SUBJECT GUIDE Academic year INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
|
|
|
- Donald Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUBJECT GUIDE Academic year INORGANIC CHEMISTRY MODULE CONTENT YEAR TERM CREDITS TYPE Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry 1º 2º 6 Basic LECTURER(S) Postal address, telephone n o, address Antonio Navarrete Guijosa- Group A Manolo Sánchez Polo- Group B Mª Teresa Fernández Martínez- Group C Josefa M. González Pérez- Group D Ricardo Navarrete Casas- Groups E and F Inorganic Department. Third floor. Faculty of Pharmacy. Postal Code, Mails: nguijosa@ugr.es, mansanch@ugr.es, mtfernan@ugr.es, jmgp@ugr.es, rncasas@ugr.es DEGREE WITHIN WHICH THE SUBJECT IS TAUGHT Degree in Pharmacy PREREQUISITES and/or RECOMMENDATIONS (if necessary) Have completed and passed the course Basic Chemical Principles, which is also offered in the first year (first semester) degree in Pharmacy. BRIEF ACCOUNT OF THE SUBJECT PROGRAMME (ACCORDING TO THE DEGREE??) - Inorganic Chemistry. - Non-metallic elements, metal and composites. - Pharmaceutical applications of inorganic elements and compounds. GENERAL AND PARTICULAR ABILITIES A. General skills Identify, design, collect, analyze, control and produce drugs and medicines, and other products and raw materials of medical interest for human or veterinary use. Learn to apply the scientific method and acquire skills in handling legislation, sources of information, literature, protocol development and other aspects that are necessary considered for the design and critical assessment of preclinical and clinical trials. Design, implement and evaluate reagents, clinical analytical methods and techniques, knowing the basics of clinical analyzes, and the characteristics and contents of the reports of laboratory diagnosis. Develop health and hygiene analysis, especially those related to food and the environment. Develop information and communication skills, both oral and written, to deal with patients and users of the center where you are working. Promote and collaboration capabilities in multidisciplinary teams and those related to other health professionals. Página 1
2 B. Specific skills Identify, design, collect, analyze and produce active ingredients, drugs and another products and materials of sanitary interest. Select appropriate techniques and procedures in the design, implementation and evaluation of reagents, methods and analytical techniques. Perform standard laboratory procedures including the use of scientific equipment for synthesis and analysis, including appropriate instrumentation. Estimating the risks associated with the use of chemical and laboratory procedures. To know the physical and chemical characteristics of the substances used for the manufacture of medicines. To know and understand the characteristics of reactions in solution, the different states of matter and the principles of thermodynamics and its application to pharmaceutical sciences. Understanding the properties of the elements and their compounds, and their application in the pharmaceutical field. OBJECTIVES (EXPRESSED IN TERMS OF EXPECTED RESULTS OF THE TEACHING PROGRAMME) - Understand the chemical elements and their compounds with focus on chemical aspects that are important in pharmaceutical practice. - Understand the role of chemical elements and their inorganic compounds in biological systems, both in normal and altered state. - To know the important role of the transition elements and coordination compounds in fundamental metabolic processes for life. DETAILED SUBJECT SYLLABUS Unit 1. Noble Gases and Chemistry of hydrogen. Group 18 elements: molecular species; physical properties; chemical behavior (reactivity); collection methods; applications. Major compounds. Hydrogen introduction. Isotopes. Molecular hydrogen. Physical Properties. Chemical behavior. Preparation methods. Applications. Biological aspects. Major compounds. Hydrides. Unit 2. Elements of Group 17. Introduction. Isotopes. Molecular species. Physical Properties. Chemical behavior. Preparation methods. Applications. Biological aspects. Lead compounds: halides, oxides (binary oxides, oxoacids and oxosalts). Unit 3. Elements of Group 16: Oxygen Introduction. Molecular species. Physical Properties. Chemical behavior. Preparation methods. Applications. Biological aspects. Major compounds. The water and hydrogen peroxide. The water in the chemicals. Inorganic aspects of water treatment and water purification. Unit 4. Orders Group 16 elements Introduction. Molecular species. Allotropy and solid phases. Physical Properties. Chemical behavior. Preparation methods. Applications. Biological aspects. Major compounds: hydrides: general aspects. Binary oxides (carbon dioxide and sulfur trioxide); oxoacids (sulfuric acid); oxosalts and other compounds. Unit 5. Elements of Group 15: Nitrogen Página 2
3 Introduction. Physical Properties. Chemical behavior. Preparation methods. Applications. Biological aspects. Major compounds: hydrides (general, ammonia and hydrazine); binary oxides; oxoacids; oxosalts (nitrates and nitrites). Unit 6. Others group 15 elements Introduction. Molecular species. Allotropy and solid phases. Physical Properties. Chemical behavior. Preparation methods. Applications. Biological aspects. Major compounds: hydrides; halides; oxides; oxoacids (phosphoric acid); oxosalts (phosphate and polyphosphate). Unit 7. Elements of Group 14: Carbon. Introduction. Molecular species. Allotropy. Physical Properties. Chemical resistance (reactivity of molecular and atomic species). Preparation methods. Applications. Biological aspects. Major compounds: halides; binary oxides (carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide); oxoacids and oxosalts (carbonates and bicarbonates, silicates). Unit 8. Orders Group 14 elements. Introduction. Molecular species. Allotropy. Physical Properties. Chemical resistance (reactivity of molecular and atomic species). Preparation methods. Applications. Biological aspects. Major compounds: hydrides; halides; oxides (silica); oxoacids and oxosalts (silicates). Unit 9. Elements of Group 13. Introduction. Molecular species and solid phases. Boro: B12 Unit. Metallic character of the other elements. Physical Properties. Chemical behavior. Preparation methods. Applications. Biological aspects. Major compounds: hydrides (boron hydrides); halides; binary oxides and hydroxides (oxides of boron and aluminum, aluminum hydroxide); oxyacids and oxosalts (borates). Unit 10. S block elements. Introduction: Electronic configuration. Physical Properties. Chemical behavior. Preparation methods. Biological function of these elements in relation to their chemical properties. Importance of calcium in pharmaceutical preparations. Major compounds : hydrides ( ionic or saline hydrides ); halides ; oxides, peroxides, superoxides ; hydroxides ; coordination compounds and organometallic compounds. Interesting applications of these compounds. Unit 11. D block elements: First transition series Introduction: Electronic configuration. Physical Properties. Chemical behavior. Preparation methods. Applications. Role in biological systems. Major compounds: hydrides; halides (simple and metal- metal) ; oxides (binary and mixed); hydroxides, oxyhydroxides, and hydroxy salts; oxoacids and oxoanions; sulfides, interstitial phases. Coordination compounds. Unit 12. D block elements: Second and third transition series. Introduction: Electronic configuration. Physical Properties. Chemical behavior. Preparation methods. Applications. Role in biological systems. Major compounds: hydrides; halides (simple and metal-metal); oxides (binary and mixed); hydroxides, oxyhydroxides, and hydroxy salts; oxoacids and oxoanions; sulfides, interstitial phases. Coordination compounds and biological systems. Unit 13. Chemistry f block elements. Introduction. Electronic configuration. Physical Properties. Characteristic chemical behavior related to their electronic configurations. Preparation methods. Applications. Major compounds. Coordination compounds. Biohealth applications of these compounds in particular gadolinium complexes used as NMR contrast Página 3
4 PRACTICAL SYLLABUS. FIRST SESSION: - Preparation of a crystallization gel. Study of the chemical properties of the halogens: reactivity and study the variation of the oxidizing capacity. Solubility of halogens and polyiodides formation. SECOND SESSION: - Study of the chemical properties of compounds formed by metallic elements belonging to the first transition series: chromium, cobalt and copper. THIRD SESSION: - [Ni(en) 3 ]SO 4 Studio System - Synthesis of the complex. Observation of the different reaction steps - Crystallization of the compound - Recording and study of IR spectrum. FOURTH SESSION: - Determination of the sulfate nickel tris (ethylenediamine) nickel (II) cation complexometric titration by Ni (II) with the anion ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA 4 - ). FIFTH SESSION: - ANTACIDS: systemic and non-systemic. - Study of the hydroxides as antacids. - Calculate the percent of magnesium hydroxide an impure sample by back-titration with excess hydrochloric acid. READING 1. Ralph H. Petrucci, F. Geoffrey Herring, Jeffry D. Madura y Carey Bissonnette. General Chemistry: principles and modern applications. Pearson Ed., S.A., Madrid, Shriver, D. F., Atkins, P. W., Langford, C. H., Química Inorgánica (2ª Edición). Editorial Reverté, Prentice Hall. Madrid, Housecroft, C., Sharpe, A. G. Química Inorgánica (2ª Edición). Ed. Pearson, Prentice Hall, Chang, R. Química (10ª Edición). Editorial Mc Graw Hill. 5. Barrett, J., Atomic Structure and Periodicity. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Henderson, W., Main Group Chemistry. Tutorial Chemistry Texts, Vol.3, Royal Society of Chemistry, Norman, N. C. Periodicity and the s- and p-block elements, Ed. Oxford Chemistry. Primers-Series Zeneca- Oxford Science Publication, Vol.51, Valenzuela Calahorro, C., Química General e Inorgánica para estudiantes de Farmacia. Editorial Universidad de Granada, Página 4
5 RECOMMENDED INTERNET LINKS Peridic system: Orbital Viewer: Free software for visualizing atomic and molecular orbitals: Inorganic Department web site: Página 5
SUBJECT GUIDE Academic year INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 SUBJECT GUIDE Academic year 2018-2019 INORGANIC CHEMISTRY (date last update: May, 10th, 2018) (Fecha de aprobación en Consejo de Departamento: 11/05/2018) MODULE CONTENT YEAR TERM CREDITS TYPE Chemistry
SUBJECT GUIDE Academic year 2018-2019 INORGANIC CHEMISTRY (date last update: May, 10th, 2018) (Fecha de aprobación en Consejo de Departamento: 11/05/2018) MODULE CONTENT YEAR TERM CREDITS TYPE Chemistry
TITLE OF COURSE: INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS* Type: DESCRIPTION Basic training, Compulsory elective, Optional Final degree project, Practicum Duration: Annual Semester/s: 3 rd and 4 th Number of credits ECTS: 12 Language/s:
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS* Type: DESCRIPTION Basic training, Compulsory elective, Optional Final degree project, Practicum Duration: Annual Semester/s: 3 rd and 4 th Number of credits ECTS: 12 Language/s:
Physics and Physical Chemistry applied to the Pharmacy
 SUBJECT GUIDE Academic year 2015-2016 Physics and Physical Chemistry applied to the Pharmacy MODULE CONTENT YEAR TERM CREDITS TYPE Physics and Mathematics LECTURER(S) Physiscs and Physical Chemistry applied
SUBJECT GUIDE Academic year 2015-2016 Physics and Physical Chemistry applied to the Pharmacy MODULE CONTENT YEAR TERM CREDITS TYPE Physics and Mathematics LECTURER(S) Physiscs and Physical Chemistry applied
1. COURSE/SUBJECT IDENTIFICATION 2. LECTURERS OF THE COURSE/SUBJECT
 COURSE DESCRIPTION INORGANIC CHEMISTRY YEAR 1 2ND SEMESTER DEGREE: PHARMACY MODALITY: ATTENDANCE IS REQUIRED ACADEMIC YEAR 2016/2017 FACULTY OF PHARMACY 1.- COURSE/SUBJECT: 1. COURSE/SUBJECT IDENTIFICATION
COURSE DESCRIPTION INORGANIC CHEMISTRY YEAR 1 2ND SEMESTER DEGREE: PHARMACY MODALITY: ATTENDANCE IS REQUIRED ACADEMIC YEAR 2016/2017 FACULTY OF PHARMACY 1.- COURSE/SUBJECT: 1. COURSE/SUBJECT IDENTIFICATION
Combined Science Chemistry Academic Overview
 Combined Science Chemistry Academic Overview 2018-2019 Science Term 1.1 Term 1.2 Term 2.1 Term 2.2 Term 3.1 Term 3.2 Year 9 States of Matter Methods of Separating and Purifying Substances Atomic Structure
Combined Science Chemistry Academic Overview 2018-2019 Science Term 1.1 Term 1.2 Term 2.1 Term 2.2 Term 3.1 Term 3.2 Year 9 States of Matter Methods of Separating and Purifying Substances Atomic Structure
EIT Review S2007 Dr. J.A. Mack.
 EIT Review S2007 Dr. J.A. Mack www.csus.edu/indiv/m/mackj/ Part 1 Atom: The smallest divisible unit of an element Compound: A substance made of two or more atoms Ion: A charged atom or molecule Cation:
EIT Review S2007 Dr. J.A. Mack www.csus.edu/indiv/m/mackj/ Part 1 Atom: The smallest divisible unit of an element Compound: A substance made of two or more atoms Ion: A charged atom or molecule Cation:
The University of Jordan
 The University of Jordan Faculty: Pharmacy Department: Pharmaceutical Sciences Program: Pharmacy and PharmD Academic Year/ Semester: 014-015 second semester Pharmaceutical Analytical Chemistry (10101)
The University of Jordan Faculty: Pharmacy Department: Pharmaceutical Sciences Program: Pharmacy and PharmD Academic Year/ Semester: 014-015 second semester Pharmaceutical Analytical Chemistry (10101)
Course Specification
 National Commission for Academic Accreditation & Assessment Course Specification Institution: King Khalid University College/Department: Faculty of Science Chemistry Department A Course Identification
National Commission for Academic Accreditation & Assessment Course Specification Institution: King Khalid University College/Department: Faculty of Science Chemistry Department A Course Identification
Study (s) Degree Center Acad. Period Grado de Química FACULTY OF CHEMISTRY 2 Second term
 COURSE DATA Data Subject Code 34199 Name Inorganic chemistry II Cycle Grade ECTS Credits 4.5 Academic year 2015-2016 Study (s) Degree Center Acad. Period year 1108 - Grado de Química FACULTY OF CHEMISTRY
COURSE DATA Data Subject Code 34199 Name Inorganic chemistry II Cycle Grade ECTS Credits 4.5 Academic year 2015-2016 Study (s) Degree Center Acad. Period year 1108 - Grado de Química FACULTY OF CHEMISTRY
Quality Assurance Unit Course Specification Assiut University
 Quality Assurance Unit Course Specification Assiut University Department of Faculty of Pharmacy Pharmaceutical analytical chemistry 2 Programme(s) on which the course is given: B. Sc. Clinical Pharmacy
Quality Assurance Unit Course Specification Assiut University Department of Faculty of Pharmacy Pharmaceutical analytical chemistry 2 Programme(s) on which the course is given: B. Sc. Clinical Pharmacy
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS AND THEIR CHARACTERISTIC PROPERTIES
 Seminar_2 1. Chemical compounds and their characteristic properties. 2. Types of chemical bonds (theses). 3. Basic types of complex compounds (theses). 4. Stability of complex compounds. TEST 2_ Chemical
Seminar_2 1. Chemical compounds and their characteristic properties. 2. Types of chemical bonds (theses). 3. Basic types of complex compounds (theses). 4. Stability of complex compounds. TEST 2_ Chemical
Nomenclature Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet #1
 Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet #1 In forming ionic compounds with non-metals, the transition metals often exhibit more than one valence. For example, in the reaction between iron and chlorine, two products
Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet #1 In forming ionic compounds with non-metals, the transition metals often exhibit more than one valence. For example, in the reaction between iron and chlorine, two products
Unit 6 Problem Set Which pair of formulas represents the empirical formula and the molecular formula of a compound?
 Unit 6 Problem Set - 2015 Name: ate: 1. Which pair of formulas represents the empirical formula and the molecular formula of a compound? 1.. H 2 O, 4 H 6 O 4. HO, 6 H 12 O 6. H 4, 5 H 12. H 2, 3 H 6 2.
Unit 6 Problem Set - 2015 Name: ate: 1. Which pair of formulas represents the empirical formula and the molecular formula of a compound? 1.. H 2 O, 4 H 6 O 4. HO, 6 H 12 O 6. H 4, 5 H 12. H 2, 3 H 6 2.
High School Chemistry - Problem Drill 08: Naming Chemical Compounds
 High School Chemistry - Problem Drill 08: Naming Chemical Compounds No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is correct for FeO? (A) Iron monoxide (B) Iron oxide (C) Iron (II) oxide (D) Iron (III) oxide (E)
High School Chemistry - Problem Drill 08: Naming Chemical Compounds No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is correct for FeO? (A) Iron monoxide (B) Iron oxide (C) Iron (II) oxide (D) Iron (III) oxide (E)
Show your work for all questions; answer all parts of all questions. No work = no credit.
 Quiz: Ch 3 & 4 Name: Version M (32 pts) September 16, 2005 AP Chem Period: 1 2 3 4 Show your work for all questions; answer all parts of all questions. No work = no credit. 1. (10 pts) A compound contains
Quiz: Ch 3 & 4 Name: Version M (32 pts) September 16, 2005 AP Chem Period: 1 2 3 4 Show your work for all questions; answer all parts of all questions. No work = no credit. 1. (10 pts) A compound contains
DETERMINING THE FORMULA OF AN IONIC COMPOUND FROM THE NAME
 DETERMINING THE FORMULA OF AN IONIC COMPOUND FROM THE NAME - The name of an ionic compound is made of the names of the CATION and ANION in the compound. - To get the FORMULA, you must figure out the SMALLEST
DETERMINING THE FORMULA OF AN IONIC COMPOUND FROM THE NAME - The name of an ionic compound is made of the names of the CATION and ANION in the compound. - To get the FORMULA, you must figure out the SMALLEST
(DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST)
 Final Prep Chap 8&9 (DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. After the correct formula for a reactant in an equation
Final Prep Chap 8&9 (DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. After the correct formula for a reactant in an equation
QAU - Car's Chemistry
 Coordinating unit: 330 - EPSEM - Manresa School of Engineering Teaching unit: 750 - EMIT - Department of Mining, Industrial and ICT Engineering Academic year: Degree: 2017 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN AUTOMOTIVE
Coordinating unit: 330 - EPSEM - Manresa School of Engineering Teaching unit: 750 - EMIT - Department of Mining, Industrial and ICT Engineering Academic year: Degree: 2017 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN AUTOMOTIVE
Unit 2. Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
 Unit 2. Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Upon successful completion of this unit, the students should be able to: 2.1 State and be able to apply the Law of Conservation of Mass, Law of Definite Proportions,
Unit 2. Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Upon successful completion of this unit, the students should be able to: 2.1 State and be able to apply the Law of Conservation of Mass, Law of Definite Proportions,
4) A specific isotope of an element is known to have 15 protons and 16 neutrons. Which symbol would properly represent this isotope?
 CHM1025 Exam 2 Chapter 4 & 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements about different elements are true
CHM1025 Exam 2 Chapter 4 & 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements about different elements are true
SNC2D1: Grade 10 Academic Science
 SNC2D1: Grade 10 Academic Science Chemistry Test date: Monday, March 24 Study tips: apple Read through your notes apple Make point form notes to summarize the topics apple Complete the review sheet apple
SNC2D1: Grade 10 Academic Science Chemistry Test date: Monday, March 24 Study tips: apple Read through your notes apple Make point form notes to summarize the topics apple Complete the review sheet apple
Chemistry Semester One Exam Review
 Chemistry Semester One Exam Review Name: 1. Compare physical and chemical changes in matter. 2. State the law on conservation of mass. 3. On which type of mixture(s) does the Tyndall Effect scatter light?
Chemistry Semester One Exam Review Name: 1. Compare physical and chemical changes in matter. 2. State the law on conservation of mass. 3. On which type of mixture(s) does the Tyndall Effect scatter light?
QI - Inorganic Chemistry
 Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 713 - EQ - Department of Chemical Engineering Academic year: Degree: 2017 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ENGINEERING
Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 713 - EQ - Department of Chemical Engineering Academic year: Degree: 2017 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ENGINEERING
: Pharmaceutical Analytical Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical analytical chemistry-1 1- Basic Information: Code Level Department Unit Lecture Tutorial Total : PHC-222 : First level (second year pharmacy) : Pharmaceutical Analytical Chemistry : 2 +
Pharmaceutical analytical chemistry-1 1- Basic Information: Code Level Department Unit Lecture Tutorial Total : PHC-222 : First level (second year pharmacy) : Pharmaceutical Analytical Chemistry : 2 +
Information on a Course offered by Department of Biology and Chemistry with effect from Semester A 2015 / 2016
 City University of Hong Kong Information on a Course offered by Department of Biology and Chemistry with effect from Semester A 2015 / 2016 Part I Course Title: Course Code: Course Duration: No. of Credit
City University of Hong Kong Information on a Course offered by Department of Biology and Chemistry with effect from Semester A 2015 / 2016 Part I Course Title: Course Code: Course Duration: No. of Credit
SCI-CH Chem Test II fall 2018 Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 SCI-CH Chem Test II fall 2018 Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:25FPCV 1 When a strontium atom loses its valence electrons, it has the same electron configuration as which element?
SCI-CH Chem Test II fall 2018 Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:25FPCV 1 When a strontium atom loses its valence electrons, it has the same electron configuration as which element?
TERMWISE SYLLABUS SESSION CLASS- XI SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY TERM-I
 TERMWISE SYLLABUS SESSION-2018-19 CLASS- XI SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY TERM-I July-2018 to Sept 2018 CONTENTS Unit I: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry General Introduction: Importance and scope of chemistry. Nature
TERMWISE SYLLABUS SESSION-2018-19 CLASS- XI SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY TERM-I July-2018 to Sept 2018 CONTENTS Unit I: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry General Introduction: Importance and scope of chemistry. Nature
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 4.0 - Chemical Formulae and Equations - the chemical symbols for the first 20 elements - And the charges of the ions they form - And use them to
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 4.0 - Chemical Formulae and Equations - the chemical symbols for the first 20 elements - And the charges of the ions they form - And use them to
Section 1 Chemical Names and Formulas. Lesson Starter
 Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Significance of a Chemical Formula Monatomic Ions Binary Ionic Compounds Writing the Formula of an Ionic Compound Naming Binary Ionic Compounds Naming Binary Molecular
Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Significance of a Chemical Formula Monatomic Ions Binary Ionic Compounds Writing the Formula of an Ionic Compound Naming Binary Ionic Compounds Naming Binary Molecular
elemental state. There are two different possibilities: DESCRIPTION 1. One cation (+ ion) replaces another. 2. One anion (- ion) replaces another.
 CHEMICAL TYPES HANDOUT In these reactions, a free element reacts with a compound to form another compound and release one of the elements of the original compound in the elemental state. There are two
CHEMICAL TYPES HANDOUT In these reactions, a free element reacts with a compound to form another compound and release one of the elements of the original compound in the elemental state. There are two
Equations. Chemical Reactions #1
 Equations Chemical Reactions #1 equations show the complete chemical formulas. Does not indicate ionic character equation shows all ions. Actually how the particles exist in the solution Steps for Writing
Equations Chemical Reactions #1 equations show the complete chemical formulas. Does not indicate ionic character equation shows all ions. Actually how the particles exist in the solution Steps for Writing
Chemical Names and Formulas
 Cool Chemistry Show Activity 3 Chemical Names and Formulas GOALS In this activity you will: Predict the charges of ions of some elements. Determine the formulas of ionic compounds. Write the conventional
Cool Chemistry Show Activity 3 Chemical Names and Formulas GOALS In this activity you will: Predict the charges of ions of some elements. Determine the formulas of ionic compounds. Write the conventional
INSTRUCTIONS ON EVERY AP EXAM:
 Most Common Reaction Types: 1. Acid-base neutralization (both weak & strong) 2. Nonmetal and metal oxides with water 3. Active metals with water 4. Single replacement redox 5. Double replacement precipitation
Most Common Reaction Types: 1. Acid-base neutralization (both weak & strong) 2. Nonmetal and metal oxides with water 3. Active metals with water 4. Single replacement redox 5. Double replacement precipitation
Unit 2: Physical Science Chemical Reactions
 Unit 2: Physical Science Chemical Reactions Chemistry Chemistry is the branch of science that with the identification of the substances deals of which matter is composed Matter is anything that contains
Unit 2: Physical Science Chemical Reactions Chemistry Chemistry is the branch of science that with the identification of the substances deals of which matter is composed Matter is anything that contains
General and Inorganic Chemistry Made Easy
 General and Inorganic Chemistry Made Easy J. Nentwig M. Kreuder K. Morgenstern VCH Contents How to use this book XIII Program 1 1 Introducüon. Chemistry as a natural science - chemical and physical processes
General and Inorganic Chemistry Made Easy J. Nentwig M. Kreuder K. Morgenstern VCH Contents How to use this book XIII Program 1 1 Introducüon. Chemistry as a natural science - chemical and physical processes
Naming and Formula Writing
 + Naming and Formula Writing + Chemical Formulas Shows the kind and number of atoms in the smallest piece of a substance Use subscripts to show the number of atoms per element Molecular formula- number
+ Naming and Formula Writing + Chemical Formulas Shows the kind and number of atoms in the smallest piece of a substance Use subscripts to show the number of atoms per element Molecular formula- number
NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS
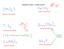 NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS iron(ii) carbonate ammonium sulfide titanium (IV) sulfide barium phosphate Spelling matters! calcium nitrate sodium phosphide DETERMINING THE FORMULA OF AN IONIC COMPOUND FROM THE
NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS iron(ii) carbonate ammonium sulfide titanium (IV) sulfide barium phosphate Spelling matters! calcium nitrate sodium phosphide DETERMINING THE FORMULA OF AN IONIC COMPOUND FROM THE
Chemical Reactions. Writing chemical reactions Types of chemical reactions Reactions in aqueous solutions. (ionic equations and solubility rules)
 Chemical Reactions Writing chemical reactions Types of chemical reactions Reactions in aqueous solutions (ionic equations and solubility rules) Writing Equations REACTANTS PRODUCTS gold (III) sulfide is
Chemical Reactions Writing chemical reactions Types of chemical reactions Reactions in aqueous solutions (ionic equations and solubility rules) Writing Equations REACTANTS PRODUCTS gold (III) sulfide is
4.4.1 Reactivity of metals Metal oxides The reactivity series. Key opportunities for skills development.
 4.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
4.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
University Studies Natural Science Course Renewal
 Chemistry 213: Principles of Chemistry II (Lecture and Lab - 4 s.h.) The purpose of this general chemistry course is to provide students with the knowledge to understand and appreciate our world/universe
Chemistry 213: Principles of Chemistry II (Lecture and Lab - 4 s.h.) The purpose of this general chemistry course is to provide students with the knowledge to understand and appreciate our world/universe
- Some MOLECULES can gain or lose electrons to form CATIONS or ANIONS. These are called POLYATOMIC IONS
 63 POLYATOMIC IONS - Some MOLECULES can gain or lose electrons to form CATIONS or ANIONS. These are called POLYATOMIC IONS - Polyatomic ions form ionic compounds in the same way that single-element ions
63 POLYATOMIC IONS - Some MOLECULES can gain or lose electrons to form CATIONS or ANIONS. These are called POLYATOMIC IONS - Polyatomic ions form ionic compounds in the same way that single-element ions
BIOO211 Biochemistry for Complementary Therapists
 BIOO211 Biochemistry for Complementary Therapists Session #1 Introduction to Chemistry Department of Bioscience www.endeavour.edu.au Introduction to Biochemistry for Complementary Therapists o Subject
BIOO211 Biochemistry for Complementary Therapists Session #1 Introduction to Chemistry Department of Bioscience www.endeavour.edu.au Introduction to Biochemistry for Complementary Therapists o Subject
Description Mole Activity. Late Lab Stamp (this stamp means you are not qualified to do lab and test corrections)
 Unit 5 Notepack: Chapters 10 Chemical Quantities NAME Unit 5 Chemical Names, and Formulas & Moles Unit Goals- As you work through this unit, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between ionic and molecular
Unit 5 Notepack: Chapters 10 Chemical Quantities NAME Unit 5 Chemical Names, and Formulas & Moles Unit Goals- As you work through this unit, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between ionic and molecular
UNIT 3 IB MATERIAL BONDING, MOLES & STOICHIOMETRY
 UNIT 3 IB MATERIAL Name: BONDING, MOLES & STOICHIOMETRY ESSENTIALS: Know, Understand, and Be Able To Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount of substance
UNIT 3 IB MATERIAL Name: BONDING, MOLES & STOICHIOMETRY ESSENTIALS: Know, Understand, and Be Able To Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount of substance
Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Ions
 Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Ions How can we classify these substances? What are their distinguishing characteristics? Can we classify them simply on the basis of appearance? 2.1 Atomic Theory How do
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Ions How can we classify these substances? What are their distinguishing characteristics? Can we classify them simply on the basis of appearance? 2.1 Atomic Theory How do
CHAPTER 7: CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS. Chemistry 1-2 Enriched Mr. Chumbley
 CHAPTER 7: CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS Chemistry 1-2 Enriched Mr. Chumbley SECTION 1: CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS While the bulk of the content will come from the Naming Chemical Compounds
CHAPTER 7: CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS Chemistry 1-2 Enriched Mr. Chumbley SECTION 1: CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS While the bulk of the content will come from the Naming Chemical Compounds
Tustin HS AP Chemistry SUMMER ASSIGNMENT
 Tustin HS AP Chemistry SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Instructor: Email: Ms. Abbey Zinsser azinsser@tustin.k12.ca.us or azinsser@mytusd.org Textbook: Chemistry: The Central Science, Brown, LeMay, Bursten, 11 th edition
Tustin HS AP Chemistry SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Instructor: Email: Ms. Abbey Zinsser azinsser@tustin.k12.ca.us or azinsser@mytusd.org Textbook: Chemistry: The Central Science, Brown, LeMay, Bursten, 11 th edition
Chapter 1. Preface (class hour: 2) Chapter 2. State of Substance (class hour: 2) Chapter 3. Atomic Structure and Period of Element (class hour: 8)
 Chapter 1. Preface (class hour: 2) [Teaching Objectives] Introduction of this course the learning process, purpose, tasks and methods. [Focus and difficulty] Introduction of this course the learning process
Chapter 1. Preface (class hour: 2) [Teaching Objectives] Introduction of this course the learning process, purpose, tasks and methods. [Focus and difficulty] Introduction of this course the learning process
Nomenclature. Formula Writing. Formula Writing 12/10/14. Rules for Writing Formulas:
 Nomenclature Formula Writing Rules for Writing Formulas: Each atom present is represented by its element symbol (Na, Mg, P, Br) The number of each type of atom is indicated by a subscript written to the
Nomenclature Formula Writing Rules for Writing Formulas: Each atom present is represented by its element symbol (Na, Mg, P, Br) The number of each type of atom is indicated by a subscript written to the
Definition 1 An element or compound is oxidized when it gains oxygen atoms
 Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
Chemistry I ETSEIB - Barcelona School of Industrial Engineering EQ - Department of Chemical Engineering
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 240 - ETSEIB - Barcelona School of Industrial Engineering 713 - EQ - Department of Chemical Engineering BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 240 - ETSEIB - Barcelona School of Industrial Engineering 713 - EQ - Department of Chemical Engineering BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN
CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS
 Name Date Class 9 CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS SECTION 9.1 NAMING IONS (pages 253 258) This section explains the use of the periodic table to determine the charge of an ion. It also defines polyatomic ion
Name Date Class 9 CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS SECTION 9.1 NAMING IONS (pages 253 258) This section explains the use of the periodic table to determine the charge of an ion. It also defines polyatomic ion
Unit 2. Chapter 4-Atoms and Elements, continued
 CHEMISTRY 110 LECTURE Unit 2 Chapter 4-Atoms and Elements, continued I Ions II ISOTOPES-Tools A. Tools 1. Atomic number, Z,, equals the number of protons 2. Mass number, A, equals the sum of protons and
CHEMISTRY 110 LECTURE Unit 2 Chapter 4-Atoms and Elements, continued I Ions II ISOTOPES-Tools A. Tools 1. Atomic number, Z,, equals the number of protons 2. Mass number, A, equals the sum of protons and
NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS. ammonium sulfide. iron(ii) carbonate. barium phosphate. titanium(iv) sulfide. Spelling matters!
 67 NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS ammonium sulfide iron(ii) carbonate titanium(iv) sulfide barium phosphate Spelling matters! barium phosphide 68 DETERMINING THE FORMULA OF AN IONIC COMPOUND FROM THE NAME - The
67 NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS ammonium sulfide iron(ii) carbonate titanium(iv) sulfide barium phosphate Spelling matters! barium phosphide 68 DETERMINING THE FORMULA OF AN IONIC COMPOUND FROM THE NAME - The
Test bank chapter (2)
 Test bank chapter (2) Choose the correct answer NOTE: A periodic table is required to work many of the problems in this chapter. 1. Which of these elements is most likely to be a good conductor of electricity?
Test bank chapter (2) Choose the correct answer NOTE: A periodic table is required to work many of the problems in this chapter. 1. Which of these elements is most likely to be a good conductor of electricity?
Unit IV: Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry
 Unit IV: Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry A. The chemical equation B. Types of chemical reactions A. Activity series of metals B. Solubility rules C. Rules for writing and balancing equations D. Calculations
Unit IV: Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry A. The chemical equation B. Types of chemical reactions A. Activity series of metals B. Solubility rules C. Rules for writing and balancing equations D. Calculations
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Atomic Theory of Matter Postulates of Dalton s Atomic Theory All matter is composed of indivisible atoms. An atom is an extremely small particle of matter that retains its identity
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Atomic Theory of Matter Postulates of Dalton s Atomic Theory All matter is composed of indivisible atoms. An atom is an extremely small particle of matter that retains its identity
FORM 4 CHEMISTRY - SUMMER REVISION WORK
 Form 3 Syllabus: FORM 4 CHEMISTRY - SUMMER REVISION WORK Chapter 1: STATES OF MATTER Converting between the 3 states of matter Application of kinetic theory to changes of state Diffusion Physical and chemical
Form 3 Syllabus: FORM 4 CHEMISTRY - SUMMER REVISION WORK Chapter 1: STATES OF MATTER Converting between the 3 states of matter Application of kinetic theory to changes of state Diffusion Physical and chemical
LOBs covered during tutorials: 7. Solve exercises related to atomic structure, electronic configurations, and periodic properties.
 Course Code Course Title ECTS Credits MED-102 General Chemistry 6 School Semester Prerequisites Medical School Fall (Semester 1) None Type of Course Field Language of Instruction Required Medicine English
Course Code Course Title ECTS Credits MED-102 General Chemistry 6 School Semester Prerequisites Medical School Fall (Semester 1) None Type of Course Field Language of Instruction Required Medicine English
Semester 1 Exam Review
 Semester 1 Exam Review 1. Compare physical and chemical changes in matter. Physical changes involve changing a substance s shape, texture, or size, not its chemical composition. Chemical changes result
Semester 1 Exam Review 1. Compare physical and chemical changes in matter. Physical changes involve changing a substance s shape, texture, or size, not its chemical composition. Chemical changes result
AP Chemistry Note Outline Chapter 4: Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry:
 AP Chemistry Note Outline Chapter 4: Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry: Water as a solvent Strong and Weak Electrolytes Solution Concentrations How to Make up a solution Types of Reactions Introduction
AP Chemistry Note Outline Chapter 4: Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry: Water as a solvent Strong and Weak Electrolytes Solution Concentrations How to Make up a solution Types of Reactions Introduction
Identify the reaction type, predict the products, and balance the equations. If it is a special decomposition or synthesis, identify which kind.
 Identify the reaction type, predict the products, and balance the equations. If it is a special decomposition or synthesis, identify which kind. 1. calcium + oxygen 2. cupric carbonate 3. aluminum + hydrochloric
Identify the reaction type, predict the products, and balance the equations. If it is a special decomposition or synthesis, identify which kind. 1. calcium + oxygen 2. cupric carbonate 3. aluminum + hydrochloric
Course specification University/Academy: Damanhour University Faculty/Institute: Faculty of Science Department: Chemistry
 Course specification University/Academy: Damanhour University Faculty/Institute: Department: Chemistry 1. Course Data: Course code: Chem. 101 Specialization: Chemistry and Physics, Biology groups Course
Course specification University/Academy: Damanhour University Faculty/Institute: Department: Chemistry 1. Course Data: Course code: Chem. 101 Specialization: Chemistry and Physics, Biology groups Course
Compounds form when elements, or electrons Ionic Compound: when one element and another element o Formed between a and a
 UNIT 5: IONIC COMPOUNDS NOTES ***Refer to Ion Charge Chart and Periodic Table for Reference Review Compounds Simple Ions All atoms want to have a full outer set of valence electrons this makes them Octet
UNIT 5: IONIC COMPOUNDS NOTES ***Refer to Ion Charge Chart and Periodic Table for Reference Review Compounds Simple Ions All atoms want to have a full outer set of valence electrons this makes them Octet
1)Ionic and Covalent compounds 2)Formulas and names 3)Mixed nomenclature 4)Calculations: a. moles-atoms-molecules, and all that
 Chem 105X Wed. Sept. 18, 2009 Today Tutors Laboratory 1)Ionic and Covalent compounds 2)Formulas and names 3)Mixed nomenclature 4)Calculations: a. moles-atoms-molecules, and all that 9/18/2009 1 Department
Chem 105X Wed. Sept. 18, 2009 Today Tutors Laboratory 1)Ionic and Covalent compounds 2)Formulas and names 3)Mixed nomenclature 4)Calculations: a. moles-atoms-molecules, and all that 9/18/2009 1 Department
Chapter 6. Chemical Reactions. Sodium reacts violently with bromine to form sodium bromide.
 Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions Sodium reacts violently with bromine to form sodium bromide. Evidence of Chemical Reactions Chemical Equations Reactants Products Reactant(s): Substance(s) present before the
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions Sodium reacts violently with bromine to form sodium bromide. Evidence of Chemical Reactions Chemical Equations Reactants Products Reactant(s): Substance(s) present before the
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonds
 Chapter 6: Chemical Bonds Section 6.1: Ionic Bonding I. Stable Electron Configurations Group # II. III. Ionic Bonds Group # A. Transfer of Electrons Group # B. Formation of Ions Group # C. Formation of
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonds Section 6.1: Ionic Bonding I. Stable Electron Configurations Group # II. III. Ionic Bonds Group # A. Transfer of Electrons Group # B. Formation of Ions Group # C. Formation of
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
 Atoms, Molecules and Ions Chapter 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Dalton s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. Elements are composed of extremely small
Atoms, Molecules and Ions Chapter 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Dalton s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. Elements are composed of extremely small
Chem 1A Dr. White Fall Handout 4
 Chem 1A Dr. White Fall 2014 1 Handout 4 4.4 Types of Chemical Reactions (Overview) A. Non-Redox Rxns B. Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) reactions 4.6. Describing Chemical Reactions in Solution A. Molecular
Chem 1A Dr. White Fall 2014 1 Handout 4 4.4 Types of Chemical Reactions (Overview) A. Non-Redox Rxns B. Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) reactions 4.6. Describing Chemical Reactions in Solution A. Molecular
How to Use This Presentation
 How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
- Use the STEM NAME of the element, then add "-ide" suffix
 65 ANIONS 2 kinds Main-group nonmetals - Use the STEM NAME of the element, then add "-ide" suffix N : "nitride" ion P : "phosphide ion" O : "oxide ion" F : "fluoride ion" Polyatomic ions - Memorize list.(see
65 ANIONS 2 kinds Main-group nonmetals - Use the STEM NAME of the element, then add "-ide" suffix N : "nitride" ion P : "phosphide ion" O : "oxide ion" F : "fluoride ion" Polyatomic ions - Memorize list.(see
ADVANCED CHEMISTRY 2
 ADVANCED CHEMISTRY 2 Philip Matthews ±m±l CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Acknowledgements How to use this book INORGANIC CHEMISTRY 88 Periodicity of physical properties 88.1 Periodicity of ionisation energies
ADVANCED CHEMISTRY 2 Philip Matthews ±m±l CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Acknowledgements How to use this book INORGANIC CHEMISTRY 88 Periodicity of physical properties 88.1 Periodicity of ionisation energies
The Thomas Hardye School Summer Preparation Task A Level Chemistry AQA 7405
 The Thomas Hardye School Summer Preparation Task A Level Chemistry AQA 7405 Purpose of task: Consolidate and develop key skills and information from GCSE that is essential and assumed knowledge for A-level
The Thomas Hardye School Summer Preparation Task A Level Chemistry AQA 7405 Purpose of task: Consolidate and develop key skills and information from GCSE that is essential and assumed knowledge for A-level
Chemistry Midterm Exam Review Sheet Spring 2012
 Chemistry Midterm Exam Review Sheet Spring 2012 1. Know your safety rules 2. A shopping mall wanted to determine whether the more expensive Tough Stuff floor wax was better than the cheaper Steel Seal
Chemistry Midterm Exam Review Sheet Spring 2012 1. Know your safety rules 2. A shopping mall wanted to determine whether the more expensive Tough Stuff floor wax was better than the cheaper Steel Seal
UNIT 8: CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND NOMENCLATURE CHEMISTRY 215, DUFFEY
 UNIT 8: CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND NOMENCLATURE CHEMISTRY 215, DUFFEY BIG IDEAS o 7.1 Ion formation - o 7.2 Ionic bonding - o 7.4 Metallic bonding - o 8.1 & 8.2 Covalent bonding - CHEMICAL BONDING o The purpose
UNIT 8: CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND NOMENCLATURE CHEMISTRY 215, DUFFEY BIG IDEAS o 7.1 Ion formation - o 7.2 Ionic bonding - o 7.4 Metallic bonding - o 8.1 & 8.2 Covalent bonding - CHEMICAL BONDING o The purpose
General Chemistry First Semester Final Exam Study Guide 60 multiple choice questions
 General Chemistry First Semester Final Exam Study Guide 60 multiple choice questions 1. Define product. 2. Define reactant. 3. Label the products and reactants in the following chemical reactions: H 2
General Chemistry First Semester Final Exam Study Guide 60 multiple choice questions 1. Define product. 2. Define reactant. 3. Label the products and reactants in the following chemical reactions: H 2
Atomic Theory and Donding
 Surrounding Name Date Atomic Theory and Donding Textbook pages 1 68-183 Summary Before You Read What do you already know about Bohr diagrams? Record your answer in the lines below. What are atoms? An atom
Surrounding Name Date Atomic Theory and Donding Textbook pages 1 68-183 Summary Before You Read What do you already know about Bohr diagrams? Record your answer in the lines below. What are atoms? An atom
Types of Reactions: Reactions
 1 Reactions On the A.P. Test there will be one question (question #4) that will say: Give the formulas to show the reactants and the products for the following chemical reactions. Each occurs in aqueous
1 Reactions On the A.P. Test there will be one question (question #4) that will say: Give the formulas to show the reactants and the products for the following chemical reactions. Each occurs in aqueous
Gilbert Kirss Foster. Chapter 4. Chemical Bonding. Understanding Climate Change
 Gilbert Kirss Foster Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding Understanding Climate Change Chapter Outline 4.1 Types of Chemical Bonds 4.2 Naming Compounds and Writing Formulas 4.3 Lewis Structures 4.4 Electronegativity,
Gilbert Kirss Foster Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding Understanding Climate Change Chapter Outline 4.1 Types of Chemical Bonds 4.2 Naming Compounds and Writing Formulas 4.3 Lewis Structures 4.4 Electronegativity,
CHAPTER 9 CHEMICAL QUANTITIES
 Chemistry Name Hour Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 9 CHEMICAL QUANTITIES Day Plans for the day Assignment(s) for the day 1 Begin Chapter
Chemistry Name Hour Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 9 CHEMICAL QUANTITIES Day Plans for the day Assignment(s) for the day 1 Begin Chapter
QUI - Chemistry
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 300 - EETAC - Castelldefels School of Telecommunications and Aerospace Engineering 745 - EAB - Department of Agri-Food Engineering
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 300 - EETAC - Castelldefels School of Telecommunications and Aerospace Engineering 745 - EAB - Department of Agri-Food Engineering
Chem 105X Fri. Sept. 17, True 2. False. Dihydrogen monoxide is toxic. Today
 Chem 105X Fri. Sept. 17, 2010 Today Written homework problem #1 Handed back #2 Due Monday in class Next week s lab 0% 0% 1) Formulas and names 2) Mixed nomenclature 3) Calculations: moles-atoms-molecules,
Chem 105X Fri. Sept. 17, 2010 Today Written homework problem #1 Handed back #2 Due Monday in class Next week s lab 0% 0% 1) Formulas and names 2) Mixed nomenclature 3) Calculations: moles-atoms-molecules,
Chemical Names and Formulas
 Cool Chemistry Show Section 3 Chemical Names and Formulas What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section you will Predict the charges of ions of some elements. Determine the formulas of ionic compounds.
Cool Chemistry Show Section 3 Chemical Names and Formulas What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section you will Predict the charges of ions of some elements. Determine the formulas of ionic compounds.
1/28/13. Naming and Writing Formulas > for Ionic Compounds
 chemistry 1 of 29 Naming and Writing Formulas A recipe is a formula for the sauce a complete list of ingredients and their proportions. Chemistry also uses formulas. Once you know the rules, you can write
chemistry 1 of 29 Naming and Writing Formulas A recipe is a formula for the sauce a complete list of ingredients and their proportions. Chemistry also uses formulas. Once you know the rules, you can write
Honors Chemistry Review for Semester One Final Exam
 Honors Chemistry Review for Semester One Final Exam Chapter 1 What is chemistry? Branches of chemistry Scientific method 1. What is chemistry? 2. Which measurement depends on gravitational force mass or
Honors Chemistry Review for Semester One Final Exam Chapter 1 What is chemistry? Branches of chemistry Scientific method 1. What is chemistry? 2. Which measurement depends on gravitational force mass or
Ions and Ionic Compounds
 Ions and Ionic Compounds Elements combine in a specific ratio to form compounds. Compounds can be categorized as ionic or covalent depending on the type of bond present within the compound. Ionic compounds
Ions and Ionic Compounds Elements combine in a specific ratio to form compounds. Compounds can be categorized as ionic or covalent depending on the type of bond present within the compound. Ionic compounds
Chemical Reactions. Chemical changes are occurring around us all the time
 Chemical changes are occurring around us all the time Food cooking Fuel being burned in a car s engine Oxygen being used in the human body The starting materials are called reactants The ending materials
Chemical changes are occurring around us all the time Food cooking Fuel being burned in a car s engine Oxygen being used in the human body The starting materials are called reactants The ending materials
September [KV 805] Sub. Code: 3805
![September [KV 805] Sub. Code: 3805 September [KV 805] Sub. Code: 3805](/thumbs/95/123019269.jpg) September 2009 [KV 805] Sub. Code: 3805 (Regulations 2008-2009) (Candidates admitted from 2008-2009 onwards) Paper V PHARMACEUTICAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY Time : Three hours Maximum : 70 marks Answer All
September 2009 [KV 805] Sub. Code: 3805 (Regulations 2008-2009) (Candidates admitted from 2008-2009 onwards) Paper V PHARMACEUTICAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY Time : Three hours Maximum : 70 marks Answer All
Column B 5. periodic table a. A vertical column of elements in the
 Unit 4 Assignment Packet Name Period: A1: The Periodic Table: Organizing the Elements A. periodic table B. metals C. nonmetals D. periods E. alkali metals F. halogens G. columns H. periodic law I. alkaline
Unit 4 Assignment Packet Name Period: A1: The Periodic Table: Organizing the Elements A. periodic table B. metals C. nonmetals D. periods E. alkali metals F. halogens G. columns H. periodic law I. alkaline
ACP Chemistry (821) - Mid-Year Review
 ACP Chemistry (821) - Mid-Year Review *Be sure you understand the concepts involved in each question. Do not simply memorize facts!* 1. What is chemistry? Chapter 1: Chemistry 2. What is the difference
ACP Chemistry (821) - Mid-Year Review *Be sure you understand the concepts involved in each question. Do not simply memorize facts!* 1. What is chemistry? Chapter 1: Chemistry 2. What is the difference
Types of Reactions: Reactions
 1 Reactions On the A.P. Test there will be one question (question #4) that will say: Give the formulas to show the reactants and the products for the following chemical reactions. Each occurs in aqueous
1 Reactions On the A.P. Test there will be one question (question #4) that will say: Give the formulas to show the reactants and the products for the following chemical reactions. Each occurs in aqueous
Spring Semester Final Exam Study Guide
 Honors Chemistry Name Period AlCl3 Cu2S NaCN HI PCl3 CrBr3 Naming and Formula Writing 1. Write the name or formula for each of the following: HClO2 (NH4)2SO4 I4O10 H3N NiN H3PO4 Mercury (II) bromide Phosphorous
Honors Chemistry Name Period AlCl3 Cu2S NaCN HI PCl3 CrBr3 Naming and Formula Writing 1. Write the name or formula for each of the following: HClO2 (NH4)2SO4 I4O10 H3N NiN H3PO4 Mercury (II) bromide Phosphorous
Properties of Compounds
 Chapter 6. Properties of Compounds Comparing properties of elements and compounds Compounds are formed when elements combine together in fixed proportions. The compound formed will often have properties
Chapter 6. Properties of Compounds Comparing properties of elements and compounds Compounds are formed when elements combine together in fixed proportions. The compound formed will often have properties
Chemical Names and Formulas
 Chemical Names and Formulas ELECTRONS AND THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS BONDING AND INTERACTIONS 91 Naming Ions For students using the Foundation edition, assign problems 4, 8 15 Essential Understanding Ions
Chemical Names and Formulas ELECTRONS AND THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS BONDING AND INTERACTIONS 91 Naming Ions For students using the Foundation edition, assign problems 4, 8 15 Essential Understanding Ions
Chemical Bonding. Chemical Bonds. Metals, Ions, or Molecules. All Matter Exists as Atoms,
 Chemical Bonding Valence electrons (the outer most electrons) are responsible for the interaction between atoms when forming chemical compounds. Another way to say that is that valence electrons are the
Chemical Bonding Valence electrons (the outer most electrons) are responsible for the interaction between atoms when forming chemical compounds. Another way to say that is that valence electrons are the
St. Thomas More High School A-LEVEL CHEMISTRY INDUCTION DAY INFORMATION and PRE-COURSE ACTIVITIES
 St. Thomas More High School A-LEVEL CHEMISTRY INDUCTION DAY INFORMATION and PRE-COURSE ACTIVITIES CHEMISTRY A-LEVEL A-level Chemistry goes into much more detail than GCSE. It attempts to answer the big
St. Thomas More High School A-LEVEL CHEMISTRY INDUCTION DAY INFORMATION and PRE-COURSE ACTIVITIES CHEMISTRY A-LEVEL A-level Chemistry goes into much more detail than GCSE. It attempts to answer the big
Chapter 5: Nomenclature
 Chem 1025 Prof George W.J. Kenney, Jr Introductory Chemistry, Zumdahl Decoste, 6th ed Last Update: 21July09 Chapter 5: Nomenclature These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text, They do NOT Replace reading the
Chem 1025 Prof George W.J. Kenney, Jr Introductory Chemistry, Zumdahl Decoste, 6th ed Last Update: 21July09 Chapter 5: Nomenclature These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text, They do NOT Replace reading the
CHEM 103 Naming Compounds
 CHEM 103 Naming Compounds Lecture Notes February 7, 2006 Prof. Sevian 1 Agenda How we name compounds depends on what kind of compounds they are Ionic compounds Molecular compounds Acids are molecular compounds
CHEM 103 Naming Compounds Lecture Notes February 7, 2006 Prof. Sevian 1 Agenda How we name compounds depends on what kind of compounds they are Ionic compounds Molecular compounds Acids are molecular compounds
5.4 Chemical changes Reactivity of metals Metal oxides The reactivity series. Key opportunities for skills development
 5.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
5.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
MODULE CONTENT YEAR TERM CREDITS TYPE. I - Fundamentals Chemistry BASIC. Postal address, telephone n o, address
 SUBJECT GUIDE Academic year 2015-2016 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY MODULE CONTENT YEAR TERM CREDITS TYPE I - Fundamentals Chemistry 1 1 6 BASIC LECTURER(S) Prof. Mónica Díaz Gavilán (MDG) Prof. Francisco Franco Montalbán
SUBJECT GUIDE Academic year 2015-2016 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY MODULE CONTENT YEAR TERM CREDITS TYPE I - Fundamentals Chemistry 1 1 6 BASIC LECTURER(S) Prof. Mónica Díaz Gavilán (MDG) Prof. Francisco Franco Montalbán
