Sophie Oberländer, Ulrike Langematz, Stefanie Meul Institut für Meteorologie, Freie Universität Berlin
|
|
|
- Juliana Lambert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Future changes in the Brewer-Dobson Circulation and possible causes derived from Chemistry-ClimateClimate Model Simulations, Ulrike Langematz, Stefanie Meul Institut für Meteorologie, Freie Universität Berlin SPARC Workshop on the Brewer-Dobson Circulation June 2012, Grindelwald
2 Introduction and Motivation Independent model simulations of future climate project intensified tropical upward mass flux (e.g. Butchart et al., 2010; Li et al., 2010; Okamoto et al., 2011;...) BDC-acceleration due to higher greenhouse gas (GHG) concentrations is expected But: Causes for the simulated trend are still under debate, e.g. changes in generation and propagation of planetary waves, or the role of gravity waves Tropical sea surface temperatures (SSTs) were found to influence the lower branch of the BDC (e.g. Garny et al., 2011) But: Changes in the deep branch still uncertain 2
3 Introduction and Motivation Sensitivity studies separating the single forcings can help to understand underlying mechanisms Here: Chemistry-Climate Model simulations in timeslice mode for present and future climate, independently changing single forcings Separation of changes due to greenhouse gas (GHG) concentrations, sea surface temperatures (SST) and sea ice concentration (SIC) as well as chlorofluorocarbons (CFC) Attention: GHGs and SSTs are connected separation only possible due to prescription of SSTs GHG : effect of rising GHGs on the atmosphere (e.g. radiation, composition) SST : effect of rising GHGs on the SSTs 3
4 Model: EMAC (in FUB-configuration) ECHAM5/MESSy Atmospheric Chemistry Model (Jöckel et al., 2006) Chemistry-Climate Model (CCM) with FUBRad-Radiation parameterization (Nissen et al., 2007) Horizontal resolution: T42 (2.8 x 2.8 ) Vertical resolution: L39 (top in 0.01 hpa, ~80 km) No interactively coupled ocean SST/SIC prescribed Gravity wave parameterization: o Non-orographic - NGW: Hines, 1997 ( model output) o Orographic - OGW: Lott and Miller, 1997 ( no output) 4
5 Timeslice-Experiments Timeslice Simulations: Integration of 20++ years under equal boundary conditions, solar mean radiation Name GHG SST/SIC CFC GHGSST SST tropsst (Tropics) : Future GHG + CFC GHG+SST GHG CFC SST Trop. SST Extra-Trop. SST 5
6 Temperature [K/decade] - DJF Future tropospheric warming (max. 0.6 K/decade) SSTs (mainly tropical SSTs) Future stratospheric cooling (max. 0.8 K/decade) GHGs 6
7 Zonal wind [m/s/decade] - DJF Changes in tropical SSTs determine zonal wind changes UTLS-changes in temperature strong T intensified subtropical jets Winter stratosphere: deceleration of stratospheric polar night jet 7
8 Mass-streamfunction [kg/m/s/decade] DJF Intensification in future masstransport Significant influence from tropical SSTs up to ~10 hpa GHG changes important in upper stratosphere 8
9 Strength of the BDC Tropical upward mass flux Integration of the mass-streamfunction within the turnaround latitudes Reference Simulation (2000) - DJF Tropical upward mass flux: (Holton, 1990) 9
10 Tropical upward mass flux [%/decade] - DJF Intensification in future mass-flux (black) within whole stratosphere Significant influence from tropical SSTs up to ~10 hpa GHG changes important in upper stratosphere Which waves are responsible for the changes? 10
11 Separation of different scale waves Application of the downward-control principle to model data Total forcing (all waves) Resolved waves (EPFlux-divergence) EPFD Unresolved waves Orographic Non-orographic gravity waves gravity waves OGWD NGWD mass-streamfunction from direct calculation (Haynes et al., 1991) mass-streamfunction due to EPFD and NGWD from model data, OGWD as residual 11
12 Tropical upward mass flux [% (direct)] - DJF Resolved waves (EPFD): 90 % in lower and 55% in upper stratosphere Unresolved waves: OGWD: important in upper stratosphere NGWD: growing influence with height (~35% at stratopause) 12
13 Tropical upward mass flux [% (direct)] - DJF Resolved waves (EPFD): Temporal (left) versus spatial (right) scale Largest amount from planetary scale, transient waves 13
14 Tropical upward mass flux [%/decade] - DJF Future change 2095 vs (n=1-3) (n 4) Resolved waves (EPFD): Lower (transient waves) and middle stratosphere (planetary waves) Unresolved waves: OGWD + NGWD: Middle and upper stratosphere 14
15 Tropical upward mass flux [%/decade] - DJF GHG SST Above ~10 hpa: ½ GHG + ½ SST: unresolved (OGWD+NGWD) waves determine mass-flux changes Below ~10 hpa: SSTs determine mass-flux: ½ OGWD + ½ EPFD (transient) 15
16 Concept of Stratospheric Age of Air Here: Mass-streamfunction and upward mass-flux include only residual masstransport through (slow) circulation But: BDC includes both: (fast) mixing & (slow) circulation Therefore : Concept of Stratospheric Age of Air Not shown here in detail, but: Age-of-air-concept points in same direction Mean age [days/decade] DJF 16
17 Summary I: What forces future changes in the BDC? Future intensification in the residual circulation shown from changes in mass-streamfunction and tropical upward mass-flux Major importance of tropical SSTs explaining nearly total future change signal in lower and middle stratosphere BDC-changes due to tropical SSTs not restricted to lower stratosphere deep circulation branch is affected as well Consideration of changes in GHGs and extra-tropical SSTs required to explain total change signal in upper levels 17
18 Summary II: Which waves are responsible? SST -effect GHG -effect Increase in wavepropagation Shallow branch Strengthened T in UTLS-region Strengthening and upward shift of subtrop. jets OGW reach higher up and account for larger drag in mid-latitudes In-situ generation of (stationary) waves upstream the (slightly) intensified stratospheric polar night jet Influences on gravity waves in upper atmosphere Changes in conditions for stationaryplanetary wave propagation Deep branch 18
Future changes in Elevated Stratopause Events
 Future changes in Elevated Stratopause Events Janice Scheffler 1, Ulrike Langematz 1, Yvan J. Orsolini 2, Blanca Ayarzagüena 1 1 Institut für Meteorologie, Freie Universität Berlin 2 Norwegian Institute
Future changes in Elevated Stratopause Events Janice Scheffler 1, Ulrike Langematz 1, Yvan J. Orsolini 2, Blanca Ayarzagüena 1 1 Institut für Meteorologie, Freie Universität Berlin 2 Norwegian Institute
Impact of wind changes in the upper troposphere lower stratosphere on tropical ozone
 Impact of wind changes in the upper troposphere lower stratosphere on tropical ozone Martin Dameris Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR) Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre, Oberpfaffenhofen
Impact of wind changes in the upper troposphere lower stratosphere on tropical ozone Martin Dameris Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR) Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre, Oberpfaffenhofen
Intensification of the shallow BDC branch: mechanism and consequences for Age of Air
 Intensification of the shallow BDC branch: mechanism and consequences for Age of Air H. Garny1,2, M. Dameris1, W. Randel2, G. Bodeker3, R. Deckert1 T. Birner4 1 Deutsches Zentrum für Luft und Raumfahrt
Intensification of the shallow BDC branch: mechanism and consequences for Age of Air H. Garny1,2, M. Dameris1, W. Randel2, G. Bodeker3, R. Deckert1 T. Birner4 1 Deutsches Zentrum für Luft und Raumfahrt
A Simulation of the Separate Climate Effects of Middle-Atmospheric and Tropospheric CO 2 Doubling
 2352 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 17 A Simulation of the Separate Climate Effects of Middle-Atmospheric and Tropospheric CO 2 Doubling M. SIGMOND Department of Applied Physics, Eindhoven University of Technology
2352 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 17 A Simulation of the Separate Climate Effects of Middle-Atmospheric and Tropospheric CO 2 Doubling M. SIGMOND Department of Applied Physics, Eindhoven University of Technology
A study of the formation and trend of the Brewer-Dobson circulation
 A study of the formation and trend of the Brewer-Dobson circulation Kota Okamoto 1, Kaoru Sato 1, and Hideharu Akiyoshi 2 1: The University of Tokyo 2: National Institute for Environmental Studies Okamoto
A study of the formation and trend of the Brewer-Dobson circulation Kota Okamoto 1, Kaoru Sato 1, and Hideharu Akiyoshi 2 1: The University of Tokyo 2: National Institute for Environmental Studies Okamoto
WACCM: The High-Top Model
 WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
Summary. Introduction The solar variability Some words about the Earth's atmosphere Simulations and results
 Summary Introduction The solar variability Some words about the Earth's atmosphere Simulations and results Introduction Understanding and quantifying the natural variability of climate on decadal and centennial
Summary Introduction The solar variability Some words about the Earth's atmosphere Simulations and results Introduction Understanding and quantifying the natural variability of climate on decadal and centennial
Separating the dynamical effects of climate change and ozone depletion. Part I: Southern Hemisphere stratosphere
 Separating the dynamical effects of climate change and ozone depletion. Part I: Southern Hemisphere stratosphere Article Published Version McLandress, C., Jonsson, A. I., Plummer, D. A., Reader, M. C.,
Separating the dynamical effects of climate change and ozone depletion. Part I: Southern Hemisphere stratosphere Article Published Version McLandress, C., Jonsson, A. I., Plummer, D. A., Reader, M. C.,
Future changes in wintertime stratospheric Arctic variability in CCMI models
 Future changes in wintertime stratospheric Arctic variability in CCMI models B. Ayarzagüena 1, U. Langematz 1, J. Abalichin 1, H. Akiyoshi 2, M. Michou 3, O. Morgenstern 4 & L. Oman 5 1 Institut für Meteorologie,
Future changes in wintertime stratospheric Arctic variability in CCMI models B. Ayarzagüena 1, U. Langematz 1, J. Abalichin 1, H. Akiyoshi 2, M. Michou 3, O. Morgenstern 4 & L. Oman 5 1 Institut für Meteorologie,
Dynamical Mechanism for the Increase in Tropical Upwelling in the Lowermost Tropical Stratosphere during Warm ENSO Events
 JULY 2010 C A L V O E T A L. 2331 Dynamical Mechanism for the Increase in Tropical Upwelling in the Lowermost Tropical Stratosphere during Warm ENSO Events N. CALVO Atmospheric Chemistry Division, NCAR,*
JULY 2010 C A L V O E T A L. 2331 Dynamical Mechanism for the Increase in Tropical Upwelling in the Lowermost Tropical Stratosphere during Warm ENSO Events N. CALVO Atmospheric Chemistry Division, NCAR,*
P4.2 THE THREE DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE AND TIME EVOLUTION OF THE DECADAL VARIABILITY REVEALED IN ECMWF REANALYSES
 P4.2 THE THREE DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE AND TIME EVOLUTION OF THE DECADAL VARIABILITY REVEALED IN ECMWF REANALYSES Taehyoun Shim 1, Gyu-Ho Lim* 1 and Dong-In Lee 2 1 School of Earth and Environmental Sciences,
P4.2 THE THREE DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE AND TIME EVOLUTION OF THE DECADAL VARIABILITY REVEALED IN ECMWF REANALYSES Taehyoun Shim 1, Gyu-Ho Lim* 1 and Dong-In Lee 2 1 School of Earth and Environmental Sciences,
WACCM: The High-Top Model
 WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
Meridional structure of the downwelling branch of the BDC Susann Tegtmeier
 Meridional structure of the downwelling branch of the BDC Susann Tegtmeier Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel (GEOMAR), Germany SPARC Brewer-Dobson Circulation Workshop, Grindelwald, June 2012 no
Meridional structure of the downwelling branch of the BDC Susann Tegtmeier Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel (GEOMAR), Germany SPARC Brewer-Dobson Circulation Workshop, Grindelwald, June 2012 no
Assessing and understanding the role of stratospheric changes on decadal climate prediction
 MiKlip II-Status seminar, Berlin, 1-3 March 2017 Assessing and understanding the role of stratospheric changes on decadal climate prediction Martin Dameris Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt, Institut
MiKlip II-Status seminar, Berlin, 1-3 March 2017 Assessing and understanding the role of stratospheric changes on decadal climate prediction Martin Dameris Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt, Institut
Stratospheric Predictability and the Arctic Polar-night Jet Oscillation
 Stratospheric Predictability and the Arctic Polar-night Jet Oscillation Peter Hitchcock1, Ted Shepherd2 University of Toronto Now at Cambridge 2Now at Reading 1 Gloria Manney JPL, NMT, Now at NWRA NAM
Stratospheric Predictability and the Arctic Polar-night Jet Oscillation Peter Hitchcock1, Ted Shepherd2 University of Toronto Now at Cambridge 2Now at Reading 1 Gloria Manney JPL, NMT, Now at NWRA NAM
The stratospheric response to extratropical torques and its relationship with the annular mode
 The stratospheric response to extratropical torques and its relationship with the annular mode Peter Watson 1, Lesley Gray 1,2 1. Atmospheric, Oceanic and Planetary Physics, Oxford University 2. National
The stratospheric response to extratropical torques and its relationship with the annular mode Peter Watson 1, Lesley Gray 1,2 1. Atmospheric, Oceanic and Planetary Physics, Oxford University 2. National
Effect of zonal asymmetries in stratospheric ozone on simulated Southern Hemisphere climate trends
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L18701, doi:10.1029/2009gl040419, 2009 Effect of zonal asymmetries in stratospheric ozone on simulated Southern Hemisphere climate trends
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L18701, doi:10.1029/2009gl040419, 2009 Effect of zonal asymmetries in stratospheric ozone on simulated Southern Hemisphere climate trends
Modelling the atmosphere. Hennie Kelder University of Technology Eindhoven
 Modelling the atmosphere Hennie Kelder University of Technology Eindhoven Content Basics of the atmosphere Atmospheric dynamics Large scale circulation Planetary waves Brewer-Dobson circulation Some Key
Modelling the atmosphere Hennie Kelder University of Technology Eindhoven Content Basics of the atmosphere Atmospheric dynamics Large scale circulation Planetary waves Brewer-Dobson circulation Some Key
Solar variability and Climate Change
 Solar variability and Climate Change Ulrich Cubasch Freie Universität, Berlin Joint work with Fidel Gonzalez-Rouco, Tom Crowley, Gabi Hegerl, Stefanie Legutke, Jürg Luterbacher, Ulrich Schlese, Hans von
Solar variability and Climate Change Ulrich Cubasch Freie Universität, Berlin Joint work with Fidel Gonzalez-Rouco, Tom Crowley, Gabi Hegerl, Stefanie Legutke, Jürg Luterbacher, Ulrich Schlese, Hans von
CHAPTER 4. Stratospheric Dynamics. Lead Authors: Neal Butchart & Andrew J. Charlton-Perez
 CHAPTER 4 Stratospheric Dynamics Lead Authors: Neal Butchart & Andrew J. Charlton-Perez Co-authors: Irene Cionni Steven C. Hardiman Kirstin Krüger Paul Kushner Paul Newman Scott M. Osprey Judith Perlwitz
CHAPTER 4 Stratospheric Dynamics Lead Authors: Neal Butchart & Andrew J. Charlton-Perez Co-authors: Irene Cionni Steven C. Hardiman Kirstin Krüger Paul Kushner Paul Newman Scott M. Osprey Judith Perlwitz
What kind of stratospheric sudden warming propagates to the troposphere?
 What kind of stratospheric sudden warming propagates to the troposphere? Ken I. Nakagawa 1, and Koji Yamazaki 2 1 Sapporo District Meteorological Observatory, Japan Meteorological Agency Kita-2, Nishi-18,
What kind of stratospheric sudden warming propagates to the troposphere? Ken I. Nakagawa 1, and Koji Yamazaki 2 1 Sapporo District Meteorological Observatory, Japan Meteorological Agency Kita-2, Nishi-18,
SC-WACCM! and! Problems with Specifying the Ozone Hole
 SC-WACCM! and! Problems with Specifying the Ozone Hole R. Neely III, K. Smith2, D. Marsh,L. Polvani2 NCAR, 2Columbia Thanks to: Mike Mills, Francis Vitt and Sean Santos Motivation To design a stratosphere-resolving
SC-WACCM! and! Problems with Specifying the Ozone Hole R. Neely III, K. Smith2, D. Marsh,L. Polvani2 NCAR, 2Columbia Thanks to: Mike Mills, Francis Vitt and Sean Santos Motivation To design a stratosphere-resolving
Dynamical balances and tropical stratospheric upwelling
 Dynamical balances and tropical stratospheric upwelling Bill Randel and Rolando Garcia NCAR Thanks to: Qiang Fu, Andrew Gettelman, Rei Ueyama, Mike Wallace, plus WACCM group at NCAR. Background: Well-known
Dynamical balances and tropical stratospheric upwelling Bill Randel and Rolando Garcia NCAR Thanks to: Qiang Fu, Andrew Gettelman, Rei Ueyama, Mike Wallace, plus WACCM group at NCAR. Background: Well-known
Linkages between Arctic sea ice loss and midlatitude
 Linkages between Arctic sea ice loss and midlatitude weather patterns Response of the wintertime atmospheric circulation to current and projected Arctic sea ice decline Gudrun Magnusdottir and Yannick
Linkages between Arctic sea ice loss and midlatitude weather patterns Response of the wintertime atmospheric circulation to current and projected Arctic sea ice decline Gudrun Magnusdottir and Yannick
The Scientific Value of Stratospheric Wind Measurements
 Working Group on Space-based Lidar Winds, Monterey, 2008 The Scientific Value of Stratospheric Wind Measurements Ted Shepherd Department of Physics University of Toronto The distribution of ozone (important
Working Group on Space-based Lidar Winds, Monterey, 2008 The Scientific Value of Stratospheric Wind Measurements Ted Shepherd Department of Physics University of Toronto The distribution of ozone (important
Transfer of the solar signal from the stratosphere to the troposphere: Northern winter
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jd006283, 2006 Transfer of the solar signal from the stratosphere to the troposphere: Northern winter Katja Matthes, 1,2 Yuhji Kuroda, 3 Kunihiko
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jd006283, 2006 Transfer of the solar signal from the stratosphere to the troposphere: Northern winter Katja Matthes, 1,2 Yuhji Kuroda, 3 Kunihiko
Mid-latitude Ocean Influence on North Pacific Sector Climate Variability
 Mid-latitude Ocean Influence on North Pacific Sector Climate Variability Guidi Zhou 1, Mojib Latif 1,2, Richard Greatbatch 1,2, Wonsun Park 1 1 GEOMAR Helmholtz-Centre for Ocean Research Kiel 2 Kiel University
Mid-latitude Ocean Influence on North Pacific Sector Climate Variability Guidi Zhou 1, Mojib Latif 1,2, Richard Greatbatch 1,2, Wonsun Park 1 1 GEOMAR Helmholtz-Centre for Ocean Research Kiel 2 Kiel University
Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of
 Article Atmospheric Science September 2013 Vol.58 No.25: 3155 3160 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5945-5 Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of 2010 2011 HU YongYun 1* & XIA
Article Atmospheric Science September 2013 Vol.58 No.25: 3155 3160 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5945-5 Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of 2010 2011 HU YongYun 1* & XIA
Math, Models, and Climate Change How shaving cream moved a jet stream, and how mathematics can help us better understand why
 Math, Models, and Climate Change How shaving cream moved a jet stream, and how mathematics can help us better understand why Edwin P. Gerber Center for Atmosphere and Ocean Science Courant Institute of
Math, Models, and Climate Change How shaving cream moved a jet stream, and how mathematics can help us better understand why Edwin P. Gerber Center for Atmosphere and Ocean Science Courant Institute of
The downward influence of uncertainty in the Northern Hemisphere wintertime stratospheric polar vortex response to climate change. Isla Simpson, NCAR
 The downward influence of uncertainty in the Northern Hemisphere wintertime stratospheric polar vortex response to climate change Isla Simpson, NCAR Peter Hitchcock (LMD), Richard Seager (LDEO), Yutian
The downward influence of uncertainty in the Northern Hemisphere wintertime stratospheric polar vortex response to climate change Isla Simpson, NCAR Peter Hitchcock (LMD), Richard Seager (LDEO), Yutian
Steven Feldstein. The link between tropical convection and the Arctic warming on intraseaonal and interdecadal time scales
 The link between tropical convection and the Arctic warming on intraseaonal and interdecadal time scales Steven Feldstein The Pennsylvania State University Collaborators: Sukyoung Lee, Hyoseok Park, Tingting
The link between tropical convection and the Arctic warming on intraseaonal and interdecadal time scales Steven Feldstein The Pennsylvania State University Collaborators: Sukyoung Lee, Hyoseok Park, Tingting
Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating
 Regional and Local Climate Modeling and Analysis Research Group R e L o C l i m Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating (1) Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change (WegCenter) and
Regional and Local Climate Modeling and Analysis Research Group R e L o C l i m Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating (1) Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change (WegCenter) and
Modeling the Downward Influence of Stratospheric Final Warming events
 Modeling the Downward Influence of Stratospheric Final Warming events Lantao Sun Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Walter A. Robinson Division of Atmospheric
Modeling the Downward Influence of Stratospheric Final Warming events Lantao Sun Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Walter A. Robinson Division of Atmospheric
Lecture #3: Gravity Waves in GCMs. Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005)
 Lecture #3: Gravity Waves in GCMs Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005) 1 Outline of Lecture 1. Role of GWs in the middle atmosphere 2. Background theory 3. Resolved GWs in GCMs 4. Parameterized
Lecture #3: Gravity Waves in GCMs Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005) 1 Outline of Lecture 1. Role of GWs in the middle atmosphere 2. Background theory 3. Resolved GWs in GCMs 4. Parameterized
Sensitivity of zonal-mean circulation to air-sea roughness in climate models
 Sensitivity of zonal-mean circulation to air-sea roughness in climate models Inna Polichtchouk & Ted Shepherd Royal Meteorological Society National Meeting 16.11.2016 MOTIVATION Question: How sensitive
Sensitivity of zonal-mean circulation to air-sea roughness in climate models Inna Polichtchouk & Ted Shepherd Royal Meteorological Society National Meeting 16.11.2016 MOTIVATION Question: How sensitive
Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~
 2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport. Recall that the most primitive equilibrium climate model can be written
 2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport The equator-to-pole temperature difference DT was stronger during the last glacial maximum, with polar temperatures down by at least twice
2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport The equator-to-pole temperature difference DT was stronger during the last glacial maximum, with polar temperatures down by at least twice
Response of the North Atlantic atmospheric circulation to increasing LGM ice-sheet elevation
 Response of the North Atlantic atmospheric circulation to increasing LGM ice-sheet elevation Marcus Löfverström NCAR Rodrigo Caballero Johan Nilsson Gabriele Messori Stockholm University The Northern Hemisphere
Response of the North Atlantic atmospheric circulation to increasing LGM ice-sheet elevation Marcus Löfverström NCAR Rodrigo Caballero Johan Nilsson Gabriele Messori Stockholm University The Northern Hemisphere
Changes in the Ventilation of the Southern Oceans, and links to Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
 Changes in the Ventilation of the Southern Oceans, and links to Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Darryn W. Waugh Dept of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Johns Hopkins University Collaborators: Francois Primeau,
Changes in the Ventilation of the Southern Oceans, and links to Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Darryn W. Waugh Dept of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Johns Hopkins University Collaborators: Francois Primeau,
The Impact of Polar Stratospheric Ozone Loss on Southern Hemisphere Stratospheric Circulation and Surface Climate
 The Impact of Polar Stratospheric Ozone Loss on Southern Hemisphere Stratospheric Circulation and Surface Climate James Keeble, Peter Braesicke, Howard Roscoe and John Pyle James.keeble@atm.ch.cam.ac.uk
The Impact of Polar Stratospheric Ozone Loss on Southern Hemisphere Stratospheric Circulation and Surface Climate James Keeble, Peter Braesicke, Howard Roscoe and John Pyle James.keeble@atm.ch.cam.ac.uk
Stratospheric Change and its Role for Climate Prediction (SHARP): A contribution to SPARC
 Stratospheric Change and its Role for Climate Prediction (SHARP): A contribution to SPARC U. Langematz, Freie Universität Berlin, Germany (ulrike.langematz@met.fu-berlin.de) and the SHARP consortium 32
Stratospheric Change and its Role for Climate Prediction (SHARP): A contribution to SPARC U. Langematz, Freie Universität Berlin, Germany (ulrike.langematz@met.fu-berlin.de) and the SHARP consortium 32
Comparing QBO and ENSO impacts on stratospheric transport in WACCM-SD and -FR
 Comparing QBO and ENSO impacts on stratospheric transport in WACCM-SD and -FR Multivariate ENSO Index + QBO shear index based on Singapore wind U50-U25 CESM Chemistry WG Meeting Boulder, CO February 10,
Comparing QBO and ENSO impacts on stratospheric transport in WACCM-SD and -FR Multivariate ENSO Index + QBO shear index based on Singapore wind U50-U25 CESM Chemistry WG Meeting Boulder, CO February 10,
The Quasi-Biennial Oscillation Analysis of the Resolved Wave Forcing
 The Quasi-Biennial Oscillation Analysis of the Resolved Wave Forcing Thomas Krismer, Marco Giorgetta Max Planck Institute for Meteorology Hamburg Introduction 1) The Quasi Biennial Oscillation is driven
The Quasi-Biennial Oscillation Analysis of the Resolved Wave Forcing Thomas Krismer, Marco Giorgetta Max Planck Institute for Meteorology Hamburg Introduction 1) The Quasi Biennial Oscillation is driven
The Climate in a World without Ozone
 The Climate in a World without Ozone Frank Selten, Richard Bintanja, Dewi Le Bars, Hylke de Vries, Michiel van Weele (KNMI) Aarnout van Delden (Univ. Utrecht) QOS 2016, 5-9 September 2016, Edinburgh Study
The Climate in a World without Ozone Frank Selten, Richard Bintanja, Dewi Le Bars, Hylke de Vries, Michiel van Weele (KNMI) Aarnout van Delden (Univ. Utrecht) QOS 2016, 5-9 September 2016, Edinburgh Study
SPARC Dynamics and Variability Project and its Connection to C20C. Paul J. Kushner (Project Coordinator) University of Toronto
 SPARC Dynamics and Variability Project and its Connection to C20C Paul J. Kushner (Project Coordinator) University of Toronto Mark Baldwin, Neil Butchart, Norm McFarlane, Alan O Neill, Judith Perlwitz,
SPARC Dynamics and Variability Project and its Connection to C20C Paul J. Kushner (Project Coordinator) University of Toronto Mark Baldwin, Neil Butchart, Norm McFarlane, Alan O Neill, Judith Perlwitz,
Role of the QBO in modulating the influence of the 11 year solar cycle on the atmosphere using constant forcings
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd013020, 2010 Role of the QBO in modulating the influence of the 11 year solar cycle on the atmosphere using constant forcings Katja Matthes,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd013020, 2010 Role of the QBO in modulating the influence of the 11 year solar cycle on the atmosphere using constant forcings Katja Matthes,
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
The general circulation: midlatitude storms
 The general circulation: midlatitude storms Motivation for this class Provide understanding basic motions of the atmosphere: Ability to diagnose individual weather systems, and predict how they will change
The general circulation: midlatitude storms Motivation for this class Provide understanding basic motions of the atmosphere: Ability to diagnose individual weather systems, and predict how they will change
Dynamics of the Atmosphere. General circulation of the atmosphere
 12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere 1 Spinup of the general circulation in an idealized model Fig. 1 Schneider, General circulation of the atmosphere, 2006 2 Sigma 0.2
12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere 1 Spinup of the general circulation in an idealized model Fig. 1 Schneider, General circulation of the atmosphere, 2006 2 Sigma 0.2
The influence of spectral solar irradiance data on stratospheric heating rates during the 11 year solar cycle
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2011gl049539, 2012 The influence of spectral solar irradiance data on stratospheric heating rates during the 11 year solar cycle S. Oberländer, 1 U.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2011gl049539, 2012 The influence of spectral solar irradiance data on stratospheric heating rates during the 11 year solar cycle S. Oberländer, 1 U.
Abrupt Circulation Responses to Tropical Upper-Tropospheric Warming in a Relatively Simple Stratosphere-Resolving AGCM
 15 JUNE 2012 W A N G E T A L. 4097 Abrupt Circulation Responses to Tropical Upper-Tropospheric Warming in a Relatively Simple Stratosphere-Resolving AGCM SHUGUANG WANG Department of Applied Physics and
15 JUNE 2012 W A N G E T A L. 4097 Abrupt Circulation Responses to Tropical Upper-Tropospheric Warming in a Relatively Simple Stratosphere-Resolving AGCM SHUGUANG WANG Department of Applied Physics and
Interannual Variations of the General Circulation and Polar Stratospheric Ozone Losses in a General Circulation Model
 Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, Vol. 80, No. 4B, pp. 877--895, 2002 877 Interannual Variations of the General Circulation and Polar Stratospheric Ozone Losses in a General Circulation Model
Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, Vol. 80, No. 4B, pp. 877--895, 2002 877 Interannual Variations of the General Circulation and Polar Stratospheric Ozone Losses in a General Circulation Model
Improved 11-year solar signal in the Freie Universität Berlin Climate Middle Atmosphere Model (FUB-CMAM)
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003jd004012, 2004 Improved 11-year solar signal in the Freie Universität Berlin Climate Middle Atmosphere Model (FUB-CMAM) Katja Matthes, 1 Ulrike
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003jd004012, 2004 Improved 11-year solar signal in the Freie Universität Berlin Climate Middle Atmosphere Model (FUB-CMAM) Katja Matthes, 1 Ulrike
Elevated stratopause and mesospheric intrusion following a stratospheric sudden warming in WACCM
 Elevated stratopause and mesospheric intrusion following a stratospheric sudden warming in WACCM Yvan J. Orsolini 1,V. Limpasuvan 2, J. Richter 3, O. K. Kvissel 4, F. Stordal 4,D. Marsh 3 1 Norwegian Institute
Elevated stratopause and mesospheric intrusion following a stratospheric sudden warming in WACCM Yvan J. Orsolini 1,V. Limpasuvan 2, J. Richter 3, O. K. Kvissel 4, F. Stordal 4,D. Marsh 3 1 Norwegian Institute
Dynamical Changes in the Arctic and Antarctic Stratosphere During Spring
 Dynamical Changes in the Arctic and Antarctic Stratosphere During Spring U. Langematz and M. Kunze Abstract Short- and long-term changes in the intensity and persistence of the Arctic and Antarctic stratospheric
Dynamical Changes in the Arctic and Antarctic Stratosphere During Spring U. Langematz and M. Kunze Abstract Short- and long-term changes in the intensity and persistence of the Arctic and Antarctic stratospheric
Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation
 Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation 8 March, 2011 Jonathon Wright Department of Applied Mathematics & Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge
Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation 8 March, 2011 Jonathon Wright Department of Applied Mathematics & Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge
Influence of Doubled CO 2 on Ozone via Changes in the Brewer Dobson Circulation
 JULY 2007 N O T E S A N D C O R R E S P O N D E N C E 2751 Influence of Doubled CO 2 on Ozone via Changes in the Brewer Dobson Circulation XUN JIANG Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences, and Department
JULY 2007 N O T E S A N D C O R R E S P O N D E N C E 2751 Influence of Doubled CO 2 on Ozone via Changes in the Brewer Dobson Circulation XUN JIANG Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences, and Department
Vertical Coupling in Climate
 Vertical Coupling in Climate Thomas Reichler (U. of Utah) NAM Polar cap averaged geopotential height anomalies height time Observations Reichler et al. (2012) SSWs seem to cluster Low-frequency power Vortex
Vertical Coupling in Climate Thomas Reichler (U. of Utah) NAM Polar cap averaged geopotential height anomalies height time Observations Reichler et al. (2012) SSWs seem to cluster Low-frequency power Vortex
Solar cycle signal in a general circulation and chemistry model with internally generated quasi biennial oscillation
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012542, 2010 Solar cycle signal in a general circulation and chemistry model with internally generated quasi biennial
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012542, 2010 Solar cycle signal in a general circulation and chemistry model with internally generated quasi biennial
Connection between NAO/AO, surface climate over Northern Eurasia: snow cover force - possible mechanism.
 Connection between NAO/AO, surface climate over Northern Eurasia: snow cover force - possible mechanism. Krupchatnikov V., Yu. Martynova (Pr. Ac. Lavrentieva, 6, Novosibirsk, 630090, Russia; tel: 330 61-51;
Connection between NAO/AO, surface climate over Northern Eurasia: snow cover force - possible mechanism. Krupchatnikov V., Yu. Martynova (Pr. Ac. Lavrentieva, 6, Novosibirsk, 630090, Russia; tel: 330 61-51;
WRF MODEL STUDY OF TROPICAL INERTIA GRAVITY WAVES WITH COMPARISONS TO OBSERVATIONS. Stephanie Evan, Joan Alexander and Jimy Dudhia.
 WRF MODEL STUDY OF TROPICAL INERTIA GRAVITY WAVES WITH COMPARISONS TO OBSERVATIONS. Stephanie Evan, Joan Alexander and Jimy Dudhia. Background Small-scale Gravity wave Inertia Gravity wave Mixed RossbyGravity
WRF MODEL STUDY OF TROPICAL INERTIA GRAVITY WAVES WITH COMPARISONS TO OBSERVATIONS. Stephanie Evan, Joan Alexander and Jimy Dudhia. Background Small-scale Gravity wave Inertia Gravity wave Mixed RossbyGravity
The Impact of the Extratropical Transition of Typhoon Dale (1996) on the Early Wintertime Stratospheric Circulation
 The Impact of the Extratropical Transition of Typhoon Dale (1996) on the Early 1996-97 Wintertime Stratospheric Circulation Andrea L. Lang 1, Jason M. Cordeira 2, Lance F. Bosart 1 and Daniel Keyser 1
The Impact of the Extratropical Transition of Typhoon Dale (1996) on the Early 1996-97 Wintertime Stratospheric Circulation Andrea L. Lang 1, Jason M. Cordeira 2, Lance F. Bosart 1 and Daniel Keyser 1
The Atmosphere. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems
 The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
Trends of Lower- to Mid-Stratospheric Water Vapor Simulated in Chemistry-Climate Models
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 1, 57 62 Trends of Lower- to Mid-Stratospheric Water Vapor Simulated in Chemistry-Climate Models HU Ding-Zhu 1, HAN Yuan-Yuan 1, SANG Wen-Jun
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 1, 57 62 Trends of Lower- to Mid-Stratospheric Water Vapor Simulated in Chemistry-Climate Models HU Ding-Zhu 1, HAN Yuan-Yuan 1, SANG Wen-Jun
Lecture 1. Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature
 Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
3D Brewer Dobson circulation derived from satellite measurements
 SPARC BDC Workshop Grindelwald, Tuesday, June 26, 202 3D Brewer Dobson circulation derived from satellite measurements Axel Gabriel, Deniz Demirhan Bari,2, Heiner Körnich 3, Dieter H.W. Peters Leibniz-Institute
SPARC BDC Workshop Grindelwald, Tuesday, June 26, 202 3D Brewer Dobson circulation derived from satellite measurements Axel Gabriel, Deniz Demirhan Bari,2, Heiner Körnich 3, Dieter H.W. Peters Leibniz-Institute
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007
 The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
Impacts of historical ozone changes on climate in GFDL-CM3
 Impacts of historical ozone changes on climate in GFDL-CM3 Larry Horowitz (GFDL) with: Vaishali Naik (GFDL), Pu Lin (CICS), and M. Daniel Schwarzkopf (GFDL) WMO (2014) Figure ADM 5-1 1 Response of tropospheric
Impacts of historical ozone changes on climate in GFDL-CM3 Larry Horowitz (GFDL) with: Vaishali Naik (GFDL), Pu Lin (CICS), and M. Daniel Schwarzkopf (GFDL) WMO (2014) Figure ADM 5-1 1 Response of tropospheric
General Circulation. Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory
 General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
Chihoko Yamashita 1,2, Han-Li Liu 1
 1 1 Gravity Waves and the High-Resolution Modeling (Using ECMWF-T799) Chihoko Yamashita 1,2, Han-Li Liu 1 1. NCAR/HAO 2. University of Colorado at Boulder AWMG/WAWG Workshop 2012-02-01 Motivations Gravity
1 1 Gravity Waves and the High-Resolution Modeling (Using ECMWF-T799) Chihoko Yamashita 1,2, Han-Li Liu 1 1. NCAR/HAO 2. University of Colorado at Boulder AWMG/WAWG Workshop 2012-02-01 Motivations Gravity
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming?
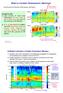 What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
Eliassen-Palm Theory
 Eliassen-Palm Theory David Painemal MPO611 April 2007 I. Introduction The separation of the flow into its zonal average and the deviations therefrom has been a dominant paradigm for analyses of the general
Eliassen-Palm Theory David Painemal MPO611 April 2007 I. Introduction The separation of the flow into its zonal average and the deviations therefrom has been a dominant paradigm for analyses of the general
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1
 CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
Vertical Structure of Atmosphere
 ATMOS 3110 Introduction to Atmospheric Sciences Distribution of atmospheric mass and gaseous constituents Because of the earth s gravitational field, the atmosphere exerts a downward forces on the earth
ATMOS 3110 Introduction to Atmospheric Sciences Distribution of atmospheric mass and gaseous constituents Because of the earth s gravitational field, the atmosphere exerts a downward forces on the earth
Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake
 Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake Shang-Ping Xie Scripps Inst of Oceanography, UCSD Ocean warming & circulation change Ocean heat uptake & meridional overturning circulation Global
Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake Shang-Ping Xie Scripps Inst of Oceanography, UCSD Ocean warming & circulation change Ocean heat uptake & meridional overturning circulation Global
The Earth s Atmosphere-II. GEOL 1350: Introduction To Meteorology
 The Earth s Atmosphere-II GEOL 1350: Introduction To Meteorology 1 Vertical Structure of Atmosphere Vertical profile of the atmosphere reveals that it can be divided into a series of layers. Each layer
The Earth s Atmosphere-II GEOL 1350: Introduction To Meteorology 1 Vertical Structure of Atmosphere Vertical profile of the atmosphere reveals that it can be divided into a series of layers. Each layer
Report on the first SOLARIS workshop 4-6 October 2006, Boulder, Colorado, USA
 Report on the first SOLARIS workshop 4-6 October 2006, Boulder, Colorado, USA K. Matthes, Freie Universität Berlin, Institut für Meteorologie, Berlin, Germany and National Center for Atmospheric Research,
Report on the first SOLARIS workshop 4-6 October 2006, Boulder, Colorado, USA K. Matthes, Freie Universität Berlin, Institut für Meteorologie, Berlin, Germany and National Center for Atmospheric Research,
On the remarkable Arctic winter in 2008/2009
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012273, 2009 On the remarkable Arctic winter in 2008/2009 K. Labitzke 1 and M. Kunze 1 Received 17 April 2009; revised 11 June 2009; accepted
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012273, 2009 On the remarkable Arctic winter in 2008/2009 K. Labitzke 1 and M. Kunze 1 Received 17 April 2009; revised 11 June 2009; accepted
Stratospheric versus Tropospheric Control of the Strength and Structure of the Brewer Dobson Circulation
 SEPTEMBER 2012 G E R B E R 2857 Stratospheric versus Tropospheric Control of the Strength and Structure of the Brewer Dobson Circulation EDWIN P. GERBER Center for Atmosphere Ocean Science, Courant Institute
SEPTEMBER 2012 G E R B E R 2857 Stratospheric versus Tropospheric Control of the Strength and Structure of the Brewer Dobson Circulation EDWIN P. GERBER Center for Atmosphere Ocean Science, Courant Institute
GPC Exeter forecast for winter Crown copyright Met Office
 GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
Effects of a convective GWD parameterization in the global forecast system of the Met Office Unified Model in Korea
 Effects of a convective GWD parameterization in the global forecast system of the Met Office Unified Model in Korea Young-Ha Kim 1, Hye-Yeong Chun 1, and Dong-Joon Kim 2 1 Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
Effects of a convective GWD parameterization in the global forecast system of the Met Office Unified Model in Korea Young-Ha Kim 1, Hye-Yeong Chun 1, and Dong-Joon Kim 2 1 Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate
 The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate Mark P. Baldwin Northwest Research Associates, USA SORCE, 27 October 2004 Overview Climatology of the
The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate Mark P. Baldwin Northwest Research Associates, USA SORCE, 27 October 2004 Overview Climatology of the
Variability and trends of major stratospheric warmings in simulations under constant and increasing GHG concentrations
 Clim Dyn () 4:7 747 DOI.7/s8--5-x Variability and trends of major stratospheric warmings in simulations under constant and increasing GHG concentrations S. Schimanke T. Spangehl H. Huebener U. Cubasch
Clim Dyn () 4:7 747 DOI.7/s8--5-x Variability and trends of major stratospheric warmings in simulations under constant and increasing GHG concentrations S. Schimanke T. Spangehl H. Huebener U. Cubasch
Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure
 Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure Hua Lu British Antarctic Survey Outline Background: Sun-Earth Climate Connection Solar wind/geomagnetic activity signals with 3 examples stratospheric
Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure Hua Lu British Antarctic Survey Outline Background: Sun-Earth Climate Connection Solar wind/geomagnetic activity signals with 3 examples stratospheric
Temperature changes in the tropical tropopause layer
 Temperature changes in the tropical tropopause layer Kohei Yoshida Division of Earth System Science, Graduate School of Environmental Science, Hokkaido University February 011 Abstract ⅰ Abstract Temperature
Temperature changes in the tropical tropopause layer Kohei Yoshida Division of Earth System Science, Graduate School of Environmental Science, Hokkaido University February 011 Abstract ⅰ Abstract Temperature
F = ma. ATS 150 Global Climate Change Winds and Weather. Scott Denning CSU CMMAP 1. Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook
 Winds and Weather Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook Circulation of the atmosphere and oceans are driven by energy imbalances Energy Imbalances What Makes the Wind Blow? Three real forces (gravity,
Winds and Weather Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook Circulation of the atmosphere and oceans are driven by energy imbalances Energy Imbalances What Makes the Wind Blow? Three real forces (gravity,
NORTH ATLANTIC DECADAL-TO- MULTIDECADAL VARIABILITY - MECHANISMS AND PREDICTABILITY
 NORTH ATLANTIC DECADAL-TO- MULTIDECADAL VARIABILITY - MECHANISMS AND PREDICTABILITY Noel Keenlyside Geophysical Institute, University of Bergen Jin Ba, Jennifer Mecking, and Nour-Eddine Omrani NTU International
NORTH ATLANTIC DECADAL-TO- MULTIDECADAL VARIABILITY - MECHANISMS AND PREDICTABILITY Noel Keenlyside Geophysical Institute, University of Bergen Jin Ba, Jennifer Mecking, and Nour-Eddine Omrani NTU International
warmest (coldest) temperatures at summer heat dispersed upward by vertical motion Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A heated by solar radiation at the base
 Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
CHAPTER 4. THE HADLEY CIRCULATION 59 smaller than that in midlatitudes. This is illustrated in Fig. 4.2 which shows the departures from zonal symmetry
 Chapter 4 THE HADLEY CIRCULATION The early work on the mean meridional circulation of the tropics was motivated by observations of the trade winds. Halley (1686) and Hadley (1735) concluded that the trade
Chapter 4 THE HADLEY CIRCULATION The early work on the mean meridional circulation of the tropics was motivated by observations of the trade winds. Halley (1686) and Hadley (1735) concluded that the trade
Chemistry climate model simulations of the effect of the 27 day solar rotational cycle on ozone
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jd015665, 2011 Chemistry climate model simulations of the effect of the 27 day solar rotational cycle on ozone A. Kubin, 1 U. Langematz, 1 and
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jd015665, 2011 Chemistry climate model simulations of the effect of the 27 day solar rotational cycle on ozone A. Kubin, 1 U. Langematz, 1 and
Dynamics of the Atmosphere
 12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere Course description: Discusses the dynamics of the atmosphere, with emphasis on the large scale. Instructor: Paul O Gorman Email: pog@mit.edu Office: 54-1712 Questions:
12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere Course description: Discusses the dynamics of the atmosphere, with emphasis on the large scale. Instructor: Paul O Gorman Email: pog@mit.edu Office: 54-1712 Questions:
Hydrodynamic conservation laws and turbulent friction in atmospheric circulation models
 Hydrodynamic conservation laws and turbulent friction in atmospheric circulation models Erich Becker Leibniz-Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Kühlungsborn, Germany Including contributions from Ulrike
Hydrodynamic conservation laws and turbulent friction in atmospheric circulation models Erich Becker Leibniz-Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Kühlungsborn, Germany Including contributions from Ulrike
Dynamics and Kinematics
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228)
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI
 Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Persistent shift of the Arctic polar vortex towards the Eurasian continent in recent decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3136 Persistent shift of the Arctic polar vortex towards the Eurasian continent in recent decades Jiankai Zhang 1, Wenshou Tian 1 *, Martyn P. Chipperfield
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3136 Persistent shift of the Arctic polar vortex towards the Eurasian continent in recent decades Jiankai Zhang 1, Wenshou Tian 1 *, Martyn P. Chipperfield
February 1989 T. Iwasaki, S. Yamada and K. Tada 29. A Parameterization Scheme of Orographic Gravity Wave Drag
 February 1989 T. Iwasaki, S. Yamada and K. Tada 29 A Parameterization Scheme of Orographic Gravity Wave Drag with Two Different Vertical Partitionings Part II: Zonally Averaged Budget Analyses Based on
February 1989 T. Iwasaki, S. Yamada and K. Tada 29 A Parameterization Scheme of Orographic Gravity Wave Drag with Two Different Vertical Partitionings Part II: Zonally Averaged Budget Analyses Based on
Seasonality of the Jet Response to Arctic Warming
 Seasonality of the Jet Response to Arctic Warming Bryn Ronalds Adv: Elizabeth Barnes CVCWG Meeting: March 2, 27 The story: Midlatitude jets are fundamental to weather and climate It is generally agreed
Seasonality of the Jet Response to Arctic Warming Bryn Ronalds Adv: Elizabeth Barnes CVCWG Meeting: March 2, 27 The story: Midlatitude jets are fundamental to weather and climate It is generally agreed
Radiative effects of ozone waves on the Northern Hemisphere polar vortex and its modulation by the QBO
 Radiative effects of ozone waves on the Northern Hemisphere polar vortex and its modulation by the QBO Vered Silverman 1, Nili Harnik 1, Katja Matthes 2, Sandro W. Lubis 3, and Sebastian Wahl 2 1 Department
Radiative effects of ozone waves on the Northern Hemisphere polar vortex and its modulation by the QBO Vered Silverman 1, Nili Harnik 1, Katja Matthes 2, Sandro W. Lubis 3, and Sebastian Wahl 2 1 Department
Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback
 Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Human Activities Climate Sensitivity Climate Feedback 1 Climate Sensitivity and Feedback (from Earth s Climate: Past and Future) 2 Definition and Mathematic
Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Human Activities Climate Sensitivity Climate Feedback 1 Climate Sensitivity and Feedback (from Earth s Climate: Past and Future) 2 Definition and Mathematic
