Answer ALL questions in Section A, and TWO questions from Section B.
|
|
|
- Clara Singleton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series Undergraduate Examination Candidate s no.: GEODYNAMICS: EARTH S ENGINE ENV-2A43 Time allowed: 2 hours. Answer ALL questions in Section A, and TWO questions from Section B. Sections A and B have equal weighting. Write all answers to Section A in the spaces provided on the paper. Answer two questions from Section B one in each answer book provided. Write your candidate s number on this paper AND on the answer books. Notes are not permitted in this examination. Do not turn over until you are told to do so by the Invigilator. ENV-2A43 Module Contact: Dr Jenni Turner, ENV Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 1
2 2 SECTION A 1. a) Why do the same volumes of oceanic crust and continental crust have different densities? b) Give two examples of how new crust may be added to a continent. c) Give one example of how the idealised Penrose model for the layered structure and composition of oceanic crust may be altered near an ocean ridge. d) Why does the elevation of the sea floor decrease with increasing distance away from an ocean ridge? e) What is the relationship between the age of oceanic crust and its depth below sea level? 2. a) Sketch and label a transtensional basin within a strike-slip fault system, show the direction of stresses that control basin formation. [3 marks]
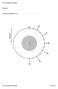
3 3 b) Briefly explain how a rift may form in the absence of tectonic plate tensional stresses. [2 marks] 3. a) By using the plot in Figure 2 determine the direction and the rate of motion at the plate boundary B-C in Figure 1. [4 marks] b) Show on Figure 1 the direction and rate of plate motion from your solution in Figure 2. Figure 1: Velocity map of relative Figure 2: Plot for scaled solution tectonic plate motion of the problem in Figure 1 PLEASE TURN OVER
4 4 4. Using shell diagrams below, and assuming a shallow focus earthquake, draw the path through the Earth of seismic rays, and label each segment of each ray: a) PcP on Figure 3a [2 marks] b) P4KP on Figure 3b [2 marks] c) PKPPKP and PKP 650 PKP on Figure 3c [4 marks] Figure 3: Shell diagrams
5 5 d) What physical change in state occurs inwards at the core-mantle boundary? Explain briefly why P wave velocity decreases but density increases inwards across this boundary. [4 marks] e) What physical changes occur at the ~650 km boundary and what mineral is involved? [3 marks] 5. a) The inversion of seismic data can be used to map magma storage regions. What basic principles does this rely on and why might interpretation be non-unique? [4 marks] PLEASE TURN OVER
6 6 b) Explain why magmatic underplating often occurs around the Moho using the principle of buoyancy. [3 marks] c) During the final stage of magma ascent the exsolution of volatiles becomes important in driving eruptions. Give three brief reasons for this. [3 marks] 6. a) Define the aspect ratio as applied to lava flows or dykes. [2 marks] b) What are the two principle controls on aspect ratio in effusive eruptions. [2 marks] c) What is the rheology of magma?
7 7 d) Name two eruptive scenarios where magma rheology governs behaviour. [2 marks] e) Briefly explain your answer for one of these scenarios. [3 marks] PLEASE TURN OVER
8 8 SECTION B [Answer TWO Questions] 7. The opening and closing of an ocean basin is simply summarised by the Wilson cycle, but no two ocean basins are the same. Explain, using your knowledge of the subsurface processes, why there are variations in ocean ridge cross-section profiles, ocean crust composition, and subduction zone characteristics. Include in your answer the type of evidence which allows us to identify these variations. [25 marks] 8. Discuss to what extent plate tectonic and magmatic processes control the occurrence of basaltic volcanism at subduction-related settings. [25 marks] 9. Relate the characteristics of strombolian, vulcanian and plinian activity to the physical properties of the magma and processes that occur, giving examples. Analyse whether each type of volcanism has a particular association with magma type and volcano-tectonic setting. [25 marks] END OF PAPER
ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B. Figure 6. Student Registration No. ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B Version 2
 ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B Figure 6 Student Registration No UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series UG Examination 014-15 SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS WITH FIELDCOURSE
ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B Figure 6 Student Registration No UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series UG Examination 014-15 SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS WITH FIELDCOURSE
Topic 12 Review Book Earth s Dynamic Crust and Interior
 Topic 12 Review Book Earth s Dynamic Crust and Interior Define the Vocabulary 1. asthenosphere 2. continental crust 3. Convection current 4. Convergent plate boundary 5. Divergent plate boundary 6. earthquake
Topic 12 Review Book Earth s Dynamic Crust and Interior Define the Vocabulary 1. asthenosphere 2. continental crust 3. Convection current 4. Convergent plate boundary 5. Divergent plate boundary 6. earthquake
Name Class Date. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?. a. core b. lithosphere c. asthenosphere d. mesosphere
 Name Class Date Assessment Geology Plate Tectonics MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?. a. core b. lithosphere
Name Class Date Assessment Geology Plate Tectonics MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?. a. core b. lithosphere
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017
 ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
Ch. 9 Review. Pgs #1-31 Write Questions and Answers
 Ch. 9 Review Pgs. 356-357 #1-31 Write Questions and Answers 356-357 #1-5 Answers 1. The layer of the upper mantle that can flow is the: A - Asthenosphere 2. Most scientists rejected Wegener s theory of
Ch. 9 Review Pgs. 356-357 #1-31 Write Questions and Answers 356-357 #1-5 Answers 1. The layer of the upper mantle that can flow is the: A - Asthenosphere 2. Most scientists rejected Wegener s theory of
Earth s Interior HW Packet HW #1 Plate Tectonics (pages )
 Name Earth s Interior HW Packet HW #1 Plate Tectonics (pages 676 683) 1. Is the following sentence true or false? According to the theory of plate tectonics, Earth s plates move about quickly on top of
Name Earth s Interior HW Packet HW #1 Plate Tectonics (pages 676 683) 1. Is the following sentence true or false? According to the theory of plate tectonics, Earth s plates move about quickly on top of
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
2. Explain why there are these two predominate elevations. (Hint: think about isostasy and the type of materials we used to demonstrate buoyancy).
 IDS 102 Plate Tectonics Questions Part I: Observations- Four maps of world are positioned around the room. Answer the questions associated with each map and record your general observations about the maps.
IDS 102 Plate Tectonics Questions Part I: Observations- Four maps of world are positioned around the room. Answer the questions associated with each map and record your general observations about the maps.
Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS. asthenosphere uplift continental drift. known as. tectonic plates move. object. UNDERSTANDING KEY IDEAS
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS 1. Use the following terms in the same sentence: crust, mantle, and core. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS 1. Use the following terms in the same sentence: crust, mantle, and core. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the
1. What is Wegener s theory of continental drift? 2. What were the 4 evidences supporting his theory? 3. Why wasn t Wegener s theory excepted?
 Notebook 7a and 7b Objective (left-side): Students will be able to explain the theory of plate tectonics and be able to make predictions about plate interactions. Mapping Reflection 1. What is Wegener
Notebook 7a and 7b Objective (left-side): Students will be able to explain the theory of plate tectonics and be able to make predictions about plate interactions. Mapping Reflection 1. What is Wegener
Benjamin N. Cardozo Dynamic Planet Test
 Names: Score: /83 Benjamin N. Cardozo Dynamic Planet Test - Labeling Questions are worth 1 Point Each (1 point per labeled/identified item) - Multiple Choice Questions are worth 2 Points Each - Short Answer
Names: Score: /83 Benjamin N. Cardozo Dynamic Planet Test - Labeling Questions are worth 1 Point Each (1 point per labeled/identified item) - Multiple Choice Questions are worth 2 Points Each - Short Answer
24. Ocean Basins p
 24. Ocean Basins p. 350-372 Background The majority of the planet is covered by ocean- about %. So the majority of the Earth s crust is. This crust is hidden from view beneath the water so it is not as
24. Ocean Basins p. 350-372 Background The majority of the planet is covered by ocean- about %. So the majority of the Earth s crust is. This crust is hidden from view beneath the water so it is not as
An Introduction to the Seafloor and Plate Tectonics 1
 An Introduction to the Seafloor and Plate Tectonics 1 Objectives 1) Investigate the components of the lithosphere and lithospheric plates. 2) Identify the associations among various seafloor features,
An Introduction to the Seafloor and Plate Tectonics 1 Objectives 1) Investigate the components of the lithosphere and lithospheric plates. 2) Identify the associations among various seafloor features,
Name: Date: Geography 12 Tectonic Processes Exercise
 Name: Date: Geography 12 Tectonic Processes Exercise 1) How has knowledge of our earth's interior been primarily obtained? 2) What are two key differences between the composition of the continents and
Name: Date: Geography 12 Tectonic Processes Exercise 1) How has knowledge of our earth's interior been primarily obtained? 2) What are two key differences between the composition of the continents and
GEOLOGY 2 THEMATIC UNIT 5 GEOLOGY OF THE LITHOSPHERE. A.M. THURSDAY, 31 January (1 hour)
 WELSH JOINT EDUCATION COMMITTEE General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Advanced Supplementary CYD-BWYLLGOR ADDYSG CYMRU Tystysgrif Addysg Gyffredinol Safon Uwch Uwch Atodol GEOLOGY 2 THEMATIC
WELSH JOINT EDUCATION COMMITTEE General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Advanced Supplementary CYD-BWYLLGOR ADDYSG CYMRU Tystysgrif Addysg Gyffredinol Safon Uwch Uwch Atodol GEOLOGY 2 THEMATIC
Core. Crust. Mesosphere. Asthenosphere. Mantle. Inner core. Lithosphere. Outer core
 Potter Name: Date: Hour: Score: /21 Learning Check 4.1 LT 4.1 Earth s Interior: I can draw and interpret models of the interior of the earth. Draw the following models (put the words in the right order)
Potter Name: Date: Hour: Score: /21 Learning Check 4.1 LT 4.1 Earth s Interior: I can draw and interpret models of the interior of the earth. Draw the following models (put the words in the right order)
Plate Tectonics Notes
 Plate Tectonics Notes Last 30 Days Earthquakes Physical Features Last 30 Days Earthquakes with Plate Boundaries Earth s Structure Earth s Layers Core: Inner Core: Center of the earth, solid ball of metal
Plate Tectonics Notes Last 30 Days Earthquakes Physical Features Last 30 Days Earthquakes with Plate Boundaries Earth s Structure Earth s Layers Core: Inner Core: Center of the earth, solid ball of metal
Earth s Interior StudyGuide
 Name Date Period Earth s Interior StudyGuide 1. The two main elements that make up the Earth s crust are and. 2. The Earth s inner core is made of solid and. 3. When one plates slides under another plate
Name Date Period Earth s Interior StudyGuide 1. The two main elements that make up the Earth s crust are and. 2. The Earth s inner core is made of solid and. 3. When one plates slides under another plate
Plates Moving Apart Types of Boundaries
 Plates Moving Apart Types of Boundaries PLATE TECTONICS IS The theory that the Earth s crust is broken into slabs of rock that move around on top of the asthenosphere. How fast are plates moving? The Arctic
Plates Moving Apart Types of Boundaries PLATE TECTONICS IS The theory that the Earth s crust is broken into slabs of rock that move around on top of the asthenosphere. How fast are plates moving? The Arctic
Refer to the map on page 173 to answer the following questions.
 Chapter 8-1 Plate Tectonics 1. Brainstorm the type of evidence that would indicate a climate change and how this evidence supports the theory of continental drift. Tropical fossils in cold regions Evidence
Chapter 8-1 Plate Tectonics 1. Brainstorm the type of evidence that would indicate a climate change and how this evidence supports the theory of continental drift. Tropical fossils in cold regions Evidence
3. PLATE TECTONICS LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: PLATES
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: PLATES 3. PLATE TECTONICS The outer layers of the Earth are divided into the lithosphere and asthenosphere. The division is based on differences in mechanical properties
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: PLATES 3. PLATE TECTONICS The outer layers of the Earth are divided into the lithosphere and asthenosphere. The division is based on differences in mechanical properties
Outcome C&D Study Guide
 Name: Class: Outcome C&D Study Guide Identify the layers of Earth s interior Lithosphere the upper most layer of the earth that includes the crust and the hard outer mantle. It is fractured into tectonic
Name: Class: Outcome C&D Study Guide Identify the layers of Earth s interior Lithosphere the upper most layer of the earth that includes the crust and the hard outer mantle. It is fractured into tectonic
Plate Boundaries. Presented by Kesler Science
 Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What is plate tectonics? 2. What are the three types of plate boundaries? 3. What crustal features are formed at plate boundaries? Quick Action INB Template
Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What is plate tectonics? 2. What are the three types of plate boundaries? 3. What crustal features are formed at plate boundaries? Quick Action INB Template
Earth s Interior. Theory of Tectonics. Tectonics & Landforms. Vocabulary
 Vocabulary Earth s Interior Theory of Tectonics Tectonics & Landforms Earthquake Volcano 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500
Vocabulary Earth s Interior Theory of Tectonics Tectonics & Landforms Earthquake Volcano 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500
Geology 101 Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics
 Geology 101 Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics Name The readings for plate tectonics will be in four different chapters: 2, 4, 10 and 11. If you have questions, please let me know. Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics:
Geology 101 Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics Name The readings for plate tectonics will be in four different chapters: 2, 4, 10 and 11. If you have questions, please let me know. Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics:
Plate Tectonics. By Destiny, Jarrek, Kaidence, and Autumn
 Plate Tectonics By Destiny, Jarrek, Kaidence, and Autumn .The Denali Fault and San Andreas Fault - The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly 1300 km (810 miles) through
Plate Tectonics By Destiny, Jarrek, Kaidence, and Autumn .The Denali Fault and San Andreas Fault - The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly 1300 km (810 miles) through
MAR110 Lecture #4 Fundamentals of Plate Tectonics
 1 MAR110 Lecture #4 Fundamentals of Plate Tectonics The Ocean Sea Floor is formed Along the Mid-Ocean Ridge Spreading Centers The Ocean Sea Floor is destroyed in the Subduction Zones Figure 4.2 Convection
1 MAR110 Lecture #4 Fundamentals of Plate Tectonics The Ocean Sea Floor is formed Along the Mid-Ocean Ridge Spreading Centers The Ocean Sea Floor is destroyed in the Subduction Zones Figure 4.2 Convection
Section 2: How Mountains Form
 Section 2: How Mountains Form Preview Objectives Mountain Ranges and Systems Plate Tectonics and Mountains Types of Mountains Objectives Identify the types of plate collisions that form mountains. Identify
Section 2: How Mountains Form Preview Objectives Mountain Ranges and Systems Plate Tectonics and Mountains Types of Mountains Objectives Identify the types of plate collisions that form mountains. Identify
Plate Tectonics 3. Where Does All the Extra Crust Go?
 Plate Tectonics 3 Where Does All the Extra Crust Go? Unless otherwise noted the artwork and photographs in this slide show are original and by Burt Carter. Permission is granted to use them for non-commercial,
Plate Tectonics 3 Where Does All the Extra Crust Go? Unless otherwise noted the artwork and photographs in this slide show are original and by Burt Carter. Permission is granted to use them for non-commercial,
Yanbu University College. General Studies Department. PHSC001 Course. Chapter9 (Basic Geology: Earthquakes and volcanoes ) Worksheet Solutions
 Yanbu University College General Studies Department PHSC001 Course Chapter9 (Basic Geology: Earthquakes and volcanoes ) Worksheet Solutions Phsc001 worksheet9 solutions, yuc Page 1-6 Chapter 9 worksheet
Yanbu University College General Studies Department PHSC001 Course Chapter9 (Basic Geology: Earthquakes and volcanoes ) Worksheet Solutions Phsc001 worksheet9 solutions, yuc Page 1-6 Chapter 9 worksheet
Mountains are then built by deforming crust: Deformation & Mountain Building. Mountains form where stresses are high!
 Deformation & Mountain Building Where are mountains located? Deformation and Folding Mountain building Mountains form where stresses are high! Mountains form at all three types of plate boundaries where
Deformation & Mountain Building Where are mountains located? Deformation and Folding Mountain building Mountains form where stresses are high! Mountains form at all three types of plate boundaries where
PLATE TECTONIC PROCESSES
 Lab 9 Name Sec PLATE TECTONIC PROCESSES 1. Fill in the blank spaces on the chart with the correct answers. Refer to figures 2.3, 2.4 p.33 (2.2 and 2.3 on p. 23) as needed. 2. With your knowledge of different
Lab 9 Name Sec PLATE TECTONIC PROCESSES 1. Fill in the blank spaces on the chart with the correct answers. Refer to figures 2.3, 2.4 p.33 (2.2 and 2.3 on p. 23) as needed. 2. With your knowledge of different
FORCES ON EARTH. An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth.
 FORCES ON EARTH An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. GEOLOGY Geologists scientists who study the forces that make and shape the Earth Geologists
FORCES ON EARTH An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. GEOLOGY Geologists scientists who study the forces that make and shape the Earth Geologists
DYNAMIC PLANET. Name: School:
 DYNAMIC PLANET November 4 th Scrimmage Name: School: Directions: DO NOT open the packet until prompted to. The test will be a 50 minute test and answer each question to the best of your abilities. Total:
DYNAMIC PLANET November 4 th Scrimmage Name: School: Directions: DO NOT open the packet until prompted to. The test will be a 50 minute test and answer each question to the best of your abilities. Total:
Diagram 1. Diagram What kind of crust is plate A, B and C made of? 2. What type of plate boundary is shown at X?
 Diagram 1 1. What kind of crust is plate A, B and C made of? 2. What type of plate boundary is shown at X? 3. What plate boundary is shown at Y? 4. What is being shown at Z? Why is plate B going underneath
Diagram 1 1. What kind of crust is plate A, B and C made of? 2. What type of plate boundary is shown at X? 3. What plate boundary is shown at Y? 4. What is being shown at Z? Why is plate B going underneath
FORCES ON EARTH UNIT 3.2. An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth.
 FORCES ON EARTH UNIT 3.2 An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. USE THESE NOTES: OUR HOME PLANET EARTH: What do you know about our planet? SO.HOW
FORCES ON EARTH UNIT 3.2 An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. USE THESE NOTES: OUR HOME PLANET EARTH: What do you know about our planet? SO.HOW
OCN 201 Seafloor Spreading and Plate Tectonics. Question
 OCN 201 Seafloor Spreading and Plate Tectonics Question What was wrong from Wegener s theory of continental drift? A. The continents were once all connected in a single supercontinent B. The continents
OCN 201 Seafloor Spreading and Plate Tectonics Question What was wrong from Wegener s theory of continental drift? A. The continents were once all connected in a single supercontinent B. The continents
Chapter 16. Mountain Building. Mountain Building. Mountains and Plate Tectonics. what s the connection?
 Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
SAC Geography Form 2 Chapter 3: Plate Tectonics Topic 3: Plate Movement
 What causes an earthquake? Plate movement causes pressure to build up along faults, or breaks, in the earth's crust. When the rocks cannot take any more pressure, the rock layers shift and an earthquake
What causes an earthquake? Plate movement causes pressure to build up along faults, or breaks, in the earth's crust. When the rocks cannot take any more pressure, the rock layers shift and an earthquake
Write It! Station Directions
 Write It! Station Directions It is recommended that you have completed at least two of the following stations before working at this station. -Read It! -Explore It! -Watch It! -Research It! Answer each
Write It! Station Directions It is recommended that you have completed at least two of the following stations before working at this station. -Read It! -Explore It! -Watch It! -Research It! Answer each
Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009
 Name: Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009 Objective: Students will be introduced to the theory of plate tectonics and different styles of plate margins and interactions. Introduction The planet can be
Name: Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009 Objective: Students will be introduced to the theory of plate tectonics and different styles of plate margins and interactions. Introduction The planet can be
Topic 12: Dynamic Earth Pracatice
 Name: Topic 12: Dynamic Earth Pracatice 1. Earth s outer core is best inferred to be A) liquid, with an average density of approximately 4 g/cm 3 B) liquid, with an average density of approximately 11
Name: Topic 12: Dynamic Earth Pracatice 1. Earth s outer core is best inferred to be A) liquid, with an average density of approximately 4 g/cm 3 B) liquid, with an average density of approximately 11
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA
 UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
Boundaries, Stresses, and Faults OH MY! How do geologic events change and shape Earth s surface?
 Boundaries, Stresses, and Faults OH MY! How do geologic events change and shape Earth s surface? Remember The Lithosphere is made of The CRUST + The Upper Rigid Mantle Plates may be called by different
Boundaries, Stresses, and Faults OH MY! How do geologic events change and shape Earth s surface? Remember The Lithosphere is made of The CRUST + The Upper Rigid Mantle Plates may be called by different
Earth and Space Science Semester 2 Exam Review. Part 1. - Convection currents circulate in the Asthenosphere located in the Upper Mantle.
 Earth and Space Science 2015 Semester 2 Exam Review Part 1 Convection -A form of heat transfer. - Convection currents circulate in the Asthenosphere located in the Upper Mantle. - Source of heat is from
Earth and Space Science 2015 Semester 2 Exam Review Part 1 Convection -A form of heat transfer. - Convection currents circulate in the Asthenosphere located in the Upper Mantle. - Source of heat is from
Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor
 Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics model describes features and processes on Earth. Plate tectonic science
Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics model describes features and processes on Earth. Plate tectonic science
1. I can describe evidence for continental drift theory (e.g., fossil evidence, mountain belts, paleoglaciation)
 Science 10 Review Earth Science Vocabulary asthenosphere continental drift theory converging plates diverging plates earthquakes epicentre fault hot spot inner core lithosphere mantle mantle convection
Science 10 Review Earth Science Vocabulary asthenosphere continental drift theory converging plates diverging plates earthquakes epicentre fault hot spot inner core lithosphere mantle mantle convection
Global Tectonics. Kearey, Philip. Table of Contents ISBN-13: Historical perspective. 2. The interior of the Earth.
 Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Plate Tectonics. Why Continents and Ocean Basins Exist
 Plate Tectonics Why Continents and Ocean Basins Exist Topics Density Structure of Earth Isostasy Sea-Floor Spreading Mechanical Structure of Earth Driving Mechanism of Plate Tectonics Lithospheric Plate
Plate Tectonics Why Continents and Ocean Basins Exist Topics Density Structure of Earth Isostasy Sea-Floor Spreading Mechanical Structure of Earth Driving Mechanism of Plate Tectonics Lithospheric Plate
Isostasy and Tectonics Lab Understanding the Nature of Mobile Floating Lithospheric Plates
 Isostasy and Tectonics Lab Understanding the Nature of Mobile Floating Lithospheric Plates Crust Mantle Dynamics Introductory Geology Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Isostasy and Tectonics Laboratory Topics
Isostasy and Tectonics Lab Understanding the Nature of Mobile Floating Lithospheric Plates Crust Mantle Dynamics Introductory Geology Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Isostasy and Tectonics Laboratory Topics
Rock Cycle. Draw the Rock cycle on your remediation page OR use a sheet of notebook paper and staple
 Earth Science Test 8.ESS2.3) Describe the relationship between the processes and forces that create igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. I can develop and use models to explain how plate movements
Earth Science Test 8.ESS2.3) Describe the relationship between the processes and forces that create igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. I can develop and use models to explain how plate movements
Geophysics Physics of the Earth
 Geophysics 210 - Physics of the Earth Final exam Section GEOPH 210 Lecture A01 Instructor Dr. Martyn Unsworth Date Friday December 12 th 2008 Time allowed 9:00 a.m. noon Total = 104 points Please attempt
Geophysics 210 - Physics of the Earth Final exam Section GEOPH 210 Lecture A01 Instructor Dr. Martyn Unsworth Date Friday December 12 th 2008 Time allowed 9:00 a.m. noon Total = 104 points Please attempt
The Theory of Plate Tectonics
 Plate Tectonics Objectives Describe how plates move. Explain the features of plate tectonics. Describe the types of plate boundaries and the features that can form and events that can occur at each. The
Plate Tectonics Objectives Describe how plates move. Explain the features of plate tectonics. Describe the types of plate boundaries and the features that can form and events that can occur at each. The
Plate Boundaries & Resulting Landforms
 Plate Boundaries & Resulting Landforms Divergent Plate Boundaries (plates being pulled apart) Type: oceanic plates Description: rising magma gently lifts the crust creating a ridge. The flow of convection
Plate Boundaries & Resulting Landforms Divergent Plate Boundaries (plates being pulled apart) Type: oceanic plates Description: rising magma gently lifts the crust creating a ridge. The flow of convection
Mineral Element Compound Atom Crystal. Silicate Nonsilicate Inorganic Luster Streak. Cleavage Fracture Hardness Density Reclamation
 6 th Grade Science Midterm Study Guide Due February 5 th * Midterm Date: February 9th (Tuesday) * Midterm will consist of 50 multiple choice questions (about 10 per chapter) YOU MUST DEFINE THE KEY TERMS
6 th Grade Science Midterm Study Guide Due February 5 th * Midterm Date: February 9th (Tuesday) * Midterm will consist of 50 multiple choice questions (about 10 per chapter) YOU MUST DEFINE THE KEY TERMS
8 th Grade Science Plate Tectonics and Topography Review
 8 th Grade Science Plate Tectonics and Topography Review #1 Scientists believe that the land masses of Earth were once joined together as one supercontinent called. A: Australia B: Wegner C: Pangaea D:
8 th Grade Science Plate Tectonics and Topography Review #1 Scientists believe that the land masses of Earth were once joined together as one supercontinent called. A: Australia B: Wegner C: Pangaea D:
Earthquakes. Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy
 Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES
 USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
Plate Tectonics Practice Test
 Plate Tectonics Practice Test 1. What is the main idea Alfred Wegner proposed in the Theory of Continental Drift that he published in 1915? a. The continents float on a liquid layer that allows them to
Plate Tectonics Practice Test 1. What is the main idea Alfred Wegner proposed in the Theory of Continental Drift that he published in 1915? a. The continents float on a liquid layer that allows them to
1. occurs when the oceanic crust slides under the continental crust.
 1. occurs when the oceanic crust slides under the continental crust. 2. What type of stress is shown? 3. Where two plates slide past one another is called a boundary. 4. What type of stress is shown? 5.
1. occurs when the oceanic crust slides under the continental crust. 2. What type of stress is shown? 3. Where two plates slide past one another is called a boundary. 4. What type of stress is shown? 5.
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
UNIT 11 PLATE TECTONICS
 UNIT 11 PLATE TECTONICS A. ALFRED WEGENER 1. Continental drift hypothesis Single supercontinent called Pangaea 200 million years ago Pangaea (all land) began to break up and started drifting to their present
UNIT 11 PLATE TECTONICS A. ALFRED WEGENER 1. Continental drift hypothesis Single supercontinent called Pangaea 200 million years ago Pangaea (all land) began to break up and started drifting to their present
Unit 11: Plate Tectonics
 Unit 11: Plate Tectonics A. Alfred Wegner 1. Continental drift hypothesis a. single supercontinent called Pangaea b. 200 million years ago Pangaea (all land) began to break up and started drifting to their
Unit 11: Plate Tectonics A. Alfred Wegner 1. Continental drift hypothesis a. single supercontinent called Pangaea b. 200 million years ago Pangaea (all land) began to break up and started drifting to their
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. Volcanoes and Eruption Types. By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner. Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Dynamic Crust Practice
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
Plate Tectonics. Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries
 Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries Continental Drift 1915, Alfred Wegener - Pangea hypothesis: suggested Earth s continents were part of a large super-continent 200
Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries Continental Drift 1915, Alfred Wegener - Pangea hypothesis: suggested Earth s continents were part of a large super-continent 200
Moho (Mohorovicic discontinuity) - boundary between crust and mantle
 Earth Layers Dynamic Crust Unit Notes Continental crust is thicker than oceanic crust Continental Crust Thicker Less Dense Made of Granite Oceanic Crust Thinner More Dense Made of Basalt Moho (Mohorovicic
Earth Layers Dynamic Crust Unit Notes Continental crust is thicker than oceanic crust Continental Crust Thicker Less Dense Made of Granite Oceanic Crust Thinner More Dense Made of Basalt Moho (Mohorovicic
Structure of the Earth
 Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
4 Deforming the Earth s Crust
 CHAPTER 7 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust SECTION Plate Tectonics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What happens when rock is placed under stress?
CHAPTER 7 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust SECTION Plate Tectonics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What happens when rock is placed under stress?
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics 9.1 Continental Drift An Idea Before Its Time Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics 9.1 Continental Drift An Idea Before Its Time Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics 9.1 Continental Drift An Idea Before Its Time Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics 9.1 Continental Drift An Idea Before Its Time Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined
The Ocean Floor Earth Science, 13e Chapter 13
 The Ocean Floor Earth Science, 13e Chapter 13 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the blue planet Seventy-one percent of Earth s surface
The Ocean Floor Earth Science, 13e Chapter 13 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the blue planet Seventy-one percent of Earth s surface
Geology 101. Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics
 Geology 101 Chapter 1: Plate Tectonics (p. 21) Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics Name You should have read this section during the first week of the quarter. You should re-read this section and review
Geology 101 Chapter 1: Plate Tectonics (p. 21) Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics Name You should have read this section during the first week of the quarter. You should re-read this section and review
Unit 4 Lesson 7 Mountain Building
 Indiana Standards 7.2.4 Explain how convection currents in the mantle cause lithospheric plates to move causing fast changes like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, and slow changes like creation of mountains
Indiana Standards 7.2.4 Explain how convection currents in the mantle cause lithospheric plates to move causing fast changes like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, and slow changes like creation of mountains
Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later...
 CHAPTER 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later... Words Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
CHAPTER 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later... Words Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
The continents are in constant! movement! Earth Science!
 The continents are in constant movement Earth Science Transitional Science 10 Note and Activity Package for Chapter 12 Note: If you lose this package it is your responsibility to print out a new copy from
The continents are in constant movement Earth Science Transitional Science 10 Note and Activity Package for Chapter 12 Note: If you lose this package it is your responsibility to print out a new copy from
The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and
 Earth s Structure The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and
Earth s Structure The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and
Plate Tectonics. How do the plates move?
 Plate Tectonics How do the plates move? Continental Drift Hypothesis In 1915, Alfred Wegener s hypothesis about Continental Drift couldn t explain the forces that could move continents. Wegener wasn t
Plate Tectonics How do the plates move? Continental Drift Hypothesis In 1915, Alfred Wegener s hypothesis about Continental Drift couldn t explain the forces that could move continents. Wegener wasn t
Mohorovicic discontinuity separates the crust and the upper mantle.
 Structure of the Earth Chapter 7 The Earth is divided into 3 Main Layers 1. Crust outermost layer 1% of the Earth s mass thickness varies: 5 100 km two types: oceanic denser continental Mohorovicic discontinuity
Structure of the Earth Chapter 7 The Earth is divided into 3 Main Layers 1. Crust outermost layer 1% of the Earth s mass thickness varies: 5 100 km two types: oceanic denser continental Mohorovicic discontinuity
Chapter Overview. Evidence for Continental Drift. Plate Tectonics. Evidence for Continental Drift. Evidence for Continental Drift 9/28/2010
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. Different plate boundaries have different features. Tectonic plates continue to move today.
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. Different plate boundaries have different features. Tectonic plates continue to move today.
Plate Tectonics Introduction
 Name Block Plate Tectonics Introduction Go to the following site: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html On the top of the screen are different tabs, click on each section as listed
Name Block Plate Tectonics Introduction Go to the following site: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html On the top of the screen are different tabs, click on each section as listed
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY
 CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY Proof or crazy idea? CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY What is Continental Drift Theory? Continental drift theory (CDT): Alfred Wegener found all the continents were once together called
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY Proof or crazy idea? CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY What is Continental Drift Theory? Continental drift theory (CDT): Alfred Wegener found all the continents were once together called
Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition
 Chapter Chapter 1 2 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
Chapter Chapter 1 2 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
Earth s Dynamic Surface
 Earth s Dynamic Surface Shaping Earth s Surface What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the
Earth s Dynamic Surface Shaping Earth s Surface What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
 Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined to form a single supercontinent. Wegener proposed that the
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined to form a single supercontinent. Wegener proposed that the
Earth Systems Science Chapter 7. Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 11/11/2010. Seismology: study of earthquakes and related phenomena
 Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 I. Structure of the Earth II. Plate Tectonics The solid part of the earth system includes processes, just like the atmosphere and oceans. However, the time scales for processes
Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 I. Structure of the Earth II. Plate Tectonics The solid part of the earth system includes processes, just like the atmosphere and oceans. However, the time scales for processes
6. In the diagram below, letters A and B represent locations near the edge of a continent.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
Plate Tectonics Unit II: Plate Boundaries (3.5 pts)
 T. James Noyes, El Camino College Plate Tectonics Unit II: The Plate Boundaries (Topic 11A-2) page 1 Name: Section: Plate Tectonics Unit II: Plate Boundaries (3.5 pts) Plate Boundaries We will now discuss
T. James Noyes, El Camino College Plate Tectonics Unit II: The Plate Boundaries (Topic 11A-2) page 1 Name: Section: Plate Tectonics Unit II: Plate Boundaries (3.5 pts) Plate Boundaries We will now discuss
Theory of Plate Tectonics
 Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
Seafloor Spreading and Paleomagnetism Activity
 Name: PART A: Ocean Bottom Profile Background: Seafloor spreading is the hypothesis that the sea floor moves sideways away from the crest of the mid- ocean ridge. It is estimated that 20 volcanic eruptions
Name: PART A: Ocean Bottom Profile Background: Seafloor spreading is the hypothesis that the sea floor moves sideways away from the crest of the mid- ocean ridge. It is estimated that 20 volcanic eruptions
10/29/13. Plate Boundaries. 3 types of plate boundaries: Divergent (divide) Convergent (collide) Transform (slide past)
 Plate Boundaries 3 types of plate boundaries: Divergent (divide) Convergent (collide) Transform (slide past) 1 Remember the plates are in motion. When plates move, they can either: A) converge (collide)
Plate Boundaries 3 types of plate boundaries: Divergent (divide) Convergent (collide) Transform (slide past) 1 Remember the plates are in motion. When plates move, they can either: A) converge (collide)
Plate Tectonics. Structure of the Earth
 Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering Prof. Deepankar Choudhury Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering Prof. Deepankar Choudhury Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module - 3 Lecture - 7 Engineering Seismology (Contd ) Let us start
Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering Prof. Deepankar Choudhury Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module - 3 Lecture - 7 Engineering Seismology (Contd ) Let us start
The Two Types of Crust. Plate Tectonics. Physical Layers of the Earth. The Asthenosphere. The Lithosphere. Chemical Layers of the Earth
 Plate Tectonics A Reminder of Earth s Structure Two physical units of Earth that are important too! How the Earth Works Plate Tectonics Plate Boundaries Chemical Layers of the Earth Crust - low density
Plate Tectonics A Reminder of Earth s Structure Two physical units of Earth that are important too! How the Earth Works Plate Tectonics Plate Boundaries Chemical Layers of the Earth Crust - low density
Tectonics. Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust
 Tectonics Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust Planetary History Planets formed HOT Denser materials fall to center Planet cools by conduction, convection, radiation to space
Tectonics Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust Planetary History Planets formed HOT Denser materials fall to center Planet cools by conduction, convection, radiation to space
NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4 MATERIAL COVERS CHAPTERS 19, 20, 21, & 2
 NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4 MATERIAL COVERS CHAPTERS 19, 20, 21, & 2 Assignment is due the beginning of the class period on December 14, 2004. Mark answers on a scantron sheet, which will be provided.
NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4 MATERIAL COVERS CHAPTERS 19, 20, 21, & 2 Assignment is due the beginning of the class period on December 14, 2004. Mark answers on a scantron sheet, which will be provided.
Introduction to Oceanography. Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Overview
 Introduction to Oceanography Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics model describes features and processes on Earth. Plate tectonic science
Introduction to Oceanography Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics model describes features and processes on Earth. Plate tectonic science
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark
 Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
b. atomic mass H What is the density of an object with a volume of 15cm 3 and a mass of 45g?
 Name Period Date Earth Science Midterm Review 2015-2016 Quarter 1 Review Assign #1 Basic Chemistry An atom is a basic chemical building block of matter. An atom consists of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Name Period Date Earth Science Midterm Review 2015-2016 Quarter 1 Review Assign #1 Basic Chemistry An atom is a basic chemical building block of matter. An atom consists of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
