Syllabus. Introduction to s-block elements, their Physical & Chemical properties, Alkali Metals. Recapitulation of s- and p- Block Elements -2
|
|
|
- Dorthy Welch
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Syllabus Weekly course details along with learning objectives and content: Week Modules Learning Objective Content Week-1 Elements -1 Elements -2 Elements -3 Week-2 Elements -4 Elements-5 Know about s-block Elements, Know about Physical properties and Chemical properties of s-block elements, Know their biological importance, Discuss complex formation, Discuss organometallic compounds of alkali metals, Understand diagonal relationship, and, anomalous behaviour of lithium. Gain basic knowledge about alkali and alkaline earth metal. Know about chemical and physical properties of s-block elements. Learn about various types of synthesis and reactivity of alkaline earth metal. Get the basic idea about organometallic compounds and complex formation Know about Abundance and occurrence of alkaline earth metal Know about biological importance of s-block elements Discuss introduction of p- elements Know significance of p-block elements Understand comparative study of p-block elements Know about hydrides of p-block elements Know about hydrogen halide Understand oxides of p-block elements Know about oxyacid of p-block elements: Boric acid, carbonic acid and silicic acid Know about oxyacids of nitrogen and phosphorous Know about Oxyacids: Arsenic acid, Sulfuric acid Know about Oxyacids of halogen Discuss halides Know about halides of Group 15 and Group 16 elements Know about hydride of boron: Diborane, Borazine Introduction to s-block elements, their Physical & Chemical properties, Alkali Metals. Alkaline earth metals. Introduction to p-block elements & their comparative study Hydride & oxides of p- block elements Oxyacids & Halides Page 1 of 10
2 Elements-6 Week-3 Elements-7 Elements-8 Elements-9 Week-4 Industries-1 and Borohydride Understand the fullerene, Understand the carbide Understand the fluorocarbon Study the synthesis, the structure and properties of fullerene Understand the classification of carbide Understand the application and uses of various steps of carbides Understand the manufacturing, properties, application and environment and health concern of different fluorocarbons Understand the chlorofluorocarbons, their structure, synthesis and major properties Study the comparison between the carbon and silicon it's similarities and dissimilarities Understand the silicates and its structure based classification Understand the Tetrasulfur tetranitride Understand the Synthesis and properties of tetrasulfurtetranitride Understand the Halogen its occurrence, electronic configuration and physical properties Understand the reactivity of the elements of the halogen Study the applications of Halogens Understand the basic properties of halogens Understand the basic properties of interhalogen compounds Understand the classification of interhalogen and its structure Understand the properties of interhalogens Understand the polyhalide, its structure and properties Discuss silicate materials. Discuss about silicate glass. Know history of glass usage. Explain the structure of a glass Explain processing technique of glass. Fullerene, Carbides, Fluorocarbon Chlorofluorocarbons and silicates. Tetrasulfur tetranitride and Halogen Halogen & Inter halogen compounds Introduction to materials & Glass. Page 2 of 10
3 Industries -2 Industries -3 Week-5 Industries -4 Discuss classification of glasses Understand the visualization of glass Know about raw materials required in glass production Know problems in glass manufacturing Understand the manufacturing of different types of glasses Understand amorphous and crystalline structure Understand characteristics of amorphous structure Understand Zachariasen s rules Understand factors affecting Glass formation, Understand Electronegativity Discuss Viscosity Discuss limit of SiO 2 to form Glass Understand the experiment : Glass formation Discuss the challenges in Glass Industry Glass: Structural Chemistry Glass- Synthesis Glass-Structural chemistry and Challenges Industries -5 Industries -6 Explain a ceramic Discuss various applications of ceramics Classify ceramics Discuss methods used to process ceramics Define porosity and also calculate true porosity Discuss processing of traditional ceramics Discuss major problems faced in ceramic processing Discuss about ceramic Describe properties and application of ceramic Define refractory material Define sintering Explain tape casing method Explain cement Discuss processing techniques of ceramics Ceramics Ceramics and Cement Page 3 of 10
4 Week-6 Industries -7 Understand the chemical constituents of cement Understand cement constituents and application Know the setting of cement Know the setting of cement and gypsum Chemistry behind Cement Industries -8 Know about development in cement industry Understand how to make cement Define concrete Know about the environmental impact Development and manufacturing of cement Industries -9 Know about superconductivity Know about types of super conductors Understand about superconducting oxides Understand ceramics superconductors Superconducting oxides Week-7 Fertilizers-1 Go back in History: Origin of fertilizer Understand Fertilizer: a chemical Know about the qualities of fertilizer Know about the abuse of fertilizer Understand the best practices Origin and History of Fertilizers Fertilizers -2 Know meaning of fertilizer. Understand significance of nutrients in fertilizer-n, P, K Learn classification of fertilizer. Know about complex or multinutrient fertilizer. Explain inorganic and organic fertilizer. Know properties of solid and liquid fertilizer. Learn about complete fertilizer. Know incomplete fertilizer. Classification of Fertilizer Page 4 of 10
5 Fertilizers -3 Explain compound fertilizer. Discuss production of compound fertilizer. Know what is complex fertilizer? Discuss various advantages of compound fertilizer. Explain mixed fertilizer and its method of preparation. Know major advantages of mixed fertilizer. Explain Potassium chloride or Muriate of Potash (MOP). Discuss how potassium chloride does manufactured? Learn about Potassium sulfate or Sulfate of Potash (SOP). Explain manufacturing of potassium sulfate. General concepts in Fertilizer Week-8 Fertilizers -4 Know about Ammonium Sulphate (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 Know about Ammonium Nitrate (NH 4 NO 3 ) Know about Ammonium Nitrate Ammonium Sulphate (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4.(NH 4 )NO 3 Know about Nitrate of Lime (Calcium Nitrate) Ca(NO 3 ) 2 Know about Calcium Cyanamide (CaCN 2 ) Know about Urea (H 2 NCONH 2 ) Fertilizers -5 Nitrogen Fertilizers Phosphorous Fertilizers Know about Super phosphate; Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 Know about Triple super phosphate; 3Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 Know about Nitrophosphate Know about Ammoniated phosphate; NH 4 (H 2 PO 4 ) Know about Metaphosphate; 3Ca(PO 3 ) 2 Understand about micronutrients Page 5 of 10
6 Fertilizers -6 Week-9 Surface Coatings -1 Know manufacturing and advantages of urea. Understand manufacturing of ammonium nitrate. Learn advantages of ammonium nitrate. Know manufacturing of calcium ammonium nitrate. Discuss advantages of calcium ammonium nitrate. Know manufacturing and advantages of ammonium phosphate. Understand manufacturing of super phosphate. Discuss about polyphosphate. Explain harmful effects of N-P-K fertilization. Understand the purpose of surface coating, its historical background and development as protective decorative technique Study its classification into various types together with understanding the basis involved Know about process of various coating their characteristics and application in domestic and engineering field. Mixed Fertilizers Introduction and Classification Surface Coatings -2 Know about experimental details and various Electroplating and Vapour type of electroplating, conditions of the deposition electroless plating Know about deposition coatings, in the deposition coating Know about physical vapour deposition and chemical vapour deposition. Week- 10 Surface Coatings -3 Surface Coatings -4 Know about varnishes, enamels Know about mechanism of film formation, Compare dyes with pigments, wax polishing, Know about special paints Study various types of organic coatings viz varnishes, enamels, lacquers, wax polish, emulsions etc. Discuss components of each of the above mentioned coatings and their applications Understand mechanism of film formation and process of drying. Paint and PVC coating Special Organic and Natural coatings Page 6 of 10
7 Know about some special paints like heat resistant, luminescent, fire retardant, cement paint etc. Familiarize with natural or eco-friendly paint and risk parameters in coating. Batteries -1 Know about the basic concepts of battery, how it was invented, its construction, components and classification of batteries with some examples. Batteries: Introduction Week- 11 Batteries -2 Batteries -3 Alloys-1 Alloys-2 Know about some examples of secondary batteries i.e. lead acid batteries, lithium batteries Know about solid-state electrolyte batteries, its advantages, disadvantages and its applications Understand about some fuel cells and its types in brief. Know about the some basic concepts of fuel cells, Know about principles & classification of the fuel cells. Know about fuel cell setup and its efficiency, Understand about solar cell and photovoltaic cell (PV), Understand about photovoltaic effect and also the solar polymer cell. Discuss history of metals Describe alloys and their types Describe ferrous and non-ferrous materials Discuss different classifications of metals Describe steels and its types Discuss heat treatment. Discuss copper alloys Discuss magnesium alloys Discuss nickel and its alloys Discuss Titanium and its alloys Discuss history of steel Discuss different approaches for steel production Discuss continuous casting method Discuss ferrous metals and its classifications Lead acid and Lithium ion batteries Fuel Cell and Solar Cell Classification Manufacture & application of steel Page 7 of 10
8 Week- 12 Alloys-3 Catalysis-1 Catalysis-2 Catalysis-3 Discuss cast iron and its classifications Discuss microstructure of different cast irons. Discuss properties of cast iron Discuss about stainless steel and its classification Discuss properties of different stainless steel Discuss about high strength low alloy steel Discuss different heat treatments of steel Discuss about the effect of heat treatment on the microstructure of steel Discuss about hardening methods of steel Define the terms Catalyst and inhibitor, catalysis and auto-catalysis. Explain the functioning of a catalyst. Know the types of Catalysis Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis and their distinguishing features Factors affecting catalyzed reactions Theory of catalysis: Intermediate Compound Theory Adsorption theory of catalysis Physical and chemical adsorption Role of physical adsorption and chemisorption is catalysis Heat of chemisorption Five step mechanism of adsorption theory Activity, selectivity and stability Choice of a catalyst Active sites Explain enzyme as nature s catalyst, Compare the activity and reactivity of man-made catalyst and enzyme, Describe the mechanism of enzyme activity and its selectivity(lock and key mechanism), Explain the factors which affect enzyme activity, Describe the homogeneous catalysis carried by Heat treatment processes General principle & properties of catalyst Homogenous & Heterogenous catalysis Industrial applications of catalysis Page 8 of 10
9 Catalysis-4 Catalysis-5 Chemical Explosives soluble metal complexes, Describe the Wilkinson s catalysis and its industrial importance, State some industrially important catalytic process- Haber s, Ostwald s, catalytic converter for controlling vehicle exhaust gases Understand about discovery of Zeolite Know about structure and composition of zeolite Understand the properties, preparation as well as catalytic applications of zeolites. Know about the role of PTC, Know about Cyanide displacement reaction, Understand probable reaction pathway Know about crown ethers as PTC Understand mechanism of PTC Discuss types of phase transfer catalysts Know the applications of PTC Understand the basic idea of explosive material. Discuss classification based on its nature as explosive. Understand essential requirement for good explosive. Understand how constructively one can think about explosives. Know about preparation of few explosives for understanding the process. Get an idea of explosive properties of few common explosives. Have a concept of explosive working as propellant. Understand how one can select a good propellant. Zeolites as catalyst Phase Transfer catalyst Chemical Explosives Course Coordinator and subject experts/ instructors 1. Prof. Prasanna S. Ghalsasi, M.Sc., Ph.D. is Professor in Chemistry at Faculty of Science, The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, Vadodara since He likes to teach undergraduate chemistry courses. He is involved in Chemistry and Science Olympiad activity. Reviewed four World Edition books from Pearson Publisher in basic chemistry. He is occupied with Page 9 of 10
10 undergraduate research activity, recently under aegis of HBCSE, Mumbai (NIUS). He is active in research in molecular materials, especially organic magnets and organic ferroelectrics. 2. Dr. R. N. Jadeja, M.Sc., Ph.D. (Chemistry), Associate Professor in Chemistry at Faculty of Science, The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, Vadodara. He has a teaching experience of over 12 years. He has published 50 research papers in national and international journals of repute along with authoring 1 book. Three students have received Ph.D. under his guidance. 3. Dr. B. V. Kamath, M.Sc., Ph.D. (Chemistry), Ex-Professor & Head in Chemistry at Faculty of Science, The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, Vadodara. He has a teaching experience of over 30 years. He has published 45 research papers in national and international journals of repute. 4. Prof. Shishir Sinha, M.Tech., Ph.D., Professor, Department of Chemical Engineering, I.I. T. Roorkee. 5. Prof. B. S. S. Daniel, M.E(I) in Metallurgy, Ph.D., Professor, Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, I.I. T. Roorkee. 6. Dr. V. K. Singh, Ph.D., M.Sc., Professor, College of Engineering (COER), Roorkee. 7. Dr. Shalini Joshi Pant, Ph.D., M.Sc., (Ex-Principal), SSDPC Girls PG College, Roorkee. Page 10 of 10
General and Inorganic Chemistry Made Easy
 General and Inorganic Chemistry Made Easy J. Nentwig M. Kreuder K. Morgenstern VCH Contents How to use this book XIII Program 1 1 Introducüon. Chemistry as a natural science - chemical and physical processes
General and Inorganic Chemistry Made Easy J. Nentwig M. Kreuder K. Morgenstern VCH Contents How to use this book XIII Program 1 1 Introducüon. Chemistry as a natural science - chemical and physical processes
Chapter 6 Notes. Section 4-5 Nonmetals
 Chapter 6 Notes Section 4-5 Nonmetals Section 4-5 Objectives 8) Contrast the reactivity and abundance of elements in the Group 3A through Group 8A. 9) Name an important element in each group of p-block
Chapter 6 Notes Section 4-5 Nonmetals Section 4-5 Objectives 8) Contrast the reactivity and abundance of elements in the Group 3A through Group 8A. 9) Name an important element in each group of p-block
Chapter 11 The Chemical Elements
 James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar Torres Chapter 11 The Chemical Elements Chemistry Chemistry a division of physical science Chemistry deals with the composition and structure
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar Torres Chapter 11 The Chemical Elements Chemistry Chemistry a division of physical science Chemistry deals with the composition and structure
Properties of Compounds
 Chapter 6. Properties of Compounds Comparing properties of elements and compounds Compounds are formed when elements combine together in fixed proportions. The compound formed will often have properties
Chapter 6. Properties of Compounds Comparing properties of elements and compounds Compounds are formed when elements combine together in fixed proportions. The compound formed will often have properties
Chemistry Class 11 Syllabus
 Chemistry Class 11 Syllabus Course Structure Unit Title Marks I Basic Concepts of Chemistry 11 II Structure of Atom III Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties 4 IV Chemical Bonding and
Chemistry Class 11 Syllabus Course Structure Unit Title Marks I Basic Concepts of Chemistry 11 II Structure of Atom III Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties 4 IV Chemical Bonding and
Fertilisers. Topic 12 National 5 Chemistry Summary Notes
 Fertilisers LI 1 Topic 12 National 5 Chemistry Summary Notes Chemistry is extremely important to the future of food production. As the population of the world increases, more and more efficient ways of
Fertilisers LI 1 Topic 12 National 5 Chemistry Summary Notes Chemistry is extremely important to the future of food production. As the population of the world increases, more and more efficient ways of
Part 8- Chemistry Paper 2 Using Resources Triple Science
 Part 8- Chemistry Paper 2 Using Resources Triple Science How bonding and structure are related to the properties of substances A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge
Part 8- Chemistry Paper 2 Using Resources Triple Science How bonding and structure are related to the properties of substances A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge
Q. Why is hydrogen located on the left side of the periodic table with the active metals, even
 REPRESENTATIVE GROUPS Q. Why is hydrogen located on the left side of the periodic table with the active metals, even though it is a gas? Hydrogen s location is related to its electron configuration, not
REPRESENTATIVE GROUPS Q. Why is hydrogen located on the left side of the periodic table with the active metals, even though it is a gas? Hydrogen s location is related to its electron configuration, not
CLASS VIII XI. Month Unit Topic Sub Topic
 April- Bridge Some Basic General Introduction : Importance and scope of May Course Concepts of chemistry. Historical approach to particulate Chemistry nature of matter, laws of chemical combination, Dalton
April- Bridge Some Basic General Introduction : Importance and scope of May Course Concepts of chemistry. Historical approach to particulate Chemistry nature of matter, laws of chemical combination, Dalton
Chapter 3-1. proton positive nucleus 1 amu neutron zero nucleus 1 amu electron negative on energy levels around the nucleus very small
 Chapter 3-1 Sub-atomic Charge Location Mass Particle proton positive nucleus 1 amu neutron zero nucleus 1 amu electron negative on energy levels around the nucleus very small The most mass of the atom
Chapter 3-1 Sub-atomic Charge Location Mass Particle proton positive nucleus 1 amu neutron zero nucleus 1 amu electron negative on energy levels around the nucleus very small The most mass of the atom
CHEMISTRY. SCIENCE Paper 2
 CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
3 rd Year Revision. (from second year: Conservation of Mass Acids, Alkalis and Indicators)
 3 rd Year Revision (from second year: Conservation of Mass Acids, Alkalis and Indicators) To revise: Elements, compounds, mixtures. Periodic table names (eg groups, periods, transition metals, alkali metals,
3 rd Year Revision (from second year: Conservation of Mass Acids, Alkalis and Indicators) To revise: Elements, compounds, mixtures. Periodic table names (eg groups, periods, transition metals, alkali metals,
Chemistry Study Guide
 Chemistry Study Guide Marking Period 3 Exam Week of 3/21/17 Study Guide due - When studying for this test, use your do nows, notes, homework, class handouts, and your textbook. Vocabulary Chapter 7 Anion
Chemistry Study Guide Marking Period 3 Exam Week of 3/21/17 Study Guide due - When studying for this test, use your do nows, notes, homework, class handouts, and your textbook. Vocabulary Chapter 7 Anion
2011 ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY - II
 Set No. 1 1. (a) with suitable examples explain addition polymerization, condensation polymerization and co-polymerization. (b) Give a brief account of conducting polymers. (c) Write the preparation, properties
Set No. 1 1. (a) with suitable examples explain addition polymerization, condensation polymerization and co-polymerization. (b) Give a brief account of conducting polymers. (c) Write the preparation, properties
Version 001 Exam 3 David Laude (53015) 1
 Version 001 Exam 3 David Laude (53015) 1 This print-out should have 30 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. V1:1, V2:1, V3:1,
Version 001 Exam 3 David Laude (53015) 1 This print-out should have 30 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. V1:1, V2:1, V3:1,
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Chemistry Paper 1
 AQA Chemistry (8462) from 2016 Topics C4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are Describe what elements and compounds are State that elements
AQA Chemistry (8462) from 2016 Topics C4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are Describe what elements and compounds are State that elements
ICSE Board. Class X Chemistry. Board Paper Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80
 ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2013 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2013 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
TERMWISE SYLLABUS SESSION CLASS- XI SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY TERM-I
 TERMWISE SYLLABUS SESSION-2018-19 CLASS- XI SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY TERM-I July-2018 to Sept 2018 CONTENTS Unit I: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry General Introduction: Importance and scope of chemistry. Nature
TERMWISE SYLLABUS SESSION-2018-19 CLASS- XI SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY TERM-I July-2018 to Sept 2018 CONTENTS Unit I: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry General Introduction: Importance and scope of chemistry. Nature
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E.
 MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - I-SET -A 008 Sulphuric acid, Ammonia, Analytical Chemistry, Organic Chemistry HCl, Nitric acid, Metallurgy Chemistry SCIENCE
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - I-SET -A 008 Sulphuric acid, Ammonia, Analytical Chemistry, Organic Chemistry HCl, Nitric acid, Metallurgy Chemistry SCIENCE
Covalent (sharing of electron pairs) Ionic ( electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions)
 Covalent (sharing of electron pairs) Ionic ( electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions) Metallic (electrostatic attraction between + metal ions and delocalised electrons) Group 1 ions 1+
Covalent (sharing of electron pairs) Ionic ( electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions) Metallic (electrostatic attraction between + metal ions and delocalised electrons) Group 1 ions 1+
NITROGEN AND ITS COMPOUNDS Q30 (i) Explain how the following would affect the yield of ammonia. An increase in (i). Pressure.
 NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE NITROGEN AND ITS COMPOUNDS 1. 1990 Q30 (i) Explain how the following would affect the yield of ammonia. An increase in (i). Pressure. (2 marks) marks)... (ii) Temperature
NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE NITROGEN AND ITS COMPOUNDS 1. 1990 Q30 (i) Explain how the following would affect the yield of ammonia. An increase in (i). Pressure. (2 marks) marks)... (ii) Temperature
Unit 5 ACIDS, BASES & SALTS
 Chemistry Form 3 Page 50 Ms. R. Buttigieg Unit 5 ACIDS, BASES & SALTS See Chemistry for You Chapter 12 pg. 142 onwards. See GCSE Chemistry Chapter 7 pg. 95 onwards INTRODUCTION ACIDS Acids have a ph less
Chemistry Form 3 Page 50 Ms. R. Buttigieg Unit 5 ACIDS, BASES & SALTS See Chemistry for You Chapter 12 pg. 142 onwards. See GCSE Chemistry Chapter 7 pg. 95 onwards INTRODUCTION ACIDS Acids have a ph less
MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL. Work sheet I. Term I. Level 9 Chemistry [PAPER 1-MCQ] Name: ELECTRICITY AND CHEMISTRY
![MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL. Work sheet I. Term I. Level 9 Chemistry [PAPER 1-MCQ] Name: ELECTRICITY AND CHEMISTRY MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL. Work sheet I. Term I. Level 9 Chemistry [PAPER 1-MCQ] Name: ELECTRICITY AND CHEMISTRY](/thumbs/90/103695152.jpg) MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Work sheet I Term I Level 9 Chemistry [PAPER 1-MCQ] Name: ELECTRICITY AND CHEMISTRY 1. The diagram shows how aluminium is manufactured by electrolysis. What are the anode and
MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Work sheet I Term I Level 9 Chemistry [PAPER 1-MCQ] Name: ELECTRICITY AND CHEMISTRY 1. The diagram shows how aluminium is manufactured by electrolysis. What are the anode and
Which fertiliser would improve the quality of this soil most effectively?
 1 farmer s soil is very low in both nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P). Which fertiliser would improve the quality of this soil most effectively? 2 Which compound is not used as a fertiliser? ammonium sulfate
1 farmer s soil is very low in both nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P). Which fertiliser would improve the quality of this soil most effectively? 2 Which compound is not used as a fertiliser? ammonium sulfate
UNDERGRADUATE COURSES. Department of Chemical Engineering (Ch.E.)
 Faculty of Engineering UNDERGRADUATE COURSES Department of Chemical Engineering (Ch.E.) Ch.E.: L-1, T-1 Chem 111: Inorganic Chemistry 3.00 Credit (3 hrs/wk) Modern concept of atomic structure, Periodic
Faculty of Engineering UNDERGRADUATE COURSES Department of Chemical Engineering (Ch.E.) Ch.E.: L-1, T-1 Chem 111: Inorganic Chemistry 3.00 Credit (3 hrs/wk) Modern concept of atomic structure, Periodic
The fertiliser industry
 The fertiliser industry The industrial production of fertilisers For more information on this section refer to the Chemical Industries Resource Pack. The industrial production of fertilisers involves several
The fertiliser industry The industrial production of fertilisers For more information on this section refer to the Chemical Industries Resource Pack. The industrial production of fertilisers involves several
SYLLABUS OF THE CHEMISTRY PRACTICALS ( ) CLASS-XII
 Experiment 1. SYLLABUS OF THE CHEMISTRY PRACTICALS (28-19) CLASS-XII Qualitative analysis: To analyze the given salt for acidic and basic radicals. (08 marks) Experiment 2. Volumetric analysis: (08 marks)
Experiment 1. SYLLABUS OF THE CHEMISTRY PRACTICALS (28-19) CLASS-XII Qualitative analysis: To analyze the given salt for acidic and basic radicals. (08 marks) Experiment 2. Volumetric analysis: (08 marks)
1. The elements on the periodic table are arranged by increasing A) atomic weight. B) atomic number. C) valence electrons. D) mass number.
 1. The elements on the periodic table are arranged by increasing A) atomic weight. B) atomic number. C) valence electrons. D) mass number. 2. Periodic law states which of the following? A) Physical and
1. The elements on the periodic table are arranged by increasing A) atomic weight. B) atomic number. C) valence electrons. D) mass number. 2. Periodic law states which of the following? A) Physical and
STANDARD GRADE CHEMISTRY : GENERAL LEVEL
 STANDARD GRADE CHEMISTRY : GENERAL LEVEL NEED TO KNOW SHEETS (BASED ON 1998 2006 EXAMS) TOPIC NO 1 -ide means two elements only ate/-ite means two elements + oxygen a solution contains a solid (solute)
STANDARD GRADE CHEMISTRY : GENERAL LEVEL NEED TO KNOW SHEETS (BASED ON 1998 2006 EXAMS) TOPIC NO 1 -ide means two elements only ate/-ite means two elements + oxygen a solution contains a solid (solute)
MC 17 C SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section.
 Question 1. (a) SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Choose from the following list of substances, as to what matches the description from to given below : [Bronze,
Question 1. (a) SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Choose from the following list of substances, as to what matches the description from to given below : [Bronze,
CHEM 103 Aqueous Solutions
 CHEM 103 Aqueous Solut Lecture Notes February 28, 2006 Prof. Sevian 1 Agenda What is a solution made of? Solubility of ionic compounds (salts), acids, and molecular compounds Exchange react that produce
CHEM 103 Aqueous Solut Lecture Notes February 28, 2006 Prof. Sevian 1 Agenda What is a solution made of? Solubility of ionic compounds (salts), acids, and molecular compounds Exchange react that produce
Some Physical Properties, Sources, and Methods of Preparation
 Group 15, 5A Valence-shell configuration: ns 2 np 3 Exhibits varied chemical properties. 1. N and P are nonmetals; 2. As and Sb are metalloids; 3. Bi is a metal (the heaviest non-radioactive element) Some
Group 15, 5A Valence-shell configuration: ns 2 np 3 Exhibits varied chemical properties. 1. N and P are nonmetals; 2. As and Sb are metalloids; 3. Bi is a metal (the heaviest non-radioactive element) Some
SUBJECT GUIDE Academic year INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 SUBJECT GUIDE Academic year 2014-2015 INORGANIC CHEMISTRY MODULE CONTENT YEAR TERM CREDITS TYPE Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry 1º 2º 6 Basic LECTURER(S) Postal address, telephone n o, e-mail address Antonio
SUBJECT GUIDE Academic year 2014-2015 INORGANIC CHEMISTRY MODULE CONTENT YEAR TERM CREDITS TYPE Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry 1º 2º 6 Basic LECTURER(S) Postal address, telephone n o, e-mail address Antonio
Fundamentals of General, Organic & Biological Chemistry 4 th Edition. Matter and Life
 Fundamentals of General, Organic & Biological Chemistry 4 th Edition Chapter One Matter and Life Mohammed Hashmat Ali Southeast Missouri State University 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. 1.1 Chemistry: The Central
Fundamentals of General, Organic & Biological Chemistry 4 th Edition Chapter One Matter and Life Mohammed Hashmat Ali Southeast Missouri State University 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. 1.1 Chemistry: The Central
Syllabus for F.4 Chemistry ( ) page 1 of 6 Sing Yin Secondary School Syllabus for Chemistry ( ) Form 4 AIMS AND OBJECTIVES
 Syllabus for F.4 Chemistry (2016-2017) page 1 of 6 Sing Yin Secondary School Syllabus for Chemistry (2016-2017) Form 4 AIMS AND OBJECTIVES According to the Curriculum Development Council, the broad aims
Syllabus for F.4 Chemistry (2016-2017) page 1 of 6 Sing Yin Secondary School Syllabus for Chemistry (2016-2017) Form 4 AIMS AND OBJECTIVES According to the Curriculum Development Council, the broad aims
Basic Digestion Principles
 Basic Digestion Principles 1 From Samples to Solutions Direct Analytical Method Solid Sample Problems: Mech. Sample Preparation (Grinding, Sieving, Weighing, Pressing, Polishing,...) Solid Sample Autosampler
Basic Digestion Principles 1 From Samples to Solutions Direct Analytical Method Solid Sample Problems: Mech. Sample Preparation (Grinding, Sieving, Weighing, Pressing, Polishing,...) Solid Sample Autosampler
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80
 ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2011 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2011 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
IB Chemistry. Topic 3: Periodicity. Name
 IB Chemistry Topic 3: Periodicity Name Topic 3 and 13 Periodicity Alkali metals: Group 1 elements. Strength of metallic bond gets weaker as atoms get larger. Anion: A charged ion. Decrease in size across
IB Chemistry Topic 3: Periodicity Name Topic 3 and 13 Periodicity Alkali metals: Group 1 elements. Strength of metallic bond gets weaker as atoms get larger. Anion: A charged ion. Decrease in size across
Column B 5. periodic table a. A vertical column of elements in the
 Unit 4 Assignment Packet Name Period: A1: The Periodic Table: Organizing the Elements A. periodic table B. metals C. nonmetals D. periods E. alkali metals F. halogens G. columns H. periodic law I. alkaline
Unit 4 Assignment Packet Name Period: A1: The Periodic Table: Organizing the Elements A. periodic table B. metals C. nonmetals D. periods E. alkali metals F. halogens G. columns H. periodic law I. alkaline
Description Computer Bonding. Late Lab Stamp (this stamp means you are not qualified to do lab and test corrections) Name: Period:
 Chemistry: Hood River Valley High School Unit 4 Note Pack and Goals Name: Period: Unit 4 Metals, Non-Metals, Metalloids, Ions, and Ionic compounds. Unit Goals- As you work through this unit, you should
Chemistry: Hood River Valley High School Unit 4 Note Pack and Goals Name: Period: Unit 4 Metals, Non-Metals, Metalloids, Ions, and Ionic compounds. Unit Goals- As you work through this unit, you should
for sodium ion (Na + )
 3.4 Unit 2 Chemistry 2 Throughout this unit candidates will be expected to write word equations for reactions specified. Higher tier candidates will also be expected to write and balance symbol equations
3.4 Unit 2 Chemistry 2 Throughout this unit candidates will be expected to write word equations for reactions specified. Higher tier candidates will also be expected to write and balance symbol equations
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan
 YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
Unit C1: Chemistry in our world Page 1 of 5
 Unit C1: Chemistry in our world Page 1 of 5 Lesson Specification learning outcomes Edexcel 360 Science Specification match Edexcel 360 Science GCSE Science Students Book page reference Additional information
Unit C1: Chemistry in our world Page 1 of 5 Lesson Specification learning outcomes Edexcel 360 Science Specification match Edexcel 360 Science GCSE Science Students Book page reference Additional information
St. Joseph s College of Arts & Science (Autonomous) Cuddalore QUESTION BANK SECTION-A
 St. Joseph s College of Arts & Science (Autonomous) Cuddalore 607001 QUESTION BANK CLASS: II - B.Sc., CHEMISTRY SUBJECT: INORGANIC CHEMISTRY-II SUBJECT CODE: CH305T UNIT-I 1) The golden spangle is a) PbCrO4
St. Joseph s College of Arts & Science (Autonomous) Cuddalore 607001 QUESTION BANK CLASS: II - B.Sc., CHEMISTRY SUBJECT: INORGANIC CHEMISTRY-II SUBJECT CODE: CH305T UNIT-I 1) The golden spangle is a) PbCrO4
Atomic Structure. Aprenda Chemistry proudly presents. Odd Answer. Flash Cards 1. Ba
 1. Ba 1. What is the chemical symbol for Barium? 3. Pt 2. What is the chemical symbol for Beryllium? 5. Sn 3. What is the chemical symbol for Platinum? 7. K 4. What is the chemical symbol for Arsenic?
1. Ba 1. What is the chemical symbol for Barium? 3. Pt 2. What is the chemical symbol for Beryllium? 5. Sn 3. What is the chemical symbol for Platinum? 7. K 4. What is the chemical symbol for Arsenic?
Agricultural Fertilizer Applicator Soil Test Results What the heck do they mean?
 Agricultural Fertilizer Applicator Soil Test Results What the heck do they mean? Northeast Ohio Pesticide Safety Education Program Lee Beers, OSU Extension Trumbull County beers.66@osu.edu 330-638-6783
Agricultural Fertilizer Applicator Soil Test Results What the heck do they mean? Northeast Ohio Pesticide Safety Education Program Lee Beers, OSU Extension Trumbull County beers.66@osu.edu 330-638-6783
MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL. Work sheet III. Term I. Level 8 Chemistry [MCQ] Name: CHEMICAL REACTIONS & SULFUR
![MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL. Work sheet III. Term I. Level 8 Chemistry [MCQ] Name: CHEMICAL REACTIONS & SULFUR MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL. Work sheet III. Term I. Level 8 Chemistry [MCQ] Name: CHEMICAL REACTIONS & SULFUR](/thumbs/95/123248955.jpg) MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Work sheet III Term I Level 8 Chemistry [MCQ] Name: CHEMICAL REACTIONS & SULFUR 1. A steel works and a chemical works are built near to a city. The limestone buildings in the
MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Work sheet III Term I Level 8 Chemistry [MCQ] Name: CHEMICAL REACTIONS & SULFUR 1. A steel works and a chemical works are built near to a city. The limestone buildings in the
National 5 Whole Course Revision Questions
 National 5 Whole Course Revision Questions Unit 1 Chemical changes 1. Describe how temperature, concentration and particle size affect the rate of a chemical reaction- mention collision theory in your
National 5 Whole Course Revision Questions Unit 1 Chemical changes 1. Describe how temperature, concentration and particle size affect the rate of a chemical reaction- mention collision theory in your
Written by: - SHAHZAD IFTIKHAR Contact # Website: s:
 SHORT QUESTION >> Question: What is Self Ionization of Water? Write the equation for self ionization of water? The reaction in which two water molecules produce ions is called as the self ionization or
SHORT QUESTION >> Question: What is Self Ionization of Water? Write the equation for self ionization of water? The reaction in which two water molecules produce ions is called as the self ionization or
C01C. References. Limiting references CPC - C01C This place does not cover: Exceptions to the last appropriate place rule:
 C01C AMMONIA; CYANOGEN; COMPOUNDS THEREOF ({metal hydrides, monoborane, diborane or addition complexes thereof C01B 6/00}; salts of oxyacids of halogens C01B 11/00; peroxides, salts of peroxyacids C01B
C01C AMMONIA; CYANOGEN; COMPOUNDS THEREOF ({metal hydrides, monoborane, diborane or addition complexes thereof C01B 6/00}; salts of oxyacids of halogens C01B 11/00; peroxides, salts of peroxyacids C01B
Q1. Methane and oxygen react together to produce carbon dioxide and water.
 Chemistry C3 Higher Questions Part 2 Q1. Methane and oxygen react together to produce carbon dioxide and water. The methane gas will not burn in oxygen until a flame is applied, but once lit it continues
Chemistry C3 Higher Questions Part 2 Q1. Methane and oxygen react together to produce carbon dioxide and water. The methane gas will not burn in oxygen until a flame is applied, but once lit it continues
CARBON. Electrochemical ond Physicochemicol Properties KIM KINOSHITA. Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Berkeley, California
 CARBON Electrochemical ond Physicochemicol Properties KIM KINOSHITA Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Berkeley, California A Wiley-Interscience Publicotion JOHN WILEY & SONS New York / Chichester / Brisbane
CARBON Electrochemical ond Physicochemicol Properties KIM KINOSHITA Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Berkeley, California A Wiley-Interscience Publicotion JOHN WILEY & SONS New York / Chichester / Brisbane
16+ ENTRANCE EXAMINATION
 ST EDWARD S OXFORD 16+ ENTRANCE EXAMINATION For entry in September 2015 CHEMISTRY Time: 1 hour Candidates Name: St Edward's School 1 1. Complete the table below. St Edward's School 2 Element calcium Symbol
ST EDWARD S OXFORD 16+ ENTRANCE EXAMINATION For entry in September 2015 CHEMISTRY Time: 1 hour Candidates Name: St Edward's School 1 1. Complete the table below. St Edward's School 2 Element calcium Symbol
BELPAHAR ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL, BELPAHAR 2 ND TRIMESTER SUB chemistry F.M. 25
 BELPAHAR ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL, BELPAHAR 2 ND TRIMESTER 2007-08 STD VI TIME 40 mins. SUB chemistry F.M. 25 Question 1 Answer in one word: a) Name an universal solvent. b) The atmospheric gas required for
BELPAHAR ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL, BELPAHAR 2 ND TRIMESTER 2007-08 STD VI TIME 40 mins. SUB chemistry F.M. 25 Question 1 Answer in one word: a) Name an universal solvent. b) The atmospheric gas required for
INORGANIC FERTILISERS NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C05B, C05C; FERTILISERS PRODUCING CARBON DIOXIDE
 CPC - C05D - 2017.08 C05D INORGANIC FERTILISERS NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C05B, C05C; FERTILISERS PRODUCING CARBON DIOXIDE Fertiliser compositions containing potassium, calcium, magnesium and others, including
CPC - C05D - 2017.08 C05D INORGANIC FERTILISERS NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C05B, C05C; FERTILISERS PRODUCING CARBON DIOXIDE Fertiliser compositions containing potassium, calcium, magnesium and others, including
AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 Topics T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table (Paper 1) To pic. Student Checklist
 Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 s T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table (Paper 1) State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are 5.1.1 A simple
Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 s T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table (Paper 1) State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are 5.1.1 A simple
Le Lycee Mauricien. Proposed Syllabus Chemistry (5070) - Form 5
 Le Lycee Mauricien Proposed Syllabus 2017 Chemistry (5070) - Form 5 First Term 1. Metals Properties of metals - Physical properties of metals - Structure of alloys and uses Reactivity Series - Place metals
Le Lycee Mauricien Proposed Syllabus 2017 Chemistry (5070) - Form 5 First Term 1. Metals Properties of metals - Physical properties of metals - Structure of alloys and uses Reactivity Series - Place metals
EDEXCEL IGCSE chemistry (double award)
 EDEXCEL IGCSE chemistry (double award) Section 1: Principles of chemistry a) States of matter 1.1 understand the three states of matter in terms of the arrangement, movement and energy of the particles
EDEXCEL IGCSE chemistry (double award) Section 1: Principles of chemistry a) States of matter 1.1 understand the three states of matter in terms of the arrangement, movement and energy of the particles
CUSTOMS TARIFF - SCHEDULE. Chapter 31 FERTILISERS
 31 - i Chapter 31 FERTILISERS Notes. 1. This Chapter does not cover: (a) Animal blood of heading 05.11; (b) Separate chemically defined compounds (other than those answering to the descriptions in Note
31 - i Chapter 31 FERTILISERS Notes. 1. This Chapter does not cover: (a) Animal blood of heading 05.11; (b) Separate chemically defined compounds (other than those answering to the descriptions in Note
Searching Inorganic Chemistry
 Searching Inorganic Chemistry Agenda: Focus Inorganic Chemistry 1. Content in SciFinder 2. Indexing of Inorganic Substances 3. Appropriate Search Strategies Chemical Name Searching Molecular Formula Structure
Searching Inorganic Chemistry Agenda: Focus Inorganic Chemistry 1. Content in SciFinder 2. Indexing of Inorganic Substances 3. Appropriate Search Strategies Chemical Name Searching Molecular Formula Structure
Dates Syllabus to be covered Remarks
 PO LEUNG KUK CENTENARY LI SHIU CHUNG MEMORIAL COLLEGE TEACHING SCHEDULE 2016/2017 FORM: 4 SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY TEXTBOOK: New 21 st Century Chemistry 2 nd Edition (Jing Kung Educational Press) Cycle 1 2 3
PO LEUNG KUK CENTENARY LI SHIU CHUNG MEMORIAL COLLEGE TEACHING SCHEDULE 2016/2017 FORM: 4 SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY TEXTBOOK: New 21 st Century Chemistry 2 nd Edition (Jing Kung Educational Press) Cycle 1 2 3
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS AND THEIR CHARACTERISTIC PROPERTIES
 Seminar_2 1. Chemical compounds and their characteristic properties. 2. Types of chemical bonds (theses). 3. Basic types of complex compounds (theses). 4. Stability of complex compounds. TEST 2_ Chemical
Seminar_2 1. Chemical compounds and their characteristic properties. 2. Types of chemical bonds (theses). 3. Basic types of complex compounds (theses). 4. Stability of complex compounds. TEST 2_ Chemical
BHARATIYA VIDYA BHAVAN S V M PUBLIC SCHOOL, VADODARA QUESTION BANK CHAPTER 5 PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
 BHARATIYA VIDYA BHAVAN S V M PUBLIC SCHOOL, VADODARA QUESTION BANK CHAPTER 5 PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS Very short answer type questions 1 mark each Q1 : Why do we need to classify elements? Q2
BHARATIYA VIDYA BHAVAN S V M PUBLIC SCHOOL, VADODARA QUESTION BANK CHAPTER 5 PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS Very short answer type questions 1 mark each Q1 : Why do we need to classify elements? Q2
CHAPTER 31 FERTILISERS
 CHAPTER 31 FERTILISERS Notes 1. This chapter does not cover: (a) animal blood heading 0511; (b) separate chemically defined compounds (other than those answering to the descriptions in Note 2(a), 3(a),
CHAPTER 31 FERTILISERS Notes 1. This chapter does not cover: (a) animal blood heading 0511; (b) separate chemically defined compounds (other than those answering to the descriptions in Note 2(a), 3(a),
Salt (sodium chloride) is added to many types of food. Sodium chloride is produced by reacting sodium with chlorine.
 Q1.This question is about salts. (a) Salt (sodium chloride) is added to many types of food. Sodium chloride is produced by reacting sodium with chlorine. sodium + chlorine sodium chloride The diagram shows
Q1.This question is about salts. (a) Salt (sodium chloride) is added to many types of food. Sodium chloride is produced by reacting sodium with chlorine. sodium + chlorine sodium chloride The diagram shows
Identify the reaction type, predict the products, and balance the equations. If it is a special decomposition or synthesis, identify which kind.
 Identify the reaction type, predict the products, and balance the equations. If it is a special decomposition or synthesis, identify which kind. 1. calcium + oxygen 2. cupric carbonate 3. aluminum + hydrochloric
Identify the reaction type, predict the products, and balance the equations. If it is a special decomposition or synthesis, identify which kind. 1. calcium + oxygen 2. cupric carbonate 3. aluminum + hydrochloric
3. Natural gas burns in a bunsen burner. (a) What happens to the temperature of the flame when the air hole is opened. (b) Explain your answer.
 Rate of reactions 1. Different chemical reactions happen at different speeds. (a) Give an example of a reaction in the lab that (i) is almost instantaneous, (ii) takes a few minutes to finish. (b) List
Rate of reactions 1. Different chemical reactions happen at different speeds. (a) Give an example of a reaction in the lab that (i) is almost instantaneous, (ii) takes a few minutes to finish. (b) List
IGCSE TEST_ (Ch. 2,3,4,5,6) Name... Date...
 IGCSE TEST_ (Ch. 2,3,4,5,6) Name... Date... 1 Winston Churchill, a British Prime Minister, had his false teeth electroplated with gold. The teeth were coated with a thin layer of carbon and were then placed
IGCSE TEST_ (Ch. 2,3,4,5,6) Name... Date... 1 Winston Churchill, a British Prime Minister, had his false teeth electroplated with gold. The teeth were coated with a thin layer of carbon and were then placed
4) A specific isotope of an element is known to have 15 protons and 16 neutrons. Which symbol would properly represent this isotope?
 CHM1025 Exam 2 Chapter 4 & 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements about different elements are true
CHM1025 Exam 2 Chapter 4 & 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements about different elements are true
Angel International SchoolManipay
 Grade OL Angel International SchoolManipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2016 Chemistry Duration: 3 Hours 1. Which property is common to calcium, potassium and sodium? a) Their atoms all lose two electrons
Grade OL Angel International SchoolManipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2016 Chemistry Duration: 3 Hours 1. Which property is common to calcium, potassium and sodium? a) Their atoms all lose two electrons
Experiment #4. Elements and Compounds.
 Experiment #4. Elements and Compounds. Goals To practice naming and classifying elements and compounds Background Properties of Elements Elements on the periodic table can be classified as metals, nonmetals
Experiment #4. Elements and Compounds. Goals To practice naming and classifying elements and compounds Background Properties of Elements Elements on the periodic table can be classified as metals, nonmetals
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox)
 Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Electrochemistry involves the study of the conversions between chemical and electrical energy. Voltaic (galvanic) cells use chemical reactions to produce an electric current.
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Electrochemistry involves the study of the conversions between chemical and electrical energy. Voltaic (galvanic) cells use chemical reactions to produce an electric current.
Periodic Table of Elements
 Periodic Table of Elements chlorine nitrogen helium gold oxygen silver mercury hydrogen neodymium sodium niobium carbon Elements Science has come along way since Aristotle s theory of Air, Water, Fire,
Periodic Table of Elements chlorine nitrogen helium gold oxygen silver mercury hydrogen neodymium sodium niobium carbon Elements Science has come along way since Aristotle s theory of Air, Water, Fire,
ADVANCED CHEMISTRY 2
 ADVANCED CHEMISTRY 2 Philip Matthews ±m±l CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Acknowledgements How to use this book INORGANIC CHEMISTRY 88 Periodicity of physical properties 88.1 Periodicity of ionisation energies
ADVANCED CHEMISTRY 2 Philip Matthews ±m±l CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Acknowledgements How to use this book INORGANIC CHEMISTRY 88 Periodicity of physical properties 88.1 Periodicity of ionisation energies
2. Read pages a. Answer the five Reading Check questions on page 47
 Chemistry Test #1 Review Chapters 1 & 2 1. Page 37, #4-6, 8, 9, 13, 14 2. Read pages 45 47 a. Answer the five Reading Check questions on page 47 3. Read pages 52 57 a. Copy the table on page 55 b. Define
Chemistry Test #1 Review Chapters 1 & 2 1. Page 37, #4-6, 8, 9, 13, 14 2. Read pages 45 47 a. Answer the five Reading Check questions on page 47 3. Read pages 52 57 a. Copy the table on page 55 b. Define
WRITING AP* NET IONIC EQUATIONS
 WRITING AP* NET IONIC EQUATIONS AP equation sets are found in the free-response section of the AP test. You are given eight equations and you must choose to answer five of these.** The equations are of
WRITING AP* NET IONIC EQUATIONS AP equation sets are found in the free-response section of the AP test. You are given eight equations and you must choose to answer five of these.** The equations are of
4.4.1 Reactivity of metals Metal oxides The reactivity series. Key opportunities for skills development.
 4.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
4.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
CHEMISTRY. SCIENCE Paper 2. (Two hours) You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes.
 CLASS IX CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent
CLASS IX CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent
0620 Chemistry Paper 3 (Extended) Paper 32 O/N/10. Paper 32 M/J/10. Paper 3 O/N/09
 0620 Chemistry Paper 3 (Extended) Paper 32 O/N/10 no. 1 properties of elements and compounds 4,21 44, 266 2 zinc and zinc blende chemistry, distillation 8,2,23 90,19,280 3 breaking down MnO 2, rate of
0620 Chemistry Paper 3 (Extended) Paper 32 O/N/10 no. 1 properties of elements and compounds 4,21 44, 266 2 zinc and zinc blende chemistry, distillation 8,2,23 90,19,280 3 breaking down MnO 2, rate of
2. Which of the following salts form coloured solutions when dissolved in water? I. Atomic radius II. Melting point III.
 1. Which pair of elements reacts most readily? A. Li + Br 2 B. Li + Cl 2 C. K + Br 2 D. K + Cl 2 2. Which of the following salts form coloured solutions when dissolved in water? I. ScCl 3 II. FeCl 3 III.
1. Which pair of elements reacts most readily? A. Li + Br 2 B. Li + Cl 2 C. K + Br 2 D. K + Cl 2 2. Which of the following salts form coloured solutions when dissolved in water? I. ScCl 3 II. FeCl 3 III.
5E Essential Lesson-SC.8.P.8.6. Element Name: Hydrogen (H) Element Name: Helium (He) Number of orbitals: 1. Number of valence electrons: 2
 Element Name: Hydrogen (H) Number of orbitals: 1 Number of protons: 1 Atomic Mass: 1.01 AMU Properties: gas, bonds with other elements, flammable Element Name: Helium (He) Number of orbitals: 1 Number
Element Name: Hydrogen (H) Number of orbitals: 1 Number of protons: 1 Atomic Mass: 1.01 AMU Properties: gas, bonds with other elements, flammable Element Name: Helium (He) Number of orbitals: 1 Number
CHEMISTRY - BROWN 13E CH.22 - CHEMISTRY OF THE NONMETALS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: YDRGEN CEMISTRY The hydrogen atom represents the simplest of the elements of the Periodic Table and consists of proton and electron. 1 1.01 Elemental hydrogen will react with
!! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: YDRGEN CEMISTRY The hydrogen atom represents the simplest of the elements of the Periodic Table and consists of proton and electron. 1 1.01 Elemental hydrogen will react with
DAPTO HIGH SCHOOL. YEAR 11 CHEMISTRY Preliminary Mid-Course Examination 2009
 DAPTO HIGH SCHOOL YEAR 11 CHEMISTRY Preliminary Mid-Course Examination 2009 General Instructions: Reading time 5 minutes Working time 1 ½ hours Write using blue or black pen Write your Student Number/Name
DAPTO HIGH SCHOOL YEAR 11 CHEMISTRY Preliminary Mid-Course Examination 2009 General Instructions: Reading time 5 minutes Working time 1 ½ hours Write using blue or black pen Write your Student Number/Name
Course Specification
 Al-Azhar University (Girls branch) Faculty of Science Department of Chemistry )فرع البنات( جامعة األزهر كلية العلوم قسم الكيمياء Course Specification Course title: Physical chemistry Code: chem. 468 Program(s)
Al-Azhar University (Girls branch) Faculty of Science Department of Chemistry )فرع البنات( جامعة األزهر كلية العلوم قسم الكيمياء Course Specification Course title: Physical chemistry Code: chem. 468 Program(s)
Inorganic Chemistry. Taro Saito
 Inorganic Chemistry Taro Saito Preface The author has tried to describe minimum chemical facts and concepts that are necessary to understand modern inorganic chemistry. All the elements except superheavy
Inorganic Chemistry Taro Saito Preface The author has tried to describe minimum chemical facts and concepts that are necessary to understand modern inorganic chemistry. All the elements except superheavy
In 1807 Davy did an electrolysis experiment to produce potassium. Davy first tried to electrolyse a solid potassium salt to produce potassium
 Q1. This question is about potassium. (a) Humphrey Davy was a professor of chemistry. In 1807 Davy did an electrolysis experiment to produce potassium. Davy first tried to electrolyse a solid potassium
Q1. This question is about potassium. (a) Humphrey Davy was a professor of chemistry. In 1807 Davy did an electrolysis experiment to produce potassium. Davy first tried to electrolyse a solid potassium
CHEMISTRY. SCIENCE Paper 2
 CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
Reducing Agent = a substance which "gives" electrons to another substance causing that substance to be reduced; a reducing agent is itself oxidized.
 Oxidation = a loss of electrons; an element which loses electrons is said to be oxidized. Reduction = a gain of electrons; an element which gains electrons is said to be reduced. Oxidizing Agent = a substance
Oxidation = a loss of electrons; an element which loses electrons is said to be oxidized. Reduction = a gain of electrons; an element which gains electrons is said to be reduced. Oxidizing Agent = a substance
THE PERIODIC TABLE. Dr Marius K Mutorwa
 THE PERIODIC TABLE Dr Marius K Mutorwa mmutorwa@polytechnic.edu.na COURSE CONTENT 1. History of the atom 2. Sub-atomic Particles protons, electrons and neutrons 3. Atomic number and Mass number 4. Isotopes
THE PERIODIC TABLE Dr Marius K Mutorwa mmutorwa@polytechnic.edu.na COURSE CONTENT 1. History of the atom 2. Sub-atomic Particles protons, electrons and neutrons 3. Atomic number and Mass number 4. Isotopes
5. Electrolytic Processes
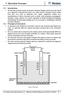 5.1 Introduction The fact that electrical energy can produce chemical changes and the processes based on it, called the electrolytic processes, are widely used for extraction of pure metals from their
5.1 Introduction The fact that electrical energy can produce chemical changes and the processes based on it, called the electrolytic processes, are widely used for extraction of pure metals from their
Equations. Chemical Reactions #1
 Equations Chemical Reactions #1 equations show the complete chemical formulas. Does not indicate ionic character equation shows all ions. Actually how the particles exist in the solution Steps for Writing
Equations Chemical Reactions #1 equations show the complete chemical formulas. Does not indicate ionic character equation shows all ions. Actually how the particles exist in the solution Steps for Writing
Exam Style Questions
 Calderglen High School Chemistry Department CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure Exam Style Questions 1 1.1 Controlling the Rate 1. The graph shows how the rate of a reaction varies
Calderglen High School Chemistry Department CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure Exam Style Questions 1 1.1 Controlling the Rate 1. The graph shows how the rate of a reaction varies
Magnetic Flowmeter Material Selection Guide
 Magnetic Flowmeter Material Selection Guide www.sparlinginstruments.com Introduction The purpose of this guide is to provide a general resource for the selection of materials for the magnetic flowmeter.
Magnetic Flowmeter Material Selection Guide www.sparlinginstruments.com Introduction The purpose of this guide is to provide a general resource for the selection of materials for the magnetic flowmeter.
5.4 Chemical changes Reactivity of metals Metal oxides The reactivity series. Key opportunities for skills development
 5.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
5.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
Or Noble-gas Atom In Bromic Acid
 Indicate The Oxidation State Of The Halogen Or Noble-gas Atom In Bromic Acid The solubility guidelines indicate all nitrate salts are soluble but that AgF is one of the hydrogen chloride gas dissolves
Indicate The Oxidation State Of The Halogen Or Noble-gas Atom In Bromic Acid The solubility guidelines indicate all nitrate salts are soluble but that AgF is one of the hydrogen chloride gas dissolves
SNC2D Chemistry Unit Test Practice
 Multiple Choice (1 mark each): SNC2D Chemistry Unit Test Practice 1. Which of the following will form positive ions? (A) the alkali metals (B) the halogens (C) the noble gases (D) all of the above 2. Which
Multiple Choice (1 mark each): SNC2D Chemistry Unit Test Practice 1. Which of the following will form positive ions? (A) the alkali metals (B) the halogens (C) the noble gases (D) all of the above 2. Which
Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015
 Grade 11B Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Chemistry - I Duration: 1.00 Hour Part 1 1) A liquid boils at a temperature of 100 o C. Which other property of the liquid
Grade 11B Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Chemistry - I Duration: 1.00 Hour Part 1 1) A liquid boils at a temperature of 100 o C. Which other property of the liquid
Name Date Class STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Chemical Reactions Section 10.1 Reactions and Equations In your textbook, read about evidence of chemical reactions. For each statement, write yes if evidence of a chemical reaction is present. Write no
Chemical Reactions Section 10.1 Reactions and Equations In your textbook, read about evidence of chemical reactions. For each statement, write yes if evidence of a chemical reaction is present. Write no
A1 Models of the atom. A2 Size of the atom
 A1 Models of the atom 1. Describe the improvements to our understanding of the atom from each of the following scientists: 1.1. Democritus 1.2. Dalton 1.3. Thomson 1.4. Rutherford 1.5. Bohr 1.6. Chadwick
A1 Models of the atom 1. Describe the improvements to our understanding of the atom from each of the following scientists: 1.1. Democritus 1.2. Dalton 1.3. Thomson 1.4. Rutherford 1.5. Bohr 1.6. Chadwick
Chemistry CRT Study Guide First Quarter
 Number AL COS # 1. #1.0 Classify sodium chloride as an element, mixture, compound, or colloid. Compound 2. #1.0 Classify air as an element, mixture, compound, or colloid. Mixture 3. #1.0 Classify a blueberry
Number AL COS # 1. #1.0 Classify sodium chloride as an element, mixture, compound, or colloid. Compound 2. #1.0 Classify air as an element, mixture, compound, or colloid. Mixture 3. #1.0 Classify a blueberry
