Observations on the 2015 February ML 5.0 and July ML 5.4 Central Queensland Earthquake Sequences
|
|
|
- Isabel Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 2015, Sydney, Australia Observations on the 2015 February ML 5.0 and July ML 5.4 Central Queensland Earthquake Sequences M.L. Turnbull Central Queensland Seismology Research Group (CQSRG), Horse Camp, Queensland, Australia. ABSTRACT: The main events and aftershocks of the February 2015 Mt Perry ML 5.0, and July 2015 Rainbow Beach ML 5.4 earthquake sequences are located and catalogued. Implications to the recurrence periods for earthquakes in the Central Queensland region are discussed. Three Central Queensland seismogenic areas are identified and their regional relationship is implied. 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Mt Perry Earthquake Sequence (MP 2015) On February at 15:57 (UTC) an earthquake measured by the Central Queensland Seismology Research Group (CQSRG) as ML 4.9, occurred 11 km north-west of the small township of Mt Perry in Central Queensland, in the Yarrol Block (Ellis & Whitaker 1976). The magnitude of this event was subsequently moderated to ML 5.0, based on data obtained from other agencies, including Geoscience Australia and the USGS. Over the next six months more than 100 aftershocks, ranging in magnitude from ML 0.7 to 4.0, were recorded and located by CQSRG; designated the Mt Perry 2015 sequence (MP 2015). These events were mostly tightly clustered in a well-defined area north-west of Mt Perry, with a south-east excursion extending some 50 km, passing 6 km to the north of Paradise Dam. 214 days after the initial event, aftershocks were still being recorded of the order of ML 1.7; however, at the time of writing, 231 days after the main event, a hiatus of 17 days was ongoing. 1.2 Rainbow Beach Earthquake Sequence (RB 2015) On July at 23:41 (UTC) an earthquake measured by CQSRG as ML 5.6, occurred out to sea,115 km north-east of the small township of Rainbow Beach in Central Queensland; about 280 km east of the Mt Perry sequence. The magnitude of this event was subsequently moderated to 5.4, based on data obtained from other agencies, including Geoscience Australia and the USGS. 51 aftershocks have been recorded and located by CQSRG, designated the Rainbow Beach 2015 sequence (RB 2015), ranging in magnitude from ML 1.9 to days after the main event, aftershocks were still being recorded of the order of ML HISTORICAL SEISMIC CONTEXT Table 1: Historical Central Queensland Earthquakes ML 4.9 and Greater. (Source: GA 2015) Magnitude (ML) Year Latitude Longitude Seismogenic Location km NE Rainbow Beach; 70 km NW of RB km N Gayndah; 40 km S MP km NW Mt Perry. Main shock of MP km NE Rainbow Beach. Aftershock of RB km NW Lady Elliot Island; 290 km NW RB km NE Rainbow Beach. Aftershock of RB km NE Rainbow Beach. Main shock of RB km N Gayndah; 40 km S MP km N Gayndah; 40 km S MP km N Lady Elliot Island; 280 km NW RB km N Lady Elliot Island; 280 km NW RB Paper Number 139
2 All earthquakes of magnitude 4.9 and greater, recorded since 1878 in the Central Queensland region, as listed in the Geoscience Australia database, are listed in Table 1. It should be noted that the locations of the 1918 events are very approximate; although the listed locations coincide with that of the 1978 ML 5.2, they may well have occurred in the RB 2015 area. It should also be noted that, although in the recent past the 1918 main event was listed as ML 6.2 by Rynn (1985, 1986) and others (Rynn et al 1987), GA currently lists it as ML 6.0. It would appear that there are two, perhaps three, historically active seismogenic areas in the Central Queensland region. The Yarrol Block; roughly bounded north of Gayndah, east of Monto, and west of Gin Gin; characterised by MP (Table 1, blue; also see Figure 3) The offshore Rainbow Beach area; characterised by RB (Table 1, green; also see Figure 3) The Elliot Island area; characterised (possibly) by the 1918 events, and the 1978 event. (Table 1, pink; also see Figure 3) 3 MAGNITUDE 6.0 EXCEEDANCE RECURRENCE PERIODS In 2001, and again in 2006, the author determined the expected magnitude exceedance recurrence periods for earthquakes within the 3 by 3 geographic square, centred on Bundaberg. This was done using Gumbel statistics of extreme events, based on the Geoscience Australia catalogue from 1878 to the time of determination. In review the author notes that he made an error in methodology in the 2006 determination that incorrectly resulted in an approximate 20% increase in the recurrence periods over those correctly determined in the 2001 analysis. The ability of the Gumbel method to extract accurate Richter-Guttenberg parameters from historical extreme event catalogues was validated by the author in 2006 (Turnbull & Weatherley 2006). The author s 2001 Gumbel analysis determined that the average recurrence period for the exceedance of an ML 6.0 event in Central Queensland was 84 years ± 4%. Recent theoretical work done by Lasse Makkonen and colleagues (Makkonen 2006 & 2011, Makkonen et al 2013) has placed the statistics of extreme events on a solid theoretical footing. The work of Makkonen has been critically examined and found to be sound (Cook 2011, Makkonen 2011). Makkonen proves that the correct methodology to be used when applying the statistics of extreme events to analyses, such as that of earthquake recurrence periods, is to use the Weibull formulation; without converting to a reduced variate, as was the case when using the Gumbel formulation. Makkonen warns that using the theoretically correct Weibull method will invariably produce lesser (but correct) recurrence periods than the empirical Gumbel method. The author has analysed the GA earthquake catalogue, including the MP 2015 main event, using the Weibull analysis, and has determined the average recurrence period for the exceedance of an ML 6.0 event in Central Queensland as 66 years (Turnbull 2015 unpublished). The error range has yet to be calculated, but is expected to be of the order of 5%. 4 AFTERSHOCK SEQUENCE CHARACTERISTICS Figure 1: Decay of the MP 2015 and RB 2015 Aftershock Decay Figure 1 shows the decay of the MP and RB 2015 sequences. The trend lines are log/linear approximations of the decays (with very poor correlation factors of 0.05). It is suggested that the sequences are, under normal circumstances, destined to continue for some further time, probably for several months. 2
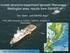
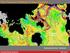
3 Figure 2: Gutenberg Richter Magnitude/Frequency Plots Analysis of the Mt Perry and Rainbow Beach sequences using Gutenberg-Richter Magnitude/Frequency regression (see Figure 2) indicates that both sequences are exhibiting the same b-value (0.45±0.05); which may be typical of intraplate earthquakes in Central Queensland. In 2001 the author (Turnbull, 2001) calculated a b-value of 0.59 using Gumbel statistics of extreme events. 5 REGIONAL RELATION OF THE SEQUENCES From the time that the Rainbow Beach main event occurred, a 23 day hiatus followed in aftershocks of the MP 2015 sequence. The author s initial interpretation of this observation was that the MP 2015 and RB 2015 sequences were related in that the RB sequence had shifted the regional geological stress expression from the Mt Perry area, and exhibited it in the offshore Rainbow Beach area. However, 22 days after the RB 2015 main event, the aftershocks of the MP 2015 sequence recommenced. Figure 1 shows that the two sequences are proceeding concurrently, but independently. Ellis & Whitaker (1976) noted three principle fault lines in the Bundaberg hinterland region. The MP 2015 events are associated with the Mt Perry Fault Zone, and the offshore events coincide with the drop off of the continental shelf. These features are shown in Figure 3. Figure 3: Map of MP and RB 2015, showing known faults and continental drop off. 3
4 Figure 3 shows all earthquakes detected by CQSRG in the 2015 calendar year to date. These events have been relocated using all available records to minimise uncertainties. MP 2015, being associated with the known Mt Perry fault zone, indicates that that group of faults is active. The RB 2015 sequence is occurring in a northeast/southwest lineation extending 70 km to the east of the continental shelf, and terminating about 20 km west of the north/south line of the Tasmantid Seamounts, with which they do not appear to be associated (see Figure 4). Figure 4: Focused view of the RB 2015 sequence. The RB 2015 sequence is positioned 15 to 20 km north of and parallel to what appears to be a relatively fresh turbidite flow, the material source of which is a narrow re-entrant in the continental drop off; which itself may be an ancient fluvial outflow. 6 CQSRG EARTHQUAKE CATALOGUE The earthquakes shown in Figures 3 and 4, and listed in Appendix A, were located using CQSRG data augmented with additional data from Geoscience Australia, SEQWater, the Seismology Research Centre, and The University of Queensland. CQSRG maintains a current earthquake catalogue online at A list of all earthquake events recorded in the MP 2015 and RB 2015 sequences (to date) is provided in Appendix A, below. 7 CONCLUSIONS The occurrence of the MP 2015 and RB 2015 earthquake and aftershock sequences, being 97 years after the previous sequence of similar magnitudes, gives credence to a proposed average ML 6.0 exceedance recurrence period, in the Central Queensland region, of 50 to 100 years. The locations of the MP 2015 and RB 2015 sequences support the observation that there are two, possibly three, principal active seismogenic areas within the Central Queensland region. 4
5 REFERENCES: Cook N. 2011, Comments on Plotting Positions in Extreme Value Analysis, Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, Volume 50 Issue 1 (January 2011), Pages Ellis P.L and Whitaker W.G. 1976, Geology of the Bundaberg 1: Sheet Area, Report No. 90, Geological Survey of Queensland, Makkonen L. 2006, Plotting Positions in Extreme Value Analysis, Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, Volume 45 Issue 2 (February 2006), Pages Makkonen L. 2011, Reply, Makkonen L, Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, Volume 50 Issue 1 (January 2011), Pages Makkonen L, Pajari M, Tikanmäki M. 2013, Closure to "Problems in the extreme value analysis", Structural Safety. Elsevier. Vol. 40 (January 2013), Pages Rynn J.M.W. 1985, A Reapraisal of Queensland.s Largest Known Earthquake The Queensland Earthquake of 6 June 1918, Magnitude ML 6.2, unpublished, Circa Rynn J.M.W. 1986, Queensland Seismic Risk Study, University of Queensland, Department of Geology and Mineralogy, Report QSRS. 4, Rynn J.M.W. Denham D. Grenhalgh S. Jones T, Gregson P.J. McCue K. & Smith R.S. 1987, Atlas of Isoseismal Maps of Australian Earthquakes Part 2, Australian Department of National Development & Energy, Bureau of Mineral resources, Geology and Geophysics, Bulletin 222, Canberra, Turnbull M.L. 2001, A Seismic Hazard Assessment and Microzonation of Bundaberg, Central Queensland University, Faculty of Engineering and Physical Systems, Master s Degree Thesis, April Turnbull M.L. 2006, Estimation of Gutenberg-Richter seismicity parameters for the Bundaberg region using Piecewise Extended Gumbel Analysis, Proceedings of the AEES 2006 Conference, Canberra, Australia, November Turnbull M.L. & Weatherly D. 2006, Validation of using Gumbel Probability Plotting to estimate Gutenberg- Richter seismicity parameters, Proceedings of the AEES 2006 Conference, Canberra, Australia, November
6 APPENDIX A: CQSRG CATALOGUE OF THE MP 2015 AND RB 2015 SEQUENCES Date (UTC) Time (UTC) Longitude Latitude Magnitude Place :24: ML Rainbow Beach :59: ML Mt Perry :25: ML Mt Perry :04: ML Mt Perry :08: ML Mt Perry :37: ML Rainbow Beach :02: ML Mt Perry :08: ML Cracow :23: ML Lady Elliot Island :34: ML Gin Gin :17: ML Paradise Dam :29: ML Mt Perry :09: ML Rainbow Beach :37: ML Rainbow Beach :04: ML Rainbow Beach :39: ML Mt Perry :05: ML Mt Perry :22: ML Rainbow Beach :06: ML Rainbow Beach :09: ML Rainbow Beach :36: ML Rainbow Beach :56: ML Rainbow Beach :36: ML Rainbow Beach :16: ML Rainbow Beach :20: ML Rainbow Beach :18: ML Rainbow Beach :42: ML Rainbow Beach :07: ML Rainbow Beach :55: ML Rainbow Beach :55: ML Rainbow Beach :52: ML Rainbow Beach :35: ML Rainbow Beach :03: ML Horse Camp :27: ML Rainbow Beach :56: ML Rainbow Beach :51: ML Rainbow Beach :20: ML Rainbow Beach :51: ML Rainbow Beach :34: ML Rainbow Beach :17: ML Rainbow Beach :10: ML Rainbow Beach :28: ML Rainbow Beach :15: ML Rainbow Beach :06: ML Rainbow Beach :56: ML Rainbow Beach :53: ML Rainbow Beach :29: ML Rainbow Beach :54: ML Rainbow Beach :08: ML Rainbow Beach :57: ML Rainbow Beach :51: ML Rainbow Beach :46: ML Rainbow Beach :29: ML Rainbow Beach :10: ML Rainbow Beach :48: ML Rainbow Beach :43: ML Rainbow Beach :38: ML Rainbow Beach :18: ML Rainbow Beach 6
7 Date (UTC) Time (UTC) Longitude Latitude Magnitude Place :05: ML Rainbow Beach :31: ML Rainbow Beach :11: ML Rainbow Beach :59: ML Rainbow Beach :44: ML Rainbow Beach :41: ML Rainbow Beach :52: ML Mt Perry :05: ML Stanthorpe : ML Horse Camp :57: ML Bundaberg :00: ML Mt Perry :12: ML Mt Perry :55: ML Mt Perry :11: ML Mt Perry :28: ML Mt Perry :29: ML Toogoolawah :29: ML Mt Perry :10: ML Mt Perry :03: ML Mt Perry :06: ML Mt Perry :08: ML Mt Perry :02: ML Mt Perry :50: ML Mt Perry :33: ML Mt Perry :13: ML Mt Perry :48: ML Mt Perry :53:: ML Mt Perry :42: ML Biggenden :09: ML Mt Perry :04: ML Mt Perry :05: ML Mt Perry : ML Horse Camp :35: ML Mt Perry :24: ML Mt Perry :35: ML Mt Perry :21: ML Mt Perry :11: ML Mt Perry :20: ML Mt Perry :41: ML Mt Perry :19: ML Mt Perry :14: ML Mt Perry :35: ML Mt Perry :56: ML Mt Perry :14: ML Mt Perry :41: ML Mt Perry :41: ML Mt Perry :12: ML Mt Perry :56: ML Mt Perry :48: ML Mt Perry :50: ML Mt Perry :28: ML Biggenden :41: ML Mt Perry :48: ML Mt Perry :19: ML Mt Perry :46: ML Mt Perry :57: ML Mt Perry :18: ML Mt Perry :23: ML Mt Perry :21: ML Mt Perry :06: ML Mt Perry 7
8 Date (UTC) Time (UTC) Longitude Latitude Magnitude Place :45: ML Mt Perry :08: ML Mt Perry :34: ML Mt Perry :15: ML Mt Perry :02: ML Mt Perry :10: ML Mt Perry :11: ML Mt Perry :37: ML Mt Perry :51: ML Mt Perry :58: ML Mt Perry :57: ML Mt Perry :17: ML Mt Perry :32: ML Bullyard :30: ML Goodnight Scrub :41: ML Mt Perry :39: ML Mt Perry :38: ML Mt Perry :39: ML Mt Perry :50: ML Mt Perry :58: ML Mt Perry :47: ML Mt Perry :35: ML Mt Perry :03: ML Mt Perry :00: ML Mt Perry :27: ML Mt Perry :22: ML Mt Perry :02: ML Mt Perry :34: ML Mt Perry :21: ML Mt Perry :54: ML Mt Perry :47: ML Mt Perry :05: ML Mt Perry :02: ML Mt Perry :56: ML Mt Perry :56: ML Mt Perry :21: ML Mt Perry :04: ML Mt Perry :00: ML Mt Perry :06: ML Mt Perry :37: ML Mt Perry : ML Mt Perry : ML Mt Perry :37: ML Mt Perry :30:57: ML Mt Perry :25: ML Mt Perry :20: ML Mt Perry :19: ML Mt Perry :14: ML Mt Perry :04: ML Mt Perry :03: ML Mt Perry :59: ML Mt Perry :57: ML Mt Perry 8
Estimation of Gutenberg-Richter seismicity parameters for the Bundaberg region using piecewise extended Gumbel analysis
 Estimation of Gutenberg-Richter seismicity parameters for the Bundaberg region using piecewise extended Gumbel analysis Abstract Mike Turnbull Central Queensland University The Gumbel statistics of extreme
Estimation of Gutenberg-Richter seismicity parameters for the Bundaberg region using piecewise extended Gumbel analysis Abstract Mike Turnbull Central Queensland University The Gumbel statistics of extreme
Years of Observation. Newcastle NSW VIII Adelaide SA VIII Sydney NSW V 1973,
 Relative earthquake hazard of Newcastle NSW by Kevin McCue Australian Seismological Centre Canberra, and Central Queensland University, Rockhampton, Qld Abstract A model-independent extreme value method
Relative earthquake hazard of Newcastle NSW by Kevin McCue Australian Seismological Centre Canberra, and Central Queensland University, Rockhampton, Qld Abstract A model-independent extreme value method
2015 Fraser Island Earthquake Sequence
 2015 Fraser Island Earthquake Sequence Elodie Borleis 1 and Vicki-Ann Dimas 2 1. Corresponding Author. Seismologist, Seismology Research Centre, Richmond VIC 3121, Australia. Email: Elodie.Borleis@src.com.au
2015 Fraser Island Earthquake Sequence Elodie Borleis 1 and Vicki-Ann Dimas 2 1. Corresponding Author. Seismologist, Seismology Research Centre, Richmond VIC 3121, Australia. Email: Elodie.Borleis@src.com.au
CQSRG Seismological Report 2014
 CENTRAL QUEENSLAND SEISMOLOGY RESEARCH GROUP CQSRG Seismological Report 2014 Edition 2015-09-21 Compiled by: Michael Turnbull BAppSc(Distinction) QUT MAppSc CQU, July 2015. Table of Contents Copyright
CENTRAL QUEENSLAND SEISMOLOGY RESEARCH GROUP CQSRG Seismological Report 2014 Edition 2015-09-21 Compiled by: Michael Turnbull BAppSc(Distinction) QUT MAppSc CQU, July 2015. Table of Contents Copyright
Coulomb stress changes due to Queensland earthquakes and the implications for seismic risk assessment
 Coulomb stress changes due to Queensland earthquakes and the implications for seismic risk assessment Abstract D. Weatherley University of Queensland Coulomb stress change analysis has been applied in
Coulomb stress changes due to Queensland earthquakes and the implications for seismic risk assessment Abstract D. Weatherley University of Queensland Coulomb stress change analysis has been applied in
Comparison of response spectra from Australian earthquakes and North American attenuation models
 Comparison of response spectra from Australian earthquakes and North American attenuation models T. Dhu, T. Allen, P. Cummins, M. Leonard, D. Robinson and J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, ACT,
Comparison of response spectra from Australian earthquakes and North American attenuation models T. Dhu, T. Allen, P. Cummins, M. Leonard, D. Robinson and J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, ACT,
Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard.
 Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard. T. Dhu, D. Robinson, C. Sinadinovski, T. Jones, A. Jones & J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, Australia.
Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard. T. Dhu, D. Robinson, C. Sinadinovski, T. Jones, A. Jones & J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, Australia.
Preliminary test of the EEPAS long term earthquake forecast model in Australia
 Preliminary test of the EEPAS long term earthquake forecast model in Australia Paul Somerville 1, Jeff Fisher 1, David Rhoades 2 and Mark Leonard 3 Abstract 1 Risk Frontiers 2 GNS Science 3 Geoscience
Preliminary test of the EEPAS long term earthquake forecast model in Australia Paul Somerville 1, Jeff Fisher 1, David Rhoades 2 and Mark Leonard 3 Abstract 1 Risk Frontiers 2 GNS Science 3 Geoscience
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS
 SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 32 Number 4 2013 A METHOD FOR THE ESTIMATION OF TSUNAMI RISK ALONG RUSSIA s FAR EAST G.V. Shevchenko, D. E. Zolotukhin,
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 32 Number 4 2013 A METHOD FOR THE ESTIMATION OF TSUNAMI RISK ALONG RUSSIA s FAR EAST G.V. Shevchenko, D. E. Zolotukhin,
The revised Australian seismic hazard map, 1991
 The revised Australian seismic hazard map, 1991 Kevin McCue Australian Seismological Centre, Australian Geological Survey Organisation GPO Box 378, Canberra ACT 2601 Introduction Large potentially destructive
The revised Australian seismic hazard map, 1991 Kevin McCue Australian Seismological Centre, Australian Geological Survey Organisation GPO Box 378, Canberra ACT 2601 Introduction Large potentially destructive
Adaptive Kernel Estimation and Continuous Probability Representation of Historical Earthquake Catalogs
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 92, No. 3, pp. 904 912, April 2002 Adaptive Kernel Estimation and Continuous Probability Representation of Historical Earthquake Catalogs by Christian
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 92, No. 3, pp. 904 912, April 2002 Adaptive Kernel Estimation and Continuous Probability Representation of Historical Earthquake Catalogs by Christian
Modelling Subduction Zone Seismogenic Hazards in Southeast Asia for Seismic Hazard Assessments
 Modelling Subduction Zone Seismogenic Hazards in Southeast Asia for Seismic Hazard Assessments Vicki-Ann Dimas 1,2 and Gary Gibson 3 1. Corresponding Author. Seismic Hazard Analyst, Seismology Research
Modelling Subduction Zone Seismogenic Hazards in Southeast Asia for Seismic Hazard Assessments Vicki-Ann Dimas 1,2 and Gary Gibson 3 1. Corresponding Author. Seismic Hazard Analyst, Seismology Research
COULOMB STRESS CHANGES DUE TO RECENT ACEH EARTHQUAKES
 COULOMB STRESS CHANGES DUE TO RECENT ACEH EARTHQUAKES Madlazim Physics Department, Faculty Mathematics and Sciences of Surabaya State University (UNESA) Jl. Ketintang, Surabaya 60231, Indonesia. e-mail:
COULOMB STRESS CHANGES DUE TO RECENT ACEH EARTHQUAKES Madlazim Physics Department, Faculty Mathematics and Sciences of Surabaya State University (UNESA) Jl. Ketintang, Surabaya 60231, Indonesia. e-mail:
Earthquake patterns in the Flinders Ranges - Temporary network , preliminary results
 Earthquake patterns in the Flinders Ranges - Temporary network 2003-2006, preliminary results Objectives David Love 1, Phil Cummins 2, Natalie Balfour 3 1 Primary Industries and Resources South Australia
Earthquake patterns in the Flinders Ranges - Temporary network 2003-2006, preliminary results Objectives David Love 1, Phil Cummins 2, Natalie Balfour 3 1 Primary Industries and Resources South Australia
Investigation of Seismic Hazard in NW-Himalayas, Pakistan using Gumbel s First Asymptotic Distribution of Extreme Values
 Pakistan Journal of Meteorology Vol. 6, Issue 12 Investigation of Seismic Hazard in NW-Himalayas, Pakistan using Gumbel s First Asymptotic Distribution of Extreme Values Naseer Ahmed 1, Dr. Zulfiqar Ahmed
Pakistan Journal of Meteorology Vol. 6, Issue 12 Investigation of Seismic Hazard in NW-Himalayas, Pakistan using Gumbel s First Asymptotic Distribution of Extreme Values Naseer Ahmed 1, Dr. Zulfiqar Ahmed
Epistemic Uncertainty in Seismic Hazard Analysis for Australia
 Australian Earthquake Engineering Society 2011 Conference, 18-20 November, Barossa Valley, South Australia Epistemic Uncertainty in Seismic Hazard Analysis for Australia Paul Somerville 1,2 and Hong Kie
Australian Earthquake Engineering Society 2011 Conference, 18-20 November, Barossa Valley, South Australia Epistemic Uncertainty in Seismic Hazard Analysis for Australia Paul Somerville 1,2 and Hong Kie
PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS AT GROUND SURFACE IN JAPAN BASED ON SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATED FROM OBSERVED STRONG-MOTION RECORDS
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 3488 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS AT GROUND SURFACE IN JAPAN BASED ON SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATED FROM
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 3488 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS AT GROUND SURFACE IN JAPAN BASED ON SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATED FROM
A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR
 A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR Annemarie CHRISTOPHERSEN 1 And Euan G C SMITH 2 SUMMARY This paper considers the distribution of aftershocks in space, abundance, magnitude and time. Investigations
A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR Annemarie CHRISTOPHERSEN 1 And Euan G C SMITH 2 SUMMARY This paper considers the distribution of aftershocks in space, abundance, magnitude and time. Investigations
Performance of national scale smoothed seismicity estimates of earthquake activity rates. Abstract
 Performance of national scale smoothed seismicity estimates of earthquake activity rates Jonathan Griffin 1, Graeme Weatherill 2 and Trevor Allen 3 1. Corresponding Author, Geoscience Australia, Symonston,
Performance of national scale smoothed seismicity estimates of earthquake activity rates Jonathan Griffin 1, Graeme Weatherill 2 and Trevor Allen 3 1. Corresponding Author, Geoscience Australia, Symonston,
Earthquakes down under: a rare but real hazard
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2015 Earthquakes down under: a rare but real hazard Solomon Buckman University
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2015 Earthquakes down under: a rare but real hazard Solomon Buckman University
A hybrid probabilistic seismic hazard analysis of a low and moderate seismic region: Sri Lanka a case study
 Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 2015, Sydney, Australia A hybrid probabilistic seismic hazard analysis of a low
Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 2015, Sydney, Australia A hybrid probabilistic seismic hazard analysis of a low
Gutenberg-Richter recurrence law to seismicity analysis of Bangladesh
 IABSE-JSCE Joint Conference on Advances in Bridge Engineering-III, August 21-22, 2015, Dhaka, Bangladesh. ISBN: 978-984-33-9313-5 Amin, Okui, Bhuiyan, Ueda (eds.) www.iabse-bd.org Gutenberg-Richter recurrence
IABSE-JSCE Joint Conference on Advances in Bridge Engineering-III, August 21-22, 2015, Dhaka, Bangladesh. ISBN: 978-984-33-9313-5 Amin, Okui, Bhuiyan, Ueda (eds.) www.iabse-bd.org Gutenberg-Richter recurrence
Seismic Network Report 2009
 Seismic Network Report 2009 Image courtesy Google Earth Compiled by Claire Payne Environmental Systems & Services Seismology Research Centre 8 River Street Richmond VIC 3121 seismology@esands.com www.esands.com
Seismic Network Report 2009 Image courtesy Google Earth Compiled by Claire Payne Environmental Systems & Services Seismology Research Centre 8 River Street Richmond VIC 3121 seismology@esands.com www.esands.com
FOCAL MECHANISMS OF SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE JAVA TRENCH: PRELIMINARY STUDY FOR THE PSHA FOR YOGYAKARTA REGION, INDONESIA
 FOCAL MECHANISMS OF SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE JAVA TRENCH: PRELIMINARY STUDY FOR THE PSHA FOR YOGYAKARTA REGION, INDONESIA Myo Thant 1, Hiroshi Kawase 2, Subagyo Pramumijoyo 3, Heru Hendrayana
FOCAL MECHANISMS OF SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE JAVA TRENCH: PRELIMINARY STUDY FOR THE PSHA FOR YOGYAKARTA REGION, INDONESIA Myo Thant 1, Hiroshi Kawase 2, Subagyo Pramumijoyo 3, Heru Hendrayana
Comparison of earthquake source spectra and attenuation in eastern North America and southeastern Australia
 Comparison of earthquake source spectra and attenuation in eastern North America and southeastern Australia Trevor Allen 1 and Gail Atkinson 2* 1 Risk Research Group Geoscience Australia GPO Box 378 Canberra,
Comparison of earthquake source spectra and attenuation in eastern North America and southeastern Australia Trevor Allen 1 and Gail Atkinson 2* 1 Risk Research Group Geoscience Australia GPO Box 378 Canberra,
;z I ~I ~ Probabilistic earthquake risk maps of southwest Western Australia. Brian A. Gaull 1 & Marion O. Michael-Leiba 1. Introduction.
 BMR Journal of Australian Geology & Geophysics 145-151 Commonwealth of Australia 1987 Probabilistic earthquake risk maps of southwest Western Australia Brian A. Gaull 1 & Marion O. Michael-Leiba 1 New
BMR Journal of Australian Geology & Geophysics 145-151 Commonwealth of Australia 1987 Probabilistic earthquake risk maps of southwest Western Australia Brian A. Gaull 1 & Marion O. Michael-Leiba 1 New
EARTHQUAKE CLUSTERS, SMALL EARTHQUAKES
 EARTHQUAKE CLUSTERS, SMALL EARTHQUAKES AND THEIR TREATMENT FOR HAZARD ESTIMATION Gary Gibson and Amy Brown RMIT University, Melbourne Seismology Research Centre, Bundoora AUTHORS Gary Gibson wrote his
EARTHQUAKE CLUSTERS, SMALL EARTHQUAKES AND THEIR TREATMENT FOR HAZARD ESTIMATION Gary Gibson and Amy Brown RMIT University, Melbourne Seismology Research Centre, Bundoora AUTHORS Gary Gibson wrote his
Time-varying and long-term mean aftershock hazard in Wellington
 Time-varying and long-term mean aftershock hazard in Wellington A. Christophersen, D.A. Rhoades, R.J. Van Dissen, C. Müller, M.W. Stirling, G.H. McVerry & M.C. Gerstenberger GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New
Time-varying and long-term mean aftershock hazard in Wellington A. Christophersen, D.A. Rhoades, R.J. Van Dissen, C. Müller, M.W. Stirling, G.H. McVerry & M.C. Gerstenberger GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New
Issues for Seismic Hazard Analysis in Regions of Low to Moderate Seismic Activity
 Proceedings of Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 2015, Sydney, Australia Issues for Seismic Hazard Analysis in Regions of Low to Moderate
Proceedings of Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 2015, Sydney, Australia Issues for Seismic Hazard Analysis in Regions of Low to Moderate
Estimation of Regional Seismic Hazard in the Korean Peninsula Using Historical Earthquake Data between A.D. 2 and 1995
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 94, No. 1, pp. 269 284, February 2004 Estimation of Regional Seismic Hazard in the Korean Peninsula Using Historical Earthquake Data between A.D.
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 94, No. 1, pp. 269 284, February 2004 Estimation of Regional Seismic Hazard in the Korean Peninsula Using Historical Earthquake Data between A.D.
SEISMIC HAZARD CHARACTERIZATION AND RISK EVALUATION USING GUMBEL S METHOD OF EXTREMES (G1 AND G3) AND G-R FORMULA FOR IRAQ
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2898 SEISMIC HAZARD CHARACTERIZATION AND RISK EVALUATION USING GUMBEL S METHOD OF EXTREMES (G1 AND G3)
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2898 SEISMIC HAZARD CHARACTERIZATION AND RISK EVALUATION USING GUMBEL S METHOD OF EXTREMES (G1 AND G3)
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis in Thailand and Adjacent Areas by Using Regional Seismic Source Zones
 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis in Thailand and Adjacent Areas by Using Regional Seismic Source Zones Santi Pailoplee 1*, Yuichi Sugiyama 2 and Punya Charusiri 1 1. Earthquake and Tectonic Geology
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis in Thailand and Adjacent Areas by Using Regional Seismic Source Zones Santi Pailoplee 1*, Yuichi Sugiyama 2 and Punya Charusiri 1 1. Earthquake and Tectonic Geology
Earthquake maximum magnitude estimation considering regional seismotectonic parameters
 Southern Cross University epublications@scu 23rd Australasian Conference on the Mechanics of Structures and Materials 2014 Earthquake maximum magnitude estimation considering regional seismotectonic parameters
Southern Cross University epublications@scu 23rd Australasian Conference on the Mechanics of Structures and Materials 2014 Earthquake maximum magnitude estimation considering regional seismotectonic parameters
CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY
 32 CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY 3.1 GENERAL In 1910, the seismological society of America identified the three groups of earthquake problems, the associated ground motions and the effect on structures. Indeed
32 CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY 3.1 GENERAL In 1910, the seismological society of America identified the three groups of earthquake problems, the associated ground motions and the effect on structures. Indeed
A NEW PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MODEL FOR NEW ZEALAND
 A NEW PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MODEL FOR NEW ZEALAND Mark W STIRLING 1 SUMMARY The Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences (GNS) has developed a new seismic hazard model for New Zealand that incorporates
A NEW PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MODEL FOR NEW ZEALAND Mark W STIRLING 1 SUMMARY The Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences (GNS) has developed a new seismic hazard model for New Zealand that incorporates
crustal structure experiment beneath Wairarapa - Wellington area: results from SAHKE
 crustal structure experiment beneath Wairarapa - Wellington area: results from SAHKE Tim Stern and SAHKE team* * VUW, GNS, University of Southern California, University of Tokyo(Japan) SAHKE = Seismic
crustal structure experiment beneath Wairarapa - Wellington area: results from SAHKE Tim Stern and SAHKE team* * VUW, GNS, University of Southern California, University of Tokyo(Japan) SAHKE = Seismic
Observations of the Bowen, Queensland ML Earthquake and its ongoing aftershock sequence. Michael L. Turnbull # and V.F.
 Observations of the Bowen, Queensland ML5.8 2016 Earthquake and its ongoing aftershock sequence. Michael L. Turnbull # and V.F. Dent ## # Corresponding Author: Adjunct Research Fellow, CQUniversity, Rockhampton,
Observations of the Bowen, Queensland ML5.8 2016 Earthquake and its ongoing aftershock sequence. Michael L. Turnbull # and V.F. Dent ## # Corresponding Author: Adjunct Research Fellow, CQUniversity, Rockhampton,
The Impact of the 2010 Darfield (Canterbury) Earthquake on the Geodetic Infrastructure in New Zealand 1
 The Impact of the 2010 Darfield (Canterbury) Earthquake on the Geodetic Infrastructure in New Zealand 1 Graeme BLICK, John BEAVAN, Chris CROOK, Nic DONNELLY Keywords: Darfield Earthquake, control, survey,
The Impact of the 2010 Darfield (Canterbury) Earthquake on the Geodetic Infrastructure in New Zealand 1 Graeme BLICK, John BEAVAN, Chris CROOK, Nic DONNELLY Keywords: Darfield Earthquake, control, survey,
Earthquake Hazard at Newcastle
 Earthquake Hazard at Newcastle Gary Gibson1 and Vicki-Ann Dimas2 1. Corresponding author. Senior seismologist, Environmental Systems & Services, Melbourne, Vic 3121. Adjunct Research Fellow, Monash University.
Earthquake Hazard at Newcastle Gary Gibson1 and Vicki-Ann Dimas2 1. Corresponding author. Senior seismologist, Environmental Systems & Services, Melbourne, Vic 3121. Adjunct Research Fellow, Monash University.
PROBABILISTIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT OF FAULT DISPLACEMENTS
 PROBABILISTIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT OF FAULT DISPLACEMENTS R. Sigbjörnsson, 1 J.Th. Snæbjörnsson, 2 S.M. Higgins, 3 S. Ólafsson 3 and B. Halldórsson 3 ABSTRACT: 1 Professor, EERC, School of Engineering and
PROBABILISTIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT OF FAULT DISPLACEMENTS R. Sigbjörnsson, 1 J.Th. Snæbjörnsson, 2 S.M. Higgins, 3 S. Ólafsson 3 and B. Halldórsson 3 ABSTRACT: 1 Professor, EERC, School of Engineering and
log (N) 2.9<M< <M< <M< <M<4.9 tot in bin [N] = Mid Point M log (N) =
![log (N) 2.9<M< <M< <M< <M<4.9 tot in bin [N] = Mid Point M log (N) = log (N) 2.9<M< <M< <M< <M<4.9 tot in bin [N] = Mid Point M log (N) =](/thumbs/92/109466632.jpg) Solution Set for Assignment Exercise : Gutenberg-Richter relationship: log() = a + b. M A) For a time period between January, 90 to December 3, 998 tot in bin [] = 450 6 57 22 7 5 Mid Point M 3.5 3.65
Solution Set for Assignment Exercise : Gutenberg-Richter relationship: log() = a + b. M A) For a time period between January, 90 to December 3, 998 tot in bin [] = 450 6 57 22 7 5 Mid Point M 3.5 3.65
Aspects of risk assessment in power-law distributed natural hazards
 Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences (2004) 4: 309 313 SRef-ID: 1684-9981/nhess/2004-4-309 European Geosciences Union 2004 Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Aspects of risk assessment in power-law
Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences (2004) 4: 309 313 SRef-ID: 1684-9981/nhess/2004-4-309 European Geosciences Union 2004 Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Aspects of risk assessment in power-law
GPS Strain & Earthquakes Unit 5: 2014 South Napa earthquake GPS strain analysis student exercise
 GPS Strain & Earthquakes Unit 5: 2014 South Napa earthquake GPS strain analysis student exercise Strain Analysis Introduction Name: The earthquake cycle can be viewed as a process of slow strain accumulation
GPS Strain & Earthquakes Unit 5: 2014 South Napa earthquake GPS strain analysis student exercise Strain Analysis Introduction Name: The earthquake cycle can be viewed as a process of slow strain accumulation
Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source
 Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Special Publication 36 Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source by Mendoza, C. 1 and Hartzell S. 2 1 Centro de Geociencias, Universidad
Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Special Publication 36 Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source by Mendoza, C. 1 and Hartzell S. 2 1 Centro de Geociencias, Universidad
Magnitude 7.1 NEAR THE EAST COAST OF HONSHU, JAPAN
 Japan was rattled by a strong aftershock and tsunami warning Thursday night nearly a month after a devastating earthquake and tsunami flattened the northeastern coast. This earthquake can be considered
Japan was rattled by a strong aftershock and tsunami warning Thursday night nearly a month after a devastating earthquake and tsunami flattened the northeastern coast. This earthquake can be considered
Recolouring GSHAP: Challenging the status quo of Australian earthquake hazard
 Recolouring GSHAP: Challenging the status quo of Australian earthquake hazard Trevor Allen, Jonathan Griffin, Dan Clark, Hadi Ghasemi, Mark Leonard & Theodora Volti Australia in the Global Context SCRs
Recolouring GSHAP: Challenging the status quo of Australian earthquake hazard Trevor Allen, Jonathan Griffin, Dan Clark, Hadi Ghasemi, Mark Leonard & Theodora Volti Australia in the Global Context SCRs
5. Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis
 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA) proposed by C.A. Cornell (1968) used to determine the design earthquake for all locations in USA. PSHA gives a relative quantification i of the design earthquake,
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA) proposed by C.A. Cornell (1968) used to determine the design earthquake for all locations in USA. PSHA gives a relative quantification i of the design earthquake,
Chapter 2 Multivariate Statistical Analysis for Seismotectonic Provinces Using Earthquake, Active Fault, and Crustal Structure Datasets
 Chapter 2 Multivariate Statistical Analysis for Seismotectonic Provinces Using Earthquake, Active Fault, and Crustal Structure Datasets Takashi Kumamoto, Masataka Tsukada, and Masatoshi Fujita Abstract
Chapter 2 Multivariate Statistical Analysis for Seismotectonic Provinces Using Earthquake, Active Fault, and Crustal Structure Datasets Takashi Kumamoto, Masataka Tsukada, and Masatoshi Fujita Abstract
Procedure for Probabilistic Tsunami Hazard Assessment for Incomplete and Uncertain Data
 Procedure for Probabilistic Tsunami Hazard Assessment for Incomplete and Uncertain Data A. Kijko (1), A. Smit (1), G.A. Papadopoulos (2), 1. University of Pretoria Natural Hazard Centre University of Pretoria,
Procedure for Probabilistic Tsunami Hazard Assessment for Incomplete and Uncertain Data A. Kijko (1), A. Smit (1), G.A. Papadopoulos (2), 1. University of Pretoria Natural Hazard Centre University of Pretoria,
NUCLEAR POWER PLANT SITE SELECTION
 NUCLEAR POWER PLANT SITE SELECTION ABDELATY B. SALMAN Ex-Chairman Nuclear Materials Authority, Cairo, Egypt I. Introduction The aim of this article is to present the requirements and characteristics for
NUCLEAR POWER PLANT SITE SELECTION ABDELATY B. SALMAN Ex-Chairman Nuclear Materials Authority, Cairo, Egypt I. Introduction The aim of this article is to present the requirements and characteristics for
An earthquake is the result of a sudden displacement across a fault that releases stresses that have accumulated in the crust of the earth.
 An earthquake is the result of a sudden displacement across a fault that releases stresses that have accumulated in the crust of the earth. Measuring an Earthquake s Size Magnitude and Moment Each can
An earthquake is the result of a sudden displacement across a fault that releases stresses that have accumulated in the crust of the earth. Measuring an Earthquake s Size Magnitude and Moment Each can
On May 4, 2001, central Arkansas experienced an M=4.4 earthquake followed by a
 1. Introduction On May 4, 2001, central Arkansas experienced an M=4.4 earthquake followed by a surprisingly large number of small earthquakes. We recorded about 2500 above the ambient noise level on a
1. Introduction On May 4, 2001, central Arkansas experienced an M=4.4 earthquake followed by a surprisingly large number of small earthquakes. We recorded about 2500 above the ambient noise level on a
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis of Nepal considering Uniform Density Model
 Proceedings of IOE Graduate Conference, 2016 pp. 115 122 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis of Nepal considering Uniform Density Model Sunita Ghimire 1, Hari Ram Parajuli 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering,
Proceedings of IOE Graduate Conference, 2016 pp. 115 122 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis of Nepal considering Uniform Density Model Sunita Ghimire 1, Hari Ram Parajuli 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering,
Indian Ocean Tsunami Warning System: Example from the 12 th September 2007 Tsunami
 Indian Ocean Tsunami Warning System: Example from the 12 th September 2007 Tsunami Charitha Pattiaratchi 1 Professor of Coastal Oceanography, The University of Western Australia Email: chari.pattiaratchi@uwa.edu.au
Indian Ocean Tsunami Warning System: Example from the 12 th September 2007 Tsunami Charitha Pattiaratchi 1 Professor of Coastal Oceanography, The University of Western Australia Email: chari.pattiaratchi@uwa.edu.au
SEISMIC INPUT FOR CHENNAI USING ADAPTIVE KERNEL DENSITY ESTIMATION TECHNIQUE
 SEISMIC INPUT FOR CHENNAI USING ADAPTIVE KERNEL DENSITY ESTIMATION TECHNIQUE G. R. Dodagoudar Associate Professor, Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai - 600036, goudar@iitm.ac.in P. Ragunathan
SEISMIC INPUT FOR CHENNAI USING ADAPTIVE KERNEL DENSITY ESTIMATION TECHNIQUE G. R. Dodagoudar Associate Professor, Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai - 600036, goudar@iitm.ac.in P. Ragunathan
On the validity of time-predictable model for earthquake generation in north-east India
 Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet. Sci.), Vol. 101, No. 4, December 1992, pp. 361-368. 9 Printed in India. On the validity of time-predictable model for earthquake generation in north-east India V
Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet. Sci.), Vol. 101, No. 4, December 1992, pp. 361-368. 9 Printed in India. On the validity of time-predictable model for earthquake generation in north-east India V
Characteristics of seismic activity before Chile M W 8.8 earthquake in 2010
 Earthq Sci (2010)23: 333 341 333 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0730-x Characteristics of seismic activity before Chile M W 8.8 earthquake in 2010 Yan Xue 1,2, Jie Liu 2 and Gang Li 2 1 Institute of Geophysics,
Earthq Sci (2010)23: 333 341 333 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0730-x Characteristics of seismic activity before Chile M W 8.8 earthquake in 2010 Yan Xue 1,2, Jie Liu 2 and Gang Li 2 1 Institute of Geophysics,
Liquefaction assessments of tailings facilities in low-seismic areas
 Page 1 Liquefaction assessments of tailings facilities in low-seismic areas Holly Rourke SRK Consulting, Perth, WA, Australia Caroline Holmes SRK Consulting, Perth, WA, Australia This paper was first presented
Page 1 Liquefaction assessments of tailings facilities in low-seismic areas Holly Rourke SRK Consulting, Perth, WA, Australia Caroline Holmes SRK Consulting, Perth, WA, Australia This paper was first presented
HARMONIZATION OF SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS FOR THE WESTERN BALKAN COUNTRIES : Overview of main BSHAP results
 Zagreb, Croatia Hotel Sheraton 12-13 May 2011 NATO SfP Project no. 983054 HARMONIZATION OF SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS FOR THE WESTERN BALKAN COUNTRIES : Overview of main BSHAP results Prof. Branislav Glavatović,
Zagreb, Croatia Hotel Sheraton 12-13 May 2011 NATO SfP Project no. 983054 HARMONIZATION OF SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS FOR THE WESTERN BALKAN COUNTRIES : Overview of main BSHAP results Prof. Branislav Glavatović,
Aftershock From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 Page 1 of 5 Aftershock From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia An aftershock is a smaller earthquake that occurs after a previous large earthquake, in the same area of the main shock. If an aftershock is
Page 1 of 5 Aftershock From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia An aftershock is a smaller earthquake that occurs after a previous large earthquake, in the same area of the main shock. If an aftershock is
Sensitivity of Liquefaction Triggering Analysis to Earthquake Magnitude
 Australian Earthquake Engineering Society 2013 Conference, Nov 15-17, Hobart, Tasmania Sensitivity of Liquefaction Triggering Analysis to Earthquake Magnitude Dr Timothy I Mote 1 and Minly M. L. So 2 1.
Australian Earthquake Engineering Society 2013 Conference, Nov 15-17, Hobart, Tasmania Sensitivity of Liquefaction Triggering Analysis to Earthquake Magnitude Dr Timothy I Mote 1 and Minly M. L. So 2 1.
EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN
 EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN Dr Ilaria Mosca 1 and Dr Natalya Silacheva 2 1 British Geological Survey, Edinburgh (UK) imosca@nerc.ac.uk 2 Institute of Seismology, Almaty (Kazakhstan) silacheva_nat@mail.ru
EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN Dr Ilaria Mosca 1 and Dr Natalya Silacheva 2 1 British Geological Survey, Edinburgh (UK) imosca@nerc.ac.uk 2 Institute of Seismology, Almaty (Kazakhstan) silacheva_nat@mail.ru
Quantifying the effect of declustering on probabilistic seismic hazard
 Proceedings of the Ninth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Society 14-16 April, 2011, Auckland, New Zealand Quantifying the effect of declustering on probabilistic
Proceedings of the Ninth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Society 14-16 April, 2011, Auckland, New Zealand Quantifying the effect of declustering on probabilistic
Geospatial application in Kiribati
 Geospatial application in Kiribati ICC-21 ST RESAP (9 TH TO 13 TH OCTOBER, 2017) BANGKOK, THAILAND Outline Kiribati Profile Natural disasters in Kiribati Achievements Challenges/Issues Ways forward 1 Kiribati
Geospatial application in Kiribati ICC-21 ST RESAP (9 TH TO 13 TH OCTOBER, 2017) BANGKOK, THAILAND Outline Kiribati Profile Natural disasters in Kiribati Achievements Challenges/Issues Ways forward 1 Kiribati
Definitions. Seismic Risk, R (Σεισμική διακινδύνευση) = risk of damage of a structure
 SEISMIC HAZARD Definitions Seismic Risk, R (Σεισμική διακινδύνευση) = risk of damage of a structure Seismic Hazard, Η (Σεισμικός κίνδυνος) = expected intensity of ground motion at a site Vulnerability,
SEISMIC HAZARD Definitions Seismic Risk, R (Σεισμική διακινδύνευση) = risk of damage of a structure Seismic Hazard, Η (Σεισμικός κίνδυνος) = expected intensity of ground motion at a site Vulnerability,
Uniform Hazard Spectrum(UHS) for performance based seismic design
 Uniform Hazard Spectrum(UHS) for performance based seismic design *Jun-Kyoung Kim 1), Soung-Hoon Wee 2) and Seong-Hwa Yoo 2) 1) Department of Fire Protection and Disaster Prevention, Semyoung University,
Uniform Hazard Spectrum(UHS) for performance based seismic design *Jun-Kyoung Kim 1), Soung-Hoon Wee 2) and Seong-Hwa Yoo 2) 1) Department of Fire Protection and Disaster Prevention, Semyoung University,
MESF CYBER JOURNAL OF GEOSCIENCE _DECEMBER 2003/
 MESF CYBER JOURNAL OF GEOSCIENCE _DECEMBER 2003/ www.meseisforum.net A PAPER PRESENTED TO THE EURO-MEDITERRANEAN SEMINAR ON NATURAL, ENVIRONMENTAL AND TECHNOLOGICAL DISASTERS- HOURTI BOUMEDIAN UNIVERSITY
MESF CYBER JOURNAL OF GEOSCIENCE _DECEMBER 2003/ www.meseisforum.net A PAPER PRESENTED TO THE EURO-MEDITERRANEAN SEMINAR ON NATURAL, ENVIRONMENTAL AND TECHNOLOGICAL DISASTERS- HOURTI BOUMEDIAN UNIVERSITY
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand
 The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
Average response spectra from some Australian earthquakes
 Average response spectra from some Australian earthquakes T.I. Allen 1, G. Gibson 1,2 & J.P. Cull 1 1 School of Geosciences, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia 2 Seismology Research Centre, Environmental
Average response spectra from some Australian earthquakes T.I. Allen 1, G. Gibson 1,2 & J.P. Cull 1 1 School of Geosciences, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia 2 Seismology Research Centre, Environmental
Seismic Activity near the Sunda and Andaman Trenches in the Sumatra Subduction Zone
 IJMS 2017 vol. 4 (2): 49-54 International Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies (IJMS) Volume 4, Issue 2, 2017 DOI: http://doi.org/10.4038/ijms.v4i2.22 Seismic Activity near the Sunda and Andaman Trenches
IJMS 2017 vol. 4 (2): 49-54 International Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies (IJMS) Volume 4, Issue 2, 2017 DOI: http://doi.org/10.4038/ijms.v4i2.22 Seismic Activity near the Sunda and Andaman Trenches
Assessment of Seismic Design Motions in Areas of Low Seismicity: Comparing Australia and New Zealand
 6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 2015 Christchurch, New Zealand Assessment of Seismic Design Motions in Areas of Low Seismicity: Comparing Australia and
6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 2015 Christchurch, New Zealand Assessment of Seismic Design Motions in Areas of Low Seismicity: Comparing Australia and
A SEISMIC SOURCE ZONE MODEL BASED ON NEOTECTONICS DATA. Dan Clark
 A SEISMIC SOURCE ZONE MODEL BASED ON NEOTECTONICS DATA. Dan Clark 1. INTRODUCTION Australia s rich neotectonic record provides an opportunity to understand the characteristics of intraplate deformation,
A SEISMIC SOURCE ZONE MODEL BASED ON NEOTECTONICS DATA. Dan Clark 1. INTRODUCTION Australia s rich neotectonic record provides an opportunity to understand the characteristics of intraplate deformation,
Seismic Quiescence before the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan, M w 7.6 Earthquake
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 96, No. 1, pp. 321 327, February 2006, doi: 10.1785/0120050069 Seismic Quiescence before the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan, M w 7.6 Earthquake by Yih-Min Wu
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 96, No. 1, pp. 321 327, February 2006, doi: 10.1785/0120050069 Seismic Quiescence before the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan, M w 7.6 Earthquake by Yih-Min Wu
EARTHQUAKE FORECASTING IN BANGLADESH AND ITS SURROUNDING REGIONS
 EARTHQUAKE FORECASTING IN BANGLADESH AND ITS SURROUNDING REGIONS B. K. Chakravorti Department of Physics, Begum Rokeya University, Rangpur, Bangladesh M. Kundar Department of Physics, Jagannath University,
EARTHQUAKE FORECASTING IN BANGLADESH AND ITS SURROUNDING REGIONS B. K. Chakravorti Department of Physics, Begum Rokeya University, Rangpur, Bangladesh M. Kundar Department of Physics, Jagannath University,
Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis (why do we live here?) Tectonic plates. Tectonic plates: Juan de Fuca. Volcanism the past 37 million years
 Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis (why do we live here?) Tectonic plates Tectonic plates: Juan de Fuca Volcanism the past 37 million years Tectonic plates: Juan de Fuca Volcanism the past 37 million
Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis (why do we live here?) Tectonic plates Tectonic plates: Juan de Fuca Volcanism the past 37 million years Tectonic plates: Juan de Fuca Volcanism the past 37 million
SOURCE PROCESS OF THE 2003 PUERTO PLATA EARTHQUAKE USING TELESEISMIC DATA AND STRONG GROUND MOTION SIMULATION
 Synopses of Master Papers Bulletin of IISEE, 47, 19-24, 2013 SOURCE PROCESS OF THE 2003 PUERTO PLATA EARTHQUAKE USING TELESEISMIC DATA AND STRONG GROUND MOTION SIMULATION Fabricio Moquete Everth* Supervisor:
Synopses of Master Papers Bulletin of IISEE, 47, 19-24, 2013 SOURCE PROCESS OF THE 2003 PUERTO PLATA EARTHQUAKE USING TELESEISMIC DATA AND STRONG GROUND MOTION SIMULATION Fabricio Moquete Everth* Supervisor:
Contemporary Tectonics and Seismicity of the Teton and Southern Yellowstone Fault Systems- Phase I
 University of Wyoming National Park Service Research Center Annual Report Volume 4 4th Annual Report, 1980 Article 16 1-1-1980 Contemporary Tectonics and Seismicity of the Teton and Southern Yellowstone
University of Wyoming National Park Service Research Center Annual Report Volume 4 4th Annual Report, 1980 Article 16 1-1-1980 Contemporary Tectonics and Seismicity of the Teton and Southern Yellowstone
Unraveling the Mysteries of Seismicity in Oklahoma. A Story Map
 Unraveling the Mysteries of Seismicity in Oklahoma A Story Map Background Why create a story map? Visualization of various types of data (graphics, text, symbols, etc.) within a geographical context to
Unraveling the Mysteries of Seismicity in Oklahoma A Story Map Background Why create a story map? Visualization of various types of data (graphics, text, symbols, etc.) within a geographical context to
EARTHQUAKE SOURCE PARAMETERS FOR SUBDUCTION ZONE EVENTS CAUSING TSUNAMIS IN AND AROUND THE PHILIPPINES
 EARTHQUAKE SOURCE PARAMETERS FOR SUBDUCTION ZONE EVENTS CAUSING TSUNAMIS IN AND AROUND THE PHILIPPINES Joan Cruz SALCEDO Supervisor: Tatsuhiko HARA MEE09186 ABSTRACT We have made a set of earthquake source
EARTHQUAKE SOURCE PARAMETERS FOR SUBDUCTION ZONE EVENTS CAUSING TSUNAMIS IN AND AROUND THE PHILIPPINES Joan Cruz SALCEDO Supervisor: Tatsuhiko HARA MEE09186 ABSTRACT We have made a set of earthquake source
Sendai Earthquake NE Japan March 11, Some explanatory slides Bob Stern, Dave Scholl, others updated March
 Sendai Earthquake NE Japan March 11, 2011 Some explanatory slides Bob Stern, Dave Scholl, others updated March 14 2011 Earth has 11 large plates and many more smaller ones. Plates are 100-200 km thick
Sendai Earthquake NE Japan March 11, 2011 Some explanatory slides Bob Stern, Dave Scholl, others updated March 14 2011 Earth has 11 large plates and many more smaller ones. Plates are 100-200 km thick
Regional Workshop on Essential Knowledge of Site Evaluation Report for Nuclear Power Plants.
 Regional Workshop on Essential Knowledge of Site Evaluation Report for Nuclear Power Plants. Development of seismotectonic models Ramon Secanell Kuala Lumpur, 26-30 August 2013 Overview of Presentation
Regional Workshop on Essential Knowledge of Site Evaluation Report for Nuclear Power Plants. Development of seismotectonic models Ramon Secanell Kuala Lumpur, 26-30 August 2013 Overview of Presentation
Magnitude 7.6 & 7.4 SOLOMON ISLANDS
 A magnitude 7.6 earthquake struck near the Solomon Islands on Sunday morning local time; there were no immediate reports of damage. The earthquake was centered 100 km (60 miles) south of Kira Kira, a town
A magnitude 7.6 earthquake struck near the Solomon Islands on Sunday morning local time; there were no immediate reports of damage. The earthquake was centered 100 km (60 miles) south of Kira Kira, a town
Susitna-Watana Hydroelectric Project (FERC No ) Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Study Study Plan Section 16.6
 (FERC No. 14241) Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Study Study Plan Section 16.6 Initial Study Report Part A: Sections 1-6, 8-9 Prepared for Prepared by MWH / Fugro June 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction...
(FERC No. 14241) Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Study Study Plan Section 16.6 Initial Study Report Part A: Sections 1-6, 8-9 Prepared for Prepared by MWH / Fugro June 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction...
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NGEO177 The Long Precursory Phase of Most Large Interplate Earthquakes Supplementary Information Supplementary Methods 1. Data and Classification We select the earthquakes
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NGEO177 The Long Precursory Phase of Most Large Interplate Earthquakes Supplementary Information Supplementary Methods 1. Data and Classification We select the earthquakes
Tsunami Response and the Enhance PTWC Alerts
 Tsunami Response and the Enhance PTWC Alerts Ken Gledhill GeoNet Project Director Chair, Intergovernmental Coordination Group, Pacific Tsunami Warning and Mitigation System (PTWS) Overview 1. Procedures
Tsunami Response and the Enhance PTWC Alerts Ken Gledhill GeoNet Project Director Chair, Intergovernmental Coordination Group, Pacific Tsunami Warning and Mitigation System (PTWS) Overview 1. Procedures
Oklahoma Earthquakes: Trends and Underlying Causes. Jeremy Boak, Oklahoma Geological Survey October 21, 2016
 Oklahoma Earthquakes: Trends and Underlying Causes Jeremy Boak, Oklahoma Geological Survey jboak@ou.edu October 21, 2016 1 The Oklahoma Geological Survey is a state agency for research and public service
Oklahoma Earthquakes: Trends and Underlying Causes Jeremy Boak, Oklahoma Geological Survey jboak@ou.edu October 21, 2016 1 The Oklahoma Geological Survey is a state agency for research and public service
4D stress sensitivity of dry rock frame moduli: constraints from geomechanical integration
 Title 4D stress sensitivity of dry rock frame moduli: constraints from geomechanical integration Authors Bloomer, D., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Reynolds, S., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Pavlova, M., Origin
Title 4D stress sensitivity of dry rock frame moduli: constraints from geomechanical integration Authors Bloomer, D., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Reynolds, S., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Pavlova, M., Origin
Seismic source modeling by clustering earthquakes and predicting earthquake magnitudes
 Seismic source modeling by clustering earthquakes and predicting earthquake magnitudes Mahdi Hashemi, Hassan A. Karimi Geoinformatics Laboratory, School of Information Sciences, University of Pittsburgh,
Seismic source modeling by clustering earthquakes and predicting earthquake magnitudes Mahdi Hashemi, Hassan A. Karimi Geoinformatics Laboratory, School of Information Sciences, University of Pittsburgh,
Thanassoulas 1, C., Klentos 2, V.
 Seismic potential map of Greece calculated for the years 2005 and 2010. Its correlation to the large (Ms>=6.0R) seismic events of the 2000 2009 period. Thanassoulas 1, C., Klentos 2, V. 1. Retired from
Seismic potential map of Greece calculated for the years 2005 and 2010. Its correlation to the large (Ms>=6.0R) seismic events of the 2000 2009 period. Thanassoulas 1, C., Klentos 2, V. 1. Retired from
Seismic Monitoring of Mine Environments
 Mapping and Monitoring the Mine Environment Paper 123 Explor97 Master Page Explor97 Contents Previous Paper G O T O Author Index Section Contents Next Paper Seismic Monitoring of Mine Environments Urbancic,
Mapping and Monitoring the Mine Environment Paper 123 Explor97 Master Page Explor97 Contents Previous Paper G O T O Author Index Section Contents Next Paper Seismic Monitoring of Mine Environments Urbancic,
Preparation of a Comprehensive Earthquake Catalog for Northeast India and its completeness analysis
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 2, Issue 6 Ver. I (Nov-Dec. 2014), PP 22-26 Preparation of a Comprehensive Earthquake Catalog for
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 2, Issue 6 Ver. I (Nov-Dec. 2014), PP 22-26 Preparation of a Comprehensive Earthquake Catalog for
Natural Hazards Mitigation in Iceland
 Natural Hazards Mitigation in Iceland With special emphasis on earthquake risk Júlíus Sólnes Professor of civil and environmental engineering Dept. of engineering, University of Iceland Cambridge, 19th
Natural Hazards Mitigation in Iceland With special emphasis on earthquake risk Júlíus Sólnes Professor of civil and environmental engineering Dept. of engineering, University of Iceland Cambridge, 19th
Earthquakes. Earthquake Magnitudes 10/1/2013. Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena
 Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Models for Seismic Hazard Assessment in Australia
 Models for Seismic Hazard Assessment in Australia Kevin McCue and Cvetan Sinadinovski Australian Geological Survey Organisation, GPO Box 378 Canberra, Australia NZSEE 2001 Conference 1 ABSTRACT: With a
Models for Seismic Hazard Assessment in Australia Kevin McCue and Cvetan Sinadinovski Australian Geological Survey Organisation, GPO Box 378 Canberra, Australia NZSEE 2001 Conference 1 ABSTRACT: With a
GROUND SURFACE VISUALIZATION USING RED RELIEF IMAGE MAP FOR A VARIETY OF MAP SCALES
 GROUND SURFACE VISUALIZATION USING RED RELIEF IMAGE MAP FOR A VARIETY OF MAP SCALES T. Chiba a, B. Hasi a * a Asia Air Survey Co., Ltd., Kawasaki, Japan (has.baator, ta.chiba,)@ajiko.co.jp Commission II,
GROUND SURFACE VISUALIZATION USING RED RELIEF IMAGE MAP FOR A VARIETY OF MAP SCALES T. Chiba a, B. Hasi a * a Asia Air Survey Co., Ltd., Kawasaki, Japan (has.baator, ta.chiba,)@ajiko.co.jp Commission II,
KNOWING WHAT WE DON T KNOW ABOUT AUSTRALIA S EARTHQUAKES
 KNOWING WHAT WE DON T KNOW ABOUT AUSTRALIA S EARTHQUAKES Kevin McCue 1 and Cvetan Sinadinovski 2 1 Corresponding Author, Adjunct Professor, CQU mccue.kevin@gmail.com 2 Advanced Research Centre, Saudi Aramco,
KNOWING WHAT WE DON T KNOW ABOUT AUSTRALIA S EARTHQUAKES Kevin McCue 1 and Cvetan Sinadinovski 2 1 Corresponding Author, Adjunct Professor, CQU mccue.kevin@gmail.com 2 Advanced Research Centre, Saudi Aramco,
Geology of the Batemans Bay region. Geological mapping
 1 During the 1960 s, 1970 s and 1980 s there was a national effort by the Commonwealth Government Bureau of Mineral Resources, Geology and Geophysics (BMR) and the Mining Departments in State and Territory
1 During the 1960 s, 1970 s and 1980 s there was a national effort by the Commonwealth Government Bureau of Mineral Resources, Geology and Geophysics (BMR) and the Mining Departments in State and Territory
Climate Change in the Pacific: Scientific Assessment and New Research Volume 1: Regional Overview
 Climate Change in the Pacific: Scientific Assessment and New Research Volume 1: Regional Overview Australian Bureau of Meteorology and Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO)
Climate Change in the Pacific: Scientific Assessment and New Research Volume 1: Regional Overview Australian Bureau of Meteorology and Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO)
Fault Length and Direction of Rupture Propagation for the 1993 Kushiro-Oki Earthquake as Derived from Strong Motion Duration
 Letter J. Phys. Earth, 41, 319-325, 1993 Fault Length and Direction of Rupture Propagation for the 1993 Kushiro-Oki Earthquake as Derived from Strong Motion Duration Yasuo Izutani Faculty of Engineering,
Letter J. Phys. Earth, 41, 319-325, 1993 Fault Length and Direction of Rupture Propagation for the 1993 Kushiro-Oki Earthquake as Derived from Strong Motion Duration Yasuo Izutani Faculty of Engineering,
Seismic Characteristics and Energy Release of Aftershock Sequences of Two Giant Sumatran Earthquakes of 2004 and 2005
 P-168 Seismic Characteristics and Energy Release of Aftershock Sequences of Two Giant Sumatran Earthquakes of 004 and 005 R. K. Jaiswal*, Harish Naswa and Anoop Singh Oil and Natural Gas Corporation, Vadodara
P-168 Seismic Characteristics and Energy Release of Aftershock Sequences of Two Giant Sumatran Earthquakes of 004 and 005 R. K. Jaiswal*, Harish Naswa and Anoop Singh Oil and Natural Gas Corporation, Vadodara
