Description of a New Deep-Water Calcareous Sponge (Porifera: Calcarea) from Northern California 1
|
|
|
- Randolph Williamson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pacific Science (2000), vol. 54, no. 1: by University of Hawai'i Press. All rights reserved Description of a New Deep-Water Calcareous Sponge (Porifera: Calcarea) from Northern California 1 KIRK DUPLESSIS 2 AND HENRY M. REISWIG 2,3 ABSTRACT: A new species, Sycon escanabensis Duplessis & Reiswig, is described from material retrieved by submersible from 3500 m depth in the Escanaba Trough, central Gorda Ridge, off northern California. The species differs from all other members of the genus by the combination of conspicuous tripartite body organization and slender, lancet-head diactins that ornament the external surface and the oscular margin. This is the first deep-water (> 1000 m) calcareous sponge described from the North Pacific Basin. MEMBERS OF THE PORIFERAN class Calcarea have often been considered to be restricted to the upper 200 m of the ocean by physical factors (Bergquist 1978), namely the calcium carbonate compensation depth, below which exposed calcareous skeletons pass fairly rapidly into solution (Gage and Tyler 1991). Indeed, the skeletal remains of calcareous sponges are rarely encountered in sediments at depths beyond 2500 m, suggesting their absence as members of deep-water faunal communities. In recent years, however, an increasing number of living calcareous specimens have been discovered at depths below 1000 m. These reports have been primarily from the Norwegian, Greenland, and Arctic Seas (Arnesen [1920]: 1 location; Borojevic and Graat-Kleeton [1965]: 7 locations; Reid [1968]: 3 locations; Tendal [1989]: 40 locations). The deepest specimen reported from the Atlantic region is Sycon abyssale from 4000 m (Borojevic and Graat-Kleeton 1965). This series of unexpected occurrences was thought to be attributable to the unusual combination of low temperatures and high overturn (dynamic instability) in this region, 1 Financial support for specimen analysis was provided by an operating grant from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council ofcanada to H.M.R. Manuscript accepted 3 April Redpath Museum and Biology Department, McGill University, 859 Sherbrooke Street West, Montreal, Quebec, Canada H3A 2K6. 3 Corresponding author ( cxhr@musica. mcgill.ca). 10 modifying the solution dynamics of calcium carbonate. However, Vacelet (1989) has found calcareous sponges at eight deep locations in the Mediterranean Sea, the deepest at 2775 m, casting serious doubt upon the unique environment hypothesis. These calcareous sponges have all been, with rare exception, members of the cosmopolitan genus Sycon. The only deep-water calcareous sponge reported from the North Pacific is an unidentified specimen discovered in the Kurile Trench at 5045 m (Koltun 1970). Here we describe a new deep-water Sycon species (four specimens) from the Northeast Pacific. This is only the second report of occurrence of deep-water Calcarea from this region and the first report with a full species determination. MATERIALS AND METHODS The two complete specimens, after being photographed and measured, were grossly dissected to provide isolated body regions. These were bulk-stained in 1% erythrosin-b in 95% ethanol and either whole-mounted in Canada balsam on slides or embedded in paraffin for thick-sectioning by hand, deparaffinized in xylene, and mounted in balsam. Pieces used for spicule sampling were deparaffinized and digested in 5.25% sodium hypocworite. Spicules were retained on 0.2-llm pore-size nitrocellulose filters, which were water-rinsed, dried, cleared in xylene,
2 New Deep-Water Calcareous Sponge-DupLESsIS AND REISWIG 11 and mounted in balsam on slides for light microscopy. Spicules were measured by computer with a microscope-coupled digitizer. Spicule drawings were prepared from videocaptured light-microscope images imported into a computer drawing program and traced on-screen. Samples for scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were digested in 5% sodium hypochlorite and were either captured on 0.2-llm pore-size polycarbonate membrane filters or deposited directly onto cover glasses after rinsing in distilled water. After gold-palladium coating, specimens were viewed and photographed with an SEM (JEOL JSM-840). Data are reported as mean ± SD (range, number of measurements). Specimens have been deposited at the California Academy of Sciences, Invertebrate Zoology Division, (CASIZ), Golden Gate Park, San Francisco, California. SYSTEMATIC TREATMENT Class CALCAREA Bowerbank, 1864 Subclass CALCARONEA Bidder, 1898 Order LEUCOSOLENIIDA Hartman, 1958 Family SYCETTIDAE Dendy, 1892 Genus Sycon Risso, 1826 Sycon escanabensis Duplessis & Reiswig, n. sp. Figures 1-3 TYPE MATERIAL: Holotype: CASIZ , length 5.6 mm (complete specimen), Esca~ naba Trough, Gorda Ridge, off Northern California; N, W; 6 September 1988; 3500 m; col. R. Zierenberg; DSS Laney Chouest and DSSV Sea Cliff, dive no Paratypes: CASIZ , length 3.4 mm (complete specimen); CASIZ , 1.3 mm (oscular tube only); CASIZ , 1.3 mm (oscular tube only); collection data as for holotype. DIAGNOSIS: Sycon with a distinctly tripartite body (oscular tube, trunk, and stalk), and short, thin, lancet-head diactins projecting from oscular margin and surrounding external surface. DESCRIPTION: Specimen: A complete specimen of Sycon escanabensis shows clear tripartite macrostructure (Figure la), consisting of an oscular tube, a trunk, and a stalk; total length: mm; width: mm. Oscular tube length: mm; diameter: mm. Oscular tube (Figure la,c) lacks choanocytes and serves only to convey exhalent water from the trunk to the superior osculum. It is composed of two bounding epithelia enclosing a well-ordered spicular skeleton of sagittal triactins, sagittal ray directed basally, and a small proportion (ca. 5%) of tetractins, curved atrial ray directed into the tube lumen and toward the osculum. Thin lancet-head diactine spicules form a marginal fringe at osculum and ornament the external surface of the tube in an oblique, osculum-directed orientation. The trunk contains the entire choanocyte population of the sponge in the flagellated chambers (radial canals). Externally the trunk is conulose and hispid, and the cones distally ornamented with small lancet-head diactins. Trunk length: mm. The flagellated chambers are coalescent for most of their length (Figure lb), a distinctive characteristic of Sycon. The chambers themselves measure Ilm wide and Ilm long. Small oocytes at low density (1-4 per flagellated chamber) occur in the holotype. Tetractins, common at the intersection of the flagellated chambers and atrial cavity, have their atrial ray oriented as in the oscular tube, but the primary rays are arranged to coincide with margins of the radial canal junctions, not the longitudinal axis of the sponge. The tapered basal stalk apparently serves only for attachment and support; it lacks choanocytes, an axial atrial cavity, and external diactin ornamentation. Stalk length: mm. Its skeleton of triactins and tetractins is less ordered than those of the other body regions. Small sand grains are attached to the stalk base of the complete paratype, CASIZ Spicules: Triactins occur in two forms: sagittal (Figure 2a-c) and irregular (Figure 2d); they are semitetrahedral (nonplanar) (Figure ld). Ray length: 231 ± 91 Ilm (28-
3 12 PACIFIC SCIENCE, Volume 54, January 2000 FIGURE 1. Sycon escanabensis, n. sp.: a, holotype, showing tripartite structure (Os, osculum; Tr, trunk; St, stalk). b, cross section of the body wall of the holotype, showing radial canals, 1% erythrosin-b stained. c, the two incomplete paratypes (oscular tubes) showing diactins of the oscular fringe. d, triactine spicule, clearly nonplanar in form (SEM). e, tetractine spicule, with atrial ray projecting vertically (SEM)./, diactine spicule (whole). g, diactine spicule (lancet head) m, 576); ray thickness: 18.4 ± m ( m, 225). Medium-sized sagittal triactins (Figure 2b) occur in oscular tube oriented with sagittal ray directed basally, and in lateral walls of the radial canals. Larger sagittal triactins (Figure 2a) occur at proximal and distal ends (terminal cones) of the radial canals. Very small triactins (Figure 2c) occur throughout the specimens. Frequency analysis of the unpaired angle of sagittal triactins (Figure 3) shows a broad, continuous distribution, establishing that only a single class of this spicule form is present; L = 125 ± 11 (97-159, 204). Irregular triactins (Figure 2d) occur throughout the specimen in small numbers and more commonly in the stalk region; largest angle: L = 134 ± 12 ( ,105). Tetractins (Figures Ie, 2e) line the atrial cavity, with atrial ray projecting inward and upward toward the osculum. They are also present in the oscular tube wall and in the
4 New Deep-Water Calcareous Sponge-DupLEsSIS AND REISWIG 13 rr c f loo~m FIGURE 2. Spicules of Sycon escanabensis, n. sp.: a, large sagittal triactins. b, medium sagittal triactins. c, small sagittal triactins. d, irregular triactin. e, tetractine spicule. f, diactine spicules g 0 "E 0.08 g: '" 0 u 15.0 '" 0.06 ~ If Angle in degrees FIGURE 3. Histogram of unpaired angle of sagittal triactine spicules of Sycon escanabensis, n. sp. trunk region at intersections of the radial canals. Dimensions of primary rays as for triactins (above); atrial ray length: 165 ± 40 flm ( flm, 20). Diactins (Figures If, 2f) always occur projecting lancet head out from the external surface on the terminal fringe of the oscular tube, along its outer walls, and at tips of the cones of the radial canals. This distinctive lancet-shaped head (Figure 19) also occurs in other Sycon species. Length: 228 ± 59 flm ( flm, 100); thickness: 2.9 ± 0.7 flm ( flm, 100). ETYMOLOGY: The species name is derived from the geographic location of collection, the Escanaba Trough. REMARKS: This species is assigned to the genus Sycon by virtue of coalescence of its radial canals. Several other species ofthis genus also show tripartite body organization, including S. ampulla, S. caminatum, S. humboldtii, S. raphanus, and S. sycandra (Burton 1963). The new species differs from S. am-
5 14 pulla by its solitary form (s. ampulla is colonial) and its solid stalk (that of S. ampulla is hollow). All of these tripartite forms differ from S. escanabensis in their possession of much larger diactine spicules. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thank M. Boudrias for providing the specimens on which this work is based. We acknowledge advice on systematics and literature from J. Vacelet and R. Borojevic. LITERATURE CITED ARNESEN, E Spongia. Report of the "Michael Sars" North Atlantic Deep-Sea Expedition 1910, 3 (2): 1-28, pis. I-V. BERGQUIST, P. R Sponges. University of California Press, Berkeley. BOROJEVIC, R., and G. GRAAT-KLEETON Sur une nouvelle espece de Sycon et quelque Demosponges recoltees par Ie "Cirrus" dans l'atlantique Nord. Beaufortia 154: BURTON, M A revision of the classifi- PACIFIC SCIENCE, Volume 54, January 2000 cation of the calcareous sponges with a catalogue of the specimens in the British Museum (Natural History). British Museum (Natural History), London. GAGE, J. D., and P. A. TYLER Deep sea biology: A natural history of organisms at the deep sea floor. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. KOLTUN, V. M Sponge fauna of the North-Western Pacific from the shallows to the ultra-abyssal depths. Pages in V. G. Bogorov, ed. Fauna of the Kurile-Kamchatka Trench and its environment. Trudy Instituta Okeanologii Akademii NAUK SSSR (Transl. from Russian, Israel Program on Scientific Translations, Jerusalem, No : ). REID, R. E. H Bathymetric distributions of Calcarea and the Hexactinellida in the present and the past. Geol. Mag. 6: TENDAL, O. S Calcareous sponges in the abyssal Norwegian and Greenland Seas. Deep-Sea Newsl. 15: VACELET, J Unexpected deep-water records of calcareous sponges (Calcarea). Deep-Sea Newsl. 15:
Lab ( 3) Kingdom: Animalia
 Lab ( 3) Kingdom: Animalia Characteristics of animals: - Multicellular - Eukaryotic organisms - Cells with out cell wall Animalia is divided in two group : A/ Invertebrate ( animals with out backbones
Lab ( 3) Kingdom: Animalia Characteristics of animals: - Multicellular - Eukaryotic organisms - Cells with out cell wall Animalia is divided in two group : A/ Invertebrate ( animals with out backbones
Zoology Name: Block: Exercise #7: The Sponges, Phylum Porifera Lab Guide
 Zoology Name: Block: Exercise #7: The Sponges, Phylum Porifera Lab Guide Members of the phylum Porifera are considered the simplest metazoans, they are little more than a loose grouping of cells, with
Zoology Name: Block: Exercise #7: The Sponges, Phylum Porifera Lab Guide Members of the phylum Porifera are considered the simplest metazoans, they are little more than a loose grouping of cells, with
INVERTEBRATE LAB. Phylum Protozoa & Porifera
 INVERTEBRATE LAB Phylum Protozoa & Porifera... These are single celled animals that are usually microscopic but some are visible to the naked eye. Many marine protozoa build themselves shells or skeletons,
INVERTEBRATE LAB Phylum Protozoa & Porifera... These are single celled animals that are usually microscopic but some are visible to the naked eye. Many marine protozoa build themselves shells or skeletons,
Order Leucosolenida Hartman, 1958
 Hoo-125.qxd 8/22/02 6:52 PM Page 1157 Systema Porifera: A Guide to the Classification of Sponges, Edited by John N.A. Hooper and Rob W.M. Van Soest Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, 2002 Order
Hoo-125.qxd 8/22/02 6:52 PM Page 1157 Systema Porifera: A Guide to the Classification of Sponges, Edited by John N.A. Hooper and Rob W.M. Van Soest Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, 2002 Order
12.1. Advent of Multicellularity A. Advantages 1. Nature s experiments with larger organisms without cellular differentiation are limited. 2. Increasi
 Phylum: Porifera The Sponges 12.1. Advent of Multicellularity A. Advantages 1. Nature s experiments with larger organisms without cellular differentiation are limited. 2. Increasing the size of a cell
Phylum: Porifera The Sponges 12.1. Advent of Multicellularity A. Advantages 1. Nature s experiments with larger organisms without cellular differentiation are limited. 2. Increasing the size of a cell
Invertebrate Zoology. Unit 2: Phylums: Porifera, Cnidaria, and Ctenophora
 Invertebrate Zoology Unit 2: Phylums: Porifera, Cnidaria, and Ctenophora Objective 1: Differentiate between the 3 types of Poriferians (Asconoids, Syconoids, and Leuconoids) and the three main classes
Invertebrate Zoology Unit 2: Phylums: Porifera, Cnidaria, and Ctenophora Objective 1: Differentiate between the 3 types of Poriferians (Asconoids, Syconoids, and Leuconoids) and the three main classes
'!.t. Deep-Sea Newsletter 20, 12-15, 1993 CHONDROCLADIA GIGANTEA (DEMOSPONGIAE) - THE GIANT CLUBSPONGE OF THE NORTHEAST ATLANTIC
 Deep-Sea Newsletter 20, 12-15, 1993 70 CHONDROCLADIA GIGANTEA (DEMOSPONGIAE) - THE GIANT CLUBSPONGE OF THE NORTHEAST ATLANTIC Chondrocladia gigantea is a most remar} able stalked sponge living on soft
Deep-Sea Newsletter 20, 12-15, 1993 70 CHONDROCLADIA GIGANTEA (DEMOSPONGIAE) - THE GIANT CLUBSPONGE OF THE NORTHEAST ATLANTIC Chondrocladia gigantea is a most remar} able stalked sponge living on soft
Earth / Environmental Science. Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR
 Earth / Environmental Science Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR The Blue Planet Nearly 70% of the Earth s surface is covered by the global ocean It was not until the 1800s that the ocean became an important focus
Earth / Environmental Science Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR The Blue Planet Nearly 70% of the Earth s surface is covered by the global ocean It was not until the 1800s that the ocean became an important focus
Calcareous sponges from New Caledonia
 Calcareous sponges from New Caledonia Radovan BOROJEVIC Departamento de Histologia e Embriologia, Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Caixa Postal 68021, 21941-970
Calcareous sponges from New Caledonia Radovan BOROJEVIC Departamento de Histologia e Embriologia, Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Caixa Postal 68021, 21941-970
Mesozoa, Parazoa, and Metazoa. Chapter 12 pg. 239
 Mesozoa, Parazoa, and Metazoa Chapter 12 pg. 239 3 Multicellular Groups: Mesozoa, Parazoa, Eumetazoa Multicellular organisms are divided into three groups: Mesozoa, Parazoa (phylum Porifera, phylum Placozoa)
Mesozoa, Parazoa, and Metazoa Chapter 12 pg. 239 3 Multicellular Groups: Mesozoa, Parazoa, Eumetazoa Multicellular organisms are divided into three groups: Mesozoa, Parazoa (phylum Porifera, phylum Placozoa)
Phyllum Porifera: Sponges
 Phyllum Porifera: Sponges Chapter 12 Ini5ally not considered animals but molecular evidence demonstrate that sponges are phylogene5cally grouped with other metazoa (animals) Sponges are the simplest mul5cellular
Phyllum Porifera: Sponges Chapter 12 Ini5ally not considered animals but molecular evidence demonstrate that sponges are phylogene5cally grouped with other metazoa (animals) Sponges are the simplest mul5cellular
Introduction to the Seafloor. Follow the steps below while taking notes in your science notebook.
 Procedure Follow the steps below while taking notes in your science notebook. 1. Name and locate all of the continents. 2. Identify linear (straight-line) and arcuate (curved-line) features on the continents.
Procedure Follow the steps below while taking notes in your science notebook. 1. Name and locate all of the continents. 2. Identify linear (straight-line) and arcuate (curved-line) features on the continents.
C. Body is platelike, no symmetry, organs, muscular or nervous systems present. D. 2-3 mm E. marine F. glide over food and secrete digestive enzyme an
 Chapter 9 (multicellularity) I. Similarities A. cells are grouped B. groups of cells are specialized for various functions C. All cells in an organism is interdependent. II. Multicelled life appeared ~
Chapter 9 (multicellularity) I. Similarities A. cells are grouped B. groups of cells are specialized for various functions C. All cells in an organism is interdependent. II. Multicelled life appeared ~
Bilateria. Radiata. Eumetazoa. Parazoa no true tissues. Multicellularity
 Quiz 1. What does porifera mean? 2. Class Hexactinellida's skeletal structure is made out of what material? 3. Characterized as large openings where water comes out 4. Cells responsible for the circulating
Quiz 1. What does porifera mean? 2. Class Hexactinellida's skeletal structure is made out of what material? 3. Characterized as large openings where water comes out 4. Cells responsible for the circulating
Small area of the ocean that is partially surrounded by land. The Ocean Basins. Three Major Oceans. Three Major Oceans. What is a SEA?
 The Ocean Basins How Deep is the Ocean? 1 2 Three Major Oceans Three Major Oceans Pacific Atlantic the shallowest ocean (3.3km average depth) Indian second shallowest ocean (3.8km average depth) Pacific
The Ocean Basins How Deep is the Ocean? 1 2 Three Major Oceans Three Major Oceans Pacific Atlantic the shallowest ocean (3.3km average depth) Indian second shallowest ocean (3.8km average depth) Pacific
Module 4: Marine Invertebrates I. Kingdom Animalia
 Module 4: Marine Invertebrates I Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia Contains the largest number of species We will split them into 2 large groups Invertebrates- Animals w/o a backbone Vertebrates- Animals
Module 4: Marine Invertebrates I Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia Contains the largest number of species We will split them into 2 large groups Invertebrates- Animals w/o a backbone Vertebrates- Animals
Sponges and Cnidarians
 The Animal Kingdom Multicellular Sponges and Cnidarians Biology : Chapter 26 Eukaryotic Heterotrophs Cells lack cell walls 95% are invertebrates What Animals Do to Survive Feeding Response Respiration
The Animal Kingdom Multicellular Sponges and Cnidarians Biology : Chapter 26 Eukaryotic Heterotrophs Cells lack cell walls 95% are invertebrates What Animals Do to Survive Feeding Response Respiration
Ocean Basins, Bathymetry and Sea Levels
 Ocean Basins, Bathymetry and Sea Levels Chapter 4 Please read chapter 5: sediments for next class and start chapter 6 on seawater for Thursday Basic concepts in Chapter 4 Bathymetry the measurement of
Ocean Basins, Bathymetry and Sea Levels Chapter 4 Please read chapter 5: sediments for next class and start chapter 6 on seawater for Thursday Basic concepts in Chapter 4 Bathymetry the measurement of
Class Calcarea Bowerbank, 1864
 Hoo-120.qxd 10/7/04 1:32 AM Page 1103 Systema Porifera: A Guide to the Classification of Sponges, Edited by John N.A. Hooper and Rob W.M. Van Soest Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, 2002 Class
Hoo-120.qxd 10/7/04 1:32 AM Page 1103 Systema Porifera: A Guide to the Classification of Sponges, Edited by John N.A. Hooper and Rob W.M. Van Soest Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, 2002 Class
Ph. Porifera and Ph. Cnidaria
 I. Phylum Porifera (sponges; pore bearer ) A. General characteristics 1. simplest animals 2. asymmetric 3. aquatic habitats a. typically marine 4. live alone or in colonies a. often members of reef habitats
I. Phylum Porifera (sponges; pore bearer ) A. General characteristics 1. simplest animals 2. asymmetric 3. aquatic habitats a. typically marine 4. live alone or in colonies a. often members of reef habitats
Directed Reading. Section: The Water Planet. surface is called the a. Earth s ocean. b. Pacific Ocean. c. salt-water ocean. d. global ocean.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Water Planet 1. The body of salt water covering nearly three-quarters of the Earth s surface is called the a. Earth s ocean. b. Pacific Ocean. c. salt-water
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Water Planet 1. The body of salt water covering nearly three-quarters of the Earth s surface is called the a. Earth s ocean. b. Pacific Ocean. c. salt-water
Site Location (Latitude/ Longitude)
 Core Identification: Expedition Site & Hole Core & Type* Pacific Cores TABLE 2.. Seafloor cores Physiographic Site Location Site Location (Latitude/ Longitude) Water Depth (m) 2-687A-2H Peru continental
Core Identification: Expedition Site & Hole Core & Type* Pacific Cores TABLE 2.. Seafloor cores Physiographic Site Location Site Location (Latitude/ Longitude) Water Depth (m) 2-687A-2H Peru continental
Lab 2 Phylum Porifera and phylum Cnidaria. Grantia. Phylum Porifera. Kingdom :- Animalia. Phylum:- Porifera. Class:- Calcarea. Order:- Leucosolenida
 Lab 2 Phylum Porifera and phylum Cnidaria Phylum Porifera Adults sessile and attached Radial symmetry or asymmetrical Multi-cellular ; loose aggregation of cells Skeleton made of collagen and spicules
Lab 2 Phylum Porifera and phylum Cnidaria Phylum Porifera Adults sessile and attached Radial symmetry or asymmetrical Multi-cellular ; loose aggregation of cells Skeleton made of collagen and spicules
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE!
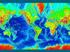
 ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
14.2 Ocean Floor Features Mapping the Ocean Floor
 14.2 Ocean Floor Features Mapping the Ocean Floor The ocean floor regions are the continental margins, the ocean basin floor, and the mid-ocean ridge. 14.2 Ocean Floor Features Continental Margins A continental
14.2 Ocean Floor Features Mapping the Ocean Floor The ocean floor regions are the continental margins, the ocean basin floor, and the mid-ocean ridge. 14.2 Ocean Floor Features Continental Margins A continental
basal animalia porifera, cnidaria
 basal animalia porifera, cnidaria PHYLUM PORIFERA porifera Sponges, no tissues or organs, cellular level of organization outer layer is made of cells called pinacocytes choanocytes (collar cells) Flagella
basal animalia porifera, cnidaria PHYLUM PORIFERA porifera Sponges, no tissues or organs, cellular level of organization outer layer is made of cells called pinacocytes choanocytes (collar cells) Flagella
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 10 - Whole Lotta Shakin' Goin' On
 General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 10 - Whole Lotta Shakin' Goin' On Name Not attempting to answer questions on expeditions will result in point deductions on course workbook (two or more blank
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 10 - Whole Lotta Shakin' Goin' On Name Not attempting to answer questions on expeditions will result in point deductions on course workbook (two or more blank
OCN 201 Physiography of the Seafloor
 OCN 201 Physiography of the Seafloor 1 Ocean Depth versus Continental Height Why do we have dry land? Solid surface of Earth is dominated by two levels: Land with a mean elevation of +840 m (29% of Earth
OCN 201 Physiography of the Seafloor 1 Ocean Depth versus Continental Height Why do we have dry land? Solid surface of Earth is dominated by two levels: Land with a mean elevation of +840 m (29% of Earth
 http://www.neic.cr.usgs.gov/neis/pands/global.html Global Seismicity and World Cities This map displays the worldwide hazard to cities by large earthquakes. When earthquakes occur near cities, the potential
http://www.neic.cr.usgs.gov/neis/pands/global.html Global Seismicity and World Cities This map displays the worldwide hazard to cities by large earthquakes. When earthquakes occur near cities, the potential
TWO NEW FOSSIL DEMOSPONGES FROM WES ONGUL ISLAND, LUTZOW-HOLM BAY, ANTA.
 Title TWO NEW FOSSIL DEMOSPONGES FROM WES ONGUL ISLAND, LUTZOW-HOLM BAY, ANTA Author(s) Hoshino, Takaharu Citation PUBLICATIONS OF THE SETO MARINE BIO LABORATORY (1977), 24(1-3): 43-48 Issue Date 1977-11-30
Title TWO NEW FOSSIL DEMOSPONGES FROM WES ONGUL ISLAND, LUTZOW-HOLM BAY, ANTA Author(s) Hoshino, Takaharu Citation PUBLICATIONS OF THE SETO MARINE BIO LABORATORY (1977), 24(1-3): 43-48 Issue Date 1977-11-30
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Oceans: The Last Frontier Foundations, 6e - Chapter 9 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Oceans: The Last Frontier Foundations, 6e - Chapter 9 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred
The Ocean Floor Chapter 14. Essentials of Geology, 8e. Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College
 The Ocean Floor Chapter 14 Essentials of Geology, 8e Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the water planet 71% of Earth s surface
The Ocean Floor Chapter 14 Essentials of Geology, 8e Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the water planet 71% of Earth s surface
PSc 201 Chapter 3 Homework. Critical Thinking Questions
 PSc 201 Chapter 3 Homework Critical Thinking Questions 1. (adapted from text) Seawater is denser than fresh water. A ship moving from the Atlantic Ocean into the Great Lakes goes from seawater to fresh
PSc 201 Chapter 3 Homework Critical Thinking Questions 1. (adapted from text) Seawater is denser than fresh water. A ship moving from the Atlantic Ocean into the Great Lakes goes from seawater to fresh
OCN 201 Physiography of the Seafloor
 OCN 201 Physiography of the Seafloor Hypsometric Curve for Earth s solid surface Note histogram Hypsometric curve of Earth shows two modes. Hypsometric curve of Venus shows only one! Why? Ocean Depth vs.
OCN 201 Physiography of the Seafloor Hypsometric Curve for Earth s solid surface Note histogram Hypsometric curve of Earth shows two modes. Hypsometric curve of Venus shows only one! Why? Ocean Depth vs.
24. Ocean Basins p
 24. Ocean Basins p. 350-372 Background The majority of the planet is covered by ocean- about %. So the majority of the Earth s crust is. This crust is hidden from view beneath the water so it is not as
24. Ocean Basins p. 350-372 Background The majority of the planet is covered by ocean- about %. So the majority of the Earth s crust is. This crust is hidden from view beneath the water so it is not as
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY
 MARINE GEOLOGY MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Marine Geology 4 LAYERS OF THE EARTH CRUST THICKNESS: VARIES BETWEEN OCEAN & CONTINENTS 5-40 KM STATE: SOLID ELEMENTS: SILICON, ALUMINUM, CALCIUM, SODIUM, POTASSIUM
MARINE GEOLOGY MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Marine Geology 4 LAYERS OF THE EARTH CRUST THICKNESS: VARIES BETWEEN OCEAN & CONTINENTS 5-40 KM STATE: SOLID ELEMENTS: SILICON, ALUMINUM, CALCIUM, SODIUM, POTASSIUM
The Indian Ocean. Copyright 2010 LessonSnips
 The Indian Ocean One of the five major geographic divisions of the world s ocean, the Indian Ocean is located in the Eastern Hemisphere. The Indian Ocean is bounded by three continents: Africa to the west,
The Indian Ocean One of the five major geographic divisions of the world s ocean, the Indian Ocean is located in the Eastern Hemisphere. The Indian Ocean is bounded by three continents: Africa to the west,
Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor
 Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 3 Marine Provinces 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 3 Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean
Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 3 Marine Provinces 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 3 Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean
1. Name at least one place that the mid-atlantic Ridge is exposed above sea level.
 Interpreting Tectonic and Bathymetric Maps. The purpose of this lab is to provide experience interpreting the bathymetry of the seafloor in terms of tectonic and geologic settings and processes. Use the
Interpreting Tectonic and Bathymetric Maps. The purpose of this lab is to provide experience interpreting the bathymetry of the seafloor in terms of tectonic and geologic settings and processes. Use the
Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans Oceans make up over 70% of the Earth s surface
 Oceanography Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans Oceans make up over 70% of the Earth s surface An ocean must be large and have features which set it apart from other oceans (currents, water
Oceanography Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans Oceans make up over 70% of the Earth s surface An ocean must be large and have features which set it apart from other oceans (currents, water
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017
 ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
Bathymetry Measures the vertical distance from the ocean surface to mountains, valleys, plains, and other sea floor features
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools.
The Bottom of the Ocean
 The Bottom of the Ocean Overview: In this lesson, students study bathymetric features of the ocean, predict how bathymetric features influence propagation and runup, then analyze an animation of a tsunami
The Bottom of the Ocean Overview: In this lesson, students study bathymetric features of the ocean, predict how bathymetric features influence propagation and runup, then analyze an animation of a tsunami
Phylum Porifera. Phylum Porifera (sponges) Defining Characteristics of Phylum. Sponges
 Phylum Porifera Sponges Ancient group of animals that dates back to the late Precambrian about 600 million years ago Phylum Porifera (sponges) Sessile, aquatic, benthic, suspension feeders on bacteria
Phylum Porifera Sponges Ancient group of animals that dates back to the late Precambrian about 600 million years ago Phylum Porifera (sponges) Sessile, aquatic, benthic, suspension feeders on bacteria
Chapter 10. Nanometrology. Oxford University Press All rights reserved.
 Chapter 10 Nanometrology Oxford University Press 2013. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands
Chapter 10 Nanometrology Oxford University Press 2013. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands
TREATISE ONLINE Number 5
 TREATISE ONLINE Number 5 Part E, Revised, Volume 4, Chapter 9A: Paleozoic Stromatoporoidea: General Introduction Colin W. Stearn 2010 Lawrence, Kansas, USA ISSN 2153-4012 paleo.ku.edu/treatiseonline PART
TREATISE ONLINE Number 5 Part E, Revised, Volume 4, Chapter 9A: Paleozoic Stromatoporoidea: General Introduction Colin W. Stearn 2010 Lawrence, Kansas, USA ISSN 2153-4012 paleo.ku.edu/treatiseonline PART
The Rise of the Animals
 The Rise of the Animals Animal or Plant? No eye spots Don t move No organs How can it be an animal? Or is it a plant? Meeting the Minimum Multicellular + Heterotrophic + Differentiated Cells + Structural
The Rise of the Animals Animal or Plant? No eye spots Don t move No organs How can it be an animal? Or is it a plant? Meeting the Minimum Multicellular + Heterotrophic + Differentiated Cells + Structural
Ocean Floor. Continental Margins. Divided into 3 major regions. Continental Margins. Ocean Basins. Mid-Ocean Ridges. Include:
 Ocean Floor Divided into 3 major regions Continental Margins Ocean Basins Mid-Ocean Ridges Continental Margins Include: Continental Shelves Continental Slopes Continental Rise 1 Continental Shelves Part
Ocean Floor Divided into 3 major regions Continental Margins Ocean Basins Mid-Ocean Ridges Continental Margins Include: Continental Shelves Continental Slopes Continental Rise 1 Continental Shelves Part
Chapter 02 The Sea Floor
 Chapter 02 The Sea Floor Multiple Choice Questions 1. One of the following is not one of the world's major ocean basins: A. Atlantic Ocean B. Arctic Ocean C. Indian Ocean D. Antarctic Ocean E. Pacific
Chapter 02 The Sea Floor Multiple Choice Questions 1. One of the following is not one of the world's major ocean basins: A. Atlantic Ocean B. Arctic Ocean C. Indian Ocean D. Antarctic Ocean E. Pacific
Chapter Overview. Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry
 CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
Bell Ringer. water cycle? gaseous water (water vapor)? How do you know? 1. What are the five components of the
 Bell Ringer 1. What are the five components of the water cycle? 2. Are clouds composed of liquid water or gaseous water (water vapor)? How do you know? 3. How are glaciers formed? Salt Water - Oceans Characteristics
Bell Ringer 1. What are the five components of the water cycle? 2. Are clouds composed of liquid water or gaseous water (water vapor)? How do you know? 3. How are glaciers formed? Salt Water - Oceans Characteristics
column Shelby A. Jones Fall 2014 Lynne Talley SIO 210: Introduction to Physical Oceanography
 Volcanic 3 He Outgassing along the East Pacific Rise, as evidenced by 3 He in the water column Shelby A. Jones Fall 2014 Lynne Talley SIO 210: Introduction to Physical Oceanography University of California,
Volcanic 3 He Outgassing along the East Pacific Rise, as evidenced by 3 He in the water column Shelby A. Jones Fall 2014 Lynne Talley SIO 210: Introduction to Physical Oceanography University of California,
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Calcareous sponge genomes reveal complex evolution of α-carbonic anhydrases and two key biomineralization enzymes
 Calcareous sponge genomes reveal comple evolution of α-carbonic anhydrases and two key biomineralization enzymes Voigt et al. Voigt et al. BMC Evolutionary Biology 2014, 14:230 Voigt et al. BMC Evolutionary
Calcareous sponge genomes reveal comple evolution of α-carbonic anhydrases and two key biomineralization enzymes Voigt et al. Voigt et al. BMC Evolutionary Biology 2014, 14:230 Voigt et al. BMC Evolutionary
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 13 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 13 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 13 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Seas. A sea is a part of an ocean that is nearly surrounded by water. The Mediterranean, Arctic and Black Sea are really part of the Atlantic Ocean.
 Exploring the Ocean Since ancient times people have studied the ocean such as waters and ocean floor It provides food and services, and serves as a route for trade and travel The World s Oceans 71% of
Exploring the Ocean Since ancient times people have studied the ocean such as waters and ocean floor It provides food and services, and serves as a route for trade and travel The World s Oceans 71% of
Lecture 05: Ocean Basins. Hypsometric Curve. Consider Ocean Basins: What is the elevation of Chambana?
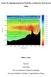
 Lecture 05: Ocean Basins 1 Hypsometric Curve What is the elevation of Chambana? Shows distribution of surface relative to sea level ~67% below sea level Mean ocean depth ~ -3.7 km (well below sea level)
Lecture 05: Ocean Basins 1 Hypsometric Curve What is the elevation of Chambana? Shows distribution of surface relative to sea level ~67% below sea level Mean ocean depth ~ -3.7 km (well below sea level)
Paleo Lab #5 - Fossilization and Fossil Identification
 Paleo Lab #5 - Fossilization and Fossil Identification page - INTRODUCTION The objectives of this exercise are to understand what fossils are, to recognize the different styles of fossil preservation,
Paleo Lab #5 - Fossilization and Fossil Identification page - INTRODUCTION The objectives of this exercise are to understand what fossils are, to recognize the different styles of fossil preservation,
Iceberg Plough Marks in the Vicinity of the Norwegian Trough
 Iceberg Plough Marks in the Vicinity of the Norwegian Trough ROBERT H. BELDERSON & JOHN B. WILSON Belderson, R. H. & Wilson, J. B.: Iceberg plough marks in the vicinity of the Norwegian Trough. Norsk Geologisk
Iceberg Plough Marks in the Vicinity of the Norwegian Trough ROBERT H. BELDERSON & JOHN B. WILSON Belderson, R. H. & Wilson, J. B.: Iceberg plough marks in the vicinity of the Norwegian Trough. Norsk Geologisk
Chapter 7 Benthic deep-sea carbonates: reefs and seeps
 Chapter 7 Benthic deep-sea carbonates: reefs and seeps Carbonates are formed across most latitudes and they are not restricted to shallow water but are also found in all but the deepest abyssal and hadal
Chapter 7 Benthic deep-sea carbonates: reefs and seeps Carbonates are formed across most latitudes and they are not restricted to shallow water but are also found in all but the deepest abyssal and hadal
On the Validity of the Name teyahalee as Applied to a Member of the Plethodon glutinosus Complex (Caudata: Plethodontidae): A New Name
 On the Validity of the Name teyahalee as Applied to a Member of the Plethodon glutinosus Complex (Caudata: Plethodontidae): A New Name NELSON G. HAIRSTON, SR. Department of Biology, University of North
On the Validity of the Name teyahalee as Applied to a Member of the Plethodon glutinosus Complex (Caudata: Plethodontidae): A New Name NELSON G. HAIRSTON, SR. Department of Biology, University of North
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2007
 BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2007 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 8 Reproduction and Development 1.Asexual reproduction: a. Is the primary form
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2007 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 8 Reproduction and Development 1.Asexual reproduction: a. Is the primary form
Earth and Space Science Semester 2 Exam Review. Part 1. - Convection currents circulate in the Asthenosphere located in the Upper Mantle.
 Earth and Space Science 2015 Semester 2 Exam Review Part 1 Convection -A form of heat transfer. - Convection currents circulate in the Asthenosphere located in the Upper Mantle. - Source of heat is from
Earth and Space Science 2015 Semester 2 Exam Review Part 1 Convection -A form of heat transfer. - Convection currents circulate in the Asthenosphere located in the Upper Mantle. - Source of heat is from
09/12/2012. Classification. Characteristics. Learning Outcome G2. Student Achievement Indicators. Phylum Porifera The Sponges
 Learning Outcome G2 Analyse the increasing complexity of the Phylum Porifera and the Phylum Cnidaria Learning Outcome G2 Phylum Porifera & Phylum Cnidaria Student Achievement Indicators Students who have
Learning Outcome G2 Analyse the increasing complexity of the Phylum Porifera and the Phylum Cnidaria Learning Outcome G2 Phylum Porifera & Phylum Cnidaria Student Achievement Indicators Students who have
COMPARISON BETWEEN PORIFERA AND CNIDARIA. Colwyn Sleep
 COMPARISON BETWEEN PORIFERA AND CNIDARIA Colwyn Sleep INTRODUCTION Porifera Cnidaria Porifera and Cnidaria are organisms which share similar characteristics with one another. -They are both multicellular,
COMPARISON BETWEEN PORIFERA AND CNIDARIA Colwyn Sleep INTRODUCTION Porifera Cnidaria Porifera and Cnidaria are organisms which share similar characteristics with one another. -They are both multicellular,
SPONGES OF PAPUA AND NEW GUINEA I. ORDER KERATOSIDA GRANT
 /. mar. biol. ASK. India, 1982, 24 (1 & 2): 1S-22 SPONGES OF PAPUA AND NEW GUINEA I. ORDER KERATOSIDA GRANT P. A. THOMAS* Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute, Cochin 682 031 ABSTRACT As the first
/. mar. biol. ASK. India, 1982, 24 (1 & 2): 1S-22 SPONGES OF PAPUA AND NEW GUINEA I. ORDER KERATOSIDA GRANT P. A. THOMAS* Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute, Cochin 682 031 ABSTRACT As the first
Oceanography, An Invitation to Marine Science 9e Tom Garrison. Ocean Basins Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
 Oceanography, An Invitation to Marine Science 9e Tom Garrison 4 Ocean Basins Key Concepts Tectonic forces shape the seabed The ocean floor is divided into continental margins and deep ocean basins The
Oceanography, An Invitation to Marine Science 9e Tom Garrison 4 Ocean Basins Key Concepts Tectonic forces shape the seabed The ocean floor is divided into continental margins and deep ocean basins The
Animal Diversity I: Porifera, Cnidaria, Ctenophora, Platyhelminthes, Rotifera, Annelida
 1 Animal Diversity I: Porifera, Cnidaria, Ctenophora, Platyhelminthes, Rotifera, Annelida Objectives: Be able to distinguish radial symmetry from bilateral symmetry. Be able to identify which of the phyla
1 Animal Diversity I: Porifera, Cnidaria, Ctenophora, Platyhelminthes, Rotifera, Annelida Objectives: Be able to distinguish radial symmetry from bilateral symmetry. Be able to identify which of the phyla
Cladorhiza corona sp. nov. (Porifera : Demospongiae : Cladorhizidae) from the Aleutian Islands (Alaska)
 The University of Maine DigitalCommons@UMaine Marine Sciences Faculty Scholarship School of Marine Sciences 12-1-2005 Cladorhiza corona sp. nov. (Porifera : Demospongiae : Cladorhizidae) from the Aleutian
The University of Maine DigitalCommons@UMaine Marine Sciences Faculty Scholarship School of Marine Sciences 12-1-2005 Cladorhiza corona sp. nov. (Porifera : Demospongiae : Cladorhizidae) from the Aleutian
I. Earth spheres A. Three major spheres 1. atmosphere, thin envelope 2. hydrosphere covers more than 71% of surface 3. geosphere from hydrosphere to
 I. Earth spheres A. Three major spheres 1. atmosphere, thin envelope 2. hydrosphere covers more than 71% of surface 3. geosphere from hydrosphere to center 4. Biosphere penetrates all three, a. only thin
I. Earth spheres A. Three major spheres 1. atmosphere, thin envelope 2. hydrosphere covers more than 71% of surface 3. geosphere from hydrosphere to center 4. Biosphere penetrates all three, a. only thin
OF PLANALVEOLITES POUGHTI
 CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE MUSEUM OF PALEONTOLOGY THE UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN VOL. XXI, No. 2, pp. 67-72 (1 pl.) MAP 10, 1967 PLANALVEOLITELLA, A NEW GENUS OF DEVONIAN TABULATE CORALS, WITH A REDESCRIPTION
CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE MUSEUM OF PALEONTOLOGY THE UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN VOL. XXI, No. 2, pp. 67-72 (1 pl.) MAP 10, 1967 PLANALVEOLITELLA, A NEW GENUS OF DEVONIAN TABULATE CORALS, WITH A REDESCRIPTION
Formation of Cold Airmasses Cold Air Outbreak
 Chapter 14: Cold Waves Formation of Cold Airmasses Cold Air Outbreak 1 Cold Wave A cold wave is an influx of unusually cold air into middle or lower latitudes. Cold waves affect much larger areas than
Chapter 14: Cold Waves Formation of Cold Airmasses Cold Air Outbreak 1 Cold Wave A cold wave is an influx of unusually cold air into middle or lower latitudes. Cold waves affect much larger areas than
BIOLOGY. An Introduction to Invertebrates CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 33 An Introduction to Invertebrates Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 33.UN08 Metazoa Eumetazoa
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 33 An Introduction to Invertebrates Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 33.UN08 Metazoa Eumetazoa
6. In the diagram below, letters A and B represent locations near the edge of a continent.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
Francisco Javier Murillo, 1 Konstantin R. Tabachnick, 2 and Larisa L. Menshenina Introduction. 2. Material and Methods
 Journal of Marine Biology Volume 2013, Article ID 438485, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/438485 Research Article Glass Sponges off the Newfoundland (Northwest Atlantic): Description of a New Species
Journal of Marine Biology Volume 2013, Article ID 438485, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/438485 Research Article Glass Sponges off the Newfoundland (Northwest Atlantic): Description of a New Species
Activity of the Month
 Activity of the Month September, 2008 It s Sedimentary, My Dear Watson Summary National Math Standards In this introductory activity, students will analyze core sample data to identify sediment composition
Activity of the Month September, 2008 It s Sedimentary, My Dear Watson Summary National Math Standards In this introductory activity, students will analyze core sample data to identify sediment composition
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY
 MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Bathymetry BATHYMETRY BATHYMETRY THE UNDERWATER EQUIVALENT TO TOPOGRAPHY THE STUDY OF WATER DEPTH A BATHYMETRIC MAP SHOWS FLOOR RELIEF OR TERRAIN AS CONTOUR LINES Bathymetry
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Bathymetry BATHYMETRY BATHYMETRY THE UNDERWATER EQUIVALENT TO TOPOGRAPHY THE STUDY OF WATER DEPTH A BATHYMETRIC MAP SHOWS FLOOR RELIEF OR TERRAIN AS CONTOUR LINES Bathymetry
Submersible investigation of unconfirmed western Miami Terrace habitat
 Submersible investigation of unconfirmed western Miami Terrace habitat Prepared By: Brian K. Walker, Ph.D. Nova Southeastern University Oceanographic Center 6/08/2015 On June 5, 2015 Nova Southeastern
Submersible investigation of unconfirmed western Miami Terrace habitat Prepared By: Brian K. Walker, Ph.D. Nova Southeastern University Oceanographic Center 6/08/2015 On June 5, 2015 Nova Southeastern
Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics: From Hypothesis to Theory
 Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics: From Hypothesis to Theory 1 Key Understandings Internal structure of the earth/structure of the crust. Difference between continental drift & plate tectonics. Evidence
Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics: From Hypothesis to Theory 1 Key Understandings Internal structure of the earth/structure of the crust. Difference between continental drift & plate tectonics. Evidence
Porifera. Thomas M. Frost Trout Lake Station Center for Limnology University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin '"'. , ' I.
 , ' Porifera Thomas M. Frost Trout Lake Station Center for Limnology University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 4 '"'. Chapter Outline I. INTRODUCTION II. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. External Morphology
, ' Porifera Thomas M. Frost Trout Lake Station Center for Limnology University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 4 '"'. Chapter Outline I. INTRODUCTION II. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. External Morphology
Chapter 8. Foundations of Geology
 Chapter 8 Foundations of Geology Structure of the Earth The earth can be divided into three parts: Crust Mantle Core The Earth s Crust The crust is the part of the earth we are most familiar with It is
Chapter 8 Foundations of Geology Structure of the Earth The earth can be divided into three parts: Crust Mantle Core The Earth s Crust The crust is the part of the earth we are most familiar with It is
Marine Sediments. Introductory Oceanography. Ray Rector: Instructor
 Marine Sediments Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector: Instructor Ocean Basins are Vast Sinks for Huge Amounts of Sediment from Numerous Different Sources Four Major Types of Seafloor Sediments 1. Lithogenous
Marine Sediments Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector: Instructor Ocean Basins are Vast Sinks for Huge Amounts of Sediment from Numerous Different Sources Four Major Types of Seafloor Sediments 1. Lithogenous
Sponge and Cnidarian Review
 Name Period Date Sponge and Cnidarian Review Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the definition that matches each term. 1. Invertebrate 2. Filter feeder 3. Asymmetry 4. Radial 5. Medusa
Name Period Date Sponge and Cnidarian Review Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the definition that matches each term. 1. Invertebrate 2. Filter feeder 3. Asymmetry 4. Radial 5. Medusa
ab Universal HIER antigen retrieval reagent (10X)
 ab208572 Universal HIER antigen retrieval reagent (10X) Instructions for use: For heat-induced epitope retrieval of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues This product is for research use only and is
ab208572 Universal HIER antigen retrieval reagent (10X) Instructions for use: For heat-induced epitope retrieval of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues This product is for research use only and is
Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics
 Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which type of plate boundary is shown? A) divergent
Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which type of plate boundary is shown? A) divergent
A SUSPECTED PARTIAL OBSCURATION OF THE FLOOR OF ALPHONSUS. Dinsmore Alter Griffith Observatory, Los Angeles, California
 A SUSPECTED PARTIAL OBSCURATION OF THE FLOOR OF ALPHONSUS Dinsmore Alter Griffith Observatory, Los Angeles, California Visual observations of the moon have been reported from time to time in which an area
A SUSPECTED PARTIAL OBSCURATION OF THE FLOOR OF ALPHONSUS Dinsmore Alter Griffith Observatory, Los Angeles, California Visual observations of the moon have been reported from time to time in which an area
Essential Question: How are the geological features that exist on land similar to the geological features on the ocean floor?
 Essential Question: How are the geological features that exist on land similar to the geological features on the ocean floor? Geography of the Oceans The world ocean can be divided into four main ocean
Essential Question: How are the geological features that exist on land similar to the geological features on the ocean floor? Geography of the Oceans The world ocean can be divided into four main ocean
Introduction to Biology
 Introduction to Biology Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
Introduction to Biology Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
Introduction to Biology
 1 Introduction to Biology 2 Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
1 Introduction to Biology 2 Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
Plate Tectonics Tutoiral. Questions. Teacher: Mrs. Zimmerman. Plate Tectonics and Mountains Practice Test
 Teacher: Mrs. Zimmerman Print Close Plate Tectonics and Mountains Practice Test Plate Tectonics Tutoiral URL: http://www.hartrao.ac.za/geodesy/tectonics.html Questions 1. Fossils of organisms that lived
Teacher: Mrs. Zimmerman Print Close Plate Tectonics and Mountains Practice Test Plate Tectonics Tutoiral URL: http://www.hartrao.ac.za/geodesy/tectonics.html Questions 1. Fossils of organisms that lived
What is a Cnidarian?
 Invertebrate What is a Cnidarian? 9000 species of jellyfishes, corals, sea anemones, hydras Mostly marine animals Radially symmetrical One body opening Two layers of cells organized into tissues with specific
Invertebrate What is a Cnidarian? 9000 species of jellyfishes, corals, sea anemones, hydras Mostly marine animals Radially symmetrical One body opening Two layers of cells organized into tissues with specific
Volcanology and Petrology of the Taney Seamounts, Northeast Pacific Ocean
 MSc Research Proposal Volcanology and Petrology of the Taney Seamounts, Northeast Pacific Ocean Jason Coumans Introduction: Short chains of seamounts are observed near mid-ocean ridges and have been previously
MSc Research Proposal Volcanology and Petrology of the Taney Seamounts, Northeast Pacific Ocean Jason Coumans Introduction: Short chains of seamounts are observed near mid-ocean ridges and have been previously
Lecture Marine Provinces
 Lecture Marine Provinces Measuring bathymetry Ocean depths and topography of ocean floor Sounding Rope/wire with heavy weight Known as lead lining Echo sounding Reflection of sound signals 1925 German
Lecture Marine Provinces Measuring bathymetry Ocean depths and topography of ocean floor Sounding Rope/wire with heavy weight Known as lead lining Echo sounding Reflection of sound signals 1925 German
Geologic Evolution of Latin America. Plate Tectonics: General Concepts & Applications to Latin America
 Geologic Evolution of Latin America Plate Tectonics: General Concepts & Applications to Latin America Structure of Earth: 3 major divisions of Core, Mantle, and Crust Upper mantle differs in the way that
Geologic Evolution of Latin America Plate Tectonics: General Concepts & Applications to Latin America Structure of Earth: 3 major divisions of Core, Mantle, and Crust Upper mantle differs in the way that
The Sea Floor. Chapter 2
 The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
UNVERSITY OF MICHIGAN THREE NEW SPECIES OF THE CYSTID GENUS LIPSANOCYSTIS FROM THE MIDDLE DEVONIAN TRAVERSE GROUP OF MICHIGAN
 CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE MUSEUM OF PALEONTOLOGY UNVERSITY OF MICHIGAN VOL. XII, No. 6, pp. 97-103 (2 pls.) APRIL 8, 1955 THREE NEW SPECIES OF THE CYSTID GENUS LIPSANOCYSTIS FROM THE MIDDLE DEVONIAN TRAVERSE
CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE MUSEUM OF PALEONTOLOGY UNVERSITY OF MICHIGAN VOL. XII, No. 6, pp. 97-103 (2 pls.) APRIL 8, 1955 THREE NEW SPECIES OF THE CYSTID GENUS LIPSANOCYSTIS FROM THE MIDDLE DEVONIAN TRAVERSE
Crustal Boundaries. As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries they interact in various ways. Convergent Transform Divergent
 Name: Date: Period: Plate Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonic plates are constantly moving and interacting As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries
Name: Date: Period: Plate Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonic plates are constantly moving and interacting As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries
Oceanic crust forms at ocean ridges and becomes part of the seafloor. Review Vocabulary. basalt: a dark-gray to black fine-grained igneous rock
 Sea-Floor Spreading Oceanic crust forms at ocean ridges and becomes part of the seafloor. Review Vocabulary basalt: a dark-gray to black fine-grained igneous rock I. Mapping the Ocean Floor Until the mid-1900
Sea-Floor Spreading Oceanic crust forms at ocean ridges and becomes part of the seafloor. Review Vocabulary basalt: a dark-gray to black fine-grained igneous rock I. Mapping the Ocean Floor Until the mid-1900
41. UPPER JURASSIC CALCISPHAERULIDAE FROM DSDP LEG 44, HOLE 391C, BLAKE-BAHAMA BASIN, WESTERN NORTH ATLANTIC
 41. UPPER JURASSIC CALCISPHAERULIDAE FROM DSDP LEG 44, HOLE 391C, BLAKE-BAHAMA BASIN, WESTERN NORTH ATLANTIC Hans M. Bolli, Department of Geology, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zurich, and University
41. UPPER JURASSIC CALCISPHAERULIDAE FROM DSDP LEG 44, HOLE 391C, BLAKE-BAHAMA BASIN, WESTERN NORTH ATLANTIC Hans M. Bolli, Department of Geology, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zurich, and University
