Delineate Location of the Last Earthquake Case Study NW of Iran
|
|
|
- Ami Clarke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Current Research in Geosciences Original Research Paper Delineate Location of the Last Earthquake Case Study NW of Iran Hadi Jarahi Department of Geosciences, North Tehran Branch, Islamic Azad University (IAU), Tehran, Iran Article history Received: Revised: Accepted: Abstract: The earthquake hazard is most important title in seismic design of buildings. One of ways to know this hazard is to know where the earthquake boundary is. Moreover, understanding of the future earthquakes location, can help to modify the seismic hazard maps. The b- values, is the effective parameter on future earthquake positioning. This study was conducted to variations of b-values in the Gutenberg-Richter relation were examined for tectonic earthquakes in the NW of Iran. Earthquake dates for this area are given from the ISC, NEIC and Engdahl catalogues for a period of 735 to 2017 were used for analysis. We separated earthquake catalogue in part 1(before 2000) and Part 2 (all events). Delineated zone from b-value distribution map in catalogue Part 1, showed us five seismic gap region (area A to E) with a potential for the occurrence of earthquakes in the near future. The results of Part 2 showed that in areas A, B and C the future earthquake had happened. Therefore, we are waiting for last seismic events in the D and E areas. This seismic gaps is a potential threat to the surrounding regions, such as the Nakhichevan and Rasht city. Keywords: B-Value, Earthquake, Potential Area, NW of Iran Introduction Main earthquakes of active fault (Berberian, 2014) of NW Iran such as N-Tabriz (Karimzadeh et al., 2013), Chaldiran (Jackson and McKenzie, 1984), Salmas (Berberian and Tchalenko, 1976) and other active faultshas widely opened up a discourse on the study of natural disasters in NW Iran earthquakes in particular (Masson et al., 2006). Lots of seismological papers tell us about the probability and prediction of an earthquake that will happen (Siame et al., 2002; Solaymani Azad, 2009; Talebian and Jackson, 2002), but the phenomenon still remains a problem and is more often wrong than right. Several research has been done on the b-value as a likely sign of a major earthquake (Zaho and Wu, 2008; Vasheghani-Farahani, 2014; Sadeghian, 2010; Nuannin, 2006). This paper focused on the b-value in the NW of Iran region where there is a history of large earthquakes occurred. The historical earthquake catalogue from the Ambraseys and Jackson (1998) and Berberian (1994; 2014) also showed that the social disaster followed these large events. In a range of last millennium, there have been number events of large earthquake in this region (Berberian, 2014). Base on Kanamori (1981) and Wyss (1973), the low value of b show the high stress areas. This is also implying very much due to fact that the great earthquake occurrences in the area are very rare even though in other regions (high b-value) have been hit by large earthquakes recently. As a step to look for other potential spots, we calculated the b-value to delineate the possible areas for large earthquakes in the future. Seismicity and Tectonic Setting The active deformation of the Iranian plateau, as a tectonically active part of the Alpine-Himalayan tectonic belt, is controlled by the Arabian-Eurasian convergence. Beneath central Iran plate, Arabian plate subduction to northwestern part of Iran. The consequences of this phenomenon manifest itself in the high number of seismicity and the existence of 2017 Hadi Jarahi. This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 3.0 license.
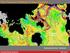
2 active volcanoes such as Sahand and Sabalan (Berberian, 1983; Berberian and King, 1981; Berberian et al., 1982). Shortening is accommodated by distribution faulting and it makes regions with different seismotectonic features and active faults. Fault plane solutions of earthquakes in the study region indicate both strike-slip and thrust faulting, though the strike-slip faulting is prominent (Sella et al., 2002). Based on the recent Global Positioning System (GPS) studies, the rate of north-south shortening throughout the NW of Iran is 13±2 mmyr 1, (Copley and Jackson, 2006) and the right-lateral shear of the overall belt occurs at a rate of 8±2 mmyr 1 (Vernant et al., 2004). Recent GPS data taken from a station south of the N-Tabriz fault in northern Central Iran, in the center of the study area, indicates northward and eastward velocities with a rate of 11.2 and 3.2 mmyr 1, respectively (Vernant et al., 2004; Masson et al., 2006). Numbers of historical earthquake have been happening in this part of the Iranian plate (Ambraseys and Melville, 1982; Berberian, 1994) by reactivate of active faults (Table 1 and Fig. 1). In 735 to 2017, record of more than 17 major earthquakes (over 6.5) shown that this area has a potential for large events. The Frequency and magnitude equation (Gutenberg and Richter, 1944) are very commonly used in the modeling of earthquake hazard, mostly related to the earthquake precursors and probabilistic seismic hazard Assessments. We use the catalogue of earthquakes from the year to be applied in the equation along NW of Iran, from 43 to 50 longitudes and 35 to 40 latitudes. An earthquake catalogue has been declustered and resulting 2450 independent earthquake events with magnitude above 3.0. We made tow kind on earthquake catalogue part 1 start from 735 to 2000 (As controlled variable) and Part 2 from 735 to All of the calculations were done for both of catalogues. We used the device ZMAP (Wyss et al., 2001) to show the result of calculation of cumulative number of earthquake and Frequency-Magnitude Distribution (FMD) (Fig. 2 and 3). From that graphic solution we ve got Mc = 4.7, b-value = , a- value = 5.94 for Part 1 and Mc = 3.0, b-value = , a-value = 3.52 for Part 2. Fig. 1. Seismotectonic Map of NW Iran. (Major earthquake description in Table 1) 8
3 Fig. 2. Cumulative number of earthquakes. The left charts are related to Part 1 and the right for Part 2 Table 1. List of main events (M>6.5) at NW of Iran No. Date Epicenter Magnitude Year month day Lat. Lon. I ommi Ms Mw Ref Ambraseys and Melville (1982) IX Berberian (1994) VIII Berberian (1994) VIII 6.6 Berberian (1994) VIII Berberian (1994) VIII Berberian (1994) Ambraseys and Melville (1982) VIII Berberian (1994) VII 6.5 Ambraseys and Melville (1982) Ambraseys and Melville (1982) VII 6.6 Ambraseys and Melville (1982) Ambraseys and Melville (1982) IX Berberian (1994) IX Berberian (1994) IX Berberian (1994) VIII Berberian (1994) VII 6.5 Ambraseys and Melville (1982) IX Berberian and Tchalenko (1976) IX Priestley et al. (1994) IX Berberian (1979) IX Berberian (2014; Zare et al., 2014) VIII Zare et al. (2014) VIII Walker et al. (2005) Talebi et al. (2015) VIII Berberian (2014) Variation of b-value Spatial Variation of B-Value To delineate the spatial variations of b-value, we divided the study area into grids, then b-value was calculated for each grid for constant radius and number of events. In this study, these parameters are determined from the area with a radius of 600 km or a minimum of 40 earthquakes with processing grid. From the b-value distribution map resulted, we find five areas named A, B, C, D and E (Fig. 4). These areas have different variation of b- value range (Table 2). As it is shown, in Fig. 4 (left 9
4 map) all of five areas have low values of b. The range of variety is 0.8 to 1.1 and all selected areas are matched to seismic sources that have potential for future earthquake. The right map in Fig. 4 showed the b-value distribution for complete earthquake catalogue. As it stands, in areas A, B and C the future earthquake happened. As it mentioned before, we separation earthquake catalogue to tow part because we need controlled variable. Therefore, it s expected that the future earthquake will happen on D and E areas. Fig. 3. Frequency- Magnitude Distribution (FMD) from earthquake catalogue. The red thin line represented Gutenberg- Richter equation, log N = a-bm. The left charts are related to Part1 and the right for Part2 10
5 A E B D C E A B D C Fig. 4. Spatial variation of b-values on the NW of Iran, five area are shown by dash rings. The left charts are related to Part 1 and the right for Part 2 11
6 Table 2. The variation of b-value in selected areas B-value Selected area Matched seismic source Part 1 Part 2 Earthquake event A Van lake fault Happened B Varzeghan fault Happened C Manjil Fault Happened D Sangavar and Talesh Faults Waiting for last E Nakhichevan Waiting for last Conclusion The concept of b-value variation has been applied properly to simulate the b-value in the NW of Iran. The b-value variation in this region is calculated based on multiple source catalogue from 735 until 2017 with a range of magnitudes from 3.0 to 7.7: The b-value maps showed that this parameter take increase depending on time Delineated zone from b-value distribution map in catalogue Part 1, showed five seismic gap regions (area A to E) with a potential for the occurrence of earthquakes in the near future. The results of Part 2 showed that in areas A, B and C the future earthquake had happened Therefore, we are waiting for last seismic events in the D and E areas. This seismic gaps is a potential threat to the surrounding regions, such as the Nakhichevan and Rasht city. Acknowledgement The author expresses his appreciation of the Miss Mahnaz Aghababaei to his valuable helps in this research. Ethics This article is original and contains unpublished materials. The corresponding author confirms that all of the other authors have read and approved the manuscript and there are no ethical issues involved. Data and Resources Data retrieved from theinternational Seismological Centre (ISC), On-line Bulletin, Internatl. Seismol. Cent., Thatcham, United Kingdom, References Ambraseys, N.N. and C.P. Melville, A History of Persian Earthquakes. 1st Edn., Cambridge University Press, New York, ISBN-10: X, pp: 236. Ambraseys, N.N. and J.A. Jackson, Faulting associated with historical and recent earthquakes in the eastern Mediterranean region. Geophys. J. Int., 133: DOI: /j X x Berberian, M. and J.S. Tchalenko, Field Study and Documentation of the 1930 Salmas (Shahpur- Azarbaidjan) Earthquake. In: Contribution to the Seismotectonics of Iran, Berberian, M. (Ed.), Geol. Surv. Iran, pp: Berberian, M., Evaluation of the instrumental and relocated epicentres of Iranian earthquakes. Geophys. J. Roy. Astr. Soc. London, 58: DOI: /j X.1979.tb04798.x Berberian, M. and G.C.P. King, Towards a paleogeography and tectonic evolution of Iran. Canad. J. Earth Sci., 18: DOI: /e Berberian, F., I.D. Muir, R.J. Pankhurst and M. Berberian, Late cretaceous and early Miocene Andeantype plutonic activity in northern Makran and Central Iran. Geol. Society, 139: DOI: /gsjgs Berberian, M., The Southern Caspian: A compressional depression floored by a trapped, modified oceanic crust. Canad. J. Earth Sci., 20: DOI: /e Berberian, M., A Natural Hazards and the First Earthquake Catalogue of Iran. Volume 1: Historical Hazards in Iran Prior to A UNESCO/IIEES Publication during UN/IDNDR. IIEES, Tehran. Berberian, M., Earthquakes and Coseismic Surface Faulting on the Iranian Plateau; A Historical, Social and Physical Approach. 1st Edn., Elsevier, ISBN-10: , pp; 770. Copley, A. and J. Jaekson, Active tectonics of the Turkish-Iranian plateau. Tectonics, 25: TC6006-TC6006. DOI: /2005TC Gutenberg, B. and C. Richter, Frequency of earthquakes in California. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am., 34: Jackson, J.A. and D.P. McKenzie, Active tectonics of the Alpine-Himalayan belt between Western Turkey and Pakistan. Geophys. J. Int., 77: DOI: /j X.1984.tb01931.x 12
7 Karimzadeh, S., Z. Cakir, B. Osmanoğlu, G. Schmalzle and M. Miyajima et al., Interseismic strain accumulation across the North Tabriz Fault (NW Iran) deduced from InSAR time series. J. Geodynam., 66: DOI: /j.jog Kanamori, H The Nature of Seismic Patterns before Large Earthquakes. In: Earthquake Prediction: An International Review, Simpson, D.W. and P.G. Richards (Eds.), Maurice Ewing Series, AGU, Washington D.C., pp: Masson, F., Y. Djamour, S. van Gorp, J. Chery and M. Tatar et al., Extension in NW Iran driven by the motion of the south Caspian Basin. Earth planet. Sci. Lett., 252: DOI: /j.epsl Nuannin, P., The potential of b-value variations as earthquake precursors for small and large events. Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Science and Technology. Priestley, K., C. Baker and J. Jackson, Implications of earthquake focal mechanism data for the active tectonics of the south Caspian Basin and surrounding regions. Geophys. J. Int., 118: DOI: /j X.1994.tb04679.x Sadeghian, R., The effects of zoning methods on forecasting of the next earthquake occurrences, according to semi-markov models. Annals Geophys., 53: DOI: /ag-4558 Sella, G.F., T.H. Dixon and A. Mao, REVEL: A model for recent plate velocities from space geodesy. J. Geophys. Res., 107: DOI: /2000JB Siame, L.L., O. Bellier, M. Sebrier, D.L. Bourlès and P. Leturmy et al., Seismic hazard reappraisal from combined structural geology, geomorphology and cosmic ray exposure dating analyses: The Eastern Precordillera thrust system (NW Argentina). Geophys. J. Int., 150: DOI: /j X x Solaymani Azad, S., Evaluation de l aleasismique pour les villes de Teheran, Tabriz etzandjandans le NW de l Iran. PhD. Theses, Approchemorphotectnique et aleosismologique [Seismic Hazard Assessment for Tehran, Tabriz and Zandjan Cities (NW Iran) Based on Morphotectonics and Palaeoseismology]. de l Universite de Montpellier. Talebi, M., M. Zare, R. Madahizadeh and A. Bali Lashak, 2015, Spatial-temporal analysis of seismicity before the 2012 Varzeghan, Iran, Mw 6.5 earthquake. Turk. J. Earth Sci., 24: DOI: /yer Talebian, M. and J. Jackson, Offset on the Main Recent Fault of NW Iran and implications for the late Cenozoic tectonics of the Arabia-Eurasia collision zone. Geophys. J. Int., 150: DOI: /j X x Vasheghani-Farahani, J., Monitoring the variations of b-value and seismicity in the Makran ranges, the absence of a notable event in west of Makran subduction zone. Geodynam. Res. Int. Bull., 2: Vernant, P., F. Nilforushan, D. Hatzfeld, M. Abassi and C. Vigney et al., Present-day crustal deformation and plate kinematics in the Middle East constrained by GPS measurements in Iran and northern Oman. Geophys. J. Int., 157: DOI: /j X x Walker, R.T., E. Bergman, J. Jackson, M. Ghorashi and M. Talebian, The 2002 June 22 Changureh (Avaj) earthquake in Qazvin province, northwest Iran: Epicentral relocation, source parameters, surface deformation and geomorphology. Geophys. J. Int., 160: DOI: /j X x Wyss, M., Towards a physical understanding of the earthquake frequency distribution. Geophys. J. Int., 31: DOI: /j X.1973.tb06506.x Wyss, M., S. Wiemer and R. Zuniga, ZMAP-a tool for analyses of seismicity patterns. Version 6,0. ETH Zürich. Zaho, Y.Z. and Z.L. Wu, Mapping the b-values along the Longmenshan fault zone before and after the 12 May 2008, Wenchuan, China, M S 8.0 earthquake. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 8: DOI: /nhess Zare, M., H. Amini, P. Yazdi, K. Sesetyan and M.B. Demircioglu et al., Recent developments of the Middle East catalog. J. Seismol., 18: DOI: /s
PSHA Study Using EZ-Frisk Software Case Study Baychebaq Dam Site
 Current Research in Geosciences Original Research Paper PSHA Study Using EZ-Frisk Software Case Study Baychebaq Dam Site Hadi Jarahi Department of Geosciences, North Tehran Branch, Islamic Azad University
Current Research in Geosciences Original Research Paper PSHA Study Using EZ-Frisk Software Case Study Baychebaq Dam Site Hadi Jarahi Department of Geosciences, North Tehran Branch, Islamic Azad University
Homogenization of Earthquake Catalogue in Terms of Magnitude in Iran and Adjoining Region
 Current Research in Geoscience Original Research Paper Homogenization of Earthquake Catalogue in Terms of Magnitude in Iran and Adjoining Region 1 Noushin Naraghiaraghi, 1 Mohd Nawawi, 1 Syed Mustafizur
Current Research in Geoscience Original Research Paper Homogenization of Earthquake Catalogue in Terms of Magnitude in Iran and Adjoining Region 1 Noushin Naraghiaraghi, 1 Mohd Nawawi, 1 Syed Mustafizur
Paleo and New Earthquakes and Evaluation of North Tabriz Fault Displacement in Relation to Recurrence Interval of Destructive Earthquakes
 Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture 9 (2015) 1012-1016 doi: 10.17265/1934-7359/2015.08.013 D DAVID PUBLISHING Paleo and New Earthquakes and Evaluation of North Tabriz Fault Displacement in Relation
Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture 9 (2015) 1012-1016 doi: 10.17265/1934-7359/2015.08.013 D DAVID PUBLISHING Paleo and New Earthquakes and Evaluation of North Tabriz Fault Displacement in Relation
Seismic versus aseismic deformation in Iran inferred from earthquakes and geodetic data
 Geophys. J. Int. (2005) 160, 217 226 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02465.x Seismic versus aseismic deformation in Iran inferred from earthquakes and geodetic data F. Masson, 1, J. Chéry, 1 D. Hatzfeld,
Geophys. J. Int. (2005) 160, 217 226 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02465.x Seismic versus aseismic deformation in Iran inferred from earthquakes and geodetic data F. Masson, 1, J. Chéry, 1 D. Hatzfeld,
(First Edition: prepared on 29/12/2003)
 (First Edition: prepared on 29/12/2003) Dr Sassan Eshghi 1 and Dr Mehdi Zaré 2 International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology, Tehran, P.O.Box: 19395/3913, IRAN e-mails: 1)s.eshghi@iiees.ac.ir,
(First Edition: prepared on 29/12/2003) Dr Sassan Eshghi 1 and Dr Mehdi Zaré 2 International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology, Tehran, P.O.Box: 19395/3913, IRAN e-mails: 1)s.eshghi@iiees.ac.ir,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/ngeo739 Supplementary Information to variability and distributed deformation in the Marmara Sea fault system Tobias Hergert 1 and Oliver Heidbach 1,* 1 Geophysical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/ngeo739 Supplementary Information to variability and distributed deformation in the Marmara Sea fault system Tobias Hergert 1 and Oliver Heidbach 1,* 1 Geophysical
Earthquake Induced Landslide Potential in Maku Dam Reservoir (NW Iran)
 Earthquake Induced Landslide Potential in Maku Dam Reservoir (NW Iran) A. Naderzadeh 1 and R. Madani 2 1 Senior Researcher, Parsayandab Consulting Engineers Company, Tehran, Iran. Email: naderzadeh@dpi.net.ir
Earthquake Induced Landslide Potential in Maku Dam Reservoir (NW Iran) A. Naderzadeh 1 and R. Madani 2 1 Senior Researcher, Parsayandab Consulting Engineers Company, Tehran, Iran. Email: naderzadeh@dpi.net.ir
P32 Temporal and Spatial Variations of b-value in the Western Anatolia
 P32 Temporal and Spatial Variations of b-value in the Western Anatolia E. Bayrak* (Karadeniz Technical University) & Y. Bayrak (Karadeniz Technical University) SUMMARY The b-value calculated in time and
P32 Temporal and Spatial Variations of b-value in the Western Anatolia E. Bayrak* (Karadeniz Technical University) & Y. Bayrak (Karadeniz Technical University) SUMMARY The b-value calculated in time and
Development of Seismic Hazard Zoning Map for Iran,
 Development of Seismic Hazard Zoning Map for Iran, BaseBased Based on New on Seismic Source Determination M. Zaré International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology (IIEES), Tehran, Iran,
Development of Seismic Hazard Zoning Map for Iran, BaseBased Based on New on Seismic Source Determination M. Zaré International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology (IIEES), Tehran, Iran,
Structural analysis of faults system in the West of Shahrood
 Structural analysis of faults system in the West of Shahrood F. Aarab 1, P. Omidi 2, A. Taheri 3 1) M.Sc. Structural Geology, Email: fa_aarab@yahoo.com 2) PhD. Structural Geology, Department of Earth Science,
Structural analysis of faults system in the West of Shahrood F. Aarab 1, P. Omidi 2, A. Taheri 3 1) M.Sc. Structural Geology, Email: fa_aarab@yahoo.com 2) PhD. Structural Geology, Department of Earth Science,
Persian Gulf Fault: New Seismotectonic Element on Seabed
 Canadian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences PEARL publication, 2015 CJBAS Vol. 03(03), 85-92, March 2015 ISSN 2292-3381 Persian Gulf Fault: New Seismotectonic Element on Seabed Hadi Jarahi a, Noushin
Canadian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences PEARL publication, 2015 CJBAS Vol. 03(03), 85-92, March 2015 ISSN 2292-3381 Persian Gulf Fault: New Seismotectonic Element on Seabed Hadi Jarahi a, Noushin
! " 89: ?+ XM - .8M- J " j! G _k EZ-FRISK.
 1395!" 95/02/26 :() *+,-., 95/05/10 :() 3,4., 1-16 :56! " 3 2 1,-.' * ( )' " #$%,+BC DE - (= -F -G8.*" 8 A- :F G " " - (?(@ =A @ >-8!+ >NK -2014 M@ @ RF 89: >8 < (= ;, - (= -F LM - 9, CF.*" +K J 63/3 58/8,+BC!F
1395!" 95/02/26 :() *+,-., 95/05/10 :() 3,4., 1-16 :56! " 3 2 1,-.' * ( )' " #$%,+BC DE - (= -F -G8.*" 8 A- :F G " " - (?(@ =A @ >-8!+ >NK -2014 M@ @ RF 89: >8 < (= ;, - (= -F LM - 9, CF.*" +K J 63/3 58/8,+BC!F
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model
 Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
SEISMIC HAZARD AND SEISMIC DESIGN REQUIREMENTS FOR THE ARABIAN PENINSULA REGION
 SEISMIC HAZARD AND SEISMIC DESIGN REQUIREMENTS FOR THE ARABIAN PENINSULA REGION V. Pascucci 1, M.W. Free 2 and Z.A. Lubkowski 2 1 Seismic Engineer, Arup, London W1T 4BQ, UK 2 Associate Director, Arup,
SEISMIC HAZARD AND SEISMIC DESIGN REQUIREMENTS FOR THE ARABIAN PENINSULA REGION V. Pascucci 1, M.W. Free 2 and Z.A. Lubkowski 2 1 Seismic Engineer, Arup, London W1T 4BQ, UK 2 Associate Director, Arup,
DEFORMATION KINEMATICS OF TIBETAN PLATEAU DETERMINED FROM GPS OBSERVATIONS
 DEFORMATION KINEMATICS OF TIBETAN PLATEAU DETERMINED FROM GPS OBSERVATIONS Jinwei Ren Institute of Geology, China Seismological Bureau, Beijing 100029 China Tel: (10)62009095; Fax: (10)62009003; email:
DEFORMATION KINEMATICS OF TIBETAN PLATEAU DETERMINED FROM GPS OBSERVATIONS Jinwei Ren Institute of Geology, China Seismological Bureau, Beijing 100029 China Tel: (10)62009095; Fax: (10)62009003; email:
FOCAL MECHANISMS OF SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE JAVA TRENCH: PRELIMINARY STUDY FOR THE PSHA FOR YOGYAKARTA REGION, INDONESIA
 FOCAL MECHANISMS OF SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE JAVA TRENCH: PRELIMINARY STUDY FOR THE PSHA FOR YOGYAKARTA REGION, INDONESIA Myo Thant 1, Hiroshi Kawase 2, Subagyo Pramumijoyo 3, Heru Hendrayana
FOCAL MECHANISMS OF SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE JAVA TRENCH: PRELIMINARY STUDY FOR THE PSHA FOR YOGYAKARTA REGION, INDONESIA Myo Thant 1, Hiroshi Kawase 2, Subagyo Pramumijoyo 3, Heru Hendrayana
Seismicity. Chapter 2 : Geographic Database Development 29
 Final Report Main Report 2.2.5. Seismicity (1) Earthquake Catalogue and Seismic Data Two earthquake catalogues are used in the Study, namely: Moinfar, A.A., Mahdavian, A. and Maleky, E. (1994): Historical
Final Report Main Report 2.2.5. Seismicity (1) Earthquake Catalogue and Seismic Data Two earthquake catalogues are used in the Study, namely: Moinfar, A.A., Mahdavian, A. and Maleky, E. (1994): Historical
Earthquake Distribution in Northeast India from
 Earthquake Distribution in Northeast India from 1961-2010 Abong A. A. 1, George A. M. 2, Awhuwhe E. A. 3 1 Department of Physics, Cross River University of Technology, P.M.B 1123, Calabar Nigeria 2 Department
Earthquake Distribution in Northeast India from 1961-2010 Abong A. A. 1, George A. M. 2, Awhuwhe E. A. 3 1 Department of Physics, Cross River University of Technology, P.M.B 1123, Calabar Nigeria 2 Department
Rudbar Lorestan Dam Design and local Faults
 Abstract Rudbar Lorestan Dam Design and local Faults Mahdavian Abbas Academic members, Dep. of Civil Eng. Power and Water University of Technology, Tehran, Iran Email: mahdavian@pwut.ac.ir The Rudbar Lorestan
Abstract Rudbar Lorestan Dam Design and local Faults Mahdavian Abbas Academic members, Dep. of Civil Eng. Power and Water University of Technology, Tehran, Iran Email: mahdavian@pwut.ac.ir The Rudbar Lorestan
Advanced Workshop on Evaluating, Monitoring and Communicating Volcanic and Seismic Hazards in East Africa.
 2053-8 Advanced Workshop on Evaluating, Monitoring and Communicating Volcanic and Seismic Hazards in East Africa 17-28 August 2009 Seismicity of the East African Rift Atalay Ayele W. Addis Ababa University
2053-8 Advanced Workshop on Evaluating, Monitoring and Communicating Volcanic and Seismic Hazards in East Africa 17-28 August 2009 Seismicity of the East African Rift Atalay Ayele W. Addis Ababa University
P33 Correlation between the Values of b and DC for the Different Regions in the Western Anatolia
 P33 Correlation between the Values of b and DC for the Different Regions in the Western Anatolia E. Bayrak* (Karadeniz Technical University) & Y. Bayrak (Karadeniz Technical University) SUMMARY The b-value
P33 Correlation between the Values of b and DC for the Different Regions in the Western Anatolia E. Bayrak* (Karadeniz Technical University) & Y. Bayrak (Karadeniz Technical University) SUMMARY The b-value
RELOCATION OF THE MACHAZE AND LACERDA EARTHQUAKES IN MOZAMBIQUE AND THE RUPTURE PROCESS OF THE 2006 Mw7.0 MACHAZE EARTHQUAKE
 RELOCATION OF THE MACHAZE AND LACERDA EARTHQUAKES IN MOZAMBIQUE AND THE RUPTURE PROCESS OF THE 2006 Mw7.0 MACHAZE EARTHQUAKE Paulino C. FEITIO* Supervisors: Nobuo HURUKAWA** MEE07165 Toshiaki YOKOI** ABSTRACT
RELOCATION OF THE MACHAZE AND LACERDA EARTHQUAKES IN MOZAMBIQUE AND THE RUPTURE PROCESS OF THE 2006 Mw7.0 MACHAZE EARTHQUAKE Paulino C. FEITIO* Supervisors: Nobuo HURUKAWA** MEE07165 Toshiaki YOKOI** ABSTRACT
Seismic Quiescence before the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan, M w 7.6 Earthquake
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 96, No. 1, pp. 321 327, February 2006, doi: 10.1785/0120050069 Seismic Quiescence before the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan, M w 7.6 Earthquake by Yih-Min Wu
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 96, No. 1, pp. 321 327, February 2006, doi: 10.1785/0120050069 Seismic Quiescence before the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan, M w 7.6 Earthquake by Yih-Min Wu
Stochastic Finite-Fault Simulation of 22 February 2005 (Mw 6.4) Zarand Earthquake (Iran), based on Dynamic Corner Frequency
 Stochastic Finite-Fault Simulation of 22 February 25 (Mw 6.4) Zarand Earthquake (Iran), based on Dynamic Corner Frequency Behzad Hassani School of Civil Engineering, University of Tehran, Email: behhassani@gmail.com
Stochastic Finite-Fault Simulation of 22 February 25 (Mw 6.4) Zarand Earthquake (Iran), based on Dynamic Corner Frequency Behzad Hassani School of Civil Engineering, University of Tehran, Email: behhassani@gmail.com
ANALYSIS OF SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL VARIATION OF EARTHQUAKE HAZARD PARAMETERS FROM A BAYESIAN APPROACH IN AND AROUND THE MARMARA SEA
 ANALYSIS OF SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL VARIATION OF EARTHQUAKE HAZARD PARAMETERS FROM A BAYESIAN APPROACH IN AND AROUND THE MARMARA SEA Y. Bayrak 1, T. Türker 2, E. Bayrak 3 ABSTRACT: 1 Prof Dr. Geophysical
ANALYSIS OF SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL VARIATION OF EARTHQUAKE HAZARD PARAMETERS FROM A BAYESIAN APPROACH IN AND AROUND THE MARMARA SEA Y. Bayrak 1, T. Türker 2, E. Bayrak 3 ABSTRACT: 1 Prof Dr. Geophysical
BEHAVIOR OF TWO EARTH-FILL DAMS DURING THE 11 AUGUST 2012 ARASBARAN, IRAN PAIR EARTHQUAKES
 BEHAVIOR OF TWO EARTH-FILL DAMS DURING THE 11 AUGUST 2012 ARASBARAN, IRAN PAIR EARTHQUAKES Ramin MADANI 1 and Ahmad NADERZADEH 2 ABSTRACT In 11 August 2012 two earthquakes with magnitudes Ms 6.4 and Ms
BEHAVIOR OF TWO EARTH-FILL DAMS DURING THE 11 AUGUST 2012 ARASBARAN, IRAN PAIR EARTHQUAKES Ramin MADANI 1 and Ahmad NADERZADEH 2 ABSTRACT In 11 August 2012 two earthquakes with magnitudes Ms 6.4 and Ms
COULOMB STRESS CHANGES DUE TO RECENT ACEH EARTHQUAKES
 COULOMB STRESS CHANGES DUE TO RECENT ACEH EARTHQUAKES Madlazim Physics Department, Faculty Mathematics and Sciences of Surabaya State University (UNESA) Jl. Ketintang, Surabaya 60231, Indonesia. e-mail:
COULOMB STRESS CHANGES DUE TO RECENT ACEH EARTHQUAKES Madlazim Physics Department, Faculty Mathematics and Sciences of Surabaya State University (UNESA) Jl. Ketintang, Surabaya 60231, Indonesia. e-mail:
Tectonic Seismogenic Index of Geothermal Reservoirs
 Tectonic Seismogenic Index of Geothermal Reservoirs C. Dinske 1, F. Wenzel 2 and S.A. Shapiro 1 1 Freie Universität Berlin 2 KIT Karlsruhe November 27, 2012 Introduction M max reservoir location -2.0 Barnett
Tectonic Seismogenic Index of Geothermal Reservoirs C. Dinske 1, F. Wenzel 2 and S.A. Shapiro 1 1 Freie Universität Berlin 2 KIT Karlsruhe November 27, 2012 Introduction M max reservoir location -2.0 Barnett
27th Seismic Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 CONTINUING ANALYSIS OF EARTH STRUCTURE AND GROUND TRUTH DATA FROM THE MIDDLE EAST Walter D. Mooney and Shane Detweiler U.S. Geological Survey Sponsored by National Nuclear Security Administration Office
CONTINUING ANALYSIS OF EARTH STRUCTURE AND GROUND TRUTH DATA FROM THE MIDDLE EAST Walter D. Mooney and Shane Detweiler U.S. Geological Survey Sponsored by National Nuclear Security Administration Office
SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences
 SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences RESEARCH PAPER September 2011 Vol.54 No.9: 1386 1393 doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4177-2 Crustal P-wave velocity structure of the Longmenshan region and its tectonic implications
SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences RESEARCH PAPER September 2011 Vol.54 No.9: 1386 1393 doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4177-2 Crustal P-wave velocity structure of the Longmenshan region and its tectonic implications
3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA
 3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA Li Xiaofan MEE09177 Supervisor: Bunichiro Shibazaki ABSTRACT We perform 3D modeling of earthquake generation of the Xianshuihe
3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA Li Xiaofan MEE09177 Supervisor: Bunichiro Shibazaki ABSTRACT We perform 3D modeling of earthquake generation of the Xianshuihe
Short Period Spectral Acceleration Zonation of Tehran a Comparison between Slip and Activity Rates Data s
 Current Research in Geoscience Original Research Paper Short Period Spectral Acceleration Zonation of Tehran a Comparison between Slip and Activity Rates Data s 1 Hadi Jarahi, 2 Noushin Naraghiaraghi and
Current Research in Geoscience Original Research Paper Short Period Spectral Acceleration Zonation of Tehran a Comparison between Slip and Activity Rates Data s 1 Hadi Jarahi, 2 Noushin Naraghiaraghi and
An analysis of correlations of seismotectonic parameter and fractal dimension preceding Roudbar-Tarom earthquake (Northwest of Iran)
 An analysis of correlations of seismotectonic parameter and fractal dimension preceding Roudbar-Tarom earthquake (Northwest of Iran) NEDA POROOHAN, KAMBIZ TEIMOURNEGAD Geology Department Islamic Azad University,Lahijan
An analysis of correlations of seismotectonic parameter and fractal dimension preceding Roudbar-Tarom earthquake (Northwest of Iran) NEDA POROOHAN, KAMBIZ TEIMOURNEGAD Geology Department Islamic Azad University,Lahijan
Integration of Seismic and Seismological Data Interpretation for Subsurface Structure Identification
 Integration of Seismic and Seismological Data Interpretation for Subsurface Structure Identification Iftikhar Ahmed Satti, and Wan Ismail Wan Yusoff Abstract The structural interpretation of a part of
Integration of Seismic and Seismological Data Interpretation for Subsurface Structure Identification Iftikhar Ahmed Satti, and Wan Ismail Wan Yusoff Abstract The structural interpretation of a part of
Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points)
 Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points) Here you will work with GPS Time Series data to explore plate motion and deformation in California. This lab modifies an exercise found here: http://www.unavco.org:8080/cws/pbonucleus/draftresources/sanandreas/
Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points) Here you will work with GPS Time Series data to explore plate motion and deformation in California. This lab modifies an exercise found here: http://www.unavco.org:8080/cws/pbonucleus/draftresources/sanandreas/
Explanatory Notes to the Map of Major Active Faults of Iran
 K. Hessami and F. Jamali Seismology Research Center, International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology (IIEES), Tehran, I.R. Iran email: hessami@iiees.ac.ir ABSTRACT: Active faulting in
K. Hessami and F. Jamali Seismology Research Center, International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology (IIEES), Tehran, I.R. Iran email: hessami@iiees.ac.ir ABSTRACT: Active faulting in
Study on the feature of surface rupture zone of the west of Kunlunshan pass earthquake ( M S 811) with high spatial resolution satellite images
 48 2 2005 3 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 48, No. 2 Mar., 2005,,. M S 811.,2005,48 (2) :321 326 Shan X J, Li J H, Ma C. Study on the feature of surface rupture zone of the West of Kunlunshan Pass
48 2 2005 3 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 48, No. 2 Mar., 2005,,. M S 811.,2005,48 (2) :321 326 Shan X J, Li J H, Ma C. Study on the feature of surface rupture zone of the West of Kunlunshan Pass
Modelling Subduction Zone Seismogenic Hazards in Southeast Asia for Seismic Hazard Assessments
 Modelling Subduction Zone Seismogenic Hazards in Southeast Asia for Seismic Hazard Assessments Vicki-Ann Dimas 1,2 and Gary Gibson 3 1. Corresponding Author. Seismic Hazard Analyst, Seismology Research
Modelling Subduction Zone Seismogenic Hazards in Southeast Asia for Seismic Hazard Assessments Vicki-Ann Dimas 1,2 and Gary Gibson 3 1. Corresponding Author. Seismic Hazard Analyst, Seismology Research
EARTHQUAKE LOCATION ACCURACY IN THE ARABIAN-EURASIAN COLLISION ZONE. Sponsored by Air Force Research Laboratory 1
 EARTHQUAKE LOCATION ACCURACY IN THE ARABIAN-EURASIAN COLLISION ZONE Eric A. Bergman, Eric R. Engdahl, Michael H. Ritzwoller, and Stephen C. Myers 2 University of Colorado and Lawrence Livermore National
EARTHQUAKE LOCATION ACCURACY IN THE ARABIAN-EURASIAN COLLISION ZONE Eric A. Bergman, Eric R. Engdahl, Michael H. Ritzwoller, and Stephen C. Myers 2 University of Colorado and Lawrence Livermore National
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2014) 197, 10 21 Advance Access publication 2014 January 29 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt509 Strain rate tensor in Iran from a new GPS velocity field Frédéric
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2014) 197, 10 21 Advance Access publication 2014 January 29 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt509 Strain rate tensor in Iran from a new GPS velocity field Frédéric
A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR
 A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR Annemarie CHRISTOPHERSEN 1 And Euan G C SMITH 2 SUMMARY This paper considers the distribution of aftershocks in space, abundance, magnitude and time. Investigations
A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR Annemarie CHRISTOPHERSEN 1 And Euan G C SMITH 2 SUMMARY This paper considers the distribution of aftershocks in space, abundance, magnitude and time. Investigations
GEOLOGICAL SURVEY OF IRAN
 MINISTRY OF INDUSTRY AND MINES GEOLOGICAL SURVEY OF IRAN TECTONIC,AND SEISMOTECTONIC SECTION CONTRIBUTION TO THE SEISMOTECTONICS OF man (PART II) BY M. BERBERIAN IN COMMEMORATION OF THE 50 TM ANNIVERSARY
MINISTRY OF INDUSTRY AND MINES GEOLOGICAL SURVEY OF IRAN TECTONIC,AND SEISMOTECTONIC SECTION CONTRIBUTION TO THE SEISMOTECTONICS OF man (PART II) BY M. BERBERIAN IN COMMEMORATION OF THE 50 TM ANNIVERSARY
Active Tectonics of Qezel Ozan River Basin, NW Iran
 2011, TextRoad Publication ISSN: 2090-4215 Journal of Applied Environmental and Biological Sciences www.textroad.com Active Tectonics of Qezel Ozan River Basin, NW Iran Mehran Arian *, Ph.D.; Vahid Hosseini
2011, TextRoad Publication ISSN: 2090-4215 Journal of Applied Environmental and Biological Sciences www.textroad.com Active Tectonics of Qezel Ozan River Basin, NW Iran Mehran Arian *, Ph.D.; Vahid Hosseini
FINITE FAULT MODELING OF FUTURE LARGE EARTHQUAKE FROM NORTH TEHRAN FAULT IN KARAJ, IRAN
 Proceedings of the 31 st Conference on Earthquake Engineering, JSCE, 2011 FINITE FAULT MODELING OF FUTURE LARGE EARTHQUAKE FROM NORTH TEHRAN FAULT IN KARAJ, IRAN Meghdad Samaei 1, Masakatsu Miyajima 2,
Proceedings of the 31 st Conference on Earthquake Engineering, JSCE, 2011 FINITE FAULT MODELING OF FUTURE LARGE EARTHQUAKE FROM NORTH TEHRAN FAULT IN KARAJ, IRAN Meghdad Samaei 1, Masakatsu Miyajima 2,
Modification of seismological parameters of Zarand earthquake (2005 February 22), in central Iran, Using Empirical Green s function method
 Modification of seismological parameters of Zarand earthquake (2005 February 22), in central Iran, Using Empirical Green s function method Ahamad Nicknam 1, Yasser Eslamian 2, Mohsen Bozorgnasab 3, Afsoon
Modification of seismological parameters of Zarand earthquake (2005 February 22), in central Iran, Using Empirical Green s function method Ahamad Nicknam 1, Yasser Eslamian 2, Mohsen Bozorgnasab 3, Afsoon
Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II
 Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II Project Representative Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo Authors Mitsuhiro
Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II Project Representative Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo Authors Mitsuhiro
Earthquakes in Barcelonnette!
 Barcelonnette in the Ubaye valley : the landscape results of large deformations during the alpine orogene (40 5 Myr in this area) and the succession of Quaternary glaciations. The sedimentary rocks are
Barcelonnette in the Ubaye valley : the landscape results of large deformations during the alpine orogene (40 5 Myr in this area) and the succession of Quaternary glaciations. The sedimentary rocks are
An Assessment on Correlations of Seismotectonic Parameters Preceding and Following Roudbar-Manjil Earthquake (Gilan, North of Iran)
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 3(4): 3443-3451, 2009 ISSN 1991-8178 An Assessment on Correlations of Seismotectonic Parameters Preceding and Following Roudbar-Manjil Earthquake (Gilan,
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 3(4): 3443-3451, 2009 ISSN 1991-8178 An Assessment on Correlations of Seismotectonic Parameters Preceding and Following Roudbar-Manjil Earthquake (Gilan,
A dynamical approach to study the time dependent behavior of the Kuhbanan fault zone (Kerman Iran)
 A dynamical approach to study the time dependent behavior of the Kuhbanan fault zone (Kerman Iran) MOHAMMADREZA TAVAKOLI 1, HOSEIN AMIRI 1. 1 Physics Department, Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Kerman,
A dynamical approach to study the time dependent behavior of the Kuhbanan fault zone (Kerman Iran) MOHAMMADREZA TAVAKOLI 1, HOSEIN AMIRI 1. 1 Physics Department, Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Kerman,
to: Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San
 Supplementary material to: Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San Andreas fault system by Yuri Fialko Methods The San Bernardino-Coachella Valley segment of the
Supplementary material to: Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San Andreas fault system by Yuri Fialko Methods The San Bernardino-Coachella Valley segment of the
Performance of national scale smoothed seismicity estimates of earthquake activity rates. Abstract
 Performance of national scale smoothed seismicity estimates of earthquake activity rates Jonathan Griffin 1, Graeme Weatherill 2 and Trevor Allen 3 1. Corresponding Author, Geoscience Australia, Symonston,
Performance of national scale smoothed seismicity estimates of earthquake activity rates Jonathan Griffin 1, Graeme Weatherill 2 and Trevor Allen 3 1. Corresponding Author, Geoscience Australia, Symonston,
An updated and refined catalog of earthquakes in Taiwan ( ) with homogenized M w magnitudes
 DOI 10.1186/s40623-016-0414-4 TECHNICAL REPORT Open Access An updated and refined catalog of earthquakes in Taiwan (1900 2014) with homogenized M w magnitudes Wen Yen Chang 1,2, Kuei Pao Chen 2* and Yi
DOI 10.1186/s40623-016-0414-4 TECHNICAL REPORT Open Access An updated and refined catalog of earthquakes in Taiwan (1900 2014) with homogenized M w magnitudes Wen Yen Chang 1,2, Kuei Pao Chen 2* and Yi
State of Stress in Seismic Gaps Along the SanJacinto Fault
 ELEVEN State of Stress in Seismic Gaps Along the SanJacinto Fault Hirao Kanamori and Harold Magistrale NTRODUCTON Data from the Southern California Seismic Network have been extensively used to map spatial
ELEVEN State of Stress in Seismic Gaps Along the SanJacinto Fault Hirao Kanamori and Harold Magistrale NTRODUCTON Data from the Southern California Seismic Network have been extensively used to map spatial
Spatial clustering and repeating of seismic events observed along the 1976 Tangshan fault, north China
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L23309, doi:10.1029/2007gl031594, 2007 Spatial clustering and repeating of seismic events observed along the 1976 Tangshan fault, north
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L23309, doi:10.1029/2007gl031594, 2007 Spatial clustering and repeating of seismic events observed along the 1976 Tangshan fault, north
Lateral extrusion and tectonic escape in Ilan Plain of northeastern Taiwan
 Lateral extrusion and tectonic escape in Ilan Plain of northeastern Taiwan Angelier, J., Chang, T.Y., Hu, J.C., Chang, C.P., Siame, L., Lee, J.C., Deffontaines, B., Chu, H.T, Lu, C.Y., Does extrusion occur
Lateral extrusion and tectonic escape in Ilan Plain of northeastern Taiwan Angelier, J., Chang, T.Y., Hu, J.C., Chang, C.P., Siame, L., Lee, J.C., Deffontaines, B., Chu, H.T, Lu, C.Y., Does extrusion occur
Contemporary Tectonics and Seismicity of the Teton and Southern Yellowstone Fault Systems- Phase I
 University of Wyoming National Park Service Research Center Annual Report Volume 4 4th Annual Report, 1980 Article 16 1-1-1980 Contemporary Tectonics and Seismicity of the Teton and Southern Yellowstone
University of Wyoming National Park Service Research Center Annual Report Volume 4 4th Annual Report, 1980 Article 16 1-1-1980 Contemporary Tectonics and Seismicity of the Teton and Southern Yellowstone
Temporal and spatial variations in the magnitude of completeness for homogenized moment magnitude catalogue for northeast India
 Temporal and spatial variations in the magnitude of completeness for homogenized moment magnitude catalogue for northeast India Ranjit Das, HRWason and M L Sharma Department of Earthquake Engineering,
Temporal and spatial variations in the magnitude of completeness for homogenized moment magnitude catalogue for northeast India Ranjit Das, HRWason and M L Sharma Department of Earthquake Engineering,
Moment tensor and stress inversion for an active fault system in west part of Lut-Block, Iran
 Journal of the Earth and Space Physics, Vol. 1, No., 201, PP. 1322 Moment tensor and stress inversion for an active fault system in west part of LutBlock, Iran Ataei, N. 1 and Rezapour, M. 2* 1. M.Sc.
Journal of the Earth and Space Physics, Vol. 1, No., 201, PP. 1322 Moment tensor and stress inversion for an active fault system in west part of LutBlock, Iran Ataei, N. 1 and Rezapour, M. 2* 1. M.Sc.
Strong Ground Motion Prediction of Future Large Earthquake from Niavaran Fault in Tehran, Iran by Finite Fault Method
 Strong Ground Motion Prediction of Future Large Earthquake from Niavaran Fault in Tehran, Iran by Finite Fault Method M. Samaei & M. Miyajima Kanazawa University, Japan M. Tsurugi Geo-Research Institute,
Strong Ground Motion Prediction of Future Large Earthquake from Niavaran Fault in Tehran, Iran by Finite Fault Method M. Samaei & M. Miyajima Kanazawa University, Japan M. Tsurugi Geo-Research Institute,
Global Tectonics. Kearey, Philip. Table of Contents ISBN-13: Historical perspective. 2. The interior of the Earth.
 Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Africa-Arabia-Eurasia plate interactions and implications for the dynamics of Mediterranean subduction and Red Sea rifting
 This page added by the GeoPRISMS office. Africa-Arabia-Eurasia plate interactions and implications for the dynamics of Mediterranean subduction and Red Sea rifting Authors: R. Reilinger, B. Hager, L. Royden,
This page added by the GeoPRISMS office. Africa-Arabia-Eurasia plate interactions and implications for the dynamics of Mediterranean subduction and Red Sea rifting Authors: R. Reilinger, B. Hager, L. Royden,
ESTIMATION AND SPATIAL MAPPING OF SEISMICITY PARAMETERS IN WESTERN HIMALAYA, CENTRAL HIMALAYA AND INDO-GANGETIC PLAIN
 ESTIMATION AND SPATIAL MAPPING OF SEISMICITY PARAMETERS IN WESTERN HIMALAYA, CENTRAL HIMALAYA AND INDO-GANGETIC PLAIN Monalisha Nayak * * Correspondent Author, Ph.D. Research Scholar, Department of Civil
ESTIMATION AND SPATIAL MAPPING OF SEISMICITY PARAMETERS IN WESTERN HIMALAYA, CENTRAL HIMALAYA AND INDO-GANGETIC PLAIN Monalisha Nayak * * Correspondent Author, Ph.D. Research Scholar, Department of Civil
NCC roles in successful disaster response I.R.IRAN
 The Second UN-GGIM-AP Plenary Meeting NCC roles in successful disaster response I.R.IRAN Teheran Iran 28-30 October 2013 Ali Javidaneh Technical Deputy of National Cartographic Center (NCC) Outline Types
The Second UN-GGIM-AP Plenary Meeting NCC roles in successful disaster response I.R.IRAN Teheran Iran 28-30 October 2013 Ali Javidaneh Technical Deputy of National Cartographic Center (NCC) Outline Types
Magnitude 7.0 PAPUA, INDONESIA
 A 7.0 magnitude earthquake struck eastern Indonesia's mountainous West Papua province on Saturday but there were no immediate reports of casualties or damage. The region is sparsely populated. According
A 7.0 magnitude earthquake struck eastern Indonesia's mountainous West Papua province on Saturday but there were no immediate reports of casualties or damage. The region is sparsely populated. According
Paleoearthquakes and slip rates of the North Tabriz Fault, NW Iran: preliminary results
 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 46, N. 5, October 2003 Paleoearthquakes and slip rates of the North Tabriz Fault, NW Iran: preliminary results Khaled Hessami ( 1 ), Daniela Pantosti ( 2 ), Hadi Tabassi ( 1
ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 46, N. 5, October 2003 Paleoearthquakes and slip rates of the North Tabriz Fault, NW Iran: preliminary results Khaled Hessami ( 1 ), Daniela Pantosti ( 2 ), Hadi Tabassi ( 1
Surface Expression of the Bam Fault Zone in Southeastern Iran: Causative Fault of the 26 December 2003 Bam Earthquake
 Surface Expression of the Bam Fault Zone in Southeastern Iran: Causative Fault of the 26 December 2003 Bam Earthquake Khaled Hessami 1, Hadi Tabassi 1, Mohammad R. Abbassi 1, Takashi Azuma 2, Koji Okumura
Surface Expression of the Bam Fault Zone in Southeastern Iran: Causative Fault of the 26 December 2003 Bam Earthquake Khaled Hessami 1, Hadi Tabassi 1, Mohammad R. Abbassi 1, Takashi Azuma 2, Koji Okumura
Review of Structural Relationship between Salt Domes in Central Zagros with Dena Fault
 28 RESEARCH JOURNAL OF FISHERIES AND HYDROBIOLOGY http://www.aensiweb.com/jasa 2015 AENSI Publisher All rights reserved ISSN:1816-9112 Open Access Journal Review of Structural Relationship between Salt
28 RESEARCH JOURNAL OF FISHERIES AND HYDROBIOLOGY http://www.aensiweb.com/jasa 2015 AENSI Publisher All rights reserved ISSN:1816-9112 Open Access Journal Review of Structural Relationship between Salt
GLOBAL SOURCE PARAMETERS OF FINITE FAULT MODEL FOR STRONG GROUND MOTION SIMULATIONS OR PREDICTIONS
 13 th orld Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2743 GLOBAL SOURCE PARAMETERS OF FINITE FAULT MODEL FOR STRONG GROUND MOTION SIMULATIONS OR PREDICTIONS
13 th orld Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2743 GLOBAL SOURCE PARAMETERS OF FINITE FAULT MODEL FOR STRONG GROUND MOTION SIMULATIONS OR PREDICTIONS
An earthquake is the result of a sudden displacement across a fault that releases stresses that have accumulated in the crust of the earth.
 An earthquake is the result of a sudden displacement across a fault that releases stresses that have accumulated in the crust of the earth. Measuring an Earthquake s Size Magnitude and Moment Each can
An earthquake is the result of a sudden displacement across a fault that releases stresses that have accumulated in the crust of the earth. Measuring an Earthquake s Size Magnitude and Moment Each can
CONTINENTAL PLATE BOUNDARY ZONES
 CONTINENTAL PLATE BOUNDARY ZONES Plate boundaries initially viewed as narrow Now recognize that many plate boundaries - especially continental - are deformation zones up to 1000 km wide, with motion spread
CONTINENTAL PLATE BOUNDARY ZONES Plate boundaries initially viewed as narrow Now recognize that many plate boundaries - especially continental - are deformation zones up to 1000 km wide, with motion spread
On the validity of time-predictable model for earthquake generation in north-east India
 Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet. Sci.), Vol. 101, No. 4, December 1992, pp. 361-368. 9 Printed in India. On the validity of time-predictable model for earthquake generation in north-east India V
Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet. Sci.), Vol. 101, No. 4, December 1992, pp. 361-368. 9 Printed in India. On the validity of time-predictable model for earthquake generation in north-east India V
REGIONAL CHARACTERISTICS OF STRESS FIELD AND ITS DYNAMICS IN AND AROUND THE NANKAI TROUGH, JAPAN
 46 4 2003 7 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 46, No. 4 July, 2003 1 1 2 3 1, 100037 2, 920-1192 3, 237-0061,,, : -. (10 22 ), (60 85km) ; (40 ), (160km)..,. GPS,, -,,.,,,.. 0001-5733(2003) 04-0488 -
46 4 2003 7 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 46, No. 4 July, 2003 1 1 2 3 1, 100037 2, 920-1192 3, 237-0061,,, : -. (10 22 ), (60 85km) ; (40 ), (160km)..,. GPS,, -,,.,,,.. 0001-5733(2003) 04-0488 -
Seismic Activity near the Sunda and Andaman Trenches in the Sumatra Subduction Zone
 IJMS 2017 vol. 4 (2): 49-54 International Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies (IJMS) Volume 4, Issue 2, 2017 DOI: http://doi.org/10.4038/ijms.v4i2.22 Seismic Activity near the Sunda and Andaman Trenches
IJMS 2017 vol. 4 (2): 49-54 International Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies (IJMS) Volume 4, Issue 2, 2017 DOI: http://doi.org/10.4038/ijms.v4i2.22 Seismic Activity near the Sunda and Andaman Trenches
Coulomb stress changes due to Queensland earthquakes and the implications for seismic risk assessment
 Coulomb stress changes due to Queensland earthquakes and the implications for seismic risk assessment Abstract D. Weatherley University of Queensland Coulomb stress change analysis has been applied in
Coulomb stress changes due to Queensland earthquakes and the implications for seismic risk assessment Abstract D. Weatherley University of Queensland Coulomb stress change analysis has been applied in
Geometry of co-seismic surface ruptures and tectonic meaning of the 23 October 2011 Mw 7.1 Van earthquake (East Anatolian Region, Turkey)
 Geometry of co-seismic surface ruptures and tectonic meaning of the 23 October 2011 Mw 7.1 Van earthquake (East Anatolian Region, Turkey) Bülent Dogan & Ahmet Karakaș. Journal of Structural Geology, 46(2013),
Geometry of co-seismic surface ruptures and tectonic meaning of the 23 October 2011 Mw 7.1 Van earthquake (East Anatolian Region, Turkey) Bülent Dogan & Ahmet Karakaș. Journal of Structural Geology, 46(2013),
Tidal triggering of earthquakes in Longmen Shan region: the relation to the fold belt and basin structures
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 64, 771 776, 2012 Tidal triggering of earthquakes in Longmen Shan region: the relation to the fold belt and basin structures Qiang Li and Gui-Ming Xu Research Center for Earthquake
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 64, 771 776, 2012 Tidal triggering of earthquakes in Longmen Shan region: the relation to the fold belt and basin structures Qiang Li and Gui-Ming Xu Research Center for Earthquake
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand
 The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
SEISMIC HAZARD CHARACTERIZATION AND RISK EVALUATION USING GUMBEL S METHOD OF EXTREMES (G1 AND G3) AND G-R FORMULA FOR IRAQ
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2898 SEISMIC HAZARD CHARACTERIZATION AND RISK EVALUATION USING GUMBEL S METHOD OF EXTREMES (G1 AND G3)
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2898 SEISMIC HAZARD CHARACTERIZATION AND RISK EVALUATION USING GUMBEL S METHOD OF EXTREMES (G1 AND G3)
Relocation of aftershocks of the Wenchuan M S 8.0 earthquake and its implication to seismotectonics
 Earthq Sci (2011)24: 107 113 107 doi:10.1007/s11589-011-0774-6 Relocation of aftershocks of the Wenchuan M S 8.0 earthquake and its implication to seismotectonics Bo Zhao Yutao Shi and Yuan Gao Institute
Earthq Sci (2011)24: 107 113 107 doi:10.1007/s11589-011-0774-6 Relocation of aftershocks of the Wenchuan M S 8.0 earthquake and its implication to seismotectonics Bo Zhao Yutao Shi and Yuan Gao Institute
Seismic hazard for some regions of the world examined using strain energy release
 JOURNAL OF THE BALKAN GEOPHYSICAL SOCIETY, Vol. 1, No 2, May 1998, p. 19-26, 4 figs. Seismic hazard for some regions of the world examined using strain energy release Theodoros M. Tsapanos Aristotle University
JOURNAL OF THE BALKAN GEOPHYSICAL SOCIETY, Vol. 1, No 2, May 1998, p. 19-26, 4 figs. Seismic hazard for some regions of the world examined using strain energy release Theodoros M. Tsapanos Aristotle University
Magnitude 7.3 IRAQ. Early reports indicate that 140 have been killed with over 800 injuries reported. Sunday, November 12, 2017 at 18:18:17 UTC
 A magnitude 7.3 earthquake has occurred in the northern border region of Iran and Iraq centered about 350 kilometers (217 miles) north of Baghdad at a depth of 33.9 km (21 miles). The earthquake was felt
A magnitude 7.3 earthquake has occurred in the northern border region of Iran and Iraq centered about 350 kilometers (217 miles) north of Baghdad at a depth of 33.9 km (21 miles). The earthquake was felt
Parts of the Sevier/ Laramide Orogeny
 Parts of the Sevier/ Laramide Orogeny AA. Accretionary Prism BB. Forearc Basin Sediment scraped off of subducting plate Sediment derived from the volcanic arc CC. Volcanic Arc Magmatic intrusion into the
Parts of the Sevier/ Laramide Orogeny AA. Accretionary Prism BB. Forearc Basin Sediment scraped off of subducting plate Sediment derived from the volcanic arc CC. Volcanic Arc Magmatic intrusion into the
MESF CYBER JOURNAL OF GEOSCIENCE _DECEMBER 2003/
 MESF CYBER JOURNAL OF GEOSCIENCE _DECEMBER 2003/ www.meseisforum.net A PAPER PRESENTED TO THE EURO-MEDITERRANEAN SEMINAR ON NATURAL, ENVIRONMENTAL AND TECHNOLOGICAL DISASTERS- HOURTI BOUMEDIAN UNIVERSITY
MESF CYBER JOURNAL OF GEOSCIENCE _DECEMBER 2003/ www.meseisforum.net A PAPER PRESENTED TO THE EURO-MEDITERRANEAN SEMINAR ON NATURAL, ENVIRONMENTAL AND TECHNOLOGICAL DISASTERS- HOURTI BOUMEDIAN UNIVERSITY
Negative repeating doublets in an aftershock sequence
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 65, 923 927, 2013 Negative repeating doublets in an aftershock sequence X. J. Ma and Z. L. Wu Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration, 100081 Beijing, China
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 65, 923 927, 2013 Negative repeating doublets in an aftershock sequence X. J. Ma and Z. L. Wu Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration, 100081 Beijing, China
Widespread Ground Motion Distribution Caused by Rupture Directivity during the 2015 Gorkha, Nepal Earthquake
 Widespread Ground Motion Distribution Caused by Rupture Directivity during the 2015 Gorkha, Nepal Earthquake Kazuki Koketsu 1, Hiroe Miyake 2, Srinagesh Davuluri 3 and Soma Nath Sapkota 4 1. Corresponding
Widespread Ground Motion Distribution Caused by Rupture Directivity during the 2015 Gorkha, Nepal Earthquake Kazuki Koketsu 1, Hiroe Miyake 2, Srinagesh Davuluri 3 and Soma Nath Sapkota 4 1. Corresponding
GPS Strain & Earthquakes Unit 5: 2014 South Napa earthquake GPS strain analysis student exercise
 GPS Strain & Earthquakes Unit 5: 2014 South Napa earthquake GPS strain analysis student exercise Strain Analysis Introduction Name: The earthquake cycle can be viewed as a process of slow strain accumulation
GPS Strain & Earthquakes Unit 5: 2014 South Napa earthquake GPS strain analysis student exercise Strain Analysis Introduction Name: The earthquake cycle can be viewed as a process of slow strain accumulation
Time-varying and long-term mean aftershock hazard in Wellington
 Time-varying and long-term mean aftershock hazard in Wellington A. Christophersen, D.A. Rhoades, R.J. Van Dissen, C. Müller, M.W. Stirling, G.H. McVerry & M.C. Gerstenberger GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New
Time-varying and long-term mean aftershock hazard in Wellington A. Christophersen, D.A. Rhoades, R.J. Van Dissen, C. Müller, M.W. Stirling, G.H. McVerry & M.C. Gerstenberger GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New
DUBAI SEISMIC NETWORK (DSN)
 DUBAI SEISMIC NETWORK (DSN) Eman Al Khatibi 1, Kamal Abou Elenean 1 1 Dubai Municipality, Survey Department, P.O. Box: 67 Dubai U.A.E. 8 th Gulf Seismic Forum, 3-6 March 2013, Muscat-Sultanate of Oman
DUBAI SEISMIC NETWORK (DSN) Eman Al Khatibi 1, Kamal Abou Elenean 1 1 Dubai Municipality, Survey Department, P.O. Box: 67 Dubai U.A.E. 8 th Gulf Seismic Forum, 3-6 March 2013, Muscat-Sultanate of Oman
SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences
 SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences RESEARCH PAPER September 2014 Vol.57 No.9: 2036 2044 doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-4827-2 A rupture blank zone in middle south part of Longmenshan Faults: Effect after Lushan M s
SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences RESEARCH PAPER September 2014 Vol.57 No.9: 2036 2044 doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-4827-2 A rupture blank zone in middle south part of Longmenshan Faults: Effect after Lushan M s
Magnitude 6.5 OFFSHORE NORTHERN CALIFORNIA
 A powerful offshore earthquake that struck near the Northern California coast left a hodgepodge of debris for communities to sort through Sunday but spared residents any serious injury. After 25,000 people
A powerful offshore earthquake that struck near the Northern California coast left a hodgepodge of debris for communities to sort through Sunday but spared residents any serious injury. After 25,000 people
NORTH OF TEHRAN SITE EFFECT MICROZONATION
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 3423 NORTH OF TEHRAN SITE EFFECT MICROZONATION M.K. Jafari 1, M.Kamalian 2, A.Razmkhah 3, A.Sohrabi 4
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 3423 NORTH OF TEHRAN SITE EFFECT MICROZONATION M.K. Jafari 1, M.Kamalian 2, A.Razmkhah 3, A.Sohrabi 4
SEISMIC VELOCITY STRUCTURE OF THE NORTHWESTERN & NORTHEASTERN HIMALAYA AND ITS IMPLICATIONS FOR EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT
 SEISMIC VELOCITY STRUCTURE OF THE NORTHWESTERN & NORTHEASTERN HIMALAYA AND ITS IMPLICATIONS FOR EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT UKIERI Thematic Partnership Supriyo Mitra Keith Priestley Motivation ~50 Ma
SEISMIC VELOCITY STRUCTURE OF THE NORTHWESTERN & NORTHEASTERN HIMALAYA AND ITS IMPLICATIONS FOR EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT UKIERI Thematic Partnership Supriyo Mitra Keith Priestley Motivation ~50 Ma
EARTHQUAKE SOURCE PARAMETERS OF MODERATELY EARTHQUAKE IN THE SOUTH EASTERN IRAN BASED ON TELESEISMIC AND REGIONAL DISTANCES
 EARTHQUAKE SOURCE PARAMETERS OF MODERATELY EARTHQUAKE IN THE SOUTH EASTERN IRAN BASED ON TELESEISMIC AND REGIONAL DISTANCES M. Mostafazadeh 1 and S.Ashkpour Motlagh 2 1 Assistant Professor,Seismology Research
EARTHQUAKE SOURCE PARAMETERS OF MODERATELY EARTHQUAKE IN THE SOUTH EASTERN IRAN BASED ON TELESEISMIC AND REGIONAL DISTANCES M. Mostafazadeh 1 and S.Ashkpour Motlagh 2 1 Assistant Professor,Seismology Research
2008 Monitoring Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 STRUCTURE OF THE KOREAN PENINSULA FROM WAVEFORM TRAVEL-TIME ANALYSIS Roland Gritto 1, Jacob E. Siegel 1, and Winston W. Chan 2 Array Information Technology 1 and Harris Corporation 2 Sponsored by Air Force
STRUCTURE OF THE KOREAN PENINSULA FROM WAVEFORM TRAVEL-TIME ANALYSIS Roland Gritto 1, Jacob E. Siegel 1, and Winston W. Chan 2 Array Information Technology 1 and Harris Corporation 2 Sponsored by Air Force
Synthetic Seismicity Models of Multiple Interacting Faults
 Synthetic Seismicity Models of Multiple Interacting Faults Russell Robinson and Rafael Benites Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences, Box 30368, Lower Hutt, New Zealand (email: r.robinson@gns.cri.nz).
Synthetic Seismicity Models of Multiple Interacting Faults Russell Robinson and Rafael Benites Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences, Box 30368, Lower Hutt, New Zealand (email: r.robinson@gns.cri.nz).
National Seismological Centre: An Overview, Prospects and Challenges
 National Seismological Centre: An Overview, Prospects and Challenges By Soma Nath Sapkota Department of Mines and Geology National Seismological Centre Nepal India Himalaya Tibetan Plateau India continental
National Seismological Centre: An Overview, Prospects and Challenges By Soma Nath Sapkota Department of Mines and Geology National Seismological Centre Nepal India Himalaya Tibetan Plateau India continental
Regional and temporal evaluation of seismicity in the Vlora-Elbasani-Dibra Transversal Fault Zone, Albania
 Regional and temporal evaluation of seismicity in the Vlora-Elbasani-Dibra Transversal Fault Zone, Albania Rrapo Ormeni 1, Serkan Öztürk 2, Olgert Gjuzi 1 1 Institute of Geosciences, Energy, Water and
Regional and temporal evaluation of seismicity in the Vlora-Elbasani-Dibra Transversal Fault Zone, Albania Rrapo Ormeni 1, Serkan Öztürk 2, Olgert Gjuzi 1 1 Institute of Geosciences, Energy, Water and
On seismic hazard analysis of the two vulnerable regions in Iran: deterministic and probabilistic approaches
 On seismic hazard analysis of the two vulnerable regions in Iran: deterministic and probabilistic approaches A. Farzampour & A. Kamali Asl Department of Civil Engineering, Sharif University of Technology,
On seismic hazard analysis of the two vulnerable regions in Iran: deterministic and probabilistic approaches A. Farzampour & A. Kamali Asl Department of Civil Engineering, Sharif University of Technology,
Is the deformation rate of the Longmenshan fault zone really small? Insight from seismic data at the two-decade time scale
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 62, 887 891, 2010 Is the deformation rate of the Longmenshan fault zone really small? Insight from seismic data at the two-decade time scale Yizhe Zhao 1, Zhongliang Wu 1,2,
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 62, 887 891, 2010 Is the deformation rate of the Longmenshan fault zone really small? Insight from seismic data at the two-decade time scale Yizhe Zhao 1, Zhongliang Wu 1,2,
An analysis of the Kefalonia seismic sequence of Jan Feb. 3, 2014
 An analysis of the Kefalonia seismic sequence of Jan. 26 - Feb. 3, 2014 Alessandro Caporali 1),Carine Bruyninx 2),Rui Fernandes 3),Athanassios Ganas 4),Ambrus Kenyeres 5),Martin Lidberg 6), Guenter Stangl
An analysis of the Kefalonia seismic sequence of Jan. 26 - Feb. 3, 2014 Alessandro Caporali 1),Carine Bruyninx 2),Rui Fernandes 3),Athanassios Ganas 4),Ambrus Kenyeres 5),Martin Lidberg 6), Guenter Stangl
