Electron Counting. It s easier to show than to explain, I think.
|
|
|
- Damian Stanley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electron Counting This, for some reason I ve never worked out, isn t as easy as it should be. It is, however, important. It allows us to say things about the stability of organometallic complexes and make predictions about the structures of complexes and deduce what oxidation state a metal centre is in. All useful information. Effectively, electron counting is a method for determining, by visual inspection, how many electrons a given complex has in its molecular orbitals (its covalent bonding system). There are certain magic numbers (which I ll go through below) that tell you your complex is happy. There are two schools as to how to go about determining this, the ionic method and the covalent method. Both must give the same answer, so although you only really need to ever use one method, using the other is a good way to double-check your answer. It s easier to show than to explain, I think. Firstly, using both ways, you need to assess which ligands are dative and which aren t. This partly comes with experience, but if you re not confident you can work it out by looking at the ligand by itself and seeing if the binding atom conforms to the octet rule (remember that?). If it s got eight electrons in its outer shell, contributed from itself and from any other atoms bound to it, it ll act as a dative ligand; if it s got seven or fewer, it ll be negatively charged.
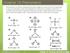
2 Then, using both methods in parallel: ionic: covalent: So, in essence, in the ionic method, you determine which bonds naturally break into ionic pairs (in this, the Pd Aryl and Pd I bonds) and which are purely dative (donation from the phosphorous lone pair). This gives you the charge on the metal centre (positive, 2+). From this, looking at your periodic table, you can determine how many outer shell electrons this metal has (eight), and add this number to the number of electrons the ligands each give (in this case, each gives two electrons). In the covalent method you treat all the bonds as covalent and determine which bonds are dative and which have electrons contributed from both the ligand and the metal. The dative ligands give 2 electrons, whilst the other ligands give one electron. You count how many electrons the metal has assuming it to be uncharged (i.e. exactly as the periodic table has it, in this case 5s 2 4d 8, ten electrons). You do also need to take account of the overall charge of the complex - if we look at Zeise s salt again, you can see how the complex itself is negatively charged as it needs to be balanced by a potassium cation.
3 You only need to count the complex itself, without the counterion. Hence, as another example: ionic: covalent: If you don t quite understand this, there s a very good page online that goes through this again, has a few more worked examples and some opportunities for you to try yourself. It also gives a very useful table which shows many of the most common ligands and how many electrons they donate in the ionic and covalent counting method. See:
4 Task 1 Provide electron-counts (using both the ionic and covalent methods) for the following complexes: [Hint - use the ligand table in the above link to help with any unfamiliar ligands] Eighteen/sixteen electron rule Right, you now know how to count electrons. This is good, though it probably seems pretty useless. It isn t. It s very important in combination with the eighteen and sixteen electron rules. These rules come from the molecular orbital analysis I briefly talked about earlier but didn t actually show. They are what is left when you boil down all the group theory stuff and get to the actually useful information. They re used to say, in essence, that a given complex is stable based on how many electrons it has in its bonding system. The (very straightforward) rules are as follows: The sixteen electron rule: if a complex has a square-planar geometry and has 16 electrons, it is stable. The eighteen electron rule: if a complex has any geometry other than a square-planar geometry and has 18 electrons, it is stable.
5 Easy. Chemistry s at its best when the maths it requires can be done with only fingers and toes. Some common inorganic complex geometries are shown in figure 3. Figure 3 - Common inorganic complex geometries - left to right: square-planar, tetrahedral, octahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, square-based pyramidal Think of the sixteen and eighteen electron rules a bit like the octet rule that you learn at GCSE, except applied to organometallic systems. They re pretty much that simple, but they re very powerful. Just one quick example of their use is in rationalising why some complexes exist in square-planar configurations (e.g. Zeise s salt) when a tetrahedral configuration would allow them to spread their ligands out more (more stable in a purely ionic compound). These rules also allow you to determine what oxidation state the metal at the centre of an organometallic complex is in. Just assume the complex to have eighteen electrons (or sixteen if it s square planar), use the ionic method to strip away the electrons contributed by the ligands, account for the overall charge, then work out how many electrons the metal has to have and how many fewer (or even more) that number is than the periodic table gives. Easy. (Disclaimer - this only works for truly covalent organometallic compounds, the maths doesn t work on some complexes like the titanium complex shown in Figure 1 Task 2 o Why might it be that the above method only works for truly covalent organometallic compounds? o Comment on the stability of all the complexes you ve electron-counted so far in this work sheet.
Organometallic Chemistry Solutions
 Organometallic Chemistry Solutions Give the denticity and hapticity of the ligands in the following complexes: Just because this complex is drawn with the iron centre bound to two distinct alkene units
Organometallic Chemistry Solutions Give the denticity and hapticity of the ligands in the following complexes: Just because this complex is drawn with the iron centre bound to two distinct alkene units
Lab Lecture on VSEPR and SPARTAN Chem 141 Lab Dr Abrash 10/3/2011
 Q: What is the purpose of this lab? Lab Lecture on VSEPR and SPARTAN Chem 141 Lab Dr Abrash 10/3/2011 To learn two methods to study and predict the shapes of molecules. One is a rule based paper method
Q: What is the purpose of this lab? Lab Lecture on VSEPR and SPARTAN Chem 141 Lab Dr Abrash 10/3/2011 To learn two methods to study and predict the shapes of molecules. One is a rule based paper method
REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS CHEMICAL BONDS: LEWIS SYMBOLS: CHEMICAL BONDING. What are valence electrons?
 REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS 13 CHEMICAL BONDING What are valence electrons? Which groups on the periodic table readily give up electrons? What group readily accepts electrons? CHEMICAL BONDS: What are chemical
REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS 13 CHEMICAL BONDING What are valence electrons? Which groups on the periodic table readily give up electrons? What group readily accepts electrons? CHEMICAL BONDS: What are chemical
Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories
 Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories Ionic Radii Ions, just like atoms, follow a periodic trend in their radii. The metal ions in a given period are smaller than the non-metal ions in the same
Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories Ionic Radii Ions, just like atoms, follow a periodic trend in their radii. The metal ions in a given period are smaller than the non-metal ions in the same
For this you need to know covalent bonds, Lewis dots, electronegativity, geometric shapes, duet & octet, single/double/triple bonds, etc...
 Lewis Structure Lab For this you need to know covalent bonds, Lewis dots, electronegativity, geometric shapes, duet & octet, single/double/triple bonds, etc... I can t assume you have had all these, so
Lewis Structure Lab For this you need to know covalent bonds, Lewis dots, electronegativity, geometric shapes, duet & octet, single/double/triple bonds, etc... I can t assume you have had all these, so
B. Electron Deficient (less than an octet) H-Be-H. Be does not need an octet Total of 4 valence electrons
 B. Electron Deficient (less than an octet) e.g. BeH 2 H-Be-H Be does not need an octet Total of 4 valence electrons Not the same as unsaturated systems that achieve the 8e - (octet) through the formation
B. Electron Deficient (less than an octet) e.g. BeH 2 H-Be-H Be does not need an octet Total of 4 valence electrons Not the same as unsaturated systems that achieve the 8e - (octet) through the formation
CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS
 CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS IONIC BONDING When an atom of a nonmetal takes one or more electrons from an atom of a metal so both atoms end up with eight valence
CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS IONIC BONDING When an atom of a nonmetal takes one or more electrons from an atom of a metal so both atoms end up with eight valence
Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules
 Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Chapters 8 and 9. Octet Rule Breakers Shapes
 Chapters 8 and 9 Octet Rule Breakers Shapes Bond Energies Bond Energy (review): The energy needed to break one mole of covalent bonds in the gas phase Breaking bonds consumes energy; forming bonds releases
Chapters 8 and 9 Octet Rule Breakers Shapes Bond Energies Bond Energy (review): The energy needed to break one mole of covalent bonds in the gas phase Breaking bonds consumes energy; forming bonds releases
The shape of simple molecules (and parts of larger molecules) can be easily predicted using the VSEPR model
 1 PREDICTING MOLECULAR SHAPE The shape of simple molecules (and parts of larger molecules) can be easily predicted using the VSEPR model VSEPR = Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model - Each BOND
1 PREDICTING MOLECULAR SHAPE The shape of simple molecules (and parts of larger molecules) can be easily predicted using the VSEPR model VSEPR = Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model - Each BOND
St Robert of Newminster Catholic School and Sixth Form College
 St Robert of Newminster Catholic School and Sixth Form College Year 12 Pre-Course Tasks: CHEMISTRY Exercise Mark Grade Atomic structure Chemical bonding Chemical equations Maths for chemists Moles Name:
St Robert of Newminster Catholic School and Sixth Form College Year 12 Pre-Course Tasks: CHEMISTRY Exercise Mark Grade Atomic structure Chemical bonding Chemical equations Maths for chemists Moles Name:
Drawing Ionic Compounds
 Drawing Molecules on Paper Structures (or Dot Structures) are one way we draw molecules on paper Since paper is 2-D and molecules aren t, it s not a perfect way to represent how molecules bond but it s
Drawing Molecules on Paper Structures (or Dot Structures) are one way we draw molecules on paper Since paper is 2-D and molecules aren t, it s not a perfect way to represent how molecules bond but it s
Honors Chemistry Unit 6 ( )
 Honors Chemistry Unit 6 (2017-2018) Lewis Dot Structures VSEPR Structures 1 We are learning to: 1. Represent compounds with Lewis structures. 2. Apply the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry
Honors Chemistry Unit 6 (2017-2018) Lewis Dot Structures VSEPR Structures 1 We are learning to: 1. Represent compounds with Lewis structures. 2. Apply the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry
Chemical Bonding. Types of Bonds. Ionic Bonding. Resonance Structures. Molecular Geometries. VSEPR Basic Shapes 3-D Notation Hybridization (Lab)
 Chemical Bonding Types of Bonds Ionic Bonding Lewis Structures Covalent Bonding Resonance Structures Octet Rule Polar Molecules Molecular Geometries VSEPR Basic Shapes 3-D Notation Hybridization (Lab)
Chemical Bonding Types of Bonds Ionic Bonding Lewis Structures Covalent Bonding Resonance Structures Octet Rule Polar Molecules Molecular Geometries VSEPR Basic Shapes 3-D Notation Hybridization (Lab)
Fill in the chart below to determine the valence electrons of elements 3-10
 Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE ETHANOL! Count valence electrons
 212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
CHM 105 & 106 MO1 UNIT THREE, LECTURE ELEVEN 1 IN OUR LAST LECTURE WE WERE LOOKING AT THE SHARING PROCESS IN CHEMICAL BONDING
 CHM 105 & 106 MO1 UNIT THREE, LECTURE ELEVEN 1 CHM 105/106 Program 28: Unit 3 Lecture 11 IN OUR LAST LECTURE WE WERE LOOKING AT THE SHARING PROCESS IN CHEMICAL BONDING AND TALKED ABOUT THE FACT THAT WE
CHM 105 & 106 MO1 UNIT THREE, LECTURE ELEVEN 1 CHM 105/106 Program 28: Unit 3 Lecture 11 IN OUR LAST LECTURE WE WERE LOOKING AT THE SHARING PROCESS IN CHEMICAL BONDING AND TALKED ABOUT THE FACT THAT WE
Notes: Covalent Compounds
 Notes: Covalent Compounds There are two ways that elements want to be like the nearest noble gas: 1) Gain or lose electrons to form an ionic compound. 2) Share electrons with other elements to form covalent
Notes: Covalent Compounds There are two ways that elements want to be like the nearest noble gas: 1) Gain or lose electrons to form an ionic compound. 2) Share electrons with other elements to form covalent
1 Electrons and Chemical Bonding
 CHAPTER 13 1 Electrons and Chemical Bonding SECTION Chemical Bonding BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is chemical bonding? What are valence
CHAPTER 13 1 Electrons and Chemical Bonding SECTION Chemical Bonding BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is chemical bonding? What are valence
Chemistry Day 30. Tuesday, November 13 th Wednesday, November 14 th, 2018
 Chemistry Day 30 Tuesday, November 13 th Wednesday, November 14 th, 2018 Do-Now: Covalent Bonding CN B 1. Write down today s FLT 2. How can you tell if atoms will form an ionic or a covalent bond? 3. What
Chemistry Day 30 Tuesday, November 13 th Wednesday, November 14 th, 2018 Do-Now: Covalent Bonding CN B 1. Write down today s FLT 2. How can you tell if atoms will form an ionic or a covalent bond? 3. What
Experiment 15. The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory of Directed Valency: An exercise
 Experiment 15 The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory of Directed Valency: An exercise Attempts to understand and predict the shapes of molecules using either the valencebond theory or
Experiment 15 The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory of Directed Valency: An exercise Attempts to understand and predict the shapes of molecules using either the valencebond theory or
CHEMICAL BONDING. Valence Electrons. Chapter Ten
 CHEMICAL BONDING Chapter Ten Valence Electrons! The electrons occupying the outermost energy level of an atom are called the valence electrons; all other electrons are called the core electrons.! The valence
CHEMICAL BONDING Chapter Ten Valence Electrons! The electrons occupying the outermost energy level of an atom are called the valence electrons; all other electrons are called the core electrons.! The valence
Outline for Today. Monday, Nov. 12. Wednesday Friday. Chapter 8: Chemical Bonding. Bond Enthalpies. Chapter 9: Theories of Bonding
 Outline for Today Monday, Nov. 12 Chapter 8: Chemical Bonding Bond Enthalpies Chapter 9: Theories of Bonding VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Theory Valence Bond Orbital ybridization Molecular
Outline for Today Monday, Nov. 12 Chapter 8: Chemical Bonding Bond Enthalpies Chapter 9: Theories of Bonding VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Theory Valence Bond Orbital ybridization Molecular
Unit 3 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Unit 3 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemical bond - A mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together 6-1 Introduction
Unit 3 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemical bond - A mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together 6-1 Introduction
Chemistry lesson 3. Study guide - Questions
 Chemistry lesson 3 Study guide - Questions This lesson builds on the understanding of the atom and electrons into the concepts of the octet rule, Lewis dot structures and chemical bonding. This is where
Chemistry lesson 3 Study guide - Questions This lesson builds on the understanding of the atom and electrons into the concepts of the octet rule, Lewis dot structures and chemical bonding. This is where
Covalent bonding does not involve electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged particles.
 SCH3U7 - Topic 4: Bonding Review SL Which of these bonding types would not be classified as strong? Metallic Covalent Ionic Dipole dipole The bond dissociation energy of NaCl is 411 kj mol -1, while that
SCH3U7 - Topic 4: Bonding Review SL Which of these bonding types would not be classified as strong? Metallic Covalent Ionic Dipole dipole The bond dissociation energy of NaCl is 411 kj mol -1, while that
The dative covalent bond acts like an ordinary covalent bond when thinking about shape so in NH 4. the shape is tetrahedral
 1.3 Bonding Definition Ionic bonding is the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions formed by electron transfer. Metal atoms lose electrons to form ve ions. Non-metal atoms gain
1.3 Bonding Definition Ionic bonding is the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions formed by electron transfer. Metal atoms lose electrons to form ve ions. Non-metal atoms gain
General and Inorganic Chemistry I.
 General and Inorganic Chemistry I. Lecture 1 István Szalai Eötvös University István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 1 / 29 Outline István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 2 / 29 Lewis Formulas
General and Inorganic Chemistry I. Lecture 1 István Szalai Eötvös University István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 1 / 29 Outline István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 2 / 29 Lewis Formulas
Molecular Orbitals. Chapter 9. Sigma bonding orbitals. Sigma bonding orbitals. Pi bonding orbitals. Sigma and pi bonds
 Molecular Orbitals Chapter 9 Orbitals and Covalent Bond The overlap of atomic orbitals from separate atoms makes molecular orbitals Each molecular orbital has room for two electrons Two types of MO Sigma
Molecular Orbitals Chapter 9 Orbitals and Covalent Bond The overlap of atomic orbitals from separate atoms makes molecular orbitals Each molecular orbital has room for two electrons Two types of MO Sigma
Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 10/11/12 October, Series & Polygonal Numbers
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L G Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Introduction Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 0//2 October, 207 Series & Polygonal Numbers Mathematicians are
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L G Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Introduction Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 0//2 October, 207 Series & Polygonal Numbers Mathematicians are
Chapter 10. Valence Electrons. Lewis dot symbols. Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding Valence Electrons Recall: the outer electrons in an atom are valence electrons. Valence electrons are related to stability Valence electrons can be represented with dots in
Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding Valence Electrons Recall: the outer electrons in an atom are valence electrons. Valence electrons are related to stability Valence electrons can be represented with dots in
CHM Simple Lewis Structures (r14) Charles Taylor 1/5
 CHM 110 - Simple Lewis Structures (r14) - 2014 Charles Taylor 1/5 Introduction In the previous note pack, you learned some about Lewis dot structures, which represent chemical compounds by showing how
CHM 110 - Simple Lewis Structures (r14) - 2014 Charles Taylor 1/5 Introduction In the previous note pack, you learned some about Lewis dot structures, which represent chemical compounds by showing how
Explain below in one sentence each (a) how we deal with overall charges on the complex in the two methods and (b) how this can be rationalized.
 An 18 Electron Guideline Worksheet Use what you learned in the primmer and the hints below to count electrons by both the losed Shell (S) and Neutral Ligand (NL) Methods. 1. First let s figure out how
An 18 Electron Guideline Worksheet Use what you learned in the primmer and the hints below to count electrons by both the losed Shell (S) and Neutral Ligand (NL) Methods. 1. First let s figure out how
Chemistry 4/2 Seite 1 von 5. You know what atoms are composed of... 3
 Chemistry 4/2 Seite 1 von 5 chemistry 2 nd Kanti study sheet for the test on the 5/10/2011 author: version: publish date: Linus Metzler 1.0b 5/9/2011 CHEMISTRY 4/2 TABLE OF CONTENTS You know what atoms
Chemistry 4/2 Seite 1 von 5 chemistry 2 nd Kanti study sheet for the test on the 5/10/2011 author: version: publish date: Linus Metzler 1.0b 5/9/2011 CHEMISTRY 4/2 TABLE OF CONTENTS You know what atoms
3. Bonding Ionic Bonding
 3. Bonding Ionic Bonding Metal atoms lose electrons to form +ve ions. on-metal atoms gain electrons to form -ve ions. Mg goes from 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 to Mg 2+ 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 goes from 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4 to
3. Bonding Ionic Bonding Metal atoms lose electrons to form +ve ions. on-metal atoms gain electrons to form -ve ions. Mg goes from 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 to Mg 2+ 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 goes from 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4 to
Structures, Shapes and Polarity. of Molecules. Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity
 Structures, Shapes and Polarity Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity of Molecules Do now: Brainstorm what you know/remember about these L2 concepts
Structures, Shapes and Polarity Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity of Molecules Do now: Brainstorm what you know/remember about these L2 concepts
Unit 1, Lesson 07: Introduction to Covalent Bonding and the Octet Rule
 Unit 1, Lesson 07: Introduction to Covalent Bonding and the Octet Rule non-metals (except Noble gases) have high electronegativity and high ionization energy. They have a strong pull on new electrons if
Unit 1, Lesson 07: Introduction to Covalent Bonding and the Octet Rule non-metals (except Noble gases) have high electronegativity and high ionization energy. They have a strong pull on new electrons if
What is a Bond? Chapter 8. Ionic Bonding. Coulomb's Law. What about covalent compounds?
 Chapter 8 What is a Bond? A force that holds atoms together. Why? We will look at it in terms of energy. Bond energy- the energy required to break a bond. Why are compounds formed? Because it gives the
Chapter 8 What is a Bond? A force that holds atoms together. Why? We will look at it in terms of energy. Bond energy- the energy required to break a bond. Why are compounds formed? Because it gives the
Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory. Lewis Theory: An Overview
 Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory Dr. Chris Kozak Memorial University of ewfoundland, Canada Lewis Theory: An verview Valence e - play a fundamental role in chemical bonding. e - transfer leads
Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory Dr. Chris Kozak Memorial University of ewfoundland, Canada Lewis Theory: An verview Valence e - play a fundamental role in chemical bonding. e - transfer leads
Covalent Bonding. Chapter 8. Diatomic elements. Covalent bonding. Molecular compounds. 1 and 7
 hapter 8 ovalent bonding ovalent Bonding A metal and a nonmetal transfer An ionic bond Two metals just mix and don t react An alloy What do two nonmetals do? Neither one will give away an electron So they
hapter 8 ovalent bonding ovalent Bonding A metal and a nonmetal transfer An ionic bond Two metals just mix and don t react An alloy What do two nonmetals do? Neither one will give away an electron So they
Chapter 6. The Chemical Bond
 Chapter 6 The Chemical Bond Some questions Why do noble gases rarely bond to other elements? How does this relate to why the atoms of other elements do form bonds? Why do certain elements combine to form
Chapter 6 The Chemical Bond Some questions Why do noble gases rarely bond to other elements? How does this relate to why the atoms of other elements do form bonds? Why do certain elements combine to form
CHEMICAL BONDING COVALENT BONDS IONIC BONDS METALLIC BONDS
 CHEMICAL BONDING COVALENT BONDS IONIC BONDS METALLIC BONDS Metallic Bonds How atoms are held together in solid metals. Metals hold onto their valence electrons very weakly. Think of them as positive ions
CHEMICAL BONDING COVALENT BONDS IONIC BONDS METALLIC BONDS Metallic Bonds How atoms are held together in solid metals. Metals hold onto their valence electrons very weakly. Think of them as positive ions
CHAPTER 3 CHEMICAL BONDING NUR FATHIN SUHANA BT AYOB SMK SULTAN ISMAIL, JB
 CHAPTER 3 CHEMICAL BONDING NUR FATHIN SUHANA BT AYOB SMK SULTAN ISMAIL, JB LEARNING OUTCOMES (ionic bonding) 1. Describe ionic (electrovalent) bonding such as NaCl and MgCl 2 LEARNING OUTCOMES (metallic
CHAPTER 3 CHEMICAL BONDING NUR FATHIN SUHANA BT AYOB SMK SULTAN ISMAIL, JB LEARNING OUTCOMES (ionic bonding) 1. Describe ionic (electrovalent) bonding such as NaCl and MgCl 2 LEARNING OUTCOMES (metallic
CHOPPED-UP CHAPTER. not too chopped up, but enough
 CHOPPED-UP CHAPTER not too chopped up, but enough chapter 12 chemical bonding what do you know? 1.When representing a water molecule as H-O-H, what do the lines between the letters symbolize? 2.Why is
CHOPPED-UP CHAPTER not too chopped up, but enough chapter 12 chemical bonding what do you know? 1.When representing a water molecule as H-O-H, what do the lines between the letters symbolize? 2.Why is
Math101, Sections 2 and 3, Spring 2008 Review Sheet for Exam #2:
 Math101, Sections 2 and 3, Spring 2008 Review Sheet for Exam #2: 03 17 08 3 All about lines 3.1 The Rectangular Coordinate System Know how to plot points in the rectangular coordinate system. Know the
Math101, Sections 2 and 3, Spring 2008 Review Sheet for Exam #2: 03 17 08 3 All about lines 3.1 The Rectangular Coordinate System Know how to plot points in the rectangular coordinate system. Know the
THE BRIDGING COURSE TO SIXTH FORM CHEMISTRY Birchwood High School
 THE BRIDGING COURSE TO SIXTH FORM CHEMISTRY Birchwood High School Mrs Ryan Chemistry Please also access the website below which is a link to a really good PPT that will help to bridge the gap between GCSE
THE BRIDGING COURSE TO SIXTH FORM CHEMISTRY Birchwood High School Mrs Ryan Chemistry Please also access the website below which is a link to a really good PPT that will help to bridge the gap between GCSE
Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes; VSEPR, Valence Bond and Molecular Orbital Theories
 C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 1 0 P a g e 1 Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes; VSEPR, Valence Bond and Molecular Orbital Theories Homework: Read Chapter 10: Work out sample/practice
C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 1 0 P a g e 1 Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes; VSEPR, Valence Bond and Molecular Orbital Theories Homework: Read Chapter 10: Work out sample/practice
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
THE BRIDGING COURSE TO SIXTH FORM CHEMISTRY AT Myton School
 THE BRIDGING COURSE TO SIXTH FORM CHEMISTRY AT Myton School Introduction Before you start the AS Chemistry course in September you should have completed this new bridging course for Chemists. It has been
THE BRIDGING COURSE TO SIXTH FORM CHEMISTRY AT Myton School Introduction Before you start the AS Chemistry course in September you should have completed this new bridging course for Chemists. It has been
Chemical bonding & structure
 Chemical bonding & structure Ionic bonding and structure Covalent bonding Covalent structures Intermolecular forces Metallic bonding Ms. Thompson - SL Chemistry Wooster High School Topic 4.3 Covalent structures
Chemical bonding & structure Ionic bonding and structure Covalent bonding Covalent structures Intermolecular forces Metallic bonding Ms. Thompson - SL Chemistry Wooster High School Topic 4.3 Covalent structures
VSEPR. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
 VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Vocabulary: domain = any electron pair or bond (single, double or triple) is considered one domain. bonding pair = shared pair = any electron pair that
VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Vocabulary: domain = any electron pair or bond (single, double or triple) is considered one domain. bonding pair = shared pair = any electron pair that
8.3 Bonding Theories > Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding. 8.3 Bonding Theories. 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding
 Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding 8.3 Bonding Theories 8.4 Polar Bonds and Molecules 1 Molecular Shape What information does a structural formula give
Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding 8.3 Bonding Theories 8.4 Polar Bonds and Molecules 1 Molecular Shape What information does a structural formula give
A. Lewis Dots and Valence electrons: Uses to represent
 Unit 5: Chemical bonding, names and formulas Ch. 7 & 8 7.1 Ions and Ionic Compounds I. Define Ion NAME Period: A. Lewis Dots and Valence electrons: Uses to represent B. Rule: Every atom wants a valence
Unit 5: Chemical bonding, names and formulas Ch. 7 & 8 7.1 Ions and Ionic Compounds I. Define Ion NAME Period: A. Lewis Dots and Valence electrons: Uses to represent B. Rule: Every atom wants a valence
Cannot be determined from this information. A. Incorrect. The electronegativity difference isn t great enough to be an ionic bond.
 AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 14: Chemical Bonding Theories No. 1 of 10 1. What type of bond is H O? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Ionic Non-polar Covalent Polar Covalent Metallic Cannot be determined from this information.
AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 14: Chemical Bonding Theories No. 1 of 10 1. What type of bond is H O? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Ionic Non-polar Covalent Polar Covalent Metallic Cannot be determined from this information.
Chemical Bonding. There are 3 ways atoms come together to form larger, more complex structures. That is to say, there are 3 bond types:
 Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding There are 3 ways atoms come together to form larger, more complex structures. That is to say, there are 3 bond types: Ionic Covalent Metallic But why would atoms even
Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding There are 3 ways atoms come together to form larger, more complex structures. That is to say, there are 3 bond types: Ionic Covalent Metallic But why would atoms even
CHEMICAL BONDING. Chemical Bonds. Ionic Bonding. Lewis Symbols
 CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
10: Modeling Molecular Structure CH141L November 24, 2015
 10: Modeling Molecular Structure CH141L November 24, 2015 This week, we ll use ball and stick models to explore molecular structure. At the end of the lab period, hand in the completed packet of Molecular
10: Modeling Molecular Structure CH141L November 24, 2015 This week, we ll use ball and stick models to explore molecular structure. At the end of the lab period, hand in the completed packet of Molecular
Chapter 13: Phenomena
 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY
 Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES (covalent bonding) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of covalent molecules (octet rule such as NH 3, CCl 4, H 2 O, CO 2, N 2 O 4, and exception to
Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES (covalent bonding) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of covalent molecules (octet rule such as NH 3, CCl 4, H 2 O, CO 2, N 2 O 4, and exception to
Lesson 6-1: Relations and Functions
 I ll bet you think numbers are pretty boring, don t you? I ll bet you think numbers have no life. For instance, numbers don t have relationships do they? And if you had no relationships, life would be
I ll bet you think numbers are pretty boring, don t you? I ll bet you think numbers have no life. For instance, numbers don t have relationships do they? And if you had no relationships, life would be
2 Ionic Bonds. What is ionic bonding? What happens to atoms that gain or lose electrons? What kinds of solids are formed from ionic bonds?
 CHAPTER 8 2 Ionic Bonds SECTION Chemical Bonding BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is ionic bonding? What happens to atoms that gain or lose
CHAPTER 8 2 Ionic Bonds SECTION Chemical Bonding BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is ionic bonding? What happens to atoms that gain or lose
A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE ETHANOL! Count valence electrons
 212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
Section 12: Lewis Structures
 Section 12: Lewis Structures The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 12.01 Electronegativity Chemistry (5)(C) 12.02 Electron
Section 12: Lewis Structures The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 12.01 Electronegativity Chemistry (5)(C) 12.02 Electron
Definition: An Ionic bond is the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions formed by electron transfer.
 3 Bonding Definition An Ionic bond is the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions formed by electron transfer. Metal atoms lose electrons to form +ve ions. on-metal atoms gain
3 Bonding Definition An Ionic bond is the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions formed by electron transfer. Metal atoms lose electrons to form +ve ions. on-metal atoms gain
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Geometry James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs, but do not denote shape. However, we use Lewis Structures to
Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Geometry James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs, but do not denote shape. However, we use Lewis Structures to
Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Now explore the Compare Two Structures link. Try changing the display to explore different combinations.
 Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Exploring The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model. Go to the Purdue University website to explore VSEPR theory. http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/vsepr/structur2.html
Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Exploring The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model. Go to the Purdue University website to explore VSEPR theory. http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/vsepr/structur2.html
Chemistry for Biology Students, Student Learning Guide
 Name: Period: Date: Chemistry for Biology Students, Student Learning Guide Getting to the website Go to www.sciencemusicvideos.com; Click on the AP Biology tab; Click on Module 3. Basic Chemistry Start
Name: Period: Date: Chemistry for Biology Students, Student Learning Guide Getting to the website Go to www.sciencemusicvideos.com; Click on the AP Biology tab; Click on Module 3. Basic Chemistry Start
Lewis Structure. Lewis Structures & VSEPR. Octet & Duet Rules. Steps for drawing Lewis Structures
 Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
 CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
Chapter Molecules are 3D. Shapes and Bonds. Chapter 9 1. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure 1 Shape 9.1 Molecules are 3D Angle Linear 180 Planar triangular (trigonal planar) 120 Tetrahedral 109.5 2 Shapes and Bonds Imagine a molecule where the
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure 1 Shape 9.1 Molecules are 3D Angle Linear 180 Planar triangular (trigonal planar) 120 Tetrahedral 109.5 2 Shapes and Bonds Imagine a molecule where the
Molecular shapes. Balls and sticks
 Molecular shapes Balls and sticks Learning objectives Apply VSEPR to predict electronic geometry and shapes of simple molecules Determine molecule shape from electronic geometry Distinguish between polar
Molecular shapes Balls and sticks Learning objectives Apply VSEPR to predict electronic geometry and shapes of simple molecules Determine molecule shape from electronic geometry Distinguish between polar
MI 4 Mathematical Induction Name. Mathematical Induction
 Mathematical Induction It turns out that the most efficient solution to the Towers of Hanoi problem with n disks takes n 1 moves. If this isn t the formula you determined, make sure to check your data
Mathematical Induction It turns out that the most efficient solution to the Towers of Hanoi problem with n disks takes n 1 moves. If this isn t the formula you determined, make sure to check your data
Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory
 Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory Introduction 1. Lewis Structures and Formal Charge LG.N. Lewis, at the University of California at Berkeley devised a simple way to understand the nature
Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory Introduction 1. Lewis Structures and Formal Charge LG.N. Lewis, at the University of California at Berkeley devised a simple way to understand the nature
Ex. 1) F F bond in F = 0 < % covalent, no transfer of electrons
 #60 Notes Unit 8: Bonding Ch. Bonding I. Bond Character Bonds are usually combinations of ionic and covalent character. The electronegativity difference is used to determine a bond s character. Electronegativity
#60 Notes Unit 8: Bonding Ch. Bonding I. Bond Character Bonds are usually combinations of ionic and covalent character. The electronegativity difference is used to determine a bond s character. Electronegativity
Chapter 7. Ionic & Covalent Bonds
 Chapter 7 Ionic & Covalent Bonds Ionic Compounds Covalent Compounds 7.1 EN difference and bond character >1.7 = ionic 0.4 1.7 = polar covalent 1.7 Electrons not shared at
Chapter 7 Ionic & Covalent Bonds Ionic Compounds Covalent Compounds 7.1 EN difference and bond character >1.7 = ionic 0.4 1.7 = polar covalent 1.7 Electrons not shared at
Hypothesis testing I. - In particular, we are talking about statistical hypotheses. [get everyone s finger length!] n =
![Hypothesis testing I. - In particular, we are talking about statistical hypotheses. [get everyone s finger length!] n = Hypothesis testing I. - In particular, we are talking about statistical hypotheses. [get everyone s finger length!] n =](/thumbs/86/94764601.jpg) Hypothesis testing I I. What is hypothesis testing? [Note we re temporarily bouncing around in the book a lot! Things will settle down again in a week or so] - Exactly what it says. We develop a hypothesis,
Hypothesis testing I I. What is hypothesis testing? [Note we re temporarily bouncing around in the book a lot! Things will settle down again in a week or so] - Exactly what it says. We develop a hypothesis,
Alex s Guide to Word Problems and Linear Equations Following Glencoe Algebra 1
 Alex s Guide to Word Problems and Linear Equations Following Glencoe Algebra 1 What is a linear equation? It sounds fancy, but linear equation means the same thing as a line. In other words, it s an equation
Alex s Guide to Word Problems and Linear Equations Following Glencoe Algebra 1 What is a linear equation? It sounds fancy, but linear equation means the same thing as a line. In other words, it s an equation
Ch 6 Chemical Bonding
 Ch 6 Chemical Bonding What you should learn in this section (objectives): Define chemical bond Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds Describe ionic and covalent bonding Explain why most chemical bonding
Ch 6 Chemical Bonding What you should learn in this section (objectives): Define chemical bond Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds Describe ionic and covalent bonding Explain why most chemical bonding
5 Polyatomic molecules
 s manual for Burrows et.al. Chemistry 3 Third edition 5 Polyatomic molecules Answers to worked examples WE 5.1 Formal charges in N 2 (on p. 221 in Chemistry 3 ) Use formal charges to decide whether oxygen
s manual for Burrows et.al. Chemistry 3 Third edition 5 Polyatomic molecules Answers to worked examples WE 5.1 Formal charges in N 2 (on p. 221 in Chemistry 3 ) Use formal charges to decide whether oxygen
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, Valence Bond Theory, and Molecular Orbital Theory
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, Valence Bond Theory, and Molecular Orbital Theory Predicting Molecular Geometry 1. Draw the Lewis structure. 2. Determine the number
Lecture Presentation Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, Valence Bond Theory, and Molecular Orbital Theory Predicting Molecular Geometry 1. Draw the Lewis structure. 2. Determine the number
Regression, part II. I. What does it all mean? A) Notice that so far all we ve done is math.
 Regression, part II I. What does it all mean? A) Notice that so far all we ve done is math. 1) One can calculate the Least Squares Regression Line for anything, regardless of any assumptions. 2) But, if
Regression, part II I. What does it all mean? A) Notice that so far all we ve done is math. 1) One can calculate the Least Squares Regression Line for anything, regardless of any assumptions. 2) But, if
Molecular Structure and Bonding. Assis.Prof.Dr.Mohammed Hassan Lecture 2
 Molecular Structure and Bonding Assis.Prof.Dr.Mohammed Hassan Lecture 2 Lewis structures: Lewis Theory The octet rule All elements except hydrogen ( hydrogen have a duet of electrons) have octet of electrons
Molecular Structure and Bonding Assis.Prof.Dr.Mohammed Hassan Lecture 2 Lewis structures: Lewis Theory The octet rule All elements except hydrogen ( hydrogen have a duet of electrons) have octet of electrons
Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond
 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the and electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together. Ionic Bond o that results from the attraction between large
Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the and electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together. Ionic Bond o that results from the attraction between large
Chapter 12. Molecular Structure
 Chapter 12 Molecular Structure Chapter Map Models Advantages and Disadvantages (1) They help us to visualize, explain, and predict chemical changes. Because a model is a simplified version of what we think
Chapter 12 Molecular Structure Chapter Map Models Advantages and Disadvantages (1) They help us to visualize, explain, and predict chemical changes. Because a model is a simplified version of what we think
Lecture 10: Powers of Matrices, Difference Equations
 Lecture 10: Powers of Matrices, Difference Equations Difference Equations A difference equation, also sometimes called a recurrence equation is an equation that defines a sequence recursively, i.e. each
Lecture 10: Powers of Matrices, Difference Equations Difference Equations A difference equation, also sometimes called a recurrence equation is an equation that defines a sequence recursively, i.e. each
CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions
 CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions 1D 1 has a triple bond. 2 has a double bond. 3 and 4 have single bonds. The stronger the bond, the shorter the length. 2A A 1:1 ratio means there must be the
CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions 1D 1 has a triple bond. 2 has a double bond. 3 and 4 have single bonds. The stronger the bond, the shorter the length. 2A A 1:1 ratio means there must be the
Elements combine to form compounds chemical bonds. Chemical Bonding
 Elements combine to form compounds chemical bonds Chemical Bonding Review Valence electrons Using periodic table to determine them. General bonding rules: If an atom has 1 to 3 valence electrons, it will
Elements combine to form compounds chemical bonds Chemical Bonding Review Valence electrons Using periodic table to determine them. General bonding rules: If an atom has 1 to 3 valence electrons, it will
Do now: Brainstorm how you would draw the Lewis diagram for: H 2 O CO 2
 Do now: Brainstorm how you would draw the Lewis diagram for: 2 O CO 2 Shapes of molecules C 4 N 3 2 O C 2 O CO 2 Shapes of molecules Shapes of molecules are determined by the number of bonding and non-bonding
Do now: Brainstorm how you would draw the Lewis diagram for: 2 O CO 2 Shapes of molecules C 4 N 3 2 O C 2 O CO 2 Shapes of molecules Shapes of molecules are determined by the number of bonding and non-bonding
base 2 4 The EXPONENT tells you how many times to write the base as a factor. Evaluate the following expressions in standard notation.
 EXPONENTIALS Exponential is a number written with an exponent. The rules for exponents make computing with very large or very small numbers easier. Students will come across exponentials in geometric sequences
EXPONENTIALS Exponential is a number written with an exponent. The rules for exponents make computing with very large or very small numbers easier. Students will come across exponentials in geometric sequences
The Chemistry of Life Chapter 2. Prof. J. Dodd
 The Chemistry of Life Chapter 2 Prof. J. Dodd Why should we study chemistry in C, H, O, N Atoms are composed of 3 main particles: (subatomic particles) Protons (+) Neutrons Electrons (-) Protons and Neutrons
The Chemistry of Life Chapter 2 Prof. J. Dodd Why should we study chemistry in C, H, O, N Atoms are composed of 3 main particles: (subatomic particles) Protons (+) Neutrons Electrons (-) Protons and Neutrons
8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook. September 10, 2015
 chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook Chapter 8: Bonding: General Concepts Mar 13 11:15 AM 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. Bonds are forces that hold groups of
chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook Chapter 8: Bonding: General Concepts Mar 13 11:15 AM 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. Bonds are forces that hold groups of
Chemistry for Biology Students, Student Learning Guide
 Name: Period: Date: Chemistry for Biology Students, Student Learning Guide Getting to the website Go to www.sciencemusicvideos.com Click on the AP Biology tab Click on Module 3. Basic Chemistry Start with
Name: Period: Date: Chemistry for Biology Students, Student Learning Guide Getting to the website Go to www.sciencemusicvideos.com Click on the AP Biology tab Click on Module 3. Basic Chemistry Start with
Unit Six --- Ionic and Covalent Bonds
 Unit Six --- Ionic and Covalent Bonds Electron Configuration in Ionic Bonding Ionic Bonds Bonding in Metals Valence Electrons Electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element s atoms Examples
Unit Six --- Ionic and Covalent Bonds Electron Configuration in Ionic Bonding Ionic Bonds Bonding in Metals Valence Electrons Electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element s atoms Examples
Molecular Models: The shape of simple molecules and ions
 Molecular Models: The shape of simple molecules and ions Background The shape of a molecule is very important when investigating its properties and reactivity. For example, compare CO 2 and SO 2. Carbon
Molecular Models: The shape of simple molecules and ions Background The shape of a molecule is very important when investigating its properties and reactivity. For example, compare CO 2 and SO 2. Carbon
General Chemistry 1 CHM201 Unit 4 Practice Test. 4. What is the orbital designation for an electron with the quantum numbers n 4, 3?
 General Chemistry 1 CHM201 Unit 4 Practice Test 1. An orbital s orientation in space is determined by a. the quantum number. d. the n quantum number. b. the m l quantum number. e. both the and m l quantum
General Chemistry 1 CHM201 Unit 4 Practice Test 1. An orbital s orientation in space is determined by a. the quantum number. d. the n quantum number. b. the m l quantum number. e. both the and m l quantum
Lecture 3A 09/30/11. How many of you have read the sections assigned for the first two days of class?
 Lecture 3A 09/30/11 How many of you have read the sections assigned for the first two days of class? We re going to start with a classical version of bonding, and we re going to use the hydrogen molecule
Lecture 3A 09/30/11 How many of you have read the sections assigned for the first two days of class? We re going to start with a classical version of bonding, and we re going to use the hydrogen molecule
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories. Molecular Shapes. Molecular Shapes. Chapter 9 Part 2 November 16 th, 2004
 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Part 2 November 16 th, 2004 8 Molecular Shapes When considering the geometry about the central atom, we consider all electrons (lone pairs and bonding
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Part 2 November 16 th, 2004 8 Molecular Shapes When considering the geometry about the central atom, we consider all electrons (lone pairs and bonding
Non-covalent bonding
 on-covalent bonding Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Topic Booklet Pre U Chemistry Cambridge International Examinations on-covalent bonding-chemical forces Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 44 minutes Score:
on-covalent bonding Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Topic Booklet Pre U Chemistry Cambridge International Examinations on-covalent bonding-chemical forces Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 44 minutes Score:
Chapter 12. Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chapter 12 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell (highest energy level) of an atom. A chemical bond is a mutual
Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chapter 12 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell (highest energy level) of an atom. A chemical bond is a mutual
Covalent bonding occurs in nonmetal compounds. Use the highlighter to select the compounds that are covalently bonded. HCl
 Covalent bonding occurs in nonmetal compounds. Use the highlighter to select the compounds that are covalently bonded. 2 C 2 Cl Li NaF Mg C 4 N NaCl 3 Drag this to the target to reveal the answers. Properties
Covalent bonding occurs in nonmetal compounds. Use the highlighter to select the compounds that are covalently bonded. 2 C 2 Cl Li NaF Mg C 4 N NaCl 3 Drag this to the target to reveal the answers. Properties
