 Mean patterns of sea ice drift in the Arctic for winter (top) and for summer, (bottom) based primarily on data from the IABP, the North Pole program and other sources with overlay of sea level pressure from NCEP/NCAR [ice drift field courtesy of I. Rigor, Polar Science Center, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, sea level pressure field by the authors]. Note he stronger ice flux through Fram Strait in winter, consistent with the stronger sea level pressure gradient across the strait and hence stronger winds.
48 Time series of the parameterized monthly ice volume flux through Fram Strait (grey columns) and the 12-month running mean (black line) [from Vinje, 2001, by permission of AMS]. The flux is quite variable.
49 Global mean surface salinity The North Atlantic is saltier than the north Pacific, hence sea surface height is higher in the North Pacific. This means a flow of water downhill from the Pacific to the Atlantic across the Arctic Ocean NOAA, World Ocean Atlas,
50 Conceptual model of the present-day atmospheric and oceanic transports and its consequences. DM is diapycnal mixing, PA (PP) is pressure in the Atlantic (Pacific) and S is salinity [from Stigebrandt, 2000, by permission of Springer-Verlag]. The upper conveyor is the back door, which transports low salinity water from the North Pacific through Bering Strait, through the Arctic Ocean and into the North Atlantic.
Arctic sea ice falls below 4 million square kilometers
 SOURCE : http://nsidc.org/arcticseaicenews/ Arctic sea ice falls below 4 million square kilometers September 5, 2012 The National Snow and Ice Data Center : Advancing knowledge of Earth's frozen regions
SOURCE : http://nsidc.org/arcticseaicenews/ Arctic sea ice falls below 4 million square kilometers September 5, 2012 The National Snow and Ice Data Center : Advancing knowledge of Earth's frozen regions
The Arctic Energy Budget
 The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
What makes the Arctic hot?
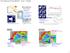 1/3 total USA UN Environ Prog What makes the Arctic hot? Local communities subsistence Arctic Shipping Routes? Decreasing Ice cover Sept 2007 -ice extent (Pink=1979-2000 mean min) Source: NSIDC Oil/Gas
1/3 total USA UN Environ Prog What makes the Arctic hot? Local communities subsistence Arctic Shipping Routes? Decreasing Ice cover Sept 2007 -ice extent (Pink=1979-2000 mean min) Source: NSIDC Oil/Gas
The Arctic Climate System GEOG 4271/5271. Mark C. Serreze Department of Geography University of Colorado, Boulder CO
 The Arctic Climate System GEOG 4271/5271 Mark C. Serreze Department of Geography University of Colorado, Boulder CO serreze@nsidc.org Why study the Arctic climate system? The fascinating processes that
The Arctic Climate System GEOG 4271/5271 Mark C. Serreze Department of Geography University of Colorado, Boulder CO serreze@nsidc.org Why study the Arctic climate system? The fascinating processes that
The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change. Renguang Wu
 The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change Renguang Wu Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing World Conference on Climate Change
The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change Renguang Wu Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing World Conference on Climate Change
 Page 1 of 10 Search NSIDC... Search Education Center Photo Gallery Home Data Programs & Projects Science Publications News & Events About Overview Global Temperatures Northern Hemisphere Snow Glaciers
Page 1 of 10 Search NSIDC... Search Education Center Photo Gallery Home Data Programs & Projects Science Publications News & Events About Overview Global Temperatures Northern Hemisphere Snow Glaciers
Causes of Changes in Arctic Sea Ice
 Causes of Changes in Arctic Sea Ice Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Outline 1. Rationale 2. Observational background 3. Modeling insights on Arctic change Pacific / Atlantic Water inflow 4.
Causes of Changes in Arctic Sea Ice Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Outline 1. Rationale 2. Observational background 3. Modeling insights on Arctic change Pacific / Atlantic Water inflow 4.
June Report: Outlook Based on May Data Regional Outlook: Beaufort and Chuckchi Seas, High Arctic, and Northwest Passage
 June Report: Outlook Based on May Data Regional Outlook: Beaufort and Chuckchi Seas, High Arctic, and Northwest Passage Charles Fowler, Sheldon Drobot, James Maslanik; University of Colorado James.Maslanik@colorado.edu
June Report: Outlook Based on May Data Regional Outlook: Beaufort and Chuckchi Seas, High Arctic, and Northwest Passage Charles Fowler, Sheldon Drobot, James Maslanik; University of Colorado James.Maslanik@colorado.edu
Canadian Ice Service
 Canadian Ice Service Key Points and Details concerning the 2009 Arctic Minimum Summer Sea Ice Extent October 1 st, 2009 http://ice-glaces.ec.gc.ca 1 Key Points of Interest Arctic-wide The Arctic-wide minimum
Canadian Ice Service Key Points and Details concerning the 2009 Arctic Minimum Summer Sea Ice Extent October 1 st, 2009 http://ice-glaces.ec.gc.ca 1 Key Points of Interest Arctic-wide The Arctic-wide minimum
Spectral Albedos. a: dry snow. b: wet new snow. c: melting old snow. a: cold MY ice. b: melting MY ice. d: frozen pond. c: melting FY white ice
 Spectral Albedos a: dry snow b: wet new snow a: cold MY ice c: melting old snow b: melting MY ice d: frozen pond c: melting FY white ice d: melting FY blue ice e: early MY pond e: ageing ponds Extinction
Spectral Albedos a: dry snow b: wet new snow a: cold MY ice c: melting old snow b: melting MY ice d: frozen pond c: melting FY white ice d: melting FY blue ice e: early MY pond e: ageing ponds Extinction
Outline: 1) Extremes were triggered by anomalous synoptic patterns 2) Cloud-Radiation-PWV positive feedback on 2007 low SIE
 Identifying Dynamical Forcing and Cloud-Radiative Feedbacks Critical to the Formation of Extreme Arctic Sea-Ice Extent in the Summers of 2007 and 1996 Xiquan Dong University of North Dakota Outline: 1)
Identifying Dynamical Forcing and Cloud-Radiative Feedbacks Critical to the Formation of Extreme Arctic Sea-Ice Extent in the Summers of 2007 and 1996 Xiquan Dong University of North Dakota Outline: 1)
Regional Outlook for the Bering-Chukchi-Beaufort Seas Contribution to the 2018 Sea Ice Outlook
 Regional Outlook for the Bering-Chukchi-Beaufort Seas Contribution to the 2018 Sea Ice Outlook 25 July 2018 Matthew Druckenmiller (National Snow and Ice Data Center, Univ. Colorado Boulder) & Hajo Eicken
Regional Outlook for the Bering-Chukchi-Beaufort Seas Contribution to the 2018 Sea Ice Outlook 25 July 2018 Matthew Druckenmiller (National Snow and Ice Data Center, Univ. Colorado Boulder) & Hajo Eicken
On Modeling the Oceanic Heat Fluxes from the North Pacific / Atlantic into the Arctic Ocean
 On Modeling the Oceanic Heat Fluxes from the North Pacific / Atlantic into the Arctic Ocean Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Collaborators: Jaclyn Clement Kinney Terry McNamara, John Whelan
On Modeling the Oceanic Heat Fluxes from the North Pacific / Atlantic into the Arctic Ocean Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Collaborators: Jaclyn Clement Kinney Terry McNamara, John Whelan
Polar Portal Season Report 2013
 Polar Portal Season Report 2013 All in all, 2013 has been a year with large melting from both the Greenland Ice Sheet and the Arctic sea ice but not nearly as large as the record-setting year of 2012.
Polar Portal Season Report 2013 All in all, 2013 has been a year with large melting from both the Greenland Ice Sheet and the Arctic sea ice but not nearly as large as the record-setting year of 2012.
Sea Ice Motion: Physics and Observations Ron Kwok Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA
 Sea Ice Motion: Physics and Observations Ron Kwok Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 7 th ESA Earth Observation Summer School ESRIN, Frascati, Italy 4-14 August
Sea Ice Motion: Physics and Observations Ron Kwok Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 7 th ESA Earth Observation Summer School ESRIN, Frascati, Italy 4-14 August
NSIDC Sea Ice Outlook Contribution, 31 May 2012
 Summary NSIDC Sea Ice Outlook Contribution, 31 May 2012 Julienne Stroeve, Walt Meier, Mark Serreze, Ted Scambos, Mark Tschudi NSIDC is using the same approach as the last 2 years: survival of ice of different
Summary NSIDC Sea Ice Outlook Contribution, 31 May 2012 Julienne Stroeve, Walt Meier, Mark Serreze, Ted Scambos, Mark Tschudi NSIDC is using the same approach as the last 2 years: survival of ice of different
Advancements and Limitations in Understanding and Predicting Arctic Climate Change
 Advancements and Limitations in Understanding and Predicting Arctic Climate Change Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Collaborators: Jaclyn Clement Kinney, Rose Tseng, Timothy McGeehan - NPS Jaromir
Advancements and Limitations in Understanding and Predicting Arctic Climate Change Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Collaborators: Jaclyn Clement Kinney, Rose Tseng, Timothy McGeehan - NPS Jaromir
Arctic Ocean simulation in the CCSM4
 Arctic Ocean simulation in the CCSM4 Alexandra Jahn National Center for Atmospheric Sciences, Boulder, USA Collaborators: K. Sterling, M.M. Holland, J. Kay, J.A. Maslanik, C.M. Bitz, D.A. Bailey, J. Stroeve,
Arctic Ocean simulation in the CCSM4 Alexandra Jahn National Center for Atmospheric Sciences, Boulder, USA Collaborators: K. Sterling, M.M. Holland, J. Kay, J.A. Maslanik, C.M. Bitz, D.A. Bailey, J. Stroeve,
The Atmospheric Circulation
 The Atmospheric Circulation Vertical structure of the Atmosphere http://www.uwsp.edu/geo/faculty/ritter/geog101/textbook/atmosphere/atmospheric_structure.html The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth,
The Atmospheric Circulation Vertical structure of the Atmosphere http://www.uwsp.edu/geo/faculty/ritter/geog101/textbook/atmosphere/atmospheric_structure.html The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth,
Observing Arctic Sea Ice Change. Christian Haas
 Observing Arctic Sea Ice Change Christian Haas Decreasing Arctic sea ice extent in September Ice extent is decreasing, but regional patterns are very different every year The Cryosphere Today, http://arctic.atmos.uiuc.edu;
Observing Arctic Sea Ice Change Christian Haas Decreasing Arctic sea ice extent in September Ice extent is decreasing, but regional patterns are very different every year The Cryosphere Today, http://arctic.atmos.uiuc.edu;
Observed rate of loss of Arctic ice extent is faster than IPCC AR4 predictions
 When will Summer Arctic Sea Ice Disappear? Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Collaborators: Jaclyn Clement Kinney, Andrew Miller, Terry McNamara, John Whelan - Naval Postgraduate School Jay Zwally
When will Summer Arctic Sea Ice Disappear? Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Collaborators: Jaclyn Clement Kinney, Andrew Miller, Terry McNamara, John Whelan - Naval Postgraduate School Jay Zwally
Recent changes in the dynamic properties of declining Arctic sea ice: A model study
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053545, 2012 Recent changes in the dynamic properties of declining Arctic sea ice: A model study Jinlun Zhang, 1 Ron Lindsay, 1 Axel Schweiger,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053545, 2012 Recent changes in the dynamic properties of declining Arctic sea ice: A model study Jinlun Zhang, 1 Ron Lindsay, 1 Axel Schweiger,
Estimate for sea ice extent for September, 2009 is comparable to the 2008 minimum in sea ice extent, or ~ km 2.
 September 2009 Sea Ice Outlook: July Report By: Jennifer V. Lukovich and David G. Barber Centre for Earth Observation Science (CEOS) University of Manitoba Estimate for sea ice extent for September, 2009
September 2009 Sea Ice Outlook: July Report By: Jennifer V. Lukovich and David G. Barber Centre for Earth Observation Science (CEOS) University of Manitoba Estimate for sea ice extent for September, 2009
Origins of the SHEBA freshwater anomaly in the Mackenzie River delta
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L09601, doi:10.1029/2005gl024813, 2006 Origins of the SHEBA freshwater anomaly in the Mackenzie River delta M. Steele, 1 A. Porcelli, 1 and J. Zhang 1 Received 29
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L09601, doi:10.1029/2005gl024813, 2006 Origins of the SHEBA freshwater anomaly in the Mackenzie River delta M. Steele, 1 A. Porcelli, 1 and J. Zhang 1 Received 29
Sea Ice Observations: Where Would We Be Without the Arctic Observing Network? Jackie Richter-Menge ERDC-CRREL
 Sea Ice Observations: Where Would We Be Without the Arctic Observing Network? Jackie Richter-Menge ERDC-CRREL Sea Ice Observations: Where Would We Be Without the Arctic Observing Network? Jackie Richter-Menge
Sea Ice Observations: Where Would We Be Without the Arctic Observing Network? Jackie Richter-Menge ERDC-CRREL Sea Ice Observations: Where Would We Be Without the Arctic Observing Network? Jackie Richter-Menge
CAM Tutorial. Sea Ice Modeling 31 July 2009 David Bailey and Marika Holland, NCAR
 CAM Tutorial Sea Ice Modeling 31 July 2009 David Bailey and Marika Holland, NCAR Sea ice influences in the climate system Surface albedo in March > 0.8 < 0.1 Ice-Ocean Freshwater Exchange Contrasting the
CAM Tutorial Sea Ice Modeling 31 July 2009 David Bailey and Marika Holland, NCAR Sea ice influences in the climate system Surface albedo in March > 0.8 < 0.1 Ice-Ocean Freshwater Exchange Contrasting the
APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1
 APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1 1 By David B. Fissel, Mar Martínez de Saavedra Álvarez, and Randy C. Kerr, ASL Environmental Sciences Inc. (Feb. 2012) West Greenland Seismic
APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1 1 By David B. Fissel, Mar Martínez de Saavedra Álvarez, and Randy C. Kerr, ASL Environmental Sciences Inc. (Feb. 2012) West Greenland Seismic
The Arctic Ocean Climate a balance between local radiation, advected heat and freshwater
 The Arctic Ocean Climate a balance between local radiation, advected heat and freshwater Bert Rudels Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland French Arctic Initiative, Collège de France, Paris,
The Arctic Ocean Climate a balance between local radiation, advected heat and freshwater Bert Rudels Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland French Arctic Initiative, Collège de France, Paris,
The impact of an intense summer cyclone on 2012 Arctic sea ice retreat. Jinlun Zhang*, Ron Lindsay, Axel Schweiger, and Michael Steele
 The impact of an intense summer cyclone on 2012 Arctic sea ice retreat Jinlun Zhang*, Ron Lindsay, Axel Schweiger, and Michael Steele *Corresponding author Polar Science Center, Applied Physics Laboratory
The impact of an intense summer cyclone on 2012 Arctic sea ice retreat Jinlun Zhang*, Ron Lindsay, Axel Schweiger, and Michael Steele *Corresponding author Polar Science Center, Applied Physics Laboratory
The Hydrologic Cycle
 The Hydrologic Cycle Monthly precipitation for the central Arctic Ocean based on data from the Russian North Pole manned camps with daily bias adjustments. Raw precipitation totals are shown along with
The Hydrologic Cycle Monthly precipitation for the central Arctic Ocean based on data from the Russian North Pole manned camps with daily bias adjustments. Raw precipitation totals are shown along with
Arctic decadal and interdecadal variability
 Arctic decadal and interdecadal variability Igor V. Polyakov International Arctic Research Center, University of Alaska Fairbanks Mark A. Johnson Institute of Marine Science, University of Alaska Fairbanks
Arctic decadal and interdecadal variability Igor V. Polyakov International Arctic Research Center, University of Alaska Fairbanks Mark A. Johnson Institute of Marine Science, University of Alaska Fairbanks
Sea ice: physical properties, processes and trends. Stephen Howell Climate Research Division, Environment and Climate Change Canada July 18, 2017
 Sea ice: physical properties, processes and trends Stephen Howell Climate Research Division, Environment and Climate Change Canada July 18, 2017 3-Part Sea Ice Lecture Overview 1. Physical properties,
Sea ice: physical properties, processes and trends Stephen Howell Climate Research Division, Environment and Climate Change Canada July 18, 2017 3-Part Sea Ice Lecture Overview 1. Physical properties,
Global Atmospheric Circulation
 Global Atmospheric Circulation Polar Climatology & Climate Variability Lecture 11 Nov. 22, 2010 Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation The Polar Vortex
Global Atmospheric Circulation Polar Climatology & Climate Variability Lecture 11 Nov. 22, 2010 Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation The Polar Vortex
Arctic climate projections and progress towards a new CCSM. Marika Holland NCAR
 Arctic climate projections and progress towards a new CCSM Marika Holland NCAR The Arctic is changing! Loss of Sept Arctic Sea Ice 2002 Loss of about 8% per decade Or >20% since 1979 (Courtesy I. Rigor
Arctic climate projections and progress towards a new CCSM Marika Holland NCAR The Arctic is changing! Loss of Sept Arctic Sea Ice 2002 Loss of about 8% per decade Or >20% since 1979 (Courtesy I. Rigor
REVISING THE BERING STRAIT FRESHWATER FLUX INTO THE ARCTIC OCEAN
 REVISING THE BERING STRAIT FRESHWATER FLUX INTO THE ARCTIC OCEAN Rebecca A. Woodgate and Knut Aagaard, Polar Science Center, Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington, Corresponding Author:
REVISING THE BERING STRAIT FRESHWATER FLUX INTO THE ARCTIC OCEAN Rebecca A. Woodgate and Knut Aagaard, Polar Science Center, Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington, Corresponding Author:
The Bering Sea/Bering Strait Relationship. Bering Strait and the Chukchi Sea
 The Bering Sea/ Relationship ANSF= Aleutian North Slope Current BSC = Bering Slope Current Anadyr (colder, saltier, nutrient-rich) Bering Shelf Waters (in between!) Exit route! From Stabeno, Schumacher
The Bering Sea/ Relationship ANSF= Aleutian North Slope Current BSC = Bering Slope Current Anadyr (colder, saltier, nutrient-rich) Bering Shelf Waters (in between!) Exit route! From Stabeno, Schumacher
Where is Earth s Water?
 PASSAGE 1 Where is Earth s Water? Our planet contains a limited amount of water that is always in motion. The water that comes out of your faucet moved through the atmosphere, flowed across Earth s surface,
PASSAGE 1 Where is Earth s Water? Our planet contains a limited amount of water that is always in motion. The water that comes out of your faucet moved through the atmosphere, flowed across Earth s surface,
MONTHLY TEMPERATURE, SALINITY AND TRANSPORT VARIABILITY OF THE BERING STRAIT THROUGHFLOW
 MONTHLY TEMPERATURE, SALINITY AND TRANSPORT VARIABILITY OF THE BERING STRAIT THROUGHFLOW Rebecca A. Woodgate, Knut Aagaard, Polar Science Center, Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington, Seattle,
MONTHLY TEMPERATURE, SALINITY AND TRANSPORT VARIABILITY OF THE BERING STRAIT THROUGHFLOW Rebecca A. Woodgate, Knut Aagaard, Polar Science Center, Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington, Seattle,
Sea-ice change around Alaska & Impacts on Human Activities
 Sea-ice change around Alaska & Impacts on Human Activities Hajo Eicken Geophysical Institute University of Alaska Fairbanks, hajo.eicken@gi.alaska.edu Introduction The Arctic sea-ice cover: Observations
Sea-ice change around Alaska & Impacts on Human Activities Hajo Eicken Geophysical Institute University of Alaska Fairbanks, hajo.eicken@gi.alaska.edu Introduction The Arctic sea-ice cover: Observations
Arctic sea ice thickness, volume, and multiyear ice coverage: losses and coupled variability ( )
 Environmental Research Letters LETTER OPEN ACCESS Arctic sea ice thickness, volume, and multiyear ice coverage: losses and coupled variability (1958 2018) To cite this article: R Kwok 2018 Environ. Res.
Environmental Research Letters LETTER OPEN ACCESS Arctic sea ice thickness, volume, and multiyear ice coverage: losses and coupled variability (1958 2018) To cite this article: R Kwok 2018 Environ. Res.
Surface Circulation Ocean current Surface Currents:
 All Write Round Robin G1. What makes up the ocean water? G2. What is the source of the salt found in ocean water? G3. How does the water temperature affect the density of ocean water? G4. How does the
All Write Round Robin G1. What makes up the ocean water? G2. What is the source of the salt found in ocean water? G3. How does the water temperature affect the density of ocean water? G4. How does the
Changing Arctic: climate, environment, metocean conditions, with a special focus on sea ice
 Changing Arctic: climate, environment, metocean conditions, with a special focus on sea ice (IPCC AR4, WG II, Ch.15) Julienne Stroeve National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), Cooperative Institute for
Changing Arctic: climate, environment, metocean conditions, with a special focus on sea ice (IPCC AR4, WG II, Ch.15) Julienne Stroeve National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), Cooperative Institute for
Ice and Ocean Mooring Data Statistics from Barrow Strait, the Central Section of the NW Passage in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago
 Ice and Ocean Mooring Data Statistics from Barrow Strait, the Central Section of the NW Passage in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago Simon Prinsenberg and Roger Pettipas Bedford Institute of Oceanography,
Ice and Ocean Mooring Data Statistics from Barrow Strait, the Central Section of the NW Passage in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago Simon Prinsenberg and Roger Pettipas Bedford Institute of Oceanography,
Understanding the Polar Regions in Climate Change
 AWG Glenwood Sprs, Oct 2007 Understanding the Polar Regions in Climate Change STEM Polar Connections Outline -- What are the Polar Regions Important to Everyone? Geography of the Poles Oceans, land, sea
AWG Glenwood Sprs, Oct 2007 Understanding the Polar Regions in Climate Change STEM Polar Connections Outline -- What are the Polar Regions Important to Everyone? Geography of the Poles Oceans, land, sea
Recent Climate Variability, Trends and the Future
 Recent Climate Variability, Trends and the Future Summary of observed variability and change While there is no doubt that the global average surface air temperature has risen over the period of instrumental
Recent Climate Variability, Trends and the Future Summary of observed variability and change While there is no doubt that the global average surface air temperature has risen over the period of instrumental
f r o m a H i g h - R e s o l u t i o n I c e - O c e a n M o d e l
 Circulation and Variability in the Western Arctic Ocean f r o m a H i g h - R e s o l u t i o n I c e - O c e a n M o d e l Jeffrey S. Dixon 1, Wieslaw Maslowski 1, Jaclyn Clement 1, Waldemar Walczowski
Circulation and Variability in the Western Arctic Ocean f r o m a H i g h - R e s o l u t i o n I c e - O c e a n M o d e l Jeffrey S. Dixon 1, Wieslaw Maslowski 1, Jaclyn Clement 1, Waldemar Walczowski
Don't let your PBL scheme be rejected by brine: Parameterization of salt plumes under sea ice in climate models
 Don't let your PBL scheme be rejected by brine: Parameterization of salt plumes under sea ice in climate models Dimitris Menemenlis California Institute of Technology, Jet Propulsion Laboratory Frontiers
Don't let your PBL scheme be rejected by brine: Parameterization of salt plumes under sea ice in climate models Dimitris Menemenlis California Institute of Technology, Jet Propulsion Laboratory Frontiers
MiSP Ecology/Pollution Global Warming Worksheet #1, L2 GLOBAL WARMING AND ICE EXTENT
 MiSP Ecology/Pollution Global Warming Worksheet #1, L2 Name Date GLOBAL WARMING AND ICE EXTENT Introduction: Sea ice is found in remote polar oceans. On average, sea ice covers about 25 million square
MiSP Ecology/Pollution Global Warming Worksheet #1, L2 Name Date GLOBAL WARMING AND ICE EXTENT Introduction: Sea ice is found in remote polar oceans. On average, sea ice covers about 25 million square
Climate Regimes of the Arctic
 Climate Regimes of the Arctic The climate of Greenland, recent changes and the ice sheet mass balance Map of Greenland, showing elevation and the location of GC- Net automatic weather stations (+), expedition
Climate Regimes of the Arctic The climate of Greenland, recent changes and the ice sheet mass balance Map of Greenland, showing elevation and the location of GC- Net automatic weather stations (+), expedition
Weather & Ocean Currents
 Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
Arctic oceanography; the path of North Atlantic Deep Water
 Chapter 7 Arctic oceanography; the path of North Atlantic Deep Water The importance of the Southern Ocean for the formation of the water masses of the world ocean poses the question whether similar conditions
Chapter 7 Arctic oceanography; the path of North Atlantic Deep Water The importance of the Southern Ocean for the formation of the water masses of the world ocean poses the question whether similar conditions
Homework 5: Background Ocean Water Properties & Stratification
 14 August 2008 MAR 110 HW5: Ocean Properties 1 Homework 5: Background Ocean Water Properties & Stratification The ocean is a heterogeneous mixture of water types - each with its own temperature, salinity,
14 August 2008 MAR 110 HW5: Ocean Properties 1 Homework 5: Background Ocean Water Properties & Stratification The ocean is a heterogeneous mixture of water types - each with its own temperature, salinity,
Extreme, transient Moisture Transport in the high-latitude North Atlantic sector and Impacts on Sea-ice concentration:
 AR conference, June 26, 2018 Extreme, transient Moisture Transport in the high-latitude North Atlantic sector and Impacts on Sea-ice concentration: associated Dynamics, including Weather Regimes & RWB
AR conference, June 26, 2018 Extreme, transient Moisture Transport in the high-latitude North Atlantic sector and Impacts on Sea-ice concentration: associated Dynamics, including Weather Regimes & RWB
Mass Balance of Multiyear Sea Ice in the Southern Beaufort Sea
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Mass Balance of Multiyear Sea Ice in the Southern Beaufort Sea PI Andrew R. Mahoney Geophysical Institute University of
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Mass Balance of Multiyear Sea Ice in the Southern Beaufort Sea PI Andrew R. Mahoney Geophysical Institute University of
The forcings and feedbacks of rapid Arctic sea ice loss
 The forcings and feedbacks of rapid Arctic sea ice loss Marika Holland, NCAR With: C. Bitz (U.WA), B. Tremblay (McGill), D. Bailey (NCAR), J. Stroeve (NSIDC), M. Serreze (NSIDC), D. Lawrence (NCAR), S
The forcings and feedbacks of rapid Arctic sea ice loss Marika Holland, NCAR With: C. Bitz (U.WA), B. Tremblay (McGill), D. Bailey (NCAR), J. Stroeve (NSIDC), M. Serreze (NSIDC), D. Lawrence (NCAR), S
Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty
 Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty David R. Easterling National Climatic Data Center Asheville, North Carolina Overview Some examples of observed climate
Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty David R. Easterling National Climatic Data Center Asheville, North Carolina Overview Some examples of observed climate
Climate Regimes of the Arctic
 Climate Regimes of the Arctic The climate of Greenland Map of Greenland, showing elevation and the location of GC- Net automatic weather stations (+), expedition stations (x), and coastal settlements (o)
Climate Regimes of the Arctic The climate of Greenland Map of Greenland, showing elevation and the location of GC- Net automatic weather stations (+), expedition stations (x), and coastal settlements (o)
Comparison of the Siberian shelf seas in the Arctic Ocean
 Comparison of the Siberian shelf seas in the Arctic Ocean by Audun Scheide & Marit Muren SIO 210 - Introduction to Physical Oceanography November 2014 Acknowledgements Special thanks to James Swift for
Comparison of the Siberian shelf seas in the Arctic Ocean by Audun Scheide & Marit Muren SIO 210 - Introduction to Physical Oceanography November 2014 Acknowledgements Special thanks to James Swift for
Research Interests: variability of sea ice thickness interactions among ocean, seaice and atmosphere climate modelling
 Dr. Richard Moritz Department Chair, Polar Science Center M.S. (Yale University, 1979), M.A. (University of Colorado, 1979), PhD (Yale University, 1988) Research Interests: variability of sea ice thickness
Dr. Richard Moritz Department Chair, Polar Science Center M.S. (Yale University, 1979), M.A. (University of Colorado, 1979), PhD (Yale University, 1988) Research Interests: variability of sea ice thickness
Variability of Sea Ice Extent Along The East Coast of Greenland
 Variability of Sea Ice Extent Along The East Coast of Greenland 2013-06-01 Author: Isabella Grönfeldt Bachelor thesis, 15 hp Lund University Supervisors: Martin Nissen, Centre for Ocean and Ice, DMI Elna
Variability of Sea Ice Extent Along The East Coast of Greenland 2013-06-01 Author: Isabella Grönfeldt Bachelor thesis, 15 hp Lund University Supervisors: Martin Nissen, Centre for Ocean and Ice, DMI Elna
Trends in Climate Teleconnections and Effects on the Midwest
 Trends in Climate Teleconnections and Effects on the Midwest Don Wuebbles Zachary Zobel Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois, Urbana November 11, 2015 Date Name of Meeting 1 Arctic
Trends in Climate Teleconnections and Effects on the Midwest Don Wuebbles Zachary Zobel Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois, Urbana November 11, 2015 Date Name of Meeting 1 Arctic
Annual September Arctic Sea ice extent
 Annual September Arctic Sea ice extent 1979-2012 Annual September Arctic Sea ice extent 1979-2012 Notes: The month of September has the minimum sea ice cover each year. Passive microwave instruments on
Annual September Arctic Sea ice extent 1979-2012 Annual September Arctic Sea ice extent 1979-2012 Notes: The month of September has the minimum sea ice cover each year. Passive microwave instruments on
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Last updated: September 2008
 North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: September 2008 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2007
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: September 2008 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2007
TEMPERATURE AND DEEP OCEAN CIRCULATION
 TEMPERATURE AND DEEP OCEAN CIRCULATION OVERVIEW Ocean currents arise in several ways. For example, wind pushes the water along the surface to form wind-driven currents. Over larger areas, circular wind
TEMPERATURE AND DEEP OCEAN CIRCULATION OVERVIEW Ocean currents arise in several ways. For example, wind pushes the water along the surface to form wind-driven currents. Over larger areas, circular wind
Interannual Variations of Arctic Cloud Types:
 Interannual Variations of Arctic Cloud Types: Relationships with Sea Ice and Surface Temperature Ryan Eastman Stephen Warren University of Washington Department of Atmospheric Sciences Changes in Arctic
Interannual Variations of Arctic Cloud Types: Relationships with Sea Ice and Surface Temperature Ryan Eastman Stephen Warren University of Washington Department of Atmospheric Sciences Changes in Arctic
Record low sea ice concentration in the central Arctic during the summer of Jinping Zhao Ocean University of China
 Record low sea ice concentration in the central Arctic during the summer of 2010 Jinping Zhao Ocean University of China Expedition to the north pole in 1995 Sea ice retreat in the Arctic 3 Replacement
Record low sea ice concentration in the central Arctic during the summer of 2010 Jinping Zhao Ocean University of China Expedition to the north pole in 1995 Sea ice retreat in the Arctic 3 Replacement
(1) Arctic Sea Ice Predictability,
 (1) Arctic Sea Ice Predictability, (2) It s Long-term Loss and Implications for Ocean Conditions Marika Holland, NCAR With contributions from: David Bailey, Alex Jahn, Jennifer Kay, Laura Landrum, Steve
(1) Arctic Sea Ice Predictability, (2) It s Long-term Loss and Implications for Ocean Conditions Marika Holland, NCAR With contributions from: David Bailey, Alex Jahn, Jennifer Kay, Laura Landrum, Steve
Sea Ice Metrics in CMIP5
 Sea Ice Metrics in CMIP5 Detelina Ivanova (PCMDI,LLNL) CESM, Breckenridge, 2012 Acknowledgements Program for Climate Models Diagnostics and Intercomparison Funding agency - DOE Motivation/Goals Follow
Sea Ice Metrics in CMIP5 Detelina Ivanova (PCMDI,LLNL) CESM, Breckenridge, 2012 Acknowledgements Program for Climate Models Diagnostics and Intercomparison Funding agency - DOE Motivation/Goals Follow
LET NOT THAT ICE MELT IN SVALBARD S. RAJAN, INCOIS NEELU SINGH, NCAOR
 LET NOT THAT ICE MELT IN SVALBARD S. RAJAN, INCOIS NEELU SINGH, NCAOR 1. Arctic (surface air) temperatures are rising twice as fast as the temperatures in the rest of the world (Amplification). The Arctic
LET NOT THAT ICE MELT IN SVALBARD S. RAJAN, INCOIS NEELU SINGH, NCAOR 1. Arctic (surface air) temperatures are rising twice as fast as the temperatures in the rest of the world (Amplification). The Arctic
The Dynamic Earth Section 3. Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 3: The Hydrosphere and Biosphere DAY 1
 Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 3: The Hydrosphere and Biosphere DAY 1 The Hydrosphere The hydrosphere includes all of the water on or near the Earth s surface. This includes water in the oceans, lakes,
Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 3: The Hydrosphere and Biosphere DAY 1 The Hydrosphere The hydrosphere includes all of the water on or near the Earth s surface. This includes water in the oceans, lakes,
Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044988, 2010 Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability Jinlun Zhang,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044988, 2010 Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability Jinlun Zhang,
Accelerated decline in the Arctic sea ice cover
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L01703, doi:10.1029/2007gl031972, 2008 Accelerated decline in the Arctic sea ice cover Josefino C. Comiso, 1 Claire L. Parkinson, 1 Robert
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L01703, doi:10.1029/2007gl031972, 2008 Accelerated decline in the Arctic sea ice cover Josefino C. Comiso, 1 Claire L. Parkinson, 1 Robert
Polar Portal Season Report 2016
 Polar Portal Season Report 2016 Less ice both on land and at sea This year s report is the fourth since the Polar Portal was launched, and as an introduction, we have chosen to take a look at the trends
Polar Portal Season Report 2016 Less ice both on land and at sea This year s report is the fourth since the Polar Portal was launched, and as an introduction, we have chosen to take a look at the trends
The Thinning of Arctic Sea Ice, : Have We Passed a Tipping Point?
 The Thinning of Arctic Sea Ice, 1988-2003: Have We Passed a Tipping Point? R. W. Lindsay and J. Zhang Polar Science Center, University of Washington, Seattle, WA Submitted to Journal of Climate, 12 November
The Thinning of Arctic Sea Ice, 1988-2003: Have We Passed a Tipping Point? R. W. Lindsay and J. Zhang Polar Science Center, University of Washington, Seattle, WA Submitted to Journal of Climate, 12 November
Arctic Climate Change. Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013
 Arctic Climate Change Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013 When was this published? Observational Evidence for Arctic
Arctic Climate Change Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013 When was this published? Observational Evidence for Arctic
introduction National Council of Teachers of Mathematics.
 1 introduction The National Science Education Standards developed under the auspices of the National Research Council specifies Science as Inquiry as major content standard for all grade levels. The activities
1 introduction The National Science Education Standards developed under the auspices of the National Research Council specifies Science as Inquiry as major content standard for all grade levels. The activities
1. Introduction 2. Ocean circulation a) Temperature, salinity, density b) Thermohaline circulation c) Wind-driven surface currents d) Circulation and
 1. Introduction 2. Ocean circulation a) Temperature, salinity, density b) Thermohaline circulation c) Wind-driven surface currents d) Circulation and climate change e) Oceanic water residence times 3.
1. Introduction 2. Ocean circulation a) Temperature, salinity, density b) Thermohaline circulation c) Wind-driven surface currents d) Circulation and climate change e) Oceanic water residence times 3.
Arctic sea ice in IPCC climate scenarios in view of the 2007 record low sea ice event A comment by Ralf Döscher, Michael Karcher and Frank Kauker
 Arctic sea ice in IPCC climate scenarios in view of the 2007 record low sea ice event A comment by Ralf Döscher, Michael Karcher and Frank Kauker Fig. 1: Arctic September sea ice extent in observations
Arctic sea ice in IPCC climate scenarios in view of the 2007 record low sea ice event A comment by Ralf Döscher, Michael Karcher and Frank Kauker Fig. 1: Arctic September sea ice extent in observations
Title. Author(s)Maslowski, Wieslaw. Citation 地球温暖化による劇変を解明する. 平成 20 年 6 月 24 日. 札幌市. Issue Date Doc URL. Type.
 Title When will Summer Arctic Sea Ice Disappear? Author(s)Maslowski, Wieslaw Citation 地球温暖化による劇変を解明する. 平成 20 年 6 月 24 日. 札幌市 Issue Date 2008-06-24 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/34395 Type conference
Title When will Summer Arctic Sea Ice Disappear? Author(s)Maslowski, Wieslaw Citation 地球温暖化による劇変を解明する. 平成 20 年 6 月 24 日. 札幌市 Issue Date 2008-06-24 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/34395 Type conference
IMPACTS OF A WARMING ARCTIC
 The Earth s Greenhouse Effect Most of the heat energy emitted from the surface is absorbed by greenhouse gases which radiate heat back down to warm the lower atmosphere and the surface. Increasing the
The Earth s Greenhouse Effect Most of the heat energy emitted from the surface is absorbed by greenhouse gases which radiate heat back down to warm the lower atmosphere and the surface. Increasing the
Sea Ice Lecture Notes ESS 431. Bonnie Light Polar Science Center / Applied Physics Lab 11/26/18, 11/28/18
 Sea Ice Lecture Notes ESS 431 Bonnie Light Polar Science Center / Applied Physics Lab bonnie@apl.washington.edu 11/26/18, 11/28/18 What is sea ice? - Frozen ocean water - Forms, grows, melts in the ocean
Sea Ice Lecture Notes ESS 431 Bonnie Light Polar Science Center / Applied Physics Lab bonnie@apl.washington.edu 11/26/18, 11/28/18 What is sea ice? - Frozen ocean water - Forms, grows, melts in the ocean
Figure 1: Two schematic views of the global overturning circulation. The Southern Ocean plays two key roles in the global overturning: (1) the
 Figure 1: Two schematic views of the global overturning circulation. The Southern Ocean plays two key roles in the global overturning: (1) the Antarctic Circumpolar Current connects the ocean basins, establishing
Figure 1: Two schematic views of the global overturning circulation. The Southern Ocean plays two key roles in the global overturning: (1) the Antarctic Circumpolar Current connects the ocean basins, establishing
Chapter 4. Understanding the Weather. Weather is short-term and caused by various air and ocean circulations
 Video: Meteorologist Paul Douglas April 2013 Understanding the Weather Weather is short-term and caused by various air and ocean circulations There are natural climate cycle that cause large climate changes
Video: Meteorologist Paul Douglas April 2013 Understanding the Weather Weather is short-term and caused by various air and ocean circulations There are natural climate cycle that cause large climate changes
NASA Images of Antarctica and the Arctic covered in both land and sea ice
 ICE SHELVES ACTIVITY 1: DECODING THE ROLE OF ANTARCTIC ICE IN GLOBAL CLIMATE Ice Shelves play a critical role in Antarctica, serving as a buffer between the ocean and the continental ice sheet covering
ICE SHELVES ACTIVITY 1: DECODING THE ROLE OF ANTARCTIC ICE IN GLOBAL CLIMATE Ice Shelves play a critical role in Antarctica, serving as a buffer between the ocean and the continental ice sheet covering
Visible and Thermal Imaging of Sea Ice and Open Water from Coast Guard Arctic Domain Awareness Flights
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Visible and Thermal Imaging of Sea Ice and Open Water from Coast Guard Arctic Domain Awareness Flights Ronald Lindsay Applied
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Visible and Thermal Imaging of Sea Ice and Open Water from Coast Guard Arctic Domain Awareness Flights Ronald Lindsay Applied
THE ATMOSPHERE IN MOTION
 Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project THE ATMOSPHERE IN MOTION Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey Factor 1: Our Energy Source Hi, I m the Sun! I provide 99.9999+
Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project THE ATMOSPHERE IN MOTION Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey Factor 1: Our Energy Source Hi, I m the Sun! I provide 99.9999+
Climatic Conditions Around Greenland 1995
 NAFO Sci. Coun. Studies, 27: 39 47 Climatic Conditions Around Greenland 1995 M. Stein Institut fur Seefischerei, Palmaille 9 D-22767 Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany Abstract The annual review of variability
NAFO Sci. Coun. Studies, 27: 39 47 Climatic Conditions Around Greenland 1995 M. Stein Institut fur Seefischerei, Palmaille 9 D-22767 Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany Abstract The annual review of variability
Storm-driven mixing and potential impact on the Arctic Ocean
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2001jc001248, 2004 Storm-driven mixing and potential impact on the Arctic Ocean Jiayan Yang, 1 Josefino Comiso, 2 David Walsh, 3 Richard Krishfield,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2001jc001248, 2004 Storm-driven mixing and potential impact on the Arctic Ocean Jiayan Yang, 1 Josefino Comiso, 2 David Walsh, 3 Richard Krishfield,
Seasonal variations of vertical structure in the deep waters of the Southern Caspian Sea
 278 Research in Marine Sciences Volume 3, Issue 1, 2018 Pages 278-286 Seasonal variations of vertical structure in the deep waters of the Southern Caspian Sea Somayeh Nahavandian 1,*, and Alireza Vasel
278 Research in Marine Sciences Volume 3, Issue 1, 2018 Pages 278-286 Seasonal variations of vertical structure in the deep waters of the Southern Caspian Sea Somayeh Nahavandian 1,*, and Alireza Vasel
Whither Arctic sea ice? A clear signal of decline regionally, seasonally and extending beyond the satellite record
 428 Annals of Glaciology 46 2007 Whither Arctic sea ice? A clear signal of decline regionally, seasonally and extending beyond the satellite record Walter N. MEIER, Julienne STROEVE, Florence FETTERER
428 Annals of Glaciology 46 2007 Whither Arctic sea ice? A clear signal of decline regionally, seasonally and extending beyond the satellite record Walter N. MEIER, Julienne STROEVE, Florence FETTERER
ARCTIC SEA ICE ALBEDO VARIABILITY AND TRENDS,
 ARCTIC SEA ICE ALBEDO VARIABILITY AND TRENDS, 1982-1998 Vesa Laine Finnish Meteorological Institute (FMI), Helsinki, Finland Abstract Whole-summer and monthly sea ice regional albedo averages, variations
ARCTIC SEA ICE ALBEDO VARIABILITY AND TRENDS, 1982-1998 Vesa Laine Finnish Meteorological Institute (FMI), Helsinki, Finland Abstract Whole-summer and monthly sea ice regional albedo averages, variations
Typical Arctic profiles. How to form halocline water? 2012 Changing Arctic Ocean 506E/497E - Lecture 7 - Woodgate
 Schematic Surface and Atlantic Circulation Typical Arctic profiles MIXED LAYER Usually thin (no wind stirring) PACIFIC WATER High nutrients Shallow (
Schematic Surface and Atlantic Circulation Typical Arctic profiles MIXED LAYER Usually thin (no wind stirring) PACIFIC WATER High nutrients Shallow (
FAMOS for YOPP Forum for Arctic Modeling and Observational Synthesis (FAMOS) for Year of Polar Prediction (YOPP)
 FAMOS for YOPP Forum for Arctic Modeling and Observational Synthesis (FAMOS) for Year of Polar Prediction (YOPP) Andrey Proshutinsky (Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution) and research FAMOS team YOPP-Summit
FAMOS for YOPP Forum for Arctic Modeling and Observational Synthesis (FAMOS) for Year of Polar Prediction (YOPP) Andrey Proshutinsky (Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution) and research FAMOS team YOPP-Summit
Rapid reduction of Arctic perennial sea ice. J. W. Weatherly 3, and G. Neumann 1 USA
 Rapid reduction of Arctic perennial sea ice S. V. Nghiem 1, I. G. Rigor 2, D. K. Perovich 3, P. Clemente-Colón 4, J. W. Weatherly 3, and G. Neumann 1 1 Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of
Rapid reduction of Arctic perennial sea ice S. V. Nghiem 1, I. G. Rigor 2, D. K. Perovich 3, P. Clemente-Colón 4, J. W. Weatherly 3, and G. Neumann 1 1 Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of
Changing predictability characteristics of Arctic sea ice in a warming climate
 Changing predictability characteristics of Arctic sea ice in a warming climate Marika Holland 1 Laura Landrum 1, John Mioduszewski 2, Steve Vavrus 2, Muyin Wang 3 1. NCAR, 2. U. Wisconsin-Madison, 3. NOAA
Changing predictability characteristics of Arctic sea ice in a warming climate Marika Holland 1 Laura Landrum 1, John Mioduszewski 2, Steve Vavrus 2, Muyin Wang 3 1. NCAR, 2. U. Wisconsin-Madison, 3. NOAA
ICE DRIFT IN THE FRAM STRAIT FROM ENVISAT ASAR DATA
 ICE DRIFT IN THE FRAM STRAIT FROM ENVISAT ASAR DATA Stein Sandven (1), Kjell Kloster (1), and Knut F. Dagestad (1) (1) Nansen Environmental and Remote Sensing Center (NERSC), Thormøhlensgte 47, N-5006
ICE DRIFT IN THE FRAM STRAIT FROM ENVISAT ASAR DATA Stein Sandven (1), Kjell Kloster (1), and Knut F. Dagestad (1) (1) Nansen Environmental and Remote Sensing Center (NERSC), Thormøhlensgte 47, N-5006
Polar Portal Season Report 2018
 Polar Portal Season Report 2018 Unusual weather resulted in an atypical melting season in the Arctic The 2017-18 season in the Arctic has once again been extraordinary. A cold summer with high levels of
Polar Portal Season Report 2018 Unusual weather resulted in an atypical melting season in the Arctic The 2017-18 season in the Arctic has once again been extraordinary. A cold summer with high levels of
4.3 Climate (6.3.3) Explore this Phenomena. The same sun shines on the entire Earth. Explain why these two areas have such different climates.
 Explore this Phenomena The same sun shines on the entire Earth. 4.3 Climate (6.3.3) Explain why these two areas have such different climates. 89 6.3.3 Climate Develop and use a model to show how unequal
Explore this Phenomena The same sun shines on the entire Earth. 4.3 Climate (6.3.3) Explain why these two areas have such different climates. 89 6.3.3 Climate Develop and use a model to show how unequal
Influence of changes in sea ice concentration and cloud cover on recent Arctic surface temperature trends
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L20710, doi:10.1029/2009gl040708, 2009 Influence of changes in sea ice concentration and cloud cover on recent Arctic surface temperature
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L20710, doi:10.1029/2009gl040708, 2009 Influence of changes in sea ice concentration and cloud cover on recent Arctic surface temperature
What drove the dramatic retreat of arctic sea ice during summer 2007?
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L11505, doi:10.1029/2008gl034005, 2008 What drove the dramatic retreat of arctic sea ice during summer 2007? Jinlun Zhang, 1 Ron Lindsay,
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L11505, doi:10.1029/2008gl034005, 2008 What drove the dramatic retreat of arctic sea ice during summer 2007? Jinlun Zhang, 1 Ron Lindsay,
