Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 Darin Toohey CU PAOS. Some resources that I borrowed from
|
|
|
- Elwin Skinner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 Darin Toohey CU PAS Why Do We Care? zone Discovery and History Circulation Chapman Chemistry Catalytic Destruction The Controversy The Big Surprise of 1985 Some resources that I borrowed from m
2 Why do we care? Phytoplankton Melanoma The Human Connection The EPA estimates that 60 million Americans born by the year 075 will get skin cancer because of ozone depletion. About one million of these people will die. (thinkquest.org) DNA isn t just for humans plants and animals too!
3 zone History In 1785, Martinus Van Marum noted the odor of electrical matter in the description of the discharge of air. Note this was before it was accepted that oxygen was a component of air! fficially named as a chemical in 1840 by Christian Schönbein, after he noted that it had a smell that was similar to that of phosphorus when exposed to air It was soon realized that ozone was a good disinfectant. tto was first to market a water purifier based on ozone Marius Paul tto
4 In 19, Gordon Dobson developed the first spectrometer to measure ozone in the atmosphere, and he characterized its latitudinal seasonal variability Brewer-Dobson circulation Brewer-Dobson circulation 4
5 198 Thomas Midgley develops chlorofluorcarbons for DuPont, inhaling them to prove that they nontoxic. These non-flammable compounds soon replace the deadly compounds (such as ammonia and S ) in home refrigerators CFCs become popular in the 1960s when americans want to live in sun belts, drive cars with air conditioning, and use spray cans for just about everything! In 190, Sydney Chapman published several theoretical papers on upper-atmospheric ozone now known as the Chapman Cycle + hυ + (λ < 4 nm) (1) + + M + M () + hυ + (λ < 6 nm) () + + (4)
6 hν rate 1 = J (J s -1, 0 km) rate = k M (k cm 6 s -1 at 50 K) rate = J (J 10 - s -1 at 0 km) hν rate 4 = k 4 (k cm s -1 at 50 K) d = J dt k M + J k4 d = k M J dt k4 dd oxygen hν Rate 1 = J Rate = k M Rate = J hν Rate 4 = k 4 d( + ) d x = = J dt dt d x In Steady State: = 0 = J dt k4 k4 P-L (note, you get the same by assuming is in steady state) 6
7 7 Substituting back: ~ 4 J M k k J M k dt d = J M k = At steady state: 1 M k J = 4 k J = M J J k k =
8 Problem Chapman mechanism predicts more ozone than what is observed! What s missing? Faster + + 8
9 Water in the stratosphere would lead to catalytic destruction of ozone by speeding up reaction (4) of Chapman s mechanism thus, introducing the concept of catalytic destruction of ozone H + H + H + H + Net Bates, D.R. and M. Nicolet, The Photochemistry of the Atmospheric Water Vapor, J. Geophys. Res., 55, 01, 1950 Catalysis H + H + rate = k a H H + H + rate = k b H Net d k4 k H b dt Replace k 4 with apparent loss k app 4 k = + b H k4 1 k4 1 1 k J = 0.1 M app k J 4 > k 4 9
10 hν hν Catalysts (N, H, Cl, etc.) Production stays the same (it s due to photolysis of ) Loss increases Paul Crutzen proposes that N x from bacterial N can participate in atmospheric chemistry as N formed in the stratosphere N + ( 1 D) N + N "Influence of Nitrogen xides on Atmospheric zone Content" Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society 96 (1970):0. 10
11 Formation of N + hν + ( 1 D) J ( 1 D) + N / ( P) + N / ~ gas kinetic N + hν N + ( 1 D) J N N + ( 1 D) N + k a = cm s -1 N + N k b = cm s -1 Yield k ( D) 1 = b 1 { k b+ ka} ( D) + J Loss of N N Production of N ~.5-4.0% of the N becomes N y Key connections made by Crutzen mankind can increase N emissions by fertilizing crops N has a long lifetime in troposphere, so can reach the stratosphere Increase in tropospheric N will increase stratospheric N x Increase in N x will result in decrease in steady state ozone e.g. Mankind can alter stratospheric ozone without leaving the ground! 11
12 Harold Johnston N + N + N + N + d ( k + k ) H H + kn N Net dt Richard Stolarski and Ralph Cicerone Cl + Cl + Cl + Cl + Net Stratospheric Chlorine: A Possible Sink for zone, Can. J. Chem., 5, , 1974 d dt ( k + k H + k N k ) H N + clo Cl (also McElroy and Wofsy, but more on them in Part ) 1
13 Dr. James E. Lovelock, Inventor The electron capture detector are unusually stable chemically and only slightly soluble in water and might therefore persist and accumulate in the atmosphere The presence of these compounds constitutes no conceivable hazard. Distribution of CCl F in and over the North and South Atlantic cean, Nature, Vol. 41, January 19, 197 1
14 Mario Molina and F. Sherwood Rowland CFCl + hν CFCl + Cl CF Cl hν CF Cl + Cl Predicted tens of percents of ozone loss The deadly weapon! M. J. Molina and F. S. Rowland "Stratospheric Sink for Chlorofluoromethanes: Chlorine atomic-atalysed destruction of ozone," Nature 49 (8 June 1974): citations even with typo! The pieces come together! Brewer-Dobson circulation CFCl + hν CFCl + Cl CF Cl hν CF Cl + Cl release spark Cl + Cl + Cl + Cl + transport Net flame un reactivity source + hυ M + M + hυ destruction 14
15 Rowland (1974): The work is going very well, but it may mean the end of the world. x10! Spray cans banned/voluntarily boycotted 15
16 A field is born! All we need to do is to observe ozone losses in conjunction with increases in CFCs Easy!? r Not? CFCs nearly double! But no ozone loss! 16
17 What really goes on? Cl + Cl + Cl + Cl + Couples Cl x to N x Cl + N Cl + N Cl + N + M ClN ClN + hν Cl + N Cl + N Cl + H HCl + Cl + CH 4 HCl + CH Couples Cl x to H x Cl + H HCl + CH Cl + H HCl + H H + Cl Cl + H HCl + HCl + hν Cl + H And N x is coupled to H x! H + H + H + + H H + C C + H H + + M H + M H + H + H + H + H + H H + Couples H x to N x H + H H + H + N N + H H + N + M HN + M HN + H H + N HN + hν H + N H + N H N + M H N + hν H + N + halogen reactions 17
18 Build a model HCl H hν ClN, H N hν N 1. Source gas. Release of radical H CH 4 H Cl Cl. Catalytic cycle 4. Rate determining step hν H H hν HCl 5. Short-lived reserviors 6. Long-lived reserviors 7. Removal Halocarbon RAINUT How the radical families contribute to ozone loss H x (H, CH 4 ) Cl x (CFCs) N x (N ) 18
19 Meanwhile, scientists refine their understanding But Industry is ready, and they come our firing! CFCs are heavier than air, and don t rise to the stratosphere they sink! There is more chlorine in sea spray than from CFCs! Chlorine may get to the stratosphere, but it doesn t form Cl! The natural variability of ozone is greater than any change expected due to man-made chemicals! Even if there is ozone loss, there is no proof that more ultraviolet light will reach the surface! Which one is it? The SST story evolves SSTs make ozone (smog chemistry) SSTs destroy ozone Those darned lab chemists 19
20 The World Breathes a Sign of Relief In the form of CFCs CFC production back on the rise! The Big Surprise of 1985! 0
21 Summary of important points Stratospheric ozone is produced by photolysis of, a process that is governed by abundances of and UV output of the sun. Mankind can t easily tamper with these parameters Sir Sydney Chapman (who spent a lot of time in Boulder) nearly got it right. He was able to account for ozone in the stratosphere to within about a factor of two with just four simple reactions. You might as well memorize these they will reappear on comps and cumulative exams (and it beats what you need to know to get the other factor of two! Gases that are long-lived in the troposphere will eventually reach the stratosphere, where they nearly all break down ( oxidize ) to produce highly reactive radicals that catalytically destroy ozone. It doesn t matter where these gases originate from the troposphere is the great homogenizer. The 1995 Nobel Prizes in Chemistry were awarded to Paul Crutzen, Mario Molina, and Sherry Rowland for recognizing the importance of this concept. The radical families are highly coupled changes in abundances of one family will result in changes in the others. Thus, the system is non-linear (although reasonably well behaved). However, it means that you can t just scale ozone losses with emissions. A simple stratospheric model has dozens of chemical species and hundreds of chemical reactions. It will run on a PC (I have one written by Michael Prather on the computer that I am using for this lecture). Having a good idea isn t good enough. It takes a lot of measurements to prove your point or a global crisis stay tuned for Part! 1
Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 (Chapter 4, p , , , )
 Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 (Chapter 4, p 155-169, 174-176, 198-222, 231-238) zone Discovery and History The Stratosphere and circulation Chapman Chemistry Catalysts The Controversy The zone Hole International
Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 (Chapter 4, p 155-169, 174-176, 198-222, 231-238) zone Discovery and History The Stratosphere and circulation Chapman Chemistry Catalysts The Controversy The zone Hole International
Gases, ozone, and CFCs. An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop
 Gases, ozone, and CFCs An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Gas Gas Model Gases are composed of tiny, widely-spaced particles. For a typical gas, the average distance between particles is about
Gases, ozone, and CFCs An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Gas Gas Model Gases are composed of tiny, widely-spaced particles. For a typical gas, the average distance between particles is about
Stratospheric Ozone Depletion, Regional Ozone, Aerosols: Connections to Climate Change
 Stratospheric Ozone Depletion, Regional Ozone, Aerosols: Connections to Climate Change Jeff Gaffney Chemistry Department University of Arkansas at Little Rock DOE Biological and Environmental Science Climate
Stratospheric Ozone Depletion, Regional Ozone, Aerosols: Connections to Climate Change Jeff Gaffney Chemistry Department University of Arkansas at Little Rock DOE Biological and Environmental Science Climate
Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation
 Outline Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation Review electromagnetic radiation absorptivity by selective gases temperature vs. height in atmosphere Ozone production and destruction natural balance anthropogenic
Outline Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation Review electromagnetic radiation absorptivity by selective gases temperature vs. height in atmosphere Ozone production and destruction natural balance anthropogenic
Measurements of Ozone. Why is Ozone Important?
 Anthropogenic Climate Changes CO 2 CFC CH 4 Human production of freons (CFCs) Ozone Hole Depletion Human production of CO2 and CH4 Global Warming Human change of land use Deforestation (from Earth s Climate:
Anthropogenic Climate Changes CO 2 CFC CH 4 Human production of freons (CFCs) Ozone Hole Depletion Human production of CO2 and CH4 Global Warming Human change of land use Deforestation (from Earth s Climate:
Ozone. In the upper atmosphere. At the surface pollution (not discussed)
 Ozone In the upper atmosphere At the surface pollution (not discussed) What is Ozone? Oxygen molecule with 3 oxygen atoms O 3 Normal form of oxygen: 2 oxygen atoms O 2 Where does Ozone occur? Stratosphere
Ozone In the upper atmosphere At the surface pollution (not discussed) What is Ozone? Oxygen molecule with 3 oxygen atoms O 3 Normal form of oxygen: 2 oxygen atoms O 2 Where does Ozone occur? Stratosphere
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 9, 2016 The Game Changer. Some perspective The British Antarctic Survey The Ozone Hole International Regulations
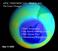 ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 9, 2016 The Game Changer Some perspective The British Antarctic Survey The Ozone Hole International Regulations Rowland (1974): The work is going very well, but it may mean the
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 9, 2016 The Game Changer Some perspective The British Antarctic Survey The Ozone Hole International Regulations Rowland (1974): The work is going very well, but it may mean the
Chapter 2 Protecting the Ozone Layer. The Ozone Hole
 Today (Tues 2/24) Newspaper Articles: Ciara Rodwell and Melissa Regan Intro to Ozone, Ozone Hole, & Chapter 2 Light, matter, and human health! Laboratory: Experiment 4 You design investigation Start Ozone
Today (Tues 2/24) Newspaper Articles: Ciara Rodwell and Melissa Regan Intro to Ozone, Ozone Hole, & Chapter 2 Light, matter, and human health! Laboratory: Experiment 4 You design investigation Start Ozone
atmosphere: a mixture a gases that surrounds the planet Earth.
 atmosphere: a mixture a gases that surrounds the planet Earth. 78% nitrogen 21% oxygen the atmosphere is held to the Earth by the force of gravity. Due to the smaller mass of planets like Mercury, less
atmosphere: a mixture a gases that surrounds the planet Earth. 78% nitrogen 21% oxygen the atmosphere is held to the Earth by the force of gravity. Due to the smaller mass of planets like Mercury, less
Chemistry 471/671. Atmospheric Chemistry III: Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
 Chemistry 471/671 Atmospheric Chemistry III: Stratospheric Ozone Depletion 2 The Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hn 2 O( 1 D) O( 1 D) + O 2 + M O 3 + M Exothermic O( 1 D) + O 3 2 O 2 O 3 + hn O( 1 D) + O 2 ( 1
Chemistry 471/671 Atmospheric Chemistry III: Stratospheric Ozone Depletion 2 The Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hn 2 O( 1 D) O( 1 D) + O 2 + M O 3 + M Exothermic O( 1 D) + O 3 2 O 2 O 3 + hn O( 1 D) + O 2 ( 1
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II
 Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes REVIEW... Q Is the depletion of STRATOSPHERIC OZONE (in
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes REVIEW... Q Is the depletion of STRATOSPHERIC OZONE (in
Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven
 Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven Prevention of the atmosphere KÖRNYEZETGAZDÁLKODÁSI AGRÁRMÉRNÖKI MSC (MSc IN AGRO-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES) Fundamentals to atmospheric chemical reactions. The stratospheric
Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven Prevention of the atmosphere KÖRNYEZETGAZDÁLKODÁSI AGRÁRMÉRNÖKI MSC (MSc IN AGRO-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES) Fundamentals to atmospheric chemical reactions. The stratospheric
Mario Molina puts the atmosphere and ozone on the political agenda
 Mario Molina puts the atmosphere and ozone on the political agenda (Version 1) A. Understanding ozone 60 km stratosphere 40 km 20 km troposphere Diagram of our atmosphere (Reproduced with permission from
Mario Molina puts the atmosphere and ozone on the political agenda (Version 1) A. Understanding ozone 60 km stratosphere 40 km 20 km troposphere Diagram of our atmosphere (Reproduced with permission from
Chapter 8. Energy and Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 8 Energy and Chemical Reactions Chapter Map Some Chemical Changes Release Energy Combustion of Methane CH 4 (g) + 2O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + 2H 2 O(l) + Some Chemical Changes Absorb Energy Energy Terms
Chapter 8 Energy and Chemical Reactions Chapter Map Some Chemical Changes Release Energy Combustion of Methane CH 4 (g) + 2O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + 2H 2 O(l) + Some Chemical Changes Absorb Energy Energy Terms
January 23, Lecture 3. The Ozone Chemistry.
 Lecture 3 January 23, 2018 The Ozone Chemistry http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a010000/a010015/index.html The atmosphere is divided vertically into four layers based on temperature: the troposphere,
Lecture 3 January 23, 2018 The Ozone Chemistry http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a010000/a010015/index.html The atmosphere is divided vertically into four layers based on temperature: the troposphere,
Chapman. 4. O + O 3 2 O 2 ; k 4 5. NO + O 3 NO 2 + O 2 ; k 5 6. NO 2 + O NO + O 2 ; k 6 7. NO 2 + hν NO + O; k 7. NO X Catalytic.
 ATM 507 Lecture 8 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Note: next week class as usual Tuesday, no class on Thursday Today s topics Mid-latitude Stratosphere Lower Stratosphere 1 Let s
ATM 507 Lecture 8 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Note: next week class as usual Tuesday, no class on Thursday Today s topics Mid-latitude Stratosphere Lower Stratosphere 1 Let s
Atmospheric Chemistry III
 Atmospheric Chemistry III Chapman chemistry, catalytic cycles: reminder Source of catalysts, transport to stratosphere: reminder Effect of major (O 2 ) and minor (N 2 O, CH 4 ) biogenic gases on [O 3 ]:
Atmospheric Chemistry III Chapman chemistry, catalytic cycles: reminder Source of catalysts, transport to stratosphere: reminder Effect of major (O 2 ) and minor (N 2 O, CH 4 ) biogenic gases on [O 3 ]:
Stratospheric O 3 : Overview
 Stratospheric Chemistry READING: Chapter 10 of text Mid-latitude Ozone Chemistry (and depletion) Polar Ozone Destruction (the Ozone Hole) Stratospheric O 3 : Overview Most O 3 (90%) in stratosphere. Remaining
Stratospheric Chemistry READING: Chapter 10 of text Mid-latitude Ozone Chemistry (and depletion) Polar Ozone Destruction (the Ozone Hole) Stratospheric O 3 : Overview Most O 3 (90%) in stratosphere. Remaining
Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics II. Chem 102 Dr. Eloranta
 Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics II Chem 102 Dr. Eloranta Rate Laws If you are familiar with calculus Experiments would allow you to determine the reaction order and rate constant, but what if you wanted
Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics II Chem 102 Dr. Eloranta Rate Laws If you are familiar with calculus Experiments would allow you to determine the reaction order and rate constant, but what if you wanted
2.1 Ozone. Ozone O 3. Oxygen O 2 1/30/2015 CHM 107
 CHM 107 2.1 Ozone In the stratosphere way up high Protects Earth from solar radiation There is a hole in the ozone layer above Antarctica Do we care? Why? Energy + 3 O 2 (g) g 2 O 3 (g) Lightning can serve
CHM 107 2.1 Ozone In the stratosphere way up high Protects Earth from solar radiation There is a hole in the ozone layer above Antarctica Do we care? Why? Energy + 3 O 2 (g) g 2 O 3 (g) Lightning can serve
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Air Pollution Chemistry Lecture 1
 ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Air Pollution Chemistry Lecture 1 Note Page numbers refer to Daniel Jacob s online textbook: http://acmg.seas.harvard.edu/publications/ jacobbook/index.html Atmos = vapor + sphaira
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Air Pollution Chemistry Lecture 1 Note Page numbers refer to Daniel Jacob s online textbook: http://acmg.seas.harvard.edu/publications/ jacobbook/index.html Atmos = vapor + sphaira
Class: Chemistry Topic:_atomic structure & ozone layer
 Class: Chemistry Topic:_atomic structure & ozone layer Directions: Please read both articles and write a 5 paragraph comparative essay on each. You should include examples provided in the articles to prove
Class: Chemistry Topic:_atomic structure & ozone layer Directions: Please read both articles and write a 5 paragraph comparative essay on each. You should include examples provided in the articles to prove
SCIAMACHY book. Ozone variability and long-term changes Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA-IASB
 SCIAMACHY book Ozone variability and long-term changes Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA-IASB 1928: start of CFC production 1971: 1 st observation of CFC in the atmosphere (J. Lovelock) 1974: identification
SCIAMACHY book Ozone variability and long-term changes Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA-IASB 1928: start of CFC production 1971: 1 st observation of CFC in the atmosphere (J. Lovelock) 1974: identification
Math 19a - Reading 8.1 outline for discussion section
 Math 9a - Reading 8. outline for discussion section due Monday, February 25, 28. How do you, guys, feel about vectors and matrices? Have you seen such things before? What did you think of the lecture on
Math 9a - Reading 8. outline for discussion section due Monday, February 25, 28. How do you, guys, feel about vectors and matrices? Have you seen such things before? What did you think of the lecture on
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore O ZO NE L AYER For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore O ZO NE L AYER For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 31. Air Pollution Part II
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 31 Air Pollution Part II Last time we talked mainly about two types of smog:. 1. London-type smog 2. L.A.-type smog or photochemical smog What are the necessary ingredients
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 31 Air Pollution Part II Last time we talked mainly about two types of smog:. 1. London-type smog 2. L.A.-type smog or photochemical smog What are the necessary ingredients
SUSTAINABILITY MATTERS FACT SHEET 7: THE HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER
 SUSTAINABILITY MATTERS FACT SHEET 7: THE HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER What is the ozone layer? Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen, which means it is a pure element, but has a different chemical structure to that
SUSTAINABILITY MATTERS FACT SHEET 7: THE HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER What is the ozone layer? Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen, which means it is a pure element, but has a different chemical structure to that
Chapter 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer
 Chapter 2: Protecting the zone Layer Why do we need to do to protect the ozone layer? Isn t ozone hazardous to human health? Why is the ozone layer getting smaller? What can we do (if anything) to help
Chapter 2: Protecting the zone Layer Why do we need to do to protect the ozone layer? Isn t ozone hazardous to human health? Why is the ozone layer getting smaller? What can we do (if anything) to help
(Figure 2) Science coursework
 Dobson was a scientist that devoted most of his life to the observation of the atmospheric ozone. The results of his devotion to the study of the atmospheric led to a great understanding of the structure
Dobson was a scientist that devoted most of his life to the observation of the atmospheric ozone. The results of his devotion to the study of the atmospheric led to a great understanding of the structure
ClO + O -> Cl + O 2 Net: O 3 + O -> O 2 + O 2
 Lecture 36. Stratospheric ozone chemistry. Part2: Threats against ozone. Objectives: 1. Chlorine chemistry. 2. Volcanic stratospheric aerosols. 3. Polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs). Readings: Turco: p.
Lecture 36. Stratospheric ozone chemistry. Part2: Threats against ozone. Objectives: 1. Chlorine chemistry. 2. Volcanic stratospheric aerosols. 3. Polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs). Readings: Turco: p.
14.4 Reaction Mechanism
 14.4 Reaction Mechanism Steps of a Reaction Fred Omega Garces Chemistry 201 Miramar College 1 Reaction Mechanism The Ozone Layer Ozone is most important in the stratosphere, at this level in the atmosphere,
14.4 Reaction Mechanism Steps of a Reaction Fred Omega Garces Chemistry 201 Miramar College 1 Reaction Mechanism The Ozone Layer Ozone is most important in the stratosphere, at this level in the atmosphere,
Stratospheric Ozone: An Online Learning Module
 Stratospheric Ozone: An Online Learning Module Using your favorite browser open Ozone/index.htm or go to http://cs.clark.edu/~mac/geol390/stratosphericozone/startozoneactivity.html Work through the web
Stratospheric Ozone: An Online Learning Module Using your favorite browser open Ozone/index.htm or go to http://cs.clark.edu/~mac/geol390/stratosphericozone/startozoneactivity.html Work through the web
Atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere is a mixture of gases, solids, and liquids that surround the planet.
 Atmosphere Atmosphere- a thin layer of air that forms a protective covering around the planet. If Earth had no atmosphere, days would be extremely hot and nights would be extremely cold. Earth's atmosphere
Atmosphere Atmosphere- a thin layer of air that forms a protective covering around the planet. If Earth had no atmosphere, days would be extremely hot and nights would be extremely cold. Earth's atmosphere
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II
 Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes THE DESTRUCTION OF STRATOSPHERIC OZONE The ozone hole
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes THE DESTRUCTION OF STRATOSPHERIC OZONE The ozone hole
Protecting the Ozone Layer. Allotropes. Comparison of Allotropes
 Protecting the Ozone Layer Practice Problems: All Ch. 2 problems with the blue codes or answers on Page 520-521 Properties of Ozone Triatomic oxygen gas or O 3 to smell in Greek; odor at 10 ppb Lightning;
Protecting the Ozone Layer Practice Problems: All Ch. 2 problems with the blue codes or answers on Page 520-521 Properties of Ozone Triatomic oxygen gas or O 3 to smell in Greek; odor at 10 ppb Lightning;
CHEM/ENVS 380 S14, Midterm Exam ANSWERS 1 Apr 2014
 PART- A. Multiple Choice Questions (5 points each): Each question may have more than one correct answer. You must select ALL correct answers, and correct answers only, to receive full credit. 1. Which
PART- A. Multiple Choice Questions (5 points each): Each question may have more than one correct answer. You must select ALL correct answers, and correct answers only, to receive full credit. 1. Which
Chapter 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer
 Chapter 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer Student: 1. O2 and O3 molecules are A. allotropes. B. structural isomers. C. isotopes. D. geometrical isomers. 2. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are there
Chapter 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer Student: 1. O2 and O3 molecules are A. allotropes. B. structural isomers. C. isotopes. D. geometrical isomers. 2. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are there
An Interpretation of Natural Healing of Ozone Holes
 ISSN 2278 0211 (Online) An Interpretation of Natural Healing of Ozone Holes Vasudevan Tachoth Nirvan Industries, Private Industrial Estate, Post Sidco Near Railway Gate, Kuruchi Coimbatore, India Abstract:
ISSN 2278 0211 (Online) An Interpretation of Natural Healing of Ozone Holes Vasudevan Tachoth Nirvan Industries, Private Industrial Estate, Post Sidco Near Railway Gate, Kuruchi Coimbatore, India Abstract:
OZONE AND ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION
 OZONE AND ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION Alfio Parisi, Michael Kimlin Imagine if the earth s protective atmosphere did not exist and the earth was subjected to the harmful ultraviolet energy from the sun. Life
OZONE AND ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION Alfio Parisi, Michael Kimlin Imagine if the earth s protective atmosphere did not exist and the earth was subjected to the harmful ultraviolet energy from the sun. Life
CONTENTS 1 MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION
 i CONTENTS 1 MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION 1 1.1 MIXING RATIO 1 1.2 NUMBER DENSITY 2 1.3 PARTIAL PRESSURE 6 PROBLEMS 10 1.1 Fog formation 10 1.2 Phase partitioning of water in cloud 10 1.3 The ozone
i CONTENTS 1 MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION 1 1.1 MIXING RATIO 1 1.2 NUMBER DENSITY 2 1.3 PARTIAL PRESSURE 6 PROBLEMS 10 1.1 Fog formation 10 1.2 Phase partitioning of water in cloud 10 1.3 The ozone
Lecture 25: Atmosphere & environment
 Lecture 25: Atmosphere & environment Read: BLB 18.1 4 HW: BLB 18:9,11,15,29,69 Sup 18:1 3 Know: ozone chemistry chemistry of the lower atmosphere sulfer compounds & acid rain nitrogen oxides & smog check
Lecture 25: Atmosphere & environment Read: BLB 18.1 4 HW: BLB 18:9,11,15,29,69 Sup 18:1 3 Know: ozone chemistry chemistry of the lower atmosphere sulfer compounds & acid rain nitrogen oxides & smog check
Lecture 15 Antarctic Ozone Hole ATOC/CHEM 5151
 Lecture 15 Antarctic Ozone Hole ATOC/CHEM 5151 1 Ozone Hole Theories 1. Solar activity: During periods of high solar activity, energetic particles are deposited high in the atmosphere, creating NOx. Perhaps
Lecture 15 Antarctic Ozone Hole ATOC/CHEM 5151 1 Ozone Hole Theories 1. Solar activity: During periods of high solar activity, energetic particles are deposited high in the atmosphere, creating NOx. Perhaps
CHEM Chemical Kinetics
 Chemical Kinetics Catalysts A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of the reaction but is neither created nor destroyed in the process. Catalysts can be divided into two broad categories. Homogeneous
Chemical Kinetics Catalysts A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of the reaction but is neither created nor destroyed in the process. Catalysts can be divided into two broad categories. Homogeneous
Chapter 7. Stratospheric Chemistry.
 Chapter 7. Stratospheric Chemistry. Stratospheric chemistry became environmental chemistry in the early 1970 s when scientists studied the potential stratospheric effects of supersonic aircraft (Crutzen,
Chapter 7. Stratospheric Chemistry. Stratospheric chemistry became environmental chemistry in the early 1970 s when scientists studied the potential stratospheric effects of supersonic aircraft (Crutzen,
2. Sketch a plot of R vs. z. Comment on the shape. Explain physically why R(z) has a maximum in the atmospheric column.
 190 PROBLEMS 10. 1 Shape of the ozone layer Consider a beam of solar radiation of wavelength λ propagating downward in the vertical direction with an actinic flux I at the top of the atmosphere. Assume
190 PROBLEMS 10. 1 Shape of the ozone layer Consider a beam of solar radiation of wavelength λ propagating downward in the vertical direction with an actinic flux I at the top of the atmosphere. Assume
Ozone Student Activity Book
 Ozone Student Activity Book I. Introduction Ozone is similar to oxygen that we breathe. Air contains oxygen molecules that are made up of two oxygen atoms combined together (O 2 ). Ozone is a molecule
Ozone Student Activity Book I. Introduction Ozone is similar to oxygen that we breathe. Air contains oxygen molecules that are made up of two oxygen atoms combined together (O 2 ). Ozone is a molecule
CHEMICAL KINETICS (RATES OF REACTION)
 Kinetics F322 1 CHEMICAL KINETICS (RATES OF REACTION) Introduction Chemical kinetics is concerned with the dynamics of chemical reactions such as the way reactions take place and the rate (speed) of the
Kinetics F322 1 CHEMICAL KINETICS (RATES OF REACTION) Introduction Chemical kinetics is concerned with the dynamics of chemical reactions such as the way reactions take place and the rate (speed) of the
The Earth is surrounded by a blanket of air, which we call the atmosphere. It reaches over 560 kilometers
 A t m o s f e r a Atmosphere The Earth is surrounded by a blanket of air, which we call the atmosphere. It reaches over 560 kilometers (348 miles) from the surface of the Earth, so we are only able to
A t m o s f e r a Atmosphere The Earth is surrounded by a blanket of air, which we call the atmosphere. It reaches over 560 kilometers (348 miles) from the surface of the Earth, so we are only able to
Chemistry of Ozone. Explain the following terms: resonance, resonance hybrid, delocalisation
 Chemistry of Ozone Ozone is triatomic oxygen, O 3. (Ozone is from the Greek ozein, to smell. ) It is a form of oxygen in which the atoms combine in threes, (correct IUPAC name: trioxygen, O 3 ), rather
Chemistry of Ozone Ozone is triatomic oxygen, O 3. (Ozone is from the Greek ozein, to smell. ) It is a form of oxygen in which the atoms combine in threes, (correct IUPAC name: trioxygen, O 3 ), rather
Chapman Cycle. The cycle describes reactions of O 2 and O 3 in stratosphere
 Chapman Cycle The cycle describes reactions of O 2 and O 3 in stratosphere Even though reactions are happening, the concentration of O 3 remains constant This is an example of a dynamic equilibrium or
Chapman Cycle The cycle describes reactions of O 2 and O 3 in stratosphere Even though reactions are happening, the concentration of O 3 remains constant This is an example of a dynamic equilibrium or
8.2 Tropospheric ozone
 8.2 Tropospheric ozone Prev Chapter 8. Ozone Next 8.2 Tropospheric ozone Tropospheric ozone is only about 10% of the total amount of ozone contained in a vertical column in the atmosphere. However, this
8.2 Tropospheric ozone Prev Chapter 8. Ozone Next 8.2 Tropospheric ozone Tropospheric ozone is only about 10% of the total amount of ozone contained in a vertical column in the atmosphere. However, this
Student Workbook California Education and the Environment Initiative. Earth Science Standard E.8.c. Living Under One Roof
 E Student Workbook California Education and the Environment Initiative Earth Science Standard E.8.c. Living Under One Roof California Education and the Environment Initiative Approved by the California
E Student Workbook California Education and the Environment Initiative Earth Science Standard E.8.c. Living Under One Roof California Education and the Environment Initiative Approved by the California
10. Stratospheric chemistry. Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017
 10. Stratospheric chemistry Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 The ozone layer Dobson unit: physical thickness (0.01 mm) of ozone layer if compressed to 1 atm, 0 o
10. Stratospheric chemistry Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 The ozone layer Dobson unit: physical thickness (0.01 mm) of ozone layer if compressed to 1 atm, 0 o
Chemical Kinetics. What quantities do we study regarding chemical reactions? 15 Chemical Kinetics
 Chemical Kinetics Chemical kinetics: the study of reaction rate, a quantity conditions affecting it, the molecular events during a chemical reaction (mechanism), and presence of other components (catalysis).
Chemical Kinetics Chemical kinetics: the study of reaction rate, a quantity conditions affecting it, the molecular events during a chemical reaction (mechanism), and presence of other components (catalysis).
Sodium, Na. Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 11.1 to 11.4.
 Sodium, Na Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 11.1 to 11.4 Forms of Carbon The Chalcogens (Group 16) What is a chalcogen? Any element in
Sodium, Na Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 11.1 to 11.4 Forms of Carbon The Chalcogens (Group 16) What is a chalcogen? Any element in
On Stationary state, also called steady state. Lifetimes and spatial scales of variability
 On sources and sinks ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 5-6 Additional Notes February 16/18, 2016 On lifetimes, variability, and models On Stationary state, also called steady state Lifetimes and spatial scales
On sources and sinks ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 5-6 Additional Notes February 16/18, 2016 On lifetimes, variability, and models On Stationary state, also called steady state Lifetimes and spatial scales
Enhanced UV radiation a new problem for the marine environment
 1 Enhanced UV radiation a new problem for the marine environment Robert F. Whitehead, Stephen J. de Mora* and Serge Demers 1.1 Introduction UV irradiance at the earth s surface is intimately related to
1 Enhanced UV radiation a new problem for the marine environment Robert F. Whitehead, Stephen J. de Mora* and Serge Demers 1.1 Introduction UV irradiance at the earth s surface is intimately related to
Introduction to Atmospheric Photochemistry AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch
 Introduction to Atmospheric Photochemistry AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2015 Lecture 9 9 March 2015 1 Chapman Chemistry Production of stratospheric
Introduction to Atmospheric Photochemistry AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2015 Lecture 9 9 March 2015 1 Chapman Chemistry Production of stratospheric
Earth s Atmosphere. Composition
 Earth s Atmosphere Earth s atmosphere is a layer of gases surrounding the planet that is held in place by gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet radiation, warming the
Earth s Atmosphere Earth s atmosphere is a layer of gases surrounding the planet that is held in place by gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet radiation, warming the
Ozone Depletion. Dana Desonie, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click (No sign in required)
 Ozone Depletion Dana Desonie, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content,
Ozone Depletion Dana Desonie, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content,
Stratosphere and Ozone
 Stratosphere and Ozone Ozone (Greek, ozein, to smell) O 3 Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hv O + O O + O 3 2O 2 O 3 + hv O 2 + O O + O 2 + M O 3 + M third-body. anything What units are used to report the amount
Stratosphere and Ozone Ozone (Greek, ozein, to smell) O 3 Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hv O + O O + O 3 2O 2 O 3 + hv O 2 + O O + O 2 + M O 3 + M third-body. anything What units are used to report the amount
TYPES OF CATALYSIS Reading Supplement
 TYPES OF CATALYSIS Reading Supplement This page looks at the the different types of catalyst (heterogeneous and homogeneous) with examples of each kind, and explanations of how they work. You will also
TYPES OF CATALYSIS Reading Supplement This page looks at the the different types of catalyst (heterogeneous and homogeneous) with examples of each kind, and explanations of how they work. You will also
This article was published in 1996 and has not been updated or revised.
 BEYOND DISCOVERY THE PATH FROM RESEARCH TO HUMAN BENEFIT THE OZONE DEPLETION PHENOMENON Like an infection that grows more and more virulent, the continent-size hole in Earth s ozone layer keeps getting
BEYOND DISCOVERY THE PATH FROM RESEARCH TO HUMAN BENEFIT THE OZONE DEPLETION PHENOMENON Like an infection that grows more and more virulent, the continent-size hole in Earth s ozone layer keeps getting
Chapter 2 Protecting the Ozone Layer
 Chapter 2 Protecting the Ozone Layer Multiple Choice Questions 1. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are there in a neutral atom of? A. A B. B C. C D. D Remember that the mass is protons plus neutrons
Chapter 2 Protecting the Ozone Layer Multiple Choice Questions 1. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are there in a neutral atom of? A. A B. B C. C D. D Remember that the mass is protons plus neutrons
Chemistry 1500: Chemistry in Modern Living. Topic 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer. Atoms and Light
 Chemistry 1500 Dr. unter s Class Topic 2 - Page 1 Chemistry 1500: Chemistry in Modern Living Topic 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer Atoms and Light Chemistry in Context, 2 nd Edition (1997): Chapter 2, Pages
Chemistry 1500 Dr. unter s Class Topic 2 - Page 1 Chemistry 1500: Chemistry in Modern Living Topic 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer Atoms and Light Chemistry in Context, 2 nd Edition (1997): Chapter 2, Pages
STRATOSPHERIC OZONE DEPLETION. Adapted from K. Sturges at MBHS
 STRATOSPHERIC OZONE DEPLETION Adapted from K. Sturges at MBHS Ozone Layer Ozone is Good up high Stratosphere Bad nearby Troposphere Solar Radiation - range of electromagnetic waves UV shortest we see if
STRATOSPHERIC OZONE DEPLETION Adapted from K. Sturges at MBHS Ozone Layer Ozone is Good up high Stratosphere Bad nearby Troposphere Solar Radiation - range of electromagnetic waves UV shortest we see if
2. (i) Infrared (radiation absorbed) by (C H) bond vibration ALLOW bond stretching OR bond bending DO NOT ALLOW molecules vibrating 2
 . (i) Species with an unpaired electron ALLOW atom, molecule or particle with an unpaired electron ALLOW has an unpaired electron ALLOW particle formed by homolytic fission DO NOT ALLOW particle with a
. (i) Species with an unpaired electron ALLOW atom, molecule or particle with an unpaired electron ALLOW has an unpaired electron ALLOW particle formed by homolytic fission DO NOT ALLOW particle with a
Discuss Yesterday s Lab. What Do We Know? Funny Ozone Video. Ozone Layer Defined! Ozone Layer. Warm-Up 3/3/2015
 Warm-Up March 3, 2015 Today you will need your notebook, pencil and whiteboards. HW due Friday. Attach the Ozone Table into your notebook Pick up ozone table in the red box Complete the Predictions Column
Warm-Up March 3, 2015 Today you will need your notebook, pencil and whiteboards. HW due Friday. Attach the Ozone Table into your notebook Pick up ozone table in the red box Complete the Predictions Column
 Part I Short Answer Choose a letter to fill in the blanks. Use choices as many times as you wish. Only one choice is needed per blank. All are 3 points each. 1. First set. How can you tell these apart?
Part I Short Answer Choose a letter to fill in the blanks. Use choices as many times as you wish. Only one choice is needed per blank. All are 3 points each. 1. First set. How can you tell these apart?
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere
 Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
 ATM 507 Lecture 9 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Next Class Tuesday, Sept. 30 Today s topics Polar Stratospheric Chemistry and the Ozone Hole, Required reading: 20 Questions and
ATM 507 Lecture 9 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Next Class Tuesday, Sept. 30 Today s topics Polar Stratospheric Chemistry and the Ozone Hole, Required reading: 20 Questions and
Ultraviolet Spectroscopy of Stratospheric Molecular O3
 Ultraviolet Spectroscopy of Stratospheric Molecular O3 Christine Predaina * Colorado Space Grant Consortium, University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado, 80309 The study of O3 (Ozone) remains a current topic
Ultraviolet Spectroscopy of Stratospheric Molecular O3 Christine Predaina * Colorado Space Grant Consortium, University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado, 80309 The study of O3 (Ozone) remains a current topic
(for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes)
 www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. chem10b 18.2-30 What is the final stage in municipal water treatment? A. aeration B. settling C. removal of added fluoride
www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. chem10b 18.2-30 What is the final stage in municipal water treatment? A. aeration B. settling C. removal of added fluoride
The Atmosphere. All of it. In one hour. Mikael Witte 10/27/2010
 The Atmosphere All of it. In one hour. Mikael Witte 10/27/2010 Outline Structure Dynamics - heat transport Composition Trace constituent compounds Some Atmospheric Processes Ozone destruction in stratosphere
The Atmosphere All of it. In one hour. Mikael Witte 10/27/2010 Outline Structure Dynamics - heat transport Composition Trace constituent compounds Some Atmospheric Processes Ozone destruction in stratosphere
In 2002, a group of university researchers joined together under the title of the Canadian Network for the Detection of Atmospheric Change (CANDAC)
 1 In 2002, a group of university researchers joined together under the title of the Canadian Network for the Detection of Atmospheric Change (CANDAC) with the objective of improving the state of observational
1 In 2002, a group of university researchers joined together under the title of the Canadian Network for the Detection of Atmospheric Change (CANDAC) with the objective of improving the state of observational
F325: Equilibria, Energetics and Elements How Far?
 F325: Equilibria, Energetics and Elements 5.1.2 How Far? 100 marks 1. Syngas is a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen gases, used as a feedstock for the manufacture of methanol. A dynamic equilibrium
F325: Equilibria, Energetics and Elements 5.1.2 How Far? 100 marks 1. Syngas is a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen gases, used as a feedstock for the manufacture of methanol. A dynamic equilibrium
LECTURE 6 - THE EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE
 LECTURE 6 - THE EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE Note: Slide numbers refer to the PowerPoint presentation which accompanies the lecture. Earth s Atmosphere, slide 1 here INTRODUCTION Earth s Atmosphere, slide 2 here
LECTURE 6 - THE EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE Note: Slide numbers refer to the PowerPoint presentation which accompanies the lecture. Earth s Atmosphere, slide 1 here INTRODUCTION Earth s Atmosphere, slide 2 here
CHAPTER 10. STRATOSPHERIC OZONE
 The stratospheric ozone layer, centered at about 20 km above the surface of the Earth ( Figure 10-1 ), protects life on Earth by absorbing UV radiation from the Sun. In this chapter we examine the mechanisms
The stratospheric ozone layer, centered at about 20 km above the surface of the Earth ( Figure 10-1 ), protects life on Earth by absorbing UV radiation from the Sun. In this chapter we examine the mechanisms
Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review
 Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Climate in a region is a. the long-term,
Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Climate in a region is a. the long-term,
Identify the condition that causes a bond in CCl 4 to break in the upper atmosphere. Deduce an equation for the formation of the reactive species.
 Q1.CCl 4 is an effective fire extinguisher but it is no longer used because of its toxicity and its role in the depletion of the ozone layer. In the upper atmosphere, a bond in CCl 4 breaks and reactive
Q1.CCl 4 is an effective fire extinguisher but it is no longer used because of its toxicity and its role in the depletion of the ozone layer. In the upper atmosphere, a bond in CCl 4 breaks and reactive
Layer Protection Glossary
 Page 1 of 7 Ozone Layer Protection Last updated on Wednesday, December 15, 2010 You are here: EPA Home Ozone Layer Protection Ozone Layer Protection Glossary Layer Protection Glossary In order to understand
Page 1 of 7 Ozone Layer Protection Last updated on Wednesday, December 15, 2010 You are here: EPA Home Ozone Layer Protection Ozone Layer Protection Glossary Layer Protection Glossary In order to understand
POLAR OZONE DEPLETION
 POLAR OZONE DEPLETION Nobel Lecture, December 8, 1995 by MARIO J. MOLINA Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, and Department of Chemistry, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge,
POLAR OZONE DEPLETION Nobel Lecture, December 8, 1995 by MARIO J. MOLINA Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, and Department of Chemistry, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge,
Reaction Mechanisms. Chemical Kinetics. Reaction Mechanisms. Reaction Mechanisms. Reaction Mechanisms. Reaction Mechanisms
 Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is a study of the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. The study of kinetics may be done in steps: Determination of reaction mechanism Prediction of rate law Measurement
Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is a study of the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. The study of kinetics may be done in steps: Determination of reaction mechanism Prediction of rate law Measurement
Do Now pg 87. Solve this riddle!
 Do Now pg 87 Solve this riddle! You can t see me You can t taste me You can t feel me But you need me I kill 7 million people a year But you kill what keeps me clear What am I? Lesson 15.1 Earth s Atmosphere
Do Now pg 87 Solve this riddle! You can t see me You can t taste me You can t feel me But you need me I kill 7 million people a year But you kill what keeps me clear What am I? Lesson 15.1 Earth s Atmosphere
This site aims to provide information on the chemistry of ozone and provide some useful links to other pages.
 OZONE CHEMISTRY: This site aims to provide information on the chemistry of ozone and provide some useful links to other pages. Ozone is an atmospheric compound, found both at ground level and in the stratosphere.
OZONE CHEMISTRY: This site aims to provide information on the chemistry of ozone and provide some useful links to other pages. Ozone is an atmospheric compound, found both at ground level and in the stratosphere.
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming?
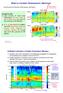 What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
Table of Contents. Chapter: Atmosphere. Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere. Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere. Section 3: Air Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement 1 Earth s Atmosphere Importance of the Atmosphere Earth's atmosphere
Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement 1 Earth s Atmosphere Importance of the Atmosphere Earth's atmosphere
Chapter 6 Notes. Section 4-5 Nonmetals
 Chapter 6 Notes Section 4-5 Nonmetals Section 4-5 Objectives 8) Contrast the reactivity and abundance of elements in the Group 3A through Group 8A. 9) Name an important element in each group of p-block
Chapter 6 Notes Section 4-5 Nonmetals Section 4-5 Objectives 8) Contrast the reactivity and abundance of elements in the Group 3A through Group 8A. 9) Name an important element in each group of p-block
Chemical Kinetics deals with rate (speed of chemical reactions how fast? Rate equation represents rate, which depends on various reactants
 Kinetics Introduction Chemical Kinetics deals with rate (speed of chemical reactions how fast? Rate equation represents rate, which depends on various reactants Reaction mechanism is the details of how
Kinetics Introduction Chemical Kinetics deals with rate (speed of chemical reactions how fast? Rate equation represents rate, which depends on various reactants Reaction mechanism is the details of how
General A haloalkane is a compound in which one or more H atoms of an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms.
 aloalkanes General A haloalkane is a compound in which one or more atoms of an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms. If one hydrogen atom is replaced, the general formula is n 2n+1 X where X = F, l, Br
aloalkanes General A haloalkane is a compound in which one or more atoms of an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms. If one hydrogen atom is replaced, the general formula is n 2n+1 X where X = F, l, Br
Atmospheric Basics AOSC 200 Tim Canty
 Atmospheric Basics AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Structure of the Atmosphere Temperature vs height Atmospheric pressure Atmospheric composition
Atmospheric Basics AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Structure of the Atmosphere Temperature vs height Atmospheric pressure Atmospheric composition
Chemical Kinetics. Reaction Mechanisms
 Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is a study of the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. The study of kinetics may be done in steps: Determination of reaction mechanism Prediction of rate law Measurement
Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is a study of the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. The study of kinetics may be done in steps: Determination of reaction mechanism Prediction of rate law Measurement
TEST 1 APCH 211 (2012) Review, Solutions & Feedback
 TEST 1 APCH 11 (01) Review, Solutions & Feedback Question 1 What is the concentration of nitrogen in the atmosphere (0 C and 1 atm) in g/l? N in the atmosphere ~ 78% Gas concentration unit s means that
TEST 1 APCH 11 (01) Review, Solutions & Feedback Question 1 What is the concentration of nitrogen in the atmosphere (0 C and 1 atm) in g/l? N in the atmosphere ~ 78% Gas concentration unit s means that
UTTAM SCHOOL FOR GIRLS PSA WORKSHEET: SCIENCE GRADE: VI
 UTTAM SCHOOL FOR GIRLS PSA WORKSHEET: SCIENCE GRADE: VI PASSAGE 1: EVERYDAY COMPOUNDS OR POISON? All elements found on the periodic table have certain distinct properties. Elements are single types of
UTTAM SCHOOL FOR GIRLS PSA WORKSHEET: SCIENCE GRADE: VI PASSAGE 1: EVERYDAY COMPOUNDS OR POISON? All elements found on the periodic table have certain distinct properties. Elements are single types of
Day 1 of Global Warming. Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Day 1 of Global Warming Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings The Atmosphere Atmosphere = the thin layer (1/100 th of Earth s diameter) of gases that surrounds
Day 1 of Global Warming Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings The Atmosphere Atmosphere = the thin layer (1/100 th of Earth s diameter) of gases that surrounds
3.2 Alkanes. Refining crude oil. N Goalby chemrevise.org 40 C 110 C 180 C. 250 C fuel oil 300 C 340 C. Fractional Distillation: Industrially
 3.2 Alkanes Refining crude oil Fractional Distillation: Industrially Petroleum is a mixture consisting mainly of alkane hydrocarbons Petroleum fraction: mixture of hydrocarbons with a similar chain length
3.2 Alkanes Refining crude oil Fractional Distillation: Industrially Petroleum is a mixture consisting mainly of alkane hydrocarbons Petroleum fraction: mixture of hydrocarbons with a similar chain length
CHAPTER 1. MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION
 1 CHAPTER 1. MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION The objective of atmospheric chemistry is to understand the factors that control the concentrations of chemical species in the atmosphere. In this book
1 CHAPTER 1. MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION The objective of atmospheric chemistry is to understand the factors that control the concentrations of chemical species in the atmosphere. In this book
Planetary Atmospheres Part 2
 Planetary Atmospheres Part 2 Atmospheric Layers: The temperature gradient (whether it increases or decreases with altitude) is set by the type of absorption that occurs. We can affect this! Photo- disassocia,on
Planetary Atmospheres Part 2 Atmospheric Layers: The temperature gradient (whether it increases or decreases with altitude) is set by the type of absorption that occurs. We can affect this! Photo- disassocia,on
Chapter 1. Thursday, April 10, Chapter 1: Introduction to the Atmosphere
 Thursday, April 10, 2014 Chapter 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to the Atmosphere Weather and Climate The Earth s 4 Spheres Earth System Science Atmospheric Composition Air Pressure Atmospheric Structures 1
Thursday, April 10, 2014 Chapter 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to the Atmosphere Weather and Climate The Earth s 4 Spheres Earth System Science Atmospheric Composition Air Pressure Atmospheric Structures 1
O 3 + UV photon (λ < 320 nm) O 2 * + O* O 3 + O 2O 2
 Tro Chpt 13 Chemical Kinetics Rate of a chemical reaction Effect of concentration on reaction rate Integrated rate laws: How concentrations change with time Effect of temperature on rate Reaction mechanisms
Tro Chpt 13 Chemical Kinetics Rate of a chemical reaction Effect of concentration on reaction rate Integrated rate laws: How concentrations change with time Effect of temperature on rate Reaction mechanisms
