CAM Tutorial. Sea Ice Modeling 31 July 2009 David Bailey and Marika Holland, NCAR
|
|
|
- Cleopatra McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CAM Tutorial Sea Ice Modeling 31 July 2009 David Bailey and Marika Holland, NCAR
2 Sea ice influences in the climate system Surface albedo in March > 0.8 < 0.1 Ice-Ocean Freshwater Exchange
3 Contrasting the Hemispheres Arctic Ocean surrounded by land (thicker ice). Southern Ocean unbounded (free drift). Larger seasonal cycle in south. Winter extent set by ocean in south and land/ ocean in north.
4 Source: NSIDC Sept Ice Extent : 23% less than previous minimum Arctic summer sea ice Source: Cryosphere Today, U. Illinois
5 Loss of the summer Arctic ice cover in context From 1980 to 2005: summer ice loss equal to 24 states; most of the US east of the Mississippi To 2007: 5 additional states (courtesy of Harry Stern, U. Washington) (courtesy of Dr. Don Perovich, CRREL)
6 We really need thickness data! Bourke and Garrett 1987 Laxon et al. 2003
7 Transition Towards Younger, Thinner Ice Ice age tracking algorithm from C. Fowler and J. Maslanik By 2007 ice >5 years is only 10% of the perennial ice pack. Younger ice is generally thinner ice Consistent with ULS data; hindcast model experiments Spring 1986 Spring 1990 Spring 2007 Maslanik et al., 2007
8 The data through 2007, however suggest more warming! Antarctic temperature trend from shows a slight cooling. (Earth Observatory.)
9 CCSM Sea Ice Model Three primary components Thermodynamics Solves for ice temperature, vertical melt/growth rates Dynamics Ice motion Ice Thickness Distribution Subgridscale parameterization, redistribution resulting from ridging/rafting, etc
10 CCSM Sea Ice Model (2) Physical Processes (included above) Radiative transfer in ice and snow. Ridging / Rafting. Snow-ice formation.
11 Sea ice thermodynamics F sw αf sw F LW F SH F LH Simulate vertical heat transfer (conduction, SW absorption) h i T 1 T 2 T 3 T 4 F ocn -k dt/dz h s Balance of fluxes at ice surface (iceatm exchange, conduction, ice melt) Balance of fluxes at ice base (ice-ocn exchange, conduction, ice melt/growth)
12 Vertical heat transfer ρc T t = z k T z + Q SW Assume brine pockets are in thermal equilibrium with ice Heat capacity and conductivity are functions of T/S of ice Assume constant salinity profile Assume non-varying density Assume pockets/channels are brine filled Q SW = d dz I SW e κz where I SW = i 0 (1 α)f SW (from Light, Maykut, Grenfell, 2003) (Maykut and Untersteiner, 1971; Bitz and Lipscomb, 1999; others)
13 Albedo Melt ponds are prevalent on sea ice. Influence surface albedo and ice mass budget. Parameterized albedo depends on surface state (snow, temp, h i, ponds). 1 km Albedo Evolution During SHEBA (Perovich et al. 2002)
14 Ice Dynamics m u t = mfk u + τ a + τ o Coriolis Air stress Ocean stress mg H + σ Sea Slope Internal Ice Stress Force balance between wind stress, water stress, internal ice stress, coriolis and stress associated with sea surface slope Ice freely diverges (no tensile strength) Ice resists convergence and shear Each ice category advected with same velocity field u = 0
15 Ice Thickness Distribution g t = h ( fg) + L(g) ( v g) + Ψ(h,g, v ) (Thorndike et al., 1975) g = obs, h = 2 or 1 Evolution depends on: Ice growth, lateral melt, ice divergence, and mechanical redistribution (riding/rafting)
16 CICE model is discretized on an Arakawa B-grid using a dipole or tripole grid.
17 Computational Decomposition y x
18 Coupling with Atmosphere Sea ice receives temperature, density, humidity, incoming radiation fields, rain, and snow. Sea ice returns grid cell aggregate ice fraction and thickness, surface temperature, albedo, surface stresses, turbulent heat fluxes, and upward radiative fluxes.
19 CCSM4 Sea Ice Component Community Ice CodE (CICE) 4.0 Base Code Delta-Eddington Radiative Transfer in sea ice and snow. (Briegleb and Light) Melt Pond Parameterization. (Bailey and Holland) Arbitrary Number of Tracers (for example age, melt ponds, aerosols). Simple (linear) snow aging. Aerosol cycling and deposition on sea ice / snow.
20 1850 control and 20 th Century Runs
21 1850 control and 20 th Century Runs (2)
22 Summary Sea ice is important! Complicated discontinuous surface represented by continuum model. Specified ice fraction for standalone CAM is a simplification. Ongoing research into new sea ice physics and parameterizations.
Sea Ice Modeling for Climate Applications. Marika M Holland (NCAR) David Bailey (NCAR), Cecilia Bitz (U. Washington), Elizabeth Hunke (LANL)
 Sea Ice Modeling for Climate Applications Marika M Holland (NCAR) David Bailey (NCAR), Cecilia Bitz (U. Washington), Elizabeth Hunke (LANL) Surface albedo > 0.8 < 0.1 Why do we care about sea ice? Surface
Sea Ice Modeling for Climate Applications Marika M Holland (NCAR) David Bailey (NCAR), Cecilia Bitz (U. Washington), Elizabeth Hunke (LANL) Surface albedo > 0.8 < 0.1 Why do we care about sea ice? Surface
Arctic climate projections and progress towards a new CCSM. Marika Holland NCAR
 Arctic climate projections and progress towards a new CCSM Marika Holland NCAR The Arctic is changing! Loss of Sept Arctic Sea Ice 2002 Loss of about 8% per decade Or >20% since 1979 (Courtesy I. Rigor
Arctic climate projections and progress towards a new CCSM Marika Holland NCAR The Arctic is changing! Loss of Sept Arctic Sea Ice 2002 Loss of about 8% per decade Or >20% since 1979 (Courtesy I. Rigor
Sea Ice Update. Marika Holland and David Bailey. National Center for Atmospheric Research. CESM Workshop. University of Toronto
 Sea Ice Update Marika Holland and David Bailey National Center for Atmospheric Research CESM Workshop University of Toronto November June 2017 2012 NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation
Sea Ice Update Marika Holland and David Bailey National Center for Atmospheric Research CESM Workshop University of Toronto November June 2017 2012 NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation
The forcings and feedbacks of rapid Arctic sea ice loss
 The forcings and feedbacks of rapid Arctic sea ice loss Marika Holland, NCAR With: C. Bitz (U.WA), B. Tremblay (McGill), D. Bailey (NCAR), J. Stroeve (NSIDC), M. Serreze (NSIDC), D. Lawrence (NCAR), S
The forcings and feedbacks of rapid Arctic sea ice loss Marika Holland, NCAR With: C. Bitz (U.WA), B. Tremblay (McGill), D. Bailey (NCAR), J. Stroeve (NSIDC), M. Serreze (NSIDC), D. Lawrence (NCAR), S
Influence of the Sea Ice Thickness Distribution on Polar Climate in CCSM3
 2398 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 19 Influence of the Sea Ice Thickness Distribution on Polar Climate in CCSM3 MARIKA M. HOLLAND National Center for Atmospheric Research,* Boulder, Colorado CECILIA
2398 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 19 Influence of the Sea Ice Thickness Distribution on Polar Climate in CCSM3 MARIKA M. HOLLAND National Center for Atmospheric Research,* Boulder, Colorado CECILIA
Influence of the Sea Ice Thickness Distribution on Polar Climate in CCSM3
 Influence of the Sea Ice Thickness Distribution on Polar Climate in CCSM3 Marika M. Holland, National Center for Atmospheric Research PO Box 3000 Boulder, CO 80307 Phone: 303-497-1734 Fax: 303-497-1700
Influence of the Sea Ice Thickness Distribution on Polar Climate in CCSM3 Marika M. Holland, National Center for Atmospheric Research PO Box 3000 Boulder, CO 80307 Phone: 303-497-1734 Fax: 303-497-1700
Early Student Support to Investigate the Role of Sea Ice-Albedo Feedback in Sea Ice Predictions
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Early Student Support to Investigate the Role of Sea Ice-Albedo Feedback in Sea Ice Predictions Cecilia M. Bitz Atmospheric
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Early Student Support to Investigate the Role of Sea Ice-Albedo Feedback in Sea Ice Predictions Cecilia M. Bitz Atmospheric
Importance of physics, resolution and forcing in hindcast simulations of Arctic and Antarctic sea ice variability and trends
 WCRP Workshop on Seasonal to Multi-Decadal Predictability of Polar Climate Bergen, 25-29 October 2010 Importance of physics, resolution and forcing in hindcast simulations of Arctic and Antarctic sea ice
WCRP Workshop on Seasonal to Multi-Decadal Predictability of Polar Climate Bergen, 25-29 October 2010 Importance of physics, resolution and forcing in hindcast simulations of Arctic and Antarctic sea ice
Modeling sea-ice and its interactions with the ocean and the atmosphere
 Modeling sea-ice and its interactions with the ocean and the atmosphere H. Goosse, T. Fichefet, R. Timmermann, M. Vancoppenolle Institut d Astronomie et de Géophysique G. Lemaître. UCL, Louvain-la-Neuve,
Modeling sea-ice and its interactions with the ocean and the atmosphere H. Goosse, T. Fichefet, R. Timmermann, M. Vancoppenolle Institut d Astronomie et de Géophysique G. Lemaître. UCL, Louvain-la-Neuve,
Spectral Albedos. a: dry snow. b: wet new snow. c: melting old snow. a: cold MY ice. b: melting MY ice. d: frozen pond. c: melting FY white ice
 Spectral Albedos a: dry snow b: wet new snow a: cold MY ice c: melting old snow b: melting MY ice d: frozen pond c: melting FY white ice d: melting FY blue ice e: early MY pond e: ageing ponds Extinction
Spectral Albedos a: dry snow b: wet new snow a: cold MY ice c: melting old snow b: melting MY ice d: frozen pond c: melting FY white ice d: melting FY blue ice e: early MY pond e: ageing ponds Extinction
(1) Arctic Sea Ice Predictability,
 (1) Arctic Sea Ice Predictability, (2) It s Long-term Loss and Implications for Ocean Conditions Marika Holland, NCAR With contributions from: David Bailey, Alex Jahn, Jennifer Kay, Laura Landrum, Steve
(1) Arctic Sea Ice Predictability, (2) It s Long-term Loss and Implications for Ocean Conditions Marika Holland, NCAR With contributions from: David Bailey, Alex Jahn, Jennifer Kay, Laura Landrum, Steve
Update on CICE activities
 CLIMATE, OCEAN AND SEA ICE MODELING PROGRAM Update on CICE activities Elizabeth Hunke October 30, 2009 Outline 1 The Current State of the Model 2 Community Development Examples 3 LANL Development Outline
CLIMATE, OCEAN AND SEA ICE MODELING PROGRAM Update on CICE activities Elizabeth Hunke October 30, 2009 Outline 1 The Current State of the Model 2 Community Development Examples 3 LANL Development Outline
Ice-Albedo Feedback Process in the Arctic Ocean
 Ice-Albedo Feedback Process in the Arctic Ocean Donald K. Perovich John Weatherly Mark Hopkins Jacqueline A. Richter-Menge U. S. Army Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory 72 Lyme Road Hanover
Ice-Albedo Feedback Process in the Arctic Ocean Donald K. Perovich John Weatherly Mark Hopkins Jacqueline A. Richter-Menge U. S. Army Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory 72 Lyme Road Hanover
Sea Ice Motion: Physics and Observations Ron Kwok Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA
 Sea Ice Motion: Physics and Observations Ron Kwok Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 7 th ESA Earth Observation Summer School ESRIN, Frascati, Italy 4-14 August
Sea Ice Motion: Physics and Observations Ron Kwok Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 7 th ESA Earth Observation Summer School ESRIN, Frascati, Italy 4-14 August
Sea ice modelling for climate applications
 Sea ice modelling for climate applications Helene Banks Ann Keen, Jeff Ridley, Jonathan Gregory, Alison McLaren William Connolley (BAS) Martin Vancoppenolle (UCL) Bill Lipscomb (Los Alamos) 7 th September
Sea ice modelling for climate applications Helene Banks Ann Keen, Jeff Ridley, Jonathan Gregory, Alison McLaren William Connolley (BAS) Martin Vancoppenolle (UCL) Bill Lipscomb (Los Alamos) 7 th September
Sea ice: physical properties, processes and trends. Stephen Howell Climate Research Division, Environment and Climate Change Canada July 18, 2017
 Sea ice: physical properties, processes and trends Stephen Howell Climate Research Division, Environment and Climate Change Canada July 18, 2017 3-Part Sea Ice Lecture Overview 1. Physical properties,
Sea ice: physical properties, processes and trends Stephen Howell Climate Research Division, Environment and Climate Change Canada July 18, 2017 3-Part Sea Ice Lecture Overview 1. Physical properties,
Sea-Ice Prediction in the GFDL model framework
 Sea-Ice Prediction in the GFDL model framework NGGPS Sea Ice Model Workshop February 3, 2016 Mitch Bushuk Princeton University and GFDL With contributions from: Michael Winton, Robert Hallberg, Rym Msadek,
Sea-Ice Prediction in the GFDL model framework NGGPS Sea Ice Model Workshop February 3, 2016 Mitch Bushuk Princeton University and GFDL With contributions from: Michael Winton, Robert Hallberg, Rym Msadek,
Impact of refreezing melt ponds on Arctic sea ice basal growth
 1 2 Impact of refreezing melt ponds on Arctic sea ice basal growth Daniela Flocco (1), Daniel L. Feltham (1), David Schröeder (1), Michel Tsamados (2) 3 4 5 6 7 (1) Centre for Polar Observations and Modelling
1 2 Impact of refreezing melt ponds on Arctic sea ice basal growth Daniela Flocco (1), Daniel L. Feltham (1), David Schröeder (1), Michel Tsamados (2) 3 4 5 6 7 (1) Centre for Polar Observations and Modelling
The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change. Renguang Wu
 The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change Renguang Wu Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing World Conference on Climate Change
The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change Renguang Wu Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing World Conference on Climate Change
Outline: 1) Extremes were triggered by anomalous synoptic patterns 2) Cloud-Radiation-PWV positive feedback on 2007 low SIE
 Identifying Dynamical Forcing and Cloud-Radiative Feedbacks Critical to the Formation of Extreme Arctic Sea-Ice Extent in the Summers of 2007 and 1996 Xiquan Dong University of North Dakota Outline: 1)
Identifying Dynamical Forcing and Cloud-Radiative Feedbacks Critical to the Formation of Extreme Arctic Sea-Ice Extent in the Summers of 2007 and 1996 Xiquan Dong University of North Dakota Outline: 1)
Arctic Ocean simulation in the CCSM4
 Arctic Ocean simulation in the CCSM4 Alexandra Jahn National Center for Atmospheric Sciences, Boulder, USA Collaborators: K. Sterling, M.M. Holland, J. Kay, J.A. Maslanik, C.M. Bitz, D.A. Bailey, J. Stroeve,
Arctic Ocean simulation in the CCSM4 Alexandra Jahn National Center for Atmospheric Sciences, Boulder, USA Collaborators: K. Sterling, M.M. Holland, J. Kay, J.A. Maslanik, C.M. Bitz, D.A. Bailey, J. Stroeve,
Arctic Ocean-Sea Ice-Climate Interactions
 Arctic Ocean-Sea Ice-Climate Interactions Sea Ice Ice extent waxes and wanes with the seasons. Ice extent is at a maximum in March (typically 14 million square km, about twice the area of the contiguous
Arctic Ocean-Sea Ice-Climate Interactions Sea Ice Ice extent waxes and wanes with the seasons. Ice extent is at a maximum in March (typically 14 million square km, about twice the area of the contiguous
ATOC OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow
![ATOC OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow ATOC OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow](/thumbs/95/126309683.jpg) ATOC 1060-002 OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow cover, permafrost, river and lake ice, ; [3]Glaciers and
ATOC 1060-002 OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow cover, permafrost, river and lake ice, ; [3]Glaciers and
Research Interests: variability of sea ice thickness interactions among ocean, seaice and atmosphere climate modelling
 Dr. Richard Moritz Department Chair, Polar Science Center M.S. (Yale University, 1979), M.A. (University of Colorado, 1979), PhD (Yale University, 1988) Research Interests: variability of sea ice thickness
Dr. Richard Moritz Department Chair, Polar Science Center M.S. (Yale University, 1979), M.A. (University of Colorado, 1979), PhD (Yale University, 1988) Research Interests: variability of sea ice thickness
Modeling Salinity of First-Year Sea Ice
 GFDL, Ocean Climate Model Development Barrow, AK, Jan 2009 Meeting, Oct 30, 2009 037 047 Modeling Salinity of First-Year Sea Ice Chris Petrich, Hajo Eicken, Pat Langhore Geophysical Institute University
GFDL, Ocean Climate Model Development Barrow, AK, Jan 2009 Meeting, Oct 30, 2009 037 047 Modeling Salinity of First-Year Sea Ice Chris Petrich, Hajo Eicken, Pat Langhore Geophysical Institute University
Evaluating the Discrete Element Method as a Tool for Predicting the Seasonal Evolution of the MIZ
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Evaluating the Discrete Element Method as a Tool for Predicting the Seasonal Evolution of the MIZ Arnold J. Song Cold Regions
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Evaluating the Discrete Element Method as a Tool for Predicting the Seasonal Evolution of the MIZ Arnold J. Song Cold Regions
CLIMATE, OCEAN AND SEA ICE MODELING PROGRAM. The Los Alamos Sea Ice Model A CICE 5.0 Update
 CLIMATE, OCEAN AND SEA ICE MODELING PROGRAM The Los Alamos Sea Ice Model A CICE 5.0 Update Outline 1 For Release in 2013 Infrastructure & efficiency improvements 2 multiphase physics approaches 2 new melt
CLIMATE, OCEAN AND SEA ICE MODELING PROGRAM The Los Alamos Sea Ice Model A CICE 5.0 Update Outline 1 For Release in 2013 Infrastructure & efficiency improvements 2 multiphase physics approaches 2 new melt
Changing Arctic: climate, environment, metocean conditions, with a special focus on sea ice
 Changing Arctic: climate, environment, metocean conditions, with a special focus on sea ice (IPCC AR4, WG II, Ch.15) Julienne Stroeve National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), Cooperative Institute for
Changing Arctic: climate, environment, metocean conditions, with a special focus on sea ice (IPCC AR4, WG II, Ch.15) Julienne Stroeve National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), Cooperative Institute for
Observing Arctic Sea Ice Change. Christian Haas
 Observing Arctic Sea Ice Change Christian Haas Decreasing Arctic sea ice extent in September Ice extent is decreasing, but regional patterns are very different every year The Cryosphere Today, http://arctic.atmos.uiuc.edu;
Observing Arctic Sea Ice Change Christian Haas Decreasing Arctic sea ice extent in September Ice extent is decreasing, but regional patterns are very different every year The Cryosphere Today, http://arctic.atmos.uiuc.edu;
Photo courtesy National Geographic
 Welcome to the Polar Climate WG! Quick update: 1. CSL proposal (~85% allocation awarded, 16 month POP starts October 1) 2. All NCAR CMIP5 data on ESG within next month 3. Observational needs/uses living
Welcome to the Polar Climate WG! Quick update: 1. CSL proposal (~85% allocation awarded, 16 month POP starts October 1) 2. All NCAR CMIP5 data on ESG within next month 3. Observational needs/uses living
The Seasonal Evolution of Sea Ice Floe Size Distribution
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. The Seasonal Evolution of Sea Ice Floe Size Distribution Jacqueline A. Richter-Menge and Donald K. Perovich CRREL 72 Lyme
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. The Seasonal Evolution of Sea Ice Floe Size Distribution Jacqueline A. Richter-Menge and Donald K. Perovich CRREL 72 Lyme
The Arctic Energy Budget
 The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Ice-Albedo Feedback Processes in the Arctic Basin
 LONG TERM GOALS Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Ice-Albedo Feedback Processes in the Arctic Basin D.K. Perovich J.A. Richter-Menge W.B. Tucker III M. Sturm U. S. Army Cold Regions Research and
LONG TERM GOALS Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Ice-Albedo Feedback Processes in the Arctic Basin D.K. Perovich J.A. Richter-Menge W.B. Tucker III M. Sturm U. S. Army Cold Regions Research and
Arctic Climate Change. Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013
 Arctic Climate Change Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013 When was this published? Observational Evidence for Arctic
Arctic Climate Change Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013 When was this published? Observational Evidence for Arctic
Sea-ice change around Alaska & Impacts on Human Activities
 Sea-ice change around Alaska & Impacts on Human Activities Hajo Eicken Geophysical Institute University of Alaska Fairbanks, hajo.eicken@gi.alaska.edu Introduction The Arctic sea-ice cover: Observations
Sea-ice change around Alaska & Impacts on Human Activities Hajo Eicken Geophysical Institute University of Alaska Fairbanks, hajo.eicken@gi.alaska.edu Introduction The Arctic sea-ice cover: Observations
Earth s Heat Budget. What causes the seasons? Seasons
 Earth s Heat Budget Solar energy and the global heat budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation A. Rotation of the Earth B. Distance from the Sun C. Variations of Earth s orbit
Earth s Heat Budget Solar energy and the global heat budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation A. Rotation of the Earth B. Distance from the Sun C. Variations of Earth s orbit
Seasonal & Diurnal Temp Variations. Earth-Sun Distance. Eccentricity 2/2/2010. ATS351 Lecture 3
 Seasonal & Diurnal Temp Variations ATS351 Lecture 3 Earth-Sun Distance Change in distance has only a minimal effect on seasonal temperature. Note that during the N. hemisphere winter, we are CLOSER to
Seasonal & Diurnal Temp Variations ATS351 Lecture 3 Earth-Sun Distance Change in distance has only a minimal effect on seasonal temperature. Note that during the N. hemisphere winter, we are CLOSER to
Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes. Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology
 Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology Physical Process Parameterizations Radiative transfer Surface turbulent fluxes Cloudy boundary layer Cloud microphysics
Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology Physical Process Parameterizations Radiative transfer Surface turbulent fluxes Cloudy boundary layer Cloud microphysics
Age Characteristics in a Multidecadal Arctic Sea Ice Simulation
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, 1 2 Age Characteristics in a Multidecadal Arctic Sea Ice Simulation Elizabeth C. Hunke 3 4 T-3 Fluid Dynamics and Solid Mechanics Group, Theoretical
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, 1 2 Age Characteristics in a Multidecadal Arctic Sea Ice Simulation Elizabeth C. Hunke 3 4 T-3 Fluid Dynamics and Solid Mechanics Group, Theoretical
Modelling the Evolution of Arctic Melt Ponds
 Modelling the Evolution of Arctic Melt Ponds Fern Scott Centre for Polar Observation and Modelling Department of Earth Science University College London A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Modelling the Evolution of Arctic Melt Ponds Fern Scott Centre for Polar Observation and Modelling Department of Earth Science University College London A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Antarctic Sea Ice: Mean state and variability in CCSM control run. Laura Landrum, Marika Holland, Dave Schneider, Elizabeth Hunke
 Antarctic Sea Ice: Mean state and variability in CCSM4 1850 control run Laura Landrum, Marika Holland, Dave Schneider, Elizabeth Hunke Overview Model years and variables Mean state and some comparisons
Antarctic Sea Ice: Mean state and variability in CCSM4 1850 control run Laura Landrum, Marika Holland, Dave Schneider, Elizabeth Hunke Overview Model years and variables Mean state and some comparisons
Reconciling different observational data sets from Surface Heat Budget of the Arctic Ocean (SHEBA) for model validation purposes
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2003jc002221, 2005 Reconciling different observational data sets from Surface Heat Budget of the Arctic Ocean (SHEBA) for model validation purposes
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2003jc002221, 2005 Reconciling different observational data sets from Surface Heat Budget of the Arctic Ocean (SHEBA) for model validation purposes
CICE: The LANL sea- ice model. Adrian Turner, Elizabeth Hunke, Nicole Jeffery
 CICE: The LANL sea- ice model Adrian Turner, Elizabeth Hunke, Nicole Jeffery Model overview Structured quadrilateral B grid Both components of velocity at verlces Ice concentralon and mass a cell centres
CICE: The LANL sea- ice model Adrian Turner, Elizabeth Hunke, Nicole Jeffery Model overview Structured quadrilateral B grid Both components of velocity at verlces Ice concentralon and mass a cell centres
Arctic sea ice in IPCC climate scenarios in view of the 2007 record low sea ice event A comment by Ralf Döscher, Michael Karcher and Frank Kauker
 Arctic sea ice in IPCC climate scenarios in view of the 2007 record low sea ice event A comment by Ralf Döscher, Michael Karcher and Frank Kauker Fig. 1: Arctic September sea ice extent in observations
Arctic sea ice in IPCC climate scenarios in view of the 2007 record low sea ice event A comment by Ralf Döscher, Michael Karcher and Frank Kauker Fig. 1: Arctic September sea ice extent in observations
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model
 The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Ice-Albedo Feedback Processes in the Arctic Basin
 LONG TERM GOALS Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Ice-Albedo Feedback Processes in the Arctic Basin D.K. Perovich J.A. Richter-Menge W.B. Tucker III M. Sturm U. S. Army Cold Regions Research and
LONG TERM GOALS Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Ice-Albedo Feedback Processes in the Arctic Basin D.K. Perovich J.A. Richter-Menge W.B. Tucker III M. Sturm U. S. Army Cold Regions Research and
The Cryosphere Radiative Effect in CESM. Justin Perket Mark Flanner CESM Polar Climate Working Group Meeting Wednesday June 19, 2013
 The Cryosphere Radiative Effect in CESM Justin Perket Mark Flanner CESM Polar Climate Working Group Meeting Wednesday June 19, 2013 Cryosphere Radiative Effect (CrRE) A new diagnostic feature is available
The Cryosphere Radiative Effect in CESM Justin Perket Mark Flanner CESM Polar Climate Working Group Meeting Wednesday June 19, 2013 Cryosphere Radiative Effect (CrRE) A new diagnostic feature is available
Radiative Climatology of the North Slope of Alaska and the Adjacent Arctic Ocean
 Radiative Climatology of the North Slope of Alaska and the Adjacent Arctic Ocean C. Marty, R. Storvold, and X. Xiong Geophysical Institute University of Alaska Fairbanks, Alaska K. H. Stamnes Stevens Institute
Radiative Climatology of the North Slope of Alaska and the Adjacent Arctic Ocean C. Marty, R. Storvold, and X. Xiong Geophysical Institute University of Alaska Fairbanks, Alaska K. H. Stamnes Stevens Institute
Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate
 Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Early Student Support to Investigate the Role of Sea Ice-Albedo Feedback in Sea Ice Predictions
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Early Student Support to Investigate the Role of Sea Ice-Albedo Feedback in Sea Ice Predictions Cecilia M. Bitz Atmospheric
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Early Student Support to Investigate the Role of Sea Ice-Albedo Feedback in Sea Ice Predictions Cecilia M. Bitz Atmospheric
Tale of Two Sea-ice Models. Kate Hedstrom, UAF
 Tale of Two Sea-ice Models Kate Hedstrom, UAF Outline Sea ice model features Dynamics Thermodynamics Ice models in ROMS Budgell ice CICE Examples Future directions Dynamics Momentum equation: Assumptions:
Tale of Two Sea-ice Models Kate Hedstrom, UAF Outline Sea ice model features Dynamics Thermodynamics Ice models in ROMS Budgell ice CICE Examples Future directions Dynamics Momentum equation: Assumptions:
Recent Improvements in the U.S. Navy s Ice Modeling Efforts Using CryoSat-2 Ice Thickness for Model Initialization
 Recent Improvements in the U.S. Navy s Ice Modeling Efforts Using CryoSat-2 Ice Thickness for Model Initialization Richard Allard 1, David Hebert 1, Pamela Posey 1, Alan Wallcraft 1, Li Li 2, William Johnston
Recent Improvements in the U.S. Navy s Ice Modeling Efforts Using CryoSat-2 Ice Thickness for Model Initialization Richard Allard 1, David Hebert 1, Pamela Posey 1, Alan Wallcraft 1, Li Li 2, William Johnston
Controls on Arctic Sea Ice from First-Year and Multiyear Ice Survivability
 2378 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 24 Controls on Arctic Sea Ice from First-Year and Multiyear Ice Survivability KYLE C. ARMOUR Department of Physics, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
2378 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 24 Controls on Arctic Sea Ice from First-Year and Multiyear Ice Survivability KYLE C. ARMOUR Department of Physics, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Ice-Albedo Feedback Processes in the Arctic Basin
 Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Ice-Albedo Feedback Processes in the Arctic Basin Gary A. Maykut Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington Seattle, Washington 98195-1640 Voice:
Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Ice-Albedo Feedback Processes in the Arctic Basin Gary A. Maykut Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington Seattle, Washington 98195-1640 Voice:
Causes of Changes in Arctic Sea Ice
 Causes of Changes in Arctic Sea Ice Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Outline 1. Rationale 2. Observational background 3. Modeling insights on Arctic change Pacific / Atlantic Water inflow 4.
Causes of Changes in Arctic Sea Ice Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Outline 1. Rationale 2. Observational background 3. Modeling insights on Arctic change Pacific / Atlantic Water inflow 4.
EFFECTS OF DATA ASSIMILATION OF ICE MOTION IN A BASIN-SCALE SEA ICE MODEL
 Ice in the Environment: Proceedings of the 16th IAHR International Symposium on Ice Dunedin, New Zealand, 2nd 6th December 2002 International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research EFFECTS OF
Ice in the Environment: Proceedings of the 16th IAHR International Symposium on Ice Dunedin, New Zealand, 2nd 6th December 2002 International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research EFFECTS OF
MOSAiC Science Implementation The Multidisciplinary drifting Observatory for the Study of Arctic Climate
 MOSAiC Science Implementation The Multidisciplinary drifting Observatory for the Study of Arctic Climate MOSAiC Coordination Team M. Shupe. 13 March 2016 MOSAiC Plan Drifting, interdisciplinary process
MOSAiC Science Implementation The Multidisciplinary drifting Observatory for the Study of Arctic Climate MOSAiC Coordination Team M. Shupe. 13 March 2016 MOSAiC Plan Drifting, interdisciplinary process
Observed State of the Global Climate
 WMO Observed State of the Global Climate Jerry Lengoasa WMO June 2013 WMO Observations of Changes of the physical state of the climate ESSENTIAL CLIMATE VARIABLES OCEANIC ATMOSPHERIC TERRESTRIAL Surface
WMO Observed State of the Global Climate Jerry Lengoasa WMO June 2013 WMO Observations of Changes of the physical state of the climate ESSENTIAL CLIMATE VARIABLES OCEANIC ATMOSPHERIC TERRESTRIAL Surface
Tropical Pacific responses to Neogene Andean uplift and highlatitude. Ran Feng and Chris Poulsen University of Michigan
 Tropical Pacific responses to Neogene Andean uplift and highlatitude sea ice expansion Ran Feng and Chris Poulsen University of Michigan Reconstructions of Neogene equatorial Pacific SSTs SST difference
Tropical Pacific responses to Neogene Andean uplift and highlatitude sea ice expansion Ran Feng and Chris Poulsen University of Michigan Reconstructions of Neogene equatorial Pacific SSTs SST difference
Lower Stratospheric Cooling. and. Abrupt Change in Arctic Sea Ice
 Lower Stratospheric Cooling and Abrupt Change in Arctic Sea Ice Carl Drews March 16, 2007 ATOC 7500-002 Human Influences on Weather and Climate University of Colorado at Boulder Dr. Roger Pielke Sr, Instructor
Lower Stratospheric Cooling and Abrupt Change in Arctic Sea Ice Carl Drews March 16, 2007 ATOC 7500-002 Human Influences on Weather and Climate University of Colorado at Boulder Dr. Roger Pielke Sr, Instructor
The Rossby Centre Ocean model applied to the Arctic Ocean using ERA-40
 The Ocean model applied to the Arctic Ocean using ERA-40 H.E. Markus Meier, R. Döscher, K. Wyser /SMHI, Norrköping and K. Döös MISU, Stockholm University, Stockholm Ocean model (RCO) based on the BRYAN-COX-SEMTNER
The Ocean model applied to the Arctic Ocean using ERA-40 H.E. Markus Meier, R. Döscher, K. Wyser /SMHI, Norrköping and K. Döös MISU, Stockholm University, Stockholm Ocean model (RCO) based on the BRYAN-COX-SEMTNER
Arctic climate: Unique vulnerability and complex response to aerosols
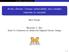 Arctic climate: Unique vulnerability and complex response to aerosols Mark Flanner November 2, 2011 Santa Fe Conference on Global and Regional Climate Change 1 / 18 Arctic: Unique vulnerability to positive
Arctic climate: Unique vulnerability and complex response to aerosols Mark Flanner November 2, 2011 Santa Fe Conference on Global and Regional Climate Change 1 / 18 Arctic: Unique vulnerability to positive
Changing predictability characteristics of Arctic sea ice in a warming climate
 Changing predictability characteristics of Arctic sea ice in a warming climate Marika Holland 1 Laura Landrum 1, John Mioduszewski 2, Steve Vavrus 2, Muyin Wang 3 1. NCAR, 2. U. Wisconsin-Madison, 3. NOAA
Changing predictability characteristics of Arctic sea ice in a warming climate Marika Holland 1 Laura Landrum 1, John Mioduszewski 2, Steve Vavrus 2, Muyin Wang 3 1. NCAR, 2. U. Wisconsin-Madison, 3. NOAA
The Oceans in a Warming World
 The Oceans in a Warming World John Marshall Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences 1. Review global observations of warming trends. Ocean temperature trends key part of the puzzle. 2. Discuss timing
The Oceans in a Warming World John Marshall Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences 1. Review global observations of warming trends. Ocean temperature trends key part of the puzzle. 2. Discuss timing
Ocean Mixing with Lead-Dependent Subgrid Scale Brine Rejection Parameterization in a Climate Model
 J. Ocean Univ. China (Oceanic and Coastal Sea Research) DOI 10.1007/s11802-012-2094-4 ISSN 1672-5182, 2012 11 (4): 473-480 http://www.ouc.edu.cn/xbywb/ E-mail:xbywb@ouc.edu.cn Ocean Mixing with Lead-Dependent
J. Ocean Univ. China (Oceanic and Coastal Sea Research) DOI 10.1007/s11802-012-2094-4 ISSN 1672-5182, 2012 11 (4): 473-480 http://www.ouc.edu.cn/xbywb/ E-mail:xbywb@ouc.edu.cn Ocean Mixing with Lead-Dependent
Centennial-scale Climate Change from Decadally-paced Explosive Volcanism
 Centennial-scale Climate Change from Decadally-paced Explosive Volcanism Yafang Zhong and Gifford Miller INSTAAR, University of Colorado at Boulder, USA Bette Otto-Bliesner, Caspar Ammann, Marika Holland,
Centennial-scale Climate Change from Decadally-paced Explosive Volcanism Yafang Zhong and Gifford Miller INSTAAR, University of Colorado at Boulder, USA Bette Otto-Bliesner, Caspar Ammann, Marika Holland,
Evaluation of snow/ice albedo parameterizations and their impacts on sea ice simulations
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 27: 81 91 (27) Published online 23 June 26 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com) DOI: 1.12/joc.1373 Evaluation of snow/ice albedo parameterizations
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 27: 81 91 (27) Published online 23 June 26 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com) DOI: 1.12/joc.1373 Evaluation of snow/ice albedo parameterizations
Climate Roles of Land Surface
 Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System
 Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
COURSE CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION
 COURSE CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION DATE 4 JUNE 2014 LEADER CHRIS BRIERLEY Course Outline 1. Current climate 2. Changing climate 3. Future climate change 4. Consequences 5. Human
COURSE CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION DATE 4 JUNE 2014 LEADER CHRIS BRIERLEY Course Outline 1. Current climate 2. Changing climate 3. Future climate change 4. Consequences 5. Human
OCN/ATM/ESS 587. Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics.
 OCN/ATM/ESS 587 Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics. Equation of state for seawater General T/S properties of the upper ocean Heat balance of the upper ocean Upper ocean circulation Deep circulation
OCN/ATM/ESS 587 Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics. Equation of state for seawater General T/S properties of the upper ocean Heat balance of the upper ocean Upper ocean circulation Deep circulation
Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Ice-Albedo Feedback Processes in the Arctic Basin
 Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Ice-Albedo Feedback Processes in the Arctic Basin Gary A. Maykut Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington Seattle, Washington 98195-1640 maykut@atmos.washington.edu
Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Ice-Albedo Feedback Processes in the Arctic Basin Gary A. Maykut Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington Seattle, Washington 98195-1640 maykut@atmos.washington.edu
Albedo evolution of seasonal Arctic sea ice
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051432, 2012 Albedo evolution of seasonal Arctic sea ice Donald K. Perovich 1,2 and Christopher Polashenski 1 Received 19 February 2012; revised
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051432, 2012 Albedo evolution of seasonal Arctic sea ice Donald K. Perovich 1,2 and Christopher Polashenski 1 Received 19 February 2012; revised
Interannual Variations of Arctic Cloud Types:
 Interannual Variations of Arctic Cloud Types: Relationships with Sea Ice and Surface Temperature Ryan Eastman Stephen Warren University of Washington Department of Atmospheric Sciences Changes in Arctic
Interannual Variations of Arctic Cloud Types: Relationships with Sea Ice and Surface Temperature Ryan Eastman Stephen Warren University of Washington Department of Atmospheric Sciences Changes in Arctic
Course Outline CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION. 1. Current climate. 2. Changing climate. 3. Future climate change
 COURSE CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION DATE 4 JUNE 2014 LEADER CHRIS BRIERLEY Course Outline 1. Current climate 2. Changing climate 3. Future climate change 4. Consequences 5. Human
COURSE CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION DATE 4 JUNE 2014 LEADER CHRIS BRIERLEY Course Outline 1. Current climate 2. Changing climate 3. Future climate change 4. Consequences 5. Human
What makes the Arctic hot?
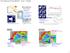 1/3 total USA UN Environ Prog What makes the Arctic hot? Local communities subsistence Arctic Shipping Routes? Decreasing Ice cover Sept 2007 -ice extent (Pink=1979-2000 mean min) Source: NSIDC Oil/Gas
1/3 total USA UN Environ Prog What makes the Arctic hot? Local communities subsistence Arctic Shipping Routes? Decreasing Ice cover Sept 2007 -ice extent (Pink=1979-2000 mean min) Source: NSIDC Oil/Gas
The Regional Arctic System Model (RASM) for Studying High Resolution Climate Changes in the Arctic
 The Regional Arctic System Model (RASM) for Studying High Resolution Climate Changes in the Arctic Mark W. Seefeldt, John J. Cassano, Alice K. Duvivier, and Mimi H. Hughes University of Colorado Boulder
The Regional Arctic System Model (RASM) for Studying High Resolution Climate Changes in the Arctic Mark W. Seefeldt, John J. Cassano, Alice K. Duvivier, and Mimi H. Hughes University of Colorado Boulder
Late-Twentieth-Century Simulation of Arctic Sea Ice and Ocean Properties in the CCSM4
 1MARCH 2012 J A H N E T A L. 1431 Late-Twentieth-Century Simulation of Arctic Sea Ice and Ocean Properties in the CCSM4 ALEXANDRA JAHN,* KARA STERLING, 1 MARIKA M. HOLLAND,* JENNIFER E. KAY,* JAMES A.
1MARCH 2012 J A H N E T A L. 1431 Late-Twentieth-Century Simulation of Arctic Sea Ice and Ocean Properties in the CCSM4 ALEXANDRA JAHN,* KARA STERLING, 1 MARIKA M. HOLLAND,* JENNIFER E. KAY,* JAMES A.
Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI
 Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Electromagnetic Radiation. Radiation and the Planetary Energy Balance. Electromagnetic Spectrum of the Sun
 Radiation and the Planetary Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Solar radiation warms the planet Conversion of solar energy at the surface Absorption and emission by the atmosphere The greenhouse
Radiation and the Planetary Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Solar radiation warms the planet Conversion of solar energy at the surface Absorption and emission by the atmosphere The greenhouse
Benchmarking Polar WRF in the Antarctic *
 Benchmarking Polar WRF in the Antarctic * David H. Bromwich 1,2, Elad Shilo 1,3, and Keith M. Hines 1 1 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, USA
Benchmarking Polar WRF in the Antarctic * David H. Bromwich 1,2, Elad Shilo 1,3, and Keith M. Hines 1 1 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, USA
The Role of Surface Albedo Feedback. in Internal Climate Variability, Transient Climate Change, and Equilibrium Climate Sensitivity
 The Role of Surface Albedo Feedback in Internal Climate Variability, Transient Climate Change, and Equilibrium Climate Sensitivity Alex Hall University of California Los Angeles Department of Atmospheric
The Role of Surface Albedo Feedback in Internal Climate Variability, Transient Climate Change, and Equilibrium Climate Sensitivity Alex Hall University of California Los Angeles Department of Atmospheric
The Ice Age sequence in the Quaternary
 The Ice Age sequence in the Quaternary Subdivisions of the Quaternary Period System Series Stage Age (Ma) Holocene 0 0.0117 Tarantian (Upper) 0.0117 0.126 Quaternary Ionian (Middle) 0.126 0.781 Pleistocene
The Ice Age sequence in the Quaternary Subdivisions of the Quaternary Period System Series Stage Age (Ma) Holocene 0 0.0117 Tarantian (Upper) 0.0117 0.126 Quaternary Ionian (Middle) 0.126 0.781 Pleistocene
Numerical modeling of sea ice in the climate system
 Numerical modeling of sea ice in the climate system by Cecilia M. Bitz Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington Worldwide emissions of CO 2 from human energy-related activities are currently about
Numerical modeling of sea ice in the climate system by Cecilia M. Bitz Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington Worldwide emissions of CO 2 from human energy-related activities are currently about
Worrying about Snow. Ed B-W, UW, Seattle with CC Bitz. Thanks to NCAR (Jen Kay, PCWG)
 Worrying about Snow Ed B-W, UW, Seattle with CC Bitz Thanks to NCAR (Jen Kay, PCWG) or investigating the influence that snow on sea ice has on predictability (and sea ice mean state/trends) Eduardo Blanchard-Wrigglesworth,
Worrying about Snow Ed B-W, UW, Seattle with CC Bitz Thanks to NCAR (Jen Kay, PCWG) or investigating the influence that snow on sea ice has on predictability (and sea ice mean state/trends) Eduardo Blanchard-Wrigglesworth,
Course Outline. About Me. Today s Outline CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION. 1. Current climate. 2.
 Course Outline 1. Current climate 2. Changing climate 3. Future climate change 4. Consequences COURSE CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION DATE 4 JUNE 2014 LEADER 5. Human impacts 6.
Course Outline 1. Current climate 2. Changing climate 3. Future climate change 4. Consequences COURSE CLIMATE SCIENCE A SHORT COURSE AT THE ROYAL INSTITUTION DATE 4 JUNE 2014 LEADER 5. Human impacts 6.
Optimization of a sea ice model using basinwide observations of Arctic sea ice thickness, extent, and velocity
 Optimization of a sea ice model using basinwide observations of Arctic sea ice thickness, extent, and velocity Article Published Version Miller, P. A., Laxon, S. W., Feltham, D. L. and Cresswell, D. J.
Optimization of a sea ice model using basinwide observations of Arctic sea ice thickness, extent, and velocity Article Published Version Miller, P. A., Laxon, S. W., Feltham, D. L. and Cresswell, D. J.
Arctic Climate Response to Forcing from Light-Absorbing Particles in Snow and Sea Ice in CESM
 Manuscript prepared for Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. with version 3.5 of the LATEX class copernicus discussions.cls. Date: 30 December 11 Arctic Climate Response to Forcing from Light-Absorbing Particles
Manuscript prepared for Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. with version 3.5 of the LATEX class copernicus discussions.cls. Date: 30 December 11 Arctic Climate Response to Forcing from Light-Absorbing Particles
Arctic catastrophes in an idealized sea ice model
 Arctic catastrophes in an idealized sea ice model Ian Eisenman March 15, 27 Abstract With recent observations of diminishing summer Arctic sea ice extent, the hypothesis of a tipping point in summer ice
Arctic catastrophes in an idealized sea ice model Ian Eisenman March 15, 27 Abstract With recent observations of diminishing summer Arctic sea ice extent, the hypothesis of a tipping point in summer ice
Whither Arctic Sea Ice?
 Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences University of Colorado Whither Arctic Sea Ice? Walt Meier http://nsidc.org Climate Literacy and Energy Awareness Network May 9, 2011 1 The Cryosphere
Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences University of Colorado Whither Arctic Sea Ice? Walt Meier http://nsidc.org Climate Literacy and Energy Awareness Network May 9, 2011 1 The Cryosphere
Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice. (from Our Changing Planet)
 Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Earth s s Climate System Solar forcing Atmosphere Ocean Land Solid Earth Energy, Water, and Biochemistry
Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Earth s s Climate System Solar forcing Atmosphere Ocean Land Solid Earth Energy, Water, and Biochemistry
Earth s Climate System. Surface Albedo. Climate Roles of Land Surface. Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice
 Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Earth s Climate System Solar forcing Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice Atmosphere Ocean Land Solid Earth Energy, Water, and Biochemistry Cycles (from Our Changing
Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Earth s Climate System Solar forcing Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice Atmosphere Ocean Land Solid Earth Energy, Water, and Biochemistry Cycles (from Our Changing
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1
 CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
Earth s Heat Budget. What causes the seasons? Seasons
 Earth s Heat Budget Solar energy and the global heat budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation A. Rotation of the Earth B. Distance from the Sun C. Variations of Earth s orbit
Earth s Heat Budget Solar energy and the global heat budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation A. Rotation of the Earth B. Distance from the Sun C. Variations of Earth s orbit
How de-coupling cloud radiative feedbacks strengthens the AMOC
 How de-coupling cloud radiative feedbacks strengthens the AMOC Elizabeth Maroon1, Eleanor Middlemas2, Jennifer Kay1, Brian Medeiros3 1CIRES, University of Colorado Boulder, 2University of Miami, 3National
How de-coupling cloud radiative feedbacks strengthens the AMOC Elizabeth Maroon1, Eleanor Middlemas2, Jennifer Kay1, Brian Medeiros3 1CIRES, University of Colorado Boulder, 2University of Miami, 3National
Snow and Sea Ice Physics, Thermodynamics, Dynamics and Remote Sensing
 Snow and Sea Ice Physics, Thermodynamics, Dynamics and Remote Sensing Ryan Galley Center for Earth Observation Science Clayton H. Riddell Faculty of Earth, Environment and Resources Freezing point of seawater
Snow and Sea Ice Physics, Thermodynamics, Dynamics and Remote Sensing Ryan Galley Center for Earth Observation Science Clayton H. Riddell Faculty of Earth, Environment and Resources Freezing point of seawater
The spatial distribution and radiative effects of soot in the snow and sea ice during the SHEBA experiment
 The spatial distribution and radiative effects of soot in the snow and sea ice during the SHEBA experiment Thomas C. Grenfell and Bonnie Light Department of Atmospheric Sciences, Box 35164, University
The spatial distribution and radiative effects of soot in the snow and sea ice during the SHEBA experiment Thomas C. Grenfell and Bonnie Light Department of Atmospheric Sciences, Box 35164, University
Observed rate of loss of Arctic ice extent is faster than IPCC AR4 predictions
 When will Summer Arctic Sea Ice Disappear? Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Collaborators: Jaclyn Clement Kinney, Andrew Miller, Terry McNamara, John Whelan - Naval Postgraduate School Jay Zwally
When will Summer Arctic Sea Ice Disappear? Wieslaw Maslowski Naval Postgraduate School Collaborators: Jaclyn Clement Kinney, Andrew Miller, Terry McNamara, John Whelan - Naval Postgraduate School Jay Zwally
Influence of clouds on radiative fluxes in the Arctic. J. English, J. Kay, A. Gettelman CESM Workshop / PCWG Meeting June 20, 2012
 Influence of clouds on radiative fluxes in the Arctic J. English, J. Kay, A. Gettelman CESM Workshop / PCWG Meeting June 20, 2012 The complexity of arctic clouds Arctic Mixed-Phase Clouds Morrison et al.,
Influence of clouds on radiative fluxes in the Arctic J. English, J. Kay, A. Gettelman CESM Workshop / PCWG Meeting June 20, 2012 The complexity of arctic clouds Arctic Mixed-Phase Clouds Morrison et al.,
