Changing Arctic: climate, environment, metocean conditions, with a special focus on sea ice
|
|
|
- Moses Duane Fields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Changing Arctic: climate, environment, metocean conditions, with a special focus on sea ice (IPCC AR4, WG II, Ch.15) Julienne Stroeve National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES), University of Colorado (CU) Vladimir Ryabinin Joint Planning Staff (JPS) for World Climate Research Programme (WCRP)
2 Global Map of Impacts on the Ocean: Cumulative Impact Scores (vulnerability-weighted sum across all stressors and ecosystems for each 1km 2 pixel but without taking into account changes in sea ice) Less than 4% subject to very low impact 41% of the ocean subject to medium to very high impact (B. Halpern et al., Science, 2008)
3 Industrial Development Shipping (UNEP)
4 (Kevin Kallaugher, The Economist August 2008)
5 IPCC Projections (IPCC AR4, WG I, Ch.10)
6 Detected temperature increases (IPCC AR4, WG I, Ch.10) Increases in mean annual temperatures for relative to (Hansen et al., 2006)
7 How much do we know about the Arctic and from what? I P Y (Toward an Integrated Arctic Observing Network, NAS 2008)
8 Major Relevant Assessments Arctic Climate Impact Assessment Millennium Ecosystem Assessment IPCC AR4 Arctic Human Development Report Global Outlook by UNEP WWF Update since ACIA Global International Waters Assessment 2008 (?)
9 10 Main Messages from ACIA 1. Arctic climate is warming rapidly and much larger changes are projected. 2. Arctic warming and its consequences have worldwide implications. 3. Arctic vegetation zones are projected to shift, bringing wide-ranging impacts. 4. Animal species' diversity, ranges, and distribution will change. 5. Many coastal communities and facilities face increasing exposure to storms. 6. Reduced sea ice is very likely to increase marine transport and access to resources. 7. Thawing ground will disrupt transportation, buildings, and other infrastructure. 8. Indigenous communities are facing major economic and cultural impacts. 9. Elevated UV radiation levels will affect people, plants, and animals. 10. Multiple influences interact to cause impacts to people and ecosystems.
10 Examples of observed changes Over to Julienne! Annual Arctic Sea Ice Extent 13 Melt Area mln km 2 Extent (million sq-km) (Huff and Steffen) Year Snow Area, million km 2 Petersen et al., 2002 IPCC AR4, SfPM, WG1 Arctic River Run-off
11 Poster Child of Climate Change: Arctic Sea Ice 10 Arctic September Sea September Sea Ice Extent 9 Rate of decline:-10%/decade Extent (10 6 km 2 ) Ice Extent (million sq-km) % reduction 5 pre-satellite satellite 27% drop Year
12 Ice Loss in 2007 Extended Further Into Central Arctic 2007 also saw the Opening of the NWP 2005 Median September Ice Extent Median September Ice Extent Median September Ice Extent
13 Transition Towards Younger Ice Ice age tracking algorithm from C. Fowler and J. Maslanik show ice 5 years or older now only makes up 10% of the perennial ice pack. Spring 1986 Spring 1990 Spring 2007 Maslanik et al., 2007
14 Younger Ice is Thinner Ice Maslanik et al., 2007 Comparison between ice age and ice thickness from 4 years of spring ICESat GLAS-derived thickness fields from J. Zwally and D. Yi. Results suggest a decrease in mean thickness of 2.6 m in March 1987 to 2.0 m in March 2007
15 What about 2008? Given the dramatic ice loss in summer 2007 Did the sea ice recover this winter? How likely is another record in summer 2008?
16 Conditions for 2008: Ice Extent/Concentration Some recovery in winter extent, but still well-below normal
17 Conditions for 2008: Ice Age Data from C. Fowler and J. Maslanik First-year ice now covers 72% of the Arctic Basin, whereas in 2007 it covered 59%.
18 Conditions for 2008: Freeboard Image courtesy of R. Kwok Comparison between 2007 and 2008 suggests the seasonal ice cover is 5-10 cm thinner and covers more area in 2008
19 Thinner Ice Already Showing Weakness MODIS Image May 21
20 Survival of Winter Formed First Year Ice FYI week 11 (70-90N) FYI remaining at end of Summer Melt Season Survival of Winter FYI FYI Fraction (%) Year
21 Estimated 2008 Minimum Sea Ice Extent 5.0 Estimated end-of-summer minimum sea ice extent for 2008 based on previous years' melt data Record minimum extent: 4.13 mil. sq-km Average estimate: 3.48 mil. sq-km Extent (million sq-km)
22 Climate Model Projections GCMs suggest decreasing Arctic ice cover will continue. 50% of the IPCC AR4 climate models reach seasonally ice free conditions by Observations suggest it may happen much sooner. Updated from Stroeve et al. (2007)
23 Abrupt Sea Ice Loss Climate models suggest that once the ice thins sufficiently, it becomes vulnerable to natural variability such that abrupt ice losses may occur (Holland et al., 2006). September Sea Ice Extent Model drop 1.8 million sq km, Ice Extent (million sq-km) NCAR CCSM3 model simulation Observations Observed drop 1.6 million sq km, Year
24 The Set up Looks Right Mean thickness (70-90N) in CCSM3 before abrupt change: 1.71 m Mean thickness (70-90N) from ICESat in Spring 2007: 1.75 m (data from J. Zwally)
25 Natural Variability Remains Important! NCAR CCSM3 Mean Ice Thickness vs. Std. Dev. Ice Extent Natural variability increases with a thinning ice pack until the ice is gone
26 Thus, Sea Ice May Recover this Summer If we have a strong cyclonic pattern with attendant cold temperatures as in 1996, we may not set a new record in summer September Ice Extent 10 Extent (million sq-km CCSM3 Run 6 Observations Year
27 Does the Thin Ice Imply a Tipping Point? If the simulated abrupt transitions are the manifestation of a tipping point, then it is likely they would be preceded by a similar critical state. Run 1: Year 2024 Run 2: Year 2025 Run 3: Year 2030 Run 4: Year 2027 Run 5: Year 2029 Solid line ice extent preceding the event, dashed line, extent after the event From M. Holland Over to Vladimir!
28 Changes in the Atmosphere - new warming/circulation pattern (J.E. Overland)
29 Atmospheric Circulation Does Not Appear to Explain Recent Warming over the Arctic From C. Deser and J. Stroeve
30 Complexity of feedbacks (Chapin III et al., 2005)
31 In the result, are we capable to predict the expected changes in the Arctic atmosphere? DJF sea-level pressure response to 2xCO 2 (J.E. Overland) (Sigmond et al.) High-top model Low-top (IPCC) model So far, there has been no adequate large-scale forcing available for regional climate models in the Arctic!
32 Changes in the Ocean State of the Arctic Ocean in 2007: warmth spreading poleward along the boundary (I. Polyakov) (P. Holliday)
33 Time series Changes in the ocean, from freshening to more saline waters Temperature Salinity (Dickson et al., 2002) (P. Holliday, 2008)
34 Simulated changes of ph & [CO 3 2- ] in two Polar Oceans: Arctic ph Carbonate Southern Ocean (J. Orr et al., pers. comm.)
35 Resilience of ecosystems in the Arctic (OASYS) (UNEP) (Stram & Oliver, 2008) Resilience of ecosystems is related to ability of species to migrate, accommodate the change, or evolve. It strongly depends on the rate of change and combination of stressors: e.g. acidification and pollution weaken resilience to temperature change Migration to colder regions is not an option in the Arctic: nowhere to go! Sea ice is a very valuable but vulnerable habitat for the Arctic ecosystem
36 Other changes (1) Changing marine cryosphere (beyond sea-ice): - iceberg calving, - ice phases shifting, - changes in fast ice, (AARI) (UNEP) - probable changes in pressure ridge properties, (AARI) -etc.
37 Other changes (2) Where once was sea ice, one now has to predict waves! (V. Dymov) Changes in (long-return) wind waves due to - changes in fetch and - storminess. Changes in storm surges due to - changes in fetch, - storminess, - tides, - mean sea-level rise, - and evolution of coasts. (D. Atkinson) (D. Atkinson)
38 Other changes (3) Accelerated coastal erosion due to likely higher wave impact, exposure of the coast to action of wind waves and ice, thawing of coastal permafrost. (D. Atkinson) (D. Atkinson) Elevated risk of ice storms (wave + ice action): an event, which is highly dangerous for shipping and destructive for coasts.
39 Implications of the changes for Arctic metocean interests 1. A host of changes in the Arctic may occur faster than anticipated in ACIA, IPCC AR4 and other assessments. Dramatic ice loss as in 2007 does not occur until midcentury in climate models. There will likely be some changes ( surprises ) in the Arctic that have not been observed in the past. Changes may happen abruptly without crossing a threshold (or tipping point), affecting our ability to predict events. 2. Past observations in the Arctic may be not representative for the future because of climate change and decadal variability. 3. This may affect the validity of conclusions made in various previous EIAs for Arctic projects and in the design considerations ( previous meaning made on past data records without taking into account the projected changes).
40 Proposal for consideration One meaningful way forward for development of required offshore metocean applications in the Arctic would be to a) run ensembles of updated global climate models with best sea-ice modules (and some other enhancements), (validation on the pan-arctic domain using past observations) b) undertake regional downscaling of the projections, (validation in regional domains on the past record) c) use regionally downscaled projections for development of industrial applications. Consider how to take into account decadal variability: WCRP s intensive work on predicting it is ongoing. Need to focus now on hemispheric impact assessments of the loss of Arctic sea ice. This could potentially form a joint project between climate change and offshore industry communities.
The forcings and feedbacks of rapid Arctic sea ice loss
 The forcings and feedbacks of rapid Arctic sea ice loss Marika Holland, NCAR With: C. Bitz (U.WA), B. Tremblay (McGill), D. Bailey (NCAR), J. Stroeve (NSIDC), M. Serreze (NSIDC), D. Lawrence (NCAR), S
The forcings and feedbacks of rapid Arctic sea ice loss Marika Holland, NCAR With: C. Bitz (U.WA), B. Tremblay (McGill), D. Bailey (NCAR), J. Stroeve (NSIDC), M. Serreze (NSIDC), D. Lawrence (NCAR), S
NSIDC Sea Ice Outlook Contribution, 31 May 2012
 Summary NSIDC Sea Ice Outlook Contribution, 31 May 2012 Julienne Stroeve, Walt Meier, Mark Serreze, Ted Scambos, Mark Tschudi NSIDC is using the same approach as the last 2 years: survival of ice of different
Summary NSIDC Sea Ice Outlook Contribution, 31 May 2012 Julienne Stroeve, Walt Meier, Mark Serreze, Ted Scambos, Mark Tschudi NSIDC is using the same approach as the last 2 years: survival of ice of different
Arctic sea ice falls below 4 million square kilometers
 SOURCE : http://nsidc.org/arcticseaicenews/ Arctic sea ice falls below 4 million square kilometers September 5, 2012 The National Snow and Ice Data Center : Advancing knowledge of Earth's frozen regions
SOURCE : http://nsidc.org/arcticseaicenews/ Arctic sea ice falls below 4 million square kilometers September 5, 2012 The National Snow and Ice Data Center : Advancing knowledge of Earth's frozen regions
The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change. Renguang Wu
 The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change Renguang Wu Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing World Conference on Climate Change
The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change Renguang Wu Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing World Conference on Climate Change
Whither Arctic Sea Ice?
 Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences University of Colorado Whither Arctic Sea Ice? Walt Meier http://nsidc.org Climate Literacy and Energy Awareness Network May 9, 2011 1 The Cryosphere
Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences University of Colorado Whither Arctic Sea Ice? Walt Meier http://nsidc.org Climate Literacy and Energy Awareness Network May 9, 2011 1 The Cryosphere
AMAP. Climate Change in the Cryosphere: Snow, Water, Ice and Permafrost in the Arctic (SWIPA) Assessment Summary
 Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences University of Colorado AMAP Climate Change in the Cryosphere: Snow, Water, Ice and Permafrost in the Arctic (SWIPA) Assessment Summary Arctic
Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences University of Colorado AMAP Climate Change in the Cryosphere: Snow, Water, Ice and Permafrost in the Arctic (SWIPA) Assessment Summary Arctic
How Will Melting Ice Sheets Affect Us?
 PASSAGE 4 How Will Melting Ice Sheets Affect Us? Variation is normal. During the last ice age, for example, ice sheets also covered much of North America and Scandinavia. Why is what s happening now different
PASSAGE 4 How Will Melting Ice Sheets Affect Us? Variation is normal. During the last ice age, for example, ice sheets also covered much of North America and Scandinavia. Why is what s happening now different
Sea-ice change around Alaska & Impacts on Human Activities
 Sea-ice change around Alaska & Impacts on Human Activities Hajo Eicken Geophysical Institute University of Alaska Fairbanks, hajo.eicken@gi.alaska.edu Introduction The Arctic sea-ice cover: Observations
Sea-ice change around Alaska & Impacts on Human Activities Hajo Eicken Geophysical Institute University of Alaska Fairbanks, hajo.eicken@gi.alaska.edu Introduction The Arctic sea-ice cover: Observations
Climate Change in Newfoundland & Labrador
 Climate Change in Newfoundland & Labrador Impacts and Adaptation Newleef Conference 08 October 2015 Met-Ocean Services The Team 55 personnel; 24/7 operational weather forecast desk; Equipment technician
Climate Change in Newfoundland & Labrador Impacts and Adaptation Newleef Conference 08 October 2015 Met-Ocean Services The Team 55 personnel; 24/7 operational weather forecast desk; Equipment technician
This satellite image of an Ellesmere Island glacier that reaches the sea in the Greely Fjord reveals growing meltwater ponds on the glacier's surface
 This satellite image of an Ellesmere Island glacier that reaches the sea in the Greely Fjord reveals growing meltwater ponds on the glacier's surface as well as icebergs that have calved off the glacier
This satellite image of an Ellesmere Island glacier that reaches the sea in the Greely Fjord reveals growing meltwater ponds on the glacier's surface as well as icebergs that have calved off the glacier
Changing Marine Access in the Arctic Ocean: The Arctic Climate Impact Assessment Panama Canal Authority 11 January 2005
 Changing Marine Access in the Arctic Ocean: The Arctic Climate Impact Assessment Panama Canal Authority 11 January 2005 Lawson Brigham Deputy Director, U.S. Arctic Research Commission ACIA Contributing
Changing Marine Access in the Arctic Ocean: The Arctic Climate Impact Assessment Panama Canal Authority 11 January 2005 Lawson Brigham Deputy Director, U.S. Arctic Research Commission ACIA Contributing
 Page 1 of 10 Search NSIDC... Search Education Center Photo Gallery Home Data Programs & Projects Science Publications News & Events About Overview Global Temperatures Northern Hemisphere Snow Glaciers
Page 1 of 10 Search NSIDC... Search Education Center Photo Gallery Home Data Programs & Projects Science Publications News & Events About Overview Global Temperatures Northern Hemisphere Snow Glaciers
The known requirements for Arctic climate services
 The known requirements for Arctic climate services based on findings described in STT White paper 8/2015 Johanna Ekman / EC PHORS STT Regional drivers The Arctic region is home to almost four million people
The known requirements for Arctic climate services based on findings described in STT White paper 8/2015 Johanna Ekman / EC PHORS STT Regional drivers The Arctic region is home to almost four million people
IMPACTS OF A WARMING ARCTIC
 The Earth s Greenhouse Effect Most of the heat energy emitted from the surface is absorbed by greenhouse gases which radiate heat back down to warm the lower atmosphere and the surface. Increasing the
The Earth s Greenhouse Effect Most of the heat energy emitted from the surface is absorbed by greenhouse gases which radiate heat back down to warm the lower atmosphere and the surface. Increasing the
(1) Arctic Sea Ice Predictability,
 (1) Arctic Sea Ice Predictability, (2) It s Long-term Loss and Implications for Ocean Conditions Marika Holland, NCAR With contributions from: David Bailey, Alex Jahn, Jennifer Kay, Laura Landrum, Steve
(1) Arctic Sea Ice Predictability, (2) It s Long-term Loss and Implications for Ocean Conditions Marika Holland, NCAR With contributions from: David Bailey, Alex Jahn, Jennifer Kay, Laura Landrum, Steve
Arctic sea ice in IPCC climate scenarios in view of the 2007 record low sea ice event A comment by Ralf Döscher, Michael Karcher and Frank Kauker
 Arctic sea ice in IPCC climate scenarios in view of the 2007 record low sea ice event A comment by Ralf Döscher, Michael Karcher and Frank Kauker Fig. 1: Arctic September sea ice extent in observations
Arctic sea ice in IPCC climate scenarios in view of the 2007 record low sea ice event A comment by Ralf Döscher, Michael Karcher and Frank Kauker Fig. 1: Arctic September sea ice extent in observations
Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty
 Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty David R. Easterling National Climatic Data Center Asheville, North Carolina Overview Some examples of observed climate
Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty David R. Easterling National Climatic Data Center Asheville, North Carolina Overview Some examples of observed climate
Can Arctic winter sea ice disappear abruptly?
 Can Arctic winter sea ice disappear abruptly? In a new study, Sebastian Bathiany and his colleagues Dirk Notz, Thorsten Mauritsen, Victor Brovkin and Gaby Raedel from MPI-M have examined the loss of Arctic
Can Arctic winter sea ice disappear abruptly? In a new study, Sebastian Bathiany and his colleagues Dirk Notz, Thorsten Mauritsen, Victor Brovkin and Gaby Raedel from MPI-M have examined the loss of Arctic
Recent Climate Variability, Trends and the Future
 Recent Climate Variability, Trends and the Future Summary of observed variability and change While there is no doubt that the global average surface air temperature has risen over the period of instrumental
Recent Climate Variability, Trends and the Future Summary of observed variability and change While there is no doubt that the global average surface air temperature has risen over the period of instrumental
Today s Lecture: Land, biosphere, cryosphere (All that stuff we don t have equations for... )
 Today s Lecture: Land, biosphere, cryosphere (All that stuff we don t have equations for... ) 4 Land, biosphere, cryosphere 1. Introduction 2. Atmosphere 3. Ocean 4. Land, biosphere, cryosphere 4.1 Land
Today s Lecture: Land, biosphere, cryosphere (All that stuff we don t have equations for... ) 4 Land, biosphere, cryosphere 1. Introduction 2. Atmosphere 3. Ocean 4. Land, biosphere, cryosphere 4.1 Land
Observed rate of loss of Arctic ice extent is faster than IPCC AR4 predictions
 When will Summer Arctic Sea Ice Disappear? Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Collaborators: Jaclyn Clement Kinney, Andrew Miller, Terry McNamara, John Whelan - Naval Postgraduate School Jay Zwally
When will Summer Arctic Sea Ice Disappear? Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Collaborators: Jaclyn Clement Kinney, Andrew Miller, Terry McNamara, John Whelan - Naval Postgraduate School Jay Zwally
Polar Portal Season Report 2013
 Polar Portal Season Report 2013 All in all, 2013 has been a year with large melting from both the Greenland Ice Sheet and the Arctic sea ice but not nearly as large as the record-setting year of 2012.
Polar Portal Season Report 2013 All in all, 2013 has been a year with large melting from both the Greenland Ice Sheet and the Arctic sea ice but not nearly as large as the record-setting year of 2012.
CAM Tutorial. Sea Ice Modeling 31 July 2009 David Bailey and Marika Holland, NCAR
 CAM Tutorial Sea Ice Modeling 31 July 2009 David Bailey and Marika Holland, NCAR Sea ice influences in the climate system Surface albedo in March > 0.8 < 0.1 Ice-Ocean Freshwater Exchange Contrasting the
CAM Tutorial Sea Ice Modeling 31 July 2009 David Bailey and Marika Holland, NCAR Sea ice influences in the climate system Surface albedo in March > 0.8 < 0.1 Ice-Ocean Freshwater Exchange Contrasting the
Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044988, 2010 Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability Jinlun Zhang,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044988, 2010 Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability Jinlun Zhang,
CLIMATE SIMULATIONS AND PROJECTIONS OVER RUSSIA AND THE ADJACENT SEAS: а CMIP5 Update
 CLIMATE SIMULATIONS AND PROJECTIONS OVER RUSSIA AND THE ADJACENT SEAS: а CMIP5 Update Tatiana Pavlova and Vladimir Kattsov Voeikov Main Geophysical Observatory, St. Petersburg, Russia Workshop on Global
CLIMATE SIMULATIONS AND PROJECTIONS OVER RUSSIA AND THE ADJACENT SEAS: а CMIP5 Update Tatiana Pavlova and Vladimir Kattsov Voeikov Main Geophysical Observatory, St. Petersburg, Russia Workshop on Global
On Modeling the Oceanic Heat Fluxes from the North Pacific / Atlantic into the Arctic Ocean
 On Modeling the Oceanic Heat Fluxes from the North Pacific / Atlantic into the Arctic Ocean Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Collaborators: Jaclyn Clement Kinney Terry McNamara, John Whelan
On Modeling the Oceanic Heat Fluxes from the North Pacific / Atlantic into the Arctic Ocean Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Collaborators: Jaclyn Clement Kinney Terry McNamara, John Whelan
Arctic Ocean-Sea Ice-Climate Interactions
 Arctic Ocean-Sea Ice-Climate Interactions Sea Ice Ice extent waxes and wanes with the seasons. Ice extent is at a maximum in March (typically 14 million square km, about twice the area of the contiguous
Arctic Ocean-Sea Ice-Climate Interactions Sea Ice Ice extent waxes and wanes with the seasons. Ice extent is at a maximum in March (typically 14 million square km, about twice the area of the contiguous
What is the IPCC? Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
 IPCC WG1 FAQ What is the IPCC? Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change The IPCC is a scientific intergovernmental body set up by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and by the United Nations
IPCC WG1 FAQ What is the IPCC? Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change The IPCC is a scientific intergovernmental body set up by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and by the United Nations
Sea ice: physical properties, processes and trends. Stephen Howell Climate Research Division, Environment and Climate Change Canada July 18, 2017
 Sea ice: physical properties, processes and trends Stephen Howell Climate Research Division, Environment and Climate Change Canada July 18, 2017 3-Part Sea Ice Lecture Overview 1. Physical properties,
Sea ice: physical properties, processes and trends Stephen Howell Climate Research Division, Environment and Climate Change Canada July 18, 2017 3-Part Sea Ice Lecture Overview 1. Physical properties,
MiSP Ecology/Pollution Global Warming Worksheet #1, L2 GLOBAL WARMING AND ICE EXTENT
 MiSP Ecology/Pollution Global Warming Worksheet #1, L2 Name Date GLOBAL WARMING AND ICE EXTENT Introduction: Sea ice is found in remote polar oceans. On average, sea ice covers about 25 million square
MiSP Ecology/Pollution Global Warming Worksheet #1, L2 Name Date GLOBAL WARMING AND ICE EXTENT Introduction: Sea ice is found in remote polar oceans. On average, sea ice covers about 25 million square
Earth Science and Climate Change
 Earth Science and Climate Change Dr. Mary L. Cleave February 7, 2007 YOU ARE HERE 3 Land Use Changes Over Time Lingering Doubts on Temperature Trends Have Been Resolved 1st CCSP Synthesis & Assessment
Earth Science and Climate Change Dr. Mary L. Cleave February 7, 2007 YOU ARE HERE 3 Land Use Changes Over Time Lingering Doubts on Temperature Trends Have Been Resolved 1st CCSP Synthesis & Assessment
Annual September Arctic Sea ice extent
 Annual September Arctic Sea ice extent 1979-2012 Annual September Arctic Sea ice extent 1979-2012 Notes: The month of September has the minimum sea ice cover each year. Passive microwave instruments on
Annual September Arctic Sea ice extent 1979-2012 Annual September Arctic Sea ice extent 1979-2012 Notes: The month of September has the minimum sea ice cover each year. Passive microwave instruments on
Climate change projections for Ontario: an updated synthesis for policymakers and planners
 Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry Climate change projections for Ontario: an updated synthesis for policymakers and planners Shannon Fera and Adam Hogg Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources and
Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry Climate change projections for Ontario: an updated synthesis for policymakers and planners Shannon Fera and Adam Hogg Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources and
Changes in Frequency of Extreme Wind Events in the Arctic
 Changes in Frequency of Extreme Wind Events in the Arctic John E. Walsh Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois 105 S. Gregory Avenue Urbana, IL 61801 phone: (217) 333-7521 fax: (217)
Changes in Frequency of Extreme Wind Events in the Arctic John E. Walsh Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois 105 S. Gregory Avenue Urbana, IL 61801 phone: (217) 333-7521 fax: (217)
Nancy N. Soreide NOAA/PMEL, Seattle, WA. J. E. Overland, J. A. Richter-Menge, H. Eicken, H. Wiggins and and J. Calder
 Nancy N. Soreide NOAA/PMEL, Seattle, WA J. E. Overland, J. A. Richter-Menge, H. Eicken, H. Wiggins and and J. Calder ARCUS State of the Arctic Meeting, March 16-19, 2010 Communicating Changes in Arctic
Nancy N. Soreide NOAA/PMEL, Seattle, WA J. E. Overland, J. A. Richter-Menge, H. Eicken, H. Wiggins and and J. Calder ARCUS State of the Arctic Meeting, March 16-19, 2010 Communicating Changes in Arctic
ATOC OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow
![ATOC OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow ATOC OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow](/thumbs/95/126309683.jpg) ATOC 1060-002 OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow cover, permafrost, river and lake ice, ; [3]Glaciers and
ATOC 1060-002 OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow cover, permafrost, river and lake ice, ; [3]Glaciers and
Observed changes in climate and their effects
 1 1.1 Observations of climate change Since the TAR, progress in understanding how climate is changing in space and time has been gained through improvements and extensions of numerous datasets and data
1 1.1 Observations of climate change Since the TAR, progress in understanding how climate is changing in space and time has been gained through improvements and extensions of numerous datasets and data
World Geography Chapter 3
 World Geography Chapter 3 Section 1 A. Introduction a. Weather b. Climate c. Both weather and climate are influenced by i. direct sunlight. ii. iii. iv. the features of the earth s surface. B. The Greenhouse
World Geography Chapter 3 Section 1 A. Introduction a. Weather b. Climate c. Both weather and climate are influenced by i. direct sunlight. ii. iii. iv. the features of the earth s surface. B. The Greenhouse
8.1.2 Climate Projections
 Chapter 8 Nauru 167 8.1 Climate Summary 8.1.1 Current Climate Over the past half century it is likely that there has been a warming air temperature trend at Nauru which is partly associated with warming
Chapter 8 Nauru 167 8.1 Climate Summary 8.1.1 Current Climate Over the past half century it is likely that there has been a warming air temperature trend at Nauru which is partly associated with warming
Arctic climate projections and progress towards a new CCSM. Marika Holland NCAR
 Arctic climate projections and progress towards a new CCSM Marika Holland NCAR The Arctic is changing! Loss of Sept Arctic Sea Ice 2002 Loss of about 8% per decade Or >20% since 1979 (Courtesy I. Rigor
Arctic climate projections and progress towards a new CCSM Marika Holland NCAR The Arctic is changing! Loss of Sept Arctic Sea Ice 2002 Loss of about 8% per decade Or >20% since 1979 (Courtesy I. Rigor
Mozambique. General Climate. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Mozambique C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2.Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Mozambique C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2.Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
Lower Stratospheric Cooling. and. Abrupt Change in Arctic Sea Ice
 Lower Stratospheric Cooling and Abrupt Change in Arctic Sea Ice Carl Drews March 16, 2007 ATOC 7500-002 Human Influences on Weather and Climate University of Colorado at Boulder Dr. Roger Pielke Sr, Instructor
Lower Stratospheric Cooling and Abrupt Change in Arctic Sea Ice Carl Drews March 16, 2007 ATOC 7500-002 Human Influences on Weather and Climate University of Colorado at Boulder Dr. Roger Pielke Sr, Instructor
Future Climate Change
 Future Climate Change How do you know whether to trust a prediction about the future? All predictions are based on global circulation models (GCMs, AOGCMs) - model accuracy is verified by its ability to
Future Climate Change How do you know whether to trust a prediction about the future? All predictions are based on global circulation models (GCMs, AOGCMs) - model accuracy is verified by its ability to
Observed State of the Global Climate
 WMO Observed State of the Global Climate Jerry Lengoasa WMO June 2013 WMO Observations of Changes of the physical state of the climate ESSENTIAL CLIMATE VARIABLES OCEANIC ATMOSPHERIC TERRESTRIAL Surface
WMO Observed State of the Global Climate Jerry Lengoasa WMO June 2013 WMO Observations of Changes of the physical state of the climate ESSENTIAL CLIMATE VARIABLES OCEANIC ATMOSPHERIC TERRESTRIAL Surface
Global Climate Change and the Implications for Oklahoma. Gary McManus Associate State Climatologist Oklahoma Climatological Survey
 Global Climate Change and the Implications for Oklahoma Gary McManus Associate State Climatologist Oklahoma Climatological Survey Our previous stance on global warming Why the anxiety? Extreme Viewpoints!
Global Climate Change and the Implications for Oklahoma Gary McManus Associate State Climatologist Oklahoma Climatological Survey Our previous stance on global warming Why the anxiety? Extreme Viewpoints!
Global Climate Change and the Implications for Oklahoma. Gary McManus Associate State Climatologist Oklahoma Climatological Survey
 Global Climate Change and the Implications for Oklahoma Gary McManus Associate State Climatologist Oklahoma Climatological Survey OCS LEGISLATIVE MANDATES Conduct and report on studies of climate and weather
Global Climate Change and the Implications for Oklahoma Gary McManus Associate State Climatologist Oklahoma Climatological Survey OCS LEGISLATIVE MANDATES Conduct and report on studies of climate and weather
Seamless weather and climate for security planning
 Seamless weather and climate for security planning Kirsty Lewis, Principal Climate Change Consultant, Met Office Hadley Centre 28 June 2010 Global Climate Models Mitigation timescale changes could be avoided
Seamless weather and climate for security planning Kirsty Lewis, Principal Climate Change Consultant, Met Office Hadley Centre 28 June 2010 Global Climate Models Mitigation timescale changes could be avoided
Arctic climate simulations by coupled models - an overview -
 Arctic climate simulations by coupled models - an overview - Annette Rinke and Klaus Dethloff Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research, Research Department Potsdam, Germany Surface temperature
Arctic climate simulations by coupled models - an overview - Annette Rinke and Klaus Dethloff Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research, Research Department Potsdam, Germany Surface temperature
1 IntroductIon to the cryosphere
 1 IntroductIon to the cryosphere in this place, nostalgia roams, patient as slow hands on skin, transparent as melt-water. nights are light and long. Shadows settle on the shoulders of air. time steps
1 IntroductIon to the cryosphere in this place, nostalgia roams, patient as slow hands on skin, transparent as melt-water. nights are light and long. Shadows settle on the shoulders of air. time steps
Arctic Climate Change. Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013
 Arctic Climate Change Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013 When was this published? Observational Evidence for Arctic
Arctic Climate Change Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013 When was this published? Observational Evidence for Arctic
How de-coupling cloud radiative feedbacks strengthens the AMOC
 How de-coupling cloud radiative feedbacks strengthens the AMOC Elizabeth Maroon1, Eleanor Middlemas2, Jennifer Kay1, Brian Medeiros3 1CIRES, University of Colorado Boulder, 2University of Miami, 3National
How de-coupling cloud radiative feedbacks strengthens the AMOC Elizabeth Maroon1, Eleanor Middlemas2, Jennifer Kay1, Brian Medeiros3 1CIRES, University of Colorado Boulder, 2University of Miami, 3National
Arctic sea ice prediction from days to centuries
 21-26 January 2018 Arctic sea ice prediction from days to centuries Are we there yet? François Massonnet September 2007: the Arctic black swan Arctic sea ice prediction: an emerging area of research Number
21-26 January 2018 Arctic sea ice prediction from days to centuries Are we there yet? François Massonnet September 2007: the Arctic black swan Arctic sea ice prediction: an emerging area of research Number
6. What has been the most effective erosive agent in the climate system? a. Water b. Ice c. Wind
 Multiple Choice. 1. Heinrich Events a. Show increased abundance of warm-water species of planktic foraminifera b. Show greater intensity since the last deglaciation c. Show increased accumulation of ice-rafted
Multiple Choice. 1. Heinrich Events a. Show increased abundance of warm-water species of planktic foraminifera b. Show greater intensity since the last deglaciation c. Show increased accumulation of ice-rafted
A Synthesis of Results from the Norwegian ESSAS (N-ESSAS) Project
 A Synthesis of Results from the Norwegian ESSAS (N-ESSAS) Project Ken Drinkwater Institute of Marine Research Bergen, Norway ken.drinkwater@imr.no ESSAS has several formally recognized national research
A Synthesis of Results from the Norwegian ESSAS (N-ESSAS) Project Ken Drinkwater Institute of Marine Research Bergen, Norway ken.drinkwater@imr.no ESSAS has several formally recognized national research
Trends in Climate Teleconnections and Effects on the Midwest
 Trends in Climate Teleconnections and Effects on the Midwest Don Wuebbles Zachary Zobel Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois, Urbana November 11, 2015 Date Name of Meeting 1 Arctic
Trends in Climate Teleconnections and Effects on the Midwest Don Wuebbles Zachary Zobel Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois, Urbana November 11, 2015 Date Name of Meeting 1 Arctic
What makes the Arctic hot?
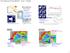 1/3 total USA UN Environ Prog What makes the Arctic hot? Local communities subsistence Arctic Shipping Routes? Decreasing Ice cover Sept 2007 -ice extent (Pink=1979-2000 mean min) Source: NSIDC Oil/Gas
1/3 total USA UN Environ Prog What makes the Arctic hot? Local communities subsistence Arctic Shipping Routes? Decreasing Ice cover Sept 2007 -ice extent (Pink=1979-2000 mean min) Source: NSIDC Oil/Gas
New perspectives of climate change impacts on marine anthropogenic radioactivity in Arctic regions
 New perspectives of climate change impacts on marine anthropogenic radioactivity in Arctic regions M. Karcher 1,3, I. Harms 2, R. Gerdes 3, W.J.F. Standring 4, M. Dowdall 4, P. Strand 4 1 O.A.Sys Ocean
New perspectives of climate change impacts on marine anthropogenic radioactivity in Arctic regions M. Karcher 1,3, I. Harms 2, R. Gerdes 3, W.J.F. Standring 4, M. Dowdall 4, P. Strand 4 1 O.A.Sys Ocean
Deke Arndt, Chief, Climate Monitoring Branch, NOAA s National Climatic Data Center
 Thomas R. Karl, L.H.D., Director, NOAA s National Climatic Data Center, and Chair of the Subcommittee on Global Change Research Peter Thorne, PhD, Senior Scientist, Cooperative Institute for Climate and
Thomas R. Karl, L.H.D., Director, NOAA s National Climatic Data Center, and Chair of the Subcommittee on Global Change Research Peter Thorne, PhD, Senior Scientist, Cooperative Institute for Climate and
Arctic Adaptation Research Considerations and Challenges
 Arctic Adaptation Research Considerations and Challenges Dr Grete K. Hovelsrud, Research Director CICERO- Center for International Climate and Environmental Research Oslo, Norway Many Strong Voices Stakeholder
Arctic Adaptation Research Considerations and Challenges Dr Grete K. Hovelsrud, Research Director CICERO- Center for International Climate and Environmental Research Oslo, Norway Many Strong Voices Stakeholder
Weather & Ocean Currents
 Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
Recent climate variability, trends and the future
 Recent climate variability, trends and the future Summary of observed variability and change While there is no doubt that the global average surface air temperatures has risen over the period of instrumental
Recent climate variability, trends and the future Summary of observed variability and change While there is no doubt that the global average surface air temperatures has risen over the period of instrumental
June Report: Outlook Based on May Data Regional Outlook: Beaufort and Chuckchi Seas, High Arctic, and Northwest Passage
 June Report: Outlook Based on May Data Regional Outlook: Beaufort and Chuckchi Seas, High Arctic, and Northwest Passage Charles Fowler, Sheldon Drobot, James Maslanik; University of Colorado James.Maslanik@colorado.edu
June Report: Outlook Based on May Data Regional Outlook: Beaufort and Chuckchi Seas, High Arctic, and Northwest Passage Charles Fowler, Sheldon Drobot, James Maslanik; University of Colorado James.Maslanik@colorado.edu
Chapter outline. Reference 12/13/2016
 Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
Changes in Marine Extremes. Professor Mikis Tsimplis. The LRET Research Collegium Southampton, 11 July 2 September 2011
 Changes in Marine Extremes by Professor Mikis Tsimplis The LRET Research Collegium Southampton, 11 July 2 September 2011 1 Changes in marine extremes Mikis Tsimplis, School of Law and National Oceanography
Changes in Marine Extremes by Professor Mikis Tsimplis The LRET Research Collegium Southampton, 11 July 2 September 2011 1 Changes in marine extremes Mikis Tsimplis, School of Law and National Oceanography
Advancements and Limitations in Understanding and Predicting Arctic Climate Change
 Advancements and Limitations in Understanding and Predicting Arctic Climate Change Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Collaborators: Jaclyn Clement Kinney, Rose Tseng, Timothy McGeehan - NPS Jaromir
Advancements and Limitations in Understanding and Predicting Arctic Climate Change Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Collaborators: Jaclyn Clement Kinney, Rose Tseng, Timothy McGeehan - NPS Jaromir
Winter. Here s what a weak La Nina usually brings to the nation with tempseraures:
 2017-2018 Winter Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2017-2018. El Nino /
2017-2018 Winter Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2017-2018. El Nino /
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Last updated: September 2008
 North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: September 2008 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2007
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: September 2008 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2007
Storm and Storm Systems Related Vocabulary and Definitions. Magnitudes are measured differently for different hazard types:
 Storm and Storm Systems Related Vocabulary and Definitions Magnitude: this is an indication of the scale of an event, often synonymous with intensity or size. In natural systems, magnitude is also related
Storm and Storm Systems Related Vocabulary and Definitions Magnitude: this is an indication of the scale of an event, often synonymous with intensity or size. In natural systems, magnitude is also related
Global warming and Extremes of Weather. Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Global warming and Extremes of Weather Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate change Can we
Global warming and Extremes of Weather Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate change Can we
The recent retreat of glaciers in the world
 The recent retreat of glaciers in the world Consequences for the global environment Dr Bernard Francou Director of Research Emeritus Grenoble-Alpes University - France Glaciers are part of the cryosphere
The recent retreat of glaciers in the world Consequences for the global environment Dr Bernard Francou Director of Research Emeritus Grenoble-Alpes University - France Glaciers are part of the cryosphere
Don t like the weather? Wait ten minutes. has been a phrase used by many in the Great
 Climate Change in the Great Lakes Michael John Michalek Don t like the weather? Wait ten minutes. has been a phrase used by many in the Great Lakes region. With weather and temperature extremes being pushed
Climate Change in the Great Lakes Michael John Michalek Don t like the weather? Wait ten minutes. has been a phrase used by many in the Great Lakes region. With weather and temperature extremes being pushed
Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis
 Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report Presented by R.K. Pachauri, IPCC Chair and Bubu Jallow, WG 1 Vice Chair Nairobi, 6 February
Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report Presented by R.K. Pachauri, IPCC Chair and Bubu Jallow, WG 1 Vice Chair Nairobi, 6 February
Possible Applications of Deep Neural Networks in Climate and Weather. David M. Hall Assistant Research Professor Dept. Computer Science, CU Boulder
 Possible Applications of Deep Neural Networks in Climate and Weather David M. Hall Assistant Research Professor Dept. Computer Science, CU Boulder Quick overview of climate and weather models Weather models
Possible Applications of Deep Neural Networks in Climate and Weather David M. Hall Assistant Research Professor Dept. Computer Science, CU Boulder Quick overview of climate and weather models Weather models
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Last updated: August 2009
 North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: August 2009 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2008 through
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: August 2009 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2008 through
LET NOT THAT ICE MELT IN SVALBARD S. RAJAN, INCOIS NEELU SINGH, NCAOR
 LET NOT THAT ICE MELT IN SVALBARD S. RAJAN, INCOIS NEELU SINGH, NCAOR 1. Arctic (surface air) temperatures are rising twice as fast as the temperatures in the rest of the world (Amplification). The Arctic
LET NOT THAT ICE MELT IN SVALBARD S. RAJAN, INCOIS NEELU SINGH, NCAOR 1. Arctic (surface air) temperatures are rising twice as fast as the temperatures in the rest of the world (Amplification). The Arctic
Polar Portal Season Report 2016
 Polar Portal Season Report 2016 Less ice both on land and at sea This year s report is the fourth since the Polar Portal was launched, and as an introduction, we have chosen to take a look at the trends
Polar Portal Season Report 2016 Less ice both on land and at sea This year s report is the fourth since the Polar Portal was launched, and as an introduction, we have chosen to take a look at the trends
Regional Outlook for the Bering-Chukchi-Beaufort Seas Contribution to the 2018 Sea Ice Outlook
 Regional Outlook for the Bering-Chukchi-Beaufort Seas Contribution to the 2018 Sea Ice Outlook 25 July 2018 Matthew Druckenmiller (National Snow and Ice Data Center, Univ. Colorado Boulder) & Hajo Eicken
Regional Outlook for the Bering-Chukchi-Beaufort Seas Contribution to the 2018 Sea Ice Outlook 25 July 2018 Matthew Druckenmiller (National Snow and Ice Data Center, Univ. Colorado Boulder) & Hajo Eicken
Spectral Albedos. a: dry snow. b: wet new snow. c: melting old snow. a: cold MY ice. b: melting MY ice. d: frozen pond. c: melting FY white ice
 Spectral Albedos a: dry snow b: wet new snow a: cold MY ice c: melting old snow b: melting MY ice d: frozen pond c: melting FY white ice d: melting FY blue ice e: early MY pond e: ageing ponds Extinction
Spectral Albedos a: dry snow b: wet new snow a: cold MY ice c: melting old snow b: melting MY ice d: frozen pond c: melting FY white ice d: melting FY blue ice e: early MY pond e: ageing ponds Extinction
Here s what a weak El Nino usually brings to the nation with temperatures:
 Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2018-2019. El Nino / La Nina: When looking
Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2018-2019. El Nino / La Nina: When looking
The Atmospheric Circulation
 The Atmospheric Circulation Vertical structure of the Atmosphere http://www.uwsp.edu/geo/faculty/ritter/geog101/textbook/atmosphere/atmospheric_structure.html The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth,
The Atmospheric Circulation Vertical structure of the Atmosphere http://www.uwsp.edu/geo/faculty/ritter/geog101/textbook/atmosphere/atmospheric_structure.html The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth,
XVI. Warming and the cryosphere
 XVI. Warming and the cryosphere review temperature from thermometers, satellites, glacier lengths and boreholes all show significant warming in the 20th C+ reconstruction of past temperatures from corals,
XVI. Warming and the cryosphere review temperature from thermometers, satellites, glacier lengths and boreholes all show significant warming in the 20th C+ reconstruction of past temperatures from corals,
Resolution XIII.23. Wetlands in the Arctic and sub-arctic
 13th Meeting of the Conference of the Contracting Parties to the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands Wetlands for a Sustainable Urban Future Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 21-29 October 2018 Resolution XIII.23
13th Meeting of the Conference of the Contracting Parties to the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands Wetlands for a Sustainable Urban Future Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 21-29 October 2018 Resolution XIII.23
Observing Arctic Sea Ice Change. Christian Haas
 Observing Arctic Sea Ice Change Christian Haas Decreasing Arctic sea ice extent in September Ice extent is decreasing, but regional patterns are very different every year The Cryosphere Today, http://arctic.atmos.uiuc.edu;
Observing Arctic Sea Ice Change Christian Haas Decreasing Arctic sea ice extent in September Ice extent is decreasing, but regional patterns are very different every year The Cryosphere Today, http://arctic.atmos.uiuc.edu;
Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future. Basic Concepts
 Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future Basic Concepts Weather instantaneous or synoptic measurements Climate time / space average Weather - the state of the air and atmosphere at a particular
Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future Basic Concepts Weather instantaneous or synoptic measurements Climate time / space average Weather - the state of the air and atmosphere at a particular
Chapter 2. Changes in Sea Level Melting Cryosphere Atmospheric Changes Summary IPCC (2013)
 IPCC (2013) Ice is melting faster (sea ice, glaciers, ice sheets, snow) Sea level is rising More ocean heat content More intense rainfall More severe drought Fewer frosts More heat waves Spring is arriving
IPCC (2013) Ice is melting faster (sea ice, glaciers, ice sheets, snow) Sea level is rising More ocean heat content More intense rainfall More severe drought Fewer frosts More heat waves Spring is arriving
Second Session of the Pan-Arctic Regional Climate Outlook Forum (PARCOF-2), virtual forum, October 2018
 Second Session of the Pan-Arctic Regional Climate Outlook Forum (PARCOF-2), virtual forum, October 2018 Consensus Statement for the Arctic Winter 2018-2019 Season Outlook Climate change in the Arctic is
Second Session of the Pan-Arctic Regional Climate Outlook Forum (PARCOF-2), virtual forum, October 2018 Consensus Statement for the Arctic Winter 2018-2019 Season Outlook Climate change in the Arctic is
Arctic Oxidation Chemistry
 19 July 2016 Connaught Summer Institute 1 Arctic Oxidation Chemistry Connaught Summer Institute 2016 William (Bill) Simpson Geophysical Institute and Department of Chemistry, University of Alaska Fairbanks
19 July 2016 Connaught Summer Institute 1 Arctic Oxidation Chemistry Connaught Summer Institute 2016 William (Bill) Simpson Geophysical Institute and Department of Chemistry, University of Alaska Fairbanks
CLIMATE READY BOSTON. Climate Projections Consensus ADAPTED FROM THE BOSTON RESEARCH ADVISORY GROUP REPORT MAY 2016
 CLIMATE READY BOSTON Sasaki Steering Committee Meeting, March 28 nd, 2016 Climate Projections Consensus ADAPTED FROM THE BOSTON RESEARCH ADVISORY GROUP REPORT MAY 2016 WHAT S IN STORE FOR BOSTON S CLIMATE?
CLIMATE READY BOSTON Sasaki Steering Committee Meeting, March 28 nd, 2016 Climate Projections Consensus ADAPTED FROM THE BOSTON RESEARCH ADVISORY GROUP REPORT MAY 2016 WHAT S IN STORE FOR BOSTON S CLIMATE?
EC-PORS III Research. Sodankylä, February Developing a Polar Prediction System
 EC-PORS III Research Sodankylä, February 2012 Developing a Polar Prediction System Polar Prediction System - Status 1. EC-PORS I (Oct. 2009) -> initial discussions 2. WWRP/THORPEX Polar Prediction Workshop,
EC-PORS III Research Sodankylä, February 2012 Developing a Polar Prediction System Polar Prediction System - Status 1. EC-PORS I (Oct. 2009) -> initial discussions 2. WWRP/THORPEX Polar Prediction Workshop,
Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review
 Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Climate in a region is a. the long-term,
Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Climate in a region is a. the long-term,
Projected Impacts of Climate Change in Southern California and the Western U.S.
 Projected Impacts of Climate Change in Southern California and the Western U.S. Sam Iacobellis and Dan Cayan Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego Sponsors: NOAA RISA
Projected Impacts of Climate Change in Southern California and the Western U.S. Sam Iacobellis and Dan Cayan Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego Sponsors: NOAA RISA
Global warming is unequivocal: The 2007 IPCC Assessment
 Global warming is unequivocal: The 2007 IPCC Assessment Kevin E. Trenberth * March 2, 2007 * Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the author
Global warming is unequivocal: The 2007 IPCC Assessment Kevin E. Trenberth * March 2, 2007 * Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the author
Chapter 3 East Timor (Timor-Leste)
 Chapter 3 East Timor (Timor-Leste) 49 3.1 Climate Summary 3.1.1 Current Climate Despite missing temperature records for Dili Airport, it is probable that over the past half century there has been a warming
Chapter 3 East Timor (Timor-Leste) 49 3.1 Climate Summary 3.1.1 Current Climate Despite missing temperature records for Dili Airport, it is probable that over the past half century there has been a warming
Lithosphere: (Rocky Sphere) Solid, rocky, outer layer of the Earth. Includes the crust and part of the upper mantle. Lithosphere
 Lithosphere: (Rocky Sphere) Solid, rocky, outer layer of the Earth. Includes the crust and part of the upper mantle. Lithosphere Permafrost Permafrost Ground that is at a temperature of 0 or below for
Lithosphere: (Rocky Sphere) Solid, rocky, outer layer of the Earth. Includes the crust and part of the upper mantle. Lithosphere Permafrost Permafrost Ground that is at a temperature of 0 or below for
The continent of Antarctica Resource N1
 The continent of Antarctica Resource N1 Prepared by Gillian Bunting Mapping and Geographic Information Centre, British Antarctic Survey February 1999 Equal area projection map of the world Resource N2
The continent of Antarctica Resource N1 Prepared by Gillian Bunting Mapping and Geographic Information Centre, British Antarctic Survey February 1999 Equal area projection map of the world Resource N2
Title. Author(s)Maslowski, Wieslaw. Citation 地球温暖化による劇変を解明する. 平成 20 年 6 月 24 日. 札幌市. Issue Date Doc URL. Type.
 Title When will Summer Arctic Sea Ice Disappear? Author(s)Maslowski, Wieslaw Citation 地球温暖化による劇変を解明する. 平成 20 年 6 月 24 日. 札幌市 Issue Date 2008-06-24 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/34395 Type conference
Title When will Summer Arctic Sea Ice Disappear? Author(s)Maslowski, Wieslaw Citation 地球温暖化による劇変を解明する. 平成 20 年 6 月 24 日. 札幌市 Issue Date 2008-06-24 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/34395 Type conference
APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1
 APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1 1 By David B. Fissel, Mar Martínez de Saavedra Álvarez, and Randy C. Kerr, ASL Environmental Sciences Inc. (Feb. 2012) West Greenland Seismic
APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1 1 By David B. Fissel, Mar Martínez de Saavedra Álvarez, and Randy C. Kerr, ASL Environmental Sciences Inc. (Feb. 2012) West Greenland Seismic
Terrestrial Climate Change Variables
 Terrestrial Climate Change Variables Content Terrestrial Climate Change Variables Surface Air Temperature Land Surface Temperature Sea Level Ice Level Aerosol Particles (acid rain) Terrestrial Climate
Terrestrial Climate Change Variables Content Terrestrial Climate Change Variables Surface Air Temperature Land Surface Temperature Sea Level Ice Level Aerosol Particles (acid rain) Terrestrial Climate
A Tutorial on Climate Change Science: The. 4 th National Climate Assessment CLIMATE SCIENCE. Don Wuebbles
 CLIMATE SCIENCE S P E C I A L R E P O R T A Tutorial on Climate Change Science: The Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume I 4 th National Climate Assessment Don Wuebbles Department of Atmospheric Sciences
CLIMATE SCIENCE S P E C I A L R E P O R T A Tutorial on Climate Change Science: The Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume I 4 th National Climate Assessment Don Wuebbles Department of Atmospheric Sciences
What the Science Tells Us & How Practitioners Can Use the Science
 What the Science Tells Us & How Practitioners Can Use the Science Presented at APTA Los Angeles, CA Presented by Dr. B. Tod Delaney President, First Environment, Inc. Wed. August 3, 2011 1 Agenda 1. What
What the Science Tells Us & How Practitioners Can Use the Science Presented at APTA Los Angeles, CA Presented by Dr. B. Tod Delaney President, First Environment, Inc. Wed. August 3, 2011 1 Agenda 1. What
