Seismic Risk Assessments for Border Area of Shanxi, Hebei and Inner Mongolia, China
|
|
|
- Buck Collins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
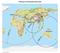
1 Seismic Risk Assessments for Border Area of, and Inner Mongolia, China Jianming Yu Inner Mongolia Earthquake Administration, Hohhot, China Abstract With a large amount of information, materials of seismic intensity in history include PGA, seismic intensity attenuation and effects of site and buildings etc. By analyzing well-recorded materials of seismic intensity in border areas of, and Inner Mongolia within 500 years, this paper proposes the method of seismic tendency assessment, which is similar to seismic risk analysis. The key to that way is establishing relation curve of seismic intensity and average repetition period, and applying it to the assessment of seismic risk. First, based on ArcGIS, we built a data bank of seismic intensity, and turned administrative map of border areas into longitude and latitude grid line with basic unit of ; second, we got seismic intensity frequency relation (namely hazard curve) of each unit by using the least squares fitting on seismic intensity materials; last, based on the hypothesis that the earthquake has cycle, we use hazard curve to estimate the repetition period of different intensities, intensity distribution of every 100 year, and exceeding probability of certain intensity (such as VI, VII andviii) in 50 years in representative cities and counties of, and Inner Mongolia border areas;the calculation indicates that Datong-Huairen-Hunyuan and HuailaiYanqing have high seismic risk and should be paid attention to. technology level and the economy development of the country according to the basic documents in seismic subject. Rich and detailed historical seismic data offers beneficial advantages for researching the seismic hazard. The paper carries on the seismic hazard analyzing and risk predicting with the seismic intensity documents from A.D to A.D in, and Inner Mongolia bording area so as to obtain time features of the region earthquake activeness [4]. Index Terms seismic intensity, hazard curve, repetition period, exceeding probability, seismic risk Figure 1. The study area I. INTRODUCTION The, and Inner Mongolia bording area locates roughly in 112 to 116 in longitude and 39 to 42 in latitude (Fig. 1), which includes the central and southern parts of Inner Mongolia (Liangcheng, Fengzhen, Chayouqianqi, Helinger and so on), North (Datong, Yanggao, Youyu and so on), Northwest (Zhangbei, Shangyi, Huaian and so on) [5]. The bording area is the annual key risk region to the above three provinces and even the country. Since the beginning of history there had been a great deal of strong earthquakes happened in this region, such as the Lingqiu M7.0 earthquake in 1626, the Yuanping M7.0 earthquake in 1683, the latest medium magnitude earthquake was the Zhangbei M6.2 earthquake on Jan. 10th, In the paper the seismic hazard is evaluated and the seismic risk is predicted by the historical intensity documents [6], [7] of the bording area to get the exceeding probability for the specific intensity in the next 50 years. Results could be regarded as the references for anti-seismic design of building and project construction facilities. The earthquake always causes huge casualties and property loss among all the natural calamities on the planet. There happened many destructive earthquakes [1] in the history of China since the country locates between the two tremendous seismic belts: Circum-Pacific Seismic belts and Mediterranean Himalayan Seismic belts, such as the Guanzhong earthquake with a magnitude of 8.0 in 1556(over 830 thousand people died or disappeared) and the Sichuan Wenchuan earthquake with the same magnitude in 2008(over 80 thousand people died or lost) [2]. The most primary factors causing giant lives loss and property damaging are always surrounding construction and region environment destroying by the earthquake. So far on the fact that the earthquake could not be predicted precisely, seismic fortification step is the best way to reduce economy loss and death [3], which is closely correlated to the Manuscript received January 14, 2017; revised May 4, doi: /ijscer
2 II. SOURCE AND DIGITALIZING OF HISTORICAL SEISMIC INTENSITY DATA The paper divides the study area into many square frames with same size to reflect the spatial distribution features for the seismic activities of the area and evaluate the seismic risk of each place by regarding the frame as an independent statistics unit. Considering synthetically the region range, geology feature, density of population and so on, the study area is divided into many base units with in latitude. Get the sequence number of each unit by numbering it from bottom to top and from left to right. Then digitalizing every seismic intensity map with ArcGIS [11] under the Xi an 80 geographical coordinate system to get the intensity observations distribution grid map, the sample number for the seismic intensity in each unit is from 3 to 45 (Fig. 2). Earthquakes after A.D were recorded in detail as the intensity degree reaches v [8], hence, the paper chooses all the earthquakes with the magnitude greater or equals to 4.75 after A.D from the earthquake catalogues, including 32 ancient earthquakes (A.D. 1500A.D. 1911) and 15 modern times earthquakes (A.D A.D. 2000), parts of which are listed in Table I. However, there are 26 earthquakes with no complete earthquake examples, which could not lead to assured intensity level. The experiments adopt the mean axis intensity decaying formula [9] suitable to and of North China: I M 1.39ln( R 11) =0.377 (1) and the earthquake intensity decaying relation suitable to medium and west region of Inner Mongolia [10]: I a M ln( Ra 12) =0.519 (2) Ib M ln( Rb 6) =0.536 (3) to estimate the intensity in the study area, where I represents the intensity degree, M represents the magnitude level, R represents mean-axis radius (in km), the index a, b respectively equals to the direction of the long axis and the short axis, Ra and Rb represents the long axis radius and the short axis radius of the intensity isoseismal, σ is the standard deviation. TABLE I. Province Inner Mongolia III. Seismogenic data Figure 2. Distribution number of intensity observations PART OF INTENSITY OBSERVATIONS Epicenter (latitude longitude) The seismic intensity frequency relation, namely the hazard curve to the unit could be obtained by analyzing the digitalized base unit, the relation describes the frequency of earthquake occurrence at a certain intensity degree. According to references [12], [13], the relation between the seismic magnitude and frequency obeys the Gutenberg-Richter formula, which indicates seismic events distribute adequately in all magnitude levels and Gutenberg-Richter relationship has high goodness of fit. Replacing the magnitude with the intensity, yields, Lingqiu Yuanping Tianzhen Datong Shacheng Huaian Shangyi Laishui Helin Magnitude Ms Intensity I Ⅴ-Ⅸ Ⅴ-Ⅸ Ⅴ-Ⅶ Ⅴ-Ⅶ Ⅴ-Ⅶ Spindle direction where I represents the intensity, f represents annual rate of the intensity occurrence when it is greater than or equals to I, a and b are parameters obtained by the least square method. Among all units with the size , a varies within the range between and 1.73, b varies between and Fig. 3 shows the intensityfrequency fitting curves of Fengzhen, Lingqiu, Shuozhou and Zhangjiakou, as well as the value of a and b. After the fitting finished, the curve slope is close to zero since the intensity observations of part units are much at one, which runs counter to a fact that the intensity observations distribution of any unit reduces as the intensity degree grows. On the above basis the average value of minus b, is seen as the average curve slope and applied to each unit, that is the slope for the intensity- SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYZING lg f a b I Toponymy (4) 206
3 frequency relationship of each unit equals to minus Re-fitting the intensity-frequency curves of all the units in the study area with a certain slope minus 0.29 keeping the curves distribute on the two sides of the intensityfrequency points [14] (Fig. 3). Figure 3. The frequency-intensity curves for Fengzhen, Lingqiu, Shuozhou and Zhangjiakou cell TABLE II. RETURN PERIOD OF DIFFERENT INTENSITY FOR VARIOUS CITIES AND COUNTIES OF THE STUDY AREA Toponymy Jining Fengzhen Yanggao Hunyuan Lingqiu Shangyi Zhangbei Shuozhou Zhangjiakou Epicenter Latitude longitude No. observations The minimum variance of the curve is given by = (lg f i lg f c ) 2 NI frequency relation and the truth while the unit contains no enough intensity observations, which leads to low correlation (Fig. 4). The annual occurrence rate f or the average return period τ corresponding to a certain intensity could be estimated with the slope value b and intercept value a according to the hazard curve formula (4), the above process also can be used for calculating the intensity corresponding to the certain annual occurrence rate or the average return period [15], for example, the intensity value corresponding to an average return period of 100 (5) where NI represents the intensity observation number, f represents the annual occurrence rate (fi represents the frequentness by intensity observations, fc represents the frequentness by the fitting curve). The minimum variance varies between and , there will be giant difference between the fitting value of the intensity- Return period (years) I Ⅴ I Ⅵ I Ⅶ I Ⅷ 207
4 years could be given by the formula (6) using the relation that the τ and f are the inverse of each other, a 2 I b IV. SEISMIC RISK EVALUATION The key phases for making the anti-seismic standard or other anti-seismic actions are evaluating the upper magnitude limit and the criticality for the researching place to predict the location and intensity of the earthquake in the future several decades, the above process is called evaluation for the seismic risk. The paper proposed the Poisson Model to take the evaluation under the assument that occurrence of two different earthquakes independent to each other. The seismic risk, namely the seismic probability P of some certain place over a specific intensity(i) over a period of time(t) can be calculated by, (6) the return periods corresponding to the intensity value V, VI, VII and VIII in the main counties and cities of the study area are listed in Table II, the intensity distribution to the average return period of 100 years is shown in Fig. 5. p 1 exp( t ) where τ expresses the mean return period for I is greater than or equals to I, t expresses the existence time of the certain buildings or facilities. The steady Poisson process for the earthquake indicates the earthquakes could be seen as a series of independent events in time and space. After a massive earthquake happened, the occurrence probability of another massive earthquake will not be changed. The formula (7) could also be used to evaluate the risk of other types of natural hazard, such as the flood and hurricane. Using the formula (4) and (7) to estimate the seismic risk of each unit. The different exceeding probability in the future 50 years is shown in Fig. 6 and Table III when the intensity I is greater than or equals to VI, VII and VIII, respectively. The overall distribution trend for the exceeding probability in the next 50 years with the different intensity varying between VI and IX is described as following: the intensity of the medium and southern part of the study area is higher than that in the north part, the highest intensity value is mainly in Liangcheng-Helin district, most of and Zhuolu-Yanqing district. There is a high probability with the intensity greater than of equals to VI, the value in the area south of 41.2 N reaches more than 50%, Liangcheng-Helin district, enclosed area by Lingqiu-Guangling-Fengzhen-YouyuShuozhou and Yanqing-Xuanhua-Zhuolu district has a probability over 70%, by comparison, the probability value in the area north of 41.2 N decreases when the longitude increases; the distribution areas keeping the highest probabilities varying between 40% and 60% with the intensity greater than or equals to VII are LiangchengHelin district, enclosed area by Hunyuan-Datong-YouyuShangyin-Daixian-Fanzhi, Guangling-Lingqiu district and Zhuolu-Huailai-Yanqing district; most parts of the study area have low probabilities under 15% with the intensity greater than or equals to VIII except the Datonghuairen and Yanqing district, which have the exceeding probability over 30%. Figure 4. The least squares residual ( ) Figure 5. Intensity distribution for return period of 100 years It is shown in Table II that, (a), except Shangyi area, the return periods in the main cities and counties spread from 60 to 100 years under the premise the intensity I reaches VI. (b), under the premise the intensity I reaches VII the return periods within the same region spread from 110 to 260 years. (c), when the intensity I reaches VIII, except a minority of places, such as Yanggao, Hunyuan, Shuozhou and so on, most counties and cities have the return periods of over 300 years. As shown in Fig. 5, (a), only the intensity in No. 225 unit of Lingqiu reaches VIII with the return period of 100 years. (b), the intensity in most parts of, part of and Beijing in the study area reaches VII. (c), the intensity decreases when the latitude grows and the minimum intensity value is IV. (7) V. CONCLUSIONS The key to seismic risk evaluation is establishing the curve of the seismic intensity and its frequency(in year), 208
5 Table II the return periods to the intensity VIof most parts of the study area is less than or equals to 100 years; the return periods to the intensity VII vary between 100 and 300 years; while the return periods to the intensity VIII change from 200 to 500 years. which mainly based on (a), rich historical seismic intensity data is the reliable resource for evaluating seismic risk, (b), evaluation results in the form of probability could be applied for anti-seismic project construction appropriately [16]. It is noted that from the return periods to different intensity in the study area in TABLE III. SEISMIC RISK FOR MAJOR COUNTIES IN THE STUDY AREA Toponymy Jining Fengzhen Yanggao Hunyuan Lingqiu Shangyi Zhangbei Shuozhou Zhangjiakou Epicenter Latitude longitude No. Exceeding probability to I Ⅵ(%) Exceeding probability to I Ⅶ(%) Exceeding probability to I Ⅷ(%) Figure 6. Exceedance probability of I VI, VII, VIII in 50 years in the study area Evaluation results for seismic risk of the study area are listed as following; (a), the exceeding probability in the next 50 years with the intensity greater than or equals to VI in most region of the study area except the Shangyi area is over 50%, the highest probability value is 84% in Shuozhou; (b), the exceeding probability in the next 50 years with the intensity greater than or equals to VII varies between 20% and 50%, in a word, its value decreases when the latitude increases; (c), the exceeding probability in the next 50 years with the intensity greater than or equals to VIII is less than or equals to 20%, the lowest value is 9% in Jining and the highest value is 20% in Lingqiu and Zhangjiakou. According to the seismicity trend at present, in the future 50 years, the probability encountering the intensity VI, VII and VIIIof the study area is greater than 53%, 30% and 14%, respectively(fig. 6). The intensity-frequency relationship from G-R empirical correlation is suitable for most types of earthquakes. Since the actual magnitude distributions 209
6 have great deviations with that by G-R relationship[17], based on which, then intensity-frequency curve has the same defects. The magnitude and frequency relation of the sensible and weak shocks happened in the incubation of the few strong earthquakes does not obey G-R relationship[]. The bias of the two relationships should be discussed in the future work to provide the right supplement. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT This work is supported by both the director fund of Inner Mongolia Earthquake Administration under Grant No. 2016YJ02 and the project for tracking the earthquake situation in 2016 under Grant No REFERENCES [1] Z. P. Song, J. Y. Yin, Y. Xue, et al., The global and sub~zone period characteristics for large earthquakes, Chinese J. Geophys, vol. 56, no. 6, pp , [2] Y. T. Chen, Z. X. Yang, Y. Zhang, et al., From 2008 wenchuan earthquake to 2013 lushan earthquake, Scientia Sinica Terrae, vol. 43, no. 6, pp , [3] M. Z. Zhang, Reflection on the seismic fortification and design in light of the Wenchuan Earthquake, China Civil Engineering Journal, vol. 42, no. 5, pp , [4] W. Y. Li and Q. R. Zhang, A parameter for the time-distribution of seismic activity, Journal of Seismology, vol. 6, no. 2, pp , [5] H. B. Zhu, H. Li, M. J. Wu, et al., Quiescence-seismic - quiescence evolution of medium-earthquakes before moderatestrong shocks in junction region of, and Neimenggu, Progress in Geophysics, vol. 29, no. 3, pp , [6] China Earthquake Administration, Recent earthquake catalog of China ( , Ms 4.7), Beijing: Chinese Science and Technology Press, [7] China Earthquake Administration. Historical strong earthquake catalog of China (2300 B.C A.C.), Beijing: Earthquake Publishing House, [8] W. Q. Huang, W. X. Li, and X. F. Cao, Research on the integrity of seismic data in Chinese mainland, Acta Seismologica Sinica, vol. 16, no. 3, pp , [9] H. J. Sha, Research on Seismic Attenuation Relationship in North China, Beijing: Institute of China Seismological Bureau crustal Stress, [10] Y. M. Yang, Y. Dai, G. Q. Zhang, et al., Attenuation relation of seismic intensity in the middle and western regions of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research, vol. 37, no. 1, pp , [11] M. Han, B. C. Dai, D. C. Zheng, et al, Research and application of electronic map based on ArcGIS server, Science of Surveying and Mapping, vol. 36, no. 3, pp , [12] B. Gutenberg and C. F. Richter, Frequency of earthquakes in California, Nature, vol. 156, no. 3960, pp. 371, [13] Z. H. Li, J. Z. Qing, and Y. J. Su, The relationship of earthquake magnitude and frequency under the condition of discrete magnitude, Chinese J. Geophys, vol. 54, no. 4, pp , [14] S. B. Bozkurt, R. S. Stein, and S. Toda, Forecasting probabilistic seismic shaking for greater Tokyo from 400 years of intensity observations, Earthquake Spectra, vol. 23, no. 3, pp , [15] J. W. Liu, Z. M. Wang, and F. R. Xie, Seismic hazard and risk assessments for Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan area, China, Chinese J Geophys, vol. 53, no. 2, pp , [16] J. W. Liu, The Study on the Method of Seismic Hazard Assessment Based on Historical Intensity Observations, Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, [17] S. Okuda, T. Ouchi, and T. Terashima, Deviation of magnitude frequency distribution of earthquakes from the gutenberg-richter law: Detection of precursory anomalies prior to large earthquakes, Phys. Earth Planet. Inter., vol. 73, no. 3-4, pp , [] Z. X. Li, B. Z. Tao, A. V. Ponomarev, et al., Laboratory experimental and seismicity analysis on deviation of magnitudefrequency relationship, J. Wuhan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.), vol. 55, no. 6, pp , Jianming Yu was born in Hohhot, China, on May 24, He received B.S. and M.S. degrees in automation from Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot, China, in 2009 and 2013, respectively. From 2013 to 2016, he was an engineer at the Inner Mongolia Earthquake Administration in Hohhot, China. His main research interests are in the fields of earthquake emergency processing and ArcGIS application on the Seismology. 210
Tomographic imaging of P wave velocity structure beneath the region around Beijing
 403 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0403-9 Tomographic imaging of P wave velocity structure beneath the region around Beijing Zhifeng Ding Xiaofeng Zhou Yan Wu Guiyin Li and Hong Zhang Institute of Geophysics,
403 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0403-9 Tomographic imaging of P wave velocity structure beneath the region around Beijing Zhifeng Ding Xiaofeng Zhou Yan Wu Guiyin Li and Hong Zhang Institute of Geophysics,
Seismic Hazard and Risk Assessments for Beijing Tianjin Tangshan, China, Area
 Pure Appl. Geophys. Ó 2010 Birkhäuser / Springer Basel AG DOI 10.1007/s00024-010-0115-z Pure and Applied Geophysics Seismic Hazard and Risk Assessments for Beijing Tianjin Tangshan, China, Area FUREN XIE,
Pure Appl. Geophys. Ó 2010 Birkhäuser / Springer Basel AG DOI 10.1007/s00024-010-0115-z Pure and Applied Geophysics Seismic Hazard and Risk Assessments for Beijing Tianjin Tangshan, China, Area FUREN XIE,
Ground motion attenuation relations of small and moderate earthquakes in Sichuan region
 Earthq Sci (2009)22: 277 282 277 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0277-x Ground motion attenuation relations of small and moderate earthquakes in Sichuan region Lanchi Kang 1, and Xing Jin 1,2 1 Fuzhou University,
Earthq Sci (2009)22: 277 282 277 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0277-x Ground motion attenuation relations of small and moderate earthquakes in Sichuan region Lanchi Kang 1, and Xing Jin 1,2 1 Fuzhou University,
Relocation of aftershocks of the Wenchuan M S 8.0 earthquake and its implication to seismotectonics
 Earthq Sci (2011)24: 107 113 107 doi:10.1007/s11589-011-0774-6 Relocation of aftershocks of the Wenchuan M S 8.0 earthquake and its implication to seismotectonics Bo Zhao Yutao Shi and Yuan Gao Institute
Earthq Sci (2011)24: 107 113 107 doi:10.1007/s11589-011-0774-6 Relocation of aftershocks of the Wenchuan M S 8.0 earthquake and its implication to seismotectonics Bo Zhao Yutao Shi and Yuan Gao Institute
DESIGN HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTION SYSTEM TO BUILD ISOSEISMAL.
 ABSTRACT : DESIGN HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTION SYSTEM TO BUILD ISOSEISMAL. Ping Li 1 and Xiaxin Tao 2 1. PHD candidate, School of Civil Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin. China 2. Professor,
ABSTRACT : DESIGN HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTION SYSTEM TO BUILD ISOSEISMAL. Ping Li 1 and Xiaxin Tao 2 1. PHD candidate, School of Civil Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin. China 2. Professor,
A BROADBAND SEISMIC EXPERIMENT IN YUNNAN, SOUTHWEST CHINA. Sponsored by Defense Threat Reduction Agency. Contract No.
 A BROADBAND SEISMIC EXPERIMENT IN YUNNAN, SOUTHWEST CHINA Wenjie Jiao, 1 Winston Chan, 1 and Chunyong Wang 2 Multimax Inc., 1 Institute of Geophysics, China Seismological Bureau 2 Sponsored by Defense
A BROADBAND SEISMIC EXPERIMENT IN YUNNAN, SOUTHWEST CHINA Wenjie Jiao, 1 Winston Chan, 1 and Chunyong Wang 2 Multimax Inc., 1 Institute of Geophysics, China Seismological Bureau 2 Sponsored by Defense
Seismic hazard expression in risk assessment
 Earthquae Resistant Engineering Structures VI 299 Seismic hazard expression in ris assessment X.-X. Tao 1, 2, Z.-R. Tao 2 & P. Li 1 1 Harbin Institute of Technology, People s Republic of China 2 Institute
Earthquae Resistant Engineering Structures VI 299 Seismic hazard expression in ris assessment X.-X. Tao 1, 2, Z.-R. Tao 2 & P. Li 1 1 Harbin Institute of Technology, People s Republic of China 2 Institute
Research on the Spatial Distribution Characteristics of b-value in Southwest Yunnan
 International Symposium on Computers & Informatics (ISCI 2015) Research on the Spatial Distribution Characteristics of b-value in Southwest Yunnan XIE ZHUOJUAN1, a, LU YUEJUN1, b 1Institute of Crustal
International Symposium on Computers & Informatics (ISCI 2015) Research on the Spatial Distribution Characteristics of b-value in Southwest Yunnan XIE ZHUOJUAN1, a, LU YUEJUN1, b 1Institute of Crustal
GIS: Assessment Model and Evaluation of an Earthquake-stricken Area with a Case Study in Shangri-La
 , pp.123-138 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijhit.2014.7.4.11 GIS: Assessment Model and Evaluation of an Earthquake-stricken Area with a Case Study in Shangri-La Shuangyun Peng 1, Kun Yang 1 and Yanbo Cao
, pp.123-138 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijhit.2014.7.4.11 GIS: Assessment Model and Evaluation of an Earthquake-stricken Area with a Case Study in Shangri-La Shuangyun Peng 1, Kun Yang 1 and Yanbo Cao
A Prototype Earthquake Early Warning (EEW) System in Beijing Capital Region of China
 The 2th International Workshop On Earthquake Early Warning, April 21-22, 2009, Kyoto, Japan A Prototype Earthquake Early Warning (EEW) System in Beijing Capital Region of China Hanshu Peng 1, Zhongliang
The 2th International Workshop On Earthquake Early Warning, April 21-22, 2009, Kyoto, Japan A Prototype Earthquake Early Warning (EEW) System in Beijing Capital Region of China Hanshu Peng 1, Zhongliang
Characteristics of seismic activity before Chile M W 8.8 earthquake in 2010
 Earthq Sci (2010)23: 333 341 333 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0730-x Characteristics of seismic activity before Chile M W 8.8 earthquake in 2010 Yan Xue 1,2, Jie Liu 2 and Gang Li 2 1 Institute of Geophysics,
Earthq Sci (2010)23: 333 341 333 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0730-x Characteristics of seismic activity before Chile M W 8.8 earthquake in 2010 Yan Xue 1,2, Jie Liu 2 and Gang Li 2 1 Institute of Geophysics,
Reliability Analysis of Liquefaction Evaluation Discriminant of Chinese Seismic Code
 Reliability Analysis of Liquefaction Evaluation Discriminant of Chinese Seismic Code Zhenzhong CAO 1, Xiaoming YUA 2, Rui Sun 3 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Geotechnical Engineering, Institute of Engineering
Reliability Analysis of Liquefaction Evaluation Discriminant of Chinese Seismic Code Zhenzhong CAO 1, Xiaoming YUA 2, Rui Sun 3 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Geotechnical Engineering, Institute of Engineering
Statistical Analysis on the Characteristics of Normalized Response Spectra of Ground Motion Records from Wenchuan Earthquake
 Statistical Analysis on the Characteristics of Normalized Response Spectra of Ground Motion Records from Wenchuan Earthquake Y.Q. Yang, J.J. Hu, L.L. Xie, J.W. Dai, H.Y. Yu Key Laboratory of Earthquake
Statistical Analysis on the Characteristics of Normalized Response Spectra of Ground Motion Records from Wenchuan Earthquake Y.Q. Yang, J.J. Hu, L.L. Xie, J.W. Dai, H.Y. Yu Key Laboratory of Earthquake
PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS AT GROUND SURFACE IN JAPAN BASED ON SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATED FROM OBSERVED STRONG-MOTION RECORDS
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 3488 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS AT GROUND SURFACE IN JAPAN BASED ON SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATED FROM
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 3488 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS AT GROUND SURFACE IN JAPAN BASED ON SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATED FROM
The Application of Global Scale Data in a Global Earthquake Disaster Alert System
 The Application of Global Scale Data in a Global Earthquake Disaster Alert System LI Yigang 1 QU Guosheng 1 HUANG Jianfa 2 1,National Earthquake Response Support Service,China 2,China Earthquake Administration,China
The Application of Global Scale Data in a Global Earthquake Disaster Alert System LI Yigang 1 QU Guosheng 1 HUANG Jianfa 2 1,National Earthquake Response Support Service,China 2,China Earthquake Administration,China
EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION RESEARCH IN CHINA: STATUS AND PROSPECTS
 J. Phys. Earth, 34, Suppl., S1-S11, 1 986 EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION RESEARCH IN CHINA: STATUS AND PROSPECTS Zhangli CHEN State Seismological Bureau, Beijing, China (Received June 22, 1985; Revised May 22,
J. Phys. Earth, 34, Suppl., S1-S11, 1 986 EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION RESEARCH IN CHINA: STATUS AND PROSPECTS Zhangli CHEN State Seismological Bureau, Beijing, China (Received June 22, 1985; Revised May 22,
EARTH OBSERVATION SERVICES IN REPUBLIC OF MOLDOVA
 EARTH OBSERVATION SERVICES IN REPUBLIC OF MOLDOVA Vasile ALCAZ 1 Ion APOSTOL 2 1 Institute of Geology and Seismology Moldavian Academy of Sciences 2 Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources Republic
EARTH OBSERVATION SERVICES IN REPUBLIC OF MOLDOVA Vasile ALCAZ 1 Ion APOSTOL 2 1 Institute of Geology and Seismology Moldavian Academy of Sciences 2 Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources Republic
Uniform Hazard Spectrum(UHS) for performance based seismic design
 Uniform Hazard Spectrum(UHS) for performance based seismic design *Jun-Kyoung Kim 1), Soung-Hoon Wee 2) and Seong-Hwa Yoo 2) 1) Department of Fire Protection and Disaster Prevention, Semyoung University,
Uniform Hazard Spectrum(UHS) for performance based seismic design *Jun-Kyoung Kim 1), Soung-Hoon Wee 2) and Seong-Hwa Yoo 2) 1) Department of Fire Protection and Disaster Prevention, Semyoung University,
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis of Nepal considering Uniform Density Model
 Proceedings of IOE Graduate Conference, 2016 pp. 115 122 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis of Nepal considering Uniform Density Model Sunita Ghimire 1, Hari Ram Parajuli 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering,
Proceedings of IOE Graduate Conference, 2016 pp. 115 122 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis of Nepal considering Uniform Density Model Sunita Ghimire 1, Hari Ram Parajuli 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering,
Soil geochemical characteristics and prospecting direction of Pengboshan area Inner Mongolia
 34 4 2015 12 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 34 No. 4 Dec. 2015 1004-5589 2015 04-0993 - 09 1 2 3 4 1 1 3 1. 150036 2. 157000 3. 130061 4. 024005 66 4 P632. 1 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1004-5589. 2015. 04. 011 Soil
34 4 2015 12 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 34 No. 4 Dec. 2015 1004-5589 2015 04-0993 - 09 1 2 3 4 1 1 3 1. 150036 2. 157000 3. 130061 4. 024005 66 4 P632. 1 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1004-5589. 2015. 04. 011 Soil
Estimation of Peak Ground Acceleration for Delhi Region using Finsim, a Finite Fault Simulation Technique
 215 Estimation of Peak Ground Acceleration for Delhi Region using Finsim, a Finite Fault Simulation Technique NEELIMA SATYAM. D* and K. S. RAO** * Earthquake Engineering Research Centre, International
215 Estimation of Peak Ground Acceleration for Delhi Region using Finsim, a Finite Fault Simulation Technique NEELIMA SATYAM. D* and K. S. RAO** * Earthquake Engineering Research Centre, International
INTRODUCTION AND PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS OF STRONG MOTION RECORDINGS FROM THE 12 MAY 2005 Ms8.0 WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE OF CHINA
 INTRODUCTION AND PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS OF STRONG MOTION RECORDINGS FROM THE 12 MAY 2005 Ms8.0 WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE OF CHINA Li Xiaojun 1, Zhou Zhenghua 1, Huang Moh 3, Wen Ruizhi 1, Yu Haiyin 1, Lu Dawei
INTRODUCTION AND PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS OF STRONG MOTION RECORDINGS FROM THE 12 MAY 2005 Ms8.0 WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE OF CHINA Li Xiaojun 1, Zhou Zhenghua 1, Huang Moh 3, Wen Ruizhi 1, Yu Haiyin 1, Lu Dawei
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS. Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1
 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 Seismic Hazard Analysis Deterministic procedures Probabilistic procedures USGS hazard
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 Seismic Hazard Analysis Deterministic procedures Probabilistic procedures USGS hazard
Earthquakes and Earth s Interior
 - What are Earthquakes? Earthquakes and Earth s Interior - The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy - Usually associated with faulting or breaking of rocks - Continuing adjustment
- What are Earthquakes? Earthquakes and Earth s Interior - The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy - Usually associated with faulting or breaking of rocks - Continuing adjustment
Natural Hazards Mitigation in Iceland
 Natural Hazards Mitigation in Iceland With special emphasis on earthquake risk Júlíus Sólnes Professor of civil and environmental engineering Dept. of engineering, University of Iceland Cambridge, 19th
Natural Hazards Mitigation in Iceland With special emphasis on earthquake risk Júlíus Sólnes Professor of civil and environmental engineering Dept. of engineering, University of Iceland Cambridge, 19th
Preliminary test of the EEPAS long term earthquake forecast model in Australia
 Preliminary test of the EEPAS long term earthquake forecast model in Australia Paul Somerville 1, Jeff Fisher 1, David Rhoades 2 and Mark Leonard 3 Abstract 1 Risk Frontiers 2 GNS Science 3 Geoscience
Preliminary test of the EEPAS long term earthquake forecast model in Australia Paul Somerville 1, Jeff Fisher 1, David Rhoades 2 and Mark Leonard 3 Abstract 1 Risk Frontiers 2 GNS Science 3 Geoscience
A BROADBAND SEISMIC EXPERIMENT IN YUNNAN, SOUTHWEST CHINA. Sponsored by Defense Threat Reduction Agency. Contract No.
 A BROADBAND SEISMIC EXPERIMENT IN YUNNAN, SOUTHWEST CHINA Wenjie Jiao, 1 Winston Chan, 1 and Chunyong Wang 2 Multimax Inc., 1 Institute of Geophysics, China Seismological Bureau 2 Sponsored by Defense
A BROADBAND SEISMIC EXPERIMENT IN YUNNAN, SOUTHWEST CHINA Wenjie Jiao, 1 Winston Chan, 1 and Chunyong Wang 2 Multimax Inc., 1 Institute of Geophysics, China Seismological Bureau 2 Sponsored by Defense
Seismic Quiescence before the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan, M w 7.6 Earthquake
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 96, No. 1, pp. 321 327, February 2006, doi: 10.1785/0120050069 Seismic Quiescence before the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan, M w 7.6 Earthquake by Yih-Min Wu
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 96, No. 1, pp. 321 327, February 2006, doi: 10.1785/0120050069 Seismic Quiescence before the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan, M w 7.6 Earthquake by Yih-Min Wu
Gutenberg-Richter recurrence law to seismicity analysis of Bangladesh
 IABSE-JSCE Joint Conference on Advances in Bridge Engineering-III, August 21-22, 2015, Dhaka, Bangladesh. ISBN: 978-984-33-9313-5 Amin, Okui, Bhuiyan, Ueda (eds.) www.iabse-bd.org Gutenberg-Richter recurrence
IABSE-JSCE Joint Conference on Advances in Bridge Engineering-III, August 21-22, 2015, Dhaka, Bangladesh. ISBN: 978-984-33-9313-5 Amin, Okui, Bhuiyan, Ueda (eds.) www.iabse-bd.org Gutenberg-Richter recurrence
EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN
 EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN Dr Ilaria Mosca 1 and Dr Natalya Silacheva 2 1 British Geological Survey, Edinburgh (UK) imosca@nerc.ac.uk 2 Institute of Seismology, Almaty (Kazakhstan) silacheva_nat@mail.ru
EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN Dr Ilaria Mosca 1 and Dr Natalya Silacheva 2 1 British Geological Survey, Edinburgh (UK) imosca@nerc.ac.uk 2 Institute of Seismology, Almaty (Kazakhstan) silacheva_nat@mail.ru
V r : A new index to represent the variation rate of geomagnetic activity
 Earthq Sci (2010)23: 343 348 343 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0731-9 V r : A new index to represent the variation rate of geomagnetic activity Dongmei Yang 1, Yufei He 1 Chuanhua Chen 2 and Jiadong Qian 3 1
Earthq Sci (2010)23: 343 348 343 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0731-9 V r : A new index to represent the variation rate of geomagnetic activity Dongmei Yang 1, Yufei He 1 Chuanhua Chen 2 and Jiadong Qian 3 1
CHARACTERIZING SPATIAL CROSS-CORRELATION BETWEEN GROUND- MOTION SPECTRAL ACCELERATIONS AT MULTIPLE PERIODS. Nirmal Jayaram 1 and Jack W.
 Proceedings of the 9th U.S. National and 10th Canadian Conference on Earthquake Engineering Compte Rendu de la 9ième Conférence Nationale Américaine et 10ième Conférence Canadienne de Génie Parasismique
Proceedings of the 9th U.S. National and 10th Canadian Conference on Earthquake Engineering Compte Rendu de la 9ième Conférence Nationale Américaine et 10ième Conférence Canadienne de Génie Parasismique
State of art of seismic design and seismic hazard analysis for oil and gas pipeline system
 Earthq Sci (2010)23: 259 263 259 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0721-y State of art of seismic design and seismic hazard analysis for oil and gas pipeline system Aiwen Liu Kun Chen and Jian Wu Institute of Geophysics,
Earthq Sci (2010)23: 259 263 259 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0721-y State of art of seismic design and seismic hazard analysis for oil and gas pipeline system Aiwen Liu Kun Chen and Jian Wu Institute of Geophysics,
Study on the feature of surface rupture zone of the west of Kunlunshan pass earthquake ( M S 811) with high spatial resolution satellite images
 48 2 2005 3 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 48, No. 2 Mar., 2005,,. M S 811.,2005,48 (2) :321 326 Shan X J, Li J H, Ma C. Study on the feature of surface rupture zone of the West of Kunlunshan Pass
48 2 2005 3 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 48, No. 2 Mar., 2005,,. M S 811.,2005,48 (2) :321 326 Shan X J, Li J H, Ma C. Study on the feature of surface rupture zone of the West of Kunlunshan Pass
Definitions. Seismic Risk, R (Σεισμική διακινδύνευση) = risk of damage of a structure
 SEISMIC HAZARD Definitions Seismic Risk, R (Σεισμική διακινδύνευση) = risk of damage of a structure Seismic Hazard, Η (Σεισμικός κίνδυνος) = expected intensity of ground motion at a site Vulnerability,
SEISMIC HAZARD Definitions Seismic Risk, R (Σεισμική διακινδύνευση) = risk of damage of a structure Seismic Hazard, Η (Σεισμικός κίνδυνος) = expected intensity of ground motion at a site Vulnerability,
Observations on the 2015 February ML 5.0 and July ML 5.4 Central Queensland Earthquake Sequences
 Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 2015, Sydney, Australia Observations on the 2015 February ML 5.0 and July ML
Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 2015, Sydney, Australia Observations on the 2015 February ML 5.0 and July ML
APPLICATIONS OF FUZZY MATHEMATICS IN EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION
 J. Phys. Earth, 34, Suppl., S213-S221, 1986 APPLICATIONS OF FUZZY MATHEMATICS IN EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION Deyi FENG,* Mingzhou LIN,** Chun JIANG,* and Ronghua CHENG*** * Seismological Bureau of Tianjin, Tianjin,
J. Phys. Earth, 34, Suppl., S213-S221, 1986 APPLICATIONS OF FUZZY MATHEMATICS IN EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION Deyi FENG,* Mingzhou LIN,** Chun JIANG,* and Ronghua CHENG*** * Seismological Bureau of Tianjin, Tianjin,
Students will be able, using GIS, to locate the largest and most destructive earthquakes;
 Exploring Earthquake Hazards with GIS Laboratory for Introduction to Geophysics, Spring 2007 Prof. Constantin Cranganu Brooklyn College of the City University of New York Learning Objectives: Students
Exploring Earthquake Hazards with GIS Laboratory for Introduction to Geophysics, Spring 2007 Prof. Constantin Cranganu Brooklyn College of the City University of New York Learning Objectives: Students
TAO Zhengru ( 陶正如 ) , Sendai, Japan 1
 TAO Zhengru ( 陶正如 ) Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration 013.6.17, Sendai, Japan 1 Contents Background Methodology Demonstration region Sichuan-Yunnan region Data of paleo-eq
TAO Zhengru ( 陶正如 ) Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration 013.6.17, Sendai, Japan 1 Contents Background Methodology Demonstration region Sichuan-Yunnan region Data of paleo-eq
Finding an Earthquake Epicenter Pearson Education, Inc.
 Finding an Earthquake Epicenter Measuring the Size of Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the size of an earthquake are: 1. Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale
Finding an Earthquake Epicenter Measuring the Size of Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the size of an earthquake are: 1. Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative
 Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative TIMOR-LESTE September Timor-Leste is expected to incur, on average, 5.9 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones.
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative TIMOR-LESTE September Timor-Leste is expected to incur, on average, 5.9 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones.
Relationships between ground motion parameters and landslides induced by Wenchuan earthquake
 Earthq Sci (2010)23: 233 242 233 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0719-5 Relationships between ground motion parameters and landslides induced by Wenchuan earthquake Xiuying Wang 1, Gaozhong Nie 2 and Dengwei Wang
Earthq Sci (2010)23: 233 242 233 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0719-5 Relationships between ground motion parameters and landslides induced by Wenchuan earthquake Xiuying Wang 1, Gaozhong Nie 2 and Dengwei Wang
AN OVERVIEW AND GUIDELINES FOR PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPPING
 CO 2 TRACCS INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP Bucharest, 2 September, 2012 AN OVERVIEW AND GUIDELINES FOR PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPPING M. Semih YÜCEMEN Department of Civil Engineering and Earthquake Studies
CO 2 TRACCS INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP Bucharest, 2 September, 2012 AN OVERVIEW AND GUIDELINES FOR PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPPING M. Semih YÜCEMEN Department of Civil Engineering and Earthquake Studies
Research Article Seismic Structure of Local Crustal Earthquakes beneath the Zipingpu Reservoir of Longmenshan Fault Zone
 International Geophysics Volume 11, Article ID 773, pages doi:.11/11/773 Research Article Seismic Structure of Local Crustal Earthquakes beneath the Zipingpu Reservoir of Longmenshan Fault Zone Haiou Li,
International Geophysics Volume 11, Article ID 773, pages doi:.11/11/773 Research Article Seismic Structure of Local Crustal Earthquakes beneath the Zipingpu Reservoir of Longmenshan Fault Zone Haiou Li,
THE INTEGRATED INFORMATION SYSTEM FOR NATURAL
 THE INTEGRATED INFORMATION SYSTEM FOR NATURAL DISASTER MITIGATION Junxiu Wu 1, Qiang Feng 2*, Bijun Liang 3, and Angsheng Wang 4 1 Department of Computer System, Technological Bureau of Xinhua News Agency,
THE INTEGRATED INFORMATION SYSTEM FOR NATURAL DISASTER MITIGATION Junxiu Wu 1, Qiang Feng 2*, Bijun Liang 3, and Angsheng Wang 4 1 Department of Computer System, Technological Bureau of Xinhua News Agency,
Songlin Li 1, Xiaoling Lai 1 Zhixiang Yao 2 and Qing Yang 1. 1 Introduction
 Earthq Sci (2009)22: 417 424 417 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0417-3 Fault zone structures of northern and southern portions of the main central fault generated by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake using fault zone
Earthq Sci (2009)22: 417 424 417 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0417-3 Fault zone structures of northern and southern portions of the main central fault generated by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake using fault zone
27th Seismic Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 P AND S WAVE VELOCITY STRUCTURE OF THE CRUST AND UPPER MANTLE UNDER CHINA AND SURROUNDING AREAS FROM BODY AND SURFACE WAVE TOMOGRAPHY M. Nafi Toksöz, Robert D. Van der Hilst, Youshun Sun, and Chang Li
P AND S WAVE VELOCITY STRUCTURE OF THE CRUST AND UPPER MANTLE UNDER CHINA AND SURROUNDING AREAS FROM BODY AND SURFACE WAVE TOMOGRAPHY M. Nafi Toksöz, Robert D. Van der Hilst, Youshun Sun, and Chang Li
log 4 0.7m log m Seismic Analysis of Structures by TK Dutta, Civil Department, IIT Delhi, New Delhi. Module 1 Seismology Exercise Problems :
 Seismic Analysis of Structures by TK Dutta, Civil Department, IIT Delhi, New Delhi. Module Seismology Exercise Problems :.4. Estimate the probabilities of surface rupture length, rupture area and maximum
Seismic Analysis of Structures by TK Dutta, Civil Department, IIT Delhi, New Delhi. Module Seismology Exercise Problems :.4. Estimate the probabilities of surface rupture length, rupture area and maximum
SEISMIC HAZARD CHARACTERIZATION AND RISK EVALUATION USING GUMBEL S METHOD OF EXTREMES (G1 AND G3) AND G-R FORMULA FOR IRAQ
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2898 SEISMIC HAZARD CHARACTERIZATION AND RISK EVALUATION USING GUMBEL S METHOD OF EXTREMES (G1 AND G3)
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2898 SEISMIC HAZARD CHARACTERIZATION AND RISK EVALUATION USING GUMBEL S METHOD OF EXTREMES (G1 AND G3)
Electromagnetic anomaly before earthquakes measured by electromagnetic experiments
 395 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0395-5 Electromagnetic anomaly before earthquakes measured by electromagnetic experiments Guoze Zhao Yan Zhan Lifeng Wang Jijun Wang Ji Tang Qibin Xiao and Xiaobin Chen Institute
395 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0395-5 Electromagnetic anomaly before earthquakes measured by electromagnetic experiments Guoze Zhao Yan Zhan Lifeng Wang Jijun Wang Ji Tang Qibin Xiao and Xiaobin Chen Institute
Initiative. Country Risk Profile: papua new guinea. Better Risk Information for Smarter Investments PAPUA NEW GUINEA.
 Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative PAPUA NEW GUINEA September 211 Country Risk Profile: papua new is expected to incur, on average, 85 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative PAPUA NEW GUINEA September 211 Country Risk Profile: papua new is expected to incur, on average, 85 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Maps in Dam Foundation
 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Maps in Dam Foundation by Hideaki Kawasaki 1, Masafumi Kondo 2, Akira Nakamura 3, Kenji Inagaki 4 ABSTRACT Because Japan is one of the world s most earthquake prone countries,
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Maps in Dam Foundation by Hideaki Kawasaki 1, Masafumi Kondo 2, Akira Nakamura 3, Kenji Inagaki 4 ABSTRACT Because Japan is one of the world s most earthquake prone countries,
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis in Thailand and Adjacent Areas by Using Regional Seismic Source Zones
 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis in Thailand and Adjacent Areas by Using Regional Seismic Source Zones Santi Pailoplee 1*, Yuichi Sugiyama 2 and Punya Charusiri 1 1. Earthquake and Tectonic Geology
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis in Thailand and Adjacent Areas by Using Regional Seismic Source Zones Santi Pailoplee 1*, Yuichi Sugiyama 2 and Punya Charusiri 1 1. Earthquake and Tectonic Geology
Response Analysis of a Buried Pipeline Considering the
 Response Analysis of a Buried Pipeline Considering the process Process of fault Fault movement Movement A.W. Liu, X.H. Jia Institute of Geophysics, CEA, China SUMMARY: For the seismic design of a pipeline
Response Analysis of a Buried Pipeline Considering the process Process of fault Fault movement Movement A.W. Liu, X.H. Jia Institute of Geophysics, CEA, China SUMMARY: For the seismic design of a pipeline
Geometric effects resulting from the asymmetry of dipping fault: Hanging wall/ footwall
 Vol.21 No.3 (275~282) ACTA SEISMOLOGICA SINICA May, 2008 Article ID: 1000-9116(2008)03-0275-08 doi: 10.1007/s11589-008-0275-4 Geometric effects resulting from the asymmetry of dipping fault: Hanging wall/
Vol.21 No.3 (275~282) ACTA SEISMOLOGICA SINICA May, 2008 Article ID: 1000-9116(2008)03-0275-08 doi: 10.1007/s11589-008-0275-4 Geometric effects resulting from the asymmetry of dipping fault: Hanging wall/
Characteristics of seismic activity before the M S 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake
 Earthq Sci (2009)22: 519 529 519 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0519-4 Characteristics of seismic activity before the M S 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake Yan Xue 1,2, Jie Liu 2 Shirong Mei 3 and Zhiping Song 4 1 Institute
Earthq Sci (2009)22: 519 529 519 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0519-4 Characteristics of seismic activity before the M S 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake Yan Xue 1,2, Jie Liu 2 Shirong Mei 3 and Zhiping Song 4 1 Institute
A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR
 A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR Annemarie CHRISTOPHERSEN 1 And Euan G C SMITH 2 SUMMARY This paper considers the distribution of aftershocks in space, abundance, magnitude and time. Investigations
A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR Annemarie CHRISTOPHERSEN 1 And Euan G C SMITH 2 SUMMARY This paper considers the distribution of aftershocks in space, abundance, magnitude and time. Investigations
5. Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis
 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA) proposed by C.A. Cornell (1968) used to determine the design earthquake for all locations in USA. PSHA gives a relative quantification i of the design earthquake,
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA) proposed by C.A. Cornell (1968) used to determine the design earthquake for all locations in USA. PSHA gives a relative quantification i of the design earthquake,
Deterministic Seismic Hazard Assessment of Quetta, Pakistan
 Deterministic Seismic Hazard Assessment of Quetta, Pakistan M.A. Shah Micro Seismic Studies Programme, Islamabad, Pakistan Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Islamabad, Pakistan M.
Deterministic Seismic Hazard Assessment of Quetta, Pakistan M.A. Shah Micro Seismic Studies Programme, Islamabad, Pakistan Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Islamabad, Pakistan M.
SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT FOR JAPAN AFTER THE 2011 TOHOKU-OKI MEGA-THRUST EARTHQUAKE (Mw9.0)
 Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering Lessons Learned from the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake, March 1-4, 2012, Tokyo, Japan SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT FOR JAPAN AFTER THE 2011 TOHOKU-OKI
Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering Lessons Learned from the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake, March 1-4, 2012, Tokyo, Japan SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT FOR JAPAN AFTER THE 2011 TOHOKU-OKI
Road & Railway Network Density Dataset at 1 km over the Belt and Road and Surround Region
 Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery. 2017, 1(4): 402-407 DOI:10.3974/geodp.2017.04.03 www.geodoi.ac.cn 2017 GCdataPR Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository Road & Railway Network Density
Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery. 2017, 1(4): 402-407 DOI:10.3974/geodp.2017.04.03 www.geodoi.ac.cn 2017 GCdataPR Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository Road & Railway Network Density
Earthquakes Chapter 19
 Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
Fig. 1 Location of the New Shanghai No. 1 Mine in Inner Mongolia, China.
 An Interdisciplinary Response to Mine Water Challenges - Sui, Sun & Wang (eds) 2014 China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou, ISBN 978-7-5646-2437-8 A Water-Inrush Risk Assessment Based
An Interdisciplinary Response to Mine Water Challenges - Sui, Sun & Wang (eds) 2014 China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou, ISBN 978-7-5646-2437-8 A Water-Inrush Risk Assessment Based
Earthquakes Earth, 9th edition, Chapter 11 Key Concepts What is an earthquake? Earthquake focus and epicenter What is an earthquake?
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Earthquakes Earth, 9 th edition, Chapter 11 Key Concepts Earthquake basics. "" and locating earthquakes.. Destruction resulting from earthquakes. Predicting earthquakes. Earthquakes
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Earthquakes Earth, 9 th edition, Chapter 11 Key Concepts Earthquake basics. "" and locating earthquakes.. Destruction resulting from earthquakes. Predicting earthquakes. Earthquakes
Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Logistic Regression in Garut District, West Java, Indonesia
 Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Logistic Regression in Garut District, West Java, Indonesia N. Lakmal Deshapriya 1, Udhi Catur Nugroho 2, Sesa Wiguna 3, Manzul Hazarika 1, Lal Samarakoon 1 1 Geoinformatics
Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Logistic Regression in Garut District, West Java, Indonesia N. Lakmal Deshapriya 1, Udhi Catur Nugroho 2, Sesa Wiguna 3, Manzul Hazarika 1, Lal Samarakoon 1 1 Geoinformatics
Tidal triggering of earthquakes in Longmen Shan region: the relation to the fold belt and basin structures
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 64, 771 776, 2012 Tidal triggering of earthquakes in Longmen Shan region: the relation to the fold belt and basin structures Qiang Li and Gui-Ming Xu Research Center for Earthquake
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 64, 771 776, 2012 Tidal triggering of earthquakes in Longmen Shan region: the relation to the fold belt and basin structures Qiang Li and Gui-Ming Xu Research Center for Earthquake
Time-varying and long-term mean aftershock hazard in Wellington
 Time-varying and long-term mean aftershock hazard in Wellington A. Christophersen, D.A. Rhoades, R.J. Van Dissen, C. Müller, M.W. Stirling, G.H. McVerry & M.C. Gerstenberger GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New
Time-varying and long-term mean aftershock hazard in Wellington A. Christophersen, D.A. Rhoades, R.J. Van Dissen, C. Müller, M.W. Stirling, G.H. McVerry & M.C. Gerstenberger GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New
arxiv: v1 [physics.geo-ph] 19 Jul 2016
![arxiv: v1 [physics.geo-ph] 19 Jul 2016 arxiv: v1 [physics.geo-ph] 19 Jul 2016](/thumbs/75/71784129.jpg) The sinusoidal periodicity nature for M 5 global earthquakes July 20, 2016 arxiv:1607.05391v1 [physics.geo-ph] 19 Jul 2016 Z. X. Zhang,, 1 X. Q. Li,2 National Earthquake Infrastructure Service, Beijing,
The sinusoidal periodicity nature for M 5 global earthquakes July 20, 2016 arxiv:1607.05391v1 [physics.geo-ph] 19 Jul 2016 Z. X. Zhang,, 1 X. Q. Li,2 National Earthquake Infrastructure Service, Beijing,
Seismic Response Analysis of selected sites in Wenxian urban area, China
 Seismic Response Analysis of selected sites in Wenxian urban area, China Y. Lu, K. Liu & Q. Li Earthquake Administration of Gansu Province (Key Laboratory of Loess Earthquake Engineering, CEA),China Y.
Seismic Response Analysis of selected sites in Wenxian urban area, China Y. Lu, K. Liu & Q. Li Earthquake Administration of Gansu Province (Key Laboratory of Loess Earthquake Engineering, CEA),China Y.
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Once you have opened the website with the link provided choose a force: Earthquakes
 Name: Once you have opened the website with the link provided choose a force: Earthquakes When do earthquakes happen? On the upper left menu, choose number 1. Read What is an Earthquake? Earthquakes happen
Name: Once you have opened the website with the link provided choose a force: Earthquakes When do earthquakes happen? On the upper left menu, choose number 1. Read What is an Earthquake? Earthquakes happen
CASUALTY IN EARTHQUAKE AND TSUNAMI DISASTERS: INTERNET-BASED MONITORING AND EARLY ESTIMATION OF THE FINAL DEATH TOLL
 CASUALTY IN EARTHQUAKE AND TSUNAMI DISASTERS: INTERNET-BASED MONITORING AND EARLY ESTIMATION OF THE FINAL DEATH TOLL ABSTRACT : Y.Z. Zhao 1, Z.L. Wu 2 and Y.T. Li 2, 3 1 College of Earth Science, Graduate
CASUALTY IN EARTHQUAKE AND TSUNAMI DISASTERS: INTERNET-BASED MONITORING AND EARLY ESTIMATION OF THE FINAL DEATH TOLL ABSTRACT : Y.Z. Zhao 1, Z.L. Wu 2 and Y.T. Li 2, 3 1 College of Earth Science, Graduate
Directivity of near-fault ground motion generated by thrust-fault earthquake: a case study of the 1999 M w 7.6 Chi-Chi earthquake
 October -7, 8, Beijing, China Directivity of near-fault ground motion generated by thrust-fault earthquake: a case study of the 999 M w 7.6 Chi-Chi earthquake J.J. Hu and L.L. Xie Assistant Professor,
October -7, 8, Beijing, China Directivity of near-fault ground motion generated by thrust-fault earthquake: a case study of the 999 M w 7.6 Chi-Chi earthquake J.J. Hu and L.L. Xie Assistant Professor,
Effects of Surface Geology on Seismic Motion
 4 th IASPEI / IAEE International Symposium: Effects of Surface Geology on Seismic Motion August 23 26, 2011 University of California Santa Barbara RECENT EXPERIENCE AND PRACTICE FOR STRONG MOTION OBSERVATION
4 th IASPEI / IAEE International Symposium: Effects of Surface Geology on Seismic Motion August 23 26, 2011 University of California Santa Barbara RECENT EXPERIENCE AND PRACTICE FOR STRONG MOTION OBSERVATION
Specific gravity field and deep crustal structure of the Himalayas east structural knot
 49 4 2006 7 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 49, No. 4 Jul., 2006,,.., 2006, 49 (4) :1045 1052 Teng J W, Wang Q S, Wang GJ, et al. Specific gravity field and deep crustal structure of the Himalayas east
49 4 2006 7 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 49, No. 4 Jul., 2006,,.., 2006, 49 (4) :1045 1052 Teng J W, Wang Q S, Wang GJ, et al. Specific gravity field and deep crustal structure of the Himalayas east
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative
 Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative PALAU September is expected to incur, on average,.7 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones. In the next 5 years,
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative PALAU September is expected to incur, on average,.7 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones. In the next 5 years,
AVERAGE AND VARIATION OF FOCAL MECHANISM AROUND TOHOKU SUBDUCTION ZONE
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 414 AVERAGE AND VARIATION OF FOCAL MECHANISM AROUND TOHOKU SUBDUCTION ZONE Shunroku YAMAMOTO 1 Naohito
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 414 AVERAGE AND VARIATION OF FOCAL MECHANISM AROUND TOHOKU SUBDUCTION ZONE Shunroku YAMAMOTO 1 Naohito
Understanding China Census Data with GIS By Shuming Bao and Susan Haynie China Data Center, University of Michigan
 Understanding China Census Data with GIS By Shuming Bao and Susan Haynie China Data Center, University of Michigan The Census data for China provides comprehensive demographic and business information
Understanding China Census Data with GIS By Shuming Bao and Susan Haynie China Data Center, University of Michigan The Census data for China provides comprehensive demographic and business information
A study on crustal structures of Changbaishan2Jingpohu volcanic area using receiver functions
 48 2 2005 3 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 48, No. 2 Mar., 2005,,..,2005,48 (2) :352 358 Duan Y H, Zhang X K, Liu Z,et al. A study on crustal structures of Changbaishan2Jingpohu volcanic area using
48 2 2005 3 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 48, No. 2 Mar., 2005,,..,2005,48 (2) :352 358 Duan Y H, Zhang X K, Liu Z,et al. A study on crustal structures of Changbaishan2Jingpohu volcanic area using
Estimation of Regional Seismic Hazard in the Korean Peninsula Using Historical Earthquake Data between A.D. 2 and 1995
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 94, No. 1, pp. 269 284, February 2004 Estimation of Regional Seismic Hazard in the Korean Peninsula Using Historical Earthquake Data between A.D.
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 94, No. 1, pp. 269 284, February 2004 Estimation of Regional Seismic Hazard in the Korean Peninsula Using Historical Earthquake Data between A.D.
Geographic Information Systems
 Geographic Information Systems What is a Geographic Information System (GIS)? definition of GIS - An internally referenced, automated, spatial information system for data mapping, management, and analysis
Geographic Information Systems What is a Geographic Information System (GIS)? definition of GIS - An internally referenced, automated, spatial information system for data mapping, management, and analysis
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative
 Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative VANUATU September 211 Country Risk Profile: VANUATU is expected to incur, on average, 48 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative VANUATU September 211 Country Risk Profile: VANUATU is expected to incur, on average, 48 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and
"Research Note" PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS OF QUETTA PAKISTAN * A. Q. BHATTI **
 IJST, Transactions of Civil Engineering, Vol. 37, No. C1, pp 157-162 Printed in The Islamic Republic of Iran, 2013 Shiraz University "Research Note" PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS OF QUETTA PAKISTAN
IJST, Transactions of Civil Engineering, Vol. 37, No. C1, pp 157-162 Printed in The Islamic Republic of Iran, 2013 Shiraz University "Research Note" PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS OF QUETTA PAKISTAN
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS
 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 This topic addresses deterministic and probabilistic seismic hazard analysis, ground
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 This topic addresses deterministic and probabilistic seismic hazard analysis, ground
Earthquakes. Earthquake Magnitudes 10/1/2013. Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena
 Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Multifractal Analysis of Seismicity of Kutch Region (Gujarat)
 P-382 Multifractal Analysis of Seismicity of Kutch Region (Gujarat) Priyanka Midha *, IIT Roorkee Summary The geographical distribution of past earthquakes is not uniform over the globe. Also, in one region
P-382 Multifractal Analysis of Seismicity of Kutch Region (Gujarat) Priyanka Midha *, IIT Roorkee Summary The geographical distribution of past earthquakes is not uniform over the globe. Also, in one region
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative
 Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative TUVALU is expected to incur, on average,. million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones. In the next 5 years, has
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative TUVALU is expected to incur, on average,. million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones. In the next 5 years, has
Impacts of 2014 Chiangrai Earthquake from Geotechnical Perspectives
 EIT-JSCE Joint International Symposium on Human Resource Development for Disaster-Resilient Countries 214 Impacts of 214 Chiangrai Earthquake from Geotechnical Perspectives Suttisak Soralump 1, Jessada
EIT-JSCE Joint International Symposium on Human Resource Development for Disaster-Resilient Countries 214 Impacts of 214 Chiangrai Earthquake from Geotechnical Perspectives Suttisak Soralump 1, Jessada
A Short Story About Earthquakes Ein kurzer Vortrag über Erdbeben
 A Short Story About Earthquakes Ein kurzer Vortrag über Erdbeben Wolfgang Rattay Reuters BBC Kurt Decker Universität Wien Department für Geodynamik und Sedimentologie The short sumary of a short story
A Short Story About Earthquakes Ein kurzer Vortrag über Erdbeben Wolfgang Rattay Reuters BBC Kurt Decker Universität Wien Department für Geodynamik und Sedimentologie The short sumary of a short story
Uncertainties in a probabilistic model for seismic hazard analysis in Japan
 Uncertainties in a probabilistic model for seismic hazard analysis in Japan T. Annaka* and H. Yashiro* * Tokyo Electric Power Services Co., Ltd., Japan ** The Tokio Marine and Fire Insurance Co., Ltd.,
Uncertainties in a probabilistic model for seismic hazard analysis in Japan T. Annaka* and H. Yashiro* * Tokyo Electric Power Services Co., Ltd., Japan ** The Tokio Marine and Fire Insurance Co., Ltd.,
Seismic Analysis of Structures Prof. T.K. Datta Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi. Lecture 03 Seismology (Contd.
 Seismic Analysis of Structures Prof. T.K. Datta Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 03 Seismology (Contd.) In the previous lecture, we discussed about the earth
Seismic Analysis of Structures Prof. T.K. Datta Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 03 Seismology (Contd.) In the previous lecture, we discussed about the earth
Students will be able, using GIS, to locate the largest and most destructive earthquakes;
 Exploring Earthquake Hazards with GIS Laboratory for Introduction to Geophysics, Spring 2007 Prof. Constantin Cranganu Brooklyn College of the City University of New York Learning Objectives: Students
Exploring Earthquake Hazards with GIS Laboratory for Introduction to Geophysics, Spring 2007 Prof. Constantin Cranganu Brooklyn College of the City University of New York Learning Objectives: Students
Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI) Dataset in Yunnan Province, China
 Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery. 2017, 1(4): 447-451 DOI:10.3974/geodp.2017.04.11 www.geodoi.ac.cn 2017 GCdataPR Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository Standardized Precipitation
Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery. 2017, 1(4): 447-451 DOI:10.3974/geodp.2017.04.11 www.geodoi.ac.cn 2017 GCdataPR Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository Standardized Precipitation
Seismic Hazard Switzerland. When, where, and how often does certain shaking occur in Switzerland?
 Seismic Hazard Switzerland When, where, and how often does certain shaking occur in Switzerland? Hazard The hazard map shows where and how often certain incidents of horizontal acceleration are likely.
Seismic Hazard Switzerland When, where, and how often does certain shaking occur in Switzerland? Hazard The hazard map shows where and how often certain incidents of horizontal acceleration are likely.
2/8/2016 Magnitude-6.3 earthquake near Tainan, Taiwan, highlights the danger of blind thrust faults around the world
 Temblor.net Earthquake News & Blog Magnitude-6.3 earthquake near Tainan, Taiwan, highlights the danger of blind thrust faults around the world 6 February 2016 Quake Insight Revised The 5 Feb 2016 M=6.3
Temblor.net Earthquake News & Blog Magnitude-6.3 earthquake near Tainan, Taiwan, highlights the danger of blind thrust faults around the world 6 February 2016 Quake Insight Revised The 5 Feb 2016 M=6.3
IGC. 50 th INDIAN GEOTECHNICAL CONFERENCE PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS FOR WARANGAL CONSIDERING SINGLE SEISMOGENIC ZONING
 50 th IGC 50 th INDIAN GEOTECHNICAL CONFERENCE 17 th 19 th DECEMBER 2015, Pune, Maharashtra, India Venue: College of Engineering (Estd. 1854), Pune, India PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS FOR WARANGAL
50 th IGC 50 th INDIAN GEOTECHNICAL CONFERENCE 17 th 19 th DECEMBER 2015, Pune, Maharashtra, India Venue: College of Engineering (Estd. 1854), Pune, India PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS FOR WARANGAL
Preliminary numerical simulation of potential earthquake-induced tsunami in East China Sea
 Vol.1 No.5 (456~463) ACTA SEISMOLOGICA SINICA Sep., 008 Article ID: 1000-9116(008)05-0456-08 doi: 10.1007/s11589-008-0456-1 Preliminary numerical simulation of potential earthquake-induced tsunami in East
Vol.1 No.5 (456~463) ACTA SEISMOLOGICA SINICA Sep., 008 Article ID: 1000-9116(008)05-0456-08 doi: 10.1007/s11589-008-0456-1 Preliminary numerical simulation of potential earthquake-induced tsunami in East
Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon
 Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon By the Oregon Board of Geologist Examiners and the Oregon
Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon By the Oregon Board of Geologist Examiners and the Oregon
Deformation Forecasting of Huangtupo Riverside Landslide in the Case of Frequent Microseisms
 Journal of Earth Science, Vol. 27, No. 1, p. 160 166, February 2016 ISSN 1674-487X Printed in China DOI: 10.1007/s12583-016-0617-4 Deformation Forecasting of Huangtupo Riverside Landslide in the Case of
Journal of Earth Science, Vol. 27, No. 1, p. 160 166, February 2016 ISSN 1674-487X Printed in China DOI: 10.1007/s12583-016-0617-4 Deformation Forecasting of Huangtupo Riverside Landslide in the Case of
Analysis of China s Haze Days in the Winter Half-Year and the Climatic Background during
 ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 5(1): 1-6, 2014 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2014.001 CHANGES IN CLIMATE SYSTEM Analysis of China s Haze Days in the Winter Half-Year and the Climatic
ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 5(1): 1-6, 2014 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2014.001 CHANGES IN CLIMATE SYSTEM Analysis of China s Haze Days in the Winter Half-Year and the Climatic
