Landslide Hazard Zonation Study in Eastern Indian Himalayan Region
|
|
|
- Josephine Singleton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Section Geohazards and Environment International Journal of Georesources and Environment ijgecamdemia.ca IJGE 07 ): 54 Available at Technical Note Landslide Hazard Zonation Study in Eastern Indian Himalayan Region Manmohan Singh Rawat, Rajendra Dobhal, Varun Joshi, Yaspal Sundriyal Uttarakhand State Council for Science and Technology, Vigyan Dham Jhara, Dehradun, India Guru Govind Singh Indra Prastha University, Sector C, Dwaraka, New Delhi, India Hemawati Nandan Bahuguna Garhwal University, Srinagar 474 Abstract: Sikkim State in the eastern Indian Himalayan Region experiences intensive landslides because of its geologically brittle terrain coupled with heavy rainfall and anthropogenic influences. Based on satellite images and a toposheet from the Survey of India, a total of 50 landslides were identified in a study area of.8 km. Among them, 4 were validated in field survey. The important factors for landslide hazard are identified and thematic maps are prepared in ArcGIS. Impacting factors including geomorphologic properties, drainage and soil conditions are assigned weight factors according to our work knowledge in this region to generate thematic layers in ArcGIS for landslide hazard analysis. A landslide hazard zonation map containing five classes, ranging from very low hazard to very high hazard, is produced. The results provide a reliable database for disaster detection and post disaster management, which is essential to planning developmental activities in this district. Keywords: landslide inventory, morphometry, landslide hazard zonation, satellite data, thematic layers Introduction Hill slopes in the Himalayan region are often prone to instability due to unfavourable geological conditions, river systems with active hydraulic erosion, groundwater conditions, deforestation and other anthropogenic influences Rawat et al 05a). In addition, external triggering factors such as high annual precipitation and seismic activities also increase the probability of instability of hill slopes. With landslide hazards, the Himalayan region is facing major problems of environmental degradation. Therefore, all civil constructions and associated excavations should be properly planned with adequate geological and geotechnical inputs. For this purpose, there is a great need of landslide susceptibility mapping to identify potential landslide areas. Sikkim State in the eastern Indian Himalayan Region IHR) covers an area of 7,0 km and bound in the south by the Great Rangit River, Chumbi valley in the east, Nepal in the west and Tibet China) in the north Raina and Srivastava ). Sikkim Himalayan region is characterized by high denudation rates, its suspended load reaches up to ton/km /year Starkel and Basu 000). Most of its rivers constantly shift channels due to suddenly high discharges during monsoon seasons Jana 00). The study area is in the southern part of Sikkim state. Landslide is a common disaster in the East district of Sikkim under influences of a variety of causative factors, including geological structures, geotectonic activities, changes of river regimes, high slope variation, deforestation, inappropriate land use as well as huge amount of rainfall that acts as a triggering factor. Damages caused by those frequent, sudden and unexpected landslides are enormous and becoming increasingly costly to tackle the associated problems. Various corrective and protective measures have been adopted from time to time but the frequency and magnitude of landslide occurrences have superseded the controlling measures. A partial reason is due to lack of proper understanding of individual landslide characters, mechanisms of slide initiation, as well as indepth information of the concerned area. It is true that this type of natural disasters cannot be checked thoroughly, but proper remedial measures can reduce the magnitude of occurrences. Thus, it is the high time to prepare such a data base and detailed landslide hazard zonation map to take necessary measures to control those hazards in the study area. Materials and Methodology. Study Methods This study includes three components: map interpretation, field surveys and factor analysis. Detail steps are shown in Figure ). * Corresponding Author: Manmohan Singh Rawat, manmohansinghrwtgmail.com, Tel: + 8) 078 Copyright Canamaple Academia Services, DOI: 0.57/ijge
2 IJGE 07 ): 54 Rawat et al Methodology Flow Chart Topo Maps Satellite Image Feild Investigation Georeference Image Processing & GIS Software PreFeild Proximity to Fault Slope Slope Aspect Lithology Landslide density Activity map generated from different layers \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ Geomorphology Lineament Buffer Landuse Polygon to Raster Weight all Layers PostFeild SlopeDip Soil Texture Dissection Index Ruggedness Number Relative Relief Lineament Density!!! Based on Expert Knowledge!!!!!!!!! Rank all Layers!!!!!!!!! Landslide Hazard Zonation!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Result Validation!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Ground Truthing!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Result Generation!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Figure. Flow chart depicting the methodology used in the study.. Geological Setting Sikkim State is located in the Teesta River watershed. Teesta and its tributaries erode deeply on the foothills of the Himalaya. Precambrian rocks cover a major portion of the Sikkim Himalaya and are represented by the following four major rock formations, listed from youngest to oldest: Everest Pelitic Formation, Sikkim Group, Chungthang Formation, and Kanchanjunga Gneiss Group. The central and eastern Himalaya regions near the Teesta River are characterized by largescale thrust movements from northwest to southeast. The East Sikkim Himalaya is mainly traversed by two thrusts called the Chungthang Thrust and the Main Central Thrust MCT), both trending in a NW SE direction. The MCT is a wellknown tectonic boundary between sedimentary and crystalline rocks, separating the Lesser and Greater Himalaya in entire Indian Himalayan Region. It is characterized by crushed rock and fracture zones. The Nepal Sikkim Himalaya and adjacent fore deep area are dominated by conjugate strike slip faults that face the wedges of the Indian shield. Rocks of this terrain are characterized by intense folding, metamorphism,
3 Landslide hazard zonation study in eastern Indian Himalayan region IJGE 07 ): 54 and thrusting in a number of tectonostatigraphy units, which exhibit inversion in stratigraphic succession as well as in metamorphic grading. Within the study area, a total of 5 lineaments are identified from the LISSIII Satellite image Figure a). Lineaments in hilly terrain indicate joints, fractures, faults and other structural features of weakness Figure b) and therefore bear a direct relationship with landslides... Land use/land cover Land use pattern is highly controlled by the underlying lithological properties, topography and hydrology. Human settlements are mainly located in water seepage zones or near to springs. Agricultural practices are confined to areas of low relief which are underlain by weak rock formation, i.e., schists, phyllite, weathered gneisses and crushed quartzites. Forest is more frequent over moderate and steep slopes. Land use/land cover classes are classified into seven categories Joshi et al 00): Tree Clad area, Forest/Semi EvergreenDenseOpen/Closed, WastelandScrub land Open scrub, Natural/Semi Natural, Agriculture land, settlements and Water bodies Figure a). Visual interpretation of Indian Satellite data was carried out at :50,000 scale to generate a geomorphic map Figure b). Three major geomorphic units dissected hills, terraces and piedmont alluvial plains were delineated for Landslide Hazard Zonation mapping. Dissected hills cover most of the study area, 0.5 km out of the total of.8 km. The hills are dissected by major and numerous tributaries which inflict severe erosion down hills. Alluvial fans are formed following hydraulic sediments. Elevation in this area is highly variable, ranging from 800 m in the southeastern of the study area to over 4,000 m northwest... Drainage Basin Morphometry Drainage basin morphometry was delineated from SOI topographical map 78A/ of the Survey of India and satellite images using Arc GIS.. Morphometric analysis using the method suggested by Strahler 5) and Goudie 0) for the following parameters: Drainage density Dd), Ruggedness Number Rn), Dissection Index Di) and Relative Relief Rh). ) Drainage Density Drainage lines were digitized from Survey of India toposheet 78A/. Channel lengths were measured and drainage density was calculated by dividing the total channel length to catchment area. Drainage density is an important indicator of the linear scale of the landform element in stream eroded topography. A low drainage density is favoured in regions of highly permeable subsoil material, under dense vegetative cover, and where relief is low. Drainage density is also related to climate, surface roughness and runoff. Drainage density in the study area is low, varying between.0 to 7.5 km/km Table, Figure 4a & b). It is classified into four classes: I, II, III and IV, denoting drainage density ranges <, 5, 57, and >7 km/km respectively. a) b) Thrust Lineaments Lineaments Buffer 500m Fault Kanchendzonga Gneiss Buxa Formation Lingtse Gneiss Chungthang Formation Metabasic rocks Figure. a) Lithological map of the study b) Lineament buffer) map 7
4 IJGE 07 ): 54 Rawat et al a) b) Agriciultural Land Built Up area Forest/SemiEvergreen Tree Clad area Open) WastelandScrub land Cliff & Precipetous slope Escarpments Moderately Steeply Sloping 50%) Steeply Sloping 50%) Summit & Ridge Very Steeply Sloping >50%) Natural/Semi natural Alpine Water bodiesriver Figure. Land use / land cover b) Geomorphological map of the study area a) b) First Order Second Order Third Order Forth Order Fifth Order < 5 57 >7 Figure 4. a) Drainage Order b) Drainage Density of the study area 8
5 Landslide hazard zonation study in eastern Indian Himalayan region IJGE 07 ): 54 Table. Distribution of Drainage Density in the study area Range of Drainage Density km/km ) Area km ) Area %) Attribute Zone < Low I Moderate II Moderately High III > High IV Table. Distribution of Ruggedness Number in the study area Ruggedness Number Area km ) Area %) Attribute Zone < Low I Moderate II Moderately High III > High IV Table. Distribution of Dissection Index in the study area Dissection Index Area km ) Area %) Attribute Zone < Low I Moderate II Moderately High III > High IV Table 4. Distribution of Relative Relief in the study area Relative Relief m) Area km ) Area %) Attribute < Low Moderate Moderately High > High ) Ruggedness Number Topographic Ruggedness Number Rn) is the product of maximum basin relief H) and drainage density Dd), where both parameters are in the same unit. An extremely high value of Ruggedness number occurs when both variables are large and slope is steep and long Strahler 5). Equation for the computation of Ruggedness Number is: Rn= Rh Dd 000 where, Rn is ruggedness index, Rh is relative relief, and Dd is drainage density. Ruggedness Number in the study area varies from 700 to 4,70 Figure 5a and Table ). They increase towards east and southwest in the study area. ) Dissection Index Dissection index is the ratio of the maximum relative relief to maximum absolute relief. It reflects the dynamic potential of the area and range is from '0' complete absence of vertical dissection) to '' vertical cliffs on hill slope or at sea level). The higher the dissection index is, the greater potential of the undulation and instability of the terrain. The dissection index in the study area varies from 0.0 to 0. Figure 5b and Table ). High dissection index >0.) occurs in 8.05% of the total area;.5% of the area falls in middle to low dissection index categories and majority areas are moderately dissected. Di= Rh Ra where, Di is Dissection index, Rh is relative relief, and Ra is Absolute relief 4) Relative Relief Relative Relief denotes the difference between the highest and the lowest points in a spatial unit. It plays an important role to understand the morphological characteristics of the terrain, degree of dissection and denudational characteristics of the area, which together control the stream gradient, thereby influencing flood patterns Hadley and Schumm ). Relative relief varies significantly in the study area Figure ). About 4.78% of the study area have extremely low to moderately low relative relief observed mostly in the whole southern part Table 4). Moderate and moderately high relative relief together accounts 5.7% of the study area, Rh=H h) where, Rh is relative relief, H is maximum elevation, and h is minimum elevation.
6 IJGE 07 ): 54 Rawat et al a) b) < >750 < >0. Figure 5. a) Ruggedness number b) Dissection Index of the study area < >750 Figure. Relative relief of the study area..4 Slope and Aspect A DEM Digital Elevation Model) for the study area was built based on Advanced Space borne Thermal Emission and Reflection radiometer ASTER) 0 m) elevation data. GCPs were added to the ASTER imagery and processed using GIS. The most common method of landslide hazard assessment using weighted overlay, which are heavily dependent on dimensional terrain visualization. Minimum 40
7 Landslide hazard zonation study in eastern Indian Himalayan region IJGE 07 ): 54 elevation of the study area is 800 m and maximum elevation is 4, m. Digital Elevation Model was used to delineate slope in the study area. Slopes are classed to: >5 0, 50 0, 45 0, 40 0, 75 0 and >75 0 Figure 7a). Landslides are more frequent in rugged areas than in gently sloping terrain. Majority landslides occur on slopes of , though the highest occurrences on slopes >75 0. The aspect of a slope can have significant influences on microclimate. In the Himalayas, this effect can be seen to an extreme degree, southfacing slopes are warm, wet and forested, whereas northfacing slopes cold, dry and much more heavily glaciated. The aspect effect also leads to differences in hydrology and sediment transport rates. Slope aspects in the study area are divided into eight cardinal directions Figure 7b). There is some association of landslides with slope aspect, with trend of landslides developing preferentially on Southeast to east facing slopes. Recorded landslides in these faces are SE %, SW 0%, NW 8%, W % and South facing 4% in the year 7 Figure 7b). This is consistent with a directional trigger mechanism such as intense rainfall from tropical storm that are more frequent from ESE or SSE. Deepseated landslides are less likely to be influenced by slope aspect, due to the overriding controls of lithology and structure...5 Rainfall Effects Local climate varies from subtropical monsoon to tropical upland type, specifically the northern part of the study area features with severe winter and comparatively higher rainfall. Mean annual rainfall recorded in station from 5 to 00 is,450 mm. Peek rainfall occurs in monsoon season between June and September. The maximum annual rainfall occurred in was 4,0 mm in the year and minimum was,787 mm in 00. Rainfall plays a vital role in landslide genesis and reactivation. An analysis of year record of landslides and rainfall events in the Sikkim Himalaya suggests that many landslides occurred under the influence of extensive rainfall reference). This study concludes that when daily rainfall amount exceeds 00 mm, there are always risks of landslides in Himalayan slopes. It was observed that in the year of 7, 8, and 000 the annual rainfall were very high during monsoon periods. These years experienced occurrences of calamitous landslides, causing serious loss of lives and properties Rawat et al 00).. Major Historic Landslides Landslide inventory map was prepared Figure 8) base on the Survey of India Toposheet 78A/ ), in which 50 landslides were identified. Remote sensing data Cartosate 008), IRS C/D LISS III 00) and LISS IV 008) were used to validate those landslides. Of them 4 landslides were found in our field survey. Out of 4 landslides were considered as significant having direct impact on roads Supplementary pictures Plate).. Numerical Rating Scheme The identification of potential landslide areas requires an integrative analysis of impacting factors according to their relative importance to landslide occurrence. This can be achieved in a rating scheme, which the impacting factors and their magnitude/classes are assigned a ranking and weight value, respectively NRSA 00). a) b) < >75 North 0.5) Northeast.57.5) East 7.5.5) Southeast.557.5) South ) Southwest ) West ) Northwest.57.5) North 7.50) Figure 7. a) Slope map b) Aspect map of the study area 4
8 IJGE 07 ): 54 Rawat et al Very High Hazard High Hazard Low Hazard Very Low Hazard Moderate Hazard Landslide Figure 8. Landslide Hazard Zonation map of the study area Based on our field survey and knowledge from previous work Rawat et al 05b), the causative factors for landslides surveyed were assigned a numerical ranking scale from to in an order of impacting importance. Weights were assigned to each class of these factors Appendix Table ). A higher value indicates more influence towards landslide occurrence. Results Landslide hazard zonation is categorized into five hazard classes, 'Very High', 'High', 'Moderate', 'Low' and 'Very Low'. Details of each hazard class are described as follows Figure 8).. Very High Hazard Zone Steep slopes with unconsolidated materials which are located near faults and tectonically weak zones, making this zone highly unstable and at a constant threat from landslides. This zone constitutes an area of.0 km and.04% of the total study area. It is mainly located in the northern and central part of the town. Because it is highly susceptible to landslides, it is recommended that no human induced activities should be undertaken in this zone. Such areas have to be entirely avoided for settlement or other developmental purposes.. High Hazard Zone High Hazard Zone covers steep slopes that are prone to landslides when disturbed. It also includes areas where the probability of sliding debris is high due to weathered rock and soil debris. Several lineaments, fractured zones and fault planes also traverse the high hazard zone. Areas that experience constant erosion by streams also fall under this class. This zone is commonly found to surround the Very High Hazard Zone occupying 5.50 km or.5% of the 4
9 Landslide hazard zonation study in eastern Indian Himalayan region IJGE 07 ): 54 total area. Since the High Hazard Zone is geologically unstable, allocation and execution of major housing structures and other projects within the vicinity of this zone should be discouraged. Also, it is recommended that proper canalization of the streams and improvement of the drainage system should be undertaken along the streams where toeerosional activities are intense.. Moderate Hazard Zone Moderate Hazard zone is generally considered stable as long as its present status is maintained. It comprises areas with a moderate slope angle and relatively compact and hard rocks. Several human settlements are found in this zone. Seismic activity and continuous heavy rainfall can reduce land stability. As such, it is important not to disturb its natural drainage. Slope alteration should also be avoided as far as possible. It is recommended that human activities that may potentially destabilize the slope and trigger landslides should not be undertaken within this zone. Although this zone comprises areas that are stable in the present condition, future land use activities have to be properly planned to maintain its status. This zone covers 4.4 km, which is.8 % of the total study area..4 Low Hazard Zone This zone comprises of areas where the impacting factors are unlikely to have adverse pressure on the slope stability. As far as the risk factor is concerned, no evidence of instability is observed within this zone, and mass movement is not expected unless major site changes occur. In addition, slope angles generally are less than 0 degree, covering with light vegetation or scrublands. It spreads over an area of 7.4 km, or.04% of the total study area. This zone is suitable for development..5 Very Low Hazard Zone This zone includes areas of low slopes with thick vegetation. As such, it is assumed to be free from present and future landslide hazards. The dip and slope angles of bedrocks are fairly low. Although it comprises soft rocks and overlying soil debris in some areas, the chance of slope failure is minimized by low slope angle. This zone extends over an area of 7.48 km or 0.5% of the total area. 4 Discussion Geomorphic factors such as geology and relief factors have a major control on landslide processes in this region given that slope, slope shape, aspect and lithology are proven to be the major contributing factors to landslides. Areas most sensitive to landslides are slopes at an angle between 4º and 75º. The output zonation map divides the study area into five hazard zones. The High Hazard Zone is in geologically unstable area, and slope failure can be triggered particularly in this zone after heavy rain. The results are validated by landslide distribution in the area during field study. As such, allocation and execution of major housing construction and other projects within this zone should be discouraged. Afforestation scheme should be implemented in this zone. Further, future land use activities have to be properly planned to maintain its present status. The results obtained from the study show a positive relationship between landslides and drainage density, which may be due to higher surface runoff and concomitant weather and erosion. Rock types like phyllite and gneiss with high drainage density are more prone to land sliding. Higher landslide frequency also corresponds to high lineament density, indicating that the areas with high dissection are more susceptible to landslides. The maximum landslide frequency within a range of 00 m distance from the road corroborates the fact that road construction is one of the prominent anthropogenic activities leading to the occurrence of landslides. Nevertheless, landslides in this area are likely to continue increasing when local population are growing, so does the demand for lands. Settlements will continually expand into areas prone to landslide hazards. According to an openended questionnaire assessing local residents understanding of the main causes of landslides, it listed steep slopes, slope shape and continuous rainfall as the major factors Karmakar 0). This is consistent with our findings in this study. A good understanding and perceptions of local people on landslides are important to maintain land stability and eliminate potential landslides. The methodology for landslide hazard zonation mapping presented here involves thematic data layers generation, spatial data integration, numerical rating scheme design and results validation. The merging of multispectral and panchromatic satellite data greatly improved the understanding of terrain features in the images. The numerical rating scheme allows an improved evaluation. However, because the landslide contributing factors vary from region to region, this rating may not be hold for other regions in the Himalaya. Acknowledgement The authors wish to thank the local people of Sikkim for sharing their wisdoms with us during this research. We also thank reviewers for their insightful inputs. References Goudie, A., 0. Geomorphological techniques. Unwin Hyman Pub.) Ltd., Boston, 570. Hadley, R.F., and S.A. Schumm,. Sediment Sources and Drainage Basin Characteristics in Upper Cheyenne River Basin. USGS WaterSupply Paper, 5B, 8. Jana, M.M., 00. Application of remote sensing in the study of geomorphic processes and landforms in piedmont zone of Darjeeling SubHimalaya. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 0): 7. Joshi, V., A. Naithani and G.C.S. Negi, 00. Study of landslides in Mandakini river valley, Ganhwal Himalaya, India. Gaia Lisbon, : Karmakar, M., 0. Landslide hazard in Darjeeling Himalayan Region and its management: a study of 4
10 IJGE 07 ): 54 geographical perspective. IJHMS, 4): 0. NRSA, 00. Landslide Hazard Zonation Mapping in the Himalayas of Uttaranchal and Himachal Pradesh States Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. ATLAS 00, National Remote Sensing Agency, Hyderabad. Rawat, M.S., V. Joshi, A.K. Sharma, K. Kumar and Y.P. Sundriyal. 00. Study of landslides in parts of Sikkim Himalaya. Indian Landslides, ): Rawat, M.S., V. Joshi, D.P. Uniyal and B.S. Rawat, 05a. Investigation of hill slope stability and mitigation measures in Sikkim Himalaya. Intl. J. Lsld. Env., ): 8 5. Rawat et al Rawat, M.S., D.P. Uniyal, R. Dobhal, V. Joshi, B.S. Rawat, A. Bartwal, D. Singh and A. Aswal, 05b. Study of landslide hazard zonation in Mandakini valley, Rudraprayag district of Uttarakhand using remote sensing & GIS. Curr. Sci., 0): Starkel, L. and S.R. Basun Ed.), 000. Rains, landslides and floods in the Darjeeling Himalaya. Indian National Science Academy, New Delhi, 8p. Strahler, A.N., 5. Quantitative slope analysis. Bull. Geol. Societ. Am., 7: 7 5. Supplementary Pictures: Plate. Chandmari slide along Nathula road Plate. th Mile Slide along NH A Plate. Bakthang slide in JN road Plate 4. Andha bridge slide along Nathula road 007) 44
11 Landslide hazard zonation study in eastern Indian Himalayan region IJGE 07 ): 54 Plate 5. Kyangnosala slide along Nathula road Plate. Manbir colony slide along Bypass road Appendix Table : Ranks and weights of thematic layers used in zonation analysis Parameter Rank Category Weight 0 Major fault 0500 m 8 Thrust 0500 m 0 Proximity to faultlength Buffer distance on either side) Slope Lithology. Phyllite/Quartzite Quartzite alternating with Shale/Slate/Phyllite Quartzite alternating with Schist Schist Schist with Slate/Phyllite Granites Gneiss Basic/Metabasic/Ulterabasic Volcanics/Meta volcanic Semiconsolidated sediments SlopeDip Bedding, joint) Dip facets parallel to slope Relation Dip facets opposite to slope Geomorphology 8.5 Low dissected hills and valleys Moderately dissected hills and valleys Highly dissected hills and valleys Alluvial fans River terraces Valley Escarpment Toe removal /erosion/cuttingby river) Density of Lineament 8 Low Moderate Moderately high High Drainage Density 7.5 Low Moderate Moderately high
12 IJGE 07 ): 54 Rawat et al High 0 Lineament Buffer m buffer 0 Land use/land cover 7 Dense vegetation >40% canopy cover) Medium vegetation040% canopy cover) Degraded vegetation<0% canopy cover) Scrub sand/grass sand Forest blank Barren land rocky) Waste land Agricultural land Builtup area Snow covered area Dissection Index Low Moderate Moderately high High Ruggedness Number 5.5 Low Moderate Moderately high High Relative Relief Low Moderate Moderately high High Soil Texture 4.5 Sandy skeletal soil Loamy skeletal soil Sandy soil Silty soil Clayey soil Loamy soil Rock outcrop Slope Aspects 4 North 7.5.5) NE.57.5) East 7.5.5) SE.557.5) South ) SW ) West ) NW.57.5)
LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING USING INFO VALUE METHOD BASED ON GIS
 LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING USING INFO VALUE METHOD BASED ON GIS ABSTRACT 1 Sonia Sharma, 2 Mitali Gupta and 3 Robin Mahajan 1,2,3 Assistant Professor, AP Goyal Shimla University Email: sonia23790@gmail.com
LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING USING INFO VALUE METHOD BASED ON GIS ABSTRACT 1 Sonia Sharma, 2 Mitali Gupta and 3 Robin Mahajan 1,2,3 Assistant Professor, AP Goyal Shimla University Email: sonia23790@gmail.com
Geospatial Approach for Delineation of Landslide Susceptible Areas in Karnaprayag, Chamoli district, Uttrakhand, India
 Geospatial Approach for Delineation of Landslide Susceptible Areas in Karnaprayag, Chamoli district, Uttrakhand, India Ajay Kumar Sharma & Anand Mohan Singh Overview Landslide - movement of a mass of rock,
Geospatial Approach for Delineation of Landslide Susceptible Areas in Karnaprayag, Chamoli district, Uttrakhand, India Ajay Kumar Sharma & Anand Mohan Singh Overview Landslide - movement of a mass of rock,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 1, No 1, 2010
 An Integrated Approach with GIS and Remote Sensing Technique for Landslide Hazard Zonation S.Evany Nithya 1 P. Rajesh Prasanna 2 1. Lecturer, 2. Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering, Anna
An Integrated Approach with GIS and Remote Sensing Technique for Landslide Hazard Zonation S.Evany Nithya 1 P. Rajesh Prasanna 2 1. Lecturer, 2. Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering, Anna
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research e-issn No.: , Date: April, 2016
 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 28-30 April, 2016 Landslide Hazard Management Maps for Settlements in Yelwandi River Basin,
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 28-30 April, 2016 Landslide Hazard Management Maps for Settlements in Yelwandi River Basin,
GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH
 GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH Prof.P.Jagadeesara Rao Department of Geo-Engineering and Centre for Remote Sensing, College
GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH Prof.P.Jagadeesara Rao Department of Geo-Engineering and Centre for Remote Sensing, College
Landslide Disasters in Uttarakhand: A Case of Landslide Susceptibility Zonation of Alaknanda Valley in Garhwal Himalaya
 Global Journal of Current Research Vol. 2 No. 1. 2013. Pp. 19-26 Copyright by CRDEEP. All Rights Reserved. Full Length Research Paper Landslide Disasters in Uttarakhand: A Case of Landslide Susceptibility
Global Journal of Current Research Vol. 2 No. 1. 2013. Pp. 19-26 Copyright by CRDEEP. All Rights Reserved. Full Length Research Paper Landslide Disasters in Uttarakhand: A Case of Landslide Susceptibility
ASTER DEM Based Studies for Geological and Geomorphological Investigation in and around Gola block, Ramgarh District, Jharkhand, India
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 3, Issue 2, February-2012 1 ASTER DEM Based Studies for Geological and Geomorphological Investigation in and around Gola block, Ramgarh
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 3, Issue 2, February-2012 1 ASTER DEM Based Studies for Geological and Geomorphological Investigation in and around Gola block, Ramgarh
Using Weather and Climate Information for Landslide Prevention and Mitigation
 Using Weather and Climate Information for Landslide Prevention and Mitigation Professor Roy C. Sidle Disaster Prevention Research Institute Kyoto University, Japan International Workshop on Climate and
Using Weather and Climate Information for Landslide Prevention and Mitigation Professor Roy C. Sidle Disaster Prevention Research Institute Kyoto University, Japan International Workshop on Climate and
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHEDS IN THE KUNIGAL AREA OF TUMKUR DISTRICT, SOUTH INDIA USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNOLOGY
 MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHEDS IN THE KUNIGAL AREA OF TUMKUR DISTRICT, SOUTH INDIA USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNOLOGY PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1170 COLLEGE : SIDDAGANGA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY,
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHEDS IN THE KUNIGAL AREA OF TUMKUR DISTRICT, SOUTH INDIA USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNOLOGY PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1170 COLLEGE : SIDDAGANGA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY,
7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.2 OBJECTIVE
 7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered as an essential element for modeling and
7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered as an essential element for modeling and
IDENTIFICATION OF LANDSLIDE-PRONE AREAS USING REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES
 5.1 IDENTIFICATION OF LANDSLIDE-PRONE AREAS USING REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES P.V. Seethapathi National Institute of Hydrology Jal Vigyan Bhawan, Roorkee-247 667, Uttarakhand Email: neriwalam@gwl.net.in
5.1 IDENTIFICATION OF LANDSLIDE-PRONE AREAS USING REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES P.V. Seethapathi National Institute of Hydrology Jal Vigyan Bhawan, Roorkee-247 667, Uttarakhand Email: neriwalam@gwl.net.in
Paper presented in the Annual Meeting of Association of American Geographers, Las Vegas, USA, March 2009 ABSTRACT
 Paper presented in the Annual Meeting of Association of American Geographers, Las Vegas, USA, March 2009 ABSTRACT CHANGING GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE KOSI RIVER SYSTEM IN THE INDIAN SUBCONTINENT Nupur Bose,
Paper presented in the Annual Meeting of Association of American Geographers, Las Vegas, USA, March 2009 ABSTRACT CHANGING GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE KOSI RIVER SYSTEM IN THE INDIAN SUBCONTINENT Nupur Bose,
LANDSLIDE HAZARD ZONATION IN AND AROUND KEDARNATH REGION AND ITS VALIDATION BASED ON REAL TIME KEDARNATH DISASTER USING GEOSPATIAL TECHNIQUES
 LANDSLIDE HAZARD ZONATION IN AND AROUND KEDARNATH REGION AND ITS VALIDATION BASED ON REAL TIME KEDARNATH DISASTER USING GEOSPATIAL TECHNIQUES Divya Uniyal 1,*, Saurabh Purohit 2, Sourabh Dangwal 1, Ashok
LANDSLIDE HAZARD ZONATION IN AND AROUND KEDARNATH REGION AND ITS VALIDATION BASED ON REAL TIME KEDARNATH DISASTER USING GEOSPATIAL TECHNIQUES Divya Uniyal 1,*, Saurabh Purohit 2, Sourabh Dangwal 1, Ashok
GIS Based Delineation of Micro-watershed and its Applications: Mahendergarh District, Haryana
 Kamla-Raj 2012 J Hum Ecol, 38(2): 155-164 (2012) GIS Based Delineation of Micro-watershed and its Applications: Mahendergarh District, Haryana Gulshan Mehra and Rajeshwari * Department of Geography, Kurukshetra
Kamla-Raj 2012 J Hum Ecol, 38(2): 155-164 (2012) GIS Based Delineation of Micro-watershed and its Applications: Mahendergarh District, Haryana Gulshan Mehra and Rajeshwari * Department of Geography, Kurukshetra
Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study
 Water Resources Management VI 139 Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study J. Letha, B. Thulasidharan Nair & B. Amruth Chand College of Engineering, Trivandrum, Kerala,
Water Resources Management VI 139 Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study J. Letha, B. Thulasidharan Nair & B. Amruth Chand College of Engineering, Trivandrum, Kerala,
Geo-Environmental Study of Kaliasaur Landslide in District Rudraprayag of Garhwal Himalaya, Uttarakhand, India
 International Journal of Humanities and Social Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 7722, ISSN (Print): 2319 7714 Volume 5 Issue 3 March. 2016 PP.07-13 Geo-Environmental Study of Kaliasaur Landslide in
International Journal of Humanities and Social Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 7722, ISSN (Print): 2319 7714 Volume 5 Issue 3 March. 2016 PP.07-13 Geo-Environmental Study of Kaliasaur Landslide in
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Hypsometric Analysis of Varattaru
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Hypsometric Analysis of Varattaru
APPLICATION OF REMOTE SENSING & GIS ON LANDSLIDE HAZARD ZONE IDENTIFICATION & MANAGEMENT
 APPLICATION OF REMOTE SENSING & GIS ON LANDSLIDE HAZARD ZONE IDENTIFICATION & MANAGEMENT PRESENTED BY SUPRITI PRAMANIK M.TECH IN ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY NIT,DURGAPUR 25-04-2015 1 INTRODUCTION
APPLICATION OF REMOTE SENSING & GIS ON LANDSLIDE HAZARD ZONE IDENTIFICATION & MANAGEMENT PRESENTED BY SUPRITI PRAMANIK M.TECH IN ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY NIT,DURGAPUR 25-04-2015 1 INTRODUCTION
Need of Proper Development in Hilly Urban Areas to Avoid
 Need of Proper Development in Hilly Urban Areas to Avoid Landslide Hazard Dr. Arvind Phukan, P.E. Cosultant/Former Professor of Civil Engineering University of Alaska, Anchorage, USA RI District Governor
Need of Proper Development in Hilly Urban Areas to Avoid Landslide Hazard Dr. Arvind Phukan, P.E. Cosultant/Former Professor of Civil Engineering University of Alaska, Anchorage, USA RI District Governor
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 2, 2011
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 2, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Geomorphological study of Atagad
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 2, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Geomorphological study of Atagad
Introduction. About the Author:
 Remote sensing and GIS for Landslide Hazard Mapping in India - A Review 1 Er. Balwinder Lallotra, 2 Dr. Bushra Zaman 1,2 Department of Civil Engineering, MM University, Sadopur, Ambala Abstract: Landslides
Remote sensing and GIS for Landslide Hazard Mapping in India - A Review 1 Er. Balwinder Lallotra, 2 Dr. Bushra Zaman 1,2 Department of Civil Engineering, MM University, Sadopur, Ambala Abstract: Landslides
Sub-watershed prioritization based on potential zones of Kuttiadi river basin, A Geo-Morphometric approach using GIS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 8, No 1, 2018 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Sub-watershed prioritization
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 8, No 1, 2018 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Sub-watershed prioritization
Environmental Impact Assessment Land Use and Land Cover CISMHE 7.1 INTRODUCTION
 7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered an essential element for modeling and understanding
7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered an essential element for modeling and understanding
Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70. Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills
 Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70 Sr. No. 01 Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills Nature and Scope Definition, nature, i)
Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70 Sr. No. 01 Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills Nature and Scope Definition, nature, i)
International Journal of Remote Sensing & Geoscience (IJRSG) ASTER DEM BASED GEOLOGICAL AND GEOMOR-
 ASTER DEM BASED GEOLOGICAL AND GEOMOR- PHOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION USING GIS TECHNOLOGY IN KOLLI HILL, SOUTH INDIA Gurugnanam.B, Centre for Applied Geology, Gandhigram Rural Institute-Deemed University, Tamilnadu,
ASTER DEM BASED GEOLOGICAL AND GEOMOR- PHOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION USING GIS TECHNOLOGY IN KOLLI HILL, SOUTH INDIA Gurugnanam.B, Centre for Applied Geology, Gandhigram Rural Institute-Deemed University, Tamilnadu,
CHAPTER VII FULLY DISTRIBUTED RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL USING GIS
 80 CHAPTER VII FULLY DISTRIBUTED RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL USING GIS 7.1GENERAL This chapter is discussed in six parts. Introduction to Runoff estimation using fully Distributed model is discussed in first
80 CHAPTER VII FULLY DISTRIBUTED RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL USING GIS 7.1GENERAL This chapter is discussed in six parts. Introduction to Runoff estimation using fully Distributed model is discussed in first
Figure 2.1: Constituent Area
 2 The Region 2.1 CONSTITUENT AREA The National Capital Region includes NCT-Delhi, nine districts of Haryana, six districts of Uttar Pradesh and one district of Rajasthan. Total area of the region is 34,144
2 The Region 2.1 CONSTITUENT AREA The National Capital Region includes NCT-Delhi, nine districts of Haryana, six districts of Uttar Pradesh and one district of Rajasthan. Total area of the region is 34,144
Morphometric Analysis of Chamundi Hills, Mysuru, India Using Geographical Information System
 Volume-7, Issue-1, January-February 2017 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 279-283 Morphometric Analysis of s, Mysuru, India Using Geographical Information System
Volume-7, Issue-1, January-February 2017 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 279-283 Morphometric Analysis of s, Mysuru, India Using Geographical Information System
Paradoxes of Fluvial Evolution in Young Orogenic Systems
 Journal of Indian Geomorphology Volume 5, 2017 ISSN 2320-0731 Indian Institute of Geomorphologists (IGI) Paradoxes of Fluvial Evolution in Young Orogenic Systems Leszek Starkel Department of Geoenvironmental
Journal of Indian Geomorphology Volume 5, 2017 ISSN 2320-0731 Indian Institute of Geomorphologists (IGI) Paradoxes of Fluvial Evolution in Young Orogenic Systems Leszek Starkel Department of Geoenvironmental
Hydrological parameters Controls Vulnerable Zones in Calicut Nilambur Gudalur Ghat section, Gudalur, The Nilgiris, Tamil Nadu.
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: 0974-4290 Vol.9, No.03 pp 248-253, 2016 Hydrological parameters Controls Vulnerable Zones in Calicut Nilambur Gudalur Ghat section,
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: 0974-4290 Vol.9, No.03 pp 248-253, 2016 Hydrological parameters Controls Vulnerable Zones in Calicut Nilambur Gudalur Ghat section,
Watershed Development Prioritization by Applying WERM Model and GIS Techniques in Takoli Watershed of District Tehri (Uttarakhand)
 Watershed Development Prioritization by Applying WERM Model and GIS Techniques in Takoli Watershed of District Tehri (Uttarakhand) Anju Panwar Uttarakhand Space Application Centre Dehradun, Uttarkhand
Watershed Development Prioritization by Applying WERM Model and GIS Techniques in Takoli Watershed of District Tehri (Uttarakhand) Anju Panwar Uttarakhand Space Application Centre Dehradun, Uttarkhand
Landslide Hazard Zonation Methods: A Critical Review
 International Journal of Civil Engineering Research. ISSN 2278-3652 Volume 5, Number 3 (2014), pp. 215-220 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcer.htm Landslide Hazard Zonation Methods:
International Journal of Civil Engineering Research. ISSN 2278-3652 Volume 5, Number 3 (2014), pp. 215-220 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcer.htm Landslide Hazard Zonation Methods:
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 3, No 1, 2012
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 3, No 1, 2012 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Geo-Hydrological study
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 3, No 1, 2012 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Geo-Hydrological study
Virtual Reality Modeling of Landslide for Alerting in Chiang Rai Area Banphot Nobaew 1 and Worasak Reangsirarak 2
 Virtual Reality Modeling of Landslide for Alerting in Chiang Rai Area Banphot Nobaew 1 and Worasak Reangsirarak 2 1 Banphot Nobaew MFU, Chiang Rai, Thailand 2 Worasak Reangsirarak MFU, Chiang Rai, Thailand
Virtual Reality Modeling of Landslide for Alerting in Chiang Rai Area Banphot Nobaew 1 and Worasak Reangsirarak 2 1 Banphot Nobaew MFU, Chiang Rai, Thailand 2 Worasak Reangsirarak MFU, Chiang Rai, Thailand
Chapter 2. Regional Landscapes and the Hydrologic Cycle
 Chapter 2. Regional Landscapes and the Hydrologic Cycle W. Lee Daniels Department of Crop and Soil Environmental Sciences, Virginia Tech Table of Contents Introduction... 23 Soils and landscapes of the
Chapter 2. Regional Landscapes and the Hydrologic Cycle W. Lee Daniels Department of Crop and Soil Environmental Sciences, Virginia Tech Table of Contents Introduction... 23 Soils and landscapes of the
3.8 Geology/Soils. Environmental Setting. Topography. Geology and Soils
 3.8 Geology/Soils This section examines whether implementation of the 2004 Land Use Mobility Elements, Zoning Code Revisions, and Central District Specific Plan the will expose people or structures to
3.8 Geology/Soils This section examines whether implementation of the 2004 Land Use Mobility Elements, Zoning Code Revisions, and Central District Specific Plan the will expose people or structures to
LAND SUITABILITY STUDY IN LAND DEGRADED AREA DUE TO MINING IN DHANBAD DISTRICT, JHARKHAND.
 LAND SUITABILITY STUDY IN LAND DEGRADED AREA DUE TO MINING IN DHANBAD DISTRICT, JHARKHAND. Saranathan, E a*, Loveson, V.J b. and Victor Rajamanickam, G c a School of Civil Engineering, SASTRA, Thanjavur
LAND SUITABILITY STUDY IN LAND DEGRADED AREA DUE TO MINING IN DHANBAD DISTRICT, JHARKHAND. Saranathan, E a*, Loveson, V.J b. and Victor Rajamanickam, G c a School of Civil Engineering, SASTRA, Thanjavur
Dr. S.SURIYA. Assistant professor. Department of Civil Engineering. B. S. Abdur Rahman University. Chennai
 Hydrograph simulation for a rural watershed using SCS curve number and Geographic Information System Dr. S.SURIYA Assistant professor Department of Civil Engineering B. S. Abdur Rahman University Chennai
Hydrograph simulation for a rural watershed using SCS curve number and Geographic Information System Dr. S.SURIYA Assistant professor Department of Civil Engineering B. S. Abdur Rahman University Chennai
Landslides Zones of Nearby Areas of Malin Village, Pune District, Maharashtra Using GIS Techniques
 Landslides Zones of Nearby Areas of Malin Village, Pune District, Maharashtra Using GIS Techniques Pooja Gujarathi 1, S. J. Mane 2 1 Savitribai Phule Pune University, D. Y. Patil College of Engineering,
Landslides Zones of Nearby Areas of Malin Village, Pune District, Maharashtra Using GIS Techniques Pooja Gujarathi 1, S. J. Mane 2 1 Savitribai Phule Pune University, D. Y. Patil College of Engineering,
FOREST RESEARCH INSTITUTE, DEHRADUN
 PROJECT REPORT DRAINAGE AND REPLENISHMENT STUDY OF MINED AREA OF GANGA SHYAMPUR RIVER HARIDWAR Submitted to UTTARAKHAND FOREST DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION (UFDC) 73, Nehru Road, Deharadun Prepared&Submitted
PROJECT REPORT DRAINAGE AND REPLENISHMENT STUDY OF MINED AREA OF GANGA SHYAMPUR RIVER HARIDWAR Submitted to UTTARAKHAND FOREST DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION (UFDC) 73, Nehru Road, Deharadun Prepared&Submitted
ENGINEER S CERTIFICATION OF FAULT AREA DEMONSTRATION (40 CFR )
 PLATTE RIVER POWER AUTHORITY RAWHIDE ENERGY STATION BOTTOM ASH TRANSFER (BAT) IMPOUNDMENTS LARIMER COUNTY, CO ENGINEER S CERTIFICATION OF FAULT AREA DEMONSTRATION (40 CFR 257.62) FOR COAL COMBUSTION RESIDUALS
PLATTE RIVER POWER AUTHORITY RAWHIDE ENERGY STATION BOTTOM ASH TRANSFER (BAT) IMPOUNDMENTS LARIMER COUNTY, CO ENGINEER S CERTIFICATION OF FAULT AREA DEMONSTRATION (40 CFR 257.62) FOR COAL COMBUSTION RESIDUALS
INTRODUCTION. Climate
 INTRODUCTION Climate Landslides are serious natural disasters in many parts of the world. Since the past 30 years, rainfall triggered landslides and debris flows had been one of the natural disasters of
INTRODUCTION Climate Landslides are serious natural disasters in many parts of the world. Since the past 30 years, rainfall triggered landslides and debris flows had been one of the natural disasters of
Abstract: About the Author:
 REMOTE SENSING AND GIS IN LAND USE PLANNING Sathees kumar P 1, Nisha Radhakrishnan 2 1 1 Ph.D Research Scholar, Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli- 620015,
REMOTE SENSING AND GIS IN LAND USE PLANNING Sathees kumar P 1, Nisha Radhakrishnan 2 1 1 Ph.D Research Scholar, Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli- 620015,
2014 Summer Training Courses on Slope Land Disaster Reduction Hydrotech Research Institute, National Taiwan University, Taiwan August 04-15, 2014
 Final Project Report 2014 Summer Training Courses on Slope Land Disaster Reduction Hydrotech Research Institute, National Taiwan University, Taiwan August 04-15, 2014 Landslides in Mt. Umyeon Susceptibility
Final Project Report 2014 Summer Training Courses on Slope Land Disaster Reduction Hydrotech Research Institute, National Taiwan University, Taiwan August 04-15, 2014 Landslides in Mt. Umyeon Susceptibility
Remote Sensing and GIS Applications for Hilly Watersheds SUBASHISA DUTTA DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING IIT GUWAHATI
 Remote Sensing and GIS Applications for Hilly Watersheds SUBASHISA DUTTA DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING IIT GUWAHATI Deciding Alternative Land Use Options in a Watershed Using GIS Source: Anita Prakash
Remote Sensing and GIS Applications for Hilly Watersheds SUBASHISA DUTTA DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING IIT GUWAHATI Deciding Alternative Land Use Options in a Watershed Using GIS Source: Anita Prakash
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10)
 Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
Assessment of solid load and siltation potential of dams reservoirs in the High Atlas of Marrakech (Moorcco) using SWAT Model
 Assessment of solid load and siltation potential of dams reservoirs in the High Atlas of Marrakech (Moorcco) using SWAT Model Amal Markhi: Phd Student Supervisor: Pr :N.Laftrouhi Contextualization Facing
Assessment of solid load and siltation potential of dams reservoirs in the High Atlas of Marrakech (Moorcco) using SWAT Model Amal Markhi: Phd Student Supervisor: Pr :N.Laftrouhi Contextualization Facing
Landslide analysis to estimate probability occurrence of earthquakes by software ArcGIS in central of Iran
 Research Journal of Recent Sciences ISSN 2277-2502 Res.J.Recent Sci. Landslide analysis to estimate probability occurrence of earthquakes by software ArcGIS in central of Iran Abstract Hamid Reza Samadi
Research Journal of Recent Sciences ISSN 2277-2502 Res.J.Recent Sci. Landslide analysis to estimate probability occurrence of earthquakes by software ArcGIS in central of Iran Abstract Hamid Reza Samadi
Hydrologic Modelling of the Upper Malaprabha Catchment using ArcView SWAT
 Hydrologic Modelling of the Upper Malaprabha Catchment using ArcView SWAT Technical briefs are short summaries of the models used in the project aimed at nontechnical readers. The aim of the PES India
Hydrologic Modelling of the Upper Malaprabha Catchment using ArcView SWAT Technical briefs are short summaries of the models used in the project aimed at nontechnical readers. The aim of the PES India
Debris flow: categories, characteristics, hazard assessment, mitigation measures. Hariklia D. SKILODIMOU, George D. BATHRELLOS
 Debris flow: categories, characteristics, hazard assessment, mitigation measures Hariklia D. SKILODIMOU, George D. BATHRELLOS Natural hazards: physical phenomena, active in geological time capable of producing
Debris flow: categories, characteristics, hazard assessment, mitigation measures Hariklia D. SKILODIMOU, George D. BATHRELLOS Natural hazards: physical phenomena, active in geological time capable of producing
Report for Area Drainage Studies for 1320 MW (2x660 MW) THERMAL POWER PROJECT AT MIRZAPUR, U.P.
 Report for Area Drainage Studies for 1320 MW (2x660 MW) THERMAL POWER PROJECT AT MIRZAPUR, U.P. 1. Introduction M/s Welspun Energy Uttar Pradesh Ltd. (WEUPL) is putting up 1320 MW (2 x 660 MW) coal fired
Report for Area Drainage Studies for 1320 MW (2x660 MW) THERMAL POWER PROJECT AT MIRZAPUR, U.P. 1. Introduction M/s Welspun Energy Uttar Pradesh Ltd. (WEUPL) is putting up 1320 MW (2 x 660 MW) coal fired
Block Level Micro Watershed Prioritization Based on Morphometric and Runoff Parameters
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2016, Volume 5, Issue 11, pp. 1981-1987 ISSN 2320-0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.76 Research Article Open Access Block
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2016, Volume 5, Issue 11, pp. 1981-1987 ISSN 2320-0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.76 Research Article Open Access Block
LANDSAT-TM IMAGES IN GEOLOGICAL MAPPING OF SURNAYA GAD AREA, DADELDHURA DISTRICT WEST NEPAL
 LANDSAT-TM IMAGES IN GEOLOGICAL MAPPING OF SURNAYA GAD AREA, DADELDHURA DISTRICT WEST NEPAL L. N. Rimal* A. K. Duvadi* S. P. Manandhar* *Department of Mines and Geology Lainchaur, Kathmandu, Nepal E-mail:
LANDSAT-TM IMAGES IN GEOLOGICAL MAPPING OF SURNAYA GAD AREA, DADELDHURA DISTRICT WEST NEPAL L. N. Rimal* A. K. Duvadi* S. P. Manandhar* *Department of Mines and Geology Lainchaur, Kathmandu, Nepal E-mail:
About the Author: E mail ID: Contact: proceedings. Page 1 of 8
 Catchment Delineation and Morphometric Analysis Using Geographical Information System of Naina Gorma Basin of Rewa District, M.P., India Vimala Singh 1, L.K. Sinha 2 Research Associate 1, DTRL, DRDO Scientist
Catchment Delineation and Morphometric Analysis Using Geographical Information System of Naina Gorma Basin of Rewa District, M.P., India Vimala Singh 1, L.K. Sinha 2 Research Associate 1, DTRL, DRDO Scientist
[Penumaka, 7(1): January-March 2017] ISSN Impact Factor
![[Penumaka, 7(1): January-March 2017] ISSN Impact Factor [Penumaka, 7(1): January-March 2017] ISSN Impact Factor](/thumbs/95/124653515.jpg) INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES &MANAGEMENT HYDROGEOMORPHOLOGY OF CHEVELLA BASIN, RANGA REDDY DISTRICT, TELANGANA STATE Penumaka Ramesh* 1 & Podila Sankara Pitchaiah 2 * 1&2 Department of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES &MANAGEMENT HYDROGEOMORPHOLOGY OF CHEVELLA BASIN, RANGA REDDY DISTRICT, TELANGANA STATE Penumaka Ramesh* 1 & Podila Sankara Pitchaiah 2 * 1&2 Department of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK SPECIAL ISSUE FOR NATIONAL LEVEL CONFERENCE "SUSTAINABLE TECHNOLOGIES IN CIVIL
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK SPECIAL ISSUE FOR NATIONAL LEVEL CONFERENCE "SUSTAINABLE TECHNOLOGIES IN CIVIL
Morphometric Analysis of Jiya Dhol River Basin
 Morphometric Analysis of Jiya Dhol River Basin Luna Moin Das North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong Abstract: Basin morphometry is an important means of understanding a drainage basin using mathematically
Morphometric Analysis of Jiya Dhol River Basin Luna Moin Das North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong Abstract: Basin morphometry is an important means of understanding a drainage basin using mathematically
Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Coimbatore district, Tamil Nadu, using Remote sensing and GIS techniques
 Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Coimbatore district, Tamil Nadu, using Remote sensing and GIS techniques Vasudevan S*, MUNGANYINKA Jeanne Pauline, Balamurugan P, Sumanta Kumar Sahoo and Ashis
Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Coimbatore district, Tamil Nadu, using Remote sensing and GIS techniques Vasudevan S*, MUNGANYINKA Jeanne Pauline, Balamurugan P, Sumanta Kumar Sahoo and Ashis
Quick Response Report #126 Hurricane Floyd Flood Mapping Integrating Landsat 7 TM Satellite Imagery and DEM Data
 Quick Response Report #126 Hurricane Floyd Flood Mapping Integrating Landsat 7 TM Satellite Imagery and DEM Data Jeffrey D. Colby Yong Wang Karen Mulcahy Department of Geography East Carolina University
Quick Response Report #126 Hurricane Floyd Flood Mapping Integrating Landsat 7 TM Satellite Imagery and DEM Data Jeffrey D. Colby Yong Wang Karen Mulcahy Department of Geography East Carolina University
CHAPTER GEOLOGICALLY HAZARDOUS AREAS Applicability Regulations.
 CHAPTER 19.07 GEOLOGICALLY HAZARDOUS AREAS 19.07.010 Applicability. Geologically hazardous areas may pose a threat to the health and safety of citizens when incompatible development is sited in areas of
CHAPTER 19.07 GEOLOGICALLY HAZARDOUS AREAS 19.07.010 Applicability. Geologically hazardous areas may pose a threat to the health and safety of citizens when incompatible development is sited in areas of
A STUDY ON MORPHOMETRIC PARAMETER OF A WATERSHED FOR SUSTAINABLE WATER CONSERVATION
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 9, September 2017, pp. 271 278, Article ID: IJCIET_08_09_031 Available online at http://http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=8&itype=9
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 9, September 2017, pp. 271 278, Article ID: IJCIET_08_09_031 Available online at http://http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=8&itype=9
Landslide Hazard Investigation in Papua New Guinea-A Remote Sensing & GIS Approach
 Landslide Hazard Investigation in Papua New Guinea-A Remote Sensing & GIS Approach Sujoy Kumar Jana 1, Tingneyuc Sekac 2, Dilip Kumar Pal 3 Abstract: Tribal communities living in the mountainous regions
Landslide Hazard Investigation in Papua New Guinea-A Remote Sensing & GIS Approach Sujoy Kumar Jana 1, Tingneyuc Sekac 2, Dilip Kumar Pal 3 Abstract: Tribal communities living in the mountainous regions
Geomorphic Evidence of Active Tectonics in the Dhundsir Gad Watershed of Alaknada Basin, Uttarakhand, India
 Geomorphic Evidence of Active Tectonics in the Dhundsir Gad Watershed of Alaknada Basin, Uttarakhand, India Hari Ballabh 1, Devi Datt Chauniyal 1 & Mahendra Singh Lodhi 2, * 1. Department of Geography,
Geomorphic Evidence of Active Tectonics in the Dhundsir Gad Watershed of Alaknada Basin, Uttarakhand, India Hari Ballabh 1, Devi Datt Chauniyal 1 & Mahendra Singh Lodhi 2, * 1. Department of Geography,
ESTIMATION OF MORPHOMETRIC PARAMETERS AND RUNOFF USING RS & GIS TECHNIQUES
 ESTIMATION OF MORPHOMETRIC PARAMETERS AND RUNOFF USING RS & GIS TECHNIQUES Shrudha. V. K¹, Hafeezunnisa² 1 Assistant Professor, Rajarajeshwari College of Engineering Bangalore 2 Assistant Engineer, WRDO
ESTIMATION OF MORPHOMETRIC PARAMETERS AND RUNOFF USING RS & GIS TECHNIQUES Shrudha. V. K¹, Hafeezunnisa² 1 Assistant Professor, Rajarajeshwari College of Engineering Bangalore 2 Assistant Engineer, WRDO
Unit 7.2 W.E.D. & Topography Test
 Name: Score: Unit 7.2 W.E.D. & Topography Test 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 1. The formation of mountains is due mainly to while the destruction
Name: Score: Unit 7.2 W.E.D. & Topography Test 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 1. The formation of mountains is due mainly to while the destruction
EMERGENCY PLANNING IN NORTHERN ALGERIA BASED ON REMOTE SENSING DATA IN RESPECT TO TSUNAMI HAZARD PREPAREDNESS
 EMERGENCY PLANNING IN NORTHERN ALGERIA BASED ON REMOTE SENSING DATA IN RESPECT TO TSUNAMI HAZARD PREPAREDNESS Barbara Theilen-Willige Technical University of Berlin, Institute of Applied Geosciences Department
EMERGENCY PLANNING IN NORTHERN ALGERIA BASED ON REMOTE SENSING DATA IN RESPECT TO TSUNAMI HAZARD PREPAREDNESS Barbara Theilen-Willige Technical University of Berlin, Institute of Applied Geosciences Department
Vulnerability of Flood Hazard in Selected Ayeyarwady Delta Region, Myanmar
 Vulnerability of Flood Hazard in Selected Ayeyarwady Delta Region, Myanmar Khin Thandar Win Department of Civil Engineering Nilar Aye Department of Civil Engineering Kyaw Zaya Htun Department of Remote
Vulnerability of Flood Hazard in Selected Ayeyarwady Delta Region, Myanmar Khin Thandar Win Department of Civil Engineering Nilar Aye Department of Civil Engineering Kyaw Zaya Htun Department of Remote
Grant 0299-NEP: Water Resources Project Preparatory Facility
 Document Produced under Grant Project Number: 45206 May 2016 Grant 0299-NEP: Water Resources Project Preparatory Facility Final Report Volume 3 East Rapti (1 of 9) Prepared by Pvt. Ltd. For Ministry of
Document Produced under Grant Project Number: 45206 May 2016 Grant 0299-NEP: Water Resources Project Preparatory Facility Final Report Volume 3 East Rapti (1 of 9) Prepared by Pvt. Ltd. For Ministry of
Chapter 1 Quantitative Analysis of Geomorphometric Parameters of Wadi Kerak, Jordan, Using Remote Sensing and GIS
 Chapter 1 Quantitative Analysis of Geomorphometric Parameters of Wadi Kerak, Jordan, Using Remote Sensing and GIS Yahya Farhan, Ali Anbar, Omar Enaba, Nisrin Al-Shaikh Geomorphometric analysis was carried
Chapter 1 Quantitative Analysis of Geomorphometric Parameters of Wadi Kerak, Jordan, Using Remote Sensing and GIS Yahya Farhan, Ali Anbar, Omar Enaba, Nisrin Al-Shaikh Geomorphometric analysis was carried
DEVELOPMENT OF FLOOD HAZARD VULNERABILITY MAP FOR ALAPPUZHA DISTRICT
 DEVELOPMENT OF FLOOD HAZARD VULNERABILITY MAP FOR ALAPPUZHA DISTRICT Ciya Maria Roy 1, Elsa Manoj 2, Harsha Joy 3, Sarin Ravi 4, Abhinanda Roy 5 1,2,3,4 U.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, MITS
DEVELOPMENT OF FLOOD HAZARD VULNERABILITY MAP FOR ALAPPUZHA DISTRICT Ciya Maria Roy 1, Elsa Manoj 2, Harsha Joy 3, Sarin Ravi 4, Abhinanda Roy 5 1,2,3,4 U.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, MITS
Hendra Pachri, Yasuhiro Mitani, Hiro Ikemi, and Ryunosuke Nakanishi
 21 2nd International Conference on Geological and Civil Engineering IPCBEE vol. 8 (21) (21) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 1.7763/IPCBEE. 21. V8. 2 Relationships between Morphology Aspect and Slope Failure
21 2nd International Conference on Geological and Civil Engineering IPCBEE vol. 8 (21) (21) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 1.7763/IPCBEE. 21. V8. 2 Relationships between Morphology Aspect and Slope Failure
Morphometric Analysis for Hard Rock Terrain of Upper Ponnaiyar Watershed, Tamilnadu A GIS Approach
 International Journal of Research Studies in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 1, Issue 9, December 2014, PP 205-209 ISSN 2349-4751 (Print) & ISSN 2349-476X (Online) Morphometric Analysis for
International Journal of Research Studies in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 1, Issue 9, December 2014, PP 205-209 ISSN 2349-4751 (Print) & ISSN 2349-476X (Online) Morphometric Analysis for
Morphometric Estimation of Parameters of Uttar Mand River Basin, Satara District, Maharashtra, India.
 Morphometric Estimation of Parameters of Uttar Mand River Basin, Satara District, Maharashtra, India. Mr.S.S.Chokakkar 1, Mr.G.N.ChavanPatil, Dr.D.N.Mudgal 3, Dr..Shreenivasa 4 1M.Sc., B.Ed, NET, PhD(Pur.)
Morphometric Estimation of Parameters of Uttar Mand River Basin, Satara District, Maharashtra, India. Mr.S.S.Chokakkar 1, Mr.G.N.ChavanPatil, Dr.D.N.Mudgal 3, Dr..Shreenivasa 4 1M.Sc., B.Ed, NET, PhD(Pur.)
Each basin is surrounded & defined by a drainage divide (high point from which water flows away) Channel initiation
 DRAINAGE BASINS A drainage basin or watershed is defined from a downstream point, working upstream, to include all of the hillslope & channel areas which drain to that point Each basin is surrounded &
DRAINAGE BASINS A drainage basin or watershed is defined from a downstream point, working upstream, to include all of the hillslope & channel areas which drain to that point Each basin is surrounded &
GIS Application in Landslide Hazard Analysis An Example from the Shihmen Reservoir Catchment Area in Northern Taiwan
 GIS Application in Landslide Hazard Analysis An Example from the Shihmen Reservoir Catchment Area in Northern Taiwan Chyi-Tyi Lee Institute of Applied Geology, National Central University, No.300, Jungda
GIS Application in Landslide Hazard Analysis An Example from the Shihmen Reservoir Catchment Area in Northern Taiwan Chyi-Tyi Lee Institute of Applied Geology, National Central University, No.300, Jungda
Satellite Based Seismic Technology
 Satellite Based Seismic Technology Dr. V.K. Srivastava, R. Ghosh*, B.B Chhualsingh Department of Applied Geophysics, Indian School of mines, Dhanbad. E- mail: ismkvinay@hotmail.com, ghosh.ramesh@rediffmail.com,
Satellite Based Seismic Technology Dr. V.K. Srivastava, R. Ghosh*, B.B Chhualsingh Department of Applied Geophysics, Indian School of mines, Dhanbad. E- mail: ismkvinay@hotmail.com, ghosh.ramesh@rediffmail.com,
Mass Wasting. Revisit: Erosion, Transportation, and Deposition
 Mass Wasting Revisit: Erosion, Transportation, and Deposition While landslides are a normal part of erosion and surface processes, they can be very destructive to life and property! - Mass wasting: downslope
Mass Wasting Revisit: Erosion, Transportation, and Deposition While landslides are a normal part of erosion and surface processes, they can be very destructive to life and property! - Mass wasting: downslope
BASIC DETAILS. Morphometric features for landslide zonation A case study for Ooty Mettupalayam highway
 BASIC DETAILS Paper reference number : MWF PN 121 Title of the paper Name of the Presenter Author affiliation Mailing address Email address : Extraction of Topographic and Morphometric features for landslide
BASIC DETAILS Paper reference number : MWF PN 121 Title of the paper Name of the Presenter Author affiliation Mailing address Email address : Extraction of Topographic and Morphometric features for landslide
Continental Landscapes
 Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
August 31, 2006 Embankment Failure Debris Flow at the Cascades Development Haywood County, North Carolina. Introduction. Findings
 August 31, 2006 Embankment Failure Debris Flow at the Cascades Development Haywood County, North Carolina Introduction North Carolina Geological Survey (NCGS) staff members visited the site of the August
August 31, 2006 Embankment Failure Debris Flow at the Cascades Development Haywood County, North Carolina Introduction North Carolina Geological Survey (NCGS) staff members visited the site of the August
Landslides Management in Rural Roads of Pauri District (Uttarakhand): Challenges & Opportunities
 Landslides Management in Rural Roads of Pauri District (Uttarakhand): Challenges & Opportunities Shakti Prakash 1 & V.V.S. Gulati 2 1 Corrosponding author, Environment Specialist, 2 Team Leader (Uttarakhand
Landslides Management in Rural Roads of Pauri District (Uttarakhand): Challenges & Opportunities Shakti Prakash 1 & V.V.S. Gulati 2 1 Corrosponding author, Environment Specialist, 2 Team Leader (Uttarakhand
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1)
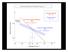 Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
5/3/2018 Susceptibility analysis of landslide due to earthquake due in Gorkha (25th April 2015) Animesh Bahadur Pradhan GIS IN WATER RESOURCES CE 547
 Susceptibility 5/3/2018 analysis of landslide due to earthquake due in Gorkha (25th April 2015) Animesh Bahadur Pradhan GIS IN WATER RESOURCES CE 547 Contents 1. Acknowledgement:... 2 2. Motivation and
Susceptibility 5/3/2018 analysis of landslide due to earthquake due in Gorkha (25th April 2015) Animesh Bahadur Pradhan GIS IN WATER RESOURCES CE 547 Contents 1. Acknowledgement:... 2 2. Motivation and
VILLAGE INFORMATION SYSTEM (V.I.S) FOR WATERSHED MANAGEMENT IN THE NORTH AHMADNAGAR DISTRICT, MAHARASHTRA
 VILLAGE INFORMATION SYSTEM (V.I.S) FOR WATERSHED MANAGEMENT IN THE NORTH AHMADNAGAR DISTRICT, MAHARASHTRA Abstract: The drought prone zone in the Western Maharashtra is not in position to achieve the agricultural
VILLAGE INFORMATION SYSTEM (V.I.S) FOR WATERSHED MANAGEMENT IN THE NORTH AHMADNAGAR DISTRICT, MAHARASHTRA Abstract: The drought prone zone in the Western Maharashtra is not in position to achieve the agricultural
Eagle Creek Post Fire Erosion Hazard Analysis Using the WEPP Model. John Rogers & Lauren McKinney
 Eagle Creek Post Fire Erosion Hazard Analysis Using the WEPP Model John Rogers & Lauren McKinney Columbia River Gorge at Risk: Using LiDAR and GIS-based predictive modeling for regional-scale erosion susceptibility
Eagle Creek Post Fire Erosion Hazard Analysis Using the WEPP Model John Rogers & Lauren McKinney Columbia River Gorge at Risk: Using LiDAR and GIS-based predictive modeling for regional-scale erosion susceptibility
UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT
 UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT I. PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY TAKE OUT YOUR PHYSICAL MAP OF SOUTH ASIA A. The Himalayan Mountains form the northern boundary of the region (color
UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT I. PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY TAKE OUT YOUR PHYSICAL MAP OF SOUTH ASIA A. The Himalayan Mountains form the northern boundary of the region (color
Impact : Changes to Existing Topography (Less than Significant)
 4.2 Land Resources 4.2.1 Alternative A Proposed Action Impact 4.2.1-1: Changes to Existing Topography (Less than Significant) Development of the project site would involve grading and other earthwork as
4.2 Land Resources 4.2.1 Alternative A Proposed Action Impact 4.2.1-1: Changes to Existing Topography (Less than Significant) Development of the project site would involve grading and other earthwork as
Geospatial Data Integration For Groundwater Recharge Estimation In Hard Rock Terrain. Authors,
 Geospatial Data Integration For Groundwater Recharge Estimation In Hard Rock Terrain Authors, Dr. Y. B. Katpatal Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering, Visvesvaraya National Institute of
Geospatial Data Integration For Groundwater Recharge Estimation In Hard Rock Terrain Authors, Dr. Y. B. Katpatal Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering, Visvesvaraya National Institute of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 1, No 3, 2010
 Integrated approach using RS and GIS techniques for mapping of ground water prospects in Lower Sanjai Watershed, Jharkhand Binay Kumar 1, Uday Kumar 2 1 Geomatics Solutions Development Group, Centre for
Integrated approach using RS and GIS techniques for mapping of ground water prospects in Lower Sanjai Watershed, Jharkhand Binay Kumar 1, Uday Kumar 2 1 Geomatics Solutions Development Group, Centre for
Prepared By: John Blair Sean Donahue Celeste Hoffman Kimberly Klinkers Megan Slater
 Prepared By: John Blair Sean Donahue Celeste Hoffman Kimberly Klinkers Megan Slater Green River Basin Location Green River Basin Stratigraphic Correlation Chart showing Study Map Units Sample of Existing
Prepared By: John Blair Sean Donahue Celeste Hoffman Kimberly Klinkers Megan Slater Green River Basin Location Green River Basin Stratigraphic Correlation Chart showing Study Map Units Sample of Existing
Landslide hazard zonation (LHZ) mapping on meso-scale for systematic town planning in mountainous terrain
 Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research 486 Vol. 67, July 2008, pp. 486-497 J SCI IND RES VOL 67 JULY 2008 Landslide hazard zonation (LHZ mapping on meso-scale for systematic town planning in mountainous
Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research 486 Vol. 67, July 2008, pp. 486-497 J SCI IND RES VOL 67 JULY 2008 Landslide hazard zonation (LHZ mapping on meso-scale for systematic town planning in mountainous
Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands
 Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Flood and Flood Hazards Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG, Legon College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Flood and Flood Hazards Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG, Legon College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
River Response. Sediment Water Wood. Confinement. Bank material. Channel morphology. Valley slope. Riparian vegetation.
 River Response River Response Sediment Water Wood Confinement Valley slope Channel morphology Bank material Flow obstructions Riparian vegetation climate catchment vegetation hydrological regime channel
River Response River Response Sediment Water Wood Confinement Valley slope Channel morphology Bank material Flow obstructions Riparian vegetation climate catchment vegetation hydrological regime channel
About the Author: Abstract:
 Identification of groundwater prospecting zones using Remote Sensing and GIS techniques in upper Vena river watersheds Nagpur district, Maharashtra, India B.S. Manjare Department of Geology RTM Nagpur
Identification of groundwater prospecting zones using Remote Sensing and GIS techniques in upper Vena river watersheds Nagpur district, Maharashtra, India B.S. Manjare Department of Geology RTM Nagpur
Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Logistic Regression in Garut District, West Java, Indonesia
 Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Logistic Regression in Garut District, West Java, Indonesia N. Lakmal Deshapriya 1, Udhi Catur Nugroho 2, Sesa Wiguna 3, Manzul Hazarika 1, Lal Samarakoon 1 1 Geoinformatics
Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Logistic Regression in Garut District, West Java, Indonesia N. Lakmal Deshapriya 1, Udhi Catur Nugroho 2, Sesa Wiguna 3, Manzul Hazarika 1, Lal Samarakoon 1 1 Geoinformatics
Assessing Vulnerability to Soil Erosion of a Watershed of Tons River Basin in Madhya Pradesh using Remote Sensing and GIS
 International Journal of Environmental Research and Development. ISSN 2249-3131 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 153-164 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijerd.htm Assessing Vulnerability
International Journal of Environmental Research and Development. ISSN 2249-3131 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 153-164 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijerd.htm Assessing Vulnerability
Downloaded from Downloaded from
 IV SEMESTER BACK-PAPER EXAMINATION-2004 Q. [1] [a] Describe internal structure of the earth with a neat sketch. Write down the major land forms and their characteristics on the earth surface. [8] [b] What
IV SEMESTER BACK-PAPER EXAMINATION-2004 Q. [1] [a] Describe internal structure of the earth with a neat sketch. Write down the major land forms and their characteristics on the earth surface. [8] [b] What
ESTIMATION OF LANDFORM CLASSIFICATION BASED ON LAND USE AND ITS CHANGE - Use of Object-based Classification and Altitude Data -
 ESTIMATION OF LANDFORM CLASSIFICATION BASED ON LAND USE AND ITS CHANGE - Use of Object-based Classification and Altitude Data - Shoichi NAKAI 1 and Jaegyu BAE 2 1 Professor, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan.
ESTIMATION OF LANDFORM CLASSIFICATION BASED ON LAND USE AND ITS CHANGE - Use of Object-based Classification and Altitude Data - Shoichi NAKAI 1 and Jaegyu BAE 2 1 Professor, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan.
International Journal of Research (IJR) Vol-1, Issue-10 November 2014 ISSN
 Morphological Parameter Estimation Derived From ASTER-DEM Using GIS and Remote Sensing Techniques A Study on Hosakote Watershed of Dakshina Pinakini River Basin, Karnataka, India K. Satish 1* and H.C.
Morphological Parameter Estimation Derived From ASTER-DEM Using GIS and Remote Sensing Techniques A Study on Hosakote Watershed of Dakshina Pinakini River Basin, Karnataka, India K. Satish 1* and H.C.
