Measurements of Ozone. Why is Ozone Important?
|
|
|
- Anabel Osborne
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anthropogenic Climate Changes CO 2 CFC CH 4 Human production of freons (CFCs) Ozone Hole Depletion Human production of CO2 and CH4 Global Warming Human change of land use Deforestation (from Earth s Climate: Past and Future) Measurements of Ozone (1) Number Density Number of molecules per cubic centimeter (molecules/cm 3 ). The number density is typically about 5x10 12 molecules/cm 3 near 20 to 25 km altitude, near the peak of ozone concentration in the stratosphere. (2) Layer Thickness The thickness of pure ozone would have at 1 atm pressure. One atmosphere-centimeter (1 atm-cm) is equal to 2.687x10 19 molecules/cm 2. One Dobson Unit (DU) is equivalent to a layer of pure ozone cm thick at 1 atm pressure. A typical midlatitude ozone column depth is about 300 DU (0.3 atm-cm). Standard Atmosphere (from Understanding Weather & Climate) Why is Ozone Important? The stratospheric ozone layer reduces the amount of UV-B radiation from the sun reaching Earth s surface. UV-B exposure can damage human s immune system, increase risk of skin cancer, and damage terrestrial plant life, single-cell organisms, and aquatic ecosystem. 1
2 How Is Ozone Formed? Polar Vortex Ozone Distribution Antarctic Ozone Hole The greatest production of ozone occurs in the tropics, where the solar UV flux is the highest. However, the general circulation in the stratosphere transport ozone-rich air from the tropical upper stratosphere to mid-to-high latitudes. Ozone column depths are highest during springtime at mid-to-high latitudes. Ozone column depths are the lowest over the equator. Ozone Production and Destruction Photodissociation (or photolysis) visible light destroy O3 permanently 2
3 Radiation and Ozone Ozone Production UV photons are required for ozone production: O2 + UV photon O + O Below about 20 km, UV photons are absorbed by ozone. Therefore, O2 can be photolyzed only above 20 km. This is why the ozone layer is located in the stratosphere and not near Earth s surface. Ozone Destruction O3 can be split by radiation in the visible-light range: O3 + photon O 2 + O Because many more visible photons than UV photons are available, O3 is photolyzed (ozone destruction) much faster than O 2 (ozone production). Also, O3 can be photolyzed all the way sown to Earth s surface. The Chlorine Catalytic Cycle The Catalyst Other Ozone Destruction Processes Other atmospheric trace constituents, such as nitrous oxide (N2O), water vapor, and freons, can also be photolyzed. They produce highly reactive radicals that keep ozone abundances lower than they would otherwise be. These radicals include: nitric oxide (NO), atomic chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br) radicals, and hydroxyl (OH) radicals. These radicals can destroy stratospheric ozone through catalytic cycles. A catalytic cycle is a set of chemical reactions facilitated by the presence of a catalyst. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction but is itself unchanged by the reaction. The Chlorine Catalytic Cycle 3
4 The Nitrogen Catalytic Cycle The Catalyst The Odd Nitrogen Cycle from UV photolysis of ozone N2O: from Earth s surface, where it is produced by microbial activity in soil and in the ocean. In the stratosphere, some of N2O reacts to form NO, the rest is photolyzed back to N2 and O2. The NO so produced participates in the ozone-destroying nitrogen catalytic cycle. Once for a while, the resulting NO2 molecule interacts with a hydroxyl radical (OH), producing nitric acid (HNO3). Nitric Acid (HNO3) then diffuses down into the troposphere and dissolves into rain. Where do those ozone-depleting catalysts come from? (1) Cl related to natural and man-made substances (2) Br related to natural and man-made substances (3) NO2 reacts with Cl and Br to produce reservoirs for Cl and Br. Other Sources of NO N2O is currently the largest source of stratospheric odd nitrogen (NO and NO2). How human activity affect NO? high-flying, supersonic transport airplanes Jet plane-produced high temperatures from combustion. combine N2 and O2 to form NO. injected NO goes to the stratosphere and destroy ozone This is why jet plans can affect stratospheric ozone layer (even though jet plans fly in the upper troposphere). 4
5 The Chlorine Cycle Chlorine Sources Natural sources of chlorine: (1) Methyl chloride (CH3Cl): produced by marine plankton. (2) Hydrogen chloride (HCl): produced by volcanic eruption and by evaporation of sea spray. These natural-generated chlorine are most removed by precipitation before they reach the stratosphere. The largest sources of stratospheric chlorine today are freons (CFCs), which are thropogenic compounds. CFCs do not react in either the troposphere or lower stratosphere CFCs go all the way to the upper stratosphere and are photolyzed by UV radiation. The Cl so produced proceeds to destroy ozone. Eventually, Cl react with CH4 and is diffused to the troposphere, where it is precipitated out. Man-Made Sources for CFCs The Bromine Cycle Br is also a ozone-depleting catalyst There are two kinds of CFCs: freon-11 (CCl3F) and freon-12 (CCl2F2). Freon-11 has been used: (1) as a propellant in spray cans (2) as a blowing agent for producing foams (3) to clean semiconductor chips. The bromine cycle is similar to the chlorine cycle. The natural source of bromine is Methyl Bromine (Ch3Br), which is a byproduct of biological activity in the ocean. These natural source reacts in the troposphere. The man-made source of bromine is two chemical compounds: Halon-1211 (CF2ClBr) and Halon-1301 (CF3Br). Freon-12 has been used as (1) a refrigerant (2) working fluid in most car air conditioners. These two halons are used in certain types of fire extinguishers. Halons diffuse up to the stratosphere, where they are photolyzed into bromine atmos. They eventually rain out. 5
6 Bromine Sources Coupling Between Odd Nitrogen and Chlorine Cycles reactive unreactive Throughout most of the lower stratosphere, the nitrogen and chlorine cycles are coupled by the above chemical reaction. The chlorine nitrate (ClONO2) formed in this reaction does not react directly with either ozone or atomic oxygen. Therefore, this coupling reaction keeps chlorine from being in its reactive forms (Cl and ClO) (which can destroy ozone). Polar Stratospheric Clouds (PSCs) How PSCs Affect Chlorine? (Sweden, January 2000; from NASA website) In winter the polar stratosphere is so cold (-80 C or below) that certain trace atmospheric constituents can condense. These clouds are called polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs). The particles that form typically consist of a mixture of water and nitric acid (HNO3). The PSCs alter the chemistry of the lower stratosphere in two ways: (1) by slow down the coupling between the odd nitrogen and chlorine cycles (2) by providing surfaces on which heterogeneous reactions can occur. In most of the seasons, there are always abundant NO2 in the stratosphere to tie up a significant fraction of the available chlorine in the form of chlorine nitrate. In the wintertime Antarctic stratosphere, NO2 concentrations are low, because most of the odd nitrogen has been converted into HNO3 and become droplets in PSCs (polar stratospheric clouds). Therefore, the formation of PSCs allow reactive chlorine concentration to increases. The PSCs particles also help convert unreactive forms of chlorine into reactive chlorine by providing surfaces on which heterogeneous reaction can occur. On PCSs destroy ozone 6
7 Three Factors for the Ozone Hole Chemical Reactions polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs) Atmospheric Circulation stratospheric polar vortex Sunlight spring season In Winter!! Antarctic Ozone Hole Mean Total Ozone Over Antarctic in October The decrease in ozone near the South Pole is most striking near the spring time (October). During the rest of the year, ozone levels have remained close to normal in the region. The Polar Vortex The wintertime circulation over the South Pole is characterized by a gigantic whirlpool of cold and dense air, called the polar vortex. The cold and dense cold air in the middle of the vortex is subsiding. The sinking air carries cloud particles along with it. Remove odd nitrogen from the stratosphere. Very little ozone and odd nitrogen can be brought into the south pole. Satellite View of the Ozone Hole September 6,
8 The 1997 Ozone Hole Global Total Ozone Change Ozone Hole Depletion Long Antarctic winter (May through September) The stratosphere is cold enough to form PSCs PSCs deplete odd nitrogen (NO) Help convert unreactive forms of chlorine (ClONO2 and HCl) into more reactive forms (such as Cl2). The reactive chlorine remains bound to the surface of clouds particles. Sunlight returns in springtime (September) The sunlight releases reactive chlorine from the particle surface. The chlorine destroy ozone in October. Ozone hole appears. At the end of winter, the polar vortex breaks down. Allow fresh ozone and odd nitrogen to be brought in from low latitudes. The ozone hole recovers (disappears) until next October. Why No Ozone Hole in Artic? 8
warmest (coldest) temperatures at summer heat dispersed upward by vertical motion Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A heated by solar radiation at the base
 Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 31. Air Pollution Part II
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 31 Air Pollution Part II Last time we talked mainly about two types of smog:. 1. London-type smog 2. L.A.-type smog or photochemical smog What are the necessary ingredients
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 31 Air Pollution Part II Last time we talked mainly about two types of smog:. 1. London-type smog 2. L.A.-type smog or photochemical smog What are the necessary ingredients
ClO + O -> Cl + O 2 Net: O 3 + O -> O 2 + O 2
 Lecture 36. Stratospheric ozone chemistry. Part2: Threats against ozone. Objectives: 1. Chlorine chemistry. 2. Volcanic stratospheric aerosols. 3. Polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs). Readings: Turco: p.
Lecture 36. Stratospheric ozone chemistry. Part2: Threats against ozone. Objectives: 1. Chlorine chemistry. 2. Volcanic stratospheric aerosols. 3. Polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs). Readings: Turco: p.
CHEM/ENVS 380 S14, Midterm Exam ANSWERS 1 Apr 2014
 PART- A. Multiple Choice Questions (5 points each): Each question may have more than one correct answer. You must select ALL correct answers, and correct answers only, to receive full credit. 1. Which
PART- A. Multiple Choice Questions (5 points each): Each question may have more than one correct answer. You must select ALL correct answers, and correct answers only, to receive full credit. 1. Which
Chemistry 471/671. Atmospheric Chemistry III: Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
 Chemistry 471/671 Atmospheric Chemistry III: Stratospheric Ozone Depletion 2 The Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hn 2 O( 1 D) O( 1 D) + O 2 + M O 3 + M Exothermic O( 1 D) + O 3 2 O 2 O 3 + hn O( 1 D) + O 2 ( 1
Chemistry 471/671 Atmospheric Chemistry III: Stratospheric Ozone Depletion 2 The Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hn 2 O( 1 D) O( 1 D) + O 2 + M O 3 + M Exothermic O( 1 D) + O 3 2 O 2 O 3 + hn O( 1 D) + O 2 ( 1
CONTENTS 1 MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION
 i CONTENTS 1 MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION 1 1.1 MIXING RATIO 1 1.2 NUMBER DENSITY 2 1.3 PARTIAL PRESSURE 6 PROBLEMS 10 1.1 Fog formation 10 1.2 Phase partitioning of water in cloud 10 1.3 The ozone
i CONTENTS 1 MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION 1 1.1 MIXING RATIO 1 1.2 NUMBER DENSITY 2 1.3 PARTIAL PRESSURE 6 PROBLEMS 10 1.1 Fog formation 10 1.2 Phase partitioning of water in cloud 10 1.3 The ozone
Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven
 Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven Prevention of the atmosphere KÖRNYEZETGAZDÁLKODÁSI AGRÁRMÉRNÖKI MSC (MSc IN AGRO-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES) Fundamentals to atmospheric chemical reactions. The stratospheric
Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven Prevention of the atmosphere KÖRNYEZETGAZDÁLKODÁSI AGRÁRMÉRNÖKI MSC (MSc IN AGRO-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES) Fundamentals to atmospheric chemical reactions. The stratospheric
Lecture 15 Antarctic Ozone Hole ATOC/CHEM 5151
 Lecture 15 Antarctic Ozone Hole ATOC/CHEM 5151 1 Ozone Hole Theories 1. Solar activity: During periods of high solar activity, energetic particles are deposited high in the atmosphere, creating NOx. Perhaps
Lecture 15 Antarctic Ozone Hole ATOC/CHEM 5151 1 Ozone Hole Theories 1. Solar activity: During periods of high solar activity, energetic particles are deposited high in the atmosphere, creating NOx. Perhaps
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere
 Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
STRATOSPHERIC OZONE DEPLETION. Adapted from K. Sturges at MBHS
 STRATOSPHERIC OZONE DEPLETION Adapted from K. Sturges at MBHS Ozone Layer Ozone is Good up high Stratosphere Bad nearby Troposphere Solar Radiation - range of electromagnetic waves UV shortest we see if
STRATOSPHERIC OZONE DEPLETION Adapted from K. Sturges at MBHS Ozone Layer Ozone is Good up high Stratosphere Bad nearby Troposphere Solar Radiation - range of electromagnetic waves UV shortest we see if
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 9, 2016 The Game Changer. Some perspective The British Antarctic Survey The Ozone Hole International Regulations
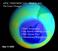 ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 9, 2016 The Game Changer Some perspective The British Antarctic Survey The Ozone Hole International Regulations Rowland (1974): The work is going very well, but it may mean the
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 9, 2016 The Game Changer Some perspective The British Antarctic Survey The Ozone Hole International Regulations Rowland (1974): The work is going very well, but it may mean the
atmosphere: a mixture a gases that surrounds the planet Earth.
 atmosphere: a mixture a gases that surrounds the planet Earth. 78% nitrogen 21% oxygen the atmosphere is held to the Earth by the force of gravity. Due to the smaller mass of planets like Mercury, less
atmosphere: a mixture a gases that surrounds the planet Earth. 78% nitrogen 21% oxygen the atmosphere is held to the Earth by the force of gravity. Due to the smaller mass of planets like Mercury, less
Stratospheric Ozone: An Online Learning Module
 Stratospheric Ozone: An Online Learning Module Using your favorite browser open Ozone/index.htm or go to http://cs.clark.edu/~mac/geol390/stratosphericozone/startozoneactivity.html Work through the web
Stratospheric Ozone: An Online Learning Module Using your favorite browser open Ozone/index.htm or go to http://cs.clark.edu/~mac/geol390/stratosphericozone/startozoneactivity.html Work through the web
SUSTAINABILITY MATTERS FACT SHEET 7: THE HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER
 SUSTAINABILITY MATTERS FACT SHEET 7: THE HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER What is the ozone layer? Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen, which means it is a pure element, but has a different chemical structure to that
SUSTAINABILITY MATTERS FACT SHEET 7: THE HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER What is the ozone layer? Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen, which means it is a pure element, but has a different chemical structure to that
The Atmosphere. All of it. In one hour. Mikael Witte 10/27/2010
 The Atmosphere All of it. In one hour. Mikael Witte 10/27/2010 Outline Structure Dynamics - heat transport Composition Trace constituent compounds Some Atmospheric Processes Ozone destruction in stratosphere
The Atmosphere All of it. In one hour. Mikael Witte 10/27/2010 Outline Structure Dynamics - heat transport Composition Trace constituent compounds Some Atmospheric Processes Ozone destruction in stratosphere
Atmospheric Chemistry III
 Atmospheric Chemistry III Chapman chemistry, catalytic cycles: reminder Source of catalysts, transport to stratosphere: reminder Effect of major (O 2 ) and minor (N 2 O, CH 4 ) biogenic gases on [O 3 ]:
Atmospheric Chemistry III Chapman chemistry, catalytic cycles: reminder Source of catalysts, transport to stratosphere: reminder Effect of major (O 2 ) and minor (N 2 O, CH 4 ) biogenic gases on [O 3 ]:
10. Stratospheric chemistry. Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017
 10. Stratospheric chemistry Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 The ozone layer Dobson unit: physical thickness (0.01 mm) of ozone layer if compressed to 1 atm, 0 o
10. Stratospheric chemistry Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 The ozone layer Dobson unit: physical thickness (0.01 mm) of ozone layer if compressed to 1 atm, 0 o
2. Sketch a plot of R vs. z. Comment on the shape. Explain physically why R(z) has a maximum in the atmospheric column.
 190 PROBLEMS 10. 1 Shape of the ozone layer Consider a beam of solar radiation of wavelength λ propagating downward in the vertical direction with an actinic flux I at the top of the atmosphere. Assume
190 PROBLEMS 10. 1 Shape of the ozone layer Consider a beam of solar radiation of wavelength λ propagating downward in the vertical direction with an actinic flux I at the top of the atmosphere. Assume
Table of Contents. Chapter: Atmosphere. Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere. Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere. Section 3: Air Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement Table of Contents Chapter 4: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere
Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement Table of Contents Chapter 4: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere
Stratosphere and Ozone
 Stratosphere and Ozone Ozone (Greek, ozein, to smell) O 3 Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hv O + O O + O 3 2O 2 O 3 + hv O 2 + O O + O 2 + M O 3 + M third-body. anything What units are used to report the amount
Stratosphere and Ozone Ozone (Greek, ozein, to smell) O 3 Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hv O + O O + O 3 2O 2 O 3 + hv O 2 + O O + O 2 + M O 3 + M third-body. anything What units are used to report the amount
Chapter 2 Protecting the Ozone Layer. The Ozone Hole
 Today (Tues 2/24) Newspaper Articles: Ciara Rodwell and Melissa Regan Intro to Ozone, Ozone Hole, & Chapter 2 Light, matter, and human health! Laboratory: Experiment 4 You design investigation Start Ozone
Today (Tues 2/24) Newspaper Articles: Ciara Rodwell and Melissa Regan Intro to Ozone, Ozone Hole, & Chapter 2 Light, matter, and human health! Laboratory: Experiment 4 You design investigation Start Ozone
An Interpretation of Natural Healing of Ozone Holes
 ISSN 2278 0211 (Online) An Interpretation of Natural Healing of Ozone Holes Vasudevan Tachoth Nirvan Industries, Private Industrial Estate, Post Sidco Near Railway Gate, Kuruchi Coimbatore, India Abstract:
ISSN 2278 0211 (Online) An Interpretation of Natural Healing of Ozone Holes Vasudevan Tachoth Nirvan Industries, Private Industrial Estate, Post Sidco Near Railway Gate, Kuruchi Coimbatore, India Abstract:
Ozone Depletion. Dana Desonie, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click (No sign in required)
 Ozone Depletion Dana Desonie, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content,
Ozone Depletion Dana Desonie, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content,
OZONE AND ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION
 OZONE AND ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION Alfio Parisi, Michael Kimlin Imagine if the earth s protective atmosphere did not exist and the earth was subjected to the harmful ultraviolet energy from the sun. Life
OZONE AND ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION Alfio Parisi, Michael Kimlin Imagine if the earth s protective atmosphere did not exist and the earth was subjected to the harmful ultraviolet energy from the sun. Life
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II
 Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes THE DESTRUCTION OF STRATOSPHERIC OZONE The ozone hole
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes THE DESTRUCTION OF STRATOSPHERIC OZONE The ozone hole
Stratospheric O 3 : Overview
 Stratospheric Chemistry READING: Chapter 10 of text Mid-latitude Ozone Chemistry (and depletion) Polar Ozone Destruction (the Ozone Hole) Stratospheric O 3 : Overview Most O 3 (90%) in stratosphere. Remaining
Stratospheric Chemistry READING: Chapter 10 of text Mid-latitude Ozone Chemistry (and depletion) Polar Ozone Destruction (the Ozone Hole) Stratospheric O 3 : Overview Most O 3 (90%) in stratosphere. Remaining
1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely
 CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Air Pollution Chemistry Lecture 1
 ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Air Pollution Chemistry Lecture 1 Note Page numbers refer to Daniel Jacob s online textbook: http://acmg.seas.harvard.edu/publications/ jacobbook/index.html Atmos = vapor + sphaira
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Air Pollution Chemistry Lecture 1 Note Page numbers refer to Daniel Jacob s online textbook: http://acmg.seas.harvard.edu/publications/ jacobbook/index.html Atmos = vapor + sphaira
Table of Contents. Chapter: Atmosphere. Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere. Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere. Section 3: Air Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement 1 Earth s Atmosphere Importance of the Atmosphere Earth's atmosphere
Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement 1 Earth s Atmosphere Importance of the Atmosphere Earth's atmosphere
Section 2: The Atmosphere
 Section 2: The Atmosphere Preview Classroom Catalyst Objectives The Atmosphere Composition of the Atmosphere Air Pressure Layers of the Atmosphere The Troposphere Section 2: The Atmosphere Preview, continued
Section 2: The Atmosphere Preview Classroom Catalyst Objectives The Atmosphere Composition of the Atmosphere Air Pressure Layers of the Atmosphere The Troposphere Section 2: The Atmosphere Preview, continued
The Earth is surrounded by a blanket of air, which we call the atmosphere. It reaches over 560 kilometers
 A t m o s f e r a Atmosphere The Earth is surrounded by a blanket of air, which we call the atmosphere. It reaches over 560 kilometers (348 miles) from the surface of the Earth, so we are only able to
A t m o s f e r a Atmosphere The Earth is surrounded by a blanket of air, which we call the atmosphere. It reaches over 560 kilometers (348 miles) from the surface of the Earth, so we are only able to
Website Lecture 3 The Physical Environment Part 1
 Website http://websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 3 The Physical Environment Part 1 1 Lectures 3 & 4 1. Biogeochemical Cycling 2. Solar Radiation 3. The Atmosphere 4. The Global Ocean 5. Weather and Climate
Website http://websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 3 The Physical Environment Part 1 1 Lectures 3 & 4 1. Biogeochemical Cycling 2. Solar Radiation 3. The Atmosphere 4. The Global Ocean 5. Weather and Climate
Chapman Cycle. The cycle describes reactions of O 2 and O 3 in stratosphere
 Chapman Cycle The cycle describes reactions of O 2 and O 3 in stratosphere Even though reactions are happening, the concentration of O 3 remains constant This is an example of a dynamic equilibrium or
Chapman Cycle The cycle describes reactions of O 2 and O 3 in stratosphere Even though reactions are happening, the concentration of O 3 remains constant This is an example of a dynamic equilibrium or
Ozone. In the upper atmosphere. At the surface pollution (not discussed)
 Ozone In the upper atmosphere At the surface pollution (not discussed) What is Ozone? Oxygen molecule with 3 oxygen atoms O 3 Normal form of oxygen: 2 oxygen atoms O 2 Where does Ozone occur? Stratosphere
Ozone In the upper atmosphere At the surface pollution (not discussed) What is Ozone? Oxygen molecule with 3 oxygen atoms O 3 Normal form of oxygen: 2 oxygen atoms O 2 Where does Ozone occur? Stratosphere
Temperature. Vertical Thermal Structure. Earth s Climate System. Lecture 1: Introduction to the Climate System
 Lecture 1: Introduction to the Climate System T mass (& radiation) T & mass relation in vertical mass (& energy, weather..) Energy T vertical stability vertical motion thunderstorm What are included in
Lecture 1: Introduction to the Climate System T mass (& radiation) T & mass relation in vertical mass (& energy, weather..) Energy T vertical stability vertical motion thunderstorm What are included in
Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation
 Outline Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation Review electromagnetic radiation absorptivity by selective gases temperature vs. height in atmosphere Ozone production and destruction natural balance anthropogenic
Outline Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation Review electromagnetic radiation absorptivity by selective gases temperature vs. height in atmosphere Ozone production and destruction natural balance anthropogenic
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds. What is an atmosphere? About 10 km thick
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? Sources of Gas Losses of Gas Thermal Escape Earth s Atmosphere About 10 km thick Consists mostly of molecular
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? Sources of Gas Losses of Gas Thermal Escape Earth s Atmosphere About 10 km thick Consists mostly of molecular
 ATM 507 Lecture 9 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Next Class Tuesday, Sept. 30 Today s topics Polar Stratospheric Chemistry and the Ozone Hole, Required reading: 20 Questions and
ATM 507 Lecture 9 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Next Class Tuesday, Sept. 30 Today s topics Polar Stratospheric Chemistry and the Ozone Hole, Required reading: 20 Questions and
IV. Atmospheric Science Section
 EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines IV. Atmospheric Science Section 1. Introduction, Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere Learning objectives: Understand the basic characteristics
EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines IV. Atmospheric Science Section 1. Introduction, Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere Learning objectives: Understand the basic characteristics
Chapter 4 Lesson 1: Describing Earth s Atmosphere
 Chapter 4 Lesson 1: Describing Earth s Atmosphere Vocabulary Importance of Earth s Atmosphere The atmosphere is a thin layer of gases surrounding Earth. o Contains the oxygen and water needed for life.
Chapter 4 Lesson 1: Describing Earth s Atmosphere Vocabulary Importance of Earth s Atmosphere The atmosphere is a thin layer of gases surrounding Earth. o Contains the oxygen and water needed for life.
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds. What is an atmosphere? Earth s Atmosphere. Atmospheric Pressure
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Day 1 of Global Warming. Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Day 1 of Global Warming Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings The Atmosphere Atmosphere = the thin layer (1/100 th of Earth s diameter) of gases that surrounds
Day 1 of Global Warming Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings The Atmosphere Atmosphere = the thin layer (1/100 th of Earth s diameter) of gases that surrounds
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Mario Molina puts the atmosphere and ozone on the political agenda
 Mario Molina puts the atmosphere and ozone on the political agenda (Version 1) A. Understanding ozone 60 km stratosphere 40 km 20 km troposphere Diagram of our atmosphere (Reproduced with permission from
Mario Molina puts the atmosphere and ozone on the political agenda (Version 1) A. Understanding ozone 60 km stratosphere 40 km 20 km troposphere Diagram of our atmosphere (Reproduced with permission from
1. Composition and Structure
 Atmospheric sciences focuses on understanding the atmosphere of the earth and other planets. The motivations for studying atmospheric sciences are largely: weather forecasting, climate studies, atmospheric
Atmospheric sciences focuses on understanding the atmosphere of the earth and other planets. The motivations for studying atmospheric sciences are largely: weather forecasting, climate studies, atmospheric
I T A T I O N H B I T B T V A O C J K M R S A T M O S P H E R E
 Word Search Directions: Below are definitions of vocabulary terms. Figure out each term and then find and circle it in the puzzle. Words may appear horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. K E M I S S
Word Search Directions: Below are definitions of vocabulary terms. Figure out each term and then find and circle it in the puzzle. Words may appear horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. K E M I S S
Layer Protection Glossary
 Page 1 of 7 Ozone Layer Protection Last updated on Wednesday, December 15, 2010 You are here: EPA Home Ozone Layer Protection Ozone Layer Protection Glossary Layer Protection Glossary In order to understand
Page 1 of 7 Ozone Layer Protection Last updated on Wednesday, December 15, 2010 You are here: EPA Home Ozone Layer Protection Ozone Layer Protection Glossary Layer Protection Glossary In order to understand
2/22/ Atmospheric Characteristics
 17.1 Atmospheric Characteristics Atmosphere: the gaseous layer that surrounds the Earth I. In the past, gases came from volcanic eruptions A. Water vapor was a major component of outgassing B. Other gases
17.1 Atmospheric Characteristics Atmosphere: the gaseous layer that surrounds the Earth I. In the past, gases came from volcanic eruptions A. Water vapor was a major component of outgassing B. Other gases
Lecture 25: Atmosphere & environment
 Lecture 25: Atmosphere & environment Read: BLB 18.1 4 HW: BLB 18:9,11,15,29,69 Sup 18:1 3 Know: ozone chemistry chemistry of the lower atmosphere sulfer compounds & acid rain nitrogen oxides & smog check
Lecture 25: Atmosphere & environment Read: BLB 18.1 4 HW: BLB 18:9,11,15,29,69 Sup 18:1 3 Know: ozone chemistry chemistry of the lower atmosphere sulfer compounds & acid rain nitrogen oxides & smog check
Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review
 Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Climate in a region is a. the long-term,
Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Climate in a region is a. the long-term,
The Atmosphere. Characteristics of the Atmosphere. Section 23.1 Objectives. Chapter 23. Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science. Section 1
 The Atmosphere Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of the Atmosphere Chapter 23 Section 1 Section 23.1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers
The Atmosphere Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of the Atmosphere Chapter 23 Section 1 Section 23.1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers
Chemistry of Ozone. Explain the following terms: resonance, resonance hybrid, delocalisation
 Chemistry of Ozone Ozone is triatomic oxygen, O 3. (Ozone is from the Greek ozein, to smell. ) It is a form of oxygen in which the atoms combine in threes, (correct IUPAC name: trioxygen, O 3 ), rather
Chemistry of Ozone Ozone is triatomic oxygen, O 3. (Ozone is from the Greek ozein, to smell. ) It is a form of oxygen in which the atoms combine in threes, (correct IUPAC name: trioxygen, O 3 ), rather
Overview Atmosphere. Meeting Individual Needs. Directed Reading for Content Mastery
 Directed Reading for Content Mastery Overview Atmosphere Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. weather exosphere coldest air temperature ionosphere stratosphere 1. which
Directed Reading for Content Mastery Overview Atmosphere Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. weather exosphere coldest air temperature ionosphere stratosphere 1. which
The Atmosphere - Chapter Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 Section Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers work. Identify the layers of the atmosphere. Identify two effects of air pollution. The Atmosphere
Section Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers work. Identify the layers of the atmosphere. Identify two effects of air pollution. The Atmosphere
Atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere is a mixture of gases, solids, and liquids that surround the planet.
 Atmosphere Atmosphere- a thin layer of air that forms a protective covering around the planet. If Earth had no atmosphere, days would be extremely hot and nights would be extremely cold. Earth's atmosphere
Atmosphere Atmosphere- a thin layer of air that forms a protective covering around the planet. If Earth had no atmosphere, days would be extremely hot and nights would be extremely cold. Earth's atmosphere
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning:! What is an atmosphere?! How does the greenhouse effect warm
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning:! What is an atmosphere?! How does the greenhouse effect warm
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds. What is an atmosphere? Planetary Atmospheres
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? Planetary Atmospheres Pressure Composition Greenhouse effect Atmospheric structure Color of the sky 1 Atmospheres
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? Planetary Atmospheres Pressure Composition Greenhouse effect Atmospheric structure Color of the sky 1 Atmospheres
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II
 Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes REVIEW... Q Is the depletion of STRATOSPHERIC OZONE (in
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes REVIEW... Q Is the depletion of STRATOSPHERIC OZONE (in
Stratospheric Chemistry
 Stratospheric Chemistry Stratospheric Chemistry Why Ozone? Part of global energy balance determines T and hence u. Protection of the biosphere from UV. Sensitive to human pollution. Search for extraterrestrial
Stratospheric Chemistry Stratospheric Chemistry Why Ozone? Part of global energy balance determines T and hence u. Protection of the biosphere from UV. Sensitive to human pollution. Search for extraterrestrial
Gases, ozone, and CFCs. An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop
 Gases, ozone, and CFCs An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Gas Gas Model Gases are composed of tiny, widely-spaced particles. For a typical gas, the average distance between particles is about
Gases, ozone, and CFCs An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Gas Gas Model Gases are composed of tiny, widely-spaced particles. For a typical gas, the average distance between particles is about
Chapter 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer
 Chapter 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer Student: 1. O2 and O3 molecules are A. allotropes. B. structural isomers. C. isotopes. D. geometrical isomers. 2. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are there
Chapter 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer Student: 1. O2 and O3 molecules are A. allotropes. B. structural isomers. C. isotopes. D. geometrical isomers. 2. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are there
ATM 507 Meeting 6. ftp://ftp.nilu.no/pub/nilu/geir/assessment-2006/10%20q&aschapter.pdf
 ATM 507 Meeting 6 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 4 due Oct. 11 Today s topics Polar Stratospheric Chemistry and the Ozone Hole, Global Ozone Trends Required reading: 20 Questions and Answers from
ATM 507 Meeting 6 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 4 due Oct. 11 Today s topics Polar Stratospheric Chemistry and the Ozone Hole, Global Ozone Trends Required reading: 20 Questions and Answers from
The Atmosphere Made up of mainly two gases: Nitrogen 78% Oxygen 21% Trace Gases 1%
 The Atmosphere 18.1 The Atmosphere Made up of mainly two gases: Nitrogen 78% Oxygen 21% Trace Gases 1% Layers of the Atmosphere made made up of 5 layers: Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Ionosphere
The Atmosphere 18.1 The Atmosphere Made up of mainly two gases: Nitrogen 78% Oxygen 21% Trace Gases 1% Layers of the Atmosphere made made up of 5 layers: Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Ionosphere
The Atmosphere. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems
 The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
Website Lecture 3 The Physical Environment Part 1
 Website http://websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 3 The Physical Environment Part 1 1 Lectures 3 & 4 1. Biogeochemical Cycling 2. Solar Radiation 3. The Atmosphere 4. The Global Ocean 5. Weather and Climate
Website http://websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 3 The Physical Environment Part 1 1 Lectures 3 & 4 1. Biogeochemical Cycling 2. Solar Radiation 3. The Atmosphere 4. The Global Ocean 5. Weather and Climate
8.2 Tropospheric ozone
 8.2 Tropospheric ozone Prev Chapter 8. Ozone Next 8.2 Tropospheric ozone Tropospheric ozone is only about 10% of the total amount of ozone contained in a vertical column in the atmosphere. However, this
8.2 Tropospheric ozone Prev Chapter 8. Ozone Next 8.2 Tropospheric ozone Tropospheric ozone is only about 10% of the total amount of ozone contained in a vertical column in the atmosphere. However, this
Biomes and Biodiversity
 Biomes and Biodiversity Agenda 2/4/13 Biomes review terrestrial and aquatic Biodiversity Climate Change Introduction Weather Terrestrial Biomes Review Tundra Boreal Forest (Taiga) Temperate Forest Temperate
Biomes and Biodiversity Agenda 2/4/13 Biomes review terrestrial and aquatic Biodiversity Climate Change Introduction Weather Terrestrial Biomes Review Tundra Boreal Forest (Taiga) Temperate Forest Temperate
Chapman. 4. O + O 3 2 O 2 ; k 4 5. NO + O 3 NO 2 + O 2 ; k 5 6. NO 2 + O NO + O 2 ; k 6 7. NO 2 + hν NO + O; k 7. NO X Catalytic.
 ATM 507 Lecture 8 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Note: next week class as usual Tuesday, no class on Thursday Today s topics Mid-latitude Stratosphere Lower Stratosphere 1 Let s
ATM 507 Lecture 8 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Note: next week class as usual Tuesday, no class on Thursday Today s topics Mid-latitude Stratosphere Lower Stratosphere 1 Let s
2. (i) Infrared (radiation absorbed) by (C H) bond vibration ALLOW bond stretching OR bond bending DO NOT ALLOW molecules vibrating 2
 . (i) Species with an unpaired electron ALLOW atom, molecule or particle with an unpaired electron ALLOW has an unpaired electron ALLOW particle formed by homolytic fission DO NOT ALLOW particle with a
. (i) Species with an unpaired electron ALLOW atom, molecule or particle with an unpaired electron ALLOW has an unpaired electron ALLOW particle formed by homolytic fission DO NOT ALLOW particle with a
(for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes)
 www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. chem10b 18.2-30 What is the final stage in municipal water treatment? A. aeration B. settling C. removal of added fluoride
www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. chem10b 18.2-30 What is the final stage in municipal water treatment? A. aeration B. settling C. removal of added fluoride
Thermal / Solar. When air is warmed it... Rises. Solar Energy. Evaporation. Condensation Forms Clouds
 Thermal / Solar Light from the Sun is transformed into what type of energy when it hits Earth's surface? Rises When air is warmed it... Solar Energy Water moves through the water cycle using what type
Thermal / Solar Light from the Sun is transformed into what type of energy when it hits Earth's surface? Rises When air is warmed it... Solar Energy Water moves through the water cycle using what type
Layers of the Earth, Ozone Layer and Spheres of the Earth
 Layers of the Earth, Ozone Layer and Spheres of the Earth Importance of the Atmosphere: Earth s atmosphere is a thin layer of air that forms a protective covering around the planet, without which days
Layers of the Earth, Ozone Layer and Spheres of the Earth Importance of the Atmosphere: Earth s atmosphere is a thin layer of air that forms a protective covering around the planet, without which days
Space Atmospheric Gases. the two most common gases; found throughout all the layers a form of oxygen found in the stratosphere
 Earth s atmospheric layers Earth s atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the planet and makes conditions on Earth suitable for living things. Layers Earth s atmosphere is divided into several
Earth s atmospheric layers Earth s atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the planet and makes conditions on Earth suitable for living things. Layers Earth s atmosphere is divided into several
General Comments about the Atmospheres of Terrestrial Planets
 General Comments about the Atmospheres of Terrestrial Planets Mercury Very little atmosphere Contents: vaporized micrometeorites, solar wind Sky is black Venus Very thick (10% density of water), dense
General Comments about the Atmospheres of Terrestrial Planets Mercury Very little atmosphere Contents: vaporized micrometeorites, solar wind Sky is black Venus Very thick (10% density of water), dense
Climate & Earth System Science. Introduction to Meteorology & Climate CHAPTER 1 LECTURE 1. Question: Introduction to the Atmosphere
 Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Outline. Planetary Atmospheres. General Comments about the Atmospheres of Terrestrial Planets. General Comments, continued
 Outline Planetary Atmospheres Chapter 10 General comments about terrestrial planet atmospheres Atmospheric structure & the generic atmosphere Greenhouse effect Magnetosphere & the aurora Weather & climate
Outline Planetary Atmospheres Chapter 10 General comments about terrestrial planet atmospheres Atmospheric structure & the generic atmosphere Greenhouse effect Magnetosphere & the aurora Weather & climate
Attendance Sign-Up Sheet. A L: Light Yellow-Green. M Y: Bright Orange
 Attendance Sign-Up Sheet Last Name A L: Light Yellow-Green M Y: Bright Orange Lecture #02 January 13, 2010, Wednesday (1) Thickness of the atmosphere (2) Composition of the atmosphere (3) Thermodynamic
Attendance Sign-Up Sheet Last Name A L: Light Yellow-Green M Y: Bright Orange Lecture #02 January 13, 2010, Wednesday (1) Thickness of the atmosphere (2) Composition of the atmosphere (3) Thermodynamic
EOH 468: Air Pollution and Health. Introduction. History of Air Pollution. Dr. Peter Bellin, CIH, Ph.D. Spring 2008
 EOH 468: Air Pollution and Health Dr. Peter Bellin, CIH, Ph.D. Spring 2008 Introduction Syllabus posted on-line. Lecture notes. Texts: recommend they be purchased. Try to do readings, draft answers to
EOH 468: Air Pollution and Health Dr. Peter Bellin, CIH, Ph.D. Spring 2008 Introduction Syllabus posted on-line. Lecture notes. Texts: recommend they be purchased. Try to do readings, draft answers to
Today. Events. Terrestrial Planet Geology - Earth. Terrestrial Planet Atmospheres. Homework DUE next time
 Today Terrestrial Planet Geology - Earth Terrestrial Planet Atmospheres Events Homework DUE next time Ring of Fire Boundaries of plates traced by Earthquakes and Volcanos Plate Motions Measurements of
Today Terrestrial Planet Geology - Earth Terrestrial Planet Atmospheres Events Homework DUE next time Ring of Fire Boundaries of plates traced by Earthquakes and Volcanos Plate Motions Measurements of
Scholarship 2015 Earth and Space Science
 S 93104R Scholarship 2015 Earth and Space Science 2.00 p.m. Tuesday 1 December 2015 RESOURCE BOOKLET Refer to this booklet to answer the questions for Scholarship Earth and Space Science 93104. Check that
S 93104R Scholarship 2015 Earth and Space Science 2.00 p.m. Tuesday 1 December 2015 RESOURCE BOOKLET Refer to this booklet to answer the questions for Scholarship Earth and Space Science 93104. Check that
SCIAMACHY book. Ozone variability and long-term changes Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA-IASB
 SCIAMACHY book Ozone variability and long-term changes Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA-IASB 1928: start of CFC production 1971: 1 st observation of CFC in the atmosphere (J. Lovelock) 1974: identification
SCIAMACHY book Ozone variability and long-term changes Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA-IASB 1928: start of CFC production 1971: 1 st observation of CFC in the atmosphere (J. Lovelock) 1974: identification
General A haloalkane is a compound in which one or more H atoms of an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms.
 aloalkanes General A haloalkane is a compound in which one or more atoms of an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms. If one hydrogen atom is replaced, the general formula is n 2n+1 X where X = F, l, Br
aloalkanes General A haloalkane is a compound in which one or more atoms of an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms. If one hydrogen atom is replaced, the general formula is n 2n+1 X where X = F, l, Br
Atmosphere. Transfer in the Atmosphere
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Earth s Atmosphere Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Air Currents Air Quality Chapter Wrap-Up How does Earth s atmosphere affect life on Earth?
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Earth s Atmosphere Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Air Currents Air Quality Chapter Wrap-Up How does Earth s atmosphere affect life on Earth?
Unit 9. Atmosphere. Natural Science 1º ESO Antonio Jesús Moreno Quintero. Colegio Guadalete. Attendis.
 9. Atmosphere Unit 9. Atmosphere. 1 1. The Earth s atmosphere. Atmosphere: envelope of gases and particles which surrounds the Earth. Evolution of the atmosphere 1 st state: hydrogen and helium. It was
9. Atmosphere Unit 9. Atmosphere. 1 1. The Earth s atmosphere. Atmosphere: envelope of gases and particles which surrounds the Earth. Evolution of the atmosphere 1 st state: hydrogen and helium. It was
Chapter 7. Stratospheric Chemistry.
 Chapter 7. Stratospheric Chemistry. Stratospheric chemistry became environmental chemistry in the early 1970 s when scientists studied the potential stratospheric effects of supersonic aircraft (Crutzen,
Chapter 7. Stratospheric Chemistry. Stratospheric chemistry became environmental chemistry in the early 1970 s when scientists studied the potential stratospheric effects of supersonic aircraft (Crutzen,
Assessment Schedule 2017 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of processes in the atmosphere system (91414)
 NCEA Level 3 Earth and Space Science (91414) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of processes in the atmosphere system (91414) Evidence Statement
NCEA Level 3 Earth and Space Science (91414) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of processes in the atmosphere system (91414) Evidence Statement
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate
 Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 16 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 16 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 16 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
). It is a gas produced naturally in the stratosphere where it strongly absorbs incoming
 Page 1 of 6 What Determines How Much Ultraviolet Radiation Reaches the Earth s Surface? The amount of UV radiation reaching the Earth s surface varies widely around the globe and through time. Several
Page 1 of 6 What Determines How Much Ultraviolet Radiation Reaches the Earth s Surface? The amount of UV radiation reaching the Earth s surface varies widely around the globe and through time. Several
CHEM Chemical Kinetics
 Chemical Kinetics Catalysts A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of the reaction but is neither created nor destroyed in the process. Catalysts can be divided into two broad categories. Homogeneous
Chemical Kinetics Catalysts A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of the reaction but is neither created nor destroyed in the process. Catalysts can be divided into two broad categories. Homogeneous
 Part I Short Answer Choose a letter to fill in the blanks. Use choices as many times as you wish. Only one choice is needed per blank. All are 3 points each. 1. First set. How can you tell these apart?
Part I Short Answer Choose a letter to fill in the blanks. Use choices as many times as you wish. Only one choice is needed per blank. All are 3 points each. 1. First set. How can you tell these apart?
Name Period Date L.O: SWBAT DESCRIBE THE PROPERTIES OF THE ATMOSPHERE.(
 Name Period Date L.O: SWBAT DESCRIBE THE PROPERTIES OF THE ATMOSPHERE.( 1. Scientists have inferred that Earth s original atmosphere was formed by the A) outgassing from Earth s interior B) erosion of
Name Period Date L.O: SWBAT DESCRIBE THE PROPERTIES OF THE ATMOSPHERE.( 1. Scientists have inferred that Earth s original atmosphere was formed by the A) outgassing from Earth s interior B) erosion of
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE During a rainstorm, the air feels moist On a clear, cloudless day, the air may feel dry As the sun heats the land and oceans, the amount of water in the atmosphere changes Water
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE During a rainstorm, the air feels moist On a clear, cloudless day, the air may feel dry As the sun heats the land and oceans, the amount of water in the atmosphere changes Water
The Cosmic Perspective Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds
 Chapter 10 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics
Chapter 10 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics
The Atmosphere. Composition of the Atmosphere. Section 2
 The Atmosphere Earth is surrounded by a mixture of gases known as the Nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other gases are all parts of this mixture. Earth s atmosphere changes constantly as these gases
The Atmosphere Earth is surrounded by a mixture of gases known as the Nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other gases are all parts of this mixture. Earth s atmosphere changes constantly as these gases
5. In which diagram is the observer experiencing the greatest intensity of insolation? A) B)
 1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
1. Which factor has the greatest influence on the number of daylight hours that a particular Earth surface location receives? A) longitude B) latitude C) diameter of Earth D) distance from the Sun 2. In
Evolution of the Atmosphere
 Evolution of the Atmosphere Anticipation Guide Oxygen is the main gas found in the atmosphere The current atmosphere is the same atmosphere that the Earth had when it formed Water vapor is a gas found
Evolution of the Atmosphere Anticipation Guide Oxygen is the main gas found in the atmosphere The current atmosphere is the same atmosphere that the Earth had when it formed Water vapor is a gas found
Science Chapter 13,14,15
 Science 1206 Chapter 13,14,15 1 Weather dynamics is the study of how the motion of water and air causes weather patterns. Energy from the Sun drives the motion of clouds, air, and water. Earth s tilt at
Science 1206 Chapter 13,14,15 1 Weather dynamics is the study of how the motion of water and air causes weather patterns. Energy from the Sun drives the motion of clouds, air, and water. Earth s tilt at
Global Warming and Climate Change Part I: Ozone Depletion
 GCOE-ARS : November 18, 2010 Global Warming and Climate Change Part I: Ozone Depletion YODEN Shigeo Department of Geophysics, Kyoto University 1. Stratospheric Ozone and History of the Earth 2. Observations
GCOE-ARS : November 18, 2010 Global Warming and Climate Change Part I: Ozone Depletion YODEN Shigeo Department of Geophysics, Kyoto University 1. Stratospheric Ozone and History of the Earth 2. Observations
