Free Radicals A TEMPO, free radical, 98+%
|
|
|
- Jonas Kennedy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Alfa Aesar offers an extensive range of free radicals for a variety of research and development purposes. Described below are the free radicals offered by Alfa Aesar and a technical product review with literature references. A12733 TEMP, free radical, 98+% [2,2,6,6-Tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxy, free radical] [ ], C 9 H 18, F.W , m.p º, b.p. 193º dec., f.p. 67º(152ºF), Merck 14,9140, Fieser 14,302 16,324 11,160 16,324 17,332 21,418, U1759, EIECS , RTECS T , BR , MDL MFCD For brief features on TEMP and related reagents, see: Synlett, 563 (2001); 1757 (2003); 657 (2006). For reviews on nitroxide radicals, see: Synthesis, 190, 401 (1971); Chem. Rev., 78, 37 (1978); J. Sci. Ind. Res., 54, 623 (1995). In the presence of a catalytic amount of KBr, catalyzes the selective oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones by buffered acl: J. rg. Chem., 50, 4888 (1985); 52, 2559 (1987); rg. Synth. Coll., 8, 367 (1993). High yields of aldehydes can also be obtained under mild, phase-transfer conditions with xone : rg. Lett., 2, 1173 (2000). In the presence of CuCl, aerobic oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes and ketones has been accomplished in the ionic liquid 1-n-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, L19086: rg. Lett., 4, 1507 (2002). With acl, α-amino or α-alkoxy alcohols have also been oxidized to the aldehydes: Tetrahedron Lett., 33, 5029 (1992). The use of I 2 as cooxidant is useful for sensitive substrates: rg. Lett., 5, 235 (2003). The addition of quaternary salts to the reaction mixture permits further oxidation of aldehydes to acids. Selective oxidation of a primary H to an aldehyde can be achieved in the presence of a secondary H: J. rg. Chem., 54, 2970 (1989); Tetrahedron Lett., 31, 2177 (1990). The oxidation can also be performed using CS under phase-transfer conditions: J. rg. Chem., 61, 7452 (1996), with Iodosobenzene diacetate, B24531: J. rg. Chem., 62, 6974 (1997), or Trichloroisocyanuric acid, B23906: rg. Lett., 3, 3041 (2001). For a review of the use of stable nitroxyl radicals for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols, see: Synthesis, 1153 (1996). Compare also 4-Hydroxy-TEMP, A12497, and 4-Acetamido-TEMP, B23456.
2 B Acetamido-TEMP, free radical, 98% [4-Acetamido-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxy, free radical] [ ], C 11 H , F.W , m.p º, EIECS , BR , MDL MFCD HC In the presence of an acid disproportionates to the oxoammonium salt, a highly selective reagent for alcohol oxidation. For a review of oxoammonium (nitrosonium) salts, see: Heterocycles, 27, 509 (1988); for a brief feature on oxoammonium salts, see: Synlett, 1757 (2003). In combination with tosic acid, oxidizes alcohols to aldehydes and ketones: J. rg. Chem., 56, 6110 (1991). For oxidation of diols to α-dicarbonyl compounds, see: J. rg. Chem., 59, 6338 (1994). Review of the use of stable nitroxyl radicals for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols: Synthesis, 1153 (1996). Compare also 4-Hydroxy-TEMP, A12497, and TEMP A A Hydroxy-TEMP, free radical, 98+% H [4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidin-1-yloxy, free radical] [ ], C 9 H 18 2, F.W , m.p º, Fieser 9,247, EIECS , RTECS T , BR , MDL MFCD Reviews: Synthesis and reactions of stable nitroxyl radicals: Synthesis, 190, 401 (1971); Advances in the chemistry of nitroxide spin labels: Chem. Rev., 78, 37 (1978); Recent advances in the chemistry of nitroxides and their applications in spin labelling: J. Sci. Ind. Res., 54, 623 (1995). For a brief feature on derived oxoammonium salts, see: Synlett, 1757 (2003). Compare also 4-Acetamido-TEMP, B23456, and TEMP, A Recommended as a stabilizer (antioxidant) for the protection of unsaturated fatty acids and their derivatives: J. Am. Chem. Soc., 101, 6748 (1979). L Methoxy-TEMP, free radical, 98+% [4-Methoxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinyloxy, free radical] [ ], C 10 H 20 2, F.W , m.p º, BR ,MDL MFCD CH 3. Reviews: Synthesis and reactions of stable nitroxyl radicals: Synthesis, 190, 401 (1971); Advances in the chemistry of nitroxide spin labels: Chem. Rev., 78, 37 (1978); Recent advances in the chemistry of nitroxides and their applications in spin labelling: J. Sci. Ind. Res., 54, 623 (1995). The oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes has been effected catalytically, in the presence of a stoichiometric cooxidant such as ferricyanide: J. Mol. Catal., 31, 217 (1985), or with hypochlorite in a two-phase system: J. rg. Chem., 52, 2559 (1987). For a review of the use of stable nitroxyl radicals for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols, see: Synthesis, 1153 (1996). Compare also TEMP, A12733 and 4-Acetamido-TEMP, B23456.
3 L xo-TEMP, free radical, 96% [4-xo-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxy, free radical] [ ], C 9 H 16 2, F.W , m.p º, EIECS ,RTECS T , BR , MDL MFCD Reviews: Synthesis and reactions of stable nitroxyl radicals: Synthesis, 190, 401 (1971); Advances in the chemistry of nitroxide spin labels: Chem. Rev., 78, 37 (1978); Recent advances in the chemistry of nitroxides and their applications in spin labelling: J. Sci. Ind. Res., 54, 623 (1995).. A17381 Carbamoyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-3-pyrrolin-1-yloxy, free radical, 99% [2,2,5,5-Tetramethyl-3-pyrrolin-1-oxyl-3-carboxamide] [ ], C 9 H , F.W , m.p º, EIECS , BR , MDL MFCD CH 2 L Carboxy-PRXYL, free radical, 98% [3-Carboxy-2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-1-pyrrolidinyloxy, free radical] [ ], C 9 H 16 3, F.W , m.p. ca 200º dec., EIECS , BR , MDL MFCD Reviews: Synthesis and reactions of stable nitroxyl radicals: Synthesis, 190, 401 (1971); Advances in the chemistry of nitroxide spin labels: Chem. Rev., 78, 37 (1978); Recent advances in the chemistry of nitroxides and their applications in spin labelling: J. Sci. Ind. Res., 54, 623 (1995).. CH
4 A Bromosuccinimide, 99% [BS] [ ], C 4 Br 2, F.W , m.p º dec., d , Merck 14,1438, Fieser 1,78 12,79 13,49 14,57 15,50 16,49 18,65 19,50 20,58 21,72, U3261, EIECS , BR , MDL MFCD Source of free-radical or positive bromine. For examples of radical benzylic bromination (Wohl-Ziegler), see: rg. Synth. Coll., 4, 921 (1963); 5, 145, 329, 825 (1973). The use of the ozone depleting solvent CCl 4 has been avoided by the use of the ionic liquid 1-n-Butyl-3- methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, L19086: Synlett, 702 (2003). Cleavage of carbohydrate benzyl ethers: J. rg. Chem., 55, 378 (1990), and of benzyl esters: Synlett, 219 (1994), occur under mild conditions; the benzyl group is converted to benzaldehyde. For allylic bromination, see e.g.: rg. Synth. Coll., 4, 108 (1963);.9, 112, 191 (1998) review: Chem. Rev., 43, 271 (1948). For free-radical α-bromination of a Boc glycine ester, see: rg. Synth. Coll., 9, 526 (1998). Both aliphatic and aromatic aldehydes are converted to acyl bromides under free-radical conditions: Tetrahedron Lett., 3809 (1979); Synlett, 347 (1990); Tetrahedron Lett., 31, 7237 (1990). In acetonitrile, BS is a mild and regiospecific nuclear brominating agent for activated aromatics such as methoxybenzenes and naphthalenes: J. rg. Chem., 60, 5328 (1995). Deactivated aromatics, e.g. nitroarenes and benzotrifluorides, can be m-brominated under mild conditions in good yield with BS in TFA, in the presence of H 2 S 4 : Synlett, 1245 (1999). In the presence of a phosphine or phosphite, converts alcohols to alkyl bromides with inversion: Tetrahedron Lett., 3937 (1973). For a review of this and related reactions, see: rg. React., 29, 1 (1983). Alkenes undergo trans-addition reactions with BS in combination with a nucleophile. For examples, see: rg. Synth. Coll., 6, 184, 560 (1988). With alcohols, bromohydrin ethers are formed. For use in the synthesis of cyclopropenone, see: rg. Synth. Coll., 6, 361 (1988): Br Cl Cl BS, MeH Me Br Me Cl i) KH 2 ii) H 2 S 4, CH 2 Cl 2 In the presence of DBU in MeH, amides rearrange to amines in good yields, providing a mild and efficient alternative to the classical Hofmann halogen/caustic alkali conditions: J. rg. Chem., 62, 7495 (1997). Examples of the use of BS as a mild, selective oxidizing agent: Sulfides to sulfoxides: J. rg. Chem., 37, 3976 (1968). ximes to nitrile oxides: J. rg. Chem., 37, 436 (1968). Secondary alcohol in the presence of primary: Tetrahedron Lett., 2745 (1979). (In DMS): Alkynes to α-diketones: Can. J. Chem., 49, 1099 (1979). (Free radical): Aldehydes to acyl bromides or amides: Tetrahedron Lett., 31, 7237 (1990). Benzyl silyl ethers to aldehydes: Synlett, 345 (1990). Aldehydes to esters: Synlett, 347 (1990). For use as a mild catalyst in acetalization reactions, see Triethyl orthoformate, A For a brief feature on uses in synthesis, see: Synlett, 498 (2006). See also 1,3-Dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin, A15510.
5 A Iodosuccinimide, 97+% [ ], C 4 I 2, F.W , m.p. ca 196º dec., d , Merck 14,5045, Fieser 1,510 10,216 12,258 15,178 16,185 18,193 19,177 21,234, EIECS , RTECS W , BR , MDL MFCD I Source of positive iodine. Iodinates methoxy benzenes and naphthalenes in acetonitrile, e.g. anisole gives 95% yield of 4-iodoanisole: Tetrahedron Lett., 37, 4081 (1996). In combination with TFA and TFA anhydride, iodinates 2,4-diethoxypyrimidines or -alkyluracils specifically to their 5-iodo-derivatives: Synth. Commun., 18, 855 (1988). With triflic acid, the "superelectrophile" iodine(i) triflate is formed. This species will iodinate even deactivated aromatics, e.g. nitrobenzene to the m-iodo derivative: J. rg. Chem., 58, 3194 (1993). Alone or with a catalytic amount of triflic acid, is a powerful coupling agent in oligosaccharide synthesis, particularly for thioglycosyl donors; see, e.g.: Tetrahedron Lett., 34, 8523 (1993). For reviews, see: Chem. Rev., 93, 1503 (1993); Contemp. rg. Synth., 3, 173 (1996). In the presence of triphenylphosphine or triphenyl phosphite, converts alcohols to iodides stereoselectively with inversion: Tetrahedron Lett., 3937 (1973). See also: Carbohydr. Res., 24, 45 (1972). In combination with the phase-transfer catalyst, Tetra-n-butylammonium iodide, A15484, oxidizes alcohols to carbonyl compounds in high yield under neutral conditions: Synthesis, 394 (1981). Glycols are cleaved to carbonyl compounds; the rate of reaction is increased by u.v. irradiation: J. rg. Chem., 46, 1927 (1981). Similarly, α-hydroxyacids are oxidatively decarboxylated to ketones: J. rg. Chem., 47, 3006 (1982). With K 2 C 3 in MeH, aldehydes can be oxidized directly to methyl esters: J. rg. Chem., 54, 1213 (1989). xidative coupling of dianions of acyclic tertiary amides gives a stereoselective preparation of β-lactams: J. rg. Chem., 57, 1864 (1992): Me Ar CBu t i) Bu t Li, THF, 78 o ii) Ph 4 PBr, 78 o Me CBu t iii) IS, 95 to 70 o 72% Ar Has been used in the construction of disulfide bridges in cystine peptides, from cysteine in a DMFdichloromethane solvent: J. rg. Chem., 58, 3003 (1993). For a brief feature on uses of the reagent in synthesis, see: Synlett, 960 (2006).
6 A Chlorosuccinimide, 98% [CS] [ ], C 4 Cl 2, F.W , m.p º, d. 1.65, Merck 14,2164, Fieser 1,139 13,79 14,87 15,86 16,84 18,101 19,95 20,108 21,131, U1759, EIECS , RTECS UY , BR , MDL MFCD Cl Source of positive chlorine in chlorination and oxidation reactions. Methyl ketones may be monochlorinated via their Li enolates: J. rg. Chem., 49, 1286 (1984). For the α-chlorination of acid chlorides formed in situ, see: Tetrahedron Lett., 3235 (1974). For chlorination of deactivated anilines, see: Synthesis, 669 (1985). In the presence of triphenylphosphine or triphenyl phosphite, converts alcohols to alkyl chlorides stereospecifically with inversion: Tetrahedron Lett., 3937 (1973). For a review, see: rg. React., 29, 1 (1983). Amides have been prepared by treatment of a carboxylic acid with CS/PPh 3 followed by an amine: Synth. Commun., 25, 959 (1995). With dimethyl sulfide, forms the Corey-Kim reagent, a mild, selective oxidant for alcohols. For a review, see: Synthesis, 857 (1990); for tabulated examples, see: rg. Synth. Coll., 6, 220 (1988). Primary alcohols are oxidized cleanly to aldehydes using CS and a catalytic amount of TEMP, A12733, under phase-transfer conditions: J. rg. Chem., 61, 7452 (1996). CS in ether is a convenient alternative to hypochlorite for the conversion of amines to -chloroamines, for use, e.g. in the Hofmann-Loeffler reaction, see: Chem. Ber., 88, 883 (1955). A Bromophthalimide, 98+% [ ], C 8 Br 2, F.W , m.p º, EIECS , BR , MDL MFCD Brominating agent comparable to -Bromosuccinimide, A Br ,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl,free radical, 95% [DPPH] [ ], C 18 H , F.W , Powder, Merck 14,3330, U2811, EIECS , MDL MFCD , ote: Store cold, Ph
7 H27530 xynitrox S100, free radical, 99+% (Avge MW ca 2250) [Poly[[6-[1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)amino]1,3,5-triazin-2,4-diyl][(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-oxy-4-piperidinyl)- imino]-1,6-hexa, PIP] ] ther Products Selected Alfa Aesar products with applications in free radical chemistry. Most are referred to in the text of this publication. A15510 L19086 B24531 A15484 B23906 A ,3-Dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin 1-n-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate Iodosobenzene diacetate Tetra-n-butylammonium iodide Trichloroisocyanuric acid Triethyl orthoformate xone is a registered trademark of E.I. du Pont de emours and Co., Inc. xynitrox is a registered trademark of Arkema Group.
New bond. ph 4.0. Fischer esterification. New bond 2 O * New bond. New bond H 2N. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. O Cl.
 Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions.
 ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK
 Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Module9. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy - Chemical shift - Integration of signal area
 1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry
 UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry Topic 4.1 Kinetics a) Define the terms: rate of a reaction, rate constant, order of reaction and overall order of reaction b) Deduce the orders of reaction
UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry Topic 4.1 Kinetics a) Define the terms: rate of a reaction, rate constant, order of reaction and overall order of reaction b) Deduce the orders of reaction
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 15, 2010 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
Aromatic Compounds II
 2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 2 Aromatic Compounds II Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 17 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 2 Aromatic Compounds II Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 17 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
CHEM 203. Midterm Exam 1 October 31, 2008 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Midterm Exam 1 ctober 31, 2008 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This exam contains 8 pages Time: 1h 30 min 1. / 15 2. / 16 3. /
CEM 203 Midterm Exam 1 ctober 31, 2008 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This exam contains 8 pages Time: 1h 30 min 1. / 15 2. / 16 3. /
3.7. Pyridinium Chloro Chromate (PCC):
 xidation 3.7. Pyridinium hloro hromate (P): 97 l l r r 3 r l P is a very important oxidising reagent which will give controlled oxidation in the case of primary alcohol. It does not give over oxidation
xidation 3.7. Pyridinium hloro hromate (P): 97 l l r r 3 r l P is a very important oxidising reagent which will give controlled oxidation in the case of primary alcohol. It does not give over oxidation
Lecture Topics: I. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS)
 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Suggested solutions for Chapter 40
 s for Chapter 40 40 PBLEM 1 Suggest mechanisms for these reactions, explaining the role of palladium in the first step. Ac Et Et BS () 4 2 1. 2. K 2 C 3 evision of enol ethers and bromination, the Wittig
s for Chapter 40 40 PBLEM 1 Suggest mechanisms for these reactions, explaining the role of palladium in the first step. Ac Et Et BS () 4 2 1. 2. K 2 C 3 evision of enol ethers and bromination, the Wittig
Alcohols. Have seen many reactions to synthesize alcohols: In this chapter we will study reactions of the alcohols
 Alcohols ave seen many reactions to synthesize alcohols: In this chapter we will study reactions of the alcohols Oxidation Need to understand the nomenclature of organic reduction/oxidation In general
Alcohols ave seen many reactions to synthesize alcohols: In this chapter we will study reactions of the alcohols Oxidation Need to understand the nomenclature of organic reduction/oxidation In general
Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions. Alpha Substitution
 Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
1. What is the major organic product obtained from the following sequence of reactions?
 CH320 N N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. Carefully record your answers on the Scantron
CH320 N N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. Carefully record your answers on the Scantron
N_HW1 N_HW1. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this sequence?
 N_HW1 N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this
N_HW1 N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
Background Information
 ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
ROADMAP FOR REACTIONS Chapter 6
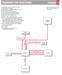 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapter 6 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L) (M) (N) () Regiochemistry: Markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: anti-addition Regiochemistry: non-markovnikov addition
RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapter 6 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L) (M) (N) () Regiochemistry: Markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: anti-addition Regiochemistry: non-markovnikov addition
Chapter 19: Amines. Introduction
 Chapter 19: Amines Chap 19 HW: (be able to name amines); 37, 39, 41, 42, 44, 46, 47, 48, 53-55, 57, 58 Introduction Organic derivatives of ammonia. Many are biologically active. Chap 19: Amines Slide 19-2
Chapter 19: Amines Chap 19 HW: (be able to name amines); 37, 39, 41, 42, 44, 46, 47, 48, 53-55, 57, 58 Introduction Organic derivatives of ammonia. Many are biologically active. Chap 19: Amines Slide 19-2
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophile substitutes for a hydrogen on the benzene ring. Chapter 17: Aromatics 2-Reactions Slide 17-2 1 Mechanism Step
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophile substitutes for a hydrogen on the benzene ring. Chapter 17: Aromatics 2-Reactions Slide 17-2 1 Mechanism Step
Introduction & Definitions Catalytic Hydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of H- and H+ Oxidation of Alcohols Oxidation of
 CEM 241- UNIT 4 xidation/reduction Reactions Redox chemistry 1 utline Introduction & Definitions Catalytic ydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of - and + xidation of Alcohols
CEM 241- UNIT 4 xidation/reduction Reactions Redox chemistry 1 utline Introduction & Definitions Catalytic ydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of - and + xidation of Alcohols
Tips for taking exams in 852
 Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry Problem Set 1. Functional Group Transformations Study Guide
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology rganic Chemistry 5.511 Problem Set 1 September, 2007 Prof. Rick L. Danheiser Functional Group Transformations Study Guide The purpose of this three-part study guide
Massachusetts Institute of Technology rganic Chemistry 5.511 Problem Set 1 September, 2007 Prof. Rick L. Danheiser Functional Group Transformations Study Guide The purpose of this three-part study guide
Table 8.2 Detailed Table of Characteristic Infrared Absorption Frequencies
 Table 8.2 Detailed Table of Characteristic Infrared Absorption Frequencies The hydrogen stretch region (3600 2500 cm 1 ). Absorption in this region is associated with the stretching vibration of hydrogen
Table 8.2 Detailed Table of Characteristic Infrared Absorption Frequencies The hydrogen stretch region (3600 2500 cm 1 ). Absorption in this region is associated with the stretching vibration of hydrogen
Chapter 20. Amines. Nomenclature for amines. Aryl amines
 Nomenclature for amines Chapter 20 Common names are widely used, named as alkylamines Systematic (IUPAC) nomenclature replaces the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -amine Amines Simple secondary
Nomenclature for amines Chapter 20 Common names are widely used, named as alkylamines Systematic (IUPAC) nomenclature replaces the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -amine Amines Simple secondary
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II
 KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level. Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis
 OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
Exam 1 (Monday, July 6, 2015)
 Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Name/CG: 2012 Term 2 Organic Chemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question
 Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
Ch 22 Carbonyl Alpha ( ) Substitution
 Ch 22 Carbonyl Alpha () Substitution The overall reaction replaces an H with an E + The acid-catalyzed reaction has an enol intermediate The base-catalyzed reaction has an enolate intermediate Keto-Enol
Ch 22 Carbonyl Alpha () Substitution The overall reaction replaces an H with an E + The acid-catalyzed reaction has an enol intermediate The base-catalyzed reaction has an enolate intermediate Keto-Enol
Chem 1220 Midterm points Dr. Luther Giddings
 Chem 1220 Midterm 1 100 points r. Luther Giddings Name Instructions: This is a closed book, closed notebook test. You may not discuss this exam with anyone, either during or after the exam, until it has
Chem 1220 Midterm 1 100 points r. Luther Giddings Name Instructions: This is a closed book, closed notebook test. You may not discuss this exam with anyone, either during or after the exam, until it has
Although we won t go into this, the reactions can be regioselective if non-symmetrical alkenes are used.
 2.1 rganic ynthesis A. Armstrong - 2004-2005 Functional Group Interconversions - Lecture 5 ection 5: xidation of C- bonds bearing no heteroatom 5.1 xidation of allylic positions Many reagents will do this
2.1 rganic ynthesis A. Armstrong - 2004-2005 Functional Group Interconversions - Lecture 5 ection 5: xidation of C- bonds bearing no heteroatom 5.1 xidation of allylic positions Many reagents will do this
Topic 4.10 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS AND ANALYSIS. Organic analysis Organic synthesis
 Topic 4.10 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS AND ANALYSIS Organic analysis Organic synthesis DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN DIFFERENT ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Many of the organic compounds prepared in AS Unit 2 and in A2 Unit 4 can
Topic 4.10 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS AND ANALYSIS Organic analysis Organic synthesis DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN DIFFERENT ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Many of the organic compounds prepared in AS Unit 2 and in A2 Unit 4 can
CHAPTER 20: MORE ABOUT OXIDATION REDUCTION REACTIONS Oxidation Reduction Reactions of Organic Compounds: An Overview
 CHAPTER 20: MORE ABOUT OXIDATION REDUCTION REACTIONS In an oxidation-reduction reaction (redox reaction), one species loses electrons and one gains electrons. The species that loses electrons is oxidized,
CHAPTER 20: MORE ABOUT OXIDATION REDUCTION REACTIONS In an oxidation-reduction reaction (redox reaction), one species loses electrons and one gains electrons. The species that loses electrons is oxidized,
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 18, This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 18, 2013 Your name: This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3. / 30 4.
CEM 203 Final Exam December 18, 2013 Your name: This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3. / 30 4.
1/4/2011. Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds
 Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Spring Term 2012 Dr. Williams (309 Zurn, ex 2386)
 Chemistry 242 Organic Chemistry II Spring Term 2012 Dr. Williams (309 Zurn, ex 2386) Web Page: http://math.mercyhurst.edu/~jwilliams/ jwilliams@mercyhurst.edu (or just visit Department web site and look
Chemistry 242 Organic Chemistry II Spring Term 2012 Dr. Williams (309 Zurn, ex 2386) Web Page: http://math.mercyhurst.edu/~jwilliams/ jwilliams@mercyhurst.edu (or just visit Department web site and look
Preparation of Alkyl Halides, R-X. Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): R + X X 2.
 Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Chapter 24. Amines. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 Chapter 24. Amines Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Amines Organic Nitrogen Compounds Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH 3, Nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons, making amines
Chapter 24. Amines Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Amines Organic Nitrogen Compounds Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH 3, Nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons, making amines
20.5 Preparation of Amines
 RGANIC CHEMISTRY 20.5 Preparation of Amines RGANIC CHEMISTRY 20.5A Through Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Alkylation of Ammonia or Amines NaH NH 3 + R X RNH 3 X RNH2 R + R X R 2 X NaH R 2 NH R 2 NH
RGANIC CHEMISTRY 20.5 Preparation of Amines RGANIC CHEMISTRY 20.5A Through Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Alkylation of Ammonia or Amines NaH NH 3 + R X RNH 3 X RNH2 R + R X R 2 X NaH R 2 NH R 2 NH
GENERAL METHODS OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY; APPARATUS THEREFOR (preparation of carboxylic acid esters by telomerisation C07C 67/47; telomerisation C08F)
 CPC - C07B - 2017.08 C07B GENERAL METHODS OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY; APPARATUS THEREFOR (preparation of carboxylic acid esters by telomerisation C07C 67/47; telomerisation C08F) General methods for the preparation
CPC - C07B - 2017.08 C07B GENERAL METHODS OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY; APPARATUS THEREFOR (preparation of carboxylic acid esters by telomerisation C07C 67/47; telomerisation C08F) General methods for the preparation
Hyperlearning MCAT Instructor Qualifying Exam Organic Chemistry
 Hyperlearning MCAT Instructor Qualifying Exam Organic Chemistry 30 Questions (5 pages); Time limit = 45 minutes Use of books or notes is not permitted. 1. When analyzed with a polarimeter, which of the
Hyperlearning MCAT Instructor Qualifying Exam Organic Chemistry 30 Questions (5 pages); Time limit = 45 minutes Use of books or notes is not permitted. 1. When analyzed with a polarimeter, which of the
Chem 251 Fall Learning Objectives
 Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
5. Clemmension Reduction: The reduction of >C=O group to methyl group (>CH2) with amalgamated zinc and conc. HCl is known as Clemmension reduction.
 Organic Chemistry Name Reactions 1. Aldol Condensation: condensation between two molecule of an aldehyde or a ketone having atleast one α-hydrogen atom to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or a β-hydroxyketone
Organic Chemistry Name Reactions 1. Aldol Condensation: condensation between two molecule of an aldehyde or a ketone having atleast one α-hydrogen atom to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or a β-hydroxyketone
Suggested solutions for Chapter 28
 s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
Mechanisms. . CCl2 F + Cl.
 Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Synthesis and Structure of Alcohols Alcohols can be considered organic analogues of water.
 Synthesis and Structure of Alcohols Alcohols can be considered organic analogues of water. Alcohols are usually classified as primary, secondary and tertiary. Alcohols with the hydroxyl bound directly
Synthesis and Structure of Alcohols Alcohols can be considered organic analogues of water. Alcohols are usually classified as primary, secondary and tertiary. Alcohols with the hydroxyl bound directly
Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Why this Chapter? Much of organic chemistry involves the chemistry of carbonyl compounds Aldehydes/ketones are intermediates in synthesis of pharmaceutical
Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Why this Chapter? Much of organic chemistry involves the chemistry of carbonyl compounds Aldehydes/ketones are intermediates in synthesis of pharmaceutical
Structural Determination Of Compounds
 EXPERIMENT 10 Mass Spectroscopy Structural Determination Of Compounds. Introduction - In mass spectrometry, a substance is bombarded with an electron beam having sufficient energy to fragment the molecule.
EXPERIMENT 10 Mass Spectroscopy Structural Determination Of Compounds. Introduction - In mass spectrometry, a substance is bombarded with an electron beam having sufficient energy to fragment the molecule.
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
Loudon Chapter 23 Review: Amines CHEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall Page 1
 Loudon Chapter 23 eview: Amines CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions
Loudon Chapter 23 eview: Amines CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions and Condensation Reactions
 Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Carbon-heteroatom single bonds basic C N C X. X= F, Cl, Br, I Alkyl Halide C O. epoxide Chapter 14 H. alcohols acidic H C S C. thiols.
 hapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols 13.1 Structure and Properties of Alcohols Alkanes arbon - arbon Multiple Bonds arbon-heteroatom single bonds basic Alkenes X X= F, l,, I Alkyl alide amines hapter 23 nitro
hapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols 13.1 Structure and Properties of Alcohols Alkanes arbon - arbon Multiple Bonds arbon-heteroatom single bonds basic Alkenes X X= F, l,, I Alkyl alide amines hapter 23 nitro
A Novel Approach of Using NBS as an Effective and Convenient Oxidizing Agent for Various Compounds a Survey
 Journal of Chemistry and Chemical Sciences, Vol.8(1), 59-65, January 2018 (An International Research Journal), www.chemistry-journal.org ISSN 2229-760X (Print) ISSN 2319-7625 (Online) A Novel Approach
Journal of Chemistry and Chemical Sciences, Vol.8(1), 59-65, January 2018 (An International Research Journal), www.chemistry-journal.org ISSN 2229-760X (Print) ISSN 2319-7625 (Online) A Novel Approach
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
12/27/2010. Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
Physical Properties. Alcohols can be: CH CH 2 OH CH 2 CH 3 C OH CH 3. Secondary alcohol. Primary alcohol. Tertiary alcohol
 Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
Organic Chemistry CHM 224
 rganic Chemistry CM 224 Final Exam Review Questions This is a compilation example final exam questions. Provide IUPAC names for each of the structures below. 2 ! Propose a structure for the compound that
rganic Chemistry CM 224 Final Exam Review Questions This is a compilation example final exam questions. Provide IUPAC names for each of the structures below. 2 ! Propose a structure for the compound that
Synthesis of Amines Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction II. Reductive Amination
 Synthesis of Amines I. Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction Amines can be alkylated in SN2 fashion by alkyl halides; primary halides are best for this purpose. This is not a practical reaction for formation
Synthesis of Amines I. Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction Amines can be alkylated in SN2 fashion by alkyl halides; primary halides are best for this purpose. This is not a practical reaction for formation
ζ ε δ γ β α α β γ δ ε ζ
 hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY. Fifth Edition. Stanley H. Pine
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Fifth Edition Stanley H. Pine Professor of Chemistry California State University, Los Angeles McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Fifth Edition Stanley H. Pine Professor of Chemistry California State University, Los Angeles McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London
Isomerism CH 4 C 2 H 6 C 3 H 8 C 4 H 10 C 5 H 12. Constitutional isomers...
 Isomerism 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 5 12 onstitutional isomers... 3 8 Positional isomers... Functional isomers... ow many constitutional isomers are there for the formula 4 8? arbon atoms are often classified as
Isomerism 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 5 12 onstitutional isomers... 3 8 Positional isomers... Functional isomers... ow many constitutional isomers are there for the formula 4 8? arbon atoms are often classified as
Organic Chemistry Lecture 2 - Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Substitutions
 ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
Organic Chemistry Curriculum Content Outline
 Organic Chemistry 2014-15 Curriculum Content Outline CHEM 0203: Organic Structure and Reactivity 1. Structure & Bonding (Brief Review from General Chemistry) a. Ionic & Covalent Bonding b. Lewis Structures
Organic Chemistry 2014-15 Curriculum Content Outline CHEM 0203: Organic Structure and Reactivity 1. Structure & Bonding (Brief Review from General Chemistry) a. Ionic & Covalent Bonding b. Lewis Structures
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FACULTY OF SCIENCE FINAL EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 353 READ THE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY
 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FACULTY OF SCIENCE FINAL EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 353 Version 1 April 18th, 2018 Time: 3 Hours READ THE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY PLEASE WRITE YOUR NAME & STUDENT I.D. NUMBER ON BOTH YOUR
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FACULTY OF SCIENCE FINAL EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 353 Version 1 April 18th, 2018 Time: 3 Hours READ THE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY PLEASE WRITE YOUR NAME & STUDENT I.D. NUMBER ON BOTH YOUR
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds. Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
22.7 Reactions of Amines: A Review and a Preview
 22.7 Reactions of Amines: A Review and a Preview Preparation of Amines Two questions to answer: 1) How is the C N C N bond to be formed? 2) How do we obtain the correct oxidation state of nitrogen (and
22.7 Reactions of Amines: A Review and a Preview Preparation of Amines Two questions to answer: 1) How is the C N C N bond to be formed? 2) How do we obtain the correct oxidation state of nitrogen (and
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 18, 2013 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Your name: Final Exam December 18, 2013 ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3.
CEM 203 Your name: Final Exam December 18, 2013 ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3.
Chem 316/422 Beauchamp 1 Match the step number in the synthesis with the letter of the reagents listed just below.
 hem 316/422 Beauchamp 1 Match the step number in the synthesis with the letter of the reagents listed just below. TP l Et step 8 4 5 eagents used in synthesis A B D E F a DMF (solvent) 1. (i-pr) 2 Li (LDA)/TF
hem 316/422 Beauchamp 1 Match the step number in the synthesis with the letter of the reagents listed just below. TP l Et step 8 4 5 eagents used in synthesis A B D E F a DMF (solvent) 1. (i-pr) 2 Li (LDA)/TF
Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols
 hapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols sp 3 alcohol phenol (aromatic alcohol) pka~ 16-18 pka~ 10 Alcohols contain an group connected to a saturated carbon (sp 3 ) Phenols contain an group connected to a carbon
hapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols sp 3 alcohol phenol (aromatic alcohol) pka~ 16-18 pka~ 10 Alcohols contain an group connected to a saturated carbon (sp 3 ) Phenols contain an group connected to a carbon
Organic Chemistry, 7 L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter , Prentice Hall
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although h benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although h benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES. 3. Predict the relative acidity and basicity of compounds and ions. Important criteria include:
 CARBXYLIC ACIDS AND TEIR DERIVATIVES A STUDENT SULD BE ABLE T: 1. Give the IUPAC name given the structure, and draw the structure given the name, of carboxylic acids and their metal salts, acyl chlorides,
CARBXYLIC ACIDS AND TEIR DERIVATIVES A STUDENT SULD BE ABLE T: 1. Give the IUPAC name given the structure, and draw the structure given the name, of carboxylic acids and their metal salts, acyl chlorides,
Tautomerism and Keto Enol Equilibrium
 Tautomerism and Keto Enol Equilibrium Enols & enolates are important nucleophiles in organic & biochemistry. Keto-Enol Equilibrium: Tautomerisation can be catalyzed by either acids or bases. Relative stability
Tautomerism and Keto Enol Equilibrium Enols & enolates are important nucleophiles in organic & biochemistry. Keto-Enol Equilibrium: Tautomerisation can be catalyzed by either acids or bases. Relative stability
Suggested solutions for Chapter 41
 s for Chapter 41 41 PBLEM 1 Explain how this synthesis of amino acids, starting with natural proline, works. Explain the stereoselectivity of each step after the first. C 2 C 2 3 CF 3 C 2 2 Pd 2 C 2 +
s for Chapter 41 41 PBLEM 1 Explain how this synthesis of amino acids, starting with natural proline, works. Explain the stereoselectivity of each step after the first. C 2 C 2 3 CF 3 C 2 2 Pd 2 C 2 +
Electrophilic Carbenes
 Electrophilic Carbenes The reaction of so-called stabilized diazo compounds with late transition metals produces a metal carbene intermediate that is electrophilic. The most common catalysts are Cu(I)
Electrophilic Carbenes The reaction of so-called stabilized diazo compounds with late transition metals produces a metal carbene intermediate that is electrophilic. The most common catalysts are Cu(I)
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 6 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Oxidation States Easy for inorganic salts: CrO 4 2- reduced to Cr 2 O 3. KMnO 4 reduced to MnO 2. Oxidation: Gain of O,
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 6 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Oxidation States Easy for inorganic salts: CrO 4 2- reduced to Cr 2 O 3. KMnO 4 reduced to MnO 2. Oxidation: Gain of O,
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
 Aromatic Hydrocarbons Aromatic hydrocarbons contain six-membered rings of carbon atoms with alternating single and double carbon-carbon bonds. The ring is sometimes shown with a circle in the center instead
Aromatic Hydrocarbons Aromatic hydrocarbons contain six-membered rings of carbon atoms with alternating single and double carbon-carbon bonds. The ring is sometimes shown with a circle in the center instead
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
896 Chapter 21 Amines H H N R R R N R H R N R H O H R 3 N CH 2 NH 2 NHCH 3
 896 Chapter 21 Amines 21.20 Summary Section 21.1 Section 21.2 Section 21.3 Section 21.4 Alkylamines are compounds of the type shown, where R, R, and R are alkyl groups. ne or more of these groups is an
896 Chapter 21 Amines 21.20 Summary Section 21.1 Section 21.2 Section 21.3 Section 21.4 Alkylamines are compounds of the type shown, where R, R, and R are alkyl groups. ne or more of these groups is an
OAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 19: NMR Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry
 OAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 19: NMR Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which statement concerning NMR spectroscopy is incorrect? Question #01 (A) Only nuclei
OAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 19: NMR Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which statement concerning NMR spectroscopy is incorrect? Question #01 (A) Only nuclei
Organic Chemistry Review: Topic 10 & Topic 20
 Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
CHEM 2312 practice final. Version - II
 EM 2312 practice final Version - II The following standardized final examination covers the entire introductory year of organic chemistry (EM 2311 and 2312 at Georgia Tech). The exam consists of 70 multiple
EM 2312 practice final Version - II The following standardized final examination covers the entire introductory year of organic chemistry (EM 2311 and 2312 at Georgia Tech). The exam consists of 70 multiple
Chapter 17. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
3) Oxidation of tertiary alcohol yields A) Aldehyde B) No reaction C) Ketone D) Carboxylic acid
 ALKYL HALIDES 18- The reaction of Propyl bromide with Na is A) Nucleophilic addition. B) Nucleophilic substitution. C) Electrophilic substitution. D) Electrophilic addition. 25) Which of the following
ALKYL HALIDES 18- The reaction of Propyl bromide with Na is A) Nucleophilic addition. B) Nucleophilic substitution. C) Electrophilic substitution. D) Electrophilic addition. 25) Which of the following
Electrophile = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor = Lewis acid, (often an acidic proton)
 314 Arrow Pushing practice/eauchamp 1 Electrophile = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor = Lewis acid, (often an acidic proton) ucleophile = nucleus/positive loving = any general electron
314 Arrow Pushing practice/eauchamp 1 Electrophile = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor = Lewis acid, (often an acidic proton) ucleophile = nucleus/positive loving = any general electron
CHAPTER 16 - CHEMISTRY OF BENZENE: ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION
 CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
Cape Cod Community College
 Cape Cod Community College Departmental Syllabus Prepared by the Department of Natural Sciences & Applied Technology Date of Departmental Approval: February 3, 2014 Date Approved by Curriculum and Programs:
Cape Cod Community College Departmental Syllabus Prepared by the Department of Natural Sciences & Applied Technology Date of Departmental Approval: February 3, 2014 Date Approved by Curriculum and Programs:
Ch 16 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Ch 16 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Mechanism - Aromatic rings typically undergo substitution, where an H is replaced with an electrophile (E+). - The rings do not typically undergo addition across
Ch 16 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Mechanism - Aromatic rings typically undergo substitution, where an H is replaced with an electrophile (E+). - The rings do not typically undergo addition across
Organic Chemistry 1 CHM 2210 Exam 4 (December 10, 2001)
 Exam 4 (December 10, 2001) Name (print): Signature: Student ID Number: There are 12 multiple choice problems (4 points each) on this exam. Record the answers to the multiple choice questions on THIS PAGE.
Exam 4 (December 10, 2001) Name (print): Signature: Student ID Number: There are 12 multiple choice problems (4 points each) on this exam. Record the answers to the multiple choice questions on THIS PAGE.
Synthetic possibilities Chem 315 Beauchamp 1
 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Propose reasonable syntheses f the following target molecules (TM-#). You can use the given starting materials and any typical ganic reagents studied in our course
Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Propose reasonable syntheses f the following target molecules (TM-#). You can use the given starting materials and any typical ganic reagents studied in our course
Ammonia Primary Secondary Tertiary Quarternary Ammonium Ion
 1 Chapter 19: Amines I. Introduction: Classification: NH 3 RNH 2 R 2 NH R 3 N R 4 N + Ammonia Primary Secondary Tertiary Quarternary Ammonium Ion Amines are a very common functional group in organic chemistry,
1 Chapter 19: Amines I. Introduction: Classification: NH 3 RNH 2 R 2 NH R 3 N R 4 N + Ammonia Primary Secondary Tertiary Quarternary Ammonium Ion Amines are a very common functional group in organic chemistry,
CH 320/328 N Summer II 2018
 CH 320/328 N Summer II 2018 HW 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. (5 pts each) 1. Which
CH 320/328 N Summer II 2018 HW 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. (5 pts each) 1. Which
Reducing Agents. Linda M. Sweeting 1998
 Reducing Agents Linda M. Sweeting 1998 Reduction is defined in chemistry as loss of oxygen, gain of hydrogen or gain of electrons; the gain of electrons enables you to calculate an oxidation state. Hydride
Reducing Agents Linda M. Sweeting 1998 Reduction is defined in chemistry as loss of oxygen, gain of hydrogen or gain of electrons; the gain of electrons enables you to calculate an oxidation state. Hydride
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Keywords: amination ate complexes carbomagnesiation carbometalation Grignard reagents homocoupling magnesates magnesium compounds metalation
 VII Abstracts 2010 p1 7.6.5.6 Aryl Grignard Reagents H. Yorimitsu Halogen magnesium exchange between aryl iodides or bromides and an isopropylmagnesium chloride lithium chloride complex or lithium trialkylmagnesates
VII Abstracts 2010 p1 7.6.5.6 Aryl Grignard Reagents H. Yorimitsu Halogen magnesium exchange between aryl iodides or bromides and an isopropylmagnesium chloride lithium chloride complex or lithium trialkylmagnesates
Organic Chemistry 112 A B C - Syllabus Addendum for Prospective Teachers
 Chapter Organic Chemistry 112 A B C - Syllabus Addendum for Prospective Teachers Ch 1-Structure and bonding Ch 2-Polar covalent bonds: Acids and bases McMurry, J. (2004) Organic Chemistry 6 th Edition
Chapter Organic Chemistry 112 A B C - Syllabus Addendum for Prospective Teachers Ch 1-Structure and bonding Ch 2-Polar covalent bonds: Acids and bases McMurry, J. (2004) Organic Chemistry 6 th Edition
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
 ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS Alcohols contain an OH group connected to a a saturated C (sp3) They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to
ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS Alcohols contain an OH group connected to a a saturated C (sp3) They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to
Dr. Munther Abdujaleel M.A. Assist. Prof. Org. Chem.
 Dr. Munther Abdujaleel M.A. Assist. Prof. Org. Chem. Amines An amine, derivatives of ammonia NH 3 has the general formula RNH 2, R 2 NH, or R 3 N, where R is any alkyl or aryl group. For example: Adernalin
Dr. Munther Abdujaleel M.A. Assist. Prof. Org. Chem. Amines An amine, derivatives of ammonia NH 3 has the general formula RNH 2, R 2 NH, or R 3 N, where R is any alkyl or aryl group. For example: Adernalin
Downloaded from
 ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids are important classes of organic compounds containing carbonyl groups. They are highly polar molecules. They boil at higher
ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids are important classes of organic compounds containing carbonyl groups. They are highly polar molecules. They boil at higher
