ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 9, 2016 The Game Changer. Some perspective The British Antarctic Survey The Ozone Hole International Regulations
|
|
|
- Alberta Hubbard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 9, 2016 The Game Changer Some perspective The British Antarctic Survey The Ozone Hole International Regulations
2 Rowland (1974): The work is going very well, but it may mean the end of the world. (quote to his wife after he realized the importance of his discovery) Industry pauses while it waits for word that ozone is, in fact, being depleted i.e., let scientists look for the smoking gun!
3 But by the mid-1980s, CFCs had risen dramatically in the atmosphere, yet studies failed to find any of the predicted ozone losses! This was a credibility issue for ozone scientists.
4 But by the mid-1980s, CFCs had risen dramatically in the atmosphere, yet studies failed to find any of the predicted ozone losses! This was a credibility issue for ozone scientists.
5 Before we talk about the ozone hole, let s take a quick look at why ozone losses from the buildup of CFCs that were predicted in the 1970s didn t materialize. When CFCs break down in the stratosphere, they certainly do release chlorine atoms: CF 3 Cl + UV Cl + CF 3 And, when chlorine atoms react with ozone, they start a catalytic cycle: Cl + O 3 ClO + O 2 ClO + O O 2 + Cl Net: O + O 3 O 2 + O 2 One complication is that ClO reacts with other molecules in the stratosphere to form compounds that do not destroy ozone.
6 We can use observations of ClO to define the catalytic loss rate of ozone due to chlorine. In the late 1970 s and early 1980 s, atmospheric researchers began looking for the smoking gun of ozone loss due to CFCs. This entailed measuring ozone, Cl, ClO, and O. When these results came in, it was clear that the reason for a lack of observed ozone loss from CFCs was that the reactive chlorine species Cl and ClO were much smaller than had been predicted. So, how do we explain this?
7 The complete chlorine cycle!! (page 348) These destroy ozone These reservoirs of chlorine do not destroy ozone
8 When we consider all these reactions, we find that most of the chlorine from CFCs ends up as HCl and ClONO 2 Cl + ClO + HOCl ClNO 3 5% 45% HCl 50%
9 By 1985, with improved understanding of chlorine photochemistry, it was clear that ozone losses expected from the amounts of CFCs already emitted to the atmosphere were much smaller than had been predicted. The was a sigh of relief, life went on, and many new and innovative uses for CFCs were found. Abundances once again increased in the atmosphere, with less worry about the consequences???
10 The pause ends, and industry comes up with many more beneficial uses of CFCs. Atmospheric abundances continue to increase.
11 Meanwhile, something strange had been brewing down under
12 Three theories were put forward at the time to explain the odd ozone observations of the British Antarctic Survey (1) Natural solar variability (which produces NO x at high altitudes) (2) Change in atmospheric circulation, with enhanced lofting of low-ozone, tropospheric air over Antarctica (3) A repartitioning of chlorine from unreactive forms (HCl + ClNO 3 ) to reactive forms (Cl + ClO)
13 Three theories were put forward at the time to explain the odd ozone observations of the British Antarctic Survey Balloon profiles of ozone ruled the first one out (1) Natural solar variability (which produces NO x at high altitudes) (2) Change in atmospheric circulation, with enhanced lofting of low-ozone, tropospheric air over Antarctica (3) A repartitioning of chlorine from unreactive forms (HCl + ClNO 3 ) to reactive forms (Cl + ClO)
14
15 Still not proof of ClO/ozone connection
16 The Smoking Gun came with aircraft measurements of ClO and ozone in 1987 (1) Ozone decreases from Aug to Sept only in the regions where ClO is high (2) ClO abundances of 1200 ppt are nearly 15 times higher than normal abundances of ClO at these altitudes (nearly 50% of the total chlorine, instead of the usual 2-3%) (3) The observed rate at which ozone decreases is equal to the rate calculated from the proposed photochemical reactions From Anderson, Toohey, and Brune (1991)
17 All that was left was to tie some of the unexpected pieces together. First, how was it that ozone losses occurred over Antarctica, and not everywhere? Up to now, scientists had ignored ozone chemistry in the cold, dark polar regions. This is because Chapman chemistry clearly shows that ultraviolet light is needed to make oxygen atoms (O), and O is a necessary reactant in all catalytic cycles known at the time. So without UV to photolyze ozone to produce O, ozone must have a very long lifetime over the polar regions. Second, it was known that the normal chemistry of the stratosphere partitions chlorine into the unreactive forms HCl and ClNO 3 (ClONO 2, chlorine nitrate). The only known way (in 1985) to convert HCl and ClNO 3 back into ClO involved ultraviolet light and reactions with OH (a species that is also formed by ultraviolet light). Clearly, the observations showed high ClO so something had to be converting HCl and ClNO 3 into ClO and clearly there was ozone loss without O atoms How could this be?
18 Three theories were proposed for catalytic cycles that did not require O atoms. Two of them ultimately were needed to explain the results: ClO + BrO and ClO + ClO. It took several years to confirm this in the laboratory.
19 The key to this heterogeneous chemistry is that relatively unreactive species HCl and ClNO 3 are converted into Cl 2, a molecule that is green and photolyzes in visible light, so ultraviolet light isn t required! This means that as soon as even the faintest sunlight appears over Antarctica, reactive chlorine is released from the more stable forms. As an added bonus, if the PSC particles grow large enough (> 20 µm in diameter), they fall out, carrying H 2 O and HNO 3 (nitric acid) with them The stranger piece of the puzzle was that laboratory work by Margaret Tolbert, coupled with Brian Toon s aerosol models, showed that at very low temperatures found only over the poles in winter, ice crystals form (they are called polar stratospheric clouds or PSCs) and that HCl and ClNO 3 react with each other on these clouds to produce Cl 2.
20 The heterogeneous ( two-phases ) reaction that occurs on PSCs is: HCl + ClNO 3 Cl 2 + HNO 3 This reaction does not occur when the gases HCl and ClNO 3 are put together in a bottle! The reason is that these neutral species don t react with each other. In order to react, they need to form ions, and this requires that they dissolve in water or ice. Amazingly, even at low temperatures, this ionic reaction becomes quite fast: (H + Cl - ) aq + (Cl + NO 3- ) aq (H + NO 3- ) aq + Cl 2(g) The subscripts aq and (g) refer to aqueous (in solution) and gaseous.
21 Note that this heterogeneous reaction also removes HNO 3 from the vapor phase. This is because HNO 3 is a very strong acid, so it remains in the ice crystals, until they evaporate. If they are large enough to sediment out of the stratosphere, they will remove the HNO 3 from the air. This has very important consequences. Without HNO 3, when bright sunlight returns to Antarctica there will be no way to regenerate NOx, and without NOx, ClO cannot be converted back into the reservoirs HCl and ClNO 3, so ozone loss just keeps going and going like the Energizer Bunny! HNO 3 + hν OH + NO 2 NO 2 + hν NO + O ClO + NO Cl + NO 2 Cl + CH 4 HCl + CH 3 ClO + NO 2 + M ClNO 3 + M
22 The final two pieces of the puzzle that solidly proved the connection between CFCs and ozone loss were studies by Webster et al. (right) and Toohey et al. (below) that showed that abundances of ClO rose sharply within the ozone hole and that this coincided with a decrease in HCl. and that this remarkable transformation occurred only when temperatures dropped below 198 K, precisely at the point where other studies showed that PSCs should form.
23 This might have been where the story ended. In 1989, the world agreed to cutbacks on production of CFCs and other ozone depleting substances. However, the previous studies by Webster and Toohey were carried out over the North Pole in 1992! Yet, at that time, no ozone hole had been observed there. Subsequent work by NASA showed that ozone indeed was decreasing dramatically over the North Pole and other parts of the earth. This sealed the fate of CFCs. By the end of the 1990s, du Pont voluntarily stopped producing CFCs.
Measurements of Ozone. Why is Ozone Important?
 Anthropogenic Climate Changes CO 2 CFC CH 4 Human production of freons (CFCs) Ozone Hole Depletion Human production of CO2 and CH4 Global Warming Human change of land use Deforestation (from Earth s Climate:
Anthropogenic Climate Changes CO 2 CFC CH 4 Human production of freons (CFCs) Ozone Hole Depletion Human production of CO2 and CH4 Global Warming Human change of land use Deforestation (from Earth s Climate:
ClO + O -> Cl + O 2 Net: O 3 + O -> O 2 + O 2
 Lecture 36. Stratospheric ozone chemistry. Part2: Threats against ozone. Objectives: 1. Chlorine chemistry. 2. Volcanic stratospheric aerosols. 3. Polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs). Readings: Turco: p.
Lecture 36. Stratospheric ozone chemistry. Part2: Threats against ozone. Objectives: 1. Chlorine chemistry. 2. Volcanic stratospheric aerosols. 3. Polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs). Readings: Turco: p.
 ATM 507 Lecture 9 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Next Class Tuesday, Sept. 30 Today s topics Polar Stratospheric Chemistry and the Ozone Hole, Required reading: 20 Questions and
ATM 507 Lecture 9 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Next Class Tuesday, Sept. 30 Today s topics Polar Stratospheric Chemistry and the Ozone Hole, Required reading: 20 Questions and
Lecture 15 Antarctic Ozone Hole ATOC/CHEM 5151
 Lecture 15 Antarctic Ozone Hole ATOC/CHEM 5151 1 Ozone Hole Theories 1. Solar activity: During periods of high solar activity, energetic particles are deposited high in the atmosphere, creating NOx. Perhaps
Lecture 15 Antarctic Ozone Hole ATOC/CHEM 5151 1 Ozone Hole Theories 1. Solar activity: During periods of high solar activity, energetic particles are deposited high in the atmosphere, creating NOx. Perhaps
2. Sketch a plot of R vs. z. Comment on the shape. Explain physically why R(z) has a maximum in the atmospheric column.
 190 PROBLEMS 10. 1 Shape of the ozone layer Consider a beam of solar radiation of wavelength λ propagating downward in the vertical direction with an actinic flux I at the top of the atmosphere. Assume
190 PROBLEMS 10. 1 Shape of the ozone layer Consider a beam of solar radiation of wavelength λ propagating downward in the vertical direction with an actinic flux I at the top of the atmosphere. Assume
Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven
 Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven Prevention of the atmosphere KÖRNYEZETGAZDÁLKODÁSI AGRÁRMÉRNÖKI MSC (MSc IN AGRO-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES) Fundamentals to atmospheric chemical reactions. The stratospheric
Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven Prevention of the atmosphere KÖRNYEZETGAZDÁLKODÁSI AGRÁRMÉRNÖKI MSC (MSc IN AGRO-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES) Fundamentals to atmospheric chemical reactions. The stratospheric
SUSTAINABILITY MATTERS FACT SHEET 7: THE HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER
 SUSTAINABILITY MATTERS FACT SHEET 7: THE HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER What is the ozone layer? Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen, which means it is a pure element, but has a different chemical structure to that
SUSTAINABILITY MATTERS FACT SHEET 7: THE HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER What is the ozone layer? Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen, which means it is a pure element, but has a different chemical structure to that
Atmospheric Chemistry III
 Atmospheric Chemistry III Chapman chemistry, catalytic cycles: reminder Source of catalysts, transport to stratosphere: reminder Effect of major (O 2 ) and minor (N 2 O, CH 4 ) biogenic gases on [O 3 ]:
Atmospheric Chemistry III Chapman chemistry, catalytic cycles: reminder Source of catalysts, transport to stratosphere: reminder Effect of major (O 2 ) and minor (N 2 O, CH 4 ) biogenic gases on [O 3 ]:
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Air Pollution Chemistry Lecture 1
 ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Air Pollution Chemistry Lecture 1 Note Page numbers refer to Daniel Jacob s online textbook: http://acmg.seas.harvard.edu/publications/ jacobbook/index.html Atmos = vapor + sphaira
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Air Pollution Chemistry Lecture 1 Note Page numbers refer to Daniel Jacob s online textbook: http://acmg.seas.harvard.edu/publications/ jacobbook/index.html Atmos = vapor + sphaira
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 31. Air Pollution Part II
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 31 Air Pollution Part II Last time we talked mainly about two types of smog:. 1. London-type smog 2. L.A.-type smog or photochemical smog What are the necessary ingredients
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 31 Air Pollution Part II Last time we talked mainly about two types of smog:. 1. London-type smog 2. L.A.-type smog or photochemical smog What are the necessary ingredients
10. Stratospheric chemistry. Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017
 10. Stratospheric chemistry Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 The ozone layer Dobson unit: physical thickness (0.01 mm) of ozone layer if compressed to 1 atm, 0 o
10. Stratospheric chemistry Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 The ozone layer Dobson unit: physical thickness (0.01 mm) of ozone layer if compressed to 1 atm, 0 o
Chapman. 4. O + O 3 2 O 2 ; k 4 5. NO + O 3 NO 2 + O 2 ; k 5 6. NO 2 + O NO + O 2 ; k 6 7. NO 2 + hν NO + O; k 7. NO X Catalytic.
 ATM 507 Lecture 8 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Note: next week class as usual Tuesday, no class on Thursday Today s topics Mid-latitude Stratosphere Lower Stratosphere 1 Let s
ATM 507 Lecture 8 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Note: next week class as usual Tuesday, no class on Thursday Today s topics Mid-latitude Stratosphere Lower Stratosphere 1 Let s
Stratospheric Chemistry: Polar Ozone Depletion AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433. Ross Salawitch
 Stratospheric Chemistry: Polar Ozone Depletion AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2017 Today: Processes that govern the formation of the Antarctic
Stratospheric Chemistry: Polar Ozone Depletion AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2017 Today: Processes that govern the formation of the Antarctic
Chemistry 471/671. Atmospheric Chemistry III: Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
 Chemistry 471/671 Atmospheric Chemistry III: Stratospheric Ozone Depletion 2 The Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hn 2 O( 1 D) O( 1 D) + O 2 + M O 3 + M Exothermic O( 1 D) + O 3 2 O 2 O 3 + hn O( 1 D) + O 2 ( 1
Chemistry 471/671 Atmospheric Chemistry III: Stratospheric Ozone Depletion 2 The Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hn 2 O( 1 D) O( 1 D) + O 2 + M O 3 + M Exothermic O( 1 D) + O 3 2 O 2 O 3 + hn O( 1 D) + O 2 ( 1
Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 (Chapter 4, p , , , )
 Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 (Chapter 4, p 155-169, 174-176, 198-222, 231-238) zone Discovery and History The Stratosphere and circulation Chapman Chemistry Catalysts The Controversy The zone Hole International
Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 (Chapter 4, p 155-169, 174-176, 198-222, 231-238) zone Discovery and History The Stratosphere and circulation Chapman Chemistry Catalysts The Controversy The zone Hole International
On Stationary state, also called steady state. Lifetimes and spatial scales of variability
 On sources and sinks ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 5-6 Additional Notes February 16/18, 2016 On lifetimes, variability, and models On Stationary state, also called steady state Lifetimes and spatial scales
On sources and sinks ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 5-6 Additional Notes February 16/18, 2016 On lifetimes, variability, and models On Stationary state, also called steady state Lifetimes and spatial scales
Stratospheric Ozone: An Online Learning Module
 Stratospheric Ozone: An Online Learning Module Using your favorite browser open Ozone/index.htm or go to http://cs.clark.edu/~mac/geol390/stratosphericozone/startozoneactivity.html Work through the web
Stratospheric Ozone: An Online Learning Module Using your favorite browser open Ozone/index.htm or go to http://cs.clark.edu/~mac/geol390/stratosphericozone/startozoneactivity.html Work through the web
An Interpretation of Natural Healing of Ozone Holes
 ISSN 2278 0211 (Online) An Interpretation of Natural Healing of Ozone Holes Vasudevan Tachoth Nirvan Industries, Private Industrial Estate, Post Sidco Near Railway Gate, Kuruchi Coimbatore, India Abstract:
ISSN 2278 0211 (Online) An Interpretation of Natural Healing of Ozone Holes Vasudevan Tachoth Nirvan Industries, Private Industrial Estate, Post Sidco Near Railway Gate, Kuruchi Coimbatore, India Abstract:
Stratospheric Chemistry: Polar Ozone Depletion AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433/633. Ross Salawitch
 Stratospheric Chemistry: Polar Ozone Depletion AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433/633 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2013 Today: Processes that govern the formation of the Antarctic
Stratospheric Chemistry: Polar Ozone Depletion AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433/633 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2013 Today: Processes that govern the formation of the Antarctic
ATM 507 Meeting 6. ftp://ftp.nilu.no/pub/nilu/geir/assessment-2006/10%20q&aschapter.pdf
 ATM 507 Meeting 6 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 4 due Oct. 11 Today s topics Polar Stratospheric Chemistry and the Ozone Hole, Global Ozone Trends Required reading: 20 Questions and Answers from
ATM 507 Meeting 6 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 4 due Oct. 11 Today s topics Polar Stratospheric Chemistry and the Ozone Hole, Global Ozone Trends Required reading: 20 Questions and Answers from
CHEM/ENVS 380 S14, Midterm Exam ANSWERS 1 Apr 2014
 PART- A. Multiple Choice Questions (5 points each): Each question may have more than one correct answer. You must select ALL correct answers, and correct answers only, to receive full credit. 1. Which
PART- A. Multiple Choice Questions (5 points each): Each question may have more than one correct answer. You must select ALL correct answers, and correct answers only, to receive full credit. 1. Which
Chapter 7. Stratospheric Chemistry.
 Chapter 7. Stratospheric Chemistry. Stratospheric chemistry became environmental chemistry in the early 1970 s when scientists studied the potential stratospheric effects of supersonic aircraft (Crutzen,
Chapter 7. Stratospheric Chemistry. Stratospheric chemistry became environmental chemistry in the early 1970 s when scientists studied the potential stratospheric effects of supersonic aircraft (Crutzen,
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II
 Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes THE DESTRUCTION OF STRATOSPHERIC OZONE The ozone hole
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes THE DESTRUCTION OF STRATOSPHERIC OZONE The ozone hole
Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation
 Outline Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation Review electromagnetic radiation absorptivity by selective gases temperature vs. height in atmosphere Ozone production and destruction natural balance anthropogenic
Outline Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation Review electromagnetic radiation absorptivity by selective gases temperature vs. height in atmosphere Ozone production and destruction natural balance anthropogenic
Stratospheric Ozone Depletion, Regional Ozone, Aerosols: Connections to Climate Change
 Stratospheric Ozone Depletion, Regional Ozone, Aerosols: Connections to Climate Change Jeff Gaffney Chemistry Department University of Arkansas at Little Rock DOE Biological and Environmental Science Climate
Stratospheric Ozone Depletion, Regional Ozone, Aerosols: Connections to Climate Change Jeff Gaffney Chemistry Department University of Arkansas at Little Rock DOE Biological and Environmental Science Climate
Global Warming and Climate Change Part I: Ozone Depletion
 GCOE-ARS : November 18, 2010 Global Warming and Climate Change Part I: Ozone Depletion YODEN Shigeo Department of Geophysics, Kyoto University 1. Stratospheric Ozone and History of the Earth 2. Observations
GCOE-ARS : November 18, 2010 Global Warming and Climate Change Part I: Ozone Depletion YODEN Shigeo Department of Geophysics, Kyoto University 1. Stratospheric Ozone and History of the Earth 2. Observations
Stratospheric O 3 : Overview
 Stratospheric Chemistry READING: Chapter 10 of text Mid-latitude Ozone Chemistry (and depletion) Polar Ozone Destruction (the Ozone Hole) Stratospheric O 3 : Overview Most O 3 (90%) in stratosphere. Remaining
Stratospheric Chemistry READING: Chapter 10 of text Mid-latitude Ozone Chemistry (and depletion) Polar Ozone Destruction (the Ozone Hole) Stratospheric O 3 : Overview Most O 3 (90%) in stratosphere. Remaining
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II
 Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes REVIEW... Q Is the depletion of STRATOSPHERIC OZONE (in
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes REVIEW... Q Is the depletion of STRATOSPHERIC OZONE (in
STRATOSPHERIC OZONE DEPLETION. Adapted from K. Sturges at MBHS
 STRATOSPHERIC OZONE DEPLETION Adapted from K. Sturges at MBHS Ozone Layer Ozone is Good up high Stratosphere Bad nearby Troposphere Solar Radiation - range of electromagnetic waves UV shortest we see if
STRATOSPHERIC OZONE DEPLETION Adapted from K. Sturges at MBHS Ozone Layer Ozone is Good up high Stratosphere Bad nearby Troposphere Solar Radiation - range of electromagnetic waves UV shortest we see if
SCIAMACHY book. Ozone variability and long-term changes Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA-IASB
 SCIAMACHY book Ozone variability and long-term changes Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA-IASB 1928: start of CFC production 1971: 1 st observation of CFC in the atmosphere (J. Lovelock) 1974: identification
SCIAMACHY book Ozone variability and long-term changes Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA-IASB 1928: start of CFC production 1971: 1 st observation of CFC in the atmosphere (J. Lovelock) 1974: identification
Outline. Chemical lifetime. Photochemistry. Ozone chemistry Chapman model Catalytic cycles Ozone hole. Institute of Applied Physics University of Bern
 Institute of Applied Physics University of Bern Outline Introduction Chemical reactions between stable molecules are quite slow in planetary s Absorption of solar UV-radiation leads to the production of
Institute of Applied Physics University of Bern Outline Introduction Chemical reactions between stable molecules are quite slow in planetary s Absorption of solar UV-radiation leads to the production of
The Atmosphere. All of it. In one hour. Mikael Witte 10/27/2010
 The Atmosphere All of it. In one hour. Mikael Witte 10/27/2010 Outline Structure Dynamics - heat transport Composition Trace constituent compounds Some Atmospheric Processes Ozone destruction in stratosphere
The Atmosphere All of it. In one hour. Mikael Witte 10/27/2010 Outline Structure Dynamics - heat transport Composition Trace constituent compounds Some Atmospheric Processes Ozone destruction in stratosphere
Simulation of Polar Ozone Depletion: An Update
 Simulation of Polar Ozone Depletion: An Update Image taken from www.zmescience.com D. Kinnison (NCAR), S. Solomon (MIT), and J. Bandoro (MIT) February 17, 2015 WACCM Working Group Meeting, Boulder Co.
Simulation of Polar Ozone Depletion: An Update Image taken from www.zmescience.com D. Kinnison (NCAR), S. Solomon (MIT), and J. Bandoro (MIT) February 17, 2015 WACCM Working Group Meeting, Boulder Co.
Class: Chemistry Topic:_atomic structure & ozone layer
 Class: Chemistry Topic:_atomic structure & ozone layer Directions: Please read both articles and write a 5 paragraph comparative essay on each. You should include examples provided in the articles to prove
Class: Chemistry Topic:_atomic structure & ozone layer Directions: Please read both articles and write a 5 paragraph comparative essay on each. You should include examples provided in the articles to prove
Chapman Cycle. The cycle describes reactions of O 2 and O 3 in stratosphere
 Chapman Cycle The cycle describes reactions of O 2 and O 3 in stratosphere Even though reactions are happening, the concentration of O 3 remains constant This is an example of a dynamic equilibrium or
Chapman Cycle The cycle describes reactions of O 2 and O 3 in stratosphere Even though reactions are happening, the concentration of O 3 remains constant This is an example of a dynamic equilibrium or
Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 Darin Toohey CU PAOS. Some resources that I borrowed from
 Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 Darin Toohey CU PAS Why Do We Care? zone Discovery and History Circulation Chapman Chemistry Catalytic Destruction The Controversy The Big Surprise of 1985 Some resources
Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 Darin Toohey CU PAS Why Do We Care? zone Discovery and History Circulation Chapman Chemistry Catalytic Destruction The Controversy The Big Surprise of 1985 Some resources
2.1 Ozone. Ozone O 3. Oxygen O 2 1/30/2015 CHM 107
 CHM 107 2.1 Ozone In the stratosphere way up high Protects Earth from solar radiation There is a hole in the ozone layer above Antarctica Do we care? Why? Energy + 3 O 2 (g) g 2 O 3 (g) Lightning can serve
CHM 107 2.1 Ozone In the stratosphere way up high Protects Earth from solar radiation There is a hole in the ozone layer above Antarctica Do we care? Why? Energy + 3 O 2 (g) g 2 O 3 (g) Lightning can serve
Chapter 2 Protecting the Ozone Layer. The Ozone Hole
 Today (Tues 2/24) Newspaper Articles: Ciara Rodwell and Melissa Regan Intro to Ozone, Ozone Hole, & Chapter 2 Light, matter, and human health! Laboratory: Experiment 4 You design investigation Start Ozone
Today (Tues 2/24) Newspaper Articles: Ciara Rodwell and Melissa Regan Intro to Ozone, Ozone Hole, & Chapter 2 Light, matter, and human health! Laboratory: Experiment 4 You design investigation Start Ozone
CONTENTS 1 MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION
 i CONTENTS 1 MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION 1 1.1 MIXING RATIO 1 1.2 NUMBER DENSITY 2 1.3 PARTIAL PRESSURE 6 PROBLEMS 10 1.1 Fog formation 10 1.2 Phase partitioning of water in cloud 10 1.3 The ozone
i CONTENTS 1 MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION 1 1.1 MIXING RATIO 1 1.2 NUMBER DENSITY 2 1.3 PARTIAL PRESSURE 6 PROBLEMS 10 1.1 Fog formation 10 1.2 Phase partitioning of water in cloud 10 1.3 The ozone
Discuss Yesterday s Lab. What Do We Know? Funny Ozone Video. Ozone Layer Defined! Ozone Layer. Warm-Up 3/3/2015
 Warm-Up March 3, 2015 Today you will need your notebook, pencil and whiteboards. HW due Friday. Attach the Ozone Table into your notebook Pick up ozone table in the red box Complete the Predictions Column
Warm-Up March 3, 2015 Today you will need your notebook, pencil and whiteboards. HW due Friday. Attach the Ozone Table into your notebook Pick up ozone table in the red box Complete the Predictions Column
The Earth is surrounded by a blanket of air, which we call the atmosphere. It reaches over 560 kilometers
 A t m o s f e r a Atmosphere The Earth is surrounded by a blanket of air, which we call the atmosphere. It reaches over 560 kilometers (348 miles) from the surface of the Earth, so we are only able to
A t m o s f e r a Atmosphere The Earth is surrounded by a blanket of air, which we call the atmosphere. It reaches over 560 kilometers (348 miles) from the surface of the Earth, so we are only able to
Reaction Mechanisms. Chemical Kinetics. Reaction Mechanisms. Reaction Mechanisms. Reaction Mechanisms. Reaction Mechanisms
 Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is a study of the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. The study of kinetics may be done in steps: Determination of reaction mechanism Prediction of rate law Measurement
Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is a study of the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. The study of kinetics may be done in steps: Determination of reaction mechanism Prediction of rate law Measurement
Chemical Kinetics. Reaction Mechanisms
 Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is a study of the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. The study of kinetics may be done in steps: Determination of reaction mechanism Prediction of rate law Measurement
Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is a study of the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. The study of kinetics may be done in steps: Determination of reaction mechanism Prediction of rate law Measurement
Stratospheric Chemistry
 Stratospheric Chemistry Stratospheric Chemistry Why Ozone? Part of global energy balance determines T and hence u. Protection of the biosphere from UV. Sensitive to human pollution. Search for extraterrestrial
Stratospheric Chemistry Stratospheric Chemistry Why Ozone? Part of global energy balance determines T and hence u. Protection of the biosphere from UV. Sensitive to human pollution. Search for extraterrestrial
Chemistry of Ozone. Explain the following terms: resonance, resonance hybrid, delocalisation
 Chemistry of Ozone Ozone is triatomic oxygen, O 3. (Ozone is from the Greek ozein, to smell. ) It is a form of oxygen in which the atoms combine in threes, (correct IUPAC name: trioxygen, O 3 ), rather
Chemistry of Ozone Ozone is triatomic oxygen, O 3. (Ozone is from the Greek ozein, to smell. ) It is a form of oxygen in which the atoms combine in threes, (correct IUPAC name: trioxygen, O 3 ), rather
(Figure 2) Science coursework
 Dobson was a scientist that devoted most of his life to the observation of the atmospheric ozone. The results of his devotion to the study of the atmospheric led to a great understanding of the structure
Dobson was a scientist that devoted most of his life to the observation of the atmospheric ozone. The results of his devotion to the study of the atmospheric led to a great understanding of the structure
Stratosphere and Ozone
 Stratosphere and Ozone Ozone (Greek, ozein, to smell) O 3 Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hv O + O O + O 3 2O 2 O 3 + hv O 2 + O O + O 2 + M O 3 + M third-body. anything What units are used to report the amount
Stratosphere and Ozone Ozone (Greek, ozein, to smell) O 3 Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hv O + O O + O 3 2O 2 O 3 + hv O 2 + O O + O 2 + M O 3 + M third-body. anything What units are used to report the amount
CHAPTER 10. STRATOSPHERIC OZONE
 The stratospheric ozone layer, centered at about 20 km above the surface of the Earth ( Figure 10-1 ), protects life on Earth by absorbing UV radiation from the Sun. In this chapter we examine the mechanisms
The stratospheric ozone layer, centered at about 20 km above the surface of the Earth ( Figure 10-1 ), protects life on Earth by absorbing UV radiation from the Sun. In this chapter we examine the mechanisms
Enhanced UV radiation a new problem for the marine environment
 1 Enhanced UV radiation a new problem for the marine environment Robert F. Whitehead, Stephen J. de Mora* and Serge Demers 1.1 Introduction UV irradiance at the earth s surface is intimately related to
1 Enhanced UV radiation a new problem for the marine environment Robert F. Whitehead, Stephen J. de Mora* and Serge Demers 1.1 Introduction UV irradiance at the earth s surface is intimately related to
Introduction to Atmospheric Photochemistry AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch
 Introduction to Atmospheric Photochemistry AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2015 Lecture 9 9 March 2015 1 Chapman Chemistry Production of stratospheric
Introduction to Atmospheric Photochemistry AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2015 Lecture 9 9 March 2015 1 Chapman Chemistry Production of stratospheric
Ozone Depletion. Dana Desonie, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click (No sign in required)
 Ozone Depletion Dana Desonie, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content,
Ozone Depletion Dana Desonie, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content,
Review of Lectures 9 to 16 AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433. Ross Salawitch
 Review of Lectures 9 to 16 AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2015 Review of Problem Set #4 will be held Mon, 13 April 6:30 pm Unfortunately the
Review of Lectures 9 to 16 AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2015 Review of Problem Set #4 will be held Mon, 13 April 6:30 pm Unfortunately the
Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review
 Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Climate in a region is a. the long-term,
Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Climate in a region is a. the long-term,
Gases, ozone, and CFCs. An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop
 Gases, ozone, and CFCs An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Gas Gas Model Gases are composed of tiny, widely-spaced particles. For a typical gas, the average distance between particles is about
Gases, ozone, and CFCs An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Gas Gas Model Gases are composed of tiny, widely-spaced particles. For a typical gas, the average distance between particles is about
Conservation The Law of Conservation of Matter states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in ordinary chemical reactions. This means that no
 Chemical Reactions Conservation The Law of Conservation of Matter states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in ordinary chemical reactions. This means that no atoms can be lost or gained. This
Chemical Reactions Conservation The Law of Conservation of Matter states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in ordinary chemical reactions. This means that no atoms can be lost or gained. This
warmest (coldest) temperatures at summer heat dispersed upward by vertical motion Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A heated by solar radiation at the base
 Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
CREATE Summer School. Tim Canty
 CREATE Summer School Tim Canty Understanding Halogens in the Arctic Today: Will focus on chlorine and bromine How lab studies affect our view of ozone loss Using observations and models to probe the atmosphere
CREATE Summer School Tim Canty Understanding Halogens in the Arctic Today: Will focus on chlorine and bromine How lab studies affect our view of ozone loss Using observations and models to probe the atmosphere
OZONE AND ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION
 OZONE AND ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION Alfio Parisi, Michael Kimlin Imagine if the earth s protective atmosphere did not exist and the earth was subjected to the harmful ultraviolet energy from the sun. Life
OZONE AND ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION Alfio Parisi, Michael Kimlin Imagine if the earth s protective atmosphere did not exist and the earth was subjected to the harmful ultraviolet energy from the sun. Life
O 3 + UV photon (λ < 320 nm) O 2 * + O* O 3 + O 2O 2
 Tro Chpt 13 Chemical Kinetics Rate of a chemical reaction Effect of concentration on reaction rate Integrated rate laws: How concentrations change with time Effect of temperature on rate Reaction mechanisms
Tro Chpt 13 Chemical Kinetics Rate of a chemical reaction Effect of concentration on reaction rate Integrated rate laws: How concentrations change with time Effect of temperature on rate Reaction mechanisms
Lecture 25: Atmosphere & environment
 Lecture 25: Atmosphere & environment Read: BLB 18.1 4 HW: BLB 18:9,11,15,29,69 Sup 18:1 3 Know: ozone chemistry chemistry of the lower atmosphere sulfer compounds & acid rain nitrogen oxides & smog check
Lecture 25: Atmosphere & environment Read: BLB 18.1 4 HW: BLB 18:9,11,15,29,69 Sup 18:1 3 Know: ozone chemistry chemistry of the lower atmosphere sulfer compounds & acid rain nitrogen oxides & smog check
Chapter 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer
 Chapter 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer Student: 1. O2 and O3 molecules are A. allotropes. B. structural isomers. C. isotopes. D. geometrical isomers. 2. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are there
Chapter 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer Student: 1. O2 and O3 molecules are A. allotropes. B. structural isomers. C. isotopes. D. geometrical isomers. 2. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are there
Chemistry 141 Samuel A. Abrash Chemical Reactions Lab Lecture 9/5/2011
 Chemistry 141 Samuel A. Abrash Chemical Reactions Lab Lecture 9/5/2011 Q: Before we start discussing this week s lab, can we talk about our lab notebooks? Sure. Q: What makes a lab notebook a good notebook?
Chemistry 141 Samuel A. Abrash Chemical Reactions Lab Lecture 9/5/2011 Q: Before we start discussing this week s lab, can we talk about our lab notebooks? Sure. Q: What makes a lab notebook a good notebook?
Measured Ozone Depletion
 Measured Ozone Depletion Global Ozone After carefully accounting for all of the known natural variations, a net decrease of about 3% per decade for the period 1978-1991 was found. This is a global average
Measured Ozone Depletion Global Ozone After carefully accounting for all of the known natural variations, a net decrease of about 3% per decade for the period 1978-1991 was found. This is a global average
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming?
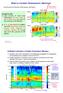 What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
Ozone. In the upper atmosphere. At the surface pollution (not discussed)
 Ozone In the upper atmosphere At the surface pollution (not discussed) What is Ozone? Oxygen molecule with 3 oxygen atoms O 3 Normal form of oxygen: 2 oxygen atoms O 2 Where does Ozone occur? Stratosphere
Ozone In the upper atmosphere At the surface pollution (not discussed) What is Ozone? Oxygen molecule with 3 oxygen atoms O 3 Normal form of oxygen: 2 oxygen atoms O 2 Where does Ozone occur? Stratosphere
Mario Molina puts the atmosphere and ozone on the political agenda
 Mario Molina puts the atmosphere and ozone on the political agenda (Version 1) A. Understanding ozone 60 km stratosphere 40 km 20 km troposphere Diagram of our atmosphere (Reproduced with permission from
Mario Molina puts the atmosphere and ozone on the political agenda (Version 1) A. Understanding ozone 60 km stratosphere 40 km 20 km troposphere Diagram of our atmosphere (Reproduced with permission from
Where is the ozone layer? Global ozone column abundance
 Where is the ozone layer? Altitude (km) 85 10 0 Thermosphere 20-30km Mesosphere Stratosphere Troposphere 100 200 300 Temperature (K) Mesopause Stratopause Tropopause Global ozone column abundance WMO,
Where is the ozone layer? Altitude (km) 85 10 0 Thermosphere 20-30km Mesosphere Stratosphere Troposphere 100 200 300 Temperature (K) Mesopause Stratopause Tropopause Global ozone column abundance WMO,
PROBLEMS Sources of CO Sources of tropospheric ozone
 220 PROBLEMS 11. 1 Sources of CO The two principal sources of CO to the atmosphere are oxidation of CH 4 and combustion. Mean rate constants for oxidation of CH 4 and CO by OH in the troposphere are k
220 PROBLEMS 11. 1 Sources of CO The two principal sources of CO to the atmosphere are oxidation of CH 4 and combustion. Mean rate constants for oxidation of CH 4 and CO by OH in the troposphere are k
The Mole. Relative Atomic Mass Ar
 STOICHIOMETRY The Mole Relative Atomic Mass Ar Relative Molecular Mass Mr Defined as mass of one atom of the element when compared with 1/12 of an atom of carbon-12 Some Ar values are not whole numbers
STOICHIOMETRY The Mole Relative Atomic Mass Ar Relative Molecular Mass Mr Defined as mass of one atom of the element when compared with 1/12 of an atom of carbon-12 Some Ar values are not whole numbers
Topic # 15 OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE. see pp in Class Notes
 Topic # 15 OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE see pp 81-85 in Class Notes [ The Ozone Treaty is ] the first truly global treaty that offers protection to every single human being. ~ Mostofa K. Tolba,
Topic # 15 OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE see pp 81-85 in Class Notes [ The Ozone Treaty is ] the first truly global treaty that offers protection to every single human being. ~ Mostofa K. Tolba,
I T A T I O N H B I T B T V A O C J K M R S A T M O S P H E R E
 Word Search Directions: Below are definitions of vocabulary terms. Figure out each term and then find and circle it in the puzzle. Words may appear horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. K E M I S S
Word Search Directions: Below are definitions of vocabulary terms. Figure out each term and then find and circle it in the puzzle. Words may appear horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. K E M I S S
Exam Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics June 4, 2015 at 8:00-13:00 separate sheets. 1. The Atmosphere Mauna Loa CO2 (ppmv) 2 CO Year
 Exam Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics June 4, 015 at 8:00-1:00 You may use: Calculator, Table booklet (Tefyma or similar), Equation sheet of the course Answer each question (1-5) on separate sheets. 1.
Exam Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics June 4, 015 at 8:00-1:00 You may use: Calculator, Table booklet (Tefyma or similar), Equation sheet of the course Answer each question (1-5) on separate sheets. 1.
Metal + water -> metal hydroxide + hydrogen Metal + acid -> metal salt + hydrogen
 Name of Formula Formula of ion Name of salt Hydrochloric Sulphuric HCl Cl - Chloride H 2 SO 4 SO 4-2 Sulphate Key words: Oxidation: loss of electrons Reduction: gain of electrons Displacement reaction:
Name of Formula Formula of ion Name of salt Hydrochloric Sulphuric HCl Cl - Chloride H 2 SO 4 SO 4-2 Sulphate Key words: Oxidation: loss of electrons Reduction: gain of electrons Displacement reaction:
Temperature. Vertical Thermal Structure. Earth s Climate System. Lecture 1: Introduction to the Climate System
 Lecture 1: Introduction to the Climate System T mass (& radiation) T & mass relation in vertical mass (& energy, weather..) Energy T vertical stability vertical motion thunderstorm What are included in
Lecture 1: Introduction to the Climate System T mass (& radiation) T & mass relation in vertical mass (& energy, weather..) Energy T vertical stability vertical motion thunderstorm What are included in
 Part I Short Answer Choose a letter to fill in the blanks. Use choices as many times as you wish. Only one choice is needed per blank. All are 3 points each. 1. First set. How can you tell these apart?
Part I Short Answer Choose a letter to fill in the blanks. Use choices as many times as you wish. Only one choice is needed per blank. All are 3 points each. 1. First set. How can you tell these apart?
The Atmosphere. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems
 The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
Planetary Atmospheres Part 2
 Planetary Atmospheres Part 2 Atmospheric Layers: The temperature gradient (whether it increases or decreases with altitude) is set by the type of absorption that occurs. We can affect this! Photo- disassocia,on
Planetary Atmospheres Part 2 Atmospheric Layers: The temperature gradient (whether it increases or decreases with altitude) is set by the type of absorption that occurs. We can affect this! Photo- disassocia,on
Raman spectroscopy measurements of Polar Stratospheric Cloud (PSC) mimics
 Raman spectroscopy measurements of Polar Stratospheric Cloud (PSC) mimics Eoin Riordan and John R Sodeau CRAC - Department of Chemistry & Environment Research Institute, University College Cork, Ireland.
Raman spectroscopy measurements of Polar Stratospheric Cloud (PSC) mimics Eoin Riordan and John R Sodeau CRAC - Department of Chemistry & Environment Research Institute, University College Cork, Ireland.
Introduction to Chemical Kinetics AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch
 Introduction to Chemical Kinetics AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2017 Goals for today: Loose ends from last lecture Overview of Chemical Kinetics
Introduction to Chemical Kinetics AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2017 Goals for today: Loose ends from last lecture Overview of Chemical Kinetics
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere
 Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
January 23, Lecture 3. The Ozone Chemistry.
 Lecture 3 January 23, 2018 The Ozone Chemistry http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a010000/a010015/index.html The atmosphere is divided vertically into four layers based on temperature: the troposphere,
Lecture 3 January 23, 2018 The Ozone Chemistry http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a010000/a010015/index.html The atmosphere is divided vertically into four layers based on temperature: the troposphere,
ATM 507 Lecture 5. Text reading Chapter 4 Problem Set #2 due Sept. 20 Today s topics Photochemistry and Photostationary State Relation
 ATM 507 Lecture 5 Text reading Chapter 4 Problem Set #2 due Sept. 20 Today s topics Photochemistry and Photostationary State Relation Beer-Lambert Law (for the absorption of light) Used to describe the
ATM 507 Lecture 5 Text reading Chapter 4 Problem Set #2 due Sept. 20 Today s topics Photochemistry and Photostationary State Relation Beer-Lambert Law (for the absorption of light) Used to describe the
). It is a gas produced naturally in the stratosphere where it strongly absorbs incoming
 Page 1 of 6 What Determines How Much Ultraviolet Radiation Reaches the Earth s Surface? The amount of UV radiation reaching the Earth s surface varies widely around the globe and through time. Several
Page 1 of 6 What Determines How Much Ultraviolet Radiation Reaches the Earth s Surface? The amount of UV radiation reaching the Earth s surface varies widely around the globe and through time. Several
IMPULSIVE NITRATE DEPOSITION EVENTS IN POLAR ICE THE RESULT OF SOLAR PROTON EVENTS. D. F. Smart and M. A. Shea SYNOPSIS
 IMPULSIVE NITRATE DEPOSITION EVENTS IN POLAR ICE THE RESULT OF SOLAR PROTON EVENTS D. F. Smart and M. A. Shea Emeritus at AFRL (RVBXS), Bedford, MA, 01731, USA SYNOPSIS The endothermic chemical reaction
IMPULSIVE NITRATE DEPOSITION EVENTS IN POLAR ICE THE RESULT OF SOLAR PROTON EVENTS D. F. Smart and M. A. Shea Emeritus at AFRL (RVBXS), Bedford, MA, 01731, USA SYNOPSIS The endothermic chemical reaction
CHAPTER 7 HOW DEEP IS THE OZONE HOLE? Questions Answered in this Chapter. Characteristics and Consequences of the Ozone Layer
 CHAPTER 7 HOW DEEP IS THE OZONE HOLE? The ozone hole has been in the news periodically since it was first discovered in 1985. Most scientists accept the explanations offered by atmospheric scientists for
CHAPTER 7 HOW DEEP IS THE OZONE HOLE? The ozone hole has been in the news periodically since it was first discovered in 1985. Most scientists accept the explanations offered by atmospheric scientists for
Math 19a - Reading 8.1 outline for discussion section
 Math 9a - Reading 8. outline for discussion section due Monday, February 25, 28. How do you, guys, feel about vectors and matrices? Have you seen such things before? What did you think of the lecture on
Math 9a - Reading 8. outline for discussion section due Monday, February 25, 28. How do you, guys, feel about vectors and matrices? Have you seen such things before? What did you think of the lecture on
1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely
 CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
Environment Canada:
 2010 2011 Polar Stratospheric t Ozone David W. Tarasick, Air Quality Research Division : http://exp-studies.tor.ec.gc.ca/ tor ec ca/ 2014 Connaught Summer School in Arctic Science, July 14 18, 18, 2014-1
2010 2011 Polar Stratospheric t Ozone David W. Tarasick, Air Quality Research Division : http://exp-studies.tor.ec.gc.ca/ tor ec ca/ 2014 Connaught Summer School in Arctic Science, July 14 18, 18, 2014-1
Evolution of inorganic chlorine partitioning in the Arctic polar vortex
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jd006951, 2006 Evolution of inorganic chlorine partitioning in the Arctic polar vortex D. M. Wilmouth, 1 R. M. Stimpfle, 1 J. G. Anderson, 1
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jd006951, 2006 Evolution of inorganic chlorine partitioning in the Arctic polar vortex D. M. Wilmouth, 1 R. M. Stimpfle, 1 J. G. Anderson, 1
Chapter 19. Molecules and Compounds
 Chapter 19 Molecules and Compounds 1 Mini Quiz Which elements will react with water the same way that Na does? A. Ar B. B C. Cl D. K E. Mg 2 Another Which of the following has the highest ionization energy?
Chapter 19 Molecules and Compounds 1 Mini Quiz Which elements will react with water the same way that Na does? A. Ar B. B C. Cl D. K E. Mg 2 Another Which of the following has the highest ionization energy?
1. Composition and Structure
 Atmospheric sciences focuses on understanding the atmosphere of the earth and other planets. The motivations for studying atmospheric sciences are largely: weather forecasting, climate studies, atmospheric
Atmospheric sciences focuses on understanding the atmosphere of the earth and other planets. The motivations for studying atmospheric sciences are largely: weather forecasting, climate studies, atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds. What is an atmosphere? Earth s Atmosphere. Atmospheric Pressure
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
A quantitative analysis of the reactions involved in stratospheric ozone depletion in the polar vortex core
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 7, 55 56, 7 https://doi.org/.594/acp-7-55-7 Author(s) 7. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution. License. A quantitative analysis of the reactions involved
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 7, 55 56, 7 https://doi.org/.594/acp-7-55-7 Author(s) 7. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution. License. A quantitative analysis of the reactions involved
2 EQUILIBRIUM 2.1 WHAT IS EQUILIBRIUM? 2.2 WHEN IS A SYSTEM AT EQUILIBRIUM? 2.3 THE EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT
 2 EQUILIBRIUM 2.1 WHAT IS EQUILIBRIUM? In general terms equilibrium implies a situation that is unchanging or steady. This is generally achieved through a balance of opposing forces. In chemistry equilibrium
2 EQUILIBRIUM 2.1 WHAT IS EQUILIBRIUM? In general terms equilibrium implies a situation that is unchanging or steady. This is generally achieved through a balance of opposing forces. In chemistry equilibrium
Fundamental differences between Arctic and Antarctic ozone depletion
 Fundamental differences between Arctic and Antarctic ozone depletion Susan Solomon 1, Jessica Haskins, Diane J. Ivy, and Flora Min Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences, Massachusetts
Fundamental differences between Arctic and Antarctic ozone depletion Susan Solomon 1, Jessica Haskins, Diane J. Ivy, and Flora Min Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences, Massachusetts
Attendance Sign-Up Sheet. A L: Light Yellow-Green. M Y: Bright Orange
 Attendance Sign-Up Sheet Last Name A L: Light Yellow-Green M Y: Bright Orange Lecture #02 January 13, 2010, Wednesday (1) Thickness of the atmosphere (2) Composition of the atmosphere (3) Thermodynamic
Attendance Sign-Up Sheet Last Name A L: Light Yellow-Green M Y: Bright Orange Lecture #02 January 13, 2010, Wednesday (1) Thickness of the atmosphere (2) Composition of the atmosphere (3) Thermodynamic
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds. What is an atmosphere? Planetary Atmospheres
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? Planetary Atmospheres Pressure Composition Greenhouse effect Atmospheric structure Color of the sky 1 Atmospheres
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? Planetary Atmospheres Pressure Composition Greenhouse effect Atmospheric structure Color of the sky 1 Atmospheres
Update of the Polar SWIFT model for polar stratospheric ozone loss (Polar SWIFT version 2)
 https://doi.org/94/gmd--67-7 Author(s) 7. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution. License. Update of the Polar SWIFT model for polar stratospheric ozone loss (Polar SWIFT version
https://doi.org/94/gmd--67-7 Author(s) 7. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution. License. Update of the Polar SWIFT model for polar stratospheric ozone loss (Polar SWIFT version
