Measurement of 59 Ni(n, p) 59 Co Reaction Cross-section through Surrogate Technique for Fusion Technology Applications
|
|
|
- Loraine Meredith Palmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Measurement of 59 Ni(n, p) 59 Co Reaction Cross-section through Surrogate Technique for Fusion Technology Applications Presented By Jyoti Pandey Department of Physics G.B. Pant University, Pantnagar Uttarakhand, India
2 59 Ni(n, p) 59 Co q In the first generation fusion reactor thousands oftons stainless steel will be used for different components (structural materials) of a fusion reactor. Iron, nickel and chromium are the main constituents of stainless steel. SUBSYSTEM CANDIDATE MATERIAL Plasma Facing Component Cu-Cr-Zr, Be, SS316 LN Divertor W, Water, Inconel 718 Shielding Blanket Breeding Blanket SS316LN & H 2 O Li, LiPb ( 83 Pb 17 Li) Vacuum Vessel Magnets Cryostat SS304, Borated steel NbSn, NbTi SS304
3 q Natural Nickel (Ni) [ 58 Ni(68.077%), 60 Ni(26.223%), 61 Ni(1.140%), 62 Ni (3.635%), 64 Ni(0.926%)]. q 59 Ni (t 1/2 = years) is one of the radio-nuclide which is produced in large quantities inside the fusion reactor. 59 Ni (t 1/2 = y ) (n,g) 59 Ni (n,2n) 60 Ni 58 Ni nat Ni 61 Ni 64 Ni 63 Ni 62 Ni 63 Ni (t 1/2 = 100 y )
4 n 55 Fe 59 Ni 63 Ni 53 Mn (n,p), (n,a), (n,n ), (n,2n), (n,3n), (n,d) and many other reactions takes place Second generation reaction 54 Mn
5 Helium Generation due to the different isotopes of Nickel (Preliminary calculation with TALYS-1.8)
6 Hydrogen Generation due to the different isotopes of Nickel (Preliminary calculation with TALYS-1.8)
7 Major Pathways of the production of 59 Ni in the fusion reactor environment 5 p)
8 Present status of 59 Ni(n,p) Large discrepancy in the data libraries Not based on measured data No experimental data is available for this reaction in IAEA EXFOR databse
9 FOCUSED OBJECTIVES Ø To measure the cross-section of 59 Ni(n, p) 59 Co from E n = 9-20 MeV. Ø Cross-section measurement is not possible directly for this reaction due to non-existence of this isotope in nature. Ø This is the main reason for using surrogate method for the measurement of this crosssection.
10 Different Types of Nuclear Reaction Mechanism Direct A single interaction before emission Pre-equilibrium A small number of interaction before emission A large number of interaction before emission Compound Nucleus
11 Bohr s Compound Nucleus Theory According to Bohr Compound Nucleus Theory 1. The formation of the compound nucleus and it s break up are independent of each other. This is known as the independence hypothesis. 2. The compound nucleus forgets it s mode of formation. The decay of compound nucleus depends only on the properties of compound nucleus and not upon how it was formed. The life time of compound nucleus is around seconds. 3. The cross section for the compound nucleus is defined as the product of formation of compound nucleus and it s decay probability. X + x C* Y + y Z + z s ( x, y) = s x G y G
12 According to H-F theory the compound nuclear cross-section is given by Applying W-E Approximation, the formula for desired cross-section is simplified as ( Applicable only at High Excitation Energy) Calculated Measured 12
13 SURROGATE TECHNIQUE
14 Desired Reaction n + 59 Ni 60 Ni p + 59 Co Surrogate Reaction 6 Li + 56 Fe 60 Ni + d p + 59 Co
15 Reference Reaction n + 60 Ni 61 Ni p + 60 Co Surrogate Reaction 6 Li + 59 Co 61 Ni + a p + 60 Co
16 Condition for using the surrogate technique Ø The Surrogate method is limited to Compound nuclear reactions. Ø Same Compound Nucleus should be formed through Desired and Surrogate reaction channels. Ø Compound Nucleus Excitation Energy should be same in both desired reaction and surrogate reaction. Ø Excitation energy formula of the compound nucleus is E exc = K.E. of the incident particle in CM frame + B.E. of the particle in compound nucleus
17 THEORETICAL STUDY OF THE PROPOSED EXPERIMENT
18 TALYS -1.8 (Nuclear Reaction Modular Code ) Software for the simulation of nuclear reactions in the energy range 1 kev 200 MeV User-friendly Code containing an optimal combination of reliable nuclear models. Developed by Arjan Koning, Stephane Hilarie, Stephane Goriely Created at NRG in Petten, the Netherlands, and is available free of charge. Versatile tool to analyse basic microscopic experiments and to
19 From 2-14 MeV the reaction mainly goes through compound nucleus process THEORETICAL STUDY Excitation function of 59 Ni(n,p) reaction along with the contribution from the different reaction mechanism (Direct + Pre-equilibrium +Compound) [ Using TALYS 1.8 ] TALYS-1.8 is used to check the different nuclear reaction mechanism contribution Theoretical variations in DDX with angle of emission for energy proton emitted through 59 Ni(n,p) reaction at 14 MeV neutrons [ Using TALYS 1.8 ] Angular Distribution of outgoing protons is symmetric.
20 Selection of Li-6 beam energy Main Condition - Compound Nucleus Excitation Energy should be same in both desired reaction and surrogate reaction. Ø Excitation Energy of ( 60 Ni*) in the Desired Reaction n + 59 Ni à ( 60 Ni)* à p+ 59 Co. at neutron energy 14 MeV ~ E*(25) MeV. Ø Excitation Energy of ( 60 Ni*) in the Surrogate Reaction 6 Li+ 56 Fe à d + ( 60 Ni)* at lithium energy 35 MeV ~ E*(25) MeV.
21 P P CN surrodecay 60Ni surrodecay ( E ( E ex ex ) = ) = N N coin ejec-decay N single coin d - p N d ( E ( E 59 1 ( Ni + 0n 28Ni E n =14MeV )* 56 6 ( Fe + 3Li d + 28Ni ex ) ex E Li ~ MeV ) ) * E exc ~ 25 MeV 59 Co H Detection of deuteron singles with DE-E telescope [( E*)] Detection of deuteron and decay particle (proton) in coincidence with DE-E telescope [ ( E*)] 21
22 EXPERIMENTAL HALL ( At TIFR )
23 EXPERIMENTAL DETAILS
24 Beam Requirments --- o Beam and it s energy --- Lithium -6 and MeV Targets and Detectors used Targets- 56 Fe(~700µg/cm 2 ), 59 Co(~600µg/cm 2 ) Ø Ø Detector- Two ΔE-E telescope detectors for PLFs A Large Area Solid State (16 Strip Detector) for Decay particle from compound nucleus 2 detectors Ø Both are SSB ( Silicon Surface Barrier ) Detector Used for Charged particle detection. Telescope Detector Ø Detectors are useful for measuring the energy deposition of passing charged particles, i.e. de/dx. Ø DE - Particle identification by mass E - Particle will go further and will completely stop there and convert it s Kinetic Energy into Current Energy 16-Strip Detector
25 EXPERIMENTAL SETUP ( INSIDE OF SCATTERING CHAMBER ) PLFs Detector E (1.0mm) DE (150 µm) Target Li Beam Large area Solid State Detector (450mm 2 )
26 Excitation energy spectra of the target like fragments produced 6 Li+ 56 Fe and 6 Li+ 59 Co reactions corresponding to PLF deuteron and alpha with and without coincidence with evaporated spectra
27 RESULTS
28 Conclusion q Scientists are becoming increasingly excited about the successful completion of the fusion reactor work. A reactor which can replicate the sun s energy source on Earth through scientific and technological innovation which are earlier unimagined. q q 59 Ni(n,p) reaction cross-section have been measured in the energy range MeV by surrogate-reaction method. The present experimental data have been compared with evaluated data libraries TENDL,EMPIRE and TALYS. q The experimental data is found to be reasonably consistent with TALYS. q The present measurement will be useful to improve and update the different data libraries and opens up the possibility of measuring the compound nuclear reactions involving unstable targets with the relevance to fusion technology
29 References Ø A.J. KONING et al., TALYS User Manual : A Nuclear Reaction Program, User Manual,NRG-1755 ZG Petten, The Netherlands (2011). Ø B. PANDEY et al., Estimate of (n,p) cross-section for Radionuclides 55 Fe Using EMPIRE and TALYS, Nuclear Science and Engineering 179, 313 (2015). Ø B. PANDEY et al., Measurement of 55 Fe(n,p) cross-section by the surrogate-reaction method for fusion technology applications, Physical Review C 93,021602(R) (2016). Ø J.ESCHER et al., Compound-Nuclear Reaction Cross-Sections from Surrogate Measurements, Rev. Mod. Phys., 84, 353 (2012). Ø R.A.FORREST, Data Requirements for Neutron Activation Part I : Cross-Sections, Fusion Eng. Des.,81,2143(2006);
30 List of publications 1. Jyoti Pandey, Bhawna Pandey, H.M. Agrawal Estimation of (n,p) cross-section for radionuclide 60 Co, Proceeding at DAE-BRNS National Conference on Recent Trends in Nuclear Physics organized by Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India, (2016). 2. Jyoti Pandey,Bhawna Pandey,H.M. Agrawal Estimation of (n,p) (n,α) reaction Cross-sections for unstable 59,63 Ni nuclides, Proceeding at 61 st DAE-BRNS Symposium on Nuclear Physics December, Vol.61, (2016). 3. Jyoti Pandey, Bhawna Pandey, H.M. Agrawal, P.V. Subhash, S.Vala, Akhil Sai Aiyyala Rajnikant Makwana, S.V. Suryanarayana, Neutron induced Cross-section of radionuclide 60 Co for fusion technology application, Fusion Science and Technology (Under Communication). 4. Jyoti Pandey, Bhawna Pandey, P.V.Subhash, H.M. Agrawal Helium and Hydrogen generation due to the presence of radionuclides (A~50-60) in fusion recator environment, Proceedings of the International Conference on High Energy Radiation and Applications (ICHERA),during October,2017 in the Physics Department, Faculty of Science, The Maharaja Sayajirao, University of Baroda ( Under Communication ).
31 Papers In Proceedings
32 AMU Proceeding paper
33 Papers In Proceedings at International Conference on High Energy Radiation and Applications (ICHERA)
34 Papers In Fusion Science and Technology (Accepted)
35
36 q I am very thankful to ACKNOWLEDGMENT Dr. H.M.Agrawal, G.B.Pant Universiry Pantnagar, India Dr. Bhawna Pandey, G.B.Pant Universiry Pantnagar, India Dr. Alok Saxena, BARC, Mumbai, India Dr. B.K. Nayak, BARC, Mumbai, India Dr. S.V. Suryanarayana, Mumbai, India for their constant guidance, support and valuable suggestions in doing this work. q BRNS (Board of Research in Nuclear Science), Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) for their funding in pursuing research work.
37 THANK YOU
Excitation functions and isotopic effects in (n,p) reactions for stable iron isotopes from. reaction threshold to 20 MeV.
 1 Excitation functions and isotopic effects in (n,p) reactions for stable iron isotopes from reaction threshold to 20 MeV. J. Joseph Jeremiah a, Damewan Suchiang b, B.M. Jyrwa a,* a Department of Physics,
1 Excitation functions and isotopic effects in (n,p) reactions for stable iron isotopes from reaction threshold to 20 MeV. J. Joseph Jeremiah a, Damewan Suchiang b, B.M. Jyrwa a,* a Department of Physics,
Neutron-Induced Reactions Investigations in the Neutrons Energy Range up to 16 MeV
 NUCLEAR THEORY, Vol. 33 (2014) eds. A.I. Georgieva, N. Minkov, Heron Press, Sofia Neutron-Induced Reactions Investigations in the Neutrons Energy Range up to 16 MeV R. Avetisyan, R. Avagyan, G. Bazoyan,
NUCLEAR THEORY, Vol. 33 (2014) eds. A.I. Georgieva, N. Minkov, Heron Press, Sofia Neutron-Induced Reactions Investigations in the Neutrons Energy Range up to 16 MeV R. Avetisyan, R. Avagyan, G. Bazoyan,
Nuclear contribution into single-event upset in 3D on-board electronics at moderate energy cosmic proton impact
 Nuclear contribution into single-event upset in 3D on-board electronics at moderate energy cosmic proton impact N. G. Chechenin, T. V. Chuvilskaya and A. A. Shirokova Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics,
Nuclear contribution into single-event upset in 3D on-board electronics at moderate energy cosmic proton impact N. G. Chechenin, T. V. Chuvilskaya and A. A. Shirokova Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics,
Complete activation data libraries for all incident particles, all energies and including covariance data
 Complete activation data libraries for all incident particles, all energies and including covariance data Arjan Koning NRG Petten, The Netherlands Workshop on Activation Data EAF 2011 June 1-3 2011, Prague,
Complete activation data libraries for all incident particles, all energies and including covariance data Arjan Koning NRG Petten, The Netherlands Workshop on Activation Data EAF 2011 June 1-3 2011, Prague,
Cross-section Measurements of Relativistic Deuteron Reactions on Copper by Activation Method
 Nuclear Physics Institute, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic Department of Nuclear Reactors, Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague Cross-section
Nuclear Physics Institute, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic Department of Nuclear Reactors, Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague Cross-section
da u g ht er + radiation
 RADIOACTIVITY The discovery of radioactivity can be attributed to several scientists. Wilhelm Roentgen discovered X-rays in 1895 and shortly after that Henri Becquerel observed radioactive behavior while
RADIOACTIVITY The discovery of radioactivity can be attributed to several scientists. Wilhelm Roentgen discovered X-rays in 1895 and shortly after that Henri Becquerel observed radioactive behavior while
SURROGATE REACTIONS. An overview of papers by Jason Burke from LLNL
 SURROGATE REACTIONS An overview of papers by Jason Burke from LLNL Compound Nuclear Reaction cross sections Cross sections for compound-nuclear reactions are required input for astrophysical models and
SURROGATE REACTIONS An overview of papers by Jason Burke from LLNL Compound Nuclear Reaction cross sections Cross sections for compound-nuclear reactions are required input for astrophysical models and
Nuclear Physics Questions. 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of?
 Nuclear Physics Questions 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of? 2. What is the definition of the atomic number? What is its symbol?
Nuclear Physics Questions 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of? 2. What is the definition of the atomic number? What is its symbol?
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PIGE, PIXE AND NAA ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES FOR THE DETERMINATION OF MINOR ELEMENTS IN STEELS
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PIGE, PIXE AND NAA ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES FOR THE DETERMINATION OF MINOR ELEMENTS IN STEELS ANTOANETA ENE 1, I. V. POPESCU 2, T. BÃDICÃ 3, C. BEªLIU 4 1 Department of Physics, Faculty
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PIGE, PIXE AND NAA ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES FOR THE DETERMINATION OF MINOR ELEMENTS IN STEELS ANTOANETA ENE 1, I. V. POPESCU 2, T. BÃDICÃ 3, C. BEªLIU 4 1 Department of Physics, Faculty
NJCTL.org 2015 AP Physics 2 Nuclear Physics
 AP Physics 2 Questions 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of? 2. What is the definition of the atomic number? What is its symbol?
AP Physics 2 Questions 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of? 2. What is the definition of the atomic number? What is its symbol?
UNIT VIII ATOMS AND NUCLEI
 UNIT VIII ATOMS AND NUCLEI Weightage Marks : 06 Alpha-particles scattering experiment, Rutherford s model of atom, Bohr Model, energy levels, Hydrogen spectrum. Composition and size of Nucleus, atomic
UNIT VIII ATOMS AND NUCLEI Weightage Marks : 06 Alpha-particles scattering experiment, Rutherford s model of atom, Bohr Model, energy levels, Hydrogen spectrum. Composition and size of Nucleus, atomic
Photonuclear Reaction Cross Sections for Gallium Isotopes. Serkan Akkoyun 1, Tuncay Bayram 2
 Photonuclear Reaction Cross Sections for Gallium Isotopes Serkan Akkoyun 1, Tuncay Bayram 2 1 Cumhuriyet University, Vocational School of Healt, Sivas, Turkey 2 Sinop University, Department of Physics,
Photonuclear Reaction Cross Sections for Gallium Isotopes Serkan Akkoyun 1, Tuncay Bayram 2 1 Cumhuriyet University, Vocational School of Healt, Sivas, Turkey 2 Sinop University, Department of Physics,
Chemistry 52 Chapter 11 ATOMIC STRUCTURE. The general designation for an atom is shown below:
 ATOMIC STRUCTURE An atom is composed of a positive nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. The protons and neutrons in a nucleus are referred
ATOMIC STRUCTURE An atom is composed of a positive nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. The protons and neutrons in a nucleus are referred
Elastic Recoil Detection Method using DT Neutrons for Hydrogen Isotope Analysis in Fusion Materials. Abstract
 Elastic Recoil Detection Method using DT Neutrons for Hydrogen Isotope Analysis in Fusion Materials Naoyoshi Kubota, Kentaro Ochiai, Keitaro Kondo 2 and Takeo Nishitani. :Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute,
Elastic Recoil Detection Method using DT Neutrons for Hydrogen Isotope Analysis in Fusion Materials Naoyoshi Kubota, Kentaro Ochiai, Keitaro Kondo 2 and Takeo Nishitani. :Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute,
Chapter 3: Neutron Activation and Isotope Analysis
 Chapter 3: Neutron Activation and Isotope Analysis 3.1. Neutron Activation Techniques 3.2. Neutron Activation of Paintings 3.3. From Qumran to Napoleon 3.4. Neutron Activation with Accelerators 3.5. Isotope
Chapter 3: Neutron Activation and Isotope Analysis 3.1. Neutron Activation Techniques 3.2. Neutron Activation of Paintings 3.3. From Qumran to Napoleon 3.4. Neutron Activation with Accelerators 3.5. Isotope
MockTime.com. Ans: (b) Q6. Curie is a unit of [1989] (a) energy of gamma-rays (b) half-life (c) radioactivity (d) intensity of gamma-rays Ans: (c)
![MockTime.com. Ans: (b) Q6. Curie is a unit of [1989] (a) energy of gamma-rays (b) half-life (c) radioactivity (d) intensity of gamma-rays Ans: (c) MockTime.com. Ans: (b) Q6. Curie is a unit of [1989] (a) energy of gamma-rays (b) half-life (c) radioactivity (d) intensity of gamma-rays Ans: (c)](/thumbs/95/125098222.jpg) Chapter Nuclei Q1. A radioactive sample with a half life of 1 month has the label: Activity = 2 micro curies on 1 8 1991. What would be its activity two months earlier? [1988] 1.0 micro curie 0.5 micro
Chapter Nuclei Q1. A radioactive sample with a half life of 1 month has the label: Activity = 2 micro curies on 1 8 1991. What would be its activity two months earlier? [1988] 1.0 micro curie 0.5 micro
Class XII Chapter 13 - Nuclei Physics
 Question 13.1: (a) Two stable isotopes of lithium and have respective abundances of 7.5% and 92.5%. These isotopes have masses 6.01512 u and 7.01600 u, respectively. Find the atomic mass of lithium. (b)
Question 13.1: (a) Two stable isotopes of lithium and have respective abundances of 7.5% and 92.5%. These isotopes have masses 6.01512 u and 7.01600 u, respectively. Find the atomic mass of lithium. (b)
Application and Validation of Event Generator in the PHITS Code for the Low-Energy Neutron-Induced Reactions
 Progress in NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY, Vol. 2, pp.931-935 (2011) ARTICLE Application and Validation of Event Generator in the PHITS Code for the Low-Energy Neutron-Induced Reactions Yosuke IWAMOTO
Progress in NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY, Vol. 2, pp.931-935 (2011) ARTICLE Application and Validation of Event Generator in the PHITS Code for the Low-Energy Neutron-Induced Reactions Yosuke IWAMOTO
Quality Assurance. Purity control. Polycrystalline Ingots
 Quality Assurance Purity control Polycrystalline Ingots 1 Gamma Spectrometry Nuclide Identification Detection of Impurity Traces 1.1 Nuclides Notation: Atomic Mass Atomic Number Element Neutron Atomic
Quality Assurance Purity control Polycrystalline Ingots 1 Gamma Spectrometry Nuclide Identification Detection of Impurity Traces 1.1 Nuclides Notation: Atomic Mass Atomic Number Element Neutron Atomic
Calculations of Excitation Functions of (n, p), (n, ) and (n, 2n) Reaction Cross-Sections for Stable Isotopes of Ni from Reaction Threshold to 20 MeV
 Journal of Nuclear and Particle Physics 2013, 3(4): 100-107 DOI: 10.5923/j.jnpp.20130304.07 Calculations of Excitation Functions of (n, p), (n, ) and (n, 2n) Reaction Cross-Sections for Stale Isotopes
Journal of Nuclear and Particle Physics 2013, 3(4): 100-107 DOI: 10.5923/j.jnpp.20130304.07 Calculations of Excitation Functions of (n, p), (n, ) and (n, 2n) Reaction Cross-Sections for Stale Isotopes
State the main interaction when an alpha particle is scattered by a gold nucleus
 Q1.(a) Scattering experiments are used to investigate the nuclei of gold atoms. In one experiment, alpha particles, all of the same energy (monoenergetic), are incident on a foil made from a single isotope
Q1.(a) Scattering experiments are used to investigate the nuclei of gold atoms. In one experiment, alpha particles, all of the same energy (monoenergetic), are incident on a foil made from a single isotope
Phys102 Lecture 29, 30, 31 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity
 Phys10 Lecture 9, 30, 31 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity Key Points Structure and Properties of the Nucleus Alpha, Beta and Gamma Decays References 30-1,,3,4,5,6,7. Atomic Structure Nitrogen (N) Atom
Phys10 Lecture 9, 30, 31 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity Key Points Structure and Properties of the Nucleus Alpha, Beta and Gamma Decays References 30-1,,3,4,5,6,7. Atomic Structure Nitrogen (N) Atom
 Question 13.1: Two stable isotopes of lithium and have respective abundances of 7.5% and 92.5%. These isotopes have masses 6.01512 u and 7.01600 u, respectively. Find the atomic mass of lithium. Boron
Question 13.1: Two stable isotopes of lithium and have respective abundances of 7.5% and 92.5%. These isotopes have masses 6.01512 u and 7.01600 u, respectively. Find the atomic mass of lithium. Boron
Chapter 10 - Nuclear Physics
 The release of atomic energy has not created a new problem. It has merely made more urgent the necessity of solving an existing one. -Albert Einstein David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Ernest
The release of atomic energy has not created a new problem. It has merely made more urgent the necessity of solving an existing one. -Albert Einstein David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Ernest
Chapter 12: Chemistry of Solutions
 General Chemistry II (Chem 1412/LSC - Tomball) Chapter 12: Chemistry of Solutions I. Stoichiometry of Chemical Equations A. Mole Interpretation of an Equation B. Stoichiometry of a Chemical Reaction C.
General Chemistry II (Chem 1412/LSC - Tomball) Chapter 12: Chemistry of Solutions I. Stoichiometry of Chemical Equations A. Mole Interpretation of an Equation B. Stoichiometry of a Chemical Reaction C.
Compound Nucleus Reactions
 Compound Nucleus Reactions E CM a Q CN Direct CN decays Time. Energy. Two-step reaction. CN forgets how it was formed. Decay of CN depends on statistical factors that are functions of E x, J. Low energy
Compound Nucleus Reactions E CM a Q CN Direct CN decays Time. Energy. Two-step reaction. CN forgets how it was formed. Decay of CN depends on statistical factors that are functions of E x, J. Low energy
Simulation of Cross Section for the Production of Copper-67
 e-issn:3-459 p-issn:347-36 Simulation of Cross Section for the Production of Copper-67 dusei G *, Andam AB, Banini GK, Fletcher JJ and Tandoh J Graduate School of Nuclear and Allied Sciences, University
e-issn:3-459 p-issn:347-36 Simulation of Cross Section for the Production of Copper-67 dusei G *, Andam AB, Banini GK, Fletcher JJ and Tandoh J Graduate School of Nuclear and Allied Sciences, University
CHARGED PARTICLE INTERACTIONS
 CHARGED PARTICLE INTERACTIONS Background Charged Particles Heavy charged particles Charged particles with Mass > m e α, proton, deuteron, heavy ion (e.g., C +, Fe + ), fission fragment, muon, etc. α is
CHARGED PARTICLE INTERACTIONS Background Charged Particles Heavy charged particles Charged particles with Mass > m e α, proton, deuteron, heavy ion (e.g., C +, Fe + ), fission fragment, muon, etc. α is
SOURCES of RADIOACTIVITY
 Section 9: SOURCES of RADIOACTIVITY This section briefly describes various sources of radioactive nuclei, both naturally occurring and those produced artificially (man-made) in, for example, reactors or
Section 9: SOURCES of RADIOACTIVITY This section briefly describes various sources of radioactive nuclei, both naturally occurring and those produced artificially (man-made) in, for example, reactors or
Physics 3204 UNIT 3 Test Matter Energy Interface
 Physics 3204 UNIT 3 Test Matter Energy Interface 2005 2006 Time: 60 minutes Total Value: 33 Marks Formulae and Constants v = f λ E = hf h f = E k + W 0 E = m c 2 p = h λ 1 A= A T 0 2 t 1 2 E k = ½ mv 2
Physics 3204 UNIT 3 Test Matter Energy Interface 2005 2006 Time: 60 minutes Total Value: 33 Marks Formulae and Constants v = f λ E = hf h f = E k + W 0 E = m c 2 p = h λ 1 A= A T 0 2 t 1 2 E k = ½ mv 2
Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ MeV, 4 T 8 MeV
 Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = 10-25 MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ 250-350 MeV, 4 T 8 MeV γ-ray spectrum intermediate energy region 10 MeV/A E beam 100 MeV/A - large variety of emitted particles
Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = 10-25 MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ 250-350 MeV, 4 T 8 MeV γ-ray spectrum intermediate energy region 10 MeV/A E beam 100 MeV/A - large variety of emitted particles
two-proton radioactivity discovery of two-proton radioactivity experimental results with TPC s future studies
 two-proton radioactivity discovery of two-proton radioactivity experimental results with TPC s future studies Bertram Blank CEN Bordeaux-Gradignan EPS European Nuclear Physics Conference 2009 Spring meeting
two-proton radioactivity discovery of two-proton radioactivity experimental results with TPC s future studies Bertram Blank CEN Bordeaux-Gradignan EPS European Nuclear Physics Conference 2009 Spring meeting
Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter
 Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter 1 Content of the chapter Introduction Interaction processes Interaction cross sections Moderation and neutrons path For more details see «Physique des Réacteurs
Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter 1 Content of the chapter Introduction Interaction processes Interaction cross sections Moderation and neutrons path For more details see «Physique des Réacteurs
(a) (i) State the proton number and the nucleon number of X.
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Nuclei of 218 84Po decay by the emission of an particle to form a stable isotope of an element X. You may assume that no emission accompanies the decay. (a) (i) State the
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Nuclei of 218 84Po decay by the emission of an particle to form a stable isotope of an element X. You may assume that no emission accompanies the decay. (a) (i) State the
Nuclear Chemistry. The Nucleus. Isotopes. Slide 1 / 43. Slide 2 / 43. Slide 3 / 43
 Slide 1 / 43 Nuclear Chemistry The Nucleus Slide 2 / 43 Remember that the nucleus is comprised of the two nucleons, protons and neutrons. The number of protons is the atomic number. The number of protons
Slide 1 / 43 Nuclear Chemistry The Nucleus Slide 2 / 43 Remember that the nucleus is comprised of the two nucleons, protons and neutrons. The number of protons is the atomic number. The number of protons
Improved nuclear data for material damage applications in LWR spectra
 Improved nuclear data for material damage applications in LWR spectra Focus on uncertainties, 59 Ni, and stainless steel Petter Helgesson,2 Henrik Sjöstrand Arjan J. Koning 3, Dimitri Rochman 4 Stephan
Improved nuclear data for material damage applications in LWR spectra Focus on uncertainties, 59 Ni, and stainless steel Petter Helgesson,2 Henrik Sjöstrand Arjan J. Koning 3, Dimitri Rochman 4 Stephan
2. Balance the following reaction. How many electrons would be transferred?
 JASPERSE CHEM 210 Ch. 19 Electrochemistry PRACTICE TEST 4 VERSION 3 Ch. 20 Nuclear Chemistry 1 Formulas: E cell =E reduction + E oxidation G = nfe cell (for kj, use F = 96.5) E cell = E [0.0592/n]log Q
JASPERSE CHEM 210 Ch. 19 Electrochemistry PRACTICE TEST 4 VERSION 3 Ch. 20 Nuclear Chemistry 1 Formulas: E cell =E reduction + E oxidation G = nfe cell (for kj, use F = 96.5) E cell = E [0.0592/n]log Q
Reconstruction of Neutron Cross-sections and Sampling
 Reconstruction of Neutron Cross-sections and Sampling Harphool Kumawat Nuclear Physics Division, BARC 1 Outline Introduction Reconstruction of resonance cross-section Linearization of cross-section Unionization
Reconstruction of Neutron Cross-sections and Sampling Harphool Kumawat Nuclear Physics Division, BARC 1 Outline Introduction Reconstruction of resonance cross-section Linearization of cross-section Unionization
FOUNDATIONS OF NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
 FOUNDATIONS OF NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY Michele Laino January 8, 2016 Abstract In this brief tutorial, some of basics of nuclear chemistry are shown. Such tutorial it is mainly focused on binding energy of nuclei
FOUNDATIONS OF NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY Michele Laino January 8, 2016 Abstract In this brief tutorial, some of basics of nuclear chemistry are shown. Such tutorial it is mainly focused on binding energy of nuclei
Nuclear Physics. PHY232 Remco Zegers Room W109 cyclotron building.
 Nuclear Physics PHY232 Remco Zegers zegers@nscl.msu.edu Room W109 cyclotron building http://www.nscl.msu.edu/~zegers/phy232.html Periodic table of elements We saw that the periodic table of elements can
Nuclear Physics PHY232 Remco Zegers zegers@nscl.msu.edu Room W109 cyclotron building http://www.nscl.msu.edu/~zegers/phy232.html Periodic table of elements We saw that the periodic table of elements can
Subatomic Particles. proton. neutron. electron. positron. particle. 1 H or 1 p. 4 α or 4 He. 0 e or 0 β
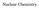 Nuclear Chemistry Subatomic Particles proton neutron 1n 0 1 H or 1 p 1 1 positron electron 0 e or 0 β +1 +1 0 e or 0 β 1 1 particle 4 α or 4 He 2 2 Nuclear Reactions A balanced nuclear equation has the
Nuclear Chemistry Subatomic Particles proton neutron 1n 0 1 H or 1 p 1 1 positron electron 0 e or 0 β +1 +1 0 e or 0 β 1 1 particle 4 α or 4 He 2 2 Nuclear Reactions A balanced nuclear equation has the
Chemistry (
 Question 2.1: (i) Calculate the number of electrons which will together weigh one gram. (ii) Calculate the mass and charge of one mole of electrons. Answer 2.1: (i) Mass of one electron = 9.10939 10 31
Question 2.1: (i) Calculate the number of electrons which will together weigh one gram. (ii) Calculate the mass and charge of one mole of electrons. Answer 2.1: (i) Mass of one electron = 9.10939 10 31
Radiation safety of the Danish Center for Proton Therapy (DCPT) Lars Hjorth Præstegaard Dept. of Medical Physics, Aarhus University Hospital
 Radiation safety of the Danish Center for Proton Therapy (DCPT) Lars Hjorth Præstegaard Dept. of Medical Physics, Aarhus University Hospital Rationale of proton therapy Dose deposition versus depth in
Radiation safety of the Danish Center for Proton Therapy (DCPT) Lars Hjorth Præstegaard Dept. of Medical Physics, Aarhus University Hospital Rationale of proton therapy Dose deposition versus depth in
UNIT 13: NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
 UNIT 13: NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY REVIEW: ISOTOPE NOTATION An isotope notation is written as Z A X, where X is the element, A is the mass number (sum of protons and neutrons), and Z is the atomic number. For
UNIT 13: NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY REVIEW: ISOTOPE NOTATION An isotope notation is written as Z A X, where X is the element, A is the mass number (sum of protons and neutrons), and Z is the atomic number. For
SIMULATION OF LASER INDUCED NUCLEAR REACTIONS
 NUCLEAR PHYSICS SIMULATION OF LASER INDUCED NUCLEAR REACTIONS K. SPOHR 1, R. CHAPMAN 1, K. LEDINGHAM 2,3, P. MCKENNA 2,3 1 The Institute of Physical Research, University of Paisley, Paisley PA1 2BE, UK
NUCLEAR PHYSICS SIMULATION OF LASER INDUCED NUCLEAR REACTIONS K. SPOHR 1, R. CHAPMAN 1, K. LEDINGHAM 2,3, P. MCKENNA 2,3 1 The Institute of Physical Research, University of Paisley, Paisley PA1 2BE, UK
Study of prompt neutron emission spectra in fast neutron induced fission of 238 U and 232 Th and 30 kev neutron induced fission on 235 U
 Study of prompt neutron emission spectra in fast neutron induced fission of 238 U and 232 Th and 30 kev neutron induced fission on 235 U S. Appannababu 1, J. Praena 2, P.F. Mastinu 1, T. Marchi 1, V.V.
Study of prompt neutron emission spectra in fast neutron induced fission of 238 U and 232 Th and 30 kev neutron induced fission on 235 U S. Appannababu 1, J. Praena 2, P.F. Mastinu 1, T. Marchi 1, V.V.
Elastic, inelastic and inclusive alpha cross sections in 6 Li+ 112 Sn system
 EPJ Web of Conferences 117, (2016) Elastic, inelastic and inclusive alpha cross sections in 6 Li+ 112 Sn system D. Chattopadhyay 1,2, S. Santra 1,2,A.Pal 1,2, A. Kundu 1, B. K. Nayak 1,2,K.Mahata 1, K.
EPJ Web of Conferences 117, (2016) Elastic, inelastic and inclusive alpha cross sections in 6 Li+ 112 Sn system D. Chattopadhyay 1,2, S. Santra 1,2,A.Pal 1,2, A. Kundu 1, B. K. Nayak 1,2,K.Mahata 1, K.
2. For the following two compounds between oxygen and hydrogen: 3. Tell what discoveries were made by each of the following scientists:
 EXTRA HOMEWORK 1A 1. When Dalton proposed that matter was composed of atoms, why was his Atomic Theory accepted? 2. For the following two compounds between oxygen and hydrogen: Mass of O Mass of H Compound
EXTRA HOMEWORK 1A 1. When Dalton proposed that matter was composed of atoms, why was his Atomic Theory accepted? 2. For the following two compounds between oxygen and hydrogen: Mass of O Mass of H Compound
RADIOACTIVITY Q32 P1 A radioactive carbon 14 decay to Nitrogen by beta emission as below 14 x 0
 NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE RADIOACTIVITY 1. 1995 Q32 P1 A radioactive carbon 14 decay to Nitrogen by beta emission as below 14 x 0 C N + e 6 7 y Determine the values of x and y in the equation (2 marks)
NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE RADIOACTIVITY 1. 1995 Q32 P1 A radioactive carbon 14 decay to Nitrogen by beta emission as below 14 x 0 C N + e 6 7 y Determine the values of x and y in the equation (2 marks)
Activation Analysis. Characteristic decay mechanisms, α, β, γ Activity A reveals the abundance N:
 2.5. Isotope analysis and neutron activation techniques The previously discussed techniques of material analysis are mainly based on the characteristic atomic structure of the elements and the associated
2.5. Isotope analysis and neutron activation techniques The previously discussed techniques of material analysis are mainly based on the characteristic atomic structure of the elements and the associated
Isotopes and Radioactive Decay
 NAME PERIOD DATE CHAPTER 4 NOTES: ISOTOPES Isotopes and Radioactive Decay ISOTOPES: Atoms that contain the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Isotopes containing more neutrons have
NAME PERIOD DATE CHAPTER 4 NOTES: ISOTOPES Isotopes and Radioactive Decay ISOTOPES: Atoms that contain the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Isotopes containing more neutrons have
 More Energetics of Alpha Decay The energy released in decay, Q, is determined by the difference in mass of the parent nucleus and the decay products, which include the daughter nucleus and the particle.
More Energetics of Alpha Decay The energy released in decay, Q, is determined by the difference in mass of the parent nucleus and the decay products, which include the daughter nucleus and the particle.
Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 3 journal of September 2015 physics pp. 379 384 Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy L S DANU, D C BISWAS, B K NAYAK and
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 3 journal of September 2015 physics pp. 379 384 Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy L S DANU, D C BISWAS, B K NAYAK and
PROGRESS OF NUCLEAR DATA MEASUREMENT IN CHINA
 PROGRESS OF NUCLEAR DATA MEASUREMENT IN CHINA (2011-2012 ) GE Zhigang RUAN Xichao China Nuclear Data Key Laboratory China Nuclear Data Center(CNDC) China Committee of Nuclear Data(CCND) China Institute
PROGRESS OF NUCLEAR DATA MEASUREMENT IN CHINA (2011-2012 ) GE Zhigang RUAN Xichao China Nuclear Data Key Laboratory China Nuclear Data Center(CNDC) China Committee of Nuclear Data(CCND) China Institute
β and γ decays, Radiation Therapies and Diagnostic, Fusion and Fission Final Exam Surveys New material Example of β-decay Beta decay Y + e # Y'+e +
 β and γ decays, Radiation Therapies and Diagnostic, Fusion and Fission Last Lecture: Radioactivity, Nuclear decay Radiation damage This lecture: nuclear physics in medicine and fusion and fission Final
β and γ decays, Radiation Therapies and Diagnostic, Fusion and Fission Last Lecture: Radioactivity, Nuclear decay Radiation damage This lecture: nuclear physics in medicine and fusion and fission Final
Basic Nuclear Theory. Lecture 1 The Atom and Nuclear Stability
 Basic Nuclear Theory Lecture 1 The Atom and Nuclear Stability Introduction Nuclear power is made possible by energy emitted from either nuclear fission or nuclear fusion. Current nuclear power plants utilize
Basic Nuclear Theory Lecture 1 The Atom and Nuclear Stability Introduction Nuclear power is made possible by energy emitted from either nuclear fission or nuclear fusion. Current nuclear power plants utilize
Neutron Interactions Part I. Rebecca M. Howell, Ph.D. Radiation Physics Y2.5321
 Neutron Interactions Part I Rebecca M. Howell, Ph.D. Radiation Physics rhowell@mdanderson.org Y2.5321 Why do we as Medical Physicists care about neutrons? Neutrons in Radiation Therapy Neutron Therapy
Neutron Interactions Part I Rebecca M. Howell, Ph.D. Radiation Physics rhowell@mdanderson.org Y2.5321 Why do we as Medical Physicists care about neutrons? Neutrons in Radiation Therapy Neutron Therapy
At low excitation, the compound nucleus de-excites by statistical emission of light particles (n,p,α)
 Does the α cluster structure in light nuclei persist through the fusion process? Justin Vadas, T.K. Steinbach, J. Schmidt, V. Singh, S. Hudan, R.T. de Souza; Indiana University L. Baby, S. Kuvin, I. Wiedenhover;
Does the α cluster structure in light nuclei persist through the fusion process? Justin Vadas, T.K. Steinbach, J. Schmidt, V. Singh, S. Hudan, R.T. de Souza; Indiana University L. Baby, S. Kuvin, I. Wiedenhover;
Experiment to validate EAF activation data: Activation on CuCrZr in NPI d-be neutron field
 Nuclear Physics Institute Řež Report NPI ASCR Řež EXP(EFDA)-03/00 Experiment to validate EAF activation data: Activation on CuCrZr in NPI d-be neutron field P. Bém, V. Burjan, M. Götz, M. Honusek, J. Hep
Nuclear Physics Institute Řež Report NPI ASCR Řež EXP(EFDA)-03/00 Experiment to validate EAF activation data: Activation on CuCrZr in NPI d-be neutron field P. Bém, V. Burjan, M. Götz, M. Honusek, J. Hep
 CHAPTER 19 THE ATOMIC NUCLEUS NUCLEAR STRUCTURE The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons. A protonis a positively charged particle having mass 1.6726 x 10(-27) kg and charge 1.6 x 10(-19) coulomb.
CHAPTER 19 THE ATOMIC NUCLEUS NUCLEAR STRUCTURE The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons. A protonis a positively charged particle having mass 1.6726 x 10(-27) kg and charge 1.6 x 10(-19) coulomb.
At the conclusion of this lesson the trainee will be able to: a) Write a typical equation for the production of each type of radiation.
 RADIOACTIVITY - SPONTANEOUS NUCLEAR PROCESSES OBJECTIVES At the conclusion of this lesson the trainee will be able to: 1. For~, p and 7 decays a) Write a typical equation for the production of each type
RADIOACTIVITY - SPONTANEOUS NUCLEAR PROCESSES OBJECTIVES At the conclusion of this lesson the trainee will be able to: 1. For~, p and 7 decays a) Write a typical equation for the production of each type
PHYSICS A2 UNIT 2 SECTION 1: RADIOACTIVITY & NUCLEAR ENERGY
 PHYSICS A2 UNIT 2 SECTION 1: RADIOACTIVITY & NUCLEAR ENERGY THE ATOMIC NUCLEUS / NUCLEAR RADIUS & DENSITY / PROPERTIES OF NUCLEAR RADIATION / INTENSITY & BACKGROUND RADIATION / EXPONENTIAL LAW OF DECAY
PHYSICS A2 UNIT 2 SECTION 1: RADIOACTIVITY & NUCLEAR ENERGY THE ATOMIC NUCLEUS / NUCLEAR RADIUS & DENSITY / PROPERTIES OF NUCLEAR RADIATION / INTENSITY & BACKGROUND RADIATION / EXPONENTIAL LAW OF DECAY
Benchmark Tests of Gamma-Ray Production Data in JENDL-3 for Some Important Nuclides
 Journal of NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECFINOLOGY, 27[9], pp. 844~852 (September 1990). TECHNICAL REPORT Benchmark Tests of Gamma-Ray Production Data in JENDL-3 for Some Important Nuclides CAI Shao-huit, Akira
Journal of NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECFINOLOGY, 27[9], pp. 844~852 (September 1990). TECHNICAL REPORT Benchmark Tests of Gamma-Ray Production Data in JENDL-3 for Some Important Nuclides CAI Shao-huit, Akira
Chapter 21. Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten
 , The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 21 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006, Prentice Hall, Inc. The
, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 21 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006, Prentice Hall, Inc. The
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Describe briefly one scattering experiment to investigate the size of the nucleus of the atom. Include a description of the properties of the incident radiation which makes
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Describe briefly one scattering experiment to investigate the size of the nucleus of the atom. Include a description of the properties of the incident radiation which makes
Integral Benchmark Experiments of the Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (JENDL)-3.3 for the Fusion Reactor Design
 1 Integral Benchmark Experiments of the Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (JENDL)-3.3 for the Fusion Reactor Design T. Nishitani 1), K. Ochiai 1), F. Maekawa 1), K. Shibata 1), M. Wada 2), I. Murata
1 Integral Benchmark Experiments of the Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (JENDL)-3.3 for the Fusion Reactor Design T. Nishitani 1), K. Ochiai 1), F. Maekawa 1), K. Shibata 1), M. Wada 2), I. Murata
The surrogate-reaction method: status and perspectives. Beatriz Jurado, CENBG, France
 The surrogate-reaction method: status and perspectives Beatriz Jurado, CENBG, France 1" Nuclear data for waste incineration and innovative fuel cycles Minor actinides incineration Th/U cycle Neutron-induced
The surrogate-reaction method: status and perspectives Beatriz Jurado, CENBG, France 1" Nuclear data for waste incineration and innovative fuel cycles Minor actinides incineration Th/U cycle Neutron-induced
Radioactivity is the emission of high energy released when the of atoms change. Radioactivity can be or.
 Chapter 19 1 RADIOACTIVITY Radioactivity is the emission of high energy released when the of atoms change. Radioactivity can be or. TYPES OF RADIATION OR EMITTED ENERGY IN NUCLEAR CHANGES Radiation is
Chapter 19 1 RADIOACTIVITY Radioactivity is the emission of high energy released when the of atoms change. Radioactivity can be or. TYPES OF RADIATION OR EMITTED ENERGY IN NUCLEAR CHANGES Radiation is
A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions
 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 39, no. 1, March, 2009 55 A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions S. Mohammadi Physics Department, Payame Noor University, Mashad 91735, IRAN (Received
Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 39, no. 1, March, 2009 55 A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions S. Mohammadi Physics Department, Payame Noor University, Mashad 91735, IRAN (Received
Accreting neutron stars provide a unique environment for nuclear reactions
 , Tracy Steinbach, Jon Schmidt, Varinderjit Singh, Sylvie Hudan, Romualdo de Souza, Lagy Baby, Sean Kuvin, Ingo Wiedenhover Accreting neutron stars provide a unique environment for nuclear reactions High
, Tracy Steinbach, Jon Schmidt, Varinderjit Singh, Sylvie Hudan, Romualdo de Souza, Lagy Baby, Sean Kuvin, Ingo Wiedenhover Accreting neutron stars provide a unique environment for nuclear reactions High
Nuclear Chemistry Notes
 Nuclear Chemistry Notes Definitions Nucleons: Subatomic particles in the nucleus : protons and neutrons Radionuclides: Radioactive nuclei. Unstable nuclei that spontaneously emit particles and electromagnetic
Nuclear Chemistry Notes Definitions Nucleons: Subatomic particles in the nucleus : protons and neutrons Radionuclides: Radioactive nuclei. Unstable nuclei that spontaneously emit particles and electromagnetic
Selected Topics in Physics a lecture course for 1st year students by W.B. von Schlippe Spring Semester 2007
 Selected Topics in Physics a lecture course for 1st year students by W.B. von Schlippe Spring Semester 2007 Lecture 11 1.) Determination of parameters of the SEMF 2.) α decay 3.) Nuclear energy levels
Selected Topics in Physics a lecture course for 1st year students by W.B. von Schlippe Spring Semester 2007 Lecture 11 1.) Determination of parameters of the SEMF 2.) α decay 3.) Nuclear energy levels
Alpha-Energies of different sources with Multi Channel Analyzer
 Physical Structure of Matter Radioactivity Alpha-Energies of different sources with Multi Channel Analyzer What you can learn about Decay series Radioactive equilibrium Isotopic properties Decay energy
Physical Structure of Matter Radioactivity Alpha-Energies of different sources with Multi Channel Analyzer What you can learn about Decay series Radioactive equilibrium Isotopic properties Decay energy
5 Atomic Physics. 1 of the isotope remains. 1 minute, 4. Atomic Physics. 1. Radioactivity 2. The nuclear atom
 5 Atomic Physics 1. Radioactivity 2. The nuclear atom 1. In a fission reactor, which particle causes a Uranium-235 nucleus to split? A. alpha-particle B. gamma ray C. neutron D. proton 2. A radioactive
5 Atomic Physics 1. Radioactivity 2. The nuclear atom 1. In a fission reactor, which particle causes a Uranium-235 nucleus to split? A. alpha-particle B. gamma ray C. neutron D. proton 2. A radioactive
Fission-yield data. Karl-Heinz Schmidt
 Fission-yield data Karl-Heinz Schmidt Topical day From nuclear data to a reliable estimate of spent fuel decay heat October 26, 2017 SCK CEN Lakehouse, Mol, Belgium Lay out Introduction Stages of the fission
Fission-yield data Karl-Heinz Schmidt Topical day From nuclear data to a reliable estimate of spent fuel decay heat October 26, 2017 SCK CEN Lakehouse, Mol, Belgium Lay out Introduction Stages of the fission
2 Give the compound nucleus resulting from 6-MeV protons bombarding a target of. my notes in the part 3 reading room or on the WEB.
 Lecture 15 Krane Enge Cohen Williams Reaction theories compound nucleus 11.10 13.7 13.1-3 direct reactions 11.11 13.11/12 ch 14 Admixed Wave functions residual interaction 5.1-4 Admixed Wave functions
Lecture 15 Krane Enge Cohen Williams Reaction theories compound nucleus 11.10 13.7 13.1-3 direct reactions 11.11 13.11/12 ch 14 Admixed Wave functions residual interaction 5.1-4 Admixed Wave functions
Neutron interactions and dosimetry. Eirik Malinen Einar Waldeland
 Neutron interactions and dosimetry Eirik Malinen Einar Waldeland Topics 1. Neutron interactions 1. Scattering 2. Absorption 2. Neutron dosimetry 3. Applications The neutron Uncharged particle, mass close
Neutron interactions and dosimetry Eirik Malinen Einar Waldeland Topics 1. Neutron interactions 1. Scattering 2. Absorption 2. Neutron dosimetry 3. Applications The neutron Uncharged particle, mass close
Unit 2 Exam - Atomic Structure and Nuclear
 1. The atomic number of an atom is always equal to the total number of. neutrons in the nucleus. protons in the nucleus 5. The mass number of an atom is equal to the number of. neutrons, only. protons,
1. The atomic number of an atom is always equal to the total number of. neutrons in the nucleus. protons in the nucleus 5. The mass number of an atom is equal to the number of. neutrons, only. protons,
SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Modern Physics SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models 1. Light of a single frequency falls on a photoelectric material but no electrons are emitted. Electrons may
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Modern Physics SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models 1. Light of a single frequency falls on a photoelectric material but no electrons are emitted. Electrons may
Properties of the nucleus. 9.1 Nuclear Physics. Isotopes. Stable Nuclei. Size of the nucleus. Size of the nucleus
 Properties of the nucleus 9. Nuclear Physics Properties of nuclei Binding Energy Radioactive decay Natural radioactivity Consists of protons and neutrons Z = no. of protons (tomic number) N = no. of neutrons
Properties of the nucleus 9. Nuclear Physics Properties of nuclei Binding Energy Radioactive decay Natural radioactivity Consists of protons and neutrons Z = no. of protons (tomic number) N = no. of neutrons
The LIONS experimental programme
 The LIONS experimental programme and its relevance for nuclear science and applications, or How can NFS help fusion? Alexander V. Prokofiev 1,*, Diego Tarrío 1, Marc O. Fregeau 2, Xavier Ledoux 2, and
The LIONS experimental programme and its relevance for nuclear science and applications, or How can NFS help fusion? Alexander V. Prokofiev 1,*, Diego Tarrío 1, Marc O. Fregeau 2, Xavier Ledoux 2, and
Nuclear Reactions A Z. Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q > 0. Exothermic Endothermic
 Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reactions A Z 4 P D+ He + Q A 4 Z 2 Q > 0 Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q = ( m + m m m ) c 2 x X Y y Q > 0 Q < 0 Exothermic Endothermic 2
Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reactions A Z 4 P D+ He + Q A 4 Z 2 Q > 0 Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q = ( m + m m m ) c 2 x X Y y Q > 0 Q < 0 Exothermic Endothermic 2
APEX CARE INSTITUTE FOR PG - TRB, SLET AND NET IN PHYSICS
 Page 1 1. Within the nucleus, the charge distribution A) Is constant, but falls to zero sharply at the nuclear radius B) Increases linearly from the centre, but falls off exponentially at the surface C)
Page 1 1. Within the nucleus, the charge distribution A) Is constant, but falls to zero sharply at the nuclear radius B) Increases linearly from the centre, but falls off exponentially at the surface C)
PHL424: Nuclear fusion
 PHL424: Nuclear fusion Hot Fusion 5 10 15 5 10 8 projectiles on target compound nuclei 1 atom Hot fusion (1961 1974) successful up to element 106 (Seaborgium) Coulomb barrier V C between projectile and
PHL424: Nuclear fusion Hot Fusion 5 10 15 5 10 8 projectiles on target compound nuclei 1 atom Hot fusion (1961 1974) successful up to element 106 (Seaborgium) Coulomb barrier V C between projectile and
Chapter 3-1. proton positive nucleus 1 amu neutron zero nucleus 1 amu electron negative on energy levels around the nucleus very small
 Chapter 3-1 Sub-atomic Charge Location Mass Particle proton positive nucleus 1 amu neutron zero nucleus 1 amu electron negative on energy levels around the nucleus very small The most mass of the atom
Chapter 3-1 Sub-atomic Charge Location Mass Particle proton positive nucleus 1 amu neutron zero nucleus 1 amu electron negative on energy levels around the nucleus very small The most mass of the atom
= : K A
 Atoms and Nuclei. State two limitations of JJ Thomson s model of atom. 2. Write the SI unit for activity of a radioactive substance. 3. What observations led JJ Thomson to conclusion that all atoms have
Atoms and Nuclei. State two limitations of JJ Thomson s model of atom. 2. Write the SI unit for activity of a radioactive substance. 3. What observations led JJ Thomson to conclusion that all atoms have
Chapter 12: Chemistry of Solutions
 CHEM 1412 LECTURE OUTLINE - Smr II 2017 - Ch 12-20 General Chemistry II (Chem 1412/LSC - Tomball) Chapter 12: Chemistry of Solutions I. Types of Solutions A. Definition of Solutions B. Components of A
CHEM 1412 LECTURE OUTLINE - Smr II 2017 - Ch 12-20 General Chemistry II (Chem 1412/LSC - Tomball) Chapter 12: Chemistry of Solutions I. Types of Solutions A. Definition of Solutions B. Components of A
A new method to acquire nuclear fission data using heavy ion reactions a way to understand the fission phenomenon
 press release date Friday 26 August 15:00 (material distribution) Education, Culture, Sports, Science Press conf., Nuclear Regulatory Agency Press conf., Ibaraki Pref.. Government press conf., Osaka Science
press release date Friday 26 August 15:00 (material distribution) Education, Culture, Sports, Science Press conf., Nuclear Regulatory Agency Press conf., Ibaraki Pref.. Government press conf., Osaka Science
CONCEPT MAP ATOMS. Atoms. 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model. 6. Hydrogen spectrum
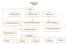 CONCEPT MAP ATOMS Atoms 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model 4.Emission line spectra 2a. Alpha scattering experiment 3a. Bohr s postulates 6. Hydrogen spectrum 8. De Broglie s explanation 5.Absorption
CONCEPT MAP ATOMS Atoms 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model 4.Emission line spectra 2a. Alpha scattering experiment 3a. Bohr s postulates 6. Hydrogen spectrum 8. De Broglie s explanation 5.Absorption
Microscopic cross sections : an utopia? S. Hilaire 1, A.J. Koning 2 & S. Goriely 3.
 Microscopic cross sections : an utopia? S. Hilaire 1, A.J. Koning 2 & S. Goriely 3 www.talys.eu 1 CEA,DAM,DIF - France 2 Nuclear Research and Consultancy Group, Petten, The Netherlands 3 Institut d Astronomie
Microscopic cross sections : an utopia? S. Hilaire 1, A.J. Koning 2 & S. Goriely 3 www.talys.eu 1 CEA,DAM,DIF - France 2 Nuclear Research and Consultancy Group, Petten, The Netherlands 3 Institut d Astronomie
Properties of the nucleus. 8.2 Nuclear Physics. Isotopes. Stable Nuclei. Size of the nucleus. Size of the nucleus
 Properties of the nucleus 8. Nuclear Physics Properties of nuclei Binding Energy Radioactive decay Natural radioactivity Consists of protons and neutrons Z = no. of protons (Atomic number) N = no. of neutrons
Properties of the nucleus 8. Nuclear Physics Properties of nuclei Binding Energy Radioactive decay Natural radioactivity Consists of protons and neutrons Z = no. of protons (Atomic number) N = no. of neutrons
Downloaded from
 constant UNIT VIII- ATOMS & NUCLEI FORMULAE ANDSHORTCUT FORMULAE. Rutherford s -Particle scattering experiment (Geiger Marsden experiment) IMPOTANT OBSERVATION Scattering of -particles by heavy nuclei
constant UNIT VIII- ATOMS & NUCLEI FORMULAE ANDSHORTCUT FORMULAE. Rutherford s -Particle scattering experiment (Geiger Marsden experiment) IMPOTANT OBSERVATION Scattering of -particles by heavy nuclei
Chapter 12: Nuclear Reaction
 Chapter 12: Nuclear Reaction A nuclear reaction occurs when a nucleus is unstable or is being bombarded by a nuclear particle. The product of a nuclear reaction is a new nuclide with an emission of a nuclear
Chapter 12: Nuclear Reaction A nuclear reaction occurs when a nucleus is unstable or is being bombarded by a nuclear particle. The product of a nuclear reaction is a new nuclide with an emission of a nuclear
Units and Definition
 RADIATION SOURCES Units and Definition Activity (Radioactivity) Definition Activity: Rate of decay (transformation or disintegration) is described by its activity Activity = number of atoms that decay
RADIATION SOURCES Units and Definition Activity (Radioactivity) Definition Activity: Rate of decay (transformation or disintegration) is described by its activity Activity = number of atoms that decay
Annax-I. Investigation of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in
 Annax-I Investigation of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in 40 Ca on 68,70 Zn at and near the Coulomb barrier. Abstract We will study the multi-nucleon transfer between two medium-heavy nuclei to find
Annax-I Investigation of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in 40 Ca on 68,70 Zn at and near the Coulomb barrier. Abstract We will study the multi-nucleon transfer between two medium-heavy nuclei to find
W. Udo Schröder Departments of Chemistry & of Physics and Astronomy
 W. Udo Schröder Departments of Chemistry & of Physics and Astronomy ANSEL Faculty Instructors ACS NuSci Acad Infrastructure 2 Prof. Frank Wolfs Prof. Udo Schrőder Research: Large Underground Xenon (LUX)
W. Udo Schröder Departments of Chemistry & of Physics and Astronomy ANSEL Faculty Instructors ACS NuSci Acad Infrastructure 2 Prof. Frank Wolfs Prof. Udo Schrőder Research: Large Underground Xenon (LUX)
Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity
 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity Structure and Properties of the Nucleus Nucleus is made of protons and neutrons Proton has positive charge: Neutron is electrically neutral: Neutrons and protons are collectively
Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity Structure and Properties of the Nucleus Nucleus is made of protons and neutrons Proton has positive charge: Neutron is electrically neutral: Neutrons and protons are collectively
FUSION NEUTRONICS EXPERIMENTS AT FNG: ACHIEVEMENTS IN THE PAST 10 YEARS AND FUTURE PERSPECTIVES
 FUSION NEUTRONICS EXPERIMENTS AT FNG: ACHIEVEMENTS IN THE PAST 10 YEARS AND FUTURE PERSPECTIVES presented by Paola Batistoni ENEA Fusion Division Fast Neutron Physics International Workshop & IEA International
FUSION NEUTRONICS EXPERIMENTS AT FNG: ACHIEVEMENTS IN THE PAST 10 YEARS AND FUTURE PERSPECTIVES presented by Paola Batistoni ENEA Fusion Division Fast Neutron Physics International Workshop & IEA International
Chapter 21 Nuclear Chemistry
 Chapter 21 Nuclear Chemistry The Nucleus Remember that the nucleus is comprised of the two nucleons, protons and neutrons. The number of protons is the atomic number. The number of protons and neutrons
Chapter 21 Nuclear Chemistry The Nucleus Remember that the nucleus is comprised of the two nucleons, protons and neutrons. The number of protons is the atomic number. The number of protons and neutrons
Issues for Neutron Calculations for ITER Fusion Reactor
 Introduction Issues for Neutron Calculations for ITER Fusion Reactor Erik Nonbøl and Bent Lauritzen Risø DTU, National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy Roskilde, Denmark Outline 1. Fusion development
Introduction Issues for Neutron Calculations for ITER Fusion Reactor Erik Nonbøl and Bent Lauritzen Risø DTU, National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy Roskilde, Denmark Outline 1. Fusion development
