Quantitative Assessment and Spatial Characteristics of Agricultural Drought Risk in the Jinghe Watershed, Northwestern China
|
|
|
- Randolph Woods
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 December, 2011 J. Resour. Ecol (4) DOI: /j.issn x Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.2 o.4 Article Quantitative Assessment and Spatial Characteristics of Agricultural Drought Risk in the Jinghe Watershed, orthwestern China LOG Xin 1, 2, ZHE Lin 1, CHEG Shengkui 1 * and DI Suchuang 3 1 Institute of Geographic Sciences and atural Resources Research, CAS, Beijing , China; 2 Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing , China; 3 Beijing Hydraulic Research Institute, Beijing , China Abstract: Though drought is a recurrent phenomenon in the Jinghe watershed, very little attention has been paid to drought mitigation and preparedness. This article presents a method for the spatial assessment of agricultural drought risk in the Jinghe watershed of western China at a 1- grid scale. A conceptual framework, which emphasizes the combined roles of hazard and vulnerability in defining risk, is used. The Z index method in a GIS environment is used to map the spatial extent of drought hazards. The key social and physical factors that define agricultural drought in the context of the Jinghe watershed are indentified and corresponding thematic maps are prepared. Risk is calculated by the integration of hazard and vulnerability. Results show that the risk gradient follows a north-south and west-east tendency and that agricultural droughts pose the highest risk to northern and northwestern sections of the Jinghe watershed. Key words: agricultural drought; natural hazards; vulnerability; risk assessment; Jinghe watershed 1 Introduction Drought is a normal, recurrent feature of climate that affects virtually all countries to some degree. The number of drought-induced natural hazards has grown significantly since the 1960s, largely as a result of increasing vulnerability to extended periods of precipitation deficiency rather than because of an increase in the frequency of meteorological droughts. This increase in drought-induced natural disasters has resulted in a considerable growth of interest in drought mitigation and preparedness worldwide. High economic costs and social vulnerability to droughts has led to increasing awareness of drought vulnerability in recent years. Agricultural drought risk assessment is essential for drought management. Previous studies are weak because of the subjectivity in the selection of risk assessment indicators and the focus on evaluation index systems and evaluation models, usually conducted on an administrative scale. Administrative scale-based risk assessment models lack accuracy to some degree. The average area affected by drought in China is about million ha per year, accounting for 60% of the total area affected by all types of meteorological disasters and annual grain losses due to drought are up to 10 billion kg (Wu et al. 2011). From , data from the China statistical yearbook showed that affected area of arable land induced by drought accounted for 77.92% of the total area affected by all types of meteorological hazards (Fig.1). The Jinghe watershed is located in a semi-arid region and characterized by high inter-annual and intra-seasonal rainfall variability. This region is regarded as one of the most drought-prone areas in China. Low and erratic rainfall, and soils with low water-holding capacity are major features of the Jinghe watershed region, where winter crops are often exposed to varying intensities of terminal drought. Agriculture in the Jinghe watershed is largely rain-fed, low-input based and highly resource dependent. Almost every year, this region experiences drought hazards, which impose high impacts on many aspects of society and environment. To help decision makers reduce the impacts Received: Accepted: Foundation: ational Key Technology R&D Program (o. 2008BAK50B05), ational Key Project for basic research (973) (o.2009cb421106) and the Knowledge Innovation Program of CAS (o. KZCX2-EW-306). * Corresponding author: CHEG Shengkui. chengsk@igsnrr.ac.cn.
2 % LOG Xin, et al.: Quantitative Assessment and Spatial Characteristics of Agricultural Drought Risk in the Jinghe Watershed of orthwestern China 339 M ha Affected area Ratio of drought to all Fig. 1 Area affected by drought ( ) of drought, it is important to improve our understanding of the characteristics and parameters that cause drought and also risk assessment spatial distributions. It is important to quantitatively analyze the spatial characteristics of agricultural drought risk at a fine resolution and comprehensively estimate potential threats and direct losses attributable to these phenomena on winter wheat production. There is an urgent need to develop a region-wide agricultural drought risk assessment model. Therefore, this study aims to determine the key factors in agricultural risk assessment and build a gird-based agricultural risk assessment model for the dominant crop, winter wheat, in the Jinghe watershed using ArcGIS. This study also aims to characterize the spatial pattern of drought hazards, identify the vulnerability of agriculture to the impact of droughts, and map drought risk zones in the Jinghe watershed. With a map of agricultural risk, decision makers can better visualize the hazard and communicate the concept of risk to agricultural producers, natural resources managers and others related to drought management Study area Jinghe River is one of the ten water systems of the Yellow River, and also the biggest branch river of Weihe River (Fig.2). It is 451 long, with a total basin river area of The watershed extends from to E longitude and from to latitude. The Jinghe watershed is a typical loess plateau hilly area with high conflicting human-land relationships (Zhen et al. 2005). The watershed involves 31 counties, of which five counties belong to the ingxia Hui Autonomous Region, 13 counties belong to Shaanxi Province and 13 counties belong to Gansu Province. The total area of the 31 involved counties is In this study, the Jinghe watershed refers to these 31 counties. We selected the 31 counties as the study area because risk management is normally based on administrative units and some data used in this study is county-based. The altitude of the area varies from m. The geographical location of the study area and an east-to-west and south-to-north elevation gradient (about 2500 m) determine several climatic gradients and precipitation gradients. Climatically, Jinghe watershed belongs to the temperate region where typical temperate continental climate prevails throughout the year with an average temperature of 8. The climate is characterized as semi-humid (in the south) to semiarid (in the north), great annual temperature variations, highly variable precipitation, and drought are dominant natural hazards. The precipitation of the study area varies between mm, gradually decreasing from south to north. These gradients mainly determine the study area s land use characteristics. Social-economically, the Jinghe watershed has a total population of , and the natural population growth rate is between The average Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita of this area in ingxia Gansu Legend County boundary Provincial boundary Shaanxi E 80 E 90 E 100 E 110 E 120 e 110 E 120 e Legend ational boundary Study area Provincial boundary 80 E 90 E 100 E 110 E 120 e 110 E Fig. 2 The extent of the study area and the location of the Jinghe watershed, China.
3 was CY , while the average value of that of the ational level is CY , meaning the region is economically undeveloped. The dominant crop in the study area is winter wheat and summer maize. Industry in this area is dominated by energy chemical engineering, which is represented by the branch company of Petro China of Changqing Company in Xifeng District of Qingyang City. 3 Materials and methods Since the dominant crop in the study area is winter wheat, this study was based on the assumption that all the arable land is cultivated by winter wheat, and the vulnerability and risk assessment results are based on 1 1 grid. 3.1 Materials Data used for the hazard assessment were downloaded from the China Meteorological Data Sharing Service system. Monthly precipitation data for hazard assessment from and daily precipitation data, highest and lowest temperature, wind speed, relative humidity and insolation duration from the year were also obtained from the China Meteorological Data Sharing Service system. Other data, such as data for validation of the risk assessment model came from Gansu Statistical Yearbook, Shaanxi Statistical Yearbook, the ingxia Hui Autonomous Region Statistical Yearbook and Gansu Rural Statistical Yearbook. Landuse data for the year 2000 was derived from Landsat TM/ETM remote sensing image at a 1: scale, with a 92.7% positioning accuracy (Liu and Buheaosier 2000) from the Data Center for Resources and Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Data on soil attributes and types and vegetation types were also from Data Center for Resources and Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences. 3.2 Methods Risk has many definitions. According to the International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (ISDR) conceptual framework, risk assessment can be broken down into a combination of hazard severity and vulnerability. Agricultural drought risk depends on a combination of the physical nature of drought and the degree to which agriculture is vulnerable to the effects of drought. To assess the risk of drought, it is essential to study the frequency, severity and spatial extent of drought hazards as well as closely related factors to agriculture, which in this study refers to winter wheat. Step 1: identify the drought hazard with regard to its spatial extent, frequency and severity; Step 2: identify and quantify the vulnerability of agriculture exposed to drought hazards; Step 3: calculate drought risk pattern and analyze its spatial characteristics. The following is a brief description of the data and Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.2 o.4, 2011 methods used for agriculture drought risk assessments in the Jinghe watershed. Based on a literature review, the proposed model was built to possess the following characteristics. First, the model needed to be cropspecific. The model was developed specifically for winter wheat as it is the dominant crop in this region. Second, the model used for agricultural risk assessment related to phonological stages during winter wheat development, providing risk information in a timely manner. Third, the agricultural drought risk model was applied with both grid data and county-based data due to the data deficiency Agriculture drought risk assessment framework According to the ISDR conceptual framework, risk is the combination of hazard severity and vulnerability. Also, Blaikie et al. (1994) defined risk as the product of hazard and vulnerability. Therefore, the risk assessment carried out in this study falls within the above two frameworks Identification of drought hazard pattern Droughts, like other natural phenomena, have spatial and temporal dimensions. In assessing drought, many researchers have used the capability of geographic information systems (GIS) to store and analyze large volumes of remotely sensed data. To investigate the spatial and temporal extent and severity of drought occurrence in the study area we used the Z index method to identify drought hazard patterns in the Jinghe watershed. The Z method has been used widely to assess drought hazard severity (Tang et al. 2009; Yang et al. 2010). The Z index method is based on the assumption that precipitation of a certain period is fitted to a Possion-III distribution, which will be transformed into a standardized normal distribution with the variable Z. In order to compute the Z index value, historic rainfall data of each station are fitted to the Possion- III distribution function: Z i s Cs 6 Cs = Fi C 2 C 6 where C s is the coefficient of skew and Φ i is the standardized variable. The value of Z index is divided into four classes which are according to study of Tang et al. (2009), as shown in Table 1. The area vulnerable to drought is identified on the basis of occurrence. For the mapping of the spatial extent of rainfall, Australian ational University Spline (AUSPLI) was used. The AUSPLI package has Table 1 Drought categories defined for Z values. Grade Drought category Z Value s 1 o drought Z 2 Mild drought Z < Moderate drought Z < Severe drought Z < (1)
4 LOG Xin, et al.: Quantitative Assessment and Spatial Characteristics of Agricultural Drought Risk in the Jinghe Watershed of orthwestern China 341 been designed to provide a facility for transparent analysis and interpolation of noisy multivariate data using thin plate smoothing splines (Hutchinson 2003). In this paper, we defined drought hazard over four categories (no drought, mild drought, moderate drought and severe drought) according to the results of the calculation. Each severity theme is given a particular weight and each feature of the theme is given a rating to compute drought severity of the integrated layer. The drought hazard index of integrated layer is calculated by the following formula: DHI = n ki Fre i (2) i=1 where DHI is the drought hazard index, k i is the weight of class i drought and Fre i is occurrence of class i drought during Weight of mild drought, moderate drought and severe drought is 1, 2 and 3, respectively Identification of vulnerability of agriculture The use of the terms vulnerable and vulnerability is often vague and equated with poor and poverty (World Food Programme 1996). Vulnerability refers to the potential for loss (Cutter 1993). Etkin et al. (2004) defines vulnerability as the propensity to suffer some degree of loss from a hazardous event, whereas Turner et al. (2003) defines it as the degree to which a system is likely to experience harm due to exposure to a hazard. Downing and Bakker (2000) stated that vulnerability is a relative measure, and the analyst must define its critical levels. Factors influencing drought vulnerability are numerous and their inclusion may depend on data availability (Wilhelmi and Wilhite 2002). Mapping of vulnerability began in the late 1970s (Currey 1978). However, a large increase in the number of studies on assessment of spatial vulnerability occurred in the last decade for two reasons: the recognition of the importance of vulnerability in hazard assessment and disaster management, and the availability of GIS technology with the capacity to integrate data of different types and from different sources, analyze data and present results in a timely and appropriate manner for environmental and agricultural decision making (Wilhelmi and Wilhite 2002). As to vulnerability, we selected four factors to assess the vulnerability of agricultural drought, which is closely related to the growth of the dominant crop in the study area. The Kriging method was used for interpolation of the station data. Kriging is a geostatistical method that uses known values and a semivariogram to predict values at some unmeasured locations. ArcGIS v9.3 offers several Kriging models: simple, ordinary, universal, indicator, disjunctive and probability. We selected the ordinary Kriging method during vulnerability calculations. The vulnerability of agriculture drought in the Jinghe watershed was calculated by the formula: V agri =W mete F mete +W soil F soil +W terr F terr +W irri F irri (3) where V agri is the agricultural vulnerability index and W mete, W soil, W terr and W irri are weights of climate factor, soil factor, topographical factor and irrigation factor, respectively. F mete, F soil, F terr and F irri are values of climate factor, soil factor, topographical factor and irrigation factor, respectively. Climate. The assumption underlying the approach taken in this study was that the best characterization of the climate factors is the probability of seasonal crop water deficiency (SCWD). Seasonal crop water use thresholds for well-watered crops were estimated using the evapotranspiration (ET) mathematical model recommended by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United ations (FAO). SCWD was used to calculate the percentage of water difference between ET and Precipitation to ET, calculated using the formula: ET-P SCWD = (4) ET where SCWD is seasonal crop water deficiency, ET is seasonal crop water evaporation and P is the precipitation during the crop growing season. Soil. Soil water-holding capacity is a significant agricultural drought vulnerability factor (Wilhelmi and Wilhite 2002). The geographic pattern of soil waterholding capacity is important for studying water stress in plants and critical to water management planning for irrigation and dryland crops (Kern 1995; Klocke and Hergert 1990). The plant-available water-holding capacity of soil is estimated as the difference in water content between field capacity and permanent wilting point. Field capacity is the amount of water retained by a wetted soil after it has been freely drained by gravity for some period of time. The water-holding capacity of the soil is mostly dependent on soil porosity, which, in turn, depends on soil texture and structure. In the Jinghe watershed, soils vary from fine texture and high water-holding capacity, to sandy soils with coarse texture and low water-holding capacity. In general, most of the study area has a poor water-holding capacity, which we can see from average soil erosion modulus data, viz t -2. We used available water capacity (AWC) as a significant vulnerability factor to identify soil of different abilities to buffer crops during periods of deficient moisture. The digital map of available water-holding capacity for the Jinghe watershed was in an ArcGIS v9.3 format with 1 spatial resolution and Albers Equal Area projection. Irrigation. The spatial and temporal ill-distribution of precipitation means that the water needs of crops in the study area are barely met. Data showed that in the northeast and northern semi-humid region of China wheat is greatly affected by water deficiency. In the northwest
5 342 Table 2 Categories defined for irrigated land to total county land at county level. Irrigation ratio class Irrigated area compared to total county land area (%) umber of counties Percentage of counties in the 31 areas (%) Very high High Moderate Low Very low of China, no irrigation means little yield (Gao 2006). Although there is no consensus in the literature whether irrigation reduces or increases vulnerability to drought (Lockeretz 1981; Opie 1989; Jackson 1991), in most cases, and especially during a short-term drought, irrigation farming provides more security for crop growers. In this study, irrigation factor was represented by percent of irrigated land compared to total county land area for each of the 31 counties. The natural break method was used to classify the percentage of irrigated land to total into five classes: very low, low, moderate, high and very high. The weights and ratings used for integration are given in Table 2. Topography. Slope was selected as the indicator Legend Low Relatively low 25 High 0 Extremely high Fig. 3 Spatial extent of agricultural drought in the Jinghe watershed Table 3 Categories defined for slopes. Slope value Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.2 o.4, 2011 Slope categories < >25 5 to represent topography because different types of physiognomy affect land use type, inputs and irrigation conditions (Shi 2006). Further, land use is one of the driving forces behind water demand and critical factors of agricultural drought vulnerability. We viewed topography as a factor influencing agriculture vulnerability. We selected the slope as the indictor, which was divided into five classes, according to the classification system of arable land slope in Loess Plateau (Table 3). We assigned arable land with a slope no more than 3 the value 1, which means it has the least vulnerability and arable land with a slope more than 25 the value 5, which means it has the highest vulnerability. 4 Results and discussion 4.1 Drought hazard severity map Drought hazard severity mapping of the Jinghe watershed is shown in Fig.3. The mapping results show that the distribution of different classes of hazard differs geographically and quantitatively. The extremely severe class occupies 2.63% of the total watershed area. The severe class occupies 46% of the total area. The moderate class and low-to-moderate class cover 39.60% and 11.78% of the total study area, respectively. Hazard mapping results also show that from north to south, hazard severity decreases, but with some variation. 4.2 Vulnerability assessment results Using formula 3, after the integration of the indicators, we obtained the vulnerability of agricultural drought in the Jinghe watershed (Fig. 4). We can see a clear gradient from the north to the south of the study area. The results showed that only 3.68% of the Jinghe watershed area was classified into the very low category, and 13.77% was classified into the low category. For the moderate category, 29.45% was classified, and 27.87% of the area was classified as the high category, while the very high category includes 25.23% of the total study area. The map also shows that the northern part of the Jinghe watershed is the comparatively high vulnerability region and the southern part of the region is of low vulnerability. We attribute this vulnerability spatial distribution between the north and the south to physiological and social-economic factors. First, the entire Jinghe watershed has a rainfall gradient from north to the south, which is highly correlated with SCWD and AWC. The
6 LOG Xin, et al.: Quantitative Assessment and Spatial Characteristics of Agricultural Drought Risk in the Jinghe Watershed of orthwestern China Vulnearability Very low Low Moderate High Very high Risk Very low Low Moderate High Very high Fig. 4 Spatial variation in vulnerability assessment of agricultural risk in the Jinghe watershed. southern part, particularly counties with a relatively flat topography located in the Weibei plain, have topographical advantages. Second, the south-north spatial variation is a result of better economic conditions in the south. Better economic conditions consequently assure more financial support to alleviate impending droughts and their impact on agriculture yield. Third, the southern region has better irrigation facilities and a higher availability of irrigation water resources than the north. 4.3 Risk assessment results By using the risk assessment of agricultural drought model, the risk assessment results at a 1 grid scale (Fig. 5) show that spatial variation is differentiated from north to south. Generally, the high risk region is located in the north, and low risk region in the south of the study area. There is also a gradient in risk spatial distribution. The northern region is almost calculated as very high and high risk areas; the south is covered very low and low risk areas. This spatial variation in risk may have arisen because of the following reasons. First, high precipitation variation between the north and the south results in different hazard zoning. Second, the SCWD indictor results showed that there is also a similar gradient in the SCWD as for precipitation. AWC results also showed a similar gradient, Fig. 5 Spatial variation in agricultural risk assessment in the Jinghe watershed. not to mention the irrigation factor. As a result of the combination of these factors, the southern part of the study area has low risk. 5 Validations of the risk assessment of agricultural drought in the Jinghe watershed Crop loss induced by drought is a direct reflection of drought impact on agriculture. Since this study mainly focused on the dominant crop of winter wheat we used the average affected area by drought from the year of 13 counties in Gansu province. The data showed that Huanxian County, Zhenyuan County and Qingcheng County have the highest affected area, and Huating County, Chongxin County and Huachi County have the lowest affected area. These results follow a similar tendency to the modeled results. 6 Conclusions An agriculture risk assessment of the Jinghe watershed was carried out at a 1- grid scale by using a GIS-based agricultural drought risk assessment model. This model is based on the ISDR and risk assessment conceptual framework of Blaikie et al. (1994), which specify that risk is a combination of hazard and vulnerability. We applied the Z index method to assess hazard severity in the study area. In our vulnerability assessment we selected
7 344 four indictors (climate, soil, irrigation and topography), represented by SCWD, AWC, irrigation ratio and slope. The spatial distribution of hazard indicated that the Jinghe watershed apparently differs from the south to the north, somewhat represented by, but not highly consistent with, precipitation. For the vulnerability assessment we concluded that the north-south difference could be attributed to physiological and social-economic factors. The spatial distribution of vulnerability showed that the Jinghe watershed has a clear north-south differentiation which showed that the northern part of the Jinghe watershed is mainly occupied by the very high and high vulnerable areas and the south part of the Jinghe watershed is mainly covered by very low and low vulnerable areas. Spatial distribution in risk assessment results were similar to those obtained for vulnerability: the north has high risk and the south has low risk. However, since the risk assessment result is a combination of hazard and vulnerability, there is a difference between the vulnerability and risk assessment. The main difference lies in the north of the Jinghe watershed (high vulnerability but moderate risk), which can be attributed to lower hazard severity. References Blaikie P M, T Cannon, I Davis, et al At risk: natural hazards, people s vulnerability, and disasters. ew York: Routledge. Currey B Mapping of areas liable to famine in Bangladesh. Ph. D. dissertation, Manoa, University of Hawaii. Cutter S L Living with risk: the geography of technological hazards. London: Edward Arnold. Downing T E, K Bakker Drought discourse and vulnerability. Chapter 45. In: Wilhite D A (ed.). Drought: A Global Assessment, atural Hazards and Disasters Series. London: Routledge Publishers. Etkin D, E Haque, L Bellisario, et al An assessment of natural hazards and disasters in Canada. The Canadian natural hazards assessment project. Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.2 o.4, 2011 Public safety and emergency preparedness Canada and environment Canada, Ottawa. Gao Z Y Development and action of irrigation in China. Journal of Economics of Water Resources, 24(1): 36 39, 82. ( in Chinese) Hutchinson M F AUSPLI Version 4.3. Canberra, Australian ational University Centre for Resource and Environmental Studies. Jackson C I Response strategies for the Great Plains: Canadian and U. S. perspectives. In: Wall G (Ed.). Symposium on the impacts of climatic change and variability on the Great Plains. Department of Geography Publication Series, Occasional Paper o. 12, University of Waterloo, Kern J S Geographic patterns of soil water-holding capacity in the contiguous United States. Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. J., 59: Klocke L, G W Hergert How soil holds water, ebguide G90-964, IAR. Lincoln: University of ebraska. Liu J Y, Buheaosier Study on spatial-temporal feature of modern land-use change in China: using remote sensing techniques. Quaternary Sciences, 20(3): ( in Chinese) Lockeretz W The dust bowl: Its relevance to contemporary environmental problems. In: Lawson M P and M E Baker (Eds.). The Great Plains: Perspectives and prospects. Lincoln: University of ebraska Press, Opie J years of climate risk assessment on the High Plains: Which farm paradigm does irrigation serve? Agric. Hist., 63: Shi X M Study on the agricultural geomorphology. Journal of Anhui Agri. Sci., 34 (20): , ( in Chinese) Tang H Y, Wang Z W, Shi J M, et al Analysis of different dryness/ wetness index in orthwest China. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 27 (5): 6 11, 64. ( in Chinese) Turner B L II, Kasperson R E, Matson P A, et al A framework for vulnerability analysis in sustainability science. Proc at Acad Sci USA 100: Wilhelmi O V, D A Wilhite Assessming vulnerability to agricultural drought: A ebraska case study. atural Hazards, 25: Wu J J, He B, Lu A F, et al Quantitative assessment and spatial characteristics analysis of agricultural drought vulnerability in China. atural Hazards, 56: Yang X H, Yang X L Aridity characteristics in East Gansu s Loess Plateau area based on Z index analysis. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 28(3): ( in Chinese) Zhen L, Xie G D, Yang L, et al Land-use change dynamics, driving forces and policy implications in Jinghe watershed of western China. Resources Science, 27 (4): ( in Chinese) 泾河流域农业旱灾风险定量评估及其空间特征 龙鑫 1,2, 甄霖 1, 成升魁 1 3, 邸苏闯 1 中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所, 北京 ; 2 中国科学院研究生院, 北京 ; 3 北京市水利科学研究所, 北京 摘要 : 泾河流域是农业旱灾的多发地区, 但是对该地农业旱灾的发生规律 旱灾影响及旱灾恢复和准备措施方面开展的研究还较少 本文根据自然灾害风险评估的理论框架, 建立了 1 栅格精度的泾河流域农业旱灾风险空间评估模型, 并对农业旱灾致灾因子危险性及农业承险体脆弱性进行评估, 最后综合评估该地区农业旱灾风险 在此基础上, 分析研究区农业旱灾危险性 承险体脆弱性及风险的空间特征 本研究采用 Z 指数方法评估泾河流域农业旱灾致灾因子的强度, 选取农作物生长季缺水率 土壤有效含水量 有效灌溉面积比以及坡度等 4 个指标评估研究区 1 空间尺度的农业旱灾脆弱性 农业旱灾风险综合评估的结果表明, 泾河流域农业旱灾风险的高风险区位于该地区北部, 低风险区位于该地区南部, 且不同等级风险区呈现出自东向西 自南向北逐渐降低的总体趋势, 但不同等级风险区呈现间隔分布的趋势 关键词 : 农业旱灾 ; 自然灾害 ; 脆弱性 ; 风险评估 ; 泾河流域
Design, Development and Application of Northeast Asia Resources and Environment Scientific Expedition Data Platform
 September, 2011 J. Resour. Ecol. 2011 2(3) 266-271 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-764x.2011.03.010 www.jorae.cn Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.2 No.3 NE Asia Design, Development and Application of Northeast
September, 2011 J. Resour. Ecol. 2011 2(3) 266-271 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-764x.2011.03.010 www.jorae.cn Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.2 No.3 NE Asia Design, Development and Application of Northeast
Quantitative Assessment of Seismic Mortality Risks in China
 March, 2011 J. Resour. Ecol. 2011 2(1) 83-90 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-764x.2011.01.012 www.jorae.cn Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.2 No.1 Article Quantitative Assessment of Seismic Mortality Risks
March, 2011 J. Resour. Ecol. 2011 2(1) 83-90 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-764x.2011.01.012 www.jorae.cn Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.2 No.1 Article Quantitative Assessment of Seismic Mortality Risks
DROUGHT ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE DERIVED METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND NDVI IN POTOHAR REGION
 DROUGHT ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE DERIVED METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND NDVI IN POTOHAR REGION Researcher: Saad-ul-Haque Supervisor: Dr. Badar Ghauri Department of RS & GISc Institute of Space Technology
DROUGHT ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE DERIVED METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND NDVI IN POTOHAR REGION Researcher: Saad-ul-Haque Supervisor: Dr. Badar Ghauri Department of RS & GISc Institute of Space Technology
2012 Typhoon Activity Prediction
 2012 Typhoon Activity Prediction Published by Shanghai Typhoon Institute of China Meteorological Administration 4 May 2012 Prediction of 2012 Northwest Pacific Basin and South China Sea Tropical Cyclone
2012 Typhoon Activity Prediction Published by Shanghai Typhoon Institute of China Meteorological Administration 4 May 2012 Prediction of 2012 Northwest Pacific Basin and South China Sea Tropical Cyclone
Spatial-temporal Changes in Ecological Risk of Land Use before and after Grain-for-Green Policy in Zhengning County, Gansu Province
 March, 2013 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.4 No.1 J. Resour. Ecol. 2013 4 (1) 036-042 DOI:10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2013.01.005 www.jorae.cn rticle Spatial-temporal Changes in Ecological Risk of Land
March, 2013 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.4 No.1 J. Resour. Ecol. 2013 4 (1) 036-042 DOI:10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2013.01.005 www.jorae.cn rticle Spatial-temporal Changes in Ecological Risk of Land
黄土丘陵区须根系作物地土壤分离季节变化研究
 土壤 (Soils), 2016, 48(5): 1015 1021 DOI: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2016.05.025 1 黄土丘陵区须根系作物地土壤分离季节变化研究 1,2 1,2 (1 721013 2 721013) : (P0.75 NSE>0.74) S147 6 9 [1 4] [5 6] 1.46 10 5 km 2 22.5% 30.9%
土壤 (Soils), 2016, 48(5): 1015 1021 DOI: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2016.05.025 1 黄土丘陵区须根系作物地土壤分离季节变化研究 1,2 1,2 (1 721013 2 721013) : (P0.75 NSE>0.74) S147 6 9 [1 4] [5 6] 1.46 10 5 km 2 22.5% 30.9%
The dynamic N1-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA 报告人 : 沈胤
 The dynamic N1-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA 报告人 : 沈胤 2016.12.26 研究背景 RNA 甲基化作为表观遗传学研究的重要内容之一, 是指发生在 RNA 分子上不同位置的甲基化修饰现象 RNA 甲基化在调控基因表达 剪接 RNA 编辑 RNA 稳定性 控制 mrna 寿命和降解等方面可能扮演重要角色
The dynamic N1-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA 报告人 : 沈胤 2016.12.26 研究背景 RNA 甲基化作为表观遗传学研究的重要内容之一, 是指发生在 RNA 分子上不同位置的甲基化修饰现象 RNA 甲基化在调控基因表达 剪接 RNA 编辑 RNA 稳定性 控制 mrna 寿命和降解等方面可能扮演重要角色
DROUGHT RISK EVALUATION USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS : A CASE STUDY IN LOP BURI PROVINCE
 DROUGHT RISK EVALUATION USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS : A CASE STUDY IN LOP BURI PROVINCE K. Prathumchai, Kiyoshi Honda, Kaew Nualchawee Asian Centre for Research on Remote Sensing STAR Program, Asian Institute
DROUGHT RISK EVALUATION USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS : A CASE STUDY IN LOP BURI PROVINCE K. Prathumchai, Kiyoshi Honda, Kaew Nualchawee Asian Centre for Research on Remote Sensing STAR Program, Asian Institute
Remote Sensing Applications in Agricultural Statistics at China NBS. Yu Xinhua Department of Rural Surveys, National Bureau of Statistics(NBS)
 Remote Sensing Applications in Agricultural Statistics at China NBS Yu Xinhua Department of Rural Surveys, National Bureau of Statistics(NBS) Outline Introduction Remote Sensing Measurement Area Frame
Remote Sensing Applications in Agricultural Statistics at China NBS Yu Xinhua Department of Rural Surveys, National Bureau of Statistics(NBS) Outline Introduction Remote Sensing Measurement Area Frame
A Study on Dynamics and Problems of Residential Suburbanization in Xi an
 Nanyang Technological University From the SelectedWorks of Man LUO Spring April 2, 2014 A Study on Dynamics and Problems of Residential Suburbanization in Xi an Man LUO Available at: https://works.bepress.com/man_luo/1/
Nanyang Technological University From the SelectedWorks of Man LUO Spring April 2, 2014 A Study on Dynamics and Problems of Residential Suburbanization in Xi an Man LUO Available at: https://works.bepress.com/man_luo/1/
Surveying,Mapping and Geoinformation Services System for the Major Natural Disasters Emergency Management in China
 Surveying,Mapping and Geoinformation Services System for the Major Natural Disasters Emergency Management in China 21 February 2013, Bangkok, Thailand Contents 2 1 2 3 4 Working Mechanism Geoinformation
Surveying,Mapping and Geoinformation Services System for the Major Natural Disasters Emergency Management in China 21 February 2013, Bangkok, Thailand Contents 2 1 2 3 4 Working Mechanism Geoinformation
Rigorous back analysis of shear strength parameters of landslide slip
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 1459 1464 Rigorous back analysis of shear strength parameters of landslide slip Ke ZHANG 1, Ping CAO 1, Rui BAO 1,2 1. School of Resources and Safety Engineering,
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 1459 1464 Rigorous back analysis of shear strength parameters of landslide slip Ke ZHANG 1, Ping CAO 1, Rui BAO 1,2 1. School of Resources and Safety Engineering,
Drought risk assessment using GIS and remote sensing: A case study of District Khushab, Pakistan
 15 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 31 August to 2 September 2017 Drought risk assessment using GIS and remote sensing: A case study of District Khushab,
15 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 31 August to 2 September 2017 Drought risk assessment using GIS and remote sensing: A case study of District Khushab,
Quantitative Measurement of Urban Expansion and Its Driving Factors in Qingdao: An Empirical Analysis Based on County Unit Data
 May, 2015 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.6 o.3 J. Resour. Ecol. 2015 6 (3) 172-179 DOI:10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2015.03.006 www.jorae.cn Article Quantitative Measurement of Urban Expansion and Its
May, 2015 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.6 o.3 J. Resour. Ecol. 2015 6 (3) 172-179 DOI:10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2015.03.006 www.jorae.cn Article Quantitative Measurement of Urban Expansion and Its
2012 AP Calculus BC 模拟试卷
 0 AP Calculus BC 模拟试卷 北京新东方罗勇 luoyong@df.cn 0-3- 说明 : 请严格按照实际考试时间进行模拟, 考试时间共 95 分钟 Multiple-Choice section A 部分 : 无计算器 B 部分 : 有计算器 Free-response section A 部分 : 有计算器 B 部分 : 无计算器 总计 45 题 /05 分钟 8 题,55 分钟
0 AP Calculus BC 模拟试卷 北京新东方罗勇 luoyong@df.cn 0-3- 说明 : 请严格按照实际考试时间进行模拟, 考试时间共 95 分钟 Multiple-Choice section A 部分 : 无计算器 B 部分 : 有计算器 Free-response section A 部分 : 有计算器 B 部分 : 无计算器 总计 45 题 /05 分钟 8 题,55 分钟
Source mechanism solution
 Source mechanism solution Contents Source mechanism solution 1 1. A general introduction 1 2. A step-by-step guide 1 Step-1: Prepare data files 1 Step-2: Start GeoTaos or GeoTaos_Map 2 Step-3: Convert
Source mechanism solution Contents Source mechanism solution 1 1. A general introduction 1 2. A step-by-step guide 1 Step-1: Prepare data files 1 Step-2: Start GeoTaos or GeoTaos_Map 2 Step-3: Convert
Extraction and Dynamic Spatial-Temporal Changes of Grassland Deterioration Research Hot Regions in China
 July, 2017 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 8 No.4 J. Resour. Ecol. 2017 8(4) 352-358 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2017.04.006 www.jorae.cn Extraction and Dynamic Spatial-Temporal Changes of Grassland
July, 2017 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 8 No.4 J. Resour. Ecol. 2017 8(4) 352-358 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2017.04.006 www.jorae.cn Extraction and Dynamic Spatial-Temporal Changes of Grassland
Spatial Differentiation of Rural Touristization and Its Determinants in China: A Geo-detector-based Case Study of Yesanpo Scenic Area
 Nov., 2016 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 7 No.6 J. Resour. Ecol. 2016 7(6) 464-471 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2016.06.006 www.jorae.cn Spatial Differentiation of Rural Touristization and Its
Nov., 2016 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 7 No.6 J. Resour. Ecol. 2016 7(6) 464-471 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2016.06.006 www.jorae.cn Spatial Differentiation of Rural Touristization and Its
通量数据质量控制的理论与方法 理加联合科技有限公司
 通量数据质量控制的理论与方法 理加联合科技有限公司 通量变量 Rn = LE + H + G (W m -2 s -1 ) 净辐射 潜热 感热 地表热 通量 通量 通量 通量 Fc (mg m -2 s -1 ) 二氧化碳通量 τ [(kg m s -1 ) m -2 s -1 ] 动量通量 质量控制 1. 概率统计方法 2. 趋势法 3. 大气物理依据 4. 测定实地诊断 5. 仪器物理依据 '
通量数据质量控制的理论与方法 理加联合科技有限公司 通量变量 Rn = LE + H + G (W m -2 s -1 ) 净辐射 潜热 感热 地表热 通量 通量 通量 通量 Fc (mg m -2 s -1 ) 二氧化碳通量 τ [(kg m s -1 ) m -2 s -1 ] 动量通量 质量控制 1. 概率统计方法 2. 趋势法 3. 大气物理依据 4. 测定实地诊断 5. 仪器物理依据 '
Effect of lengthening alkyl spacer on hydroformylation performance of tethered phosphine modified Rh/SiO2 catalyst
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (216) 268 272 催化学报 216 年第 37 卷第 2 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Effect of lengthening alkyl
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (216) 268 272 催化学报 216 年第 37 卷第 2 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Effect of lengthening alkyl
Spatio-temporal pattern of drought in Northeast of Iran
 Spatio-temporal pattern of drought in Northeast of Iran Akhtari R., Bandarabadi S.R., Saghafian B. in López-Francos A. (ed.). Drought management: scientific and technological innovations Zaragoza : CIHEAM
Spatio-temporal pattern of drought in Northeast of Iran Akhtari R., Bandarabadi S.R., Saghafian B. in López-Francos A. (ed.). Drought management: scientific and technological innovations Zaragoza : CIHEAM
三类调度问题的复合派遣算法及其在医疗运营管理中的应用
 申请上海交通大学博士学位论文 三类调度问题的复合派遣算法及其在医疗运营管理中的应用 博士生 : 苏惠荞 导师 : 万国华教授 专业 : 管理科学与工程 研究方向 : 运作管理 学校代码 : 10248 上海交通大学安泰经济与管理学院 2017 年 6 月 Dissertation Submitted to Shanghai Jiao Tong University for the Degree of
申请上海交通大学博士学位论文 三类调度问题的复合派遣算法及其在医疗运营管理中的应用 博士生 : 苏惠荞 导师 : 万国华教授 专业 : 管理科学与工程 研究方向 : 运作管理 学校代码 : 10248 上海交通大学安泰经济与管理学院 2017 年 6 月 Dissertation Submitted to Shanghai Jiao Tong University for the Degree of
Galileo Galilei ( ) Title page of Galileo's Dialogue concerning the two chief world systems, published in Florence in February 1632.
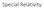 Special Relativity Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) Title page of Galileo's Dialogue concerning the two chief world systems, published in Florence in February 1632. 2 Galilean Transformation z z!!! r ' = r
Special Relativity Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) Title page of Galileo's Dialogue concerning the two chief world systems, published in Florence in February 1632. 2 Galilean Transformation z z!!! r ' = r
d) There is a Web page that includes links to both Web page A and Web page B.
 P403-406 5. Determine whether the relation R on the set of all eb pages is reflexive( 自反 ), symmetric( 对 称 ), antisymmetric( 反对称 ), and/or transitive( 传递 ), where (a, b) R if and only if a) Everyone who
P403-406 5. Determine whether the relation R on the set of all eb pages is reflexive( 自反 ), symmetric( 对 称 ), antisymmetric( 反对称 ), and/or transitive( 传递 ), where (a, b) R if and only if a) Everyone who
RESEARCH AND APPLICATION OF THE EVAPORATION CAPACITY SPATIAL INTERPOLATION METHOD FOR AGRICULUTRAL ENVIRONMENT / 面向农业环境的蒸发量空间插值方法研究和应用
 RESEARCH AND APPLICATION OF THE EVAPORATION CAPACITY SPATIAL INTERPOLATION METHOD FOR AGRICULUTRAL ENVIRONMENT / 面向农业环境的蒸发量空间插值方法研究和应用 Ph.D. Yinlong JIN 1), Prof. Ph.D. Eng. Jiesheng HUANG 1), Ph.D. Ben
RESEARCH AND APPLICATION OF THE EVAPORATION CAPACITY SPATIAL INTERPOLATION METHOD FOR AGRICULUTRAL ENVIRONMENT / 面向农业环境的蒸发量空间插值方法研究和应用 Ph.D. Yinlong JIN 1), Prof. Ph.D. Eng. Jiesheng HUANG 1), Ph.D. Ben
Measurement of accelerator neutron radiation field spectrum by Extended Range Neutron Multisphere Spectrometers and unfolding program
 Measurement of accelerator neutron radiation field spectrum by Extended Range Neutron Multisphere Spectrometers and unfolding program LI Guanjia( 李冠稼 ), WANG Qingbin( 王庆斌 ), MA Zhongjian( 马忠剑 ), GUO Siming(
Measurement of accelerator neutron radiation field spectrum by Extended Range Neutron Multisphere Spectrometers and unfolding program LI Guanjia( 李冠稼 ), WANG Qingbin( 王庆斌 ), MA Zhongjian( 马忠剑 ), GUO Siming(
A new operational medium-range numerical weather forecast system of CHINA. NWPD/NMC/CMA (Beijing,CHINA)
 A new operational medium-range numerical weather forecast system of CHINA NWPD/NMC/CMA (Beijing,CHINA) Organizational Chart of CMA NSMC (National Satellite Meteorological Center) NCC (National Climate
A new operational medium-range numerical weather forecast system of CHINA NWPD/NMC/CMA (Beijing,CHINA) Organizational Chart of CMA NSMC (National Satellite Meteorological Center) NCC (National Climate
MODELLING FROST RISK IN APPLE TREE, IRAN. Mohammad Rahimi
 WMO Regional Seminar on strategic Capacity Development of National Meteorological and Hydrological Services in RA II (Opportunity and Challenges in 21th century) Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 3-4 December 2008
WMO Regional Seminar on strategic Capacity Development of National Meteorological and Hydrological Services in RA II (Opportunity and Challenges in 21th century) Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 3-4 December 2008
Effects of check-dams on sediment storage-release in Chabagou Watershed
 第 26 卷第 2 期农业工程学报 Vol.26 No.2 64 2010 年 2 月 Transactions of the CSAE Feb. 2010 Effects of check-dams on sediment storage-release in Chabagou Watershed Zhang Luan 1,2, Shi Changxing 1, Zhang Hao 3 (1. Key
第 26 卷第 2 期农业工程学报 Vol.26 No.2 64 2010 年 2 月 Transactions of the CSAE Feb. 2010 Effects of check-dams on sediment storage-release in Chabagou Watershed Zhang Luan 1,2, Shi Changxing 1, Zhang Hao 3 (1. Key
An IntRoduction to grey methods by using R
 An IntRoduction to grey methods by using R Tan Xi Department of Statistics, NUFE Nov 6, 2009 2009-2-5 Contents: A brief introduction to Grey Methods An analysis of Degree of Grey Incidence Grey GM(, )
An IntRoduction to grey methods by using R Tan Xi Department of Statistics, NUFE Nov 6, 2009 2009-2-5 Contents: A brief introduction to Grey Methods An analysis of Degree of Grey Incidence Grey GM(, )
Integrated Algebra. Simplified Chinese. Problem Solving
 Problem Solving algebraically concept conjecture constraint equivalent formulate generalization graphically multiple representations numerically parameter pattern relative efficiency strategy verbally
Problem Solving algebraically concept conjecture constraint equivalent formulate generalization graphically multiple representations numerically parameter pattern relative efficiency strategy verbally
Modeling effects of changes in diffuse radiation on light use efficiency in forest ecosystem. Wei Nan
 Modeling effects of changes in diffuse radiation on light use efficiency in forest ecosystem Wei Nan 2018.05.04 1 Outline 1. Background 2. Material and methods 3. Results & Discussion 4. Conclusion 2 1
Modeling effects of changes in diffuse radiation on light use efficiency in forest ecosystem Wei Nan 2018.05.04 1 Outline 1. Background 2. Material and methods 3. Results & Discussion 4. Conclusion 2 1
GEOGRAPHY. In relation to the above aims, candidates should, after completing this syllabus, be able to
 GEOGRAPHY AIMS The aims of this syllabus are to enable candidates 1. to recognize and understand the arrangement of phenomena and features on Earth as well as the inter-relationship and interaction among
GEOGRAPHY AIMS The aims of this syllabus are to enable candidates 1. to recognize and understand the arrangement of phenomena and features on Earth as well as the inter-relationship and interaction among
Synthesis of PdS Au nanorods with asymmetric tips with improved H2 production efficiency in water splitting and increased photostability
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 407 412 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 3 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Communication (Special Issue of
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 407 412 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 3 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Communication (Special Issue of
Droughts are normal recurring climatic phenomena that vary in space, time, and intensity. They may affect people and agriculture at local scales for
 I. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Background Droughts are normal recurring climatic phenomena that vary in space, time, and intensity. They may affect people and agriculture at local scales for short periods or cover
I. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Background Droughts are normal recurring climatic phenomena that vary in space, time, and intensity. They may affect people and agriculture at local scales for short periods or cover
The Study of Soil Fertility Spatial Variation Feature Based on GIS and Data Mining *
 The Study of Soil Fertility Spatial Variation Feature Based on GIS and Data Mining * Chunan Li, Guifen Chen **, Guangwei Zeng, and Jiao Ye College of Information and Technology, Jilin Agricultural University,
The Study of Soil Fertility Spatial Variation Feature Based on GIS and Data Mining * Chunan Li, Guifen Chen **, Guangwei Zeng, and Jiao Ye College of Information and Technology, Jilin Agricultural University,
能源化学工程专业培养方案. Undergraduate Program for Specialty in Energy Chemical Engineering 专业负责人 : 何平分管院长 : 廖其龙院学术委员会主任 : 李玉香
 能源化学工程专业培养方案 Undergraduate Program for Specialty in Energy Chemical Engineering 专业负责人 : 何平分管院长 : 廖其龙院学术委员会主任 : 李玉香 Director of Specialty: He Ping Executive Dean: Liao Qilong Academic Committee Director:
能源化学工程专业培养方案 Undergraduate Program for Specialty in Energy Chemical Engineering 专业负责人 : 何平分管院长 : 廖其龙院学术委员会主任 : 李玉香 Director of Specialty: He Ping Executive Dean: Liao Qilong Academic Committee Director:
THE STUDY OF NUMBERS AND INTENSITY OF TROPICAL CYCLONE MOVING TOWARD THE UPPER PART OF THAILAND
 THE STUDY OF NUMBERS AND INTENSITY OF TROPICAL CYCLONE MOVING TOWARD THE UPPER PART OF THAILAND Aphantree Yuttaphan 1, Sombat Chuenchooklin 2 and Somchai Baimoung 3 ABSTRACT The upper part of Thailand
THE STUDY OF NUMBERS AND INTENSITY OF TROPICAL CYCLONE MOVING TOWARD THE UPPER PART OF THAILAND Aphantree Yuttaphan 1, Sombat Chuenchooklin 2 and Somchai Baimoung 3 ABSTRACT The upper part of Thailand
Analysis on Temperature Variation over the Past 55 Years in Guyuan City, China
 Analysis on Temperature Variation over the Past 55 Years in Guyuan City, China Liu Rui 1, 2,*, Zhang ZhiHua 1, 2 1 School of Environmental Science and Engineering, Chang an University, No.126 Yanta Road,
Analysis on Temperature Variation over the Past 55 Years in Guyuan City, China Liu Rui 1, 2,*, Zhang ZhiHua 1, 2 1 School of Environmental Science and Engineering, Chang an University, No.126 Yanta Road,
Cooling rate of water
 Cooling rate of water Group 5: Xihui Yuan, Wenjing Song, Ming Zhong, Kaiyue Chen, Yue Zhao, Xiangxie Li 目录. Abstract:... 2. Introduction:... 2 2.. Statement of the problem:... 2 2.2 objectives:... 2 2.3.
Cooling rate of water Group 5: Xihui Yuan, Wenjing Song, Ming Zhong, Kaiyue Chen, Yue Zhao, Xiangxie Li 目录. Abstract:... 2. Introduction:... 2 2.. Statement of the problem:... 2 2.2 objectives:... 2 2.3.
控释氮肥配施尿素对土壤无机氮 微生物及水稻生长的影响
 土壤 (Soils), 2018, 50(3): 469 475 DOI: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2018.03.005 1 控释氮肥配施尿素对土壤无机氮 微生物及水稻生长的影响 1 1 1* 1 1 1 昇 1 2 (1 611130 2 210008) (0 10% 20% 40% 80% 100%) 40% NH 4+ -N NO 3 -N 10.11% ~ 17.02% 12.17%
土壤 (Soils), 2018, 50(3): 469 475 DOI: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2018.03.005 1 控释氮肥配施尿素对土壤无机氮 微生物及水稻生长的影响 1 1 1* 1 1 1 昇 1 2 (1 611130 2 210008) (0 10% 20% 40% 80% 100%) 40% NH 4+ -N NO 3 -N 10.11% ~ 17.02% 12.17%
Factors Driving the Expansion of Construction Land: A Panel Data Study of Districts and Counties in Ningbo City, China
 July, 2018 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 9 No.4 J. Resour. Ecol. 2018 9(4) 365-373 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2018.04.004 www.jorae.cn Factors Driving the Expansion of Construction Land: A Panel
July, 2018 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 9 No.4 J. Resour. Ecol. 2018 9(4) 365-373 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2018.04.004 www.jorae.cn Factors Driving the Expansion of Construction Land: A Panel
Developing a Digital Elevation Model using ANUDEM for the Coarse Sandy Hilly Catchments of the Loess Plateau, China
 Developing a Digital Elevation Model using ANUDEM for the Coarse Sandy Hilly Catchments of the Loess Plateau, China QinKe Yang, Tom G. Van Niel, Tim R. McVicar Michael F. Hutchinson and LingTao Li CSIRO
Developing a Digital Elevation Model using ANUDEM for the Coarse Sandy Hilly Catchments of the Loess Plateau, China QinKe Yang, Tom G. Van Niel, Tim R. McVicar Michael F. Hutchinson and LingTao Li CSIRO
DEVELOPMENT OF FLOOD HAZARD VULNERABILITY MAP FOR ALAPPUZHA DISTRICT
 DEVELOPMENT OF FLOOD HAZARD VULNERABILITY MAP FOR ALAPPUZHA DISTRICT Ciya Maria Roy 1, Elsa Manoj 2, Harsha Joy 3, Sarin Ravi 4, Abhinanda Roy 5 1,2,3,4 U.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, MITS
DEVELOPMENT OF FLOOD HAZARD VULNERABILITY MAP FOR ALAPPUZHA DISTRICT Ciya Maria Roy 1, Elsa Manoj 2, Harsha Joy 3, Sarin Ravi 4, Abhinanda Roy 5 1,2,3,4 U.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, MITS
Workshop on Drought and Extreme Temperatures: Preparedness and Management for Sustainable Agriculture, Forestry and Fishery
 Workshop on Drought and Extreme Temperatures: Preparedness and Management for Sustainable Agriculture, Forestry and Fishery 16-17 Feb.2009, Beijing, China Modeling Apple Tree Bud burst time and frost risk
Workshop on Drought and Extreme Temperatures: Preparedness and Management for Sustainable Agriculture, Forestry and Fishery 16-17 Feb.2009, Beijing, China Modeling Apple Tree Bud burst time and frost risk
China Wenchuan Earthquake Disaster (May ) and Its Loss Assessment
 International Disaster and Risk Conference Davos 2008, August 25-29, Switzerland China Wenchuan Earthquake Disaster (May 12.2008) and Its Loss Assessment Peijun SHI Disaster Assessment Group of the National
International Disaster and Risk Conference Davos 2008, August 25-29, Switzerland China Wenchuan Earthquake Disaster (May 12.2008) and Its Loss Assessment Peijun SHI Disaster Assessment Group of the National
Chapter-1 Introduction
 Modeling of rainfall variability and drought assessment in Sabarmati basin, Gujarat, India Chapter-1 Introduction 1.1 General Many researchers had studied variability of rainfall at spatial as well as
Modeling of rainfall variability and drought assessment in Sabarmati basin, Gujarat, India Chapter-1 Introduction 1.1 General Many researchers had studied variability of rainfall at spatial as well as
Remote Sensing Classification of Marsh Wetland with Different Resolution Images
 March, 2016 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 7 No.2 J. Resour. Ecol. 2016 7(2) 107-114 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2016.02.005 www.jorae.cn Article Remote Sensing Classification of Marsh Wetland
March, 2016 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 7 No.2 J. Resour. Ecol. 2016 7(2) 107-114 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2016.02.005 www.jorae.cn Article Remote Sensing Classification of Marsh Wetland
Decadal Change in East Asian Monsoon Climate System: Natural Variability vs Anthropogenic Forcing
 International Conference on Science and Technology for Sustainability 2011 Building from Regional to Global Sustainability-Visions from Asia September 14-16, 2011, Kyoto International Conference Center
International Conference on Science and Technology for Sustainability 2011 Building from Regional to Global Sustainability-Visions from Asia September 14-16, 2011, Kyoto International Conference Center
Integrating non-precious-metal cocatalyst Ni3N with g-c3n4 for enhanced photocatalytic H2 production in water under visible-light irradiation
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 4 (219) 16 167 催化学报 219 年第 4 卷第 2 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Integrating non-precious-metal
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 4 (219) 16 167 催化学报 219 年第 4 卷第 2 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Integrating non-precious-metal
Quantitative Geography Analysis on Spatial Structure of A-grade Tourist Attractions in China
 Jan., 2015 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.6 No.1 J. Resour. Ecol. 2015 6 (1) 012-020 DOI:10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2015.01.002 www.jorae.cn Article Quantitative Geography Analysis on Spatial Structure
Jan., 2015 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.6 No.1 J. Resour. Ecol. 2015 6 (1) 012-020 DOI:10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2015.01.002 www.jorae.cn Article Quantitative Geography Analysis on Spatial Structure
A new approach for fast calculation of sloped terrace earthwork based on GIS in the hilly regions
 A new approach for fast calculation of sloped terrace earthwork based on GIS in the hilly regions Qingchun Zhang 1 1 Land Consolidation and Rehabilitation Center, the Ministry of Land and Resources; 1
A new approach for fast calculation of sloped terrace earthwork based on GIS in the hilly regions Qingchun Zhang 1 1 Land Consolidation and Rehabilitation Center, the Ministry of Land and Resources; 1
INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS FOR SOCIAL STUDIES, WORLD GEOGRAPHY. PAGE(S) WHERE TAUGHT (If submission is not a book, cite appropriate location(s))
 Prentice Hall: The Cultural Landscape, An Introduction to Human Geography 2002 Indiana Academic Standards for Social Studies, World Geography (Grades 9-12) STANDARD 1: THE WORLD IN SPATIAL TERMS Students
Prentice Hall: The Cultural Landscape, An Introduction to Human Geography 2002 Indiana Academic Standards for Social Studies, World Geography (Grades 9-12) STANDARD 1: THE WORLD IN SPATIAL TERMS Students
A Spatial Decision Support System for Agriculture and Natural Resources Management in China
 9 th APGEOSS Symposium Xiangzheng Deng A Spatial Decision Support System for Agriculture and Natural Resources Management in China Need to take decisions and make critical day-to-day and long-term planning
9 th APGEOSS Symposium Xiangzheng Deng A Spatial Decision Support System for Agriculture and Natural Resources Management in China Need to take decisions and make critical day-to-day and long-term planning
Atomic & Molecular Clusters / 原子分子团簇 /
 Atomic & Molecular Clusters / 原子分子团簇 / 王金兰 Email: jlwang@seu.edu.cn Department of Physics Southeast University What is nanometer? Nano is Small (10-7 --10-9 m; 1-100 nm) 10 0 m 10-1 m 10-2 m 10-3 m 10-4
Atomic & Molecular Clusters / 原子分子团簇 / 王金兰 Email: jlwang@seu.edu.cn Department of Physics Southeast University What is nanometer? Nano is Small (10-7 --10-9 m; 1-100 nm) 10 0 m 10-1 m 10-2 m 10-3 m 10-4
Chapter 2 the z-transform. 2.1 definition 2.2 properties of ROC 2.3 the inverse z-transform 2.4 z-transform properties
 Chapter 2 the -Transform 2.1 definition 2.2 properties of ROC 2.3 the inverse -transform 2.4 -transform properties 2.1 definition One motivation for introducing -transform is that the Fourier transform
Chapter 2 the -Transform 2.1 definition 2.2 properties of ROC 2.3 the inverse -transform 2.4 -transform properties 2.1 definition One motivation for introducing -transform is that the Fourier transform
猪发酵床废弃垫料不同配比基质对辣椒生长及品质的影响
 土壤 (Soils), 2017, 49(6): 1100 1107 DOI: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2017.06.005 1 猪发酵床废弃垫料不同配比基质对辣椒生长及品质的影响 * ( / 210014) (WD) ( ph EC ) T8 (WD.... =9.. 2.. 6) T7(WD.... =9.. 4.. 4) T8 T9(WD.. =9.. 5) ph EC T7
土壤 (Soils), 2017, 49(6): 1100 1107 DOI: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2017.06.005 1 猪发酵床废弃垫料不同配比基质对辣椒生长及品质的影响 * ( / 210014) (WD) ( ph EC ) T8 (WD.... =9.. 2.. 6) T7(WD.... =9.. 4.. 4) T8 T9(WD.. =9.. 5) ph EC T7
Synthesis of anisole by vapor phase methylation of phenol with methanol over catalysts supported on activated alumina
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (216) 72 726 催化学报 216 年第 37 卷第 5 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Synthesis of anisole by vapor
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (216) 72 726 催化学报 216 年第 37 卷第 5 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Synthesis of anisole by vapor
Soil database of China and carbon dynamics at regional scale
 Soil database of China and carbon dynamics at regional scale Xue-Zheng Shi Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China xzshi@issas.ac.cn Outline Role of soil database Multiple digital
Soil database of China and carbon dynamics at regional scale Xue-Zheng Shi Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China xzshi@issas.ac.cn Outline Role of soil database Multiple digital
Nonlinear Temperature Effects of Dust Bowl Region and Short-Run Adaptation
 Nonlinear Temperature Effects of Dust Bowl Region and Short-Run Adaptation A. John Woodill University of Hawaii at Manoa Seminar in Energy and Environmental Policy March 28, 2016 A. John Woodill Nonlinear
Nonlinear Temperature Effects of Dust Bowl Region and Short-Run Adaptation A. John Woodill University of Hawaii at Manoa Seminar in Energy and Environmental Policy March 28, 2016 A. John Woodill Nonlinear
Drought Assessment Using GIS and Remote Sensing in Amman-Zarqa Basin, Jordan
 Drought Assessment Using GIS and Remote Sensing in Amman-Zarqa Basin, Jordan Nezar Hammouri 1) and Ali El-Naqa 2) 1) Assistant Professor, Faculty of Natural Resources and Environment, Hashemite University,
Drought Assessment Using GIS and Remote Sensing in Amman-Zarqa Basin, Jordan Nezar Hammouri 1) and Ali El-Naqa 2) 1) Assistant Professor, Faculty of Natural Resources and Environment, Hashemite University,
VILLAGE INFORMATION SYSTEM (V.I.S) FOR WATERSHED MANAGEMENT IN THE NORTH AHMADNAGAR DISTRICT, MAHARASHTRA
 VILLAGE INFORMATION SYSTEM (V.I.S) FOR WATERSHED MANAGEMENT IN THE NORTH AHMADNAGAR DISTRICT, MAHARASHTRA Abstract: The drought prone zone in the Western Maharashtra is not in position to achieve the agricultural
VILLAGE INFORMATION SYSTEM (V.I.S) FOR WATERSHED MANAGEMENT IN THE NORTH AHMADNAGAR DISTRICT, MAHARASHTRA Abstract: The drought prone zone in the Western Maharashtra is not in position to achieve the agricultural
MONITORING OF SURFACE WATER RESOURCES IN THE MINAB PLAIN BY USING THE STANDARDIZED PRECIPITATION INDEX (SPI) AND THE MARKOF CHAIN MODEL
 MONITORING OF SURFACE WATER RESOURCES IN THE MINAB PLAIN BY USING THE STANDARDIZED PRECIPITATION INDEX (SPI) AND THE MARKOF CHAIN MODEL Bahari Meymandi.A Department of Hydraulic Structures, college of
MONITORING OF SURFACE WATER RESOURCES IN THE MINAB PLAIN BY USING THE STANDARDIZED PRECIPITATION INDEX (SPI) AND THE MARKOF CHAIN MODEL Bahari Meymandi.A Department of Hydraulic Structures, college of
Geomechanical Issues of CO2 Storage in Deep Saline Aquifers 二氧化碳咸水层封存的力学问题
 Geomechanical Issues of CO2 Storage in Deep Saline Aquifers 二氧化碳咸水层封存的力学问题 Li Xiaochun( 李小春 ) Yuan Wei ( 袁维 ) Institute of Rock and Soil Mechanics Chinese Academy of Science 中国科学院武汉岩土力学研究所 Outlines ( 提纲
Geomechanical Issues of CO2 Storage in Deep Saline Aquifers 二氧化碳咸水层封存的力学问题 Li Xiaochun( 李小春 ) Yuan Wei ( 袁维 ) Institute of Rock and Soil Mechanics Chinese Academy of Science 中国科学院武汉岩土力学研究所 Outlines ( 提纲
2011 Typhoon Activity Prediction
 2011 Typhoon Activity Prediction Published by Shanghai Typhoon Institute of China Meteorological Administration April 21th, 2011 Prediction of 2011 Northwest Pacific Basin and South China Sea Tropical
2011 Typhoon Activity Prediction Published by Shanghai Typhoon Institute of China Meteorological Administration April 21th, 2011 Prediction of 2011 Northwest Pacific Basin and South China Sea Tropical
A GIS-based Study on Grassland Degradation and. Increase of Dust Storms in China
 1 A GIS-based Study on Grassland Degradation and Increase of Dust Storms in China Qinxue WANG* and Kuninori OTSUBO* * National Institute for Environmental Studies, 16-2 Onogawa, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8506,
1 A GIS-based Study on Grassland Degradation and Increase of Dust Storms in China Qinxue WANG* and Kuninori OTSUBO* * National Institute for Environmental Studies, 16-2 Onogawa, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8506,
Flood hazard mapping in Urban Council limit, Vavuniya District, Sri Lanka- A GIS approach
 International Research Journal of Environment Sciences E-ISSN 2319 1414 Flood hazard mapping in Urban Council limit, Vavuniya District, Sri Lanka- A GIS approach Abstract M.S.R. Akther* and G. Tharani
International Research Journal of Environment Sciences E-ISSN 2319 1414 Flood hazard mapping in Urban Council limit, Vavuniya District, Sri Lanka- A GIS approach Abstract M.S.R. Akther* and G. Tharani
2. The lattice Boltzmann for porous flow and transport
 Lattice Boltzmann for flow and transport phenomena 2. The lattice Boltzmann for porous flow and transport Li Chen XJTU, 2016 Mail: lichennht08@mail.xjtu.edu.cn http://gr.xjtu.edu.cn/web/lichennht08 Content
Lattice Boltzmann for flow and transport phenomena 2. The lattice Boltzmann for porous flow and transport Li Chen XJTU, 2016 Mail: lichennht08@mail.xjtu.edu.cn http://gr.xjtu.edu.cn/web/lichennht08 Content
Recovering from the Recovery
 Recovering from the Recovery A Community-level View of Post- Earthquake Planning in the Historic Qiang Minority Ethnic Villages of Sichuan (A Report from the Field) Dan Abramson 艾丹, University of Washington
Recovering from the Recovery A Community-level View of Post- Earthquake Planning in the Historic Qiang Minority Ethnic Villages of Sichuan (A Report from the Field) Dan Abramson 艾丹, University of Washington
The Study of Dynamic Monitor of Rice Drought in Jiangxi Province with Remote Sensing
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 10 (2011 ) 1847 1853 2011 3rd International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Conference Application Title Technology
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 10 (2011 ) 1847 1853 2011 3rd International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Conference Application Title Technology
On the Quark model based on virtual spacetime and the origin of fractional charge
 On the Quark model based on virtual spacetime and the origin of fractional charge Zhi Cheng No. 9 Bairong st. Baiyun District, Guangzhou, China. 510400. gzchengzhi@hotmail.com Abstract: The quark model
On the Quark model based on virtual spacetime and the origin of fractional charge Zhi Cheng No. 9 Bairong st. Baiyun District, Guangzhou, China. 510400. gzchengzhi@hotmail.com Abstract: The quark model
The East Asian summer monsoon and impact of snow cover over HTP
 中国气象科学研究院 Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences ISSI meeting The East Asian summer monsoon and impact of snow cover over HTP Congwen Zhu Feb.2017 Bejing Outline East Asian Summer Monsoon Seasonal
中国气象科学研究院 Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences ISSI meeting The East Asian summer monsoon and impact of snow cover over HTP Congwen Zhu Feb.2017 Bejing Outline East Asian Summer Monsoon Seasonal
Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study
 Water Resources Management VI 139 Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study J. Letha, B. Thulasidharan Nair & B. Amruth Chand College of Engineering, Trivandrum, Kerala,
Water Resources Management VI 139 Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study J. Letha, B. Thulasidharan Nair & B. Amruth Chand College of Engineering, Trivandrum, Kerala,
World Geography. WG.1.1 Explain Earth s grid system and be able to locate places using degrees of latitude and longitude.
 Standard 1: The World in Spatial Terms Students will use maps, globes, atlases, and grid-referenced technologies, such as remote sensing, Geographic Information Systems (GIS), and Global Positioning Systems
Standard 1: The World in Spatial Terms Students will use maps, globes, atlases, and grid-referenced technologies, such as remote sensing, Geographic Information Systems (GIS), and Global Positioning Systems
La pietra da altre colline può levigare la giada di questa qui Il Classico dei Versi 可 以 攻 玉
 T r e n d s o f H e a l t h c a r e P e r f o r m a n c e E v a l u a t i o n i n C h i n a : a n E c o n o m i c a n d S o c i a l A n a l y s i s A t h e s i s p r e s e n t e d b y H a o L i T o T h
T r e n d s o f H e a l t h c a r e P e r f o r m a n c e E v a l u a t i o n i n C h i n a : a n E c o n o m i c a n d S o c i a l A n a l y s i s A t h e s i s p r e s e n t e d b y H a o L i T o T h
上海激光电子伽玛源 (SLEGS) 样机的实验介绍
 上海激光电子伽玛源 (SLEGS) 样机的实验介绍 Pan Qiangyan for SLEGS collaborators 一. 引言二. 装置布局三. 实验及其结果四. 结论 一, 引言 为建设 SLEGS 光束线提供参考和研制依据, 中科院上海应用物理研究所于 2005 年成立了以徐望研究员为组长的 SLEGS 小组, 开展 SLEGS 样机的实验工作 ; 在中科院知识创新工程方向性项目 (
上海激光电子伽玛源 (SLEGS) 样机的实验介绍 Pan Qiangyan for SLEGS collaborators 一. 引言二. 装置布局三. 实验及其结果四. 结论 一, 引言 为建设 SLEGS 光束线提供参考和研制依据, 中科院上海应用物理研究所于 2005 年成立了以徐望研究员为组长的 SLEGS 小组, 开展 SLEGS 样机的实验工作 ; 在中科院知识创新工程方向性项目 (
Report. Developing a course component on disaster management
 Report Developing a course component on disaster management By Chira Prangkio Tawee Chaipimonplin Department of Geography, Faculty of Social Sciences, Chiang Mai University Thailand Presented at Indian
Report Developing a course component on disaster management By Chira Prangkio Tawee Chaipimonplin Department of Geography, Faculty of Social Sciences, Chiang Mai University Thailand Presented at Indian
Drought Criteria. Richard J. Heggen Department of Civil Engineering University of New Mexico, USA Abstract
 Drought Criteria Richard J. Heggen Department of Civil Engineering University of New Mexico, USA rheggen@unm.edu Abstract Rainwater catchment is an anticipatory response to drought. Catchment design requires
Drought Criteria Richard J. Heggen Department of Civil Engineering University of New Mexico, USA rheggen@unm.edu Abstract Rainwater catchment is an anticipatory response to drought. Catchment design requires
Land Cover Status in the Koshi River Basin, Central Himalayas
 Jan., 2017 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 8 No.1 J. Resour. Ecol. 2017 8(1) 10-19 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2017.01.003 www.jorae.cn Land Cover Status in the Koshi River Basin, Central Himalayas
Jan., 2017 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 8 No.1 J. Resour. Ecol. 2017 8(1) 10-19 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2017.01.003 www.jorae.cn Land Cover Status in the Koshi River Basin, Central Himalayas
Service Bulletin-04 真空电容的外形尺寸
 Plasma Control Technologies Service Bulletin-04 真空电容的外形尺寸 在安装或者拆装真空电容时, 由于真空电容的电级片很容易移位, 所以要特别注意避免对电容的损伤, 这对于过去的玻璃电容来说非常明显, 但对于如今的陶瓷电容则不那么明显, 因为它们能够承载更高的机械的 电性能的负载及热负载 尽管从外表看来电容非常结实, 但是应当注意, 由于采用焊接工艺来封装铜和陶瓷,
Plasma Control Technologies Service Bulletin-04 真空电容的外形尺寸 在安装或者拆装真空电容时, 由于真空电容的电级片很容易移位, 所以要特别注意避免对电容的损伤, 这对于过去的玻璃电容来说非常明显, 但对于如今的陶瓷电容则不那么明显, 因为它们能够承载更高的机械的 电性能的负载及热负载 尽管从外表看来电容非常结实, 但是应当注意, 由于采用焊接工艺来封装铜和陶瓷,
Barnabas Chipindu, Department of Physics, University of Zimbabwe
 DEFICIENCIES IN THE OPERATIONAL APPLICATIONS OF LONG - RANGE WEATHER PREDICTIONS FOR AGRICULTURE - RECOMMENDATIONS FOR IMPROVING THE TECHNOLOGY FOR THE BENEFIT OF AGRICULTURE AT THE NATIONAL AND REGIONAL
DEFICIENCIES IN THE OPERATIONAL APPLICATIONS OF LONG - RANGE WEATHER PREDICTIONS FOR AGRICULTURE - RECOMMENDATIONS FOR IMPROVING THE TECHNOLOGY FOR THE BENEFIT OF AGRICULTURE AT THE NATIONAL AND REGIONAL
POTENTIAL EVAPOTRANSPIRATION AND DRYNESS / DROUGHT PHENOMENA IN COVURLUI FIELD AND BRATEŞ FLOODPLAIN
 PRESENT ENVIRONMENT AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT, VOL. 5, no.2, 2011 POTENTIAL EVAPOTRANSPIRATION AND DRYNESS / DROUGHT PHENOMENA IN COVURLUI FIELD AND BRATEŞ FLOODPLAIN Gigliola Elena Ureche (Dobrin) 1
PRESENT ENVIRONMENT AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT, VOL. 5, no.2, 2011 POTENTIAL EVAPOTRANSPIRATION AND DRYNESS / DROUGHT PHENOMENA IN COVURLUI FIELD AND BRATEŞ FLOODPLAIN Gigliola Elena Ureche (Dobrin) 1
Establishment and data analysis of sea-state monitoring system along Taiwan coast
 Vol. 14 No. 1 Marine Science Bulletin May 2012 Establishment and data analysis of sea-state monitoring system along Taiwan coast FENG Xiang-bo 1,2, WANG Hao 1,2, YAN Yi-xin 1,2 1. Key Laboratory of Coastal
Vol. 14 No. 1 Marine Science Bulletin May 2012 Establishment and data analysis of sea-state monitoring system along Taiwan coast FENG Xiang-bo 1,2, WANG Hao 1,2, YAN Yi-xin 1,2 1. Key Laboratory of Coastal
The Lagrange Mean Value Theorem Of Functions of n Variables
 陕西师范大学学士学位论文 The Lagrage Mea Value Theorem Of Fuctios of Variables 作 者 单 位 数学与信息科学学院 指 导 老 师 曹怀 信 作 者 姓 名 李 碧 专 业 班 级数学与应用数学专业 4 级 班 The Lagrage Mea Value Theorem of a Fuctio of Variables LI i lass, Grade
陕西师范大学学士学位论文 The Lagrage Mea Value Theorem Of Fuctios of Variables 作 者 单 位 数学与信息科学学院 指 导 老 师 曹怀 信 作 者 姓 名 李 碧 专 业 班 级数学与应用数学专业 4 级 班 The Lagrage Mea Value Theorem of a Fuctio of Variables LI i lass, Grade
Chapter 1 Linear Regression with One Predictor Variable
 Chapter 1 Linear Regression with One Predictor Variable 許湘伶 Applied Linear Regression Models (Kutner, Nachtsheim, Neter, Li) hsuhl (NUK) LR Chap 1 1 / 41 Regression analysis is a statistical methodology
Chapter 1 Linear Regression with One Predictor Variable 許湘伶 Applied Linear Regression Models (Kutner, Nachtsheim, Neter, Li) hsuhl (NUK) LR Chap 1 1 / 41 Regression analysis is a statistical methodology
GIS in Weather and Society
 GIS in Weather and Society Olga Wilhelmi Institute for the Study of Society and Environment National Center for Atmospheric Research WAS*IS November 8, 2005 Boulder, Colorado Presentation Outline GIS basic
GIS in Weather and Society Olga Wilhelmi Institute for the Study of Society and Environment National Center for Atmospheric Research WAS*IS November 8, 2005 Boulder, Colorado Presentation Outline GIS basic
World Meteorological Organization
 World Meteorological Organization Opportunities and Challenges for Development of Weather-based Insurance and Derivatives Markets in Developing Countries By Maryam Golnaraghi, Ph.D. Head of WMO Disaster
World Meteorological Organization Opportunities and Challenges for Development of Weather-based Insurance and Derivatives Markets in Developing Countries By Maryam Golnaraghi, Ph.D. Head of WMO Disaster
Growth of Cu/SSZ 13 on SiC for selective catalytic reduction of NO
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 71 78 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 1 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Growth of Cu/SSZ 13 on SiC
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 71 78 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 1 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Growth of Cu/SSZ 13 on SiC
Lecture 2. Random variables: discrete and continuous
 Lecture 2 Random variables: discrete and continuous Random variables: discrete Probability theory is concerned with situations in which the outcomes occur randomly. Generically, such situations are called
Lecture 2 Random variables: discrete and continuous Random variables: discrete Probability theory is concerned with situations in which the outcomes occur randomly. Generically, such situations are called
Analytical Report. Drought in the Horn of Africa February Executive summary. Geographical context. Likelihood of drought impact (LDI)
 Executive summary The current drought in the Horn of Africa is affecting especially Somalia, among other countries, in particular the central and southern regions, where most population is located. Overall,
Executive summary The current drought in the Horn of Africa is affecting especially Somalia, among other countries, in particular the central and southern regions, where most population is located. Overall,
YIFEI SUN. Department of Geography California State University Northridge, CA Tel: (818) (o)
 YIFEI SUN Department of Geography California State University Northridge, CA 91330-8249 Tel: (818) 677-3529 (o) Email: yifei.sun@csun.edu EDUCATION Ph.D. in Geography, 2001. State University of New York
YIFEI SUN Department of Geography California State University Northridge, CA 91330-8249 Tel: (818) 677-3529 (o) Email: yifei.sun@csun.edu EDUCATION Ph.D. in Geography, 2001. State University of New York
Effects of particle size and particle interactions on scheelite flotation
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 3682 3687 Effects of particle size and particle interactions on scheelite flotation Wan-zhong YIN, Ji-zhen WANG College of Resources and Civil Engineering, Northeastern
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 3682 3687 Effects of particle size and particle interactions on scheelite flotation Wan-zhong YIN, Ji-zhen WANG College of Resources and Civil Engineering, Northeastern
«Desertification and Drought Monitoring in Arid Tunisia based on Remote Sensing Imagery» Research Undertaken & Case-Studies.
 «Desertification and Drought Monitoring in Arid Tunisia based on Remote Sensing Imagery» Research Undertaken & Case-Studies EU COST Action September 2015, Antalya Turkey Bouajila ESSIFI INSTITUT DES REGIONS
«Desertification and Drought Monitoring in Arid Tunisia based on Remote Sensing Imagery» Research Undertaken & Case-Studies EU COST Action September 2015, Antalya Turkey Bouajila ESSIFI INSTITUT DES REGIONS
沙强 / 讲师 随时欢迎对有机化学感兴趣的同学与我交流! 理学院化学系 从事专业 有机化学. 办公室 逸夫楼 6072 实验室 逸夫楼 6081 毕业院校 南京理工大学 电子邮箱 研 究 方 向 催化不对称合成 杂环骨架构建 卡宾化学 生物活性分子设计
 沙强 / 讲师 随时欢迎对有机化学感兴趣的同学与我交流! 院系 理学院化学系 从事专业 有机化学 学历 博士研究生 学位 博士 办公室 逸夫楼 6072 实验室 逸夫楼 6081 毕业院校 南京理工大学 电子邮箱 qsha@njau.edu.cn 研 究 方 向 催化不对称合成 杂环骨架构建 卡宾化学 生物活性分子设计 研究方向汇总图个人简介 2010 年毕业于南京理工大学制药工程专业, 获得工学学士学位,
沙强 / 讲师 随时欢迎对有机化学感兴趣的同学与我交流! 院系 理学院化学系 从事专业 有机化学 学历 博士研究生 学位 博士 办公室 逸夫楼 6072 实验室 逸夫楼 6081 毕业院校 南京理工大学 电子邮箱 qsha@njau.edu.cn 研 究 方 向 催化不对称合成 杂环骨架构建 卡宾化学 生物活性分子设计 研究方向汇总图个人简介 2010 年毕业于南京理工大学制药工程专业, 获得工学学士学位,
Sustainable Cities and Communities based on Indicators on Urbanization 地理国情监测技术. Prof. Dr. John W. Z. SHI The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
 IAEG- SDGs WG on Geospatial Information, 1 st Expert Group Meeting 12-14 Dec 2016 Mexico City Measure 地理国情监测技术 Sustainable Cities and Communities 专业 based on Indicators on Urbanization Prof. Dr. John W.
IAEG- SDGs WG on Geospatial Information, 1 st Expert Group Meeting 12-14 Dec 2016 Mexico City Measure 地理国情监测技术 Sustainable Cities and Communities 专业 based on Indicators on Urbanization Prof. Dr. John W.
Using object oriented technique to extract jujube based on landsat8 OLI image in Jialuhe Basin
 Journal of Image Processing Theory and Applications (2016) 1: 16-20 Clausius Scientific Press, Canada Using object oriented technique to extract jujube based on landsat8 OLI image in Jialuhe Basin Guotao
Journal of Image Processing Theory and Applications (2016) 1: 16-20 Clausius Scientific Press, Canada Using object oriented technique to extract jujube based on landsat8 OLI image in Jialuhe Basin Guotao
Solar Radiation Climatology Calculation in China
 June, 214 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.5 o.2 J. Resour. Ecol. 214 5 (2) 132-138 DOI:1.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.214.2.5 www.jorae.cn Article Solar Radiation Climatology Calculation in China WAG Chenliang
June, 214 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.5 o.2 J. Resour. Ecol. 214 5 (2) 132-138 DOI:1.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.214.2.5 www.jorae.cn Article Solar Radiation Climatology Calculation in China WAG Chenliang
FLOOD HAZARD AND RISK ASSESSMENT IN MID- EASTERN PART OF DHAKA, BANGLADESH
 FLOOD HAZARD AND RISK ASSESSMENT IN MID- EASTERN PART OF DHAKA, BANGLADESH Muhammad MASOOD MEE07180 Supervisor: Prof. Kuniyoshi TAKEUCHI ABSTRACT An inundation simulation has been done for the mid-eastern
FLOOD HAZARD AND RISK ASSESSMENT IN MID- EASTERN PART OF DHAKA, BANGLADESH Muhammad MASOOD MEE07180 Supervisor: Prof. Kuniyoshi TAKEUCHI ABSTRACT An inundation simulation has been done for the mid-eastern
国际数值预报现状和发展 沈学顺 中国气象局数值预报中心
 国际数值预报现状和发展 沈学顺 中国气象局数值预报中心 提纲 背景介绍 国际数值预报现状和水平 未来发展 一 背景介绍 What is Numerical Weather Prediction? The technique used to obtain an objective forecast of the future weather (up to possibly two weeks) by
国际数值预报现状和发展 沈学顺 中国气象局数值预报中心 提纲 背景介绍 国际数值预报现状和水平 未来发展 一 背景介绍 What is Numerical Weather Prediction? The technique used to obtain an objective forecast of the future weather (up to possibly two weeks) by
