10: Modeling Molecular Structure CH141L November 24, 2015
|
|
|
- Posy Stewart
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 10: Modeling Molecular Structure CH141L November 24, 2015 This week, we ll use ball and stick models to explore molecular structure. At the end of the lab period, hand in the completed packet of Molecular Structure Tables. Take notes in your lab notebook as you work through this activity. You can use a pencil today! At the start of Lab 1. Define the terms appearing in bold in the first paragraph in Part C. Use this document, your textbook (Chapters 9 and 10) or online resources. 2. Write the names or formulas for each of the 20 molecules and ions listed in Part C. 3. Bring your lab notebook and a pencil to lab. Introduction Models are used to represent and understand the behavior of molecules. ne example is the ball and stick type model used to represent molecular structure. Such representations give us some sense of the way atoms are bonded and of the molecule s three-dimensional structure. However, a model must be more than an artistic representation to be really useful. Good models must serve as a tool for predicting properties and reactivity and must help us go beyond a simple appreciation of a static object to give us some sense of the object s potential. In this experiment, we will use ball and stick molecular models as a source of information on molecular behavior or as a facilitator for predicting such behavior. In addition, we will relate the molecular structure obtained from the models to two powerful tools, the Lewis Structure representation for molecules and the VSEPR theory for predicting molecular shape and polarity. This model building exercise is designed to give you a more concrete and three-dimensional view of these representations to help you to get the most information possible out of simple molecular models. The exercises described in this experiment are designed to be somewhat open-ended. Redo things that are initially confusing or build new molecules and try to predict their shapes, polarity, etc. Playing with the models is an ideal way to build your scientific understanding and intuition. Procedure 1 Using models it is relatively easy to see both geometry and polarity, as well as to deduce Lewis structures. In this exercise you will assemble models for a sizable number of common chemical species and will use them to determine geometry, polarity, and possible isomerism of the molecules. You may work in pairs. The models you will use consist of wooden balls (atoms), pegs (single bonds), and springs (used for multiple bonds). The balls represent the atomic nuclei and inner core electrons. The pegs and springs 1 Developed from The Geometrical Structure of Molecules: An Experiment using Molecular Models from Chemistry 103 Laboratory Manual, S. F. Sontum ed, Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Middlebury College, Middlebury, Vermont, 1988, pp
2 10: Modeling Molecular Structure CH141L 2 represent valence shell bonding or nonbonding (lone pair) electron pairs. Most of the heavy atoms in this exercise (C, N,, F, S,, Sb, Xe, and I) obey the octet rule. In their bonded structures, such atoms have four electron pairs around a central core and are represented in the model set as black balls with four holes. When these atoms participate in a multiple bond, more than one of their electron pairs (holes) are connected to the same atom. Springs are required for these bonds because of the rigid angles between the holes in these wooden atoms. A few of the structures will require expanded octet atoms. Atoms with an expanded octet can accommodate more than eight electrons. Atoms in the third and higher periods of the periodic table in the transition metal or representative groups (IIIA-VIIA) can have expanded octets. Initially we will assume that all heavy atoms obey the octet rule, and in our procedure we will discover the atoms that require expanded octets. A. Construction of Lewis Structures and Ball and Stick Molecular Models In assembling molecular models of the kind we are considering, it is usually desirable to use a systematic approach. The method suggested below parallels the method for writing Lewis structures that we have discussed in class. We will illustrate this method by developing a model for formaldehyde, CH Determine the total number of valence electrons and select the appropriate number of pegs. Recall that for the main group elements, (of the Periodic Table) which we will be using (H, C, N,, F, S,, Sb, Xe, and I), the number of valence electrons on an atom is equal to the group number. If the structure to be constructed has one or more electric charges (+ or -), add one electron to the total for each negative charge and subtract one electron for each positive charge. Each peg in our models represents two electrons, so once you have determined the total number of electrons, count the number of pegs to be used in your structure. For formaldehyde each H contributes one valence electron, the C contributes four valence electrons and the contributes six valence electrons to the overall structure, giving a total of 2(1) or 12 valence electrons. Therefore, our structure requires six pegs. 2. Select the appropriate wooden balls and deduce a skeletal structure for the molecule. Each hydrogen atom in our models is represented by a yellow ball with one hole (accommodating one electron pair) and, initially, each heavy atom will be represented by a black ball having four holes (accommodating four electron pairs, an octet ). Thus select one ball of the appropriate type for each atom in your molecular formula. The skeletal structure is the sequence of attachments (or the connection of atoms to one another) within the molecule. Frequently the skeletal structure can be discerned from the order in which the atoms are written in the molecular formula. ften the first atom in the formula is the central atom (especially if it is the least electronegative element) with those following all being attached to it. For more complex structures (e.g., ethyl alcohol considered below) the skeletal structure will sometimes be suggested by subdivisions in the molecular formula (CH 3 CH 2 H for ethyl alcohol). Sometimes there will be several possible and/or reasonable skeletal structures for a given molecular formula. Such molecular formulas are said to have several possible structural isomers (discussed below). If your skeletal structure requires more than four atoms to be attached to a central atom, that central atom will require
3 10: Modeling Molecular Structure CH141L 3 an expanded octet. In such cases, replace the black ball (4 holes) with an appropriate expanded octet ball (5 holes, light blue or 6 holes, white) and proceed to Step 3. Formaldehyde requires two yellow balls (two H atoms) and two black balls (one C and one atom). Build the skeletal structure with C (black ball with four holes) as the central atom with the H atoms (yellow balls with one hole) and the atom (black ball with four holes) attached to it. 3. Assemble a single-bonded structure for the molecule. Simply connect the adjacent atoms in your skeletal structure by inserting each end of a wooden peg into holes in adjacent atoms. If there are no empty holes in any of the atoms and no unused pegs after doing this, the structure is complete, 2 proceed to Part B. If there are empty holes or extra pegs, proceed to step 4. For formaldehyde, three pegs are required and our single-bonded structure has three of the holes in the C filled with pegs attached to the and two H atoms. In this case, there is one empty hole in the C, there are three empty holes in the and there are three unused pegs. Thus, we proceed to Step Add lone pairs. If you have additional pegs, place them in the empty holes. If all of the holes are filled and all of the pegs are used at this point, the structure is complete; 2 proceed to Part B. If there are empty holes or extra pegs, proceed to Step 5. For formaldehyde, we fill three of the four empty holes with lone pairs. Thus, we are left with one empty hole on either the C or the atom so we proceed to Step Add multiple bonds and/or expand octets. (a) If you have empty holes, your molecule is called unsaturated since there are insufficient electrons to fill the octets of all atoms. To reach octets, some atoms will need to share more than one electron pair with one or more of their neighbors. A double bond can be created by using a lone pair of electrons on one atom to help fill an empty hole on an adjacent atom (using two lone pairs from a single atom to fill two empty holes on a single adjacent atom produces a triple bond). To locate the most appropriate sites for multiple bonds, arrange the lone pairs in your single bonded structure so that each atom with an empty hole is adjacent to at least one atom with at least one lone pair. To complete the multiple bonds, we require more flexibility than the wooden pegs can provide, so we will use springs to form the double and triple bonds. At each site where there is an empty hole and an adjacent lone pair, replace both the lone pair peg and the peg representing the bond between the adjacent atoms with springs. Using springs provides the structural flexibility to allow you to create the multiple bond by inserting the free end of the lone pair spring into the empty hole on the adjacent atom. Complete octets of all atoms (fill all empty holes) by creating multiple bonds. Sometimes there is more than one arrangement of multiple bonds that fill all of the 2 Such completely single bonded molecules are said to be saturated molecules since they have all of the electrons they can accommodate without expanding the octet of one of their atoms.
4 10: Modeling Molecular Structure CH141L 4 holes. At this point in our exercise, any one of the possible multiply bonded structures is sufficient. Your structure should now be complete; go to Part B. For formaldehyde we use a structure with an empty hole on C and three lone pairs on or one with an empty hole on and one lone pair on C. In either case we replace the C bond peg and one lone pair with springs and then form a double bond between C and by connecting them with the two springs. This arrangement completes the structure for formaldehyde since all holes are filled and all pegs and springs are used. (b) If you have additional pegs. Your molecule has more electrons than can be accommodated by octets on all heavy atoms so that the octet of one or more of the atoms in the structure will need to be expanded. Atoms from the third row of the Periodic Table or below can accommodate more than eight valence electrons; thus they can have expanded octets. Select the central atom in your structure that can have expanded octets, and replace it in the structure with either a light blue (5 holes 10 electrons) or a white (6 holes 12 electrons) ball depending on the number of extra lone pairs of electrons they need to hold in your final structure. Fill the extra holes with your unused pegs. Your structure should be complete; proceed to Part B. B. Interpretation of Molecular Models 1. Draw the Lewis Dot Formula for your model. Simply write down the atoms, bonds, and lone pairs from your model built in Part A. This exercise should help you gain a sense of the three dimensional structure represented by Lewis dot formulas. Ultimately, it will be very useful for you to use the two dimensional Lewis formulas to visualize three-dimensional structures without the aid of ball and stick models. Lewis structures are much quicker and easier to produce and when you can see them in three dimensions they will be very powerful reasoning tools for you to use in predicting the shape and properties of molecules. For formaldehyde the Lewis dot formula is: H C H 2. Examine the Molecule s Molecular Geometry and describe the general overall shape of the molecule. Do the outer most atoms form a recognizable solid form (e.g. a cube, a pyramid, a tetrahedron, a bipyramid, an octahedron, etc.)? Is the molecule flat (planar) or are the atoms all in a line (linear)? If the molecule is planar, does it have an easily recognizable regular shape (e.g., a triangle, a square, a pentagon, etc.)? Formaldehyde is flat (all atoms lie in one plane) with its peripheral atoms forming the vertices of a triangle. Such a structure is called trigonal planar: C H H 3. Predict the Molecule s Polarity. Polar bonds are formed between two atoms with different electronegativities. The more electronegative atom attracts more than its fair share of electrons to
5 10: Modeling Molecular Structure CH141L 5 give a partial negative charge. The less electronegative atom has some electron density pulled away, so the less electronegative atom is partially positively charged. This polar bond creates a dipole (two poles) for that part of the molecule. The total dipole moment of the molecule is the vector sum of all the bond dipoles. For example, both C 2 and S 2 have polar bonds. However, the bond dipoles in carbon dioxide oppose each other and cancel out since C 2 is a linear molecule (the dipoles are vectors, in this case, of exactly the same magnitude in opposite directions). In S 2 the bond dipoles don t cancel, therefore, the whole molecule is polar. In drawings, an arrow is used to show the dipole, with the arrowhead pointing in the direction of the partial negative charge and the partial positive charge is depicted with a plus on the other end of the arrow, as shown below. C S Bond dipoles cancel nonpolar Bond dipoles don t cancel polar S Molecular dipole Symmetrically substituted linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral molecules are non-polar. For a tetrahedral example, C 4 is non-polar while CH 3 is polar. C Bond dipoles cancel nonpolar H C Bond dipoles don t cancel polar H C Molecular dipole A small electronegativity difference, such as that between C (2.5) and H (2.1) is not sufficient to create a noticeable bond dipole. However, the electronegativity difference between C (2.5) and (3.5) is large and the C bond is markedly polar. Does your molecule contain polar bonds? If so, which end of each polar bond is more positive and which is more negative? From the shape noted in 2 above, predict whether the molecule as a whole is polar. If so, indicate the direction of the molecule s dipole moment on the Lewis structure you drew in 1, above. In formaldehyde the C bond is polar, with the C atom partially positively charged and the partially negatively charged. The C H bonds are essentially nonpolar. Thus, formaldehyde is a polar molecule with a net dipole mirroring the C bond polarity. In the polarity column of Part C enter yes and draw the arrow depicting the net molecular dipole on Lewis structure. 4. Examine the Molecule s Potential for Resonance. If your molecule has multiple bonds, resonance is possible. If the multiple bonds may be arranged in more than one way, while maintaining the same skeletal structure, then each of the possible structures is a resonance structure. S 2 has two equivalent low energy resonance structures. The relative importance of inequivalent resonance structures is compared by calculating the formal charges on the atoms.
6 10: Modeling Molecular Structure CH141L 6 The formal charge on an atom is given by: fc = valence electrons 1 2 (bonding electrons) non-bonding electrons For example in S 2, the formal charge on the S-atom is fc = (6) 2 = +1, the formal charge on the doubly-bonded -atom is fc = 6 ½ 1 2 (4) 4 = 0, and the formal charge on the singly-bonded -atom is fc = (2) 6 = 1. The sum of the formal charges is equal to the charge on the ion or molecule. The actual structure of the molecule is best represented by an average of all of the resonance structures weighted such that low energy resonance structures (those with minimal formal charges on atoms) contribute more to the average structure than do high energy resonance structures (those containing atoms with large formal charges). Consider the cyanate ion, CN. The three inequivalent resonance structures of the cyanate ion are shown below with the formal charges: [ C N ] less likely [ C N ] dominant resonance structure [ C N ] least likely The C N resonance form is the dominant contributor to the structure of the molecule, since this resonance structure has the smallest formal charges. In addition, negative formal charges are most stable on the most electronegative atoms. Now back to the formaldehyde example: For formaldehyde, there is only one place for the double bond. Thus, formaldehyde has no resonance structures, so we enter no in the resonance column for the table in Part C (if there are resonance structures, indicate how many in the table and draw one additional structure in the table). For species with expanded octets, additional caution is required when comparing resonance structures. Expanded octets require the incorporation of d-atomic orbitals on the central atom into the bonding framework of the molecule. For non-metals, these d-orbitals are higher in energy than the valence s- and p-orbitals. Comparing formal charges between resonance structures, one with and one without an expanded octet, is invalid, since the expanded octet uses a different set of atomic orbitals than is used without an expanded octet. P dominant resonace structure P -1 with formal charges P -1 requires highenergy d-orbitals on P to expand octet For example, there is no evidence for significant contribution of d-orbitals in P 3 4, even though the formal charges can be minimized by expanding the octet. At our current level of approximation, the P bonds in P 3 4 are best described as single bonds. Expanding an octet requires a significant energy cost. 0 3-
7 10: Modeling Molecular Structure CH141L 7 5. Examine the Molecule s Potential for Structural Isomerism. If it is possible to arrange the atoms of your molecule in another skeletal structure that is different from the one chosen in Part A.2., then its molecular formula does not describe a unique molecule. Two or more structures that have the same molecular formula but different skeletal structures (sequences of attachment of atoms) are called structural isomers. Note, if there is only one possible structure, there are no isomers (enter no in the table constructed in Part C). If your molecule has structural isomers, build a model of at least one of them, draw it in your table in Part C, and compare it with your original model. It is possible to arrange the atoms of formaldehyde with the as the central atom and the C and two H atoms to the atom. Build a model for this structure. This second isomer is not a stable molecule, because the central has a formal charge of +2 and the C has a formal charge of 2. Molecules with such large formal charges, especially those with a positive formal charge on the more electronegative atom and a negative formal charge on the less electronegative atom are not usually stable. The isomer with as the central atom should not be listed as a stable isomer in the tables for this experiment. C. Build Models and Interpret Molecular Properties with those Models Using the provided kit, build a model for each of the following molecules or ions and then analyze your model according to the procedures above. Complete the table at the end of this document to record information on the compound or ion. Record the chemical name, chemical formula, number of valence electrons, Lewis structure (with the superimposed molecular dipole if present) and if applicable, any resonance and stable isomers. In addition, summarize the electron group geometry molecular shape, and hybridized orbitals for each central atom. Complete the worksheet (in pencil) for the 20 chemical species that follow. Remember to add or remove the appropriate number of electrons for the charges of ions when calculating the total number of electrons for these species. 1. Formaldehylde: Follow along with the example described above to complete your table. 2. Methane 3. Dicholormethane: Convert your methane molecule to dichloromethane (CH 2 2 ) by replacing two H atoms with atoms. Do the additional structural analyses described in Part B above. Draw the Lewis dot structures for all of the structural isomers of CH 2 2 that you think may exist. Build structures of all of your isomers and compare them see if they are identical (i.e., not isomers, are superimposable) or isomers, not superimposable upon each other with rotation. How many structural isomers are there with the molecular formula CH 2 2? 4. Ethanol: CH 3 CH 2 H 5. Dimethyl ether: CH 3 CH 3, Construct models for ethanol and dimethyl ether. These two compounds are structural isomers and have very different properties. Ethanol is very soluble in water, while dimethyl ether is not. The boiling point of ethanol is much higher (78.5 C) than dimethyl
8 10: Modeling Molecular Structure CH141L 8 ether (-24 C). These differences are caused by the presence of the H bond, which allows hydrogen bonding to be an important contribution to the forces between molecules in ethanol. Additional Molecules 6. H 2 7. H NH 3 9. NH C 2 H C 2 H SF S AsF I N C N 20. 3
Tinker Toys: Molecular Modeling by Hand
 Tinker Toys: Molecular Modeling by and Pre-lab Assignment: Reading: 1. hapters 8 and 9 in your course text. 2. This lab handout. ther points to note: 1. Please bring your text book to lab. 2. You may use
Tinker Toys: Molecular Modeling by and Pre-lab Assignment: Reading: 1. hapters 8 and 9 in your course text. 2. This lab handout. ther points to note: 1. Please bring your text book to lab. 2. You may use
Molecular Models: The shape of simple molecules and ions
 Molecular Models: The shape of simple molecules and ions Background The shape of a molecule is very important when investigating its properties and reactivity. For example, compare CO 2 and SO 2. Carbon
Molecular Models: The shape of simple molecules and ions Background The shape of a molecule is very important when investigating its properties and reactivity. For example, compare CO 2 and SO 2. Carbon
Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory
 Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory Introduction 1. Lewis Structures and Formal Charge LG.N. Lewis, at the University of California at Berkeley devised a simple way to understand the nature
Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory Introduction 1. Lewis Structures and Formal Charge LG.N. Lewis, at the University of California at Berkeley devised a simple way to understand the nature
: O: (1) (2) (3) (4) Page 1 of 6 : : : : : : (8) H H
 Experiment #12 MOLECULAR MODELS An aspect of chemistry, which traditionally proves to be difficult to many students, is the visualization of compounds, ions, and molecules in three dimensional space. In
Experiment #12 MOLECULAR MODELS An aspect of chemistry, which traditionally proves to be difficult to many students, is the visualization of compounds, ions, and molecules in three dimensional space. In
Molecular Geometry. Objectives N H H. The objectives of this laboratory are to:
 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are to: Molecular Geometry Write Lewis structure representations of the bonding and valence electrons in molecules. Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular
Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are to: Molecular Geometry Write Lewis structure representations of the bonding and valence electrons in molecules. Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular
A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE ETHANOL! Count valence electrons
 212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 9.1 Molecular Shapes Read Sec. 9.1 and 9.2, then complete the Sample and Practice Exercises in these sections. Sample Exercise 9.1 (p. 347) Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular geometries of a)
9.1 Molecular Shapes Read Sec. 9.1 and 9.2, then complete the Sample and Practice Exercises in these sections. Sample Exercise 9.1 (p. 347) Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular geometries of a)
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry. Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Lewis Theory of Molecular Shape and Polarity
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Lewis Theory of Molecular Shape and Polarity
EXPERIMENT 15: MOLECULAR MODELS
 EXPERIMENT 15: MLEULAR MDELS Introduction: Given formulas of some molecules and ions, you will use the periodic table, valence electron count, and electronegativities to deduce their geometry and polarities.
EXPERIMENT 15: MLEULAR MDELS Introduction: Given formulas of some molecules and ions, you will use the periodic table, valence electron count, and electronegativities to deduce their geometry and polarities.
Molecular shapes. Balls and sticks
 Molecular shapes Balls and sticks Learning objectives Apply VSEPR to predict electronic geometry and shapes of simple molecules Determine molecule shape from electronic geometry Distinguish between polar
Molecular shapes Balls and sticks Learning objectives Apply VSEPR to predict electronic geometry and shapes of simple molecules Determine molecule shape from electronic geometry Distinguish between polar
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 9. Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
LEWIS STRUCTURES - The Geometry of Covalent Molecules
 LEWIS STRUTURES - The Geometry of ovalent Molecules The formulas of many covalent compounds, especially those involving only the elements of the first few periods of the periodic table, were brought within
LEWIS STRUTURES - The Geometry of ovalent Molecules The formulas of many covalent compounds, especially those involving only the elements of the first few periods of the periodic table, were brought within
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 10 1
 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 10 1 Molecular geometry is the general shape of a molecule, as determined by the relative positions
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 10 1 Molecular geometry is the general shape of a molecule, as determined by the relative positions
CHEMISTRY. Chapter 10 Theories of Bonding and Structure. The Molecular Nature of Matter. Jespersen Brady Hyslop SIXTH EDITION
 CHEMISTRY The Molecular Nature of Matter SIXTH EDITION Jespersen Brady Hyslop Chapter 10 Theories of Bonding and Structure Copyright 2012 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Molecular Structures Molecules containing
CHEMISTRY The Molecular Nature of Matter SIXTH EDITION Jespersen Brady Hyslop Chapter 10 Theories of Bonding and Structure Copyright 2012 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Molecular Structures Molecules containing
8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook. September 10, 2015
 chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook Chapter 8: Bonding: General Concepts Mar 13 11:15 AM 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. Bonds are forces that hold groups of
chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook Chapter 8: Bonding: General Concepts Mar 13 11:15 AM 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. Bonds are forces that hold groups of
CHEMICAL BONDING. Valence Electrons. Chapter Ten
 CHEMICAL BONDING Chapter Ten Valence Electrons! The electrons occupying the outermost energy level of an atom are called the valence electrons; all other electrons are called the core electrons.! The valence
CHEMICAL BONDING Chapter Ten Valence Electrons! The electrons occupying the outermost energy level of an atom are called the valence electrons; all other electrons are called the core electrons.! The valence
Ch. 9- Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Ch. 9- Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.0 Introduction A. Lewis structures do not show one of the most important aspects of molecules- their overall shapes B. The shape and size of molecules-
Ch. 9- Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.0 Introduction A. Lewis structures do not show one of the most important aspects of molecules- their overall shapes B. The shape and size of molecules-
CHM 151LL: Geometry of Covalent Compounds
 CM 151LL: Geometry of Covalent Compounds Introduction Octet Rule A Lewis structure (or electrondot formula) is a twodimensional structural formula showing the arrangement of electrons around atoms in covalently
CM 151LL: Geometry of Covalent Compounds Introduction Octet Rule A Lewis structure (or electrondot formula) is a twodimensional structural formula showing the arrangement of electrons around atoms in covalently
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories. Molecular Shapes. Molecular Shapes. Chapter 9 Part 2 November 16 th, 2004
 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Part 2 November 16 th, 2004 8 Molecular Shapes When considering the geometry about the central atom, we consider all electrons (lone pairs and bonding
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Part 2 November 16 th, 2004 8 Molecular Shapes When considering the geometry about the central atom, we consider all electrons (lone pairs and bonding
The shape of simple molecules (and parts of larger molecules) can be easily predicted using the VSEPR model
 1 PREDICTING MOLECULAR SHAPE The shape of simple molecules (and parts of larger molecules) can be easily predicted using the VSEPR model VSEPR = Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model - Each BOND
1 PREDICTING MOLECULAR SHAPE The shape of simple molecules (and parts of larger molecules) can be easily predicted using the VSEPR model VSEPR = Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model - Each BOND
Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky
 Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky What Determines the Type of Bonding in Any Substance? Why do Atoms Bond? The key to answering the first question are found in the electronic structure of the atoms
Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky What Determines the Type of Bonding in Any Substance? Why do Atoms Bond? The key to answering the first question are found in the electronic structure of the atoms
Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 1 - VSEPR
 Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 1 - VSEPR Objectives: 1. Understand and become proficient at using VSEPR to predict the geometries of simple molecules and ions. 2. Become proficient at predicting
Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 1 - VSEPR Objectives: 1. Understand and become proficient at using VSEPR to predict the geometries of simple molecules and ions. 2. Become proficient at predicting
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Bonding - Ch. 7. Types of Bonding
 Types of Bonding I. holds everything together! II. All bonding occurs because of III. Electronegativity difference and bond character A. A between two atoms results in a when those two atoms form a bond.
Types of Bonding I. holds everything together! II. All bonding occurs because of III. Electronegativity difference and bond character A. A between two atoms results in a when those two atoms form a bond.
Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes
 Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes PRELAB ASSINGMENT Read the entire laboratory write up and answer the following questions before coming to lab. Read the entire laboratory write up
Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes PRELAB ASSINGMENT Read the entire laboratory write up and answer the following questions before coming to lab. Read the entire laboratory write up
Chapter 9 The Shapes of Molecules Cocaine
 Chapter 9 The Shapes of Molecules 1 Cocaine 10.1 Depicting Molecules & Ions with Lewis Structures 2 Number of Covalent Bonds 3 The number of covalent bonds can be determined from the number of electrons
Chapter 9 The Shapes of Molecules 1 Cocaine 10.1 Depicting Molecules & Ions with Lewis Structures 2 Number of Covalent Bonds 3 The number of covalent bonds can be determined from the number of electrons
Lab #11- Molecular Geometry
 Objectives Chesapeake Campus Chemistry 111 Laboratory Lab #11- Molecular Geometry Determine the shape of a molecule using the VSEPR. Draw the Lewis structures of a molecule including bond angles and formal
Objectives Chesapeake Campus Chemistry 111 Laboratory Lab #11- Molecular Geometry Determine the shape of a molecule using the VSEPR. Draw the Lewis structures of a molecule including bond angles and formal
SECTION II: BUILDING MODELS
 SECTION II: BUILDING MODELS Lesson 9 New Smells, New Ideas Lesson 10 Two s Company Lesson 11 Let s Build It Lesson 12 What Shape Is That Smell? Lesson 13 Sorting It Out Lesson 14 How Does the Nose Know?
SECTION II: BUILDING MODELS Lesson 9 New Smells, New Ideas Lesson 10 Two s Company Lesson 11 Let s Build It Lesson 12 What Shape Is That Smell? Lesson 13 Sorting It Out Lesson 14 How Does the Nose Know?
EXPERIMENT #13 Lewis Structures and Molecular Geometry
 OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #13 s and Draw Lewis structures of atoms, ions, and molecules Build models of linear, trigonal planar tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral arrangements of electron pairs
OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #13 s and Draw Lewis structures of atoms, ions, and molecules Build models of linear, trigonal planar tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral arrangements of electron pairs
A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE ETHANOL! Count valence electrons
 212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
Chapter 4 Lecture Outline. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 4 Lecture Outline 1 Copyright McGraw-ill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Introduction to Covalent Bonding Covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons between
Chapter 4 Lecture Outline 1 Copyright McGraw-ill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Introduction to Covalent Bonding Covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons between
Lewis Structure. Lewis Structures & VSEPR. Octet & Duet Rules. Steps for drawing Lewis Structures
 Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules
 Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Valence Bond Theory - Description
 Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 2 - Valence Bond Theory and Hybridization 1. Understand and be able to describe the Valence Bond Theory description of covalent bond formation. 2. Understand and
Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 2 - Valence Bond Theory and Hybridization 1. Understand and be able to describe the Valence Bond Theory description of covalent bond formation. 2. Understand and
Carbon and Its Compounds
 Chapter 1 Carbon and Its Compounds Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 1.2 Organic Molecules from the Inside Out I: The Modelling of Atoms Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 2 s orbitals:
Chapter 1 Carbon and Its Compounds Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 1.2 Organic Molecules from the Inside Out I: The Modelling of Atoms Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 2 s orbitals:
11/14/2014. Chemical Bonding. Richard Philips Feynman, Nobel Laureate in Physics ( )
 Chemical Bonding Lewis Theory Valence Bond VSEPR Molecular rbital Theory 1 "...he [his father] knew the difference between knowing the name of something and knowing something" Richard Philips eynman, Nobel
Chemical Bonding Lewis Theory Valence Bond VSEPR Molecular rbital Theory 1 "...he [his father] knew the difference between knowing the name of something and knowing something" Richard Philips eynman, Nobel
Lecture outline: Section 9. theory 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory. S. Ensign, Chem. 1210
 Lecture outline: Section 9 Molecular l geometry and bonding theories 1. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory 1 Ionic bonding Covalent bonding
Lecture outline: Section 9 Molecular l geometry and bonding theories 1. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory 1 Ionic bonding Covalent bonding
For this you need to know covalent bonds, Lewis dots, electronegativity, geometric shapes, duet & octet, single/double/triple bonds, etc...
 Lewis Structure Lab For this you need to know covalent bonds, Lewis dots, electronegativity, geometric shapes, duet & octet, single/double/triple bonds, etc... I can t assume you have had all these, so
Lewis Structure Lab For this you need to know covalent bonds, Lewis dots, electronegativity, geometric shapes, duet & octet, single/double/triple bonds, etc... I can t assume you have had all these, so
Lab Lecture on VSEPR and SPARTAN Chem 141 Lab Dr Abrash 10/3/2011
 Q: What is the purpose of this lab? Lab Lecture on VSEPR and SPARTAN Chem 141 Lab Dr Abrash 10/3/2011 To learn two methods to study and predict the shapes of molecules. One is a rule based paper method
Q: What is the purpose of this lab? Lab Lecture on VSEPR and SPARTAN Chem 141 Lab Dr Abrash 10/3/2011 To learn two methods to study and predict the shapes of molecules. One is a rule based paper method
Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes; VSEPR, Valence Bond and Molecular Orbital Theories
 C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 1 0 P a g e 1 Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes; VSEPR, Valence Bond and Molecular Orbital Theories Homework: Read Chapter 10: Work out sample/practice
C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 1 0 P a g e 1 Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes; VSEPR, Valence Bond and Molecular Orbital Theories Homework: Read Chapter 10: Work out sample/practice
bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction
 bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction ionic compound- a metal reacts with a nonmetal Ionic bonds form when an atom that
bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction ionic compound- a metal reacts with a nonmetal Ionic bonds form when an atom that
Structures, Shapes and Polarity. of Molecules. Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity
 Structures, Shapes and Polarity Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity of Molecules Do now: Brainstorm what you know/remember about these L2 concepts
Structures, Shapes and Polarity Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity of Molecules Do now: Brainstorm what you know/remember about these L2 concepts
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule For Lewis structures of covalent compounds least electronegative
 Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
Lewis Theory of Shapes and Polarities of Molecules
 Lewis Theory of Shapes and Polarities of Molecules Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Molecular Shape or Geometry The way in which atoms of a molecule are arranged in space
Lewis Theory of Shapes and Polarities of Molecules Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Molecular Shape or Geometry The way in which atoms of a molecule are arranged in space
Molecular Geometry & Polarity
 Molecular Geometry & Polarity Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized
Molecular Geometry & Polarity Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Models
 25 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Models A chemical bond is a force that holds groups of two or more atoms together and makes them function as a unit. Bonding involves only the valence (outer shell) electrons
25 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Models A chemical bond is a force that holds groups of two or more atoms together and makes them function as a unit. Bonding involves only the valence (outer shell) electrons
COVALENT BONDING CHEMICAL BONDING I: LEWIS MODEL. Chapter 7
 Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes
 Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes PRELAB ASSINGMENT Write an objective, and answer the following questions in your laboratory notebook before coming to lab. Read the entire laboratory
Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes PRELAB ASSINGMENT Write an objective, and answer the following questions in your laboratory notebook before coming to lab. Read the entire laboratory
Check Your Solution A comparison with the figures in Figure 4.31 on page 234 of the student textbook confirms the results.
 Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
Chemical Bonding Chapter 8
 Chemical Bonding Chapter 8 Get your Clicker, 2 magnets, goggles and your handouts Nov 15 6:15 PM Recall that: Ionic-Involves the transfer of electrons - forms between a metal and a nonmetal Covalent-Involves
Chemical Bonding Chapter 8 Get your Clicker, 2 magnets, goggles and your handouts Nov 15 6:15 PM Recall that: Ionic-Involves the transfer of electrons - forms between a metal and a nonmetal Covalent-Involves
Chemical Bonding. Types of Bonds. Ionic Bonding. Resonance Structures. Molecular Geometries. VSEPR Basic Shapes 3-D Notation Hybridization (Lab)
 Chemical Bonding Types of Bonds Ionic Bonding Lewis Structures Covalent Bonding Resonance Structures Octet Rule Polar Molecules Molecular Geometries VSEPR Basic Shapes 3-D Notation Hybridization (Lab)
Chemical Bonding Types of Bonds Ionic Bonding Lewis Structures Covalent Bonding Resonance Structures Octet Rule Polar Molecules Molecular Geometries VSEPR Basic Shapes 3-D Notation Hybridization (Lab)
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules
 Chem 220 Notes Page 1 Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules I. Types of Chemical Bonds A. Why do atoms forms bonds? Atoms want to have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas atom (noble
Chem 220 Notes Page 1 Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules I. Types of Chemical Bonds A. Why do atoms forms bonds? Atoms want to have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas atom (noble
Ex. 1) F F bond in F = 0 < % covalent, no transfer of electrons
 #60 Notes Unit 8: Bonding Ch. Bonding I. Bond Character Bonds are usually combinations of ionic and covalent character. The electronegativity difference is used to determine a bond s character. Electronegativity
#60 Notes Unit 8: Bonding Ch. Bonding I. Bond Character Bonds are usually combinations of ionic and covalent character. The electronegativity difference is used to determine a bond s character. Electronegativity
Chemical Bonding II. Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds Hybridization MO theory
 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
Organic Chemistry. Review Information for Unit 1. VSEPR Hybrid Orbitals Polar Molecules
 rganic hemistry Review Information for Unit 1 VSEPR ybrid rbitals Polar Molecules VSEPR The valence shell electron pair repulsion model (VSEPR) can be used to predict the geometry around a particular atom
rganic hemistry Review Information for Unit 1 VSEPR ybrid rbitals Polar Molecules VSEPR The valence shell electron pair repulsion model (VSEPR) can be used to predict the geometry around a particular atom
Carbon-based molecules are held together by covalent bonds between atoms
 hapter 1: hemical bonding and structure in organic compounds arbon-based molecules are held together by covalent bonds between atoms omposition: Mainly nonmetals; especially,, O, N, S, P and the halogens
hapter 1: hemical bonding and structure in organic compounds arbon-based molecules are held together by covalent bonds between atoms omposition: Mainly nonmetals; especially,, O, N, S, P and the halogens
Periodic Trends. Homework: Lewis Theory. Elements of his theory:
 Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Chapters 8 and 9. Octet Rule Breakers Shapes
 Chapters 8 and 9 Octet Rule Breakers Shapes Bond Energies Bond Energy (review): The energy needed to break one mole of covalent bonds in the gas phase Breaking bonds consumes energy; forming bonds releases
Chapters 8 and 9 Octet Rule Breakers Shapes Bond Energies Bond Energy (review): The energy needed to break one mole of covalent bonds in the gas phase Breaking bonds consumes energy; forming bonds releases
Chemistry: The Central Science. Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory The shape and size of a molecule of a particular substance, together with the strength and polarity of its bonds, largely
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory The shape and size of a molecule of a particular substance, together with the strength and polarity of its bonds, largely
Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories
 Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories Ionic Radii Ions, just like atoms, follow a periodic trend in their radii. The metal ions in a given period are smaller than the non-metal ions in the same
Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories Ionic Radii Ions, just like atoms, follow a periodic trend in their radii. The metal ions in a given period are smaller than the non-metal ions in the same
Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structures
 CHAPTERS 9 AND 10 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structures Objectives You will be able to: 1. Write a description of the formation of the covalent bond between two hydrogen atoms to form a hydrogen molecule.
CHAPTERS 9 AND 10 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structures Objectives You will be able to: 1. Write a description of the formation of the covalent bond between two hydrogen atoms to form a hydrogen molecule.
5 Polyatomic molecules
 s manual for Burrows et.al. Chemistry 3 Third edition 5 Polyatomic molecules Answers to worked examples WE 5.1 Formal charges in N 2 (on p. 221 in Chemistry 3 ) Use formal charges to decide whether oxygen
s manual for Burrows et.al. Chemistry 3 Third edition 5 Polyatomic molecules Answers to worked examples WE 5.1 Formal charges in N 2 (on p. 221 in Chemistry 3 ) Use formal charges to decide whether oxygen
To visualize the three-dimensional structures of some common molecules. To obtain bond angle, bond length, and hybridization data for molecules.
 Molecular Geometry PURPOSE A B C To explore some simple molecular structures. To explore the relationship between bond order and bond length. To explore resonance structures. GOALS To compare Lewis structures
Molecular Geometry PURPOSE A B C To explore some simple molecular structures. To explore the relationship between bond order and bond length. To explore resonance structures. GOALS To compare Lewis structures
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Electron Geometry Hybrid Orbitals
 Molecular Shape and Hybridized Orbitals CH2000: Introduction to General Chemistry, Plymouth State University, Fall 2014 Introduction: In chemistry, the three dimensional shape of a molecule is as important
Molecular Shape and Hybridized Orbitals CH2000: Introduction to General Chemistry, Plymouth State University, Fall 2014 Introduction: In chemistry, the three dimensional shape of a molecule is as important
Bonding - Ch Types of Bonding
 Types of Bonding I. holds everything together! II. All bonding occurs because of III. Electronegativity difference and bond character A. A between two atoms results in a when those two atoms form a bond.
Types of Bonding I. holds everything together! II. All bonding occurs because of III. Electronegativity difference and bond character A. A between two atoms results in a when those two atoms form a bond.
Ch 13: Covalent Bonding
 Ch 13: Covalent Bonding Section 13: Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion 1. Recall the rules for drawing Lewis dot structures 2. Remember the special situations: - Resonance structures - ormal charges
Ch 13: Covalent Bonding Section 13: Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion 1. Recall the rules for drawing Lewis dot structures 2. Remember the special situations: - Resonance structures - ormal charges
Electron Geometry Hybrid Orbitals
 Molecular Shape and Hybridized Orbitals CH2000: Introduction to General Chemistry, Plymouth State University Introduction: In chemistry, the three dimensional shape of a molecule is as important as the
Molecular Shape and Hybridized Orbitals CH2000: Introduction to General Chemistry, Plymouth State University Introduction: In chemistry, the three dimensional shape of a molecule is as important as the
10-1. The Shapes of Molecules, chapter 10
 10-1 The Shapes of Molecules, chapter 10 The Shapes of Molecules; Goals 10.1 Depicting Molecules and Ions with Lewis Structures 10.2 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory 10.3 Molecular
10-1 The Shapes of Molecules, chapter 10 The Shapes of Molecules; Goals 10.1 Depicting Molecules and Ions with Lewis Structures 10.2 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory 10.3 Molecular
Chapter 10. Geometry
 Chapter 10 Molec cular Geometry 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Molecular Geometry Molecular Polarity VSEPR Model Summary of Molecular Shapes Hybridization Molecular Orbital Theory Bond Angles 2 MOLECULAR GEOMETRY Molecular
Chapter 10 Molec cular Geometry 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Molecular Geometry Molecular Polarity VSEPR Model Summary of Molecular Shapes Hybridization Molecular Orbital Theory Bond Angles 2 MOLECULAR GEOMETRY Molecular
Review questions CHAPTER 5. Practice exercises 5.1 F F 5.3
 CHAPTER 5 Practice exercises 5.1 S 5.3 5.5 Ethane is symmetrical, so does not have a dipole moment. However, ethanol has a polar H group at one end and so has a dipole moment. 5.7 xygen has the valence
CHAPTER 5 Practice exercises 5.1 S 5.3 5.5 Ethane is symmetrical, so does not have a dipole moment. However, ethanol has a polar H group at one end and so has a dipole moment. 5.7 xygen has the valence
Molecular Modeling 1: Classic Molecular Modeling
 Molecular Modeling 1: Classic Molecular Modeling Author: J. M. McCormick* Last Update: January 31, 2011 Introduction Dalton's Atomic Theory revolutionized chemistry by explaining chemical properties in
Molecular Modeling 1: Classic Molecular Modeling Author: J. M. McCormick* Last Update: January 31, 2011 Introduction Dalton's Atomic Theory revolutionized chemistry by explaining chemical properties in
Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry
 Experiment 11 Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. Purpose
Experiment 11 Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. Purpose
CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions
 CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions 1D 1 has a triple bond. 2 has a double bond. 3 and 4 have single bonds. The stronger the bond, the shorter the length. 2A A 1:1 ratio means there must be the
CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions 1D 1 has a triple bond. 2 has a double bond. 3 and 4 have single bonds. The stronger the bond, the shorter the length. 2A A 1:1 ratio means there must be the
Geometry of Covalent Compounds
 Geometry of Covalent Compounds Introduction This laboratory exercise will give you experience working with molecular model sets so you will better understand the geometries of small covalent molecules.
Geometry of Covalent Compounds Introduction This laboratory exercise will give you experience working with molecular model sets so you will better understand the geometries of small covalent molecules.
CHAPTER TEN MOLECULAR GEOMETRY MOLECULAR GEOMETRY V S E P R CHEMICAL BONDING II: MOLECULAR GEOMETRY AND HYBRIDIZATION OF ATOMIC ORBITALS
 CHAPTER TEN CHEMICAL BONDING II: AND HYBRIDIZATION O ATOMIC ORBITALS V S E P R VSEPR Theory In VSEPR theory, multiple bonds behave like a single electron pair Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR)
CHAPTER TEN CHEMICAL BONDING II: AND HYBRIDIZATION O ATOMIC ORBITALS V S E P R VSEPR Theory In VSEPR theory, multiple bonds behave like a single electron pair Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR)
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Geometries -Bond angles: angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of the atoms in a molecule -Bond angles determine overall shape of
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Geometries -Bond angles: angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of the atoms in a molecule -Bond angles determine overall shape of
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories PART I Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories PART I Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 6. The Chemical Bond
 Chapter 6 The Chemical Bond Some questions Why do noble gases rarely bond to other elements? How does this relate to why the atoms of other elements do form bonds? Why do certain elements combine to form
Chapter 6 The Chemical Bond Some questions Why do noble gases rarely bond to other elements? How does this relate to why the atoms of other elements do form bonds? Why do certain elements combine to form
Chapter 13: Phenomena
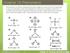 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
CHM 130LL: Molecular Models
 CM 130LL: Molecular Models In this lab, you will study covalently bonded molecules i.e., molecules where nonmetal atoms are held together because they share one or more pairs of electrons. In this experiment,
CM 130LL: Molecular Models In this lab, you will study covalently bonded molecules i.e., molecules where nonmetal atoms are held together because they share one or more pairs of electrons. In this experiment,
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model.
 Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model. Determine whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar based
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model. Determine whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar based
VSEPR. Ch10. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory allows you to predict molecular shape. Lewis Dot theory extended to 3 dimensions.
 Ch10 VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory allows you to predict molecular shape. Lewis Dot theory extended to 3 dimensions. version 1.5 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2016 Valence Shell Electron
Ch10 VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory allows you to predict molecular shape. Lewis Dot theory extended to 3 dimensions. version 1.5 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2016 Valence Shell Electron
VSEPR. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
 VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Vocabulary: domain = any electron pair or bond (single, double or triple) is considered one domain. bonding pair = shared pair = any electron pair that
VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Vocabulary: domain = any electron pair or bond (single, double or triple) is considered one domain. bonding pair = shared pair = any electron pair that
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories. Lecture Presentation. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
CHEMICAL BONDING. Chemical Bonds. Ionic Bonding. Lewis Symbols
 CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
BONDING THEORIES Chapter , Carey
 BONDING THEORIES Chapter 10.6-10.7, Carey The Covalent Chemical Bond (9.2) FIG I Potential Energy Change to Form H2 What is a chemical bond? Why do chemical bonds occur? Descriptions of bonding: Valence
BONDING THEORIES Chapter 10.6-10.7, Carey The Covalent Chemical Bond (9.2) FIG I Potential Energy Change to Form H2 What is a chemical bond? Why do chemical bonds occur? Descriptions of bonding: Valence
Atoms have the ability to do two things in order to become isoelectronic with a Noble Gas.
 CHEMICAL BONDING Atoms have the ability to do two things in order to become isoelectronic with a Noble Gas. 1.Electrons can be from one atom to another forming. Positive ions (cations) are formed when
CHEMICAL BONDING Atoms have the ability to do two things in order to become isoelectronic with a Noble Gas. 1.Electrons can be from one atom to another forming. Positive ions (cations) are formed when
Covalent Bonding. In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons
 In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization
 Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization A. Molecular Geometry Lewis structures provide us with the number and types of bonds around a central atom, as well as any NB electron pairs. They do not tell us the
Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization A. Molecular Geometry Lewis structures provide us with the number and types of bonds around a central atom, as well as any NB electron pairs. They do not tell us the
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
AP Chemistry. Unit #7. Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape. Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING. Discrete molecules formed
 AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
Lewis Structure and Electron Dot Models
 Lewis Structure and Electron Dot Models The Lewis Structure is a method of displaying the electrons present in any given atom or compound. Steps: 1. Make a skeleton structure 2. Count all e- available
Lewis Structure and Electron Dot Models The Lewis Structure is a method of displaying the electrons present in any given atom or compound. Steps: 1. Make a skeleton structure 2. Count all e- available
Geometry of Covalent Compounds
 Geometry of Covalent Compounds Introduction This laboratory exercise will give you experience working with molecular model sets so you will better understand the geometries of small covalent molecules.
Geometry of Covalent Compounds Introduction This laboratory exercise will give you experience working with molecular model sets so you will better understand the geometries of small covalent molecules.
PART 3 Chemical Bonds, Valence Bond Method, and Molecular Shapes. Reference: Chapter 9 10 in textbook
 PART 3 Chemical Bonds, Valence Bond Method, and Molecular Shapes Reference: Chapter 9 10 in textbook 1 Valence Electrons Valence ae Electron Define: the outer shell electrons Important for determination
PART 3 Chemical Bonds, Valence Bond Method, and Molecular Shapes Reference: Chapter 9 10 in textbook 1 Valence Electrons Valence ae Electron Define: the outer shell electrons Important for determination
Chemical Bonding I: Covalent Bonding. How are atoms held together in compounds?
 I: Covalent Bonding How are atoms held together in compounds? IONIC or COVALENT bonds or forces For most atoms, a filled outer shell contains 8 electrons ----- an octet Atoms want to form octets when they
I: Covalent Bonding How are atoms held together in compounds? IONIC or COVALENT bonds or forces For most atoms, a filled outer shell contains 8 electrons ----- an octet Atoms want to form octets when they
Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms.
 Chapter 9 CH 180 Major Concepts: Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms. Sublevels (s, p, d, & f) of separate atoms may overlap and result in hybrid orbitals
Chapter 9 CH 180 Major Concepts: Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms. Sublevels (s, p, d, & f) of separate atoms may overlap and result in hybrid orbitals
H O H C H H N H H. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion: Predicting Shape & Polarity
 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion: Predicting Shape & Polarity BJECTIVES Students will develop the ability to: 1. Predict the arrangement that valence e pairs assume around an atom (e pair geometry)
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion: Predicting Shape & Polarity BJECTIVES Students will develop the ability to: 1. Predict the arrangement that valence e pairs assume around an atom (e pair geometry)
