WACCM: The High-Top Model
|
|
|
- Kevin Richard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison (303) km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218, 2001
2 WACCM Additions to CAM Extends from surface to 5.1x10-6 hpa (~150 km), with 66 vertical levels Detailed neutral chemistry model for the middle atmosphere, catalytic cycles affecting ozone heterogeneous chemistry on PSCs and sulfate aerosol heating due to chemical reactions Model of ion chemistry in the mesosphere/lower thermosphere (MLT), ion drag, auroral processes, and solar proton events EUV and non-lte longwave radiation parameterizations Imposed QBO, based on cyclic, fixed-phase, or observed winds Volcanic aerosol heating calculated explicitly Gravity wave drag deposition from vertically propagating GWs generated by orography, fronts, and convection Molecular diffusion and constituent separation Thermosphere extension (WACCM-X) to ~500 km
3 WACCM Motivation Roble, Geophysical Monograph, v. 123, p. 53, 2000 Coupling between atmospheric layers: Waves transport energy and momentum from the lower atmosphere to drive the QBO, SAO, sudden warmings, mean meridional circulation Solar inputs, e.g. auroral production of NO in the mesosphere and downward transport to the stratosphere Stratosphere-troposphere exchange Climate Variability and Climate Change: What is the impact of the stratosphere on tropospheric variability? How important is coupling among radiation, chemistry, and circulation? (e.g., in the response to O3 depletion or CO2 increase) Response to solar variability: impacts mediated by chemistry? Interpretation of Satellite Observations
4 CESM-WACCM component configurations CAM atmosphere specified chemistry free-running WACCM static (pre-industrial or present-day) ocean free-running data observations specified dynamics transient climatology land sea ice free-running data observations climatology freerunning data observations climatology
5 Stratospheric Sulfate Surface Area Density Climatology 50N EQ 50S 50N EQ 50S El Chichón 17 N, 93 W Agung 8 S, 115 E Sulfate Surface Area Density, 43 hpa Mt Pinatubo: 15 N, 120 E Krakatau: 6 S, 105 E, Aug Santa Maria: 14 N, 91 W, 24 Oct Observations used: SAGE I, SAGE II, SAM II, and SME instruments. Non-volcanic periods filled with monthly mean of values. Used Pinatubo aerosol for Krakatau and Santa Maria.
6 Krakatoa 1883 Santa Maria 1902 Agung 1963 Chichón 1982 Surface Temperature Anomalies normalized to Santa Maria 1902 Pinatubo 1991 CCSM-CAM4 1deg WACCM4 Pre-Indusrtrial WACCM4 20th Century WACCM Observations (HadCRUT3) Agung 1963 Chichón 1982 Pinatubo 1991 Agung 1963 Chichón 1982 Pinatubo 1991 Krakatoa 1883 Krakatoa 1883 Santa Maria 1902
7 Volcanic heating in WACCM 2 N Surface Area (cm 2 cm -3 ) Multiple aerosol independent parameters derived from observations used as inputs. 2 N 2 N Sulfate Mass (µg m -3 ) Effective Radius (cm)
8 Volcanic heating in WACCM Pinatubo 1991 Pinatubo 1991 Temperature anomalies calculated with WACCM (black lines) and observed (grey lines) at pressures in the lower stratosphere (Tilmes et al., 2009) Pinatubo 1991
9 Grading of Chemistry in CCMs: Chapter 6 of the SPaRC CCMVal CCMs were evaluated on their ability to represent longlived constituents (precursors) and short-lived substances (radicals). WACCM graded out high in all categories (i.e., grade of 1 is the highest possible). This is a reflection of the: 1) completeness of the chemical processes included 2) accuracy of photolysis rates (J s) 3) and accuracy of the numerical solution approach. SPARC CCMVal, Report on the Evaluation of Chemistry-Climate Models, V.Eyring, T. G. Shepherd, D. W. Waugh (EDs.), SPARC Reprot No.4, WCRP-X, WMO/TD-No. X,
10 WACCM Heterogeneous Chemistry Module Sulfate Aerosols (H 2 O, H 2 SO 4 ) - LBS k=1/4*v*sad*γ (SAD from SAGEII) R lbs = 0.1 μm Temperature >200 K 188 K (T sat ) Sulfate Aerosols (H 2 O, HNO 3, H 2 SO 4 ) - STS Thermo. Model (Tabazadeh) Nitric Acid Hydrate (H 2 O, HNO 3 ) NAT R NAT = ƒ {Log Normal Size; # particles cc; width distribution; condensed phase HNO 3 }? R sts = 0.5 μm ICE (H 2 O, with NAT Coating) 185 K (T nuc ) R ice = μm
11 WACCM Ozone Trend: CCMVal and WMO Antarctic Spring WACCM does better than most models at calculating the evolution of the ozone hole. Redrawn from: Austin, J., et al., J. Geophys. Res., in press., 2010.
12 Antarctic sea-ice extent CCSM4 (CAM4) -- Pre-Industrial WACCM4 -- Pre-Industrial Observed ave -- ice-ocean hindcast Satellite CCSM4 (CAM) dashed lines: ( ave) - PI solid lines: ( ave) - PI WACCM4 The more realistic ozone loss in WACCM drives changes in winds that enhance sea-ice loss, producing sea-ice extent closer to modern observations.
13 Acceleration of the Brewer Dobson Circulation due to Increases in Greenhouse Gases Garcia and Randel, J. Atmos. Sci., vol. 65 (8), pp , faster circulation in greenhouse world due to enhanced propagation of wave activity into the lower stratosphere and its dissipation in the subtropics 20th Century Age of Air (y), ~10 hpa, tropics Future, fixed GHGs changes in meridional temperature gradient affect zonal winds, which change the regions where waves dissipate, increasing momentum deposition Future, increasing GHGs
14 Impact of geoengineered aerosols on the troposphere and stratosphere Tilmes et al., J. Geophys. Res., vol. 114, pp , ~5 years for adjustment of temperatures Constant temperature offset Temperature: Geoengineering - Baseline The fixed amount of sulfur cools the Earth s surface by ~0.9 K (Tropics), ~1.2 K (Global) Delay of global warming by ~ 40 years Dependence on continuous injection of sulfur T anomaly (K) Baseline / Geoengineering 40 km year km year km year surface year
15 Impact of geoengineered aerosols on the troposphere and stratosphere Tilmes et al., J. Geophys. Res., vol. 114, pp , Impacts of geoengineering on ozone Baseline Geoengineering Altitude (km) Latitude Impact of geoengineering Difference of annual mean zonally averaged global ozone values between present day (2010 future ( ) for (a) the baseline run and (b) the geoengineering run. (c) Difference of n zonally averaged global ozone values between geoengineering and baseline runs for future 0) conditions. Hatched areas are not significant at 95% level based on Student s t test. in the lower stratosphere compared to arcia and Randel, 2008]. Further, the tion is discussed below for the tropics, midlatitudes and polar regions.
16 Massive global ozone loss predicted following regional nuclear conflict Mills et al., PNAS, vol. 105, pp. 5307, 2008 WACCM input: new estimates of smoke produced by fires in contemporary cities following a regional nuclear war between India and Pakistan Solar radiation heats the soot, lofting it to the stratopause, heating the the entire stratosphere for 10 years, altering reaction rates affecting ozone. Calculated ozone losses exceed 20% globally, 25-45% at midlatitudes, and 50-70% at northern high latitudes persisting for 5 years, with substantial losses continuing for 5 additional years. Column ozone amounts remain below that which defines the Antarctic ozone hole everywhere outside of the tropics.
17 Nuclear winter in WACCM4 Black Carbon Input hpa GISS ModelE Year WACCM4 GISS ModelE WACCM4 GISS ModelE (Robock et al., 1997) WACCM4 Year
18 WACCM and CAM-Chem Customer Support CGD Forum: Mike Mills WACCM Liaison (303) Simone Tilmes CAM-Chem Liaison (303)
WACCM: The High-Top Model
 WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
Descrip(on of Chemistry, Aerosols in CESM and WACCM
 Descrip(on of Chemistry, Aerosols in CESM and WACCM Presented by Simone Tilmes, Mike Mills NESL: ACD/CGD Chemistry- Climate WG Co- Chairs: Louisa Emmons, Stephen Ghan, Noelle Eckley Selin WACCM WG Co-
Descrip(on of Chemistry, Aerosols in CESM and WACCM Presented by Simone Tilmes, Mike Mills NESL: ACD/CGD Chemistry- Climate WG Co- Chairs: Louisa Emmons, Stephen Ghan, Noelle Eckley Selin WACCM WG Co-
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1153966/dc1 Supporting Online Material for The Sensitivity of Polar Ozone Depletion to Proposed Geoengineering Schemes Simone Tilmes,* Rolf Müller, Ross Salawitch *To
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1153966/dc1 Supporting Online Material for The Sensitivity of Polar Ozone Depletion to Proposed Geoengineering Schemes Simone Tilmes,* Rolf Müller, Ross Salawitch *To
Impact of Solar and Sulfate Geoengineering on Surface Ozone
 Impact of Solar and Sulfate Geoengineering on Surface Ozone Lili Xia 1, Peer J. Nowack 2, Simone Tilmes 3 and Alan Robock 1 1 Department of Environmental Sciences, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ
Impact of Solar and Sulfate Geoengineering on Surface Ozone Lili Xia 1, Peer J. Nowack 2, Simone Tilmes 3 and Alan Robock 1 1 Department of Environmental Sciences, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ
CESM1-WACCM: Comparison with CCSM4/ CESM CMIP5 simulations
 CESM1-WACCM: Comparison with CCSM4/ CESM CMIP5 simulations Dan Marsh, Mike Mills, Natalia Calvo, Marika Holland, Cécile Hannay WAWG meeting, Boulder, February 2011 NCAR is sponsored by the National Science
CESM1-WACCM: Comparison with CCSM4/ CESM CMIP5 simulations Dan Marsh, Mike Mills, Natalia Calvo, Marika Holland, Cécile Hannay WAWG meeting, Boulder, February 2011 NCAR is sponsored by the National Science
Impacts of historical ozone changes on climate in GFDL-CM3
 Impacts of historical ozone changes on climate in GFDL-CM3 Larry Horowitz (GFDL) with: Vaishali Naik (GFDL), Pu Lin (CICS), and M. Daniel Schwarzkopf (GFDL) WMO (2014) Figure ADM 5-1 1 Response of tropospheric
Impacts of historical ozone changes on climate in GFDL-CM3 Larry Horowitz (GFDL) with: Vaishali Naik (GFDL), Pu Lin (CICS), and M. Daniel Schwarzkopf (GFDL) WMO (2014) Figure ADM 5-1 1 Response of tropospheric
WACCM: State of the Model
 WACCM: State of the Model Whole Atmosphere Working Group Michael Mills, liaison Andrew Gettelman, internal co-chair Lorenzo Polvani, external co-chair CESM Workshop, June 2014 Scientifically validated
WACCM: State of the Model Whole Atmosphere Working Group Michael Mills, liaison Andrew Gettelman, internal co-chair Lorenzo Polvani, external co-chair CESM Workshop, June 2014 Scientifically validated
warmest (coldest) temperatures at summer heat dispersed upward by vertical motion Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A heated by solar radiation at the base
 Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Dynamical Mechanism for the Increase in Tropical Upwelling in the Lowermost Tropical Stratosphere during Warm ENSO Events
 JULY 2010 C A L V O E T A L. 2331 Dynamical Mechanism for the Increase in Tropical Upwelling in the Lowermost Tropical Stratosphere during Warm ENSO Events N. CALVO Atmospheric Chemistry Division, NCAR,*
JULY 2010 C A L V O E T A L. 2331 Dynamical Mechanism for the Increase in Tropical Upwelling in the Lowermost Tropical Stratosphere during Warm ENSO Events N. CALVO Atmospheric Chemistry Division, NCAR,*
Atmospheric Coupling via Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP)
 Atmospheric Coupling via Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP) Cora E. Randall University of Colorado Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Acknowledgments
Atmospheric Coupling via Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP) Cora E. Randall University of Colorado Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Acknowledgments
Dynamical coupling between the middle atmosphere and lower thermosphere
 Dynamical coupling between the middle atmosphere and lower thermosphere Anne Smith, Dan Marsh, Nick Pedatella NCAR* Tomoko Matsuo CIRES/NOAA NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Model runs
Dynamical coupling between the middle atmosphere and lower thermosphere Anne Smith, Dan Marsh, Nick Pedatella NCAR* Tomoko Matsuo CIRES/NOAA NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Model runs
CESM2 (WACCM6): Stratospheric Evaluation
 CESM2 (WACCM6): Stratospheric Evaluation D. Kinnison, M. Mills, R. Garcia, D. Marsh, A. Gettelman, F. Vitt, S. Glanville, C. Bardeen, S. Tilmes, A. Smith, J-F. Lamarque, L. Emmons, A. Conley, J. Richter,
CESM2 (WACCM6): Stratospheric Evaluation D. Kinnison, M. Mills, R. Garcia, D. Marsh, A. Gettelman, F. Vitt, S. Glanville, C. Bardeen, S. Tilmes, A. Smith, J-F. Lamarque, L. Emmons, A. Conley, J. Richter,
Role of the QBO in modulating the influence of the 11 year solar cycle on the atmosphere using constant forcings
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd013020, 2010 Role of the QBO in modulating the influence of the 11 year solar cycle on the atmosphere using constant forcings Katja Matthes,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd013020, 2010 Role of the QBO in modulating the influence of the 11 year solar cycle on the atmosphere using constant forcings Katja Matthes,
State of WACCM. A. Gettelman, L. M. Polvani, M. Mills + WACCM Team
 State of WACCM A. Gettelman, L. M. Polvani, M. Mills + WACCM Team WACCM4/5 Highlights CCMI Simulations (Kinnison) WACCM Last Millennium Run GEOMIP Experiments (Mills) WACCM6 Current Plans/Progress Updated
State of WACCM A. Gettelman, L. M. Polvani, M. Mills + WACCM Team WACCM4/5 Highlights CCMI Simulations (Kinnison) WACCM Last Millennium Run GEOMIP Experiments (Mills) WACCM6 Current Plans/Progress Updated
Elevated stratopause and mesospheric intrusion following a stratospheric sudden warming in WACCM
 Elevated stratopause and mesospheric intrusion following a stratospheric sudden warming in WACCM Yvan J. Orsolini 1,V. Limpasuvan 2, J. Richter 3, O. K. Kvissel 4, F. Stordal 4,D. Marsh 3 1 Norwegian Institute
Elevated stratopause and mesospheric intrusion following a stratospheric sudden warming in WACCM Yvan J. Orsolini 1,V. Limpasuvan 2, J. Richter 3, O. K. Kvissel 4, F. Stordal 4,D. Marsh 3 1 Norwegian Institute
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric sulfate burdens
 Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric sulfate burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric sulfate burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric
The 11 year solar cycle signal in transient simulations from the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016393, 2012 The 11 year solar cycle signal in transient simulations from the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model G. Chiodo, 1 N. Calvo,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016393, 2012 The 11 year solar cycle signal in transient simulations from the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model G. Chiodo, 1 N. Calvo,
SC-WACCM! and! Problems with Specifying the Ozone Hole
 SC-WACCM! and! Problems with Specifying the Ozone Hole R. Neely III, K. Smith2, D. Marsh,L. Polvani2 NCAR, 2Columbia Thanks to: Mike Mills, Francis Vitt and Sean Santos Motivation To design a stratosphere-resolving
SC-WACCM! and! Problems with Specifying the Ozone Hole R. Neely III, K. Smith2, D. Marsh,L. Polvani2 NCAR, 2Columbia Thanks to: Mike Mills, Francis Vitt and Sean Santos Motivation To design a stratosphere-resolving
ENSO influence on zonal mean temperature and ozone in the tropical lower stratosphere
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L15822, doi:10.1029/2009gl039343, 2009 ENSO influence on zonal mean temperature and ozone in the tropical lower stratosphere William J. Randel, 1 Rolando R. Garcia,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L15822, doi:10.1029/2009gl039343, 2009 ENSO influence on zonal mean temperature and ozone in the tropical lower stratosphere William J. Randel, 1 Rolando R. Garcia,
Do large tropical volcanic eruptions influence the Southern Annular Mode?
 SPARC GA, Queenstown, NZ, January 14, 2014 Do large tropical volcanic eruptions influence the Southern Annular Mode? Kirstin Krüger 1,2, Matt Toohey 2, Doreen Metzner 2,3 ( 1 UiO, Oslo, Norway; 2 GEOMAR,
SPARC GA, Queenstown, NZ, January 14, 2014 Do large tropical volcanic eruptions influence the Southern Annular Mode? Kirstin Krüger 1,2, Matt Toohey 2, Doreen Metzner 2,3 ( 1 UiO, Oslo, Norway; 2 GEOMAR,
Impact of wind changes in the upper troposphere lower stratosphere on tropical ozone
 Impact of wind changes in the upper troposphere lower stratosphere on tropical ozone Martin Dameris Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR) Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre, Oberpfaffenhofen
Impact of wind changes in the upper troposphere lower stratosphere on tropical ozone Martin Dameris Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR) Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre, Oberpfaffenhofen
Effect of zonal asymmetries in stratospheric ozone on simulated Southern Hemisphere climate trends
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L18701, doi:10.1029/2009gl040419, 2009 Effect of zonal asymmetries in stratospheric ozone on simulated Southern Hemisphere climate trends
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L18701, doi:10.1029/2009gl040419, 2009 Effect of zonal asymmetries in stratospheric ozone on simulated Southern Hemisphere climate trends
Measurements of Ozone. Why is Ozone Important?
 Anthropogenic Climate Changes CO 2 CFC CH 4 Human production of freons (CFCs) Ozone Hole Depletion Human production of CO2 and CH4 Global Warming Human change of land use Deforestation (from Earth s Climate:
Anthropogenic Climate Changes CO 2 CFC CH 4 Human production of freons (CFCs) Ozone Hole Depletion Human production of CO2 and CH4 Global Warming Human change of land use Deforestation (from Earth s Climate:
Sophie Oberländer, Ulrike Langematz, Stefanie Meul Institut für Meteorologie, Freie Universität Berlin
 Future changes in the Brewer-Dobson Circulation and possible causes derived from Chemistry-ClimateClimate Model Simulations, Ulrike Langematz, Stefanie Meul Institut für Meteorologie, Freie Universität
Future changes in the Brewer-Dobson Circulation and possible causes derived from Chemistry-ClimateClimate Model Simulations, Ulrike Langematz, Stefanie Meul Institut für Meteorologie, Freie Universität
Climate Throughout Geologic Time Has Been Controlled Primarily by the Balance Between
 Climate Throughout Geologic Time Has Been Controlled Primarily by the Balance Between Cooling Caused by Major Explosive Eruptions of Evolved Magmas Typical of Island Arcs and Warming Caused by Voluminous
Climate Throughout Geologic Time Has Been Controlled Primarily by the Balance Between Cooling Caused by Major Explosive Eruptions of Evolved Magmas Typical of Island Arcs and Warming Caused by Voluminous
FORCING ANTHROPOGENIC
 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING Earth-Sun orbital relationships, changing landsea distribution (due to plate tectonics), solar variability & VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS vs. ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING Human-Enhanced GH Effect,
NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING Earth-Sun orbital relationships, changing landsea distribution (due to plate tectonics), solar variability & VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS vs. ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING Human-Enhanced GH Effect,
Math, Models, and Climate Change How shaving cream moved a jet stream, and how mathematics can help us better understand why
 Math, Models, and Climate Change How shaving cream moved a jet stream, and how mathematics can help us better understand why Edwin P. Gerber Center for Atmosphere and Ocean Science Courant Institute of
Math, Models, and Climate Change How shaving cream moved a jet stream, and how mathematics can help us better understand why Edwin P. Gerber Center for Atmosphere and Ocean Science Courant Institute of
Chemistry-Climate Models: What we have and what we need
 Chemistry-Climate Models: What we have and what we need Dan Marsh National Center for Atmospheric Research NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Outline Overview of processes in our current
Chemistry-Climate Models: What we have and what we need Dan Marsh National Center for Atmospheric Research NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Outline Overview of processes in our current
Separating the dynamical effects of climate change and ozone depletion. Part I: Southern Hemisphere stratosphere
 Separating the dynamical effects of climate change and ozone depletion. Part I: Southern Hemisphere stratosphere Article Published Version McLandress, C., Jonsson, A. I., Plummer, D. A., Reader, M. C.,
Separating the dynamical effects of climate change and ozone depletion. Part I: Southern Hemisphere stratosphere Article Published Version McLandress, C., Jonsson, A. I., Plummer, D. A., Reader, M. C.,
Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of
 Article Atmospheric Science September 2013 Vol.58 No.25: 3155 3160 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5945-5 Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of 2010 2011 HU YongYun 1* & XIA
Article Atmospheric Science September 2013 Vol.58 No.25: 3155 3160 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5945-5 Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of 2010 2011 HU YongYun 1* & XIA
A distinct stronger warming in the tropical tropopause layer during using GPS radio occultation: Association with minor volcanic eruptions
 A distinct stronger warming in the tropical tropopause layer during 2001-2010 using GPS radio occultation: Association with minor volcanic eruptions Sanjay Kumar Mehta 1*, Masatomo Fujiwara 2, and Toshitaka
A distinct stronger warming in the tropical tropopause layer during 2001-2010 using GPS radio occultation: Association with minor volcanic eruptions Sanjay Kumar Mehta 1*, Masatomo Fujiwara 2, and Toshitaka
Dynamical balances and tropical stratospheric upwelling
 Dynamical balances and tropical stratospheric upwelling Bill Randel and Rolando Garcia NCAR Thanks to: Qiang Fu, Andrew Gettelman, Rei Ueyama, Mike Wallace, plus WACCM group at NCAR. Background: Well-known
Dynamical balances and tropical stratospheric upwelling Bill Randel and Rolando Garcia NCAR Thanks to: Qiang Fu, Andrew Gettelman, Rei Ueyama, Mike Wallace, plus WACCM group at NCAR. Background: Well-known
Global Response to the Major Volcanic Eruptions in 9 Reanalysis Datasets
 Global Response to the Major Volcanic Eruptions in 9 Reanalysis Datasets Masatomo Fujiwara and Takashi Hibino (Hokkaido Univ., Japan) Sanjay Kumar Mehta (Kyoto Univ., Japan) Lesley Gray, Daniel Mitchell,
Global Response to the Major Volcanic Eruptions in 9 Reanalysis Datasets Masatomo Fujiwara and Takashi Hibino (Hokkaido Univ., Japan) Sanjay Kumar Mehta (Kyoto Univ., Japan) Lesley Gray, Daniel Mitchell,
Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM) and Its Thermosphere/Ionosphere Extension (WACCM-X)
 Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM) and Its Thermosphere/Ionosphere Extension (WACCM-X) WAWG Co-Chairs: Han-Li Liu, NCAR/HAO Lorenzo Polvani, Columbia University Scientific Objectives of WACCM
Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM) and Its Thermosphere/Ionosphere Extension (WACCM-X) WAWG Co-Chairs: Han-Li Liu, NCAR/HAO Lorenzo Polvani, Columbia University Scientific Objectives of WACCM
Comparing QBO and ENSO impacts on stratospheric transport in WACCM-SD and -FR
 Comparing QBO and ENSO impacts on stratospheric transport in WACCM-SD and -FR Multivariate ENSO Index + QBO shear index based on Singapore wind U50-U25 CESM Chemistry WG Meeting Boulder, CO February 10,
Comparing QBO and ENSO impacts on stratospheric transport in WACCM-SD and -FR Multivariate ENSO Index + QBO shear index based on Singapore wind U50-U25 CESM Chemistry WG Meeting Boulder, CO February 10,
IMPULSIVE NITRATE DEPOSITION EVENTS IN POLAR ICE THE RESULT OF SOLAR PROTON EVENTS. D. F. Smart and M. A. Shea SYNOPSIS
 IMPULSIVE NITRATE DEPOSITION EVENTS IN POLAR ICE THE RESULT OF SOLAR PROTON EVENTS D. F. Smart and M. A. Shea Emeritus at AFRL (RVBXS), Bedford, MA, 01731, USA SYNOPSIS The endothermic chemical reaction
IMPULSIVE NITRATE DEPOSITION EVENTS IN POLAR ICE THE RESULT OF SOLAR PROTON EVENTS D. F. Smart and M. A. Shea Emeritus at AFRL (RVBXS), Bedford, MA, 01731, USA SYNOPSIS The endothermic chemical reaction
The Impact of Polar Stratospheric Ozone Loss on Southern Hemisphere Stratospheric Circulation and Surface Climate
 The Impact of Polar Stratospheric Ozone Loss on Southern Hemisphere Stratospheric Circulation and Surface Climate James Keeble, Peter Braesicke, Howard Roscoe and John Pyle James.keeble@atm.ch.cam.ac.uk
The Impact of Polar Stratospheric Ozone Loss on Southern Hemisphere Stratospheric Circulation and Surface Climate James Keeble, Peter Braesicke, Howard Roscoe and John Pyle James.keeble@atm.ch.cam.ac.uk
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric burdens
 Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric and
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric and
Summary. Introduction The solar variability Some words about the Earth's atmosphere Simulations and results
 Summary Introduction The solar variability Some words about the Earth's atmosphere Simulations and results Introduction Understanding and quantifying the natural variability of climate on decadal and centennial
Summary Introduction The solar variability Some words about the Earth's atmosphere Simulations and results Introduction Understanding and quantifying the natural variability of climate on decadal and centennial
Recent anthropogenic increases in SO2 from Asia have minimal impact on stratospheric aerosol
 !1 Recent anthropogenic increases in SO2 from Asia have minimal impact on stratospheric aerosol Ryan R. Neely III (NCAR/ASP), O. Brian Toon, Susan Solomon, Karen H. Rosenlof, John S Daniel, J. English,
!1 Recent anthropogenic increases in SO2 from Asia have minimal impact on stratospheric aerosol Ryan R. Neely III (NCAR/ASP), O. Brian Toon, Susan Solomon, Karen H. Rosenlof, John S Daniel, J. English,
Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure
 Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure Hua Lu British Antarctic Survey Outline Background: Sun-Earth Climate Connection Solar wind/geomagnetic activity signals with 3 examples stratospheric
Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure Hua Lu British Antarctic Survey Outline Background: Sun-Earth Climate Connection Solar wind/geomagnetic activity signals with 3 examples stratospheric
On the Determination of Age of Air Trends from Atmospheric Trace Species
 JANUARY 2011 G A R C I A E T A L. 139 On the Determination of Age of Air Trends from Atmospheric Trace Species ROLANDO R. GARCIA, WILLIAM J. RANDEL, AND DOUGLAS E. KINNISON National Center for Atmospheric
JANUARY 2011 G A R C I A E T A L. 139 On the Determination of Age of Air Trends from Atmospheric Trace Species ROLANDO R. GARCIA, WILLIAM J. RANDEL, AND DOUGLAS E. KINNISON National Center for Atmospheric
NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING Part II
 TOPIC #12 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING Part II (p 72 in Class Notes) Today we will focus on the third main driver of NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING: 1) ATRONOMICAL FORCING 2) SOLAR FORCING 3) VOLCANIC FORCING VOLCANIC
TOPIC #12 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING Part II (p 72 in Class Notes) Today we will focus on the third main driver of NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING: 1) ATRONOMICAL FORCING 2) SOLAR FORCING 3) VOLCANIC FORCING VOLCANIC
Solar cycle signal in a general circulation and chemistry model with internally generated quasi biennial oscillation
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012542, 2010 Solar cycle signal in a general circulation and chemistry model with internally generated quasi biennial
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012542, 2010 Solar cycle signal in a general circulation and chemistry model with internally generated quasi biennial
Modelling the atmosphere. Hennie Kelder University of Technology Eindhoven
 Modelling the atmosphere Hennie Kelder University of Technology Eindhoven Content Basics of the atmosphere Atmospheric dynamics Large scale circulation Planetary waves Brewer-Dobson circulation Some Key
Modelling the atmosphere Hennie Kelder University of Technology Eindhoven Content Basics of the atmosphere Atmospheric dynamics Large scale circulation Planetary waves Brewer-Dobson circulation Some Key
The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate
 The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate Mark P. Baldwin Northwest Research Associates, USA SORCE, 27 October 2004 Overview Climatology of the
The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate Mark P. Baldwin Northwest Research Associates, USA SORCE, 27 October 2004 Overview Climatology of the
The Scientific Value of Stratospheric Wind Measurements
 Working Group on Space-based Lidar Winds, Monterey, 2008 The Scientific Value of Stratospheric Wind Measurements Ted Shepherd Department of Physics University of Toronto The distribution of ozone (important
Working Group on Space-based Lidar Winds, Monterey, 2008 The Scientific Value of Stratospheric Wind Measurements Ted Shepherd Department of Physics University of Toronto The distribution of ozone (important
Effects of Large Volcanic Eruptions on Global Summer Climate and East Asian Monsoon Changes
 The image cannot be displayed. Your computer may not have enough memory to open the image, or the image may have been corrupted. Restart your computer, and then open the file again. If the red x still
The image cannot be displayed. Your computer may not have enough memory to open the image, or the image may have been corrupted. Restart your computer, and then open the file again. If the red x still
The Atmosphere. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems
 The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
Physical and Optical Properties of the Stratospheric Aerosol Layer
 Physical and Optical Properties of the Stratospheric Aerosol Layer Patrick Hamill Department of Physics and Astronomy San Jose State University San Jose, California Justification for this Talk Much debate
Physical and Optical Properties of the Stratospheric Aerosol Layer Patrick Hamill Department of Physics and Astronomy San Jose State University San Jose, California Justification for this Talk Much debate
P4.2 THE THREE DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE AND TIME EVOLUTION OF THE DECADAL VARIABILITY REVEALED IN ECMWF REANALYSES
 P4.2 THE THREE DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE AND TIME EVOLUTION OF THE DECADAL VARIABILITY REVEALED IN ECMWF REANALYSES Taehyoun Shim 1, Gyu-Ho Lim* 1 and Dong-In Lee 2 1 School of Earth and Environmental Sciences,
P4.2 THE THREE DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE AND TIME EVOLUTION OF THE DECADAL VARIABILITY REVEALED IN ECMWF REANALYSES Taehyoun Shim 1, Gyu-Ho Lim* 1 and Dong-In Lee 2 1 School of Earth and Environmental Sciences,
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming?
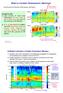 What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
Simulation of secular trends in the middle atmosphere,
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd007485, 2007 Simulation of secular trends in the middle atmosphere, 1950 2003 R. R. Garcia, 1 D. R. Marsh, 1 D.
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd007485, 2007 Simulation of secular trends in the middle atmosphere, 1950 2003 R. R. Garcia, 1 D. R. Marsh, 1 D.
Report on the first SOLARIS workshop 4-6 October 2006, Boulder, Colorado, USA
 Report on the first SOLARIS workshop 4-6 October 2006, Boulder, Colorado, USA K. Matthes, Freie Universität Berlin, Institut für Meteorologie, Berlin, Germany and National Center for Atmospheric Research,
Report on the first SOLARIS workshop 4-6 October 2006, Boulder, Colorado, USA K. Matthes, Freie Universität Berlin, Institut für Meteorologie, Berlin, Germany and National Center for Atmospheric Research,
CCM Modelling : LMDz-Reprobus
 CCM Modelling : LMDz-Reprobus Marchand Marion, Slimane Bekki, Franck Lefèvre, François Lott, David Cugnet, Line Jourdain, Perrine Lemmenais, Virginie Poulain, Julien Jumelet, Slimane Bekki, marie-pierre
CCM Modelling : LMDz-Reprobus Marchand Marion, Slimane Bekki, Franck Lefèvre, François Lott, David Cugnet, Line Jourdain, Perrine Lemmenais, Virginie Poulain, Julien Jumelet, Slimane Bekki, marie-pierre
The solar cycle effect in the MLT region. Simulations with HAMMONIA
 The solar cycle effect in the MLT region Simulations with HAMMONIA Hauke Schmidt Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg, Germany Variability of solar UV irradiance as given by UARS / SOLSTICE (Maximum:
The solar cycle effect in the MLT region Simulations with HAMMONIA Hauke Schmidt Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg, Germany Variability of solar UV irradiance as given by UARS / SOLSTICE (Maximum:
An Examination of Anomalously Low Column Ozone in the Southern Hemisphere Midlatitudes During 1997
 San Jose State University From the SelectedWorks of Eugene C. Cordero April, 2002 An Examination of Anomalously Low Column Ozone in the Southern Hemisphere Midlatitudes During 1997 Eugene C. Cordero, San
San Jose State University From the SelectedWorks of Eugene C. Cordero April, 2002 An Examination of Anomalously Low Column Ozone in the Southern Hemisphere Midlatitudes During 1997 Eugene C. Cordero, San
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales. John Houghton. C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth
 Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
Reconciling modeled and observed temperature trends over Antarctica
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052526, 2012 Reconciling modeled and observed temperature trends over Antarctica N. Calvo, 1,2,3 R. R. Garcia, 2 D. R. Marsh, 2 M. J. Mills, 2
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052526, 2012 Reconciling modeled and observed temperature trends over Antarctica N. Calvo, 1,2,3 R. R. Garcia, 2 D. R. Marsh, 2 M. J. Mills, 2
EPP contribution to (stratospheric and) tropospheric variations. Annika Seppälä Finnish Meteorological Institute Academy of Finland
 EPP contribution to (stratospheric and) tropospheric variations Annika Seppälä Finnish Meteorological Institute Academy of Finland A. Seppälä, HEPPA-SOLARIS Workshop, Boulder, Oct 0 So far... Energetic
EPP contribution to (stratospheric and) tropospheric variations Annika Seppälä Finnish Meteorological Institute Academy of Finland A. Seppälä, HEPPA-SOLARIS Workshop, Boulder, Oct 0 So far... Energetic
Polar Ozone Depletion and Trends as Represented by the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM)
 Polar Ozone Depletion and Trends as Represented by the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM) Doug Kinnison 1, Susan Solomon 2, Diane Ivy 2, Mike Mills 1, Ryan Neely III 3, and Anja Schmidt 3
Polar Ozone Depletion and Trends as Represented by the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM) Doug Kinnison 1, Susan Solomon 2, Diane Ivy 2, Mike Mills 1, Ryan Neely III 3, and Anja Schmidt 3
Whole Atmosphere Simulation of Anthropogenic Climate Change
 Whole Atmosphere Simulation of Anthropogenic Climate Change Stan Solomon, Hanli Liu, Dan Marsh, Joe McInerney, Liying Qian, and Francis Vitt High Altitude Observatory National Center for Atmospheric Research
Whole Atmosphere Simulation of Anthropogenic Climate Change Stan Solomon, Hanli Liu, Dan Marsh, Joe McInerney, Liying Qian, and Francis Vitt High Altitude Observatory National Center for Atmospheric Research
Volcanoes drive climate variability by
 Volcanoes drive climate variability by 1. emitting ozone weeks before eruptions, 2. forming lower stratospheric aerosols that cool Earth, 3. causing sustained ozone depletion, surface warming, and lower
Volcanoes drive climate variability by 1. emitting ozone weeks before eruptions, 2. forming lower stratospheric aerosols that cool Earth, 3. causing sustained ozone depletion, surface warming, and lower
The Need For Meteoritic Dust In The Stratosphere
 Global LIDAR Remote Sensing of Stratospheric Aerosols and Comparison with WACCM/CARMA: The Need For Meteoritic Dust In The Stratosphere CESM Whole Atmosphere Working Group Meeting 23 June 2011 Breckenridge,
Global LIDAR Remote Sensing of Stratospheric Aerosols and Comparison with WACCM/CARMA: The Need For Meteoritic Dust In The Stratosphere CESM Whole Atmosphere Working Group Meeting 23 June 2011 Breckenridge,
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1
 CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
Stratospheric Influence on Polar Climate. Paul Kushner, Dept. of Physics, University of Toronto
 Stratospheric Influence on Polar Climate Paul Kushner, Dept. of Physics, University of Toronto Aims for Today 1. Discuss different types of stratospheric influence. 2. Describe some dynamical aspects.
Stratospheric Influence on Polar Climate Paul Kushner, Dept. of Physics, University of Toronto Aims for Today 1. Discuss different types of stratospheric influence. 2. Describe some dynamical aspects.
Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~
 2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
A possible joint WCRP SPARC SSiRC/AeroCom initiative on stratospheric sulfur
 A possible joint WCRP SPARC SSiRC/AeroCom initiative on stratospheric sulfur Claudia Timmreck and the SSiRC team AeroCom workshop, Hamburg, 23. 9. 2013 Stratospheric Sulfur and Climate Climate Volcanic
A possible joint WCRP SPARC SSiRC/AeroCom initiative on stratospheric sulfur Claudia Timmreck and the SSiRC team AeroCom workshop, Hamburg, 23. 9. 2013 Stratospheric Sulfur and Climate Climate Volcanic
WACCM Studies at CU-Boulder
 WACCM Studies at CU-Boulder V.L. Harvey, C.E. Randall, O.B. Toon, E. Peck, S. Benze, M. Brakebusch, L. Holt, D. Wheeler, J. France, E. Wolf, Y. Zhu, X. Fang, C. Jackman, M. Mills, D. Marsh Most Topics
WACCM Studies at CU-Boulder V.L. Harvey, C.E. Randall, O.B. Toon, E. Peck, S. Benze, M. Brakebusch, L. Holt, D. Wheeler, J. France, E. Wolf, Y. Zhu, X. Fang, C. Jackman, M. Mills, D. Marsh Most Topics
The stratospheric response to extratropical torques and its relationship with the annular mode
 The stratospheric response to extratropical torques and its relationship with the annular mode Peter Watson 1, Lesley Gray 1,2 1. Atmospheric, Oceanic and Planetary Physics, Oxford University 2. National
The stratospheric response to extratropical torques and its relationship with the annular mode Peter Watson 1, Lesley Gray 1,2 1. Atmospheric, Oceanic and Planetary Physics, Oxford University 2. National
Vertical Structure of Atmosphere
 ATMOS 3110 Introduction to Atmospheric Sciences Distribution of atmospheric mass and gaseous constituents Because of the earth s gravitational field, the atmosphere exerts a downward forces on the earth
ATMOS 3110 Introduction to Atmospheric Sciences Distribution of atmospheric mass and gaseous constituents Because of the earth s gravitational field, the atmosphere exerts a downward forces on the earth
The ozone hole indirect effect: Cloud-radiative anomalies accompanying the poleward shift of the eddy-driven jet in the Southern Hemisphere
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 388 392, doi:1.12/grl.575, 213 The ozone hole indirect effect: Cloud-radiative anomalies accompanying the poleward shift of the eddy-driven jet in the Southern Hemisphere
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 388 392, doi:1.12/grl.575, 213 The ozone hole indirect effect: Cloud-radiative anomalies accompanying the poleward shift of the eddy-driven jet in the Southern Hemisphere
CESM: A platform for atmospheric prediction from the surface to geospace
 CESM: A platform for atmospheric prediction from the surface to geospace Dan Marsh, NCAR & University of Leeds Whole Atmosphere Modelling Workshop Deimos, Tres Cantos, Spain 13-15 June, 2018 Outline NCAR
CESM: A platform for atmospheric prediction from the surface to geospace Dan Marsh, NCAR & University of Leeds Whole Atmosphere Modelling Workshop Deimos, Tres Cantos, Spain 13-15 June, 2018 Outline NCAR
SPARC Dynamics and Variability Project and its Connection to C20C. Paul J. Kushner (Project Coordinator) University of Toronto
 SPARC Dynamics and Variability Project and its Connection to C20C Paul J. Kushner (Project Coordinator) University of Toronto Mark Baldwin, Neil Butchart, Norm McFarlane, Alan O Neill, Judith Perlwitz,
SPARC Dynamics and Variability Project and its Connection to C20C Paul J. Kushner (Project Coordinator) University of Toronto Mark Baldwin, Neil Butchart, Norm McFarlane, Alan O Neill, Judith Perlwitz,
Simulation of Polar Ozone Depletion: An Update
 Simulation of Polar Ozone Depletion: An Update Image taken from www.zmescience.com D. Kinnison (NCAR), S. Solomon (MIT), and J. Bandoro (MIT) February 17, 2015 WACCM Working Group Meeting, Boulder Co.
Simulation of Polar Ozone Depletion: An Update Image taken from www.zmescience.com D. Kinnison (NCAR), S. Solomon (MIT), and J. Bandoro (MIT) February 17, 2015 WACCM Working Group Meeting, Boulder Co.
WACCM CCMI Simulations: Status and Analysis
 WACCM CCMI Simulations: Status and Analysis D. Kinnison, R. Garcia, A. Smith, D. Marsh, R. Neely, A. Conley, M. Mills, S. Tilmes, J-F Lamarque, A. Gettelman, & F. Vitt. (NCAR) 13 February 2014, WACCM Working
WACCM CCMI Simulations: Status and Analysis D. Kinnison, R. Garcia, A. Smith, D. Marsh, R. Neely, A. Conley, M. Mills, S. Tilmes, J-F Lamarque, A. Gettelman, & F. Vitt. (NCAR) 13 February 2014, WACCM Working
Linkages between Arctic sea ice loss and midlatitude
 Linkages between Arctic sea ice loss and midlatitude weather patterns Response of the wintertime atmospheric circulation to current and projected Arctic sea ice decline Gudrun Magnusdottir and Yannick
Linkages between Arctic sea ice loss and midlatitude weather patterns Response of the wintertime atmospheric circulation to current and projected Arctic sea ice decline Gudrun Magnusdottir and Yannick
ECMWF global reanalyses: Resources for the wind energy community
 ECMWF global reanalyses: Resources for the wind energy community (and a few myth-busters) Paul Poli European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) Shinfield Park, RG2 9AX, Reading, UK paul.poli
ECMWF global reanalyses: Resources for the wind energy community (and a few myth-busters) Paul Poli European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) Shinfield Park, RG2 9AX, Reading, UK paul.poli
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 16 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 16 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 16 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
ttp://news.discovery.com/earth/iceland-volcano-aurora.html
 ttp://news.discovery.com/earth/iceland-volcano-aurora.html Outline Role of volcanism on the climate system Distribution of Arctic volcanoes Types of eruptions Frequency of Arctic eruptions Influence on
ttp://news.discovery.com/earth/iceland-volcano-aurora.html Outline Role of volcanism on the climate system Distribution of Arctic volcanoes Types of eruptions Frequency of Arctic eruptions Influence on
WACCM simulations of the mean circulation linking the mesosphere and thermosphere. Anne Smith, Rolando Garcia, Dan Marsh NCAR/ACD
 WACCM simulations of the mean circulation linking the mesosphere and thermosphere Anne Smith, Rolando Garcia, Dan Marsh NCAR/ACD trace species transport in the middle atmosphere wave driven mean circulation
WACCM simulations of the mean circulation linking the mesosphere and thermosphere Anne Smith, Rolando Garcia, Dan Marsh NCAR/ACD trace species transport in the middle atmosphere wave driven mean circulation
Wrap up of TOPIC # 13 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING: Volcanic Eruptions (pp 71-74)
 Wrap up of TOPIC # 13 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING: Volcanic Eruptions (pp 71-74) How the Climatic Effect Occurs.... through the ENERGY BALANCE of course! p 71 Mt Merapi Latitude: 7 32'30"S Indonesia's Mount
Wrap up of TOPIC # 13 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING: Volcanic Eruptions (pp 71-74) How the Climatic Effect Occurs.... through the ENERGY BALANCE of course! p 71 Mt Merapi Latitude: 7 32'30"S Indonesia's Mount
Global Warming and Climate Change Part I: Ozone Depletion
 GCOE-ARS : November 18, 2010 Global Warming and Climate Change Part I: Ozone Depletion YODEN Shigeo Department of Geophysics, Kyoto University 1. Stratospheric Ozone and History of the Earth 2. Observations
GCOE-ARS : November 18, 2010 Global Warming and Climate Change Part I: Ozone Depletion YODEN Shigeo Department of Geophysics, Kyoto University 1. Stratospheric Ozone and History of the Earth 2. Observations
The Oceans in a Warming World
 The Oceans in a Warming World John Marshall Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences 1. Review global observations of warming trends. Ocean temperature trends key part of the puzzle. 2. Discuss timing
The Oceans in a Warming World John Marshall Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences 1. Review global observations of warming trends. Ocean temperature trends key part of the puzzle. 2. Discuss timing
Thermospheric Winds. Astrid Maute. High Altitude Observatory (HAO) National Center for Atmospheric Science (NCAR) Boulder CO, USA
 Thermospheric Winds Astrid Maute High Altitude Observatory (HAO) National Center for Atmospheric Science (NCAR) Boulder CO, USA High Altitude Observatory (HAO) National Center for Atmospheric Research
Thermospheric Winds Astrid Maute High Altitude Observatory (HAO) National Center for Atmospheric Science (NCAR) Boulder CO, USA High Altitude Observatory (HAO) National Center for Atmospheric Research
CESM1.0/WACCM4 with CARMA3.0 Microphysics. Michael Mills Charles Bardeen
 CESM1.0/WACCM4 with CARMA3.0 Microphysics Michael Mills Charles Bardeen CAM/CARMA (C. Bardeen) CARMA Sectional Microphysics Fortran 90 Embeddable Shared with NASA Goddard CAM/CARMA Clouds & Aerosols Integrated
CESM1.0/WACCM4 with CARMA3.0 Microphysics Michael Mills Charles Bardeen CAM/CARMA (C. Bardeen) CARMA Sectional Microphysics Fortran 90 Embeddable Shared with NASA Goddard CAM/CARMA Clouds & Aerosols Integrated
Unit 2 Meteorology Test **Please do not write on this test** 5. El Nino & La Nina 6. Photosynthesis 7. Coriolis Effect 8.
 Matching (2 points each) 1. weather 2. climate 3. Greenhouse Effect 4. Convection Unit 2 Meteorology Test **Please do not write on this test** 5. El Nino & La Nina 6. Photosynthesis 7. Coriolis Effect
Matching (2 points each) 1. weather 2. climate 3. Greenhouse Effect 4. Convection Unit 2 Meteorology Test **Please do not write on this test** 5. El Nino & La Nina 6. Photosynthesis 7. Coriolis Effect
Influence of Sudden Stratosphere Warmings on the Ionosphere and Thermosphere
 Influence of Sudden Stratosphere Warmings on the Ionosphere and Thermosphere Nick Pedatella 1,2 1 High Altitude Observatory, National Center for Atmospheric Research 2 COSMIC Program Office, University
Influence of Sudden Stratosphere Warmings on the Ionosphere and Thermosphere Nick Pedatella 1,2 1 High Altitude Observatory, National Center for Atmospheric Research 2 COSMIC Program Office, University
Trends of Lower- to Mid-Stratospheric Water Vapor Simulated in Chemistry-Climate Models
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 1, 57 62 Trends of Lower- to Mid-Stratospheric Water Vapor Simulated in Chemistry-Climate Models HU Ding-Zhu 1, HAN Yuan-Yuan 1, SANG Wen-Jun
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 1, 57 62 Trends of Lower- to Mid-Stratospheric Water Vapor Simulated in Chemistry-Climate Models HU Ding-Zhu 1, HAN Yuan-Yuan 1, SANG Wen-Jun
How Volcanism Controls Climate Change
 How Volcanism Controls Climate Change V13D-2633 Peter L. Ward Teton Tectonics, Jackson, WY US Geological Survey retired peward@wyoming.com 307-413-4055 Fundamental Conclusion Large, explosive, volcanic
How Volcanism Controls Climate Change V13D-2633 Peter L. Ward Teton Tectonics, Jackson, WY US Geological Survey retired peward@wyoming.com 307-413-4055 Fundamental Conclusion Large, explosive, volcanic
Stratospheric planetary wave reflection and its influence on the troposphere
 Stratospheric planetary wave reflection and its influence on the troposphere N. Harnik, Tel Aviv University J. Perlwitz, CIRES U. Colorado/NOAA ESRL T. A. Shaw, Columbia University, NY, NY, USA The following
Stratospheric planetary wave reflection and its influence on the troposphere N. Harnik, Tel Aviv University J. Perlwitz, CIRES U. Colorado/NOAA ESRL T. A. Shaw, Columbia University, NY, NY, USA The following
Mechanisms for influence of the stratosphere on the troposphere
 Mechanisms for influence of the stratosphere on the troposphere Radiative Mass transfer/chemical Dynamical Alan Plumb M. I. T. Apr 2003 What dynamical effect does the stratosphere have on the troposphere?
Mechanisms for influence of the stratosphere on the troposphere Radiative Mass transfer/chemical Dynamical Alan Plumb M. I. T. Apr 2003 What dynamical effect does the stratosphere have on the troposphere?
Descrip(on of Chemistry, Aerosols in CESM and WACCM
 Descrip(on of Chemistry, Aerosols in CESM and WACCM Presented by Simone Tilmes, Mike Mills NESL: ACD/CGD Chemistry- Climate WG Co- Chairs: Louisa Emmons, Stephen Ghan, Noelle Eckley Selin WACCM WG Co-
Descrip(on of Chemistry, Aerosols in CESM and WACCM Presented by Simone Tilmes, Mike Mills NESL: ACD/CGD Chemistry- Climate WG Co- Chairs: Louisa Emmons, Stephen Ghan, Noelle Eckley Selin WACCM WG Co-
Coupled Chemistry in the Met Office UM: current and in a future extended (thermosphere) version
 Coupled Chemistry in the Met Office UM: current and in a future extended (thermosphere) version David Jackson QEPPA Meeting, Lancaster 13/03/2013 Overview What is the UM? UKCA chemistry Link to QEPPA goals
Coupled Chemistry in the Met Office UM: current and in a future extended (thermosphere) version David Jackson QEPPA Meeting, Lancaster 13/03/2013 Overview What is the UM? UKCA chemistry Link to QEPPA goals
Reconciling the Observed and Modeled Southern Hemisphere Circulation Response to Volcanic Eruptions Supplemental Material
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1002/, 1 2 3 Reconciling the Observed and Modeled Southern Hemisphere Circulation Response to Volcanic Eruptions Supplemental Material Marie C. McGraw
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1002/, 1 2 3 Reconciling the Observed and Modeled Southern Hemisphere Circulation Response to Volcanic Eruptions Supplemental Material Marie C. McGraw
The Quasi-Biennial Oscillation Analysis of the Resolved Wave Forcing
 The Quasi-Biennial Oscillation Analysis of the Resolved Wave Forcing Thomas Krismer, Marco Giorgetta Max Planck Institute for Meteorology Hamburg Introduction 1) The Quasi Biennial Oscillation is driven
The Quasi-Biennial Oscillation Analysis of the Resolved Wave Forcing Thomas Krismer, Marco Giorgetta Max Planck Institute for Meteorology Hamburg Introduction 1) The Quasi Biennial Oscillation is driven
The Structure and Motion of the Atmosphere OCEA 101
 The Structure and Motion of the Atmosphere OCEA 101 Why should you care? - the atmosphere is the primary driving force for the ocean circulation. - the atmosphere controls geographical variations in ocean
The Structure and Motion of the Atmosphere OCEA 101 Why should you care? - the atmosphere is the primary driving force for the ocean circulation. - the atmosphere controls geographical variations in ocean
I T A T I O N H B I T B T V A O C J K M R S A T M O S P H E R E
 Word Search Directions: Below are definitions of vocabulary terms. Figure out each term and then find and circle it in the puzzle. Words may appear horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. K E M I S S
Word Search Directions: Below are definitions of vocabulary terms. Figure out each term and then find and circle it in the puzzle. Words may appear horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. K E M I S S
Vertical Coupling in Climate
 Vertical Coupling in Climate Thomas Reichler (U. of Utah) NAM Polar cap averaged geopotential height anomalies height time Observations Reichler et al. (2012) SSWs seem to cluster Low-frequency power Vortex
Vertical Coupling in Climate Thomas Reichler (U. of Utah) NAM Polar cap averaged geopotential height anomalies height time Observations Reichler et al. (2012) SSWs seem to cluster Low-frequency power Vortex
