Chapter , Exam 2
|
|
|
- Gertrude Snow
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter , Exam 2
2 Covalent Bonding Covalent bonds are formed when two nonmetals combine The atoms share electrons. If the atoms share 2 electrons a single covalent bond is formed. If the atoms share 4 electrons a double covalent bond is formed. If the atoms share 6 electrons a triple covalent bond is formed. 2
3 Formation of Covalent Bonds Representation of the formation of an 2 molecule from atoms. 3
4 Formation of Covalent Bonds We can use Electron dot formulas to show covalent bond formation. Electron Dot formulas are a way to represent the number of valence electrons graphically. Each element in a molecule must have eight dots representing electrons when full shell is made Exceptions: (2 dots); e (2 dots); Group 3A (B, Al ) 6 dots; some transition metals and some elements at row 3 and below can have 10 or more dots. 4
5 Writing Electron Dot Formulas:The Octet Rule The octet rule states that representative elements usually attain stable noble gas electron configurations in most of their compounds. Electron dot formulas are based on the octet rule. 5
6 Writing Electron Dot Formulas:The Octet Rule Write the element symbol Write in a counter clockwise fashion, the valence electrons of the elements 6
7 Writing Electron Dot Formulas Determine the central atom Place the other atoms near the central atom Count the total number of valence electrons Make a single bond between the two atoms For a single bond, 2 dots 1 single bond Represent by Place the remaining electrons around each atom to give the atoms an octet (8 electrons, remember the exceptions) 7
8 Writing Electron Dot Formulas:The Octet Rule If the atoms do not get an octet before the electrons run out, use multiple bonds. For double bond, 4 dots double bond Represent by = For triple bond, 6 dots triple bond Represent by 8
9 Formation of Covalent Bonds 1.) molecule formation representation or 2 2. Cl molecule formation Cl..... Cl or Cl.... 9
10 Electron Dot Formulas for Molecules and Polyatomic Ions hydrogen fluoride, F. F or F hydrogen bromide, Br. Br or Br 10
11 Formation of Covalent Bonds 11
12 Writing Electron Dot Formulas:The Octet Rule Example 7-1: Write Lewis dot and dash formulas for silicon tetrafluoride, SiF 4. Total = 4 (Si) + 7x4 (F) = 32 Si is central atom, bonded to each of 4 F F F Si F F 8 electrons used for bonds (32-8=24) 24 electrons placed around the 4 Fs. 12
13 Writing Electron Dot Formulas:The Octet Rule F F Si F F Recount to make sure that all elements have 8 electrons 13
14 Writing Electron Dot Formulas:The Octet Rule Example 7-2: Write Lewis dot and dash formulas for hydrogen cyanide, CN. N = 1 () + 4 (C) + 5 (N) = 10 Carbon is central atom One bond to and one to N (4 electrons) 6 electrons left, but neither C or N have an octet Must share more electrons Triple bond give C 8 electrons and N 6 electrons. 2 left over sit on N to make 8 electrons C N or C N 14
15 Writing Electron Dot Formulas:Limitations of the Octet Rule Example 7-4: Write dot formulas for BBr 3. You do it! 15 Br B Br. B Br Br. or Br B Br Br
16 Naming Some Inorganic Compounds Covalent molecular compounds composed of two nonmetals other than hydrogen Nomenclature must include prefixes that specify the number of atoms of each element in the compound. Use the minimum number of prefixes necessary to specify the compound. Frequently drop the prefix mono-. 16
17 Naming Some Inorganic Compounds 17
18 Naming Some Inorganic Compounds Formula CO CO 2 SO 3 OF 2 P 4 O 6 Name carbon monoxide carbon dioxide sulfur trioxide oxygen difluoride You do it! 18
19 Naming Some Inorganic Compounds Formula CO CO 2 SO 3 OF 2 P 4 O 6 hexoxide P 4 O 10 Name carbon monoxide carbon dioxide sulfur trioxide oxygen difluoride tetraphosphorus You do it! 19
20 Naming Some Inorganic Compounds Formula CO?? SO 3?? P 4 O 6?? Name carbon monoxide carbon dioxide sulfur trioxide oxygen difluoride tetraphosphorus hexoxide tetraphosphorus decoxide 20
21 Naming Some Inorganic Compounds Formula N 2 O NO N 2 O 3 NO 2???? Modern Name dinitrogen monoxide nitrogen monoxide dinitrogen trioxide nitrogen dioxide dinitrogen tetroxide dinitrogen pentoxide 21
22 Covalent Compound Naming Review 22
23 Covalent Compound Naming Review 23
24 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds in which the electrons are shared equally are designated as nonpolar covalent bonds. Nonpolar covalent bonds have a symmetrical charge distribution. To be nonpolar the two atoms involved in the bond must be the same element or have the similar electronegativity to share equally. 24
25 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Bonds Some examples of nonpolar covalent bonds.. or 2 N 2 N N or N N 25
26 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds in which the electrons are not shared equally are designated as polar covalent bonds Polar covalent bonds have an asymmetrical charge distribution To be a polar covalent bond the two atoms involved in the bond must have different electronegativities. 26
27 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Bonds Some examples of polar covalent bonds. F Electronegativities F Difference = 1.9 very polar bond 27
28 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Bonds 28
29 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Bonds 29
30 Dipole Moments Molecules whose centers of positive and negative charge do not coincide, have an asymmetric charge distribution, and are polar. These molecules have a dipole moment. The dipole moment has the symbol µ. 30 δ Fδ 1.91 Debye units δ I δ 0.38 Debye units
31 Dipole Moments There are some nonpolar molecules that have polar bonds. There are two conditions that must be true for a molecule to be polar. 1. There must be at least one polar bond present or one lone pair of electrons. 2. The polar bonds, if there are more than one, and lone pairs must be arranged so that their dipole moments do not cancel one another. 31
32 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Bonds 32
33 VSEPR TEORY Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Commonly designated as VSEPR Principal originator R. J. Gillespie in the 1950 s Arrange electrons as far apart as possible to minimize repulsion Give the shape of the molecule 33
34 Predicting Shapes The same basic approach will be used in every example of molecular structure prediction: 1. Draw the correct Electron dot structure. Identify the central atom. Designate the bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons on central atom. 2. Count the regions of high electron density on the central atom. Include both bonding and lone pairs in the counting. 34
35 Predicting Shapes 3. Determine the electronic geometry around the central atom. VSEPR is a guide to the geometry. 4. Determine the molecular geometry around the central atom. Ignore the lone pairs of electrons. 5. Determine polarity from the molecular geometry using electronegativity differences. 35
36 VSEPR Theory Regions of high electron density around the central atom are arranged as far apart as possible to minimize repulsions. There are 5 basic molecular shapes that we will use. 36
37 VSEPR Theory 1 Two regions of high electron density around the central atom. 37
38 VSEPR Theory 2 Three regions of high electron density around the central atom. 38
39 VSEPR Theory 3 Four regions of high electron density around the central atom. 39
40 40
41 VSEPR Theory Frequently, we describe two geometries for each molecule. 1. Electronic geometry is determined by the locations of regions of high electron density around the central atom(s). 2. Molecular geometry determined by the arrangement of atoms around the central atom(s). Electron pairs are not used in the molecular geometry determination just the positions of the atoms in the molecule are used. 41
42 VSEPR Theory An example of a molecule that has the same electronic and molecular geometries is methane - C 4. Electronic and molecular geometries are tetrahedral. 42 C
43 VSEPR Theory An example of a molecule that has different electronic and molecular geometries is water - 2 O. Electronic geometry is tetrahedral. Molecular geometry is bent or angular. C 43
44 Polar Molecules: The Influence of Molecular Geometry Molecular geometry affects molecular polarity. Due to the effect of the bond dipoles and how they either cancel or reinforce each other. 44 A B A linear molecule nonpolar A B A angular molecule polar
45 Polar Molecules: The Influence of Molecular Geometry Polar Molecules must meet two requirements: 1. One polar bond or one lone pair of electrons on central atom. 2. Neither bonds nor lone pairs can be symmetrically arranged that their polarities cancel. 45
46 Molecular Shapes and Bonding A = central atom B = bonding pairs around central atom U = lone pairs around central atom For example: AB 3 U designates that there are 3 bonding pairs and 1 lone pair around the central atom. 46
47 Linear Electronic Geometry:AB 2 Species Some examples of molecules with this geometry are: BeCl 2, BeBr 2,BeI 2, gcl 2, CdCl 2 All of these examples are linear, nonpolar molecules. Important exceptions occur when the two substituents are not the same! BeClBr or BeIBr will be linear and polar! 47
48 Linear Electronic Geometry:AB 2 Species Dot Formula Cl Be Cl Electronic Geometry Cl Be Cl 180 o - linear 48
49 Linear Electronic Geometry:AB 2 Species A) Molecular Geometry Cl Be Cl 180 o -linear Electronegativities Cl Polarity - Be Cl bond dipolesare 2.0 symmetric 2.0 very polar bonds - Cl Be- - - Cl nonpolar molecule 49 C
50 Trigonal Planar Electronic Geometry: AB 3 Species Some examples of molecules with this geometry are: BF 3, BCl 3 All of these examples are trigonal planar, nonpolar molecules. Important exceptions occur when the three substituents are not the same! BF 2 Cl or BCI 2 Br will be trigonal planar and polar! 50
51 Trigonal Planar Electronic Geometry: AB 3 Species Dot Formula Cl B Cl Cl Electronic Geometry B 120-trigonal planar 51
52 Trigonal Planar Electronic Geometry: AB 3 Species Molecular Geometry Polarity Cl B Cl Cl 120 o -trigonal planar Cl B Electronegativities Cl Cl B - Cl very polar bonds bond dipoles are symmetric nonpolar molecule 52 C
53 Tetrahedral Electronic Geometry: AB 4 Species Some examples of molecules with this geometry are: C 4, CF 4, CCl 4, Si 4, SiF 4 All of these examples are tetrahedral, nonpolar molecules. Important exceptions occur when the four substituents are not the same! CF 3 Cl or C 2 CI 2 will be tetrahedral and polar! 53
54 Tetrahedral Electronic Geometry: AB 4 Species 54
55 Tetrahedral Electronic Geometry: AB 4 Species Dot Formula.... C C.. Electronic Geometry..... tetrahedral o bond angles. 55
56 Tetrahedral Electronic Geometry: AB 4 Species Molecular Geometry C tetrahedral Electronegativities Polarity C C slightly polar bonds symmetric dipoles nonpolar molecule 56 C
57 57 Tetrahedral Electronic Geometry: AB 3 U Some examples of molecules with this geometry are: N 3, NF 3, P 3, PCl 3, As 3 These molecules are our first examples of central atoms with lone pairs of electrons. Thus, the electronic and molecular geometries are different. All three substituents are the same but molecule is polar. N 3 and NF 3 are trigonal pyramidal, polar molecules.
58 Tetrahedral Electronic Geometry: AB 3 U Species Dot Formulas Electronic Geometry N F. N. F F... N.. tetrahedral......
59 Tetrahedral Electronic Geometry: AB 3 U Species Molecular Geometry 1 lo n e p a ir p y r a m 1 lo n e p a ir 59 F.. N.. N p y r a m F id a l F id a l.. N Electronegativities very polar bonds N Electronegativities F F Polarity N - asym m etrical dipoles polar m olecule µ = 1.5 D.. C F asym m etrical dipoles polar m olecule µ = 0.2 D bond dipoles reinforce effect of lone pair bond dipoles oppose N - effect F of lone pair very polar bonds
60 Tetrahedral Electronic Geometry: AB 2 U 2 Species Some examples of molecules with this geometry are: 2 O, OF 2, 2 S These molecules are our first examples of central atoms with two lone pairs of electrons. Thus, the electronic and molecular geometries are different. Both substituents are the same but molecule is polar. Molecules are angular, bent, or V-shaped and polar. 60
61 Tetrahedral Electronic Geometry: AB 2 U 2 Species Molecular Geometry O bent, angular or V-shaped 2 lone pairs Electronegativities O Polarity bond dipoles reinforce O - lone pairs very polar bonds C asymetric dipoles very polar molecule µ 1.7 D 61
62 Tetrahedral Electronic Geometry: ABU 3 Species Some examples of molecules with this geometry are: F, Cl, Br, I, FCl, IBr These molecules are examples of central atoms with three lone pairs of electrons. Again, the electronic and molecular geometries are different. Molecules are linear and polar when the two atoms are different. Cl 2, Br 2, I 2 are nonpolar. 62
63 Tetrahedral Electronic Geometry: ABU 3 Species Dot Formula F Electronic Geometry F tetrahedral 63
64 Tetrahedral Electronic Geometry: ABU 3 Species Molecular Geometry Polarity F is a polar molecule. F 3 lone pairs C linear 64
CHAPTER 8. Molecular Structure & Covalent Bonding Theories
 CAPTER 8 Molecular Structure & Covalent Bonding Theories 1 Chapter Goals 1. A Preview of the Chapter 2. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory 3. Polar Molecules:The Influence of Molecular
CAPTER 8 Molecular Structure & Covalent Bonding Theories 1 Chapter Goals 1. A Preview of the Chapter 2. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory 3. Polar Molecules:The Influence of Molecular
Chapter 4 Lecture Outline. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 4 Lecture Outline 1 Copyright McGraw-ill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Introduction to Covalent Bonding Covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons between
Chapter 4 Lecture Outline 1 Copyright McGraw-ill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Introduction to Covalent Bonding Covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons between
4/25/2017. VSEPR Theory. Two Electron Groups. Shapes of Molecules. Two Electron Groups with Double Bonds. Three Electron Groups.
 Chapter 10 Lecture Chapter 10 Bonding and Properties of Solids and Liquids 10.3 Shapes of Molecules and Ions (VSEPR Theory) Learning Goal Predict the three-dimensional structure of a molecule or a polyatomic
Chapter 10 Lecture Chapter 10 Bonding and Properties of Solids and Liquids 10.3 Shapes of Molecules and Ions (VSEPR Theory) Learning Goal Predict the three-dimensional structure of a molecule or a polyatomic
Hybridization and Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory
 ybridization and Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory Chapter 10 istorical Models G.N.Lewis and I. Langmuir (~1920) laid out foundations Ionic species were formed by electron transfer Covalent molecules arise
ybridization and Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory Chapter 10 istorical Models G.N.Lewis and I. Langmuir (~1920) laid out foundations Ionic species were formed by electron transfer Covalent molecules arise
Honors Chemistry Unit 6 ( )
 Honors Chemistry Unit 6 (2017-2018) Lewis Dot Structures VSEPR Structures 1 We are learning to: 1. Represent compounds with Lewis structures. 2. Apply the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry
Honors Chemistry Unit 6 (2017-2018) Lewis Dot Structures VSEPR Structures 1 We are learning to: 1. Represent compounds with Lewis structures. 2. Apply the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry
4/7/2017. Chapter 5. Chemical Bonding: The Covalent Bond Model
 Chapter 5. Chemical Bonding: The Covalent Bond Model Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor all ; Phone:
Chapter 5. Chemical Bonding: The Covalent Bond Model Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor all ; Phone:
Bonding: Part Two. Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond. transfer valence e - Metallic bond. (NaCl) (Fe) mobile valence e - Covalent bond
 Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction
 Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent
Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent
REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS CHEMICAL BONDS: LEWIS SYMBOLS: CHEMICAL BONDING. What are valence electrons?
 REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS 13 CHEMICAL BONDING What are valence electrons? Which groups on the periodic table readily give up electrons? What group readily accepts electrons? CHEMICAL BONDS: What are chemical
REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS 13 CHEMICAL BONDING What are valence electrons? Which groups on the periodic table readily give up electrons? What group readily accepts electrons? CHEMICAL BONDS: What are chemical
Lewis Dot Formulas and Molecular Shapes
 Lewis Dot Formulas and Molecular Shapes Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent chemical bonds are formed by valence electrons
Lewis Dot Formulas and Molecular Shapes Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent chemical bonds are formed by valence electrons
Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Learning Objective
 Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry 11.1 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Discuss the atomic trends Metals are located on the left side of the periodic
Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry 11.1 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Discuss the atomic trends Metals are located on the left side of the periodic
Lewis Structures and Molecular Shapes
 Lewis Structures and Molecular Shapes Drawing Lewis Structures Determine from formula if ionic or covalent Count the electrons If ionic : add valence # to charge if (-), subtract if (+) - = 7+1 electrons;
Lewis Structures and Molecular Shapes Drawing Lewis Structures Determine from formula if ionic or covalent Count the electrons If ionic : add valence # to charge if (-), subtract if (+) - = 7+1 electrons;
CHEMICAL BONDING. Chemical Bonds. Ionic Bonding. Lewis Symbols
 CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
Bonding: Part Two. Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond. transfer valence e - Metallic bond. (NaCl) (Fe) mobile valence e - Covalent bond
 Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Covalent Bonds Ch. Why do atoms bond? Atoms want noble gas configuration ( ) For bonds there is a transfer of electrons to get an octet of electrons
 Covalent Bonds Ch. Why do atoms bond? Atoms want noble gas configuration ( ) For bonds there is a transfer of electrons to get an octet of electrons For covalent bonds there is a of electrons to get an
Covalent Bonds Ch. Why do atoms bond? Atoms want noble gas configuration ( ) For bonds there is a transfer of electrons to get an octet of electrons For covalent bonds there is a of electrons to get an
LET S FIRST REVIEW IONIC BONDING
 COVALENT BONDING LET S FIRST REVIEW IONIC BONDING In an IONIC bond, electrons are lost or gained, resulting in the formation of IONS in ionic compounds. K F K F K F K F K F K F K + F _ The compound potassium
COVALENT BONDING LET S FIRST REVIEW IONIC BONDING In an IONIC bond, electrons are lost or gained, resulting in the formation of IONS in ionic compounds. K F K F K F K F K F K F K + F _ The compound potassium
CP Covalent Bonds Ch. 8 &
 CP Covalent Bonds Ch. 8 & 9 2015-2016 Why do atoms bond? Atoms want stability- to achieve a noble gas configuration ( ) For bonds there is a transfer of electrons to get an octet of electrons For covalent
CP Covalent Bonds Ch. 8 & 9 2015-2016 Why do atoms bond? Atoms want stability- to achieve a noble gas configuration ( ) For bonds there is a transfer of electrons to get an octet of electrons For covalent
Chemical bonding is the combining of elements to form new substances.
 Name Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature: Unit Objective Study Guide Class Period Date Due 1. Define chemical bonding. What is chemical bonding? Chemical bonding is the combining of elements to form new
Name Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature: Unit Objective Study Guide Class Period Date Due 1. Define chemical bonding. What is chemical bonding? Chemical bonding is the combining of elements to form new
Molecular Geometry & Polarity
 Molecular Geometry & Polarity Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized
Molecular Geometry & Polarity Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized
Chemical Bonds. Chapter 6
 Chemical Bonds Chapter 6 1 Ch. 6 Chemical Bonding I. How and Why Atoms Bond A. Vocabulary B. Chemical Bonds - Basics C. Chemical Bonds Types D. Chemical Bonds Covalent E. Drawing Lewis Diagrams F. Bond
Chemical Bonds Chapter 6 1 Ch. 6 Chemical Bonding I. How and Why Atoms Bond A. Vocabulary B. Chemical Bonds - Basics C. Chemical Bonds Types D. Chemical Bonds Covalent E. Drawing Lewis Diagrams F. Bond
4.2.7 & Shapes, and bond angles for molecules with two, three and four negative charge centers
 4.2.7 & 4.2.8 Shapes, and bond angles for molecules with two, three and four negative charge centers The shape of a molecule has an important part to play in determining its chemical (e.g. reactivity and
4.2.7 & 4.2.8 Shapes, and bond angles for molecules with two, three and four negative charge centers The shape of a molecule has an important part to play in determining its chemical (e.g. reactivity and
Class Period. 4. What distinguishes a polar covalent bond from a nonpolar covalent bond?
 Cut along dotted line. Name Assignment #1 Chemical Bonding (Predicting Bond Types) 1. What is a chemical bond? 2. Why do atoms form chemical bonds? 3. What distinguishes an ionic bond from a covalent bond?
Cut along dotted line. Name Assignment #1 Chemical Bonding (Predicting Bond Types) 1. What is a chemical bond? 2. Why do atoms form chemical bonds? 3. What distinguishes an ionic bond from a covalent bond?
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Covalent Practice CP November 2015 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Bromine, atomic number 35, belongs to Group 17. How many electrons does
Covalent Practice CP November 2015 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Bromine, atomic number 35, belongs to Group 17. How many electrons does
Chemical Bonding II. Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds Hybridization MO theory
 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Models
 25 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Models A chemical bond is a force that holds groups of two or more atoms together and makes them function as a unit. Bonding involves only the valence (outer shell) electrons
25 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Models A chemical bond is a force that holds groups of two or more atoms together and makes them function as a unit. Bonding involves only the valence (outer shell) electrons
RESONANCE STRUCTURE When a molecule has more than one possible structure. Draw all possible structures and place a double end arrow ( ) in between.
 CHEMISTRY NOTES 6.1 COVALENT BONDS Objectives Explain the role and location of electrons in a covalent bond. Describe the change in energy and stability that takes place as a covalent bond forms. Distinguish
CHEMISTRY NOTES 6.1 COVALENT BONDS Objectives Explain the role and location of electrons in a covalent bond. Describe the change in energy and stability that takes place as a covalent bond forms. Distinguish
Section 12: Lewis Structures
 Section 12: Lewis Structures The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 12.01 Electronegativity Chemistry (5)(C) 12.02 Electron
Section 12: Lewis Structures The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 12.01 Electronegativity Chemistry (5)(C) 12.02 Electron
CH 222 Chapter Seven Concept Guide
 CH 222 Chapter Seven Concept Guide 1. Lewis Structures Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for cyanide ion, CN -. 1 C at 4 electrons = 4 electrons 1 N at 5 electrons = 5 electrons -1 charge = + 1 electron Total
CH 222 Chapter Seven Concept Guide 1. Lewis Structures Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for cyanide ion, CN -. 1 C at 4 electrons = 4 electrons 1 N at 5 electrons = 5 electrons -1 charge = + 1 electron Total
Lewis Theory of Shapes and Polarities of Molecules
 Lewis Theory of Shapes and Polarities of Molecules Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Molecular Shape or Geometry The way in which atoms of a molecule are arranged in space
Lewis Theory of Shapes and Polarities of Molecules Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Molecular Shape or Geometry The way in which atoms of a molecule are arranged in space
Chapter 12 Structures and Characteristics of Bonds Objectives
 Objectives 1. To learn about ionic and covalent bonds and explain how they are formed - what holds compounds together? 2. To learn about the polar covalent bond are all covalent bonds equal? 3. To understand
Objectives 1. To learn about ionic and covalent bonds and explain how they are formed - what holds compounds together? 2. To learn about the polar covalent bond are all covalent bonds equal? 3. To understand
Fill in the chart below to determine the valence electrons of elements 3-10
 Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Chapter 13: Phenomena
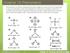 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Molecular Geometry. Valence Shell Electron Pair. What Determines the Shape of a Molecule? Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) Localized Electron Model
 Molecular Geometry Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized Electron
Molecular Geometry Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized Electron
Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Now explore the Compare Two Structures link. Try changing the display to explore different combinations.
 Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Exploring The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model. Go to the Purdue University website to explore VSEPR theory. http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/vsepr/structur2.html
Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Exploring The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model. Go to the Purdue University website to explore VSEPR theory. http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/vsepr/structur2.html
6.1 Intro to Chemical Bonding Name:
 6.1 Intro to Chemical Bonding Name: A. Chemical bond Favored by nature because: 3 main types of bonds 1. 2. 3. B. Ionic Bonds C. Covalent Bonds D. Metallic Bond E. Bond Determination RECALL: Electronegativity
6.1 Intro to Chemical Bonding Name: A. Chemical bond Favored by nature because: 3 main types of bonds 1. 2. 3. B. Ionic Bonds C. Covalent Bonds D. Metallic Bond E. Bond Determination RECALL: Electronegativity
Test Bank for Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition by Tro
 Test Bank for Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition by Tro Sample Introductory Chemistry, 5e (Tro) Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding 10.1 True/False Questions 1) Bonding theories are used to predict
Test Bank for Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition by Tro Sample Introductory Chemistry, 5e (Tro) Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding 10.1 True/False Questions 1) Bonding theories are used to predict
Chapter 12. Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chapter 12 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell (highest energy level) of an atom. A chemical bond is a mutual
Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chapter 12 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell (highest energy level) of an atom. A chemical bond is a mutual
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Section Chapter 8: Covalent Bonding CHAPTER 8 Table Of Contents Section 8.2 Section 8.3 Section 8.4 Section 8.5 Naming Molecules Molecular Structures Molecular Shapes Electronegativity
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Section Chapter 8: Covalent Bonding CHAPTER 8 Table Of Contents Section 8.2 Section 8.3 Section 8.4 Section 8.5 Naming Molecules Molecular Structures Molecular Shapes Electronegativity
Intramolecular Bonding. Chapters 4, 12 Chemistry Mr. McKenzie
 Intramolecular Bonding Chapters 4, 12 Chemistry Mr. McKenzie What determines the type of intramolecular bond? An intramolecular bond is any force that holds two atoms together to form a compound; 3 types
Intramolecular Bonding Chapters 4, 12 Chemistry Mr. McKenzie What determines the type of intramolecular bond? An intramolecular bond is any force that holds two atoms together to form a compound; 3 types
Chapter 10. Valence Electrons. Lewis dot symbols. Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding Valence Electrons Recall: the outer electrons in an atom are valence electrons. Valence electrons are related to stability Valence electrons can be represented with dots in
Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding Valence Electrons Recall: the outer electrons in an atom are valence electrons. Valence electrons are related to stability Valence electrons can be represented with dots in
Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry
 Experiment 11 Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. Purpose
Experiment 11 Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. Purpose
Name Date Class MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS. Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides
 8.1 MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Section Review Objectives Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides Vocabulary covalent bond molecule diatomic molecule
8.1 MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Section Review Objectives Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides Vocabulary covalent bond molecule diatomic molecule
(A) 1 bonding pair (B) 1 bonding pair and 1 lone pair (C) 2 bonding pairs (D) 2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs
 AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 13: Lewis Structures and VSPER No. 1 of 10 1. Lewis structure is used to model covalent bonds of a molecule or ion. Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bonding formed by
AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 13: Lewis Structures and VSPER No. 1 of 10 1. Lewis structure is used to model covalent bonds of a molecule or ion. Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bonding formed by
Chemistry 51 Chapter 5 OCTET RULE & IONS
 OCTET RULE & IONS Most elements, except noble gases, combine to form compounds. Compounds are the result of the formation of chemical bonds between two or more different elements. In the formation of a
OCTET RULE & IONS Most elements, except noble gases, combine to form compounds. Compounds are the result of the formation of chemical bonds between two or more different elements. In the formation of a
Ionic Versus Covalent Bonding. Covalent Bonding. Covalent Bonding H 2. Covalent Bonding. Keywords:
 Keywords: Covalent Bonding Valence electron Covalent bonding Single, double and triple bonds Bonding electrons and Non-bonding electrons (lone pair of electrons) Bond energy and bond length Electronegativity
Keywords: Covalent Bonding Valence electron Covalent bonding Single, double and triple bonds Bonding electrons and Non-bonding electrons (lone pair of electrons) Bond energy and bond length Electronegativity
Experiment #2. Lewis Structures
 Experiment #2. Lewis Structures A Lewis structure shows how the valence electrons are arranged and indicates the bonding between atoms in a molecule. We represent the elements by their symbols. The shared
Experiment #2. Lewis Structures A Lewis structure shows how the valence electrons are arranged and indicates the bonding between atoms in a molecule. We represent the elements by their symbols. The shared
MOLECULAR MODELS OBJECTIVES
 MOLECULAR MODELS OBJECTIVES 1. To learn to draw Lewis structures for common compounds 2. To identify electron pairs as bonding pairs or lone pairs 3. To use electron pair repulsion theory to predict electronic
MOLECULAR MODELS OBJECTIVES 1. To learn to draw Lewis structures for common compounds 2. To identify electron pairs as bonding pairs or lone pairs 3. To use electron pair repulsion theory to predict electronic
CHAPTER 6: CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS CHAPTER 16: COVALENT BONDING
 CHAPTER 6: CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS CHAPTER 16: COVALENT BONDING 6.1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding A chemical bond is a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different
CHAPTER 6: CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS CHAPTER 16: COVALENT BONDING 6.1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding A chemical bond is a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different
Covalent bonding occurs in nonmetal compounds. Use the highlighter to select the compounds that are covalently bonded. HCl
 Covalent bonding occurs in nonmetal compounds. Use the highlighter to select the compounds that are covalently bonded. 2 C 2 Cl Li NaF Mg C 4 N NaCl 3 Drag this to the target to reveal the answers. Properties
Covalent bonding occurs in nonmetal compounds. Use the highlighter to select the compounds that are covalently bonded. 2 C 2 Cl Li NaF Mg C 4 N NaCl 3 Drag this to the target to reveal the answers. Properties
Structures, Shapes and Polarity. of Molecules. Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity
 Structures, Shapes and Polarity Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity of Molecules Do now: Brainstorm what you know/remember about these L2 concepts
Structures, Shapes and Polarity Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity of Molecules Do now: Brainstorm what you know/remember about these L2 concepts
Lesson 11: Covalent Bonding
 NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lesson 11: Covalent Bonding Reminder: List of Information you can get from the Periodic Table 1. Groups/families and their names 2. Periods 3. Period number = number of electron
NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lesson 11: Covalent Bonding Reminder: List of Information you can get from the Periodic Table 1. Groups/families and their names 2. Periods 3. Period number = number of electron
CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING
 Chemistry Name Hour Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING Day Plans for the day Assignment(s) for the day 1 Begin Chapter
Chemistry Name Hour Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING Day Plans for the day Assignment(s) for the day 1 Begin Chapter
Chapter 6. The Chemical Bond
 Chapter 6 The Chemical Bond Some questions Why do noble gases rarely bond to other elements? How does this relate to why the atoms of other elements do form bonds? Why do certain elements combine to form
Chapter 6 The Chemical Bond Some questions Why do noble gases rarely bond to other elements? How does this relate to why the atoms of other elements do form bonds? Why do certain elements combine to form
Ionic and Covalent Compounds: Structures and Properties Examples of Lewis Dot Structures for the Representative Elements
 Ionic and Covalent Compounds: Structures and Properties Examples of Lewis Dot Structures for the Representative Elements Chemical bond: Attractive force between 2 atoms in a compound Lewis Dot Structure:
Ionic and Covalent Compounds: Structures and Properties Examples of Lewis Dot Structures for the Representative Elements Chemical bond: Attractive force between 2 atoms in a compound Lewis Dot Structure:
COVALENT COMPOUNDS. Back to Lewis Dot Structures and Valence Electrons!
 COVALENT COMPOUNDS Back to Lewis Dot Structures and Valence Electrons! Review of Lewis Dot Structures Electron Dot Structures contain: Element s Symbol: representing the atom s nucleus and inner electrons
COVALENT COMPOUNDS Back to Lewis Dot Structures and Valence Electrons! Review of Lewis Dot Structures Electron Dot Structures contain: Element s Symbol: representing the atom s nucleus and inner electrons
Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY
 Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES (covalent bonding) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of covalent molecules (octet rule such as NH 3, CCl 4, H 2 O, CO 2, N 2 O 4, and exception to
Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES (covalent bonding) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of covalent molecules (octet rule such as NH 3, CCl 4, H 2 O, CO 2, N 2 O 4, and exception to
Covalent & Metallic Bonding
 Covalent & Metallic Bonding Metallic Bonding Metals are made of closely packed cations. These cations have a number of valence electrons floating around them as what we call a sea of electrons. Metallic
Covalent & Metallic Bonding Metallic Bonding Metals are made of closely packed cations. These cations have a number of valence electrons floating around them as what we call a sea of electrons. Metallic
CHAPTER 12: CHEMICAL BONDING
 CHAPTER 12: CHEMICAL BONDING Problems: 1-26, 27c, 28, 33-34, 35b, 36(a-c), 37(a,b,d), 38a, 39-40, 41-42(a,c), 43-58, 67-74 12.1 THE CHEMICAL BOND CONCEPT chemical bond: what holds atoms or ions together
CHAPTER 12: CHEMICAL BONDING Problems: 1-26, 27c, 28, 33-34, 35b, 36(a-c), 37(a,b,d), 38a, 39-40, 41-42(a,c), 43-58, 67-74 12.1 THE CHEMICAL BOND CONCEPT chemical bond: what holds atoms or ions together
Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules
 Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Chapter 8: Covalent Bonding. Chapter 8
 : Covalent Bonding Bonding Ionic Bonding - attracted to each other, but not fully committed Covalent Bonding - fully committed, and shares everything Two methods to gain or lose valence electrons: Transfer
: Covalent Bonding Bonding Ionic Bonding - attracted to each other, but not fully committed Covalent Bonding - fully committed, and shares everything Two methods to gain or lose valence electrons: Transfer
Chem 1075 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Lecture Outline. Chemical Bond Concept
 Chem 1075 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Lecture Outline Slide 2 Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has and electrons. Core electrons are found to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the s
Chem 1075 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Lecture Outline Slide 2 Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has and electrons. Core electrons are found to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the s
C N O F. Carbon dioxide Triphosphorus pentoxide C 6 H 6 BF 3 I 5 H 10. Tetracarbon nonahydride. Dihydrogen monoxide
 NAMING COVALENT COMPOUNDS TYPES OF BONDS FORMED ELECTRONS & BONDS BOND FORMATION COVALENT BONDING A covalent bond forms between 2 elements because they one share or more pairs of valence electrons between
NAMING COVALENT COMPOUNDS TYPES OF BONDS FORMED ELECTRONS & BONDS BOND FORMATION COVALENT BONDING A covalent bond forms between 2 elements because they one share or more pairs of valence electrons between
Chapter 12 Structure and Shape
 Free Study Guide for Cracolice Peters Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach Second Edition www.brookscole.com/chemistry Chapter 12 Structure and Shape Chapter 12Assignment A: Lewis Diagrams
Free Study Guide for Cracolice Peters Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach Second Edition www.brookscole.com/chemistry Chapter 12 Structure and Shape Chapter 12Assignment A: Lewis Diagrams
MONDAY, Dec. 8: COVALENT NOMENCLATURE Name the following covalent compounds. 1) P 4 S 5 2) O 2 3) SeF 6 4) Si 2 Br 6 5) SCl 4 6) CH 4
 MONDAY, Dec. 8: COVALENT NOMENCLATURE Name the following covalent compounds. 1) P 4 S 5 2) O 2 3) Se 6 4) Si 2 Br 6 5) SCl 4 6) CH 4 December 10, 2014 Write the formulas for the following covalent compounds.
MONDAY, Dec. 8: COVALENT NOMENCLATURE Name the following covalent compounds. 1) P 4 S 5 2) O 2 3) Se 6 4) Si 2 Br 6 5) SCl 4 6) CH 4 December 10, 2014 Write the formulas for the following covalent compounds.
What is Bonding? The Octet Rule. Getting an Octet. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Shapes. (Chapter Three, Part Two)
 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Shapes (Chapter Three, Part Two) What is Bonding? Bonding describes how atoms interact with each other in an attractive sense. There are three types of bonding: Ionic bonding
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Shapes (Chapter Three, Part Two) What is Bonding? Bonding describes how atoms interact with each other in an attractive sense. There are three types of bonding: Ionic bonding
CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions
 CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions 1D 1 has a triple bond. 2 has a double bond. 3 and 4 have single bonds. The stronger the bond, the shorter the length. 2A A 1:1 ratio means there must be the
CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions 1D 1 has a triple bond. 2 has a double bond. 3 and 4 have single bonds. The stronger the bond, the shorter the length. 2A A 1:1 ratio means there must be the
Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes
 Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes PRELAB ASSINGMENT Read the entire laboratory write up and answer the following questions before coming to lab. Read the entire laboratory write up
Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes PRELAB ASSINGMENT Read the entire laboratory write up and answer the following questions before coming to lab. Read the entire laboratory write up
At the end of this lesson, students should be able to :
 At the end of this lesson, students should be able to : (a) Explain Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory (VSEPR) (b) Draw the basic molecular shapes: linear, planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
At the end of this lesson, students should be able to : (a) Explain Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory (VSEPR) (b) Draw the basic molecular shapes: linear, planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
Covalent Bonding. Click a hyperlink or folder tab to view the corresponding slides. Exit
 Covalent Bonding Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond Section 8.2 Naming Molecules Section 8.3 Molecular Structures Section 8.4 Molecular Shapes Section 8.5 Electronegativity and Polarity Click a hyperlink or
Covalent Bonding Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond Section 8.2 Naming Molecules Section 8.3 Molecular Structures Section 8.4 Molecular Shapes Section 8.5 Electronegativity and Polarity Click a hyperlink or
Ionic and Covalent Bonding
 1. Define the following terms: a) valence electrons Ionic and Covalent Bonding the electrons in the highest occupied energy level always electrons in the s and p orbitals maximum of 8 valence electrons
1. Define the following terms: a) valence electrons Ionic and Covalent Bonding the electrons in the highest occupied energy level always electrons in the s and p orbitals maximum of 8 valence electrons
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 1
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. How to get the book of
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. How to get the book of
SKILL-BUILDING EXERCISE
 4. O and H Solution 1. Carbon has an electronegativity of 2.5, while the value for hydrogen is 2.1. The difference is 0.3, which is rather small. The C H bond is therefore considered nonpolar. 2. Both
4. O and H Solution 1. Carbon has an electronegativity of 2.5, while the value for hydrogen is 2.1. The difference is 0.3, which is rather small. The C H bond is therefore considered nonpolar. 2. Both
Chapter 8. Bonding: General Concepts
 Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Table of Contents 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds 8.3 Bond Polarity and Dipole Moments 8.5 Energy Effects in Binary Ionic Compounds 8.6 Partial Ionic Character
Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Table of Contents 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds 8.3 Bond Polarity and Dipole Moments 8.5 Energy Effects in Binary Ionic Compounds 8.6 Partial Ionic Character
Hey, Baby. You and I Have a Bond...Ch. 8
 I. IONIC BONDING FUNDAMENTALS A. They form between... 1. A and a a. A to become b. A to become B. How it happens (Let s first focus on two atoms): 1. When a metal and a nonmetal meet, electrons get transferred
I. IONIC BONDING FUNDAMENTALS A. They form between... 1. A and a a. A to become b. A to become B. How it happens (Let s first focus on two atoms): 1. When a metal and a nonmetal meet, electrons get transferred
Valence Shell Electron Pair repulsion
 Molecular Geometry Valence Shell Electron Pair repulsion The valence shell electron pair repulsion model (VSEPR model) assumes that electron pairs repel one another. (VSEPR) model gives helps determine
Molecular Geometry Valence Shell Electron Pair repulsion The valence shell electron pair repulsion model (VSEPR model) assumes that electron pairs repel one another. (VSEPR) model gives helps determine
Chem 121 Exam 4 Practice Exam
 Chem 121 Exam 4 Practice Exam 1. What is the correct electron configuration for bromine? b. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 9 4s 2 4p 6 c. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 5 d. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p
Chem 121 Exam 4 Practice Exam 1. What is the correct electron configuration for bromine? b. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 9 4s 2 4p 6 c. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 5 d. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p
CHM 151LL: Geometry of Covalent Compounds
 CM 151LL: Geometry of Covalent Compounds Introduction Octet Rule A Lewis structure (or electrondot formula) is a twodimensional structural formula showing the arrangement of electrons around atoms in covalently
CM 151LL: Geometry of Covalent Compounds Introduction Octet Rule A Lewis structure (or electrondot formula) is a twodimensional structural formula showing the arrangement of electrons around atoms in covalently
Covalent Bonding bonding that results from the sharing of electron pairs.
 Unit 5 Notes Covalent Bonding, Covalent Compounds, and Intermolecular Forces Chemical Bond a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms
Unit 5 Notes Covalent Bonding, Covalent Compounds, and Intermolecular Forces Chemical Bond a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms
Covalent Bonding. Click a hyperlink or folder tab to view the corresponding slides. Exit
 Covalent Bonding Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond Section 8.2 Naming Molecules Section 8.3 Molecular Structures Section 8.4 Molecular Shapes Section 8.5 Electronegativity and Polarity Click a hyperlink or
Covalent Bonding Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond Section 8.2 Naming Molecules Section 8.3 Molecular Structures Section 8.4 Molecular Shapes Section 8.5 Electronegativity and Polarity Click a hyperlink or
AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam
 AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is a correct Lewis structure for
AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is a correct Lewis structure for
Molecular Geometry. Objectives N H H. The objectives of this laboratory are to:
 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are to: Molecular Geometry Write Lewis structure representations of the bonding and valence electrons in molecules. Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular
Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are to: Molecular Geometry Write Lewis structure representations of the bonding and valence electrons in molecules. Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts
 Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts Types of Chemical Bonds Information about the strength of a bonding interaction is obtained by measuring the bond energy, which is the energy
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts Types of Chemical Bonds Information about the strength of a bonding interaction is obtained by measuring the bond energy, which is the energy
Chemical bonding & structure
 Chemical bonding & structure Ionic bonding and structure Covalent bonding Covalent structures Intermolecular forces Metallic bonding Ms. Thompson - SL Chemistry Wooster High School Topic 4.3 Covalent structures
Chemical bonding & structure Ionic bonding and structure Covalent bonding Covalent structures Intermolecular forces Metallic bonding Ms. Thompson - SL Chemistry Wooster High School Topic 4.3 Covalent structures
Ch 13: Covalent Bonding
 Ch 13: Covalent Bonding Section 13: Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion 1. Recall the rules for drawing Lewis dot structures 2. Remember the special situations: - Resonance structures - ormal charges
Ch 13: Covalent Bonding Section 13: Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion 1. Recall the rules for drawing Lewis dot structures 2. Remember the special situations: - Resonance structures - ormal charges
Chemistry and the material world Lecture 3
 Chemistry and the material world 123.102 Lecture 3 Electronic bookkeeping we need a way of finding out in which proportions two or more atoms make up a molecule is it CH 3 or CH 4 or CH 5? counting valence
Chemistry and the material world 123.102 Lecture 3 Electronic bookkeeping we need a way of finding out in which proportions two or more atoms make up a molecule is it CH 3 or CH 4 or CH 5? counting valence
NAME: Chapter 12, Test 1: Chemical Bonding. Total Question(s): 20 Here are the quiz answers, in review:
 NAME: Chapter 12, Test 1: Chemical Bonding Total Question(s): 20 Here are the quiz s, in review: 1.Elements whose electronegativities are similar will form bonds that are. (A) ionic (B) polar covalent
NAME: Chapter 12, Test 1: Chemical Bonding Total Question(s): 20 Here are the quiz s, in review: 1.Elements whose electronegativities are similar will form bonds that are. (A) ionic (B) polar covalent
Name Date Class. covalent bond molecule sigma bond exothermic pi bond
 Date Class 8 Covalent Bonding Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond In your textbook, read about the nature of covalent bonds. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. covalent bond molecule
Date Class 8 Covalent Bonding Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond In your textbook, read about the nature of covalent bonds. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. covalent bond molecule
VSEPR. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
 VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Vocabulary: domain = any electron pair or bond (single, double or triple) is considered one domain. bonding pair = shared pair = any electron pair that
VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Vocabulary: domain = any electron pair or bond (single, double or triple) is considered one domain. bonding pair = shared pair = any electron pair that
Chapter 8 H H H H. Molecular Compounds & Covalent Bonding. Why do covalent bonds form? 8.1 Molecular Compounds. Properties of Molecular Compounds
 Chapter 8 Molecular Compounds & Covalent Bonding Why do covalent bonds form? If only group 5A, 6A, 7A atoms existed, ionic bonds can t form. NNMETALS Each atom needs electrons so they are not willing to
Chapter 8 Molecular Compounds & Covalent Bonding Why do covalent bonds form? If only group 5A, 6A, 7A atoms existed, ionic bonds can t form. NNMETALS Each atom needs electrons so they are not willing to
Molecular Models: The shape of simple molecules and ions
 Molecular Models: The shape of simple molecules and ions Background The shape of a molecule is very important when investigating its properties and reactivity. For example, compare CO 2 and SO 2. Carbon
Molecular Models: The shape of simple molecules and ions Background The shape of a molecule is very important when investigating its properties and reactivity. For example, compare CO 2 and SO 2. Carbon
Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms.
 Chapter 9 CH 180 Major Concepts: Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms. Sublevels (s, p, d, & f) of separate atoms may overlap and result in hybrid orbitals
Chapter 9 CH 180 Major Concepts: Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms. Sublevels (s, p, d, & f) of separate atoms may overlap and result in hybrid orbitals
Chapter 12. Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has core and valence electrons. Core electrons are found close to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the most distant s and
Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has core and valence electrons. Core electrons are found close to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the most distant s and
Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017
 Unit Three: Bonding & Molecular Geometry Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017 1. What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom in water? a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) It is not hybridized 2. When a double
Unit Three: Bonding & Molecular Geometry Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017 1. What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom in water? a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) It is not hybridized 2. When a double
5. Chemical Bonding: The Covalent Bond Model 5.1 The Covalent Bond Model
 5. Chemical Bonding: The Covalent Bond Model 5.1 The Covalent Bond Model Almost all chemical substances are found as aggregates of atoms in the form of molecules and ions produced through the reactions
5. Chemical Bonding: The Covalent Bond Model 5.1 The Covalent Bond Model Almost all chemical substances are found as aggregates of atoms in the form of molecules and ions produced through the reactions
Check Your Solution A comparison with the figures in Figure 4.31 on page 234 of the student textbook confirms the results.
 Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
Assignment 09 A. 2- The image below depicts a seesaw structure. Which of the following has such a structure?
 Assignment 09 A 1- Give the total number of electron domains, the number of bonding and nonbonding domains, and the molecular geometry, respectively, for the central atom of P 3. a) four electron domains,
Assignment 09 A 1- Give the total number of electron domains, the number of bonding and nonbonding domains, and the molecular geometry, respectively, for the central atom of P 3. a) four electron domains,
For a quick and enjoyable introduction to Covalent vs Ionic Bonding watch this video:
 Covalent Bonding Covalent Bonding is the result of sharing of electron pairs between 2 nonmetal atoms Caution: sharing can be complicated Recall the Octet Rule: Atoms tend to gain, lose or share valence
Covalent Bonding Covalent Bonding is the result of sharing of electron pairs between 2 nonmetal atoms Caution: sharing can be complicated Recall the Octet Rule: Atoms tend to gain, lose or share valence
B. (i), (iii), and (v) C. (iv) D. (i), (ii), (iii), and (v) E. (i), (iii), (iv), and (v) Answer: B. SO 3, and NO 3 - both have 24 VE and have Lewis
 SCCH 161 Homework 3 1. Give the number of lone pairs around the central atom and the molecular geometry of CBr 4. Answer: Carbon has 4 valence electrons and bonds to four bromine atoms (each has 7 VE s).
SCCH 161 Homework 3 1. Give the number of lone pairs around the central atom and the molecular geometry of CBr 4. Answer: Carbon has 4 valence electrons and bonds to four bromine atoms (each has 7 VE s).
Chapter 16 Covalent Bonding
 Chemistry/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 16 Covalent Bonding Chapter 16: 1 26; 28, 30, 31, 35-37, 40, 43-46, Extra Credit: 50-53, 55, 56, 58, 59, 62-67 Section 16.1 The Nature of Covalent Bonding Practice Problems
Chemistry/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 16 Covalent Bonding Chapter 16: 1 26; 28, 30, 31, 35-37, 40, 43-46, Extra Credit: 50-53, 55, 56, 58, 59, 62-67 Section 16.1 The Nature of Covalent Bonding Practice Problems
A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE ETHANOL! Count valence electrons
 212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
