Index. Binary molten salt mixture, schematic representation, 15 3
|
|
|
- Cecilia Terry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acid-base equilibria of water in melts, table of equilibrium constant values, 314 Acidity of metal aquo complexes, 132 Acidobasicity of water in molten salts, 311 Acids in dilute solution, pk values, 130 Activities of components of Dead Sea water, 99, 100 AgCl/ Ag 2S mixtures-collected thermodynamic data, 380 Alkali metal oxides in melts, thermodynamic data, 199 Aluminum halide-alkali metal halide molten salt systems acid-base chemistry, 408 electrochemistry of elemental and dissociated chalcogens, 410 species characterization, 409 stability of organic radical ions, 411 Anion basicity, 128 Anionic hydration, 11 scattering length and sample parameters, 12 Aqueous cesium chloride, computer simulation, 49, 50 Aqueous glasses CaZnC14 solutions, 22, 23 nitrate-bound water, 25 Basicity moderating parameter, -y, 129 Behavior of chalcogenides in chloroaluminates, 366 Binary molten salt mixture, schematic representation, 15 3 Cation-bound water in hydrate melts, relaxation rates, 16 Cation-bound water in the glassy state, reason for dielectric activity, 22 Cationic hydration, 8 parameters obtained from neutron diffraction, 10 scattering length and sample parameters, 9 Charge-transfer-to-solvent electrochemical and spectral correlations, 92 Charge-transfer-to-solvent spectra comparison of models fore max prediction, 83 concept, 80 Coulombic interaction components, 89 and Coulombic interactions, 85 effect of electrolytes, 84 expanded lattice models (of electrolyte solutions), 86 interionic distances, 88 maximum absorption energies, other models, 83 "polaron" model, 81 quantitative treatment, 81 Smith-Symons "confined" model, 82 Stein-Treinin "diffuse" model, 82 temperature dependence of E max, linearity, 91 variation with concentration,
2 446 Charge-transfer-to-solvent spectral shifts activity coefficient correlation, 90 thermodynamic correlations, 94 Chloride ion hydration, 13 Classification of molten salts, 151 Comparison of calculated and experimental molalities: sodium chloride in equilibrium with halite and potassium chloride in equilibrium with carnallite, 107 Comparison of polysulfides in melts effect of basicity, 402 electrochemistry, 403 stability, 403 Comparison of Tl, Ag, Pb, Cu results (halide-chalcogenide melts), 376, 379 Competitive polarization in melts, 426, 427,431 Complex ions in melts, 5 Computer simulation: interfaces, 51 Computer simulation techniques molecular dynamics, polarization, 36,40 Monte Carlo method, 29 review, 28 Concentration ranges for water+ salt mixtures, 148 Condition of electroneu trality, applied to aqueous solutions and melts, 156 Conductance Arrhenius plots, 6 2 data, concentrated solutions, 72 Conductivities temperature dependence, 298 and activation energies, 298 and relation to maxima, 299 water concentration dependence of, 295 and comparison of hydrated to crystallographic radii, 29 8 and position of maxima, 296 relation to hydration numbers, 297 relation to hydration numbers and cation composition, 298 Contribution of polarization to ml'<ing in mixtures of LiF-LiCl-NaF-NaCl, 429 Cooperative effects in tranport processes, 150 Copper and iron sulfide/chloride systems, 375 Dead Sea, 97 composition, 98 water compared with ocean water, 99 Debye-Hi.ickel theory ex tensions, 58 Monte Carlo tests, 32 Deleterious effects of w:1ter on extractive processes, 325 Determination of solubility of water in molten salts, 306, 7 Dielectric activity: rotational source, 24 Differing behavior of water in LiCl-KCl and NaCl-KCl, 313 DiffusioP. coefficients: data, concentrated solutions, 7 4 Distribution of electrons in metal-molten salt solutions, 442 Dynamic properties of ionic liquids, 40 Effects of water in molten salts: predictions, 331 Electric transport in binary molten salt mixtures and in aqueous solutions of binary electrolytes, 154 Electrochemistry of water in molten salts, 169 acetates, 178 autocatalytic model, 175 chlorides, 17 6 effect on double layer capacities, 175 hydroxides, 177 influence upon anodic processes, 17 2 influence on electrode processes, 178 nitrates and nitrites, 170 solvated electron model, 174 Electrodes for measuring oxide ion concentrations, 312 Electrolysis of PbS in chloride melts, 366 Electrolytes in a multicomponent electrolyte solution, equations for calculations of osmotic and activity coefficients, 101, 102, 103 Electron donor power, 129 Electrostriction in molten salts and highly concentrated electrolyte solutions, 1 Enthalpy of mixing, electrostatic energy term, 430 Enthalpy of solution of Na in NaCl, 441 Equilibrium constants for anionic oxygen reactions in NaN03-KN03, 204 Fluctuating polarization, 440
3 447 Free energy of mixing MgClrCaC12, 436 Friction coefficients for molten salts and aqueous solutions, 159 Friction coefficients for the system LiN03 + AgN03 at 260 C (table), 161 Friction coefficients for the system LiN03 + AgN03 at 260 C as a function of the mole fraction of silver nitrate, 162 Germanium sulfide/germanium iodide melts, 368 Hammett acidity function, Ho, 136 aqueous solu!ions of ZnC12, 136 Heats of mixing: MgCl2 + Ca02; MgCl2 + SrCl2, 434, 435 Hydrated melts, relaxation studies, 15 Hydration shells: ions in Dead Sea water and end brine, 109 Hydrogen density distribution contours, simulation, 48 Hydrogen in molten salts acetates, 250 bisulfates, 252 anodic hydrogen dissolution, 254 cathodic hydrogen evolution, 253 carbonates, 255 role of carbon monoxide, 255 chlorides, 25 7 electrode reactions, 25 7 chloroaluminates, 259 electrochemistry, 260 diffusion coefficients, 252!1uorides, 261 electrochemistry, 261 hydroxides, 26 2 acid-base behavior, 262 electrochemistry, 263 nitrates, 264 activation energy, 269 electrochemical studies, 2 71 C02, H20/C03 2 -,H 2 system, 278 H20/H2,0H- system, 275 mechanisms, 276 pot en tiometry, 2 72 potentiometry, catalysis, 2 73 voltammetry, 273 ESCA studies, 280 Henry's law applicability, 266 Hydrogen in molten salts (cont.) kinetics, 26 7 manometric studies, 265 pressure-time relationship, 268, 270 solubility products, 267 other melts, 264 solubility and thermodynamic data, 251 Hydrolysis of chlorides, 312 of!1uorides, 315, 317 of hydroxides, 317 of nitrates, 318 Hydroxide melts, 301 conductivities, 302 comparisons with other melts, 302 and transport mechanisms, 302 inl1uence of water, 303 and proton mobility, 303 Interdiffusion in binary molten salt mbltures and in aqueous electrolyte solutions of binary electrolytes, 155 Ion pairs and ion triplet interactions, aqueous solutions, 112 Ionic contact radii in gases and crystals, 2 Ions in water, simulation, 4 7 Isotherms for potassium chloride, Monte Carlo calculations, 33, 34 Lead sulfide-alkali chloride melts, 369 Lead sulfide-lead halide melts, 367 Loss tangent spectra, aqueous glasses, 19, 20 Madelung constants, derivation from spectral shifts, 9 3 Mechanism of transport, relation of phenomenological parameters, 3 00 Melting, 4 Melts, resonance effects, 6 Metal aqua complexes, predicted acidity, 139 Metal-electrolyte interface aqueous: Hg, 118 aqueous: solid metals, 119 C -E data, main characteristics, 120 current model, 121 internal inconsistencies, 121 effect of ion size, 124 experimental methods: C-E determinations, 119
4 448 Metal-electrolyte interface (cont.) modified diffuse layer theory, 123 molten salts: solid metals, 119 new experiments, 124 simple diffuse layer theory, 122 Methods for describing the structure of molten salts and electrolyte solutions, 14 7 Microwave dielectric measurements, 16 Mobilities anion, 67 cation, 67 interaction, 69 Molar volumes and additivity, 294 and ion hydration, 294 water concentration dependence of, 292 Ca(N03h 4H20 system, 292 LiNOrKN03 system, 293 NH4N03-NH4Cl-LiN03 system, 292 Molecular dynamics, density distribution functions, 45 Molten salt mixtures, behavior of magnesium chloride, 433 Molten salt purification methods chemical, 213, 219 desiccation, 211, 227, 232 filtration, 227, 232, 242 physical methods, 210 principles, 209 recrystallization, 212, 22 7 reduced pressure, 211,227,232 sublimation, 211, 242 zone refining, 213 Molten salt solvents, purification general considerations, 188 purity availabilities, 187 purity requirements, 186 residual impurity levels, 197, 215 technological interests, 188 Molten salt technologies, 165 Nature of chalcogenide species in melts, 365 Neutron first-order difference method, 7 nmr studies, concentrated solutions, 137 Onsager reciprocal relations, validity, 68 Oxide equilibria in chloride melts, 216 Oxide species in miscellaneous melts, 3 56 Oxide species in miscellaneous melts (cont.) carbonates, 358 fluorides, 35 8 multiple oxide equilibria in hydroxide melts, 357 oxygen electrode response in chloride melts, 356 sulfates, 357 Oxide species in molten salts, 339 acid-base equilibrium constants in KN03, 348 an acid-base scale for oxyanions in KN03, 349 cryoscopic methods, 352 manometric methods, 353 solubility determinations, 35 2 spectroscopic methods, 352 thermogravimetry, 352 voltammetric methods, 350 oxide species in nitrates, 350 volumetric analysis, 353 basicity in glasses, 341 and gas solubilities, 342 and leachability of glasses, 341 and slag formation, 341 and sulfur formation, 343 and water solubility, 343 congruent melting and compound formation, 340 optical basicity and p-block ion probes, 345 qualitative estimation, 340 quantitative estimation, 345 potentiometric methods, 345 acid titrations, 34 7 oxygen electrodes, 345 use of acid-base indicators, 344 use of organic indicators, 345 Oxide species in nitrate melts, 3 53 stabilization by silica, 354 Oxoacidity scales, molten chlorides (figure), 316 Oxygen density distribu lion con tours, simulation, 49 Oxygen electrode in melts, 199 Phase diagrams for metal chloride and metal sulfide mixtures, 364 Phenomenological coefficients, On sager relations, 158ff
5 449 pk-optical basicity relation acids, 131 acid dissociation of hydrated cations, 134 pk values for metal ions in aqueous solutions, 133 Polarization, importance in determining thermodynamic properties of molten salt mixtures, 425 Polyatomic ions in molten salts, inorganic and organic, 3 Pourbaix-type diagram for iron in molten NaCl-KCl, 329 for noble metals in molten NaOH-KOH, 332 for various species in NaCl-KCl-CeCl 3, 330 Precipitation of salts from brines, 106 from Dead Sea brines, 104 Precision, relative, of experimental data, 70 Proton chemical shift vs. Hammett acidity function (HN0 3 and HCl) relation, 138 Proton magnetic shift constant, concentrated solutions, 140 Radial distribution functions, simulated KCl, 38 Redox properties of water, 317 in chlorides, 320, 321 in hydroxides, 3 22 in nitrates, 322 Regular solutions, 430 Relation between excess entropy and enthalpy: MgClrCaCl2 and other systems, 43 7 Relationship between cation-anion distance and polarizability of anion in alkali earth halides, 432 Relaxation data, aqueous glasses, interpretation, 21 Relaxation spectra cooling techniques, 16 experimental data, 18, 19 experimental procedures, 17 Reviews of transport properties of molten salts and electrolytic solutions, 145, 146 Room-temperature chloroaluminate-based melts, 412 Room-temperature ch1oroaluminate-based melts (cont.) acid-base chemistry and pcl values, 415 as a function of composition, 417 potentiometric evidence, 415 n -butylpyridinium chloride mixtures, 413 electrochemistry and spectroscopy of aromatic hydrocarbons, 417 correlation with ionization potentials, 418 correlation with solid state complexes, 418 formation of radical cations, 419 electrochemistry of the Fe(III)/Fe(Il) system, 420 physical properties, 420 species characterization, 413 compositional variations, 414 Raman shifts, 413 use as battery electrolytes, 4 21 Separation of titanium and iron in melts, 326 Silver chloride-silver sulfate melts, electrical conductivities, 3 73 Silver chloride-sulfide melts, enthalpies of mixing, 379 Silver halide-silver chalcogenide systems, 369 densities and molar volumes, 3 71 molar volumes as function of mol% Ag2S, 372 phase studies, 3 74 Simulation, polar systems, 43 Solubility and reactivity of water in molten salts, 188 chlorides and fluorides, 189 nitrates, 203 electrochemical data, 207 oxyanion solvents, 202 temperature dependence of Henry's law constant, 194 Solubility data for water in molten salts (table), 308, 309 Solubility of metal oxides in NaOH-KOH, 327 Solubility ranges of aluminum species in LiCl-KCl, 326 Solutions of sodium in NaCl, 440 Spectral probe ions, 84
6 450 Standard molar Gibbs free energies of formation and dissolution, 105 Structural aspects in Dead Sea brines, 108 Structure of NaCl: comparison of MD and neutron-scattering experiments, 39 Sulfides in molten lead chloride, 392 importance in lead electrolysis, 392 and anodic reaction, 392 and chronopotentiometric studies, 393 influence on cathodic yield, 392 and other electrochemical methods, 393 initial oxidation step, 394 second oxidation step, 395 subsequent reaction, 396 sulfur dissolution and polysulfide formation, 395 Sulfur compounds in molten NaOH-water mixtures, 396 coulometry, 401 elemental sulfur, 397 polysulfides, 396 spectroscopic characterization, 397 stability, spectra and electrochemistry, 399 the sulfide ion, 396 voltammetry of sulfides, 399 Solubility of water (see also Solubility and reactivity of water) in chlorides, hydroxides, 307 in molten nitrates and nitrites, 206, 307 electrochemical detection, 207, 231 impurity chloride ions detection, 212 impurity nitrite ions, 208 impurity oxide ions, 208 in molten salts, 306 Solubility of water and hydrogen chloride in chloride melts, 190 effect of solute polarity, 192 electrochemical detection, 192, 234, 236 hydrolysis and dissociation, 196 hydroxide formation, 197 oxide formation, 198 nature of solution species, 19 5 Sulfur species in chloroaluminate melts acid-base chemistry, 389 electrochemistry, 3 90 acid melts, 391 basic melts, 3 90 solubility, 389 Sulfur species in LiCl-KCl, 365 electrochemistry, solubility, 387 Sulfur species in LiCl-KCl (cont.) spectroscopy, 388 Sulfur species in miscellaneous melts, NaCl-KCl, 391 thiocyanates, 391 Sulfur vapor electrode, 374 Thallous sulfide-chloride mixture, 382 activity coefficients, 383 Theories and models of water-salt mixtures for discussion of transport processes, 149 Thermodynamics and structure, 2 7 and transport properties for the system LiN03 + AgN03 at 260 C (table), 157 Tin chalcogenide-tin halide melts, 368 Transference numbers, data, concentrated solutions, 7 3 Transport application of irreversible thermodynamics to, 66 concentration dependence of, 6 3 cooperative nature of, 60 phenomenological coefficients for, 66 quasi-lattice models for, 59 temperature dependence parameters for, 61 theories of, 58 transition state models for, 59 Transport experiments and results, 156ff Transport numbers, relation to ion velocity, 152 Velocity correlation coefficients, 69 Viscosity concentration dependence of, 65 data, concentrated solutions, 71 water concentration dependence of, 299 and comparison with conductivities, 299 Water in molten salts, 165 effect on aluminum electroplating, 168 effect on corrosion and passivation, 166 role in TORCO process, 169 solubility, 166 X-ray and neutron diffraction studies of concentrated solutions, 110
7.1 Electrolyte and electrolytic solution
 Out-class reading: Levine, pp. 294-310 Section 10.6 solutions of electrolytes Section 10.9 ionic association pp. 512-515 Section 16.6 electrical conductivity of electrolyte solutions. Contents of solution
Out-class reading: Levine, pp. 294-310 Section 10.6 solutions of electrolytes Section 10.9 ionic association pp. 512-515 Section 16.6 electrical conductivity of electrolyte solutions. Contents of solution
CH 4 AP. Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
 CH 4 AP Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Water Aqueous means dissolved in H 2 O Moderates the Earth s temperature because of high specific heat H-bonds cause strong cohesive and adhesive properties Polar,
CH 4 AP Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Water Aqueous means dissolved in H 2 O Moderates the Earth s temperature because of high specific heat H-bonds cause strong cohesive and adhesive properties Polar,
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 5 - Electricity and Chemistry Electrolysis You need to know that electrolysis is: - The breakdown of ionic substances into their constituent elements
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 5 - Electricity and Chemistry Electrolysis You need to know that electrolysis is: - The breakdown of ionic substances into their constituent elements
Personalised Learning Checklists Edexcel Combined: Chemistry Paper 1
 Edexcel (combined) Chemistry Topics (1SC0) from 2016 - Paper 1 (Topic 1 parts a&b) Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe how the Dalton model of an atom has changed over time because of the discovery
Edexcel (combined) Chemistry Topics (1SC0) from 2016 - Paper 1 (Topic 1 parts a&b) Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe how the Dalton model of an atom has changed over time because of the discovery
Covalent (sharing of electron pairs) Ionic ( electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions)
 Covalent (sharing of electron pairs) Ionic ( electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions) Metallic (electrostatic attraction between + metal ions and delocalised electrons) Group 1 ions 1+
Covalent (sharing of electron pairs) Ionic ( electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions) Metallic (electrostatic attraction between + metal ions and delocalised electrons) Group 1 ions 1+
FORM 4 CHEMISTRY - SUMMER REVISION WORK
 Form 3 Syllabus: FORM 4 CHEMISTRY - SUMMER REVISION WORK Chapter 1: STATES OF MATTER Converting between the 3 states of matter Application of kinetic theory to changes of state Diffusion Physical and chemical
Form 3 Syllabus: FORM 4 CHEMISTRY - SUMMER REVISION WORK Chapter 1: STATES OF MATTER Converting between the 3 states of matter Application of kinetic theory to changes of state Diffusion Physical and chemical
Solubility Rules See also Table 4.1 in text and Appendix G in Lab Manual
 Ch 4 Chemical Reactions Ionic Theory of Solutions - Ionic substances produce freely moving ions when dissolved in water, and the ions carry electric current. (S. Arrhenius, 1884) - An electrolyte is a
Ch 4 Chemical Reactions Ionic Theory of Solutions - Ionic substances produce freely moving ions when dissolved in water, and the ions carry electric current. (S. Arrhenius, 1884) - An electrolyte is a
Stoichiometry: Chemical Calculations. Chemistry is concerned with the properties and the interchange of matter by reaction i.e. structure and change.
 Chemistry is concerned with the properties and the interchange of matter by reaction i.e. structure and change. In order to do this, we need to be able to talk about numbers of atoms. The key concept is
Chemistry is concerned with the properties and the interchange of matter by reaction i.e. structure and change. In order to do this, we need to be able to talk about numbers of atoms. The key concept is
PhET Interactive Chemistry Simulations Aligned to an Example General Chemistry Curriculum
 PhET Interactive Chemistry Simulations Aligned to an Example General Chemistry Curriculum Alignment is based on the topics and subtopics addressed by each sim. Sims that directly address the topic area
PhET Interactive Chemistry Simulations Aligned to an Example General Chemistry Curriculum Alignment is based on the topics and subtopics addressed by each sim. Sims that directly address the topic area
Balances 9, , 623, 643, , , 679 (also see Electroneutrality. Material balances)
 Handbook of Aqueous Electrolyte Thermodynamics: Theory & Application by Joseph F. Zemaitis, Jr., Diane M. Clark, Marshall Rafal and Noel C. Scrivner Copyright 1986 American Institute of Chemical Engineers,
Handbook of Aqueous Electrolyte Thermodynamics: Theory & Application by Joseph F. Zemaitis, Jr., Diane M. Clark, Marshall Rafal and Noel C. Scrivner Copyright 1986 American Institute of Chemical Engineers,
Chapter 4. Reactions in Aqueous Solution
 Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solution Topics General properties of aqueous solutions Precipitation reactions Acid base reactions Oxidation reduction reactions Concentration of solutions Aqueous reactions
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solution Topics General properties of aqueous solutions Precipitation reactions Acid base reactions Oxidation reduction reactions Concentration of solutions Aqueous reactions
Miami Dade College CHM Second Semester General Chemistry
 Miami Dade College CHM 1046 - Second Semester General Chemistry Course Description: CHM 1046 is the second semester of a two-semester general chemistry course for science, premedical science and engineering
Miami Dade College CHM 1046 - Second Semester General Chemistry Course Description: CHM 1046 is the second semester of a two-semester general chemistry course for science, premedical science and engineering
Student Achievement. Chemistry 12
 Student Achievement Chemistry 12 Key Elements: Reaction Kinetics Estimated Time: 14 16 hours By the end of this course, students will be able to explain the significance of reaction rates, demonstrate
Student Achievement Chemistry 12 Key Elements: Reaction Kinetics Estimated Time: 14 16 hours By the end of this course, students will be able to explain the significance of reaction rates, demonstrate
Chapter 6. Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
 Chapter 6 Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry Chapter 6 Table of Contents (6.1) (6.2) (6.3) (6.4) (6.5) (6.6) (6.7) (6.8) Water, the common solvent The nature of aqueous solutions: Strong
Chapter 6 Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry Chapter 6 Table of Contents (6.1) (6.2) (6.3) (6.4) (6.5) (6.6) (6.7) (6.8) Water, the common solvent The nature of aqueous solutions: Strong
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC TEXT REFERENCE. Electrochemistry. Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18. Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1
 Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan
 YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions. Copyright McGraw-Hill
 Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 4.1 General Properties of Aqueous Solutions Solution - a homogeneous mixture Solute: the component that is dissolved Solvent: the component
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 4.1 General Properties of Aqueous Solutions Solution - a homogeneous mixture Solute: the component that is dissolved Solvent: the component
Chapter 4: Chemical Reactions in Aqueous Solutions. 4.1 Some Electronic Properties of Aqueous Solutions
 Chapter : Chemical Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Water: the universal solvent ¾ of Earth s surface water in living organisms Some Electrical Properties of Aqueous Solutions Reactions of Acids and Bases
Chapter : Chemical Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Water: the universal solvent ¾ of Earth s surface water in living organisms Some Electrical Properties of Aqueous Solutions Reactions of Acids and Bases
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes
 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
Electrochemistry in Nonaqueous Solutions
 К. Izutsu Electrochemistry in Nonaqueous Solutions WILEY-VCH Contents Preface V Part I Fundamentals of Chemistry in Non-Aqueous Solutions: Electrochemical Aspects 1 Properties of Solvents and Solvent Classification
К. Izutsu Electrochemistry in Nonaqueous Solutions WILEY-VCH Contents Preface V Part I Fundamentals of Chemistry in Non-Aqueous Solutions: Electrochemical Aspects 1 Properties of Solvents and Solvent Classification
AP Chemistry Honors Unit Chemistry #4 2 Unit 3. Types of Chemical Reactions & Solution Stoichiometry
 HO AP Chemistry Honors Unit Chemistry #4 2 Unit 3 Chapter 4 Zumdahl & Zumdahl Types of Chemical Reactions & Solution Stoichiometry Students should be able to:! Predict to some extent whether a substance
HO AP Chemistry Honors Unit Chemistry #4 2 Unit 3 Chapter 4 Zumdahl & Zumdahl Types of Chemical Reactions & Solution Stoichiometry Students should be able to:! Predict to some extent whether a substance
Chapter 4. Reactions in Aqueous Solution
 Chapter 4. Reactions in Aqueous Solution 4.1 General Properties of Aqueous Solutions A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. A solution is made when one substance (the solute) is
Chapter 4. Reactions in Aqueous Solution 4.1 General Properties of Aqueous Solutions A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. A solution is made when one substance (the solute) is
Chemistry 104 Final Exam Content Evaluation and Preparation for General Chemistry I Material
 Chemistry 104 Final Exam Content Evaluation and Preparation for General Chemistry I Material What is 25 mph in mm s 1? Unit conversions What is 1025 K in o F? Which is larger 1 ft 3 or 0.1 m 3? What is
Chemistry 104 Final Exam Content Evaluation and Preparation for General Chemistry I Material What is 25 mph in mm s 1? Unit conversions What is 1025 K in o F? Which is larger 1 ft 3 or 0.1 m 3? What is
Time Allowed: 1:45 hours
 9 th LAHORE BOARD 2014 Group I 1) Explain double covalent bond with the help of an example. 2) How do atoms follow octet rule? 3) Explain polar covalent bond with an example. 4) Define pressure. Write
9 th LAHORE BOARD 2014 Group I 1) Explain double covalent bond with the help of an example. 2) How do atoms follow octet rule? 3) Explain polar covalent bond with an example. 4) Define pressure. Write
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry. Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry. Notes.
 Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry Notes Define electrolysis as The breakdown of an ionic compound, molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of electricity Describe the electrode
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry Notes Define electrolysis as The breakdown of an ionic compound, molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of electricity Describe the electrode
IGCSE TEST_ (Ch. 2,3,4,5,6) Name... Date...
 IGCSE TEST_ (Ch. 2,3,4,5,6) Name... Date... 1 Winston Churchill, a British Prime Minister, had his false teeth electroplated with gold. The teeth were coated with a thin layer of carbon and were then placed
IGCSE TEST_ (Ch. 2,3,4,5,6) Name... Date... 1 Winston Churchill, a British Prime Minister, had his false teeth electroplated with gold. The teeth were coated with a thin layer of carbon and were then placed
Unit IV: Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry
 Unit IV: Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry A. The chemical equation B. Types of chemical reactions A. Activity series of metals B. Solubility rules C. Rules for writing and balancing equations D. Calculations
Unit IV: Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry A. The chemical equation B. Types of chemical reactions A. Activity series of metals B. Solubility rules C. Rules for writing and balancing equations D. Calculations
Unit-8 Equilibrium. Rate of reaction: Consider the following chemical reactions:
 Unit-8 Equilibrium Rate of reaction: Consider the following chemical reactions: 1. The solution of sodium chloride and silver nitrate when mixed, there is an instantaneous formation of a precipitate of
Unit-8 Equilibrium Rate of reaction: Consider the following chemical reactions: 1. The solution of sodium chloride and silver nitrate when mixed, there is an instantaneous formation of a precipitate of
Chapter Four: Reactions in Aqueous Solution
 Chapter Four: Reactions in Aqueous Solution Learning Outcomes: Identify compounds as acids or bases, and as strong, weak, or nonelectrolytes Recognize reactions by type and be able to predict the products
Chapter Four: Reactions in Aqueous Solution Learning Outcomes: Identify compounds as acids or bases, and as strong, weak, or nonelectrolytes Recognize reactions by type and be able to predict the products
Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species.
 Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species. The species that loses the electron is oxidized. The species that gains the electron is reduced.
Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species. The species that loses the electron is oxidized. The species that gains the electron is reduced.
Practice I: Chemistry IGCSE
 Practice I: Chemistry IGCSE cristian.obiol@gmail.com 1) Explain the following processes related to changes of states of matter. -Melting:... -Vaporization:... -Freezing:... -Condensation:... -Sublimation:...
Practice I: Chemistry IGCSE cristian.obiol@gmail.com 1) Explain the following processes related to changes of states of matter. -Melting:... -Vaporization:... -Freezing:... -Condensation:... -Sublimation:...
Electrochemistry. Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts
 Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts What do I need to know about electrochemistry? Electrochemistry Learning Outcomes: Candidates should be able to: a) Describe
Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts What do I need to know about electrochemistry? Electrochemistry Learning Outcomes: Candidates should be able to: a) Describe
Properties of Compounds
 Chapter 6. Properties of Compounds Comparing properties of elements and compounds Compounds are formed when elements combine together in fixed proportions. The compound formed will often have properties
Chapter 6. Properties of Compounds Comparing properties of elements and compounds Compounds are formed when elements combine together in fixed proportions. The compound formed will often have properties
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
4.4.1 Reactivity of metals Metal oxides The reactivity series. Key opportunities for skills development.
 4.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
4.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
4 CO O 2. , how many moles of KCl will be produced? Use the unbalanced equation below: PbCl 2. PbSO 4
 Honors Chemistry Practice Final 2017 KEY 1. Acetylene gas, C 2, is used in welding because it generates an extremely hot flame when combusted with oxygen. How many moles of oxygen are required to react
Honors Chemistry Practice Final 2017 KEY 1. Acetylene gas, C 2, is used in welding because it generates an extremely hot flame when combusted with oxygen. How many moles of oxygen are required to react
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding Learning Objectives Describe the formation of ions by electron loss/gain to obtain the electronic configuration of a noble gas. Describe the formation of ionic bonds between
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding Learning Objectives Describe the formation of ions by electron loss/gain to obtain the electronic configuration of a noble gas. Describe the formation of ionic bonds between
Chapter 4. The Major Classes of Chemical Reactions 4-1
 Chapter 4 The Major Classes of Chemical Reactions 4-1 The Major Classes of Chemical Reactions 4.1 The Role of Water as a Solvent 4.2 Writing Equations for Aqueous Ionic Reactions 4.3 Precipitation Reactions
Chapter 4 The Major Classes of Chemical Reactions 4-1 The Major Classes of Chemical Reactions 4.1 The Role of Water as a Solvent 4.2 Writing Equations for Aqueous Ionic Reactions 4.3 Precipitation Reactions
Acids, Bases, & Neutralization Chapter 20 & 21 Assignment & Problem Set
 Acids, Bases, & Neutralization Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Acids, Bases, & Neutralization 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know
Acids, Bases, & Neutralization Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Acids, Bases, & Neutralization 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know
Electrodes are normally made out of inert (unreactive) materials. Graphite and platinum are common electrode materials.
 Electrolysis Electrolysis is using an electric current to break up an ionic compound to form elements. Covalent compounds can t be split up by electrolysis. Terms used in electrolysis: Electrolyte - the
Electrolysis Electrolysis is using an electric current to break up an ionic compound to form elements. Covalent compounds can t be split up by electrolysis. Terms used in electrolysis: Electrolyte - the
Downloaded from
 I.I.T.Foundation - XI Chemistry MCQ #10 Time: 45 min Student's Name: Roll No.: Full Marks: 90 Solutions I. MCQ - Choose Appropriate Alternative 1. Molarity is the number of moles of a solute dissolved
I.I.T.Foundation - XI Chemistry MCQ #10 Time: 45 min Student's Name: Roll No.: Full Marks: 90 Solutions I. MCQ - Choose Appropriate Alternative 1. Molarity is the number of moles of a solute dissolved
AP Chemistry Common Ion Effect; 16.6 ionization constants, will. Equilibria with Weak Acids and and the preparation of buffer
 Instructional Unit Acid-Base Equibria 16.1 Acid-Ionizaation Equilibria; Students will perform Students will distinguish Oral response, written 3.1.12C, 16.2 Polyprotic Acids; 16.3 Base- calculations involving
Instructional Unit Acid-Base Equibria 16.1 Acid-Ionizaation Equilibria; Students will perform Students will distinguish Oral response, written 3.1.12C, 16.2 Polyprotic Acids; 16.3 Base- calculations involving
CH 221 Chapter Four Part II Concept Guide
 CH 221 Chapter Four Part II Concept Guide 1. Solubility Why are some compounds soluble and others insoluble? In solid potassium permanganate, KMnO 4, the potassium ions, which have a charge of +1, are
CH 221 Chapter Four Part II Concept Guide 1. Solubility Why are some compounds soluble and others insoluble? In solid potassium permanganate, KMnO 4, the potassium ions, which have a charge of +1, are
DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS. Double your pleasure, double your fun
 DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS Double your pleasure, double your fun Industrial processes produce unwanted by-products. Dissolved toxic metal ions-copper, mercury, and cadmium-are common leftovers in the
DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS Double your pleasure, double your fun Industrial processes produce unwanted by-products. Dissolved toxic metal ions-copper, mercury, and cadmium-are common leftovers in the
ed. Brad Collins Aqueous Chemistry Chapter 5 Some images copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sunday, August 18, 13
 ed. Brad Collins Aqueous Chemistry Chapter 5 Some images copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. A solution is a homogenous mixture of 2 or more substances at the molecular level The solute(s) is(are)
ed. Brad Collins Aqueous Chemistry Chapter 5 Some images copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. A solution is a homogenous mixture of 2 or more substances at the molecular level The solute(s) is(are)
Brass, a solid solution of Zn and Cu, is used to make musical instruments and many other objects.
 Brass, a solid solution of Zn and Cu, is used to make musical instruments and many other objects. 14.1 General Properties of Solutions 14.2 Solubility 14.3 Rate of Dissolving Solids 14.4 Concentration
Brass, a solid solution of Zn and Cu, is used to make musical instruments and many other objects. 14.1 General Properties of Solutions 14.2 Solubility 14.3 Rate of Dissolving Solids 14.4 Concentration
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes
 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
HW 2. CHEM 481 Chapters 3 & 5 Chapter 3. Energetics of Ionic Bonding
 HW 2. CHEM 481 Chapters 3 & 5 Chapter 3. Energetics of Ionic Bonding Name: 1. Give coordination number for both anion and cation of the following ionic lattices. a) CsCl Structure: b) Rock Salt Structure:
HW 2. CHEM 481 Chapters 3 & 5 Chapter 3. Energetics of Ionic Bonding Name: 1. Give coordination number for both anion and cation of the following ionic lattices. a) CsCl Structure: b) Rock Salt Structure:
Chapter 4 Chemical Formulas, Reactions, Redox and Solutions
 Terms to Know: Solubility Solute Solvent Solution Chapter 4 the amount of substance that dissolves in a given volume of solvent at a given temperature. a substance dissolved in a liquid to form a solution
Terms to Know: Solubility Solute Solvent Solution Chapter 4 the amount of substance that dissolves in a given volume of solvent at a given temperature. a substance dissolved in a liquid to form a solution
AP Chemistry Unit 1 Review Guide: IUPAC Naming, Stoichiometry, Solution Chemistry
 I. IUPAC Naming AP Chemistry Unit 1 Review Guide: IUPAC Naming, Stoichiometry, Solution Chemistry For Ionic Compounds: Formula to Name: 1. Identify the cation (positive ion) by name, then identify the
I. IUPAC Naming AP Chemistry Unit 1 Review Guide: IUPAC Naming, Stoichiometry, Solution Chemistry For Ionic Compounds: Formula to Name: 1. Identify the cation (positive ion) by name, then identify the
Chemistry Study Guide
 Chemistry Study Guide Marking Period 3 Exam Week of 3/21/17 Study Guide due - When studying for this test, use your do nows, notes, homework, class handouts, and your textbook. Vocabulary Chapter 7 Anion
Chemistry Study Guide Marking Period 3 Exam Week of 3/21/17 Study Guide due - When studying for this test, use your do nows, notes, homework, class handouts, and your textbook. Vocabulary Chapter 7 Anion
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17
 Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Name Date. 9. Which substance shows the least change in solubility (grams of solute) from 0 C to 100 C?
 Solubility Curve Practice Problems Directions: Use the graph to answer the questions below. Assume you will be using 100g of water unless otherwise stated. 1. How many grams of potassium chloride (KCl)
Solubility Curve Practice Problems Directions: Use the graph to answer the questions below. Assume you will be using 100g of water unless otherwise stated. 1. How many grams of potassium chloride (KCl)
Norwich City Schools AP Chemistry
 Topic: Structure of Matter Students will use inquiry based methods to investigate scientific concepts Students will examine and investigate the structure, properties, and interactions of matter. Students
Topic: Structure of Matter Students will use inquiry based methods to investigate scientific concepts Students will examine and investigate the structure, properties, and interactions of matter. Students
Chapter 17: Additional Aspects of Aqueous equilibria. Common-ion effect
 Chapter 17: Additional Aspects of Aqueous equilibria Learning goals and key skills: Describe the common ion effect. Explain how a buffer functions. Calculate the ph of a buffer solution. Calculate the
Chapter 17: Additional Aspects of Aqueous equilibria Learning goals and key skills: Describe the common ion effect. Explain how a buffer functions. Calculate the ph of a buffer solution. Calculate the
CHEMISTRY. SCIENCE Paper 2
 CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
8. Draw Lewis structures and determine molecular geometry based on VSEPR Theory
 Chemistry Grade 12 Outcomes 1 Quantum Chemistry and Atomic Structure Unit I 1. Perform calculations on wavelength, frequency and energy. 2. Have an understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum. 3. Relate
Chemistry Grade 12 Outcomes 1 Quantum Chemistry and Atomic Structure Unit I 1. Perform calculations on wavelength, frequency and energy. 2. Have an understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum. 3. Relate
Chapter 4; Reactions in Aqueous Solutions. Chapter 4; Reactions in Aqueous Solutions. V. Molarity VI. Acid-Base Titrations VII. Dilution of Solutions
 Chapter 4; Reactions in Aqueous Solutions I. Electrolytes vs. NonElectrolytes II. Precipitation Reaction a) Solubility Rules III. Reactions of Acids a) Neutralization b) Acid and Carbonate c) Acid and
Chapter 4; Reactions in Aqueous Solutions I. Electrolytes vs. NonElectrolytes II. Precipitation Reaction a) Solubility Rules III. Reactions of Acids a) Neutralization b) Acid and Carbonate c) Acid and
The City School. Subject: Chemistry CIE Code: Curriculum Distribution Chart
 The City School Curriculum Distribution Chart Class 9: September 2014 to May 2015 Subject: Chemistry CIE Code: 5070 Syllabus Content (As taken from the CIE 2015 syllabus) Topic Content Week Learning Outcomes
The City School Curriculum Distribution Chart Class 9: September 2014 to May 2015 Subject: Chemistry CIE Code: 5070 Syllabus Content (As taken from the CIE 2015 syllabus) Topic Content Week Learning Outcomes
Chemistry 12. Resource Exam B. Exam Booklet
 Chemistry 12 Resource Exam B Exam Booklet Contents: 21 pages Examination: 2 hours 50 multiple-choice questions in the Exam Booklet Additional Time Permitted: 60 minutes Province of British Columbia PART
Chemistry 12 Resource Exam B Exam Booklet Contents: 21 pages Examination: 2 hours 50 multiple-choice questions in the Exam Booklet Additional Time Permitted: 60 minutes Province of British Columbia PART
Chemistry: The Central Science Twelfth Edition, AP* Edition 2012
 A Correlation of The Central Science Twelfth Edition, AP* Edition 2012 to the AP* Chemistry Topics I. Structure of Matter A. Atomic theory and atomic structure 1. Evidence for the atomic theory SECTIONS:
A Correlation of The Central Science Twelfth Edition, AP* Edition 2012 to the AP* Chemistry Topics I. Structure of Matter A. Atomic theory and atomic structure 1. Evidence for the atomic theory SECTIONS:
Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions 1 Chapter 4 General Properties of Aqueous Solutions (4.1) Precipitation Reactions (4.2) Acid-Base Reactions (4.3) Oxidation-Reduction Reactions (4.4) Concentration of Solutions
Reactions in Aqueous Solutions 1 Chapter 4 General Properties of Aqueous Solutions (4.1) Precipitation Reactions (4.2) Acid-Base Reactions (4.3) Oxidation-Reduction Reactions (4.4) Concentration of Solutions
Molecule smallest particle of a substance having its chemical properties Atoms connected via covalent bonds Examples:
 Ionic equations, calculations involving concentrations, stoichiometry MUDr. Jan Pláteník, PhD Molecule smallest particle of a substance having its chemical properties Atoms connected via covalent bonds
Ionic equations, calculations involving concentrations, stoichiometry MUDr. Jan Pláteník, PhD Molecule smallest particle of a substance having its chemical properties Atoms connected via covalent bonds
Section 4: Aqueous Reactions
 Section 4: Aqueous Reactions 1. Solution composition 2. Electrolytes and nonelectrolytes 3. Acids, bases, and salts 4. Neutralization ti reactions 5. Precipitation reactions 6. Oxidation/reduction reactions
Section 4: Aqueous Reactions 1. Solution composition 2. Electrolytes and nonelectrolytes 3. Acids, bases, and salts 4. Neutralization ti reactions 5. Precipitation reactions 6. Oxidation/reduction reactions
Study guide for AP test on TOPIC 1 Matter & Measurement
 Study guide for AP test on IC 1 Matter & Measurement IC 1 Recall a definition of chemistry Understand the process and stages of scientific (logical) problem solving Recall the three states of matter, their
Study guide for AP test on IC 1 Matter & Measurement IC 1 Recall a definition of chemistry Understand the process and stages of scientific (logical) problem solving Recall the three states of matter, their
CHAPTER 4 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS & SOLUTION STOICHIOMETRY
 Advanced Chemistry Name Hour Advanced Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 4 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS & SOLUTION STOICHIOMETRY Day Plans
Advanced Chemistry Name Hour Advanced Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 4 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS & SOLUTION STOICHIOMETRY Day Plans
GCSE Additional Science
 GCSE Additional Science Module C5 Chemicals of the Natural Environment: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this
GCSE Additional Science Module C5 Chemicals of the Natural Environment: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this
Electrolytic processes Notes
 Edexcel GCSE Chemistry Topic 3: Chemical changes Electrolytic processes Notes 3.22 Recall that electrolytes are ionic compounds in the molten state or dissolved in water When an ionic substance is melted
Edexcel GCSE Chemistry Topic 3: Chemical changes Electrolytic processes Notes 3.22 Recall that electrolytes are ionic compounds in the molten state or dissolved in water When an ionic substance is melted
Contents. 1 Matter: Its Properties and Measurement 1. 2 Atoms and the Atomic Theory Chemical Compounds Chemical Reactions 111
 Ed: Pls provide art About the Authors Preface xvii xvi 1 Matter: Its Properties and Measurement 1 1-1 The Scientific Method 2 1-2 Properties of Matter 4 1-3 Classification of Matter 5 1-4 Measurement of
Ed: Pls provide art About the Authors Preface xvii xvi 1 Matter: Its Properties and Measurement 1 1-1 The Scientific Method 2 1-2 Properties of Matter 4 1-3 Classification of Matter 5 1-4 Measurement of
YEAR 10 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min
 YEAR 10 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min NAME: CLASS: Useful data: Q = It. Faraday Constant = 96,500 C mol -1. Use the Periodic table, given below, where necessary. Marks Grid [For Examiners use only] Question
YEAR 10 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min NAME: CLASS: Useful data: Q = It. Faraday Constant = 96,500 C mol -1. Use the Periodic table, given below, where necessary. Marks Grid [For Examiners use only] Question
insoluble partial very soluble (< 0.1 g/100ml) solubility (> 1 g/100ml) Factors Affecting Solubility in Water
 Aqueous Solutions Solubility is a relative term since all solutes will have some solubility in water. Insoluble substances simply have extremely low solubility. The solubility rules are a general set of
Aqueous Solutions Solubility is a relative term since all solutes will have some solubility in water. Insoluble substances simply have extremely low solubility. The solubility rules are a general set of
Part A Answer all questions in this part.
 Part A Directions (1-24): For each statement or question, record on your separate answer sheet the number of the word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question.
Part A Directions (1-24): For each statement or question, record on your separate answer sheet the number of the word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question.
Chemical Equations. Chemical Reactions. The Hindenburg Reaction 5/25/11
 Chemical Reactions CHM 1032C Chemical Equations Chemical change involves a reorganization of the atoms in one or more substances. The Hindenburg Reaction Reactants are on left, products to the right. Arrow
Chemical Reactions CHM 1032C Chemical Equations Chemical change involves a reorganization of the atoms in one or more substances. The Hindenburg Reaction Reactants are on left, products to the right. Arrow
AP Chemistry Unit #4. Types of Chemical Reactions & Solution Stoichiometry
 AP Chemistry Unit #4 Chapter 4 Zumdahl & Zumdahl Types of Chemical Reactions & Solution Stoichiometry Students should be able to: Predict to some extent whether a substance will be a strong electrolyte,
AP Chemistry Unit #4 Chapter 4 Zumdahl & Zumdahl Types of Chemical Reactions & Solution Stoichiometry Students should be able to: Predict to some extent whether a substance will be a strong electrolyte,
Acids Bases and Salts Acid
 Acids Bases and Salts Acid ph less than 7.0 Sour taste Electrolyte Names of Acids Binary acids Contain only 2 elements Begin with hydro; end with ic Ternary acids Ex: H 2 S = hydrosulfuric Contain a polyatomic
Acids Bases and Salts Acid ph less than 7.0 Sour taste Electrolyte Names of Acids Binary acids Contain only 2 elements Begin with hydro; end with ic Ternary acids Ex: H 2 S = hydrosulfuric Contain a polyatomic
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry. Electrochemical Cells
 Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Colligative Properties. Compounds in Aqueous Solution. Rules for Net Ionic Equations. Rule
 Slide 1 Colligative Properties Slide 2 Compounds in Aqueous Solution Dissociation - The separation of ions that occurs when an ionic compound dissolves Precipitation Reactions - A chemical reaction in
Slide 1 Colligative Properties Slide 2 Compounds in Aqueous Solution Dissociation - The separation of ions that occurs when an ionic compound dissolves Precipitation Reactions - A chemical reaction in
Chapter 4: Types of Chemical reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
 Chapter 4: Types of Chemical reactions and Solution Stoichiometry 4.1 Water, The Common Solvent State why water acts as a common solvent. Draw the structure of water, including partial charge. Write equations
Chapter 4: Types of Chemical reactions and Solution Stoichiometry 4.1 Water, The Common Solvent State why water acts as a common solvent. Draw the structure of water, including partial charge. Write equations
Describe how the inter-conversion of solids, liquids and gases are achieved and recall names used for these inter-conversions
 Understand the arrangements, movements and energy of the particle in each of the 3 states of matter : solid, liquid and gas Describe how the inter-conversion of solids, liquids and gases are achieved and
Understand the arrangements, movements and energy of the particle in each of the 3 states of matter : solid, liquid and gas Describe how the inter-conversion of solids, liquids and gases are achieved and
Name Class Date. In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 Assessment Chapter Test A Chapter: Solutions In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. Agitation prevents settling
Assessment Chapter Test A Chapter: Solutions In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. Agitation prevents settling
ACP Chemistry (821) - Mid-Year Review
 ACP Chemistry (821) - Mid-Year Review *Be sure you understand the concepts involved in each question. Do not simply memorize facts!* 1. What is chemistry? Chapter 1: Chemistry 2. What is the difference
ACP Chemistry (821) - Mid-Year Review *Be sure you understand the concepts involved in each question. Do not simply memorize facts!* 1. What is chemistry? Chapter 1: Chemistry 2. What is the difference
Sodium, Na. Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 6.1 to 6.5 and 7.1.
 Sodium, Na Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 6.1 to 6.5 and 7.1 Forms of Carbon What is an alkali metal? Any element in Group 1 except
Sodium, Na Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 6.1 to 6.5 and 7.1 Forms of Carbon What is an alkali metal? Any element in Group 1 except
Chapter 4 - Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Chemistry
 Chapter 4 - Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Chemistry 4.1 Water, the Common Solvent - the water molecule is bent with and H-O-H angles of approx. 105 º - O-H bonds are covalent - O is slightly
Chapter 4 - Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Chemistry 4.1 Water, the Common Solvent - the water molecule is bent with and H-O-H angles of approx. 105 º - O-H bonds are covalent - O is slightly
CHEMICAL REACTIONS. The process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances
 CHEMICAL REACTIONS The process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances Equations Reactions are represented by a chemical equation Reactants Products Must have
CHEMICAL REACTIONS The process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances Equations Reactions are represented by a chemical equation Reactants Products Must have
5.4 Chemical changes Reactivity of metals Metal oxides The reactivity series. Key opportunities for skills development
 5.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
5.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
Thinkwell s Homeschool AP Chemistry Course Lesson Plan: 34 weeks
 Thinkwell s Homeschool AP Chemistry Course Lesson Plan: 34 weeks Welcome to Thinkwell s Homeschool AP Chemistry! We re thrilled that you ve decided to make us part of your homeschool curriculum. This lesson
Thinkwell s Homeschool AP Chemistry Course Lesson Plan: 34 weeks Welcome to Thinkwell s Homeschool AP Chemistry! We re thrilled that you ve decided to make us part of your homeschool curriculum. This lesson
Definition 1 An element or compound is oxidized when it gains oxygen atoms
 Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
Chapter 6. Chemical Reactions. Sodium reacts violently with bromine to form sodium bromide.
 Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions Sodium reacts violently with bromine to form sodium bromide. Evidence of Chemical Reactions Chemical Equations Reactants Products Reactant(s): Substance(s) present before the
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions Sodium reacts violently with bromine to form sodium bromide. Evidence of Chemical Reactions Chemical Equations Reactants Products Reactant(s): Substance(s) present before the
C4 Quick Revision Questions
 C4 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only Question 1... of 50 Write the equation which shows the formation of iron oxide Answer 1... of 50 4Fe + 3O 2 2Fe 2 O 3 Question
C4 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only Question 1... of 50 Write the equation which shows the formation of iron oxide Answer 1... of 50 4Fe + 3O 2 2Fe 2 O 3 Question
Identify the bonding types molecular, covalent network, ionic, and metallic - in various solids (11.8)
 Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids (Chapter 11) Very brief review of Lewis structures and molecular geometry Draw Lewis structures for and determine polarity of molecules through sp 3 8.45 8.64,
Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids (Chapter 11) Very brief review of Lewis structures and molecular geometry Draw Lewis structures for and determine polarity of molecules through sp 3 8.45 8.64,
Acid, Bases and Salts (IGCSE Chemistry Syllabus )
 Acid, Bases and Salts (IGCSE Chemistry Syllabus 2016-2018) Acid o A compound when dissolved in water produces hydrogen ions (H + ) ; proton (H + ) donor o It turns blue damp litmus paper to red o ph 1
Acid, Bases and Salts (IGCSE Chemistry Syllabus 2016-2018) Acid o A compound when dissolved in water produces hydrogen ions (H + ) ; proton (H + ) donor o It turns blue damp litmus paper to red o ph 1
Chapter Four. Chapter Four. Chemical Reactions in Aqueous Solutions. Electrostatic Forces. Conduction Illustrated
 1 Electrostatic Forces 2 Chemical Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Unlike charges (+ and ) attract one another. Like charges (+ and +, or and ) repel one another. Conduction Illustrated 3 Arrhenius s Theory
1 Electrostatic Forces 2 Chemical Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Unlike charges (+ and ) attract one another. Like charges (+ and +, or and ) repel one another. Conduction Illustrated 3 Arrhenius s Theory
GHW#3. Chapter 3. Louisiana Tech University, Chemistry 481. POGIL(Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) Exercise on Chapter 3.
 GHW#3. Chapter 3. Louisiana Tech University, Chemistry 481. POGIL(Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) Exercise on Chapter 3. Energetics of Ionic Bonding. Why? What are the properties of ionic compounds?
GHW#3. Chapter 3. Louisiana Tech University, Chemistry 481. POGIL(Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) Exercise on Chapter 3. Energetics of Ionic Bonding. Why? What are the properties of ionic compounds?
Learning Outcomes: At the end of this assignment, students will be able to:
 Chemical Equilibria & Sample Preparation Purpose: The purpose of this assignment is to predict how solute concentrations are controlled by chemical equilibria, understand the chemistry involved with sample
Chemical Equilibria & Sample Preparation Purpose: The purpose of this assignment is to predict how solute concentrations are controlled by chemical equilibria, understand the chemistry involved with sample
9/24/12. Chemistry Second Edition Julia Burdge. Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
 Chemistry Second Edition Julia Burdge 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
Chemistry Second Edition Julia Burdge 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
3. Solids cannot conduct electricity because the ions cannot move freely 4. Electrolytic cell
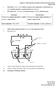 Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Ch.2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
 Ch.2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Naming Recall Ionic Bond = electrostatic attraction due to the transfer of vse - s between a metal and nonmetal Covalent Bond = sharing of valence electrons between nonmetals
Ch.2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Naming Recall Ionic Bond = electrostatic attraction due to the transfer of vse - s between a metal and nonmetal Covalent Bond = sharing of valence electrons between nonmetals
SCHOOL YEAR CH- 13 IONS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS AND COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE : 11 TEST A
 SCHOOL YEAR 2017-18 NAME: CH- 13 IONS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS AND COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE : 11 TEST A Choose the best answer from the options that follow each question. 1. A solute
SCHOOL YEAR 2017-18 NAME: CH- 13 IONS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS AND COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE : 11 TEST A Choose the best answer from the options that follow each question. 1. A solute
IONIC CHARGES. Chemistry 51 Review
 IONIC CHARGES The ionic charge of an ion is dependent on the number of electrons lost or gained to attain a noble gas configuration. For most main group elements, the ionic charges can be determined from
IONIC CHARGES The ionic charge of an ion is dependent on the number of electrons lost or gained to attain a noble gas configuration. For most main group elements, the ionic charges can be determined from
Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry
 covered by A-Level Chemistry products Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant 1.1.1 Apply the mole concept to substances. Moles and Formulae 1.1.2 Determine the number
covered by A-Level Chemistry products Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant 1.1.1 Apply the mole concept to substances. Moles and Formulae 1.1.2 Determine the number
