THE AMERICAN MINERALOGIST, VOL.51, MAY-JUNE. 1966
|
|
|
- Juniper Rich
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE AMERICAN MINERALOGIST, VOL.51, MAY-JUNE COMPOSITIONAL VARIATIONS OF PLAGIOCLASE FELDSPAR FROM A BASALTIC LAVA FLOW Jnnnv M. Honlnn, Department of Geology, Teras Western College, El Paso, Teras. Assrnecr A detailed study of the Rock Creek basalt flow reveals significant relationships between chemical composition of the plagioclase feldspar and texture. The An content of the groundmass plagioclase varies inversely with size and directly with the amount of associated glass. The rate of cooling, alter extrusion, determined the composition of the groundmass plagioclase. The plagioclase phenocrysts, averaging 20 percent more calcic than the corresponding groundmass plagioclase, are intratelluric. INrnooucrroN At the present time no detailed information is available concerning the variation in composition of any one mineral or the compositional variation of a mineral present in two distinct sizes (i.e., phenocryst and groundmass crystals) in a lava flow. In order to obtain such information a study has been completed concerning the variation in composition of groundmass and phenocryst plagioclase from a thick porphyritic flow (250 to 40 feet), the Rock Creek flow, of the Columbia River Basalt in west-central Idaho (Bond, 1963). Samples were collected from five measured sections of the Rock Creek flow and the phenocryst and groundmass plagioclase in each sample were concentrated separately with a Frantz Isodynamic separator after crushing and screening. The composition of the plagioclase, expressed as mole per cent An content, was determined by the glass fusion method (Foster, 1955). In addition, the textural relationships in each sample were studied with thin sections, with special emphasis on determination of the size of the groundmass plagioclase and the amount of associated glass so as to obtain an index of the rate of cooling for each sample. The factors that determine the texture of any igneous rock include the rate of cooling, bulk chemical composition, composition with regard to hyperfusibles, and pressure. The similarity in average composition of the plagioclase phenocrysts from all samples suggests that the first-formed crystals of plagioclase represent crystallization from the same melt. There is no evidence to indicate that the bulk chemical composition changed during crystallization. The content of hyperfusibles and the effect of pressure during crystallization are hard to appraise, but it seems likely that the influence of pressure was small because of the crvstallization at the surface. Therefore, the rate of cooling, after extrusion, was the primary factor in determining the final texture. However, in small areas variations in volatile constituents and pressure may have influenced the rate of cooling and 0
2 0 JERRY M. HOFFER Tarr,r 1. CouposrrroN.tr,.a.No Toxrunnl Dera ol Pr-a.crocr-asr FRoM THE Rocr Cnaor Fr-ow Sample Nunber An Content Pheno.rJSt An Content Average Size (width in mm) Per Cent Groundmass of Groundmass Crvstals Glass w-1 w-3 w-4 w6 w- w- w9 w-10 W-11 w-12 SKC-1 SKC-2 SKC-3 SKC.4 SKC_6 SKC- SKC-9 SKC-IO skc-11 SK-1 SK-2 SK,3 SK-4 SK-5 SK- SK-9 sk-10 SK-11 SK-12 SK-13 R-1 R-3 R-4 R-5 R-6 R R- R-9 R-10 R-11 s-1 s s-4 s-6 s- s-9 s-10 s-12 s-13 s-14 s-l t O s2.0, ,t r l 0 4, O , , q S 0 o o o t J )l
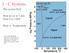
3 PLAGIOCLASE COMPOSITIONAL VARIATION hence the final texture. The average width of the groundmass plagioclase rvas determined by micrometer ocular measurements on two thin sections per sample. The percentage of associated glass was estimated from two thin sections per sample by comparison with standard percentage charts. To check the relative accuracy of these above determinations, each thin section was ranked in order of increasing size of the groundmass plagioclase and the amount of associated glass by projection from a 35 mm slide projector. In all samples, excellent agreement was obtained by both methods. The results of these determinations are summarized in Table 1. Rrsur,rs AND DrscussroN The composition of the groundmass plagiociase ranges from An36 to An5e and shows no s1'stematic spatial variation vertically or laterallv (l).. u, bo tro E ctl?o '-(L fo 33 3e E q)c N= cn9 (9 o. t5 o. to o.o5 o.oo y=o.2445-o.oo3x r= Mole Per Cent An Content Fro. 1. Variation of mole per cent An content of the groundmass plagioclase samples with size (width) of the groundmass plagioclase (y: equation of the line and r : Iinear corrclation coefficient). Each point represents a sample. through the flow. Marked correlations exist, however, between the An content and cr1'stal size of the groundmass plagioclase (Fig. 1) and between the An content of the groundmass plagioclase and the amount of associated glass (Fig.2). As the An content of the groundmass plagioclase increases, the size of the crystals decreases (r: -0.6), and the amount of associated glass increases (r: +0.5). In addition, a marked degree of negative correlation (r: -0.i9) exists between the proportion of associated glass and the size oi the groundmass plagioclase crystals. The plagioclase phenocrysts range in composition from An5e 5 to An3, with 9 per cent of the samples in the interval An5e 5 to Anoz r. Textural relationships and composition (the phenocrysts average 20 per cent more
4 10 IERRV M. HOFFER calcic than the corresponding groundmass plagioclase) suggest that the plagioclase phenocrysts are intratelluric and crystallized at depth under conditions of slow cooling, before the crystallization of the groundmass plagioclase. The relationship of the size of the groundmass plagioclase and proportion of associated glass indicates that there were variations in the rate of cooling after extrusion of the magma. In samples representing conditions of relatively slow cooling the proportion of glass is small and the average size of the groundmass plagioclase is relatively large. Conversely, small groundmass plagioclase crystals, formed under condition of rapid cooling, are found in samples containing a large amount of glass. Rock Creek samples representing rapid cooiing, inferred from the small 60 E55 :so o o4s E y=42.ooo1.o.2332x. 35 o l Per Cent Gloss Frc. 2. Variation of mole per cent An content of the groundmass plagioclase samples rnith per cent glass (y:equation of the line and r:linear correlation coefficient). Each point represents a sample. crystal size and abundant glass, possess groundmass plagioclase of high An content (An66 to An6e) whereas those that cooled more slowly contain groundmass plagioclase of low An content (Anae to Anro). With regard to the plagioclase phenocrysts, no significant relationship was found to exist between the composition and the rate of cooling, as indicated by the proportion of glass. The relationship between compositional variations of the groundmass and phenocryst plagioclase and cooling history, as indicated by textural features, during crystallization of the Rock Creek flow can best be explained by reference to the plagioclase phase diagram in Fig. 3 (Bowen, 1913). In this simplified scheme aii components of the Rock Creek magma are neglected except plagioclase. The temperatures indicated on the phase diagram do not imply the temperatures of crystallization of the magma of the Rock Creek flow.
5 P LAGIOCLASE COM POSI TION A L V ARI AT ION 11 t540 () o t420 (l) 5 E, q) CL E t300 o too An Content Frc. 3. The phase relationships of the plagioclase feldspars (A:composition of the simplified hypothetical Rock Creek magma. B:composition of the most calcic plagioclase phenocryst (Ana), C:composition of the most sodic plagioclase phenocryst (Anrr.u), D:composition of the most calcic groundmass plagioclase (An5e), E:composition of the most sodic groundmass plagioclase (Aq6), and F:composition of the hypothetical Rock Creek magma after extrusion to the surface). When the temperature of the hypothetical Rock Creek magma of composition A intersected the liquidus, the first plagioclase to crystallize had a composition of An3, the composition of the most calcic plagioclase phenocryst (B in Fig.3). As cooling continued more sodic crystals of plagioclase crystallized and some of the earlier more calcic crystals were converted to more sodic composition by reaction with the melt. The relatively small range of composition of the majority of the Rock Creek plagioclase phenocrysts suggests that, for the most part, close approach to equilibrium between the crystals and the melt was attained during
6 12 JDRRY M. HOFFI'R crystailization. Weak zoning in manv of the phenocrysts indicates, however, that equilibrium between the melt and crystals was not maintained throughout the crvstallization of the plagioclase phenocrysts. At this stage, when composition of the plagioclase phenocrysts was about An63 (average An content of all phenocryst samples), the magma and its phenocrysts, in the form of a crystal mush, were extruded to the surface. Cooling was immediately accelerated, and the phenocryst formation halted. The composition of the melt at this stage was probably close to An26, point F on the liquidus curve of Fig. 3, and the groundmass plagioclase crystals that formed initially, after or during extrusion of the magma, had an An content of approximatell'59 per cent (point D). As cooling proceeded, cr\rstals more and more sodic in composition crystal- Iized and some of the earlier more calcic crystals reacted with the melt and became more sodic. The final composition of the groundmass plagioclase was therefore dependent upon the rate of cooling after extrusion. In groundmass samples which reflect a rapid rate of cooling (small size of the groundmass plagioclase and larger amounts of associated glass), the An content of the groundmass plagioclase is high. The high An content of these groundmass plagioclases is evidently the direct result of the rapid cooling. On the other hand, the samples that show evidence of crystallization under conditions of slower cooling (groundmass plagioclase crystals are relatively large and are associated with small amounts of glass) contain groundmass plagioclase of low An content. Under these conditions of slow cooling the early-formed groundmass crystals of composition approximately An5e w re able to react with the melt and were converted in composition to more sodic forms. Therefore, the slower the rate of cooling, the more sodic are the final groundmass plagioclase crystals. CoNcr.usroNs In summary, the important features of the plagioclase from the Rock Creek flow may be stated. The composition of the groundmass plagioclase crystals (An36 to An5e) varies inversely with their size and directly with the amount of associated giass. Therefore, the variation of An content of the plagioclase groundmass crystals is due primarily to the variation in the rate of cooling under conditions of fractional crystallization. The composition of the plagioclase phenocrysts is more calcic than the corresponding groundmass (9 per cent in the interval An5e.5 to Aner s) and does not show any relationship to the amount of associated glass. The first formed crystals, the plagioclase phenocrysts, crystallized at depth under conditions of slow cooling which allowed close approach to equilibrium. At a later stage the magma was extruded to the surface and
7 PLAGIOCLASE COMPOSITIONAL VARIATION 13 variations in the accelerated cooling rate produced the compositional variations found in the groundmass plagioclase crystals. AcrNowrBocMENTS The author wishes to thank The Society of the Sigma Xi for financial support of this study. Thanks are also extended to R. K. Sorem, Washington State University, who critically read the manuscript and offered helpful suggestions during the investigation. RrprnnNcrs BoNr, J. G. (1963) Geology of the Clearwater Embayment. Iil.aho Bureau Mines Geol. Pamph. 12. Bowrx, N. L. (1913) The melting phenomena of the plagioclase feldsparc. Am. Jour. Sci.35, Fosrnn, VV. R. (1955) Simple method for the determination of plagioclase leldspar. Am. Mineral..40,
Block: Igneous Rocks. From this list, select the terms which answer the following questions.
 Geology 12 Name: Mix and Match: Igneous Rocks Refer to the following list. Block: porphyritic volatiles mafic glassy magma mixing concordant discontinuous reaction series igneous vesicular partial melting
Geology 12 Name: Mix and Match: Igneous Rocks Refer to the following list. Block: porphyritic volatiles mafic glassy magma mixing concordant discontinuous reaction series igneous vesicular partial melting
Lecture 3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Dr. Shwan Omar
 Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
INTRODUCTION ROCK COLOR
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS Instructions: Some rocks that you would be working with may have sharp edges and corners, therefore, be careful when working with them! When you are
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS Instructions: Some rocks that you would be working with may have sharp edges and corners, therefore, be careful when working with them! When you are
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100
 Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Chapter 4 8/27/2013. Igneous Rocks. and Intrusive Igneous Activity. Introduction. The Properties and Behavior of Magma and Lava
 Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
CHAPTER ROCK WERE FORMED
 HOW CHAPTER 5 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
HOW CHAPTER 5 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
CHAPTER ROCK WERE FORMED
 HOW CHAPTER 3 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
HOW CHAPTER 3 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
6. IGNEOUS ROCKS AND VOLCANIC HAZARDS
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS AND VOLCANIC HAZARDS Instructions: Refer to Laboratory 5 in your lab book on pages 129-152 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS AND VOLCANIC HAZARDS Instructions: Refer to Laboratory 5 in your lab book on pages 129-152 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will
EARTH SCIENCE. Geology, the Environment and the Universe. Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks
 EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
To get you thinking What natural process is responsible for the appearance of these rocks? Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 To get you thinking What natural process is responsible for the appearance of these rocks? Rocks and the Rock Cycle Bell Ringer Name the 3 types of rock. Is one type of rock able to change into a different
To get you thinking What natural process is responsible for the appearance of these rocks? Rocks and the Rock Cycle Bell Ringer Name the 3 types of rock. Is one type of rock able to change into a different
TWO COMPONENT (BINARY) PHASE DIAGRAMS. Experimental Determination of 2-Component Phase Diagrams
 Page 1 of 12 EENS 211 Earth Materials Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson TWO COMPONENT (BINARY) PHASE DIAGRAMS This document last updated on 08-Oct-2003 Experimental Determination of 2-Component
Page 1 of 12 EENS 211 Earth Materials Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson TWO COMPONENT (BINARY) PHASE DIAGRAMS This document last updated on 08-Oct-2003 Experimental Determination of 2-Component
Chapter 3: Igneous Rocks 3.2 IGNEOUS ROCK ORIGIN
 Chapter 3: Igneous Rocks Adapted by Lyndsay R. Hauber & Michael B. Cuggy (2018) University of Saskatchewan from Deline B, Harris R & Tefend K. (2015) "Laboratory Manual for Introductory Geology". First
Chapter 3: Igneous Rocks Adapted by Lyndsay R. Hauber & Michael B. Cuggy (2018) University of Saskatchewan from Deline B, Harris R & Tefend K. (2015) "Laboratory Manual for Introductory Geology". First
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Student Name: College: Grade:
 Student Name: College: Grade: Physical Geology Laboratory IGNEOUS MINERALS AND ROCKS IDENTIFICATION - INTRODUCTION & PURPOSE: In this lab you will learn to identify igneous rocks in hand samples from their
Student Name: College: Grade: Physical Geology Laboratory IGNEOUS MINERALS AND ROCKS IDENTIFICATION - INTRODUCTION & PURPOSE: In this lab you will learn to identify igneous rocks in hand samples from their
Igneous Rock. Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere
 Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
 1 Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Presentation modified from: Instructor Resource Center on CD-ROM, Foundations of Earth Science,, 4 th Edition, Lutgens/Tarbuck, Rock Cycle Igneous Rocks Today 2 Rock
1 Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Presentation modified from: Instructor Resource Center on CD-ROM, Foundations of Earth Science,, 4 th Edition, Lutgens/Tarbuck, Rock Cycle Igneous Rocks Today 2 Rock
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Igneous Rocks. Igneous Rocks - 1. Environment of Formation - Magma - Plutonic - rock that formed within the Earth. Intrusive - Earth s crust.
 Name: Date: Period: Minerals and Rocks The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES - Methods to classify igneous rocks: 1. Environment of Formation - Magma - Plutonic - rock that formed within the
Name: Date: Period: Minerals and Rocks The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES - Methods to classify igneous rocks: 1. Environment of Formation - Magma - Plutonic - rock that formed within the
IGNEOUS ROCKS. SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks?
 Date Period Name IGNEOUS ROCKS SECTION.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Date Period Name IGNEOUS ROCKS SECTION.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Textures of Igneous Rocks
 Page 1 of 6 EENS 212 Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Petrology Tulane University This document last updated on 12-Feb-2004 Introduction to Igneous Rocks An igneous rock is any crystalline or glassy rock that forms
Page 1 of 6 EENS 212 Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Petrology Tulane University This document last updated on 12-Feb-2004 Introduction to Igneous Rocks An igneous rock is any crystalline or glassy rock that forms
Plate tectonics, rock cycle
 Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
Engineering Geology. Igneous rocks. Hussien Al - deeky
 Igneous rocks Hussien Al - deeky 1 The Geology Definition of Rocks In Geology Rock is defined as the solid material forming the outer rocky shell or crust of the earth. There are three major groups of
Igneous rocks Hussien Al - deeky 1 The Geology Definition of Rocks In Geology Rock is defined as the solid material forming the outer rocky shell or crust of the earth. There are three major groups of
How 2 nd half labs will work
 How 2 nd half labs will work Continue to use your mineral identification skills Learn to describe, classify, interpret rock hand samples: Igneous sedimentary metamorphic volcanic plutonic (1 week) (1 wk)
How 2 nd half labs will work Continue to use your mineral identification skills Learn to describe, classify, interpret rock hand samples: Igneous sedimentary metamorphic volcanic plutonic (1 week) (1 wk)
EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Name Class Date. Chapter 3 Rocks Chapter Test. Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided.
 Chapter 3 Rocks Chapter Test Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Which of the following is true about rocks? a. Rocks are
Chapter 3 Rocks Chapter Test Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Which of the following is true about rocks? a. Rocks are
THE FORMATION OF IDDINGSITE. A. B. Eowanls, Uniaersity of M elbourne, Auslralia.
 THE FORMATION OF IDDINGSITE A. B. Eowanls, Uniaersity of M elbourne, Auslralia. h.rrnooucrton fn their comprehensive paper on the origin, occurrence, composition and physical properties of the mineral
THE FORMATION OF IDDINGSITE A. B. Eowanls, Uniaersity of M elbourne, Auslralia. h.rrnooucrton fn their comprehensive paper on the origin, occurrence, composition and physical properties of the mineral
Hirsch - Binary phase diagrams problems KEY
 Hirsch - Binary phase diagrams problems KEY Name Question 1. 1A. Using the phase rule, determine the degrees of freedom: a. at point e F = 2-3 + 1 = 0 b. within the field A + B F = 2-2 + 1 = 1 c. within
Hirsch - Binary phase diagrams problems KEY Name Question 1. 1A. Using the phase rule, determine the degrees of freedom: a. at point e F = 2-3 + 1 = 0 b. within the field A + B F = 2-2 + 1 = 1 c. within
The 3 types of rocks:
 Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Igneous Activity The 3 types of rocks:! Sedimentary! Igneous! Metamorphic Marble 1 10/7/15 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Come from rocks sediments (rock fragments, sand, silt, etc.) Fossils
Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Igneous Activity The 3 types of rocks:! Sedimentary! Igneous! Metamorphic Marble 1 10/7/15 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Come from rocks sediments (rock fragments, sand, silt, etc.) Fossils
Igneous Rocks. Sedimentary Rocks. Metamorphic Rocks
 Name: Date: Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from the solidification of magma either below (intrusive igneous rocks) or above (extrusive igneous rocks) the Earth s surface. For example, the igneous rock
Name: Date: Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from the solidification of magma either below (intrusive igneous rocks) or above (extrusive igneous rocks) the Earth s surface. For example, the igneous rock
Earth Science 11: Minerals
 lname: Date: Earth Science 11: Minerals Purpose: Text Pages: I can identify and classify minerals using their physical and chemical properties 90-111 *This is recommended reading! Matter and Atoms (5.1)
lname: Date: Earth Science 11: Minerals Purpose: Text Pages: I can identify and classify minerals using their physical and chemical properties 90-111 *This is recommended reading! Matter and Atoms (5.1)
PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS
 PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS PLATE TECTONICS TO IGNEOUS ROCKS Internal Heat Seafloor Spreading/Plate Tectonics Volcanism Plate Boundary Intra-plate (hot spot) Divergent Convergent Igneous
PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS PLATE TECTONICS TO IGNEOUS ROCKS Internal Heat Seafloor Spreading/Plate Tectonics Volcanism Plate Boundary Intra-plate (hot spot) Divergent Convergent Igneous
Rocks. Types of Rocks
 Rocks Rocks are the most common material on Earth. They are naturally occurring aggregates of one or more minerals. 1 Igneous rocks, Types of Rocks Sedimentary rocks and Metamorphic rocks. 2 1 3 4 2 IGNEOUS
Rocks Rocks are the most common material on Earth. They are naturally occurring aggregates of one or more minerals. 1 Igneous rocks, Types of Rocks Sedimentary rocks and Metamorphic rocks. 2 1 3 4 2 IGNEOUS
Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks
 Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - 1 Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly
Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - 1 Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly
Rocks. Geology: Slides 22-50
 Rocks Geology: Slides 22-50 Rocks Catastrophism versus Uniformitarianism Catastrophism The Earth s surface was created by fast drastic changes (called catastrophes) that occurred long ago and do not occur
Rocks Geology: Slides 22-50 Rocks Catastrophism versus Uniformitarianism Catastrophism The Earth s surface was created by fast drastic changes (called catastrophes) that occurred long ago and do not occur
Rocks. 3.1 The Rock Cycle. 3.1 The Rock Cycle. 3.1 The Rock Cycle. The Rock Cycle. I. Rocks
 Rocks Tarbuck Lutgens 3.1 The Rock Cycle 3.1 The Rock Cycle I. Rocks Rocks are any solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter occurring naturally as part of our planet. Types of Rocks 1. Igneous rock
Rocks Tarbuck Lutgens 3.1 The Rock Cycle 3.1 The Rock Cycle I. Rocks Rocks are any solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter occurring naturally as part of our planet. Types of Rocks 1. Igneous rock
DIFFERENTIATION OF MAGMAS BY FRACTIONAL CRYSTALLIZATION THE M&M MAGMA CHAMBER
 Geol 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2009 Name DIFFERENTIATION OF MAGMAS BY FRACTIONAL CRYSTALLIZATION THE M&M MAGMA CHAMBER Objective: This exercise is intended to improve understanding
Geol 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2009 Name DIFFERENTIATION OF MAGMAS BY FRACTIONAL CRYSTALLIZATION THE M&M MAGMA CHAMBER Objective: This exercise is intended to improve understanding
EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS ROCK CLASSIFICATION LAB 2 HANDOUT
 EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS ROCK CLASSIFICATION LAB 2 HANDOUT Sources: University of Washington, Texas A&M University, University of Southern Alabama What is an igneous rock (a
EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS ROCK CLASSIFICATION LAB 2 HANDOUT Sources: University of Washington, Texas A&M University, University of Southern Alabama What is an igneous rock (a
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 3 Rocks 3.1 The Rock Cycle Rocks Rocks are any solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter occurring naturally as part of our planet. Types of Rocks
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 3 Rocks 3.1 The Rock Cycle Rocks Rocks are any solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter occurring naturally as part of our planet. Types of Rocks
Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks
 Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly recognize
Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly recognize
This slide show is intended to help you understand important types of rocks.
 Rocks Mrs. Comer This slide show is intended to help you understand important types of rocks. The diagram in the next slide represents the ROCK CYCLE a scheme that represents the processes of continuous
Rocks Mrs. Comer This slide show is intended to help you understand important types of rocks. The diagram in the next slide represents the ROCK CYCLE a scheme that represents the processes of continuous
Chapter 6: The Phase Rule and One and Two-Component Systems aka Phase Equilibria
 Chapter 6: The Phase Rule and One and Two-Component Systems aka Phase Equilibria Makaopuhi Lava Lake Magma samples recovered from various depths beneath solid crust From Wright and Okamura, (1977) USGS
Chapter 6: The Phase Rule and One and Two-Component Systems aka Phase Equilibria Makaopuhi Lava Lake Magma samples recovered from various depths beneath solid crust From Wright and Okamura, (1977) USGS
THE ORDER OF CRYSTALLIZATION IN IGNEOUS ROCKS
 THE ORDER OF CRYSTALLIZATION IN IGNEOUS ROCKS N. L. BOWEN Massachusetts Institute of Technology The order of crystallization in igneous rocks is necessarily determined from the end product, the solid rock.
THE ORDER OF CRYSTALLIZATION IN IGNEOUS ROCKS N. L. BOWEN Massachusetts Institute of Technology The order of crystallization in igneous rocks is necessarily determined from the end product, the solid rock.
Station 2 2. Identify the type of each sample (i.e. rock type, mineral class) 3. Samples A and B have a very similar appearance. What key characterist
 Station 1 2. Identify the type of each sample (i.e. rock type, mineral class) 3. What is an important economic use of sample 1B? Station 2 2. Identify the type of each sample (i.e. rock type, mineral class)
Station 1 2. Identify the type of each sample (i.e. rock type, mineral class) 3. What is an important economic use of sample 1B? Station 2 2. Identify the type of each sample (i.e. rock type, mineral class)
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Grotzinger Jordan. Understanding Earth. Sixth Edition
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
RR#7 - Free Response
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the table below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The table shows the elements and their percent compositions by mass in the five minerals present in
Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the table below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The table shows the elements and their percent compositions by mass in the five minerals present in
SHORTER COMMUNICATIONS
 SHORTER COMMUNICATIONS CHEMICO-MINERALOGIC RELATIONSHIP IN RAJMAHAL BASALTS-BIHAR J. C. V. SASTRI Department of Geology, University of Mysore, Mysore Introduction: Recently the writer in association with
SHORTER COMMUNICATIONS CHEMICO-MINERALOGIC RELATIONSHIP IN RAJMAHAL BASALTS-BIHAR J. C. V. SASTRI Department of Geology, University of Mysore, Mysore Introduction: Recently the writer in association with
Name Class Date. 1. In your own words, write a definition for the term rock cycle.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS 1. In your own words, write a definition for the term rock cycle. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS 1. In your own words, write a definition for the term rock cycle. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
lava magma pyroclastic materials lava flow igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma
 magma lava lava flow pyroclastic materials igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma intermediate magma viscosity magma chamber Bowen s reaction
magma lava lava flow pyroclastic materials igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma intermediate magma viscosity magma chamber Bowen s reaction
Introduction. Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth
 Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Name Petrology Spring 2006 Igneous rocks lab Part II Hand samples of igneous rocks Due Tuesday 3/7
 Igneous rocks lab Part II Hand samples of igneous rocks Due Tuesday 3/7 1. Use the color index and density of the rock to establish whether it is felsic, intermediate, mafic, or ultramafic. 2. Determine
Igneous rocks lab Part II Hand samples of igneous rocks Due Tuesday 3/7 1. Use the color index and density of the rock to establish whether it is felsic, intermediate, mafic, or ultramafic. 2. Determine
Unit 2 Exam: Rocks & Minerals
 Name: Date: 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the 2001 edition of the Earth Science Reference Tables, the map and cross section below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The shaded
Name: Date: 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the 2001 edition of the Earth Science Reference Tables, the map and cross section below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The shaded
12 Chemistry (Mg,Fe) 2 SiO 4 Olivine is forms what is called an isomorphous solid solution series that ranges between two end members: Forsterite Mg
 11 Olivine Structure Olivine is a common green or brown rock forming minerals which consists of a solid-solution series between Forsterite (Fo) and Fayalite (Fa). It is an orthorhombic orthosilicate with
11 Olivine Structure Olivine is a common green or brown rock forming minerals which consists of a solid-solution series between Forsterite (Fo) and Fayalite (Fa). It is an orthorhombic orthosilicate with
Quartz. ! Naturally occurring - formed by nature. ! Solid - not liquid or gas. Liquid water is not a mineral
 GEOL 110 - Minerals, Igneous Rocks Minerals Diamond Azurite Quartz Why Study Minerals?! Rocks = aggregates of minerals! Importance to Society?! Importance to Geology? 5 part definition, must satisfy all
GEOL 110 - Minerals, Igneous Rocks Minerals Diamond Azurite Quartz Why Study Minerals?! Rocks = aggregates of minerals! Importance to Society?! Importance to Geology? 5 part definition, must satisfy all
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) What is the approximate density of a mineral with a mass of 262.2 grams that displaces 46 cubic centimeters of water? A) 6.1 g/cm 3 C) 1.8 g/cm 3 B) 5.7 g/cm 3 D) 12.2 g/cm 3 2) In which two Earth
Name: 1) What is the approximate density of a mineral with a mass of 262.2 grams that displaces 46 cubic centimeters of water? A) 6.1 g/cm 3 C) 1.8 g/cm 3 B) 5.7 g/cm 3 D) 12.2 g/cm 3 2) In which two Earth
Name Class Date. In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements.
 CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Partial melting of mantle peridotite
 Partial melting of mantle peridotite 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 (TºC) Depth (km) 50 100 150 Plag lherzolite (ol-opx-cpx-pl) Spinel lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-sp) Garnet lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-gar) Graphite Diamond
Partial melting of mantle peridotite 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 (TºC) Depth (km) 50 100 150 Plag lherzolite (ol-opx-cpx-pl) Spinel lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-sp) Garnet lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-gar) Graphite Diamond
DO NOW: HW DUE FRIDAY!!!
 DO NOW: HW DUE FRIDAY!!! 1. What is a sedimentary rock? 2. How are sedimentary rocks formed? 3. What are the characteristics of sedimentary rock? 4. What are metamorphic rocks? 5. How are metamorphic rocks
DO NOW: HW DUE FRIDAY!!! 1. What is a sedimentary rock? 2. How are sedimentary rocks formed? 3. What are the characteristics of sedimentary rock? 4. What are metamorphic rocks? 5. How are metamorphic rocks
Earth Science 232 Petrography
 Earth Science 232 Petrography Course notes by Shaun Frape and Alec Blyth Winter 2002 1 Petrology - Introduction Some Definitions Petra Greek for rock Logos Greek for disclosure or explanation Petrology
Earth Science 232 Petrography Course notes by Shaun Frape and Alec Blyth Winter 2002 1 Petrology - Introduction Some Definitions Petra Greek for rock Logos Greek for disclosure or explanation Petrology
WHAT ARE ROCKS? ROCKS are a naturally occurring SOLID MIXTURE of one or more minerals and organic matter. Rocks are ALWAYS changing.
 WHAT ARE ROCKS? ROCKS are a naturally occurring SOLID MIXTURE of one or more minerals and organic matter. Rocks are ALWAYS changing. How do we classify Rocks? Formation (where and how the rock was formed)
WHAT ARE ROCKS? ROCKS are a naturally occurring SOLID MIXTURE of one or more minerals and organic matter. Rocks are ALWAYS changing. How do we classify Rocks? Formation (where and how the rock was formed)
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks
 The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
Earth Science 11: Earth Materials: Rock Cycle
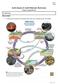 Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials: Rock Cycle Chapter 2, pages 44 to 46 2.1: Rock Cycle What is a Rock? A solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally as part of our planet
Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials: Rock Cycle Chapter 2, pages 44 to 46 2.1: Rock Cycle What is a Rock? A solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally as part of our planet
C = 3: Ternary Systems: Example 1: Ternary Eutectic
 Phase Equilibrium C = 3: Ternary Systems: Example 1: Ternary Eutectic Adding components, becomes increasingly difficult to depict 1-C: P - T diagrams easy 2-C: isobaric T-X, isothermal P-X 3-C:?? Still
Phase Equilibrium C = 3: Ternary Systems: Example 1: Ternary Eutectic Adding components, becomes increasingly difficult to depict 1-C: P - T diagrams easy 2-C: isobaric T-X, isothermal P-X 3-C:?? Still
Notes for Use of the Cpx-Plag-Ol Thermobar Workbook Last Updated:
 Notes for Use of the Cpx-Plag-Ol Thermobar Workbook Last Updated: 7-22-05 Cpx-Plag-Ol Thermobar is an Excel workbook that can be used to calculate crystallization pressures and temperatures for clinopyroxene-
Notes for Use of the Cpx-Plag-Ol Thermobar Workbook Last Updated: 7-22-05 Cpx-Plag-Ol Thermobar is an Excel workbook that can be used to calculate crystallization pressures and temperatures for clinopyroxene-
Igneous Rocks: Formed by Fire (p )
 READING QUESTIONS: Chapter 2 (Rocks) PSCI 131 18/WI 70 pts NAME DUE: Monday, January 29 Igneous Rocks: Formed by Fire (p. 34-43) 1. What is magma? 2. Extrusive igneous rocks form at the Earth s, and intrusive
READING QUESTIONS: Chapter 2 (Rocks) PSCI 131 18/WI 70 pts NAME DUE: Monday, January 29 Igneous Rocks: Formed by Fire (p. 34-43) 1. What is magma? 2. Extrusive igneous rocks form at the Earth s, and intrusive
Igneous Rock Notes. Page #:
 Page #: Igneous Rock Notes Magma and lava form very different types of igneous rocks. Igneous rocks form from molten rock, but where does molten rock come from? The temperature inside Earth with depth.
Page #: Igneous Rock Notes Magma and lava form very different types of igneous rocks. Igneous rocks form from molten rock, but where does molten rock come from? The temperature inside Earth with depth.
What Do You See? Learning Outcomes Goals Learning Outcomes Think About It Identify classify In what kinds of environments do igneous rocks form?
 Section 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Identify and classify
Section 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Identify and classify
Rock & Minerals Regents Review
 Name Rock & Minerals Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagram below, which represents a part of the rock cycle. The igneous rock granite, and the characteristics of sedimentary
Name Rock & Minerals Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagram below, which represents a part of the rock cycle. The igneous rock granite, and the characteristics of sedimentary
Unit 2: Minerals and Rocks Practice Questions
 Name: Date: 1. Which mineral is white or colorless, has a hardness of 2.5, and splits with cubic cleavage? 6. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the photograph of a sample of gneiss below.
Name: Date: 1. Which mineral is white or colorless, has a hardness of 2.5, and splits with cubic cleavage? 6. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the photograph of a sample of gneiss below.
Rocks Rock- A group of minerals, glass, mineroid bound together in some way.
 Rocks Rock- A group of minerals, glass, mineroid bound together in some way. All rocks fit into one of three categories: Igneous- formed by the cooling and hardening of hot molten rock Sedimentary- formed
Rocks Rock- A group of minerals, glass, mineroid bound together in some way. All rocks fit into one of three categories: Igneous- formed by the cooling and hardening of hot molten rock Sedimentary- formed
Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity
 Summary IGNEOUS ROCKS AND METAMORPHIC ROCKS DERIVED FROM IGNEOUS parents make up about 95 percent of Earth s crust. Furthermore, the mantle, which accounts for more than 82 percent of Earth s volume, is
Summary IGNEOUS ROCKS AND METAMORPHIC ROCKS DERIVED FROM IGNEOUS parents make up about 95 percent of Earth s crust. Furthermore, the mantle, which accounts for more than 82 percent of Earth s volume, is
Igneous Rocks. Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members:
 Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Unit 9 Lesson 3 How Can Rocks Be Classified? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Igneous Rock Rock is a natural solid that is made of one or more minerals. Rocks are classified by how they form. There are three types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous Rock Classwork
Igneous Rock Rock is a natural solid that is made of one or more minerals. Rocks are classified by how they form. There are three types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous Rock Classwork
Crystallization history of a zoned plagioclase
 MINERALOGICAL MAGAZINE, DECEMBER 1974, VOL. 39, vv. 867-77 Crystallization history of a zoned plagioclase (Microprobe analysis of zoned plagioclase from the Grand Manan tholeiite sheet) G. J. PRINGLE,
MINERALOGICAL MAGAZINE, DECEMBER 1974, VOL. 39, vv. 867-77 Crystallization history of a zoned plagioclase (Microprobe analysis of zoned plagioclase from the Grand Manan tholeiite sheet) G. J. PRINGLE,
Interpreting Phase Diagrams
 Interpreting Phase Diagrams Understanding chemical reactions requires that we know something about how materials behave as the temperature and pressure change. For a single component (like quartz or ice)
Interpreting Phase Diagrams Understanding chemical reactions requires that we know something about how materials behave as the temperature and pressure change. For a single component (like quartz or ice)
Textural Terms in Igneous Petrology
 Textural Terms in Igneous Petrology Adcumulate - Cumulus crystals continue to grow and displace the intercumulus liquid. Example: Opx adcumulate texture with minor interstitial chromite and plagioclase
Textural Terms in Igneous Petrology Adcumulate - Cumulus crystals continue to grow and displace the intercumulus liquid. Example: Opx adcumulate texture with minor interstitial chromite and plagioclase
A. IGNEOUS Rocks formed by cooling and hardening of hot molten rock called magma (within crust or at its surface).
 EARTH SCIENCE 11 CHAPTER 5 NOTES KEY How Earth's Rocks Were Formed Early geologists believed that the physical features of the Earth were formed by sudden spectacular events called CATASTROPHES. Modern
EARTH SCIENCE 11 CHAPTER 5 NOTES KEY How Earth's Rocks Were Formed Early geologists believed that the physical features of the Earth were formed by sudden spectacular events called CATASTROPHES. Modern
23/9/2013 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY. Chapter 2: Rock classification:
 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 2: Rock classification: ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks
ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 2: Rock classification: ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks
2-C Eutectic Systems
 Phase Equilibrium 2-C Eutectic Systems Example: Diopside - Anorthite No solid solution * For system at this T, X, phase(s) plot where? Fig. 6.11. Isobaric T-X phase diagram at atmospheric pressure. After
Phase Equilibrium 2-C Eutectic Systems Example: Diopside - Anorthite No solid solution * For system at this T, X, phase(s) plot where? Fig. 6.11. Isobaric T-X phase diagram at atmospheric pressure. After
Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
Physical Geography Lab Activity #07
 Physical Geography Lab Activity #07 Due date Name Rocks & Minerals COR Objective 8 7.1. Introduction One part of being a physical geographer is having a basic knowledge of the rocks around us. In this
Physical Geography Lab Activity #07 Due date Name Rocks & Minerals COR Objective 8 7.1. Introduction One part of being a physical geographer is having a basic knowledge of the rocks around us. In this
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science Seventh Edition
 INSTRUCTOR MANUAL Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Applications and Investigations in Earth Science Seventh Edition Tarbuck Lutgens Pinzke Exercise One The Study of Minerals MATERIALS
INSTRUCTOR MANUAL Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Applications and Investigations in Earth Science Seventh Edition Tarbuck Lutgens Pinzke Exercise One The Study of Minerals MATERIALS
Directed Reading. Section: Rocks and the Rock Cycle. made of a. inorganic matter. b. solid organic matter. c. liquid organic matter. d. chemicals.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Rocks and the Rock Cycle 1. The solid part of Earth is made up of material called a. glacial ice. b. lava. c. rock. d. wood. 2. Rock can be a collection of one
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Rocks and the Rock Cycle 1. The solid part of Earth is made up of material called a. glacial ice. b. lava. c. rock. d. wood. 2. Rock can be a collection of one
13. PETROLOGY OF BASALTS FROM DEEP SEA DRILLING PROJECT, LEG 38
 . PETROLOGY OF BASALTS FROM DEEP SEA DRILLING PROJECT, LEG W.I. Ridley, M.R. Perfit, and ML. Adams, LamontDoherty Geological Observatory, Columbia University, Palisades, New York INTRODUCTION We have determined
. PETROLOGY OF BASALTS FROM DEEP SEA DRILLING PROJECT, LEG W.I. Ridley, M.R. Perfit, and ML. Adams, LamontDoherty Geological Observatory, Columbia University, Palisades, New York INTRODUCTION We have determined
GEOLOGY. Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02
 GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
Happy Tuesday. Pull out a ½ sheet of paper
 Happy Tuesday Pull out a ½ sheet of paper 1. Physical properties of a mineral are predominantly related to 1. the external conditions of temperature, pressure, and amount of space available for growth.
Happy Tuesday Pull out a ½ sheet of paper 1. Physical properties of a mineral are predominantly related to 1. the external conditions of temperature, pressure, and amount of space available for growth.
Name. GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Igneous Rocks
 Name GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Igneous Rocks I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give an endless variety
Name GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Igneous Rocks I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give an endless variety
Differentiation of Magmas By Fractional Crystallization
 Wirth Magmatic Differentiation Using M&M s 1 HANDOUT Differentiation of Magmas By Fractional Crystallization Objective The objective of this exercise is to gain first-hand knowledge of the process of magmatic
Wirth Magmatic Differentiation Using M&M s 1 HANDOUT Differentiation of Magmas By Fractional Crystallization Objective The objective of this exercise is to gain first-hand knowledge of the process of magmatic
Rock Cart for High School Students
 Rock Cart for High School Students Goals and Objectives for high school students (9 th 12 th grade): 1) Define igneous rocks 2) Discuss chemical composition of rocks 3) Understand the plate tectonics and
Rock Cart for High School Students Goals and Objectives for high school students (9 th 12 th grade): 1) Define igneous rocks 2) Discuss chemical composition of rocks 3) Understand the plate tectonics and
Igneous Rocks. Definition of Igneous Rocks. Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma
 Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS REFER TO CHAPTER 2 IN YOUR MANUAL
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Section: Pre-Lab and Introduction to Physical Properties of Rocks Assignment for: Common Rocks (Chapter 2) For this assignment, you will require:
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Section: Pre-Lab and Introduction to Physical Properties of Rocks Assignment for: Common Rocks (Chapter 2) For this assignment, you will require:
1 - C Systems. The system H 2 O. Heat an ice at 1 atm from-5 to 120 o C. Heat vs. Temperature
 1 - C Systems The system H 2 O Heat an ice at 1 atm from-5 to 120 o C Heat vs. Temperature Fig. 6.7. After Bridgman (1911) Proc. Amer. Acad. Arts and Sci., 5, 441-513; (1936) J. Chem. Phys., 3, 597-605;
1 - C Systems The system H 2 O Heat an ice at 1 atm from-5 to 120 o C Heat vs. Temperature Fig. 6.7. After Bridgman (1911) Proc. Amer. Acad. Arts and Sci., 5, 441-513; (1936) J. Chem. Phys., 3, 597-605;
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
9/4/2015. Feldspars White, pink, variable Clays White perfect Quartz Colourless, white, red, None
 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks Chapter 3.0: Weathering & soils Chapter 4.0: Geological
ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks Chapter 3.0: Weathering & soils Chapter 4.0: Geological
A rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals, or organic matter
 A rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals, or organic matter Rocks are classified by how they are formed, their composition, and texture Rocks change over time through the rock
A rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals, or organic matter Rocks are classified by how they are formed, their composition, and texture Rocks change over time through the rock
REMINDER. MOVIE: Rocks that Originate Underground 5:41 to 12:40
 REMINDER 2 chapters covered next week Sedimentary Rocks Soils and Weathering (first half) Learn vocabulary for both! Turn to Neighbor: Without using your book or notes, try to remember which te mineral
REMINDER 2 chapters covered next week Sedimentary Rocks Soils and Weathering (first half) Learn vocabulary for both! Turn to Neighbor: Without using your book or notes, try to remember which te mineral
