Simulation of Polar Ozone Depletion: An Update
|
|
|
- Denis Fowler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Simulation of Polar Ozone Depletion: An Update Image taken from D. Kinnison (NCAR), S. Solomon (MIT), and J. Bandoro (MIT) February 17, 2015 WACCM Working Group Meeting, Boulder Co.
2 Polar Chemical Processes in the Lower Stratosphere While activation may take place during dark polar winter, substantial ozone losses require that sunlight as well as activated chlorine (and bromine) be present to catalytically destroy ozone.
3 CALIOP Observations (liquid => solid), Pitts et al., 2009 Antarctic Vortex, 3-year Mean area coverage. <= Supercooled Ternary Solution (STS), with some solid mixtures STS is forming in early winter (~60%) at 20km. <= Water-Ice (and STS) <= STS-NAT clouds (low NAT #density) <= STS-NAT clouds (high NAT #density)
4 Modifications to PSC Parameterization: 80/20 partitioning Equilibrium Approach for WACCM. Considine et al., JGR, Settling Velocity Kinnison et al., JGR, % total HNO 3 20% total HNO 3 80% total HNO 3 20% total HNO 3 Empirically, the partitioning of 80% total HNO 3 into STS and 20% into NAT best represents the evolution of HNO 3 (g) in WACCM. CALIOP measurements show PSCs Fractional area is >60% in early winter (Pitts et al., 2009). Wegner et al., JGR, 2013.
5 Comparison to Aura-MLS Observations 475K, between 1 May and 1 July 2005, >80 S EqL. T STS T ICE T NAT T S_NAT Mixture of NAT and STS PSCs The model shows significantly less scatter than the satellite observation due to the simplification that all PSCs form instantaneously with a prescribed size distribution.
6 HNO 3 Comparison to Aura MLS observations 475K, 80-90S 15 There is no temporal offset in gas-phase HNO 3 between model and Obs. ppbv 10 5 Model DeNOy occurs throughout the winter / spring period. 0 May June July Aug Sept Oct Mixture of NAT and STS forms in late May / early June. Model overestimates HNO 3 (g) larger NAT radius needed?
7 PSC Model Development Summary We have updated the PSC representation in WACCM using Aura MLS and CALIOP data as constraints (Wegner et al., JGR 2013). The model now has a mixed phase of STS and NAT in early winter that is more consistent with CALIOP data. The evolution of gas-phase HNO 3 also is in better agreement with Aura MLS. We also updated (not shown) the dehydration threshold for polar stratospheric H 2 O. We were dehydrating at 80% saturation of water over ICE. We are now dehydrating at 100%. 7
8 Examine PSC Assumptions on Ozone Depletion Scenario Temperature PSCS Comments No Het - NONE Zeroed halogen het. rates. Reference - ALL TYPES CCMI Version 2Kbias -2K applied ALL TYPES Only to the Het Module. 3xSAD - ALL TYPES Show the sensitivity to sulfate SAD in polar region only. REFnat - ALL TYPES 2-NAT MODES (0.0001, 5 particles cm -3 ) SOLID - NAT, ICE Liquid PSCs reactivity zeroed. LIQUID#1 T 195K LBS Test Drdla+Muller 2012 result. LIQUID#2 T 192K LBS, ~STS STS starts to form. LIQUID#3 - LBS, STS 8
9 TOZ (DU) *** 82 S *** Zonal Mean *** 2011 ~160DU 9
10 TOZ (DU) *** 82 S *** Zonal Mean *** 2011 ~100DU 10
11 TOZ (DU) *** 82 S *** Zonal Mean *** 2011 ~80 DU 11
12 TOZ (DU) *** 82 S *** Zonal Mean *** 2011 NOTE: A different Solid/Liquid approach gives similar TOZ. 12
13 TOZ (DU) *** 82 N *** Zonal Mean ***
14
15 -57 DU -96 DU -75 DU -118 DU
16 TOZ Summary In the SH, the REF case underestimates the observed TOZ (OMI) by approximately 25DU. In the SH, adding a -2K bias to the heterogeneous module overestimates the depletion. In the SH, adding a 3xSAD to the input CCM sulfate SAD (which is consistent with small volcanic eruptions) shows very good agreement with OMI TOZ. The model has difficulty representing the observed TOZ in the NH. Only when the -2K bias and 3xSAD is applied does the model come close to the observed decrease. More work is needed to understand this model/observed difference. The depletion due to LIQUIDS and SOLIDS is not additive. REF SOLID only + LIQUID#3 16
17 Activation vs Deactivation: 74 S, 61hPa REF Chlorine Activation: Sum of all het. Rates that produce chlorine. Chlorine Deactivation: Sum of the rate that produce NO 2 (JHNO 3, HNO 3 +OH) and Cl+CH 4 => HCl Both liquid PSCs and water-ice are important for chlorine activation at this location in the reference cases. Overall a very good representation of O3 depletion. HNO 3 (g), H 2 O(g) and T in good agreement with MLS =>
18 Activation vs Deactivation: 74 S, 61hPa REF LIQ#2 T 192K LIQUID#2 shuts off ozone loss process by converting a great deal of active chlorine back into the reservoir species (ClONO 2 ). If deactivation into ClONO 2 occurs too early, related chemical indicator is a reduced rate of formation of HCl at later times. 18
19 Activation vs Deactivation: 74 S, 61hPa REF LIQ#2 T 192K SOLID 19
20 HCl Rate Change as an Indicator Het. Processing. Vortex Core, 52hPa Vortex Edge, 52hPa D[HCl]/dt Cl + O 3 => ClO + O 2 Cl + CH 4 => HCl + CH 3. D[HCl]/dt Production and loss chemistry of ClONO2 is key. Cl + CH 4 => HCl + CH 3. Douglass et al., 1995
21 HCl Rate Change as an Indicator Het. Processing. LIQUID#2
22 Summary We find that the occurrence of cold temperatures and PSC chemistry at T<192K is essential to produce substantial ozone loss (O3L). This conclusion is bolstered by broad agreement of the temporal behavior of computed ozone and related species (HNO 3, H 2 O, HCl) compared to Aura MLS. The magnitude of the calculated TOZ in both polar regions is sensitive to small differences in temperature and sulfate surface area density (~10-40DU). These sensitivities are important in quantifying ozone recover due to halogens. These results confirm earlier studies suggesting that liquid PSCs particles are sufficient to simulation nearly all of the O3L using current model chemistry. However, solid PSCs do play an important role in de-noy and de-h2o. They also add to the O3L for altitudes >18km. We have shown that the results for O3L from each particle type are not additive. We ve shown that the rate of change of HCl can be used as a key indicator of ozone depletion chemistry, primarily outside of the vortex core. 22
Simulation of Polar Ozone Depletion in SD-WACCM4 / MERRA
 Simulation of Polar Ozone Depletion in SD-WACCM4 / MERRA D. Kinnison (NCAR), S. Solomon (MIT), J. Bandoro (MIT), and R. Garcia (NCAR) June 16, 2015 WACCM Working Group Meeting, Baltimore MD. Image courtesy
Simulation of Polar Ozone Depletion in SD-WACCM4 / MERRA D. Kinnison (NCAR), S. Solomon (MIT), J. Bandoro (MIT), and R. Garcia (NCAR) June 16, 2015 WACCM Working Group Meeting, Baltimore MD. Image courtesy
CESM2 (WACCM6): Stratospheric Evaluation
 CESM2 (WACCM6): Stratospheric Evaluation D. Kinnison, M. Mills, R. Garcia, D. Marsh, A. Gettelman, F. Vitt, S. Glanville, C. Bardeen, S. Tilmes, A. Smith, J-F. Lamarque, L. Emmons, A. Conley, J. Richter,
CESM2 (WACCM6): Stratospheric Evaluation D. Kinnison, M. Mills, R. Garcia, D. Marsh, A. Gettelman, F. Vitt, S. Glanville, C. Bardeen, S. Tilmes, A. Smith, J-F. Lamarque, L. Emmons, A. Conley, J. Richter,
CESM Tutorial: Stratospheric Aerosols and Chemistry
 CESM Tutorial: Stratospheric Aerosols and Chemistry Mike Mills, CESM WACCM Liaison Doug Kinnison, NCAR ACOM August 15, 2017 Image taken from www.zmescience.com The Antarctic Ozone Hole From https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/30602
CESM Tutorial: Stratospheric Aerosols and Chemistry Mike Mills, CESM WACCM Liaison Doug Kinnison, NCAR ACOM August 15, 2017 Image taken from www.zmescience.com The Antarctic Ozone Hole From https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/30602
WACCM CCMI Simulations: Status and Analysis
 WACCM CCMI Simulations: Status and Analysis D. Kinnison, R. Garcia, A. Smith, D. Marsh, R. Neely, A. Conley, M. Mills, S. Tilmes, J-F Lamarque, A. Gettelman, & F. Vitt. (NCAR) 13 February 2014, WACCM Working
WACCM CCMI Simulations: Status and Analysis D. Kinnison, R. Garcia, A. Smith, D. Marsh, R. Neely, A. Conley, M. Mills, S. Tilmes, J-F Lamarque, A. Gettelman, & F. Vitt. (NCAR) 13 February 2014, WACCM Working
Understanding the Relation between V PSC and Arctic Ozone Loss
 Understanding the Relation between V PSC and Arctic Ozone Loss Neil Harris European Ozone Research Coordinating Unit Department of Chemistry, University of Cambridge Ralph Lehmann, Markus Rex, Peter von
Understanding the Relation between V PSC and Arctic Ozone Loss Neil Harris European Ozone Research Coordinating Unit Department of Chemistry, University of Cambridge Ralph Lehmann, Markus Rex, Peter von
ClO + O -> Cl + O 2 Net: O 3 + O -> O 2 + O 2
 Lecture 36. Stratospheric ozone chemistry. Part2: Threats against ozone. Objectives: 1. Chlorine chemistry. 2. Volcanic stratospheric aerosols. 3. Polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs). Readings: Turco: p.
Lecture 36. Stratospheric ozone chemistry. Part2: Threats against ozone. Objectives: 1. Chlorine chemistry. 2. Volcanic stratospheric aerosols. 3. Polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs). Readings: Turco: p.
Lecture 15 Antarctic Ozone Hole ATOC/CHEM 5151
 Lecture 15 Antarctic Ozone Hole ATOC/CHEM 5151 1 Ozone Hole Theories 1. Solar activity: During periods of high solar activity, energetic particles are deposited high in the atmosphere, creating NOx. Perhaps
Lecture 15 Antarctic Ozone Hole ATOC/CHEM 5151 1 Ozone Hole Theories 1. Solar activity: During periods of high solar activity, energetic particles are deposited high in the atmosphere, creating NOx. Perhaps
Update of the Polar SWIFT model for polar stratospheric ozone loss (Polar SWIFT version 2)
 https://doi.org/94/gmd--67-7 Author(s) 7. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution. License. Update of the Polar SWIFT model for polar stratospheric ozone loss (Polar SWIFT version
https://doi.org/94/gmd--67-7 Author(s) 7. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution. License. Update of the Polar SWIFT model for polar stratospheric ozone loss (Polar SWIFT version
Atmospheric Chemistry III
 Atmospheric Chemistry III Chapman chemistry, catalytic cycles: reminder Source of catalysts, transport to stratosphere: reminder Effect of major (O 2 ) and minor (N 2 O, CH 4 ) biogenic gases on [O 3 ]:
Atmospheric Chemistry III Chapman chemistry, catalytic cycles: reminder Source of catalysts, transport to stratosphere: reminder Effect of major (O 2 ) and minor (N 2 O, CH 4 ) biogenic gases on [O 3 ]:
Measurements of Ozone. Why is Ozone Important?
 Anthropogenic Climate Changes CO 2 CFC CH 4 Human production of freons (CFCs) Ozone Hole Depletion Human production of CO2 and CH4 Global Warming Human change of land use Deforestation (from Earth s Climate:
Anthropogenic Climate Changes CO 2 CFC CH 4 Human production of freons (CFCs) Ozone Hole Depletion Human production of CO2 and CH4 Global Warming Human change of land use Deforestation (from Earth s Climate:
Modeling polar ozone loss at the University of Colorado
 Modeling polar ozone loss at the University of Colorado CESM workshop Breckenridge, 06/21/2012 Matthias Brakebusch, Cora E. Randall, Douglas E. Kinnison, Simone Tilmes, Michelle L. Santee, Gloria L. Manney
Modeling polar ozone loss at the University of Colorado CESM workshop Breckenridge, 06/21/2012 Matthias Brakebusch, Cora E. Randall, Douglas E. Kinnison, Simone Tilmes, Michelle L. Santee, Gloria L. Manney
Polar Ozone Depletion and Trends as Represented by the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM)
 Polar Ozone Depletion and Trends as Represented by the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM) Doug Kinnison 1, Susan Solomon 2, Diane Ivy 2, Mike Mills 1, Ryan Neely III 3, and Anja Schmidt 3
Polar Ozone Depletion and Trends as Represented by the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM) Doug Kinnison 1, Susan Solomon 2, Diane Ivy 2, Mike Mills 1, Ryan Neely III 3, and Anja Schmidt 3
2. Sketch a plot of R vs. z. Comment on the shape. Explain physically why R(z) has a maximum in the atmospheric column.
 190 PROBLEMS 10. 1 Shape of the ozone layer Consider a beam of solar radiation of wavelength λ propagating downward in the vertical direction with an actinic flux I at the top of the atmosphere. Assume
190 PROBLEMS 10. 1 Shape of the ozone layer Consider a beam of solar radiation of wavelength λ propagating downward in the vertical direction with an actinic flux I at the top of the atmosphere. Assume
Chemistry 471/671. Atmospheric Chemistry III: Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
 Chemistry 471/671 Atmospheric Chemistry III: Stratospheric Ozone Depletion 2 The Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hn 2 O( 1 D) O( 1 D) + O 2 + M O 3 + M Exothermic O( 1 D) + O 3 2 O 2 O 3 + hn O( 1 D) + O 2 ( 1
Chemistry 471/671 Atmospheric Chemistry III: Stratospheric Ozone Depletion 2 The Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hn 2 O( 1 D) O( 1 D) + O 2 + M O 3 + M Exothermic O( 1 D) + O 3 2 O 2 O 3 + hn O( 1 D) + O 2 ( 1
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 9, 2016 The Game Changer. Some perspective The British Antarctic Survey The Ozone Hole International Regulations
 ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 9, 2016 The Game Changer Some perspective The British Antarctic Survey The Ozone Hole International Regulations Rowland (1974): The work is going very well, but it may mean the
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 9, 2016 The Game Changer Some perspective The British Antarctic Survey The Ozone Hole International Regulations Rowland (1974): The work is going very well, but it may mean the
 ATM 507 Lecture 9 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Next Class Tuesday, Sept. 30 Today s topics Polar Stratospheric Chemistry and the Ozone Hole, Required reading: 20 Questions and
ATM 507 Lecture 9 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Next Class Tuesday, Sept. 30 Today s topics Polar Stratospheric Chemistry and the Ozone Hole, Required reading: 20 Questions and
Chemistry Updates for CCMI
 Chemistry Updates for CCMI Doug Kinnison 11 February 2013 WACCM Working Group Meeting NCAR Why Do Another Assessment? NESL / ACD community contribution. Increases national and international collaborations.
Chemistry Updates for CCMI Doug Kinnison 11 February 2013 WACCM Working Group Meeting NCAR Why Do Another Assessment? NESL / ACD community contribution. Increases national and international collaborations.
A quantitative analysis of the reactions involved in stratospheric ozone depletion in the polar vortex core
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 7, 55 56, 7 https://doi.org/.594/acp-7-55-7 Author(s) 7. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution. License. A quantitative analysis of the reactions involved
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 7, 55 56, 7 https://doi.org/.594/acp-7-55-7 Author(s) 7. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution. License. A quantitative analysis of the reactions involved
Gravity wave events and polar stratospheric clouds over the Antarctic Peninsula from spaceborne lidar observations
 Gravity wave events and polar stratospheric clouds over the Antarctic Peninsula from spaceborne lidar observations V. Noel, A. Hertzog, H. Chepfer Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique, IPSL/CNRS 1 1.
Gravity wave events and polar stratospheric clouds over the Antarctic Peninsula from spaceborne lidar observations V. Noel, A. Hertzog, H. Chepfer Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique, IPSL/CNRS 1 1.
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1153966/dc1 Supporting Online Material for The Sensitivity of Polar Ozone Depletion to Proposed Geoengineering Schemes Simone Tilmes,* Rolf Müller, Ross Salawitch *To
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1153966/dc1 Supporting Online Material for The Sensitivity of Polar Ozone Depletion to Proposed Geoengineering Schemes Simone Tilmes,* Rolf Müller, Ross Salawitch *To
Global Warming and Climate Change Part I: Ozone Depletion
 GCOE-ARS : November 18, 2010 Global Warming and Climate Change Part I: Ozone Depletion YODEN Shigeo Department of Geophysics, Kyoto University 1. Stratospheric Ozone and History of the Earth 2. Observations
GCOE-ARS : November 18, 2010 Global Warming and Climate Change Part I: Ozone Depletion YODEN Shigeo Department of Geophysics, Kyoto University 1. Stratospheric Ozone and History of the Earth 2. Observations
Stratospheric O 3 : Overview
 Stratospheric Chemistry READING: Chapter 10 of text Mid-latitude Ozone Chemistry (and depletion) Polar Ozone Destruction (the Ozone Hole) Stratospheric O 3 : Overview Most O 3 (90%) in stratosphere. Remaining
Stratospheric Chemistry READING: Chapter 10 of text Mid-latitude Ozone Chemistry (and depletion) Polar Ozone Destruction (the Ozone Hole) Stratospheric O 3 : Overview Most O 3 (90%) in stratosphere. Remaining
WACCM: The High-Top Model
 WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Polar processing and development of the 2004 Antarctic ozone hole: First results from MLS on Aura Citation for published version: Santee, ML, Manney, GL, Livesey, NJ, Froidevaux,
Edinburgh Research Explorer Polar processing and development of the 2004 Antarctic ozone hole: First results from MLS on Aura Citation for published version: Santee, ML, Manney, GL, Livesey, NJ, Froidevaux,
Stratospheric Chemistry: Polar Ozone Depletion AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433. Ross Salawitch
 Stratospheric Chemistry: Polar Ozone Depletion AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2017 Today: Processes that govern the formation of the Antarctic
Stratospheric Chemistry: Polar Ozone Depletion AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2017 Today: Processes that govern the formation of the Antarctic
Simulation of stratospheric water vapor trends: impact on stratospheric ozone chemistry
 Atmos. Chem. Phys.,,, www.atmos-chem-phys.org/acp/// SRef-ID: 68/acp/-- European Geosciences Union Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Simulation of stratospheric water vapor trends: impact on stratospheric
Atmos. Chem. Phys.,,, www.atmos-chem-phys.org/acp/// SRef-ID: 68/acp/-- European Geosciences Union Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Simulation of stratospheric water vapor trends: impact on stratospheric
Simulation of polar stratospheric clouds in the specified dynamics version of the whole atmosphere community climate model
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 1 1, doi:./jgrd.1, 1 Simulation of polar stratospheric clouds in the specified dynamics version of the whole atmosphere community climate model T.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 1 1, doi:./jgrd.1, 1 Simulation of polar stratospheric clouds in the specified dynamics version of the whole atmosphere community climate model T.
Observing the Impact of Calbuco Volcanic Aerosols on South Polar Ozone Depletion in 2015
 Observing the Impact of Calbuco Volcanic Aerosols on South Polar Ozone Depletion in 2015 The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Observing the Impact of Calbuco Volcanic Aerosols on South Polar Ozone Depletion in 2015 The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Stratospheric Chemistry: Polar Ozone Depletion AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433/633. Ross Salawitch
 Stratospheric Chemistry: Polar Ozone Depletion AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433/633 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2013 Today: Processes that govern the formation of the Antarctic
Stratospheric Chemistry: Polar Ozone Depletion AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433/633 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2013 Today: Processes that govern the formation of the Antarctic
An Overview of the Impact. on the Stratosphere and Mesosphere
 An Overview of the Impact of Energetic Particle Precipitation it ti on the Stratosphere and Mesosphere Charles Jackman NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD Aspen GCI Workshop 2010 Colorado June
An Overview of the Impact of Energetic Particle Precipitation it ti on the Stratosphere and Mesosphere Charles Jackman NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD Aspen GCI Workshop 2010 Colorado June
Raman spectroscopy measurements of Polar Stratospheric Cloud (PSC) mimics
 Raman spectroscopy measurements of Polar Stratospheric Cloud (PSC) mimics Eoin Riordan and John R Sodeau CRAC - Department of Chemistry & Environment Research Institute, University College Cork, Ireland.
Raman spectroscopy measurements of Polar Stratospheric Cloud (PSC) mimics Eoin Riordan and John R Sodeau CRAC - Department of Chemistry & Environment Research Institute, University College Cork, Ireland.
WACCM Studies at CU-Boulder
 WACCM Studies at CU-Boulder V.L. Harvey, C.E. Randall, O.B. Toon, E. Peck, S. Benze, M. Brakebusch, L. Holt, D. Wheeler, J. France, E. Wolf, Y. Zhu, X. Fang, C. Jackman, M. Mills, D. Marsh Most Topics
WACCM Studies at CU-Boulder V.L. Harvey, C.E. Randall, O.B. Toon, E. Peck, S. Benze, M. Brakebusch, L. Holt, D. Wheeler, J. France, E. Wolf, Y. Zhu, X. Fang, C. Jackman, M. Mills, D. Marsh Most Topics
The Impact of Polar Stratospheric Ozone Loss on Southern Hemisphere Stratospheric Circulation and Surface Climate
 The Impact of Polar Stratospheric Ozone Loss on Southern Hemisphere Stratospheric Circulation and Surface Climate James Keeble, Peter Braesicke, Howard Roscoe and John Pyle James.keeble@atm.ch.cam.ac.uk
The Impact of Polar Stratospheric Ozone Loss on Southern Hemisphere Stratospheric Circulation and Surface Climate James Keeble, Peter Braesicke, Howard Roscoe and John Pyle James.keeble@atm.ch.cam.ac.uk
Overview and quality of global observations of middle atmospheric water vapour by the Odin satellite
 Overview and quality of global observations of middle atmospheric water vapour by the Odin satellite J. Urban*, D.P. Murtagh*, M. Ekström,, P. Eriksson*, C. Sanchez*, A. Jones,* S. Lossow **, Y. Kasai
Overview and quality of global observations of middle atmospheric water vapour by the Odin satellite J. Urban*, D.P. Murtagh*, M. Ekström,, P. Eriksson*, C. Sanchez*, A. Jones,* S. Lossow **, Y. Kasai
CHEM/ENVS 380 S14, Midterm Exam ANSWERS 1 Apr 2014
 PART- A. Multiple Choice Questions (5 points each): Each question may have more than one correct answer. You must select ALL correct answers, and correct answers only, to receive full credit. 1. Which
PART- A. Multiple Choice Questions (5 points each): Each question may have more than one correct answer. You must select ALL correct answers, and correct answers only, to receive full credit. 1. Which
WACCM: The High-Top Model
 WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of
 Article Atmospheric Science September 2013 Vol.58 No.25: 3155 3160 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5945-5 Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of 2010 2011 HU YongYun 1* & XIA
Article Atmospheric Science September 2013 Vol.58 No.25: 3155 3160 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5945-5 Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of 2010 2011 HU YongYun 1* & XIA
Stratospheric Chemistry and Processes. Sophie Godin-Beekmann LATMOS, OVSQ, IPSL
 Stratospheric Chemistry and Processes Sophie Godin-Beekmann LATMOS, OVSQ, IPSL 1 The Stratosphere Layer just above the troposphere Altitude depends on latitude and season (higher in the tropics and summer)
Stratospheric Chemistry and Processes Sophie Godin-Beekmann LATMOS, OVSQ, IPSL 1 The Stratosphere Layer just above the troposphere Altitude depends on latitude and season (higher in the tropics and summer)
An assessment of changing ozone loss rates at South Pole: Twenty five years of ozonesonde measurements
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016353, 2011 An assessment of changing ozone loss rates at South Pole: Twenty five years of ozonesonde measurements B. Hassler, 1,2 J. S. Daniel,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016353, 2011 An assessment of changing ozone loss rates at South Pole: Twenty five years of ozonesonde measurements B. Hassler, 1,2 J. S. Daniel,
Stratosphere and Ozone
 Stratosphere and Ozone Ozone (Greek, ozein, to smell) O 3 Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hv O + O O + O 3 2O 2 O 3 + hv O 2 + O O + O 2 + M O 3 + M third-body. anything What units are used to report the amount
Stratosphere and Ozone Ozone (Greek, ozein, to smell) O 3 Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hv O + O O + O 3 2O 2 O 3 + hv O 2 + O O + O 2 + M O 3 + M third-body. anything What units are used to report the amount
CCM Modelling : LMDz-Reprobus
 CCM Modelling : LMDz-Reprobus Marchand Marion, Slimane Bekki, Franck Lefèvre, François Lott, David Cugnet, Line Jourdain, Perrine Lemmenais, Virginie Poulain, Julien Jumelet, Slimane Bekki, marie-pierre
CCM Modelling : LMDz-Reprobus Marchand Marion, Slimane Bekki, Franck Lefèvre, François Lott, David Cugnet, Line Jourdain, Perrine Lemmenais, Virginie Poulain, Julien Jumelet, Slimane Bekki, marie-pierre
BRAM: Reanalysis of stratospheric chemical composition based on Aura MLS
 BRAM: Reanalysis of stratospheric chemical composition based on Aura MLS quentin@oma.be Motivations BASCOE produces operational analyses of MLS since 2009 for the validation of MACC O 3 (Lefever et al.,
BRAM: Reanalysis of stratospheric chemical composition based on Aura MLS quentin@oma.be Motivations BASCOE produces operational analyses of MLS since 2009 for the validation of MACC O 3 (Lefever et al.,
State of WACCM. A. Gettelman, L. M. Polvani, M. Mills + WACCM Team
 State of WACCM A. Gettelman, L. M. Polvani, M. Mills + WACCM Team WACCM4/5 Highlights CCMI Simulations (Kinnison) WACCM Last Millennium Run GEOMIP Experiments (Mills) WACCM6 Current Plans/Progress Updated
State of WACCM A. Gettelman, L. M. Polvani, M. Mills + WACCM Team WACCM4/5 Highlights CCMI Simulations (Kinnison) WACCM Last Millennium Run GEOMIP Experiments (Mills) WACCM6 Current Plans/Progress Updated
Halogen Chemistry in CAM-CHEM & CCMVal
 Halogen Chemistry in CAM-CHEM & CCMVal D. Kinnison, A. Saiz-Lopez, J.F. Lamarque, S. Tilmes, plus A. Gettelman, J. Orlando, S. Schauffler, E. Atlas, and R. Garcia February 12 CCSM CCWG Boulder, Co dkin@ucar.edu
Halogen Chemistry in CAM-CHEM & CCMVal D. Kinnison, A. Saiz-Lopez, J.F. Lamarque, S. Tilmes, plus A. Gettelman, J. Orlando, S. Schauffler, E. Atlas, and R. Garcia February 12 CCSM CCWG Boulder, Co dkin@ucar.edu
SCIAMACHY book. Ozone variability and long-term changes Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA-IASB
 SCIAMACHY book Ozone variability and long-term changes Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA-IASB 1928: start of CFC production 1971: 1 st observation of CFC in the atmosphere (J. Lovelock) 1974: identification
SCIAMACHY book Ozone variability and long-term changes Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA-IASB 1928: start of CFC production 1971: 1 st observation of CFC in the atmosphere (J. Lovelock) 1974: identification
Chapman Cycle. The cycle describes reactions of O 2 and O 3 in stratosphere
 Chapman Cycle The cycle describes reactions of O 2 and O 3 in stratosphere Even though reactions are happening, the concentration of O 3 remains constant This is an example of a dynamic equilibrium or
Chapman Cycle The cycle describes reactions of O 2 and O 3 in stratosphere Even though reactions are happening, the concentration of O 3 remains constant This is an example of a dynamic equilibrium or
Chapter 7. Stratospheric Chemistry.
 Chapter 7. Stratospheric Chemistry. Stratospheric chemistry became environmental chemistry in the early 1970 s when scientists studied the potential stratospheric effects of supersonic aircraft (Crutzen,
Chapter 7. Stratospheric Chemistry. Stratospheric chemistry became environmental chemistry in the early 1970 s when scientists studied the potential stratospheric effects of supersonic aircraft (Crutzen,
Antarctic Ozone Bulletin
 Antarctic Ozone Bulletin No 1 / Altitude [km] 35 30 25 20 15 10 Temperature [ C] -90-80 -70-60 -50-40 -30 Neumayer 15 August Ozone Temperature Ozone sounding on 15 August from the German NDACC/GAW station
Antarctic Ozone Bulletin No 1 / Altitude [km] 35 30 25 20 15 10 Temperature [ C] -90-80 -70-60 -50-40 -30 Neumayer 15 August Ozone Temperature Ozone sounding on 15 August from the German NDACC/GAW station
Stratospheric Chemistry
 Stratospheric Chemistry Stratospheric Chemistry Why Ozone? Part of global energy balance determines T and hence u. Protection of the biosphere from UV. Sensitive to human pollution. Search for extraterrestrial
Stratospheric Chemistry Stratospheric Chemistry Why Ozone? Part of global energy balance determines T and hence u. Protection of the biosphere from UV. Sensitive to human pollution. Search for extraterrestrial
Fundamental differences between Arctic and Antarctic ozone depletion
 Fundamental differences between Arctic and Antarctic ozone depletion Susan Solomon 1, Jessica Haskins, Diane J. Ivy, and Flora Min Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences, Massachusetts
Fundamental differences between Arctic and Antarctic ozone depletion Susan Solomon 1, Jessica Haskins, Diane J. Ivy, and Flora Min Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences, Massachusetts
Shape and Chemical Diagnostics of the Polar Vortices in WACCM
 Shape and Chemical Diagnostics of the Polar Vortices in WACCM V. Lynn Harvey, Cora Randall, Jeff France, Laura Holt, Katelynn Greer Richard Collins Dan Marsh, Doug Kinnison Laboratory for Atmospheric and
Shape and Chemical Diagnostics of the Polar Vortices in WACCM V. Lynn Harvey, Cora Randall, Jeff France, Laura Holt, Katelynn Greer Richard Collins Dan Marsh, Doug Kinnison Laboratory for Atmospheric and
Atmospheric Coupling via Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP)
 Atmospheric Coupling via Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP) Cora E. Randall University of Colorado Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Acknowledgments
Atmospheric Coupling via Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP) Cora E. Randall University of Colorado Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Acknowledgments
Simulation of ozone depletion in spring 2000 with the Chemical Lagrangian Model of the Stratosphere (CLaMS)
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. D20, 8295, doi:10.1029/2001jd000456, 2002 Simulation of ozone depletion in spring 2000 with the Chemical Lagrangian Model of the Stratosphere (CLaMS) J.-U.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. D20, 8295, doi:10.1029/2001jd000456, 2002 Simulation of ozone depletion in spring 2000 with the Chemical Lagrangian Model of the Stratosphere (CLaMS) J.-U.
Measured Ozone Depletion
 Measured Ozone Depletion Global Ozone After carefully accounting for all of the known natural variations, a net decrease of about 3% per decade for the period 1978-1991 was found. This is a global average
Measured Ozone Depletion Global Ozone After carefully accounting for all of the known natural variations, a net decrease of about 3% per decade for the period 1978-1991 was found. This is a global average
ATM 507 Meeting 6. ftp://ftp.nilu.no/pub/nilu/geir/assessment-2006/10%20q&aschapter.pdf
 ATM 507 Meeting 6 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 4 due Oct. 11 Today s topics Polar Stratospheric Chemistry and the Ozone Hole, Global Ozone Trends Required reading: 20 Questions and Answers from
ATM 507 Meeting 6 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 4 due Oct. 11 Today s topics Polar Stratospheric Chemistry and the Ozone Hole, Global Ozone Trends Required reading: 20 Questions and Answers from
The contributions of chemistry and transport to low arctic ozone in March 2011 derived from Aura MLS observations
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 1563 1576, doi:10.2/jgrd.181, 2013 The contributions of chemistry and transport to low arctic ozone in March 2011 derived from Aura observations
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 1563 1576, doi:10.2/jgrd.181, 2013 The contributions of chemistry and transport to low arctic ozone in March 2011 derived from Aura observations
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming?
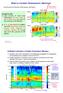 What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
Evaluation of CESM1 (WACCM) free-running and specified-dynamics atmospheric composition simulations using global multi-species satellite data records
 Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss., https://doi.org/./acp-0- Discussion started: June 0 c Author(s) 0. CC BY.0 License. 0 0 0 Evaluation of CESM (WACCM) free-running and specified-dynamics atmospheric composition
Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss., https://doi.org/./acp-0- Discussion started: June 0 c Author(s) 0. CC BY.0 License. 0 0 0 Evaluation of CESM (WACCM) free-running and specified-dynamics atmospheric composition
DANISH METEOROLOGICAL INSTITUTE
 DANISH METEOROLOGICAL INSTITUTE SCIENTIFIC REPORT 00-06 Polar Stratospheric Clouds Microphysical and optical models By Niels Larsen COPENHAGEN 2000 Polar Stratospheric Clouds Microphysical and optical
DANISH METEOROLOGICAL INSTITUTE SCIENTIFIC REPORT 00-06 Polar Stratospheric Clouds Microphysical and optical models By Niels Larsen COPENHAGEN 2000 Polar Stratospheric Clouds Microphysical and optical
Chapman. 4. O + O 3 2 O 2 ; k 4 5. NO + O 3 NO 2 + O 2 ; k 5 6. NO 2 + O NO + O 2 ; k 6 7. NO 2 + hν NO + O; k 7. NO X Catalytic.
 ATM 507 Lecture 8 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Note: next week class as usual Tuesday, no class on Thursday Today s topics Mid-latitude Stratosphere Lower Stratosphere 1 Let s
ATM 507 Lecture 8 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Note: next week class as usual Tuesday, no class on Thursday Today s topics Mid-latitude Stratosphere Lower Stratosphere 1 Let s
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II
 Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes THE DESTRUCTION OF STRATOSPHERIC OZONE The ozone hole
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes THE DESTRUCTION OF STRATOSPHERIC OZONE The ozone hole
Environment Canada:
 2010 2011 Polar Stratospheric t Ozone David W. Tarasick, Air Quality Research Division : http://exp-studies.tor.ec.gc.ca/ tor ec ca/ 2014 Connaught Summer School in Arctic Science, July 14 18, 18, 2014-1
2010 2011 Polar Stratospheric t Ozone David W. Tarasick, Air Quality Research Division : http://exp-studies.tor.ec.gc.ca/ tor ec ca/ 2014 Connaught Summer School in Arctic Science, July 14 18, 18, 2014-1
Stratospheric Ozone: An Online Learning Module
 Stratospheric Ozone: An Online Learning Module Using your favorite browser open Ozone/index.htm or go to http://cs.clark.edu/~mac/geol390/stratosphericozone/startozoneactivity.html Work through the web
Stratospheric Ozone: An Online Learning Module Using your favorite browser open Ozone/index.htm or go to http://cs.clark.edu/~mac/geol390/stratosphericozone/startozoneactivity.html Work through the web
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 31. Air Pollution Part II
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 31 Air Pollution Part II Last time we talked mainly about two types of smog:. 1. London-type smog 2. L.A.-type smog or photochemical smog What are the necessary ingredients
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 31 Air Pollution Part II Last time we talked mainly about two types of smog:. 1. London-type smog 2. L.A.-type smog or photochemical smog What are the necessary ingredients
Research Article. G. Venkata Chalapathi 1, S. Eswaraiah 2*, P. Vishnu Prasanth 3, Jaewook Lee 2, K. Niranjan Kumar 4, Yong Ha Kim 2 ABSTRACT
 International Journal of Current Research and Review DOI: 10.31782/IJCRR.2018.10108 IJCRR Section: Life sciences Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 ICV: 71.54 Research Article Unusual Changes in Stratospheric
International Journal of Current Research and Review DOI: 10.31782/IJCRR.2018.10108 IJCRR Section: Life sciences Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 ICV: 71.54 Research Article Unusual Changes in Stratospheric
STRATOSPHERIC OZONE DEPLETION. Adapted from K. Sturges at MBHS
 STRATOSPHERIC OZONE DEPLETION Adapted from K. Sturges at MBHS Ozone Layer Ozone is Good up high Stratosphere Bad nearby Troposphere Solar Radiation - range of electromagnetic waves UV shortest we see if
STRATOSPHERIC OZONE DEPLETION Adapted from K. Sturges at MBHS Ozone Layer Ozone is Good up high Stratosphere Bad nearby Troposphere Solar Radiation - range of electromagnetic waves UV shortest we see if
An Interpretation of Natural Healing of Ozone Holes
 ISSN 2278 0211 (Online) An Interpretation of Natural Healing of Ozone Holes Vasudevan Tachoth Nirvan Industries, Private Industrial Estate, Post Sidco Near Railway Gate, Kuruchi Coimbatore, India Abstract:
ISSN 2278 0211 (Online) An Interpretation of Natural Healing of Ozone Holes Vasudevan Tachoth Nirvan Industries, Private Industrial Estate, Post Sidco Near Railway Gate, Kuruchi Coimbatore, India Abstract:
On Cosmic-Ray-Driven Electron Reaction Mechanism for Ozone Hole and Chlorofluorocarbon Mechanism for Global Climate Change
 On Cosmic-Ray-Driven Electron Reaction Mechanism for Ozone Hole and Chlorofluorocarbon Mechanism for Global Climate Change Qing-Bin Lu Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Waterloo, Waterloo,
On Cosmic-Ray-Driven Electron Reaction Mechanism for Ozone Hole and Chlorofluorocarbon Mechanism for Global Climate Change Qing-Bin Lu Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Waterloo, Waterloo,
Vertical profiles of activated ClO and ozone loss in the Arctic vortex in January and March 2000: In situ observations and model simulations
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D22, 8334, doi:10.1029/2002jd002564, 2003 Vertical profiles of activated ClO and ozone loss in the Arctic vortex in January and March 2000: In situ observations
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D22, 8334, doi:10.1029/2002jd002564, 2003 Vertical profiles of activated ClO and ozone loss in the Arctic vortex in January and March 2000: In situ observations
CESM1-WACCM: Comparison with CCSM4/ CESM CMIP5 simulations
 CESM1-WACCM: Comparison with CCSM4/ CESM CMIP5 simulations Dan Marsh, Mike Mills, Natalia Calvo, Marika Holland, Cécile Hannay WAWG meeting, Boulder, February 2011 NCAR is sponsored by the National Science
CESM1-WACCM: Comparison with CCSM4/ CESM CMIP5 simulations Dan Marsh, Mike Mills, Natalia Calvo, Marika Holland, Cécile Hannay WAWG meeting, Boulder, February 2011 NCAR is sponsored by the National Science
Impacts of historical ozone changes on climate in GFDL-CM3
 Impacts of historical ozone changes on climate in GFDL-CM3 Larry Horowitz (GFDL) with: Vaishali Naik (GFDL), Pu Lin (CICS), and M. Daniel Schwarzkopf (GFDL) WMO (2014) Figure ADM 5-1 1 Response of tropospheric
Impacts of historical ozone changes on climate in GFDL-CM3 Larry Horowitz (GFDL) with: Vaishali Naik (GFDL), Pu Lin (CICS), and M. Daniel Schwarzkopf (GFDL) WMO (2014) Figure ADM 5-1 1 Response of tropospheric
CREATE Summer School. Tim Canty
 CREATE Summer School Tim Canty Understanding Halogens in the Arctic Today: Will focus on chlorine and bromine How lab studies affect our view of ozone loss Using observations and models to probe the atmosphere
CREATE Summer School Tim Canty Understanding Halogens in the Arctic Today: Will focus on chlorine and bromine How lab studies affect our view of ozone loss Using observations and models to probe the atmosphere
Chemistry-Climate Models: What we have and what we need
 Chemistry-Climate Models: What we have and what we need Dan Marsh National Center for Atmospheric Research NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Outline Overview of processes in our current
Chemistry-Climate Models: What we have and what we need Dan Marsh National Center for Atmospheric Research NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Outline Overview of processes in our current
SUSTAINABILITY MATTERS FACT SHEET 7: THE HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER
 SUSTAINABILITY MATTERS FACT SHEET 7: THE HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER What is the ozone layer? Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen, which means it is a pure element, but has a different chemical structure to that
SUSTAINABILITY MATTERS FACT SHEET 7: THE HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER What is the ozone layer? Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen, which means it is a pure element, but has a different chemical structure to that
Status/Updates of CAM4/5 Chemistry
 Status/Updates of CAM4/5 Chemistry Available Chemical Mechanisms, CAM4 Bulk Aerosol Model (BAM): Includes Black Carbon, Organic Carbon, Sea Salt, Dust, SO 2, SO 4, H 2 O 2, DMS (prescribed monthly fields
Status/Updates of CAM4/5 Chemistry Available Chemical Mechanisms, CAM4 Bulk Aerosol Model (BAM): Includes Black Carbon, Organic Carbon, Sea Salt, Dust, SO 2, SO 4, H 2 O 2, DMS (prescribed monthly fields
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI: /,
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Analysis of ozone loss in the Arctic stratosphere during the late winter and spring of 1997, using the Chemical Species Mapping on Trajectories
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Analysis of ozone loss in the Arctic stratosphere during the late winter and spring of 1997, using the Chemical Species Mapping on Trajectories
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117, D05311, doi: /2011jd016789, 2012
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016789, 2012 Ozone loss rates in the Arctic winter stratosphere during 1994 2000 derived from POAM II/III and ILAS observations: Implications
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016789, 2012 Ozone loss rates in the Arctic winter stratosphere during 1994 2000 derived from POAM II/III and ILAS observations: Implications
Variability and trends in stratospheric water vapor
 Variability and trends in stratospheric water vapor Bill Randel Atmospheric Chemistry Division NCAR, Boulder, CO Photo: Liz Moyer Climatology - Seasonal cycle (by far the largest variability) - summer
Variability and trends in stratospheric water vapor Bill Randel Atmospheric Chemistry Division NCAR, Boulder, CO Photo: Liz Moyer Climatology - Seasonal cycle (by far the largest variability) - summer
PROBLEMS Sources of CO Sources of tropospheric ozone
 220 PROBLEMS 11. 1 Sources of CO The two principal sources of CO to the atmosphere are oxidation of CH 4 and combustion. Mean rate constants for oxidation of CH 4 and CO by OH in the troposphere are k
220 PROBLEMS 11. 1 Sources of CO The two principal sources of CO to the atmosphere are oxidation of CH 4 and combustion. Mean rate constants for oxidation of CH 4 and CO by OH in the troposphere are k
10. Stratospheric chemistry. Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017
 10. Stratospheric chemistry Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 The ozone layer Dobson unit: physical thickness (0.01 mm) of ozone layer if compressed to 1 atm, 0 o
10. Stratospheric chemistry Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 The ozone layer Dobson unit: physical thickness (0.01 mm) of ozone layer if compressed to 1 atm, 0 o
CHAPTER 3. Update on Polar Ozone: Past, Present, and Future. Lead Authors: M. Dameris S. Godin-Beekmann
 CHAPTER 3 Update on Polar Ozone: Past, Present, and Future Lead Authors: M. Dameris S. Godin-Beekmann Coauthors: S. Alexander P. Braesicke M. Chipperfield A.T.J. de Laat Y. Orsolini M. Rex M.L. Santee
CHAPTER 3 Update on Polar Ozone: Past, Present, and Future Lead Authors: M. Dameris S. Godin-Beekmann Coauthors: S. Alexander P. Braesicke M. Chipperfield A.T.J. de Laat Y. Orsolini M. Rex M.L. Santee
WACCM: State of the Model
 WACCM: State of the Model Whole Atmosphere Working Group Michael Mills, liaison Andrew Gettelman, internal co-chair Lorenzo Polvani, external co-chair CESM Workshop, June 2014 Scientifically validated
WACCM: State of the Model Whole Atmosphere Working Group Michael Mills, liaison Andrew Gettelman, internal co-chair Lorenzo Polvani, external co-chair CESM Workshop, June 2014 Scientifically validated
Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven
 Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven Prevention of the atmosphere KÖRNYEZETGAZDÁLKODÁSI AGRÁRMÉRNÖKI MSC (MSc IN AGRO-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES) Fundamentals to atmospheric chemical reactions. The stratospheric
Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven Prevention of the atmosphere KÖRNYEZETGAZDÁLKODÁSI AGRÁRMÉRNÖKI MSC (MSc IN AGRO-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES) Fundamentals to atmospheric chemical reactions. The stratospheric
Peter Bernath. Old Dominion University, Norfolk, VA and University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON
 THE ATMOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY EXPERIMENT (ACE): Greenhouse Gas Measurements of CO 2, CFCs and HFCs Peter Bernath Old Dominion University, Norfolk, VA and University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON ACE Satellite
THE ATMOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY EXPERIMENT (ACE): Greenhouse Gas Measurements of CO 2, CFCs and HFCs Peter Bernath Old Dominion University, Norfolk, VA and University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON ACE Satellite
Antarctic Ozone Bulletin
 Antarctic Ozone Bulletin No 2 / 2008 View of the Argentinian station Belgrano at 79 S. The Brewer spectrophotometer can be seen on the observation platform in the middle of the photo. Data from this station
Antarctic Ozone Bulletin No 2 / 2008 View of the Argentinian station Belgrano at 79 S. The Brewer spectrophotometer can be seen on the observation platform in the middle of the photo. Data from this station
Quantitative performance metrics for stratospheric-resolving chemistry-climate models
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 8, 5699 5713, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Quantitative performance metrics for
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 8, 5699 5713, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Quantitative performance metrics for
Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) ozone profile data record characteristics, quality and applications
 Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) ozone profile data record characteristics, quality and applications A presentation for the 2016 meeting of the Committee on Earth Observation Satellites (COES) Atmospheric
Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) ozone profile data record characteristics, quality and applications A presentation for the 2016 meeting of the Committee on Earth Observation Satellites (COES) Atmospheric
Volcanoes drive climate variability by
 Volcanoes drive climate variability by 1. emitting ozone weeks before eruptions, 2. forming lower stratospheric aerosols that cool Earth, 3. causing sustained ozone depletion, surface warming, and lower
Volcanoes drive climate variability by 1. emitting ozone weeks before eruptions, 2. forming lower stratospheric aerosols that cool Earth, 3. causing sustained ozone depletion, surface warming, and lower
Comparing QBO and ENSO impacts on stratospheric transport in WACCM-SD and -FR
 Comparing QBO and ENSO impacts on stratospheric transport in WACCM-SD and -FR Multivariate ENSO Index + QBO shear index based on Singapore wind U50-U25 CESM Chemistry WG Meeting Boulder, CO February 10,
Comparing QBO and ENSO impacts on stratospheric transport in WACCM-SD and -FR Multivariate ENSO Index + QBO shear index based on Singapore wind U50-U25 CESM Chemistry WG Meeting Boulder, CO February 10,
Simulated Radiances for OMI
 Simulated Radiances for OMI document: KNMI-OMI-2000-004 version: 1.0 date: 11 February 2000 author: J.P. Veefkind approved: G.H.J. van den Oord checked: J. de Haan Index 0. Abstract 1. Introduction 2.
Simulated Radiances for OMI document: KNMI-OMI-2000-004 version: 1.0 date: 11 February 2000 author: J.P. Veefkind approved: G.H.J. van den Oord checked: J. de Haan Index 0. Abstract 1. Introduction 2.
Composition of the Atmosphere from Mid-Earth Orbit (CAMEO): Observations for air quality studies
 Community Workshop on Air Quality Remote Sensing from Space, NCAR, Boulder, 21-23 Feb 2006 Composition of the Atmosphere from Mid-Earth Orbit (CAMEO): Observations for air quality studies A future atmospheric
Community Workshop on Air Quality Remote Sensing from Space, NCAR, Boulder, 21-23 Feb 2006 Composition of the Atmosphere from Mid-Earth Orbit (CAMEO): Observations for air quality studies A future atmospheric
EPP contribution to (stratospheric and) tropospheric variations. Annika Seppälä Finnish Meteorological Institute Academy of Finland
 EPP contribution to (stratospheric and) tropospheric variations Annika Seppälä Finnish Meteorological Institute Academy of Finland A. Seppälä, HEPPA-SOLARIS Workshop, Boulder, Oct 0 So far... Energetic
EPP contribution to (stratospheric and) tropospheric variations Annika Seppälä Finnish Meteorological Institute Academy of Finland A. Seppälä, HEPPA-SOLARIS Workshop, Boulder, Oct 0 So far... Energetic
Model studies on the sensitivity of upper tropospheric chemistry to heterogeneous uptake of HNO 3 on cirrus ice particles
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. D23, 4696, doi:10.1029/2001jd000735, 2002 Model studies on the sensitivity of upper tropospheric chemistry to heterogeneous uptake of HNO 3 on cirrus ice
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. D23, 4696, doi:10.1029/2001jd000735, 2002 Model studies on the sensitivity of upper tropospheric chemistry to heterogeneous uptake of HNO 3 on cirrus ice
warmest (coldest) temperatures at summer heat dispersed upward by vertical motion Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A heated by solar radiation at the base
 Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Laura Revell, Andrea Stenke, Beiping Luo, Stefanie Kremser, Eugene Rozanov, Timofei Sukhodolov and Thomas Peter
 Impacts of Mt. Pinatubo volcanic aerosol on the tropical stratosphere in chemistry-climate model simulations using CCMI and CMIP6 stratospheric aerosol data Laura Revell, Andrea Stenke, Beiping Luo, Stefanie
Impacts of Mt. Pinatubo volcanic aerosol on the tropical stratosphere in chemistry-climate model simulations using CCMI and CMIP6 stratospheric aerosol data Laura Revell, Andrea Stenke, Beiping Luo, Stefanie
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D5, 8317, doi: /2001jd001063, 2003
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D5, 8317, doi:10.1029/2001jd001063, 2003 Large-scale chemical evolution of the Arctic vortex during the 1999/ 2000 winter: HALOE/POAM III Lagrangian photochemical
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D5, 8317, doi:10.1029/2001jd001063, 2003 Large-scale chemical evolution of the Arctic vortex during the 1999/ 2000 winter: HALOE/POAM III Lagrangian photochemical
A three-dimensional model study of long-term mid-high latitude lower stratosphere ozone changes
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 3, 1253 1265, 2003 Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics A three-dimensional model study of long-term mid-high latitude lower stratosphere ozone changes M. P. Chipperfield School of the
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 3, 1253 1265, 2003 Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics A three-dimensional model study of long-term mid-high latitude lower stratosphere ozone changes M. P. Chipperfield School of the
CLOUD DETECTION AND DISTRIBUTIONS FROM MIPAS INFRA-RED LIMB OBSERVATIONS
 CLOUD DETECTION AND DISTRIBUTIONS FROM MIPAS INFRA-RED LIMB OBSERVATIONS J. Greenhough, J. J. Remedios, and H. Sembhi EOS, Space Research Centre, Department of Physics & Astronomy, University of Leicester,
CLOUD DETECTION AND DISTRIBUTIONS FROM MIPAS INFRA-RED LIMB OBSERVATIONS J. Greenhough, J. J. Remedios, and H. Sembhi EOS, Space Research Centre, Department of Physics & Astronomy, University of Leicester,
The exceptional Arctic winter 2005/06
 SPARC data assimilation workshop, 2-4 October 2006 The exceptional Arctic winter 2005/06 An example to investigate polar processes using different assimilations systems 1, Gloria Manney 2,3, Steven Pawson
SPARC data assimilation workshop, 2-4 October 2006 The exceptional Arctic winter 2005/06 An example to investigate polar processes using different assimilations systems 1, Gloria Manney 2,3, Steven Pawson
Meridional structure of the downwelling branch of the BDC Susann Tegtmeier
 Meridional structure of the downwelling branch of the BDC Susann Tegtmeier Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel (GEOMAR), Germany SPARC Brewer-Dobson Circulation Workshop, Grindelwald, June 2012 no
Meridional structure of the downwelling branch of the BDC Susann Tegtmeier Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel (GEOMAR), Germany SPARC Brewer-Dobson Circulation Workshop, Grindelwald, June 2012 no
