Chemical bonding & structure
|
|
|
- Maud Davis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chemical bonding & structure Ionic bonding and structure Covalent bonding Covalent structures Intermolecular forces Metallic bonding Ms. Thompson - SL Chemistry Wooster High School
2 Topic 4.3 Covalent structures Lewis (electron dot) structures show all the valence electrons in a covalently bonded species. The octet rule refers to the tendency of atoms to gain a valence shell with a total of 8 electrons. Some atoms, like Be and B, might form stable compounds with incomplete octets of electrons. Resonance structures occur when there is more than one possible position for a double bond in a molecule. Shapes of species are determined by the repulsion of electron pairs according to VSEPR theory. Carbon and silicon form giant covalent/network covalent structures.
3 Nature of science Scientist use models as representations of the real world the development of the model of molecular shape (VSEPR) and to to explain observable properties.
4 Lewis (electron dot) structures Based on the formation of the covalent bond and the molecule Each pair of electrons can be represented in a number of different ways - by two dots, two crosses (or a combination of a dot and a cross), or by a line.
5 Lewis (electron dot) structures In the previous representations it is important to distinguish between: Bonding pairs of electrons (showing the covalent bond as single, double, or triple bonds) Non-bonding pairs of electrons, often call lone pairs, which are pairs of electrons not involved in the bonding Help us understand the different types of covalent bond (single, double, or triple bonds) and the existence of lone pairs in molecules. Tell us nothing about the actual shapes of molecules May be drawn with a geometrical arrangement that differs completely from its real shape in space. So we rely on the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR) to deduce the shape of molecules and predicting molecular geometries.
6 Lewis structures of cations and anions and ionic compounds Can be written for neutral molecules as well as cations and anions Notice that within the cations and anions there can be covalent bonds but the bonding between the cation and anion is ionic. covalent bonds in the cation covalent bonds in the anion Ionic bonds between the cation and anion So the compound overall is ionic
7 Lewis Dot Structure Oxygen, O2 Group 16 and has six valence electrons Needs to acquire two more electrons for a full octet and to attain noble gas configuration. If two oxygen atoms share two electrons with each other, each oxygen atom gains two more electrons to attain a complete octet of electrons, which results in the formation of a covalent bond between the two oxygen atoms. A double, covalent bond is formed and the shared pair of electrons can be represented by two lines O O O O O O O O Oxygen has 4 non-bonding pair of electrons (lone pairs) and two pair that bonds
8 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory Every molecule has a particular shape therefore, we need to have the ability to think in three-dimensional. Lewis structures are two-dimensional representations and tell us nothing about the shape. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR) can be used to deduce the shapes of covalent molecules. Since electrons are negatively charged subatomic particles, pairs of electrons repel one another to be as far apart as possible in space
9 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory Get into groups of four Send one person to grab nine balloons from the front Tie two balloons together Tie three balloons together Tie four balloons together Estimate the angles between the balloons using a protractor Hint: 180º
10 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory 180º linear 109.5º 120º tetrahedral trigonal planar
11 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory The basic molecular geometries can therefore be summarized on the basis of two, three, or four pairs of electrons. Each pair of electrons is described as occupying an electronic domain - a field of electronic density. Number of electron domains Molecular geometry Bond angle Examples of molecules or ions having this shape two linear 180º AB2 BeCl2, CO2 three trigonal planar 120º AB3 BF3, [NO3] - four tetrahedral 109.5º AB4 CH4, [NH4] +, [ClO4] -
12 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory Additional shapes can be deduced for species with fewer bonding pairs of electrons than the number of domains present. Electron domains not occupied by bonding pairs of electrons are filled by non-bonding pairs of electrons (lone pairs) AB2E (v-shaped), AB3E (trigonal pyramidal), and AB2E2 (v-shaped or bent) where represents a lone pair of electrons Electron domain geometry: based on total number of electron domains predicted by VSEPR theory Molecular geometry: gives the shape of the molecule
13 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory Number of electron domains Electron domain geometry Molecular geometry Bond angle Examples of molecules or ions having this shape three trigonal planar AB2E v-shaped (bent) <120º [NO2] -, SO2 four tetrahedral AB3E trigonal pyramidal <109.5º NH3, [SO3] 2-, H3O + four tetrahedral AB2E2 v-shaped (bent) <109.5º H2O, [NH2] -
14 Bond angles in molecular geometries Lone pairs of electrons affect bond angles in a molecule Lone pairs occupy more space than bonding pairs so they decrease the bond angle between bonding pairs. Degree of electron pair-electron pair repulsion follows this order: LP LP > LP BP > BP BP Angles are not uniform across the board! Electronegativity and multiple bonds can affect bond angles. i.e. PH3 has AB3E structure and is trigonal pyramidal but its angle is 93.5º due to the greater electronegativity effect from Phosphorus.
15 Bond angles in molecular geometries Molecule Number of electron domains Molecular geometry Bond angle CH4 four 109.5º tetrahedral (AB4) NH3 four 107º trigonal pyramidal (AB3E) H2O four 104.5º v-shaped (AB2E2)
16 Writing Lewis dot structures and electron domain and molecular geometries Writing dot structures is a process: Determine the number of valence electrons each atom contributes to the structure The number of valence electrons can usually be determined by the column in which the atom resides in the periodic table
17 Writing Lewis dot structures and electron domain and molecular geometries 1. Draw ball and stick diagram, identifying central atom. Each stick represents a pair of bonding electrons For oxoanions (anions containing oxygen) put negative charge on terminal oxygen atoms Remaining bonds should be converted into double bonds For other non-oxoanions put brackets around ion and put charge outside these. Cl Cl C Cl Cl
18 Writing Lewis dot structures and electron domain and molecular geometries 2. Make the atom that is fewest in number the central atom. For the central atom the number of valence electrons comes from periodic table. 3. Count number of sticks, these are single bonds designated as sigma (σ) bonds (add these). You subtract double (pi π bonds). a. Carbon has four valence electrons and four sigma bonds (no pi bonds) so number of valence electrons is eight Cl Cl C Cl Cl
19 Writing Lewis dot structures and electron domain and molecular geometries 4. Add one electron for a negative charge and subtract one for a positive charge (exclude this for oxoanions as you already localized them) 5. Combine steps 2-4 and divide this number by two to obtain the number of electron pairs, which equals the number of electron domains a. 8 valence electrons/2 = four electron domains 6. Deduce the electron domain geometry a. Thus, the electron domain geometry is tetrahedral, AB4 Cl Cl C Cl Cl
20 Writing Lewis dot structures and electron domain and molecular geometries 7. Determine number of lone pairs present, if applicable and deduce molecular geometry. Draw exact representation taking into account the order of electronpair repulsion: a. LP LP > LP BP > BP BP 8. Draw Lewis structure completing the octets on all terminal atoms, except Hydrogen. Remember square brackets on anions and cations. 9. Draw resonance structures, if applicable.
21 Practice Problem... I Do... Determine the Lewis structure, electron domains, and molecular geometries for [NH4] + First, draw the ball and stick diagram for the ammonium ion. Be sure to include the cation s charge in this step! H[ H N H H [ +
22 Practice Problem... I Do... Determine the Lewis structure, electron domains, and molecular geometries for [NH4] + Second, count the number of valence electrons of the central atom (N) and the number of sigma (single) bonds, add them up and divide by two to obtain the number of electron domains. N has five valence electrons [NH4] + has four sigma bonds [NH4] + has eight valence electrons 8/2= 4 electron domains for [NH4] + H[ H N H H Electron domain geometry is tetrahedral, AB4. [ +
23 Practice Problem... I Do... Determine the Lewis structure, electron domains, and molecular geometries for [NH4] + [ Last, draw the actual structure taking into consideration shape due to electron-pair repulsion. [NH4] + has no lone pairs therefore it is truly tetrahedral with bond angles of 109.5º 109.5º [ +
24 Practice Problem... We Do... Determine the Lewis structure, electron domains, and molecular geometries for NF3
25 Practice Problem 20 mins... You Do... Work with a partner and answer the following question: Determine the Lewis structure, electron domains, and molecular geometries for SF2, [NO2] -, and [SO3] 2-
26 Resonance structures Individual Lewis structures that contribute to overall structure are called resonance forms. Actual electronic structure of a species is called a resonance hybrid of these resonance forms. Shown using double headed arrow - will look at in more detail in Topic 10. Best known example is Benzene. Shows delocalization of electrons
27 Molecular polarity Unlike bond polarity, molecular polarity looks at whether the whole molecule is polar or non-polar. Non-polar molecule may have polar bonds Follow these steps to determine molecular polarity: 1. Using VSEPR theory, deduce the molecular geometry. 2. For each bond present, using electronegativity differences, Δχp, deduce the bond polarity for each bond present and draw the associated dipole moments; these are best represented as vectors. 3. Using vector addition, sum all the dipole moments present to establish whether there is a net dipole moment, μ, for the molecule. If so, the molecule is polar.
28 Practice Problem Turn to section 8 of your data booklet!!... We Do... Deduce the molecular polarities of the following: SF2. χp(s) = 2.6 χp(f) = 4.0 S F δ + δ - Fluorine is more electronegative than sulfur and the S-F bond is polar with the following dipole moment: To deduce molecular polarity, we sum the two S-F vectors. The SF2 molecule is v-shaped so we add the two vectors using the parallelogram law. F v1 S v2 F μ <109.5º vnet v1 + v2 = vnet This results in a net dipole moment, μ; the molecule is polar
29 Practice Problem Turn to section 8 of your data booklet!!... You Do... Deduce the molecular polarities of the following: CO2.
30 Allotropes Different structural modifications of the same element. Can vary in both physical and chemical properties. Carbon is most fascinating elements of periodic table and life forms on Earth are all based on carbon. Has a number of allotropes: graphite, graphene, and C60 fullerene.
31 Allotropes Covalent solid networks Graphite, diamond, and graphene are examples of covalent solid networks. Atoms are held together by covalent bonds in a giant three-dimensional lattice structure Graphite Layers of hexagonal rings consisting of carbon atoms. Connected by weak intermolecular forces of attraction (London Forces) Used as a lubricant and in pencils Diamond Each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement. Strength is due to covalently bonded interlocking structural arrangement of tetrahedra.
32 Allotropes Graphene - the super material! Not only the thinnest and strongest of known materials but first twodimensional crystal ever discovered. Differs from graphite because it is single planar sheet of carbon atoms arranged hexagonally and is only ONE ATOM thick!!!! 1mm piece of graphite consists of 3 million sheets of graphene, stacked on top of each other. When folded into sphere, becomes fullerene. C60 fullerene Not a covalent solid network Composed of individual molecules with strong covalent bonds but with weak London forces between molecules.
33 Silicon dioxide, SiO2 (quartz) Often called silica, usually found in its amorphous form as sand. Solid with no ordered structure. Quartz is another example of a three-dimensional covalent network solid. Consists of arrays of SiO4 tetrahedra arranged in a lattice Both cyrstalline and amorphous dioxide are insoluble in water and solid SiO2 does not conduct electricity or heat (no delocalized electrons present)
34 Coordinate covalent bonding Another type of covalent bonding In a typical covalent bond, the shared pair of electrons originate from both atoms that form the bond One atom contributes an electron to share and so does the other atom In coordinate covalent bonding, the shared pair of electrons comes from only one of the atoms; this atoms donates both electrons to the shared pair i.e. [NH4] +, [H3O] +, CO, Al2Cl6 and transition metal complexes
35 Coordinate covalent bonding [ Ammonium cation H3N + H + --> [NH4] + Lone pair on nitrogen combines with proton to form ammonium cation Hydronium cation H2O + H + --> [H3O] + Lone pair on oxygen combines with proton to form hydronium cation Carbon monoxide, CO 109.5º Dimer of aluminum chloride [ + The coordinate covalent bond is represented by an arrow to signify the origin of the electrons in the bond. Once formed, however, all the bonds are equivalent (whether coordinate covalent or normal covalent). Previously, the term dative covalent bonding was used for this type of bond but this term is now largely obsolete.
36 Representations of structures For tetrahedral structures it is common to use wedge and dash notation to show the various planes: A wedge indicates that the bond is in front of the defining plane (coming towards you) A dash indicates that the bond is behind the defining plane (facing away from you) A solid line indicates that the bond lies on the defining plane For example, the tetrahedral structure of methane, CH4, can be represented as follows using this notation
37 Topic 4.3 Covalent structure Lewis (electron dot) structures show all the valence electrons in a covalently bonded species. The octet rule refers to the tendency of atoms to gain a valence shell with a total of 8 electrons. Some atoms, like Be and B, might form stable compounds with incomplete octets of electrons. Resonance structures occur when there is more than one possible position for a double bond in a molecule. Shapes of species are determined by the repulsion of electron pairs according to VSEPR theory. Carbon and silicon form giant covalent/network covalent structures.
REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS CHEMICAL BONDS: LEWIS SYMBOLS: CHEMICAL BONDING. What are valence electrons?
 REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS 13 CHEMICAL BONDING What are valence electrons? Which groups on the periodic table readily give up electrons? What group readily accepts electrons? CHEMICAL BONDS: What are chemical
REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS 13 CHEMICAL BONDING What are valence electrons? Which groups on the periodic table readily give up electrons? What group readily accepts electrons? CHEMICAL BONDS: What are chemical
Molecular Compounds Compounds that are bonded covalently (like in water, or carbon dioxide) are called molecular compounds
 Chapter 8: Covalent Bonding Section 1: Molecular Compounds Bonds are Forces that hold groups of atoms together and make them function as a unit. Two types: Ionic bonds transfer of electrons (gained or
Chapter 8: Covalent Bonding Section 1: Molecular Compounds Bonds are Forces that hold groups of atoms together and make them function as a unit. Two types: Ionic bonds transfer of electrons (gained or
CHAPTER 6: CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS CHAPTER 16: COVALENT BONDING
 CHAPTER 6: CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS CHAPTER 16: COVALENT BONDING 6.1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding A chemical bond is a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different
CHAPTER 6: CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS CHAPTER 16: COVALENT BONDING 6.1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding A chemical bond is a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different
Bonding. Honors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6
 Bonding Honors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6 Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds them together. Types of Bonds Ionic Bonds Force of attraction
Bonding Honors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6 Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds them together. Types of Bonds Ionic Bonds Force of attraction
Chapter 6. Preview. Objectives. Molecular Compounds
 Section 2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds Preview Objectives Molecular Compounds Formation of a Covalent Bond Characteristics of the Covalent Bond The Octet Rule Electron-Dot Notation Lewis Structures
Section 2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds Preview Objectives Molecular Compounds Formation of a Covalent Bond Characteristics of the Covalent Bond The Octet Rule Electron-Dot Notation Lewis Structures
CHEMICAL BONDING. Chemical Bonds. Ionic Bonding. Lewis Symbols
 CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam
 AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is a correct Lewis structure for
AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is a correct Lewis structure for
Covalent Bonds Ch. Why do atoms bond? Atoms want noble gas configuration ( ) For bonds there is a transfer of electrons to get an octet of electrons
 Covalent Bonds Ch. Why do atoms bond? Atoms want noble gas configuration ( ) For bonds there is a transfer of electrons to get an octet of electrons For covalent bonds there is a of electrons to get an
Covalent Bonds Ch. Why do atoms bond? Atoms want noble gas configuration ( ) For bonds there is a transfer of electrons to get an octet of electrons For covalent bonds there is a of electrons to get an
Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules
 Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules 1. Ionic bonds 2. Covalent bonds (also co-ordinate covalent bonds) 3. Metallic bonds 4. Van der Waals forces
Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules 1. Ionic bonds 2. Covalent bonds (also co-ordinate covalent bonds) 3. Metallic bonds 4. Van der Waals forces
Chapter 6 Chemistry Review
 Chapter 6 Chemistry Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Put the LETTER of the correct answer in the blank. 1. The electrons involved in
Chapter 6 Chemistry Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Put the LETTER of the correct answer in the blank. 1. The electrons involved in
Bonding: Part Two. Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond. transfer valence e - Metallic bond. (NaCl) (Fe) mobile valence e - Covalent bond
 Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Lewis Dot Formulas and Molecular Shapes
 Lewis Dot Formulas and Molecular Shapes Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent chemical bonds are formed by valence electrons
Lewis Dot Formulas and Molecular Shapes Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent chemical bonds are formed by valence electrons
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule For Lewis structures of covalent compounds least electronegative
 Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
Covalent bonding does not involve electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged particles.
 SCH3U7 - Topic 4: Bonding Review SL Which of these bonding types would not be classified as strong? Metallic Covalent Ionic Dipole dipole The bond dissociation energy of NaCl is 411 kj mol -1, while that
SCH3U7 - Topic 4: Bonding Review SL Which of these bonding types would not be classified as strong? Metallic Covalent Ionic Dipole dipole The bond dissociation energy of NaCl is 411 kj mol -1, while that
Section 12: Lewis Structures
 Section 12: Lewis Structures The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 12.01 Electronegativity Chemistry (5)(C) 12.02 Electron
Section 12: Lewis Structures The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 12.01 Electronegativity Chemistry (5)(C) 12.02 Electron
Chemical Bonding. Section 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding. Section 2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds
 Chemical Bonding Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Section 2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds Section 3 Ionic Bonding and Ionic Compounds Section 4 Metallic Bonding Section
Chemical Bonding Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Section 2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds Section 3 Ionic Bonding and Ionic Compounds Section 4 Metallic Bonding Section
Hey, Baby. You and I Have a Bond...Ch. 8
 I. IONIC BONDING FUNDAMENTALS A. They form between... 1. A and a a. A to become b. A to become B. How it happens (Let s first focus on two atoms): 1. When a metal and a nonmetal meet, electrons get transferred
I. IONIC BONDING FUNDAMENTALS A. They form between... 1. A and a a. A to become b. A to become B. How it happens (Let s first focus on two atoms): 1. When a metal and a nonmetal meet, electrons get transferred
***Occurs when atoms of elements combine together to form compounds.*****
 CHEMICAL BONDING ***Occurs when atoms of elements combine together to form compounds.***** Formation of compounds involve adjustments in the position of one or more valence electrons. PE is lower in bonded
CHEMICAL BONDING ***Occurs when atoms of elements combine together to form compounds.***** Formation of compounds involve adjustments in the position of one or more valence electrons. PE is lower in bonded
Lewis Theory of Shapes and Polarities of Molecules
 Lewis Theory of Shapes and Polarities of Molecules Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Molecular Shape or Geometry The way in which atoms of a molecule are arranged in space
Lewis Theory of Shapes and Polarities of Molecules Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Molecular Shape or Geometry The way in which atoms of a molecule are arranged in space
Chapter 12. Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chapter 12 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell (highest energy level) of an atom. A chemical bond is a mutual
Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chapter 12 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell (highest energy level) of an atom. A chemical bond is a mutual
Chemical Bonds. Chapter 6
 Chemical Bonds Chapter 6 1 Ch. 6 Chemical Bonding I. How and Why Atoms Bond A. Vocabulary B. Chemical Bonds - Basics C. Chemical Bonds Types D. Chemical Bonds Covalent E. Drawing Lewis Diagrams F. Bond
Chemical Bonds Chapter 6 1 Ch. 6 Chemical Bonding I. How and Why Atoms Bond A. Vocabulary B. Chemical Bonds - Basics C. Chemical Bonds Types D. Chemical Bonds Covalent E. Drawing Lewis Diagrams F. Bond
Ch 6 Chemical Bonding
 Ch 6 Chemical Bonding What you should learn in this section (objectives): Define chemical bond Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds Describe ionic and covalent bonding Explain why most chemical bonding
Ch 6 Chemical Bonding What you should learn in this section (objectives): Define chemical bond Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds Describe ionic and covalent bonding Explain why most chemical bonding
4.2.7 & Shapes, and bond angles for molecules with two, three and four negative charge centers
 4.2.7 & 4.2.8 Shapes, and bond angles for molecules with two, three and four negative charge centers The shape of a molecule has an important part to play in determining its chemical (e.g. reactivity and
4.2.7 & 4.2.8 Shapes, and bond angles for molecules with two, three and four negative charge centers The shape of a molecule has an important part to play in determining its chemical (e.g. reactivity and
Chapter 12. Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has core and valence electrons. Core electrons are found close to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the most distant s and
Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has core and valence electrons. Core electrons are found close to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the most distant s and
CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS
 CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS IONIC BONDING When an atom of a nonmetal takes one or more electrons from an atom of a metal so both atoms end up with eight valence
CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS IONIC BONDING When an atom of a nonmetal takes one or more electrons from an atom of a metal so both atoms end up with eight valence
Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules
 Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Bonding: Part Two. Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond. transfer valence e - Metallic bond. (NaCl) (Fe) mobile valence e - Covalent bond
 Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Check Your Solution A comparison with the figures in Figure 4.31 on page 234 of the student textbook confirms the results.
 Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
Molecular Models: The shape of simple molecules and ions
 Molecular Models: The shape of simple molecules and ions Background The shape of a molecule is very important when investigating its properties and reactivity. For example, compare CO 2 and SO 2. Carbon
Molecular Models: The shape of simple molecules and ions Background The shape of a molecule is very important when investigating its properties and reactivity. For example, compare CO 2 and SO 2. Carbon
Chapter 12 Structures and Characteristics of Bonds Objectives
 Objectives 1. To learn about ionic and covalent bonds and explain how they are formed - what holds compounds together? 2. To learn about the polar covalent bond are all covalent bonds equal? 3. To understand
Objectives 1. To learn about ionic and covalent bonds and explain how they are formed - what holds compounds together? 2. To learn about the polar covalent bond are all covalent bonds equal? 3. To understand
A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE ETHANOL! Count valence electrons
 212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
COVALENT BONDING CHEMICAL BONDING I: LEWIS MODEL. Chapter 7
 Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
SL Score. HL Score ! /30 ! /48. Practice Exam: Paper 1 Topic 4: Bonding. Name
 Name Practice Exam: Paper 1 Topic 4: Bonding SL SL Score! /30 HL Score! /48 1. What is the correct Lewis structure for hypochlorous acid, a compound containing chlorine, hydrogen and oxygen? A. B. C. D.
Name Practice Exam: Paper 1 Topic 4: Bonding SL SL Score! /30 HL Score! /48 1. What is the correct Lewis structure for hypochlorous acid, a compound containing chlorine, hydrogen and oxygen? A. B. C. D.
Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction
 Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent
Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent
Carbon and Its Compounds
 Chapter 1 Carbon and Its Compounds Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 1.2 Organic Molecules from the Inside Out I: The Modelling of Atoms Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 2 s orbitals:
Chapter 1 Carbon and Its Compounds Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 1.2 Organic Molecules from the Inside Out I: The Modelling of Atoms Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 2 s orbitals:
Covalent Bonding. In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons
 In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
Unit Six --- Ionic and Covalent Bonds
 Unit Six --- Ionic and Covalent Bonds Electron Configuration in Ionic Bonding Ionic Bonds Bonding in Metals Valence Electrons Electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element s atoms Examples
Unit Six --- Ionic and Covalent Bonds Electron Configuration in Ionic Bonding Ionic Bonds Bonding in Metals Valence Electrons Electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element s atoms Examples
IB Topics 4 & 14 Multiple Choice Practice
 IB Topics 4 & 14 Multiple Choice Practice 1. Which compound has the shortest C N bond? CH 3NH 2 (CH 3) 3CNH 2 CH 3CN CH 3CHNH 2. Which of the following series shows increasing hydrogen bonding with water?
IB Topics 4 & 14 Multiple Choice Practice 1. Which compound has the shortest C N bond? CH 3NH 2 (CH 3) 3CNH 2 CH 3CN CH 3CHNH 2. Which of the following series shows increasing hydrogen bonding with water?
General and Inorganic Chemistry I.
 General and Inorganic Chemistry I. Lecture 1 István Szalai Eötvös University István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 1 / 29 Outline István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 2 / 29 Lewis Formulas
General and Inorganic Chemistry I. Lecture 1 István Szalai Eötvös University István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 1 / 29 Outline István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 2 / 29 Lewis Formulas
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Section Chapter 8: Covalent Bonding CHAPTER 8 Table Of Contents Section 8.2 Section 8.3 Section 8.4 Section 8.5 Naming Molecules Molecular Structures Molecular Shapes Electronegativity
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Section Chapter 8: Covalent Bonding CHAPTER 8 Table Of Contents Section 8.2 Section 8.3 Section 8.4 Section 8.5 Naming Molecules Molecular Structures Molecular Shapes Electronegativity
Honors Chemistry Unit 6 ( )
 Honors Chemistry Unit 6 (2017-2018) Lewis Dot Structures VSEPR Structures 1 We are learning to: 1. Represent compounds with Lewis structures. 2. Apply the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry
Honors Chemistry Unit 6 (2017-2018) Lewis Dot Structures VSEPR Structures 1 We are learning to: 1. Represent compounds with Lewis structures. 2. Apply the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry
* one of these choices is not used
 IONIC BONDING REVIEW WORKSHEET Part 1 - Complete each of the following sentences by filling in the appropriate word or phrase from the list below. negative noble gas octet anion positive electrons ions
IONIC BONDING REVIEW WORKSHEET Part 1 - Complete each of the following sentences by filling in the appropriate word or phrase from the list below. negative noble gas octet anion positive electrons ions
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking
 INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Sixth Edition by Charles H. Corwin Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding by Christopher Hamaker 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 12 1 Chemical Bond Concept
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Sixth Edition by Charles H. Corwin Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding by Christopher Hamaker 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 12 1 Chemical Bond Concept
Chapter 8 Covalent Boding
 Chapter 8 Covalent Boding Molecules & Molecular Compounds In nature, matter takes many forms. The noble gases exist as atoms. They are monatomic; monatomic they consist of single atoms. Hydrogen chloride
Chapter 8 Covalent Boding Molecules & Molecular Compounds In nature, matter takes many forms. The noble gases exist as atoms. They are monatomic; monatomic they consist of single atoms. Hydrogen chloride
Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry
 Experiment 11 Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. Purpose
Experiment 11 Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. Purpose
Chapter 6. Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 6 Chemical Bonding Section 6.1 Intro to Chemical Bonding 6.1 Objectives Define chemical bond. Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds. Describe ionic and covalent bonding. Explain why most chemical
Chapter 6 Chemical Bonding Section 6.1 Intro to Chemical Bonding 6.1 Objectives Define chemical bond. Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds. Describe ionic and covalent bonding. Explain why most chemical
Chapter 6. Preview. Lesson Starter Objectives Chemical Bond
 Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Chemical Bond Section 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Lesson Starter Imagine getting onto a crowded elevator. As people squeeze into the confined space, they come in
Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Chemical Bond Section 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Lesson Starter Imagine getting onto a crowded elevator. As people squeeze into the confined space, they come in
Chapter 6. Preview. Lesson Starter Objectives Chemical Bond
 Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Chemical Bond Section 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Lesson Starter Imagine getting onto a crowded elevator. As people squeeze into the confined space, they come in
Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Chemical Bond Section 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Lesson Starter Imagine getting onto a crowded elevator. As people squeeze into the confined space, they come in
CP Covalent Bonds Ch. 8 &
 CP Covalent Bonds Ch. 8 & 9 2015-2016 Why do atoms bond? Atoms want stability- to achieve a noble gas configuration ( ) For bonds there is a transfer of electrons to get an octet of electrons For covalent
CP Covalent Bonds Ch. 8 & 9 2015-2016 Why do atoms bond? Atoms want stability- to achieve a noble gas configuration ( ) For bonds there is a transfer of electrons to get an octet of electrons For covalent
Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Now explore the Compare Two Structures link. Try changing the display to explore different combinations.
 Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Exploring The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model. Go to the Purdue University website to explore VSEPR theory. http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/vsepr/structur2.html
Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Exploring The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model. Go to the Purdue University website to explore VSEPR theory. http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/vsepr/structur2.html
Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Learning Objective
 Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry 11.1 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Discuss the atomic trends Metals are located on the left side of the periodic
Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry 11.1 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Discuss the atomic trends Metals are located on the left side of the periodic
CHEMICAL BONDS A CHEMICAL BOND IS A FORCE OF ATTRACTION HOLDING THE ATOMS OR IONS TOGETHER.
 CHEMICAL BONDS A CHEMICAL BOND IS A FORCE OF ATTRACTION HOLDING THE ATOMS OR IONS TOGETHER. q Elements tend to enter into chemical reaction to gain stability q This is satisfied by completing the octet
CHEMICAL BONDS A CHEMICAL BOND IS A FORCE OF ATTRACTION HOLDING THE ATOMS OR IONS TOGETHER. q Elements tend to enter into chemical reaction to gain stability q This is satisfied by completing the octet
Bonding. Polar Vs. Nonpolar Covalent Bonds. Ionic or Covalent? Identifying Bond Types. Solutions + -
 Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds them together. Bonding onors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6 Types of Bonds Ionic Bonds Force of attraction
Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds them together. Bonding onors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6 Types of Bonds Ionic Bonds Force of attraction
AP Chemistry Chapter 7: Bonding
 AP Chemistry Chapter 7: Bonding Types of Bonding I. holds everything together! I All bonding occurs because of! Electronegativity difference and bond character A. A difference in electronegativity between
AP Chemistry Chapter 7: Bonding Types of Bonding I. holds everything together! I All bonding occurs because of! Electronegativity difference and bond character A. A difference in electronegativity between
Chapter 6. The Chemical Bond
 Chapter 6 The Chemical Bond Some questions Why do noble gases rarely bond to other elements? How does this relate to why the atoms of other elements do form bonds? Why do certain elements combine to form
Chapter 6 The Chemical Bond Some questions Why do noble gases rarely bond to other elements? How does this relate to why the atoms of other elements do form bonds? Why do certain elements combine to form
Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
 CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
of its physical and chemical properties.
 8.4 Molecular Shapes VSEPR Model The shape of a molecule determines many of its physical and chemical properties. Molecular l geometry (shape) can be determined with the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
8.4 Molecular Shapes VSEPR Model The shape of a molecule determines many of its physical and chemical properties. Molecular l geometry (shape) can be determined with the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
Fill in the chart below to determine the valence electrons of elements 3-10
 Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
 CHAPTER 6 CHEMICAL BONDING SHORT QUESTION WITH ANSWERS Q.1 Dipole moments of chlorobenzene is 1.70 D and of chlorobenzene is 2.5 D while that of paradichlorbenzene is zero; why? Benzene has zero dipole
CHAPTER 6 CHEMICAL BONDING SHORT QUESTION WITH ANSWERS Q.1 Dipole moments of chlorobenzene is 1.70 D and of chlorobenzene is 2.5 D while that of paradichlorbenzene is zero; why? Benzene has zero dipole
Chemistry I Chemical Bonding / Molecular Geometry / Intermolecular Forces Lecture Notes
 Chemistry I Chemical Bonding / Molecular Geometry / Intermolecular Forces Lecture Notes Since most elements do not have a filled outer shell, they attempt to achieve an octet arrangement by combining with
Chemistry I Chemical Bonding / Molecular Geometry / Intermolecular Forces Lecture Notes Since most elements do not have a filled outer shell, they attempt to achieve an octet arrangement by combining with
Chemical Bonding II. Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds Hybridization MO theory
 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
Introduction to Chemical Bonding
 Chemical Bonding Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical bond! is a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together Why are most
Chemical Bonding Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical bond! is a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together Why are most
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
AP Chemistry. Unit #7. Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape. Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING. Discrete molecules formed
 AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
Bonding. Each type of bonding gives rise to distinctive physical properties for the substances formed.
 Bonding History: In 55 BC, the Roman poet and philosopher Lucretius stated that a force of some kind holds atoms together. He wrote that certain atoms when they collide, do not recoil far, being driven
Bonding History: In 55 BC, the Roman poet and philosopher Lucretius stated that a force of some kind holds atoms together. He wrote that certain atoms when they collide, do not recoil far, being driven
Topic 4: Bonding. Adapted from Mr Field
 Topic 4: Bonding Adapted from Mr Field 4.1 Ionic Bonding and Structure Ionic bonding An ionic bond is: The electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions sodium fluoride lithium oxide F -
Topic 4: Bonding Adapted from Mr Field 4.1 Ionic Bonding and Structure Ionic bonding An ionic bond is: The electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions sodium fluoride lithium oxide F -
Periodic Trends. Homework: Lewis Theory. Elements of his theory:
 Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization
 Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization A. Molecular Geometry Lewis structures provide us with the number and types of bonds around a central atom, as well as any NB electron pairs. They do not tell us the
Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization A. Molecular Geometry Lewis structures provide us with the number and types of bonds around a central atom, as well as any NB electron pairs. They do not tell us the
Chem 1075 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Lecture Outline. Chemical Bond Concept
 Chem 1075 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Lecture Outline Slide 2 Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has and electrons. Core electrons are found to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the s
Chem 1075 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Lecture Outline Slide 2 Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has and electrons. Core electrons are found to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the s
What is Bonding? The Octet Rule. Getting an Octet. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Shapes. (Chapter Three, Part Two)
 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Shapes (Chapter Three, Part Two) What is Bonding? Bonding describes how atoms interact with each other in an attractive sense. There are three types of bonding: Ionic bonding
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Shapes (Chapter Three, Part Two) What is Bonding? Bonding describes how atoms interact with each other in an attractive sense. There are three types of bonding: Ionic bonding
Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chapter 9 Chang & Goldsby Modified by Dr. Hahn Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent
Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chapter 9 Chang & Goldsby Modified by Dr. Hahn Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent
Covalent Bonding. In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons
 In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
Ch. 12 Section 1: Introduction to Chemical Bonding
 Name Period Date Chemical Bonding & Intermolecular Forces (Chapter 12, 13 &14) Fill-in the blanks during the PowerPoint presentation in class. Ch. 12 Section 1: Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical
Name Period Date Chemical Bonding & Intermolecular Forces (Chapter 12, 13 &14) Fill-in the blanks during the PowerPoint presentation in class. Ch. 12 Section 1: Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical
Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY
 Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES (covalent bonding) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of covalent molecules (octet rule such as NH 3, CCl 4, H 2 O, CO 2, N 2 O 4, and exception to
Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES (covalent bonding) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of covalent molecules (octet rule such as NH 3, CCl 4, H 2 O, CO 2, N 2 O 4, and exception to
Lewis Structure. Lewis Structures & VSEPR. Octet & Duet Rules. Steps for drawing Lewis Structures
 Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
Chapter 7. Ionic & Covalent Bonds
 Chapter 7 Ionic & Covalent Bonds Ionic Compounds Covalent Compounds 7.1 EN difference and bond character >1.7 = ionic 0.4 1.7 = polar covalent 1.7 Electrons not shared at
Chapter 7 Ionic & Covalent Bonds Ionic Compounds Covalent Compounds 7.1 EN difference and bond character >1.7 = ionic 0.4 1.7 = polar covalent 1.7 Electrons not shared at
Chemical Bonding Basic Concepts
 Chemical Bonding Basic Concepts Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence electrons are the electrons that particpate in chemical bonding. Group e - configuration # of valence
Chemical Bonding Basic Concepts Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence electrons are the electrons that particpate in chemical bonding. Group e - configuration # of valence
Chapter 13: Phenomena
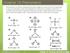 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
a) DIATOMIC ELEMENTS e.g. . MEMORIZE THEM!!
 CH 11 TOPIC 20 MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS COVALENT BONDS 1 You have mastered this topic when you can: 1) define or describe MOLECULAR ELEMENTS and DIATOMIC ELEMENTS. 2) define or describe MOLECULAR COMPOUND and
CH 11 TOPIC 20 MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS COVALENT BONDS 1 You have mastered this topic when you can: 1) define or describe MOLECULAR ELEMENTS and DIATOMIC ELEMENTS. 2) define or describe MOLECULAR COMPOUND and
Honors Chemistry - Unit 9 Chapter 6: Bonding & Molecular Structures. Unit 9 Packet Page 1 of 14
 Honors Chemistry - Unit 9 Chapter 6: Bonding & Molecular Structures Unit 9 Packet Page 1 of 14 Vocab Quiz: UT Due: Test Date: Quiz Date(s): FORMULAS/CONSTANTS Memorize VSEPR Chart First 6 Shapes!! OBJECTIVES:
Honors Chemistry - Unit 9 Chapter 6: Bonding & Molecular Structures Unit 9 Packet Page 1 of 14 Vocab Quiz: UT Due: Test Date: Quiz Date(s): FORMULAS/CONSTANTS Memorize VSEPR Chart First 6 Shapes!! OBJECTIVES:
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH
 C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE The Ionic Bond Formation of Ions The
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE The Ionic Bond Formation of Ions The
Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes
 Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes PRELAB ASSINGMENT Read the entire laboratory write up and answer the following questions before coming to lab. Read the entire laboratory write up
Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes PRELAB ASSINGMENT Read the entire laboratory write up and answer the following questions before coming to lab. Read the entire laboratory write up
Molecular Geometry & Polarity
 Molecular Geometry & Polarity Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized
Molecular Geometry & Polarity Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized
Downloaded from
 Points to Remember Class: XI Chapter Name: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Top Concepts 1. The attractive force which holds together the constituent particles (atoms, ions or molecules) in chemical
Points to Remember Class: XI Chapter Name: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Top Concepts 1. The attractive force which holds together the constituent particles (atoms, ions or molecules) in chemical
Name. Molecular Models
 Name Molecular Models Lab Day Introduction: The atom and molecule are truly small; 6 10 23 carbon atoms occupy about 4 cm 3, or each atom has a volume of about 6 10 24 cm 3. Molecules, though larger than
Name Molecular Models Lab Day Introduction: The atom and molecule are truly small; 6 10 23 carbon atoms occupy about 4 cm 3, or each atom has a volume of about 6 10 24 cm 3. Molecules, though larger than
Chapter 9. Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules
 Chem 220 Notes Page 1 Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules I. Types of Chemical Bonds A. Why do atoms forms bonds? Atoms want to have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas atom (noble
Chem 220 Notes Page 1 Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules I. Types of Chemical Bonds A. Why do atoms forms bonds? Atoms want to have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas atom (noble
Theory of knowledge: Aim 3: Use naming conventions to name ionic compounds.
 Core 44 Essential idea: Ionic compounds consist of ions held together in lattice structures by ionic bonds. 4.1 Ionic bonding and structure Use theories to explain natural phenomena molten ionic compounds
Core 44 Essential idea: Ionic compounds consist of ions held together in lattice structures by ionic bonds. 4.1 Ionic bonding and structure Use theories to explain natural phenomena molten ionic compounds
EXPERIMENT 15: MOLECULAR MODELS
 EXPERIMENT 15: MLEULAR MDELS Introduction: Given formulas of some molecules and ions, you will use the periodic table, valence electron count, and electronegativities to deduce their geometry and polarities.
EXPERIMENT 15: MLEULAR MDELS Introduction: Given formulas of some molecules and ions, you will use the periodic table, valence electron count, and electronegativities to deduce their geometry and polarities.
CHEMICAL BONDING. Valence Electrons. Chapter Ten
 CHEMICAL BONDING Chapter Ten Valence Electrons! The electrons occupying the outermost energy level of an atom are called the valence electrons; all other electrons are called the core electrons.! The valence
CHEMICAL BONDING Chapter Ten Valence Electrons! The electrons occupying the outermost energy level of an atom are called the valence electrons; all other electrons are called the core electrons.! The valence
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts
 Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts Types of Chemical Bonds Information about the strength of a bonding interaction is obtained by measuring the bond energy, which is the energy
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts Types of Chemical Bonds Information about the strength of a bonding interaction is obtained by measuring the bond energy, which is the energy
6.1 Intro to Chemical Bonding Name:
 6.1 Intro to Chemical Bonding Name: A. Chemical bond Favored by nature because: 3 main types of bonds 1. 2. 3. B. Ionic Bonds C. Covalent Bonds D. Metallic Bond E. Bond Determination RECALL: Electronegativity
6.1 Intro to Chemical Bonding Name: A. Chemical bond Favored by nature because: 3 main types of bonds 1. 2. 3. B. Ionic Bonds C. Covalent Bonds D. Metallic Bond E. Bond Determination RECALL: Electronegativity
Class XI: Chemistry Chapter 4: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Top Concepts
 1 Class XI: Chemistry Chapter 4: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Top Concepts 1. The attractive force which holds together the constituent particles (atoms, ions or molecules) in chemical species
1 Class XI: Chemistry Chapter 4: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Top Concepts 1. The attractive force which holds together the constituent particles (atoms, ions or molecules) in chemical species
bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction
 bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction ionic compound- a metal reacts with a nonmetal Ionic bonds form when an atom that
bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction ionic compound- a metal reacts with a nonmetal Ionic bonds form when an atom that
Chapter 4 Lecture Outline. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 4 Lecture Outline 1 Copyright McGraw-ill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Introduction to Covalent Bonding Covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons between
Chapter 4 Lecture Outline 1 Copyright McGraw-ill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Introduction to Covalent Bonding Covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons between
1. What is the formula for the compound formed by calcium and nitrogen?
 IB Chem 1 Name Topic 4 Bonding - Sample Test Problems 1. What is the formula for the compound formed by calcium and nitrogen? A. CaN B. Ca 2 N C. Ca 2 N 3 D. Ca 3 N 2 2. Element X is in group 2, and element
IB Chem 1 Name Topic 4 Bonding - Sample Test Problems 1. What is the formula for the compound formed by calcium and nitrogen? A. CaN B. Ca 2 N C. Ca 2 N 3 D. Ca 3 N 2 2. Element X is in group 2, and element
Edexcel Chemistry A-level
 Edexcel Chemistry A-level Topic 2 - Bonding and Structure Flashcards What are ions? What are ions? Charged particles that is formed when an atom loses or gains electrons What is the charge of the ion when
Edexcel Chemistry A-level Topic 2 - Bonding and Structure Flashcards What are ions? What are ions? Charged particles that is formed when an atom loses or gains electrons What is the charge of the ion when
Lecture outline: Section 9. theory 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory. S. Ensign, Chem. 1210
 Lecture outline: Section 9 Molecular l geometry and bonding theories 1. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory 1 Ionic bonding Covalent bonding
Lecture outline: Section 9 Molecular l geometry and bonding theories 1. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory 1 Ionic bonding Covalent bonding
8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook. September 10, 2015
 chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook Chapter 8: Bonding: General Concepts Mar 13 11:15 AM 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. Bonds are forces that hold groups of
chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook Chapter 8: Bonding: General Concepts Mar 13 11:15 AM 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. Bonds are forces that hold groups of
